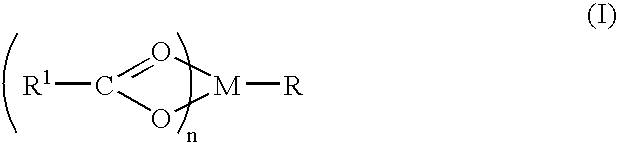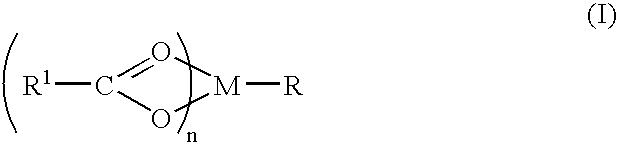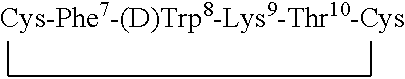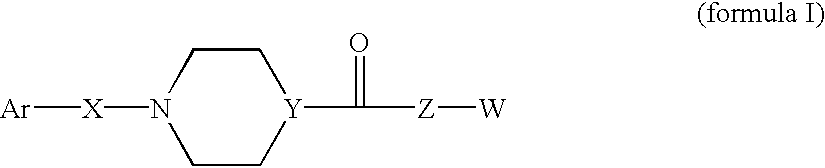Patents
Literature
269results about "Somatostatins" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dispersible macromolecule compositions and methods for their preparation and use
A process for preparing ultrafine powders of biological macromolecules comprises atomizing liquid solutions of the macromolecules, drying the droplets formed in the atomization step, and collecting the particles which result from drying. By properly controlling each of the atomization, drying, and collection steps, ultrafine dry powder compositions having characteristics particularly suitable for pulmonary delivery for therapeutic and other purposes may be prepared.
Owner:NOVARTIS FARMA
Methods of delivering stable topical drug compositions
InactiveUS20060127469A1Easy and administration routeNot to wasteOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsRoom temperatureTopical drug
A method of delivering a drug composition comprises providing a carrier having a phosphatidylcholine component and a drug entrapped therein, and applying the composition to the skin for transdermal delivery of the drug, wherein the composition is stable at room temperature.
Owner:TRANSDERMAL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Topical drug delivery using phosphatidylcholine
InactiveUS20060105955A1Topical deliveryEasier and pleasanterOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsTopical drugTransdermal medication
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for transdermal drug delivery comprising formulating a phosphatidylcholine carrier composition containing the drug and applying the composition to the skin.
Owner:TRANSDERMAL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Non-aqueous single phase vehicles and formulations utilizing such vehicles
InactiveUS20050276856A1Decrease in levelLower Level RequirementsPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineDelivery vehicle
Owner:DURECT CORP
Injectable, oral, or topical sustained release pharmaceutical formulations
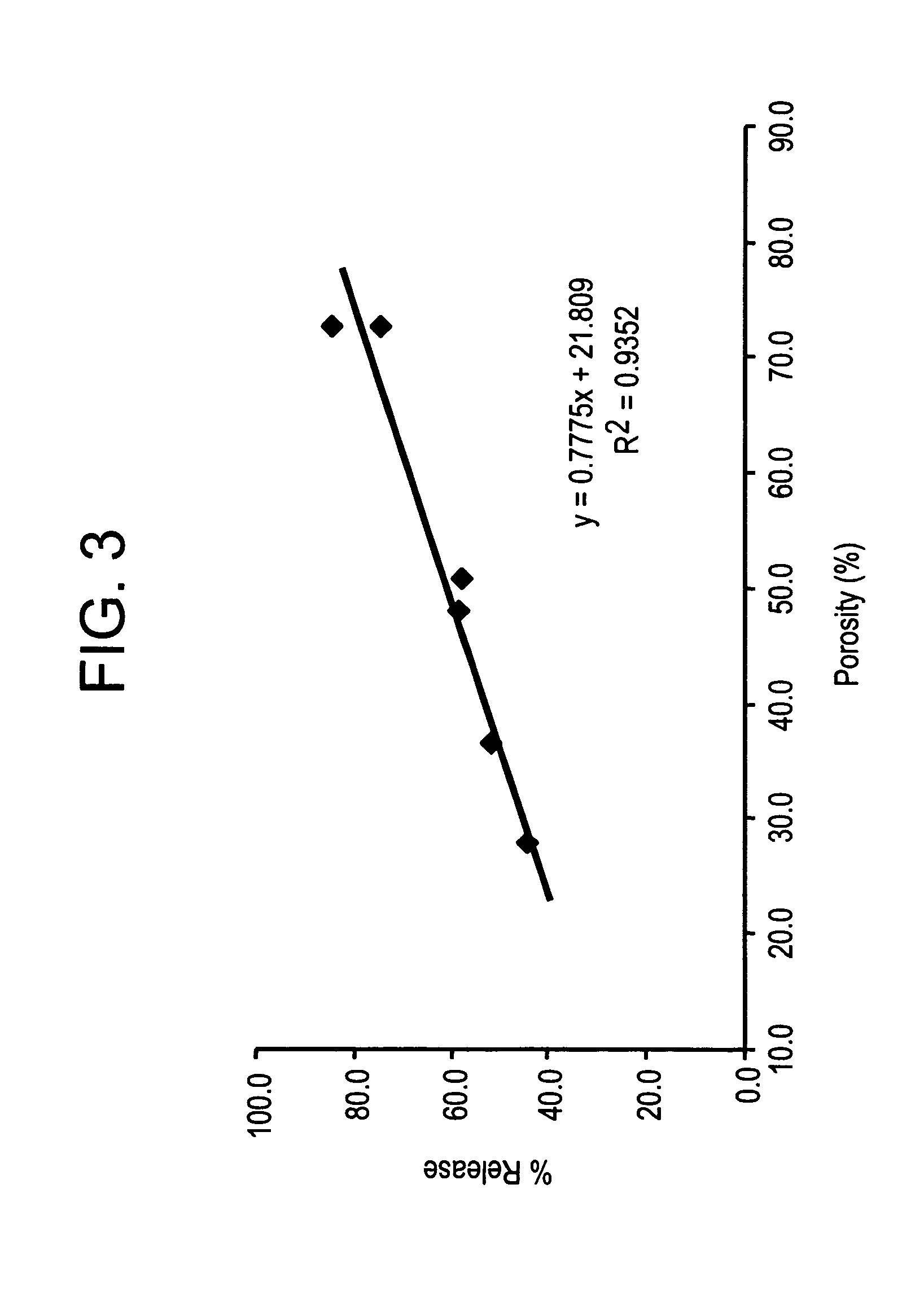
Pharmaceutical formulations and methods are provided for the sustained delivery of a pharmaceutical agent to a patient by injection, by oral administration or by topical administration. The injectable formulation includes porous microparticles which comprise a pharmaceutical agent and a matrix material, wherein upon injection of the formulation a therapeutically or prophylactically effective amount of the pharmaceutical agent is released from the microparticles for at least 24 hours. The oral formulation includes porous microparticles which comprise a pharmaceutical agent and a matrix material, wherein a therapeutically or prophylactically effective amount of the pharmaceutical agent is released from the microparticles for at least 2 hours following oral administration. The topical formulation includes porous microparticles which comprise a pharmaceutical agent and a matrix material, wherein a therapeutically or prophylactically effective amount of the pharmaceutical agent is released from the microparticles for at least 2 hours following topical administration.
Owner:ACUSPHERE INC
Use of somatostatin receptor agonists in the treatment of human disorders of sleep hypoxia and oxygen deprivation
InactiveUS20030083241A1Inhibition of activationBroad anti-inflammatory activityAntinoxious agentsSomatostatinsOxygen deprivationHypopnea
The invention relates to a method of treating diverse human disorders that may arise, in part, out of sleep hypoxia and oxygen deprivation occurring in the context of sleep apnea / hypopnea disturbances. The disorders that may be treated by the invention comprise gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), asthma-associated gastroesophageal reflux (GER), GER-associated asthma, asthma, cardiomyopathy, cardioarrhythmia, congestive heart failure, sudden infant death syndrome, and diverse neurologic conditions. The mode of treatment uses somatostatin receptor ligands (SstRLs), particularly somatostatin-receptor agonists. The invention concerns the method of treatment utilizing, and compositions comprising SstRLs and somatostatin receptor agonists, including agonists of the somatostatin receptor types 2 and 5, particularly, the type 2A receptor (SsR-2A), including octreotide and lanreotide.
Owner:YOUNG CHARLES W
Compound and method of treating neurogenic conditions using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug complexes
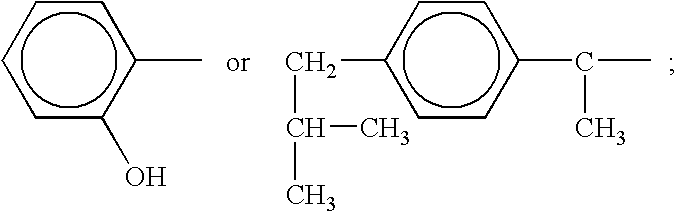
A complex is provided for the treatment of neurogenic conditions having the formula: where R1 is M is a metal ion Ca(II), Mg(II), Cu(II) or Ni(II); n is an integer 1 or 2; R is BBB peptide, transferrin, membrane transporter peptide, TAT peptide, bradykinin, beta-endorphin, bombesin, calcitonin, cholecystokinin, an enkephalin, dynorphin, insulin, gastrin, substance P, neurotensin, glucagon, secretin, somatostatin, motilin, vasopressin, oxytocin, prolactin, thyrotropin, an angiotensin, galanin, neuropeptide Y, thyrotropin-releasing hormone, gonadotropnin-releasing hormone, growth hormone-releasing hormone, luteinizing hormone, vasoactive intestinal peptidegluconate, L-lactate, L-leucine, L-tryptophan, and L-glutamate; and R is coupled to M through a carboxylate moiety. Magnesium (II) represents the preferred metal ion as magnesium is known to have neuroprotective effects. The metal ion is in part chelated by a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that does not inhibit platelet activity and includes salicylate and ibuprofenate. The complex also includes a ligand operative in transport across the blood brain barrier. A process for making an inventive complex includes the stoichiometric addition of ligands containing carboxylate groups to a solution of the metal ion. In instances where the metal ion is magnesium (II), a stoichiometric ratio of 1:1:1 is found between the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory ligand:magnesium (II):transporter ligand.
