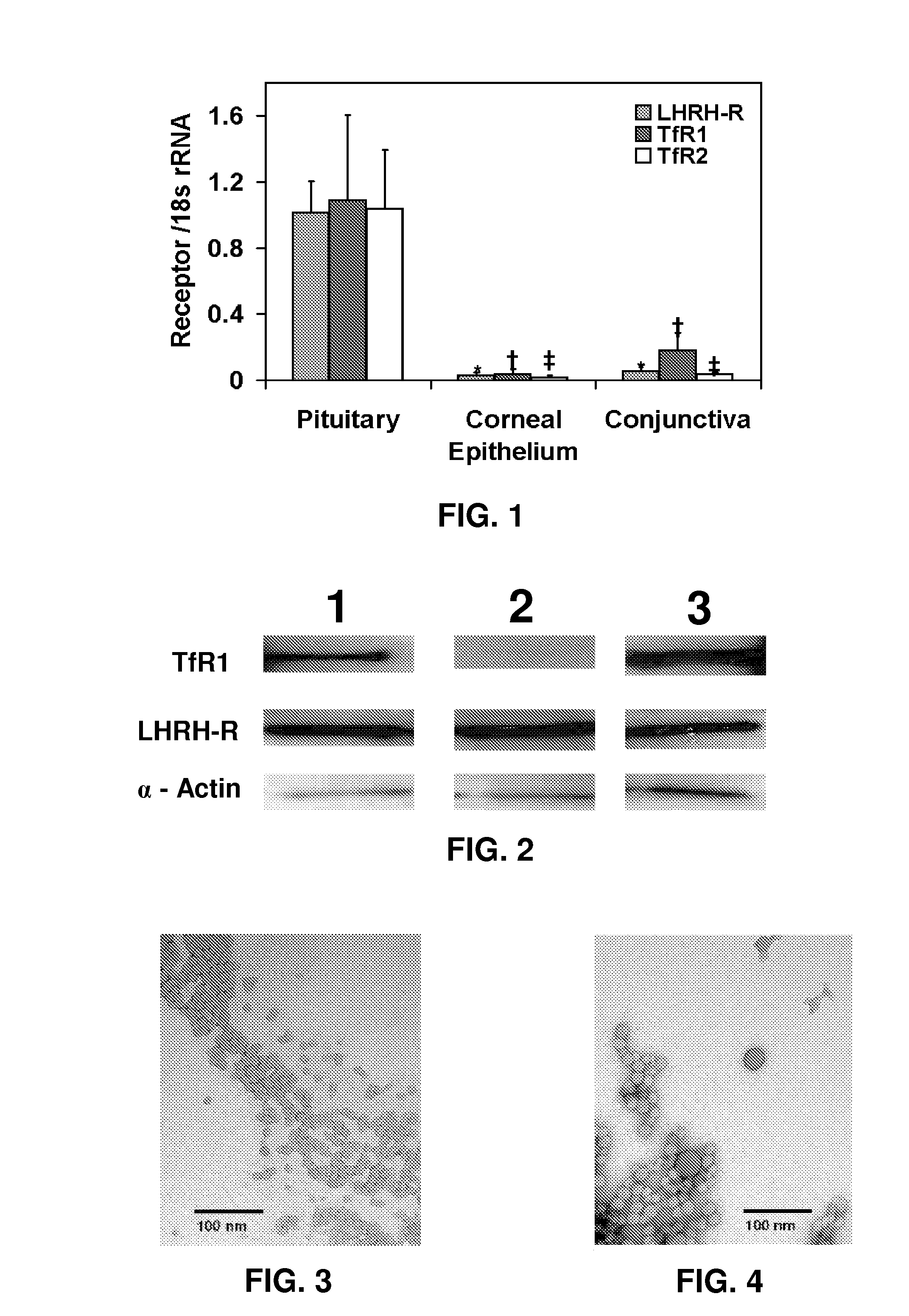
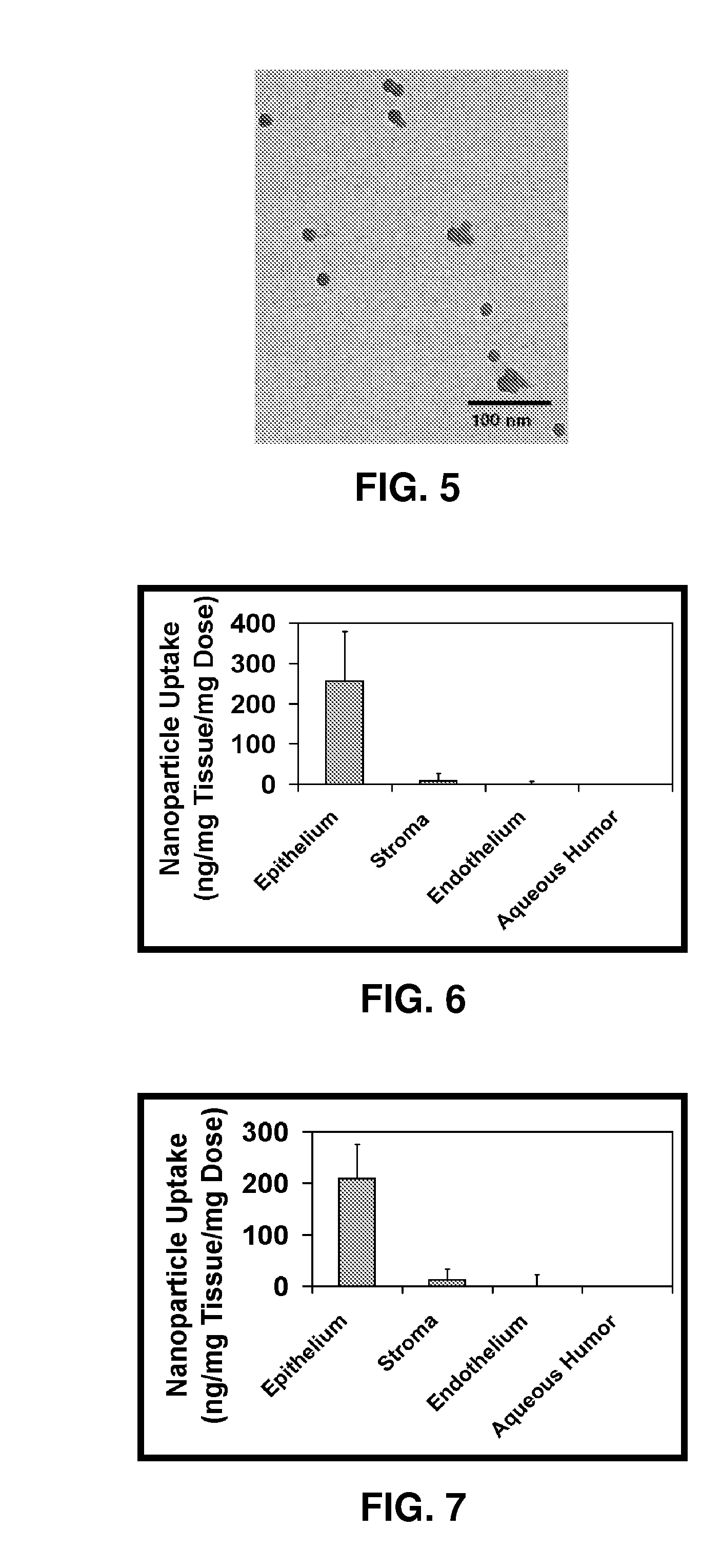
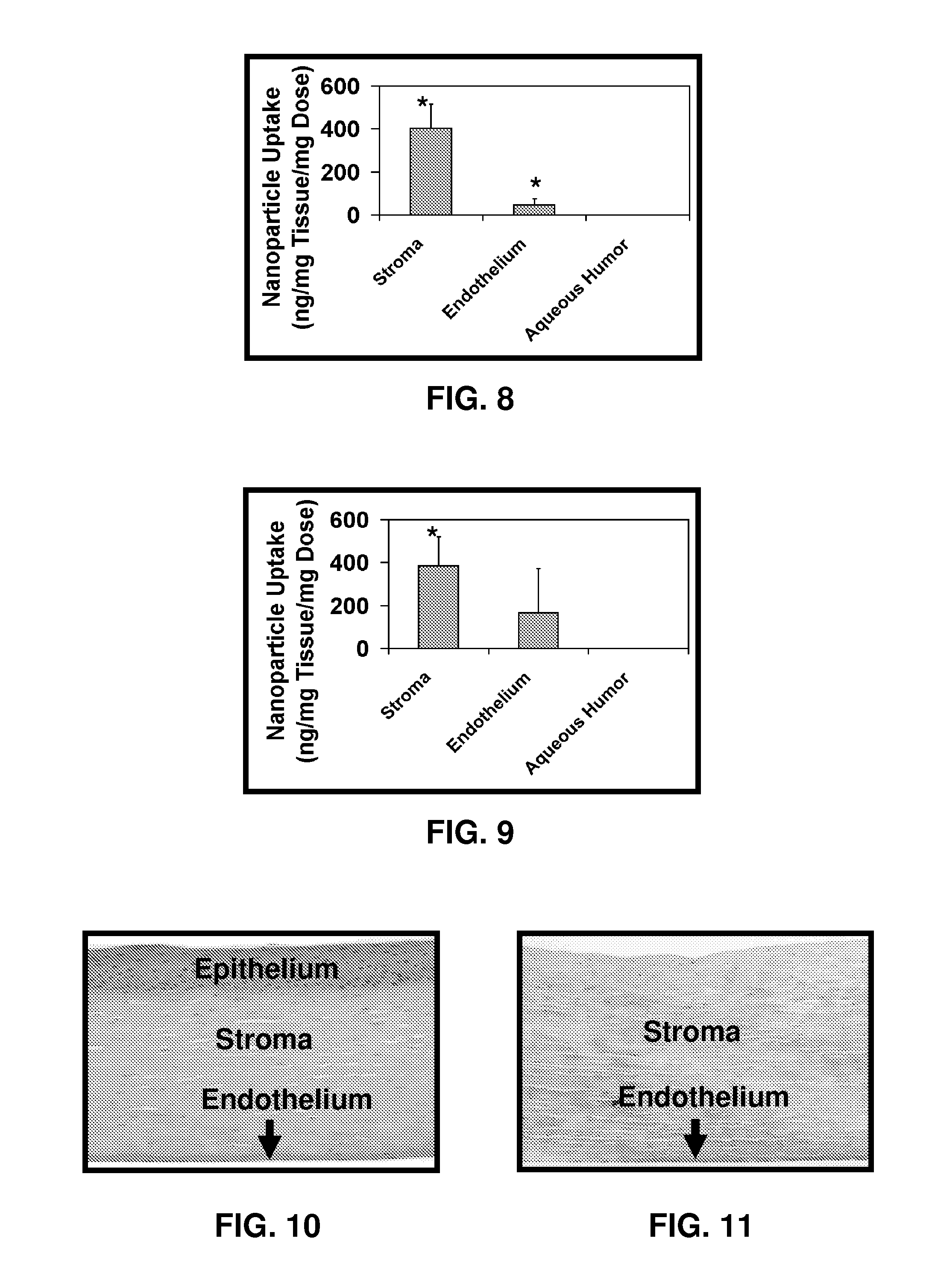
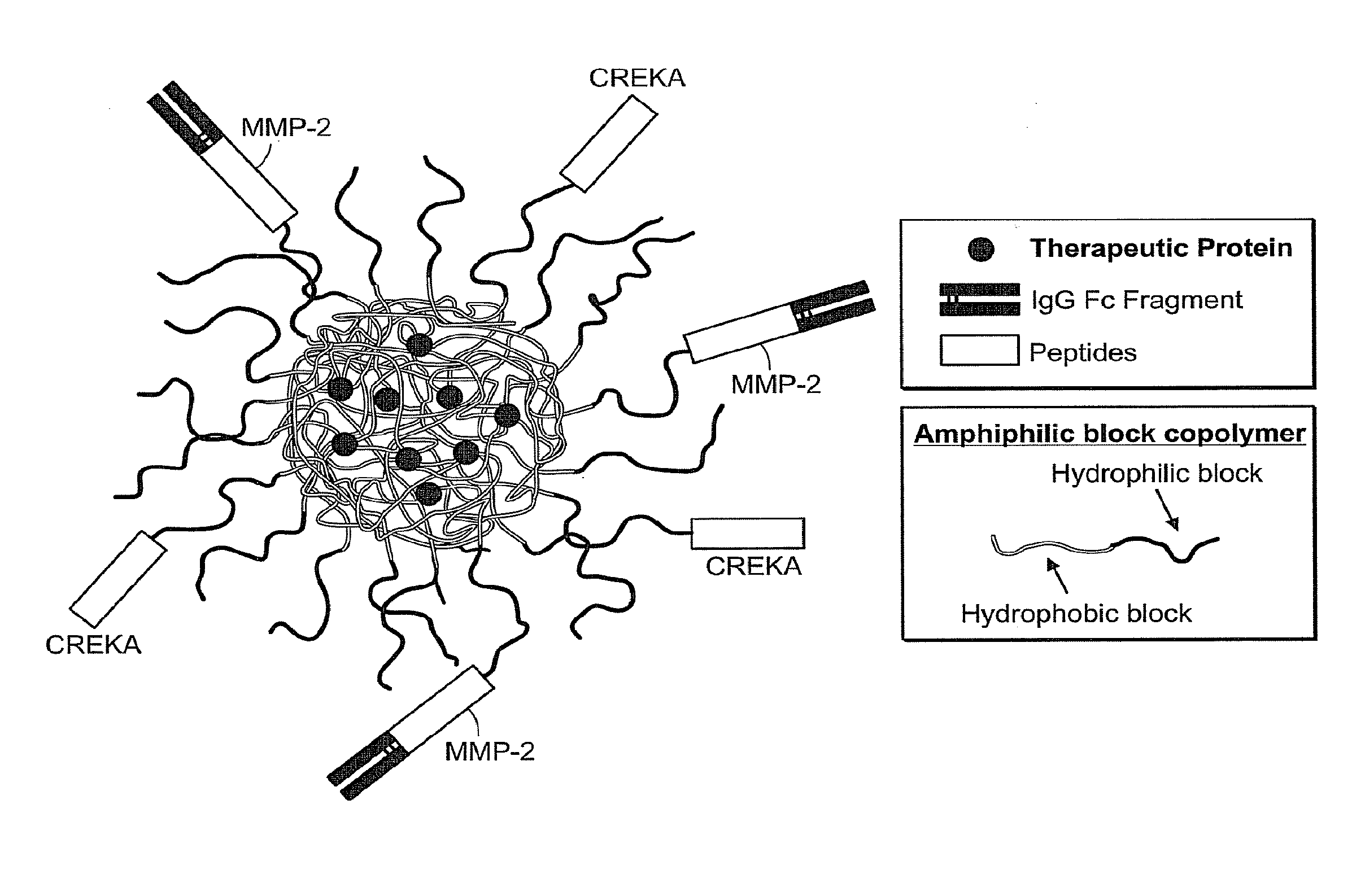
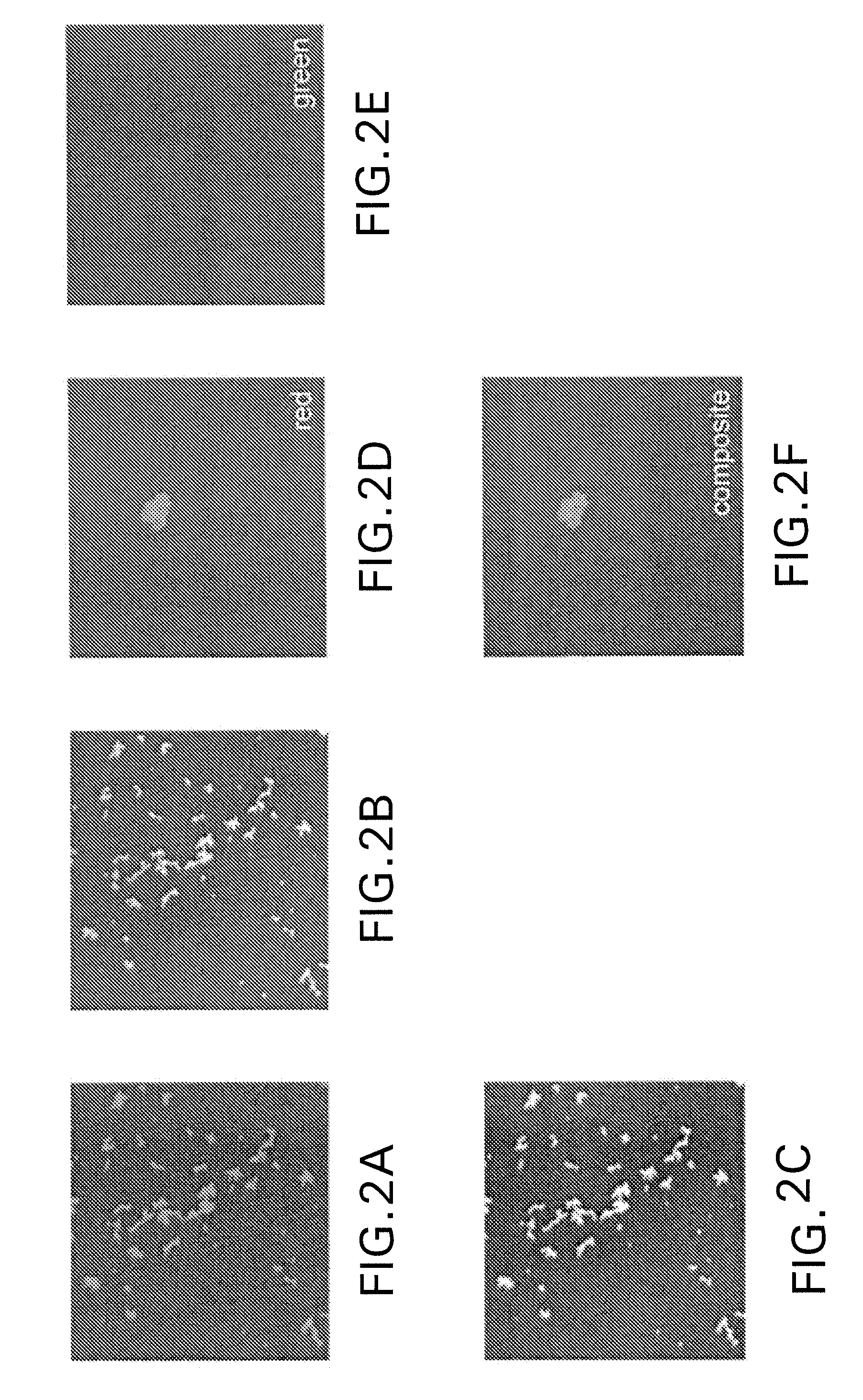
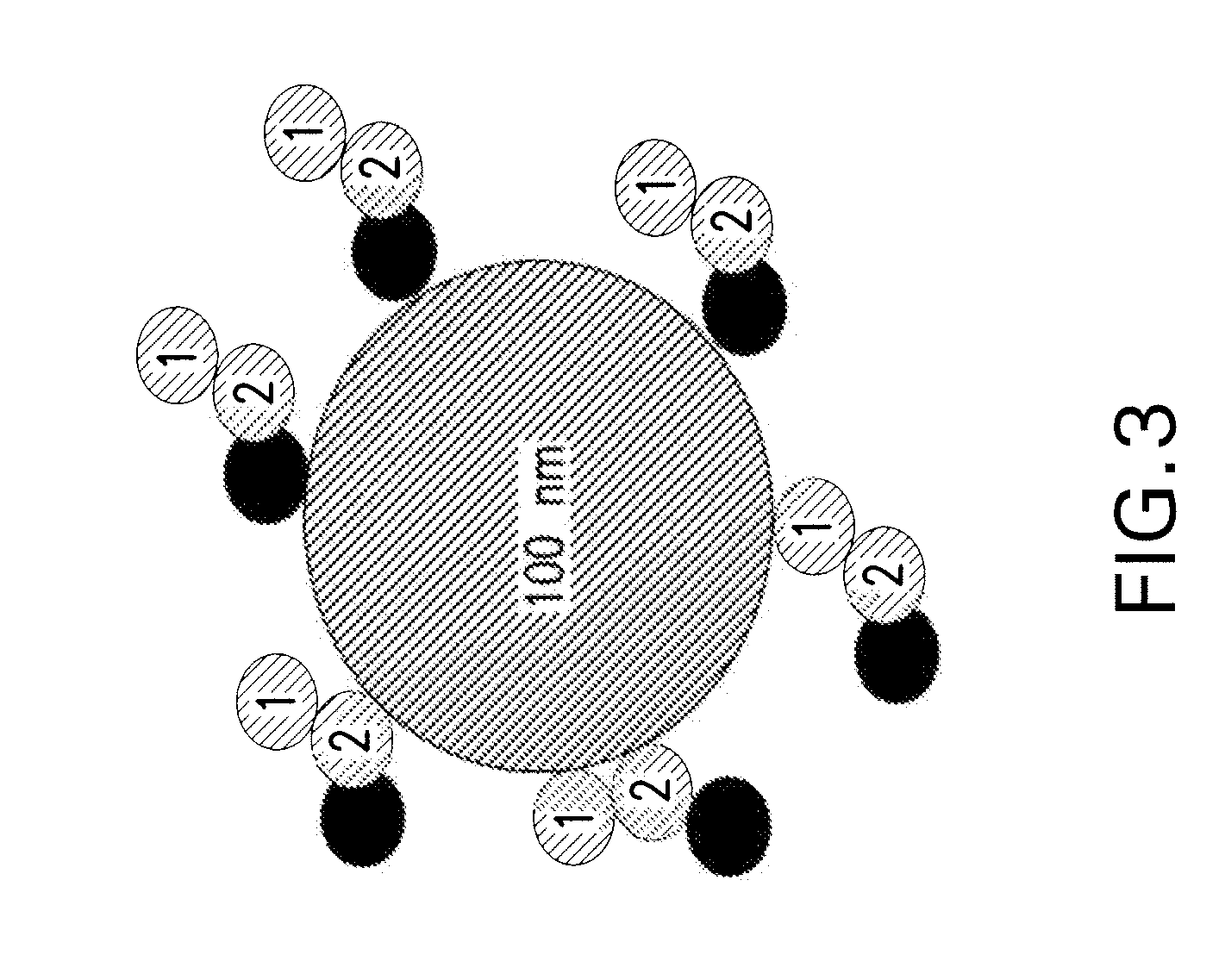
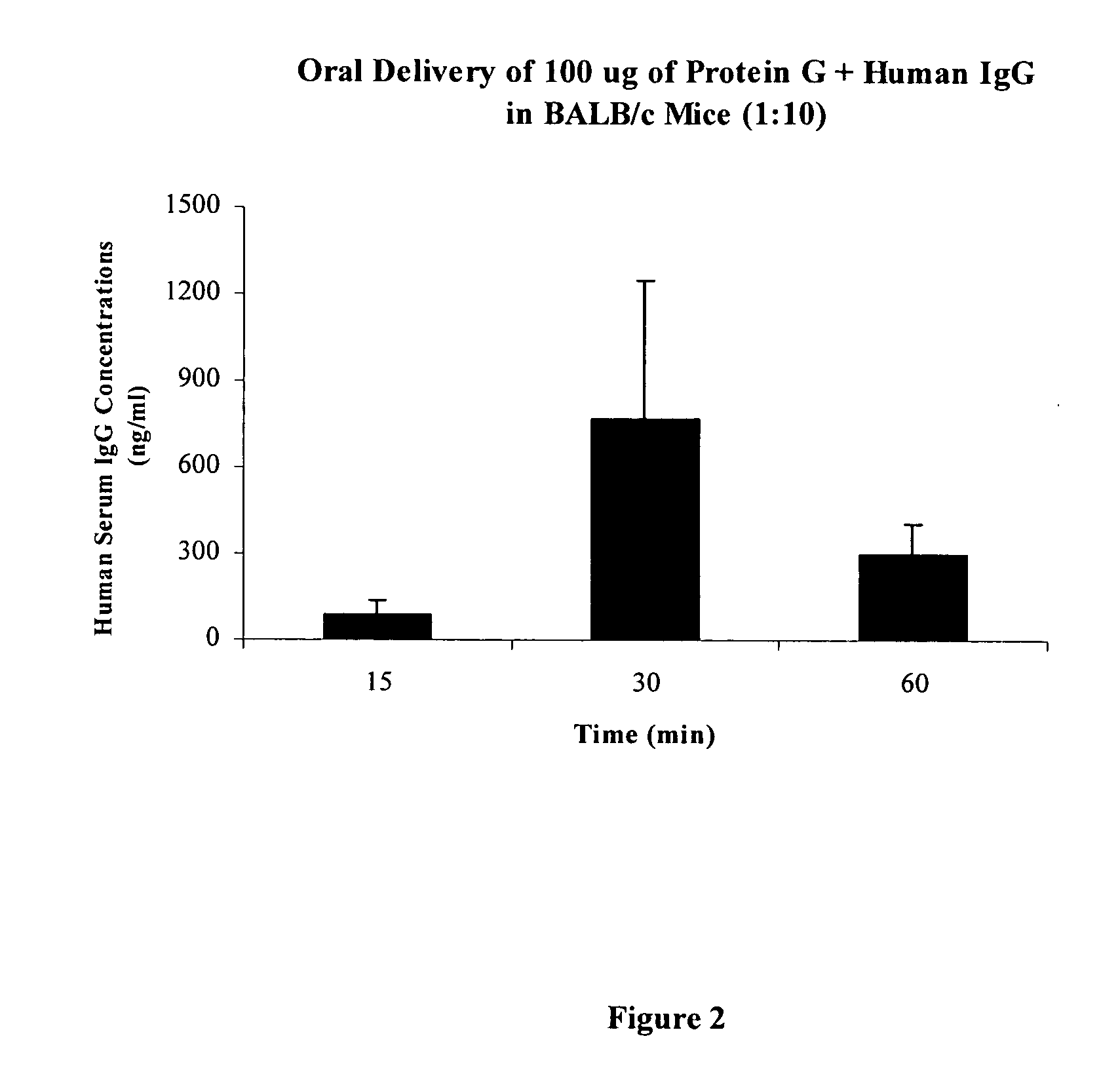
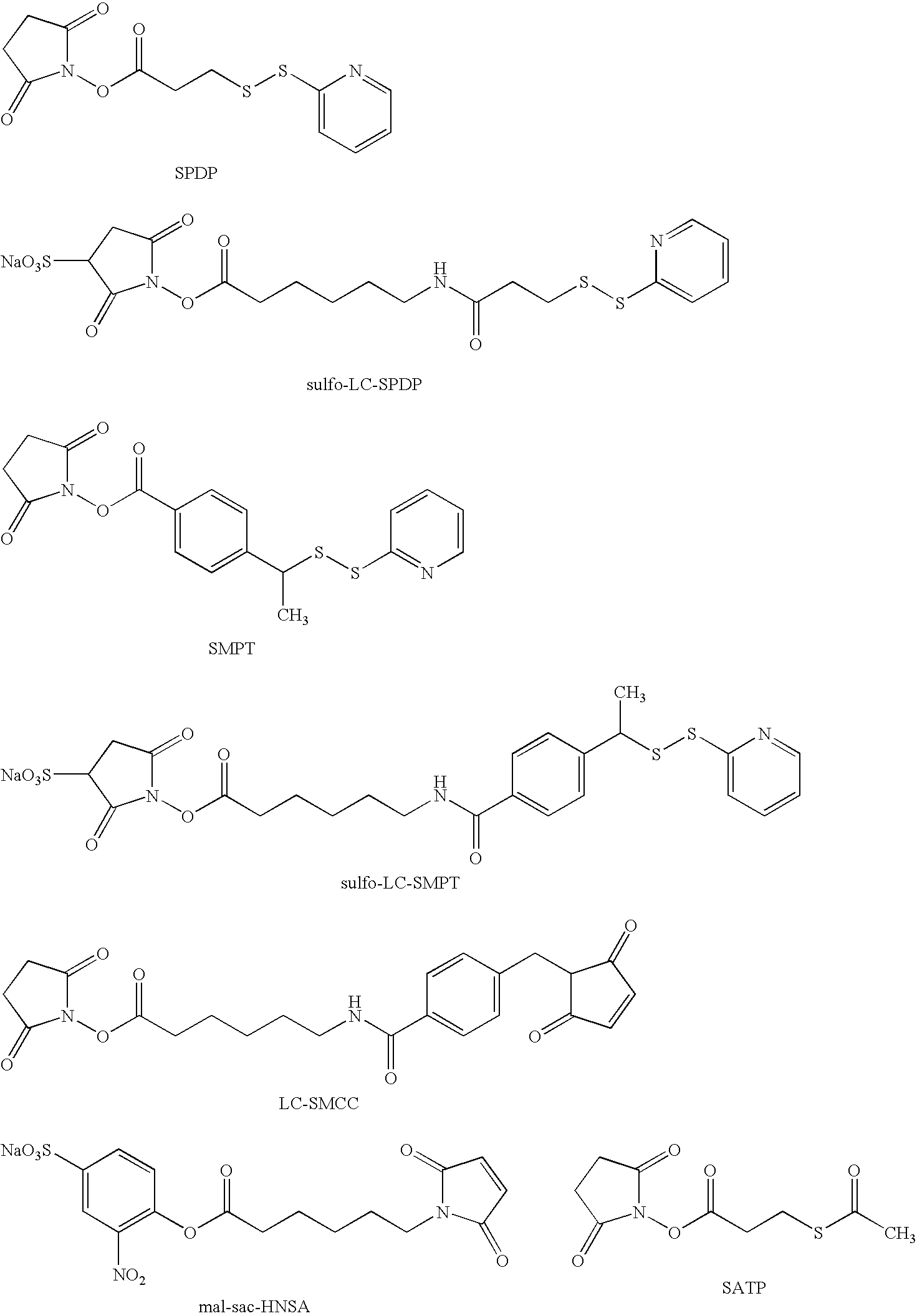
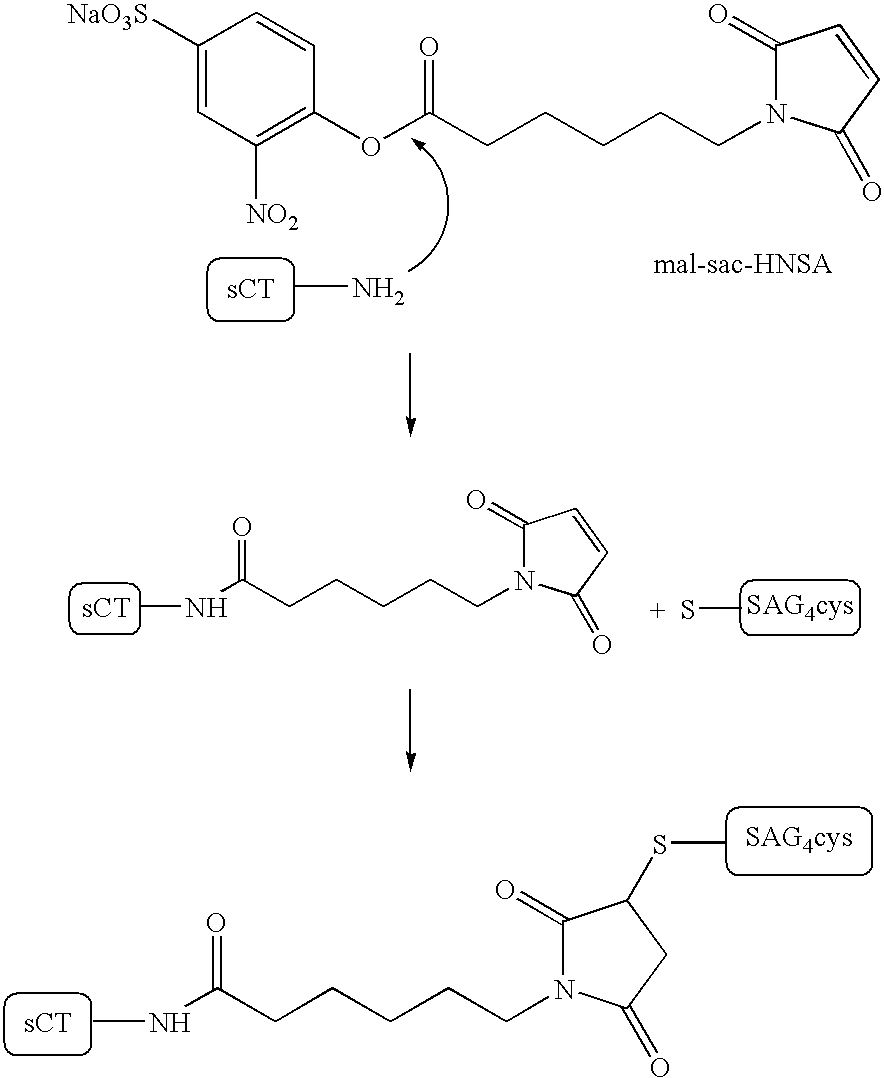
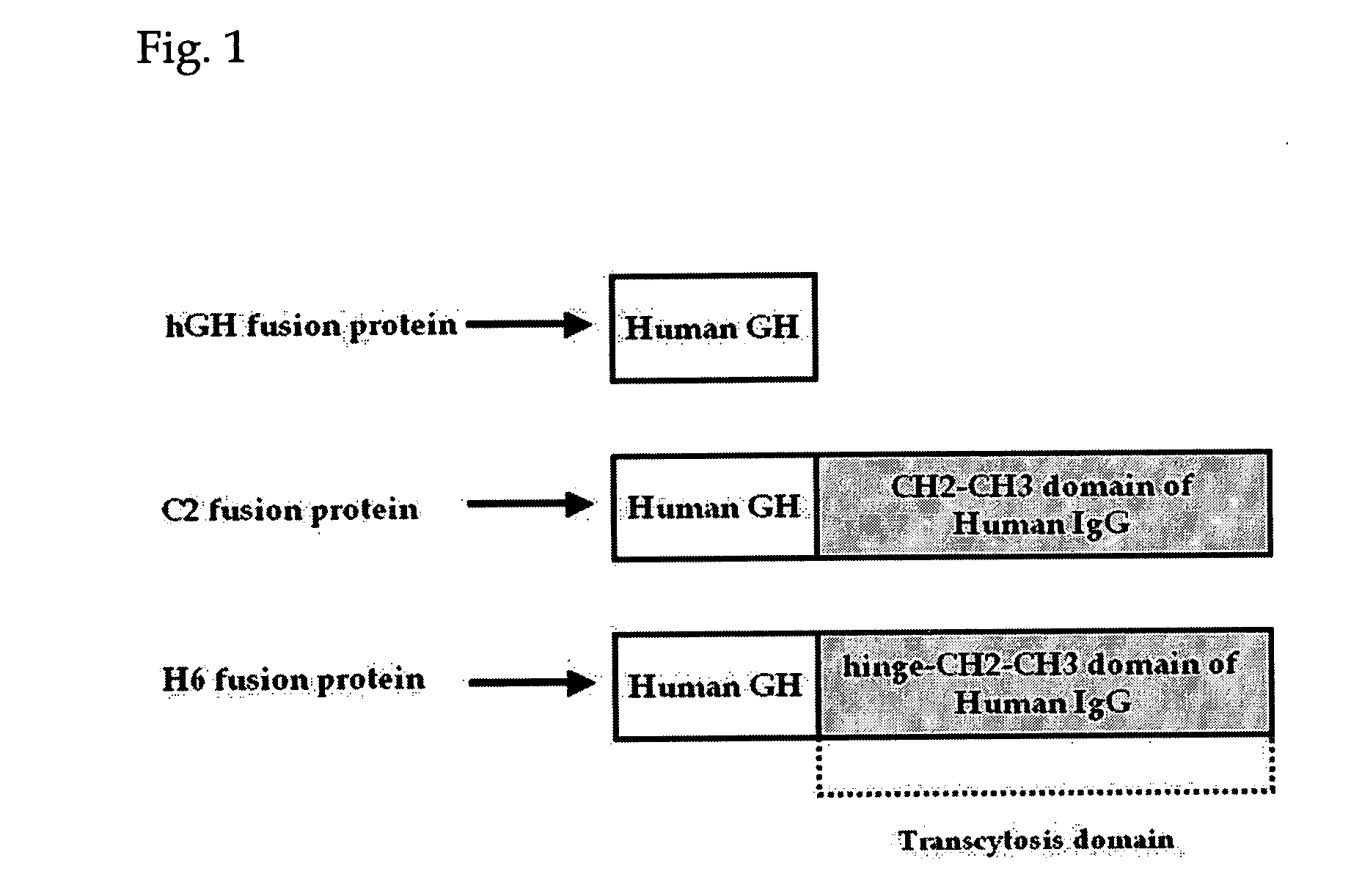
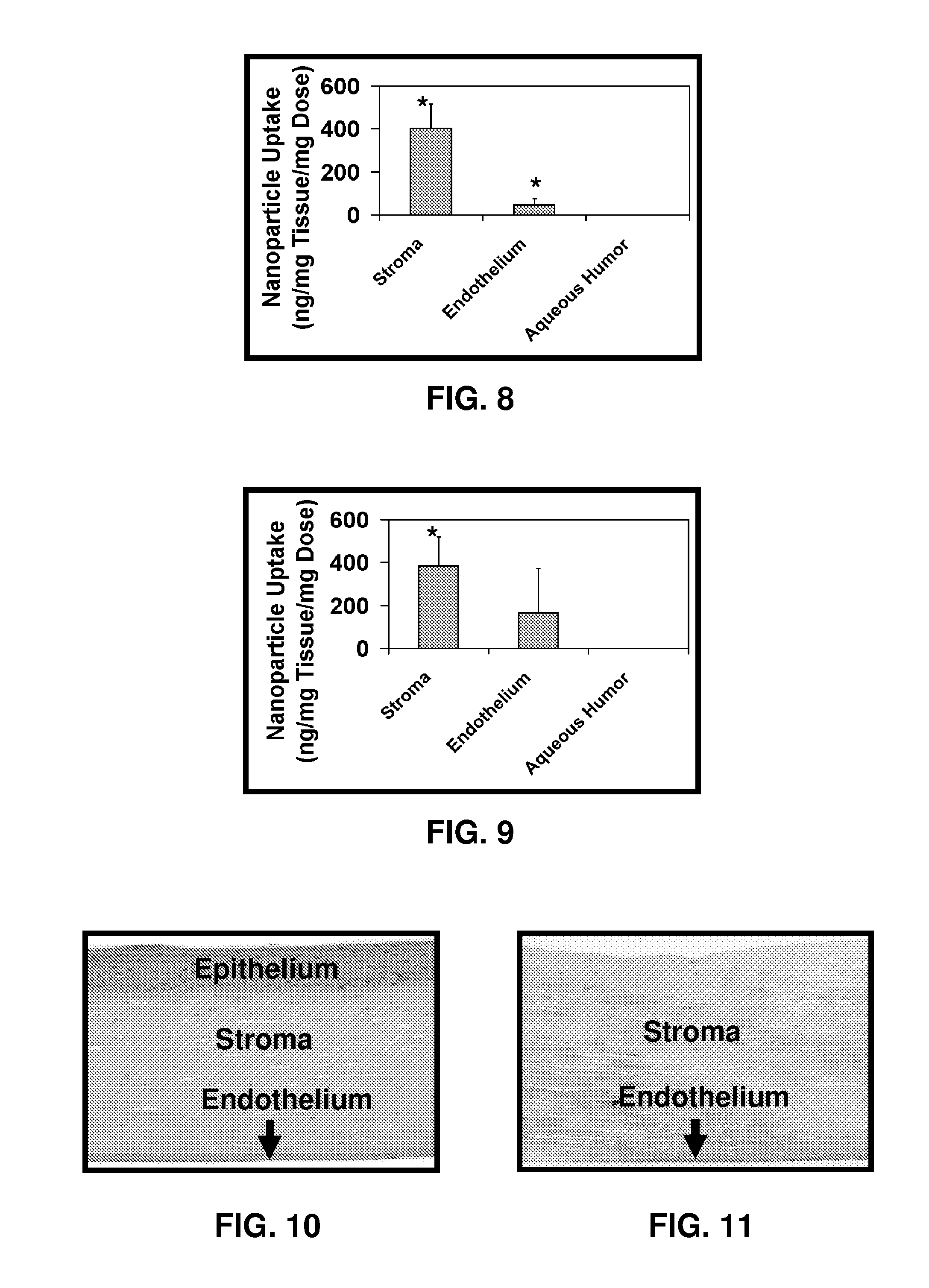
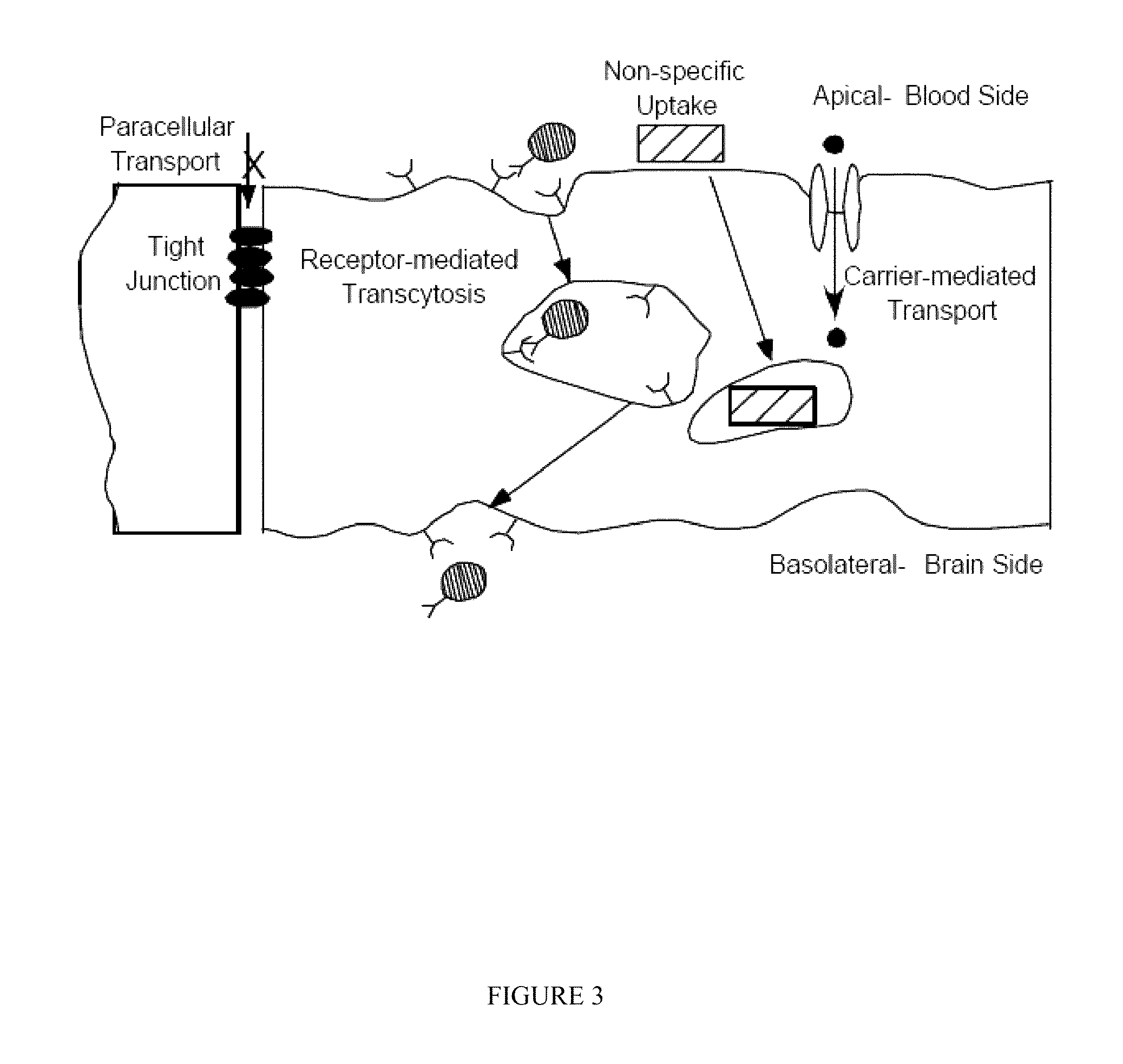
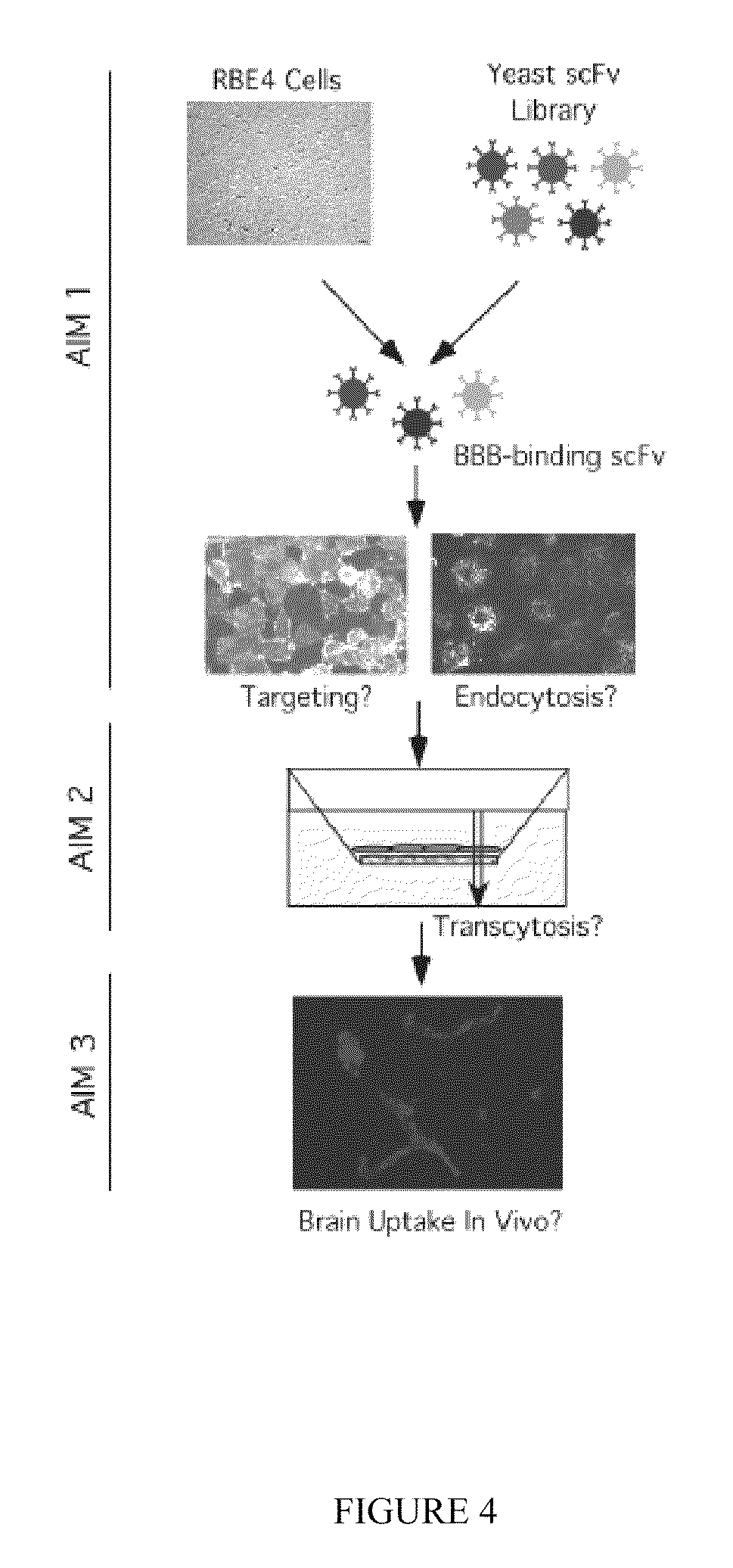
Patents
Literature
43 results about "Transcytosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
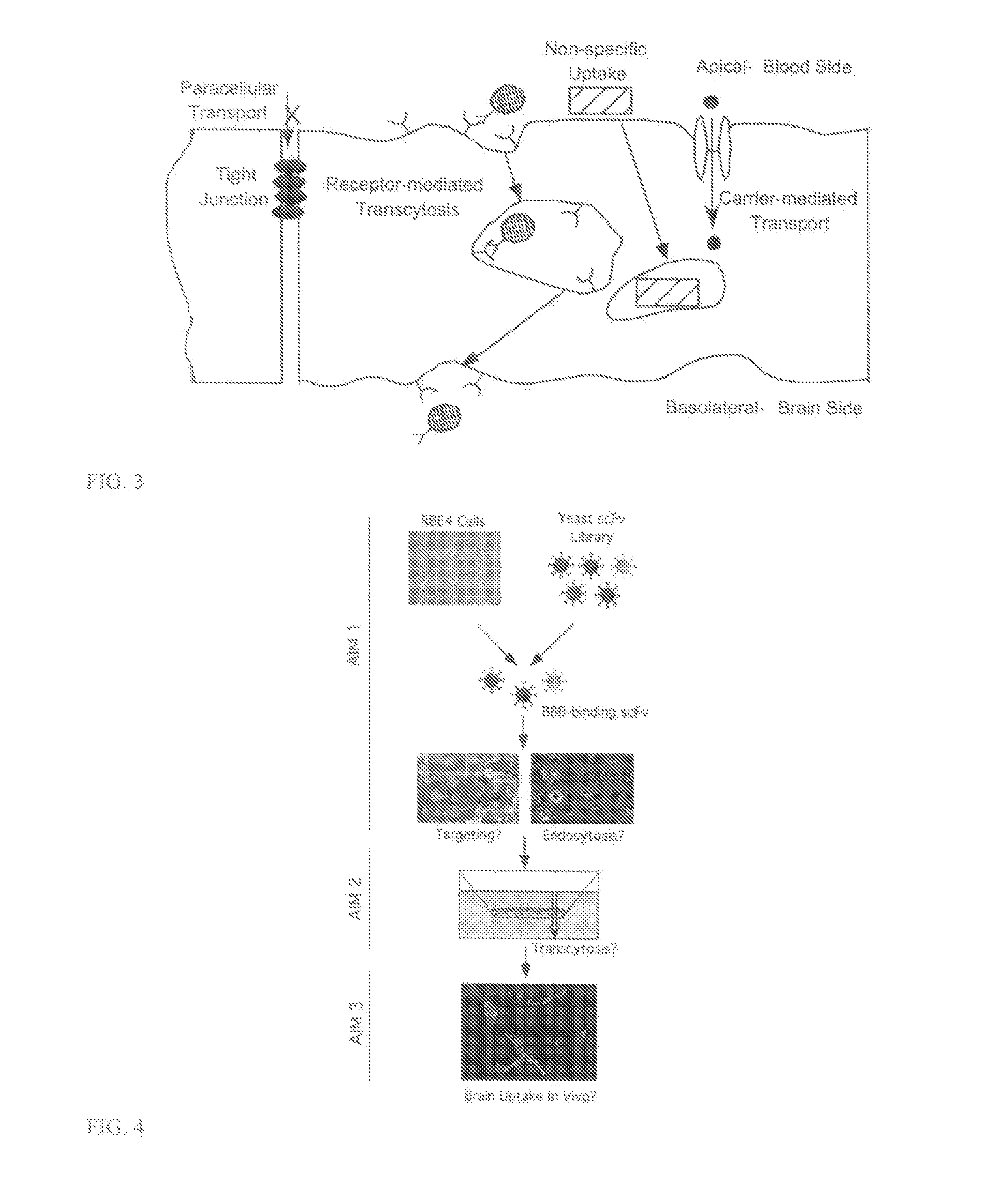
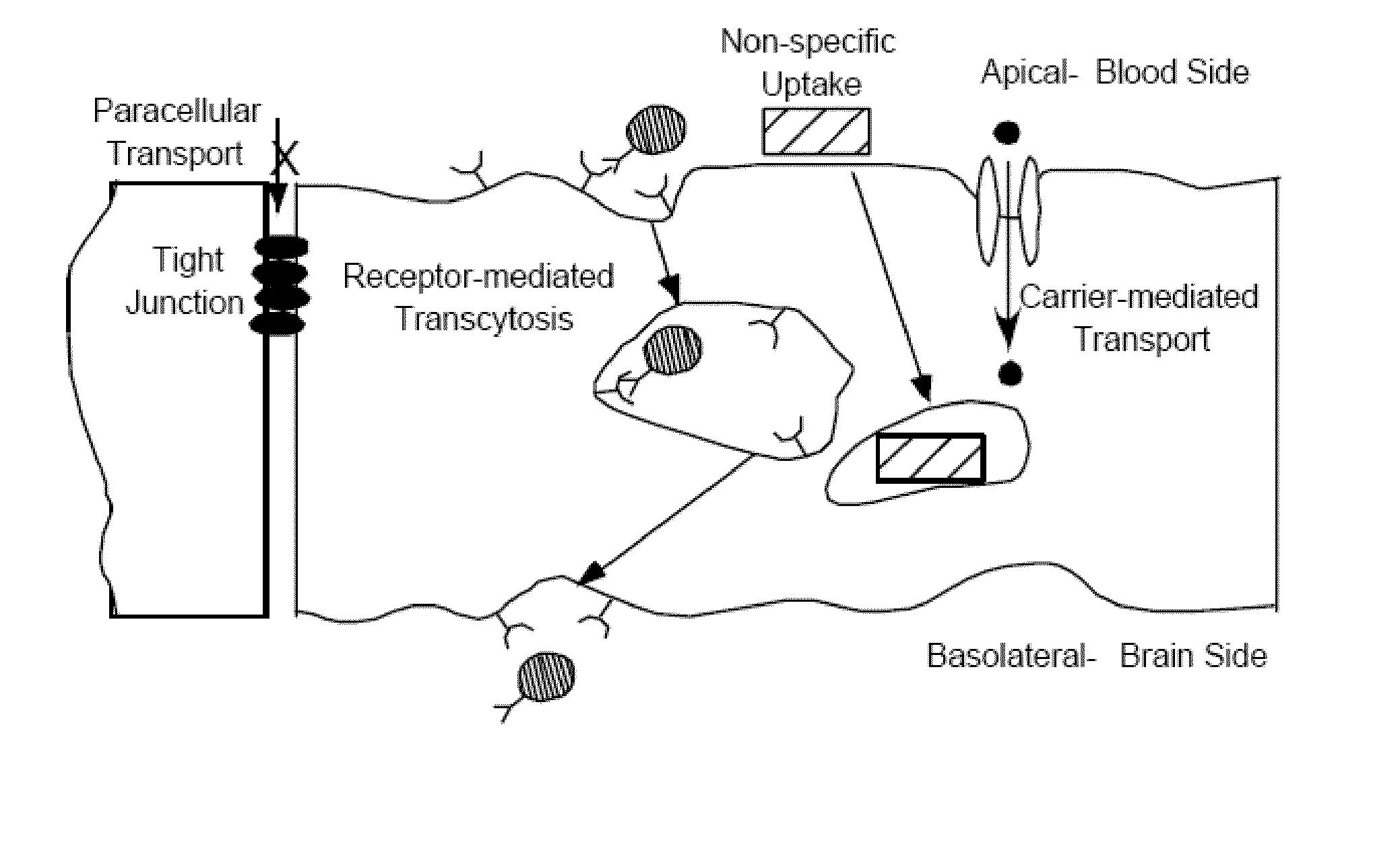
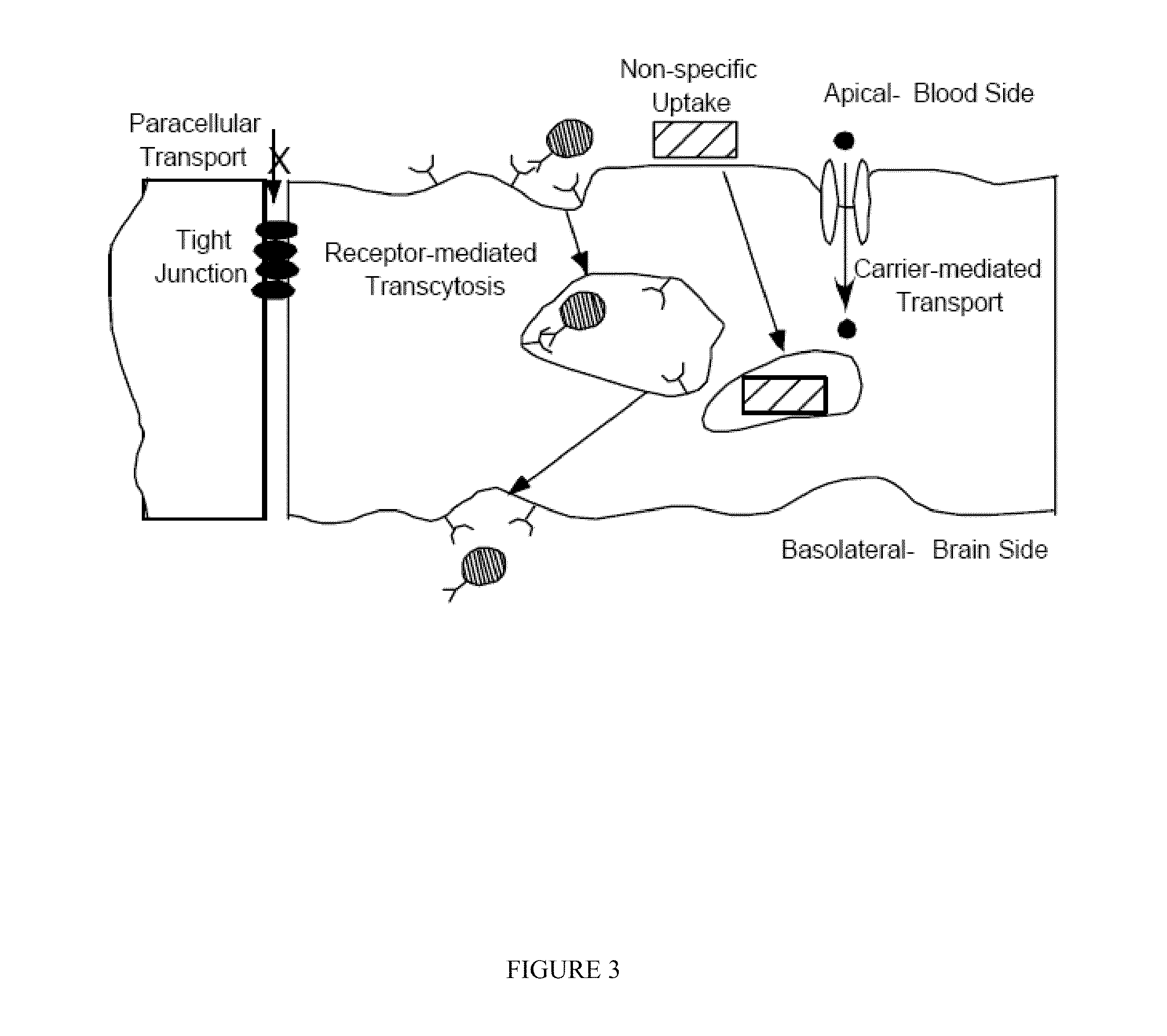
Transcytosis (also known as cytopempsis) is a type of transcellular transport in which various macromolecules are transported across the interior of a cell. Macromolecules are captured in vesicles on one side of the cell, drawn across the cell, and ejected on the other side. Examples of macromolecules transported include IgA, transferrin, and insulin. While transcytosis is most commonly observed in epithelial cells, the process is also present elsewhere. Blood capillaries are a well-known site for transcytosis, though it occurs in other cells, including neurons, osteoclasts and M cells of the intestine.
