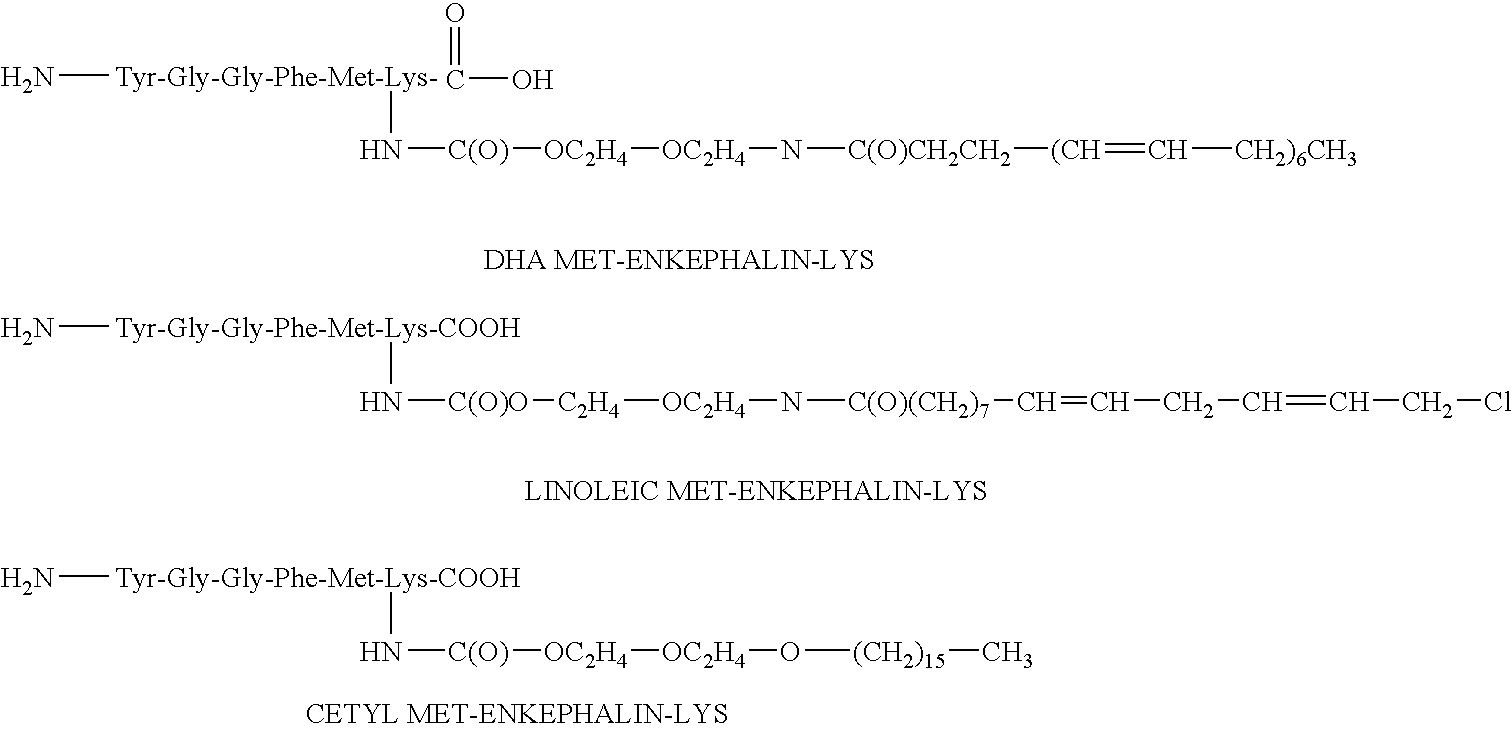Methods of altering the binding affinity of a peptide to its receptor
a technology of peptide binding affinity and amphiphilic oligomer, which is applied in the direction of parathyroid hormone, angiogenin, metabolism disorder, etc., can solve the problems of peptide delivery to the cns being metabolically unstable, limiting the use of many compounds for use as cns therapeutic agents, and not being able to protect peptides from the wide range of peptide-degrading enzymes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0097] For clarity of disclosure, and not by way of limitation, the detailed description of the invention is divided into the subsections which follow.
