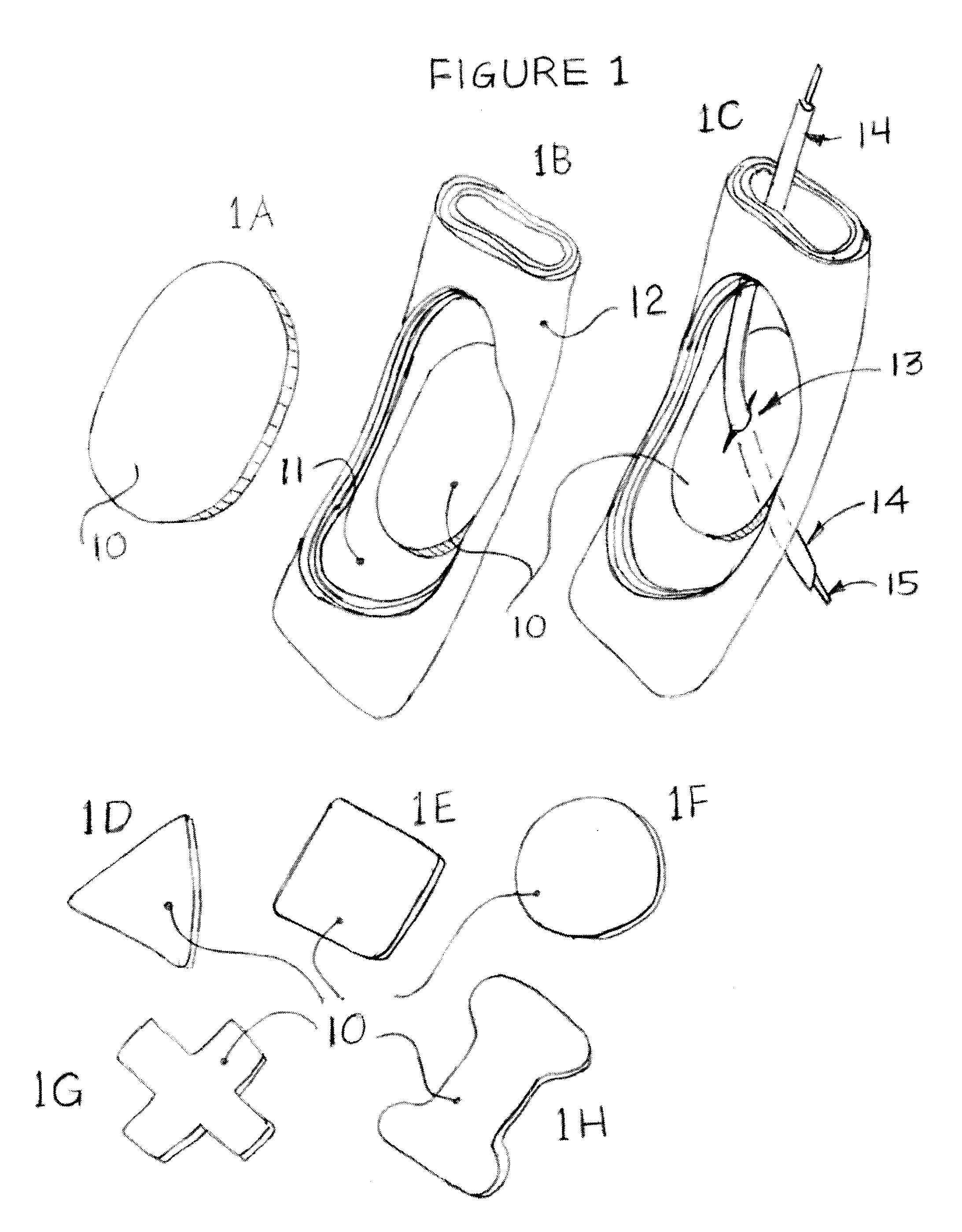
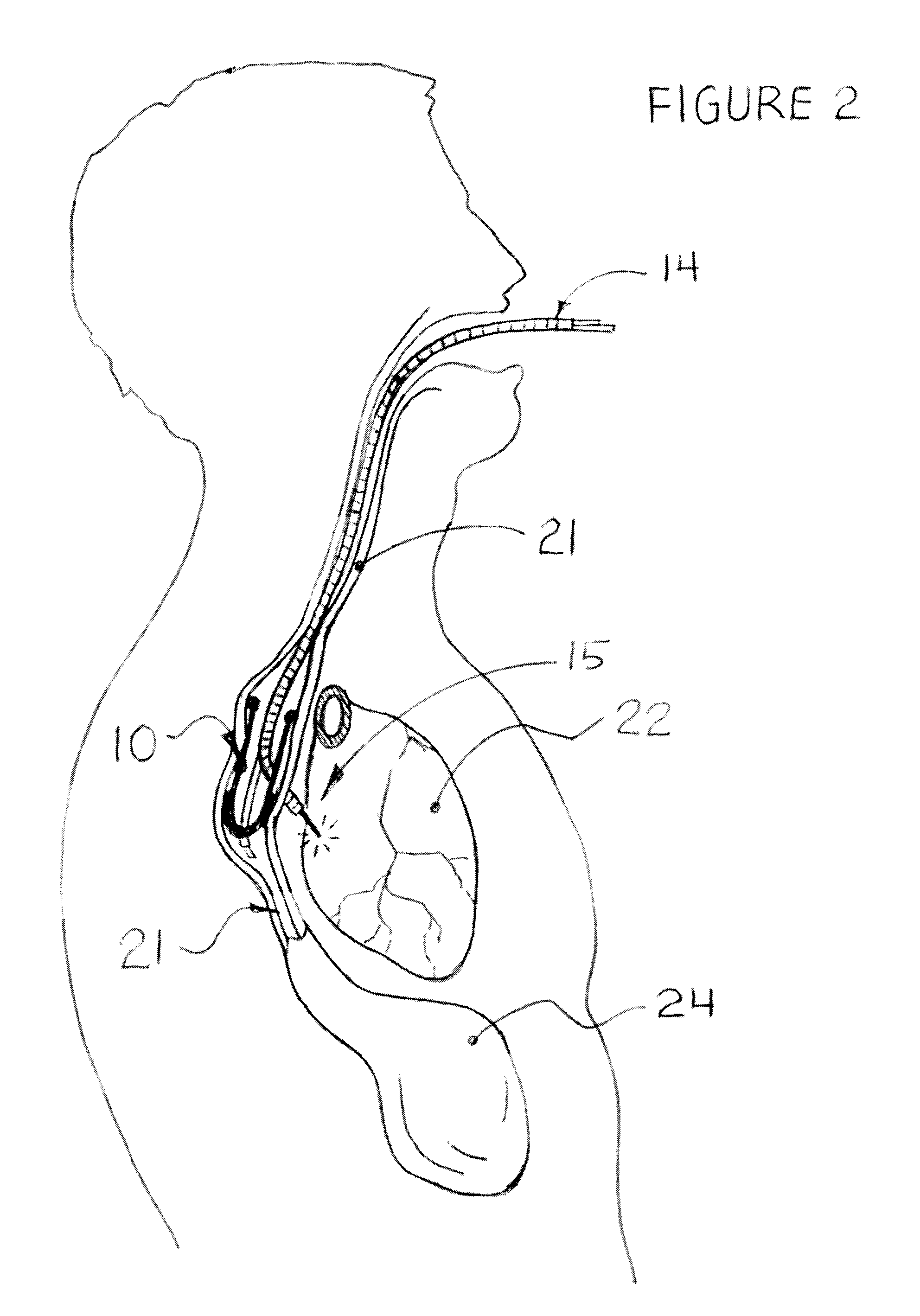
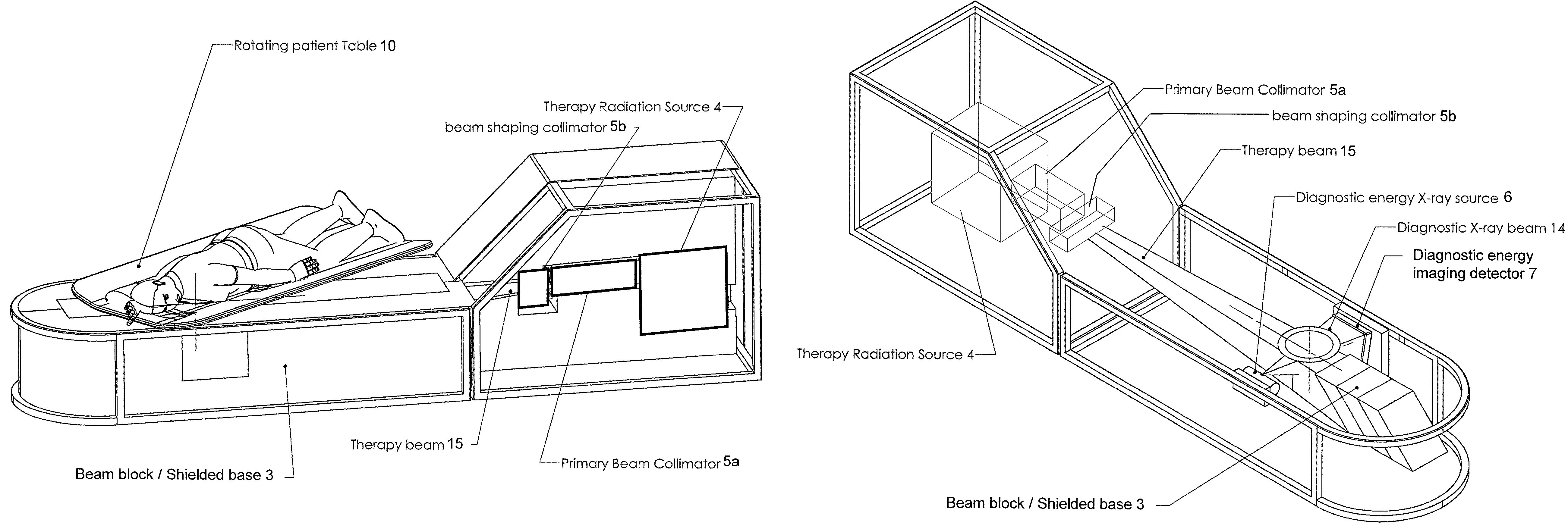
Patents
Literature
44 results about "Thoracic wall" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
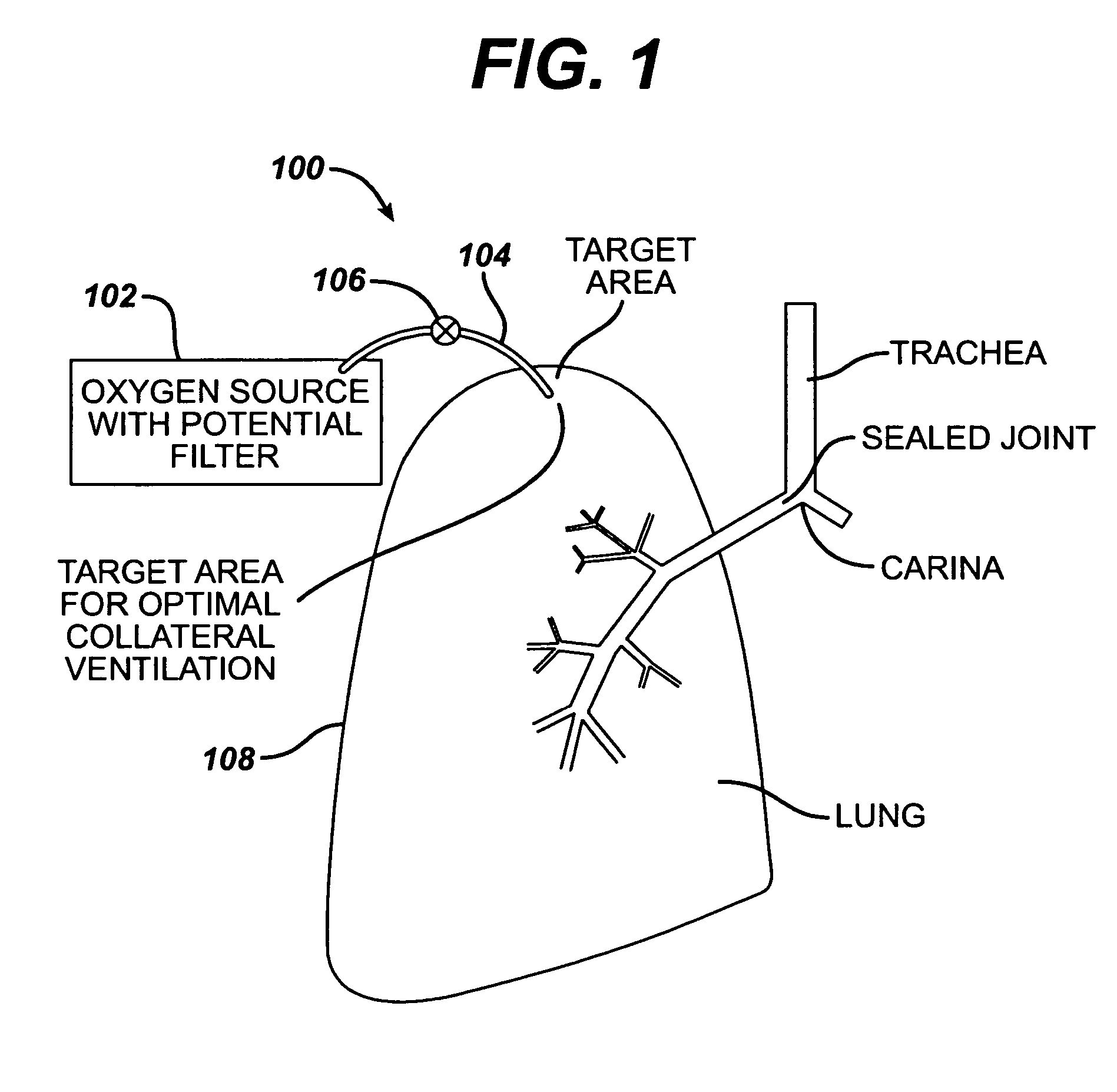
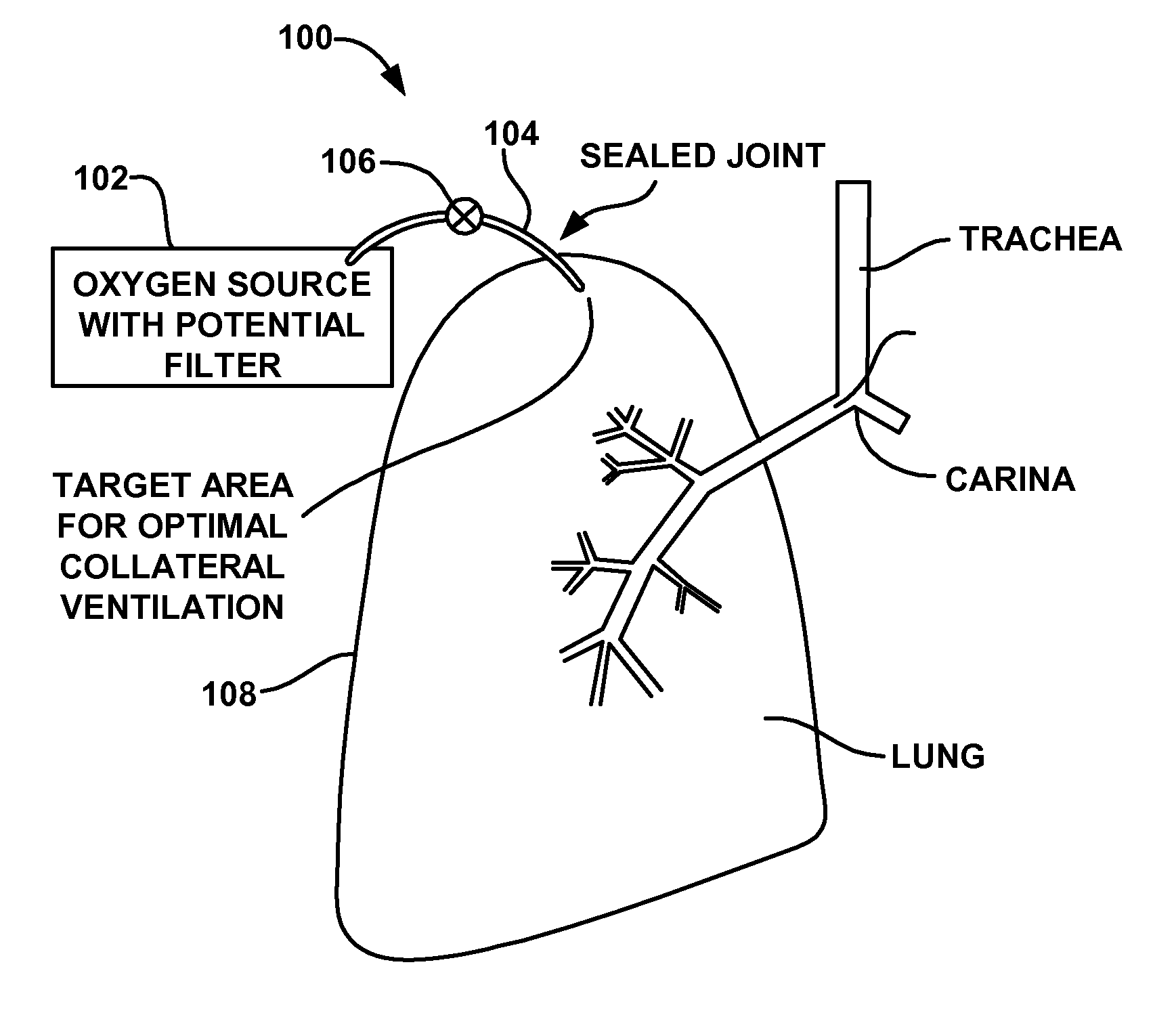
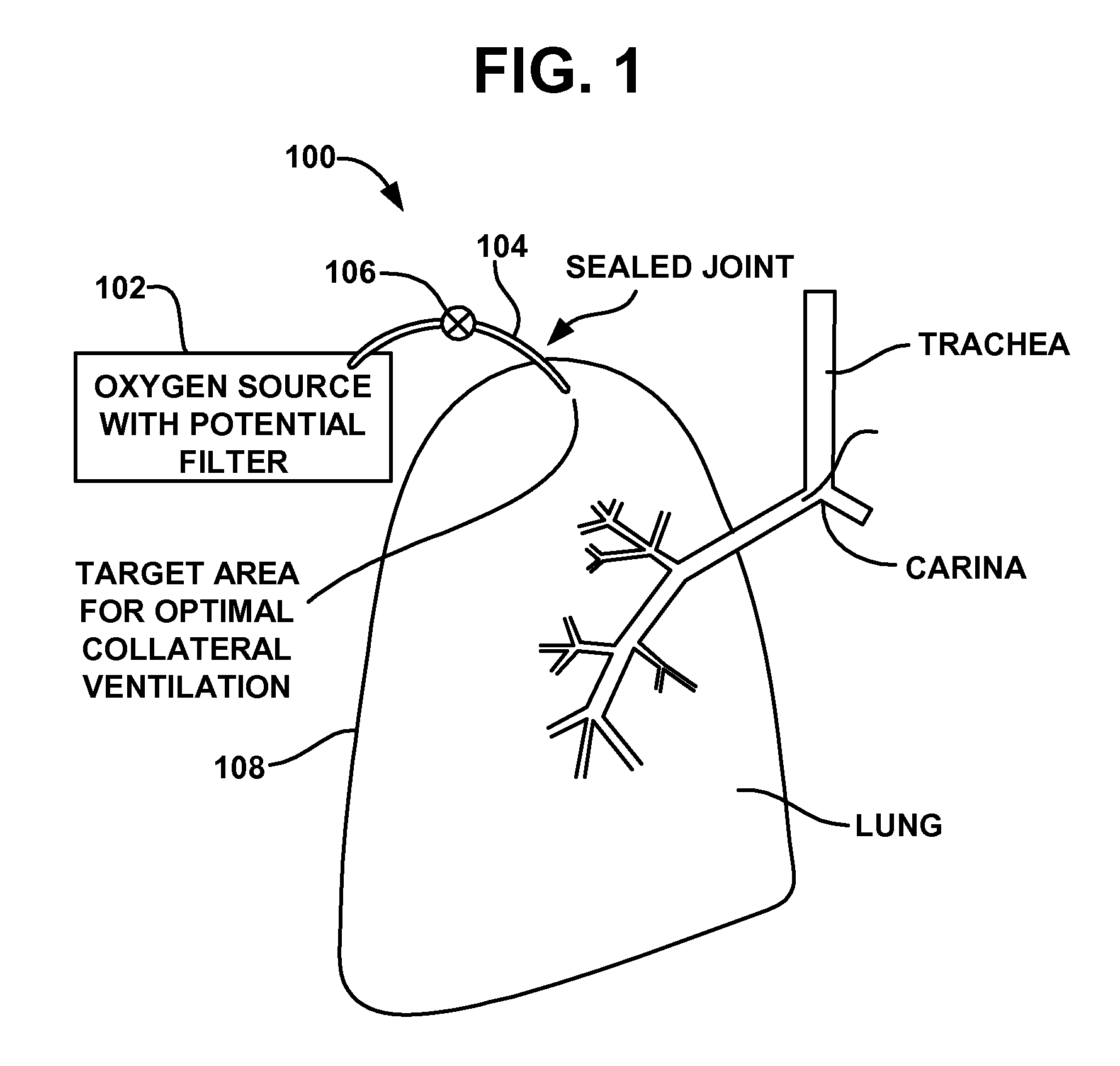
The thoracic wall or chest wall is the boundary of the thoracic cavity.
