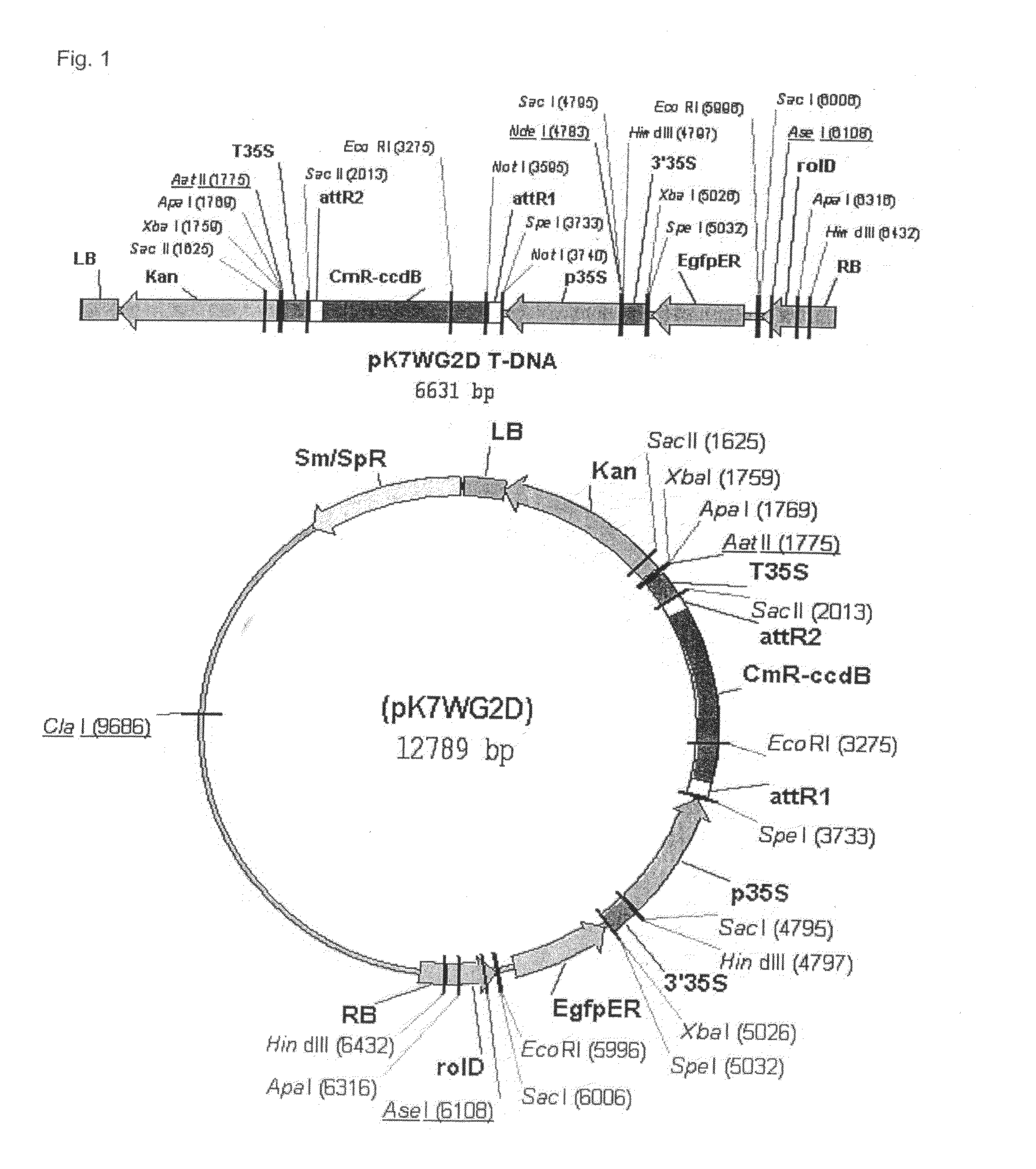
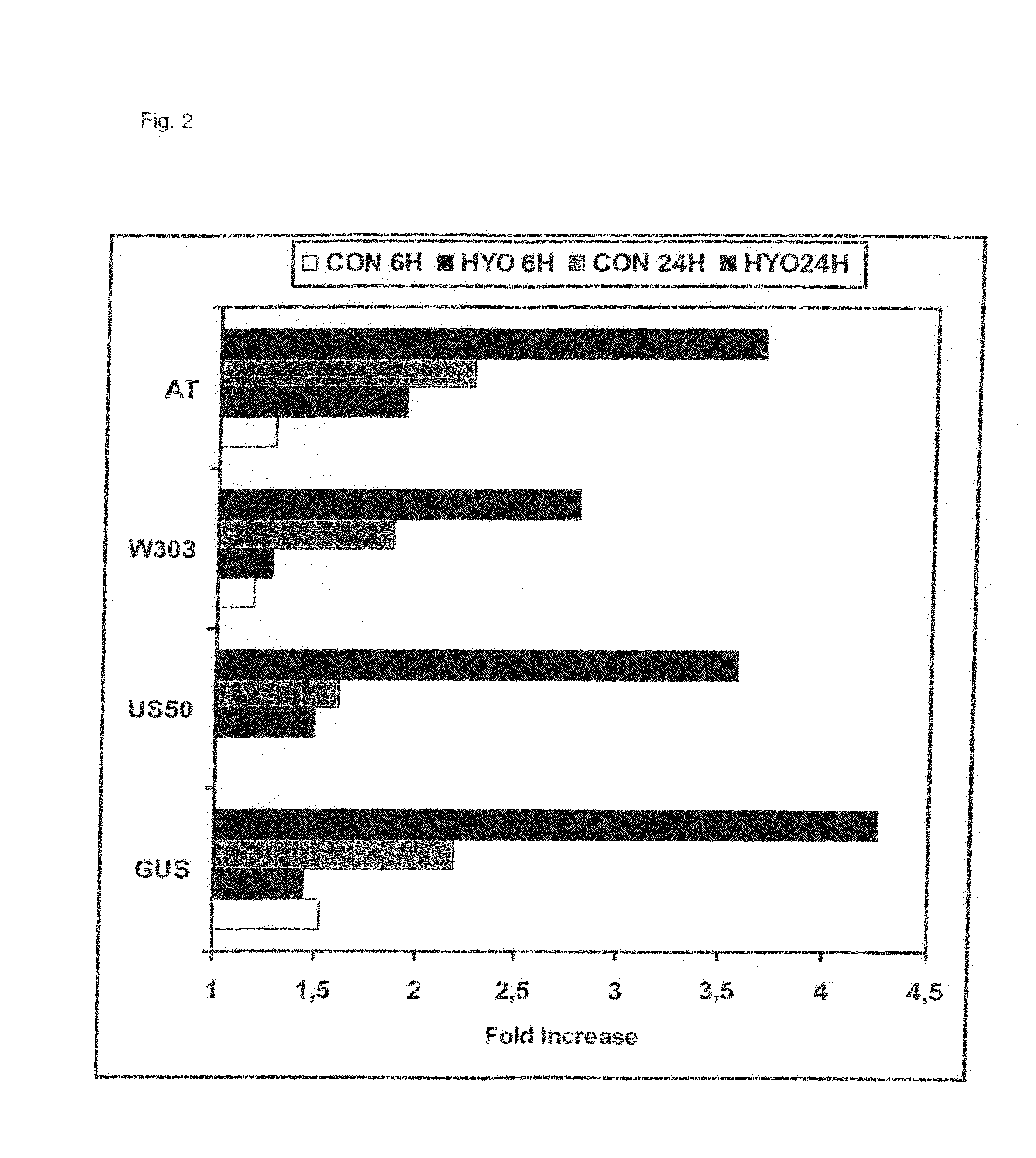
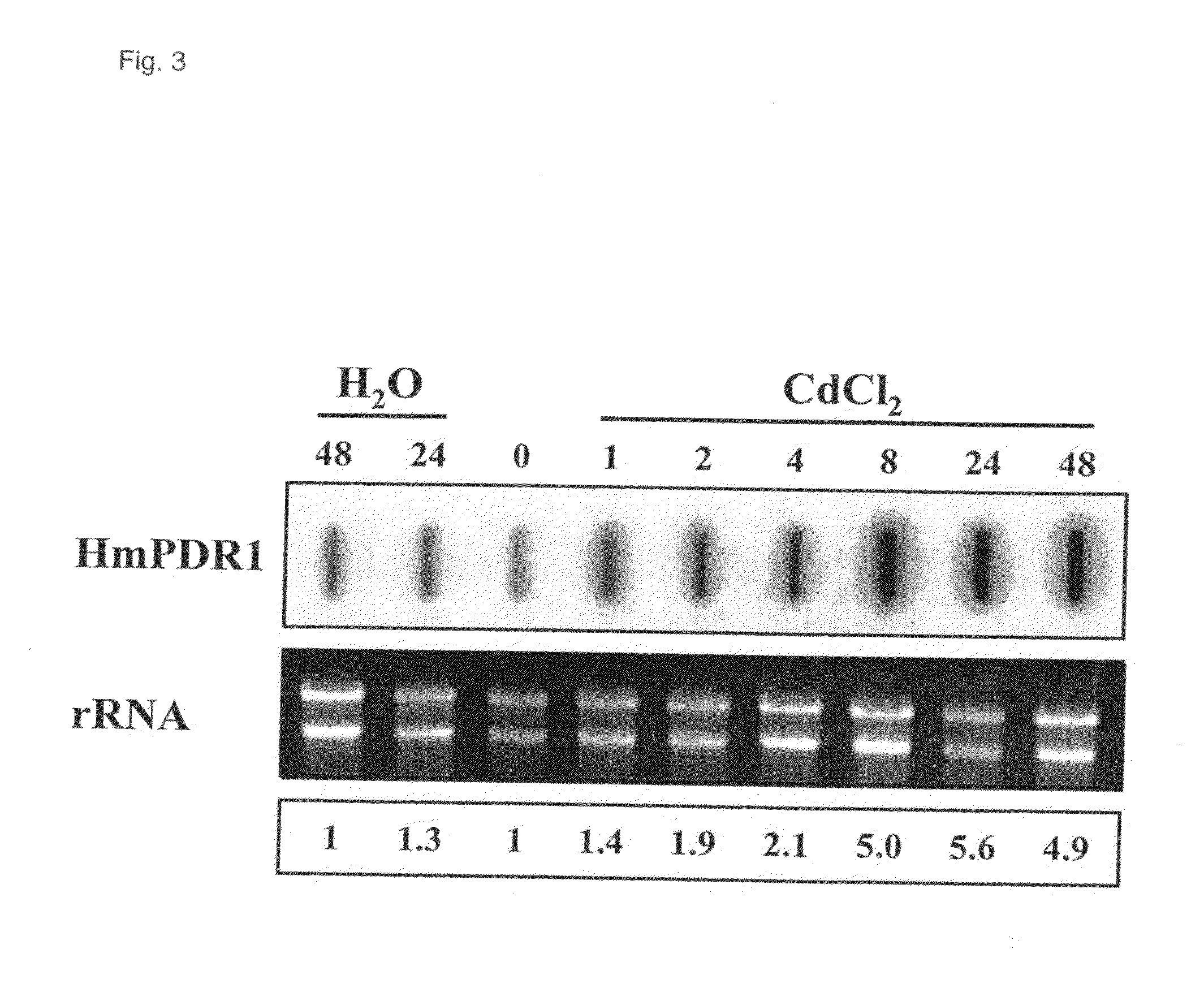
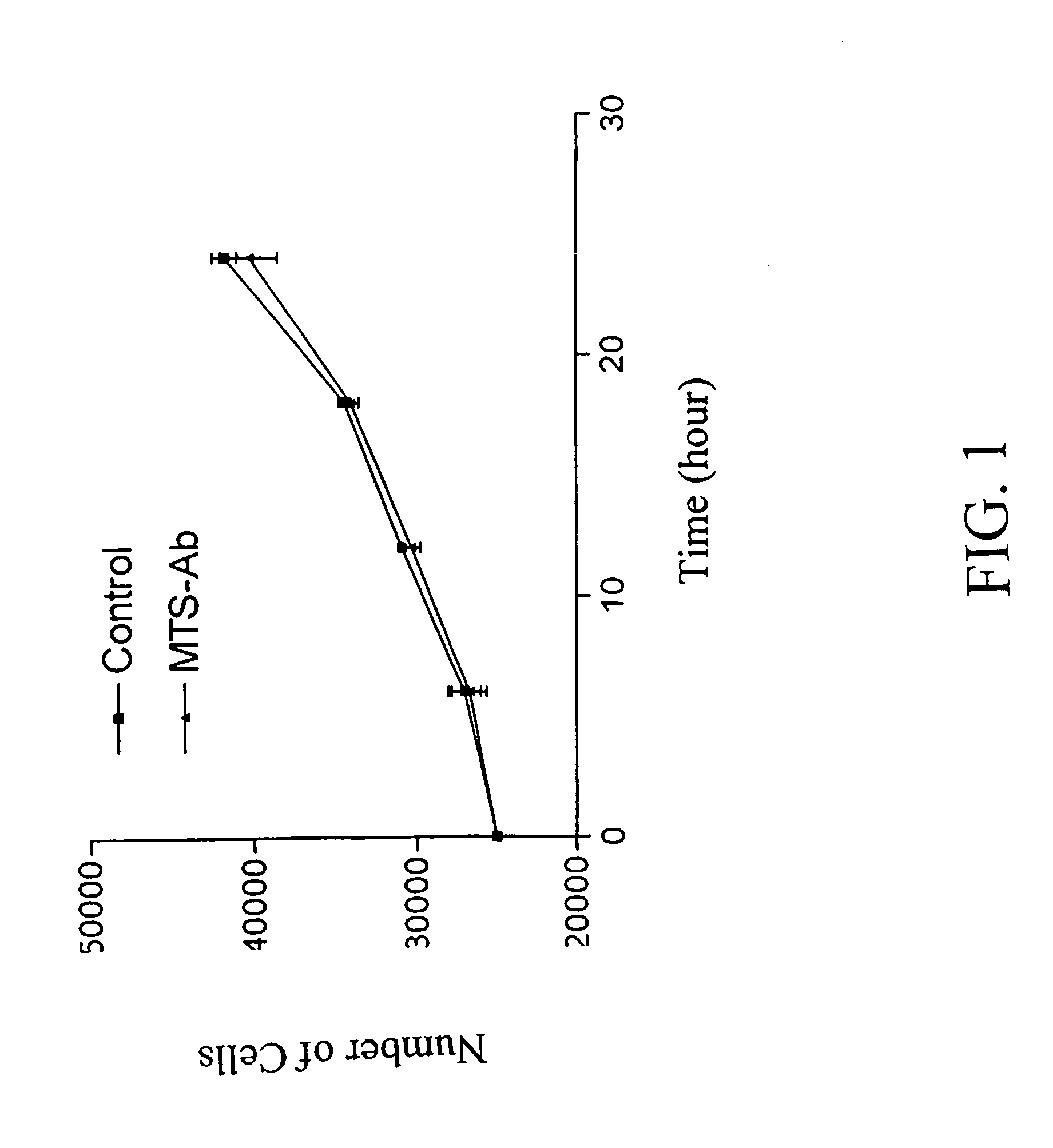
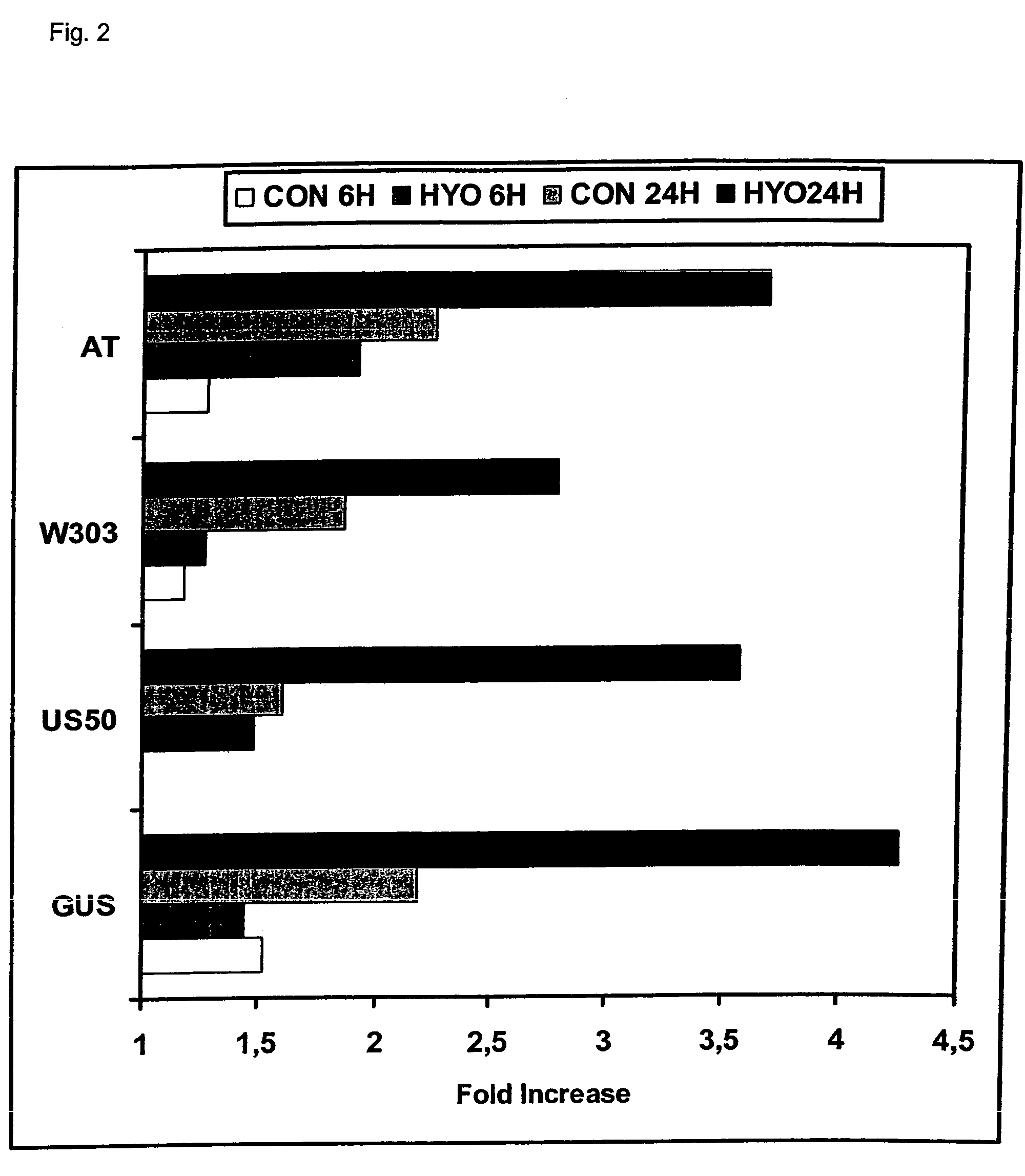
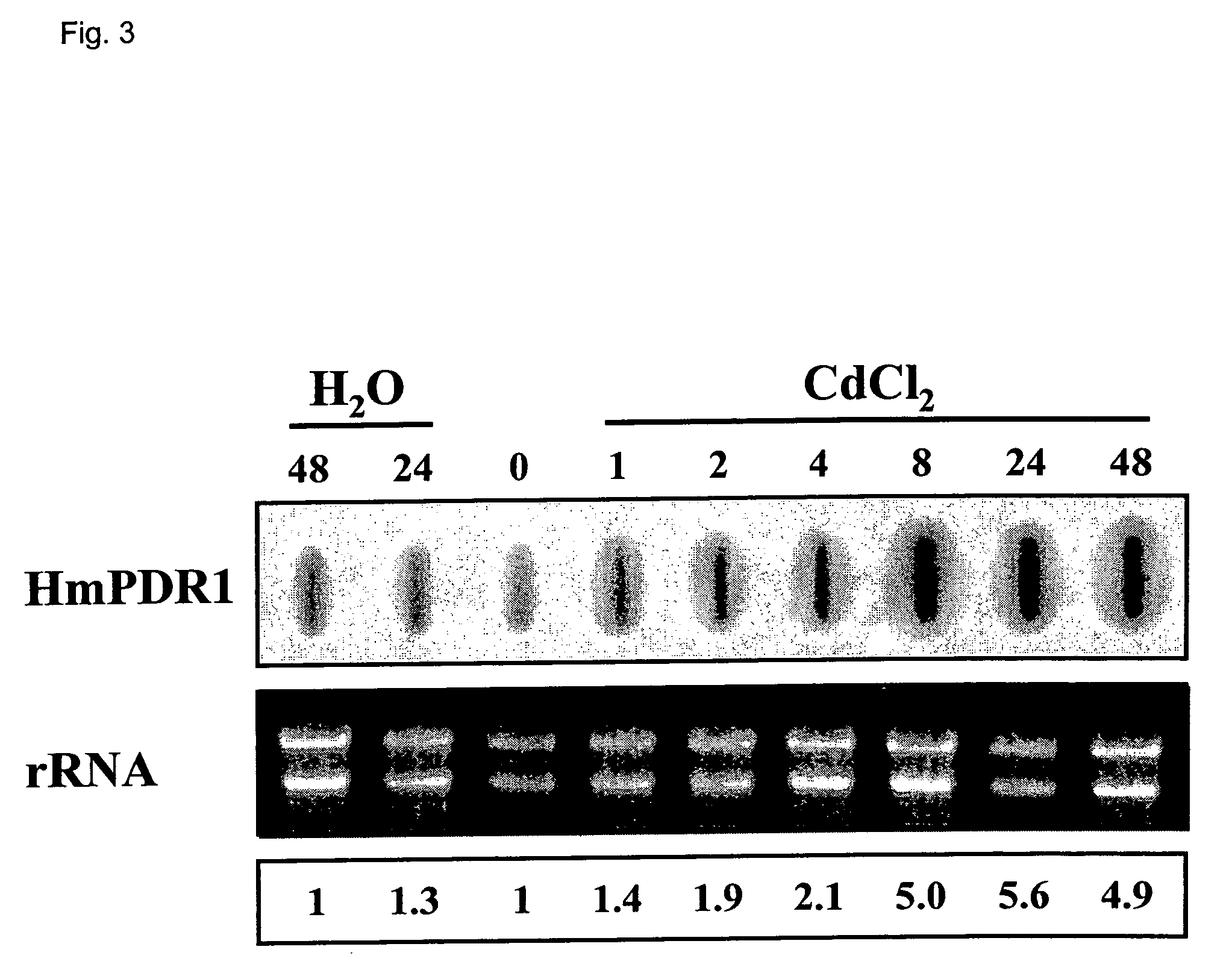
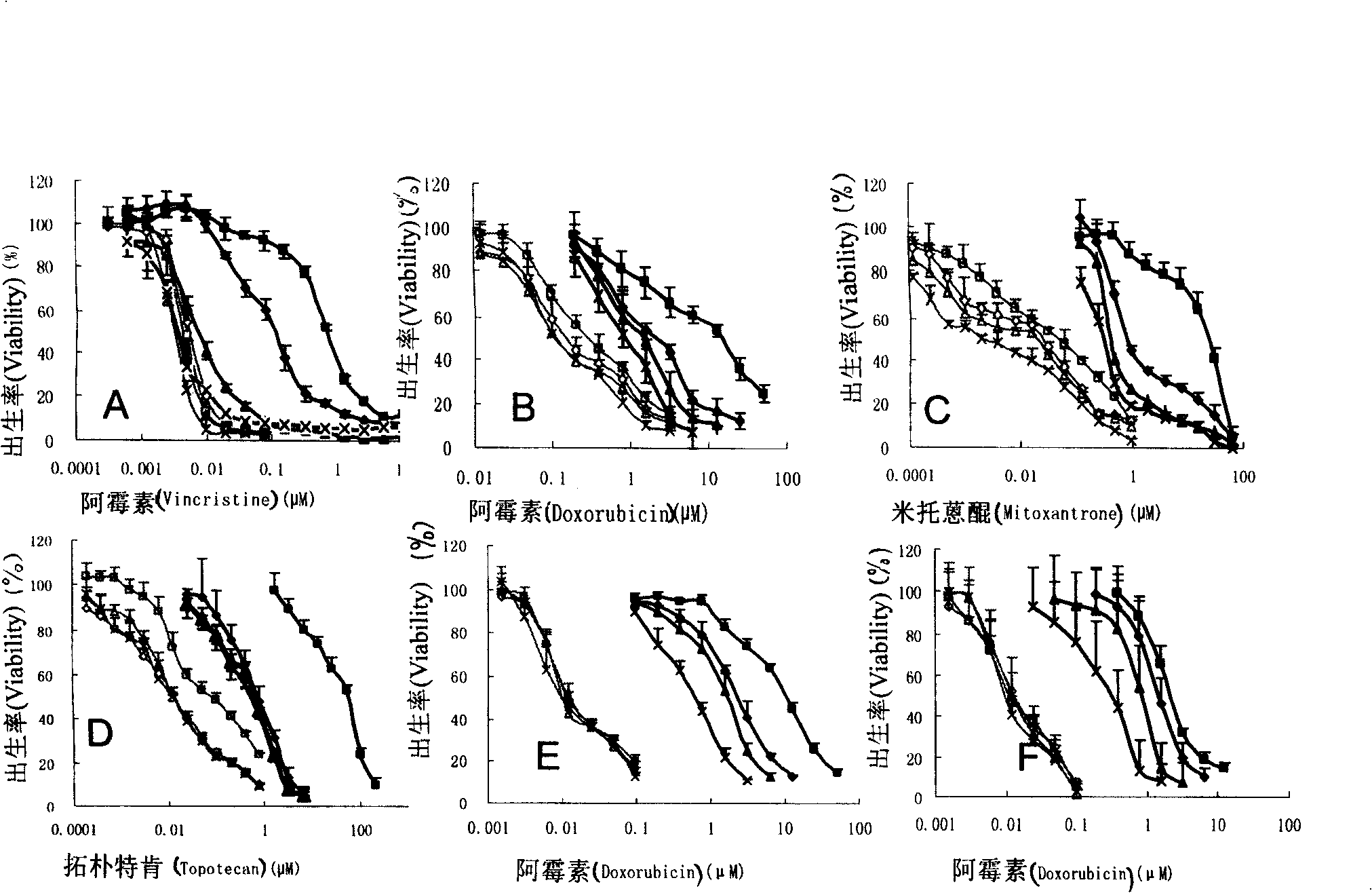
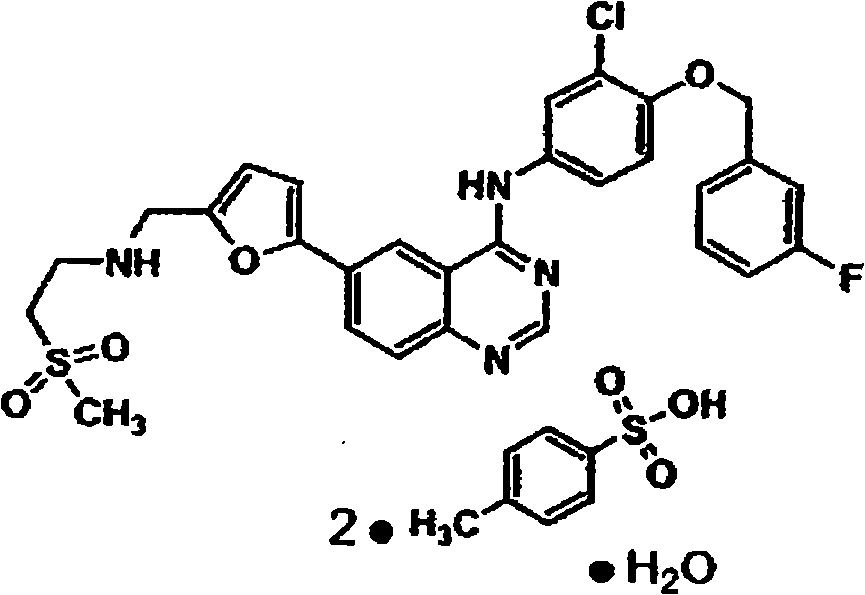
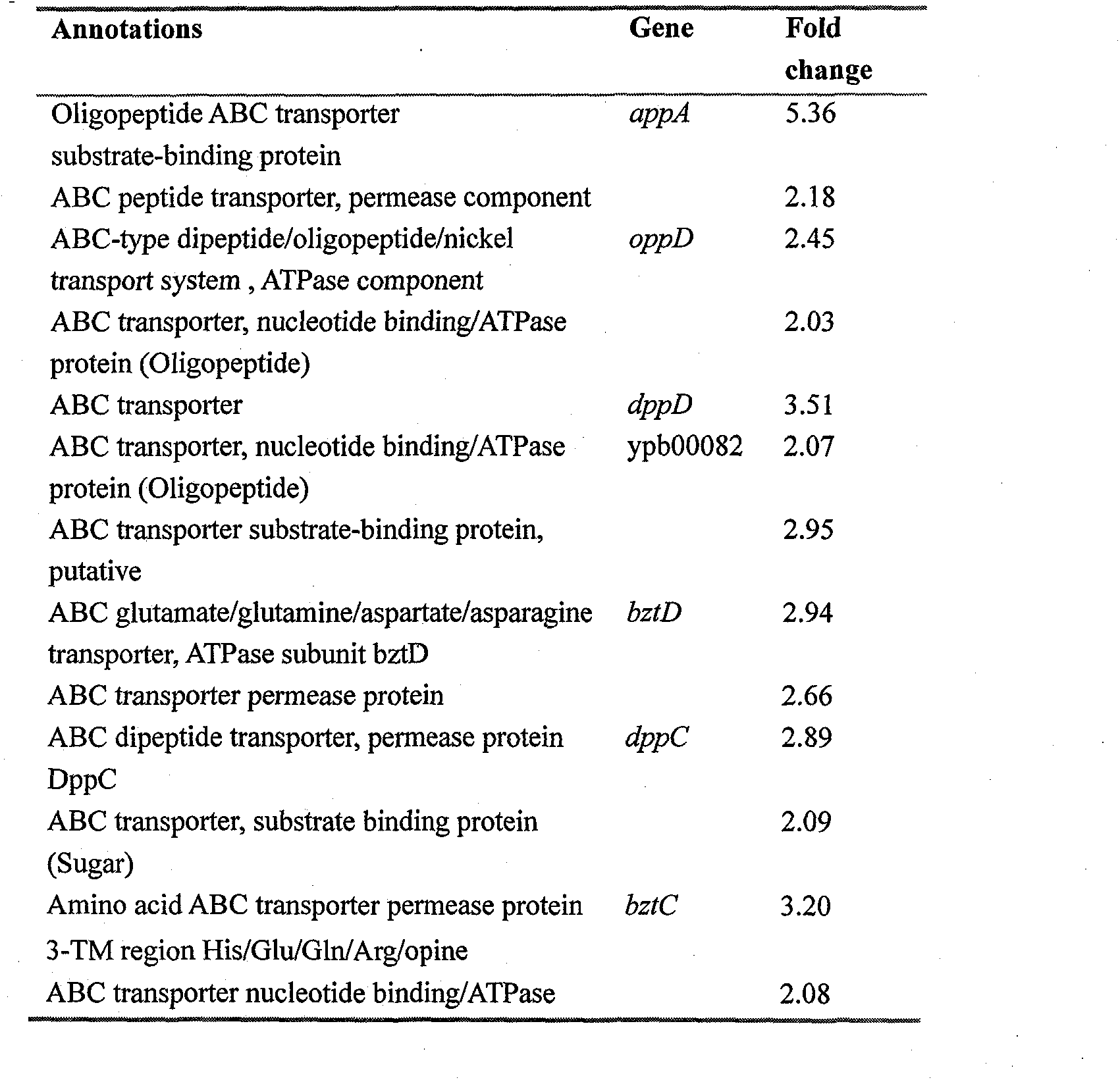
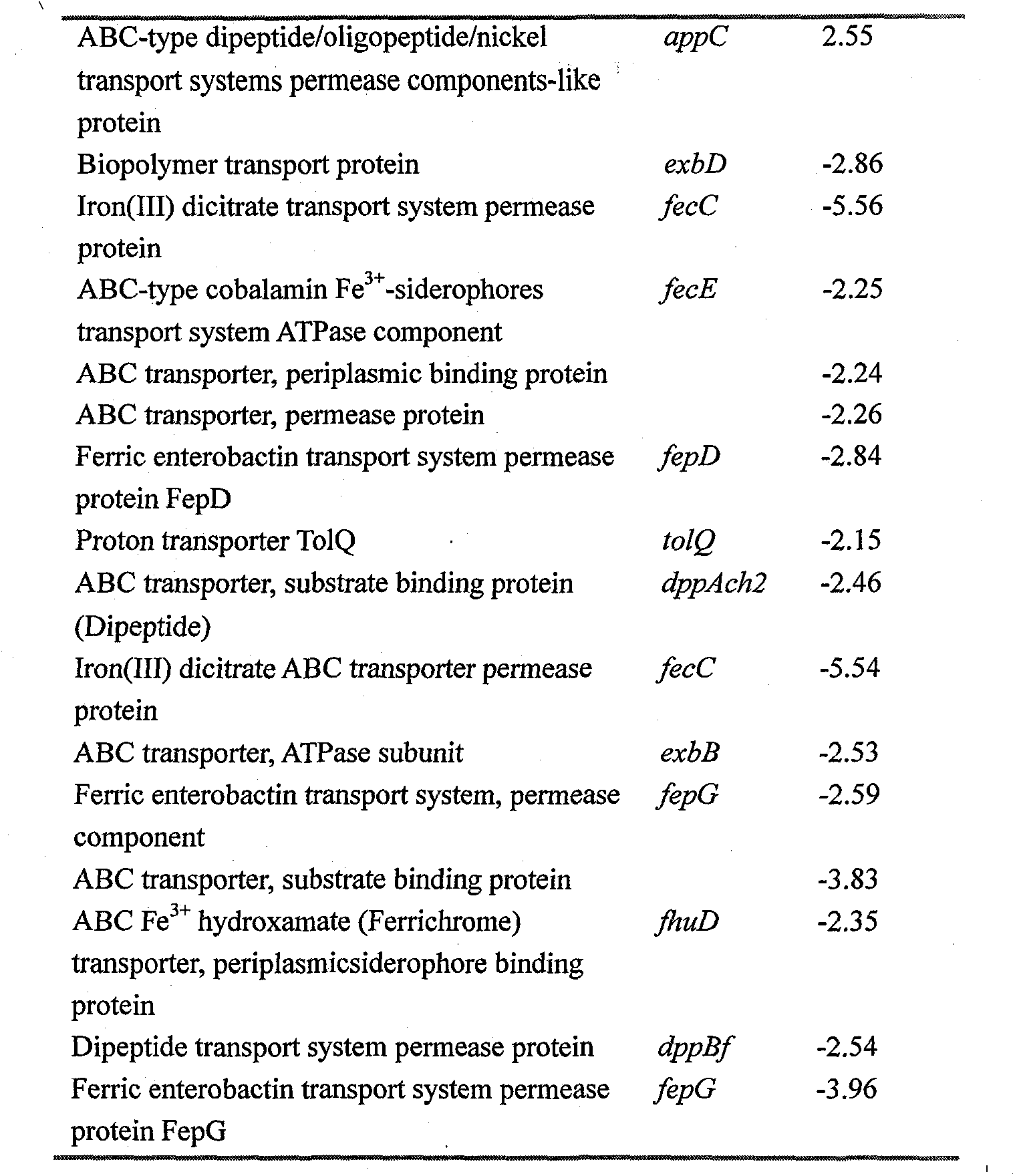
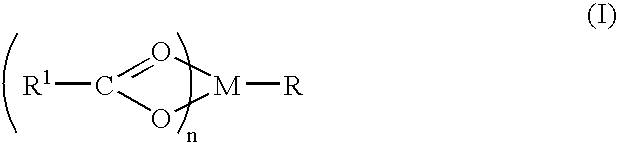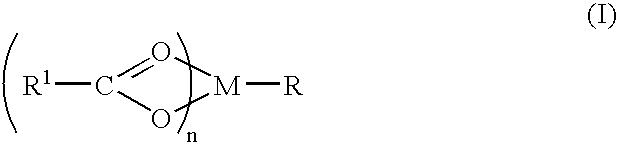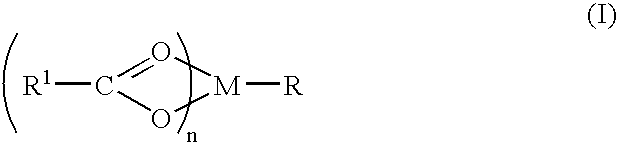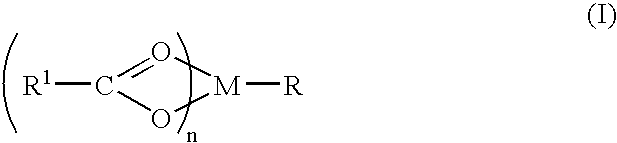Patents
Literature
34 results about "Membrane Transporters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A membrane transport protein (or simply transporter) is a membrane protein involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, or macromolecules, such as another protein, across a biological membrane.
Compound and method of treating neurogenic conditions using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug complexes
A complex is provided for the treatment of neurogenic conditions having the formula: where R1 is M is a metal ion Ca(II), Mg(II), Cu(II) or Ni(II); n is an integer 1 or 2; R is BBB peptide, transferrin, membrane transporter peptide, TAT peptide, bradykinin, beta-endorphin, bombesin, calcitonin, cholecystokinin, an enkephalin, dynorphin, insulin, gastrin, substance P, neurotensin, glucagon, secretin, somatostatin, motilin, vasopressin, oxytocin, prolactin, thyrotropin, an angiotensin, galanin, neuropeptide Y, thyrotropin-releasing hormone, gonadotropnin-releasing hormone, growth hormone-releasing hormone, luteinizing hormone, vasoactive intestinal peptidegluconate, L-lactate, L-leucine, L-tryptophan, and L-glutamate; and R is coupled to M through a carboxylate moiety. Magnesium (II) represents the preferred metal ion as magnesium is known to have neuroprotective effects. The metal ion is in part chelated by a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that does not inhibit platelet activity and includes salicylate and ibuprofenate. The complex also includes a ligand operative in transport across the blood brain barrier. A process for making an inventive complex includes the stoichiometric addition of ligands containing carboxylate groups to a solution of the metal ion. In instances where the metal ion is magnesium (II), a stoichiometric ratio of 1:1:1 is found between the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory ligand:magnesium (II):transporter ligand.