Owner:MILLER LANDON C G
Conformationally constrained backbone cyclized peptide analogs
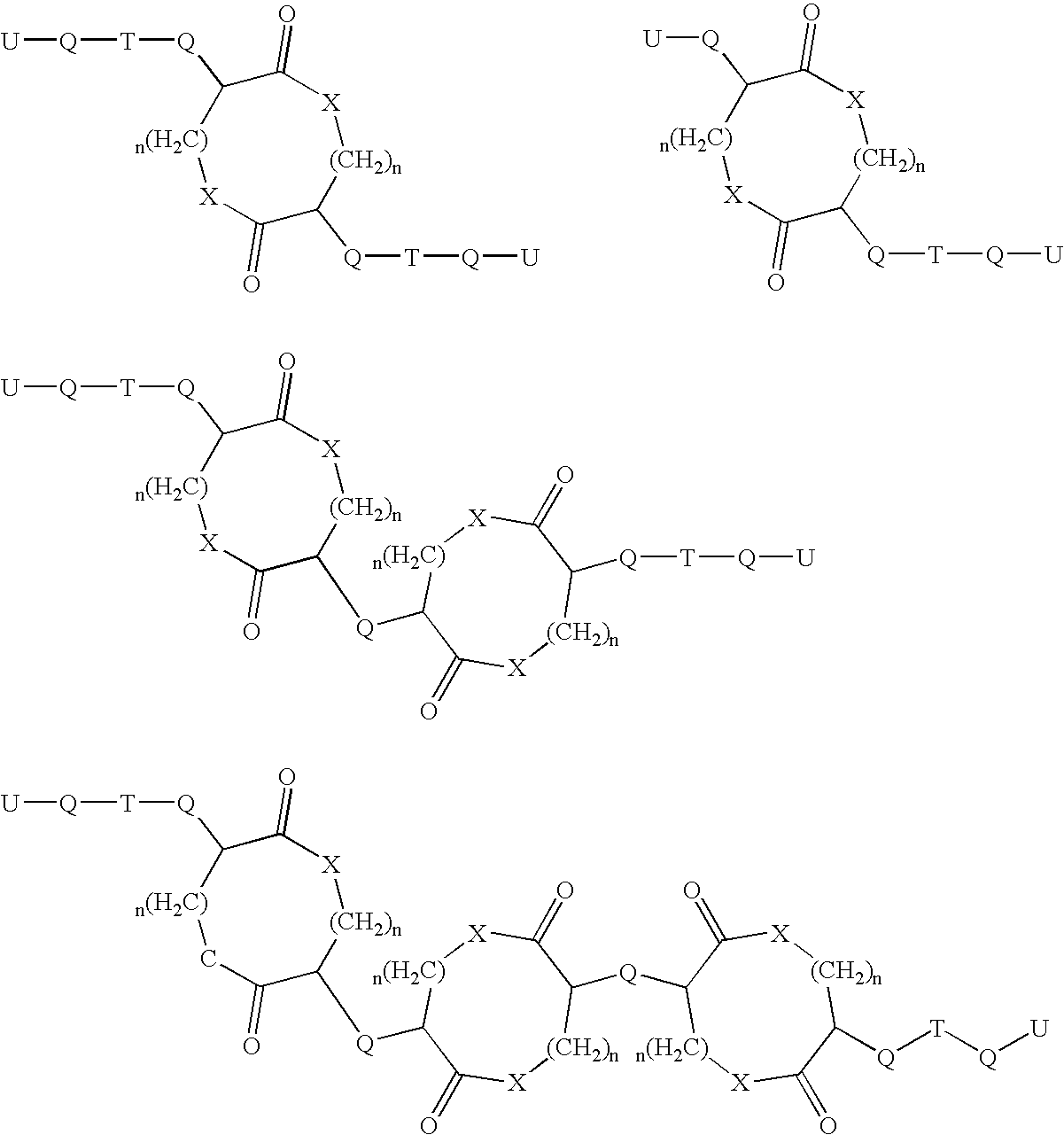
Novel backbone cyclized peptide analogs are formed by means of bridging groups attached via the alpha nitrogens of amino acid derivatives to provide novel non-peptidic linkages. Novel building units disclosed are Nα(ω-functionalized) amino acids constructed to include a spacer and a terminal functional group. One or more of these Nα(ω-functionalized) amino acids are incorporated into a peptide sequence, preferably during solid phase peptide synthesis. The reactive terminal functional groups are protected by specific protecting groups that can be selectively removed to effect either backbone-to-backbone or backbone-to-side chain cyclizations. The invention is specifically exemplified by backbone cyclized bradykinin antagonists having biological activity. Further embodiments of the invention are somatostatin analogs having one or two ring structures involving backbone cyclization.
Owner:DEVELOGEN ISRAEL
Combination therapy comprising a Cox-2 inhibitor and an antineoplastic agent
InactiveUS20050227929A1Effective amountReduce dosageBiocideSomatostatinsCOX-2 inhibitorCombination therapy
A method for treating or preventing neoplasia or a neoplasia-related disorder in a subject is provided, the method comprising administering to the subject an effective amount of a combination comprising a Cox-2 inhibitor and an antineoplastic agent.
Owner:PHARMACIA & UPJOHN CO
Method for delivery of monomeric or dimeric insulin complexed to diketopiperazine microparticles
InactiveUS7648960B2Rapid increase in blood agent concentrationEasy to transportPowder deliverySpray deliveryBlood insulinBlood agent
Methods are provided for purifying peptides and proteins by incorporating the peptide or protein into a diketopiperazine or competitive complexing agent to facilitate removal of one or more impurities from the peptide or protein. Formulations and methods also are provided for the improved transport of active agents across biological membranes, resulting for example in a rapid increase in blood agent concentration. The formulations include microparticles formed of (i) the active agent, which may be charged or neutral, and (ii) a transport enhancer that masks the charge of the agent and / or that forms hydrogen bonds with the target biological membrane in order to facilitate transport. In one embodiment insulin is administered via the pulmonary delivery of microparticles comprising fumaryl diketopiperazine and insulin in its biologically active form. This method of delivering insulin results in a rapid increase in blood insulin concentration that is comparable to the increase resulting from intravenous delivery.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Activatable clostridial toxins
InactiveUS20090018081A1Long duration of therapyOvercome resistanceHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsClostridial toxinNucleic acid
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
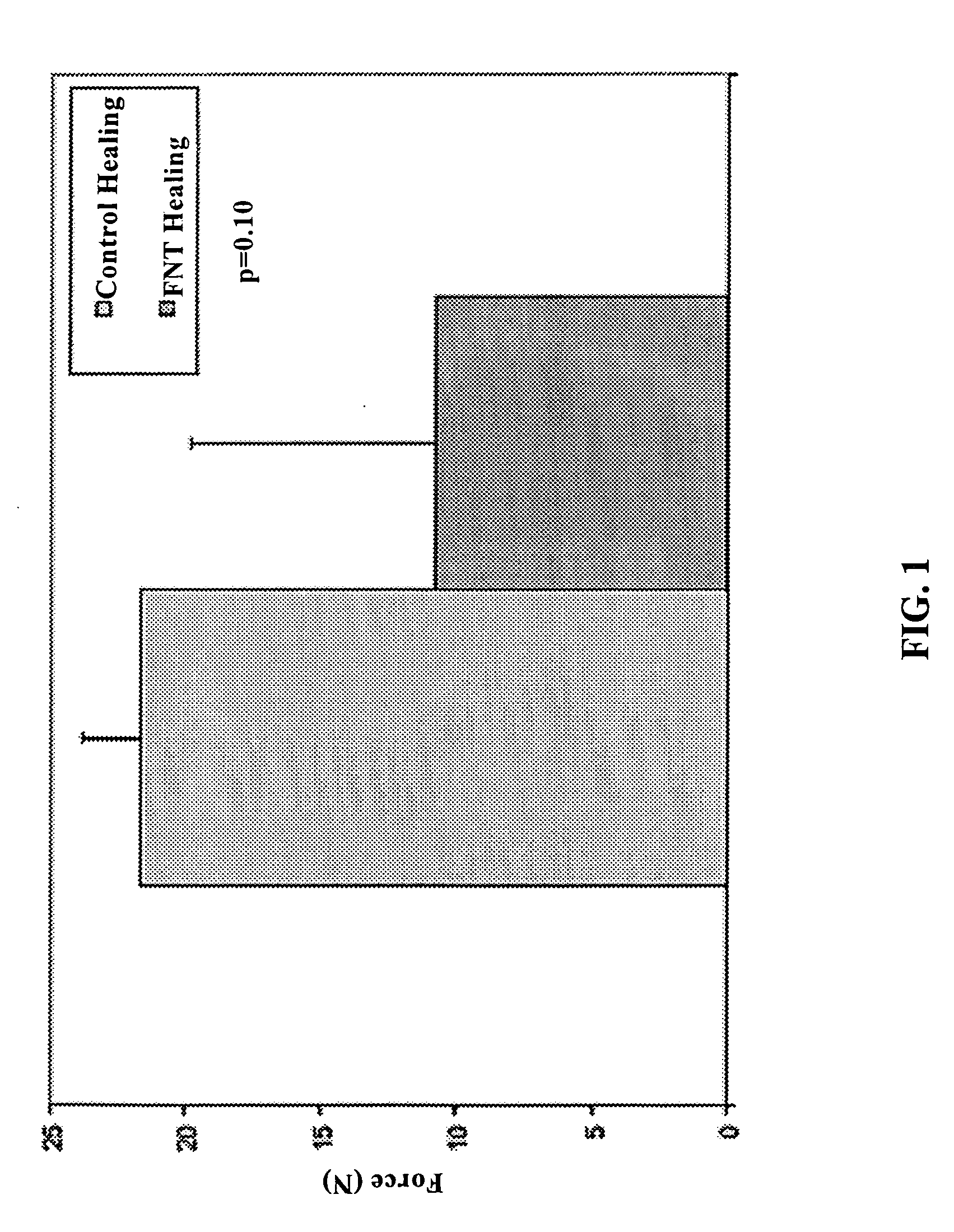
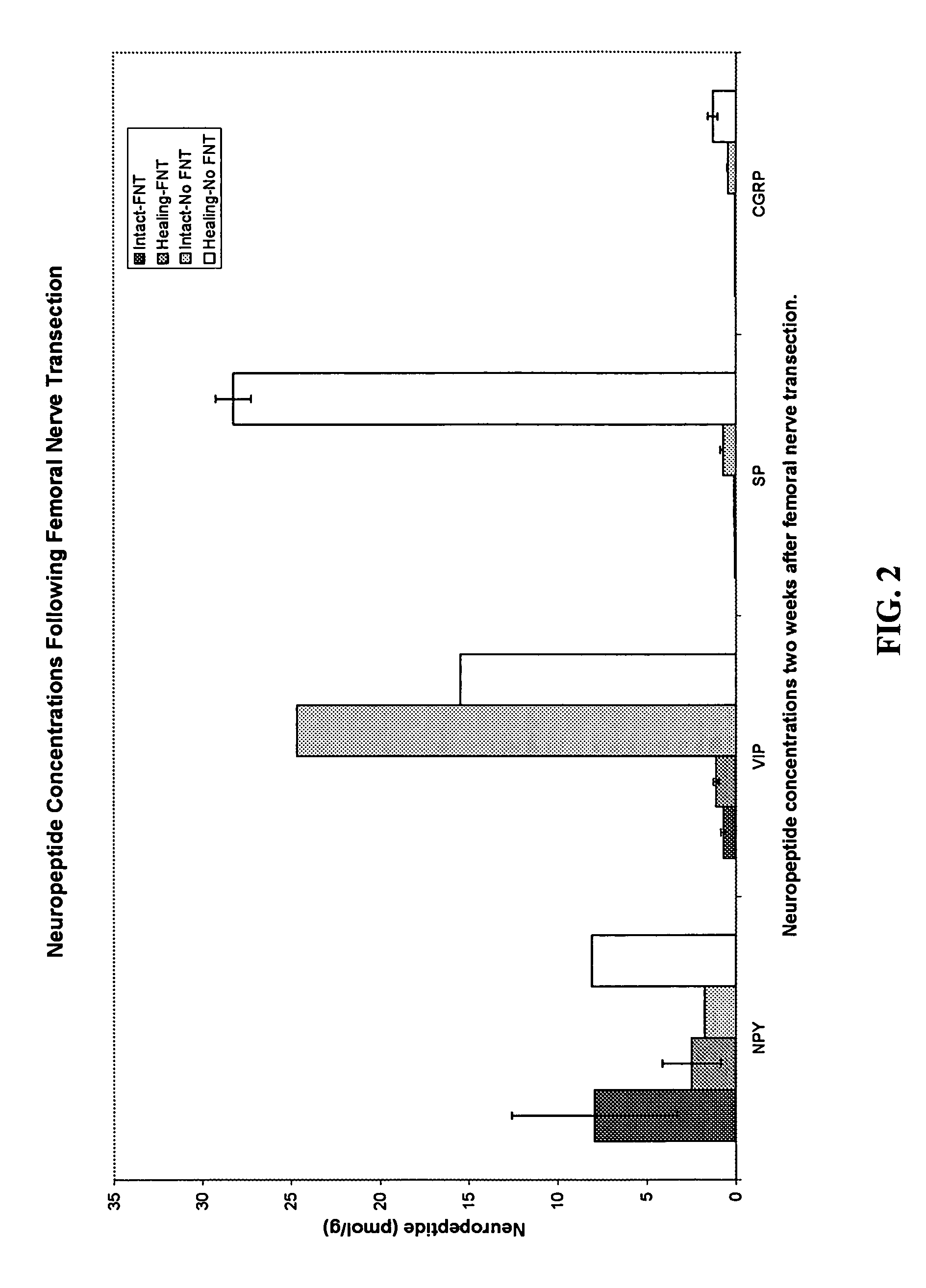
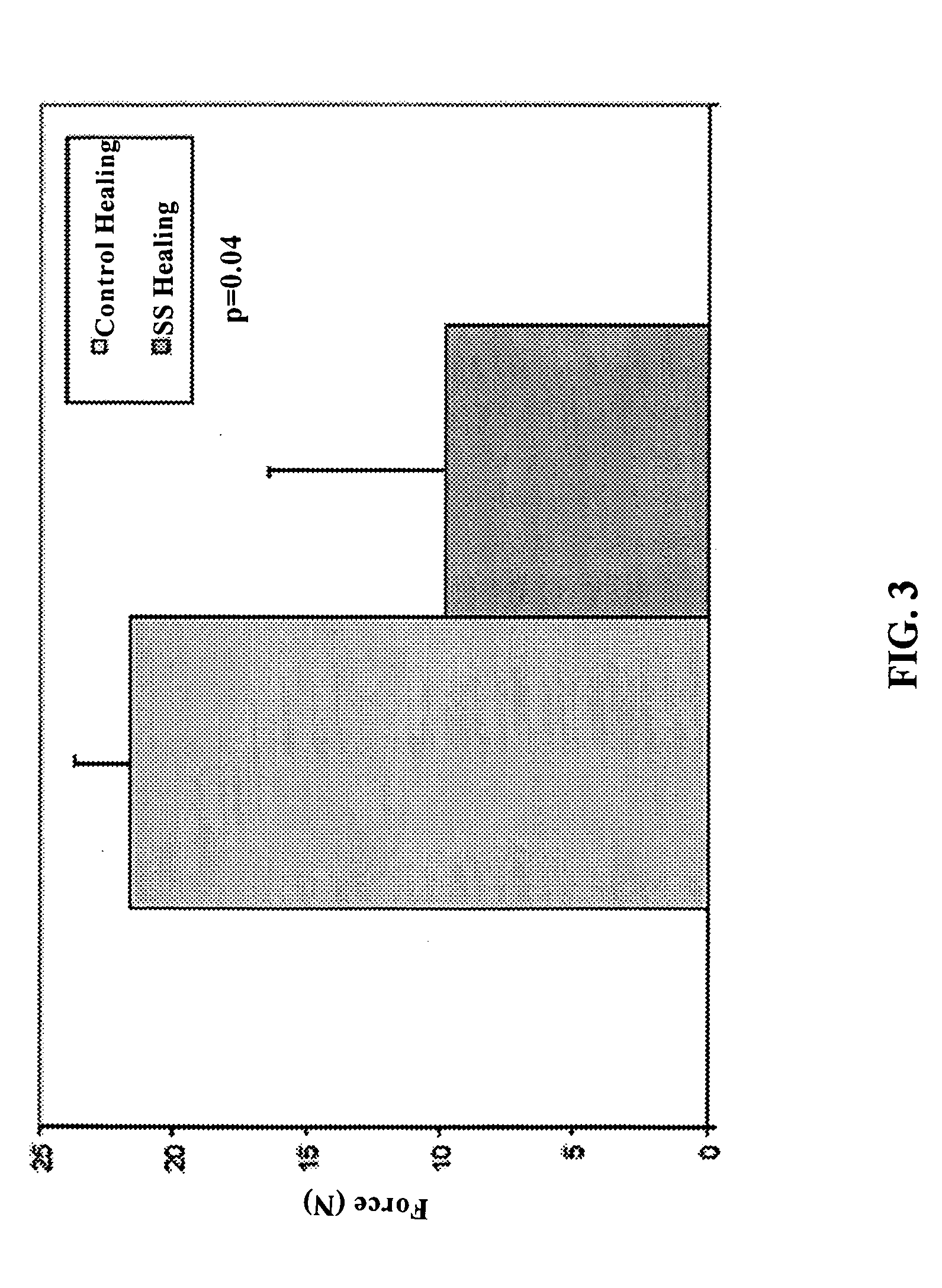
Use of neuropeptides for ligament, cartilage, and bone healing
Disclosed are a method and a corresponding pharmaceutical composition for treating damaged cartilage and subchondral bone. Neurogenic compounds in general and neuropeptides in particular have been found to be highly effective in stimulated repair of cartilage and bone damaged due to traumatic injury, ligament disease, and disuse. Preferred active ingredients for use in the method and corresponding pharmaceutical composition include calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), cholecystokinin (CCK), dynorphin, enkephalin, galanin, neuropeptide Y (NPY), neurotensin, somatostatin, substance P (SP), thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP).