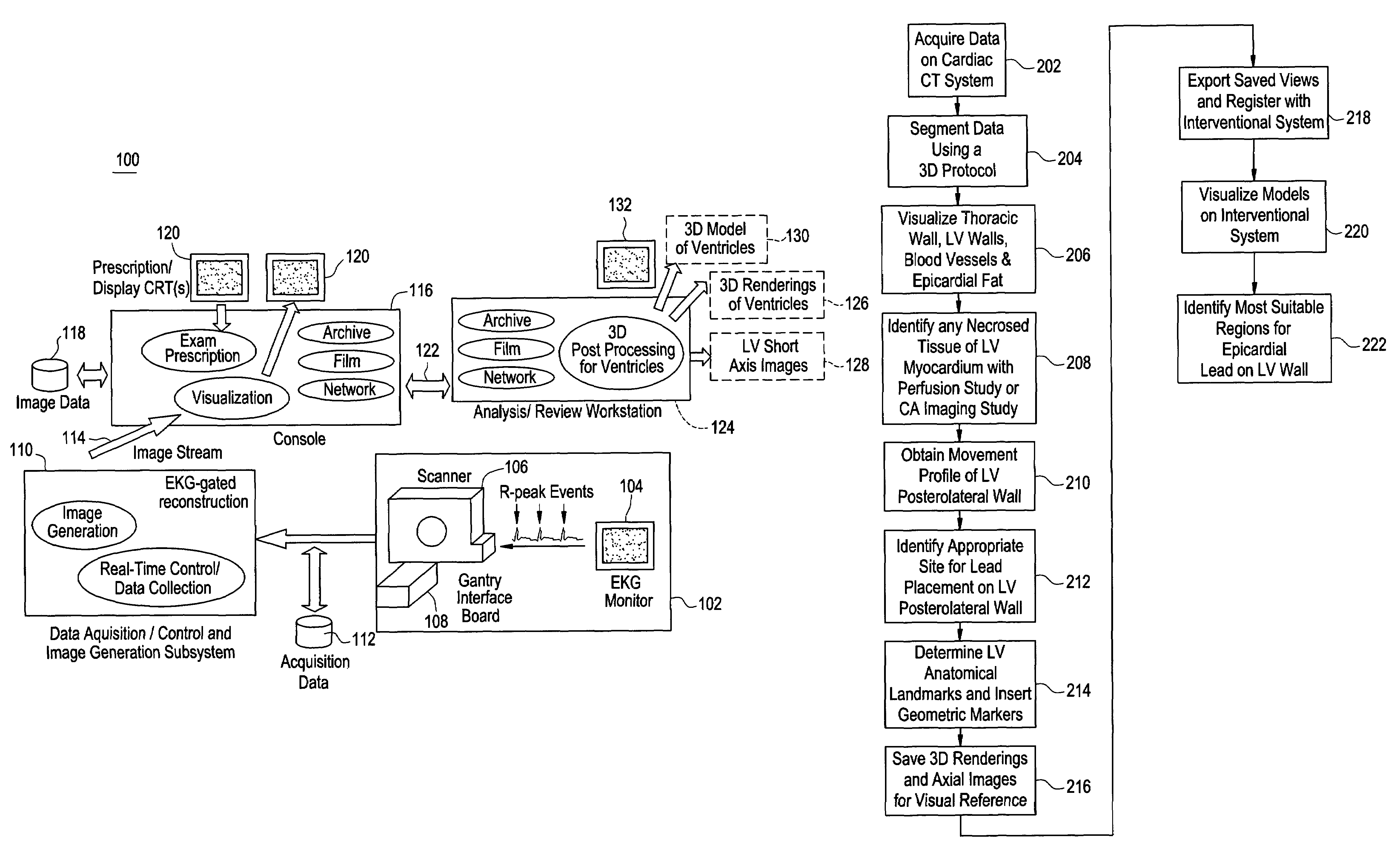
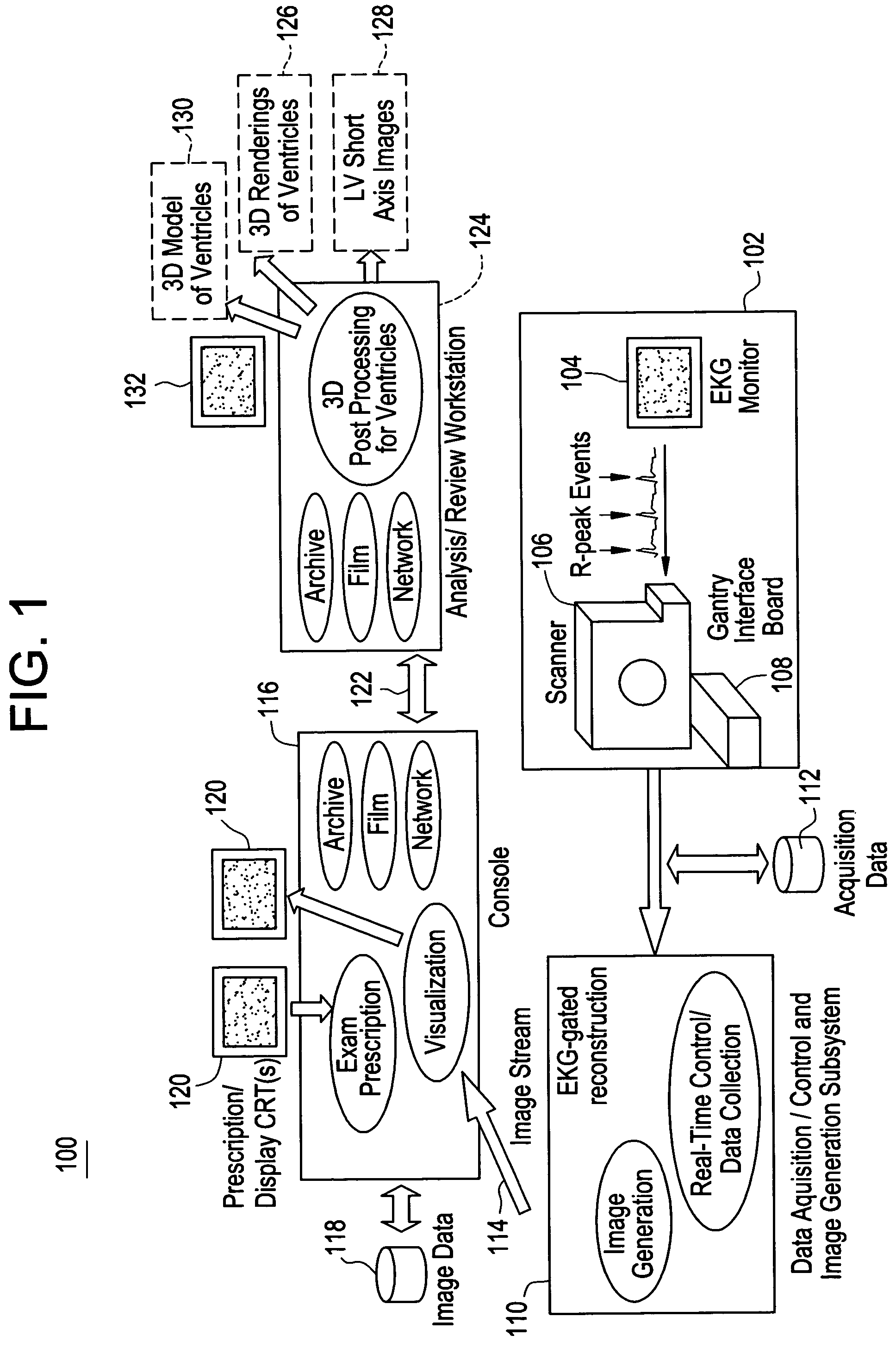
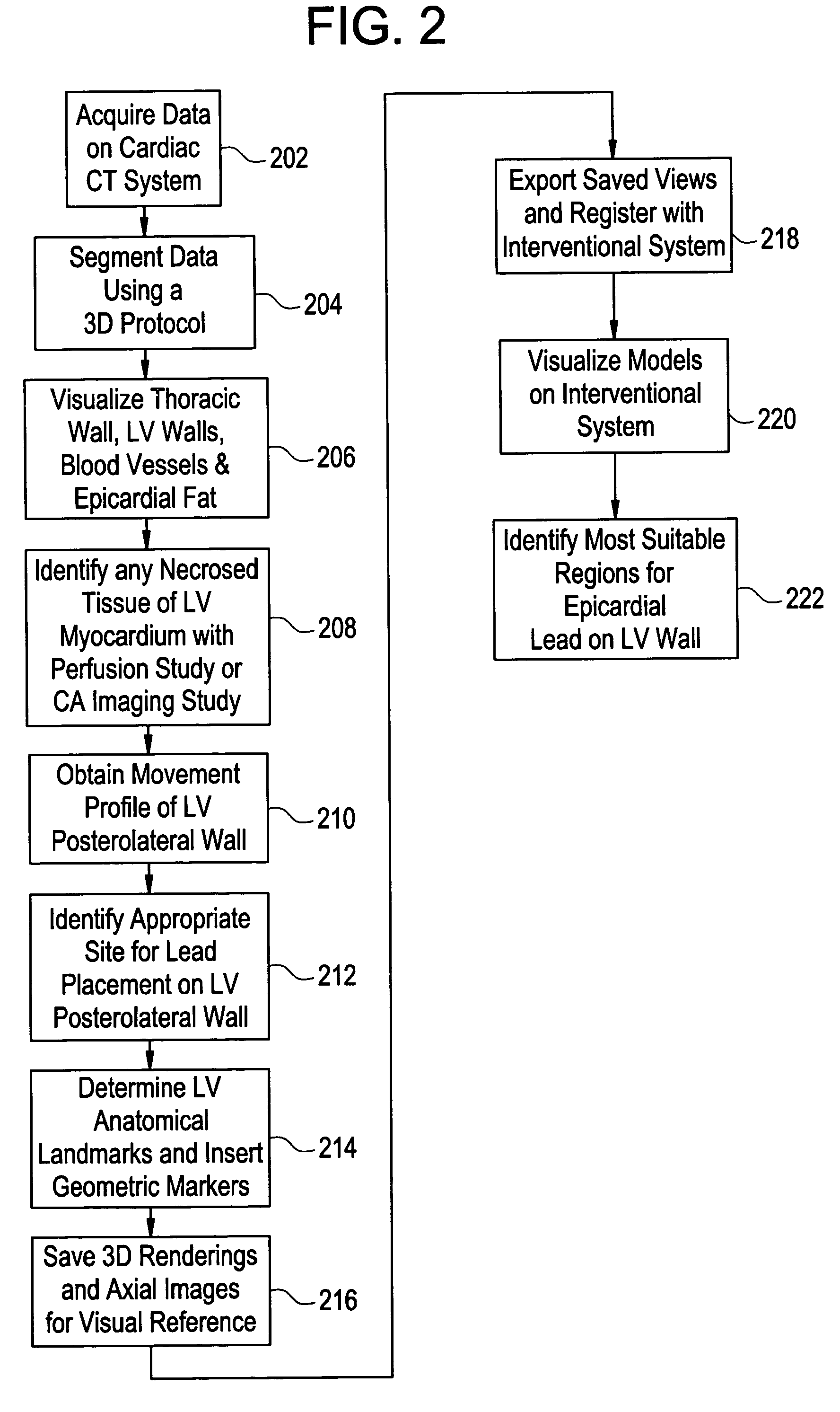
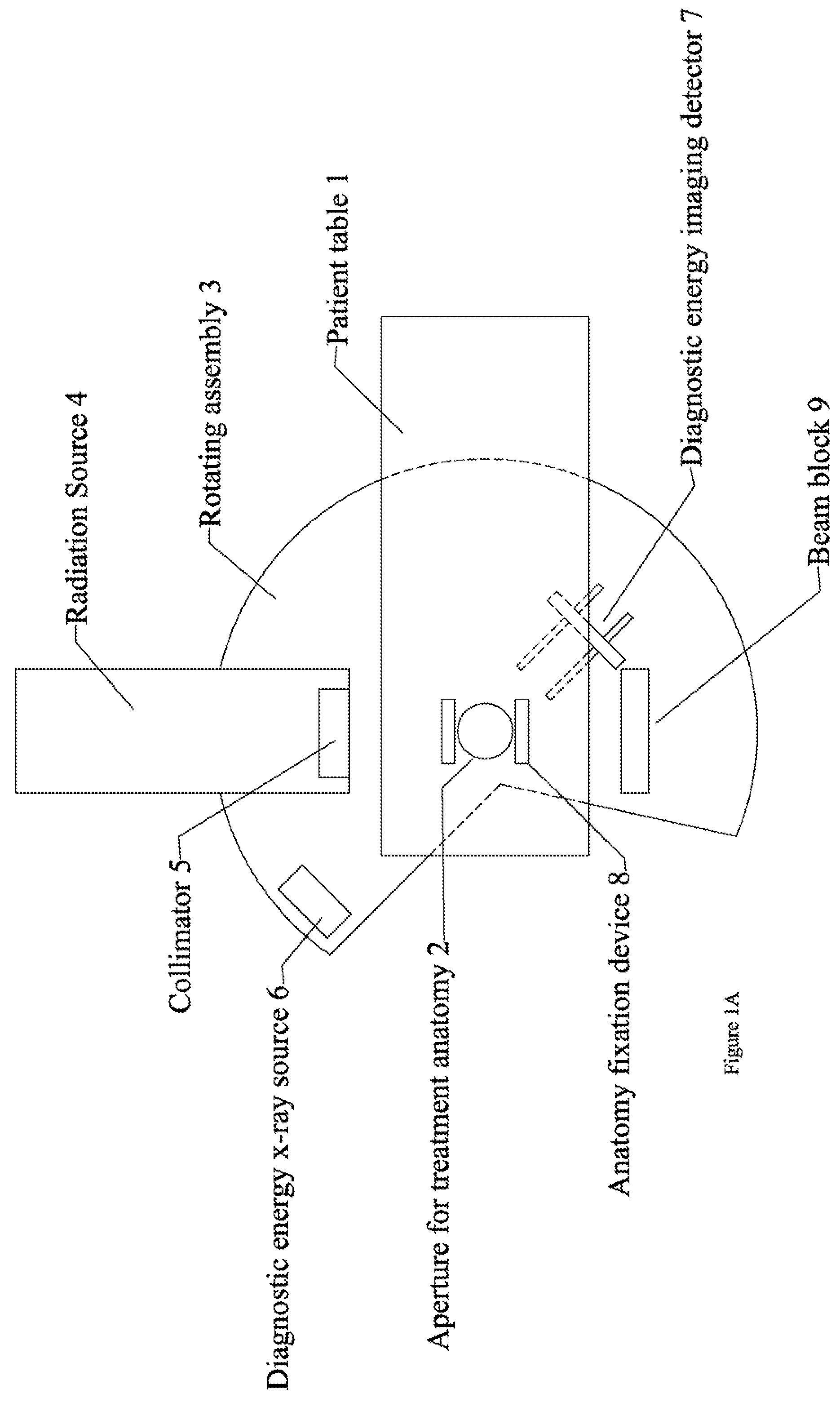
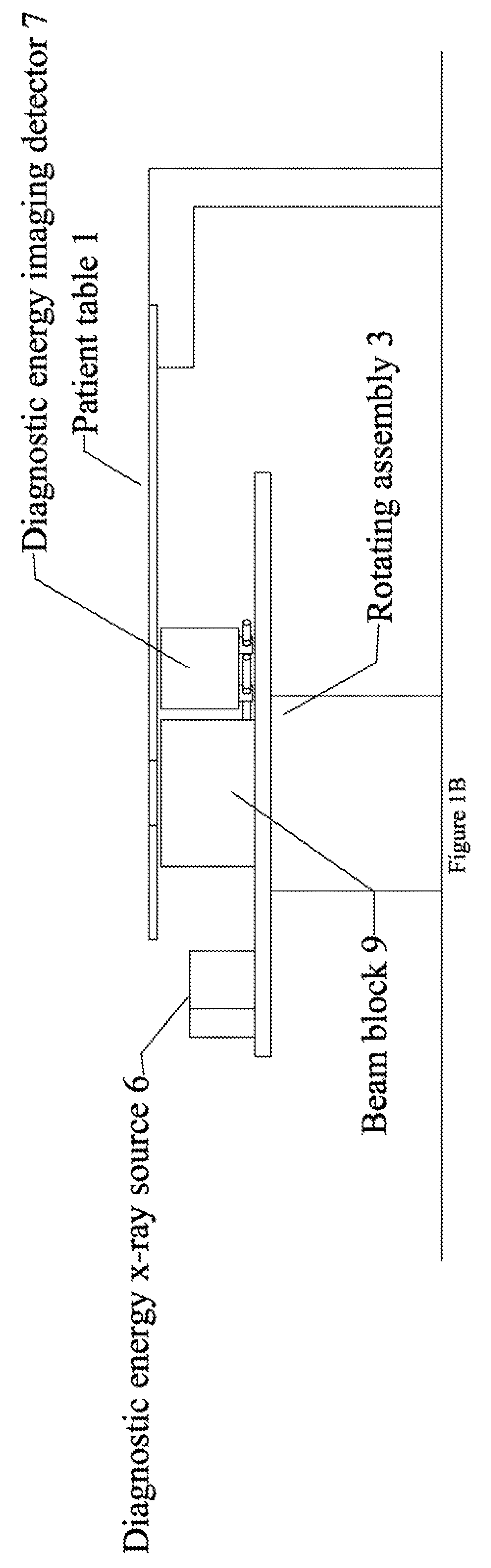
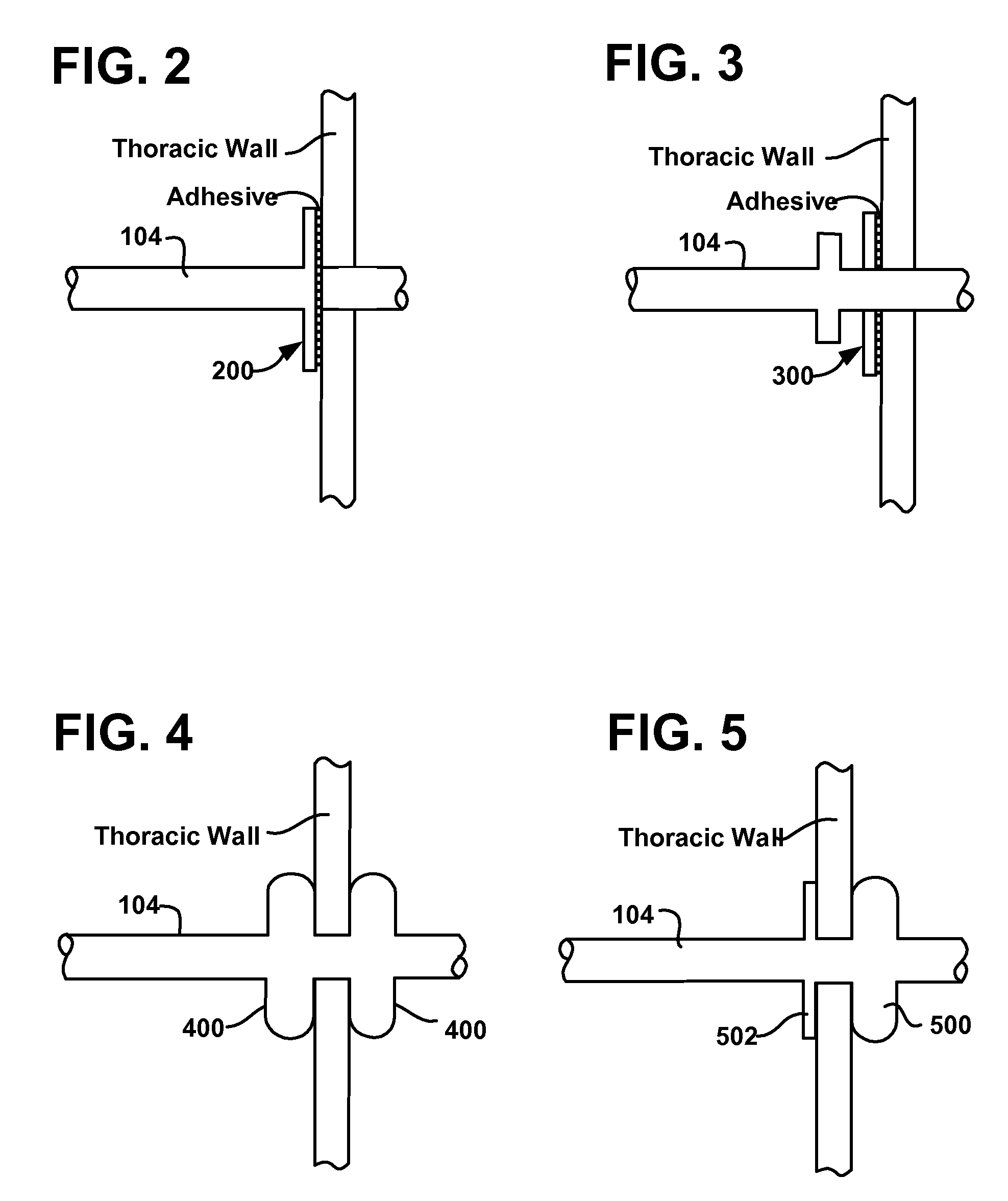
Cardiac CT system and method for planning and treatment of biventricular pacing using epicardial lead
ActiveUS7343196B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyAnatomical landmarkThoracic wall
A method for planning biventricular pacing lead placement for a patient includes obtaining acquisition data from a medical imaging system and generating a 3D model of the left ventricle and thoracic wall of the patient. One or more left ventricle anatomical landmarks are identified on the 3D model, and saved views of the 3D model are registered on an interventional system. One or more of the registered saved views are visualized with the interventional system, and at least one suitable region on the left ventricle wall is identified for epicardial lead placement.