Owner:MILLER LANDON C G
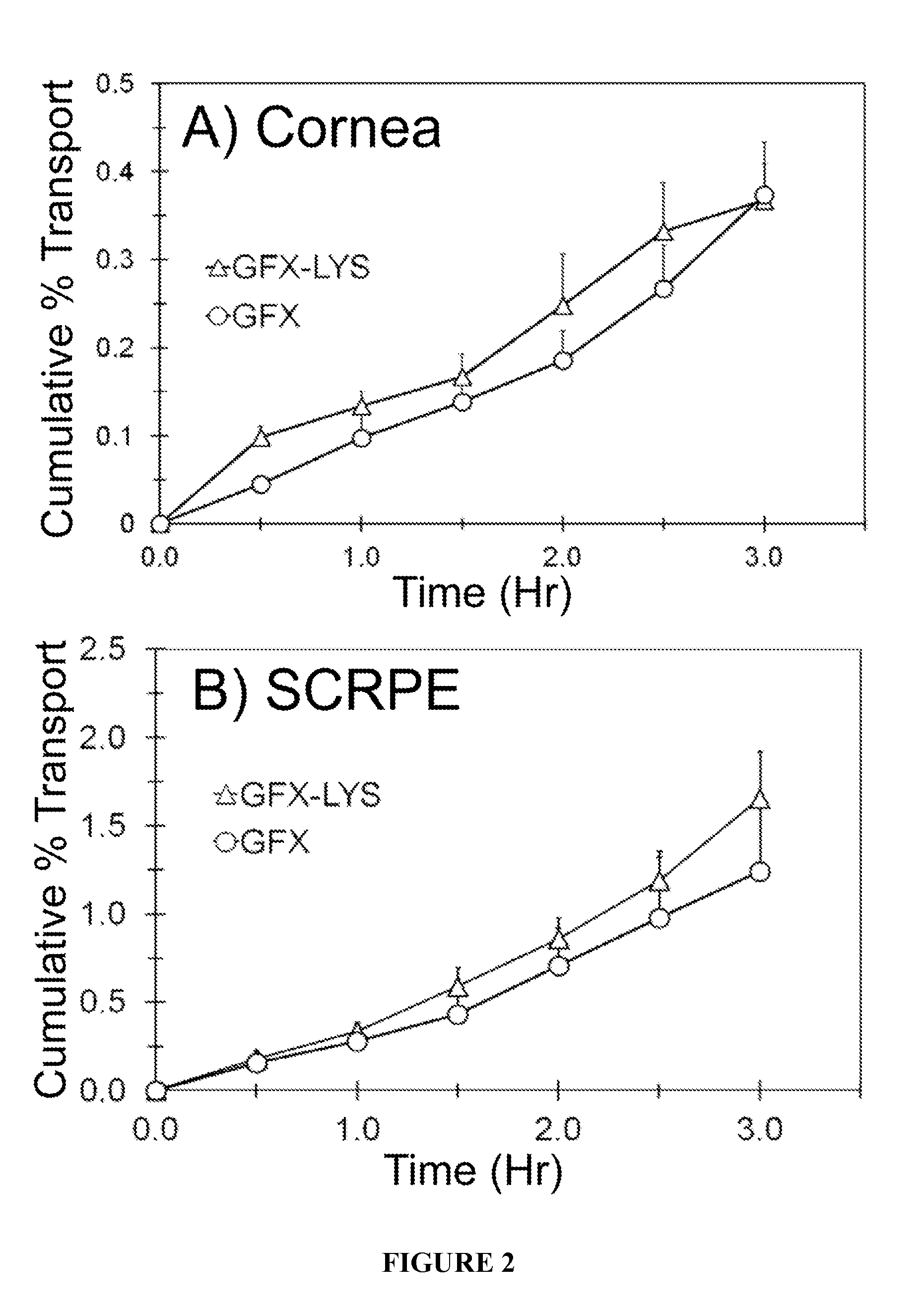
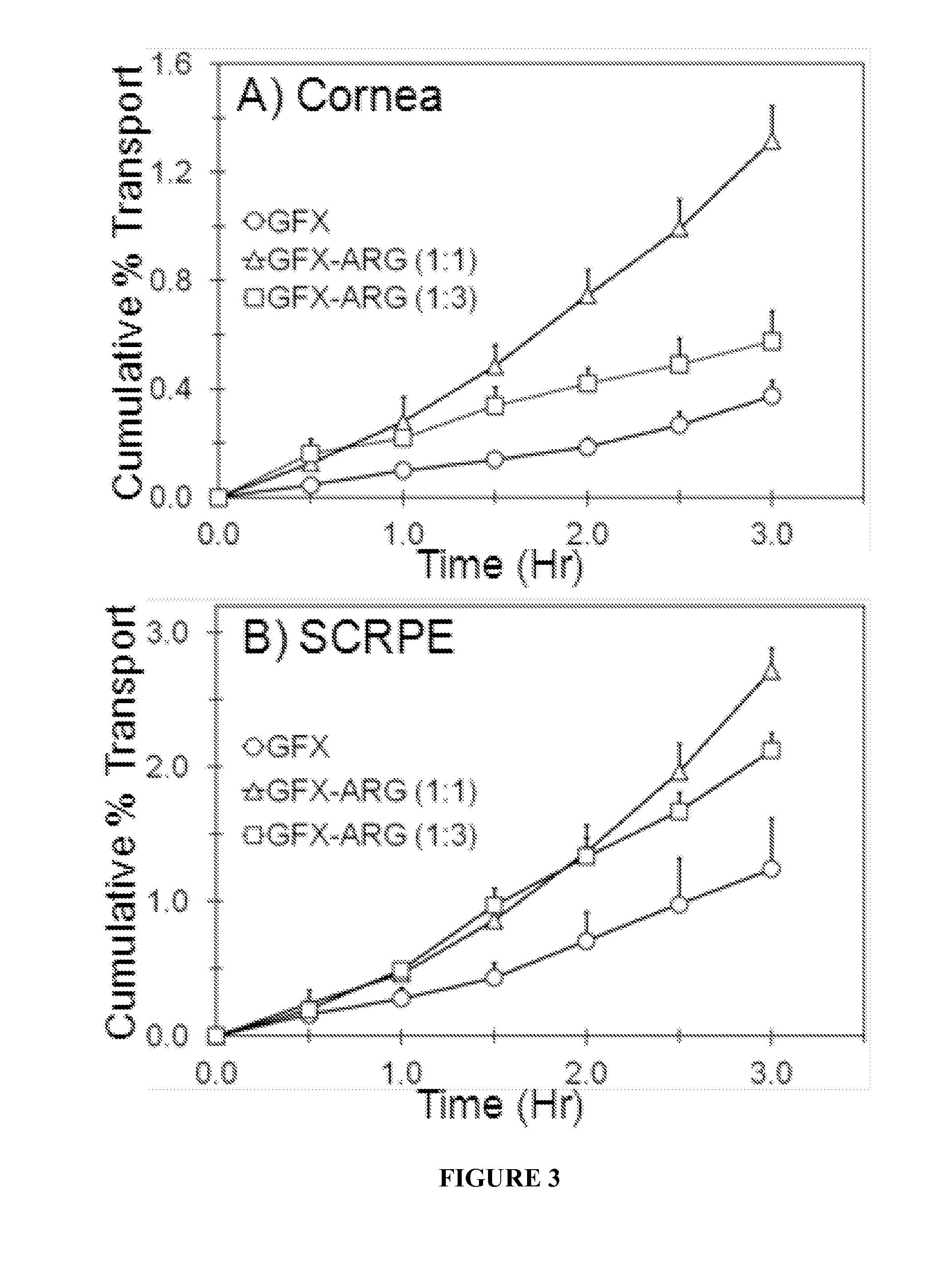
Topical ocular drug delivery
InactiveUS20130190324A1Increased transporter mediated delivery of drugReduce penetrationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsMembrane TransportersBioavailability
The present invention provides compositions and methods for increasing the delivery (i.e., bioavailability) of a compound to an ocular cell. Such compositions and methods can be used to treat an ocular clinical condition. Typically, increased bioavailability or delivery of the compound to ocular cells is achieved by utilizing a membrane transporter.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Compound and method of treating neurogenic conditions using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug complexes
InactiveUS7151084B2Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMembrane TransportersPancreatic hormone
A complex is provided for the treatment of neurogenic conditions having the formula:where R1 isM is a metal ion Ca(II), Mg(II), Cu(II) or Ni(II); n is an integer 1 or 2; R is BBB peptide, transferrin, membrane transporter peptide, TAT peptide, bradykinin, beta-endorphin, bombesin, calcitonin, cholecystokinin, an enkephalin, dynorphin, insulin, gastrin, substance P, neurotensin, glucagon, secretin, somatostatin, motilin, vasopressin, oxytocin, prolactin, thyrotropin, an angiotensin, galanin, neuropeptide Y, thyrotropin-releasing hormone, gonadotropnin-releasing hormone, growth hormone-releasing hormone, luteinizing hormone, vasoactive intestinal peptidegluconate, L-lactate, L-leucine, L-tryptophan, and L-glutamate; and R is coupled to M through a carboxylate moiety. Magnesium(II) represents the preferred metal ion as magnesium is known to have neuroprotective effects. The metal ion is in part chelated by a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that does not inhibit platelet activity and includes salicylate and ibuprofenate. The complex also includes a ligand operative in transport across the blood brain barrier. A process for making an inventive complex includes the stoichiometric addition of ligands containing carboxylate groups to a solution of the metal ion. In instances where the metal ion is magnesium(II), a stoichiometric ratio of 1:1:1 is found between the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory ligand:magnesium(II):transporter ligand.
Owner:MILLER LANDON C G
2,4,5-trisubstituted imidazole compounds and its preparing process and pharmaceutical use
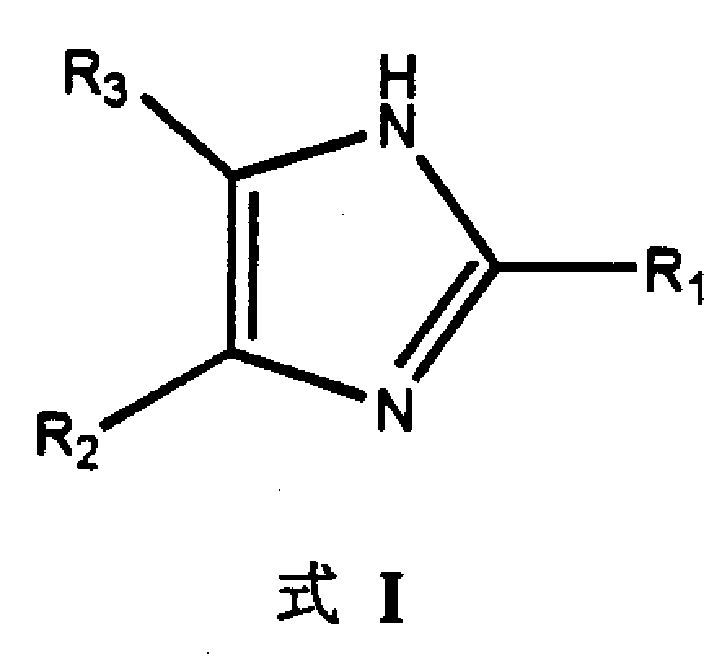
The present invention relates to 2,4,5-trisulbstituted imidazole compounds and their preparation process and their application in preparing medicines for reversing multiple drug resistance of tumor cell mediated by P-glucoprotein, multiple drug resistance relative protein, lung multiple drug resistance relative protein and other membrane transport proteins and restoring the sensitivity of tumor cells with multiple drug resistance to anticancer medicines.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
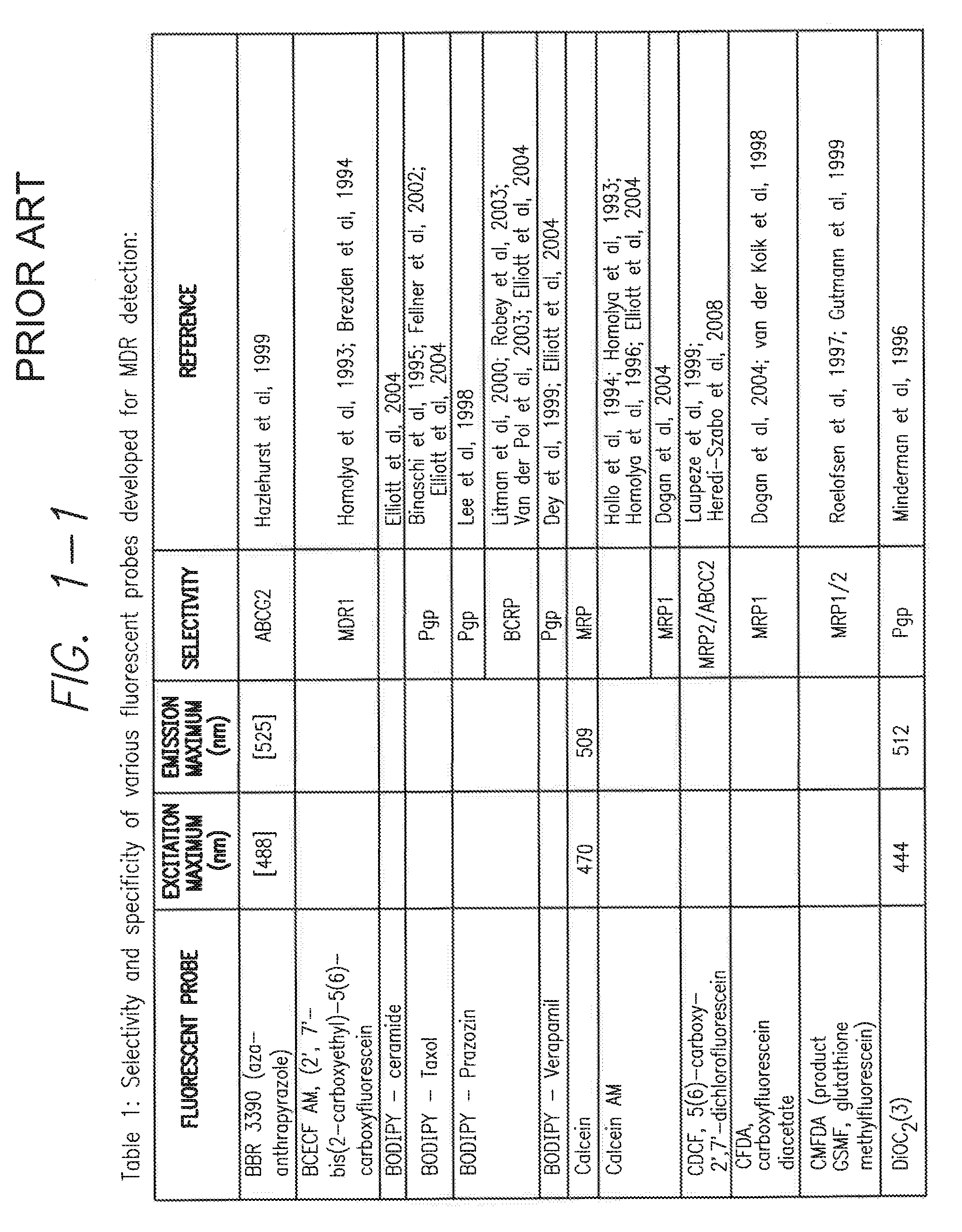
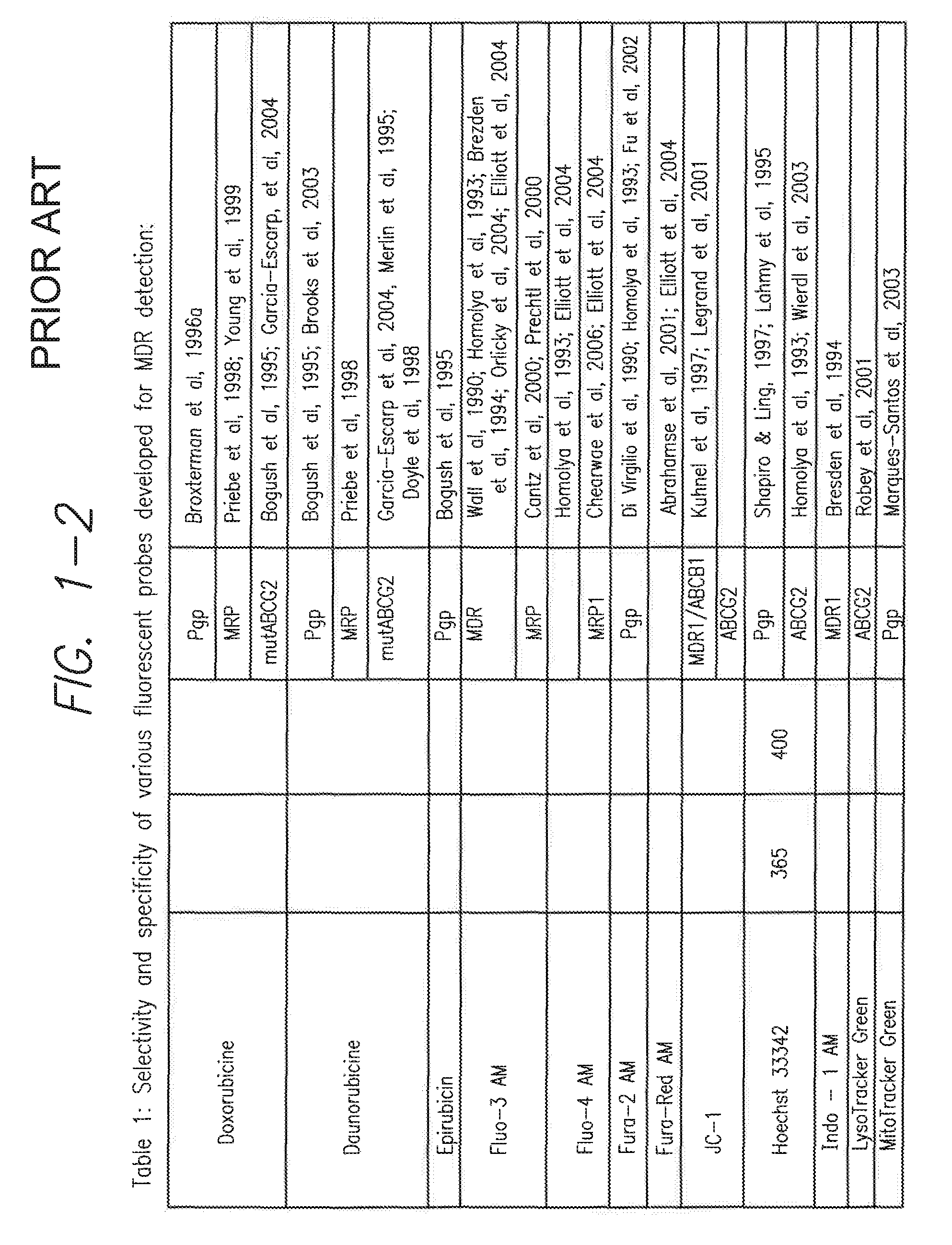
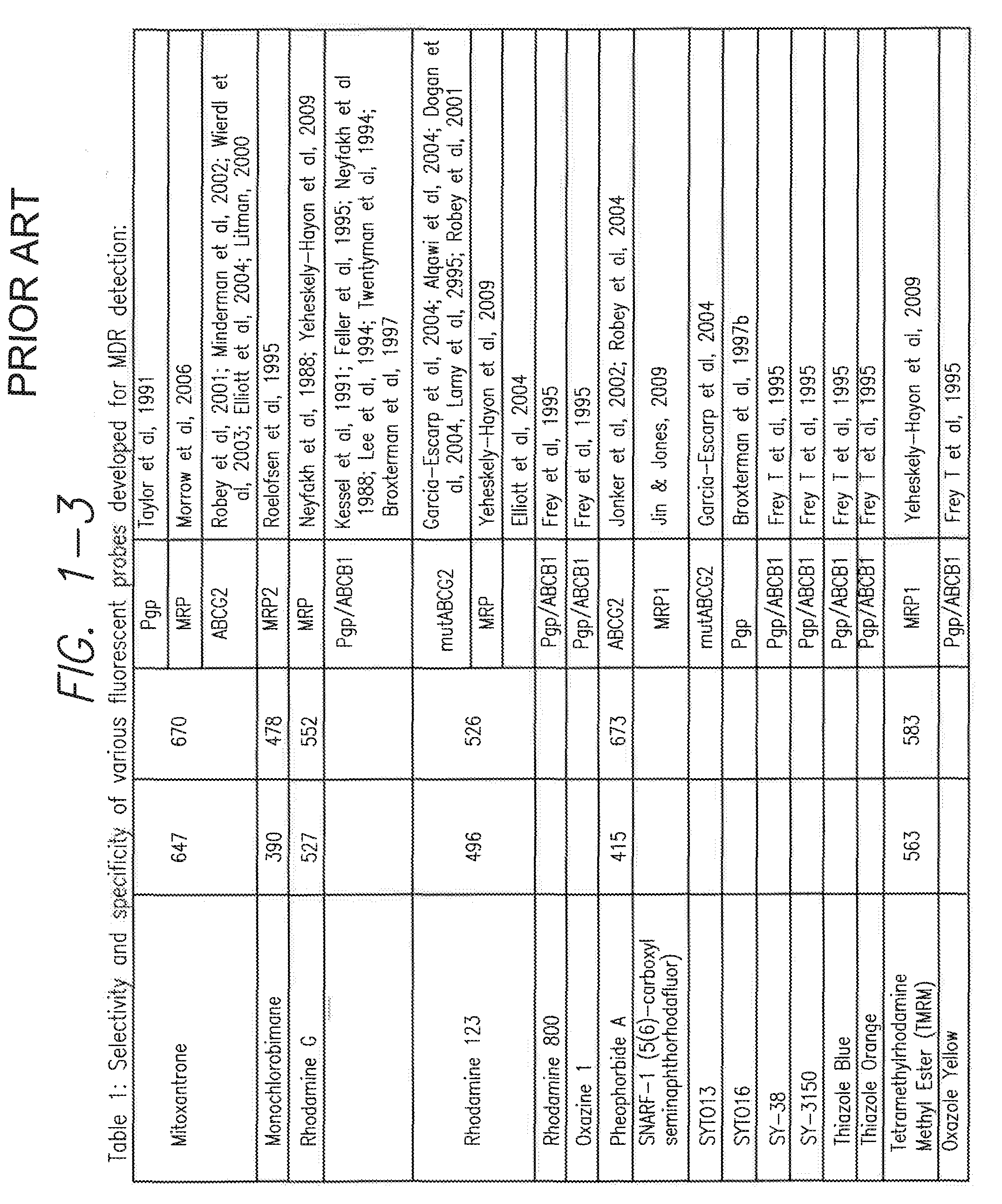
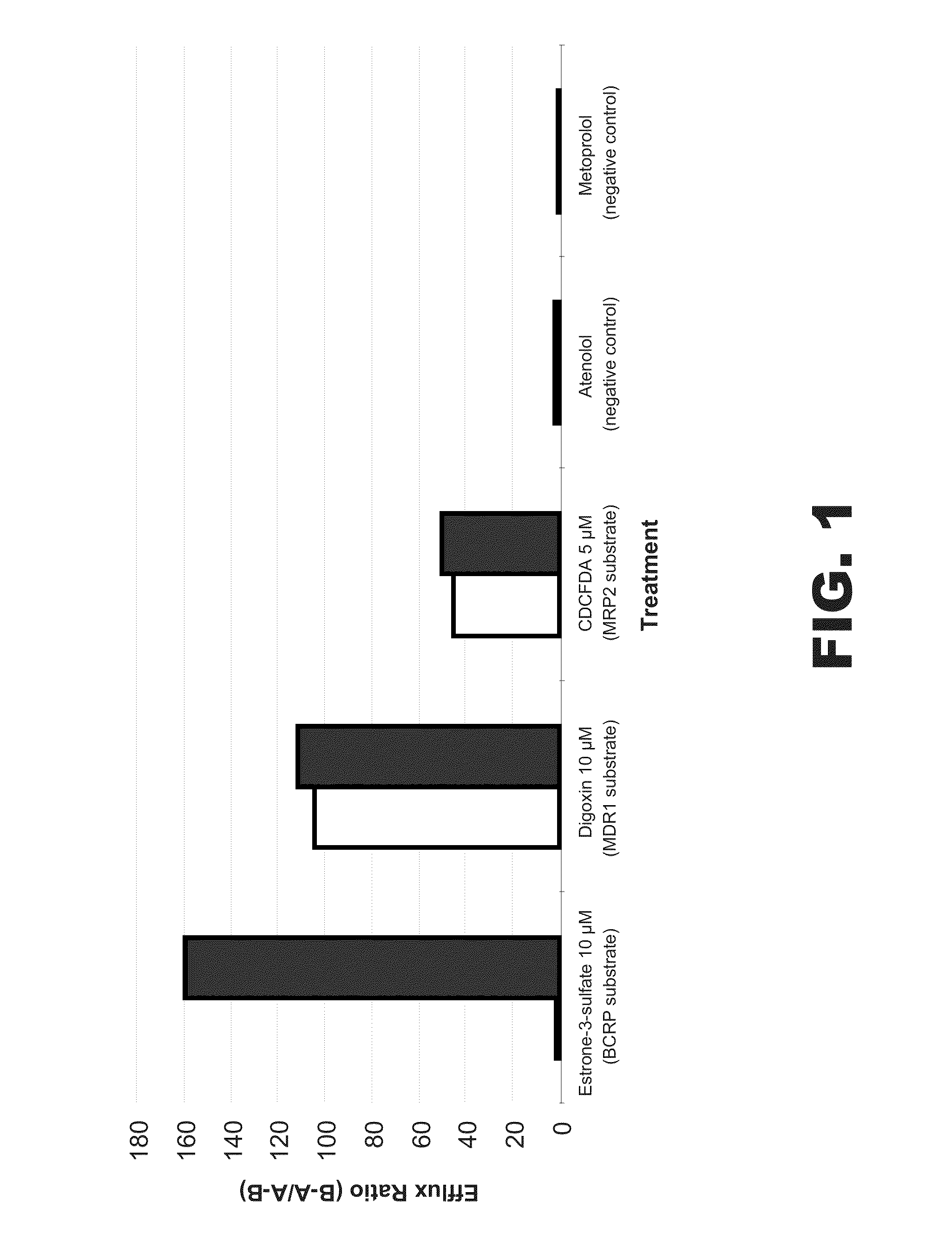
Processes and kits for determining multi-drug resistance of cells
This invention relates to multi-drug resistance (MDR) in cells, and the use of certain xanthene compounds for determining drug resistance in cells and the effect of test compounds on cell membrane transport by the membrane transporters MDR1, MRP and BCRP. Processes and kits for making these determinations and measuring these effects are described and provided.
