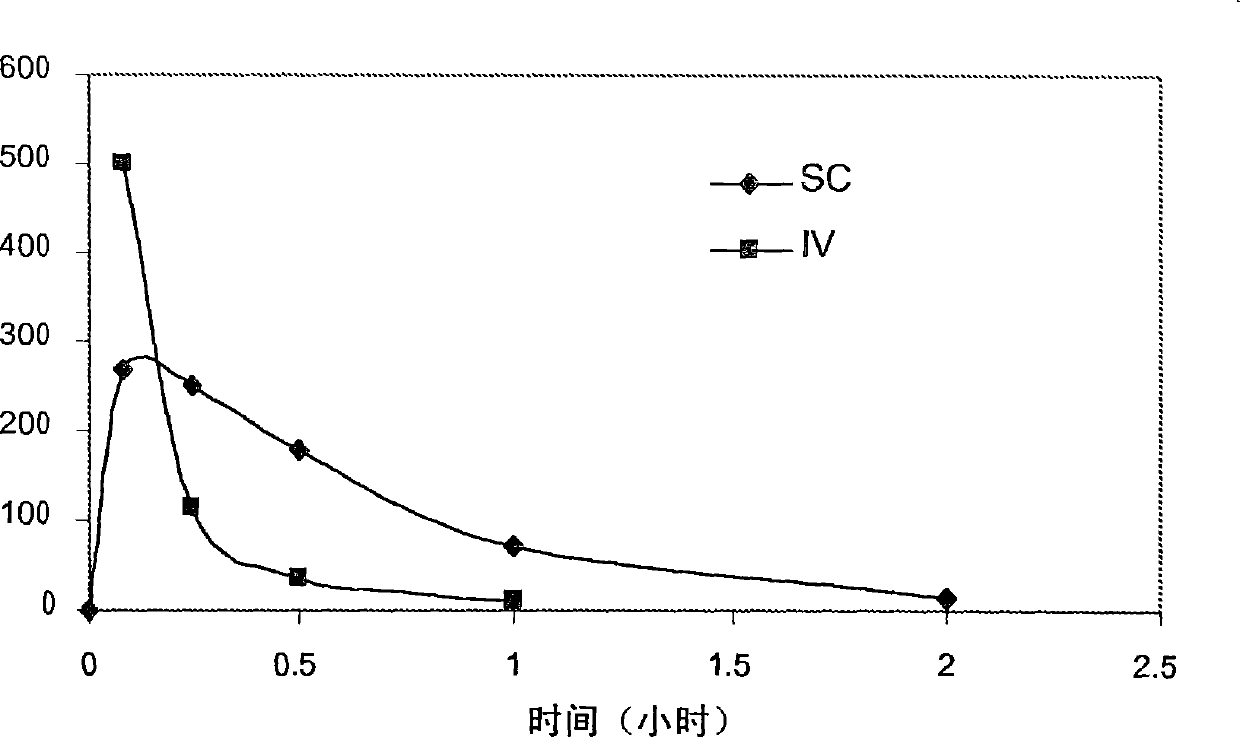
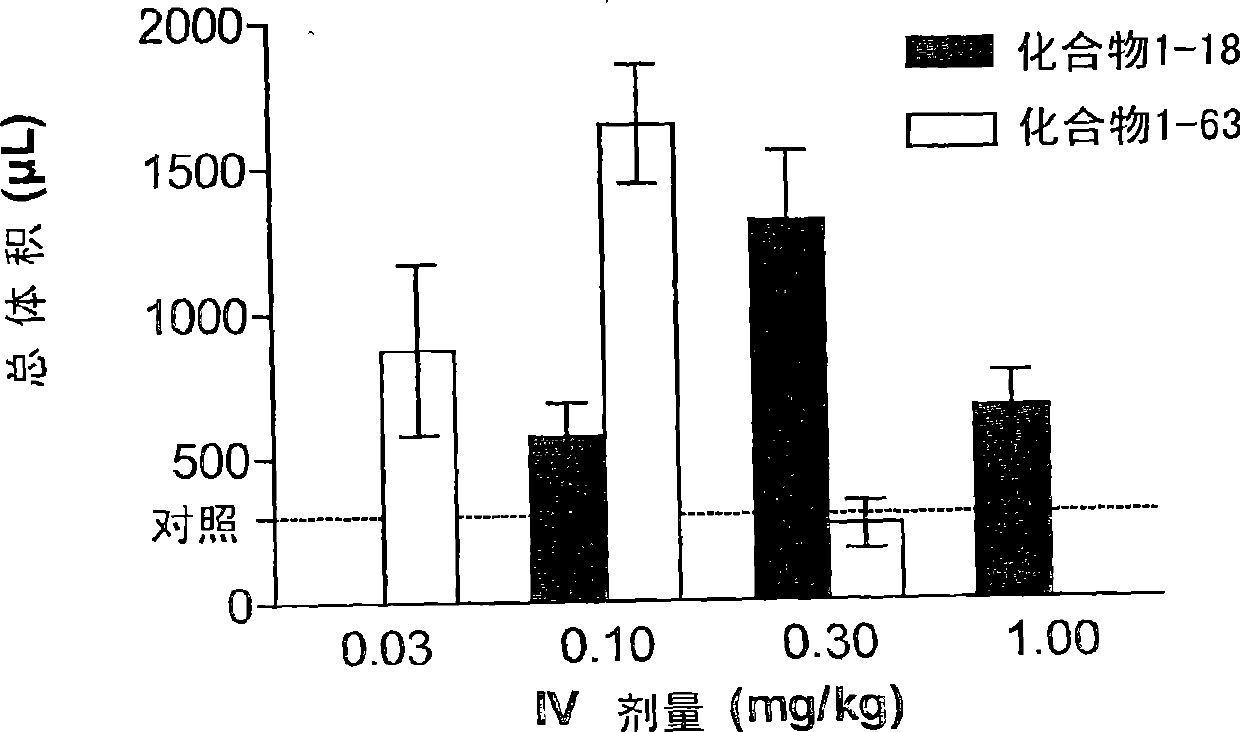
Patents
Literature
63 results about "Intracrine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Intracrine refers to a hormone that acts inside a cell, regulating intracellular events. In simple terms it means that the cell stimulates itself by cellular production of a factor that acts within the cell. Steroid hormones act through intracellular (mostly nuclear) receptors and, thus, may be considered to be intracrines. In contrast, peptide or protein hormones, in general, act as endocrines, autocrines, or paracrines by binding to their receptors present on the cell surface. Several peptide/protein hormones or their isoforms also act inside the cell through different mechanisms. These peptide/protein hormones, which have intracellular functions, are also called intracrines. The term 'intracrine' is thought to have been coined to represent peptide/protein hormones that also have intracellular actions. To better understand intracrine, we can compare it to paracrine, autocrine and endocrine. Autocrine system deal with the autocrine receptors of a cell allowing for the hormones to bind, which have been secreted from that same cell. Paracrine system is one where nearby cells get hormones from a cell, and change the functioning of those nearby cells. Endocrine system refers to when the hormones from a cell affect another cell that is very distant from the one that released the hormone.
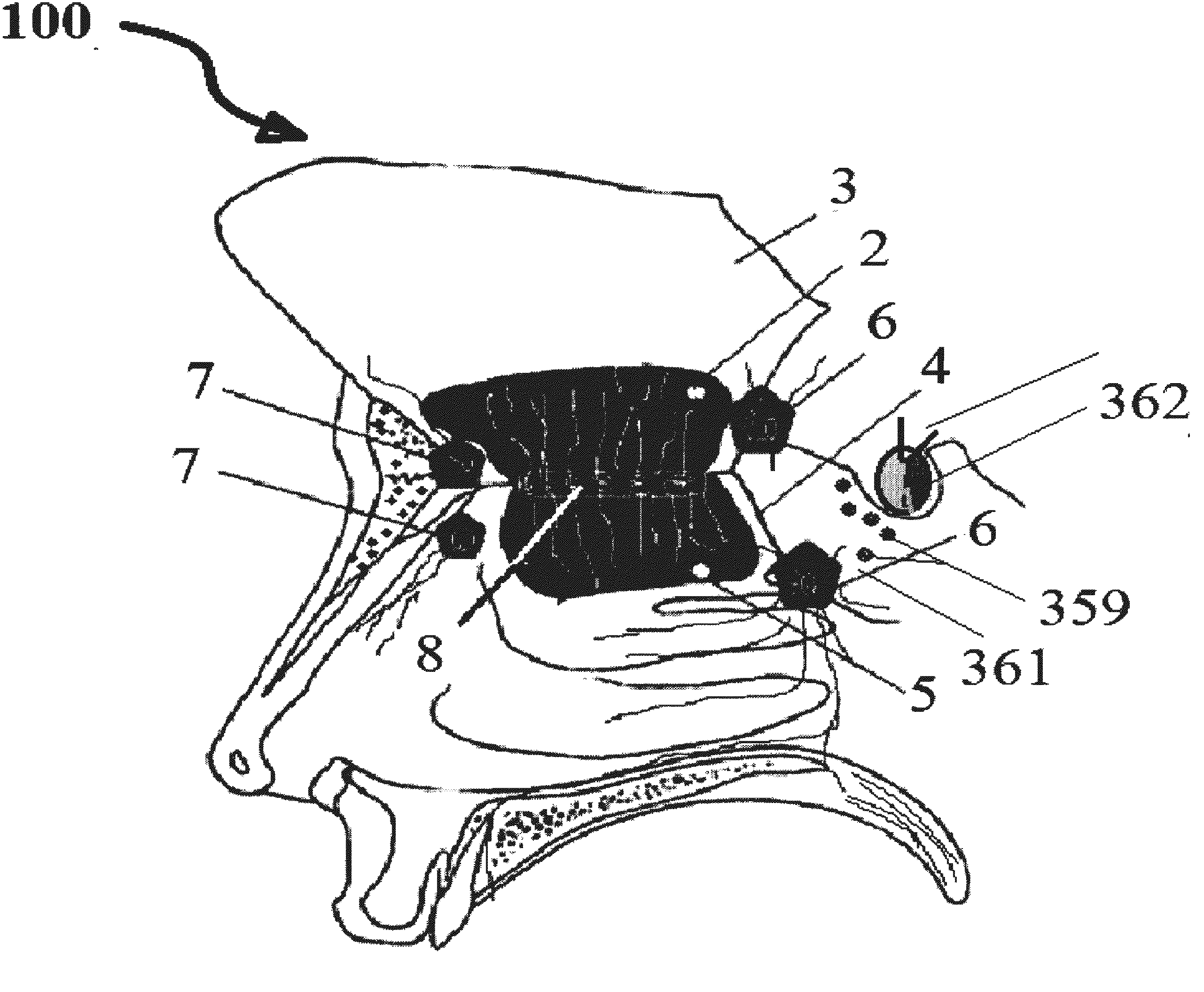
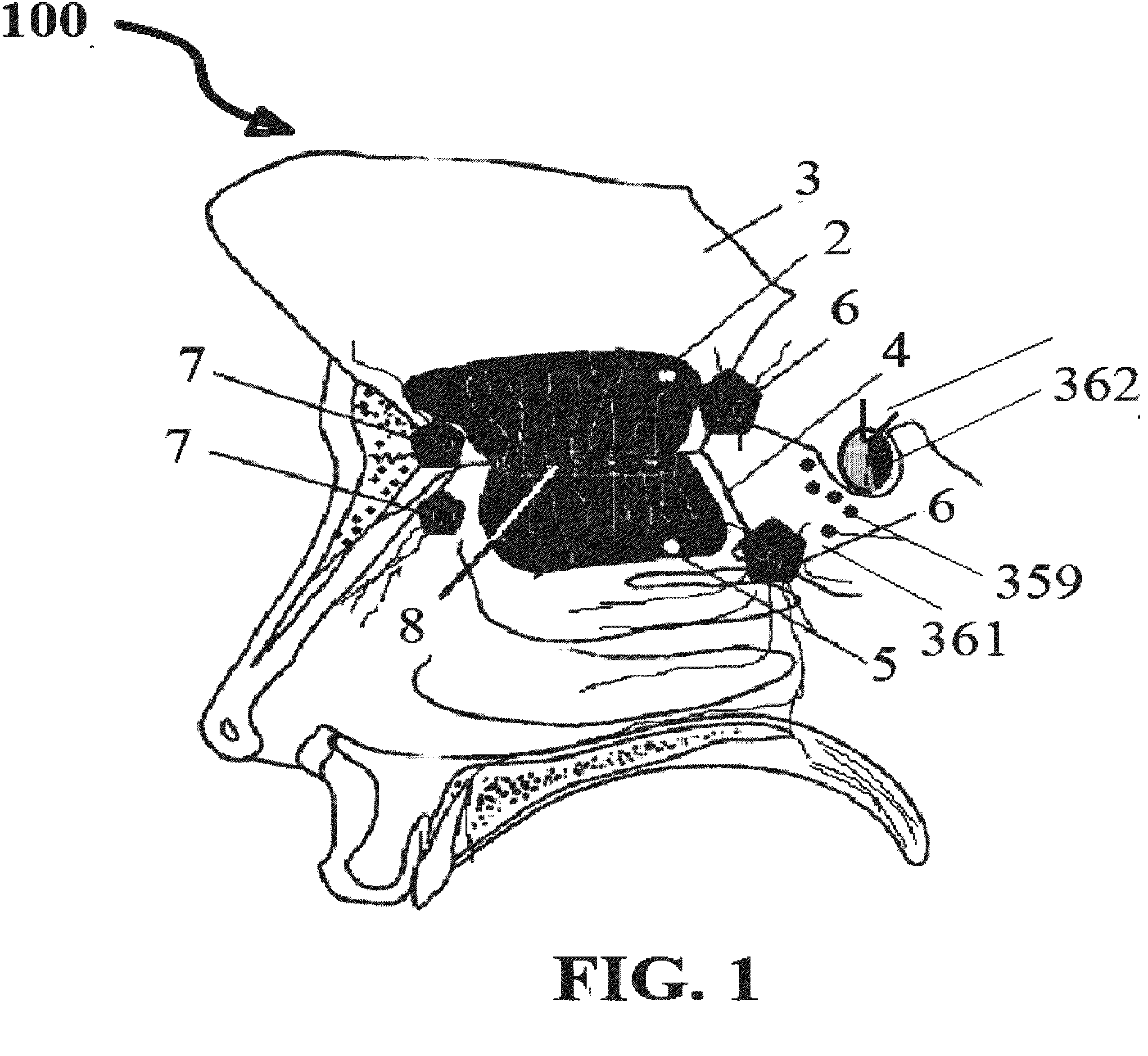
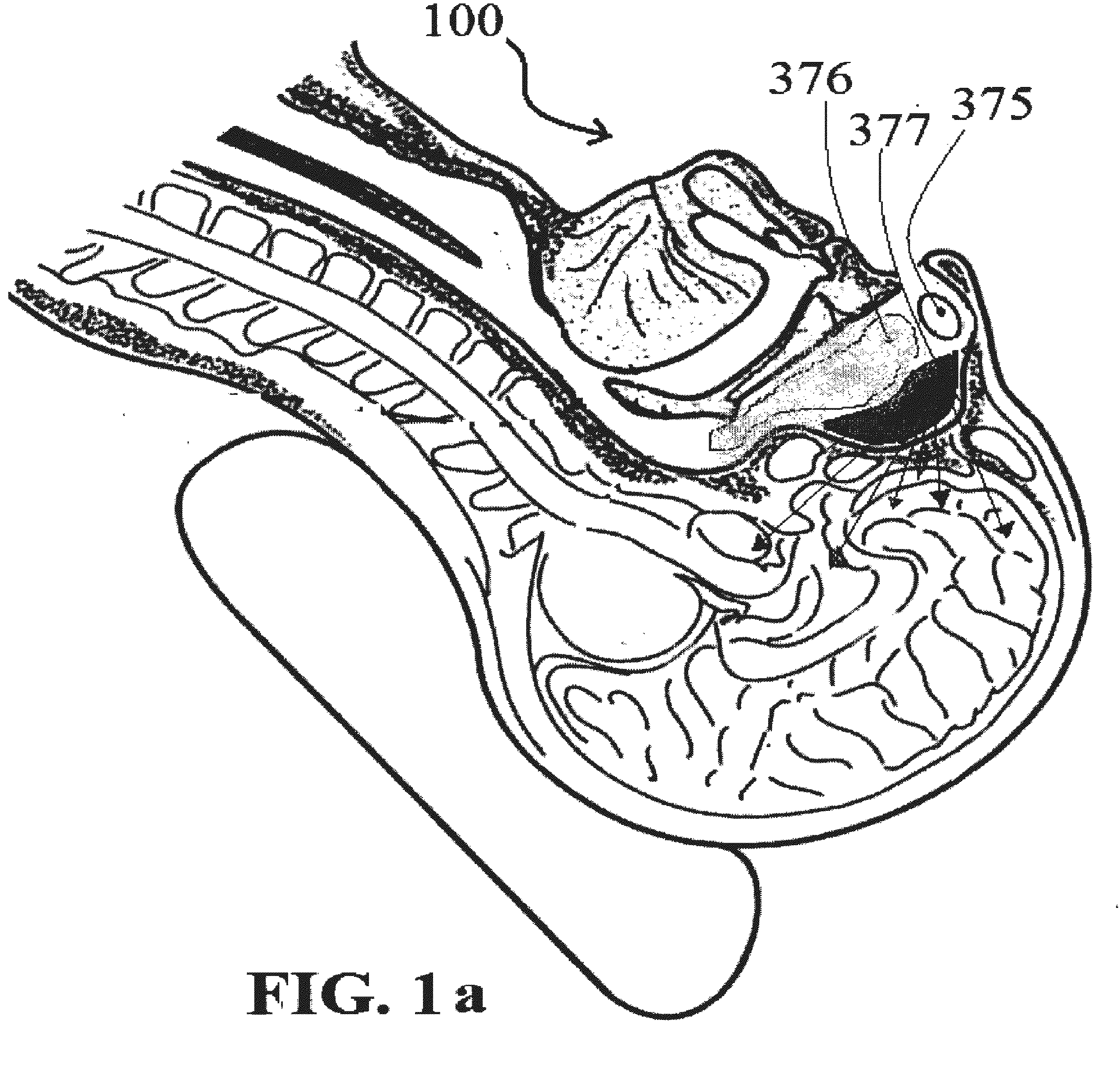
Alzheimer's disease treatment with multiple therapeutic agents delivered to the olfactory region through a special delivery catheter and iontophoresis
InactiveUS20120323214A1Reduce and preventAvoid destructionNervous disorderHead electrodesApoptosisExcitotoxicity
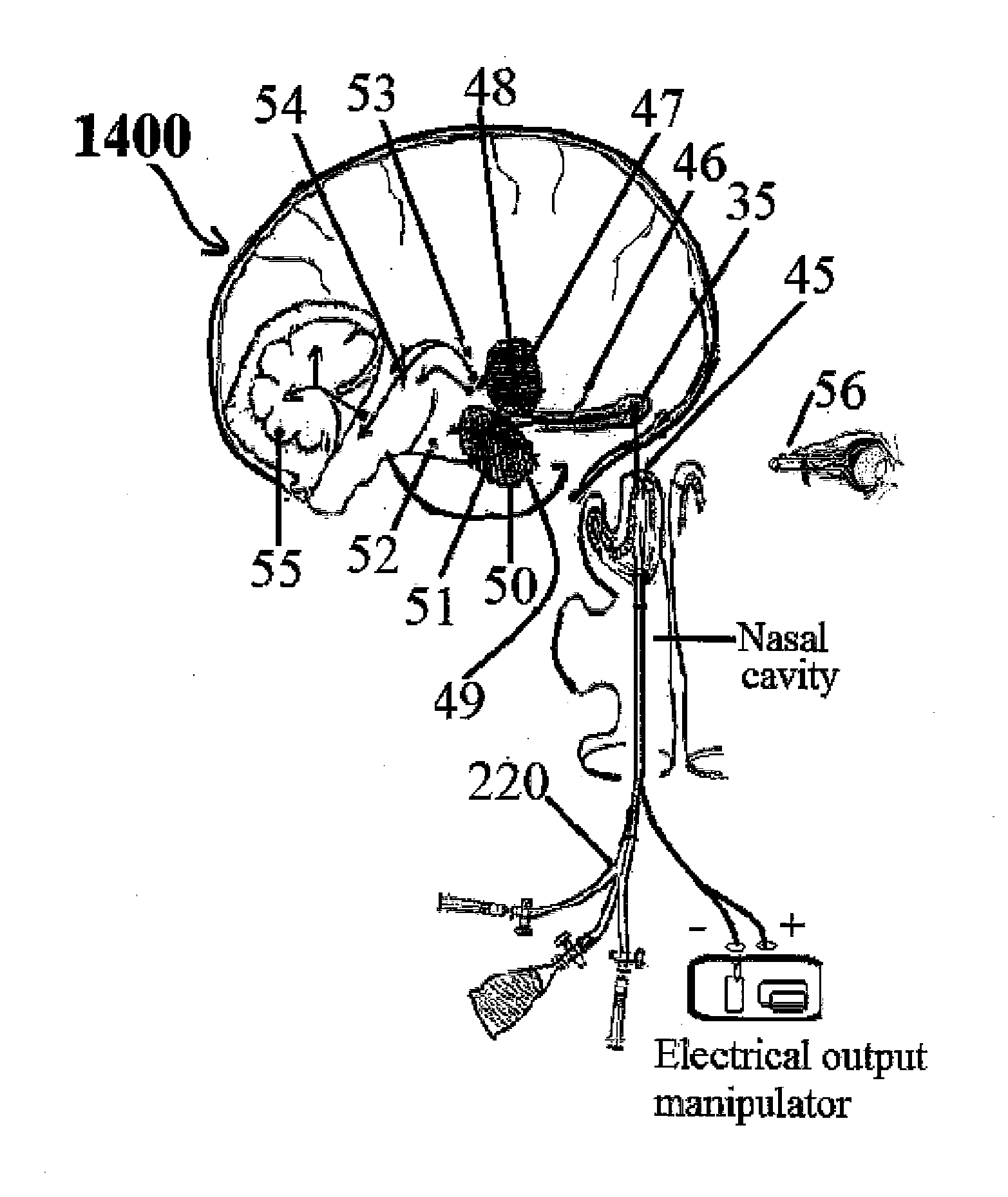
This invention describes the administration of multiple therapeutic agents with insulin in conjunction with bexarotene, ketamine, monoclonal antibodies Etanercept, IGF-1, and acetylcholine esterase inhibitors physostigmine, for treatment of Alzheimer's disease and other neurodegenerative diseases. Insulin, improves memory; also augments and amplifies the effects of the adjuvant therapeutic agents (paracrine and intracrine effects) and consequently reduces the β amyloid, its soluble precursors, prevents damage to the neuronal skeletal network (taupathy), and blocks glutamate excitotoxicity, reduces brain inflammation, prevents apoptosis, and increases the acetylcholine levels in the neurons and synapses; by using a combination of insulin, bexarotene, ketamine, Etanercept, IGF-1, and physostigmine therapeutic agents. The results are achieved by using the specially designed Iontophoresis incorporated olfactory mucosal delivery (ORE) catheter device located at the olfactory nerves, sphenoid sinus, and adjacent structures described here, to transport the large molecules of therapeutic agents to treat AD delivered to the CNS bypassing BBB from ORE.
