Compositions and methods for controlling neuronal excitation
a technology of excitation and composition, applied in the field of composition and method of controlling neuronal excitation, can solve the problems of limited system use, limited clinical application of current optogenetic approaches, and limited prior work in chemical optogenetics to cultured cells, so as to achieve the effect of reducing the functional output of the neuron and increasing the activity of the neuron
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Identification and Characterization of Optovin
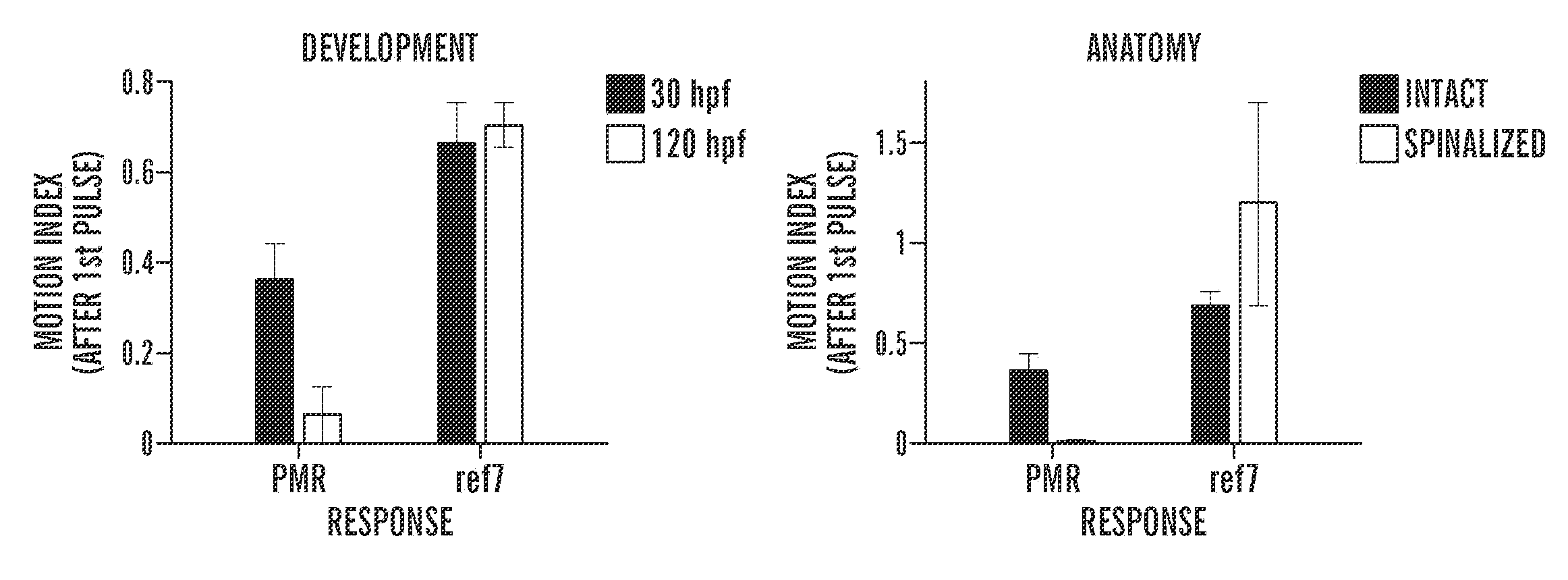
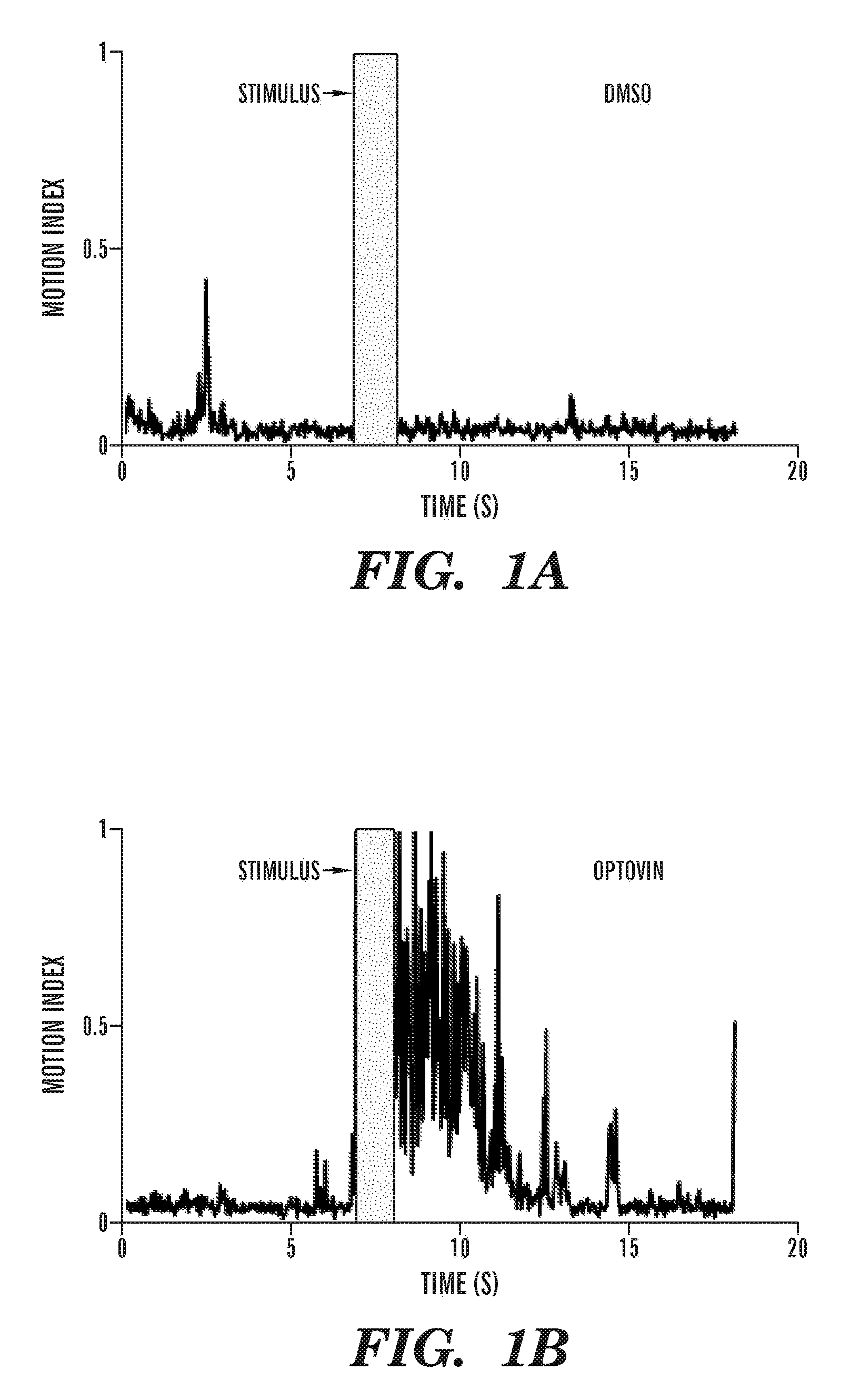
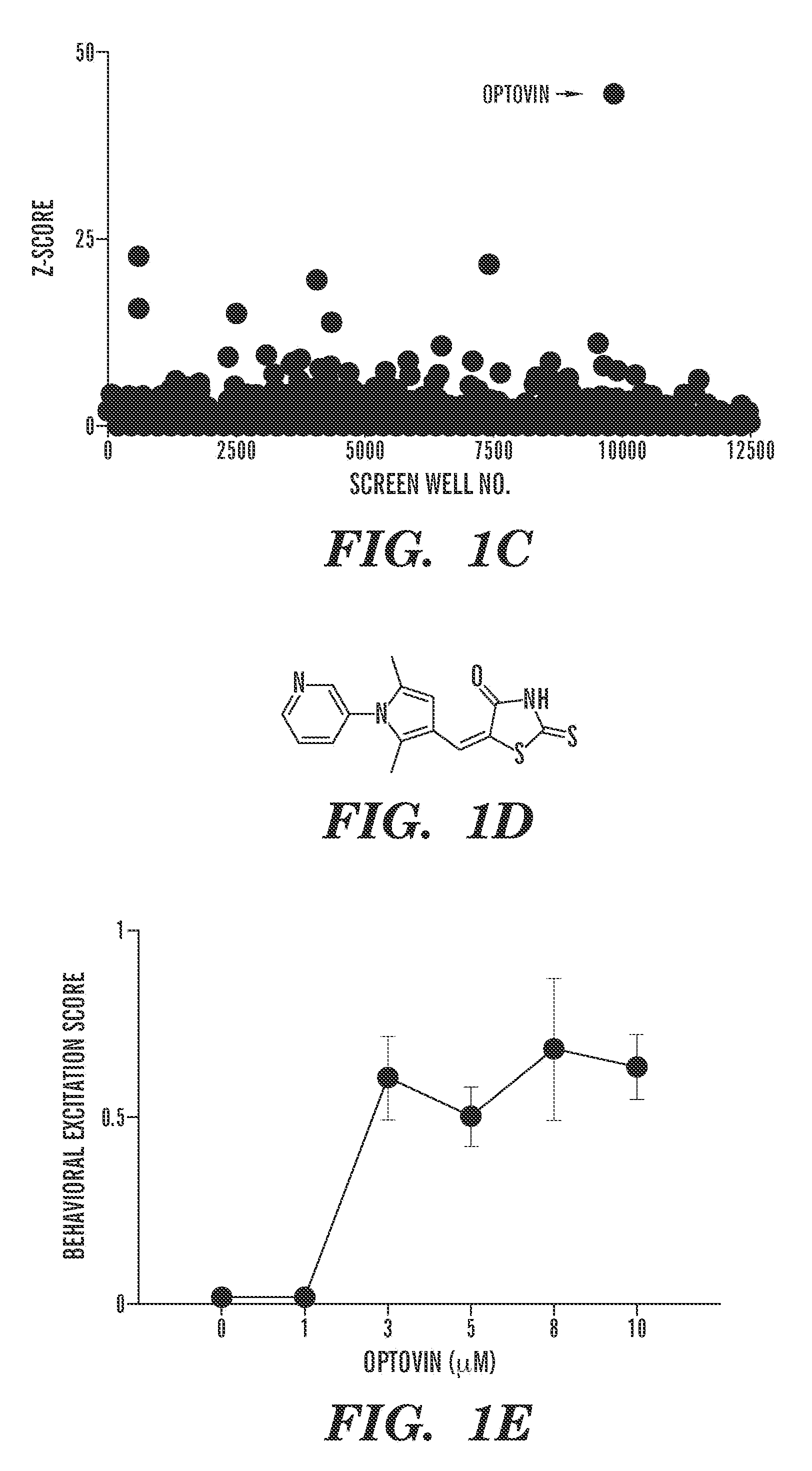
[0639]Optogenetics is a powerful research tool because it enables high-resolution optical control of neuronal activity1-14. However, current optogenetic approaches are limited to transgenic systems expressing microbial opsins and other exogenous photoreceptors. Identified herein are small molecules, including optovin, that enable repeated photoactivation of motor behaviors in wild type animals. Surprisingly, optovin's behavioral effects are not visually mediated. Rather, photodetection is performed by sensory neurons expressing the