Owner:ENZO LIFE SCI INC
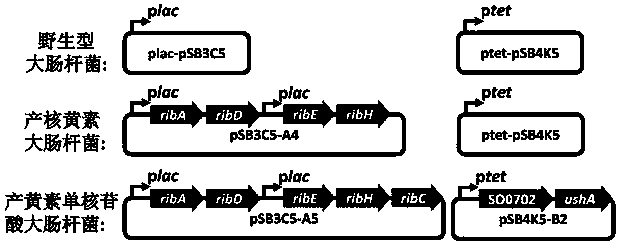
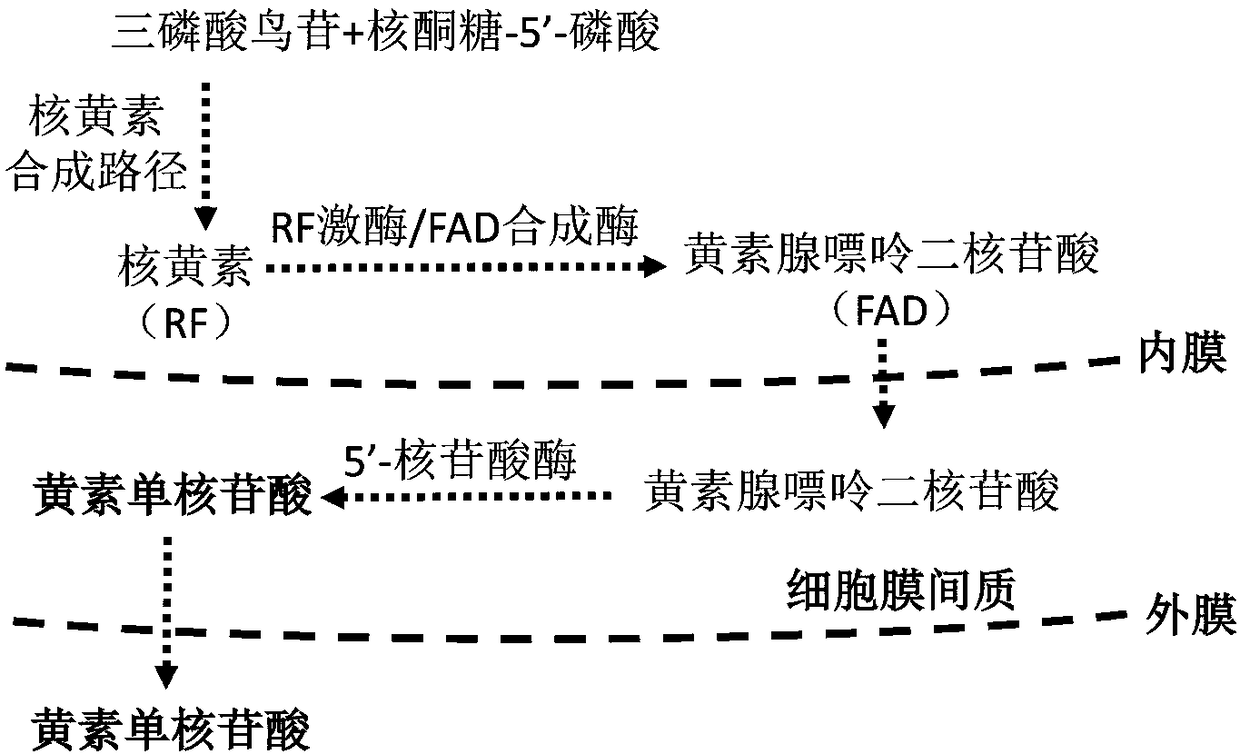
Method for constructing engineering strain for producing flavin mononucleotide, and applications of engineering strain
InactiveCN108330136AHigh purityAchieve eliminationNucleic acid vectorFermentationMembrane TransportersCell membrane
The invention discloses a method for constructing an engineering strain for producing flavin mononucleotide, and applications of the engineering strain. According to the method, by using a synthetic biology technology, an intracellular flavinpool component and endometrial secretion are regulated in newly-constructed or existing riboflavin fermenting bacteria, and an inside-cell-membrane-interstitium enzyme catalytic step is novelly added, such that the high-purity flavin mononucleotide is produced through fermentation with microorganisms; and the method specifically comprises: (1) introducinga bifunctional enzyme riboflavin kinase / flavin adenine dinucleotide producing enzyme into riboflavin fermentation bacteria to convert the intracellular flavinpool component from riboflavin to flavin adenine dinucleotide, (2) introducing a flavin adenine dinucleotide internal membrane transporter, and transporting the intracellular flavin adenine dinucleotide into cell membrane interstitium, and (3) introducing 5'-nucleotidase to lyse and convert the flavin adenine dinucleotide in the cell membrane interstitium into the flavin mononucleotide. According to the present invention, under the shaking fermentation condition, the fermentation purity of the flavin mononucleotide (accounting for the total flavin compounds) can be up to 92.4%.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Use of genes encoding membrane transporter pumps to stimulate the production of secondary metabolites in biological cells
InactiveUS20100170010A1Increase productionIncrease secretionSugar derivativesPeptidesBiological cellBiotechnology
The invention relates to the field of secondary metabolite production in plants and plant cell cultures. More specifically, the invention relates to the use of transporters and more particularly ABC-transporters to enhance the production and / or secretion of secondary metabolites in plants and plant cell cultures.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW +1
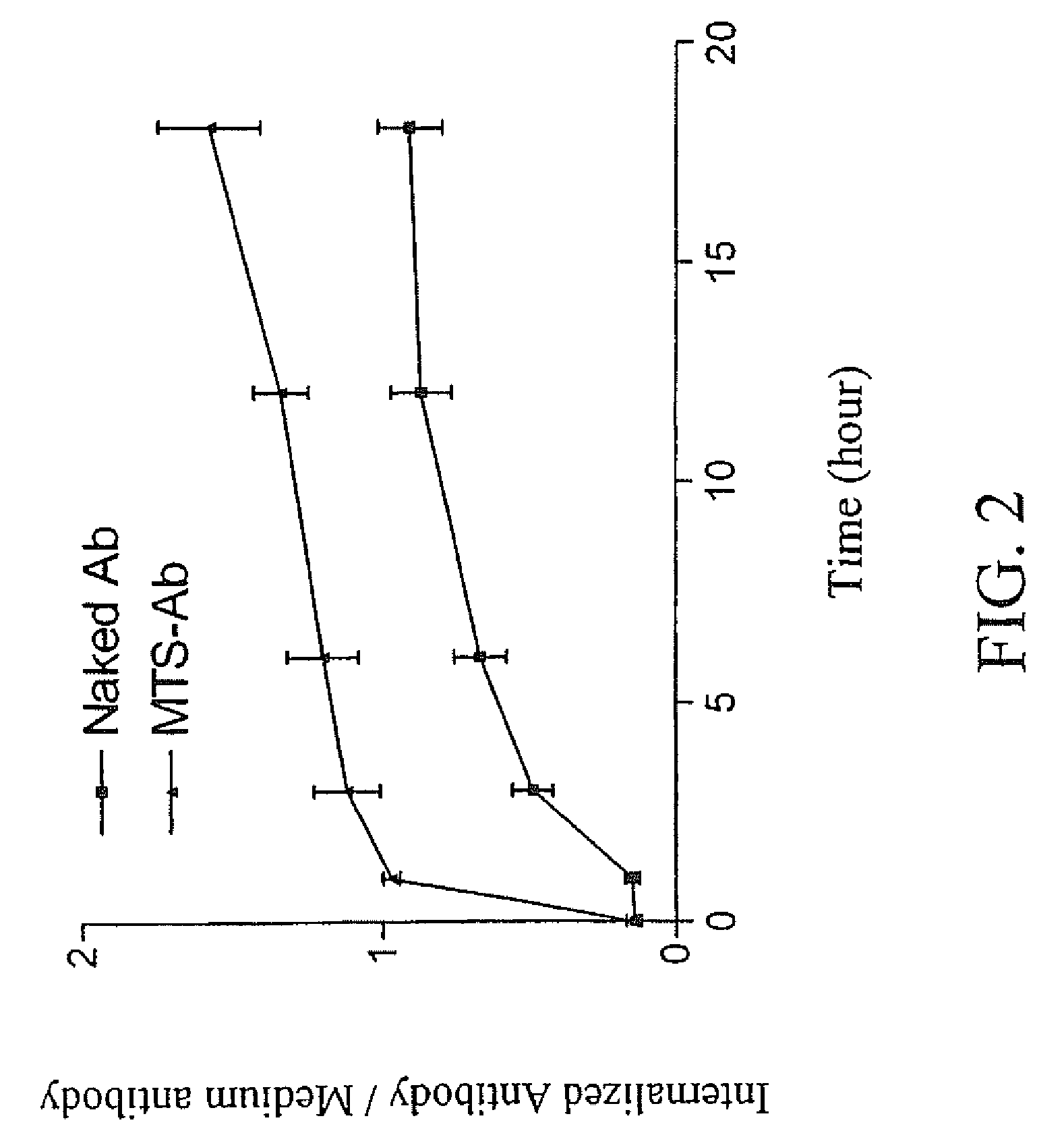
Trans-membrane-antibody induced inhibition of apoptosis
InactiveUS20050033033A1Inhibit apoptosisEffective treatmentHybrid immunoglobulinsNervous disorderAntibody conjugateMembrane Transporters
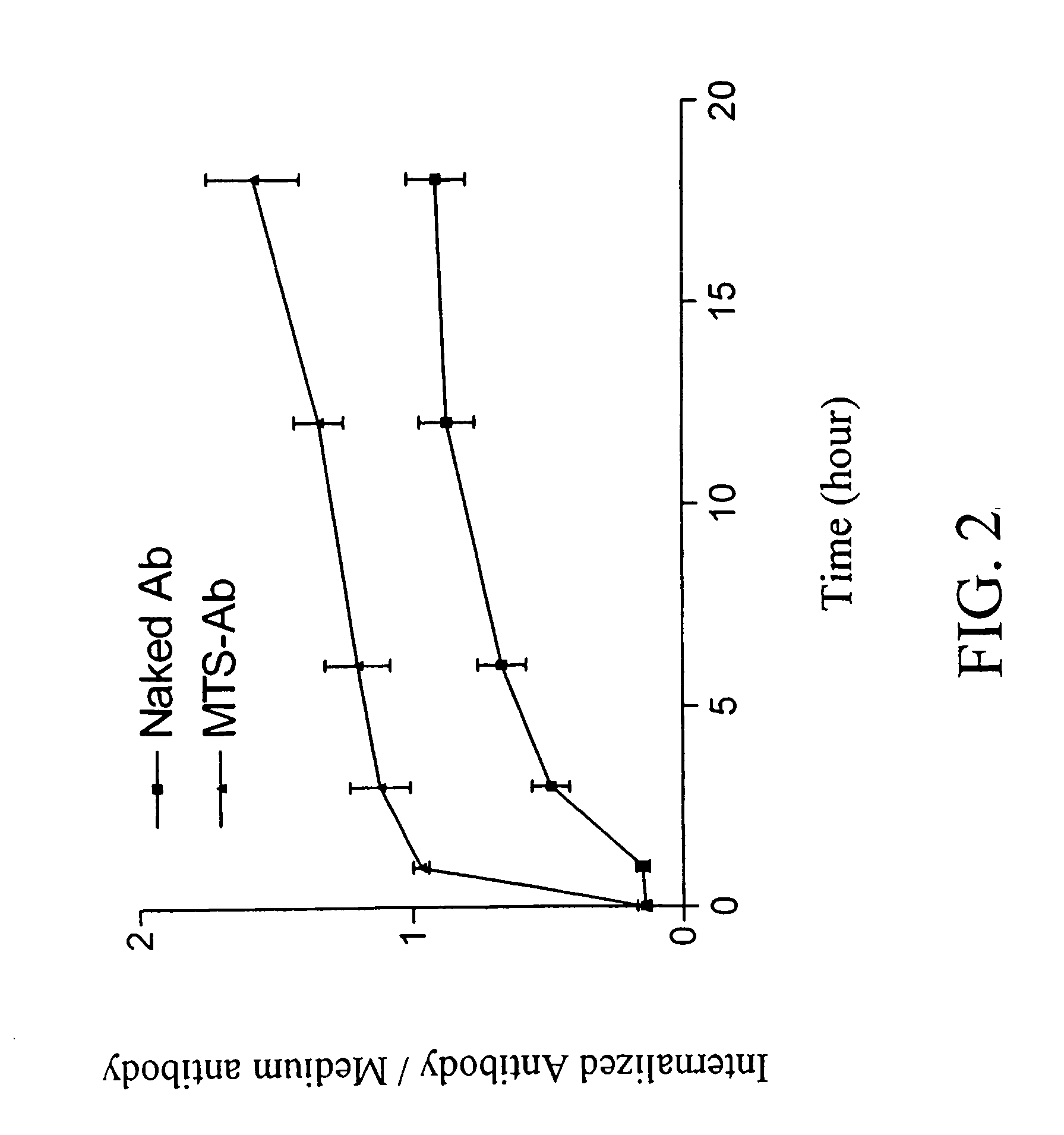
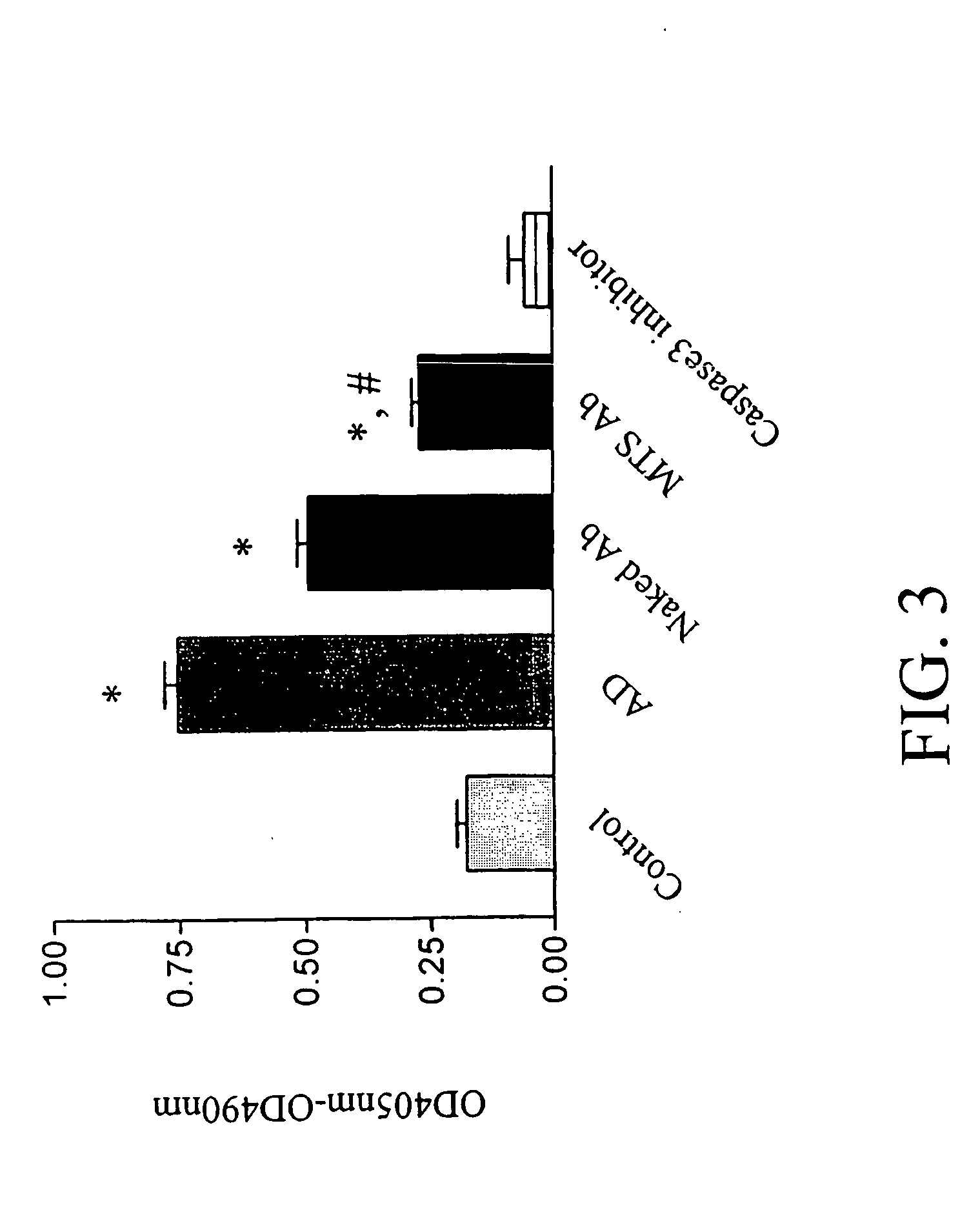
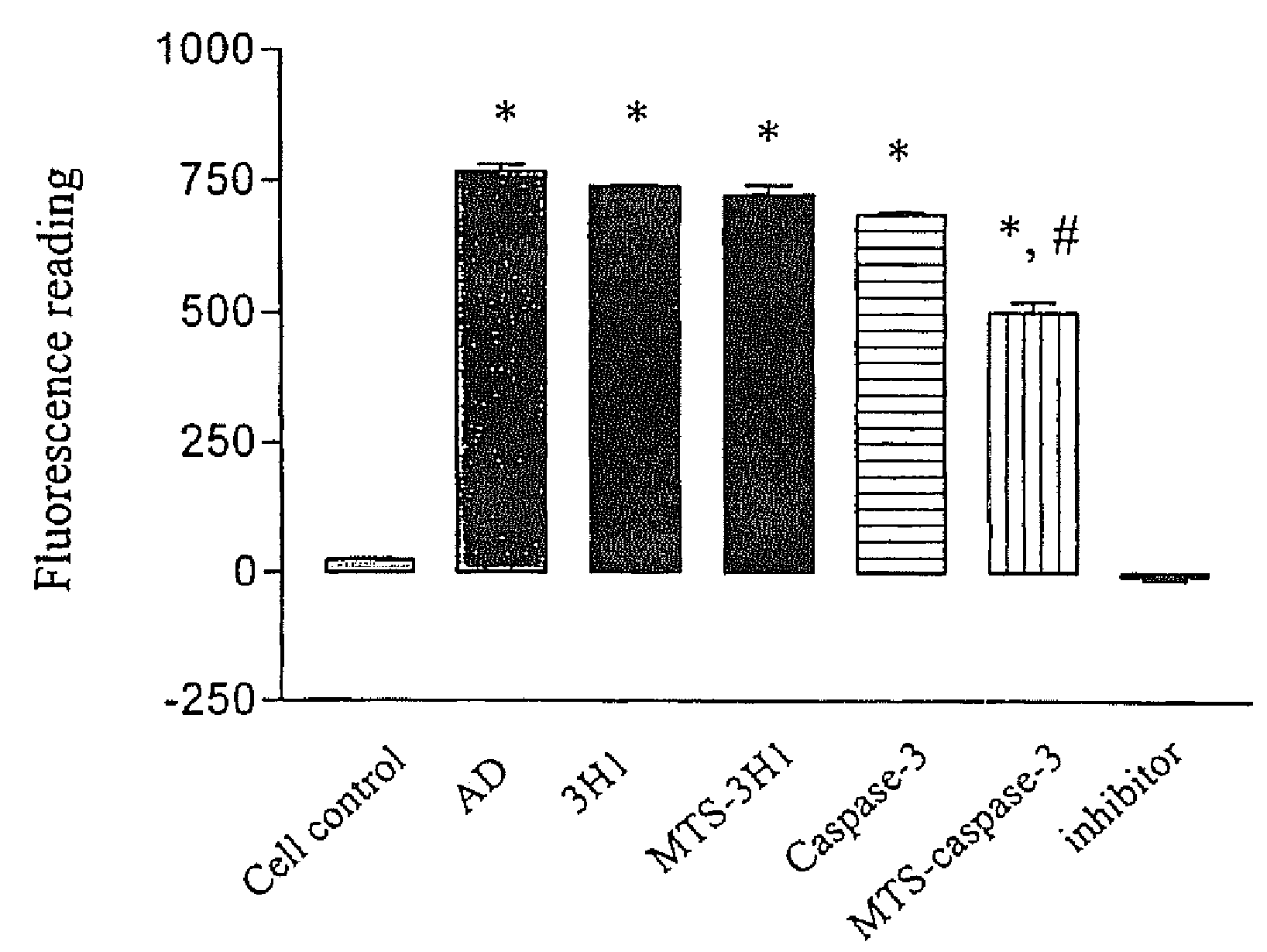
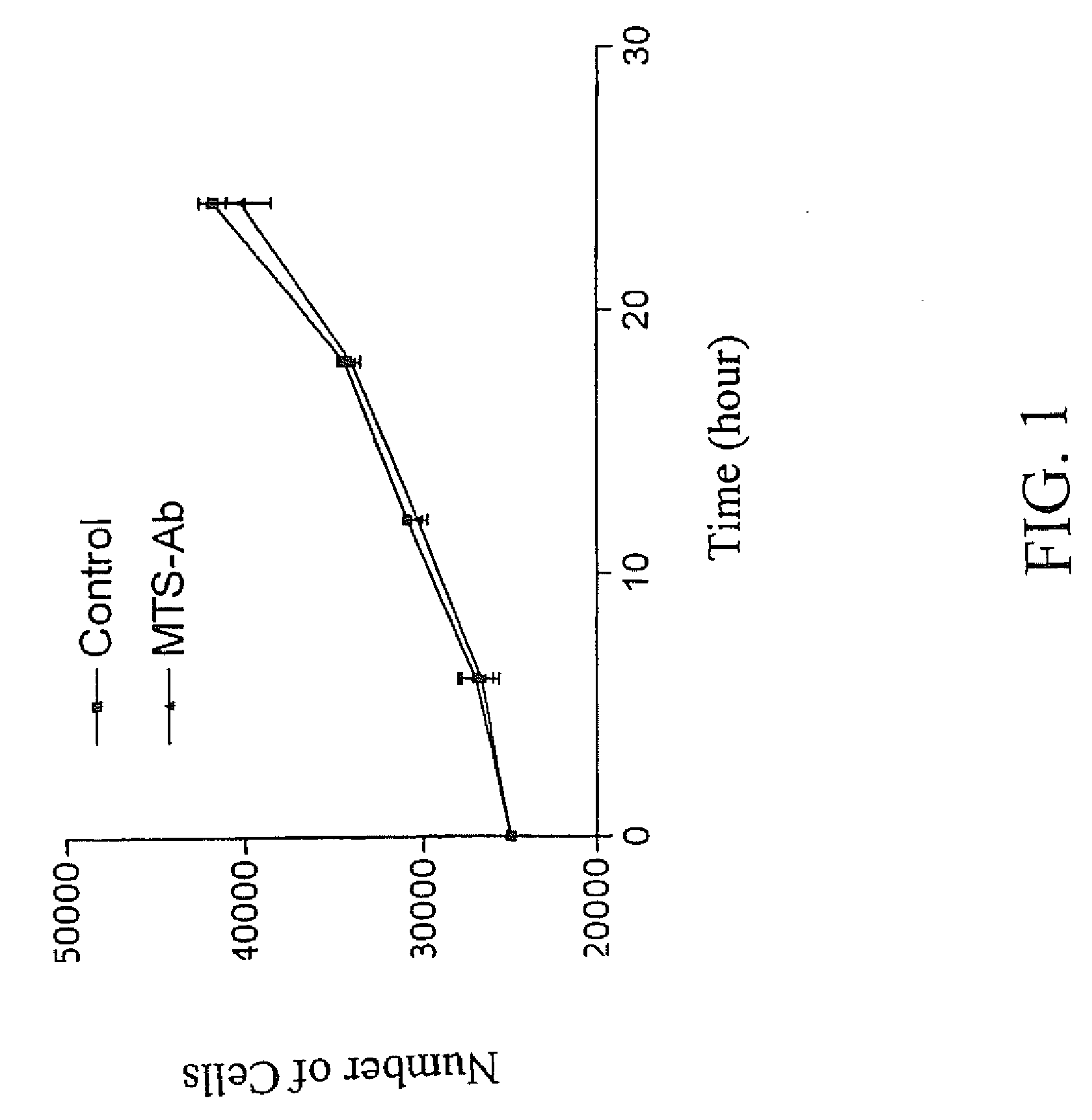
Cell suicide (apoptosis) is associated with pathogenesis, for example, it is the major cause for the loss of neurons in Alzheimer's disease. Caspase-3 is critically involved in the pathway of apoptosis. Superantibody (SAT)-trans-membrane technology has been used to produce antibodies against the caspase enzyme in an effort to inhibit apoptosis in living cells. The advantage of using trans-membrane antibodies as apoptosis inhibitors is their specific target recognition in the cell and their lower toxicity compared to conventional apoptosis inhibitors. It is shown that a MTS-transport-peptide modified monoclonal anti-caspase-3 antibody reduces actinomycin D-induced apoptosis and cleavage of spectrin in living cells. These results indicate that antibodies conjugated to a membrane transporter peptide have a therapeutic potential to inhibit apoptosis in a variety of diseases.