Owner:WEDGE THERAPEUTICS
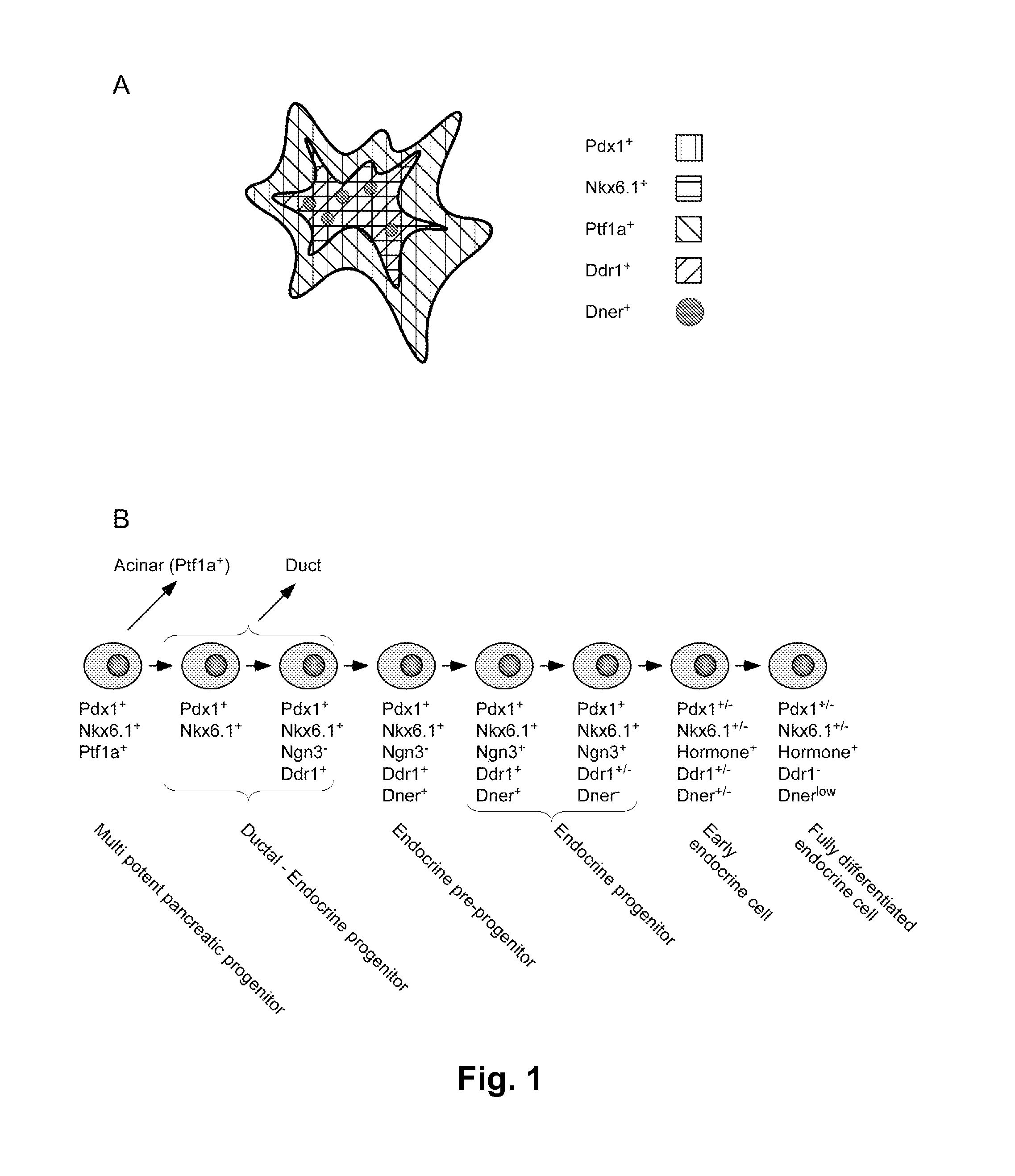
Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells
ActiveUS20110151561A1High expressionPancreatic cellsEpidermal cells/skin cellsPluripotential stem cellIntracrine
The present invention provides methods to promote the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into insulin producing cells. In particular, the present invention provides a method to increase the expression of NGN3 and NKX6.1 in populations of cells expressing markers characteristic of the pancreatic endocrine lineage.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
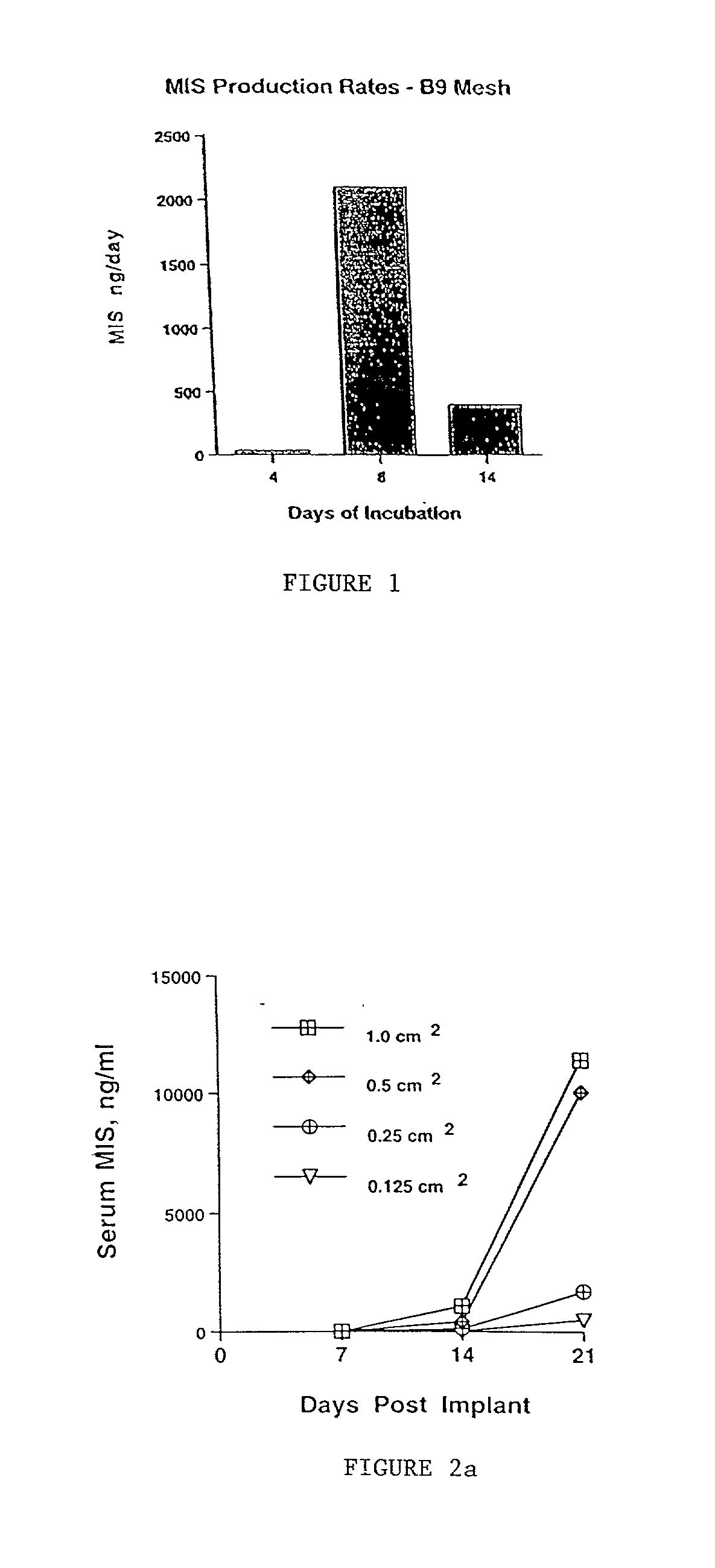
Delivery of therapeutic biologicals from implantable tissue matrices
InactiveUS20020031500A1Many of effectMany of inconveniencePowder deliveryBiocideProgenitorActive agent
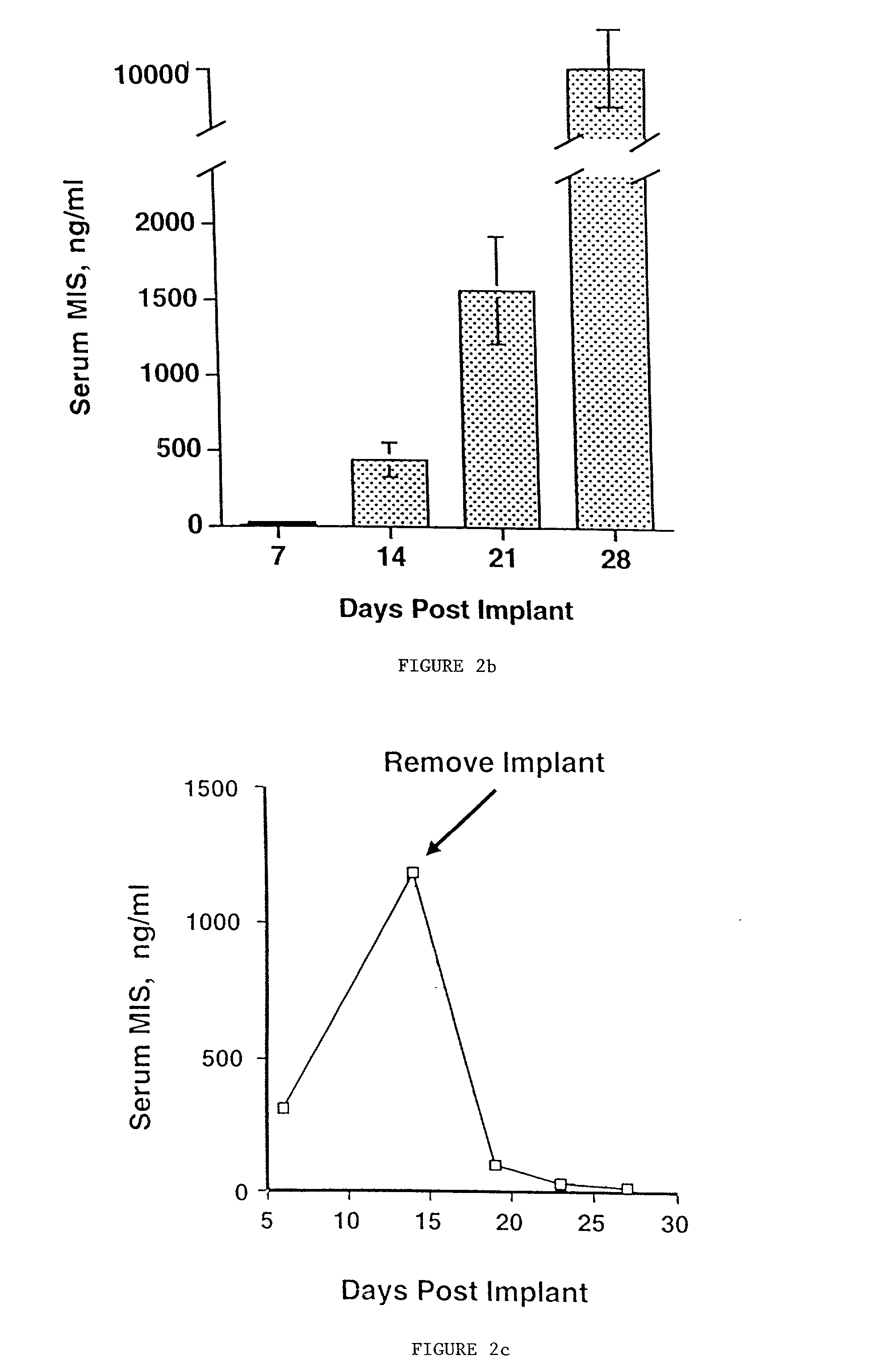
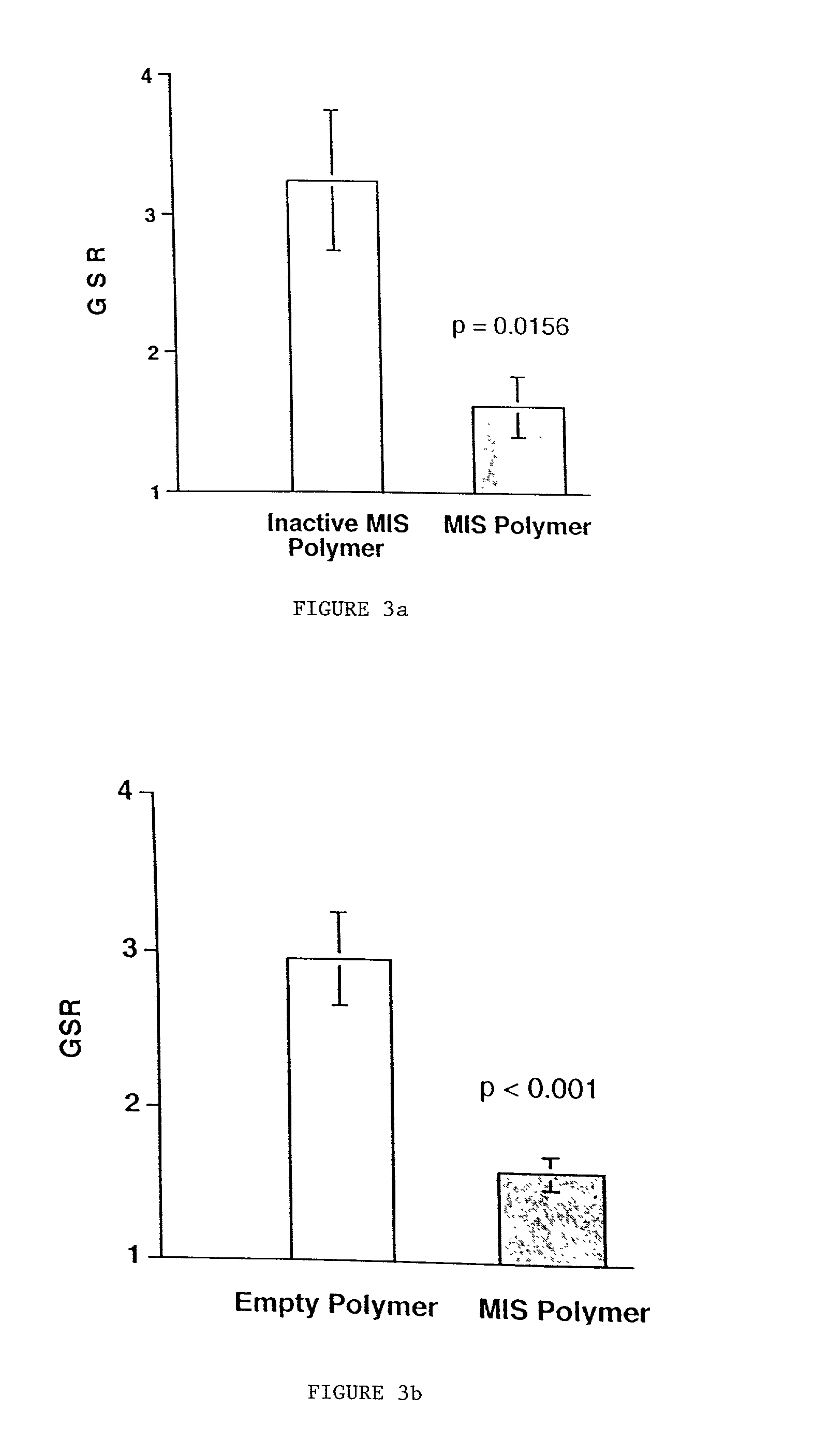
Normal cells, such as fibroblasts or other tissue or organ cell types, are genetically engineered to express biologically active, therapeutic agents, such as proteins that are normally produced in small amounts, for example, MIS, or other members of the TGF-beta family Herceptin(TM), interferons, andanti-angiogenic factors. These cells are seeded into a matrix for implantation into the patient to be treated. Cells may also be engineered to include a lethal gene, so that implanted cells can be destroyed once treatment is completed. Cells can be implanted in a variety of different matrices. In a preferred embodiment, these matrices are implantable and biodegradable over a period of time equal to or less than the expected period of treatment, when cells engraft to form a functional tissue producing the desired biologically active agent. Implantation may be ectopic or in some cases orthotopic. Representative cell types include tissue specific cells, progenitor cells, and stem cells. Matrices can be formed of synthetic or natural materials, by chemical coupling at the time of implantation, using standard techniques for formation of fibrous matrices from polymeric fibers, and using micromachining or microfabrication techniques. These devices and strategies are used as delivery systems via standard or minimally invasive implantation techniques for any number of parenterally deliverable recombinant proteins, particularly those that are difficult to produce in large amounts and / or active forms using conventional methods of purification, for the treatment of a variety of conditions that produce abnormal growth, including treatment of malignant and benign neoplasias, vascular malformations (hemangiomas), inflammatory conditions, keloid formation, abdominal or plural adhesions, endometriosis, congenital or endocrine abnormalities, and other conditions that can produce abnormal growth such as infection. Efficacy of treatment with the therapeutic biologicals is detected by determining specific criteria, for example, cessation of cell proliferation, regression of abnormal tissue, or cell death, or expression of genes or proteins reflecting the above.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Alzheimer's disease treatment with multiple therapeutic agents delivered to the olfactory region through a special delivery catheter and iontophoresis
InactiveUS20140012182A1Large deliveryAvoid destructionNervous disorderHead electrodesApoptosisExcitotoxicity
This invention describes the administration of multiple therapeutic agents with insulin in conjunction with bexarotene, ketamine, monoclonal antibodies Etanercept, IGF-1, and acetylcholine esterase inhibitors physostigmine, for treatment of Alzheimer's disease and other neurodegenerative diseases. Insulin, improves memory; also augments and amplifies the effects of the adjuvant therapeutic agents (paracrine and intracrine effects) and consequently reduces the β amyloid, its soluble precursors, prevents damage to the neuronal skeletal network (taupathy), and blocks glutamate excitotoxicity, reduces brain inflammation, prevents apoptosis, and increases the acetylcholine levels in the neurons and synapses; by using a combination of insulin, bexarotene, ketamine, Etanercept, IGF-1, and physostigmine therapeutic agents. The results are achieved by using the specially designed Iontophoresis incorporated olfactory mucosal delivery (ORE) catheter device located at the olfactory nerves, sphenoid sinus, and adjacent structures described here, to transport the large molecules of therapeutic agents to treat AD delivered to the CNS bypassing BBB from ORE.