Methods and Compositions for Targeted Delivery of Therapeutic Agents
ActiveUS20090087494A1Increase uptakeImprove transportPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsPharmacologyTranscytosis
Compositions and methods for targeted delivery of therapeutic agents, and particularly for mucosal, oral, nasal, or parenteral delivery of therapeutic agents. The compositions comprise carrier particles containing or encapsulating a therapeutic agent or agents, which have been modified on their surface to contain one or more targeting moieties that enable the enhanced uptake and transport of the therapeutic agent via receptor-mediated processes such as endocytosis or transcytosis.
Owner:NEBRASKA BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF
Drug delivery systems using fc fragments
InactiveUS20100303723A1Easy to useEffectively cross epithelial cell layersPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsEpitheliumMedicine
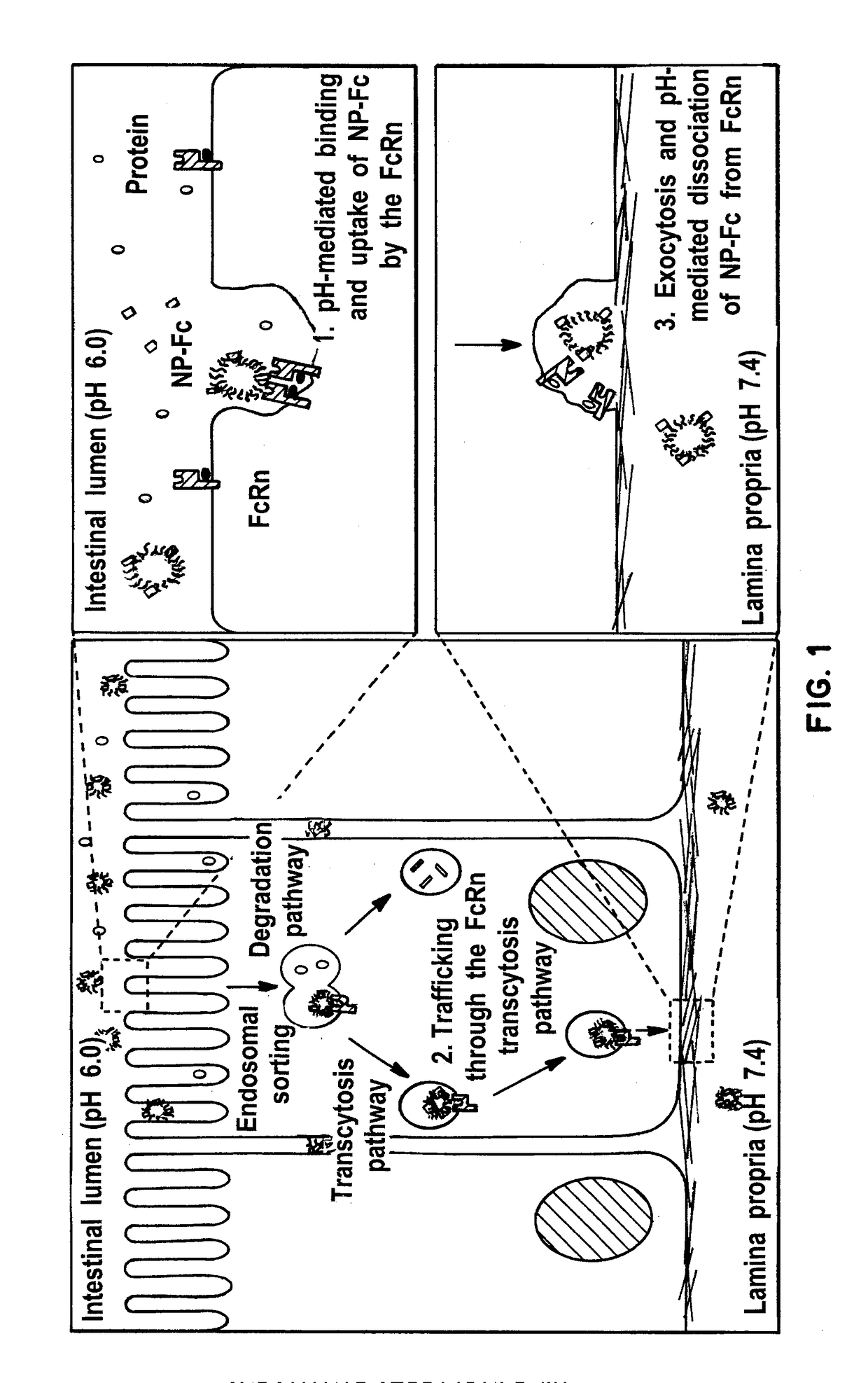
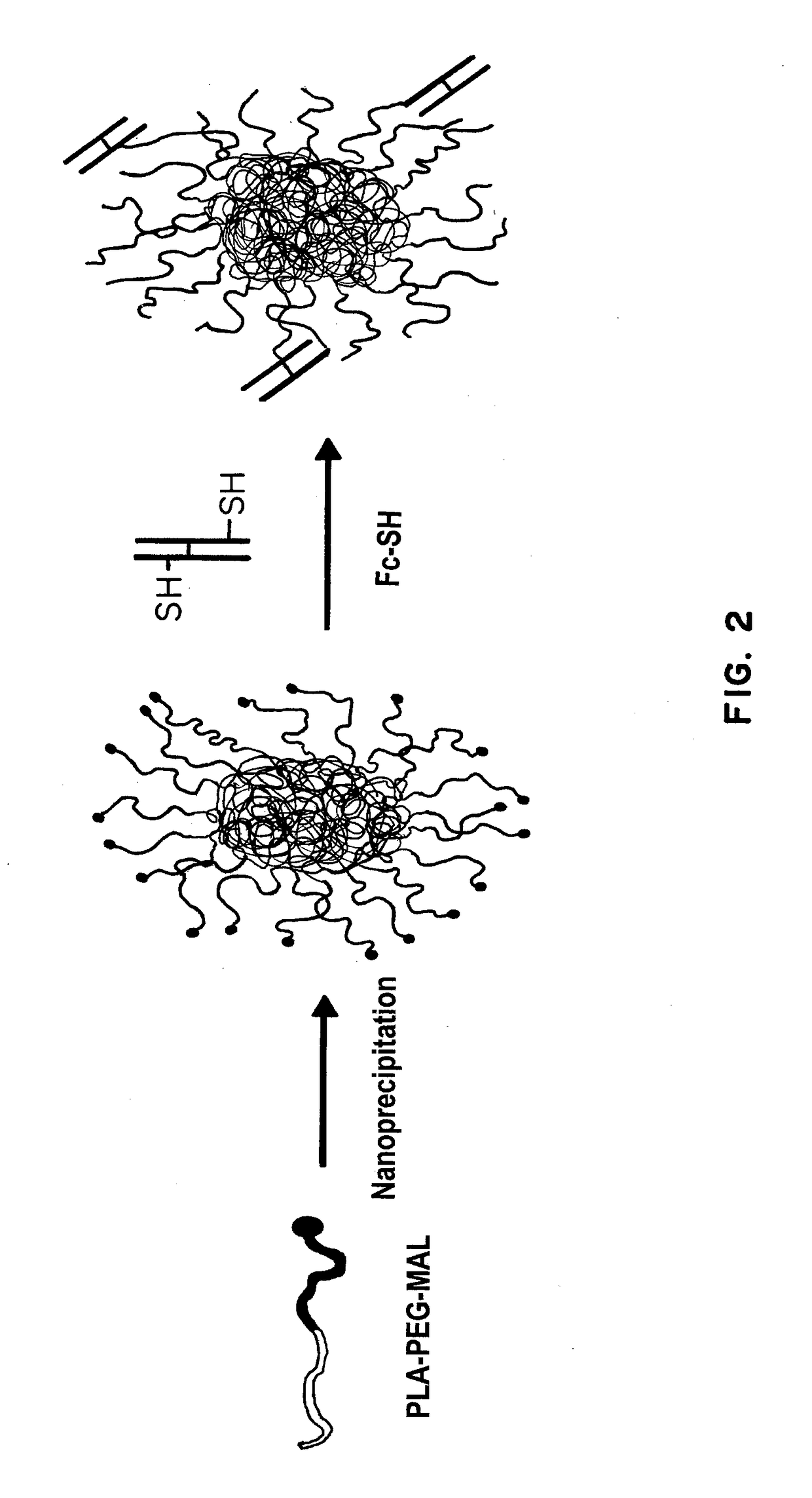
The present invention provides drug delivery systems comprising FcRn binding partners (e.g., FcRn binding partner, Fc fragment) associated with a particle or an agent to be delivered. Inventive drug delivery systems allow for binding to the FcRn receptor and transcytosis into and / or through a cell or cell layer. Inventive systems are useful for delivering therapeutic agents across the endothelium of blood vessels or the epithelium of an organ.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Methods and compositions for needleless delivery of binding partners
InactiveUS20090148401A1Extended half-lifeBetter prophylacticPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderBinding domainTranscytosis
The present invention relates, in part, to methods and compositions for needleless delivery of macromolecules to a subject. In one aspect, the methods and compositions involve administering to the subject a delivery construct comprising a carrier construct non-covalently bound to a binding partner, wherein the carrier construct comprises a receptor-binding domain, a transcytosis domain, and a macromolecule to which the binding partner non-covalently binds, wherein the binding partner binds to the macromolecule with a Ka that is at least about 104 M−1.