Owner:INNEXUS BIOTECHNOLOGY INT LTD
Processes and kits for determining multi-drug resistance of cells
ActiveUS20110269168A1Prevent outflowAnimal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementMembrane TransportersChemical compound
This invention relates to multi-drug resistance (MDR) in cells, and the use of certain xanthene compounds for determining drug resistance in cells and the effect of test compounds on cell membrane transport by the membrane transporters MDR1, MRP and BCRP. Processes and kits for making these determinations and measuring these effects are described and provided.
Owner:ENZO LIFE SCI INC
Gene capable of regulating and controlling inhibition of vitamin C fermented strain acid production during acid stress
InactiveCN102286614AReduce outputMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMembrane TransportersBasic research
The invention relates to a gene capable of regulating and controlling inhibition of vitamin C fermented strain acid production during acid stress and belongs to the technical fields of basic research on vitamin C prepared by fermentation and biological engineering. The key gene for regulating and controlling yield reduction of acid stress induced 2-Keto-L-Gulonic acid (2-KLG) in the production strains is determined, so a metabolic engineering strategy with high pertinence is generated. The expression condition of genes, in particular membrane transport protein genes, of acid-forming bacteria in the vitamin C mixed bacteria fermented system is analyzed by an expression profile chip technology. Compared with ketogenic gulonic acid bacteria subjected to single cultivation, the ketogenic gulonic acid bacteria subjected to mixed bacteria cultivation have 45 upregulated membrane transport protein genes and 15 down regulated membrane transport protein genes. The notable thing is that: 7 iron ion transport protein genes are inhibited to express. After acid stress, the iron ion transport protein genes are over expressed. During fermentation, the iron ions are added to inhibit mixed bacteria to ferment and generate acid. The result shows that the iron ion transport protein exerts reverse action in the process of yield reduction of 2-KLG generated by the acid stress induced mixed bacteria fermentation.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Use of genes encoding membrane transporter pumps to stimulate the production of secondary metabolites in biological cells
InactiveUS7622634B2Increase productionAvoid toxicityAlgae productsSugar derivativesBiological cellBiotechnology
The invention relates to the field of secondary metabolite production in plants and plant cell cultures. More specifically, the invention relates to the use of transporters and more particularly ABC-transporters to enhance the production and / or secretion of secondary metabolites in plants and plant cell cultures.
Owner:VTT BIOTECH +1
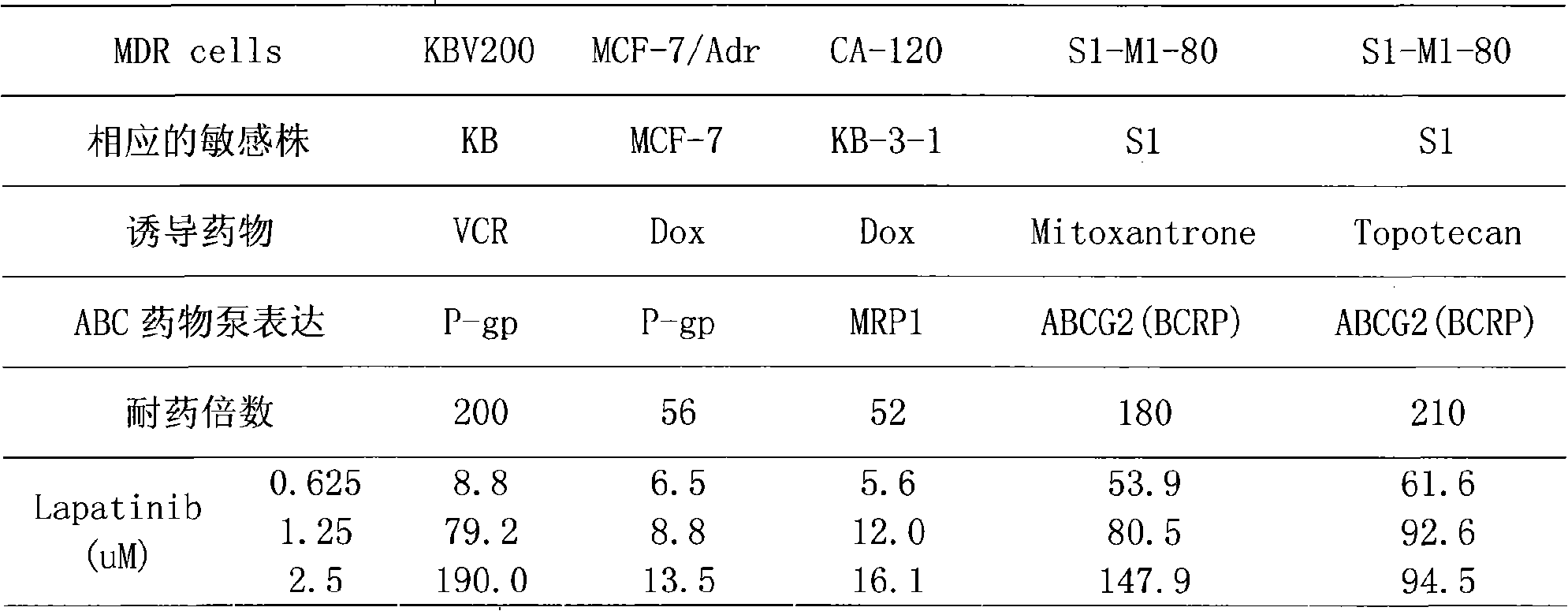
Use of lapatinib for reversing multi-drug resistance of tumor
InactiveCN101406475ASignificant reversal in vivo and in vitroSignificant reversalOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCatharanthineMembrane Transporters
The invention relates to the multi-drug resistance (MDR) of Lapatinib (formula 1) in reversing tumour cells which are mediated by membrane transport proteins (ABC) families such as P-glycoprotein (P-gp), multi-drug resistance related protein (MRP1), breast cancer multi-drug resistance related proteins (ABCG2 and BCRP) and the like. The Lapatinib is used together with anti-cancer drugs such as anthracyclines, catharanthines, taxols, podophyllotoxins, camptothecins and the like to restore the sensitivity of MDR tumor cells to the anticancer drugs. The Lapatinib is applied to combination chemotherapy of drug-resistant patients in clinical chemotherapy or the prevention of drug-resistance generation for the tumor cells.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
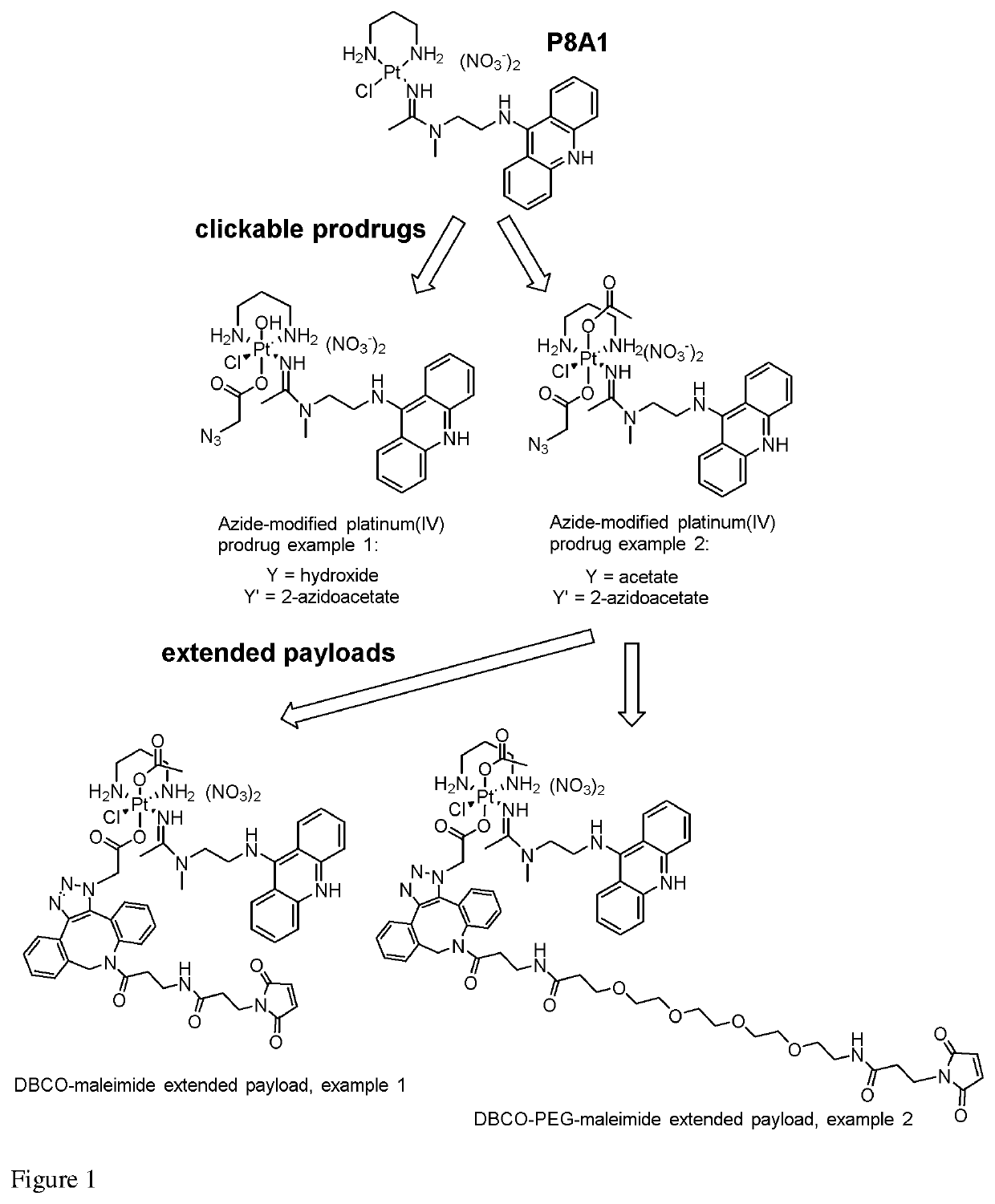
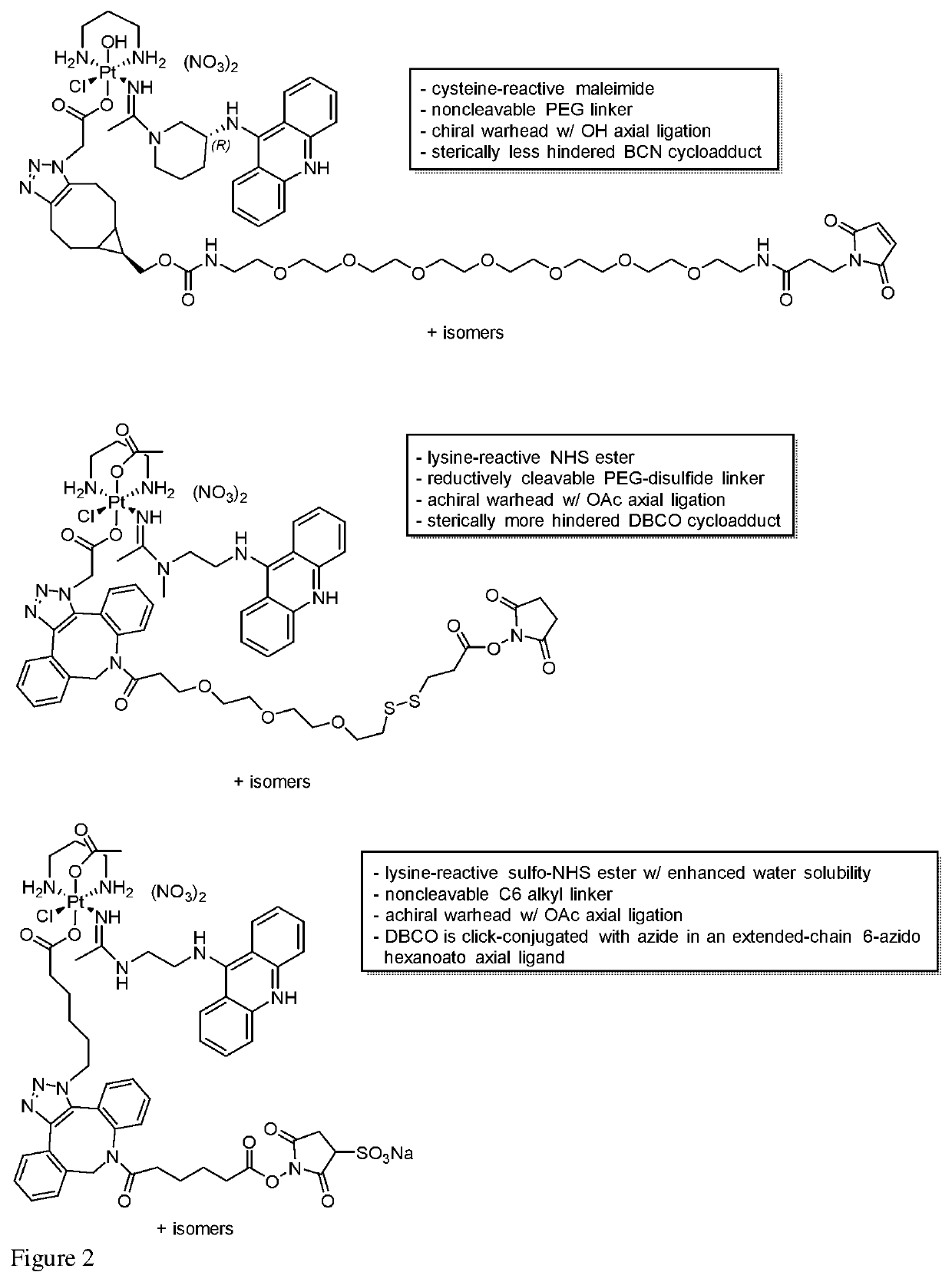
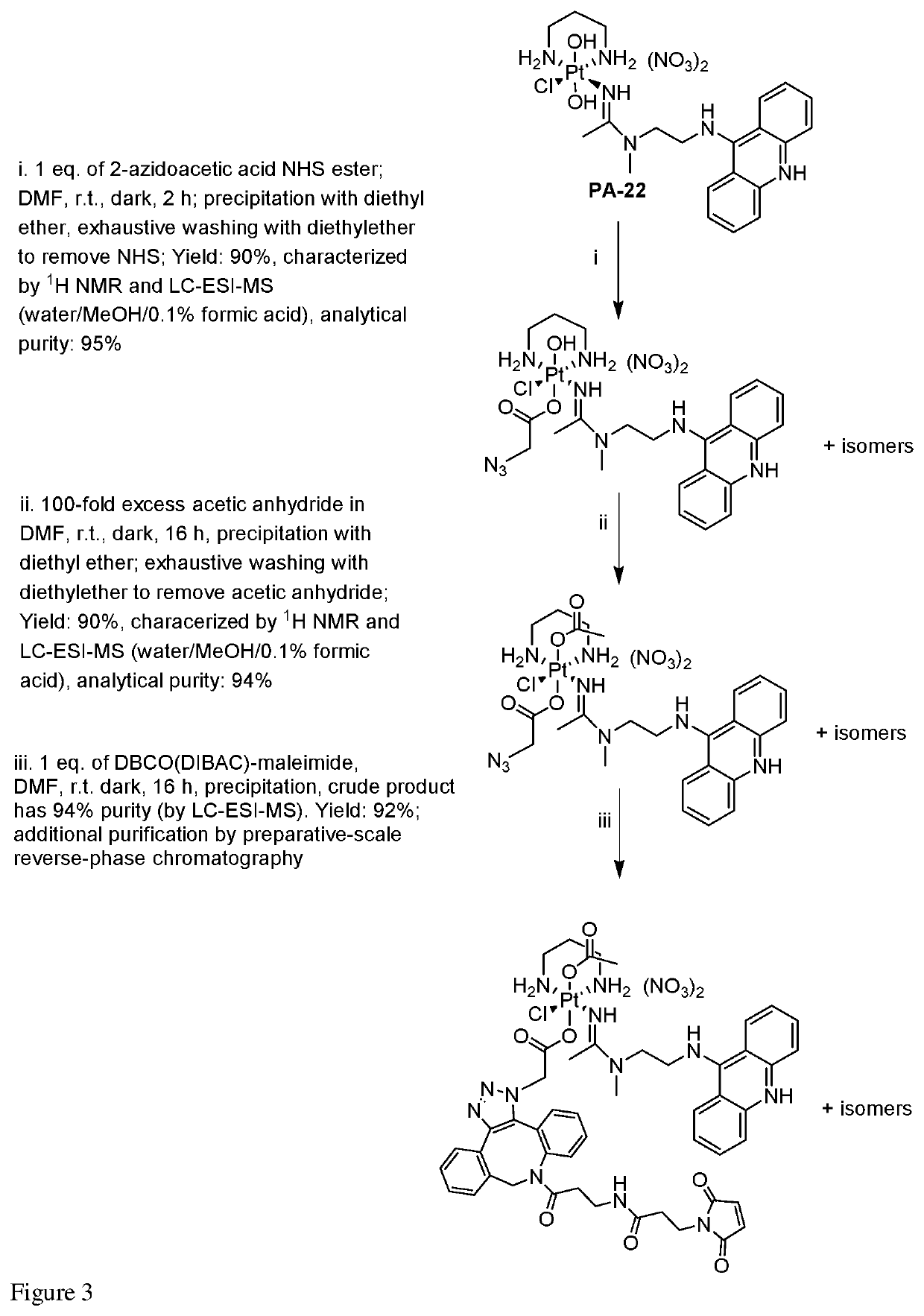
Platinum-acridine compounds and methods of treating cancers
PendingUS20210330679A1Platinum organic compoundsDepsipeptide ingredientsAcridineMembrane Transporters
Platinum-acridines and analogs thereof as cytotoxic agents for cancer treatment. Also provided methods of using hMATE1 (SLC47A1) as a biomarker to identify tumors that are likely to respond to the agents, and epigenetically sensitizing tumor tissue to anticancer drugs targeting this membrane transporter.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV
Gene capable of regulating and controlling inhibition of vitamin C fermented strain acid production during acid stress
InactiveCN102286614BReduce outputMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBiotechnologyVitamin C
The invention relates to a gene capable of regulating and controlling inhibition of vitamin C fermented strain acid production during acid stress and belongs to the technical fields of basic research on vitamin C prepared by fermentation and biological engineering. The key gene for regulating and controlling yield reduction of acid stress induced 2-KLG in the production strains is determined, so a metabolic engineering strategy with high pertinence is generated. The expression condition of genes, in particular membrane transport protein genes, of specific microorganisms in the microorganisms subjected to mixed cultivation is analyzed by an expression profile chip technology. Compared with ketogenic gulonic acid bacteria subjected to single cultivation, the ketogenic gulonic acid bacteria subjected to mixed bacteria cultivation have 45 upregulated membrane transport protein genes and 15 downregulated membrane transport protein genes. The notable thing is that: 7 iron ion transport protein genes are inhibited to express. After acid stress, the iron ion transport protein genes are overexpressed. During fermentation, the iron ions are added to inhibit mixed bacteria to ferment and generate acid. The result shows that the iron ion transport protein exerts reverse action in the process of yield reduction of 2-KLG generated by the acid stress induced mixed bacteria fermentation.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Trans-membrane-antibody induced inhibition of apoptosis
InactiveUS20090274710A1Nervous disorderHybrid immunoglobulinsAntibody conjugateMembrane Transporters
Owner:INNEXUS BIOTECHNOLOGY INT LTD
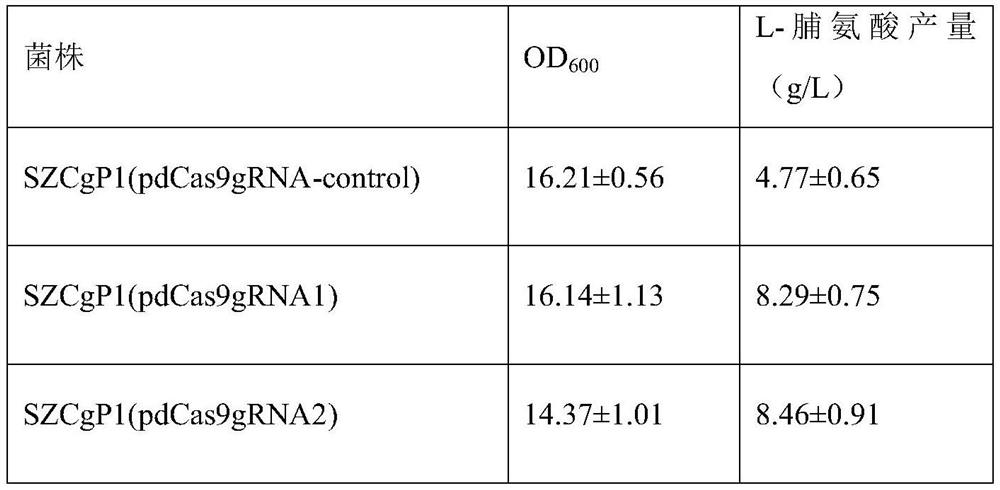
Bacterial strain for producing L-proline as well as construction method and application of bacterial strain
PendingCN114874958AIncrease productionHas industrial application valueBacteriaBiofuelsMembrane TransportersMicrobiology
The invention discloses a strain for producing L-proline as well as a construction method and application of the strain. Through screening, the inactivation of the two membrane transporters can improve the yield of the L-proline in the L-proline producing strain. The discovery of the invention can provide new thoughts and targets for technicians in the field to construct the L-proline production strain, that is, not only concern on the transformation of the L-proline synthesis route, but also increase the yield of the strain through inactivation of the membrane transporter, thereby providing reference for constructing the production strain with higher yield of L-proline.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Cells having disrupted expression of proteins involved in adme and toxicology processes
The present invention provides cells comprising disrupted expression of at least one membrane transporter, drug metabolizing enzyme, xenobiotic sensor, or cellular stress response pathway protein. Also provided are methods for assessing the effect of an agent in the cells disclosed herein relative to comparable control cells.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Membrane transporters and uses thereof
Recombinant cells expressing membrane transporters, and methods of their use in various applications, are provided. These applications include, but are not limited to, industrial biotechnology, and reproduction / simulation of biochemical pathways or components thereof (e.g., photosynthetic pathways or components thereof). The recombinant cells may be provided as a component of a transgenic organism (e.g., a transgenic plant).