Owner:WEDGE THERAPEUTICS
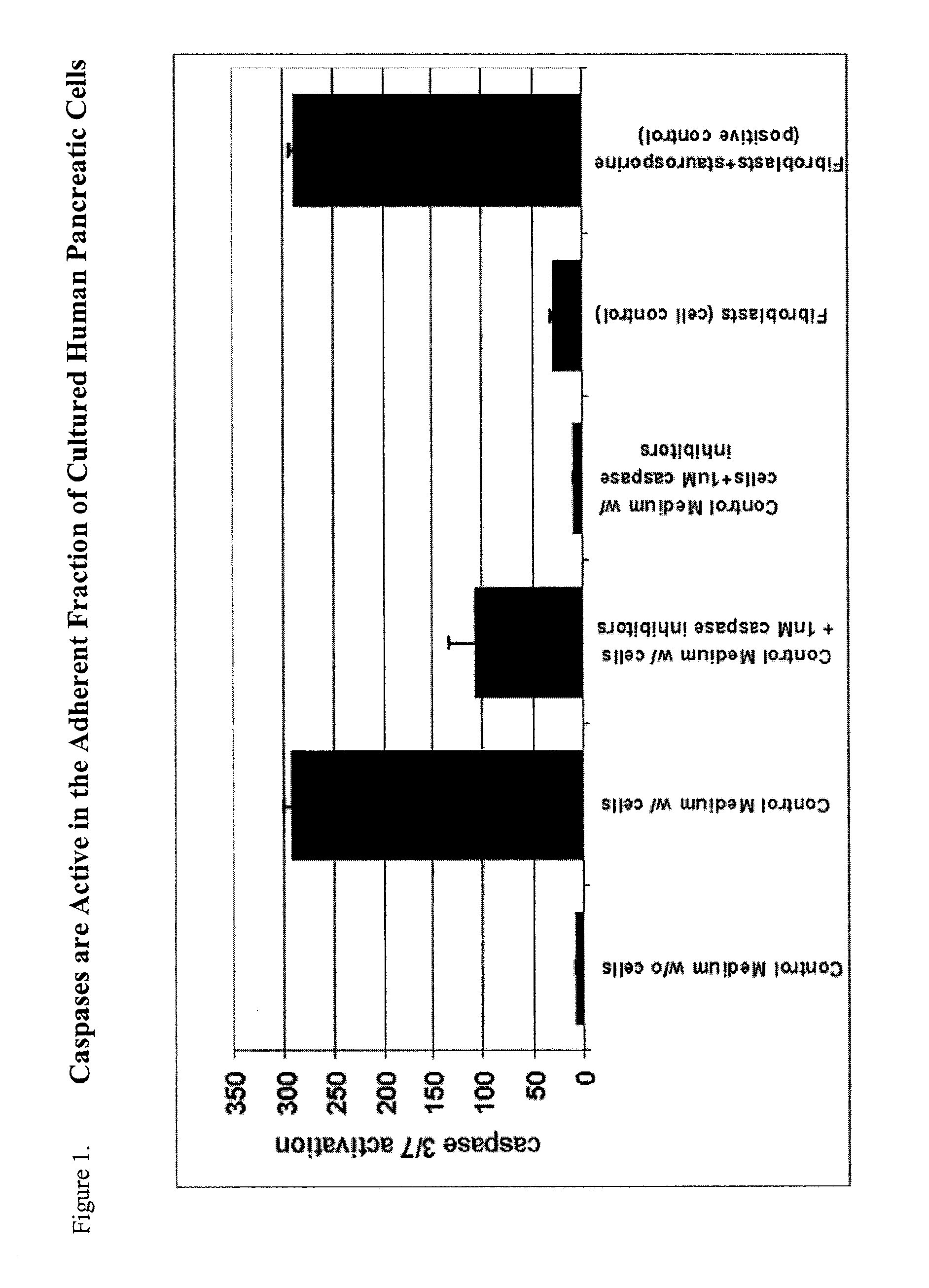
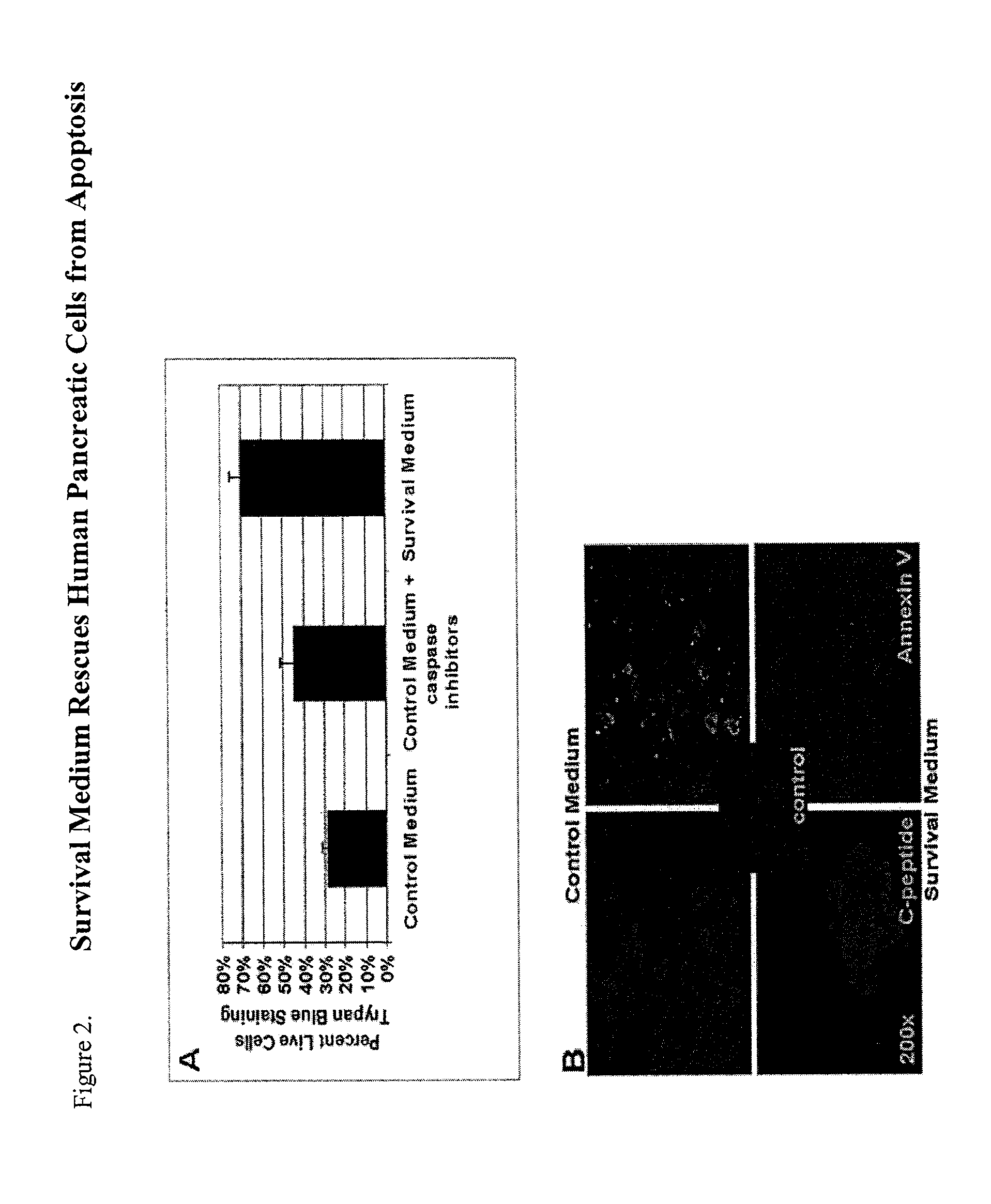
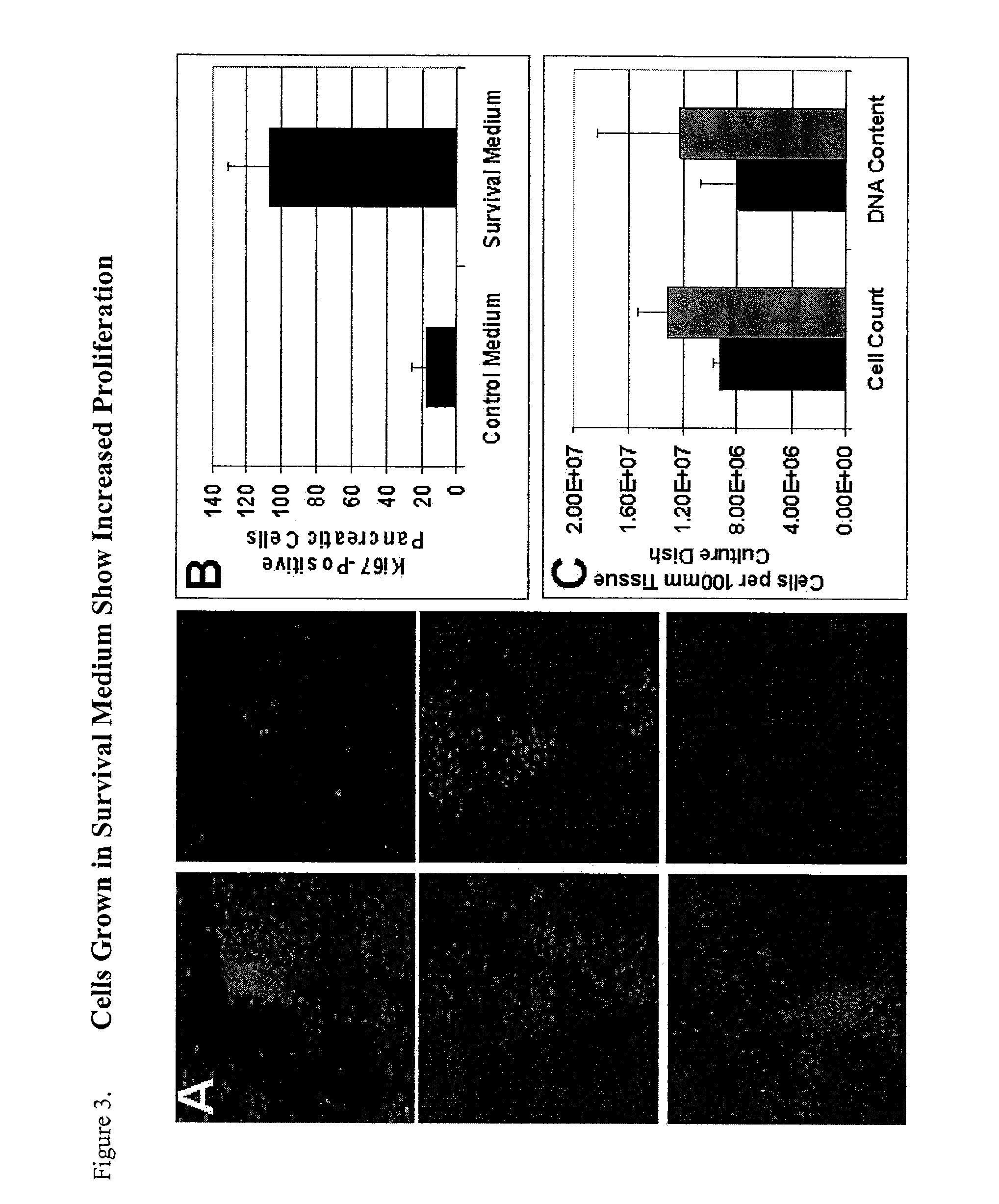
Method of improving cell proliferation of pancreatic progenitor cells in a pancreatic cell culture
InactiveUS20100311166A1Increasing cell proliferationIncreased level of activationCell dissociation methodsMetabolism disorderProgenitorCaspase inhibitors
The invention relates to the discovery that the proliferation and survival of pancreatic progenitor cells can be enhanced by contacting the cells with, (1) a caspase inhibitor sufficient to reduce apoptosis in the pancreatic endocrine cells; and, (2) a growth factor in an amount sufficient to increase the level of activated Akt in the pancreatic endocrine cells.
Owner:RENEURON INC
Population of undifferentiated neural, endocrine or neuroendocrine cells in a hydrogel support
InactiveUS7470425B2Encourage productionExtension of timeBiocideBone implantNervous systemNeuroendocrine cell
The invention features a method for generating new tissue by obtaining a liquid hydrogel-cell composition including a hydrogel and tissue precursor cells; delivering the liquid hydrogel-cell composition into a permeable, biocompatible support structure; and allowing the liquid hydrogel-cell composition to solidify within the support structure and the tissue precursor cells to grow and generate new tissue. The invention also features a tissue forming structure including a permeable, biocompatible support structure having a predetermined shape that corresponds to the shape of desired tissue; and a hydrogel-cell composition at least partially filling the support structure, wherein the hydrogel-cell composition includes a hydrogel and tissue precursor cells. The new tissue forming structure can be used in new methods to generate various tissues (e.g., to treat defective tissue) including new bone, cartilage, and nervous tissue such as spinal cord tissue. The invention also new isolated nervous system stem cells.
Owner:VCELL THERAPEUTICS +1
HER cancer protocols
InactiveUS7309486B1Reduce systemic toxicityAvoid asynchronicityOrganic active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsDual actionIntracrine
Owner:ZAMOYSKI MARK
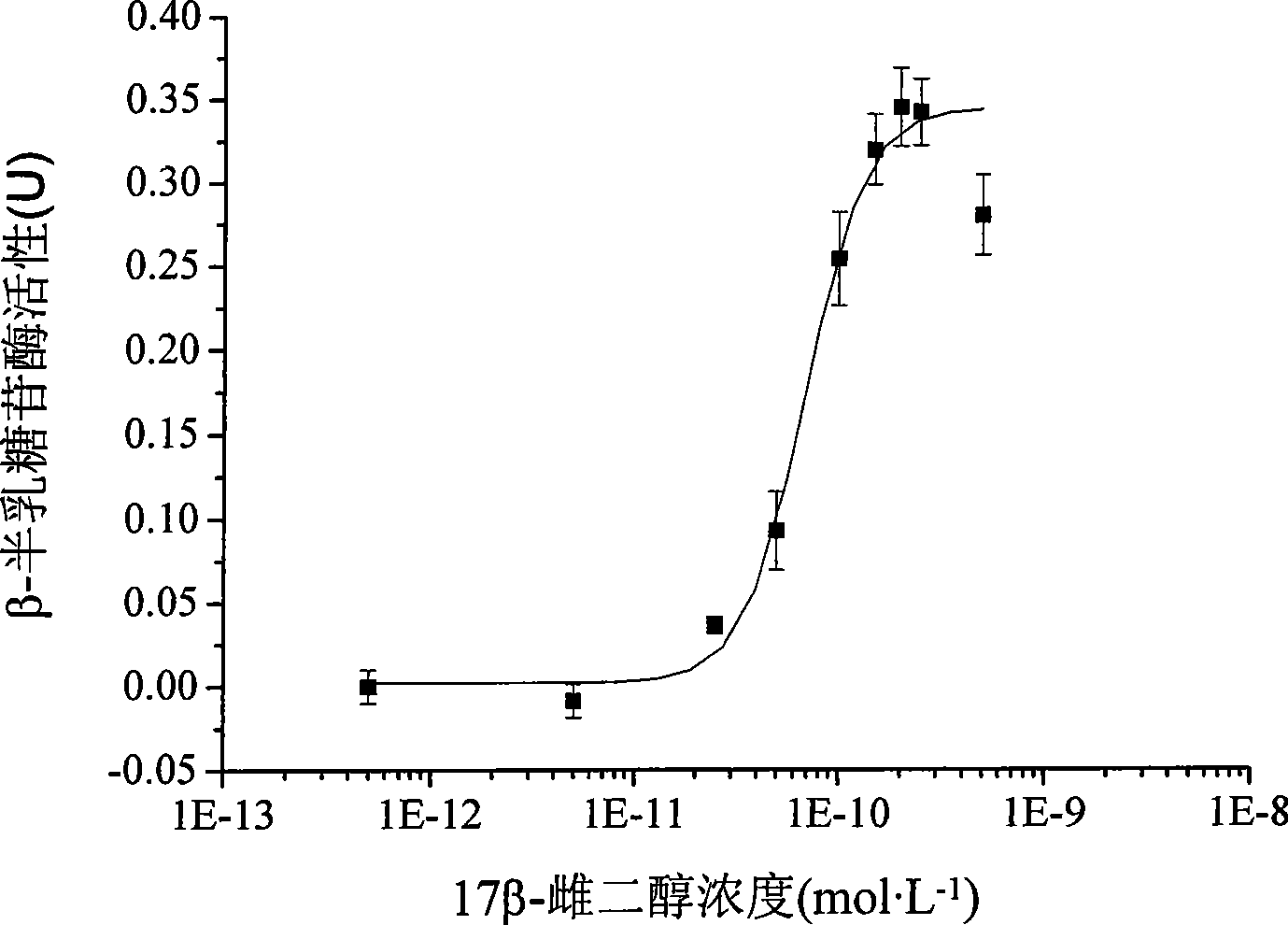
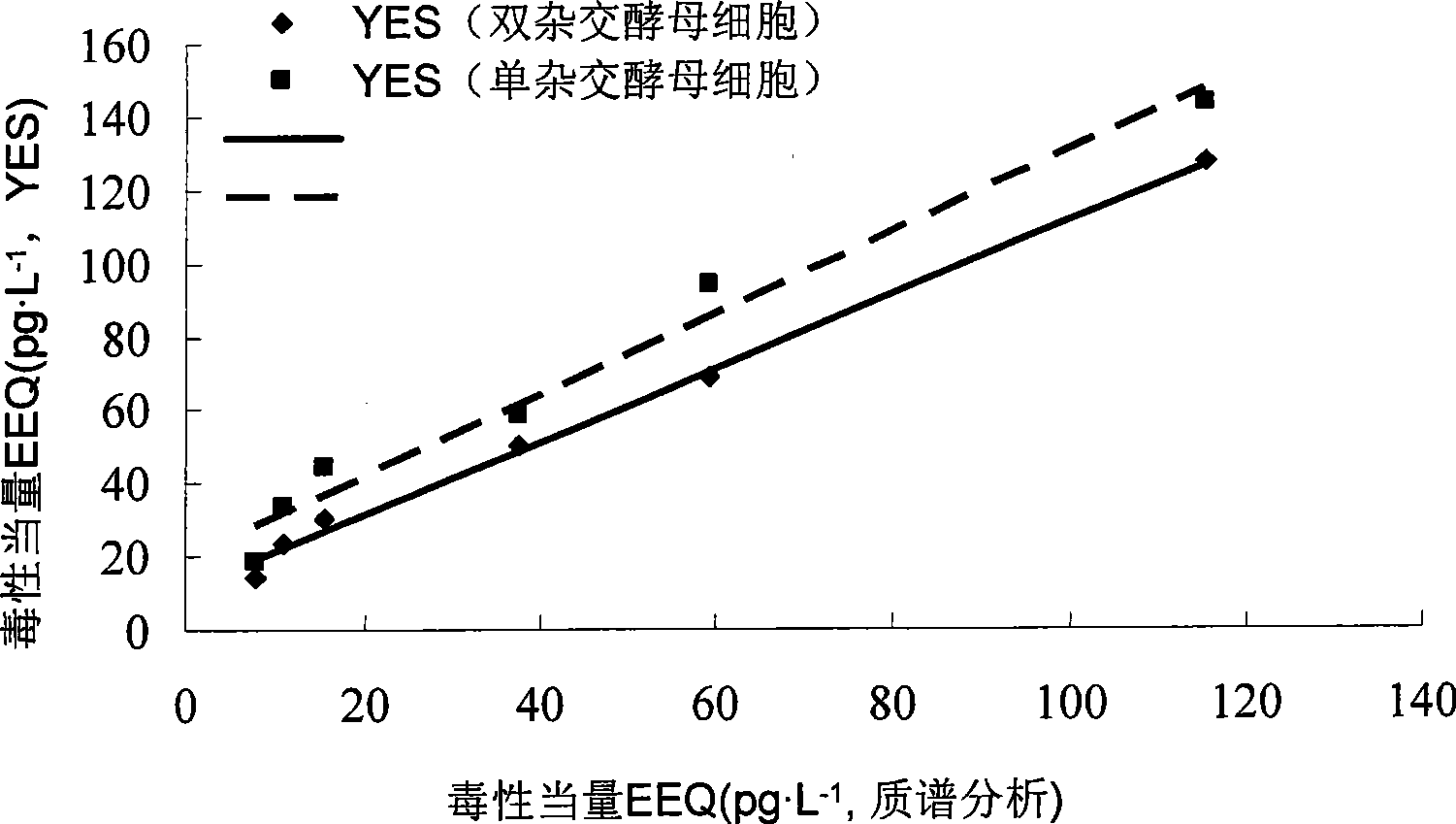
Two-hybrid yeast for detecting estrogen-like compound in environment and biological test method
ActiveCN101469315AThe test process is fastTest stableFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyMammal
The invention provides a two-hybrid yeast for detecting estrogen-like compounds in environmental samples and a preparation method thereof, wherein the yeast contains pGBKT7-ER yeast expression plasmids and pGAD424-GRIP1 yeast expression plasmids, wherein the pGBKT7-ER yeast expression plasmids contain estrogen receptor genes, and the pGAD424-GRIP1 yeast expression plasmids contain estrogen receptor coactivated factor genetic fragments with the sequence of SEQ ID No.2. The invention also provides a bioassay method for detecting the estrogen-like compounds in the environment, which comprises: co-culturing two-hybrid yeast cells and a sample to be detected, adding a reaction liquid of o-nitrobenzene-beta-D-galactopyranoside for reaction, and calculating the concentration of the estrogen-like compounds according to the detected absorbance value of supernatant at 420 nanometers after the reaction stops. The invention adopts the two-hybrid yeast of recombinant estrogen receptor genes for test, and is more close to the actual action conditions of an endocrine system of a mammal; constructed yeast cell genes have stable character and are easy to culture and screen; the screening process of the whole estrogen-like effect is simple to operate; and the required quantity of the sample is small, and the cost is low.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
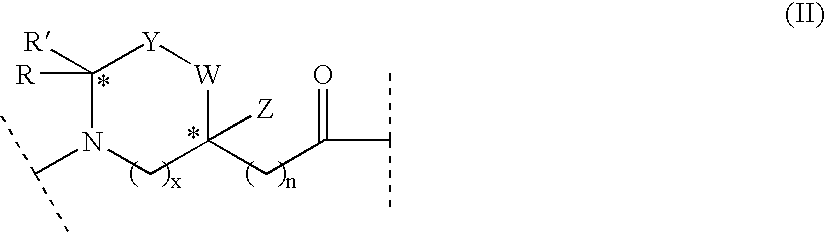
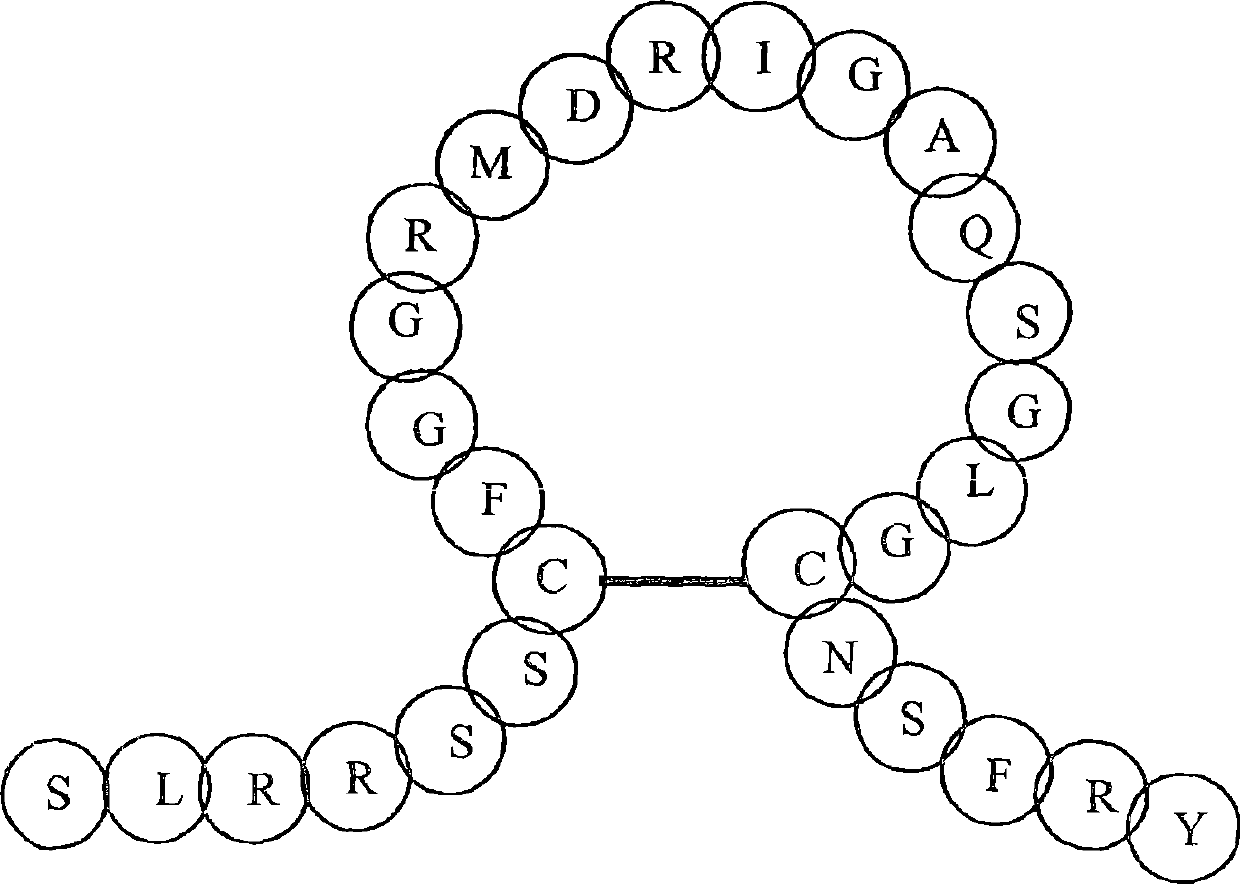
Linear natriuretic peptide constructs
ActiveUS7795221B2Prolonged duration of effectPromote degradationAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseHypertension medications
Linear constructs with an N-terminus and a C-terminus which bind to a natriuretic peptide receptor and include a plurality of amino acid residues and at least one amino acid surrogate of formula I:where R, R′, Q, Y, W, Z, J, x and n are as defined in the specification, and optionally at least one prosthetic group covalently bound to a reactive group of at least one of the amino acid residues or surrogates, pharmaceutical compositions including such linear constructs, and methods of treating congestive heart failure or other conditions, syndromes or diseases for which induction of anti-hypertensive, cardiovascular, renal or endocrine effects are desired.