cation channel TRPA1. TRPA1 is both necessary and sufficient for the optovin response. Optovin activates human TRPA1 via structure-dependent photochemical reactions with redox-sensitive cysteine residues. In animals with severed spinal cords, optovin treatment enables control of motor activity in the paralyzed extremities by localized illumination. Described herein is the identification of a light-based strate...
example 2
Photo-Sensitive TRPA1 Agonist Treatment
[0728]Dosage combinations of a photo-sensitive TrpA1 agonist as described herein and electromagnetic radiation can be used to induce muscle contractions in mice. Mice can be administered a dose of a photo-sensitive TrpA1 agonist systemically, e.g. orally or via injection, or locally, e.g. by topical application. The photo-sensitive TrpA1 agonist can cross the epidermis and enter muscle tissues or be transported to the muscle tissue systemically. The target muscle can then be exposed to electromagnetic radiation of the appropriate wavelength, i.e. a wavelength that will activate that particular photo-sensitive TrpA1 agonist. The electromagnetic radiation can be directed through the epidermis to reach the neurons in the muscle tissue. Alternatively, the radiation can be generated in or near the muscle tissue, e.g. by an implanted, wirelessly controlled LED. Alternatively, the radiation can be generated by an external or implanted radiation source...
example 3
Development of Optovin-Class Compounds
[0730]To optimize optovin for photochemical control of TrpA1, medicinal chemistry can be used to create a panel of optimized optovin derivatives that permit flexible manipulation of TrpA1 activity. Optimization can focus on developing compounds that are more potent than optovin and compounds that have desirable physicochemical properties, including altered wavelength sensitivity and rapid photoswitching kinetics. Compounds can also be optimized for low in vivo toxicity and tested for conservation across species.
[0731]Additionally, photo-dependent ligands can be developed for additional TRP channels. Compounds can be tested in a panel of cell-based calcium assays to identify compounds that cause photochemical gating of four other TRP channels, TrpC1, TrpV1, TrpC6, and TrpM8. Compounds with activity beyond TrpA1 can be further optimized to generate selective, photoswitchable probes for each of the target TRP channels.
[0732]Iterative cycles of medi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com