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
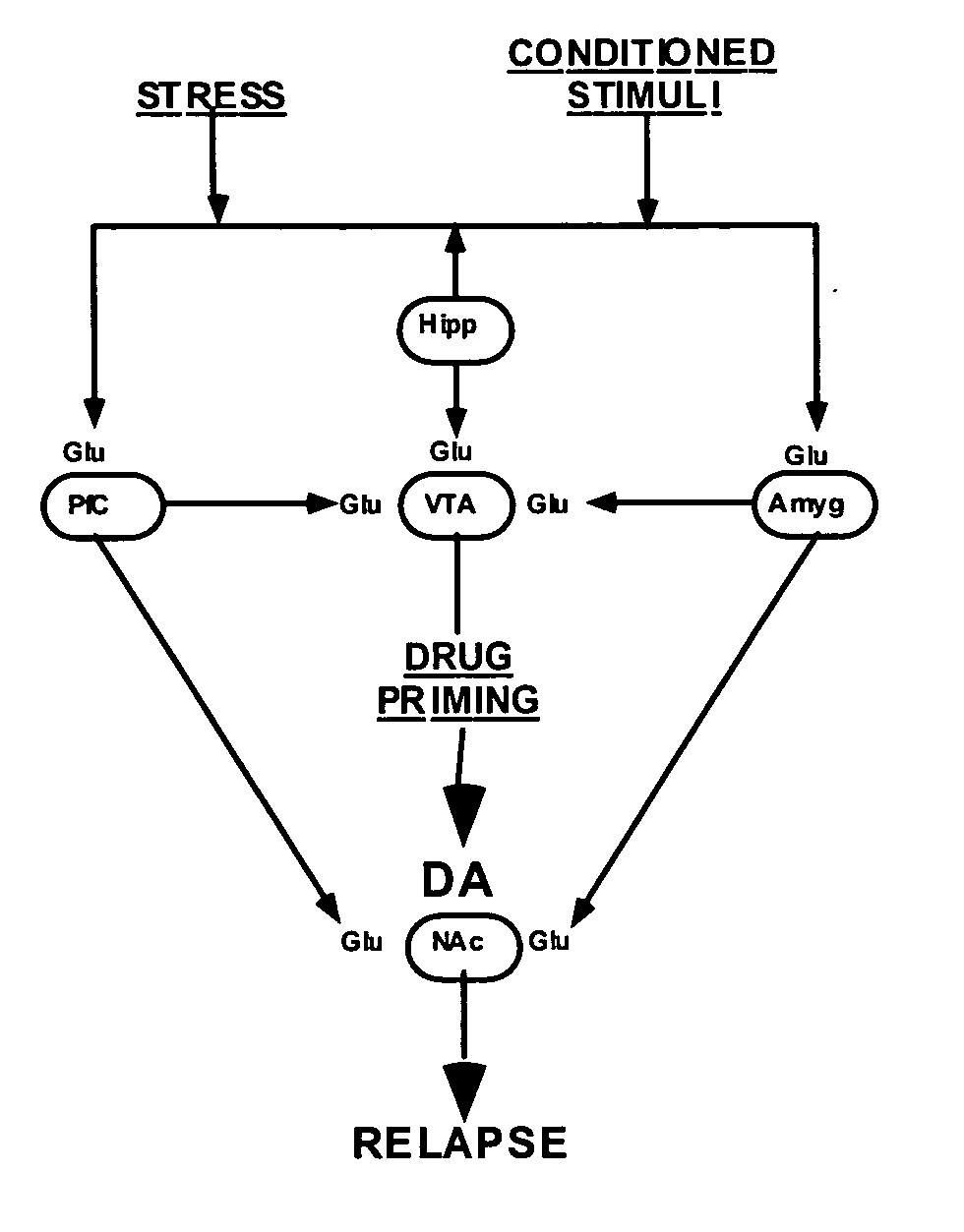
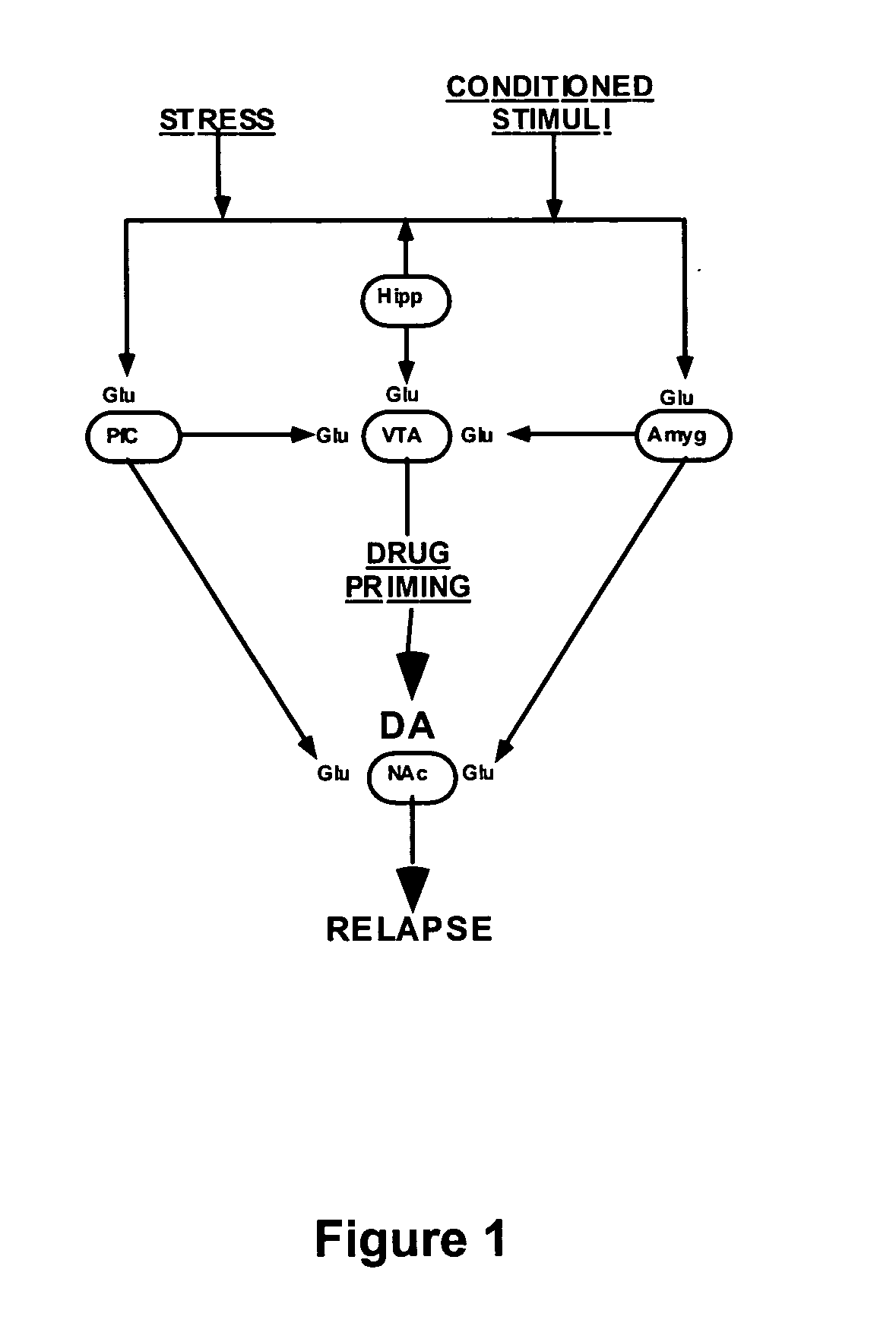
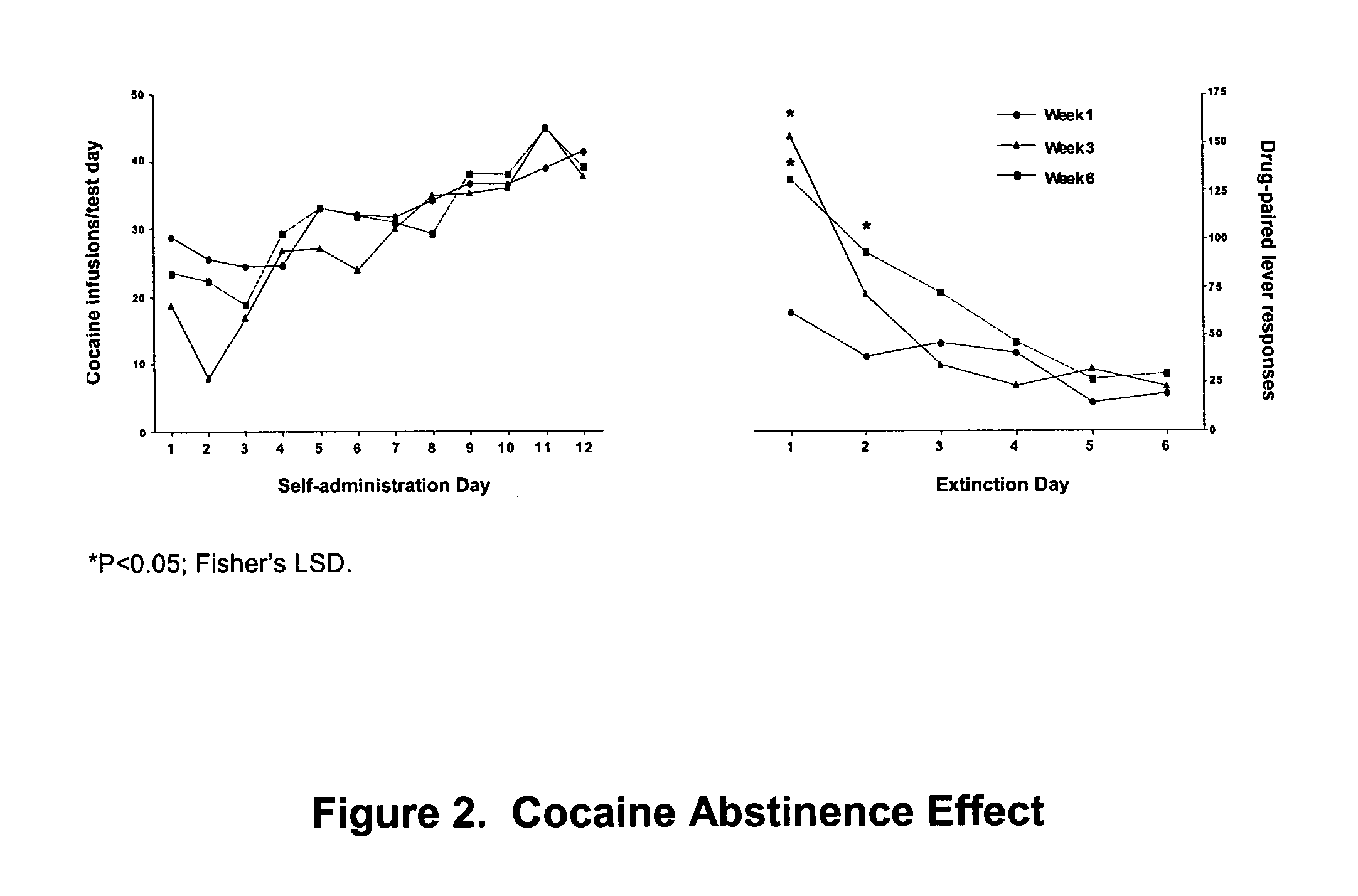
Methods for treating drug addiction
This invention describes gene targets for the development of therapeutics to treat drug addiction. Animal models of drug craving and relapse have been developed and used to find gene expression changes in key brain regions implicated in cocaine addiction. The genes whose expression levels are altered serve as pharmacological targets with the purpose of preventing or inhibiting cocaine craving and relapse in human cocaine addicts.