Owner:TRINITY ASSIGNMENT FOR THE BENEFIT OF CREDITORS
Blood-brain barrier targeting antibodies
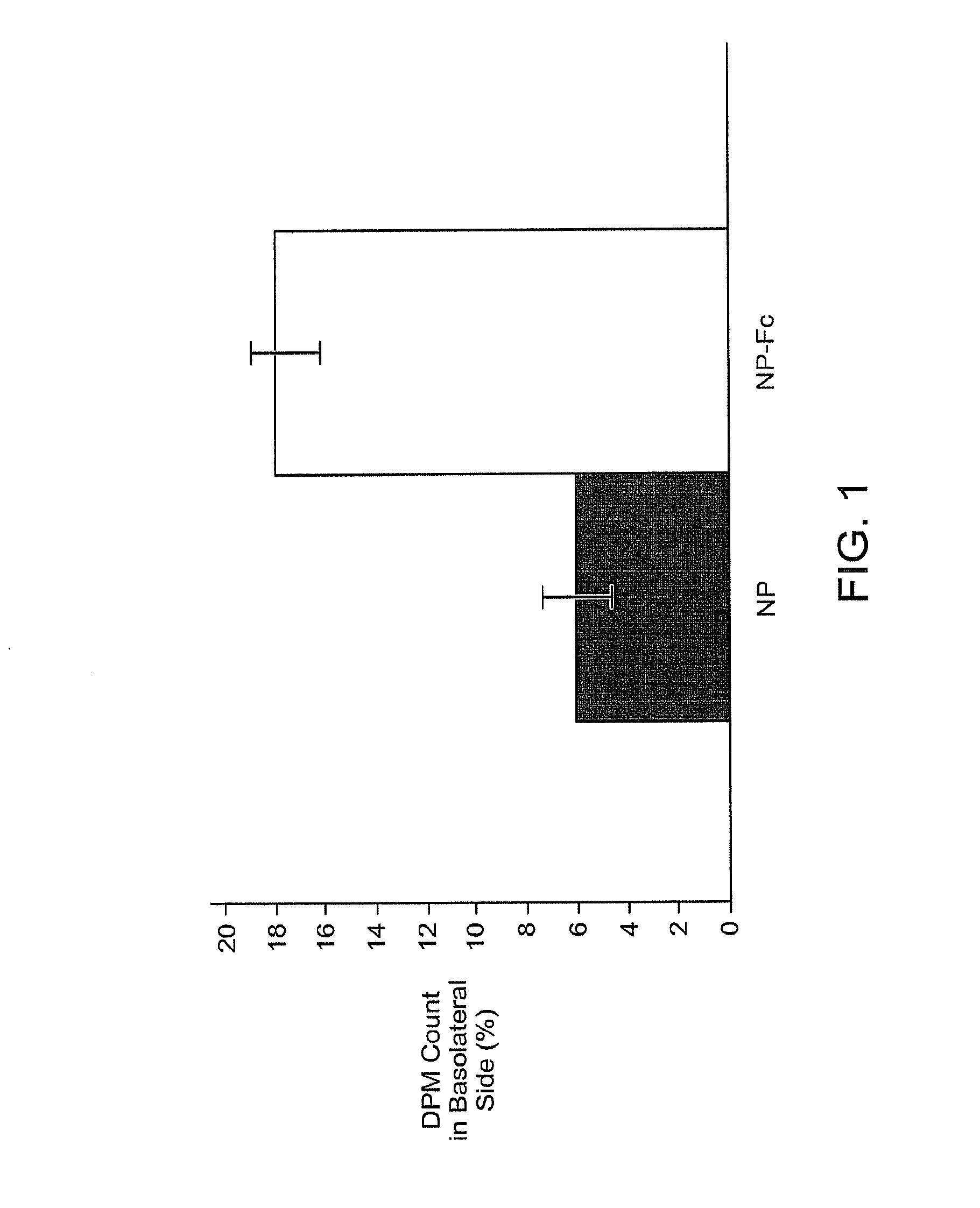
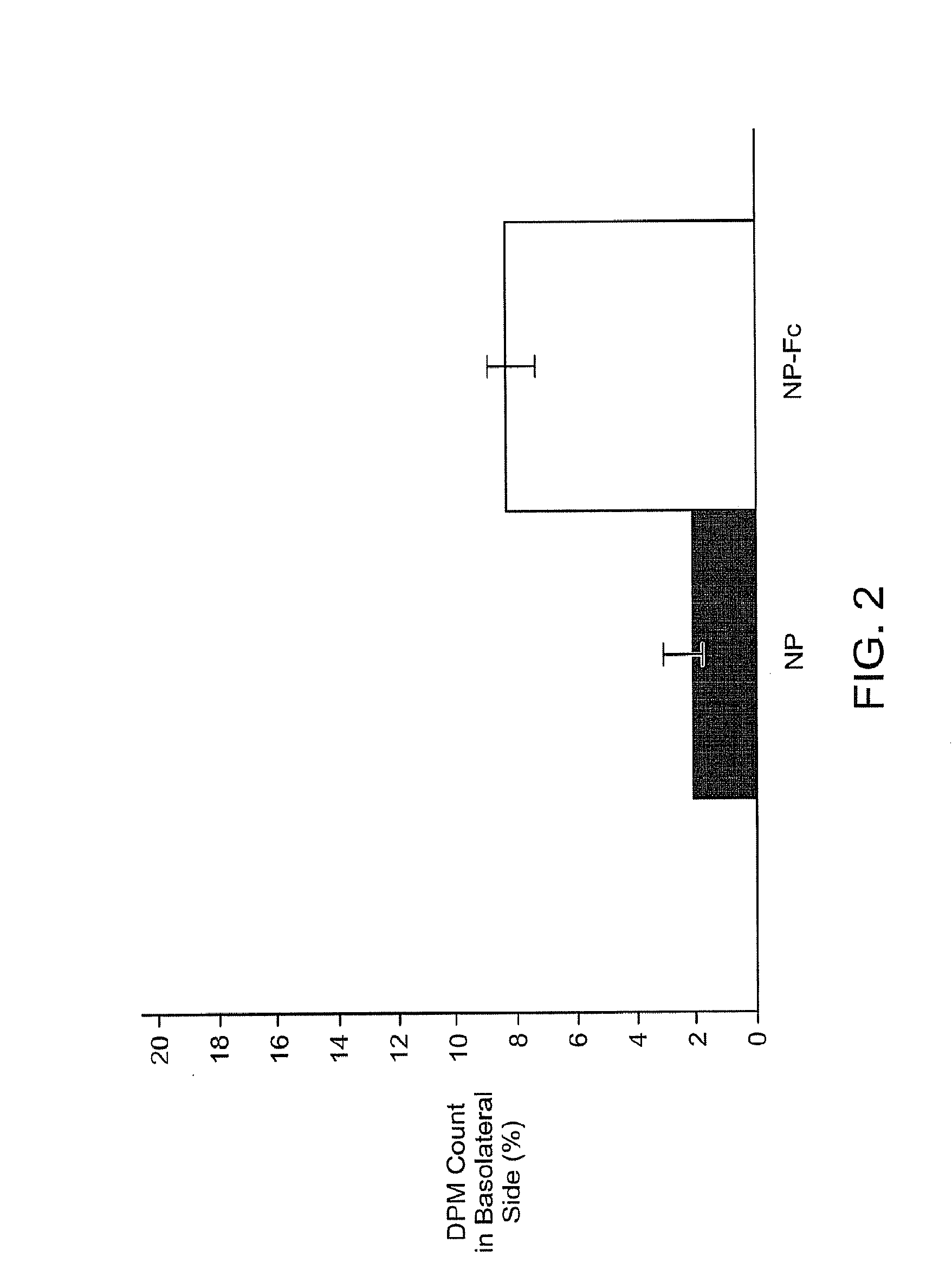
This invention provides antibodies that bind brain endothelial cell receptors resulting in endocytosis / transcytosis of the receptor and bound ligands. In some embodiments, the ligand comprises the antibody in combination with a pharmaceutically active compound and the antibody directs delivery of the compound across the blood brain barrier (BBB). The invention also provides methods of identifying endothelial cell specific antibodies by panning the library against cultured cell monolayers. The invention further allows for identifying endothelial cell receptors that bind the antibody thereby providing target receptors against which to isolate further cognate ligands and their associated transport systems and by which to identify transcytosis transporters targeted by the antibodies.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Methods and compositions for needleless delivery of particles
Methods and compositions for needleless delivery of particles to the bloodstream of a subject are provided herein. In one aspect, the invention provides a delivery construct, comprising a receptor binding domain, a transcytosis domain, a particle to be delivered to a subject, and, optionally, a cleavable linker. In other aspects, the invention provides compositions comprising delivery constructs of the invention, kits comprising delivery constructs of the invention, and methods of using delivery constructs of the invention.
Owner:TRINITY ASSIGNMENT FOR THE BENEFIT OF CREDITORS
Methods and compositions for needleless delivery of antibodies
The present invention relates, in part, to methods and compositions for needleless delivery of antibodies to a subject. The present invention also relates, in part, to methods for needleless delivery of fusion proteins comprising a bioactive molecule and an antibody fragment to subject. In one aspect, the methods and compositions involve administering to the subject a delivery construct comprising a carrier construct non-covalently bound to the antibody or fusion protein to be delivered, wherein the carrier construct comprises a receptor-binding domain, a transcytosis domain, and an antibody-binding domain to which the antibody or the antibody fragment of the fusion protein non-covalently binds.
Owner:TRINITY ASSIGNMENT FOR THE BENEFIT OF CREDITORS
Compounds and molecular complexes comprising multiple binding regions directed to transcytotic ligands
InactiveUS20060134103A1Simple processIncrease ratingsSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsExocytosisActive agent
Disclosed herein are multimeric molecular complexes and compounds that are multivalent, i.e., they have two or more targeting elements directed to a ligand that confers paracellular transporting properties and / or transcytotic properties to complexes and compounds to which it is bound. The complexes and compounds have properties that are different from the properties of monomers, complexes and compounds having only one targeting element directed to a paracellular and / or transcytotic ligand. The complexes and compounds of the invention undergo endocytosis, transcytosis and exocytosis; following endocytosis, the complexes or compounds may be transported into the cytosol or an organelle of a cell. In polarized cells, transcytosis can proceed in a “forward” or “reverse” direction. Reverse transcytosis is used for the non-invasive delivery of biologically active agents from the lumen of, e.g., the gastrointestinal tract or the airways of lungs, to the circulatory system. The complexes and compounds are incorporated in various compositions and medical devices suitable for medicinal or veterinary use.
Owner:HAWLEY STEPHEN +4
Probiotic microorganisms producing chimeric human growth hormone fused with Fc fragment of human IgG for oral delivery system and methods for producing them
The present invention relates to probiotic microorganisms producing chimeric human growth hormone for oral use and methods for preparing them. The invention provides probiotic Lactobacillus or yeast transformant expressing chimeric protein which is human growth hormone fused with Fc fragment of human IgG, in which the transformants are safely delivered into intestine though oral route. Also, the invention provides a chimeric protein-expressing vector which can induce transcytosis in intestine epithelial cells. Accordingly, the invention demonstrates that the chimeric protein for oral delivery system can be absorbed in intestine, and delivery of the chimeric protein by oral route using Lactobacillus has very excellent efficiency in vivo test in rats. Accordingly, the Lactobacillus of the present invention is an excellent deliverer of protein drugs.