Owner:APN HEALTH +1
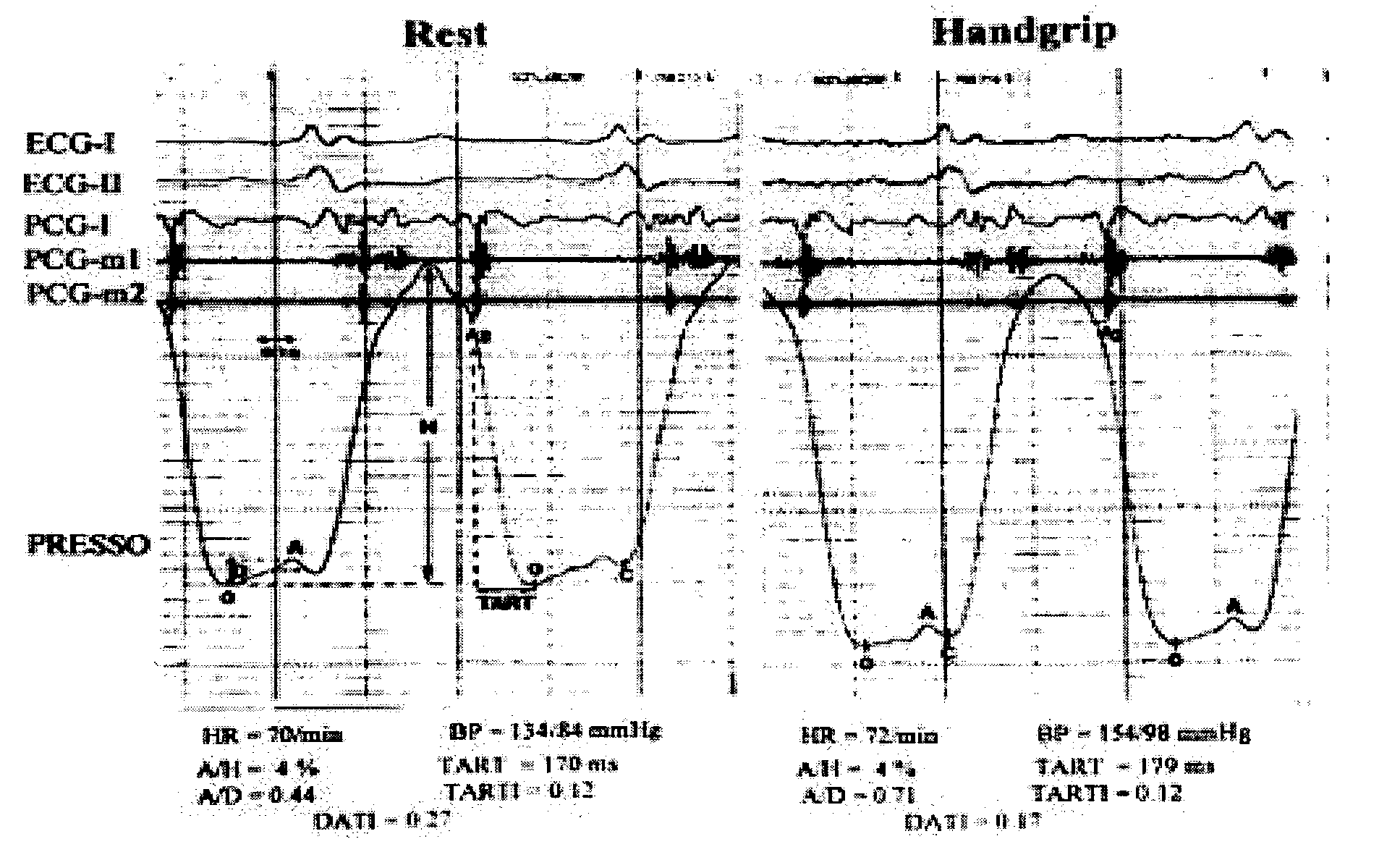
Device for and method of rapid noninvasive measurement of parameters of diastolic function of left ventricle and automated evaluation of the measured profile of left ventricular function at rest and with exercise
ActiveUS7107095B2Information can be usedSafe and convenient modalityEvaluation of blood vesselsAuscultation instrumentsLeft ventricular sizeHeart disease
In a method of noninvasive measurement of parameters of diastolic function of left ventricle and automated evaluation of the measured profile at rest and with exercise, a patient performs an isometric exercise. An external pressure sensor and heart sounds microphone are applied in a non-invasive manner on the thoracic wall to obtain a left ventricular pressure mirroring curve (pressocardiogram) and simultaneously the heart sounds (phonocardiogram). An external unit determines and calculates characteristic diastolic parameters derived from the pressocardiographic curve and phonocardiogram at rest, during and after exercise, converts each said pressocardiogram into a digital waveform in the time domain, and automatically categorizes the mentioned characteristic parameters based on exact categorization criteria for defining several differentialforms of diastolic dysfunction of left ventricle in human beings.
Owner:MANOLAS JAN
Pulmonary pulse oximetry method for the measurement of oxygen saturation in the mixed venous blood
InactiveUS20130310669A1Diagnostics using lightMaterial analysis by optical meansVenous bloodPulse oximetry
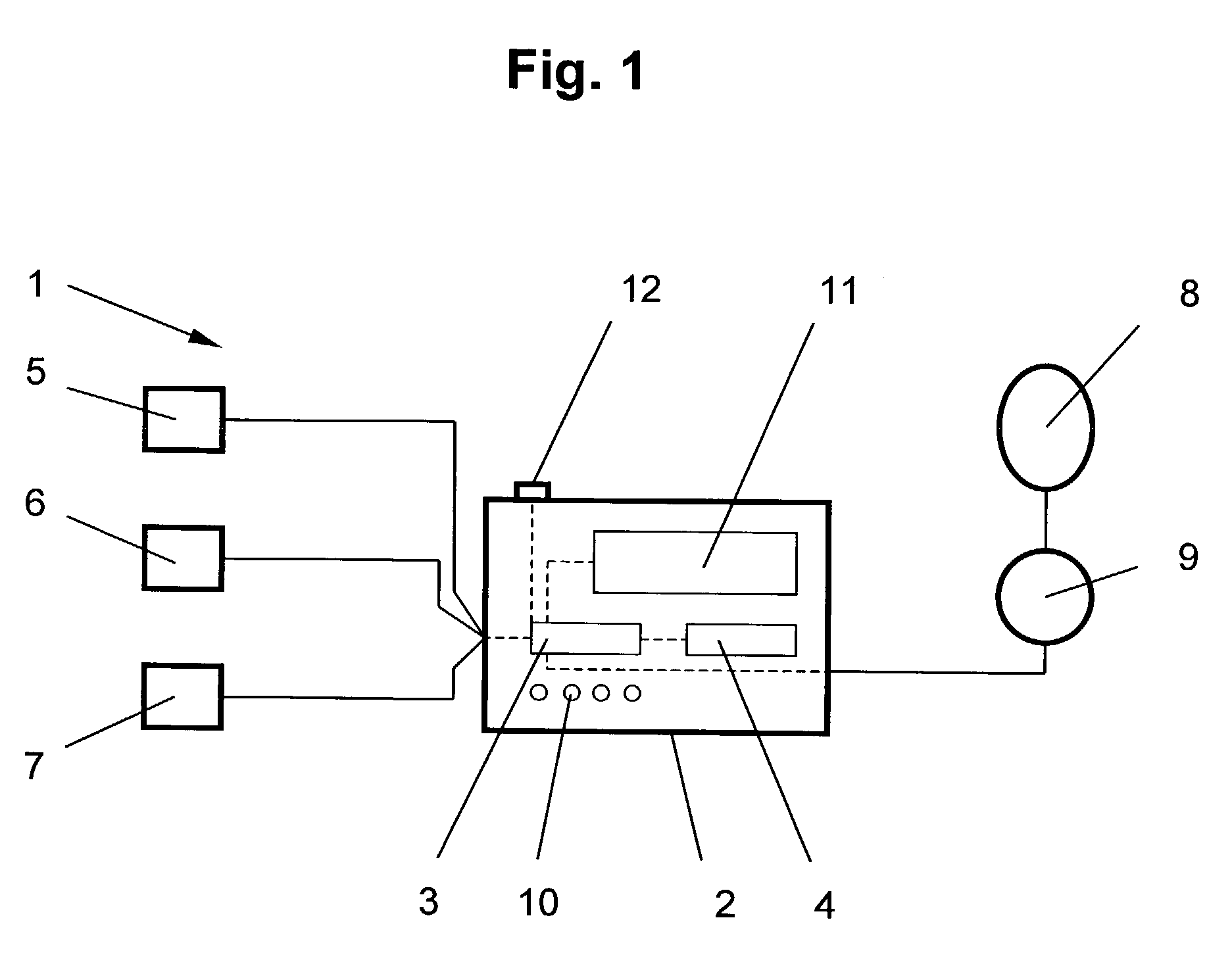
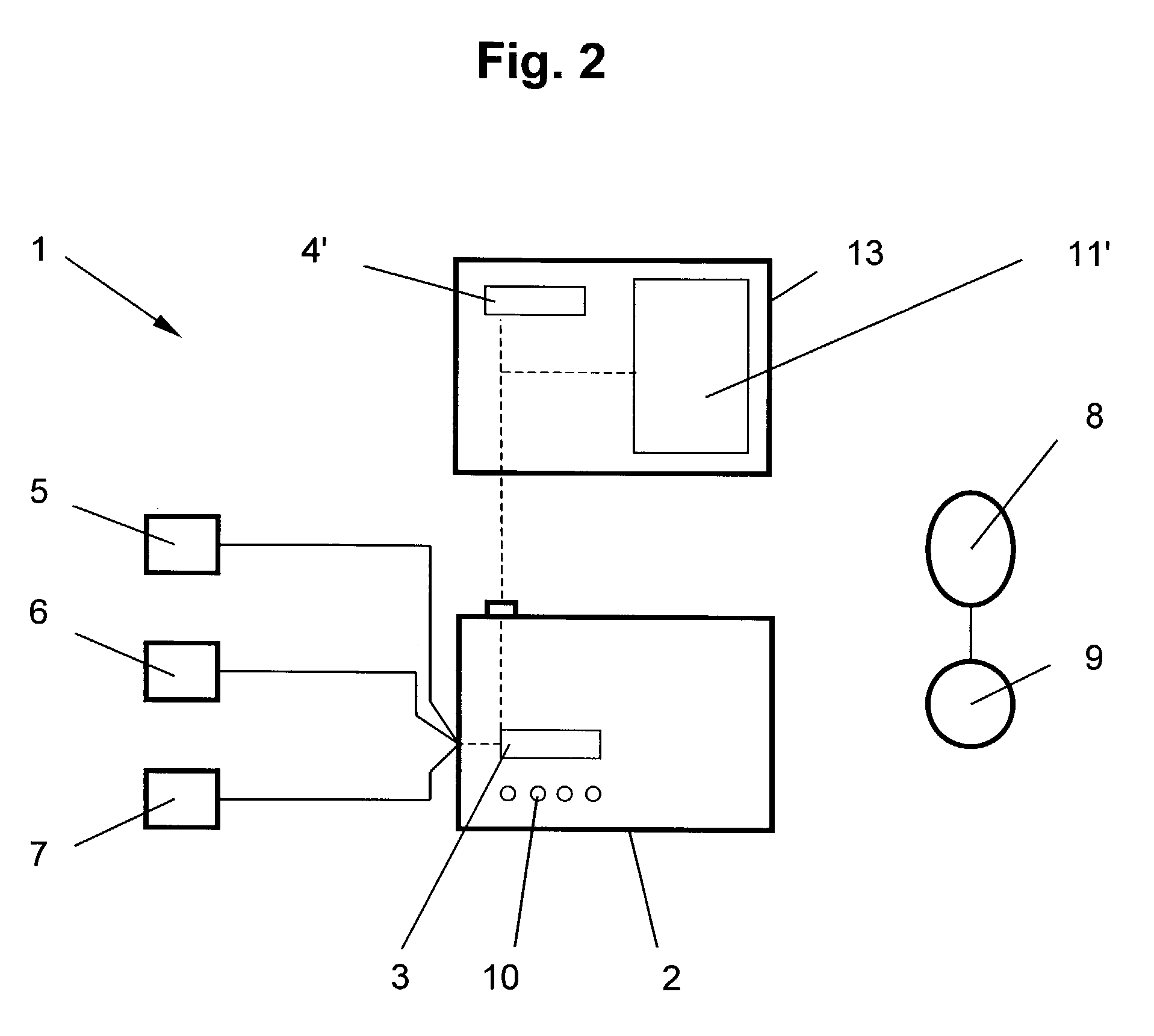
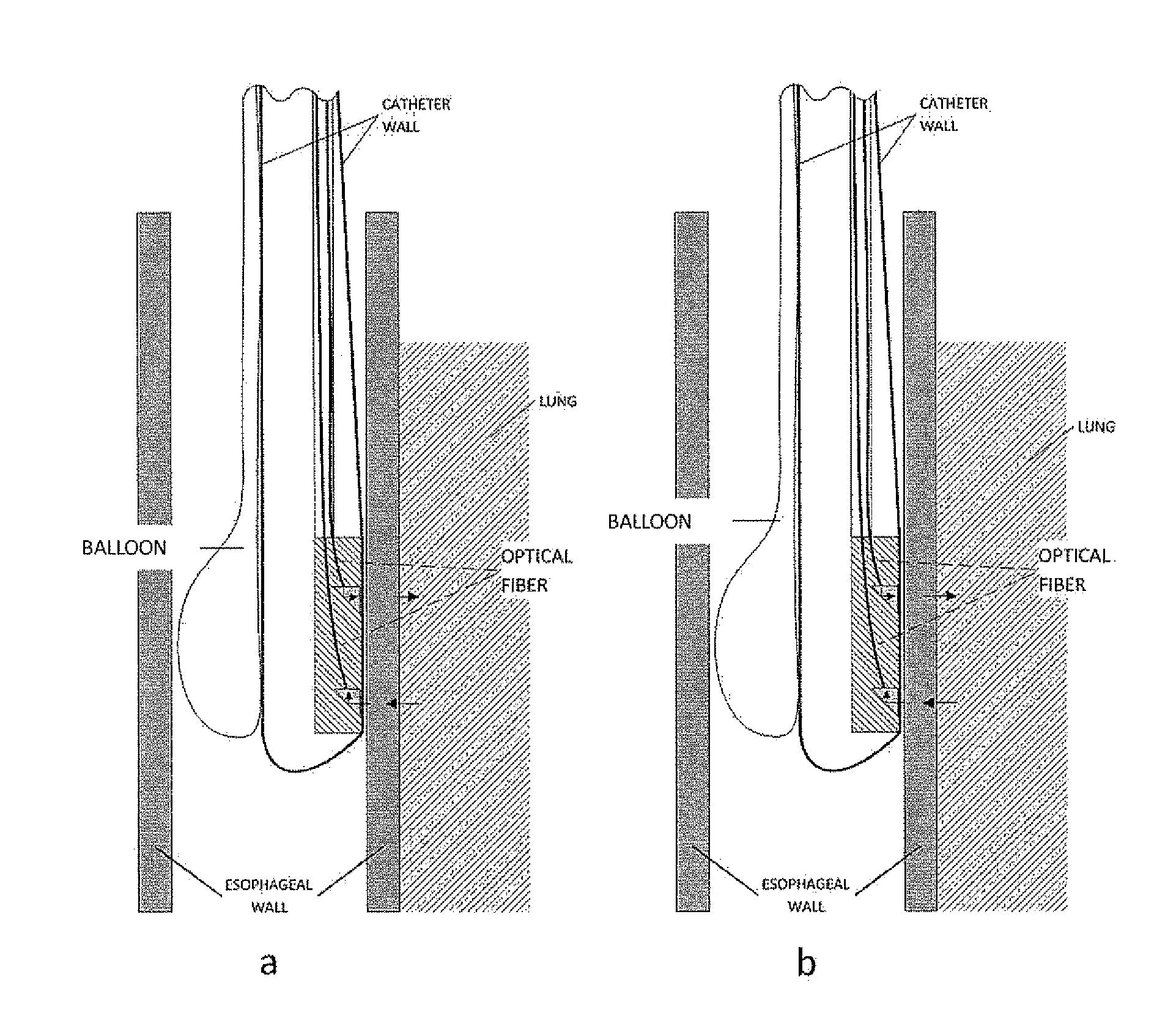
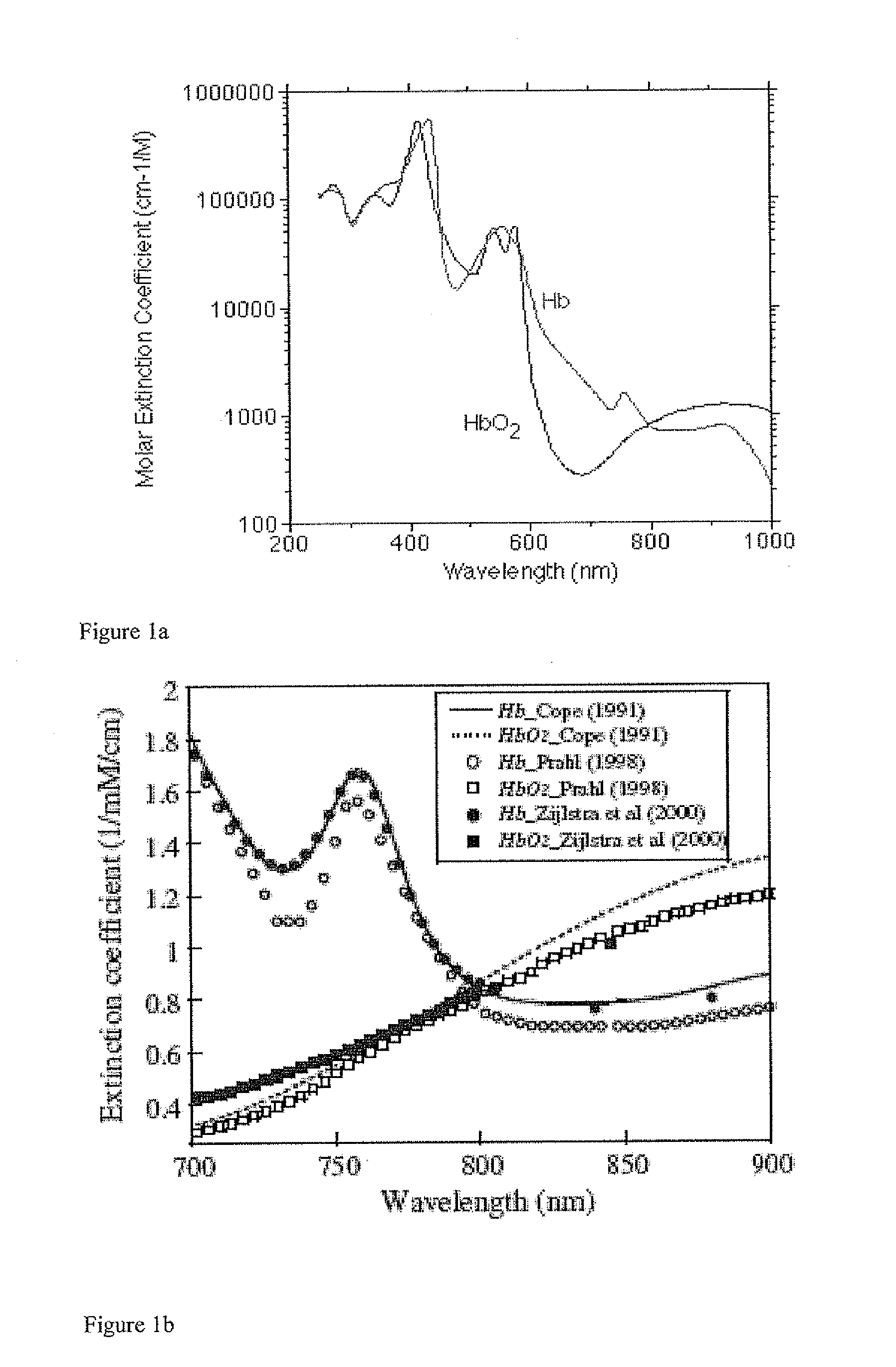
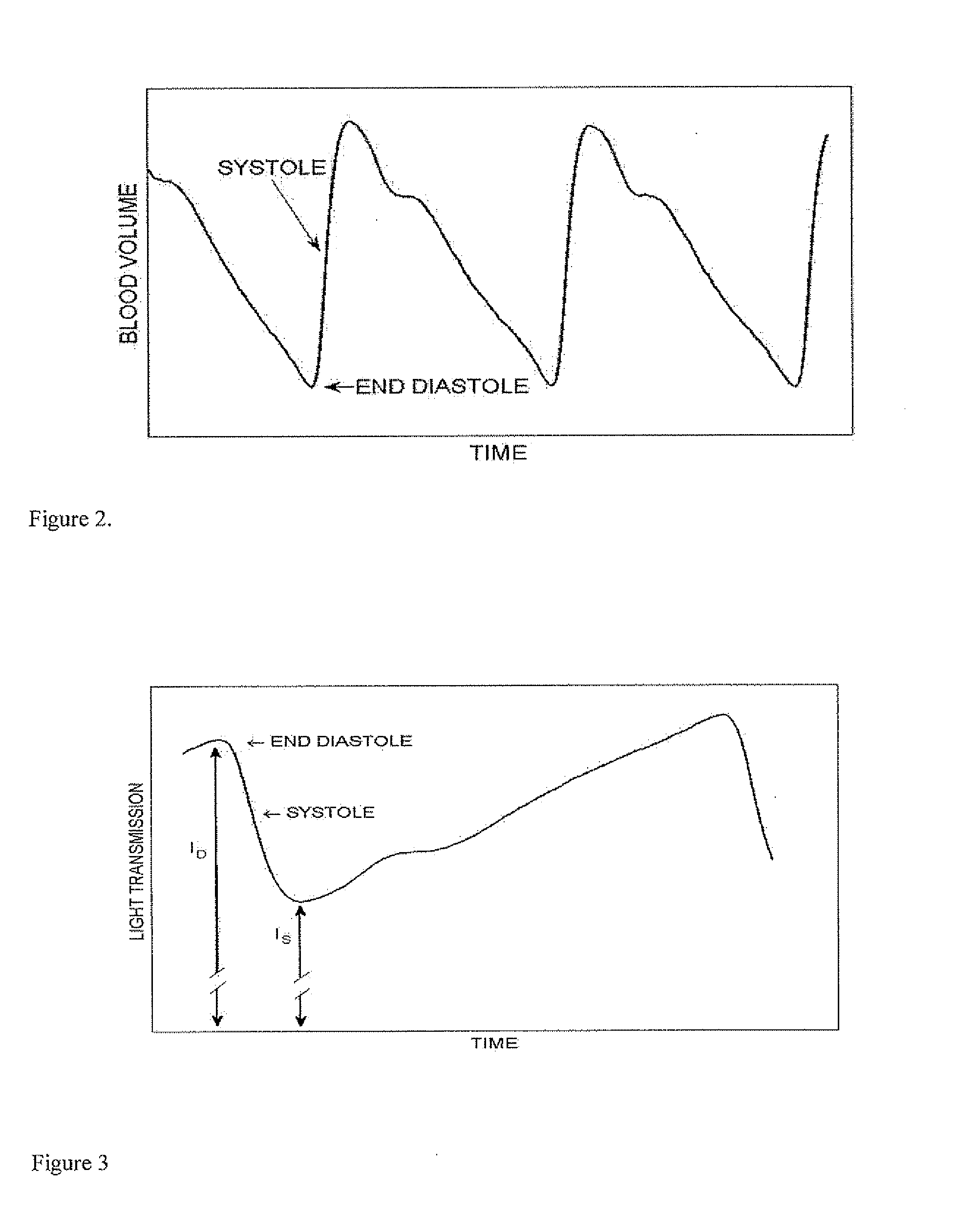
A method for obtaining diagnostic information relating to the lungs of a subject includes directing into tissue of the lungs of the subject light of a first wavelength and detecting part of the light that has passed primarily through microcirculatory tissue of the lungs and generating a signal which is a function of intensity of the detected light. The signal is then processed to derive a PPG curve for pulmonary microcirculatory arteries. The method is implemented using various locations for a light source and a detector, including various combinations of positioning on the thoracic wall, insertion into the esophagus, and in some cases, insertion of a probe through the thoracic wall to a position adjacent to the pulmonary pleura. Use of two different wavelengths allows derivation of mixed venous blood oxygen saturation.