Owner:IRM
Nanoparticle compositions of water-soluble drugs for oral administration and preparation methods thereof
InactiveUS20070154559A1Increase ratingsIncrease resistanceAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsLipid formationOral medication
The present invention relates to an orally administrable composition containing nanoparticles with the particle size of 500 nm or less, comprising 0.1˜30 weight % of a complex of a water-soluble drug and a counter-ion substance in which the charged water-soluble drug is bonded with the counter-ion substance, 0.5˜80 weight % of a lipid, 0.5˜80 weight % of a polymer, and 1˜80 weight % of an emulsifier, wherein the weight ratio of said lipid and said polymer is in the range of 1:0.05˜3, and a preparation method thereof. The composition of the present invention has high gastrointestinal absorption rate upon oral administration, and has high drug entrapping rate in the nanoparticle, and is also stable against lipases.
Owner:SAMYANG BIOPHARMLS CORP
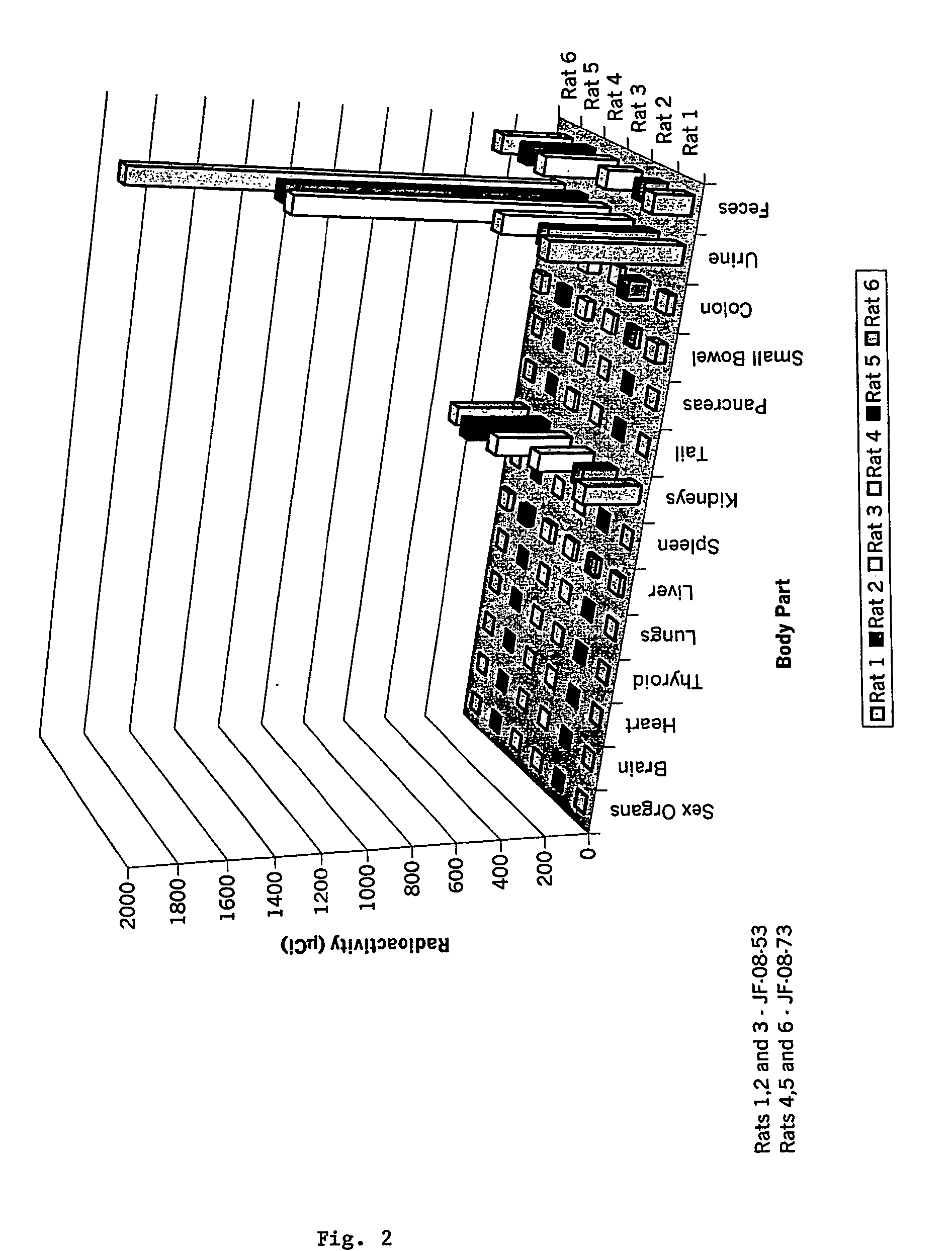
Diagnostic or therapeutic somatostatin or bombesin analog conjugates and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050070470A1Quick eliminationReduce drug toxicityOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseCytotoxicity
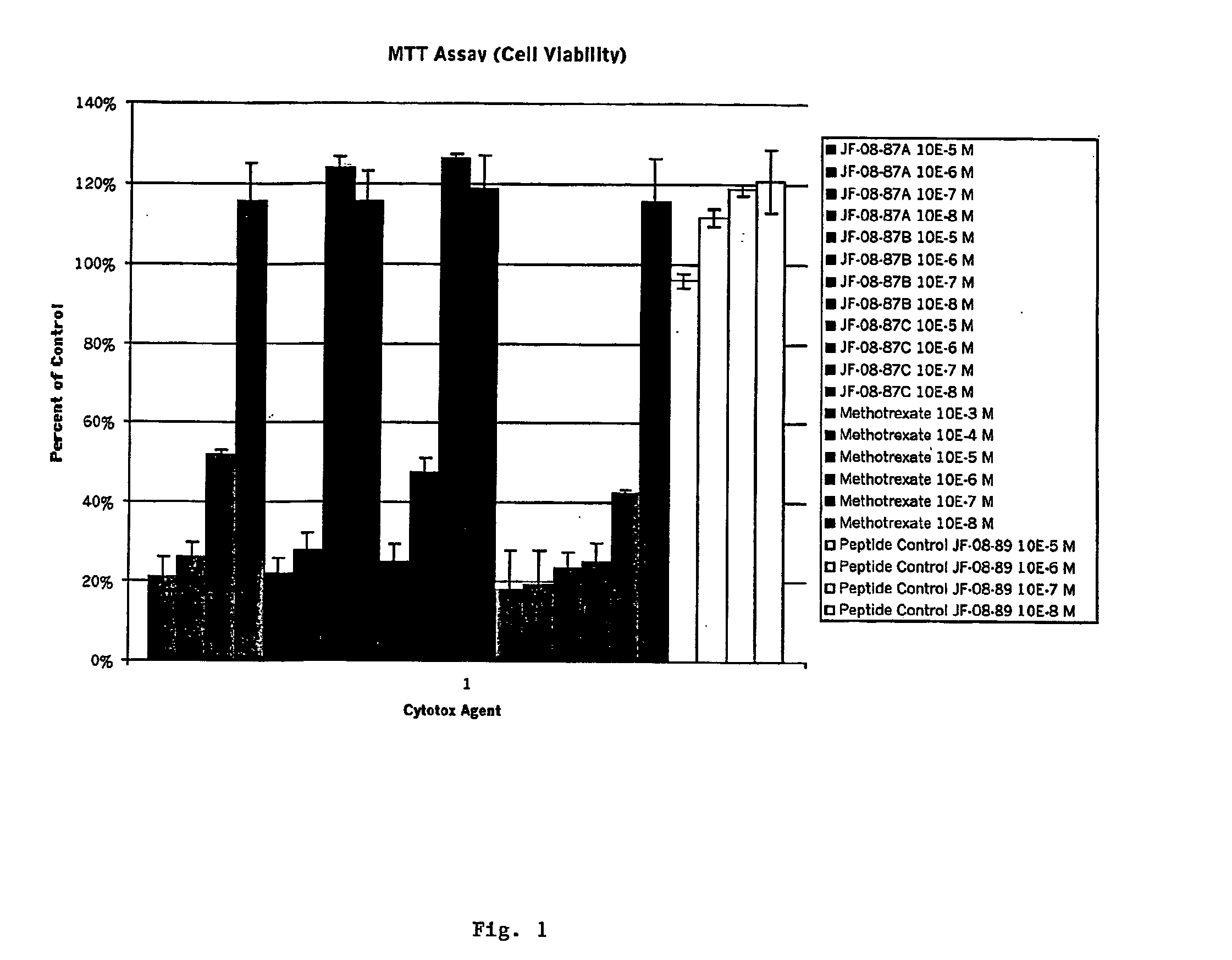
Disclosed are peptide agents and uses thereof that are analogs of biologically active peptides such as somatostatin and bombesin. The compounds of the invention have the general formula X-Y-Z-Q, where X is a cytotoxic agent, therapeutic agent, detectable label or chelating group, and Q is a biologically active peptide. In peptide agents of the invention Y is optionally a hydrophilic polymer or peptide, and Z is a linking peptide bonded to Q at the amino terminus of Q, having two, three, four, or five, amino acid residues selected to link X to Q, while retaining the biological activity of Q. Methods of using these peptide agents in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases are also disclosed.