Owner:PALATIN TECH INC
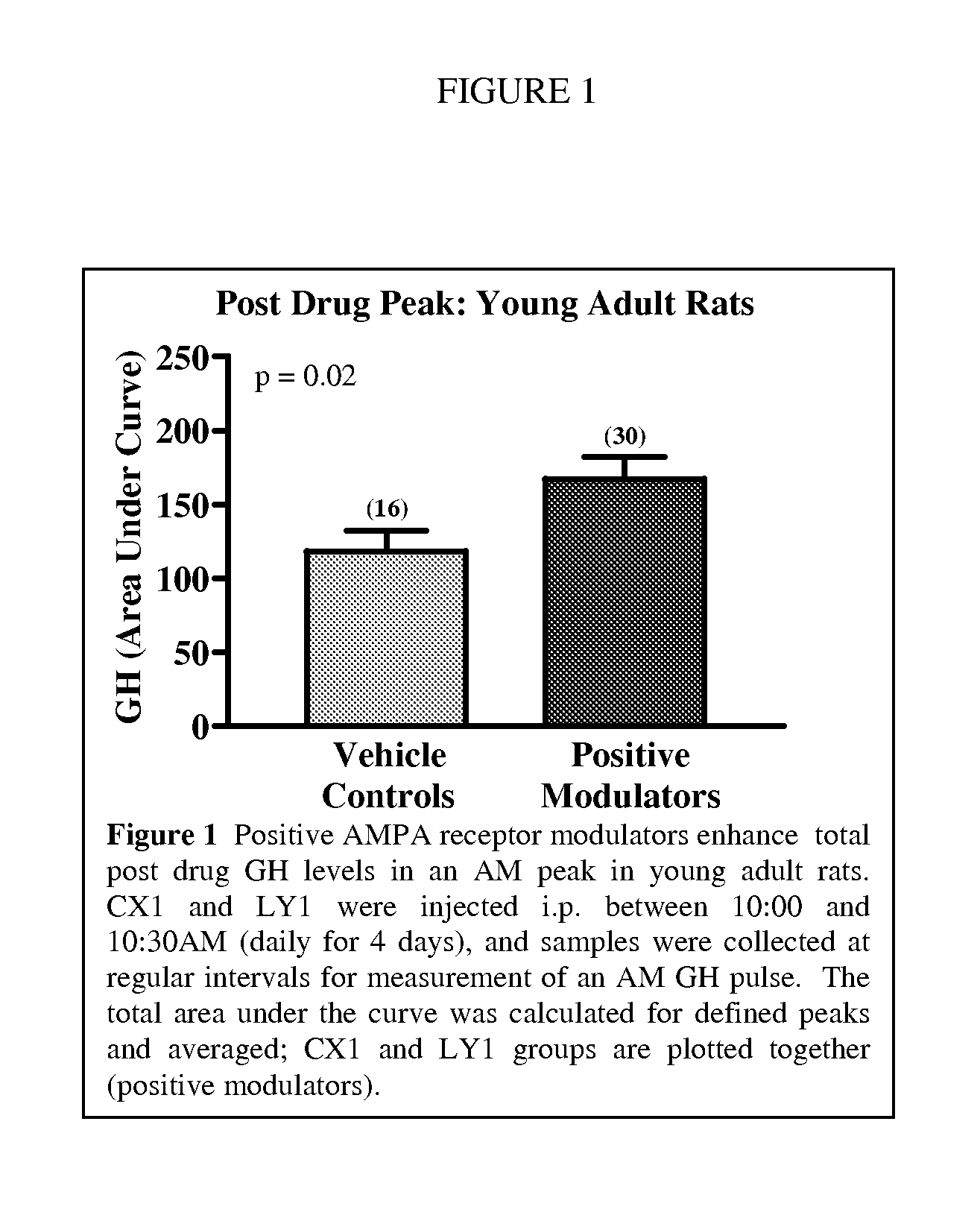
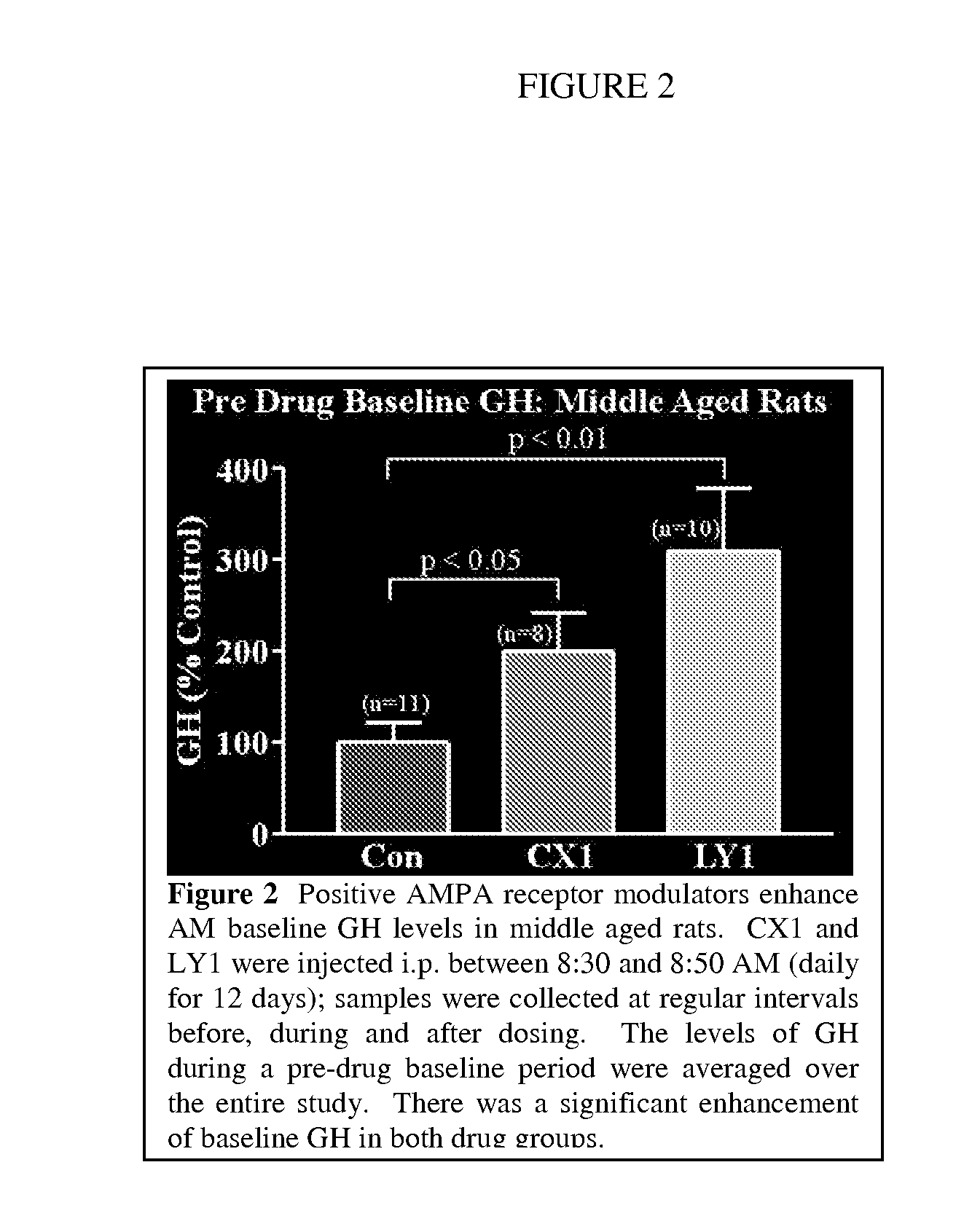
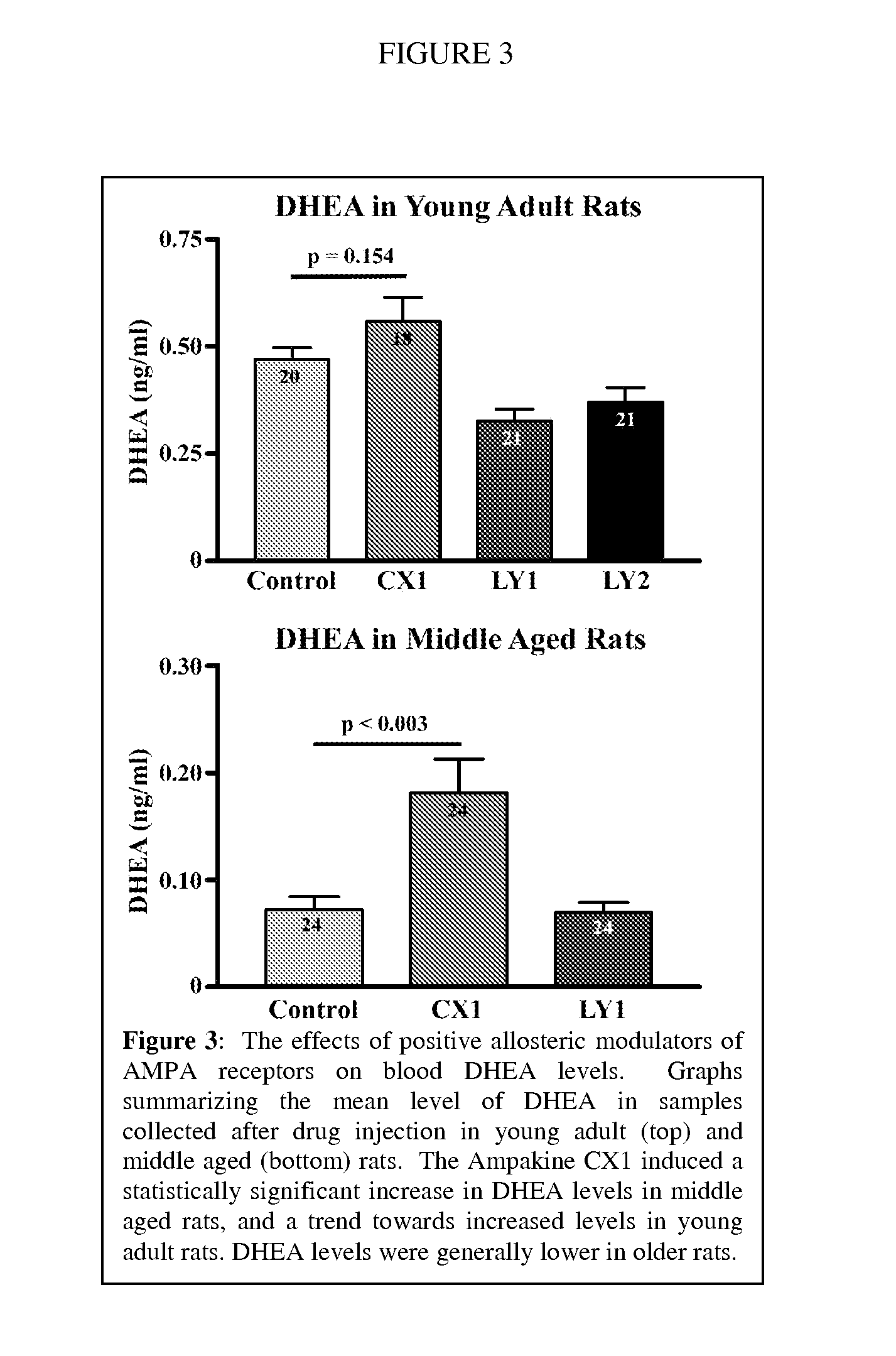
Modulation of Growth Hormone, DHEA, and Cortisol with Positive Modulators of AMPA Type Glutamate Receptors
InactiveUS20100298393A1Facilitated releaseImprove the level ofBiocideAnimal repellantsPhysiologyAllosteric modulator
Methods for modulating the endocrine system of a mammal are provided. In the subject methods, a positive allosteric modulator of AMPA receptors of the hypothalamus are administered to the host. The subject methods find use in applications where it is desired to increase the baseline circulatory level of a growth hormone in a mammalian host. The subject methods also find use in applications where it is desired to increase the circulatory level of DHEA in a mammalian host. Finally, another subject method also finds use in applications where it is desired to decrease the circulatory level of cortisol in a mammalian host.
Owner:OLAS PHARMA
SSTR1-selective analogs
InactiveUS20060155107A1Improve bindingHigh selectivityPeptide/protein ingredientsSomatostatinsNervous systemScreening method
Analogs of SRIF which are selective for SSTR1 in contrast to the other cloned SRIF receptors. These analogs are useful in determining the tissue and cellular expression of the receptor SSTR1 and its biological role in the endocrine, exocrine and nervous system, as well as in regulating tumor growth. SRIF analog peptides, such as des-AA1,2,5[D-Trp8, IAmp9, Tyr11]-SRIF and counterparts incorporating Cbm at the N-terminus, as well as radioiodinated versions thereof, inhibit the binding of a universal SRIF radioligand to the cloned human receptor SSTR1, but they do not bind with significant affinity to human SSTR2, SSTR3, SSTR4 or SSTR5. By incorporating an iodinated tyrosine in position-2 or in position-11 in these SSTR1-selective SRIF analogs, a labeled compound useful in drug-screening methods is provided. The N-terminus accommodates bulky moieties without loss of selectivity, and a carbamoyl moiety or a conjugating agent that will accept a radioactive nuclide or will link to a cytotoxin may be present at the N-terminus.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Ovary cell microcapsule
InactiveCN101229192AComplementary personalizationCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsEndocrine functionsPhysiology
The invention provides an ovarian cell microcapsule, which adopts alginate-poly-lysine- alginate (APA) to encapsulate ovarian cells and prepare a microcapsule containing ovarian cells inside. The ovarian cells in the microcapsule consists of ovarian granulosa cells and theca cells, which has endocrine function; undifferentiated ovary inner mesenchymal cells and connective tissue cells. If allogenously plant the microcapsule of the invention, the endocrine cells in the microcapsule can constantly secret sex hormone in body, and the endocrine function can be under the control of neuroendorine of the body to reach the aim of personalized supplementing the inefficiency of sex hormone endocrine. The allogenous plant of ovarian cell microcapsule has positive prevention and treatment effects to body degenerative lesion. Experiment shows that the invention can alleviate the loss of bone quantity and presents positive effect to the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis; meanwhile, the invention can affect the biological activity of islet Alpha cell and Beta cell, and regulate the endocrine of insulin and glucagons.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
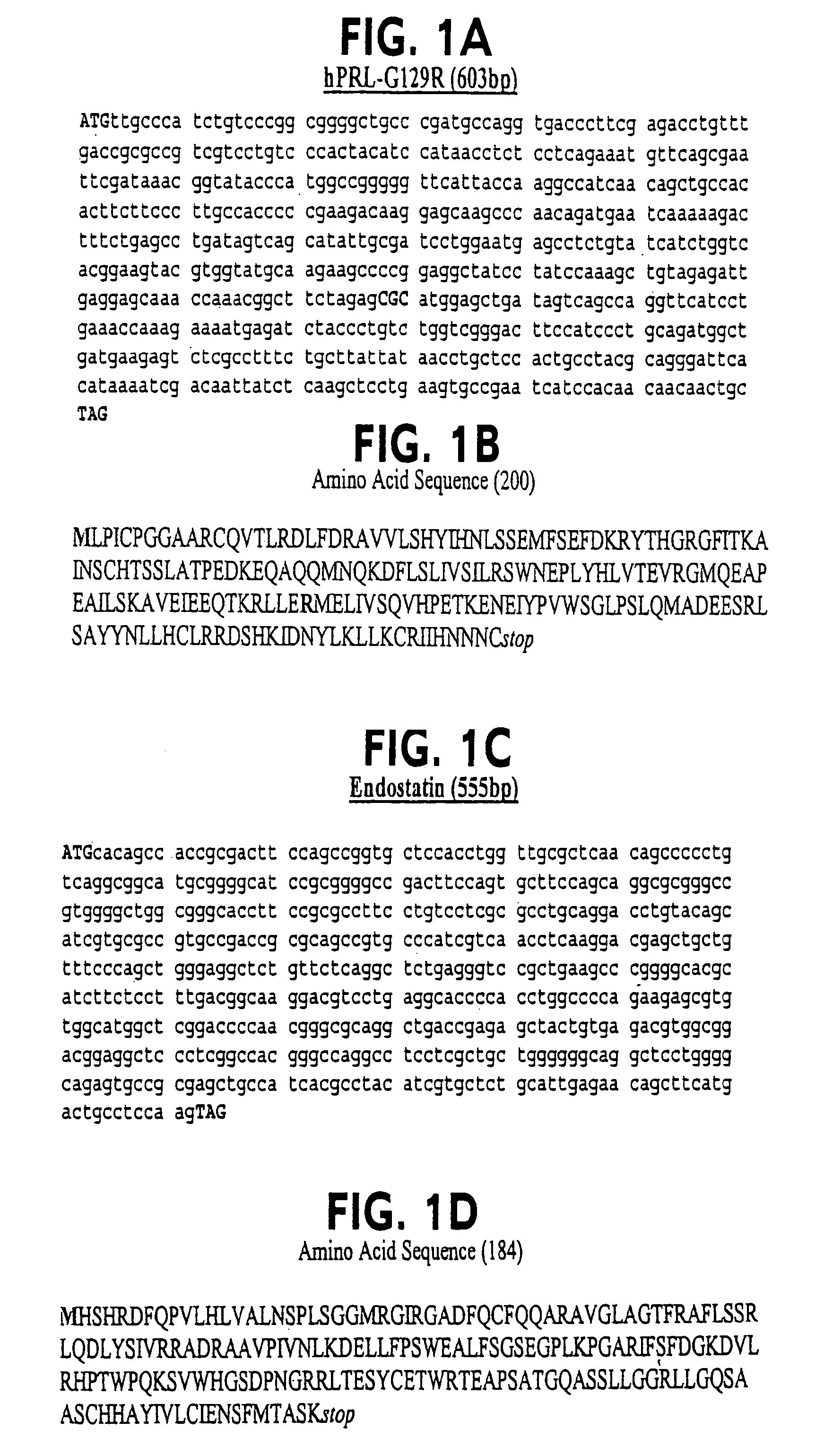
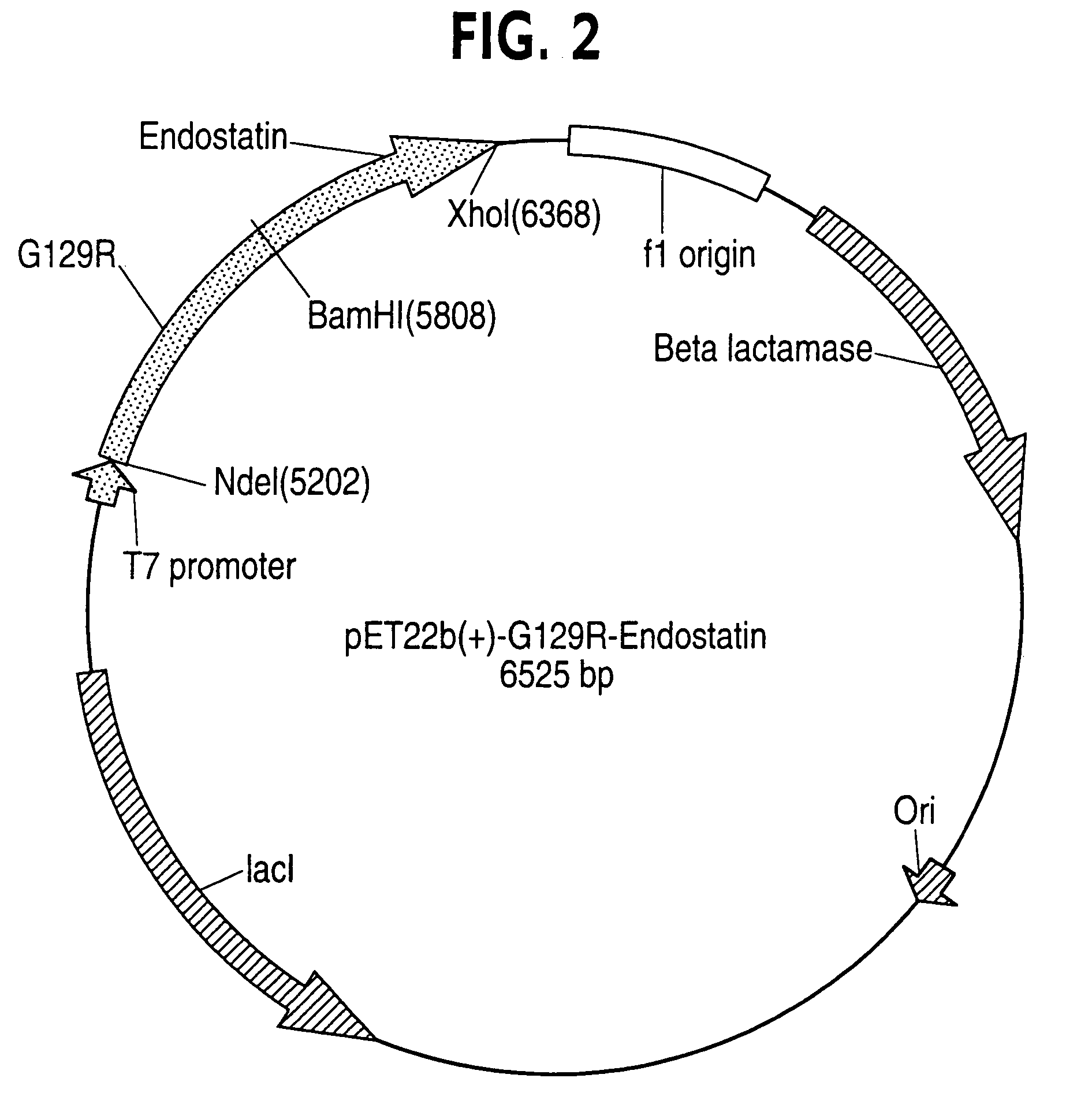
Human prolactin antagonist-angiogenesis inhibitor fusion proteins
ActiveUS7339027B2Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAngiogenesis InhibitionIntracrine
A novel fusion protein, comprising a receptor-antagonizing domain and an angiogensis inhibiting domain, characterized, for example, by its ability to block apoptosis and / or inhibit endocrine response, is useful in treating cancer. For example, a human prolactin antagonist-endostatin fusion protein combines apoptosis induction and angiogenesis inhibition to combat cancer.