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
Membrane transporter assay and methods of use
InactiveUS20190094204A1Quick measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMembrane TransportersProviding material
Owner:HOWARD HUGHES MEDICAL INST
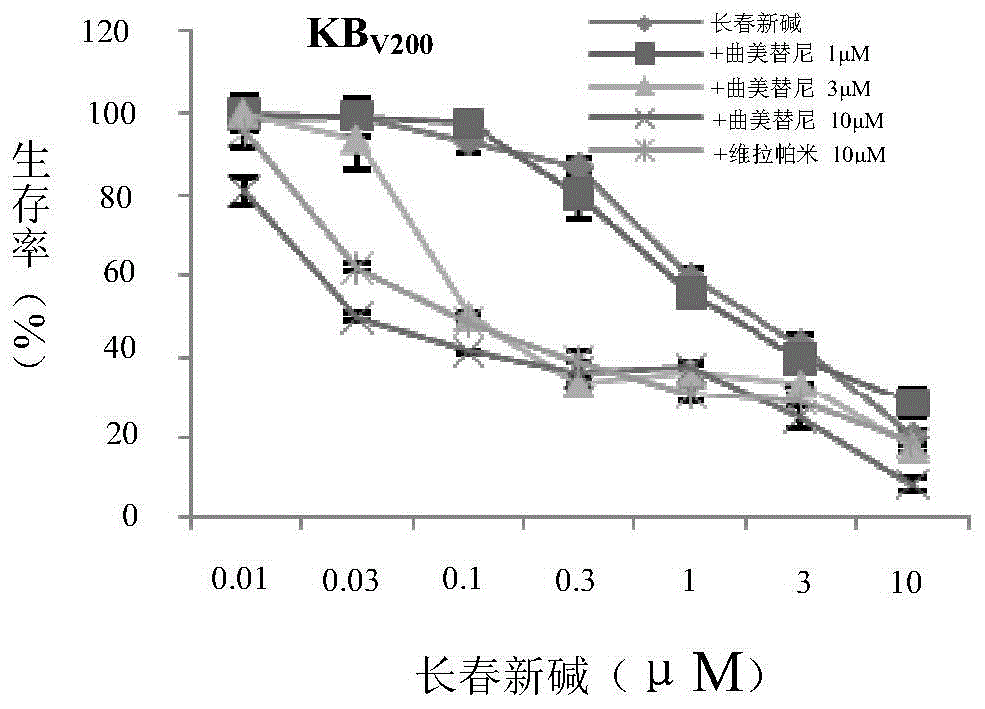
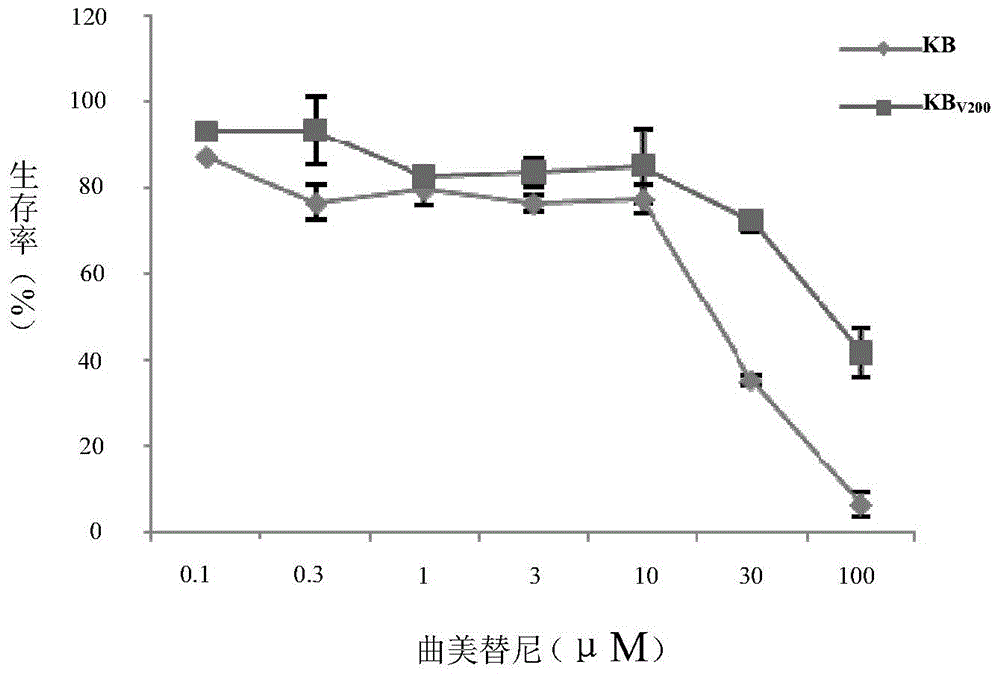
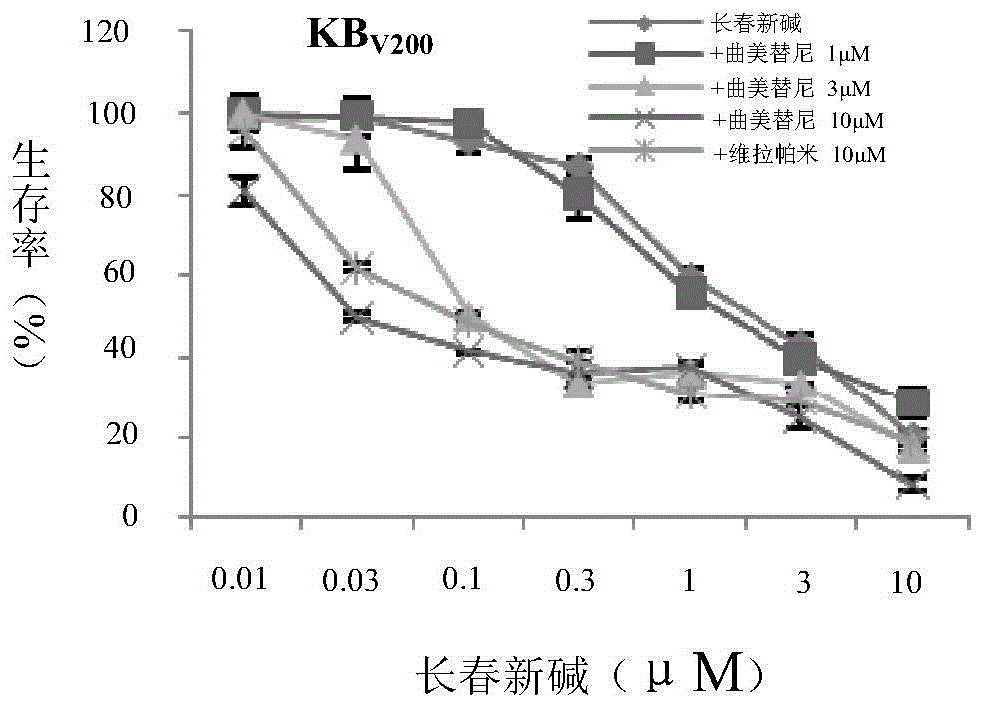
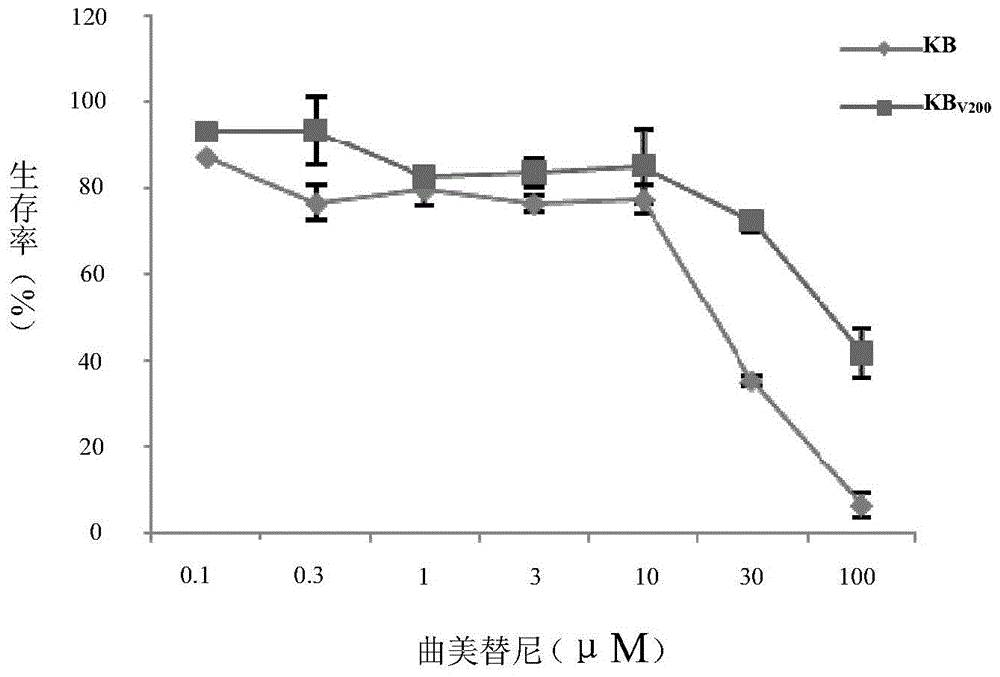
Application of trametinib in preparing medicine for reversing multi-medicine resistance of tumors
ActiveCN104434924AReverse multidrug resistanceRestore sensitivityOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsMembrane TransportersMembrane transport protein
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine application, and discloses an application of trametinib in preparing a medicine for reversing multi-medicine resistance of tumors. Trametinib can be used for significantly reversing the multi-medicine resistance of the tumors mediated by membrane transport protein to ensure that the sensitivity of P-glycoprotein high expression cells to anti-cancer medicines can be restored. According to the medicine for reversing the multi-medicine resistance of the tumors, disclosed by the invention, trametinib and the anti-cancer medicines can be combined to ensure that the effects of treating and controlling resistant tumors can be achieved by restoring the sensitivity of resistant cells to the anti-cancer medicines.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
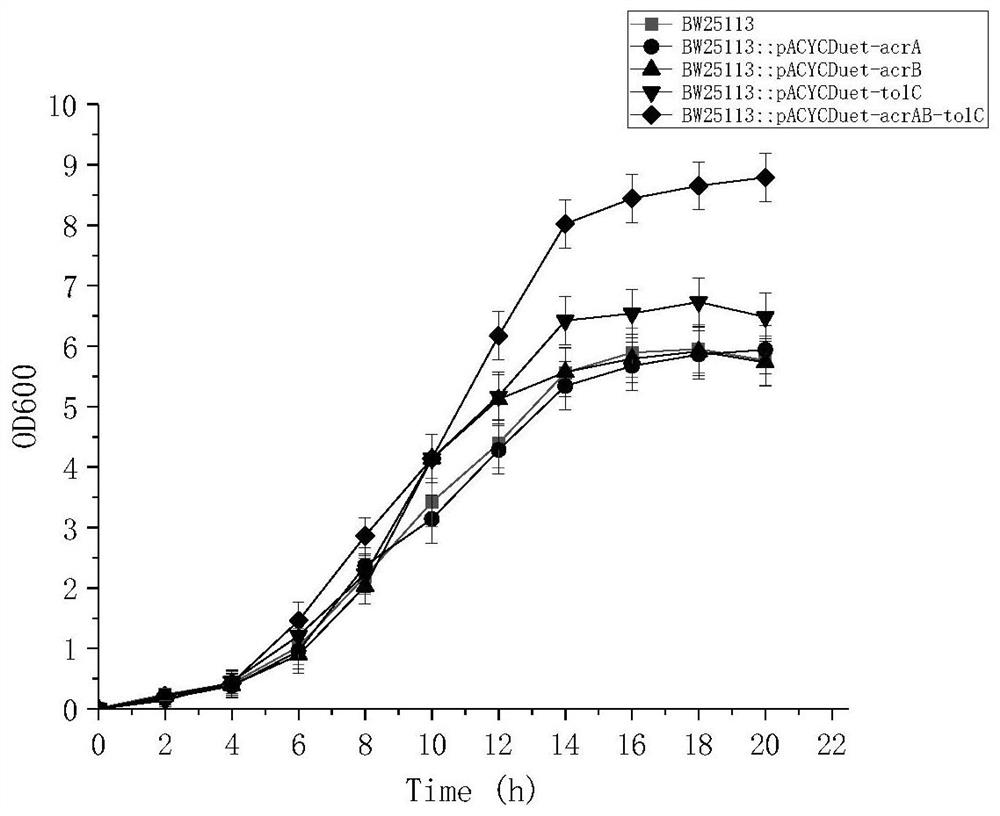
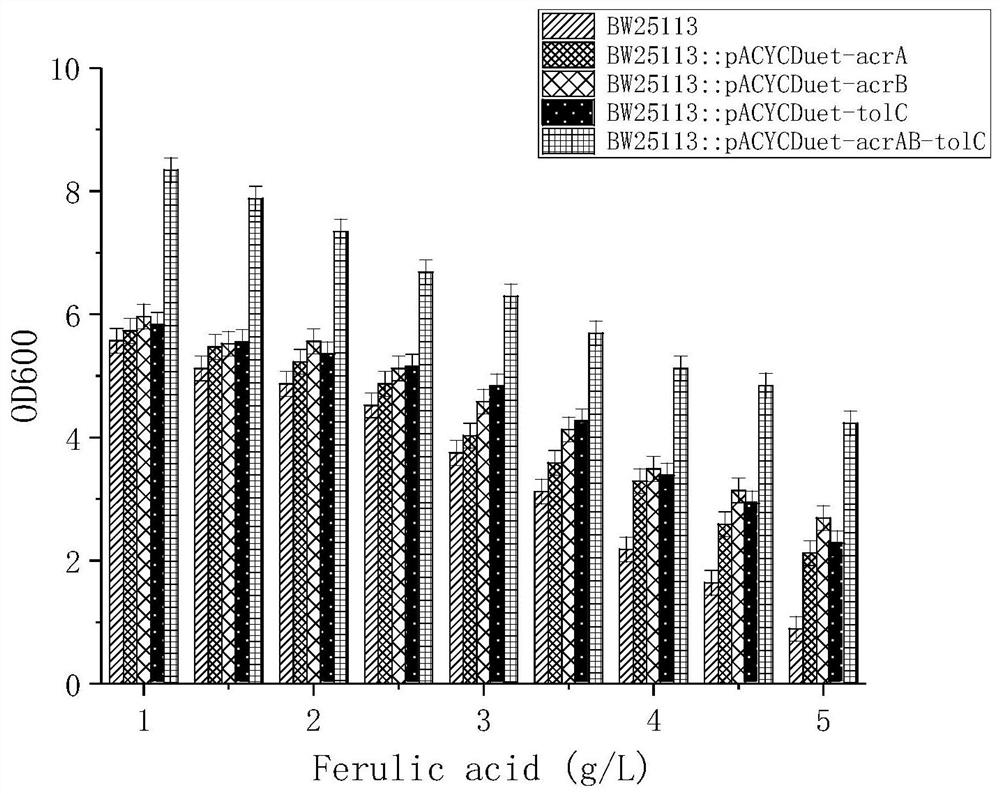
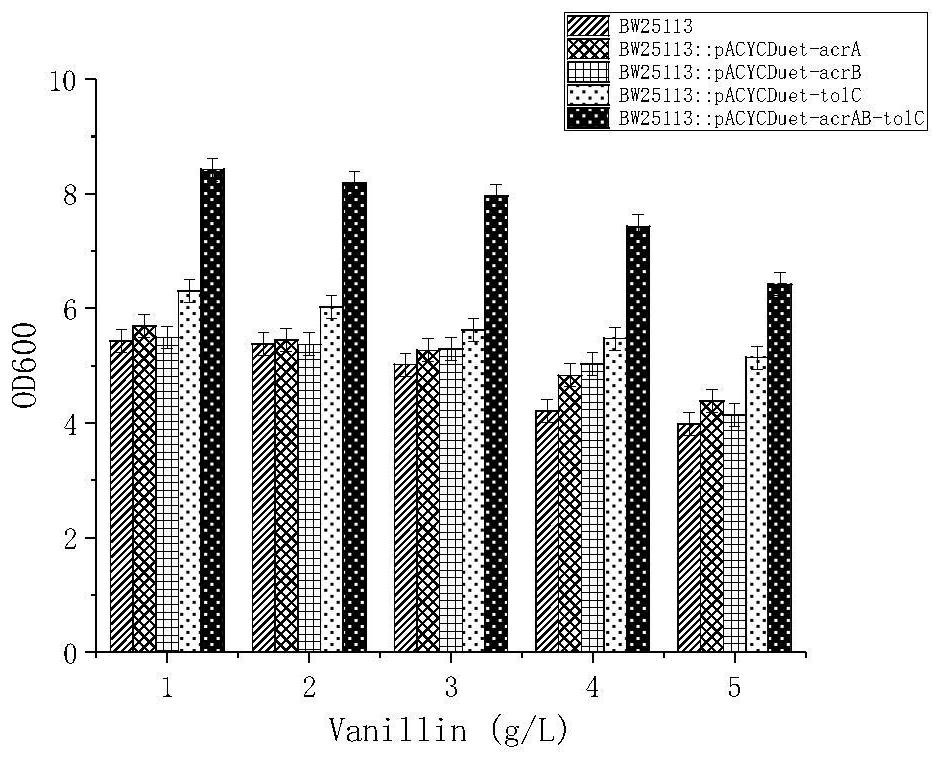
A kind of recombinant gene engineering bacterium and its fermentative application to produce vanillin
ActiveCN110257312BIncrease concentrationImproving the ability of fermentation to produce vanillinBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMembrane TransportersLarge intestine
