Cardiac CT system and method for planning and treatment of biventricular pacing using epicardial lead
a technology of epicardial lead and ct system, which is applied in the field of cardiac rhythm management system, can solve the problems of delayed left ventricular ejection, different regions of the left ventricle not contracting in a coordinated fashion, and ineffective contraction of the left ventricl
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
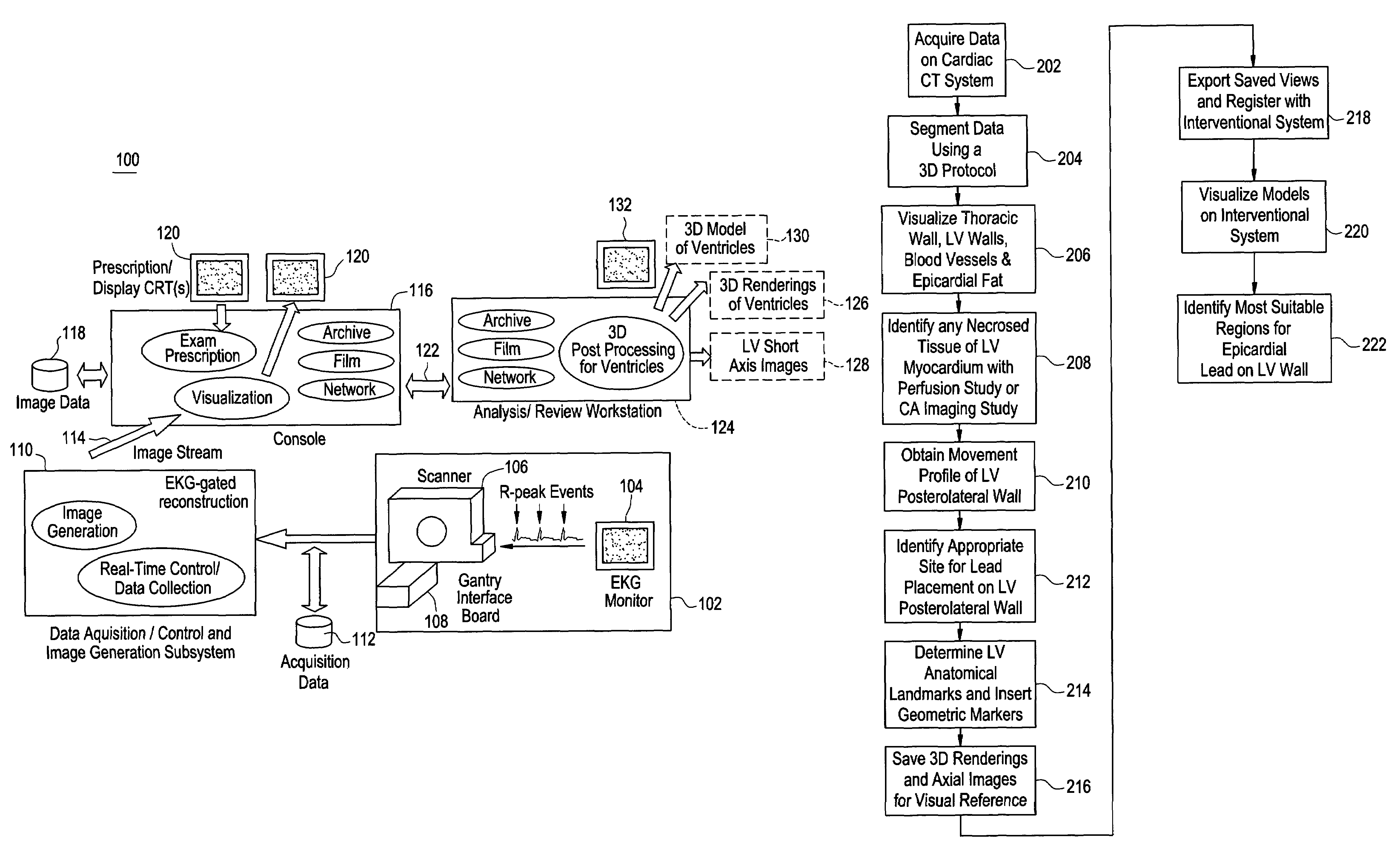
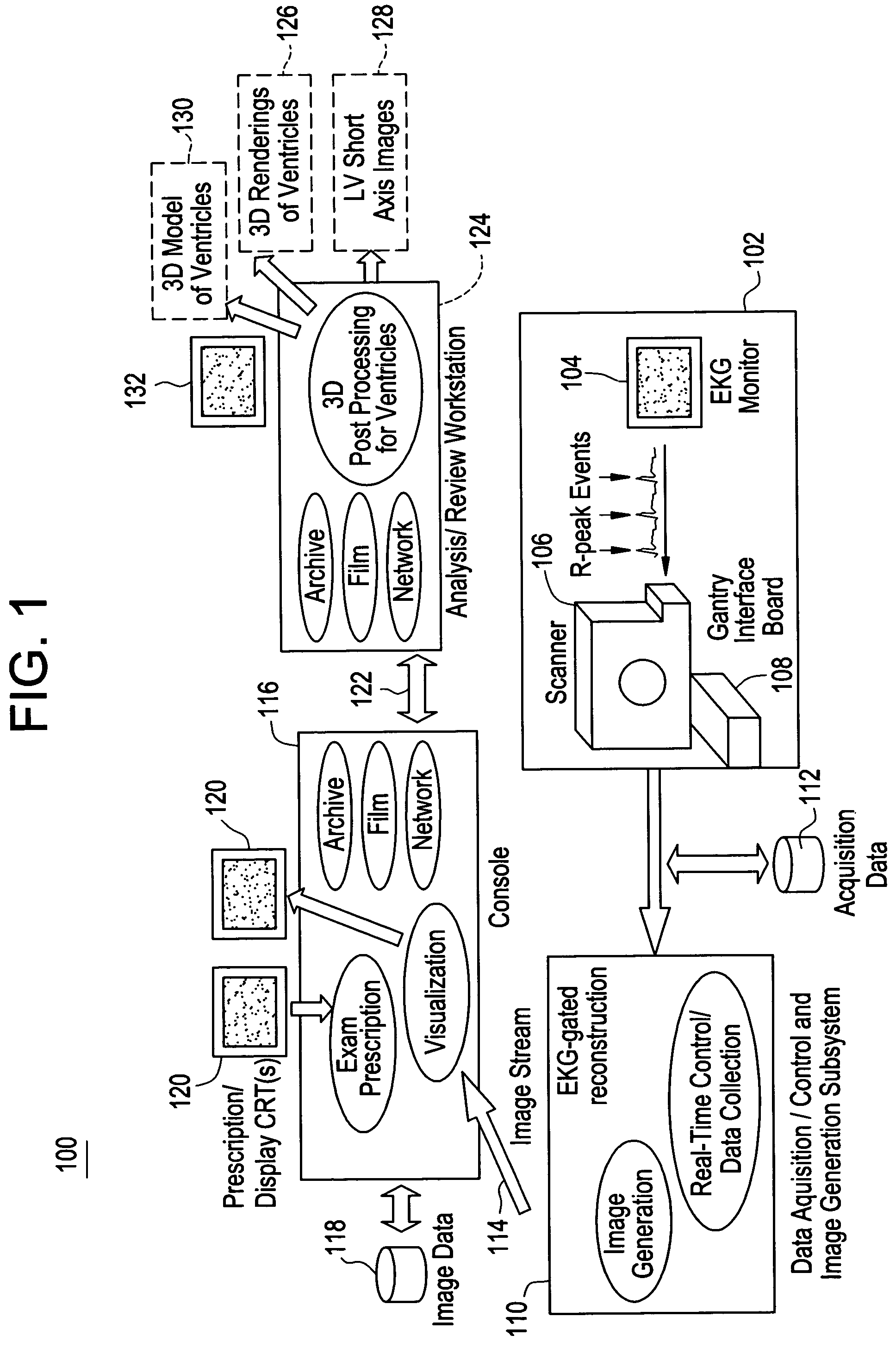