Owner:INSILICO CO LTD
Methods and compositions for needleless delivery of macromolecules
InactiveUS20060153798A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsHigh concentrationBinding domain
Methods and compositions for needleless delivery of macromolecules to the bloodstream of a subject are provided herein. In one aspect, the invention provides a delivery construct, comprising a receptor binding domain, a transcytosis domain, a macromolecule to be delivered to a subject, and a cleavable linker. In certain aspects, the cleavable linker can be cleavable by an enzyme present in higher concentration at or near the basal-lateral membrane of a polarized epithelial cell or in the plasma than elsewhere in the body, for example, at the apical side of the polarized epithelial cell. In other aspects, the invention provides nucleic acids encoding delivery constructs of the invention, kits comprising delivery constructs of the invention, cells expressing delivery constructs of the invention, and methods of using delivery constructs of the invention.
Owner:TRINITY ASSIGNMENT FOR THE BENEFIT OF CREDITORS
Methods and compositions for needleless delivery of binding partners
InactiveUS20070148131A1Extended half-lifeImprove welfarePeptide/protein ingredientsCalcitoninsNeedle freeReceptor
The present invention relates, in part, to methods and compositions for needleless delivery of macromolecules to a subject. In one aspect, the methods and compositions involve administering to the subject a delivery construct comprising a carrier construct non-covalently bound to a binding partner, wherein the carrier construct comprises a receptor-binding domain, a transcytosis domain, and a macromolecule to which the binding partner non-covalently binds, wherein the binding partner binds to the macromolecule with a Ka that is at least about 104 M−1.
Owner:TRINITY ASSIGNMENT FOR THE BENEFIT OF CREDITORS
Methods and compositions for targeted delivery of therapeutic agents
Owner:NEBRASKA BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF
Blood-brain barrier targeting anti-bodies
This invention provides antibodies that bind brain endothelial cell receptors resulting in endocytosis / transcytosis of the receptor and bound ligands. In some embodiments, the ligand comprises the antibody in combination with a pharmaceutically active compound and the antibody directs delivery of the compound across the blood brain barrier (BBB). The invention also provides methods of identifying endothelial cell specific antibodies by panning the library against cultured cell monolayers. The invention further allows for identifying endothelial cell receptors that bind the antibody thereby providing target receptors against which to isolate further cognate ligands and their associated transport systems and by which to identify transcytosis transporters targeted by the antibodies.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Blood-Brain Barrier Targeting Anti-bodies
ActiveUS20100209425A1Nervous disorderImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCell specificTransport system
This invention provides antibodies that bind brain endothelial cell receptors resulting in endocytosis / transcytosis of the receptor and bound ligands. In some embodiments, the ligand comprises the antibody in combination with a pharmaceutically active compound and the antibody directs delivery of the compound across the blood brain barrier (BBB). The invention also provides methods of identifying endothelial cell specific antibodies by panning the library against cultured cell monolayers. The invention further allows for identifying endothelial cell receptors that bind the antibody thereby providing target receptors against which to isolate further cognate ligands and their associated transport systems and by which to identify transcytosis transporters targeted by the antibodies.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Epithelial tissue targeting agent
Targeting molecules for use in delivering biological agents to epithelial tissue are disclosed. Upon delivery, the biological agent(s) may remain within an epithelial cell or may undergo transepithelial transport via transcytosis. The targeting molecules may be used, for example, for the delivery of therapeutic agents.
Owner:SYNTHON BIOPHARMACEUTICALS BV +1
Preparation of brain-targeted bionic nano-drug delivery system and application thereof to brain glioma treatment
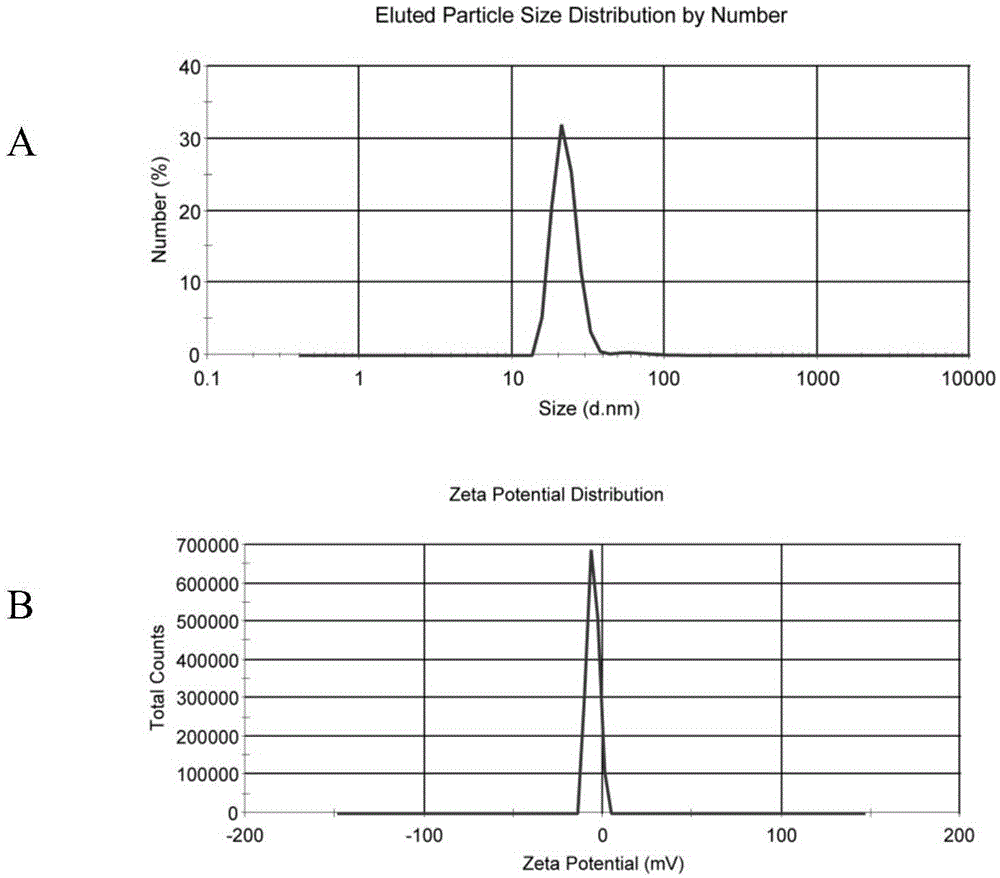
InactiveCN105078895ASmall particle sizePotential stabilityPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsBiocompatibility TestingAngiopep-2