The invention discloses a recombinant genetically engineered bacterium and its application to produce vanillin by fermentation. The genes of vanillin or ferulic acid include one or more of the periplasmic membrane fusion protein AcrA gene, the inner membrane transport protein AcrB gene or the outer membrane protein TolC gene; the host includes the large intestine containing the ech gene and the fcs gene bacilli. The recombinant genetically engineered bacteria E.coli BW25113::PegYB::pACYCDuet-acrAB-tolC of the present invention can use ferulic acid as a substrate to produce vanillin, and the highest yield of vanillin is 2335 mg / L. The fermented liquid fermented by the method of the invention contains higher vanillin and has good application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
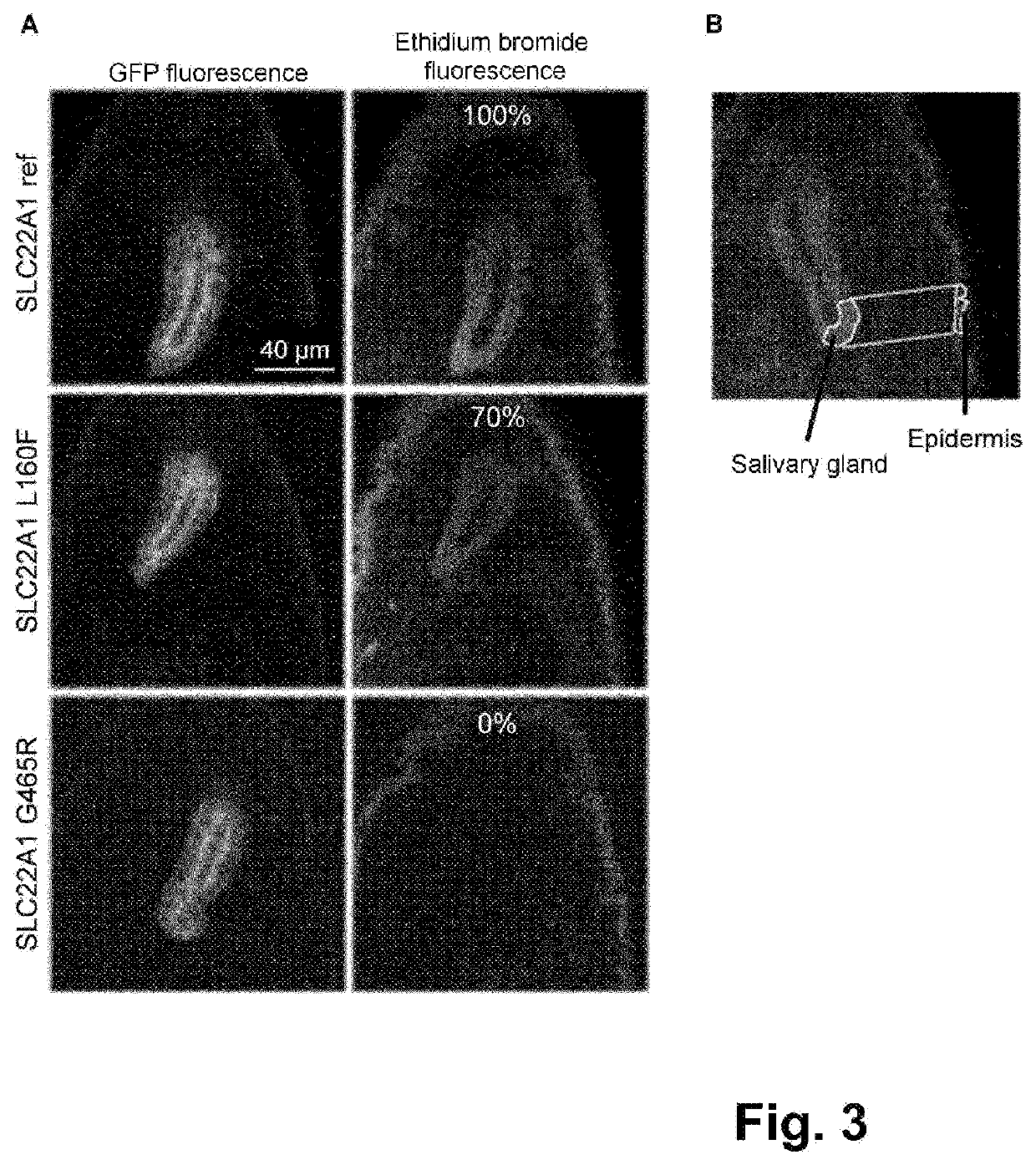
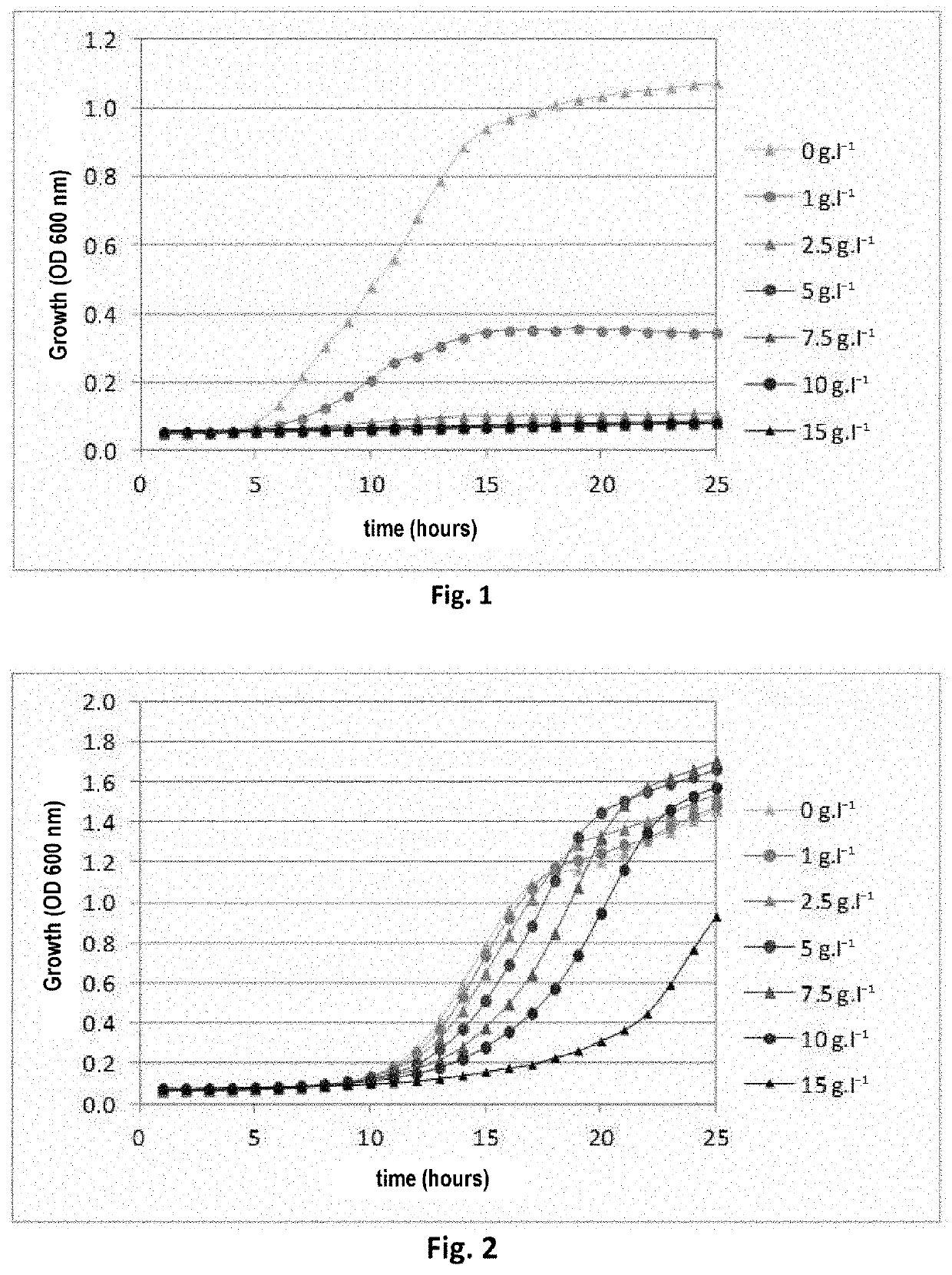
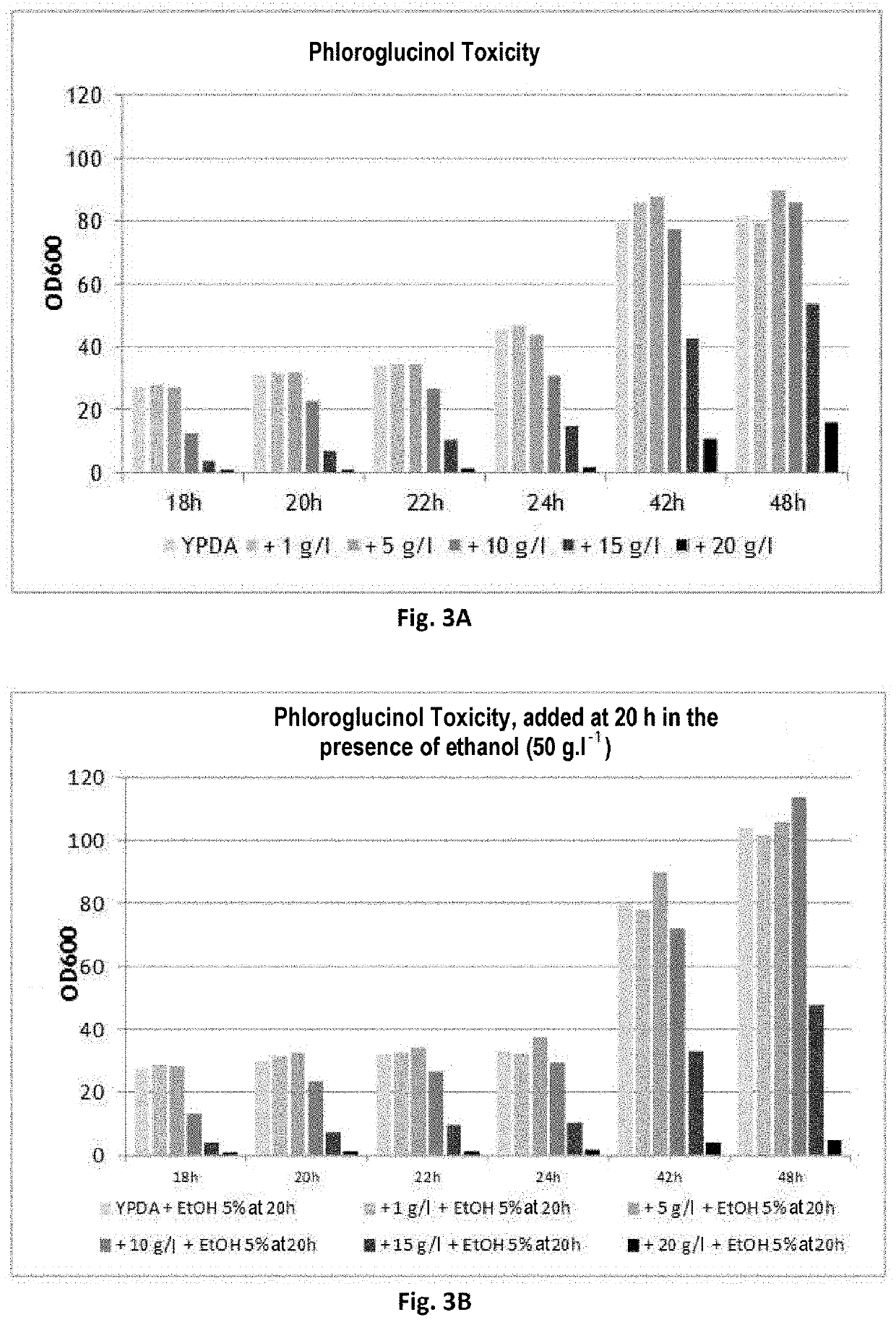
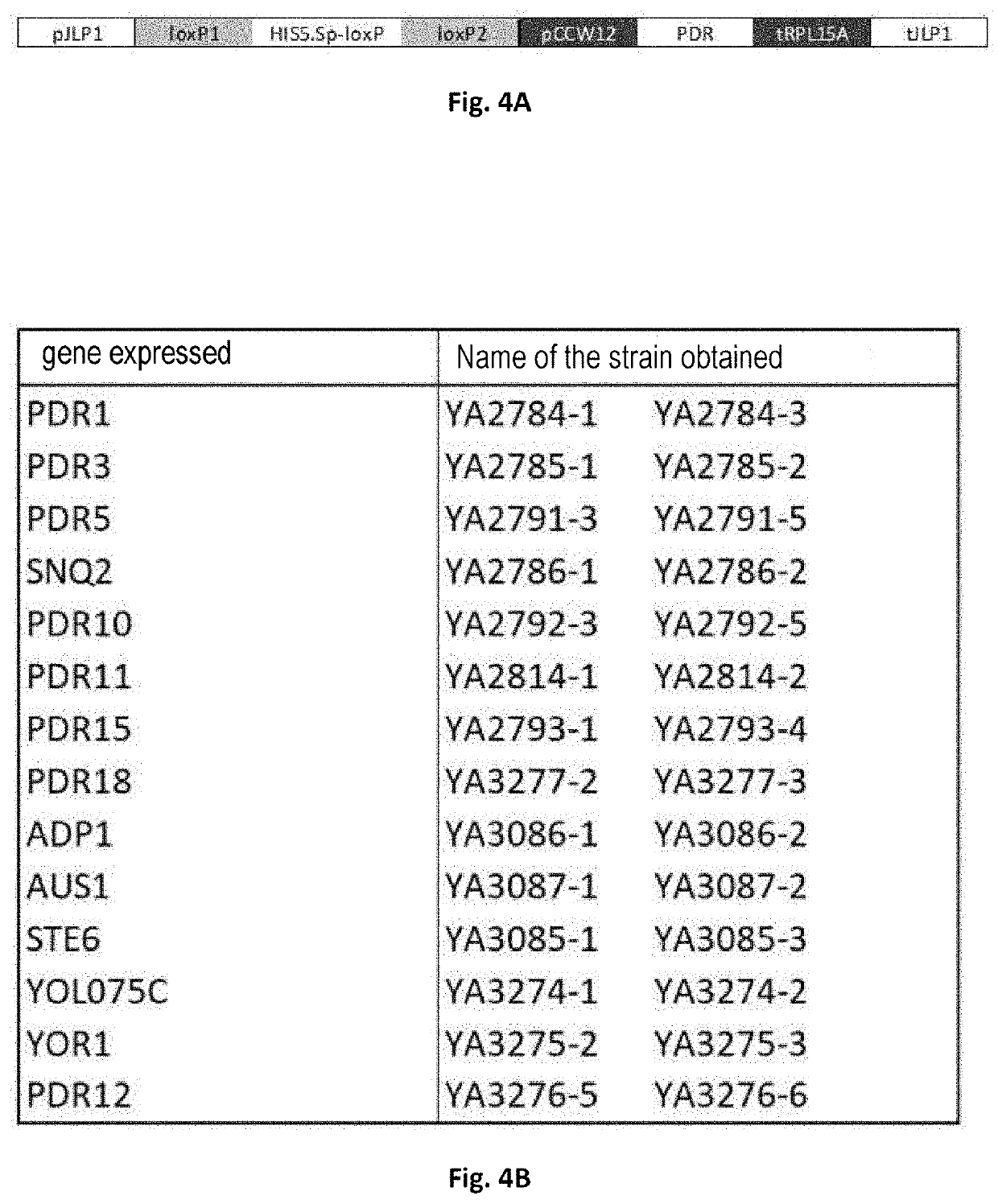
Phloroglucinol-resistant cell, in particular yeast
PendingCN113412329AFungiCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMembrane TransportersLiving cell
The present invention relates to a living cell, preferably a host cell, that is phloroglucinol-resistant. The host cell is characterised in that it overexpresses a polypeptide selected from (i) transmembrane transporters of the ABC family, in particular transmembrane transporters of the PDR subfamily, (ii) transcription factors controlling the expression of the transmembrane transporters of the PDR subfamily, and (iii) transmembrane transporters of the MFS family; preferably a polypeptide selected from SNQ2, STE6, PDR3, AQR1, DTR1, FLR1, QDR1, YHK8 and ATR1; and more preferably the SNQ2 transporter. The present invention also relates to a method for producing the phloroglucinol-resistant recombinant host cell. The present invention also relates to a method for producing phloroglucinol.