Owner:TULANE EDUCATIONAL FUND
Long-acting polypeptides and methods of producing same
ActiveUS20090312254A1Reduce dosing frequencyImprove compliancePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleotideChorionic gonadotrophin
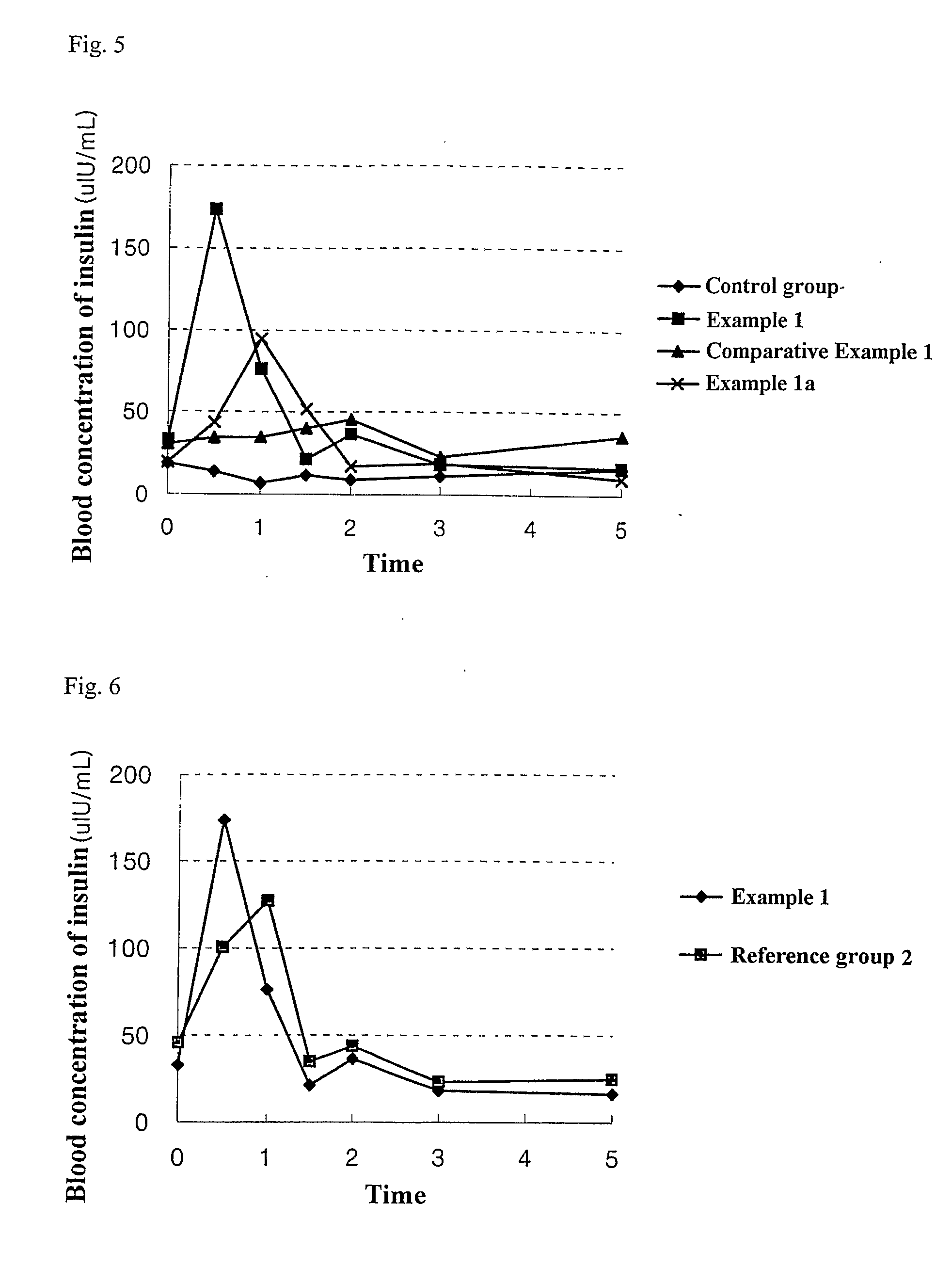
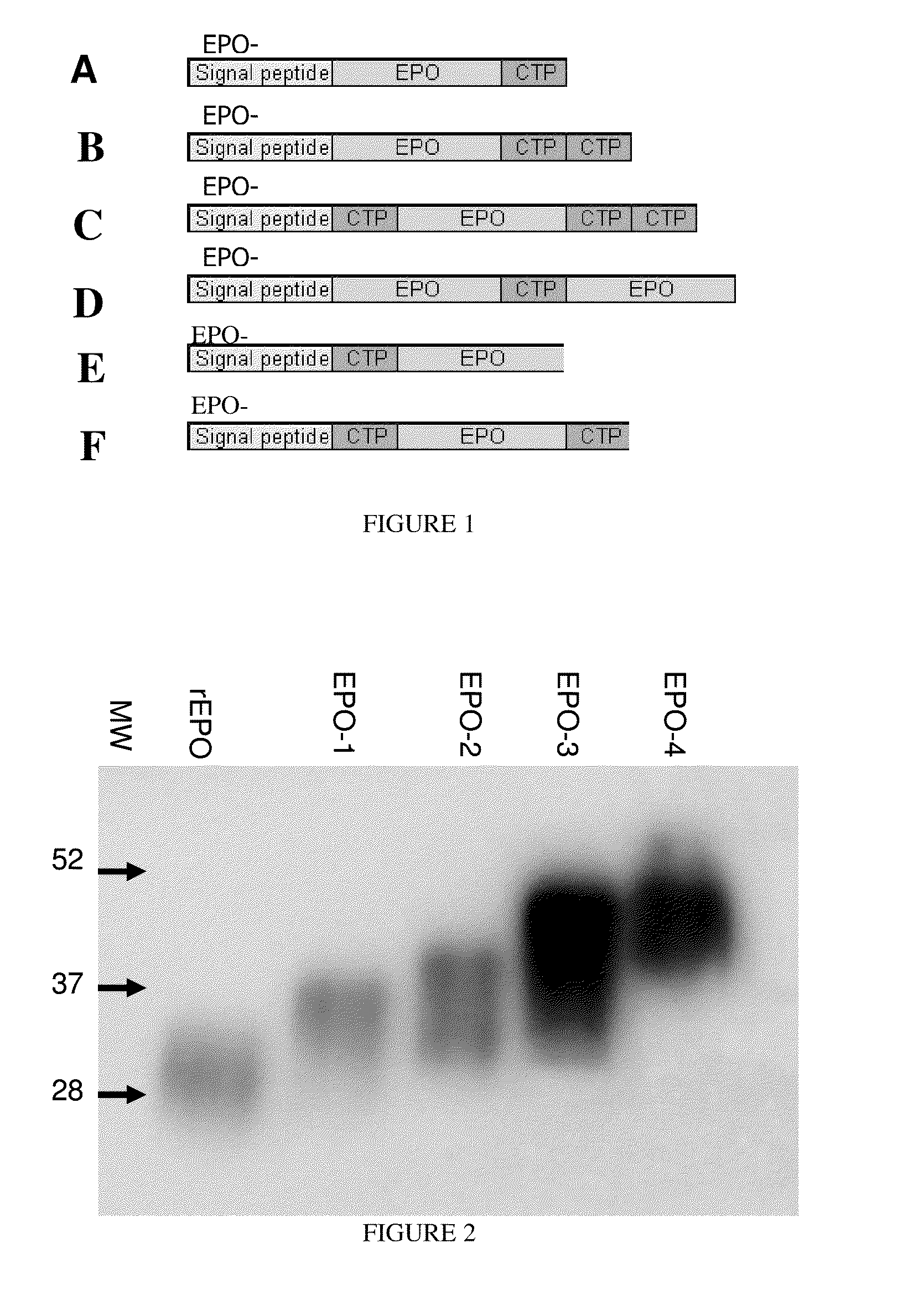
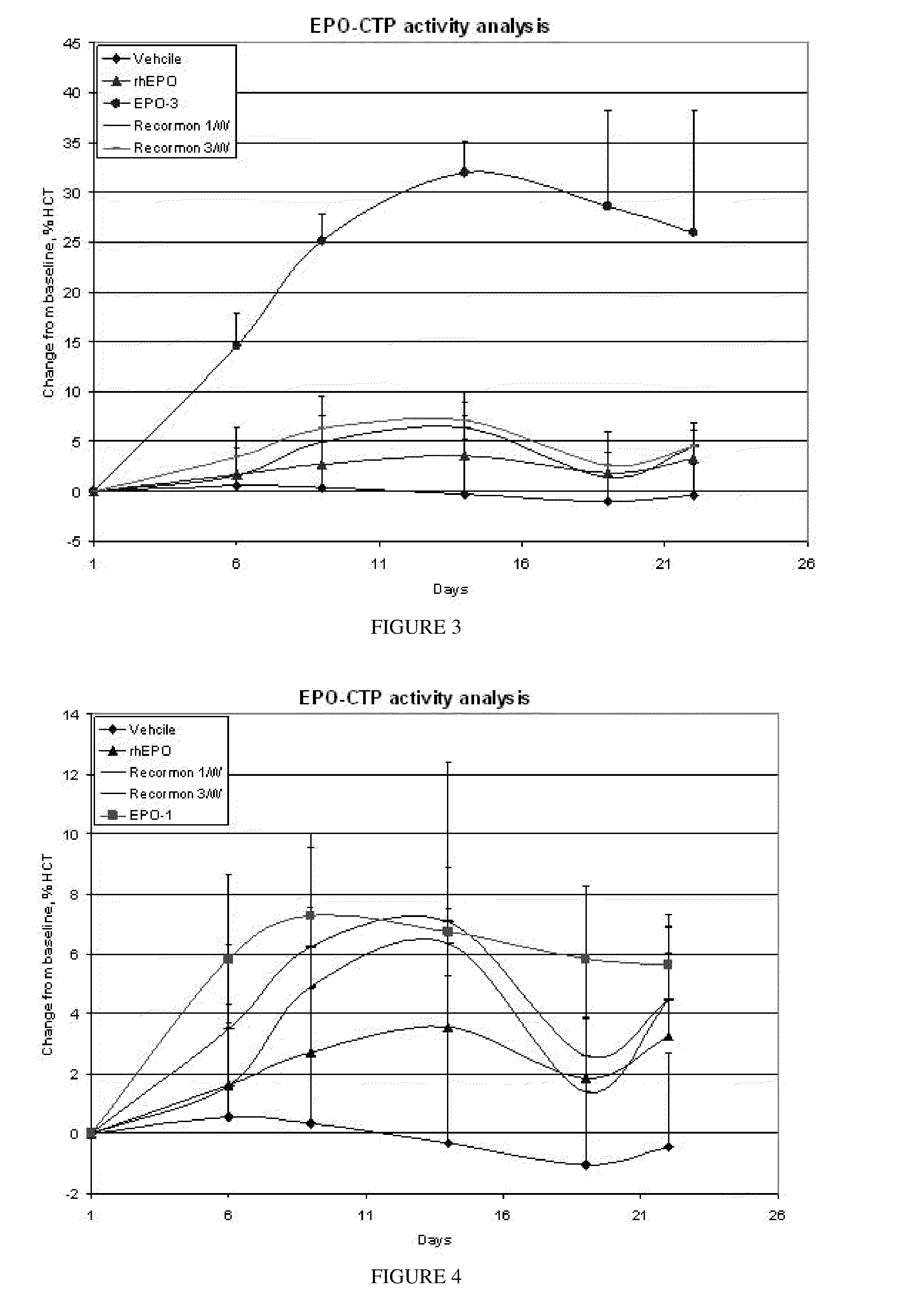
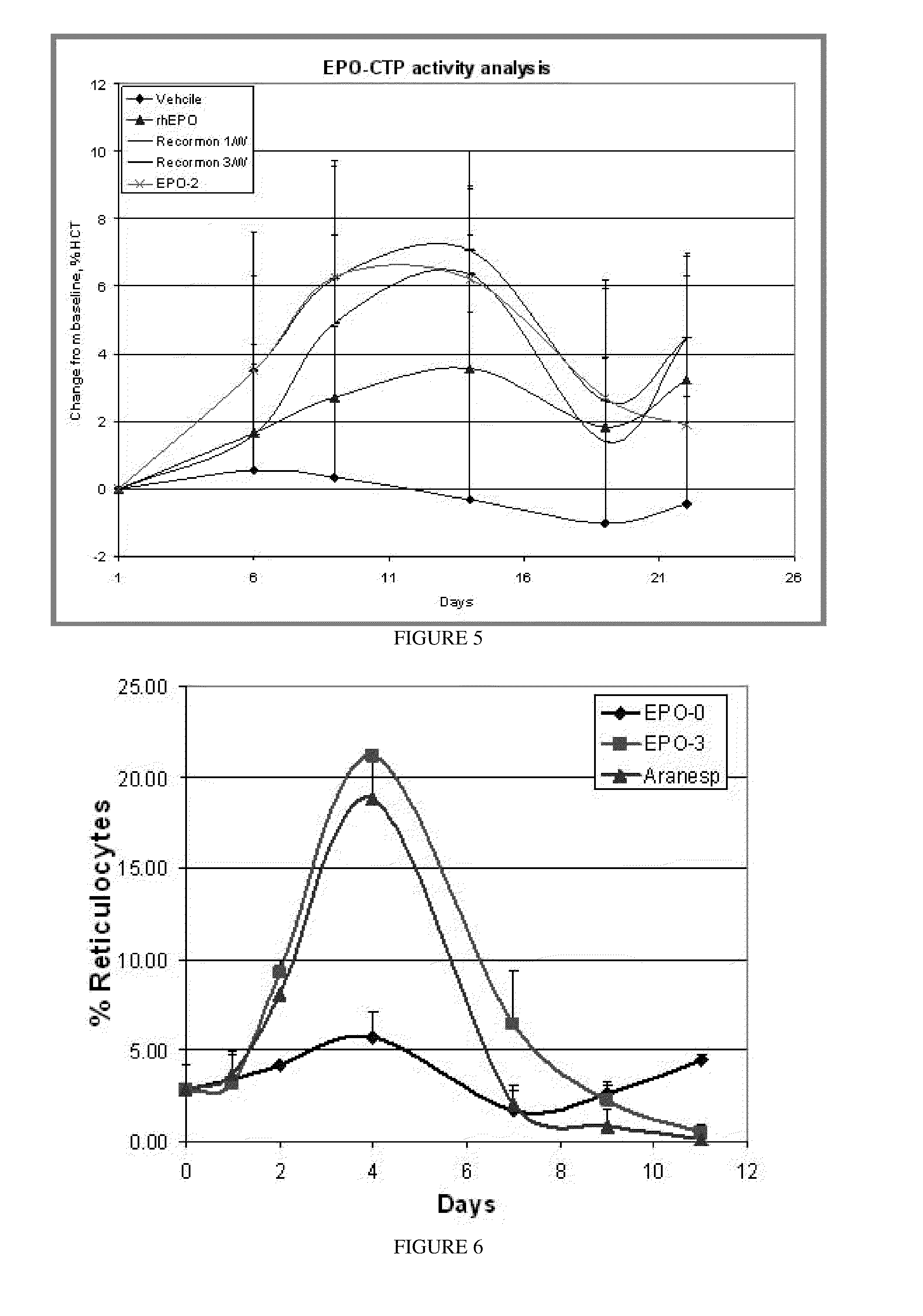
A polypeptide and polynucleotides encoding same comprising one carboxy-terminal peptide (CTP) of chorionic gonadotrophin attached to an amino terminus of a cytokine and two carboxy-terminal peptides (CTP) of chorionic gonadotrophin attached to a carboxy terminus of a cytokine are disclosed. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the polypeptide and polynucleotides of the invention and methods of using same are also disclosed.