The invention relates to the technical field of medicine, in particular to preparation of a brain-targeted bionic nano-drug delivery system and application thereof to brain glioma treatment. The brain-targeted bionic nano-drug delivery system adopts an LDL (low-density lipoprotein) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) compound as a vector to modify Angiopep-2 on surface apolipoprotein and encapsulate salinomycin. The brain-targeted bionic nano-drug delivery system has the advantages of good biocompatibility and no immunogenicity; under the action of transcytosis mediated by LRP-1 (low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1) expressed in blood brain barrier, the brain-targeted bionic nano-drug delivery system targets to penetrate the blood brain barrier actively; after entering the brain, the brain-targeted bionic nano-drug delivery system targets spongioblastoma by means of common mediation of an LDLR (low-density lipoprotein receptor) and an LRP-1 receptor, and kills tumor cells, tumor stem cells and multiple target points of tumor angiogenic blood vessels. The preparation of the brain-targeted bionic nano-drug delivery system and application thereof to brain glioma treatment provide a safer, more efficient and atraumatic drug-delivery way for treatment of tumors of the central nervous system.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
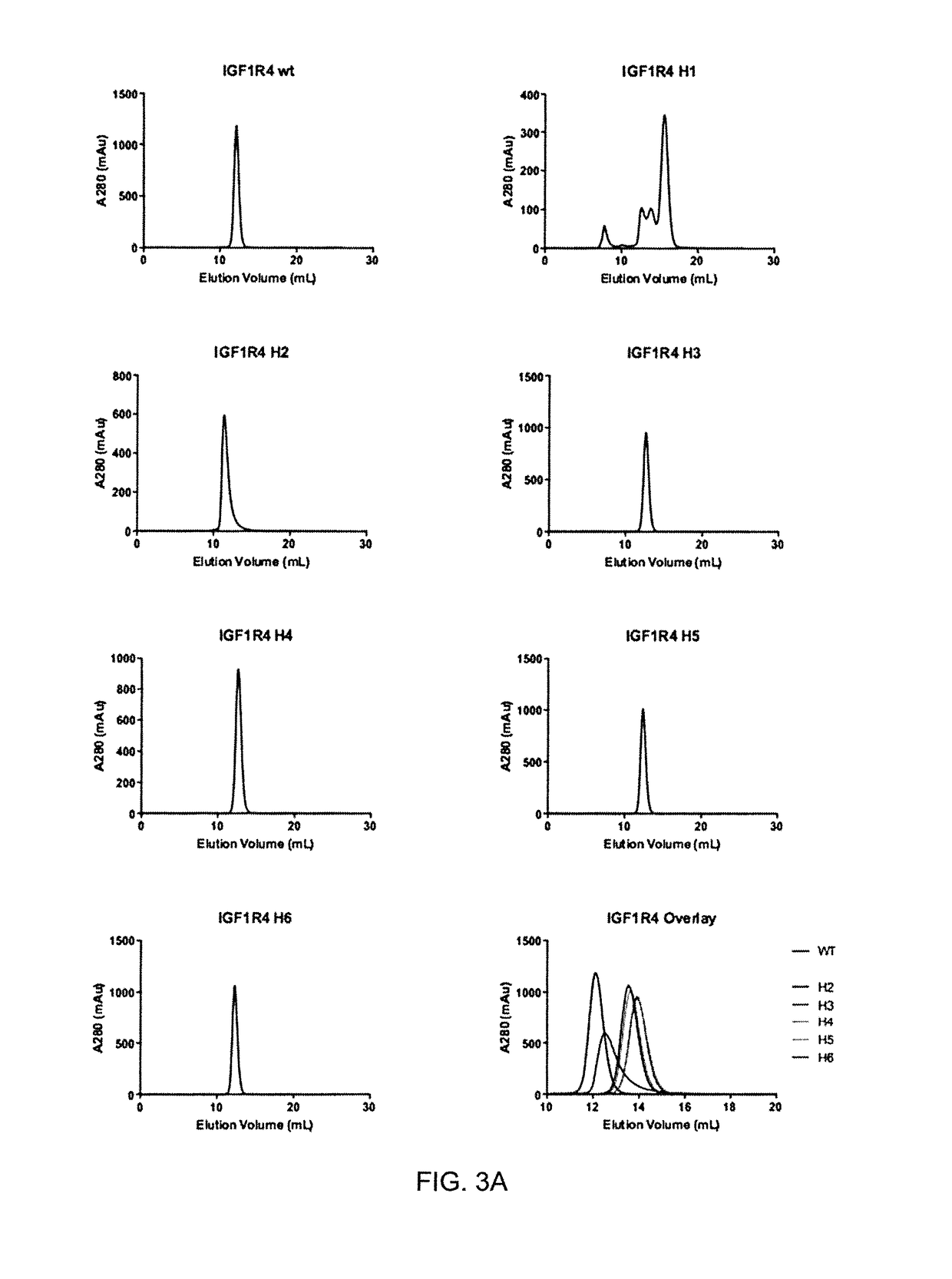
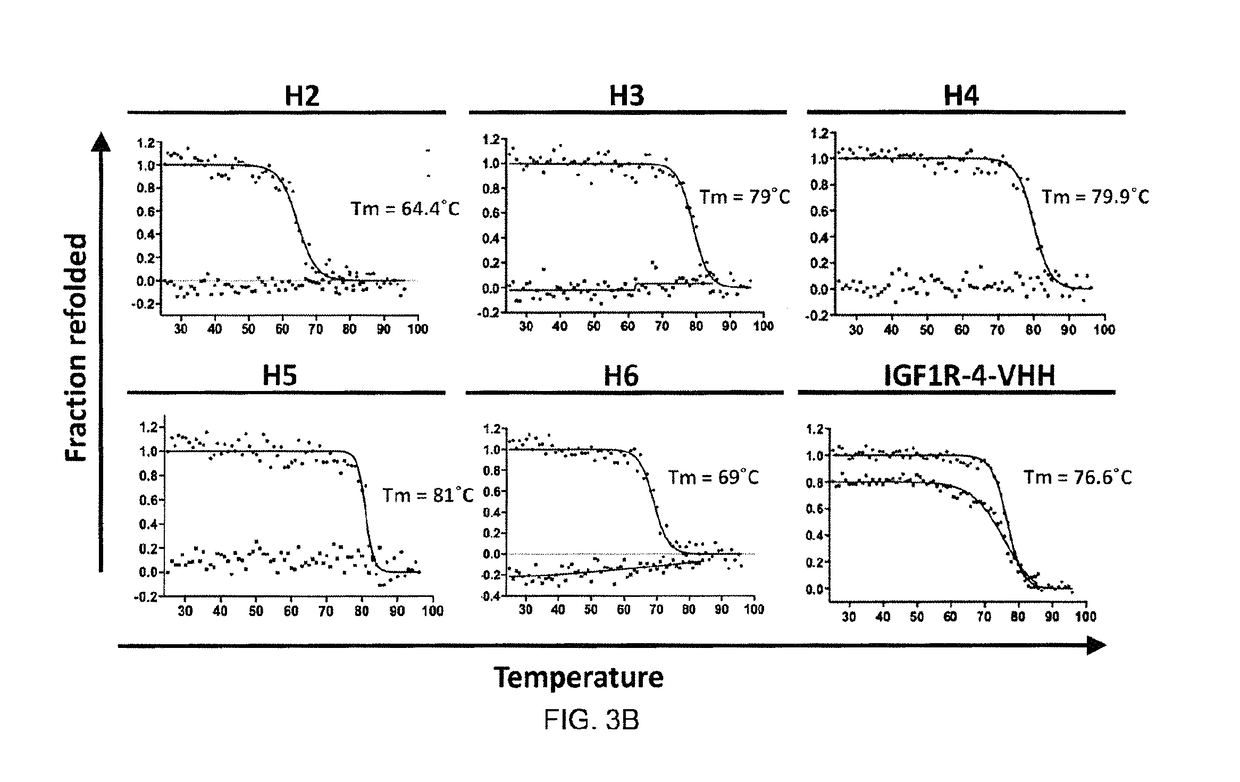
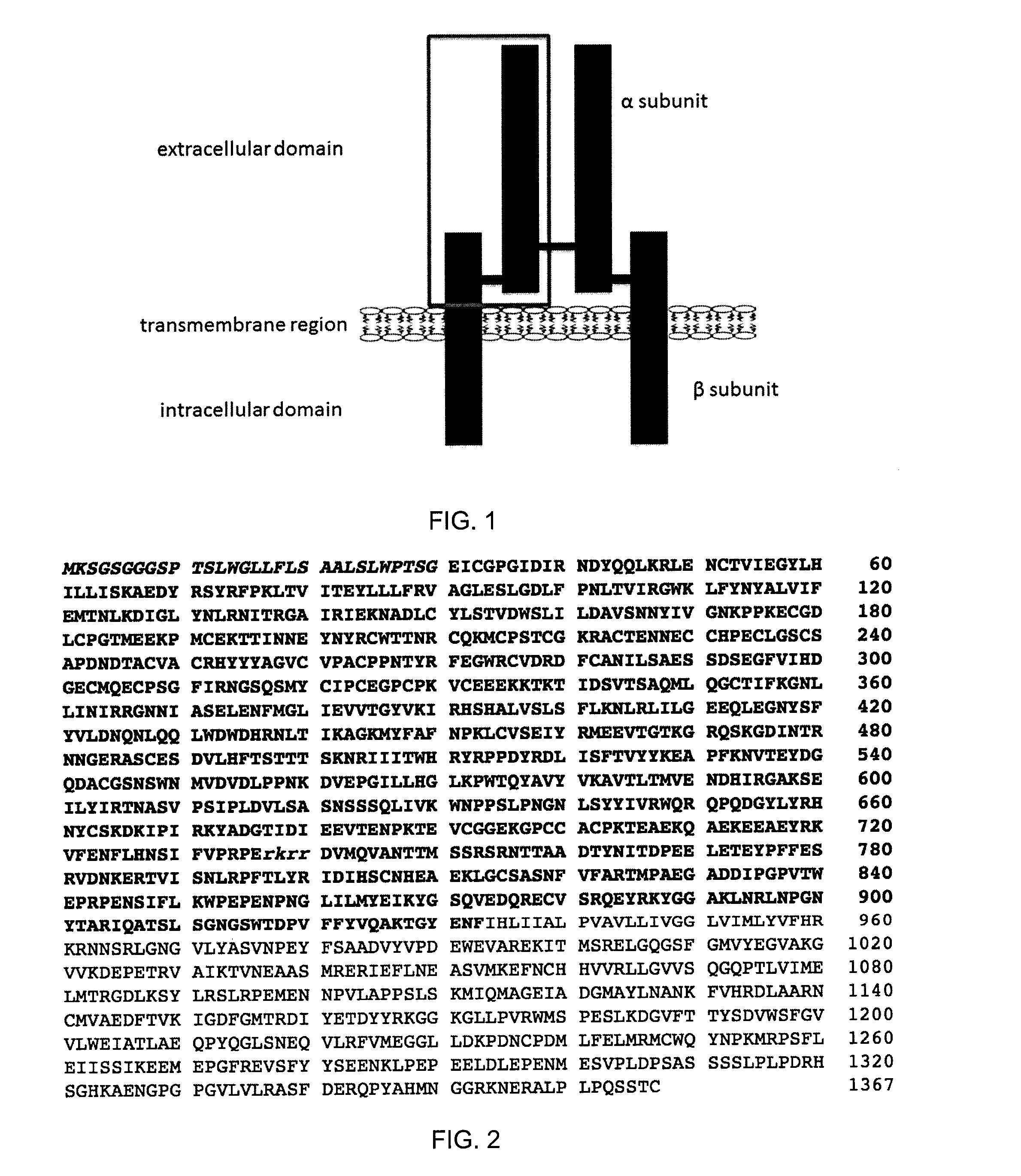
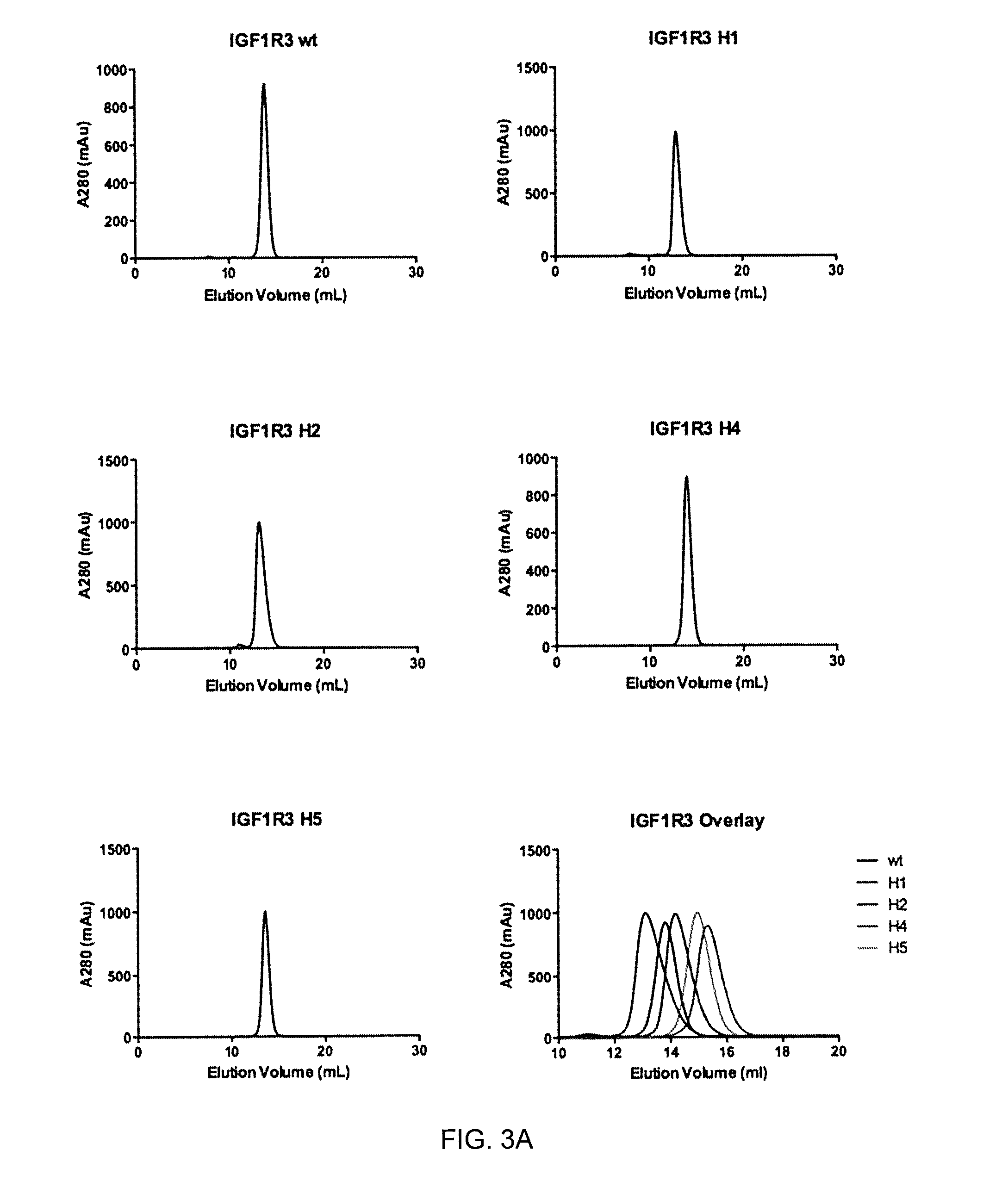
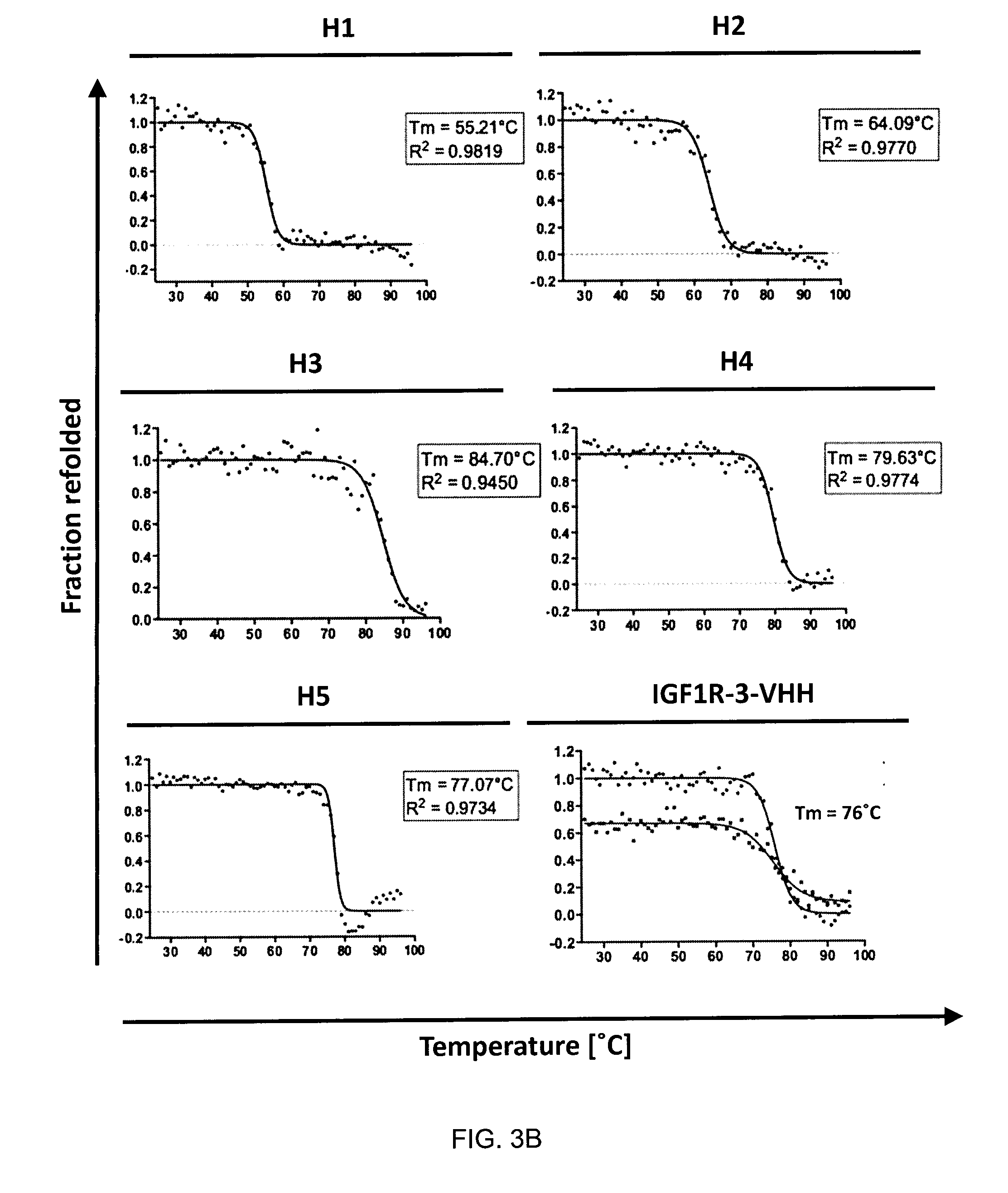
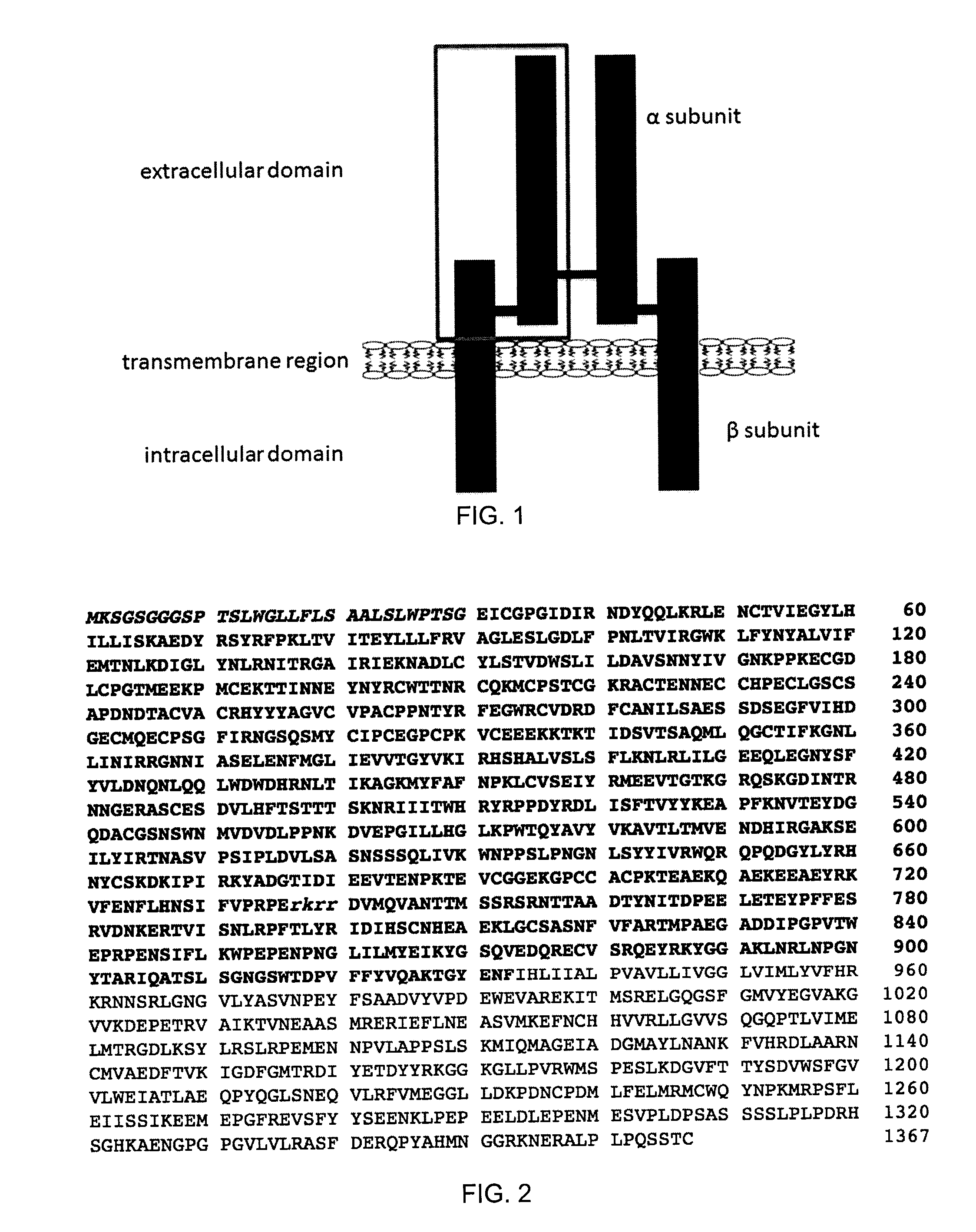
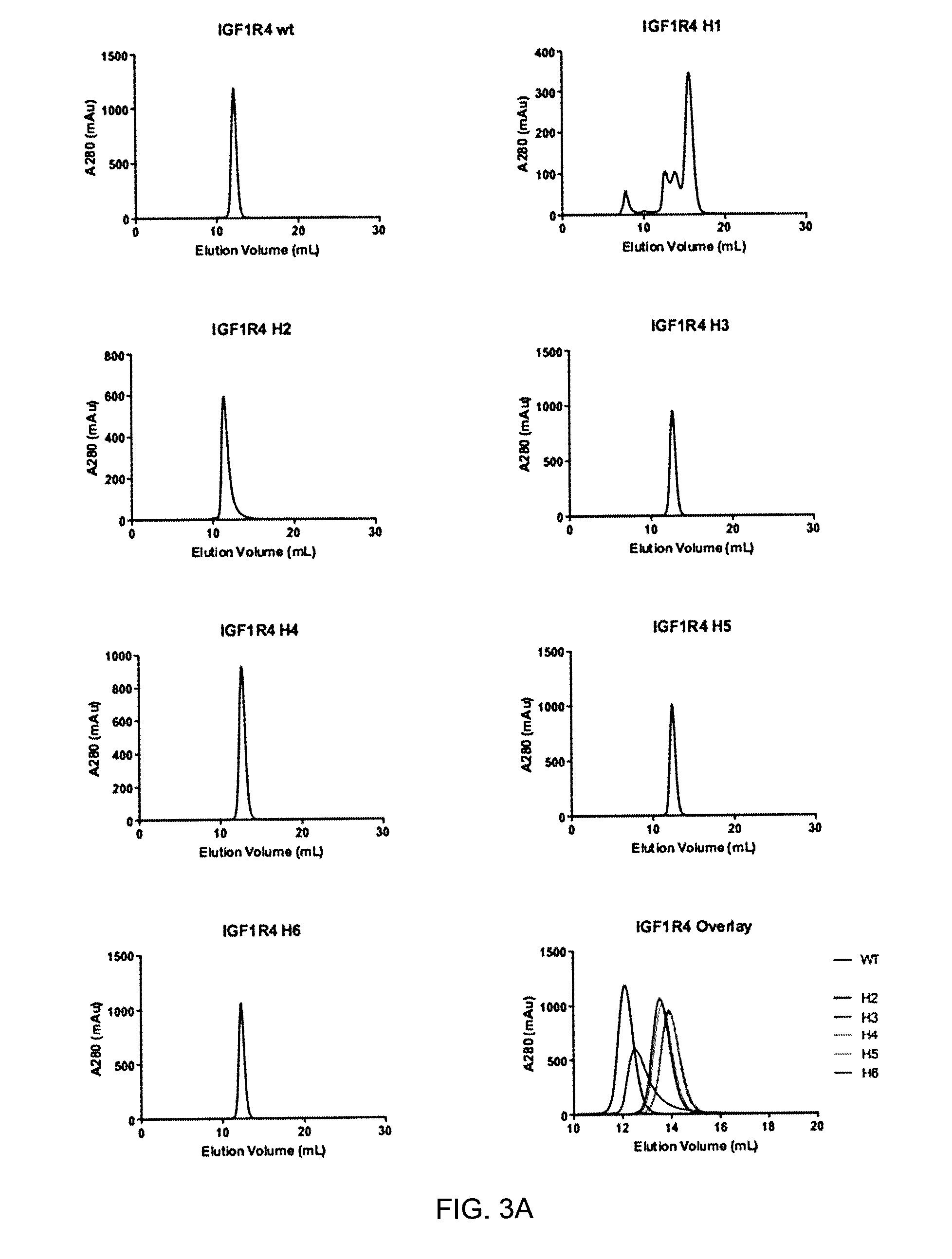
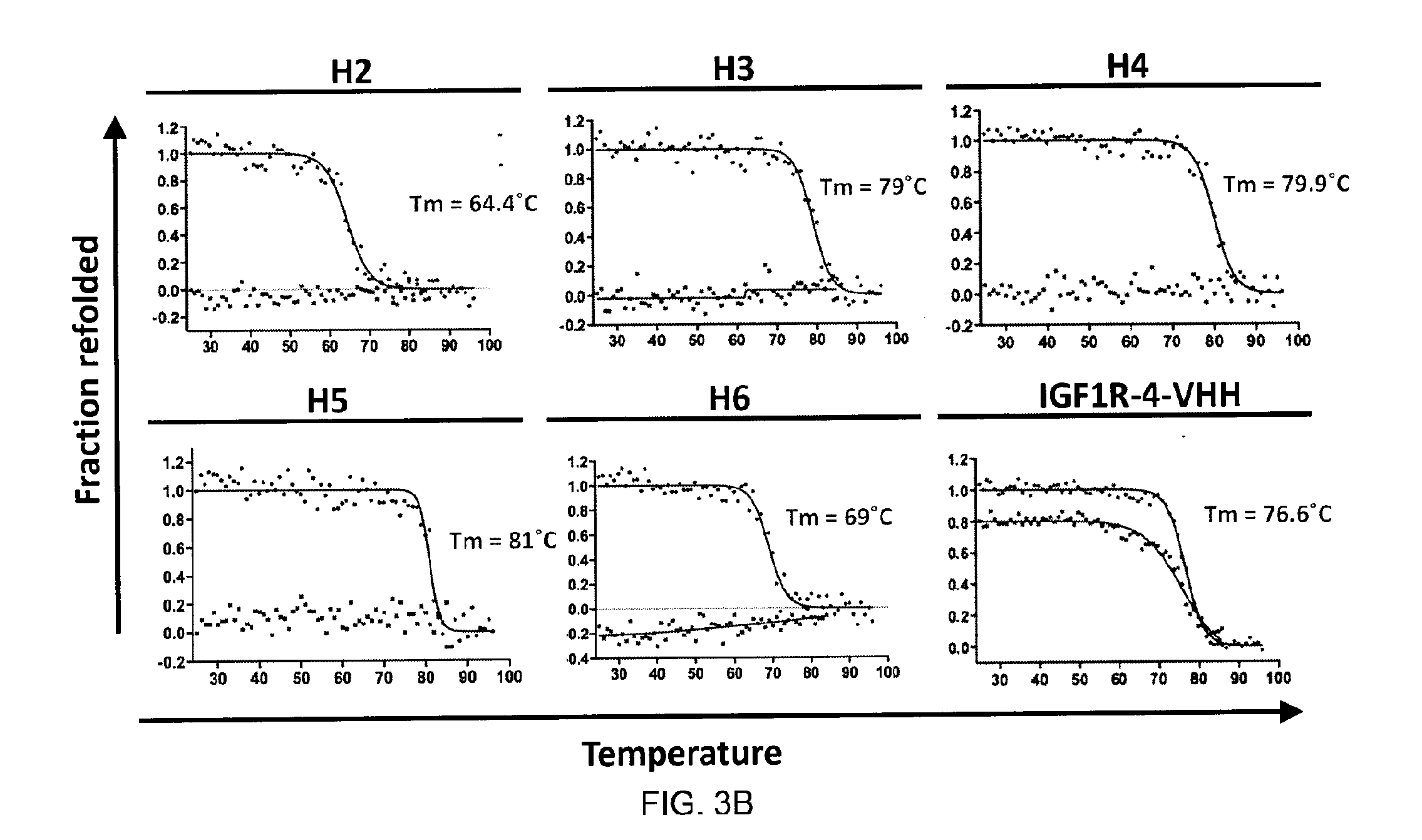
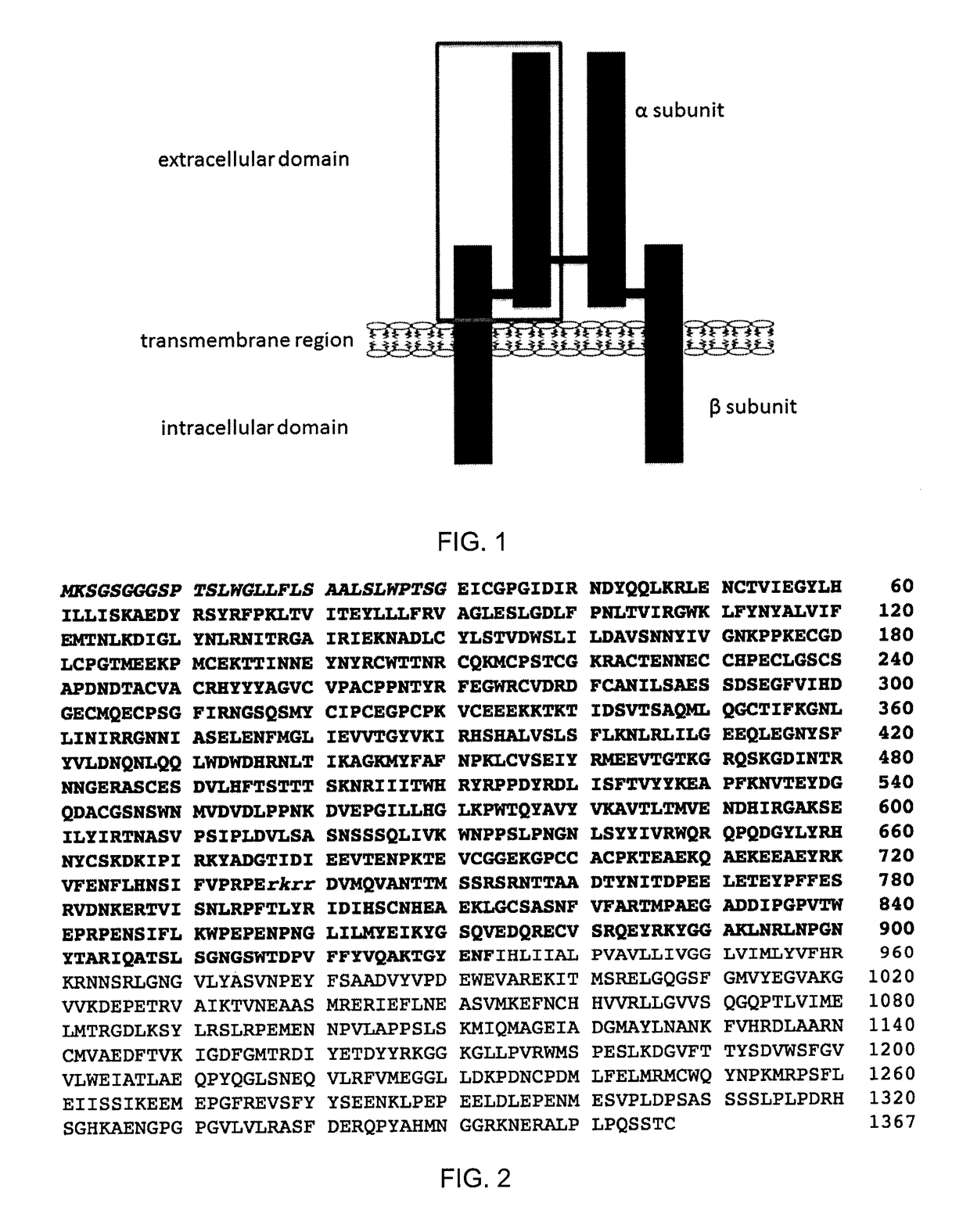
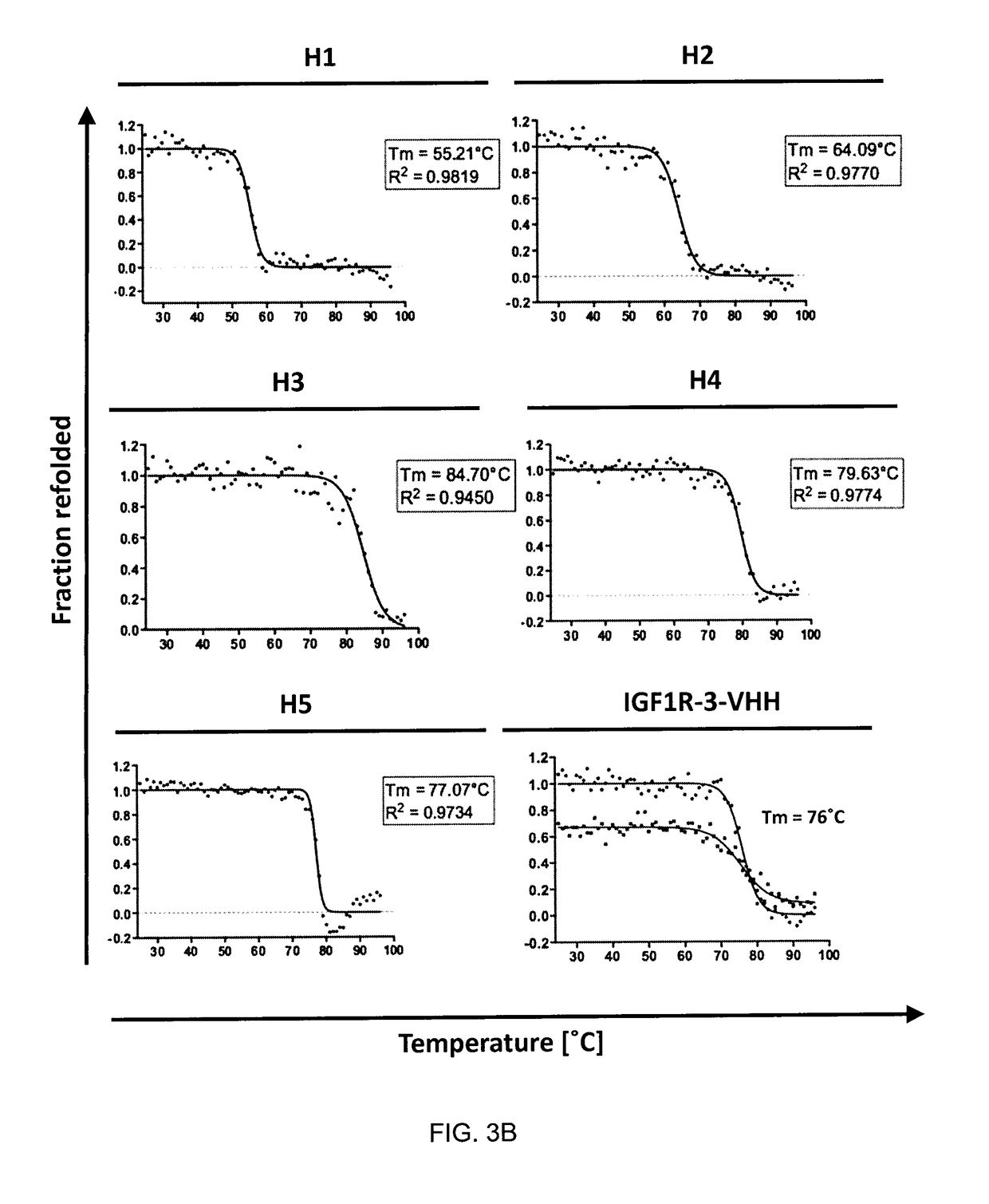
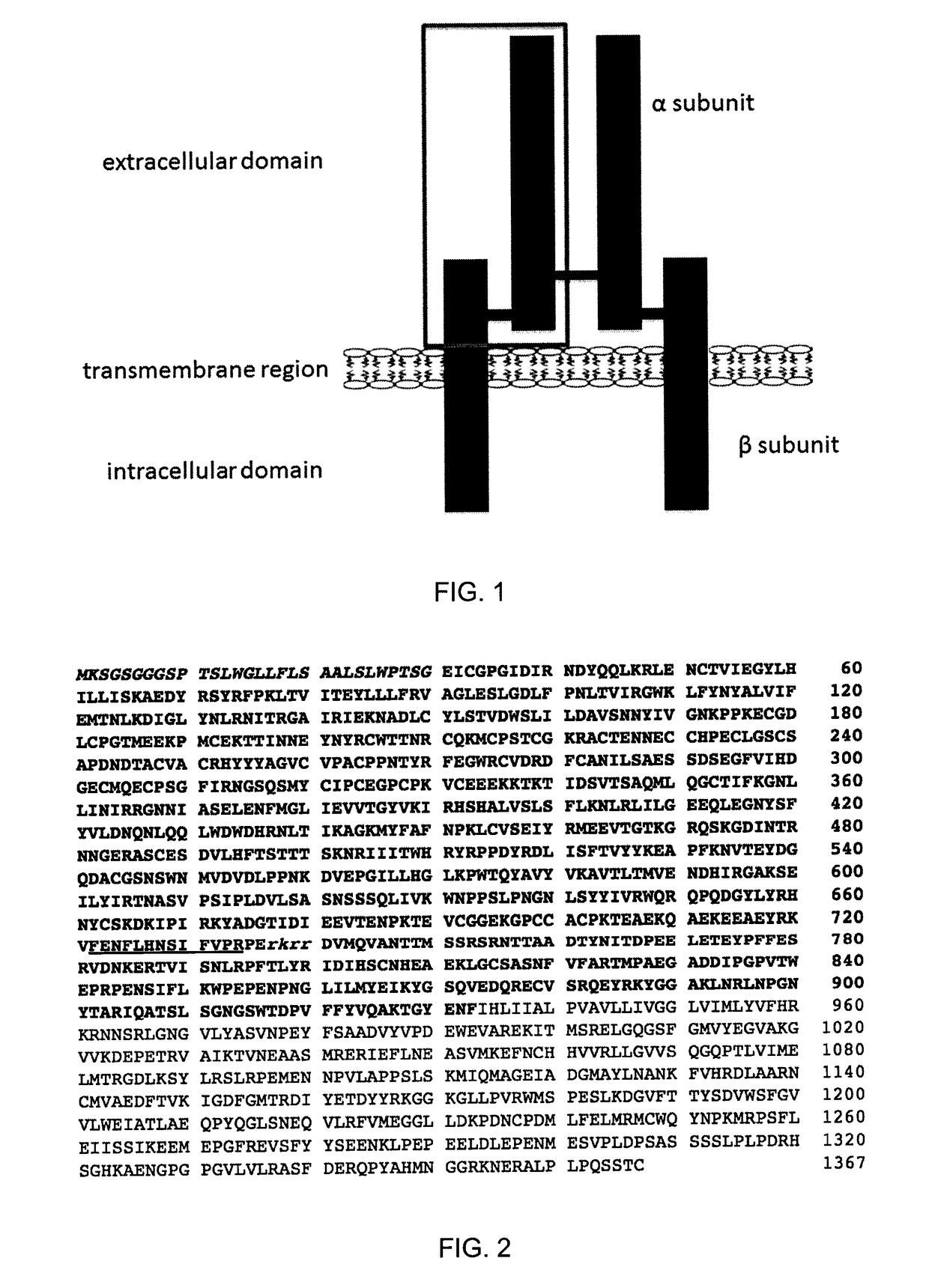
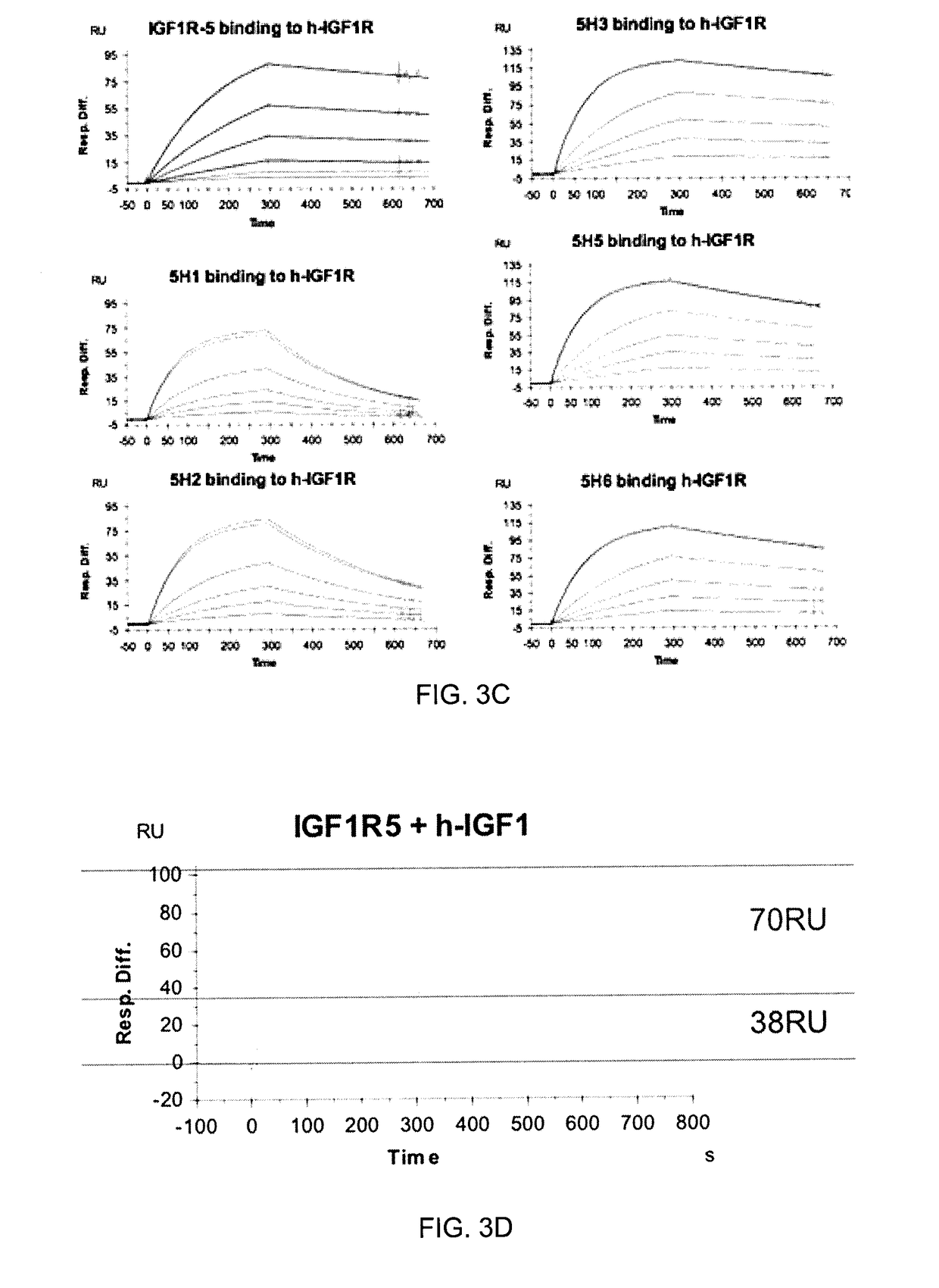
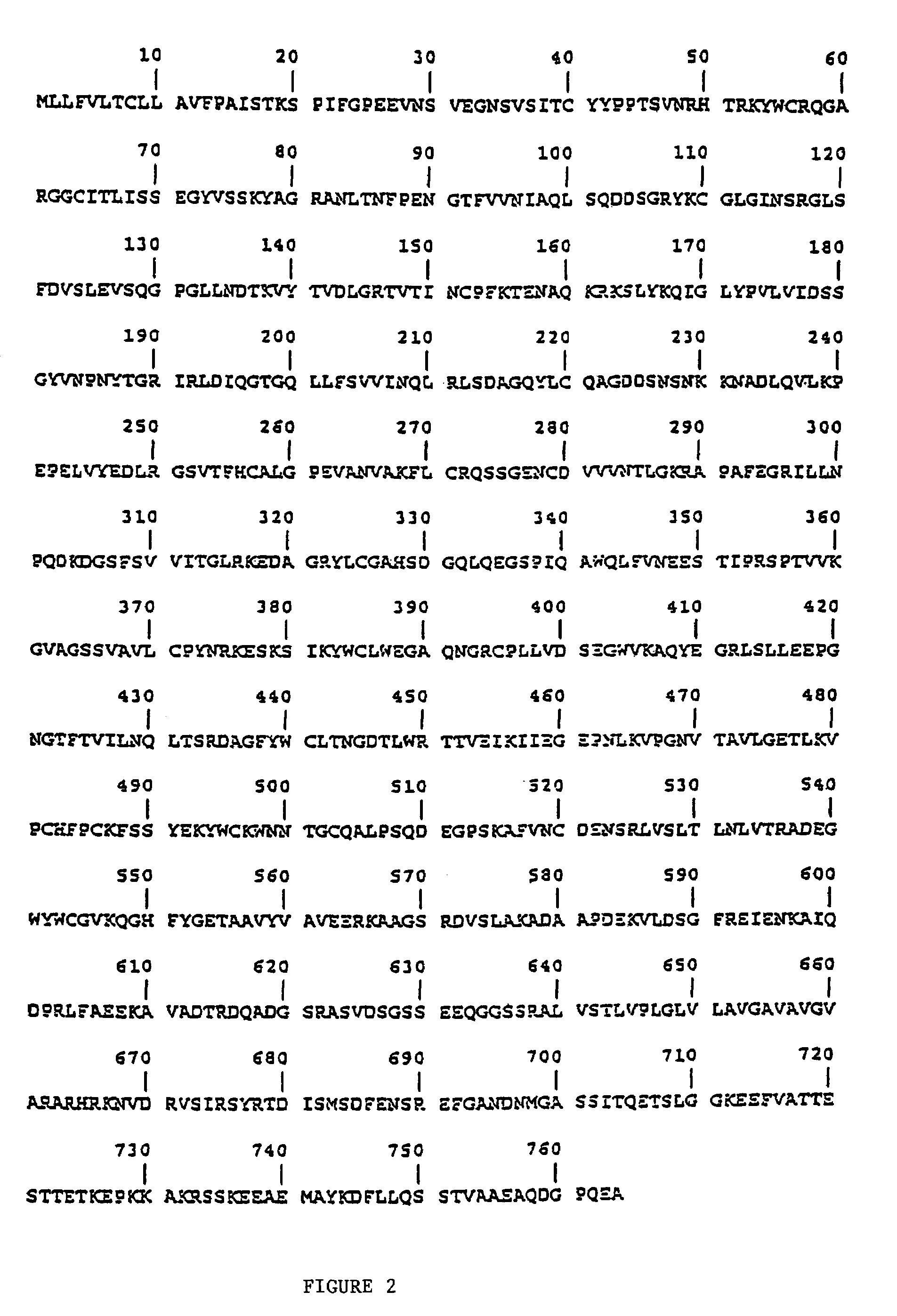
Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor -specific antibodies and uses thereof
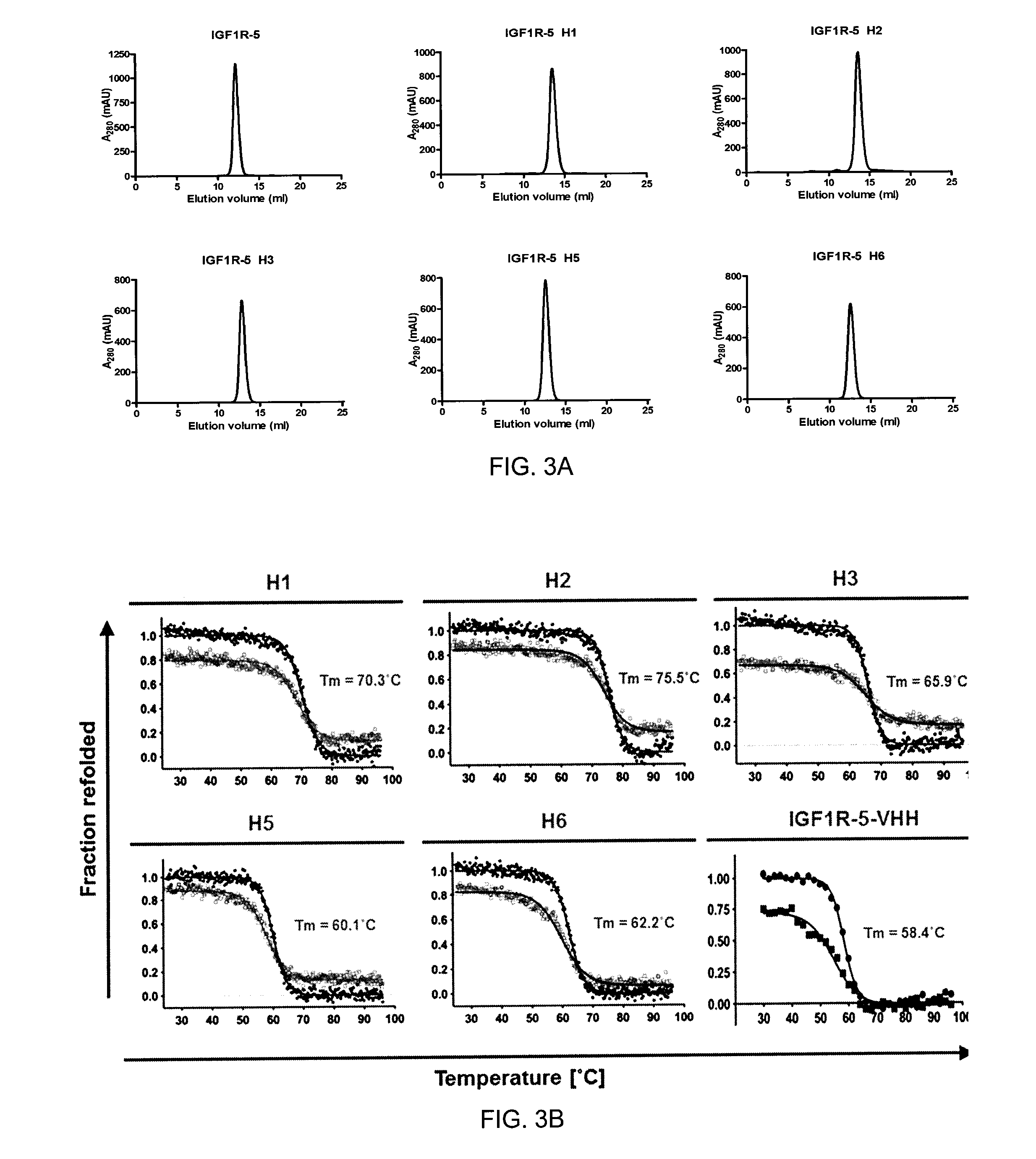
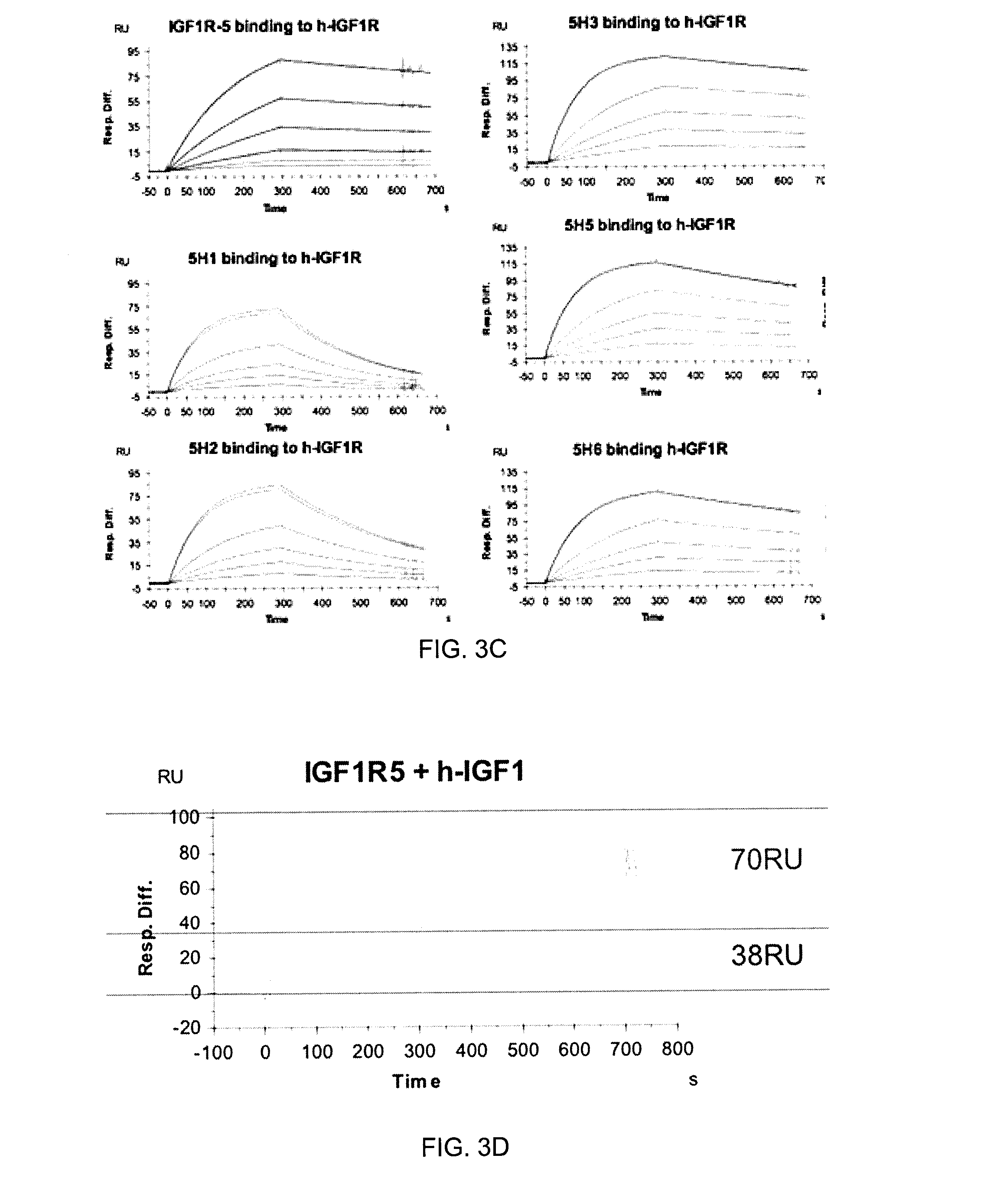
ActiveUS20170015748A1Prolonged Circulatory Half-LifeEfficient transportGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsOmicsAntigen bindingBiology
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) prevents transport of molecules larger than 500 Dal tons from blood to brain. Receptor-mediated transcytosis (RMT) facilitates transport across the BBB of specific molecules that bind receptors on brain endothelial cells that form the BBB. An insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF 1R)-binding antibody or fragment thereof is identified that transmigrates the BBB by RMT. The antibody or fragment is used to deliver a cargo molecule across the BBB, wherein the cargo molecule may be a therapeutic or detectable agent. The antibody is a camelid VHH, prepared by immunizing a llama with a 933-amino acid IGF 1R polypeptide. Humanized forms of the camelid VHH are also generated.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
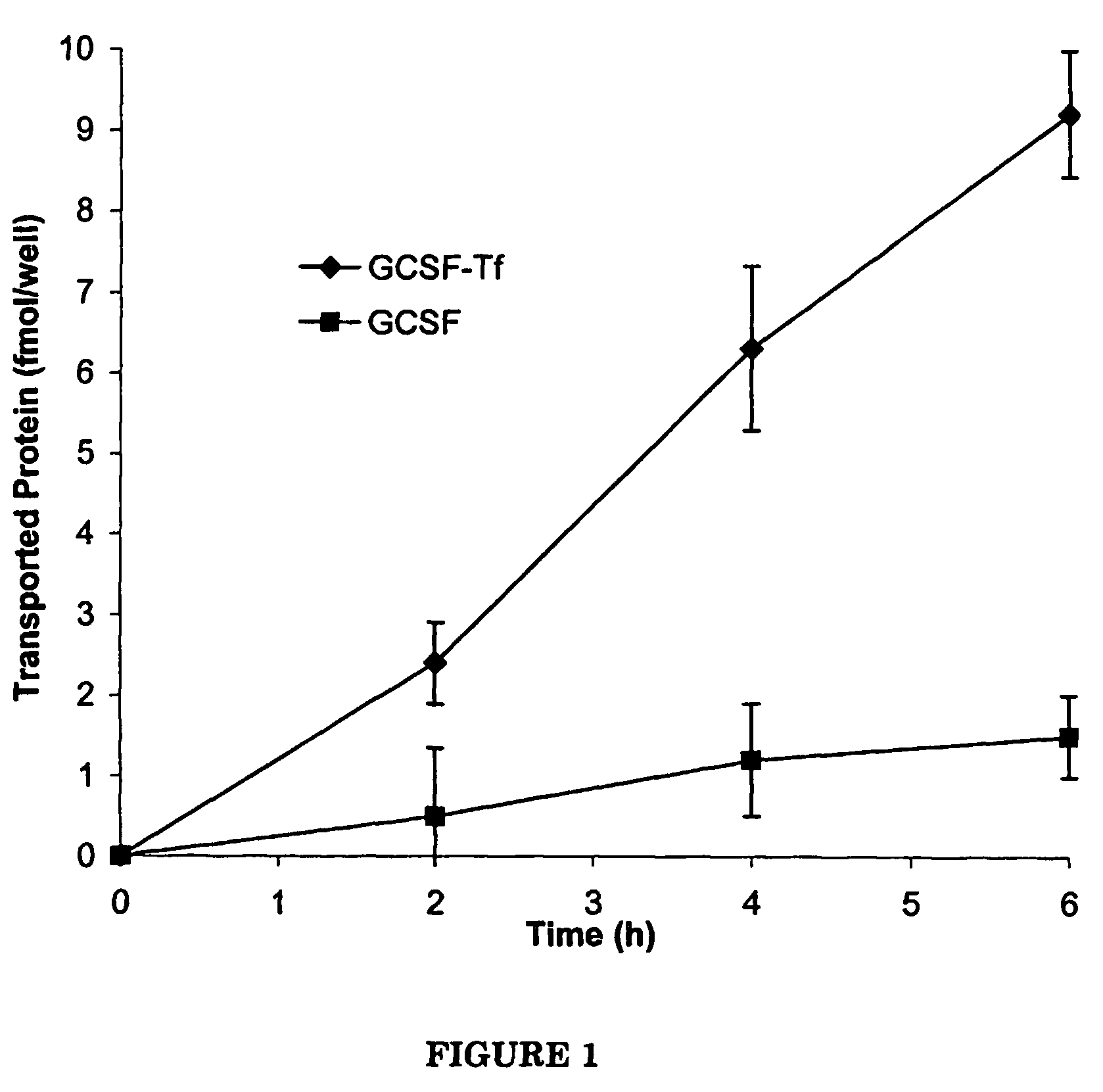
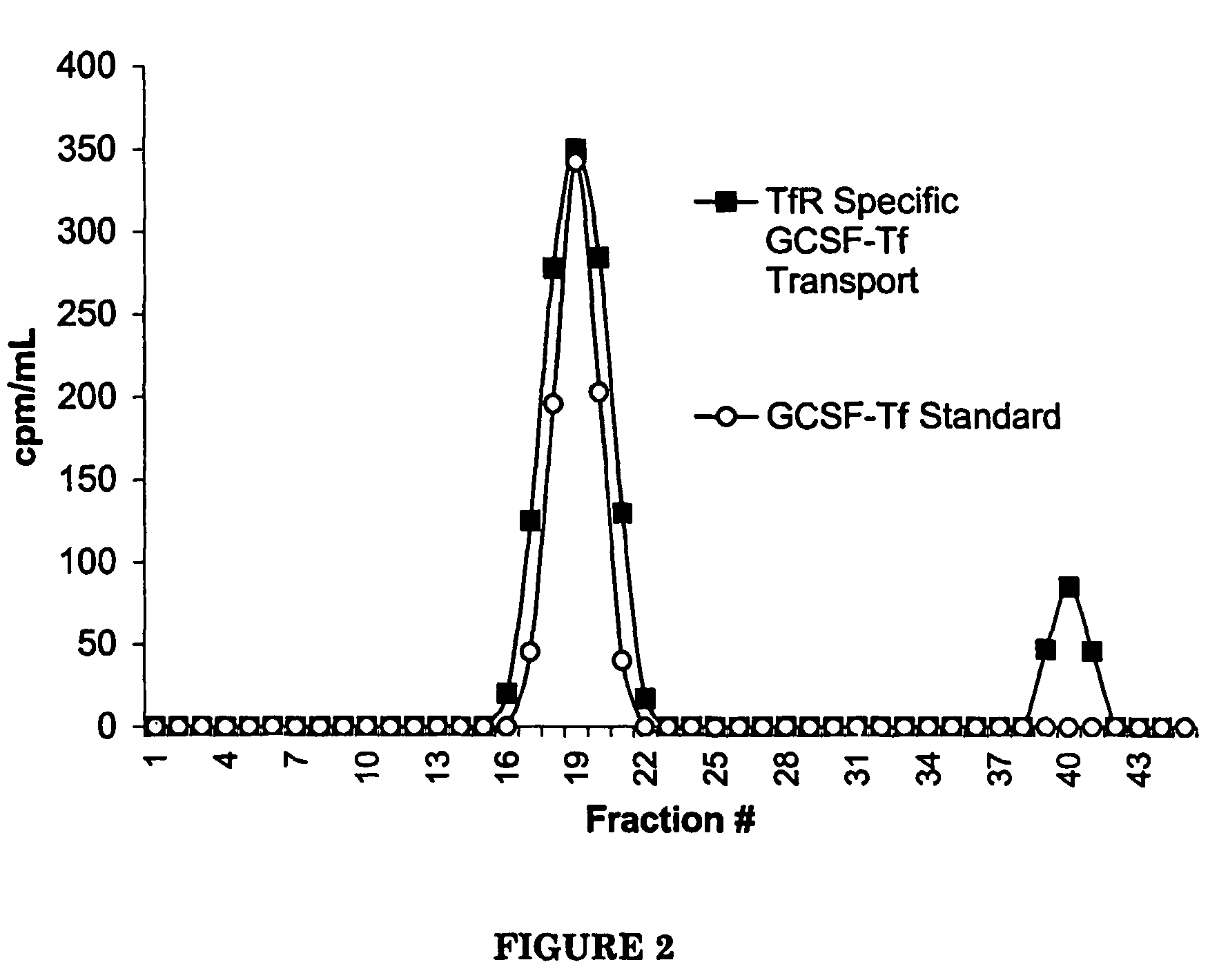
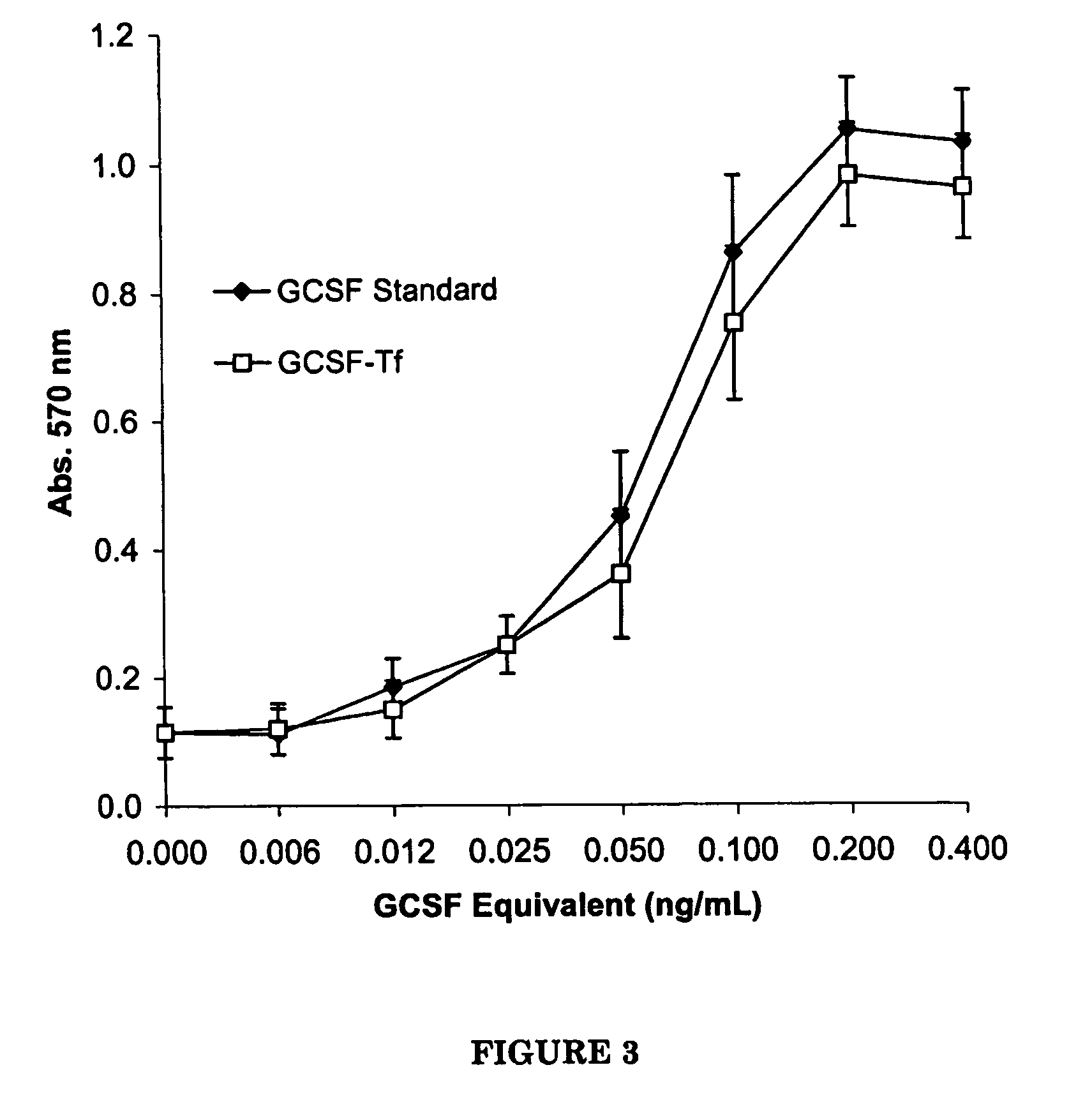
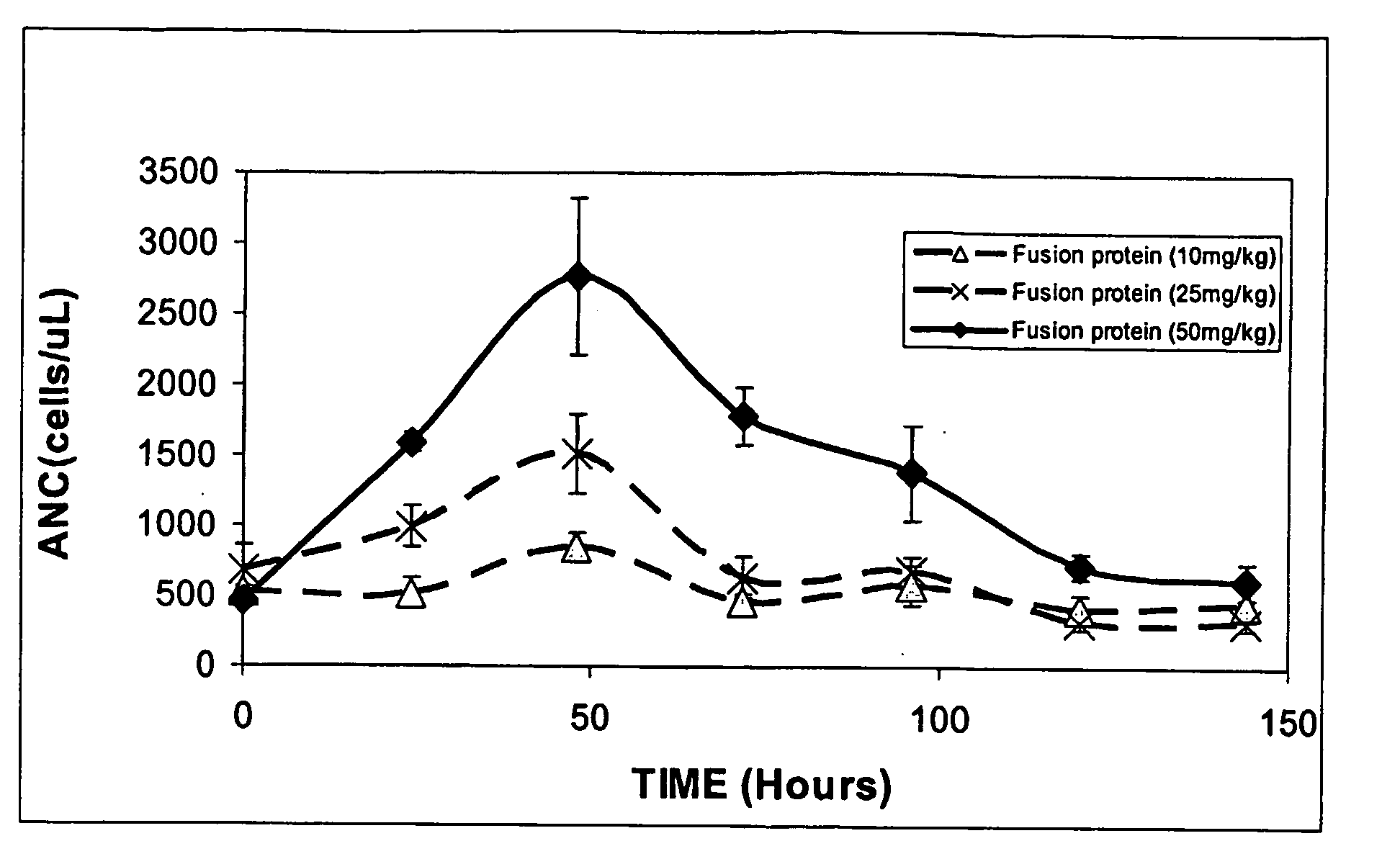
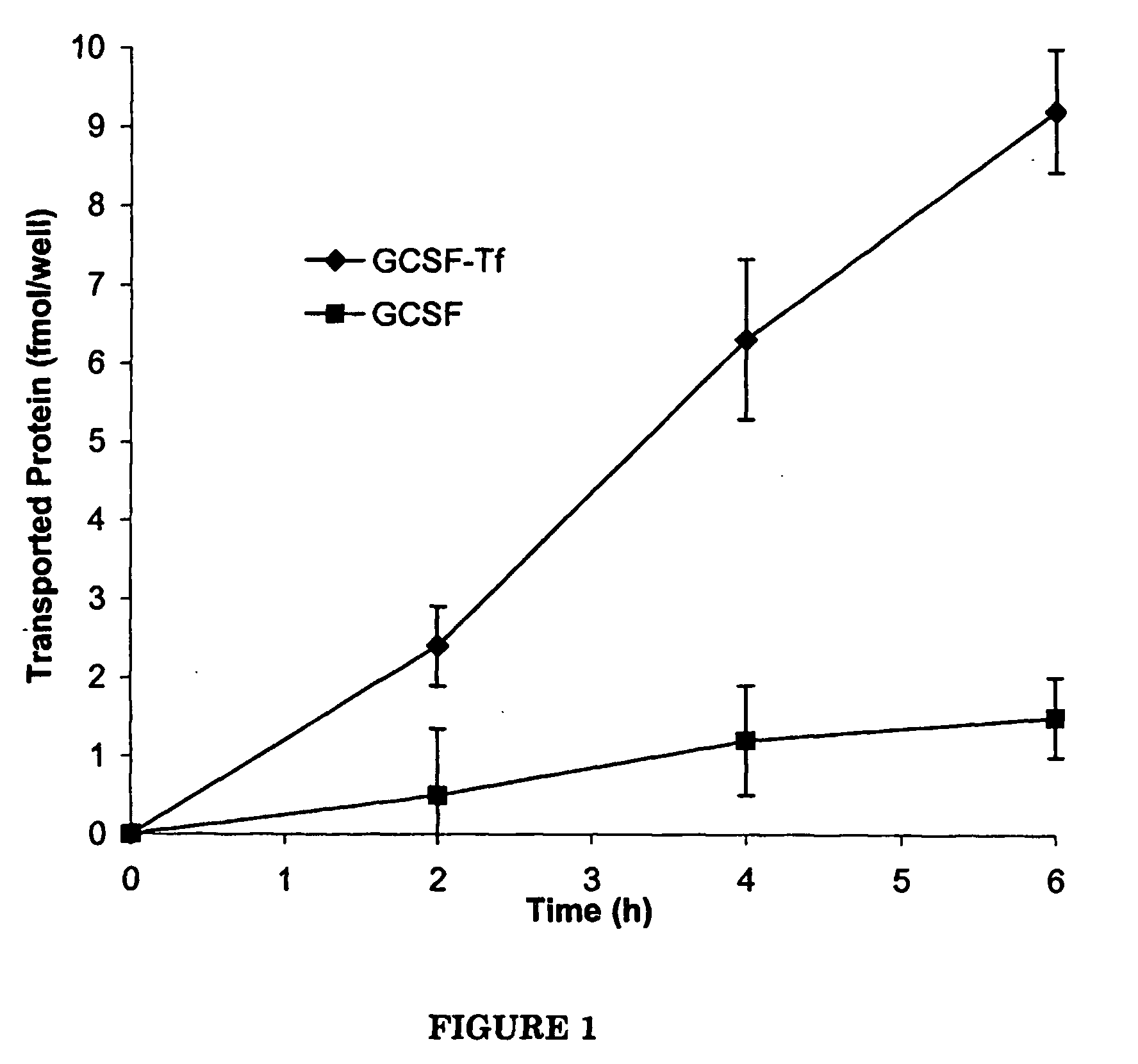
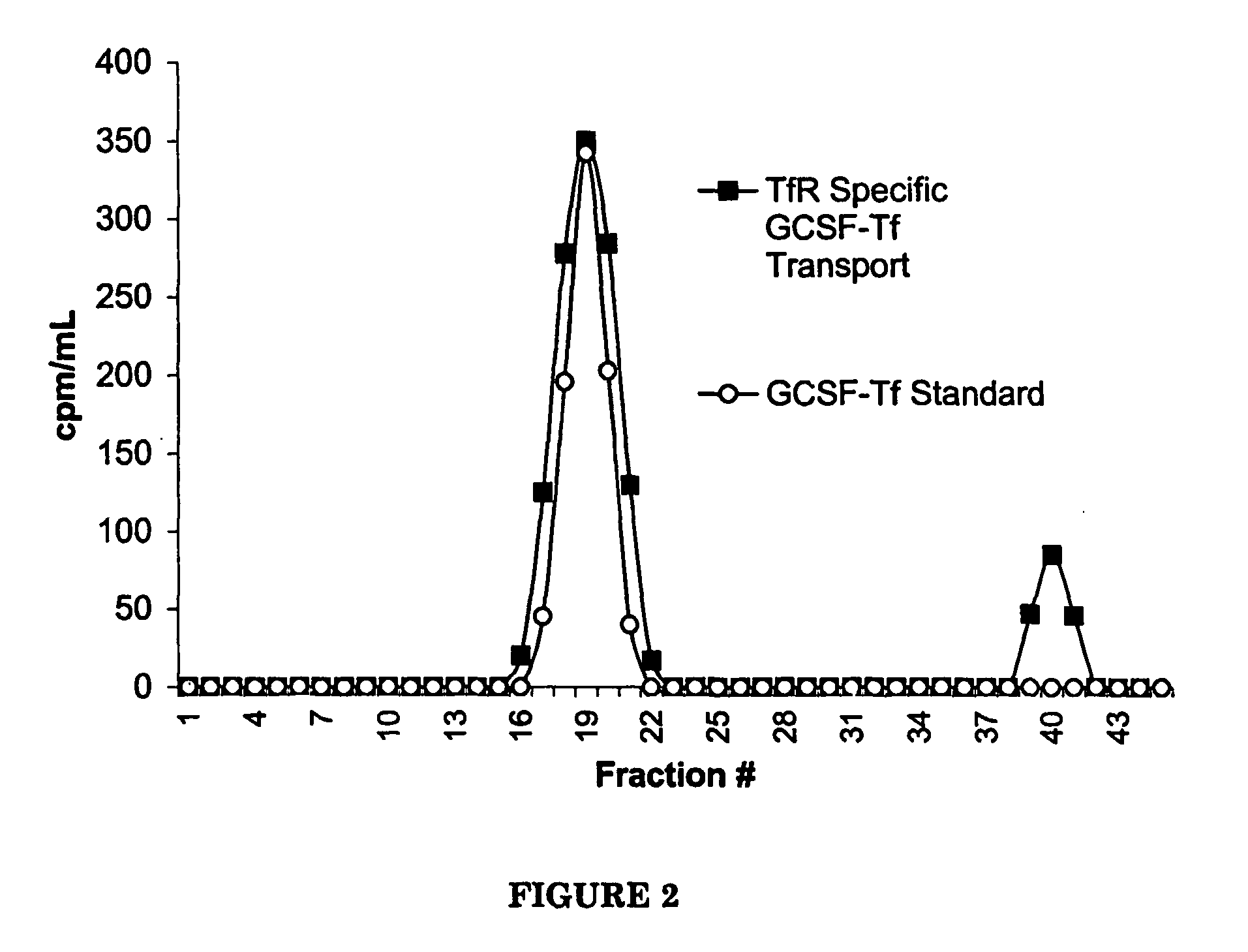
G-CSF transferrin fusion proteins
InactiveUS8188032B2Improve stabilityEasy to transportPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTranscytosisTransferrin
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH
Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor-specific antibodies and uses thereof
ActiveUS10112998B2Efficient transportEasy to detectHybrid immunoglobulinsNervous disorderInsulin-like growth factorCereblon
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) prevents transport of molecules larger than 500 Dal tons from blood to brain. Receptor-mediated transcytosis (RMT) facilitates transport across the BBB of specific molecules that bind receptors on brain endothelial cells that form the BBB. An insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF 1R)-binding antibody or fragment thereof is identified that transmigrates the BBB by RMT. The antibody or fragment is used to deliver a cargo molecule across the BBB, wherein the cargo molecule may be a therapeutic or detectable agent. The antibody is a camelid VHH, prepared by immunizing a llama with a 933-amino acid IGF 1R polypeptide. Humanized forms of the camelid VHH are also generated.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor -specific antibodies and uses thereof
ActiveUS20170015749A1Prolonged Circulatory Half-LifeEfficient transportHybrid immunoglobulinsNervous disorderInsulin-like growth factorAntigen binding