Owner:JERUSALEM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOG +1
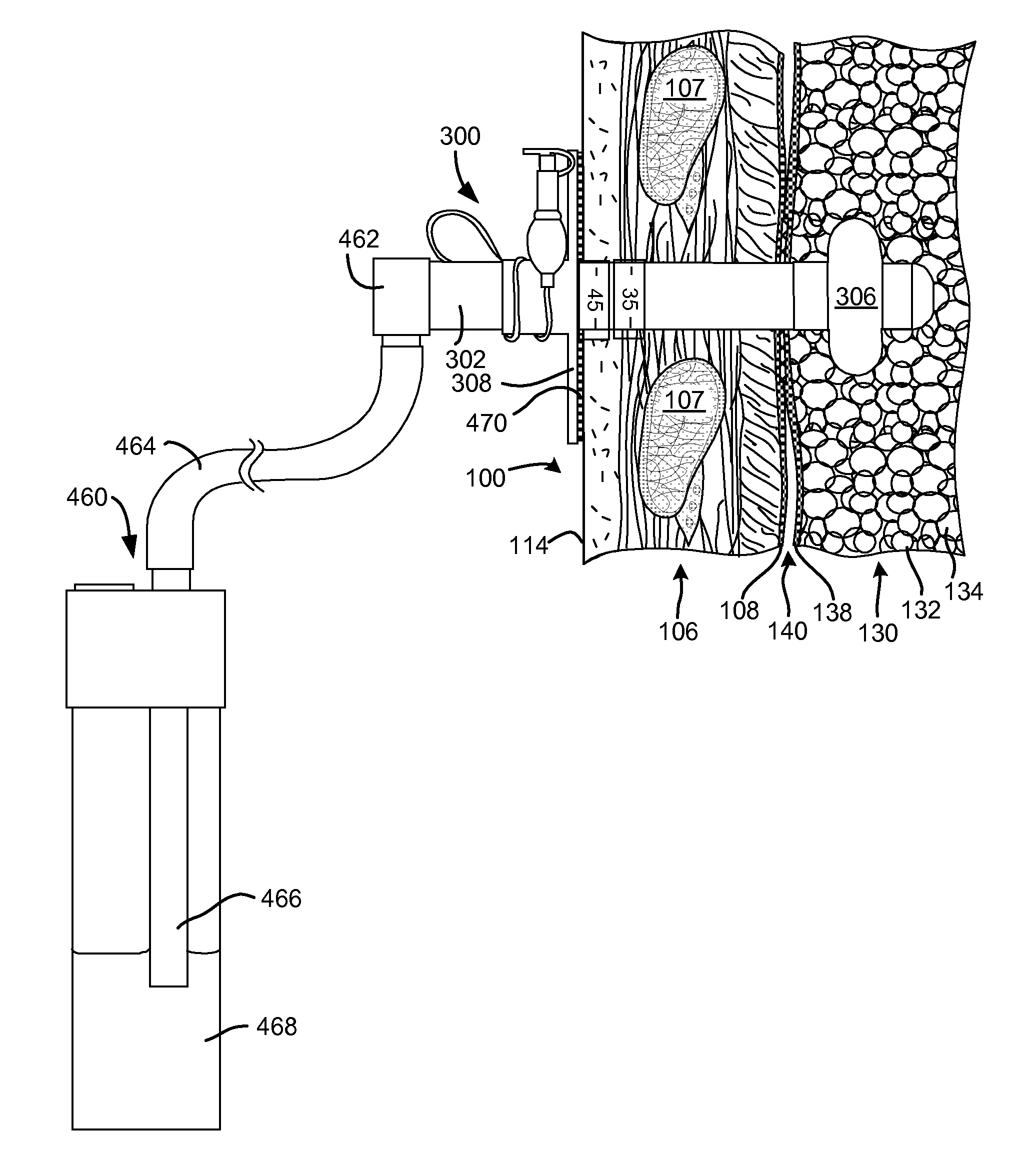
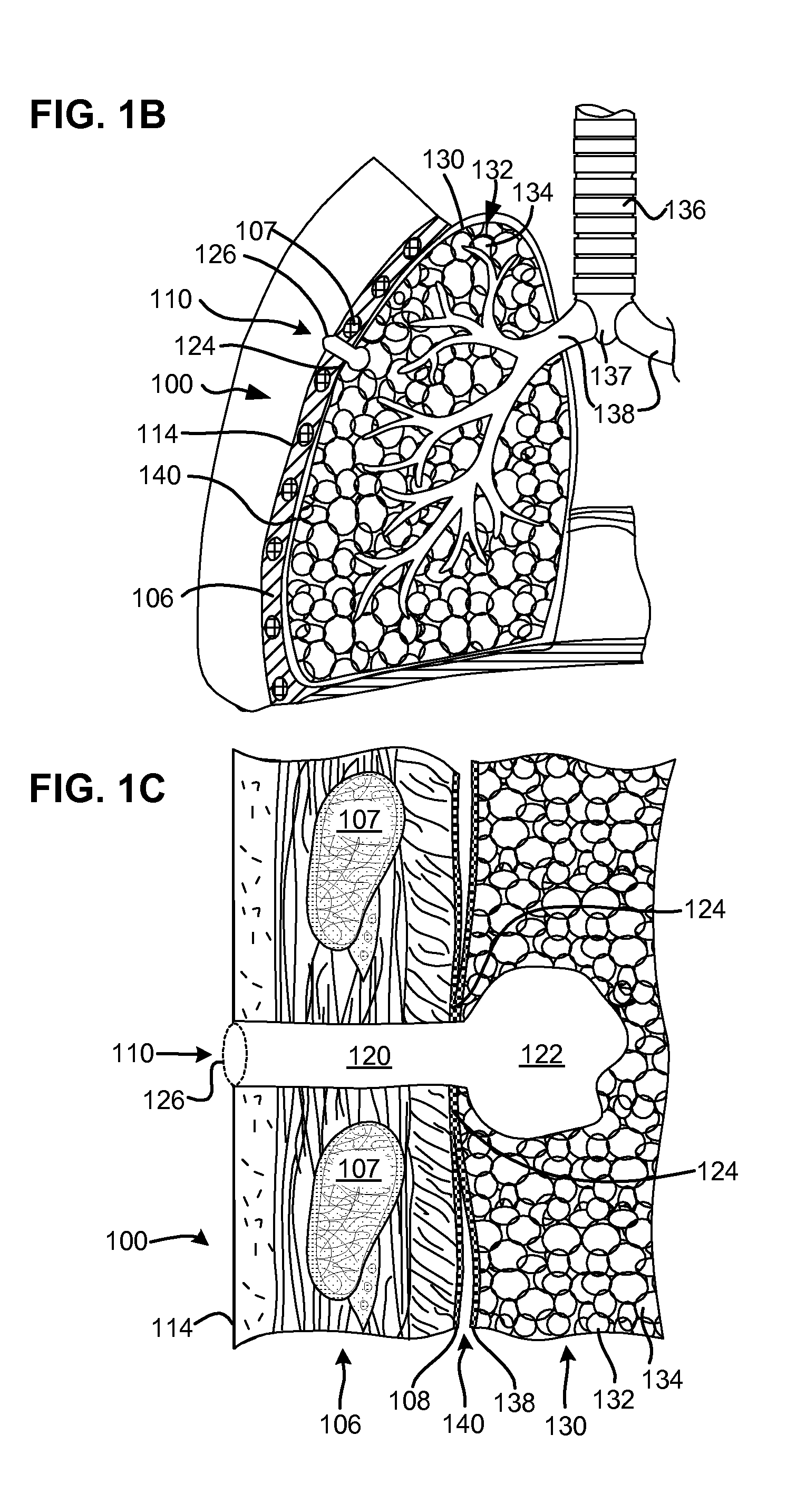
Percutaneous single-phase surgical procedure for creating a pneumostoma to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS20090209909A1Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesSuture equipmentsStapling toolsPleural cavityPleural part
A percutaneous single-phase surgical procedure is disclosed for creating a pneumostoma to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. A pneumostomy instrument is introduced percutaneously through the thoracic wall, parietal membrane, visceral membrane and into the parenchymal tissue of the lung. The pneumostomy instrument crosses the pleural cavity between the parietal membrane and visceral membrane there being no pleurodesis between the membranes prior to passage of the pneumostomy instrument. A pneumoplasty device at the distal end of the pneumostomy instrument displaces and engages the parenchymal tissue of the lung and the pneumostomy instrument is used to secure the lung and visceral membrane in contact with the parietal membrane and chest wall. The pneumostomy instrument is left in place while a pneumostoma tract heals and pleurodesis occurs between the pleural membranes surrounding the pneumostomy instrument.
Owner:PORTAERO
Methods and apparatus for transesophageal microaccess surgery
InactiveUS20100036197A1Avoid pollutionPrecise positioningBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesNODALOesophageal tube
The current invention describes methods of transesophageal access to the neck and thorax to perform surgical interventions on structures outside the esophagus in both the cervical and the thoracic cavity. It describes a liner device made of a complete or partial tubular structure, or a flat plate, the liner having means to facilitate creation of a side opening, which may include a valve. The liner with its side opening form a port structure inside the esophageal lumen. The port structure allows elongated surgical devices to pass through a perforation across the full thickness of the esophageal wall to outside location, in a controlled way. The elongated surgical devices can be diagnostic scopes, therapeutic scopes, manual elongated surgical devices, robotic arms or the like. After being deployed outside the esophagus, the surgical devices can access structures outside the esophagus, in the neck and thorax in 360 degrees of freedom around the esophageal circumference. These structures can be bony, cartilaginous, spinal, vascular, soft tissue, deep tissues, lymph nodal, cardiac, pulmonary, tracheal, nervous, muscular or diaphragmatic, skin and subcutaneous tissues of the neck, skin and subcutaneous tissues of the anterior chest wall, skin and subcutaneous tissues of the skin of the back, and skin and layers of the breast.
Owner:MICROACCESS
Radiation therapy system for treating breasts and extremities
InactiveUS7526066B2Maximize separationWeaken energyPatient positioning for diagnosticsX-ray tube vessels/containerAnatomical structuresCritical structure
Owner:ORBITAL THERAPY
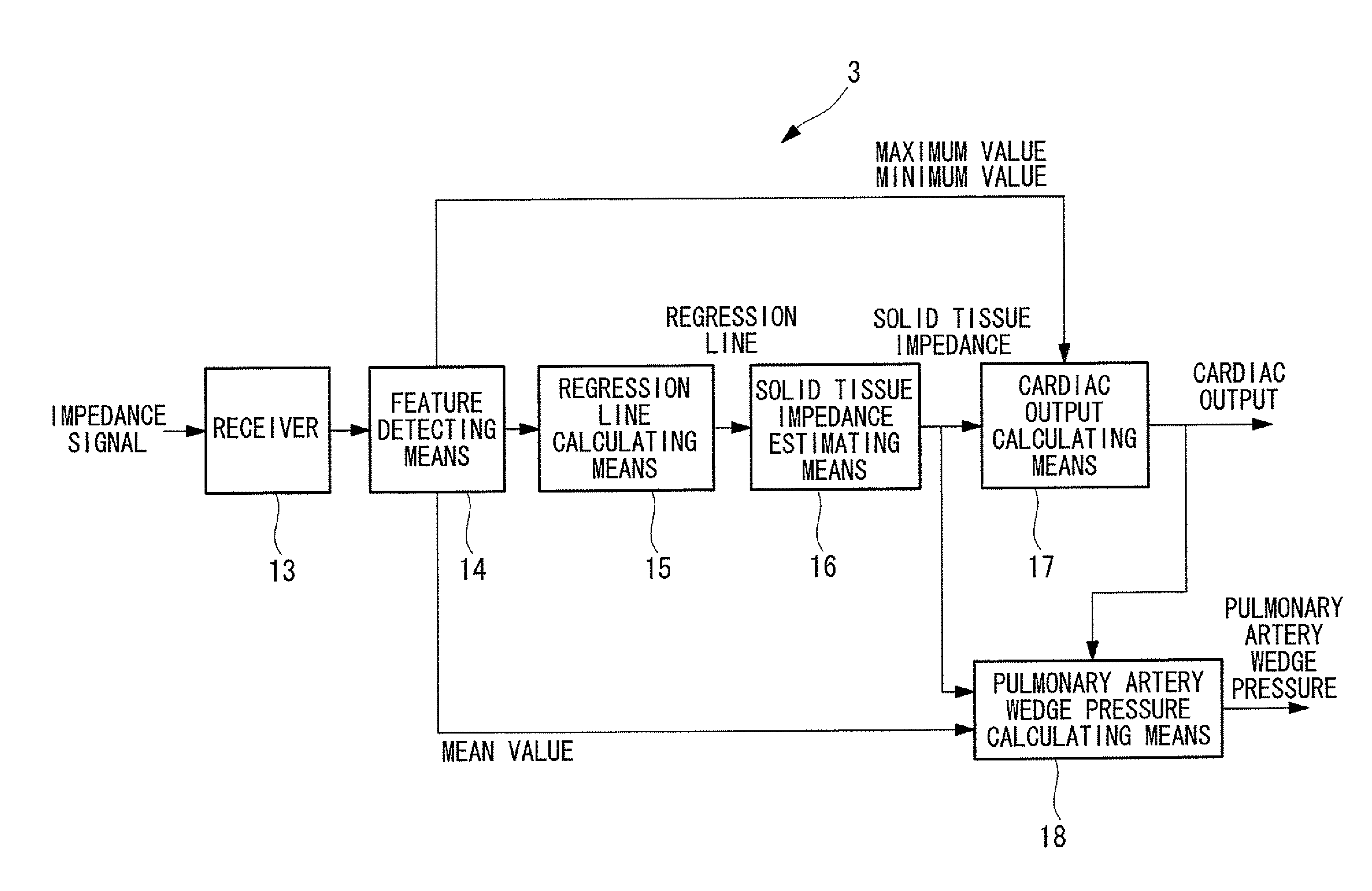
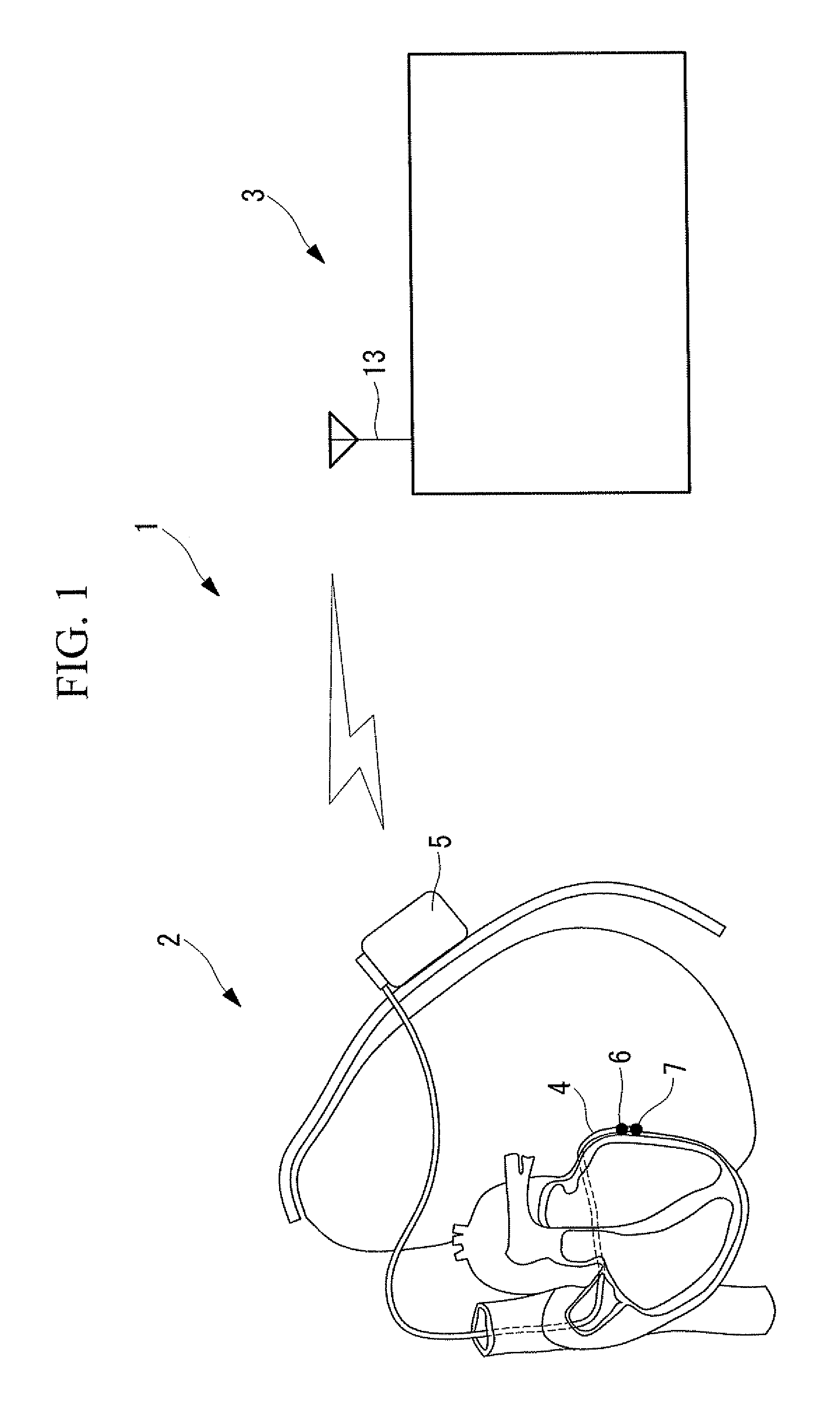
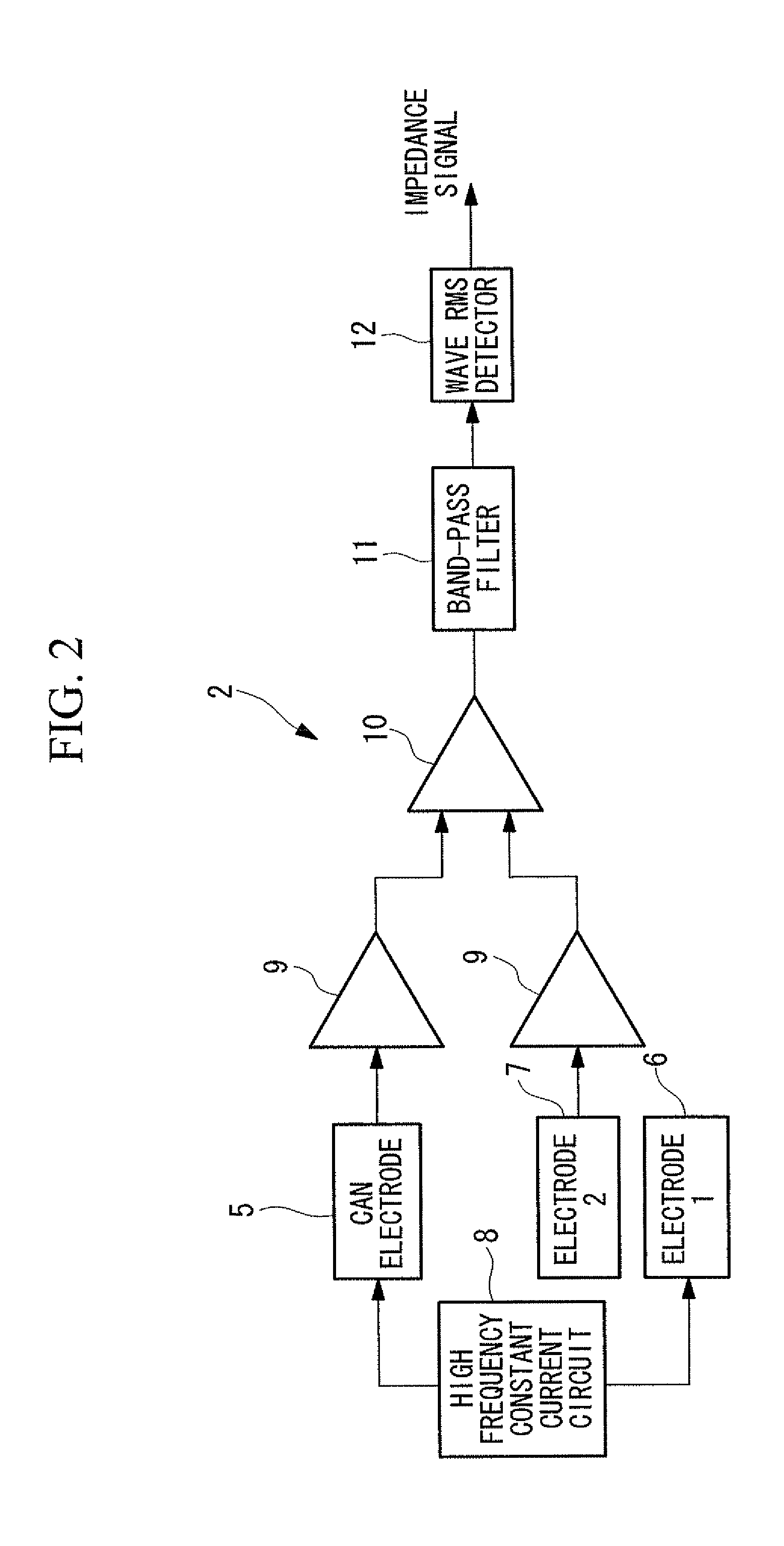
Solid tissue impedance estimating method, cardiac output calculating method, pulmonary artery wedge pressure calculating method, cardiac output monitoring device, cardiac output monitoring system, pulmonary artery wedge pressure monitoring device, and pulmonary artery wedge pressure monitoring system
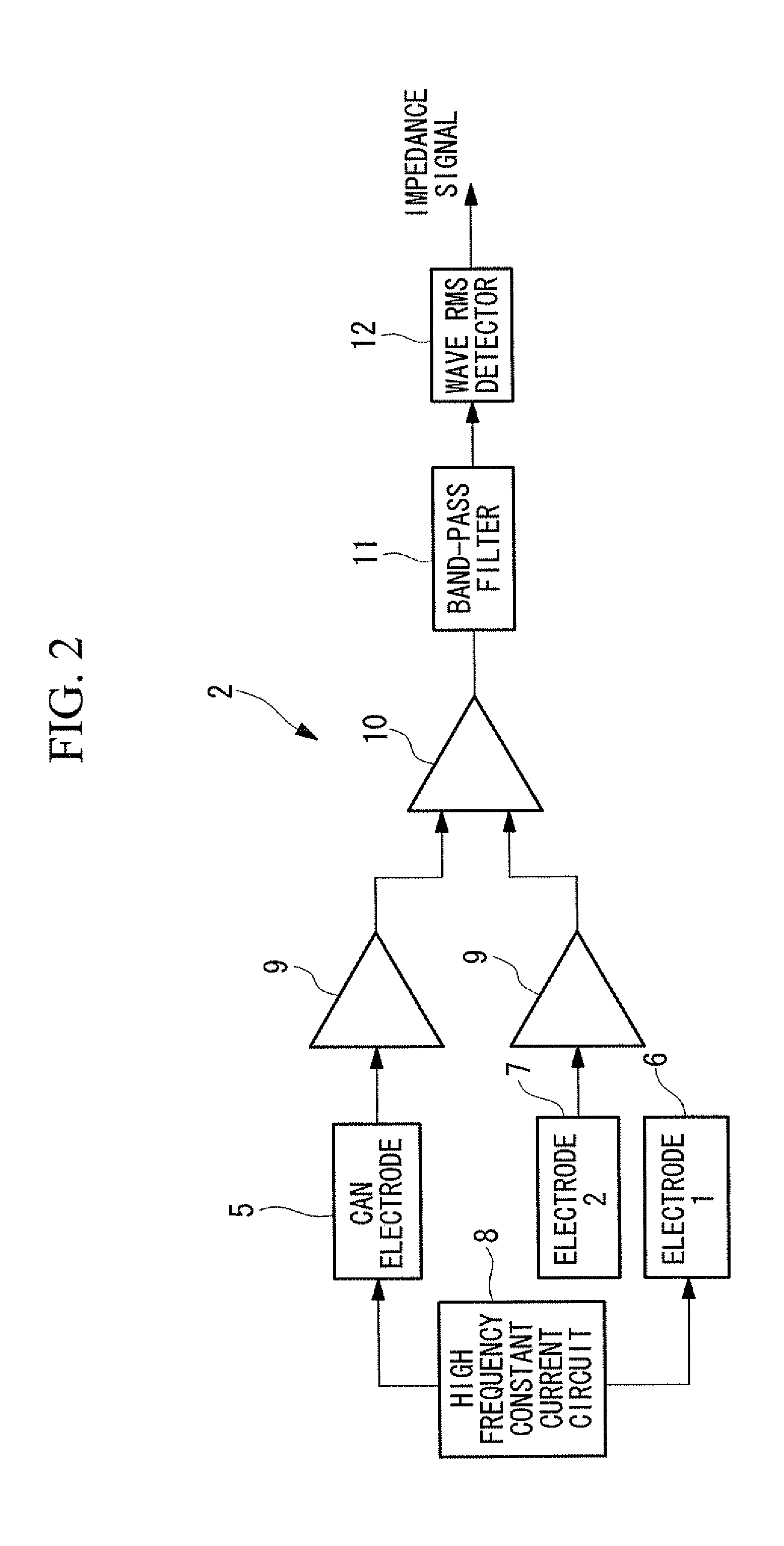
A practical method for estimating cardiac output and pulmonary artery wedge pressure with good accuracy is provided. The present invention provides a method for estimating the impedance arising from solid tissue by determining the impedance at the intersection between the line of identity and the extrapolated regression line, where the regression line is obtained by linearly regressing the maximum value to the minimum value of the impedance signal of each of multiple data sets, where each data set contains the maximum value and the minimum value of the impedance signal during one cardiac cycle, where impedance signal is obtained between a can electrode implanted in the left thoracic wall and an electrode inserted into the coronary vein, over a specific period of time following the infusion of hypertonic saline into the pulmonary circulation.