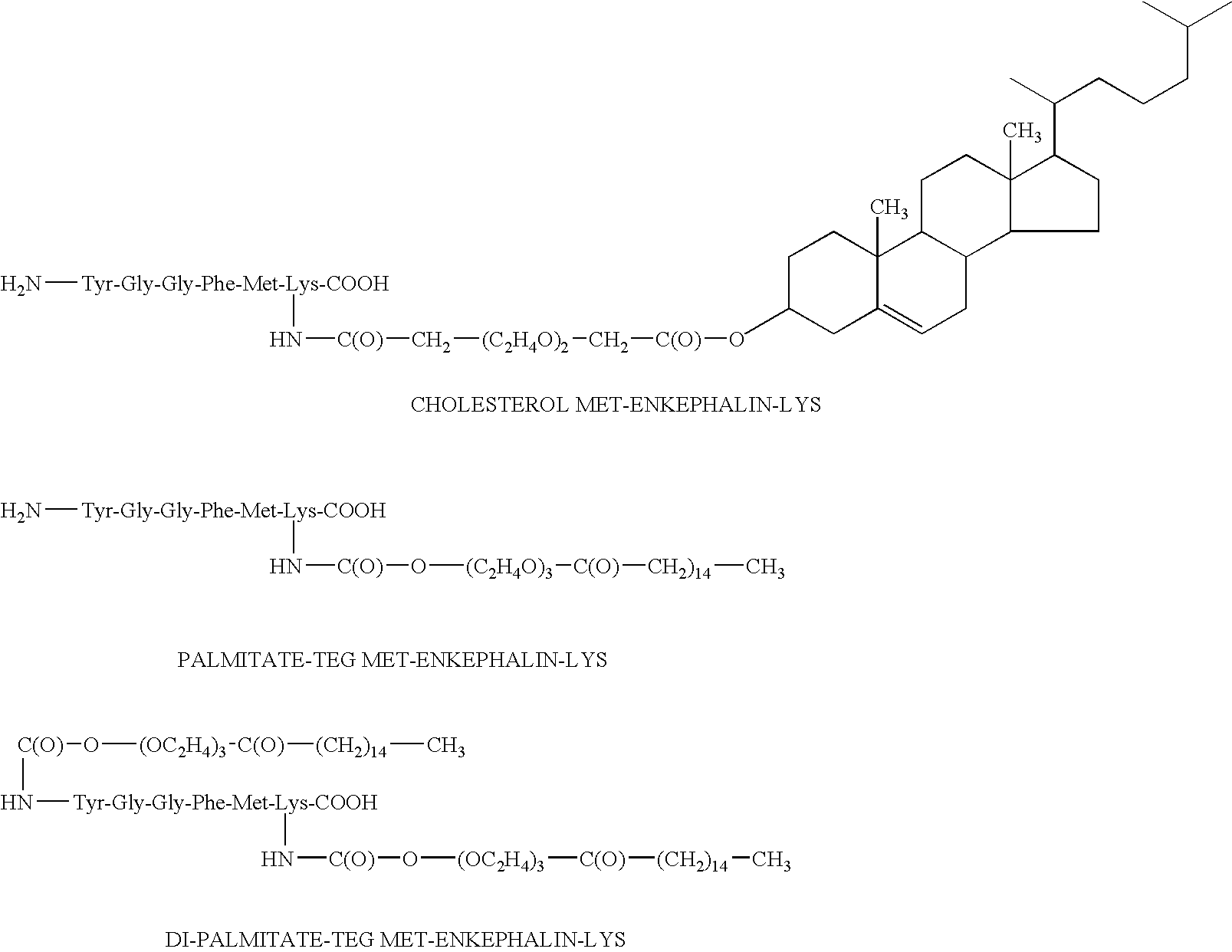
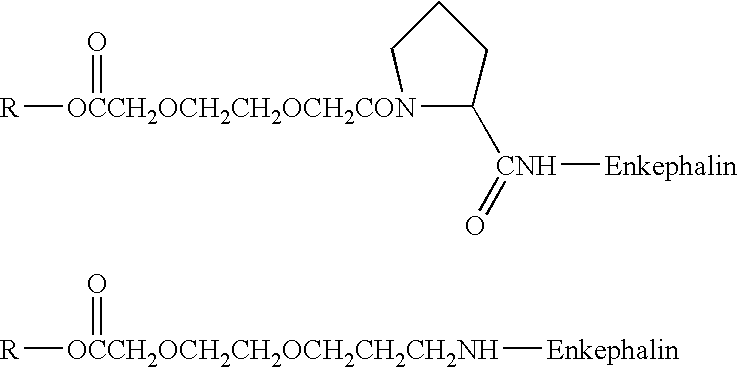
[0098] The present invention relates generally to amphiphilic drug-oligomer conjugates capable of traversing the BBB and to methods of making and using such conjugates.
[0099] The drugs are preferably neuro-active drugs, proteins, peptides and especially enkephalin analogues. The conjugates are stable in the environment of the bloodstream and resist degradation by the BBB. The conjugates readily traverse the BBB.
[0100] In one aspect, the conjugates produce their intended pharmacological effect without requiring metabolic cleavage of the oligomer. When cleavage of the oligomer occurs, the drug retains activity.
[0101] The amphiphilic oligomers are composed of lipophilic and hydrophilic moieties. The lipophilic moieties are preferably natural fatty aids or alkyl chains. The lipophilic moieties are preferably small segments of PEG, having ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com