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) prevents transport of molecules larger than 500 Daltons from blood to brain. Receptor-mediated transcytosis (RMT) facilitates transport across the BBB of specific molecules that bind receptors on brain endothelial cells that form the BBB. An insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R)-binding antibody or fragment thereof is identified that transmigrates the BBB by RMT. The antibody or fragment is used to deliver a cargo molecule across the BBB, wherein the cargo molecule may be a therapeutic or detectable agent. The antibody is a camelid VHH, prepared by immunizing a llama with a 933-amino acid IGF1R polypeptide. Humanized forms of the camelid VHH are also generated.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor -specific antibodies and uses thereof
ActiveUS20170022277A1Prolonged Circulatory Half-LifeEfficient transportNervous disorderGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsInsulin-like growth factorAntigen binding
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) prevents transport of molecules larger than 500 Dal tons from blood to brain. Receptor-mediated transcytosis (RMT) facilitates transport across the BBB of specific molecules that bind receptors on brain endothelial cells that form the BBB. An insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF 1R)-binding antibody or fragment thereof is identified that transmigrates the BBB by RMT. The antibody or fragment is used to deliver a cargo molecule across the BBB, wherein the cargo molecule may be a therapeutic or detectable agent. The antibody is a camelid VHH, prepared by immunizing a llama with a 933-amino acid IGF 1R polypeptide. Humanized forms of the camelid VHH are also generated.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Methods and compositions for needleless delivery of macromolecules
Methods and compositions for needleless delivery of macromolecules to the bloodstream of a subject are provided herein. In one aspect, the invention provides a delivery construct, comprising a receptor binding domain, a transcytosis domain, a macromolecule to be delivered to a subject, and a cleavable linker. Generally, the cleavable linker is cleavable by an enzyme present in higher concentration at or near the basal-lateral membrane of a polarized epithelial cell or in the plasma than elsewhere in the body, for example, at the apical side of the polarized epithelial cell. In other aspects, the invention provides nucleic acids encoding delivery constructs of the invention, kits comprising delivery constructs of the invention, cells expressing delivery constructs of the invention, and methods of using delivery constructs of the invention.
Owner:TRINITY ASSIGNMENT FOR THE BENEFIT OF CREDITORS
Methods and compositions for needleless delivery of antibodies
The present invention relates, in part, to methods and compositions for needleless delivery of antibodies to a subject. The present invention also relates, in part, to methods for needleless delivery of fusion proteins comprising a bioactive molecule and an antibody fragment to subject. In one aspect, the methods and compositions involve administering to the subject a delivery construct comprising a carrier construct non-covalently bound to the antibody or fusion protein to be delivered, wherein the carrier construct comprises a receptor-binding domain, a transcytosis domain, and an antibody-binding domain to which the antibody or the antibody fragment of the fusion protein non-covalently binds.
Owner:TRINITY ASSIGNMENT FOR THE BENEFIT OF CREDITORS
Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor-specific antibodies and uses thereof
ActiveUS10106614B2Efficient transportEasy to detectHybrid immunoglobulinsNervous disorderAntigen bindingBiology
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
G-CSF Transferrin Fusion Proteins
InactiveUS20090042777A1Improve stabilityEasy to transportOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsTranscytosisTransferrin
A polypeptide comprising a G-CSF domain operably linked to a Tf domain, wherein the ability of the polypeptide to be transported into a cell expressing a TfR gene or the ability of the polypeptide to be transported across a cell expressing a TfR gene via transcytosis is higher than that of the G-CSF domain alone.
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH
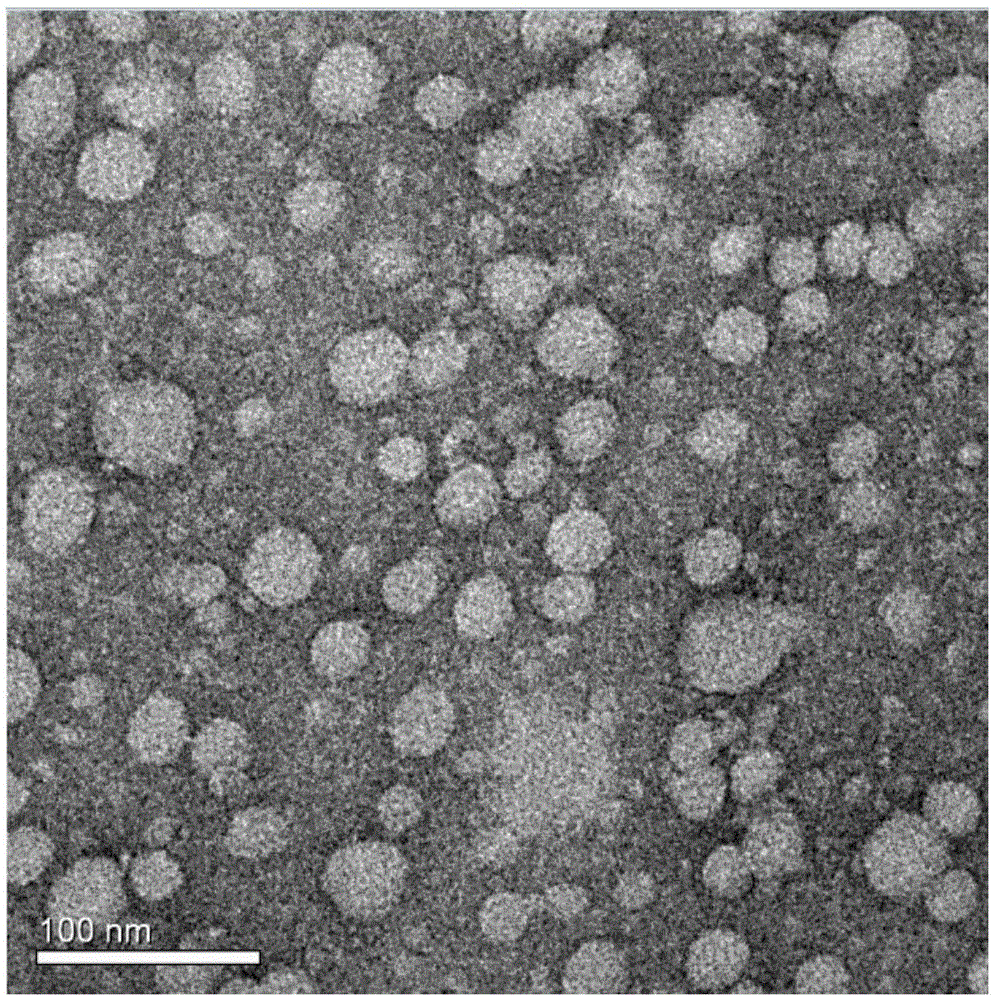
Receptor-targeted nanoparticles for enhanced transcytosis mediated drug delivery
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Bimodal nanoprobes for image-guided brain tumor resection
ActiveCN107837403ASmall particle sizeGood chemical stabilityEmulsion deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityPolyethylene glycol
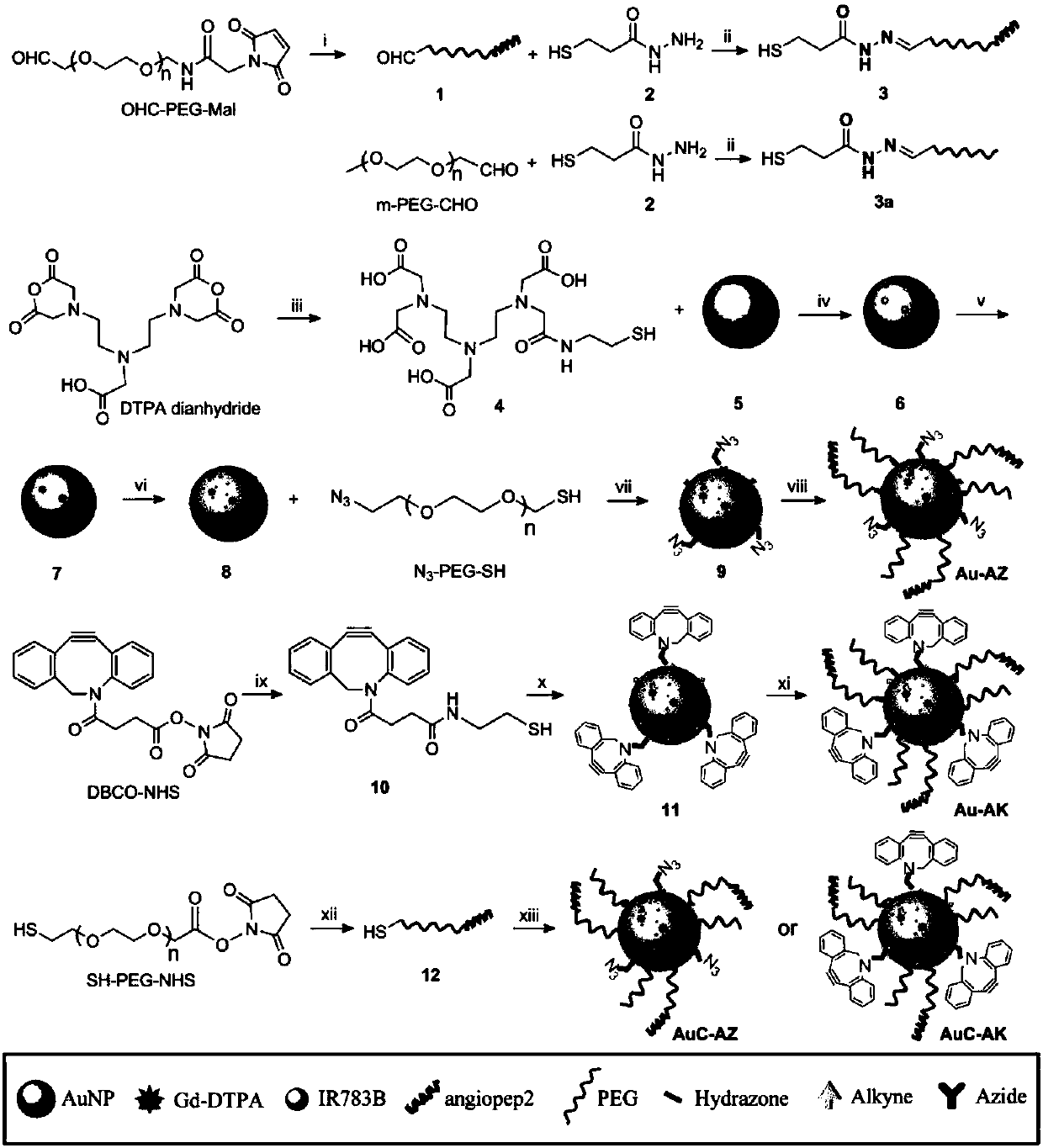