Owner:NAT CEREBRAL & CARDIOVASCULAR CENT +1
Micropower impact-type biological radar front end
InactiveCN103027670AStrong anti-motion interference abilityHigh motion interference suppression abilityRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsPalpitationsMicropower
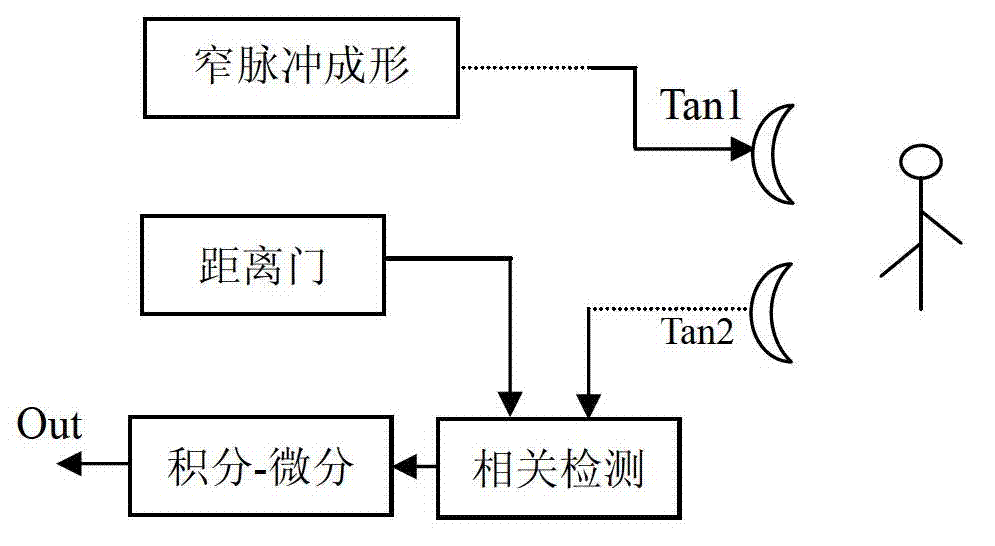
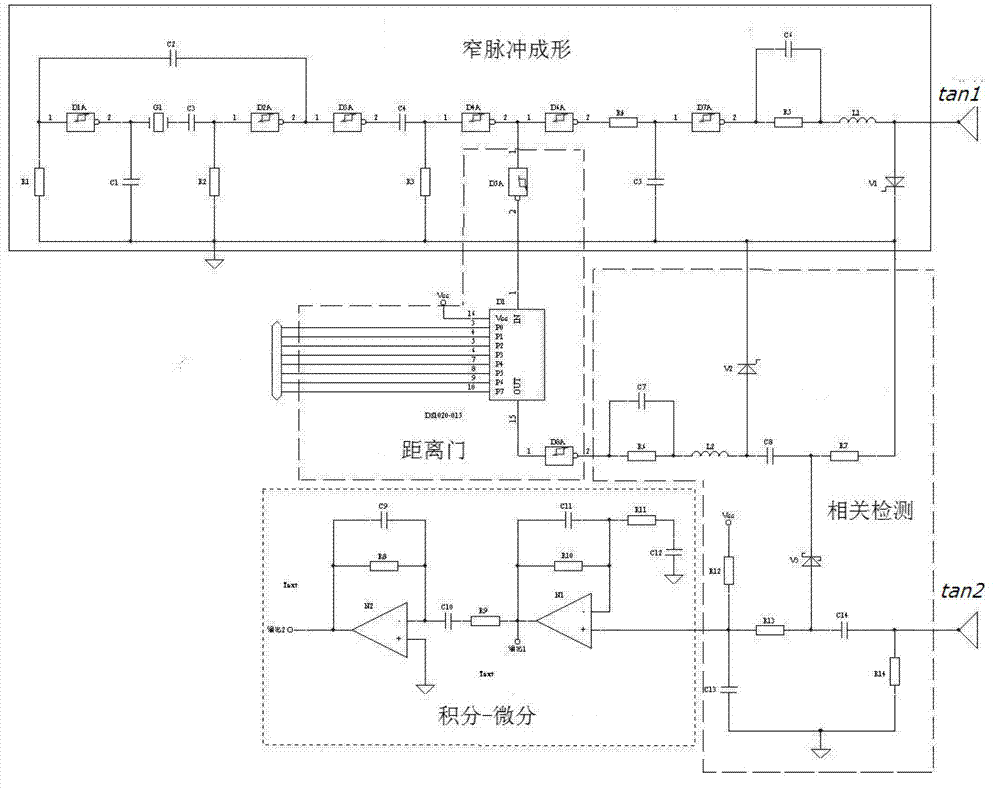
The invention discloses a micropower impact-type biological radar front end which comprises a narrow pulse forming module used for generating a narrow pulse sequence, a correlation detection module, a distance gate module and an integral-differential module, wherein the correlation detection module is used for demodulating narrow pulse echoes modulated by thoracic wall micromotion caused by breathing and palpitation of a human body; the distance gate module is used for scanning the distance in a detection region; and the integral-differential module is used for extracting breathing and palpitation micromotion information of the human body. By virtue of being externally connected with transmitting and receiving antennae, a direct current power supply and a simple amplifying circuit, the micropower impact-type biological radar front end can be used for performing nonrestraint and noncontact respiratory rate and heart rate monitoring on the human body, can be widely applied to monitoring physiologic signals of clinical special patients with empyrosis and infections, household elders and other patients with chronic diseases.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for simulating elastic curve of human body thoracic cage when pressing heart outside pulmones anabiosis thorax
InactiveCN101303812AImprove training effectStable structureEducational modelsHuman bodyDamping factor
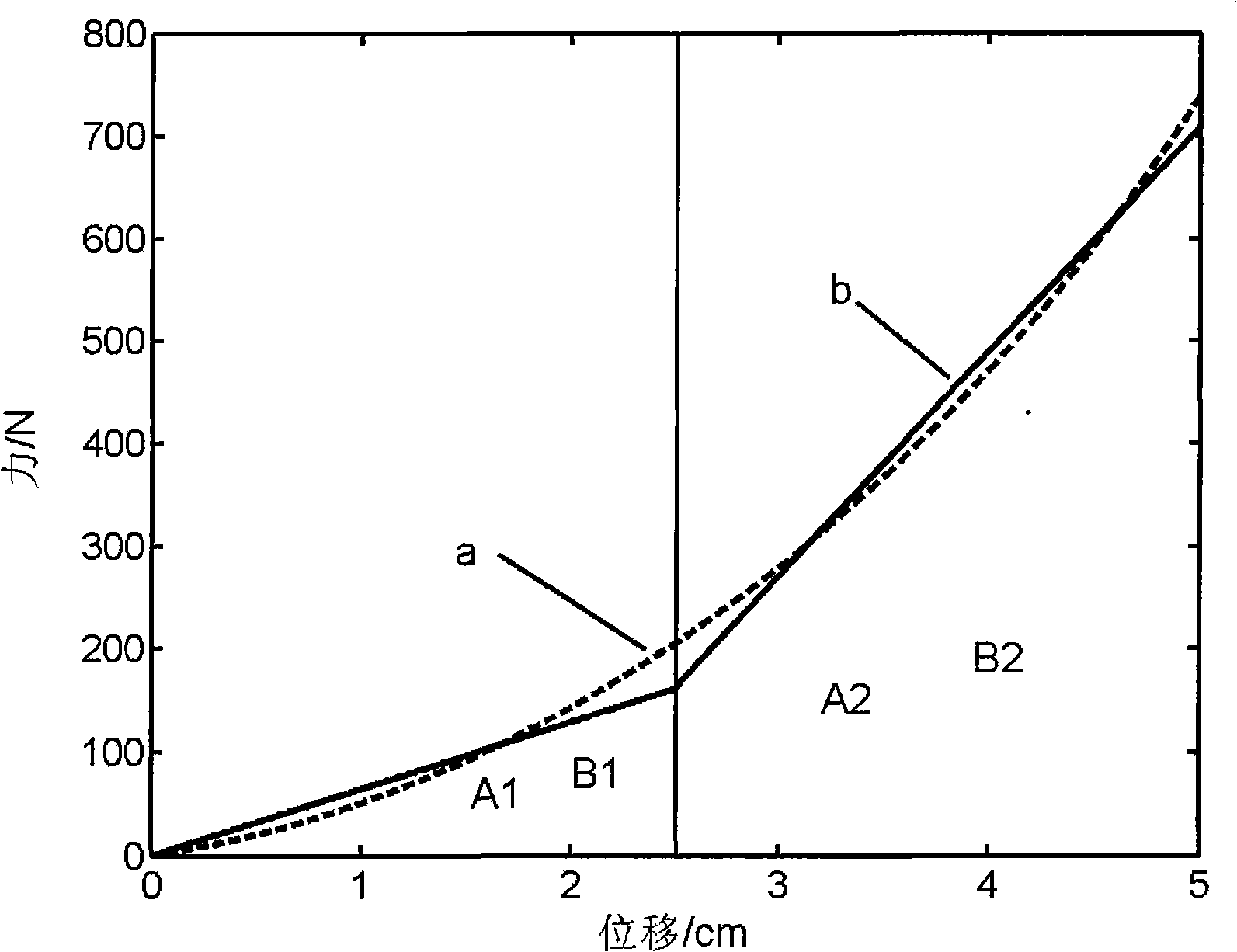
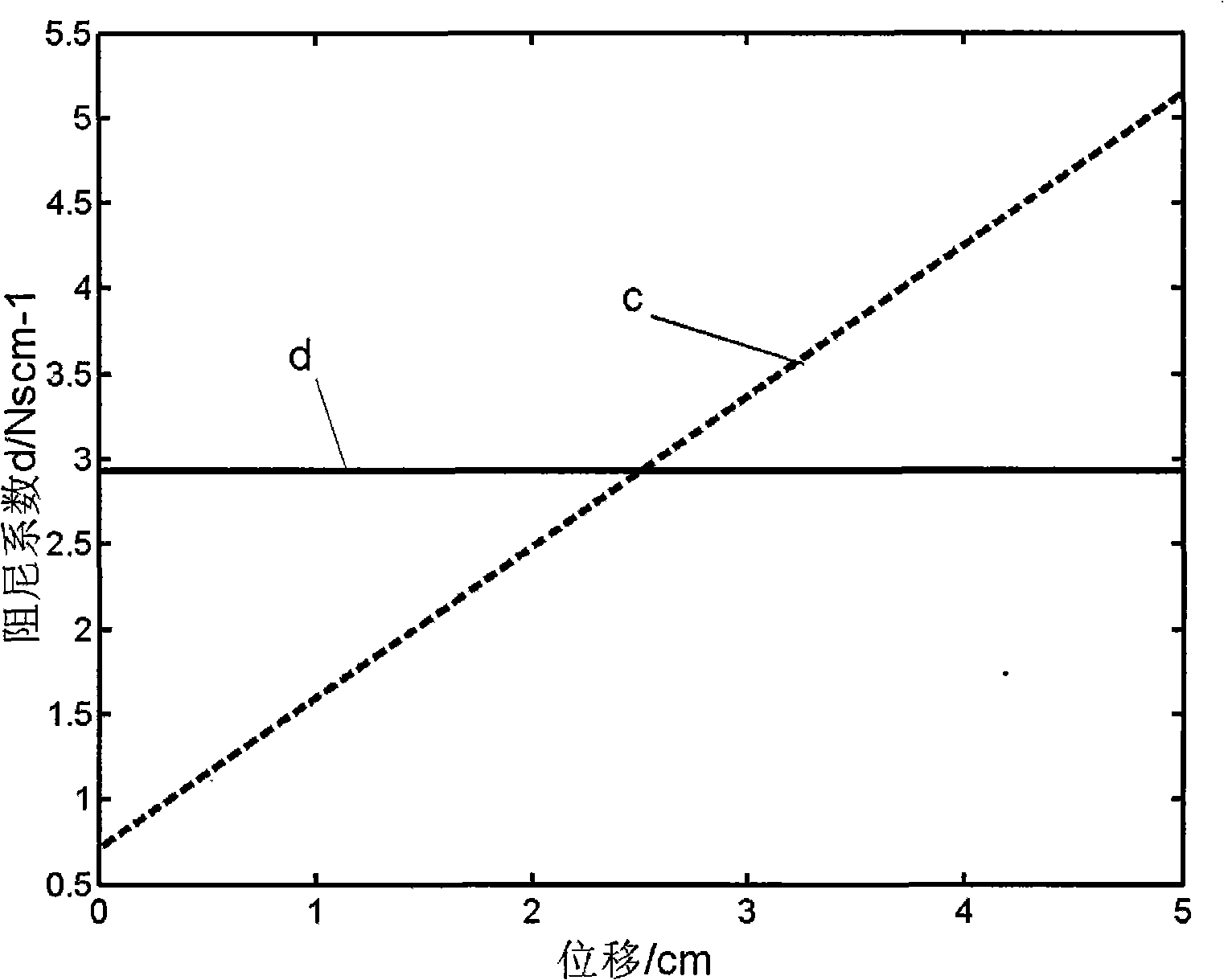
The invention discloses a simulation method of an elastic curve in cardiopulmonary resuscitation external chest compression, which has the main content that: 1. adopting an unequal deformation juxtaposed linear compression spring group to simulate the non-linear elastic force of the thorax; 2. adopting a damper (a buffer, a reducer) to simulate the damping force of the thorax, and the average value (2.93Ns / cm) of the damping coefficient of the damper between 0 to 5cm being equal; 3. respectively installing and fixing the damper and two ends of the spring group on the front and back walls of a simulation thorax which simulate the thoracic walls of the human body to form a thoracic simulating mechanism. The method adopts the combination of the spring and buffing equipment among the similar methods for the first time, thus the hysteretic curve in the process of pressing and releasing is in line with the typical hysteretic curve of the thorax of the human body in published literatures, therefore pressing hand feeling which is closer to a real human body can be acquired in the simulating mechanism and the effects of practicing cardiopulmonary resuscitation external chest compression techniques on the mechanism can be improved.
Owner:SANITARY EQUIP INST ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI PLA
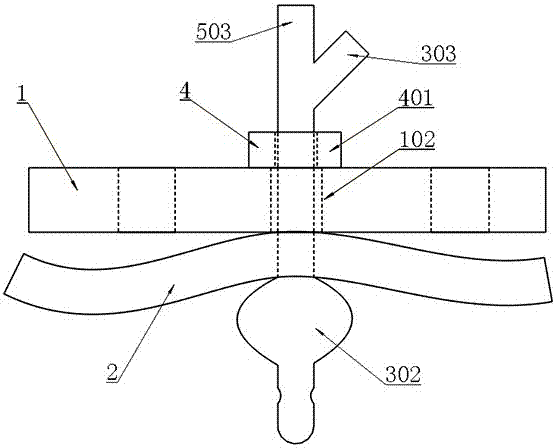
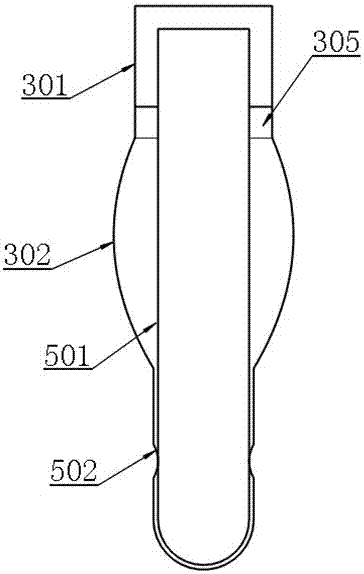
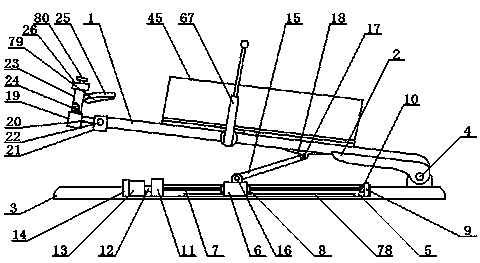
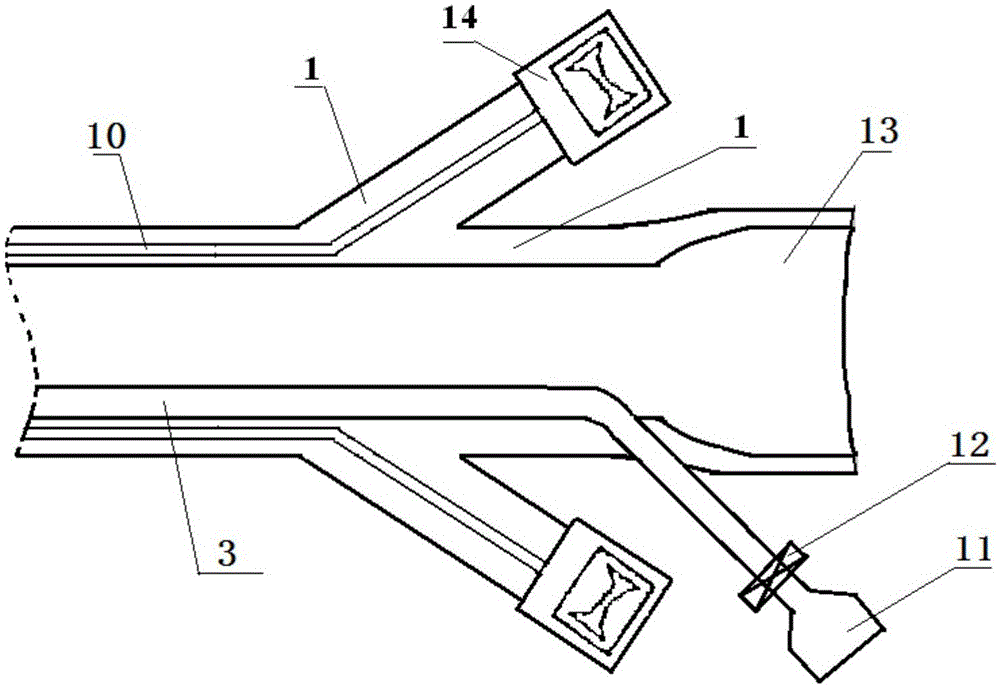
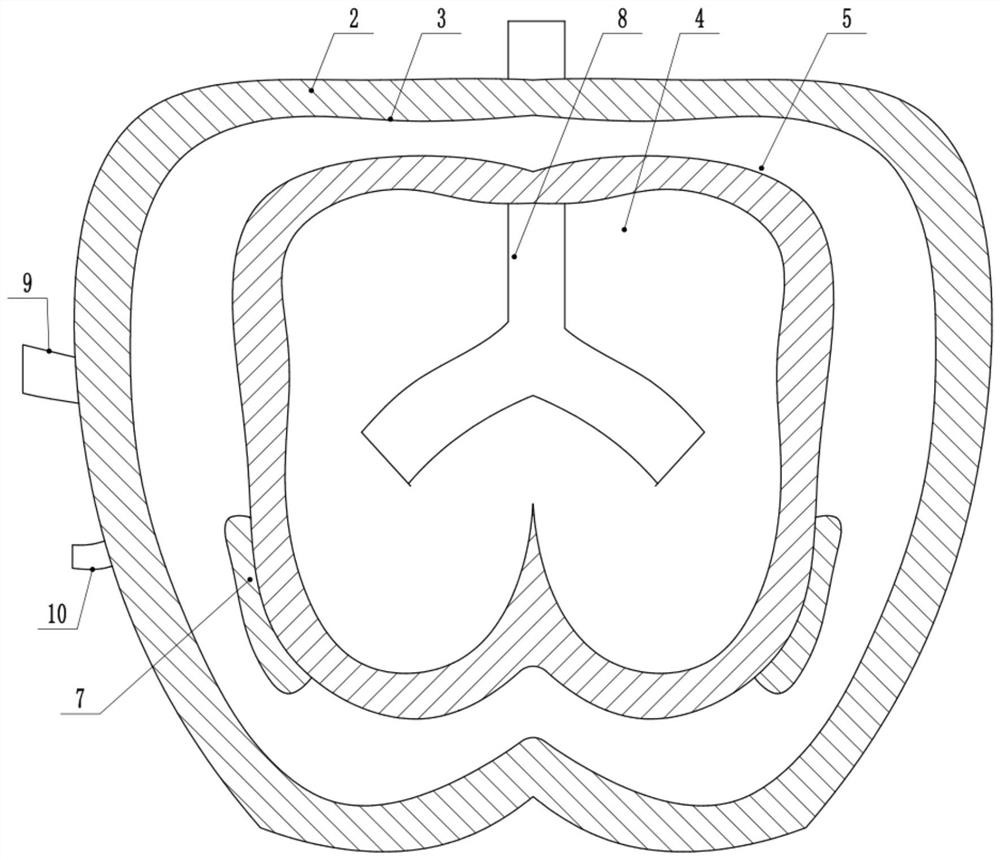
Locking compression thoracic wall external fixation device
ActiveCN107510498AImprove stabilitySimple structureIntravenous devicesSuction devicesThoracic wallActive fixation
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical devices for treating rib fracture, and in particular relates to a locking compression thoracic wall external fixation device. The locking compression thoracic wall external fixation device comprises an external fixation plate, and a penetrating expansion unit which is arranged on the external fixation plate, penetrates through the thoracic wall, and outwards presses the softened and collapsed thoracic wall to the external fixation plate in an expansion and outwards traction jacking manner for realizing external fixation of the thoracic wall. The invention aims at providing the locking compression thoracic wall external fixation device, after an expansion ball is inserted into the thoracic wall, the softened and collapsed thoracic wall is outwards pulled and jacked up and outwards pressed on the external fixation plate, and thus the purpose of active fixation is achieved. The locking compression thoracic wall external fixation device has the advantages that the structure is simple and effective, the thoracic wall fixation stability is good, the fracture end sets and realizes alignment, the fixation effect is good, and the surgical trauma is small.