Owner:MODIGENE LLC +1
Aerosolized active agent delivery
InactiveUS20050090798A1Improve bioavailabilityImprove the immunityFactor VIIPowder deliveryInspiratory flowActive agent
The present invention is directed to methods and devices for delivering an active agent formulation to the lung of a human patient. The active agent formulation may be in dry powder form, it may be nebulized, or it may be in admixture with a propellant. The active agent formulation is delivered to a patient at an inspiratory flow rate of less than 17 liters per minute. The bioavailability of the active agent was found to increase at these flow rates when compared to inspiratory flow rates of 17 liters per minute or more.
Owner:NOVARTIS FARMA
Method for the preparation of controlled release formulations
ActiveUS20060228414A1Prevent degradationReducing and preventing degradationBiocideNanotechActive agentPolymer chemistry
The methods disclosed herein are of use for the production of controlled release compositions. In particular, the methods provide the contacting of an organic phase containing a bioactive agent and a polymer with an aqueous phase containing an organic ion to create controlled release compositions containing bioactive agents. The present invention also includes controlled release compositions including a polymer, an organic ion and a bioactive agent. The present invention also includes methods of using such controlled release compositions. The usefulness of the present invention is that the methods result in the production of controlled release compositions containing bioactive agent capable of administration in a concentrated low-dose form, having low burst and reduced production of degraded bioactive agent.
Owner:PR PHARMA +1
SARMS and method of use thereof
InactiveUS7772433B2Improve bone strengthIncreased bone resorptionBiocideNervous disorderDiabetes mellitusRelated disorder
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
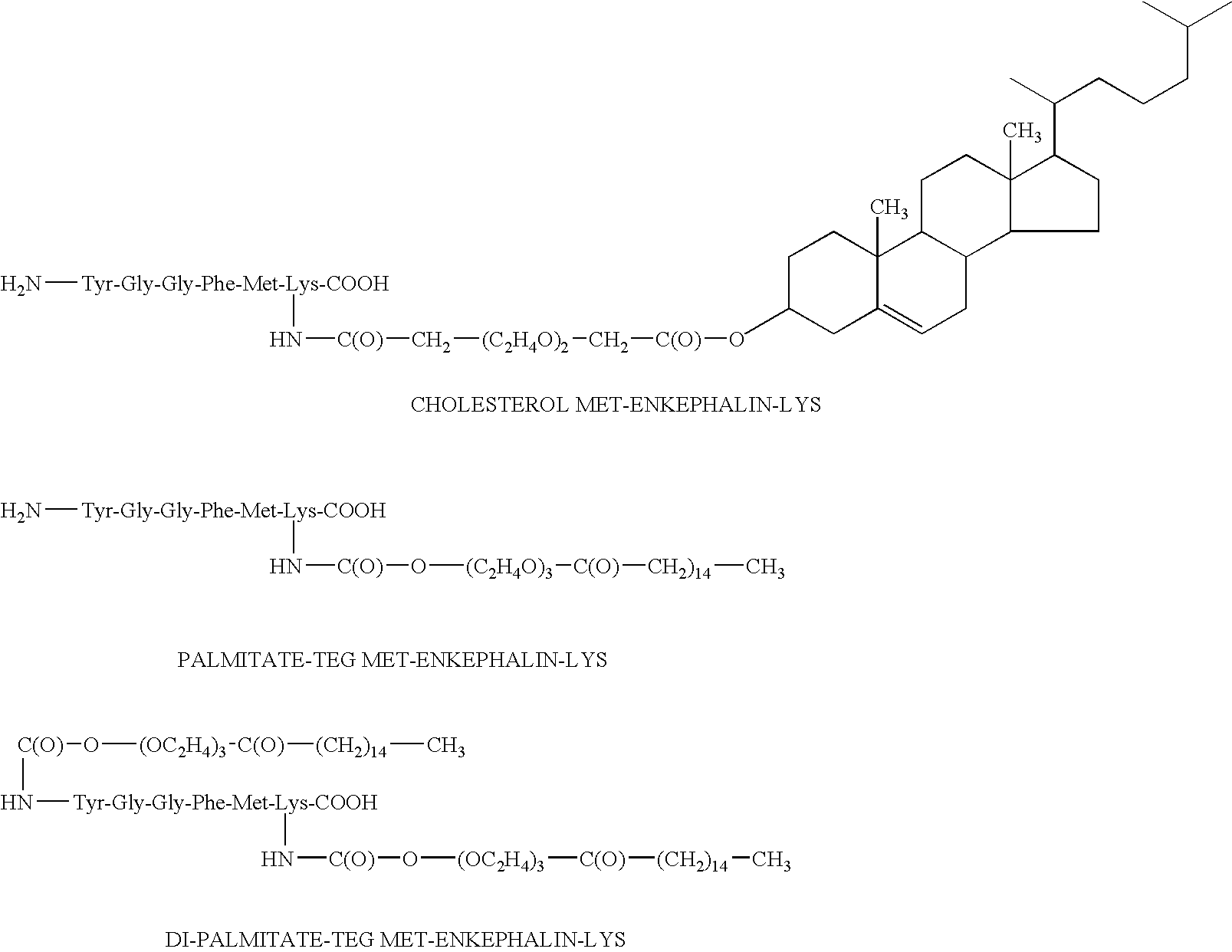
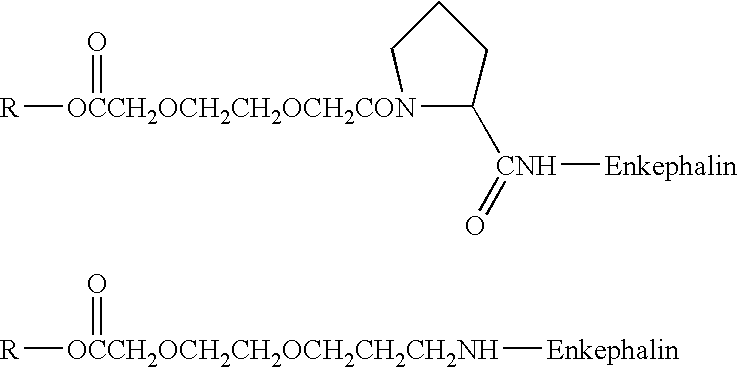
Peptide derivatives
A pharmacologically active peptide hormone derivative in which the parent peptide hormone has been modified by introducing either a lipophilic substituent, W, in the N-terminal amino acid or a lipophilic substituent, Z, in the C-terminal amino acid of the parent peptide hormone or an analogue thereof, said lipophilic substituent having from 8 to 40 carbon atoms, has a protracted profile of action.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Formulations for coated microprojections having controlled solubility
The invention provides for a formulation for coating one or more microprojections using a non-volatile counterion to improve solubility of a biologically active agent. The invention also includes formulations having a volatile counterion to reduce the solubility of a portion of the biologically active agent.