The invention relates to bimodal nanoprobes and a preparation method thereof, and application of the bimodal nanoprobes to image-guided brain tumor resection, belonging to the field of molecular imaging probes. The nanoprobes use a gold nanoparticle as a carrier; the surface of the gold nanoparticle is modified by a magnetic resonance imaging group Gd<3+>-DTPA, a Raman reporter molecule IR783B, acyclooctyne group DBCO or an azido group N=N=N, polyethylene glycol, and an across-blood-brain-barrier targeting group Angiopep-2; and the targeting group Angiopep-2 specificity guides the nanoprobesacross blood-brain barriers through transcytosis, and the nanoprobes form aggregate in the acidic environment of brain tumors, so magnetic resonance signals and Raman scattering signals are enhanced at the same time. The bimodal nanoprobes employ a bimodal image technology of combined surface-enhanced resonant Raman scattering and magnetic resonance imaging, can locate tumors through magnetic resonance imaging before an operation, and utilize surface-enhanced resonant Raman scattering imaging to guide tumor resection during the operation. The bimodal nanoprobes provided by the invention have important scientific research and clinical significance to improvement of therapeutic effect on brain tumors and promotion of the clinical and translational practice of individual-based treatment methods.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Bacterially derived, intact minicells for delivery of therapeutic agents to brain tumors
InactiveCN104114153AOrganic active ingredientsRadioactive preparation carriersActive agentTranscytosis
Systemic administration of intact, bacterially derived minicells results in rapid accumulation of the minicells in the microenvironment of a brain tumor, in therapeutically significant concentrations, without requiring endothelial endocytosis / transcytosis across the blood brain barrier or any other mechanism by which, pursuant to conventional approaches, nanoparticles have entered into that microenvironment. Accordingly, a wide variety of brain tumors, both primary and metastatic, can be treated by administering systemically a therapeutically effective amount of a composition comprised of a plurality of such minicells, each minicell being a vehicle for an active agent against the tumor, such as a radionuclide, a functional nucleic acid or a plasmid encoding one, or a chemotherapeutic agent.
Owner:ENGENEIC MOLECULAR DELIVERY PTY LTD
Bacterially derived, intact minicells for delivery of therapeutic agents to brain tumors
PendingCN109125286AOrganic active ingredientsRadioactive preparation carriersActive agentTranscytosis
Owner:ENGENEIC MOLECULAR DELIVERY PTY LTD
Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor-specific antibodies and uses thereof
ActiveUS10100117B2Efficient transportEasy to detectHybrid immunoglobulinsGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsInsulin-like growth factorCereblon
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) prevents transport of molecules larger than 500 Dal tons from blood to brain. Receptor-mediated transcytosis (RMT) facilitates transport across the BBB of specific molecules that bind receptors on brain endothelial cells that form the BBB. An insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF 1R)-binding antibody or fragment thereof is identified that transmigrates the BBB by RMT. The antibody or fragment is used to deliver a cargo molecule across the BBB, wherein the cargo molecule may be a therapeutic or detectable agent. The antibody is a camelid VHH, prepared by immunizing a llama with a 933-amino acid IGF 1R polypeptide. Humanized forms of the camelid VHH are also generated.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
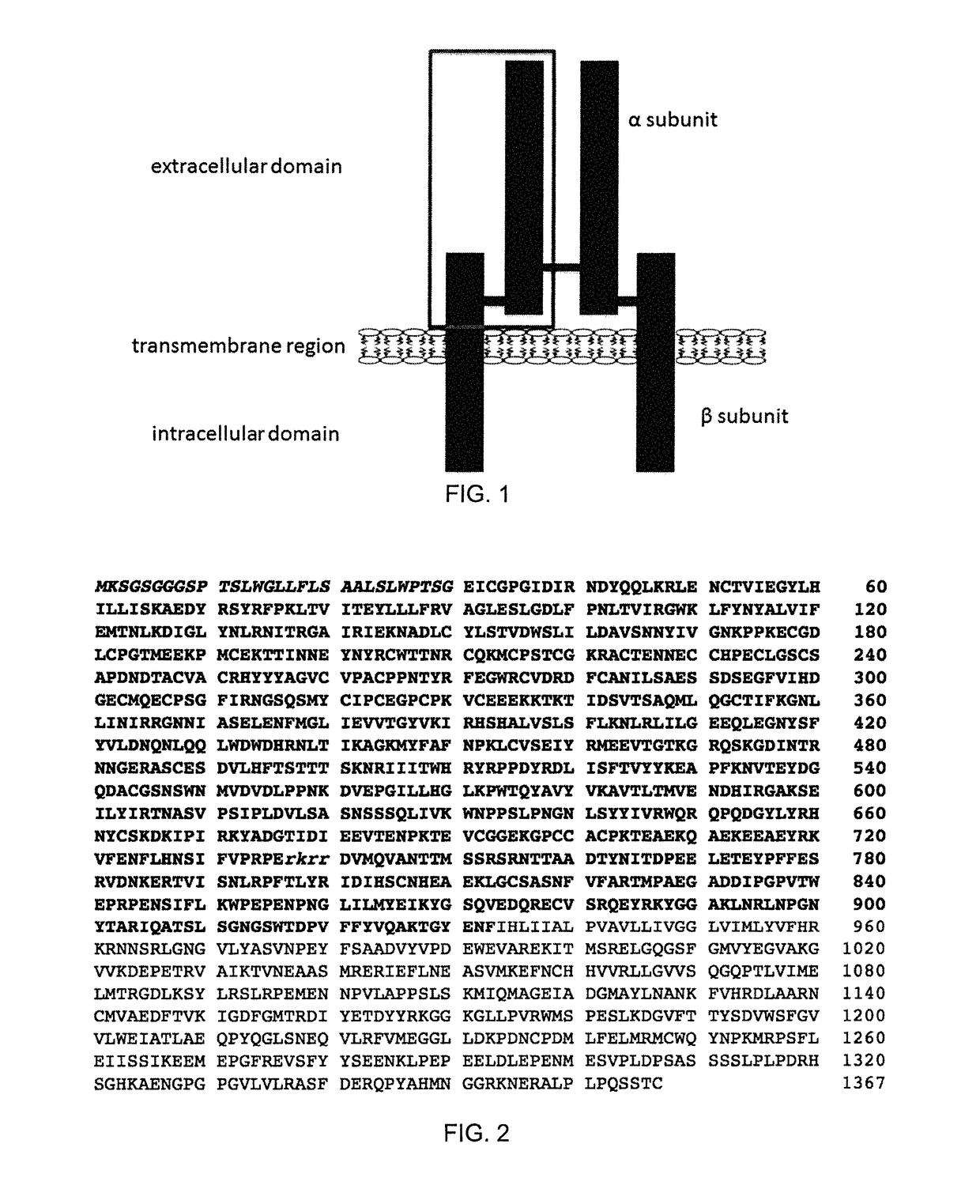
Methods of targeting agents to cells expressing the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor
InactiveUS7404954B2Increase ratingsReduces proteolytic cleavagePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMammalPolymeric immunoglobulin receptor
The invention provides compositions and methods for specific binding to a region of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR) of a cell with the provisos that the ligand does not substantially bind to the most abundant form of the secretory component (SC) of pIgR present in an organ of interest of an animal of interest under physiological conditions, and does not bind to the pIgR stalk. In some embodiments, the ligand decreases cleavage of SC from the stalk by at least one-third. The ligands and methods of the invention can be used with both birds and mammals. In more preferred embodiments, the animal is a mammal. In the most preferred embodiment, the animal is a human. The ligand may be targeted into the cell or may undergo retrograde transcytosis and release at the basolateral side of the cell, and may comprise a biologically active composition.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com