Owner:宋斌
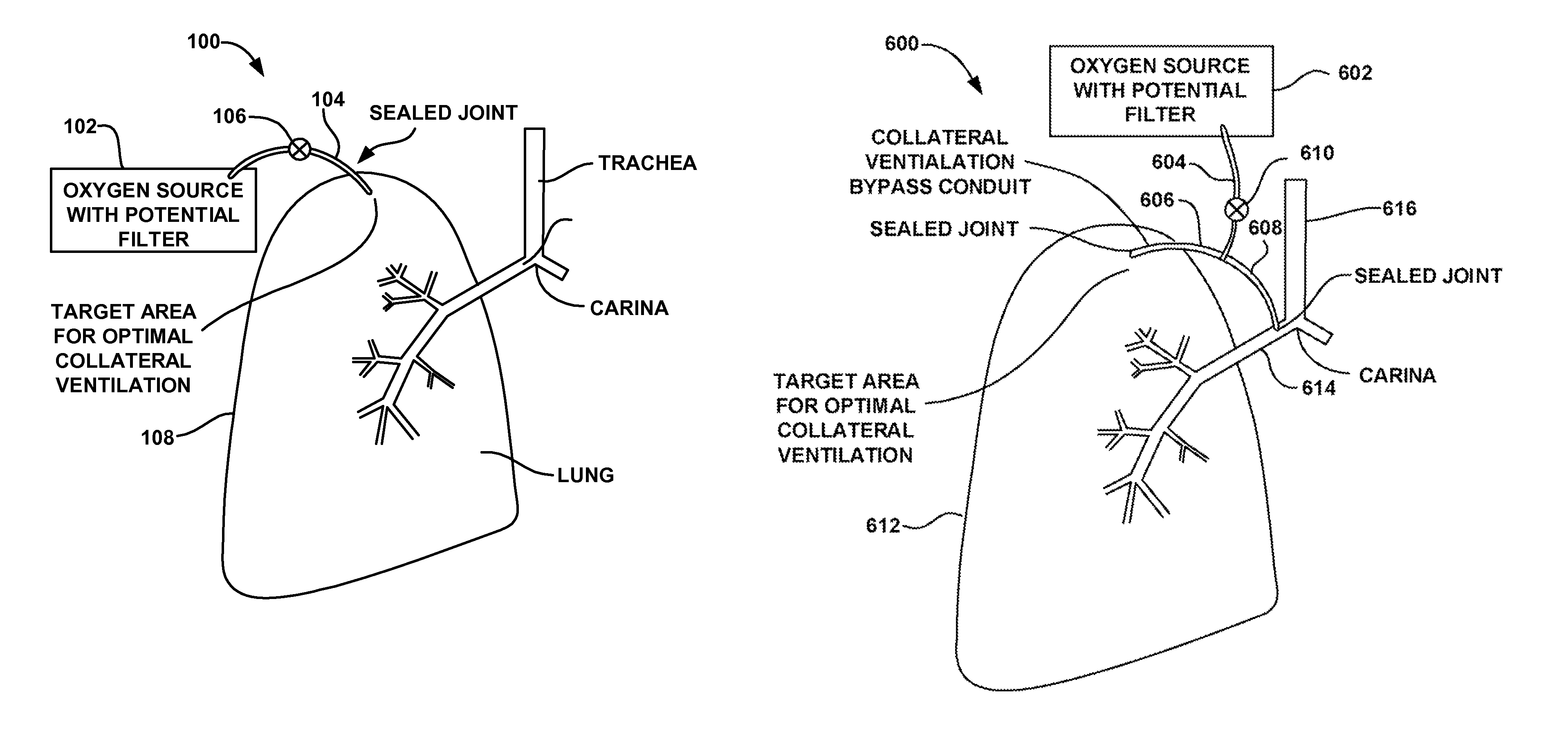
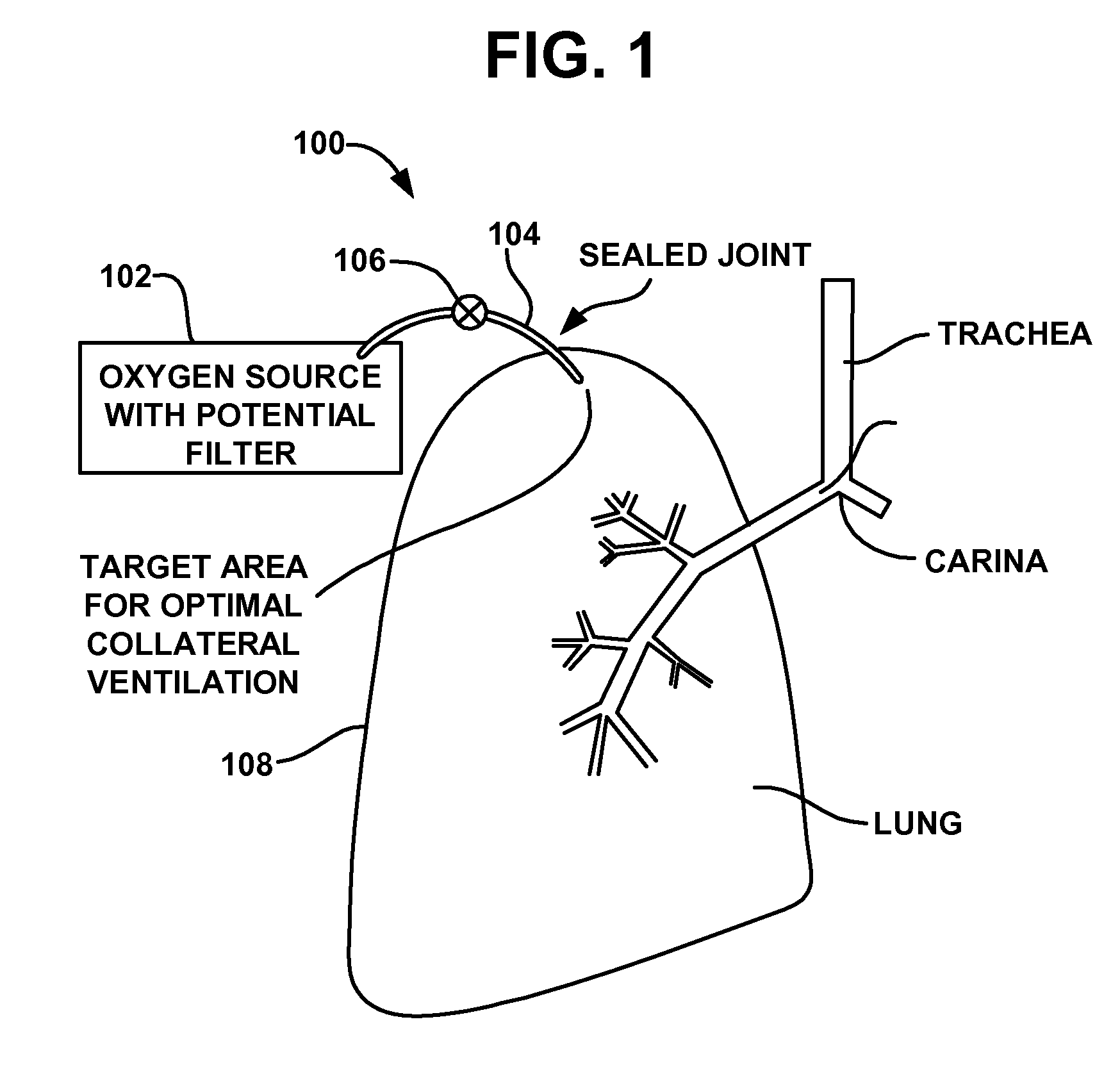
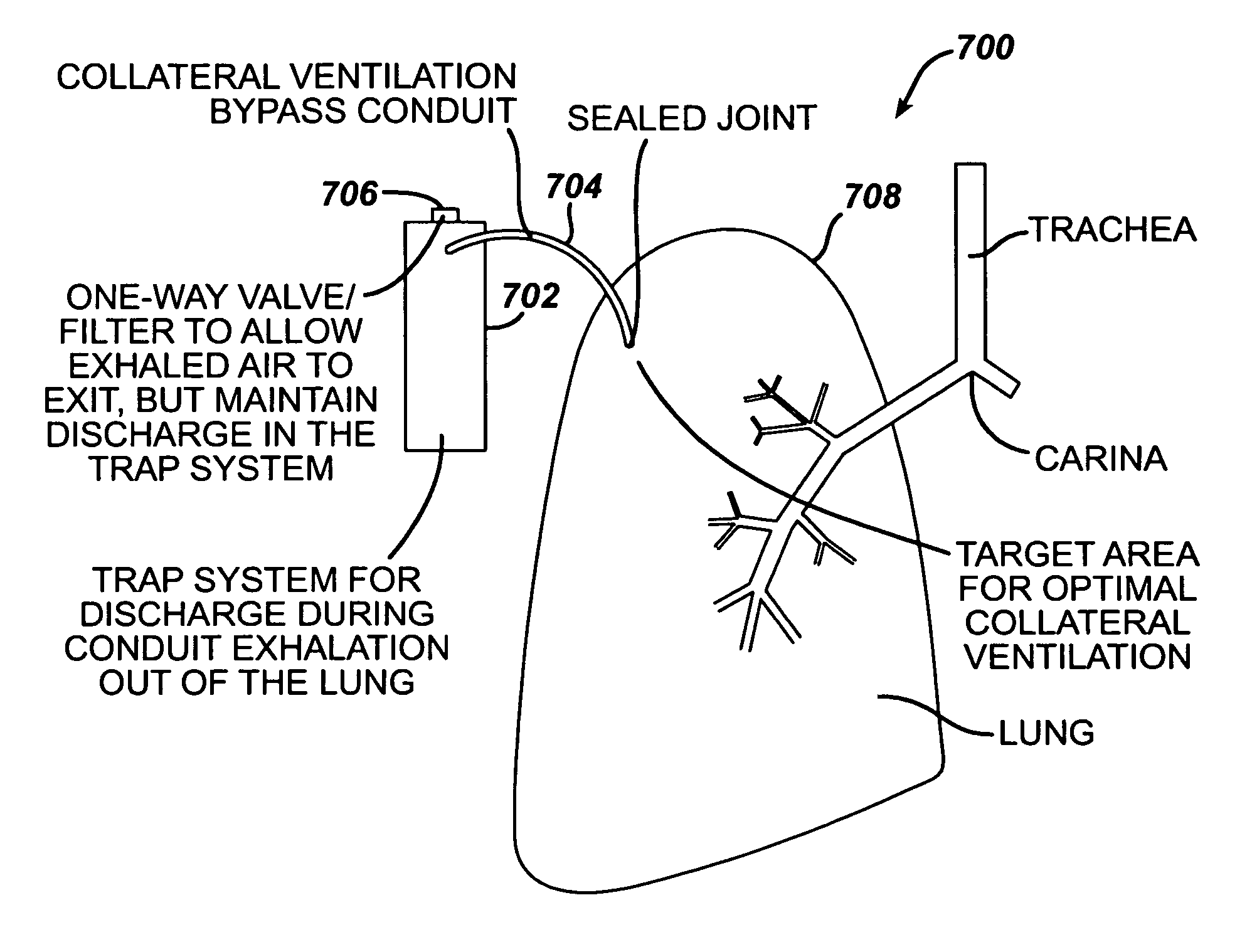
Device and method for creating a localized pleurodesis and treating a lung through the localized pleurodesis
InactiveUS7828789B2Speed up the flowPromote absorptionRespiratorsDiagnosticsPleural cavityThoracic wall
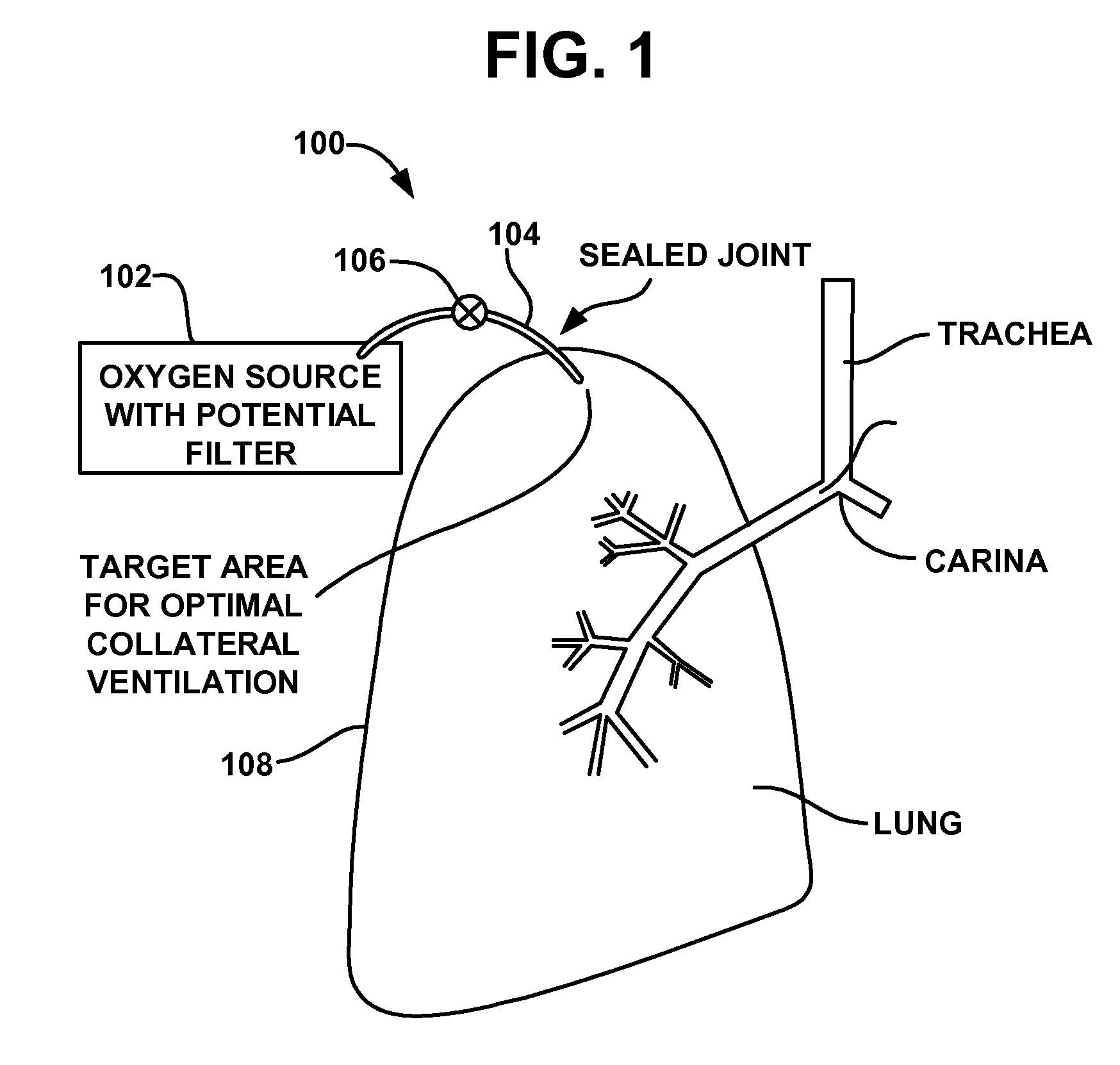
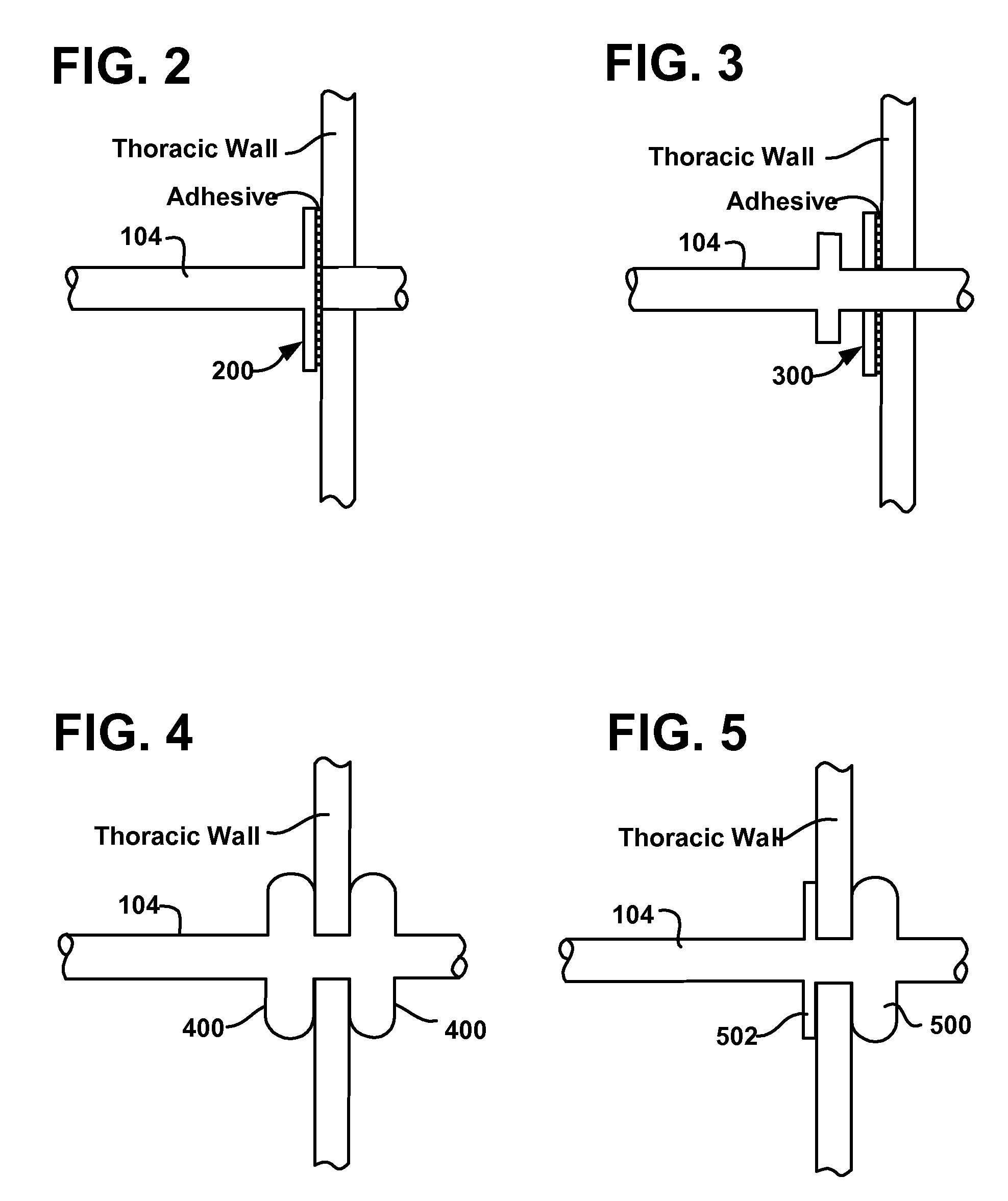
The invention provides methods and devices for creating a localized pleurodesis between the thoracic wall and the lung such that a ventilation bypass conduit may be introduced into the lung through the thoracic wall and visceral membrane without causing a pneumothorax. A medical device such as a catheter is used to enter the pleural cavity and deliver a pleurodesis agent to a localized area between the visceral and parietal membranes.
Owner:PORTAERO
Radiotherapy board and couch
ActiveUS20170028218A1Operating tablesPatient positioning for diagnosticsRadiotherapy breastPath length
Provided herein is a radiotherapy breast board and couch for use in radiotherapy treatment of breast cancer patients, which are particularly suitable for treating the patient to the breast / thoracic wall and regional lymph nodes in prone position. The radiotherapy breast board and couch comprises a caudal part for supporting the lower body of the patient and a cranial part with supports for the head and non-treated parts of the upper body. The board or couch further provides an opening allowing for the affected breast of the patient to pass through and an opening allowing for the regional lymph nodes to pass trough as said patient lies in a prone position on said board or couch. This opening allows the use of a variety of beam directions to reach the affected region via short radiological path lengths without passing elements of the breast board or couch.