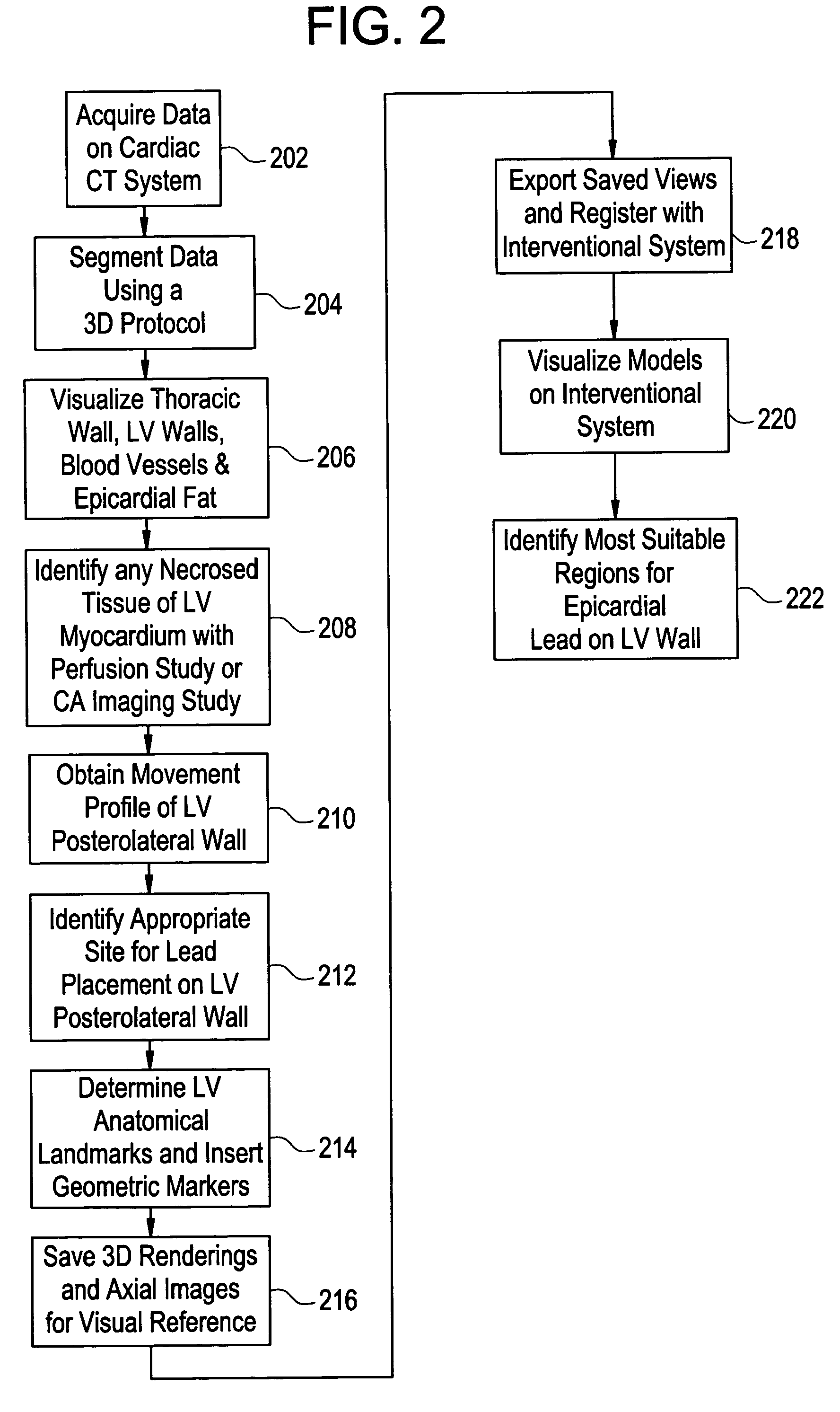
[0017]Disclosed herein is a cardiac computed tomography (CT) system and method for biventricular pacing that provides information for planning interventional procedures that enable an electrophysiologist, cardiologist and / or surgeon to plan in advance a desired approach to complete the procedure. Additionally, with a more detailed three-dimensional (3D) geometrical representation of the left ventricle (LV) and its relationship to the thoracic wall, the practitioner can also identify the presence of fat, the location and orientation of the major blood vessels and their branches, and viable tissue. This information can be used for determining the optimal placement of the LV lead. Additionally, LV contractility and regional wall motion abnormalities can be visualized to identify the best location for placement of LV epicardial pacing lead. Thus, the information obtained from cardiac CT system eliminates the need to place the lead blindly, thereby avoiding many of the problems discussed...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com