Owner:ONCOLIX
Compositions and methods for treating endocrine, gastrointestinal or autoimmune disorders
Recombinant cells and methods are provided that relate to the use of isolated, engineered recombinant cells to directly or indirectly treat diseases or disorders in a mammalian host such as endocrine, gastrointestinal or autoimmune disorders. A recombinant cell is provided that comprises a signal sequence and a promoter, wherein: the signal sequence is capable of regulating signal-dependent expression of a target nucleic acid in a host or is capable of regulating signal-dependent expression of a target nucleic acid in response to an environmental stimulus, the cell is derived from an enteric or a commensal bacterium, and the target nucleic acid encodes a mammalian factor that promotes normal functioning of a physiological process in the host or is effective in preventing onset, establishment, or spread of a non-infectious disease in the host. The recombinant cell is administered to the host to treat the disease or disorder.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Model Taste Cells and Methods of Use for Identifying Modulators of Taste Sensation
InactiveUS20080026416A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisTaste receptor ligandEnteroendocrine cell
The present invention provides model taste cells that naturally or recombinantly express taste receptors and relevant cellular proteins and / or molecules useful for taste signal transduction. The present invention further provides methods of use for these model taste cells for screening for compounds that modulate sweet and / or other taste signal transduction. Compositions comprising the compounds / modulators identified using the model taste cells are also provided. In preferred embodiments, the model taste cells are derived from human HuTu-80 enteroendocrine cells, and derivative cells thereof.
Owner:THE COCA-COLA CO
Microarray for evaluation of stress-related genes in skin
InactiveUS20070059711A1Improve the level ofBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDNA Microarray ChipCuticle
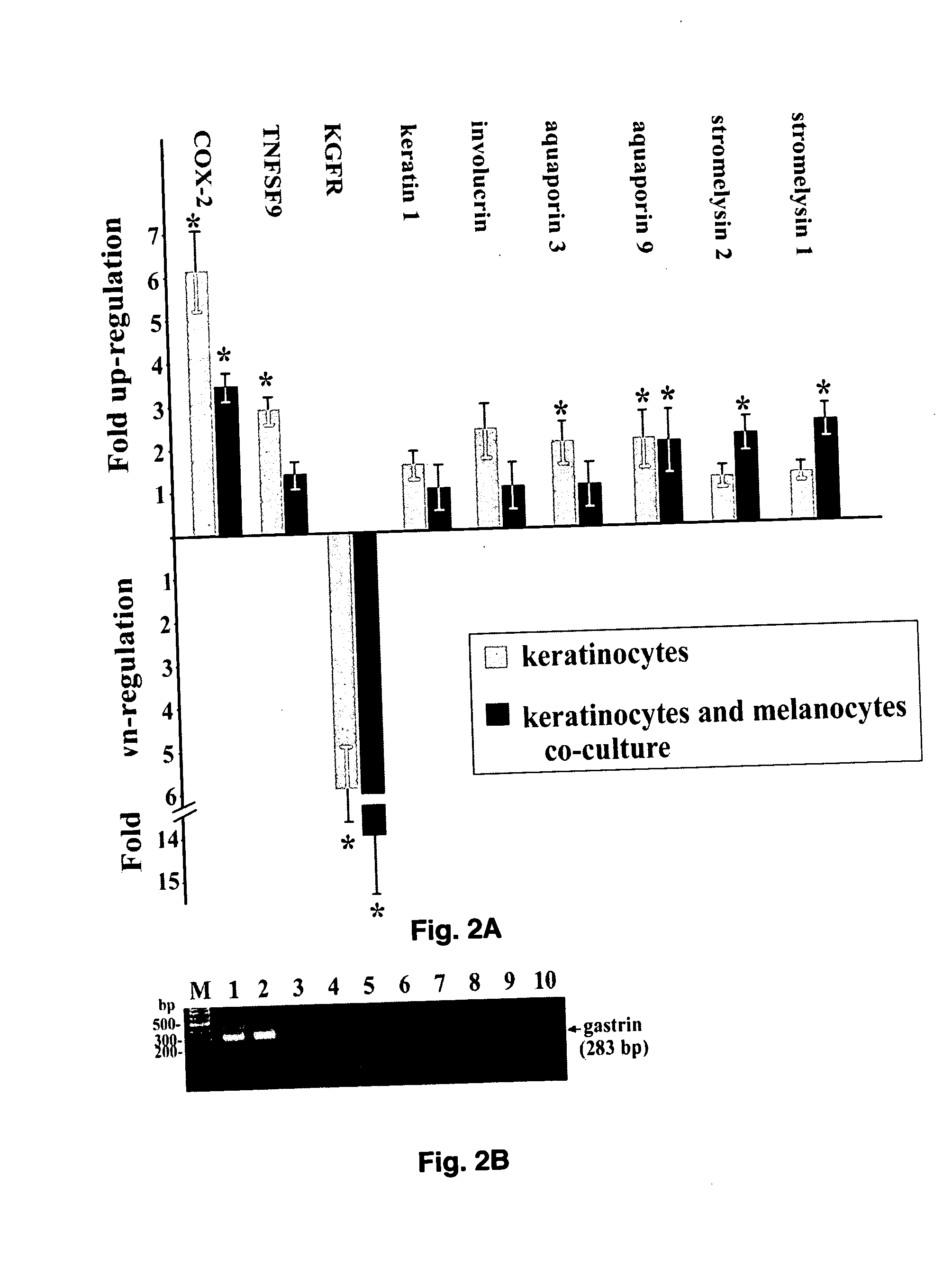
The present invention provides a novel DNA microarray chip that can be used for simultaneous testing of transcriptional responses to cutaneous stressors in the context of neuro-endocrine-immune functions of the skin. The transcriptional responses to ultraviolet radiation in epidermal keratinocytes were tested using such microarray chip containing more than 700 neuro-endocrine-immune related genes. The gene expression pattern was non-random and time dependent; it included increased expression of genes involved in water and salt balance, prostaglandin synthesis, keratinocyte differentiation as well as genes coding for stress effectors, cytokines and metalloproteinases. In contrast, expression was decreased for genes coding for growth factors and their receptors, and for elements of extracellular matrix. This stochastic pattern suggests that transcriptional responses are coordinated and aimed at preservation of epidermal barrier function, prevention of early carcinogenic events and remodeling of extracellular matrix.
Owner:SLOMINSKI ANDRZEJ +1
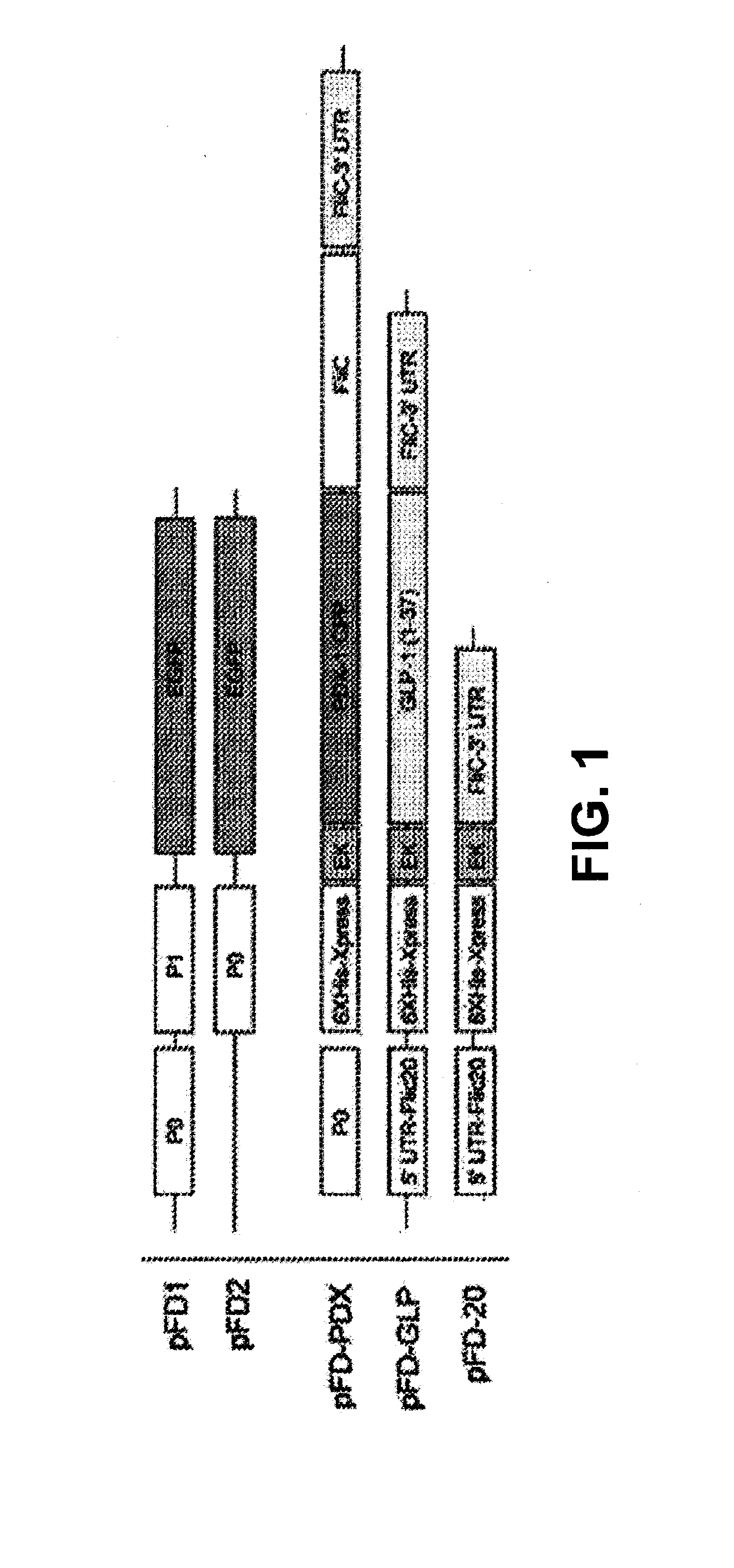
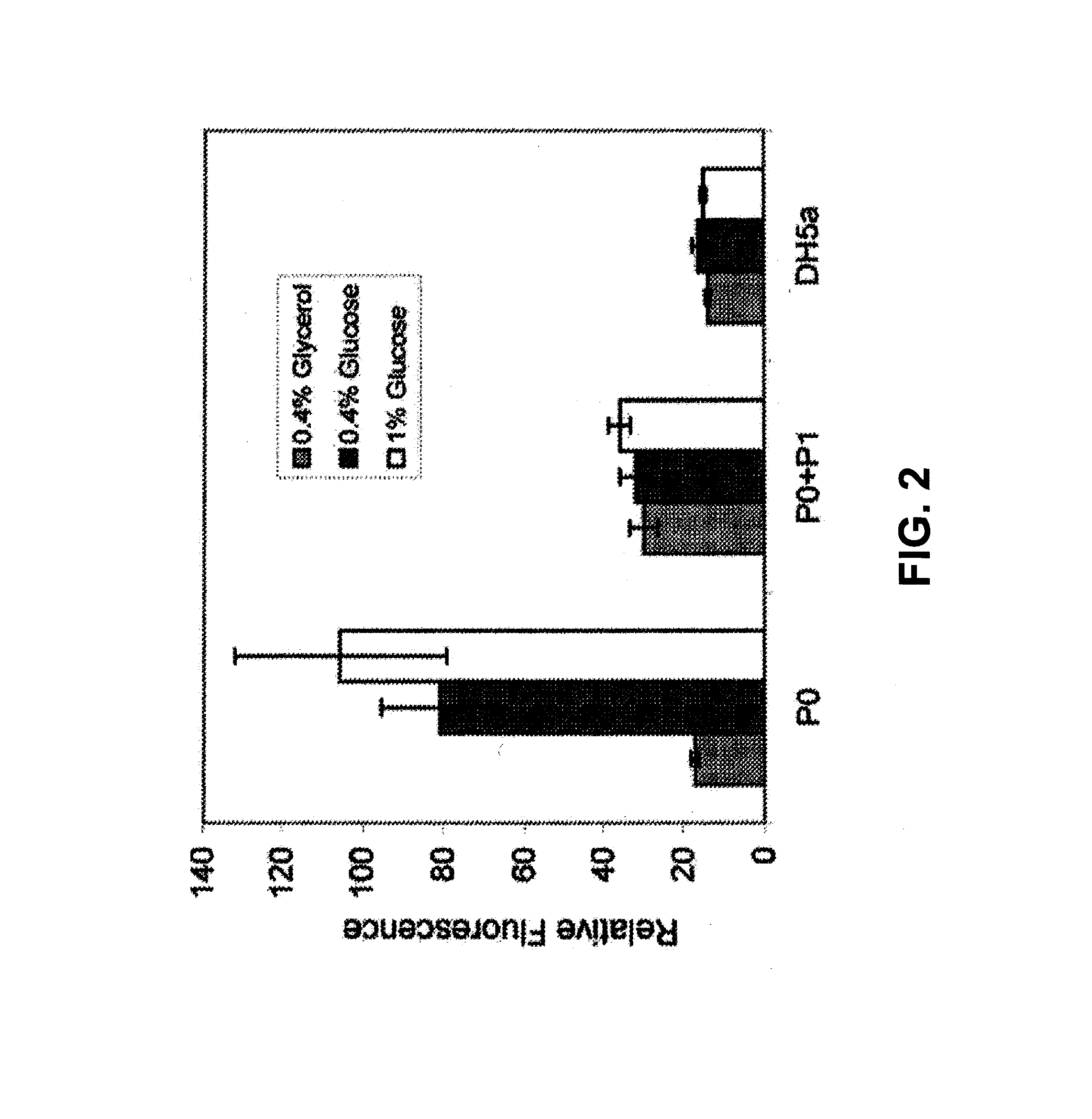
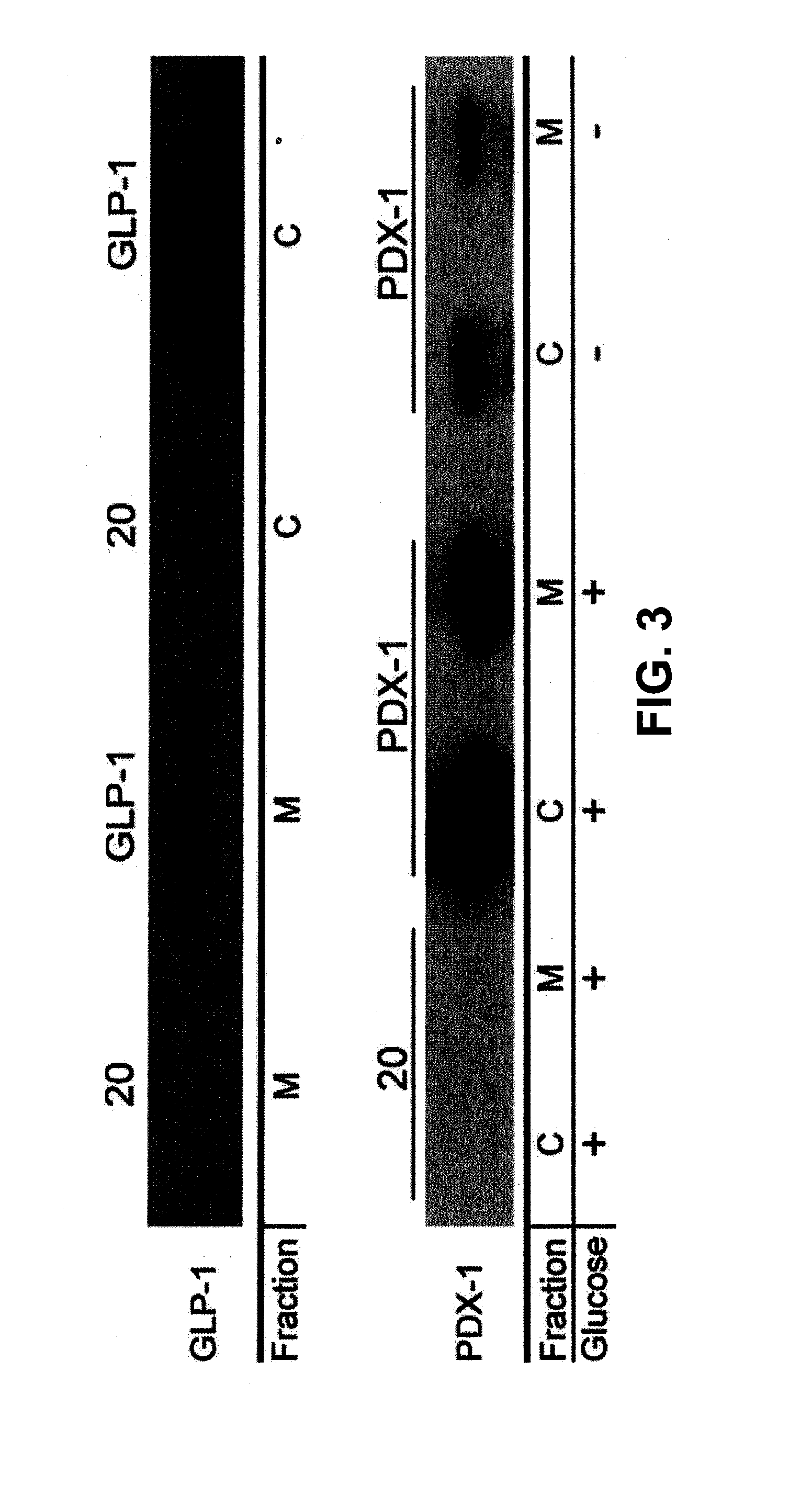
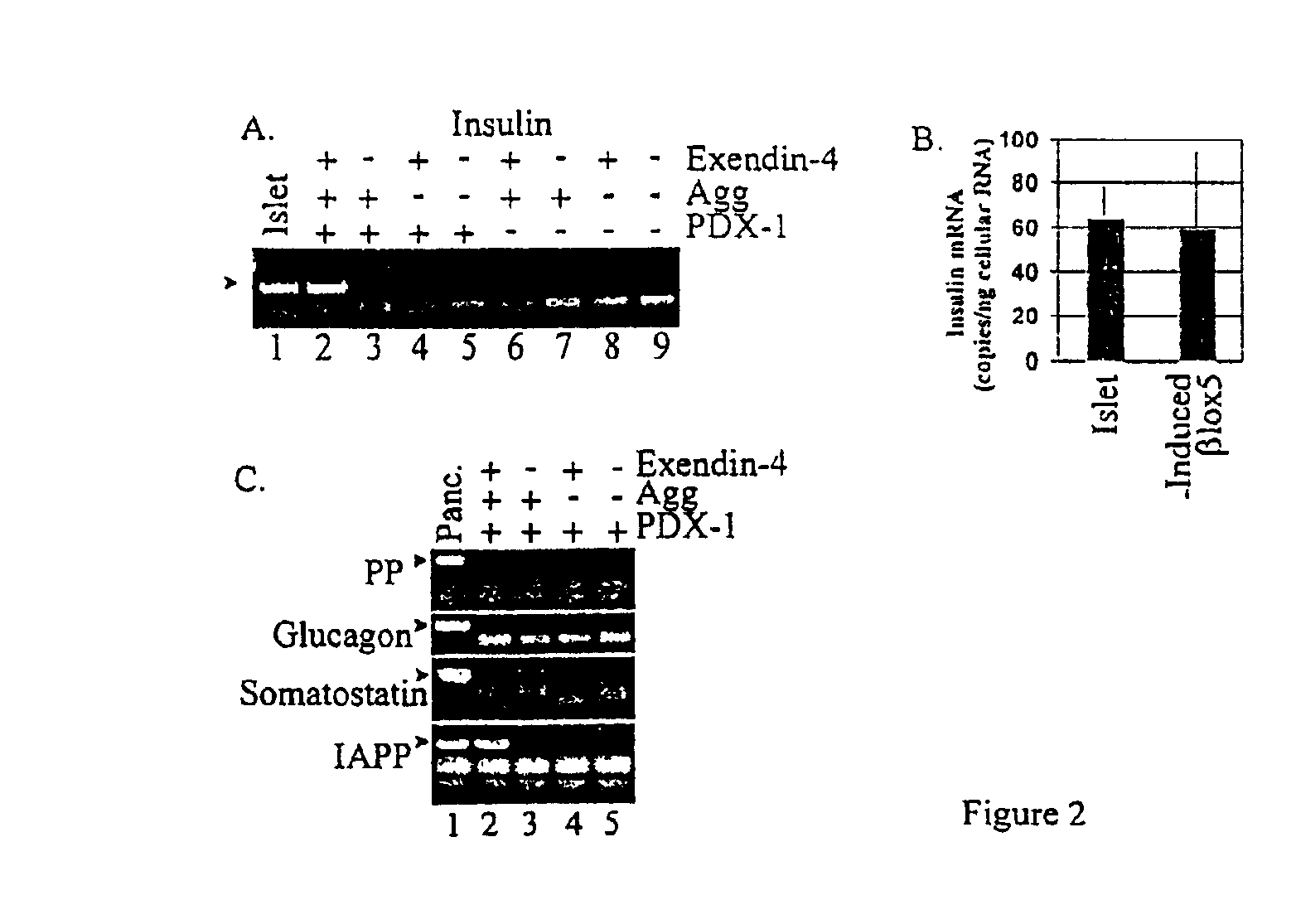
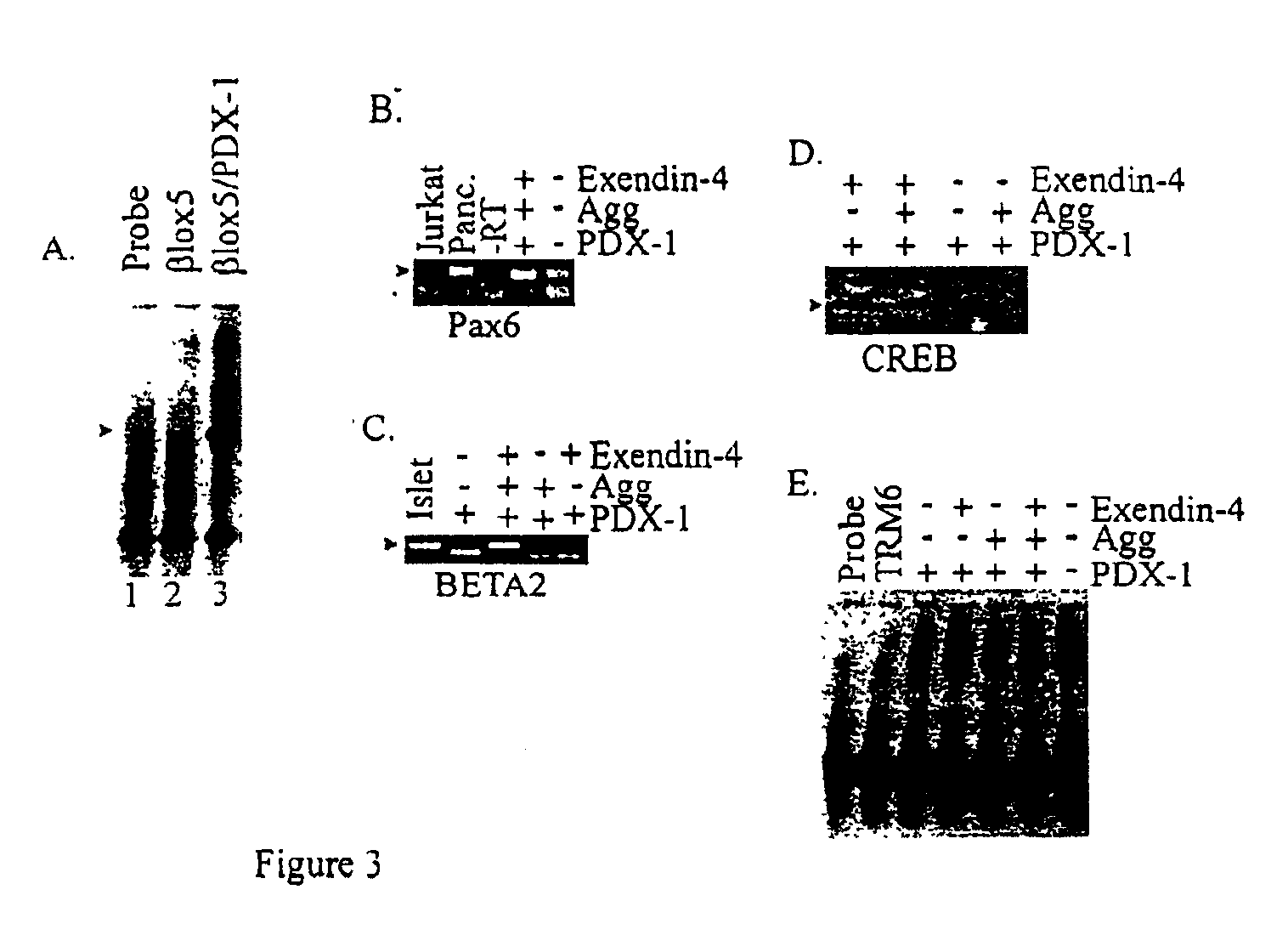
Induction of beta cell differentiation in human cells by stimulation of the GLP-1 receptor
InactiveUS6884585B2High expressionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsHuman cell
The present invention provides methods for inducing insulin gene expression in cultured pancreas cells, the method comprising contacting a culture of endocrine pancreas cells expressing a PDX-1 gene with a GLP-1 receptor agonist, wherein the cells have been cultured under conditions such that the cells are in contact with other cells in the culture, thereby inducing insulin gene expression in the cells. The invention also provides high throughput screening methods for modulators of β-cell function, stable cultures of cells made by the methods of the invention, and methods of treating a human subject using the methods of the invention.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for purifying and recognizing pancreatic endocrine cells
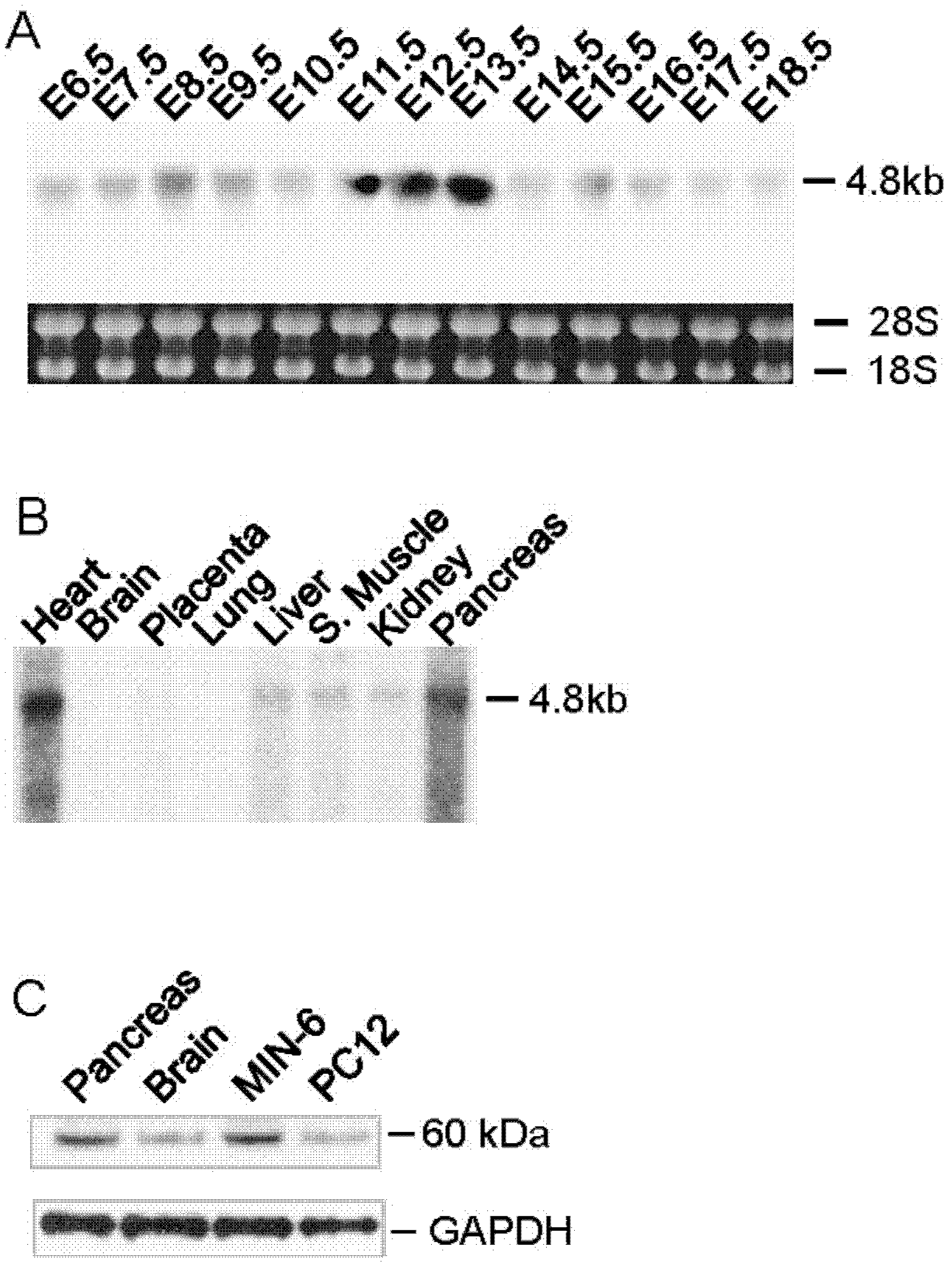
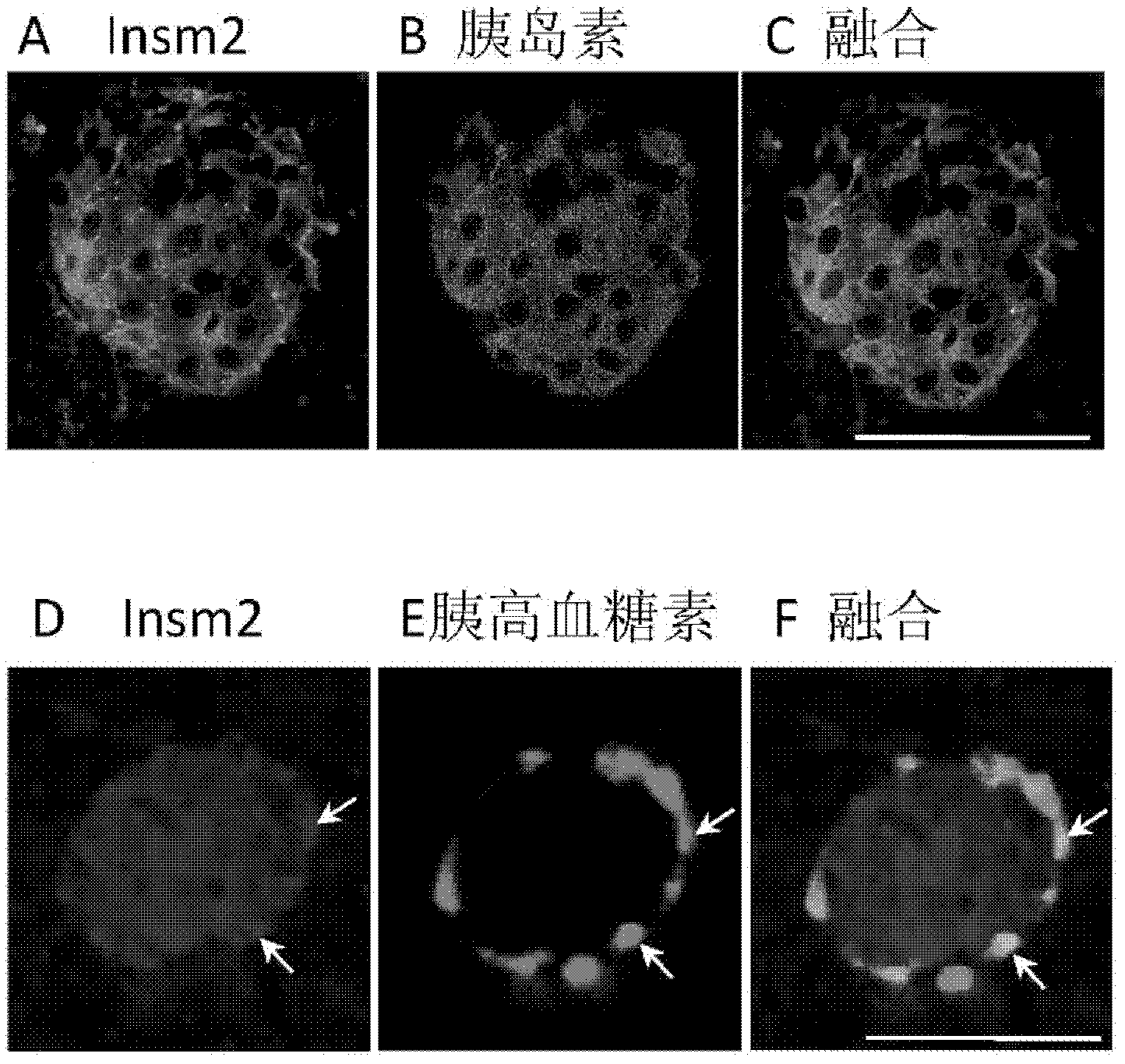
InactiveCN102321572AMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificially induced pluripotent cellsIntracrinePancreas
Owner:余跃红 +1
Biomarker metabolic pathway, and analysis method and application