Owner:UNIV GENT
Post thoracic surgery protection and fixing device
InactiveCN107714251AAvoid painAvoid fixationVibration massageCatheterThoracic structureChest Wall Pain
A post thoracic surgery protection and fixing device belongs to the technical field of medical apparatuses. A technical scheme is that the post thoracic surgery protection and fixing device comprisesa plate body. A plate body support is arranged on the lower side of the plate body; the lower side of the plate body support is provided with a fixing seat; the fixing seat is assembled to the plate body support via a supporting rotating shaft; a supporting chute is formed in the upper side of the fixing seat; a movable slide block is disposed in the supporting chute; and a supporting driving screw rod is arranged on the left side of the movable slide block. Simple operation and less time and efforts are required for post thoracic surgery binding up; new contusions due to direct contact to a wound can be avoided, so the occlusion thoracic cavity can be protected; chest wall pains can be avoided and a drainage tube can be fixed; postoperative rehabilitation and exercise can be facilitated;and work difficulty can be reduced for medical workers.
Owner:徐启良
Method for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS7811274B2Speed up the flowPromote absorptionRespiratorsSurgeryObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesThoracic cavity
A ventilation bypass system which alleviates symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by allowing air to exit the lung of a patient through the thoracic wall bypassing the natural airways. A pleurodesis is formed between the visceral and parietal membranes surrounding a lung and an opening is made through the thoracic wall into the lung via the pleurodesis. The ventilation bypass system includes a conduit placed through the opening in the thoracic wall into the lung, a flange for securing the conduit to the thoracic wall and preventing over-insertion of the conduit, and a flow control device for controlling flow of material out of the lung.
Owner:PORTAERO
Implantable device and method for creating a localized pleurodesis and treating a lung through the localized pleurodesis
InactiveUS20080188824A1Speed up the flowPromote absorptionRespiratorsSurgeryPleural cavityThoracic wall
The invention provides methods and devices for creating a localized pleurodesis between the thoracic wall and the lung such that a ventilation bypass conduit may be introduced into the lung through the thoracic wall and visceral membrane without causing a pneumothorax. A catheter or implantable device delivers the pleurodesis agent to the pleural cavity.
Owner:PORTAERO
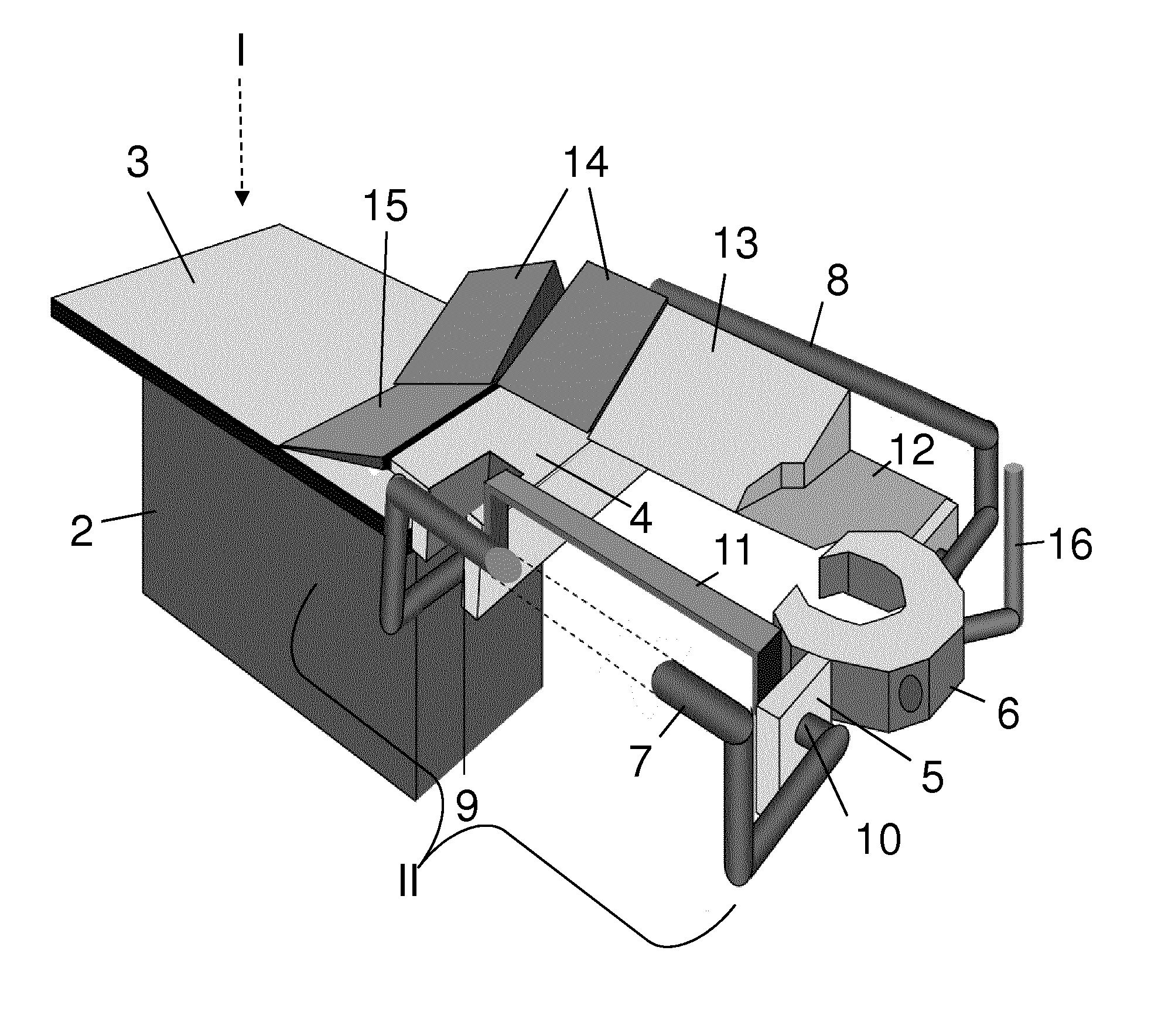
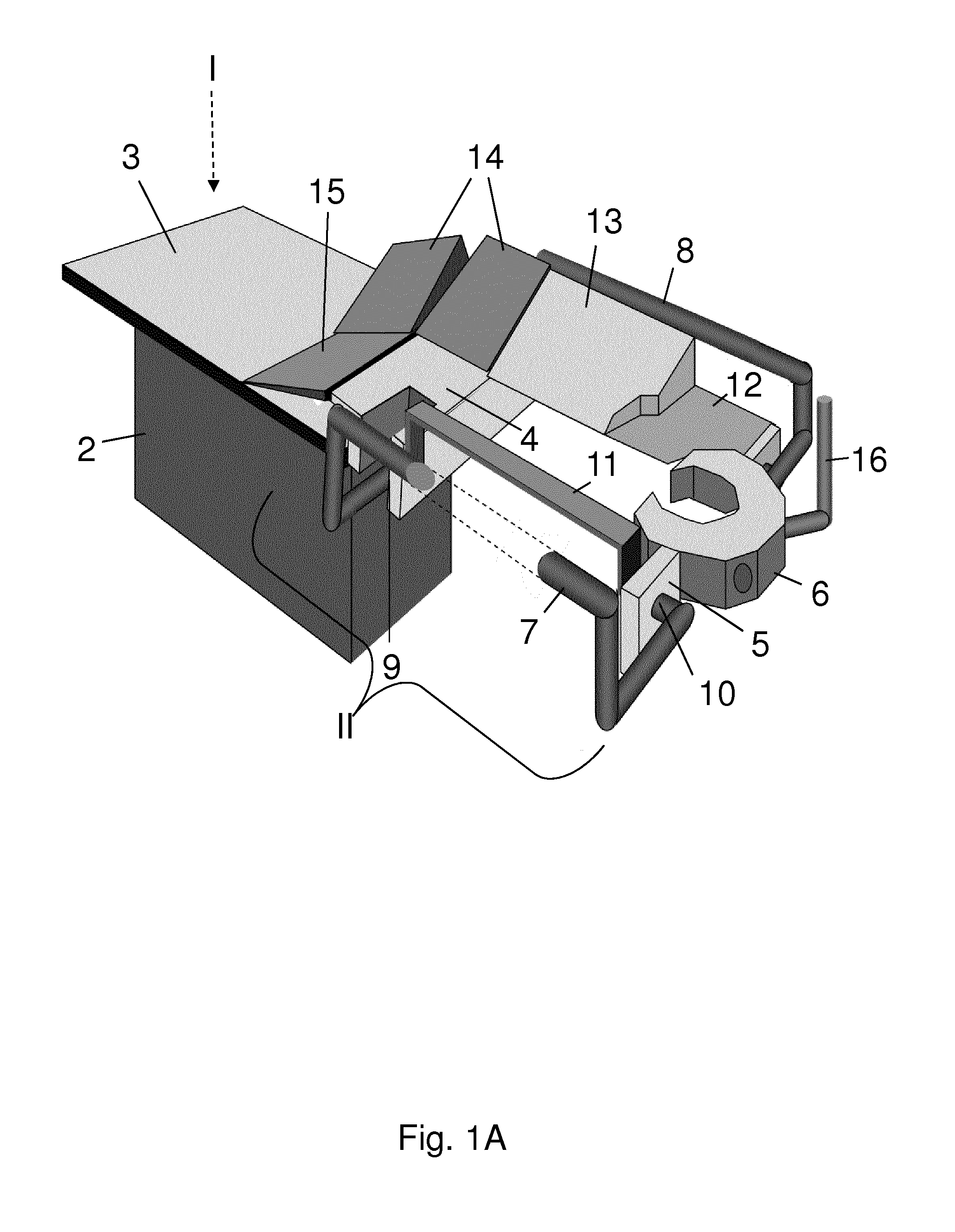
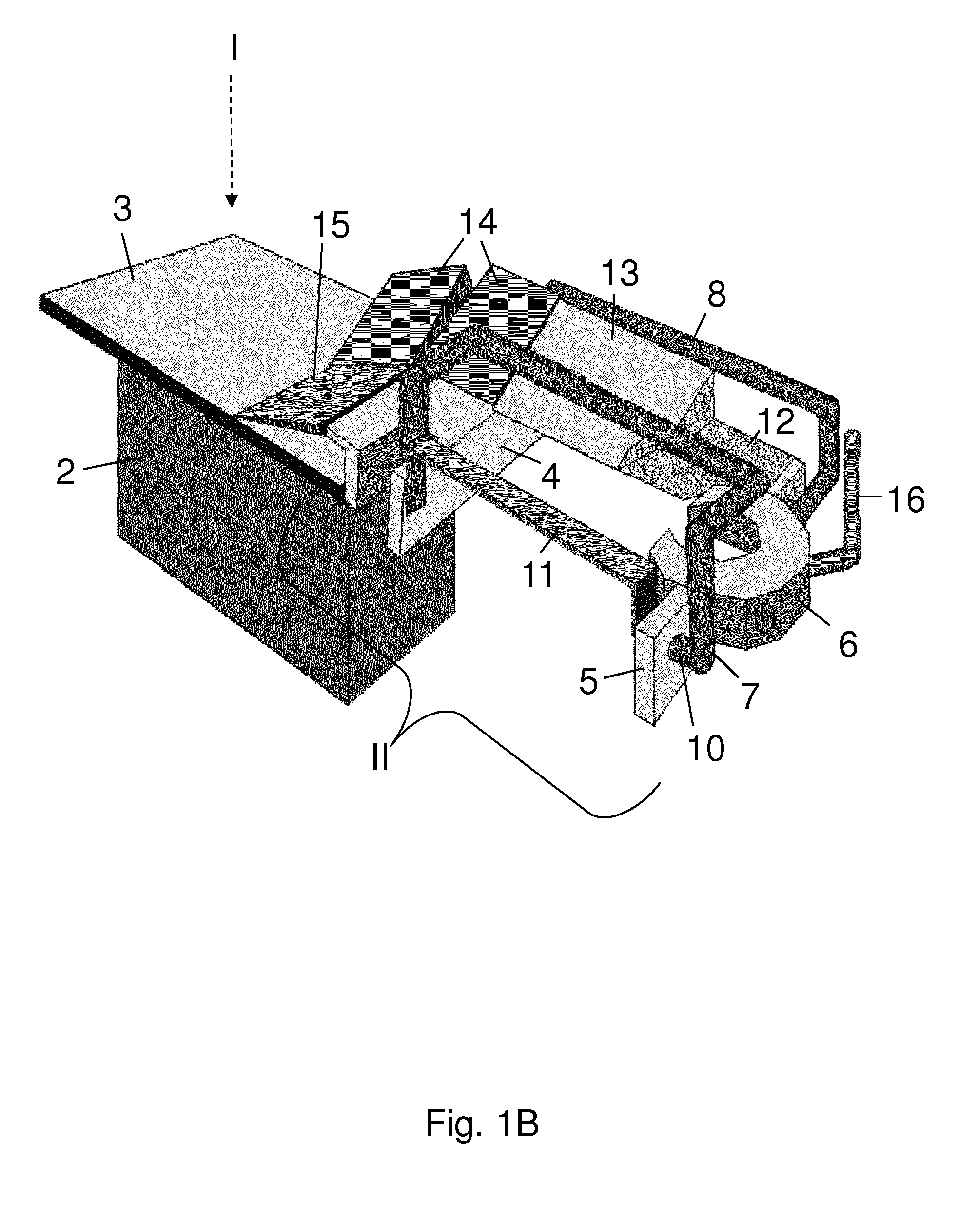
Thorax mounted stabilization platform
A thorax mounted stabilizing platform for a surgical device, such as a tissue stabilizer, can be inserted through a minimally invasive incision and affixed to the thoracic wall to stabilize the surgical device. The stabilizing platform includes a rod that is introduced into a percutaneous opening in the patient. An internal and / or an external fixing device is deployed to attach the rod to the patient. One or more surgical devices may be mounted to the distal or internal end of the rod. An adjustment knob or other actuation mechanism is located at the proximal or external end of the rod to actuate or manipulate the surgical device(s) attached to the distal end.
Owner:ESTECH ENDOSCOPIC TECH
Solid tissue impedance estimating method, cardiac output calculating method, pulmonary artery wedge pressure calculating method, cardiac output monitoring device, cardiac output monitoring system, pulmonary artery wedge pressure monitoring device, and pulmonary artery wedge pressure monitoring system
A practical method for estimating cardiac output and pulmonary artery wedge pressure with good accuracy is provided. A method is provided for estimating the impedance arising from solid tissue by determining the impedance at the intersection between the line of identity and the extrapolated regression line, where the regression line is obtained by linearly regressing the maximum value to the minimum value of the impedance signal of each of multiple data sets, where each data set contains the maximum value and the minimum value of the impedance signal during one cardiac cycle, where impedance signal is obtained between a can electrode implanted in the left thoracic wall and an electrode inserted into the coronary vein, over a specific period of time following the infusion of hypertonic saline into the pulmonary circulation.
Owner:NAT CEREBRAL & CARDIOVASCULAR CENT +1
Device and method for creating a localized pleurodesis and treating a lung through the localized pleurodesis
InactiveUS20080188809A1Increase expiratory flowSpeed up the flowRespiratorsDiagnosticsPleural cavityThoracic wall
The invention provides methods and devices for creating a localized pleurodesis between the thoracic wall and the lung such that a ventilation bypass conduit may be introduced into the lung through the thoracic wall and visceral membrane without causing a pneumothorax. A medical device such as a catheter is used to enter the pleural cavity and deliver a pleurodesis agent to a localized area between the visceral and parietal membranes.
Owner:PORTAERO
Double-balloon drainage tube for abdomen or chest
InactiveCN105013066APromote recoveryAvoid increased risk of infectionBalloon catheterThoracic wallThoracic structure
The present invention relates to a double-balloon drainage tube for an abdomen or chest. The double-balloon drainage tube comprises a tube body, a flush tube and two balloons. The tube body is a hollow tube, a hollow part is a drainage cavity, and the head of the tube body is provided with a drainage port. The flush tube is arranged in the tube body drainage cavity and is attached to the inner wall of the tube body. The upper part of the flush tube is provided with a plurality of holes. Two balloons are symmetrically arranged at two sides of the tube body close to the head part. The tube body between the two balloons is symmetrically provided with a plurality of drainage holes. Balloon cavities communicate with a balloon water injection or gas injection tube cavity in the tube body wall. After the drainage tube is placed into the abdomen or chest, water or gas can be injected, then the two balloons at the head end uniformly swell at the same time, the swelled balloons are clamped at the inner side of the abdomen or chest, and the drainage tube can be continuously fixed into the abdomen or chest and does not come off. Through the effects of adsorption, vacuum and siphoning, the fluid or blood in the abdomen or chest can be drained out of a body through the drainage port and the drainage holes on the tube body between the two balloons.