Owner:ALZA CORP
Conjugates of ligand linker and cytotoxic agent and related composition and methods of use
InactiveUS20050171014A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCytotoxicityOrganic chemistry
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE US REPRESENTED BY THE SEC
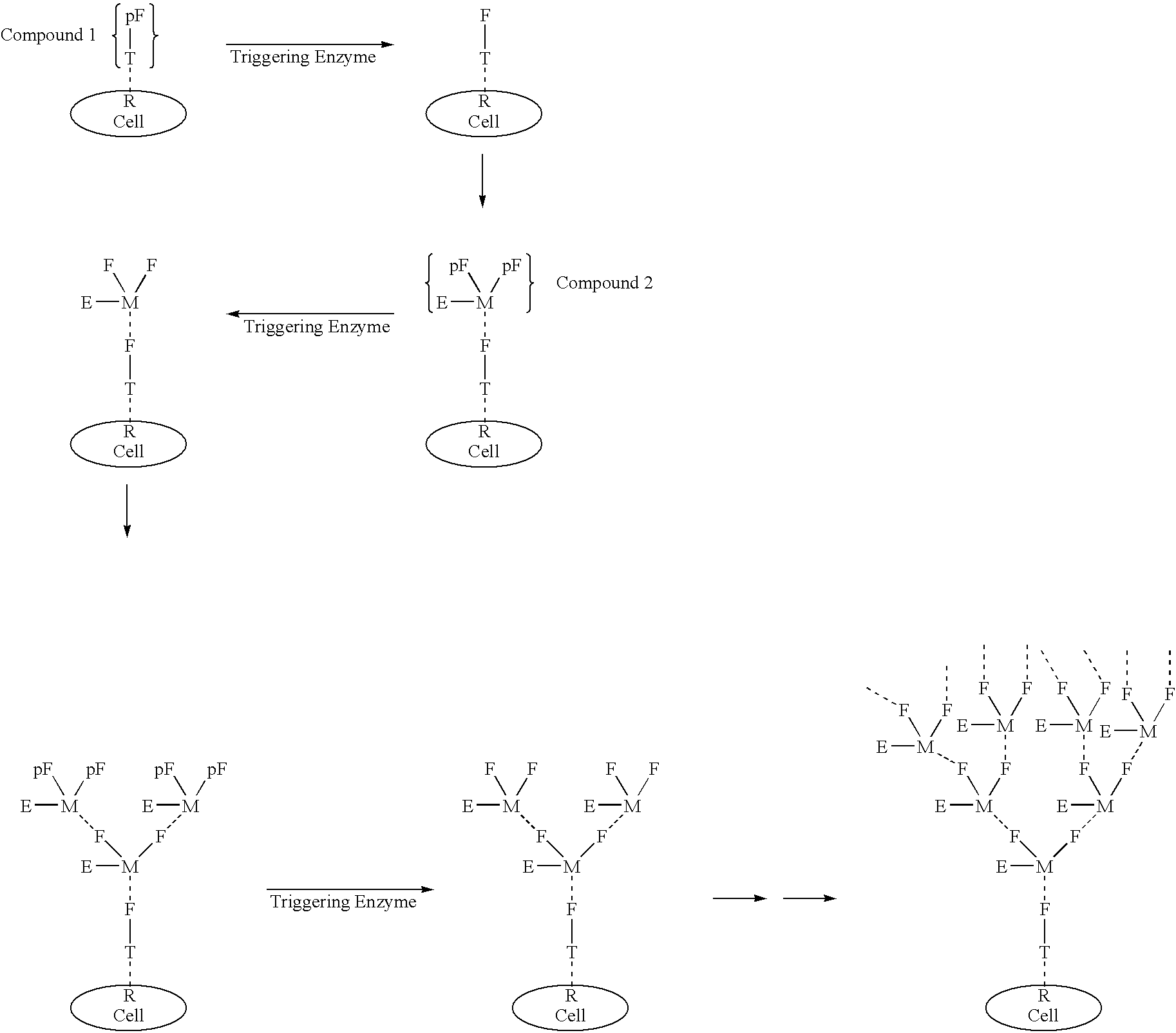
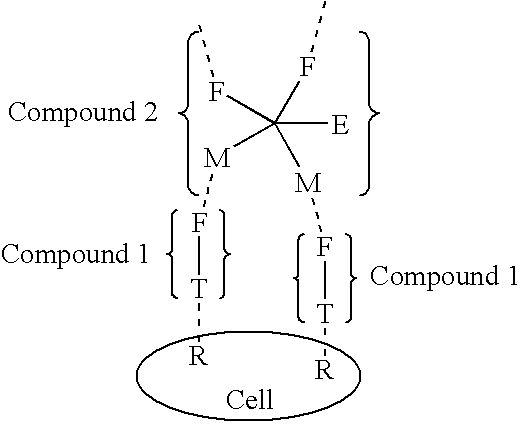
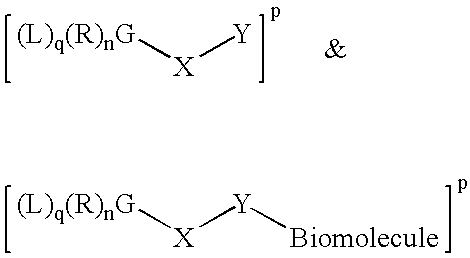
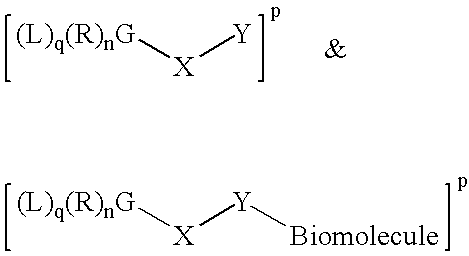
Exponential pattern recognition based cellular targeting compositions, methods and anticancer applications
InactiveUS20070172422A1Saccharide peptide ingredientsProtease inhibitorsCell bindingCellular targeting
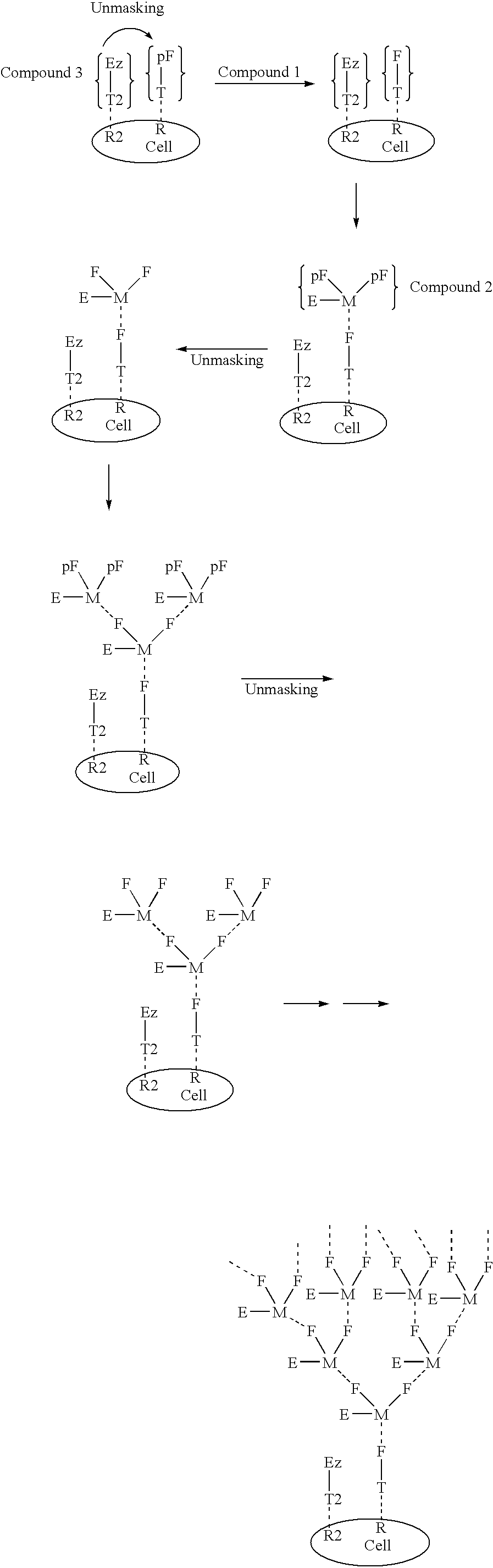
The present invention relates to the compositions, methods, and applications of a new approach to pattern recognition based targeting by which an exponential amplification of effector response can be specifically obtained at a targeted cells. The purpose of this invention is to enable the selective delivery of large quantities of an array of effector molecules to target cells for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. The invention is comprised of two components designated as “Compound 1” and “Compound 2”: Compound 1 is comprised of a cell binding agent and a masked female adaptor. Compound 2 is comprised of a male ligand, an effector agent, and two or more masked female receptors. The male ligand is selected to bind with high affinity to the female adaptor. Compound 1 can bind with high affinity to the target cell and the female receptor can then be unmasked by an enzyme enriched at the tumor cell. The male ligand of Compound 2 can then bind to the unmasked female adaptor bound to the target cell. The masked female adaptor on the bound Compound 2 can then be specifically unmasked. One receptor has in effect become two. Two new molecules of Compound 2 can bind to the unmasked adaptors receptors. After unmasking two receptors in effect become four. The process can continue in an explosive exponential like fashion resulting in enormous amplification of the number of effector molecules specifically deposited at the target cell.
Owner:GLAZIER ARNOLD
Injectable Sustained-Release Pharmaceutical Formulation and the Preparation Method Thereof
InactiveUS20110091420A1Good effectGood sustained release effectBiocideCalcitoninsOrganic acidSolvent
Disclosed are an injectable sustained-release pharmaceutical formulation and a process for preparing the same. In some embodiments, the formulation comprises an active ingredient in a therapeutically effective amount, an amphipathic molecule, an organic acid and / or a salt thereof which is hardly soluble in water, and an oily solvent. The injectable sustained-release pharmaceutical formulation provides a good sustained-release effect for various active ingredients, in particular peptides, proteins, nucleic acids and saccharides.
Owner:INST OF PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI P L A +1
Controlled released compositions
ActiveUS20070092574A1Reduce degradationEasy loadingPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseControlled release
The compositions disclosed herein are for use as controlled release therapeutics for the treatment of a wide variety of diseases. In particular, the compositions provide water soluble bioactive agents, organic ions and polymers where the bioactive agent is efficiently released over time with minimal degradation products. The resulting controlled release composition is capable of administration in a decreased dose volume due to the high drug content and predominance of non-degraded bioactive agent after release. Additionally, the compositions, of the present invention are capable of long term, sustained releases.
Owner:PR PHARMA +1
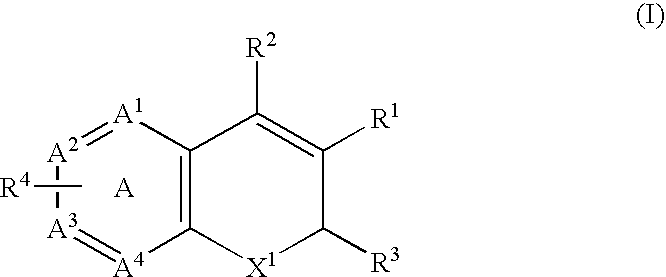
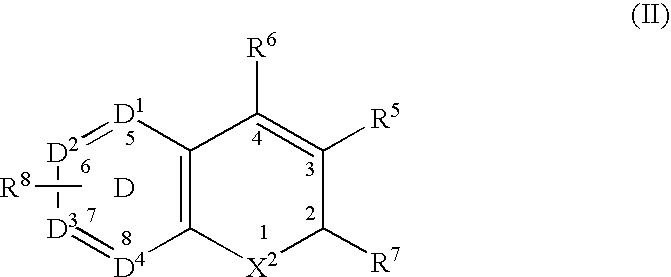
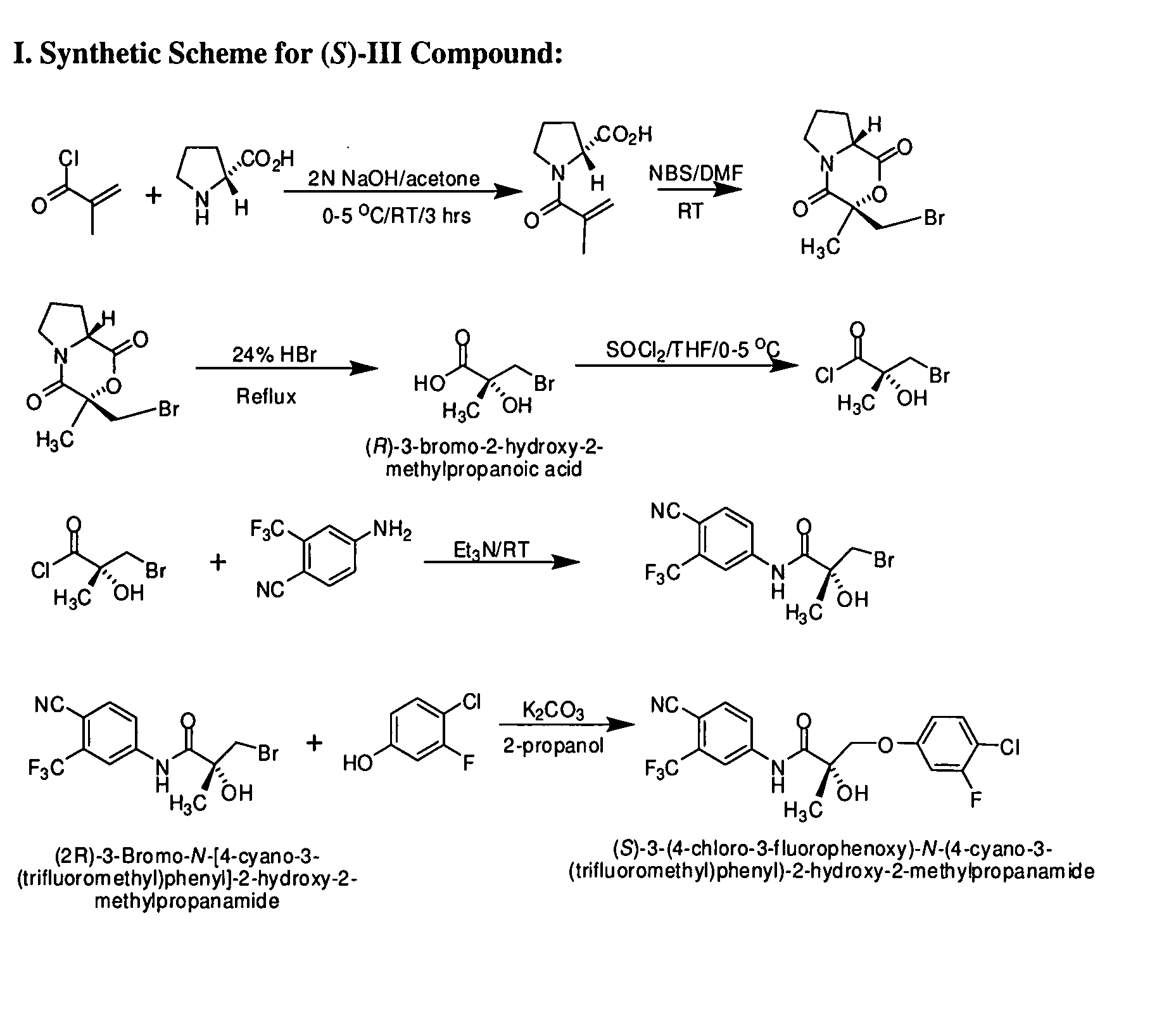
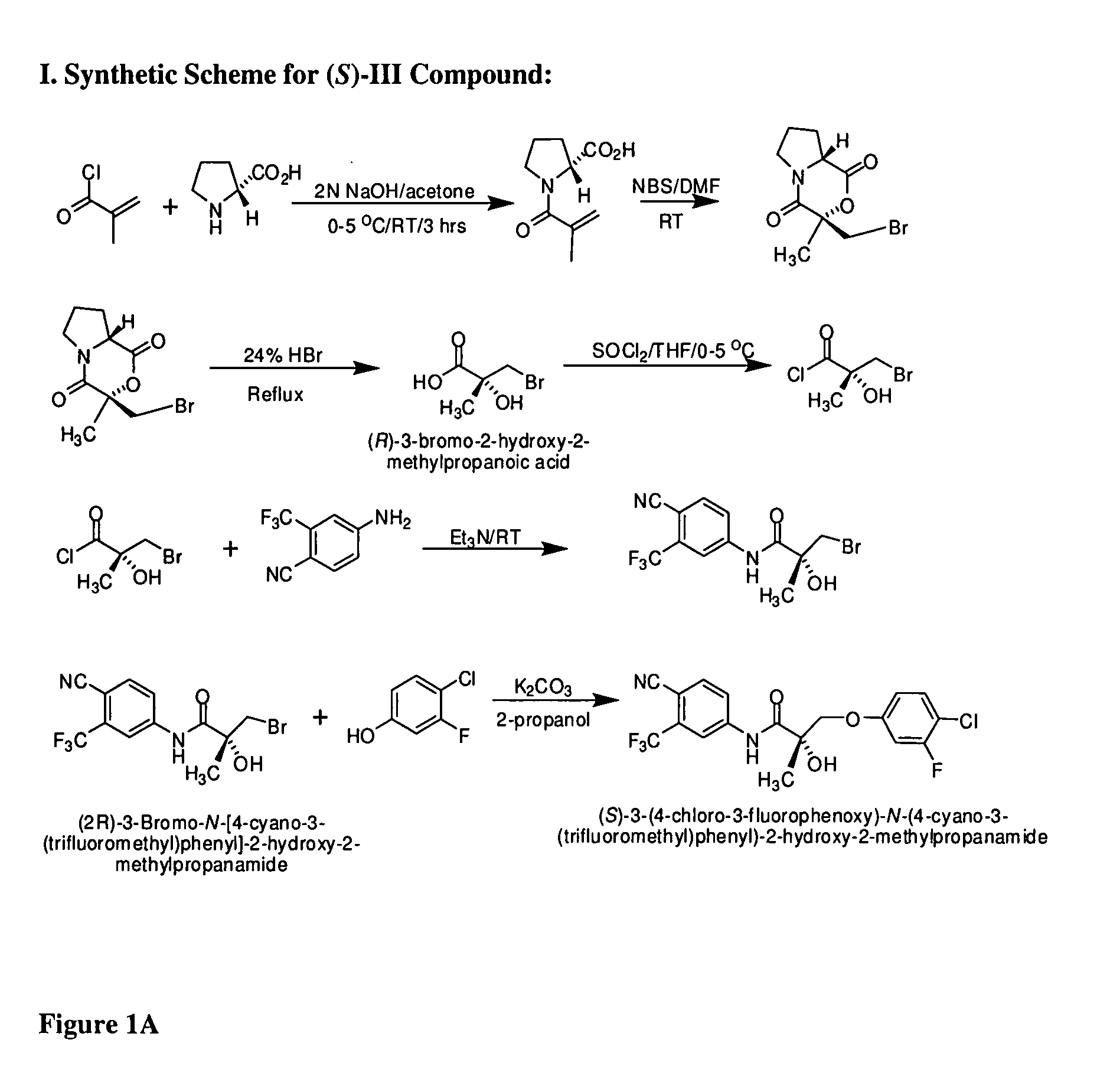
Somatostatin antagonists and agonists that act at the sst subtype 2 receptor