The invention belongs to the technical field of functional analysis methods of disease metabolism biomarkers, and provides a biomarker metabolic pathway and an analysis method. The metabolic biomarker is stearic acid, phytosphingosine, glycine, glutamine and phospholipids; an acting target spot of the metabolic biomarker is a target protein related to a depression nervous system, immune response and endocrine; and the metabolic pathway is a PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, an mTOR signaling pathway, an MAPK signaling pathway, an erbB signaling pathway, a neurenergen signaling pathway, an Rap1 signaling pathway and an Ras signaling pathway. A functional network analysis method suitable for depression characteristics is established, and the clinical application of these biomarkers helps to optimize the diagnosis of depression, and can provide some valuable clues for the subsequent depression network function researches.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
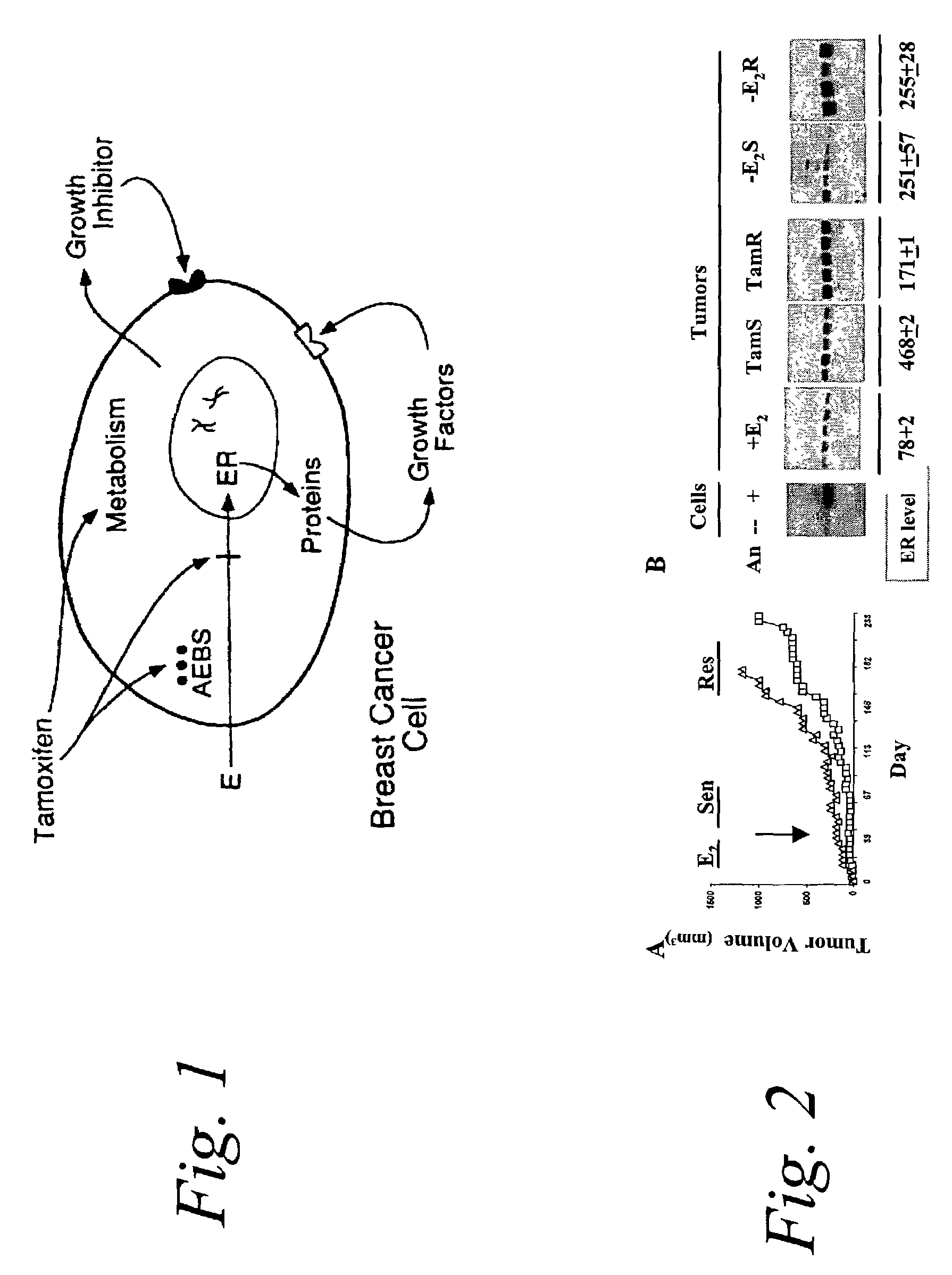
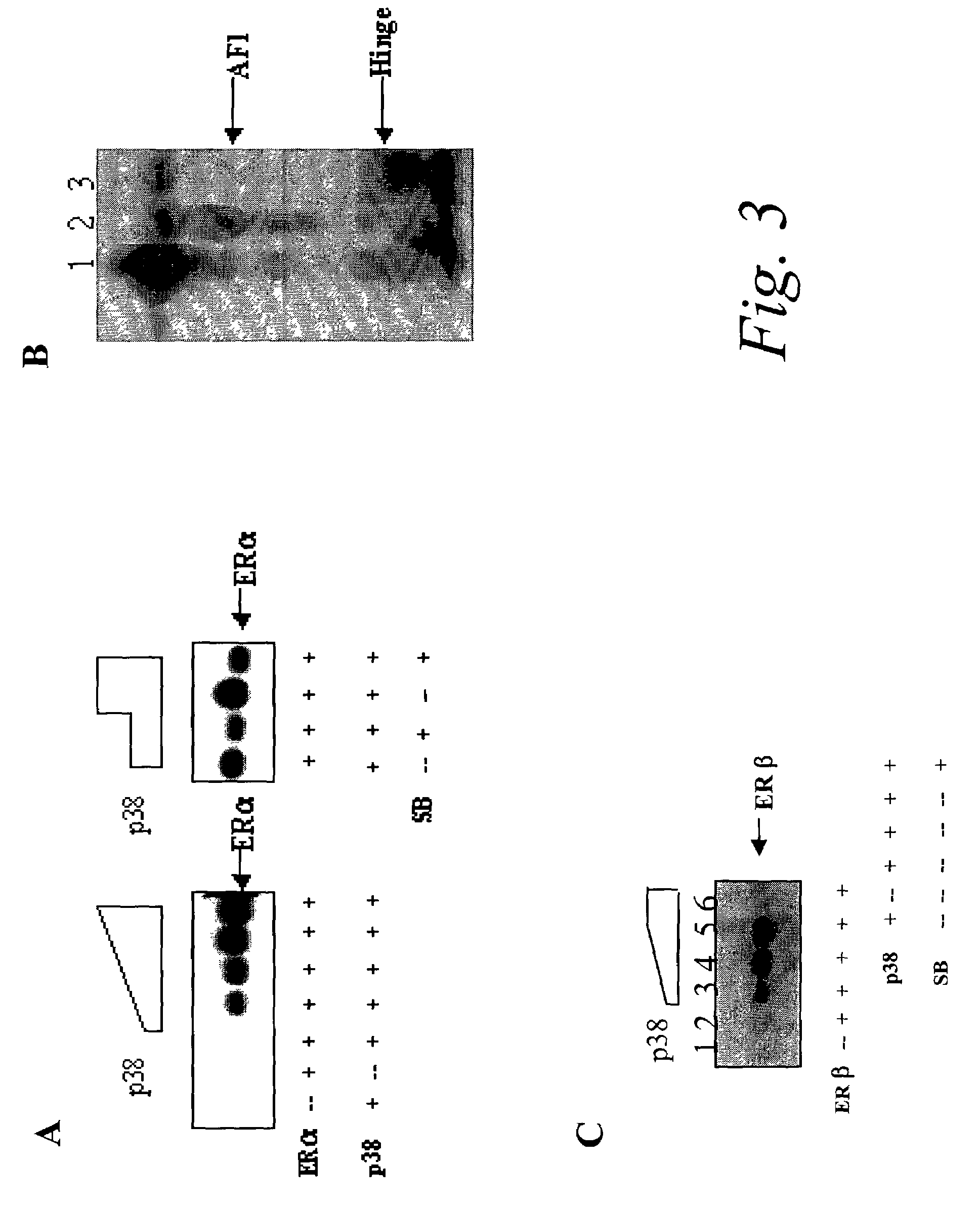
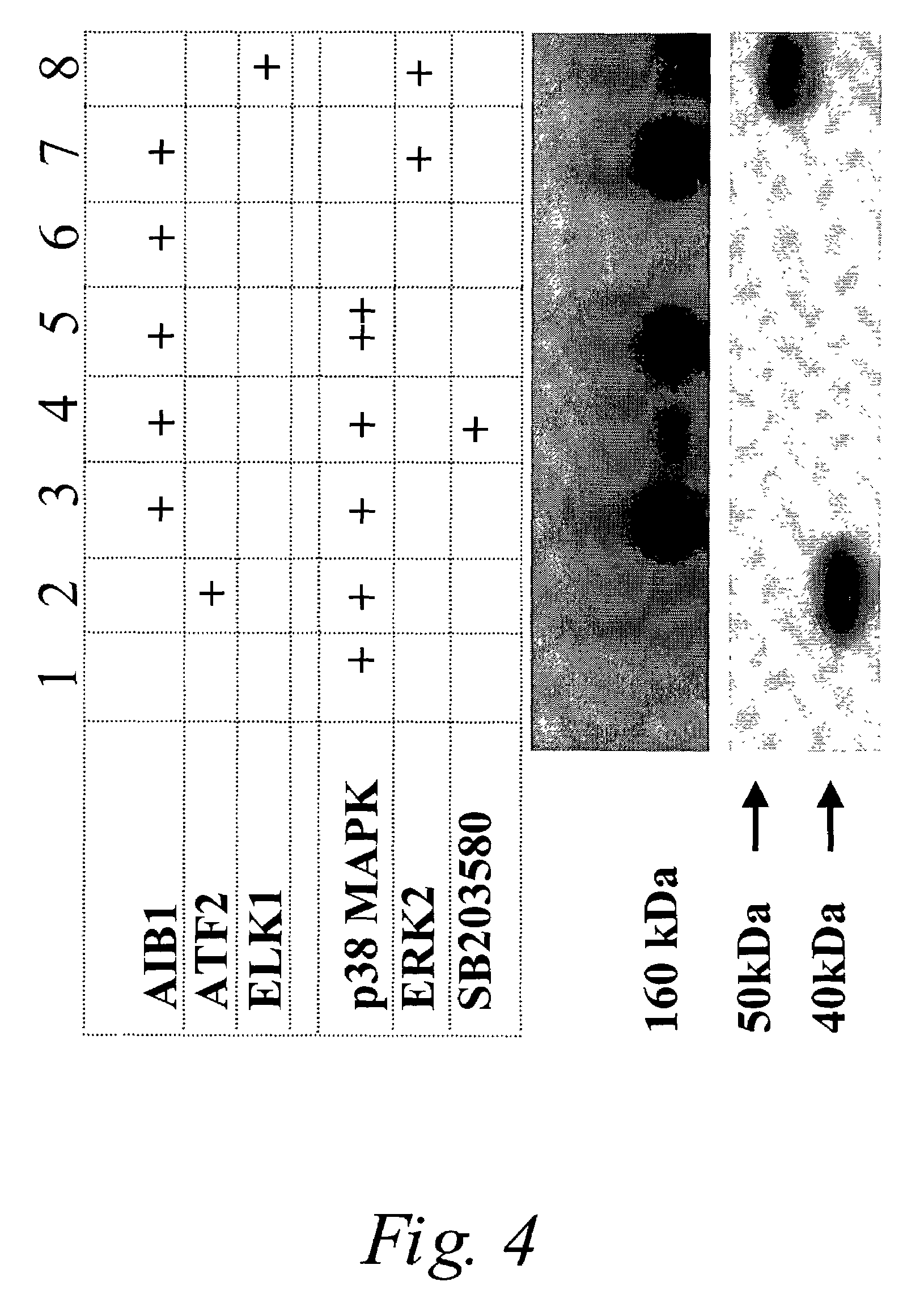
P38 MAPK pathway predicts endocrine-resistant growth of human breast cancer and provides a novel diagnostic and treatment target
InactiveUS7217533B2Avoid resistanceSamplingMicrobiological testing/measurementAdjuvantTreatment targets
Acquired and de novo endocrine resistance are major clinical problems in the management of breast cancer patients. Though the antiestrogen tamoxifen prolongs disease-free and overall survival in the adjuvant setting, and induces remissions in over half of the patients with estrogen receptor positive metastatic disease, all patients eventually acquire tamoxifen resistance. Furthermore, many of the resistant tumors actually appear to be stimulated by tamoxifen just as they are by estrogens. The present invention provides methods of predicting endocrine resistance comprising detecting the biological activity and / or expression of p38 MAPK and / or AIB1. The invention further provides methods of reducing, reversing, or preventing endocrine resistance comprising contacting a breast or prostate tumor with a p38 MAPK pathway inhibitor.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Subpopulations of spore-like cells and uses thereof
Subpopulations of spore-like cells expressing specific cell surface and gene expression markers are provided. In one embodiment, the cells express at least one cell surface or gene expression marker selected from the group consisting of Oct4, nanog, Zfp296, cripto, Gdf3, UtF1, Ecat1, Esg1, Sox2, Pax6, nestin, SCA-1, CD29, CD34, CD90, B1 integrin, cKit, SP-C, CC10, SF1, DAX1, and SCG10. Also provided are methods for purifying a subpopulation of spore-like cells of interest from a population of spore-like cells, and methods for inducing differentiation of the isolated spore-like cells into cells of endodermal, mesodermal or ectodermal origin. The spore-like cells can be used to generate cells originating from all three germ layers and can be used to treat a patient who has a deficiency of functional cells in any of a wide variety of tissues, including the retina, intestine, bladder, kidney, liver, lung, nervous system, or endocrine system.
Owner:VCELL THERAPEUTICS
Novel human G-protein coupled receptor, HGPRBMY18, expressed highly in pituitary gland and colon carcinoma cells
InactiveUS20030129653A1Pathological conditionAvoid the needPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPituitary glandPolynucleotide
The present invention describes a newly discovered human G-protein coupled receptor and its encoding polynucleotide. Also described are expression vectors, host cells, agonists, antagonists, antisense molecules, and antibodies associated with the polynucleotide and / or polypeptide of the present invention. In addition, methods for treating, diagnosing, preventing, and screening for disorders associated with aberrant cell growth, endocrine conditions, neurological conditions, and diseases or disorders related to the pituitary gland, colon, breast, lungs, and prostate are illustrated.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Model taste cells and methods of use for identifying modulators of taste sensation
InactiveCN101495508ACell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsBiological material analysisTaste receptor ligandEnteroendocrine cell
The present invention provides model taste cells that naturally or recombinant Iy express taste receptors and relevant cellular proteins and / or molecules useful for taste signal transduction. The present invention further provides methods of use for these model taste cells for screening for compounds that modulate sweet and / or other taste signal transduction. Compositions comprising the compounds / modulators identified using the model taste cells are also provided. In preferred embodiments, the model taste cells are derived from human HuTu-80 enteroendocrine cells, and derivative cells thereof.