Owner:王亮
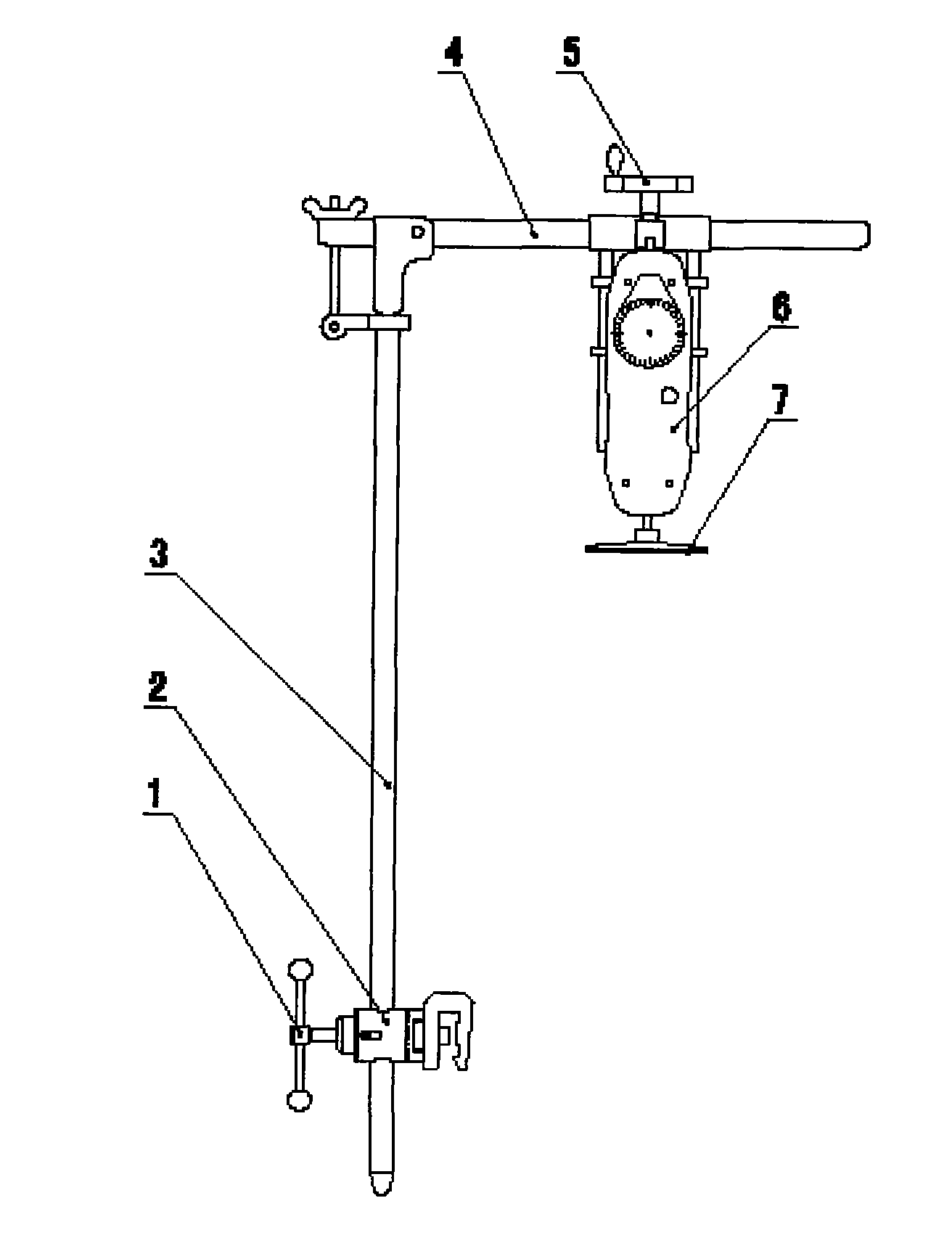
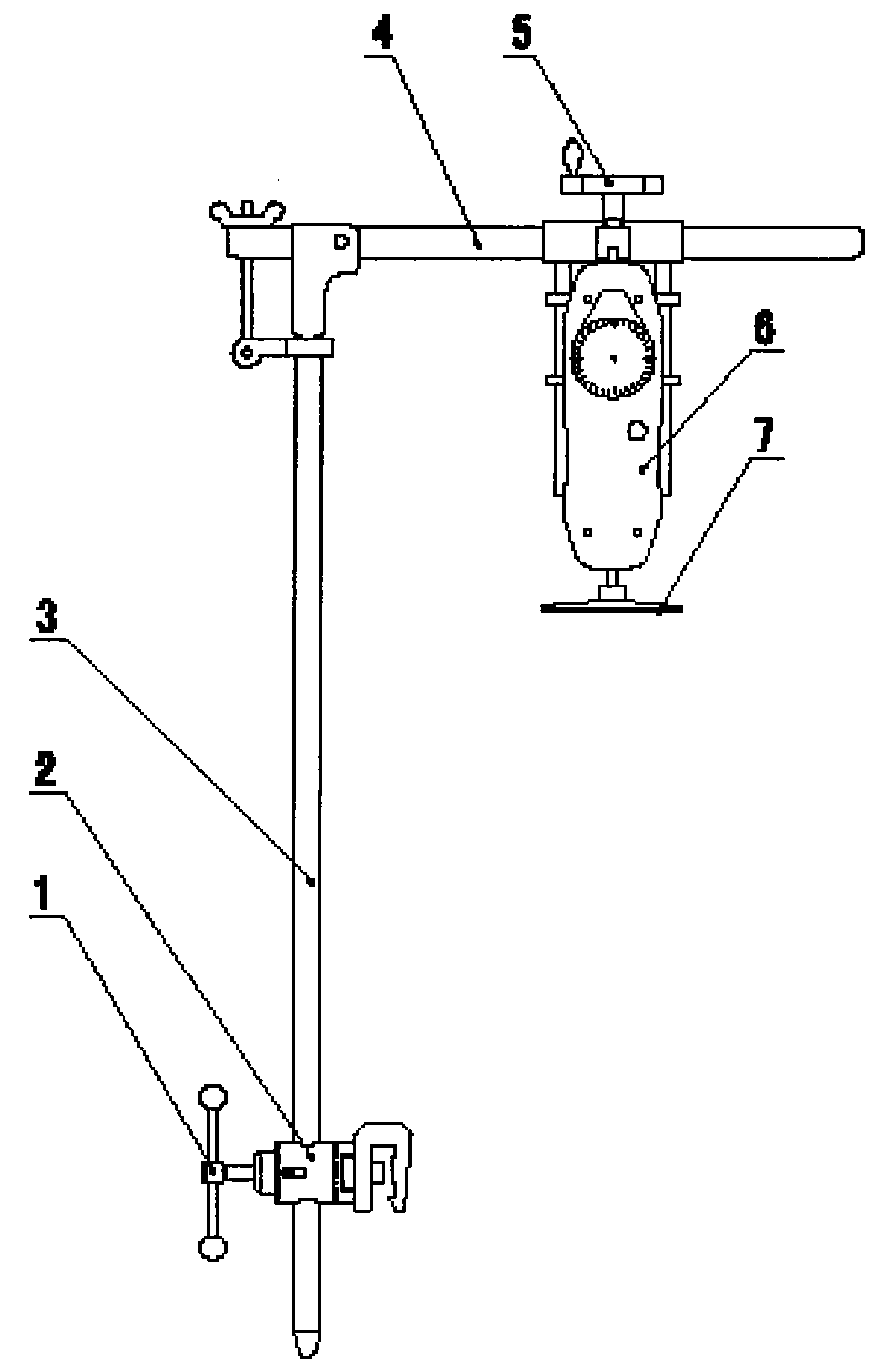
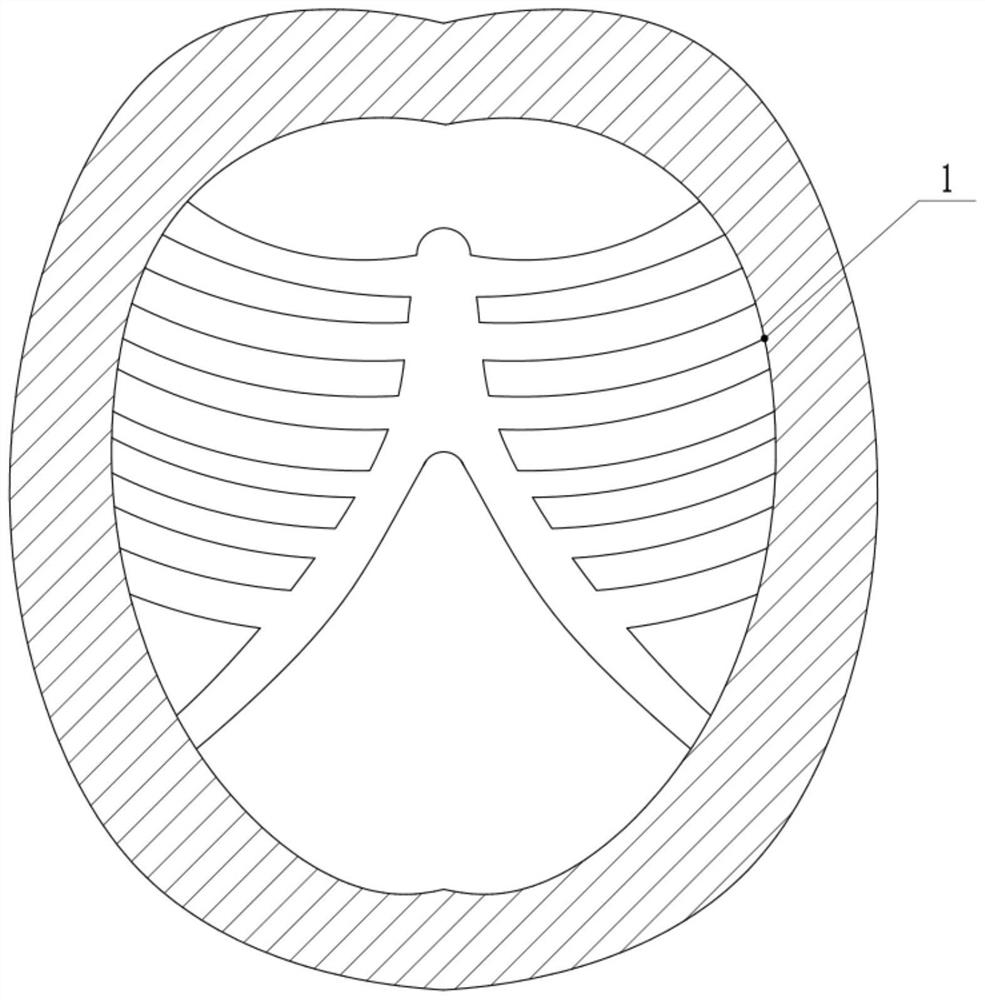
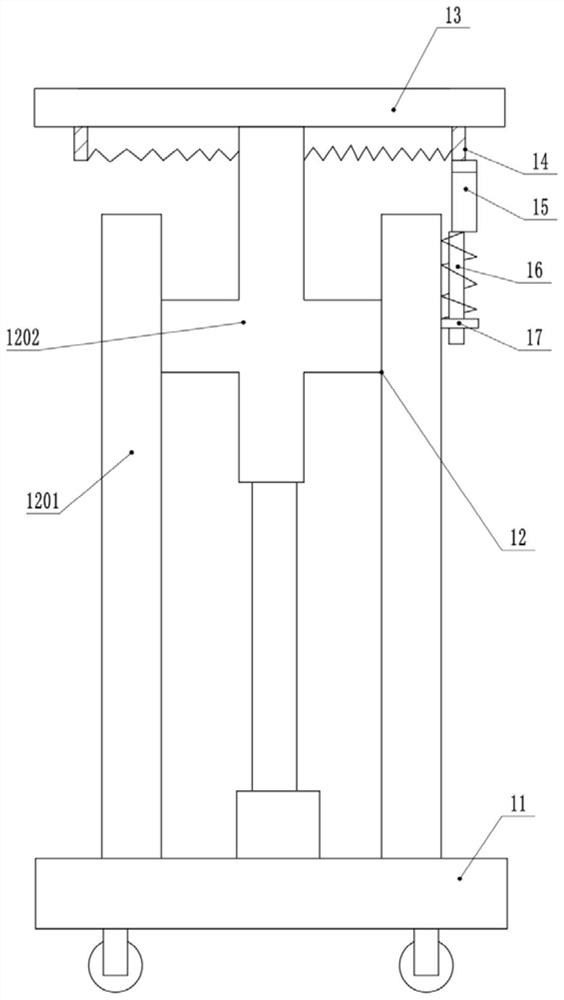
Chest rib pressure device
ActiveCN102028527AGood lookingCooperate wellOperating tablesMuscle exercising devicesThoracic wallEmergency medicine
The invention belongs to medical apparatus and instruments, and particularly relates to a chest rib pressure device used for pressing chest wall and measuring pressure in chicken chest minimally invasive surgery caused by thoracic wall deformity. The device comprises a vertical supporting rod, a locator, a clamping rod, a beam, a pressure hand wheel, a pressure gage and a press plate, wherein the locator is sleeved on the vertical supporting rod, the clamping rod is used for fixing the locator, the beam is connected with the vertical supporting rod, the pressure hand wheel is fixed on the beam, and the pressure gage and the press plate are fixed with the pressure hand wheel. The invention provides the device which replaces manual labor for pressing the chest rib in surgery, corrects deformity appearance and measures the exert pressure value.
Owner:BEIJING CHILDRENS HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Method for making artificial breast wall and artificial bone
InactiveCN1850294AAntibacterial and anti-inflammatoryLong-term tensile strengthProsthesisFiberThoracic wall
The present invention relates to a preparation method of artificial thoracic wall and artificial bone material. Said method includes the following steps: mixing polylactic acid fibre and chitosan fibre, weaving them into fabric with 100 um-350 um holes; mixing polylactic acid chips and polycaprolactone chips according to weight ratio of 1:0.05-1.25, then mixing them with chitosan fibre and pressing them to obtain plate material; wrapping said plate material with the above-mentioned obtained fabric, and adopting sewing mode to make three layers be connected together. Said material can be used for repairing thoracic wall with large-area deficiency and forming new bone.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Thoracoscope intervention training model and preparation method
PendingCN112735241AHigh degree of simulationAchieve sealingAdditive manufacturing apparatusEducational modelsCardiologyThoracic wall
The invention relates to a thoracoscope intervention training model and a preparation method. The thoracoscope intervention training model comprises a base, a lung lobe model, a rib model, a thoracic cavity membrane and a thoracic wall model, a puncture inlet is formed in the thoracic wall model, and a replacement upper cover is arranged on the puncture inlet; the lower end of the thoracic wall model is connected with the base, the thoracic wall model comprises a skin layer, a fat layer and a muscle layer which are connected in sequence, and the rib model is connected with the muscle layer; the thoracic cavity membrane is in a bag shape, a thoracic cavity membrane opening matched with the puncture inlet is formed in the top of the thoracic cavity membrane, the edge of the thoracic cavity membrane opening is detachably connected with the puncture inlet, and the thoracic cavity membrane is located above the pulmonary lobe model; and an air inlet cavity is formed in the lung lobe model, and an air channel communicated with the air inlet cavity is formed in the lung lobe model.
Owner:上海璞临医疗科技有限公司
Incision retracting fixator applicable to single-pore thoracoscopic surgery
InactiveCN104840226AEasy to fixAvoid damageSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSurgical operationSurgical risk
The invention relates to an incision retracting fixator applicable to single-pore thoracoscopic surgery. The incision retracting fixator has two kinds of structures A and B and comprises an elastic pipeline, an oval elastic pipeline is embedded in the circular elastic pipeline, the oval pipeline and the elastic pipeline are integrated, and two ends of an acute point of the oval elastic pipeline embedded in the circular elastic pipeline are closely embedded with circular elastic the pipeline. The circular elastic pipeline is an elastic waist-drum-shaped cylinder, and the oval elastic pipeline is embedded in the pipeline and is arranged in the middle to form three channels or at the edge to form two channels. During surgical operation, a thoracoscope and an operation instrument can pass the same incision, and compared with conventional thoracoscopic surgery, the single-pore thoracoscopic surgery performed with the incision retracting fixator has the advantages that two incisions can be reduced and surgical operation is more minimally invasive and has the remarkable advantages in reducing postoperative incision pain and paresthesia of the thoracic wall and accelerating postoperative recovery and the like, and for those patients with poor cardio-pulmonary function, operation risk is reduced.
Owner:杨雪鹰
Puncture sheathing canal
The invention discloses a puncture sheathing canal, which is characterized by comprising an outer sheathing canal body, wherein a puncture needle core, which is just used for piercing skin surface, isarranged in the outer sheathing canal body; in a puncture process, the head of the outer sheathing canal body is transformed into an expanded state from a closed state; the head of the outer sheathing canal body, when getting closed, can pierce into subcutaneous tissues until penetrating a thoracic wall or abdominal wall; and the head of the outer sheathing canal body, after penetrating the thoracic wall or the abdominal wall, can get expanded into the form of an umbrella. The puncture sheathing canal provided by the invention cannot cause injuries to such visceral organs as hearts, lungs andabdominal cavities easily; and the puncture sheathing canal is convenient to operate, simple in structure, easy for industrial production and excellent in medical effect.
Owner:潘湘斌
Breast cancer postoperative complication treating brace
PendingCN109907884AComfortable touchNot easy to generateBreast bandagesAbdomen bandagesPostoperative complicationAxilla
The invention discloses a breast cancer postoperative complication treating brace. The breast cancer postoperative complication treating brace comprises a thoracic wall pressurizing support, an armpitpressurizing support and a wearable breast cancer postoperative dressing fixing belt, wherein the thoracic wall pressurizing support is in a flat cushion structure; the armpit pressurizing support isin an ellipsoid structure and comprises a soft external layer and a hard internal core, and the hard internal core is arranged inside and fixedly connected with the soft external layer; the surface of the thoracic wall pressuring support and the soft external layer of the armpit pressurizing support are provided with anti-slippery structures; the wearable breast cancer postoperative dressing fixing belt is composed of an armpit-shoulder binding belt, a breast binding belt, an armpit-shoulder binding belt length adjusting device and a breast binding belt length adjusting device, and the armpit-shoulder binding belt and the breast binding belt penetrate through the armpit-shoulder binding belt length adjusting device and the breast binding belt length adjusting device respectively for adjusting the length; the wearable breast cancer postoperative dressing fixing belt can press the thoracic wall pressurizing support and the armpit pressurizing support onto a wounded part.
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Radiotherapy board and couch
ActiveUS10548542B2Operating tablesPatient positioning for diagnosticsRadiotherapy breastThoracic wall
Owner:UNIV GENT
Thorax mounted stabilization platform
Owner:ESTECH ENDOSCOPIC TECH
Treatment teaching aid for simulating pleural effusion puncture
PendingCN113096510AImprove teaching effectCosmonautic condition simulationsEducational modelsThoracic structureThoracic wall
The invention relates to the technical field of thoracocentesis teaching aids, in particular to a treatment teaching aid for simulating pleural effusion puncture. The treatment teaching aid comprises a simulated upper body model with simulated ribs and a supporting device for supporting the simulated upper body model, wherein a simulated cavity for placing a simulated thoracic cavity is arranged in the simulated upper body model, the simulated thoracic cavity comprises a simulated thoracic wall shell, a wall layer pleura is arranged on the inner side of the simulated thoracic wall shell, a simulated lung is arranged in the simulated thoracic wall shell, and the simulated lung is sleeved with a dirty layer pleura; the dirty layer pleura is sleeved with an annular air bag, and the annular air bag is connected with an air supply device through an air bag branch pipe. a simulated trachea is arranged in the simulated lung; and an air inlet joint and a liquid inlet joint which are communicated with the interior of the simulated thoracic cavity shell are arranged on the simulated thoracic cavity shell and are respectively connected with the air supply device and a liquid supply device through pipelines. The problems that low-seniority doctors cannot quickly distinguish the type of thoracocentesis, and treatment of patients is affected are solved.
Owner:PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF DEYANG CITY
Field tension pneumothorax first-aid assembly
PendingCN112263307ASimple structureEasy to operateSurgical needlesPneumothorax apparatusThoracic structureMedicine
The invention relates to the technical field of pneumothorax first aid, in particular to a field tension pneumothorax first-aid assembly. The field tension pneumothorax first-aid assembly comprises apuncture needle, wherein a needle head is arranged at the top end of the puncture needle, the puncture needle is connected with a transparent bottle body filled with water through an air pipe, a bottle opening is formed in the upper end of the bottle body, a film with a cross-shaped opening is arranged in the bottle opening, a check valve is arranged at the connecting position of the air pipe andthe puncture needle, and a one-way valve is arranged at the connecting position of the air pipe and the bottle body. The field tension pneumothorax first-aid assembly is simple in structure, convenient to operate and capable of meeting the requirements of field first aid, external air is effectively prevented from being reversely injected into the thoracic cavity through the a plurality of valves,air in the thoracic cavity can be consolidated to be exhausted from the thoracic wall, lung tissue is expanded again to recover the function, and the requirement of pneumothorax first aid is met.
Owner:周昱岐
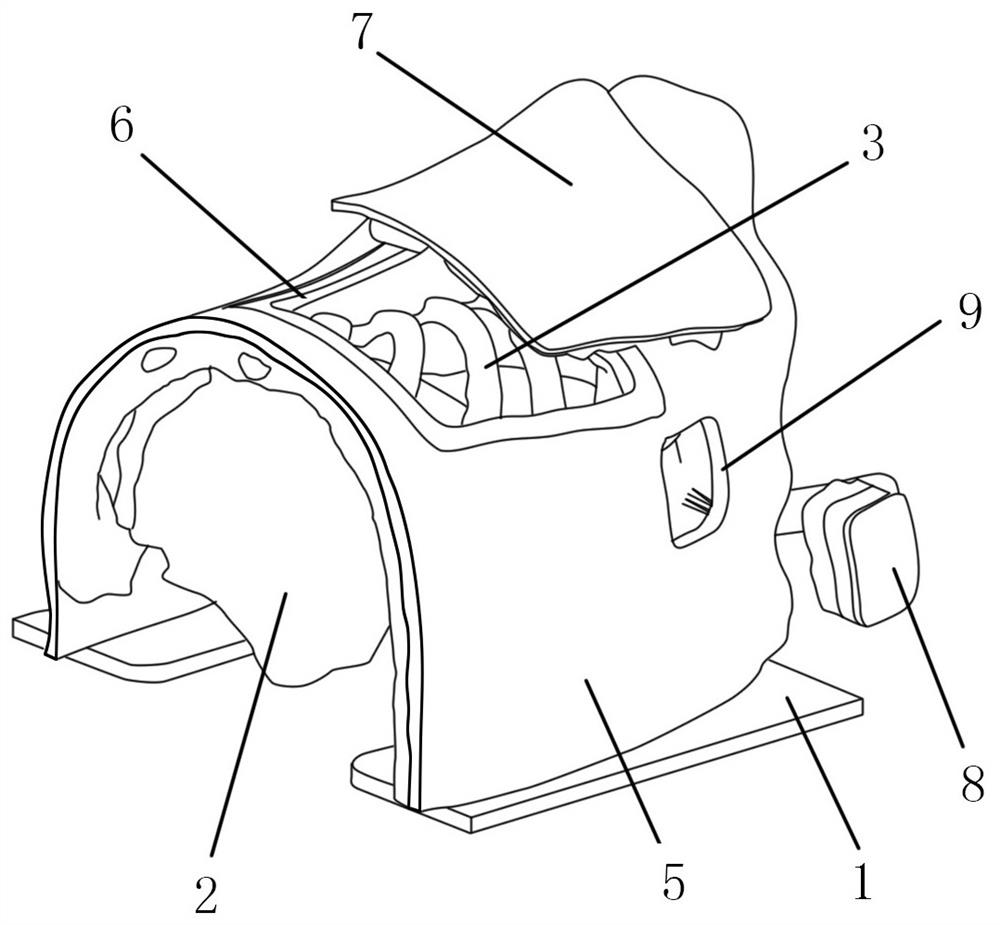
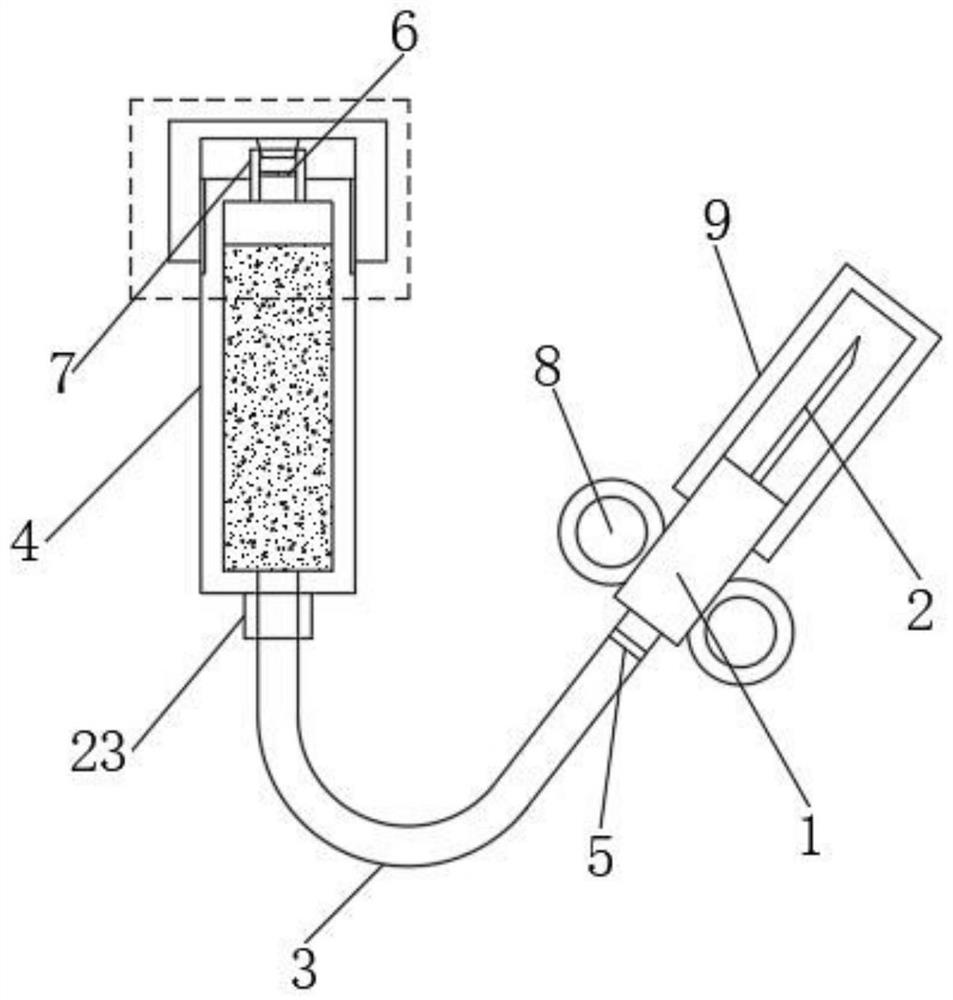
Hemostatic device and system for thoracic wall after femoral artery or pacemaker implantation
InactiveCN114848076ARealize compression intensity adjustmentErgonomic designSurgerySensorsThoracic wallFemoral artery
The invention provides hemostasis equipment and system for a thoracic wall after femoral artery or pacemaker implantation, and the hemostasis equipment and system comprises a U-shaped fixing device which comprises a U-shaped leather sheath; the air bag fixing unit is mounted at the horizontal end of the inner side of the U-shaped leather sheath; the adjusting unit is located in the U-shaped leather sheath and comprises a height adjusting unit located at the U-shaped bottom of the U-shaped leather sheath and a rotation angle adjusting unit located between the height adjusting unit and the air bag fixing unit; through mutual cooperation of the U-shaped fixing device and the external hematoma monitor alarm, the following three effects can be achieved: firstly, the disposable air bag is used as a disposable compression consumable, the inflation amount can be set by a machine according to the condition of a patient, automatic inflation is achieved, and manual inflation is not needed; secondly, whether exudation occurs in a femoral artery or a pacemaker postoperative wound can be monitored, and an alarm is given when exudation occurs; and thirdly, whether the disposable air bag is pressed to leak air or not can be monitored, and an alarm is given when air leakage occurs.
Owner:陈琼珊
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com