InactiveUS20020128206A1Ease of detectabilityEasy to prepareDipeptide ingredientsMetabolism disorderArylMammal
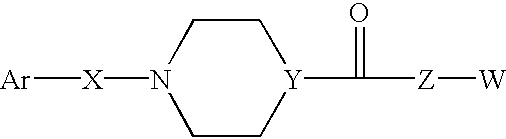
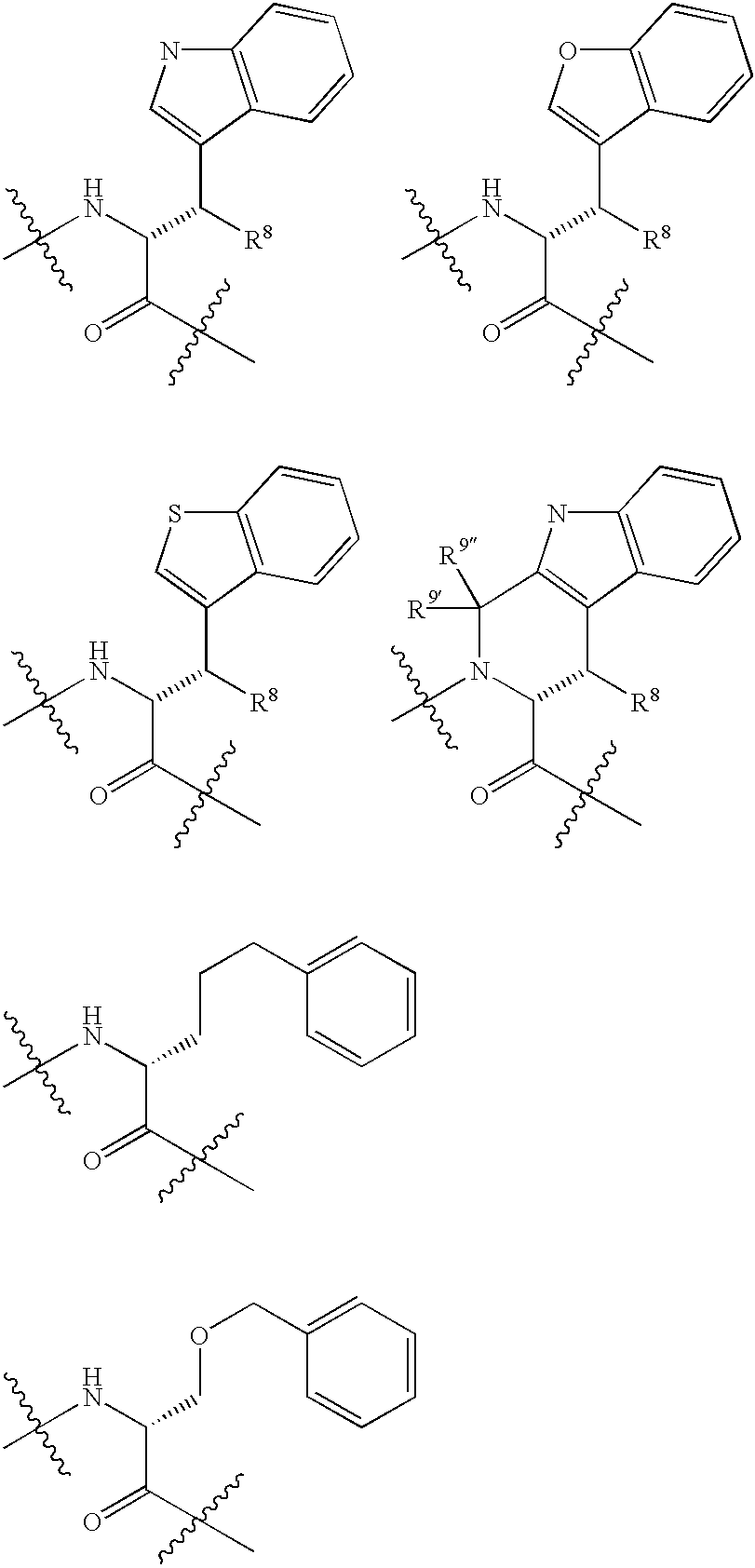
Compounds according to the formula: 1 and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, solvates or hydrates thereof, wherein group Ar is optionally substituted (C.sub.6-C.sub.10)aryl or (C.sub.1-C.sub.9)heteroaryl; X is a direct link, --CH.sub.2 --, --SO.sub.2 --, --CO--, --CHR.sup.1-- where R.sup.1 is(C.sub.1-C.sub.6) alkyl, or --CR.sup.1'R.sup.1"-where both R.sup.1' and R.sup.1" are, independently, (C.sub.1-C.sub.6)alkyl; Y is N or CH; and Z and W are as herein defined, and pharmaceutical compositions thereof, and methods useful to facilitate secretion of growth hormone(GH) in mammals.
Owner:HAY BRUCE A +2
SARMS and method of use thereof
InactiveUS20080057068A1Reduce severityReduce morbidityBiocideNervous disorderDiabetes mellitusDisease cause
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Methods of altering the binding affinity of a peptide to its receptor
InactiveUS20040102381A1Improve hydrophilicityEnhance amphipathicAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsOligomerNucleotide
The present invention relates to amphiphilic drug-oligomer conjugates capable of traversing the blood-brain barrier ("BBB") and to methods of making and using such conjugates. An amphiphilic drug-oligomer conjugate comprises a therapeutic compound conjugated to an oligomer, wherein the oligomer comprises a lipophilic moiety coupled to a hydrophilic moiety. The conjugates of the invention further comprise therapeutic agents such as proteins, peptides, nucleosides, nucleotides, antiviral agents, antineoplastic agents, antibiotics, etc., and prodrugs, precursors, derivatives and intermediates thereof, chemically coupled to amphiphilic oligomers.
Owner:BIOCON LTD
SSTR1-selective analogs
InactiveUS7019109B2High affinityEasy to markPeptide sourcesRadioactive preparation carriersNervous systemScreening method
Analogs of SRIF which are selective for SSTR1 in contrast to the other cloned SRIF receptors. These analogs are useful in determining the tissue and cellular expression of the receptor SSTR1 and its biological role in the endocrine, exocrine and nervous system, as well as in regulating tumor growth. SRIF analog peptides, such as des-AA1,2,5[D-Trp8, NαMeIAmp9, Tyr11]-SRIF and counterparts incorporating Cbm at the N-terminus and / or NαSer13, inhibit the binding of a universal SRIF radioligand to the cloned human receptor SSTR1, but they do not bind with significant affinity to human SSTR2, SSTR3, SSTR4 or SSTR5. By incorporating an iodinated tyrosine in position-2 or in position-11 in these SSTR1-selective SRIF analogs, a labeled compound useful in drug-screening methods is provided. The N-terminus accommodates bulky moieties without loss of selectivity, and a carbamoyl moiety or a conjugating agent that will accept a radioactive nuclide or will link to a cytotoxin may be present at the N-terminus.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Radiolabeled Compounds And Compositions, Their Precursors And Methods For Their Production
ActiveUS20080038191A1High densityPeptide/protein ingredientsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsCounterionSulfur
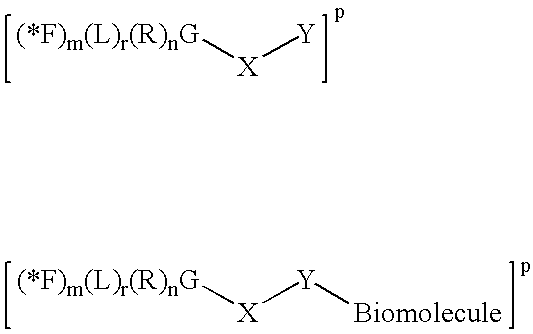
Positron emitting compounds and methods of their production are provided. The compounds have the formula: (F)m G (R)n wherein each R is a group comprising at least one carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus or sulfur atom and G is joined to R through said carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus or sulfur atom; G is silicon or boron; m is 2 to 5 and n is 1 to 3 with m+n=3 to 6 when G is silicon; m is 1 to 3 and n is 1 to 3 with m+n=3 to 4 when G is boron; and wherein the compound further comprises one or more counterions when the above formula is charged; and wherein at least one F is 18 F.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com