Owner:THE COCA COLA CO
TSH immunoassays employing scavenging reagents for cross-reacting endocrine glycoprotein hormone analogues
ActiveUS8617826B2Interference minimizationBiological testingImmunoassaysFollicle-stimulating hormoneIntracrine
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) immunoassays are performed using an ELISA sandwich assay that employs scavenging or sacrificial beads for reducing interference caused by cross-reacting endocrine glycoprotein hormone analogues such as Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH), Luteinizing Hormone (LH) and Chorionic Gonadotropin (CG).
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
Cyclic natriuretic peptide constructs
Cyclic constructs with an N-terminus and a C-terminus which bind to a natriuretic peptide receptor and include a plurality of amino acid residues, at least one amino acid surrogate of formula I: where R, R', Q, Y, W, Z, J, x and n are as defined in the specification, and optionally at least one prosthetic group, pharmaceutical compositions including such cyclic constructs, and methods of treatingcongestive heart failure or other conditions, syndromes or diseases for which induction of anti hypertensive, cardiovascular, renal or endocrine effects are desired.
Owner:PALATIN TECH INC
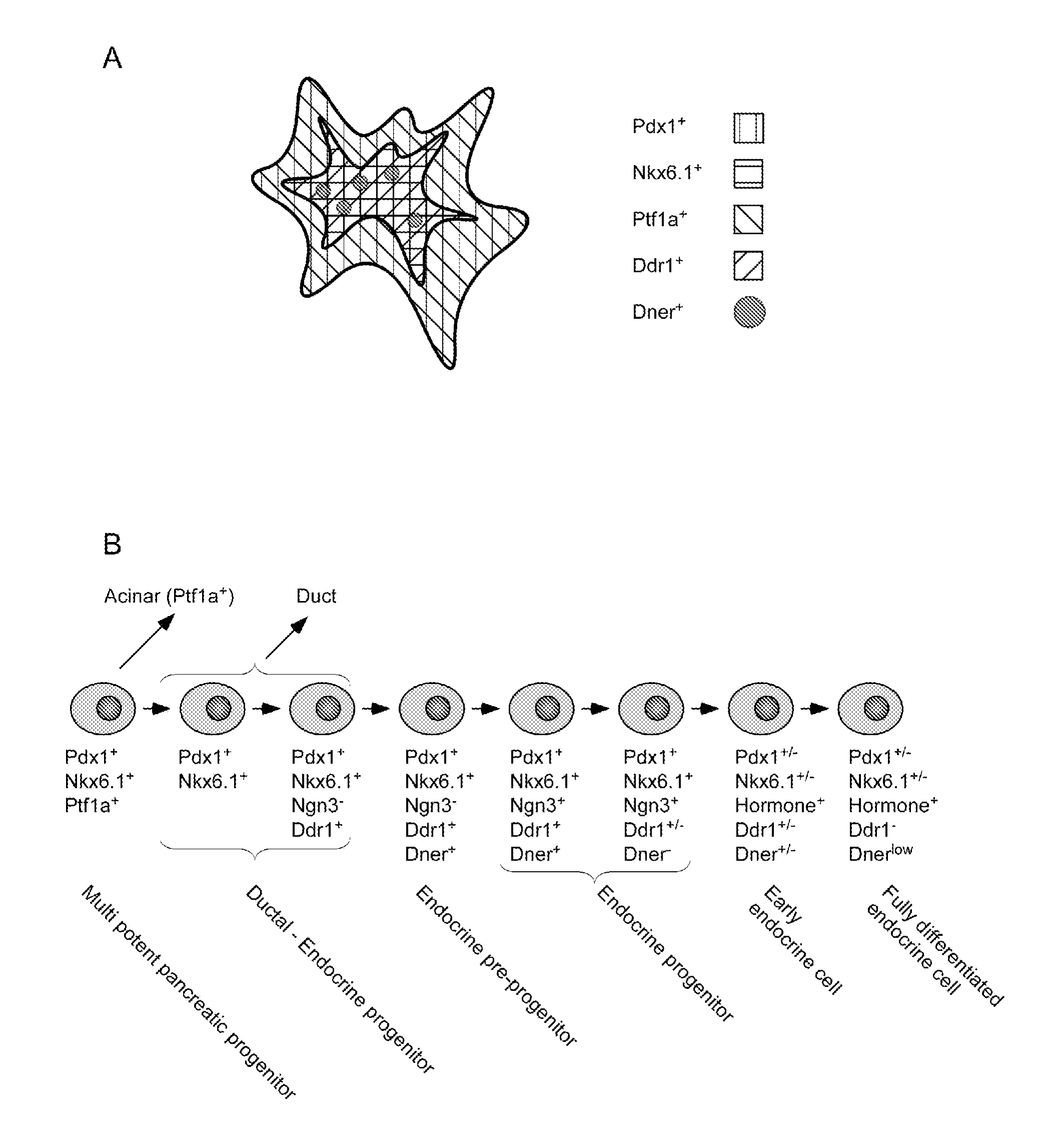
Dner-mediated cell purification of pancreatic endocrine pre-progenitor cells and their progeny
InactiveUS20110020297A1Promote differentiationImprove scalabilityBiocideMetabolism disorderSurface markerProgenitor
The invention relates to a method of identifying and obtaining a culture cells comprising cells selected from the group consisting of endocrine pre-progenitor cells, endocrine progenitor cells, early endocrine cells, and / or fully differentiated endocrine cells. Also contemplated is a method of expanding the number of such cells as well as sorting such cells. In some aspects the invention further relates to a selective cell surface marker, DNER, that permits the selection of a unique subset of cells with endocrine pre-progenitor, endocrine progenitor, early endocrine, and / or fully differentiated endocrine phenotype. In some aspects the selective cell surface marker is selected from the group consisting of DNER, DISP2, SEZ6L2, LRP1 1 and SLC30A8. Furthermore, the invention relates to isolated cells selected from such cells and compositions thereof.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
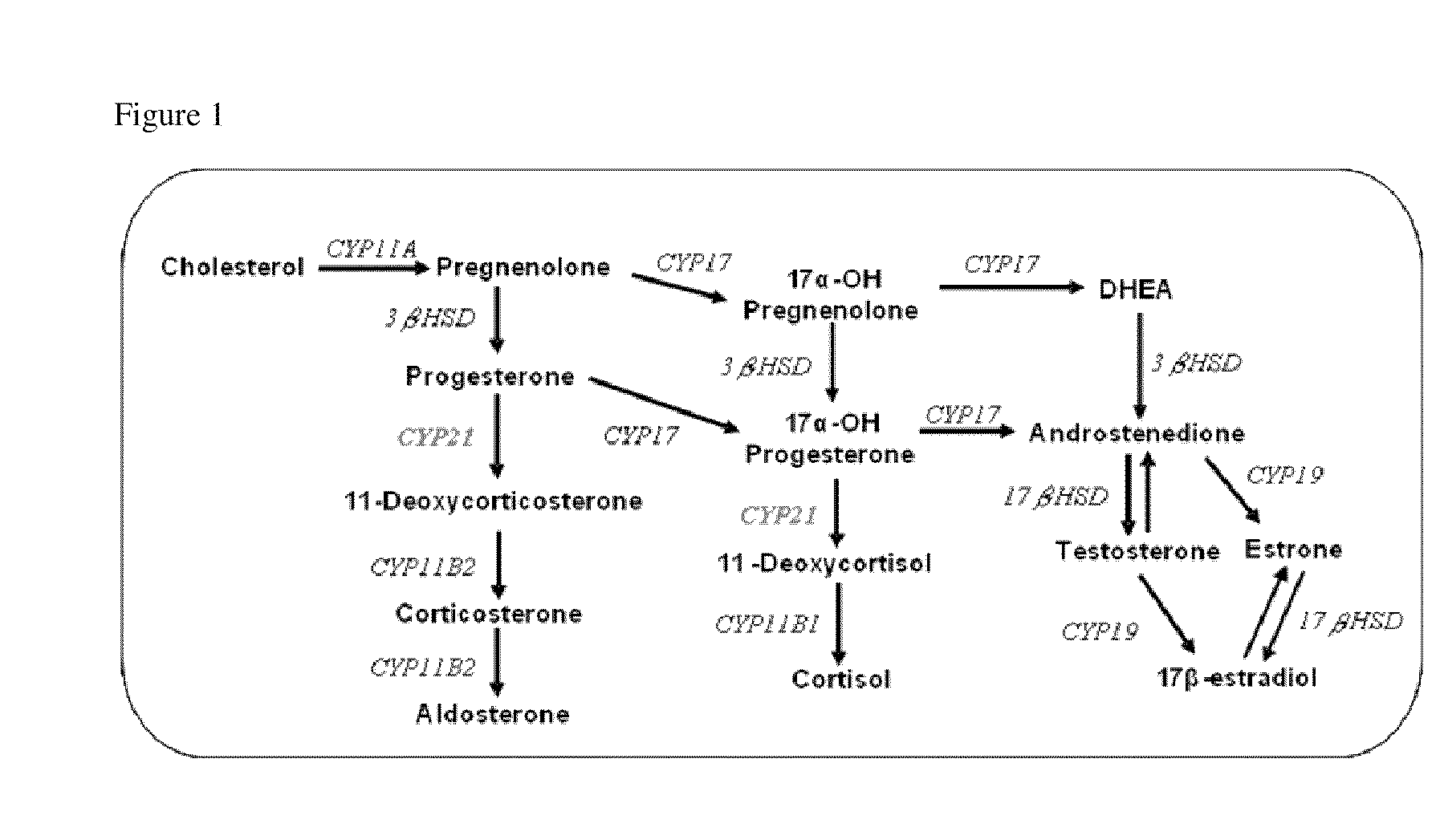
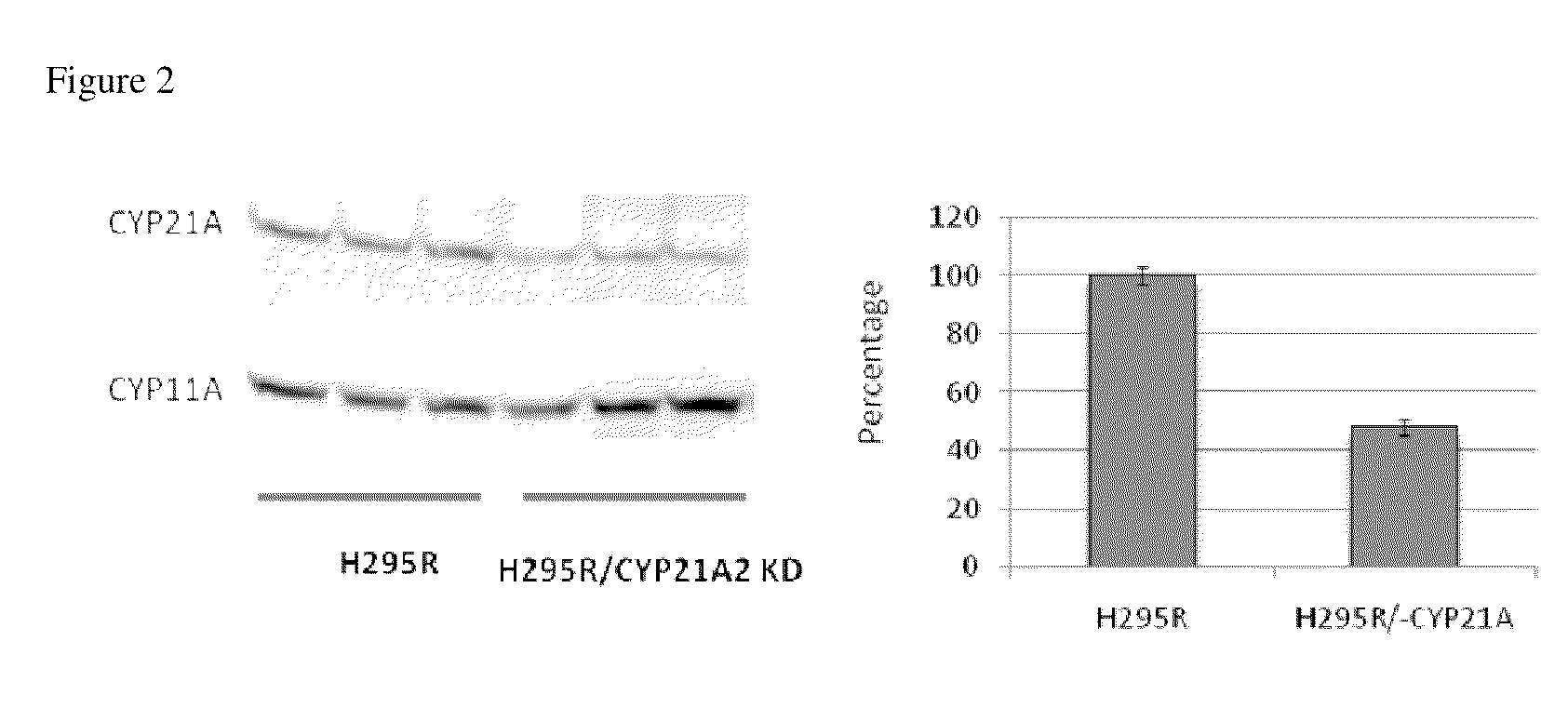
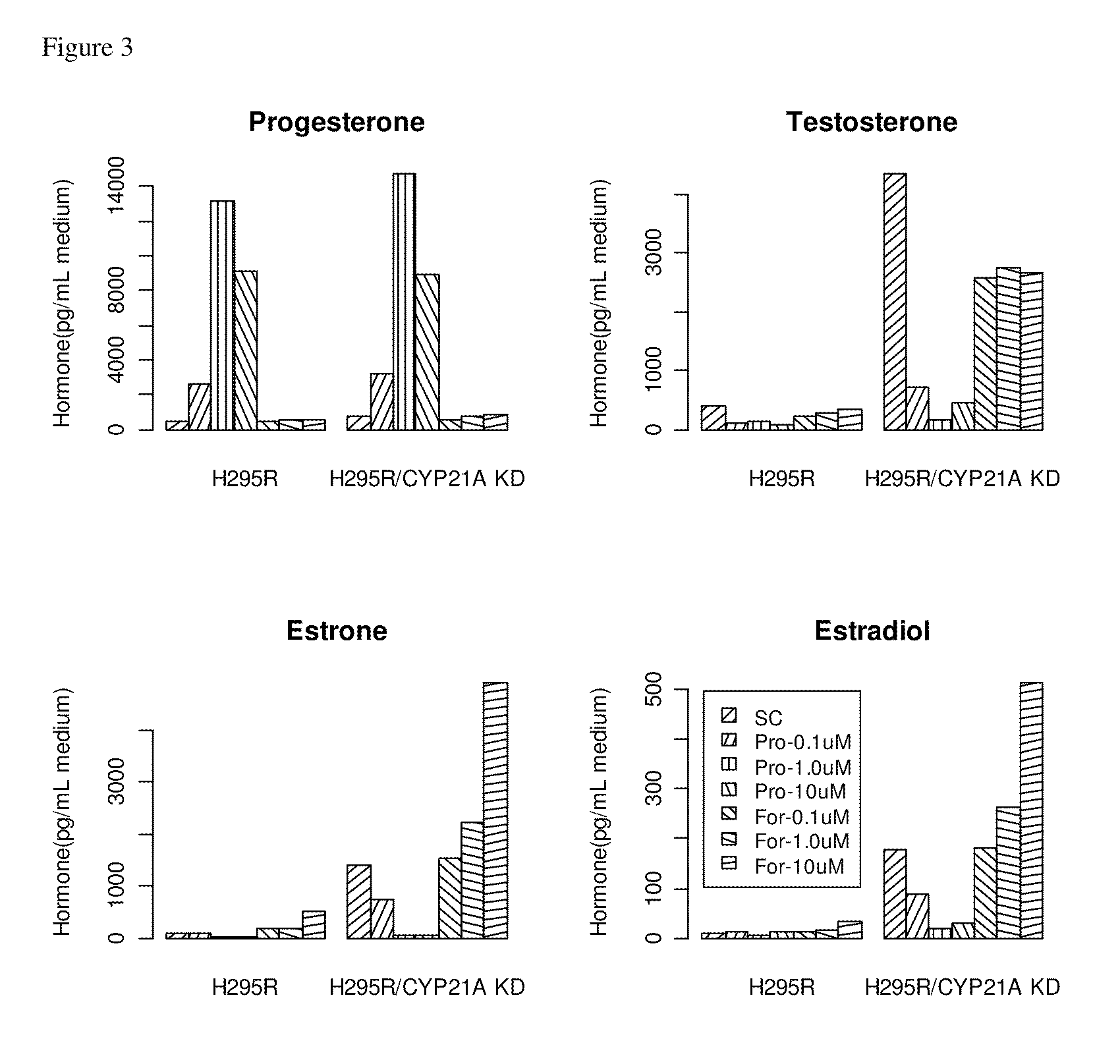
Steroidogenesis modified cells and methods for screening for endocrine disrupting chemicals
InactiveUS20110065114A1Reduce expressionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPerturbateurs endocriniensCYP17A1
An isolated steroidogenesis modified cell comprising one or more steroid biosynthesis knock down nucleic acid operatively linked to a promoter, wherein the steroid biosynthesis knock down nucleic acid reduces the expression of a gene selected from the group CYP21A2, CYP11A1, CYP17A1, CYP19A1, 3-βHSD1, 3-βHSD2, 17-βHSD1, StAR, HMGR, CYP11B2, CYP11B1, 5α-Reductase 2, SULT1E1, CYP3A4 and UTG1A1, wherein the cell comprises reduced expression of one or more of said genes. The cells are useful for identifying endocrine disruptors. Accordingly, the disclosure includes in a further aspect a screening assay for identifying an endocrine disruptor comprising:a) contacting a cell described herein with a test substance;b) determining a level of at least one steroid or steroidogenic gene mRNA or enzyme activity;wherein a modulation in the level of the at least one steroid or steroidogenic gene mRNA or enzyme activity compared to a control is indicative that the test substance is an endocrine disruptor.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN
Monoclonal antibody for immunologically analyzing or concentrating endocrine disruptor or its degradation product and utilization of the same
A hybridoma which produces a monoclonal antibody against an endocrine disruptor or its degradation product obtained by fusing spleen cells or lymphoid cells of an animal having been immunized with a complex of the endocrine disruptor or a compound similar thereto with a protein with myeloma cells; the monoclonal antibody produced thereby; and a method for immunologically detecting the endocrine disruptor or its degradation product and a method for immunologically concentrating the same each by using the above antibody.
Owner:JAPAN ENVIROCHEM
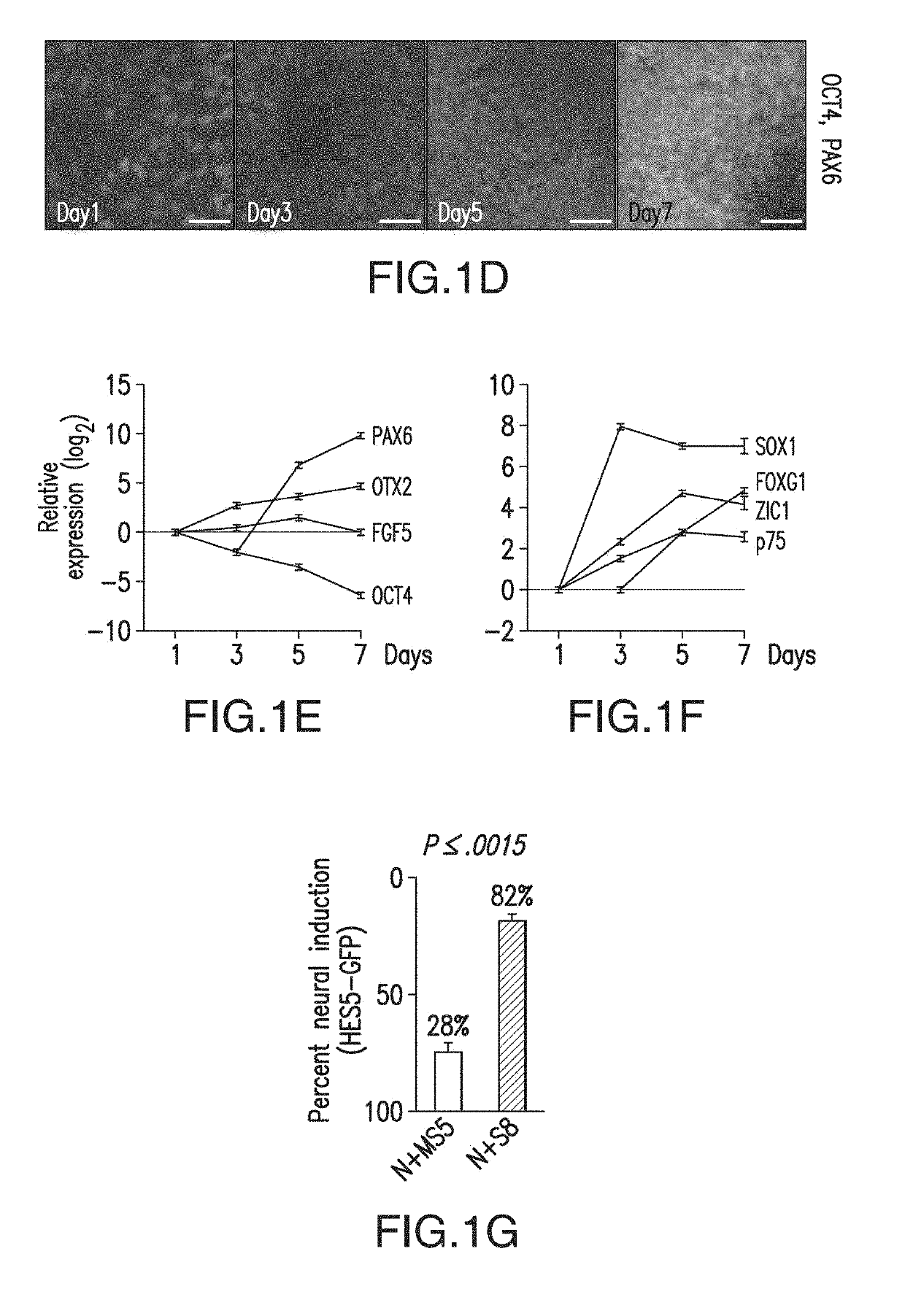
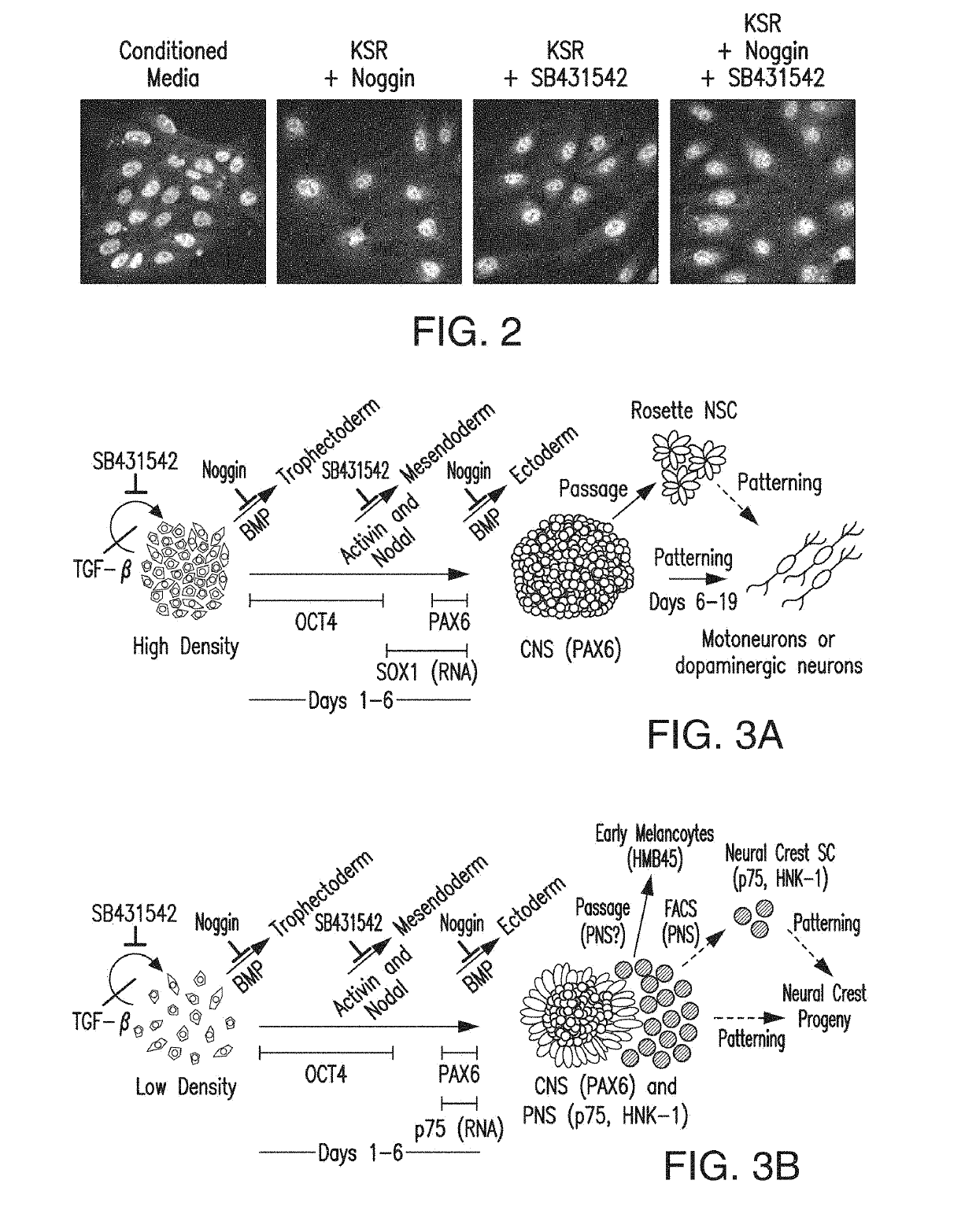
Specification of functional cranial placode derivatives from human pluripotent stem cells
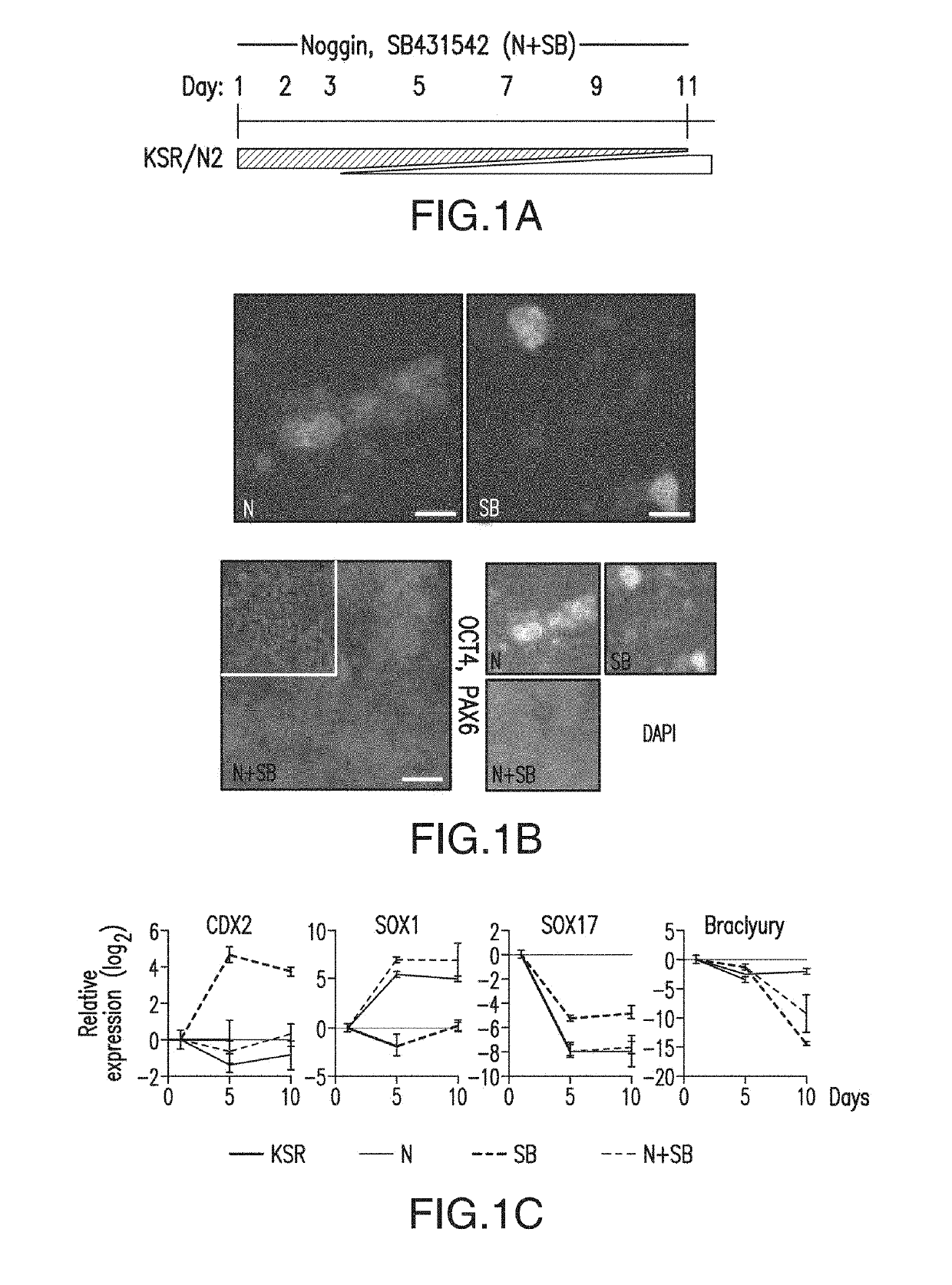
ActiveUS10273452B2Reduce functionInhibit phosphorylationSenses disorderNervous disorderInduced pluripotent stem cellLens Fiber
Cranial placodes are embryonic structures essential for sensory and endocrine organ development. The efficient derivation of cranial placodes from human pluripotent stem cells is disclosed where the timed removal of the BMP inhibitor Noggin, a component of the dual-SMAD inhibition strategy of neural induction, triggers placode induction at the expense of CNS fates. Further fate specification at the pre-placode stage enables the selective generation of placode-derived trigeminal ganglia capable of in vivo engraftment, mature lens fibers and anterior pituitary hormone-producing cells that upon transplantation produce hormones including, but not limited to, human growth hormone and adrenocortiocotropic hormone in vivo. Alternatively, anterior pituitary hormone-producing cells are generated in cell culture systems in vitro.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
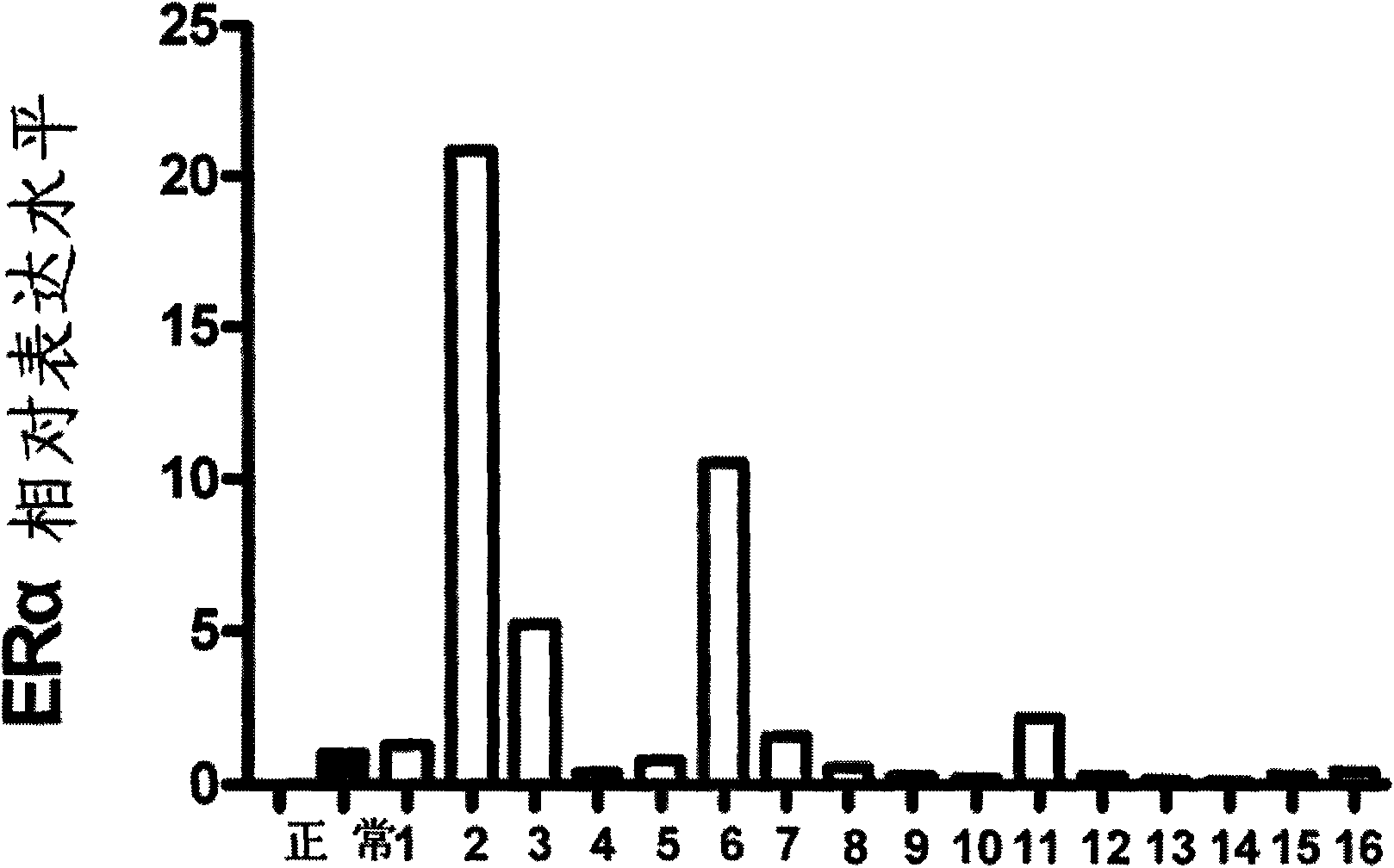
Method for predicting drug tolerance of endocrine medicament in estrogen receptor antagonists
InactiveCN101659994AReduced responseEliminate side effectsMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceSide effectIntracrine
The invention discloses a method for predicting the drug tolerance of an endocrine medicament in estrogen receptor antagonists, which adopts a real-time quantitative method to detect the relative express level of ER alpha and ER beta in breast cancer so as to predict the drug tolerance of the endocrine medicament in the estrogen receptor antagonists. The method comprises the following steps: comparing the relative express level of ER alpha and ER beta genes of a target to be detected with that of a normal contrast, and analyzing the drug tolerance of the endocrine medicament in the estrogen receptor antagonists, wherein the drug tolerance of the endocrine medicament in the estrogen receptor antagonists is negative when the ratio of ER alpha / ER beta of the target to be detected is more than that of the normal contrast; and the drug tolerance of the endocrine medicament in the estrogen receptor antagonists is positive when the ratio of ER alpha / ER beta of the target to be detected is less than that of the normal contrast. The method for predicting the drug tolerance provides a feasible basis for directing the medication of the breast caner individuals in clinic, and can reduce thedrug tolerance reaction and side effect caused by blind use of drugs.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com