Owner:MICHELIN & CO CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN
Application of cucumis sativus CsHMGB gene in reducing pesticide residue and relieving pesticide toxicity
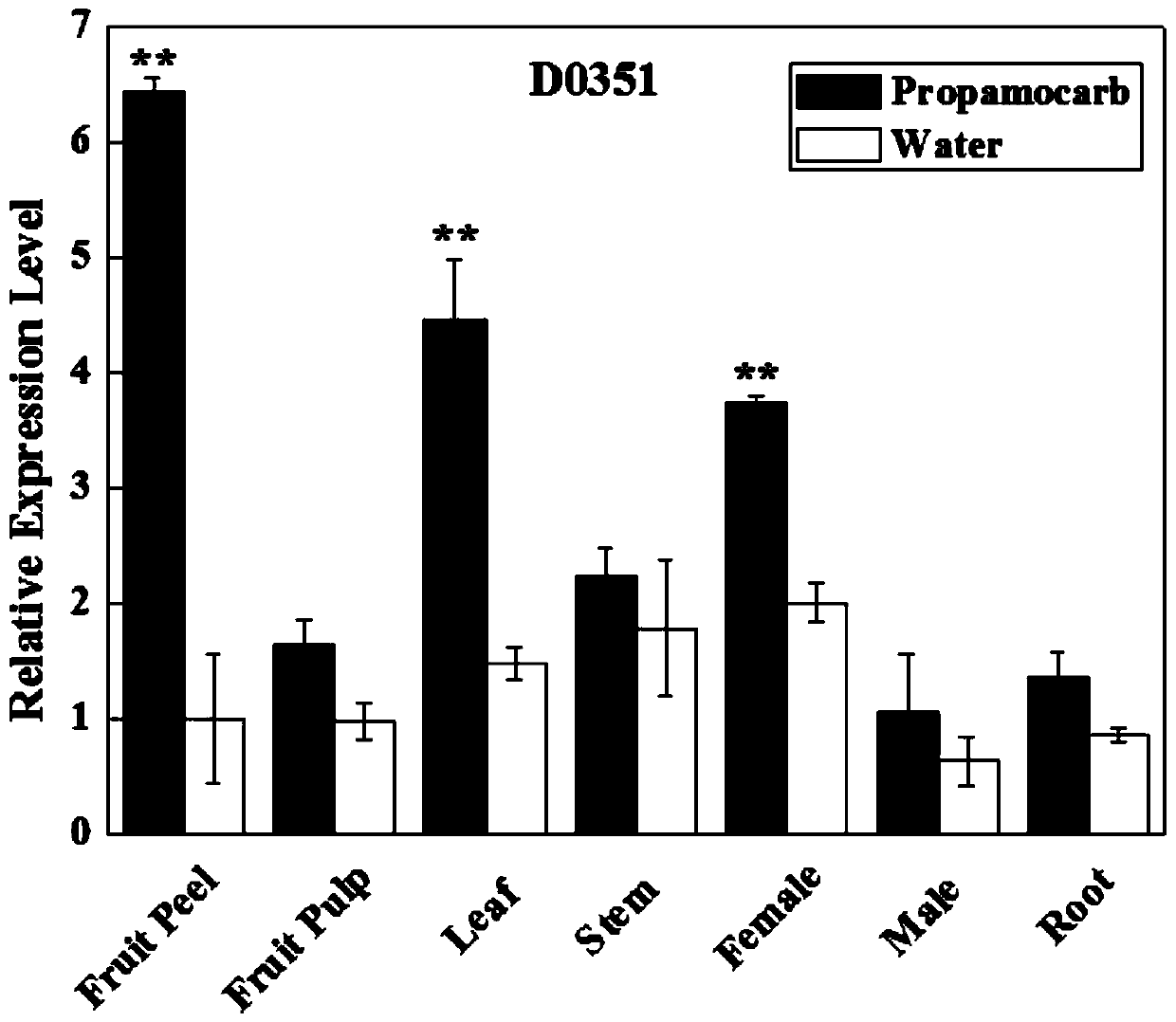
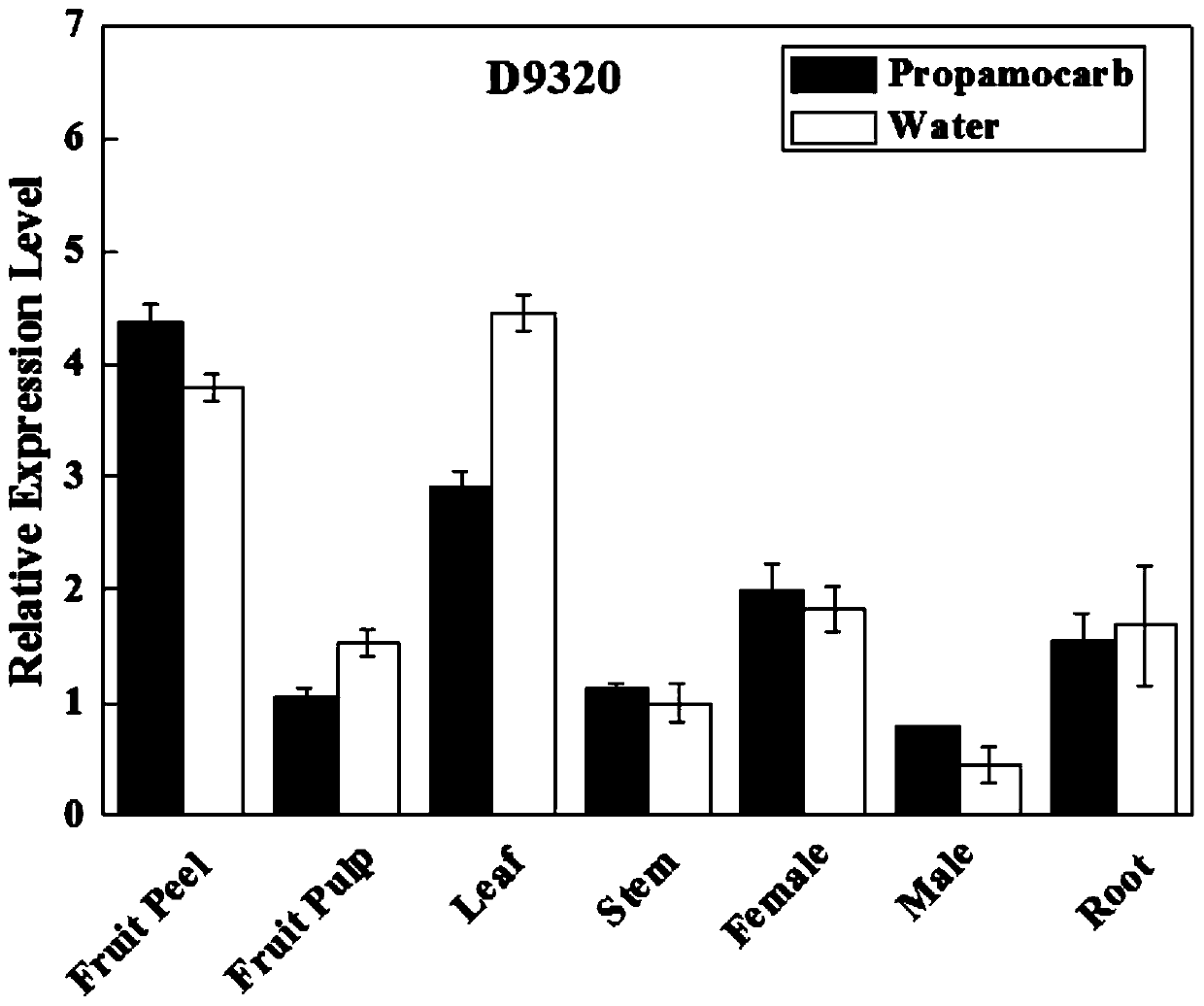
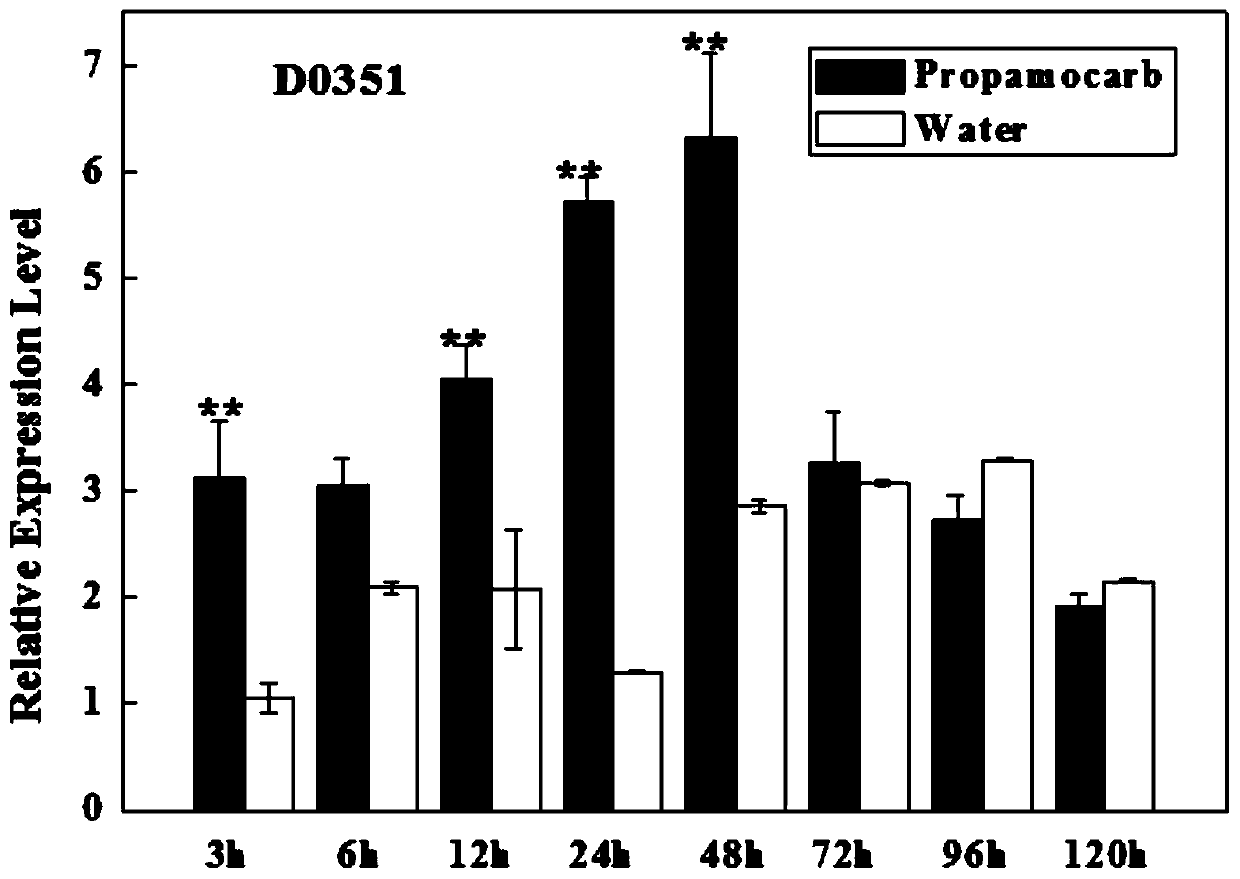
ActiveCN111534540AResidue reductionImprove safety qualityPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyPesticide toxicity
The invention discloses an application of a cucumis sativus CsHMGB gene in reducing pesticide residue and relieving pesticide toxicity, and relates to an application of the CsHMGB gene in the field ofagriculture. From the perspective of genetics, pesticides are metabolized in plants, the safety quality of cucumis sativuss is improved, pesticide residues are reduced, and meanwhile the problems ofenvironmental pollution and the like are avoided. The residual quantity of propamocarb in a cucumis sativus strain for silencing CsHMGB is increased, and the residual quantity of propamocarb in a cucumis sativus strain for overexpressing CsHMGB is reduced. Cucumis sativus is interfered by ROS after being threatened by propamocarb, the overexpressed CsHMGB can improve the activity of antioxidant enzymes SOD, POD, CAT and the like, and the ASA-GSH circulation capacity is improved. The overexpressed CsHMGB induces up-regulated expression of a detoxifying gene and some genes of a glutathione family and a membrane transporter ABC family. The CsHMGB can relieve poison of propamocarb through an antioxidant enzyme system.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
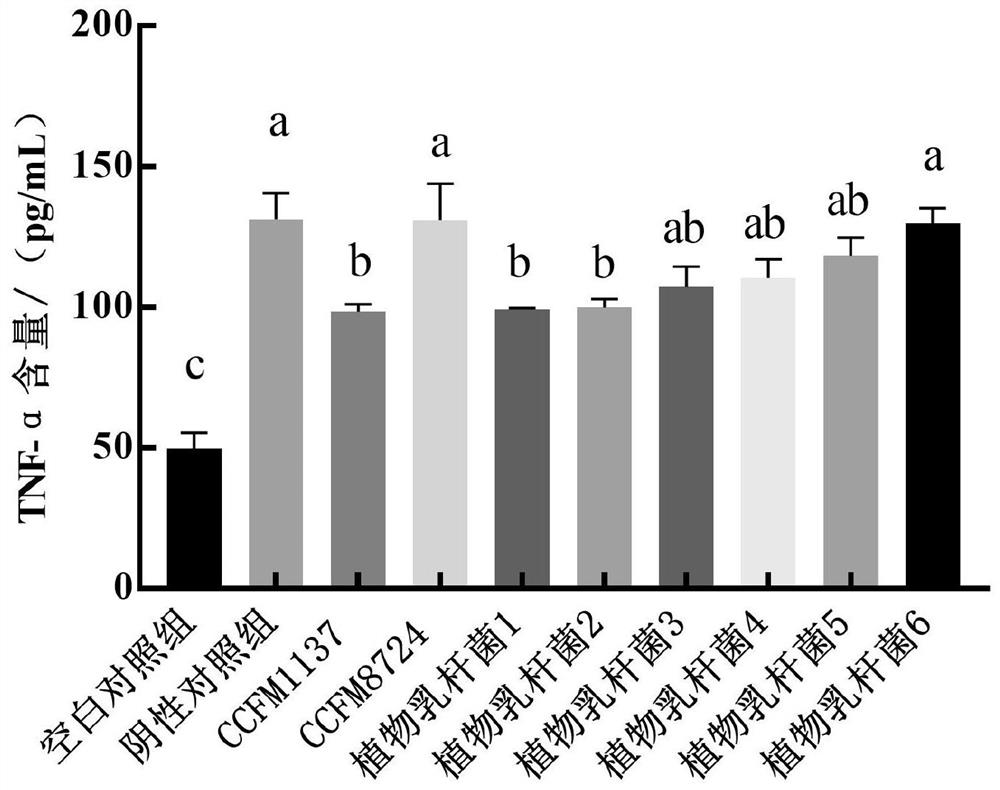
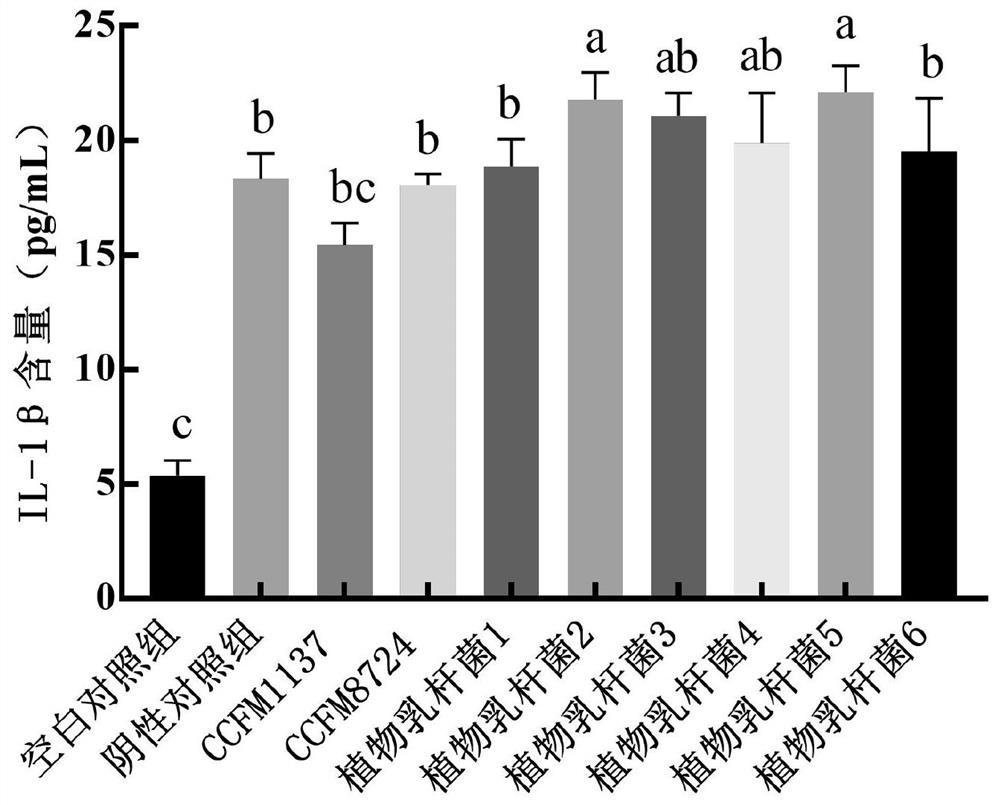
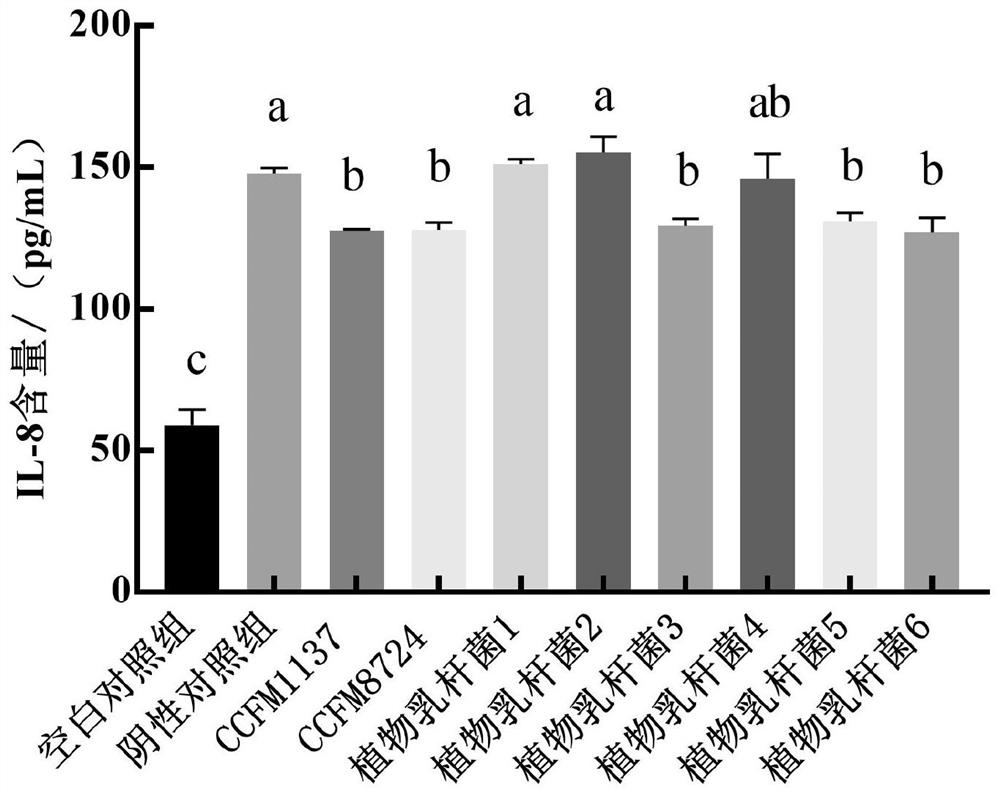
Lactobacillus plantarum for preventing and/or treating periodontitis, its culture and its preparation and application
ActiveCN113005055BReduce the content of inflammatory factorsHigh expressionAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsInflammatory factorsMembrane Transporters
The invention relates to the technical field of microbes, and discloses Lactobacillus plantarum for preventing and / or treating periodontitis, its culture and its preparation and application. The Lactobacillus plantarum, named Lactobacillus plantarum (Lactobacillus plantarum) CCFM1137, was preserved on August 1, 2020 at the Guangdong Provincial Microbial Culture Collection Center on the 5th Floor, Building 59, Compound No. 100, Xianlie Middle Road, Guangzhou City, and the preservation number is GDMCC No: 61114. The plantarum lactobacillus can inhibit the formation of Porphyromonas gingivalis, Prevotella intermedia and Fusobacterium nucleatum mixed bacteria biofilm; it can reduce the content of inflammatory factors in the periodontitis cell model; it can make the periodontitis cell model The expression level of the transmembrane transport protein is increased; it can be used for preventing and / or treating oral diseases and inhibiting Prevotella intermedium, Porphyromonas gingivalis and / or Fusobacterium nucleatum.
Owner:INFINITUS (CHINA) CO LTD
Transgenic Insect and Use of Same in Methods for Testing Natural or Synthetic Substances
InactiveUS20200260700A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsAnimal husbandryBiotechnologyMembrane Transporters
A transgenic insect includes a genome which has at least one first exogenic DNA sequence, which is coded for a human membrane transporter protein. The expression of the first exogenic DNA sequence leads to a functional human membrane transporter protein in the transgenic insect.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH FUR MEDIZINISCHE FORSCHUNG MBH +1
Phloroglucinol-resistant cell, in particular yeast
PendingUS20220098626A1Increase its phloroglucinolCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsTransferasesMembrane TransportersLiving cell
The present invention relates to a living cell, preferably a host cell, that is phloroglucinol resistant, said host cell being characterized in that it overexpresses a polypeptide selected from (i) transmembrane transporters of the ABC family, in particular transmembrane transporters of the PDR subfamily, (ii) transcription factors which control the expression of the transmembrane transporters of the PDR subfamily, and (iii) transmembrane transporters of the MFS family; preferably a polypeptide selected from SNQ2, STE6, PDR3, AQR1, DTR1, FLR1, QDR1, YHK8 and ATR1; and more preferably the SNQ2 transporter. The present invention also relates to a method for producing a phloroglucinol-resistant recombinant host cell. The present invention also relates to a method for producing phloroglucinol.
Owner:MICHELIN & CO CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN
A nano-filter film transfer cutting tool
ActiveCN106584533BKeep safeReduce insecurityWork holdersMetal working apparatusMembrane TransportersLight filter
The invention discloses a transferring and cutting tool for a nano light filtering film. According to the nano film storage and cutting tool, the effect that the nano film is safely and reliably stored can be ensured; complete cutting of the nano film can be finished at a time in a specified shape; burrs, cracks and defects do not exist; a step spigot and a circular arc spigot are designed, double-spigot laminating is formed, and the problem that a nano material cannot be pressed when an upper pressing frame and a lower pressing frame are laminated can be solved; unsafe factors in a tool cavity can be eliminated during transferring of the nano light filtering film by designing an upper protection cover; and a boss of the upper protection cover is attached to the light filtering film, thus, an attachment stabilizing effect is achieved, and the safety of the light filtering film is protected.
Owner:SHANDONG INST OF AEROSPACE ELECTRONICS TECH
Application of trametinib in the preparation of drugs for reversing tumor multidrug resistance
ActiveCN104434924BReverse multidrug resistanceRestore sensitivityOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsMembrane TransportersMembrane transport protein
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
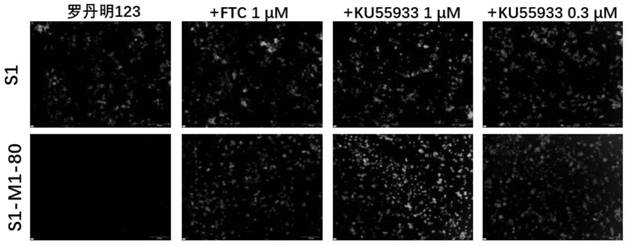
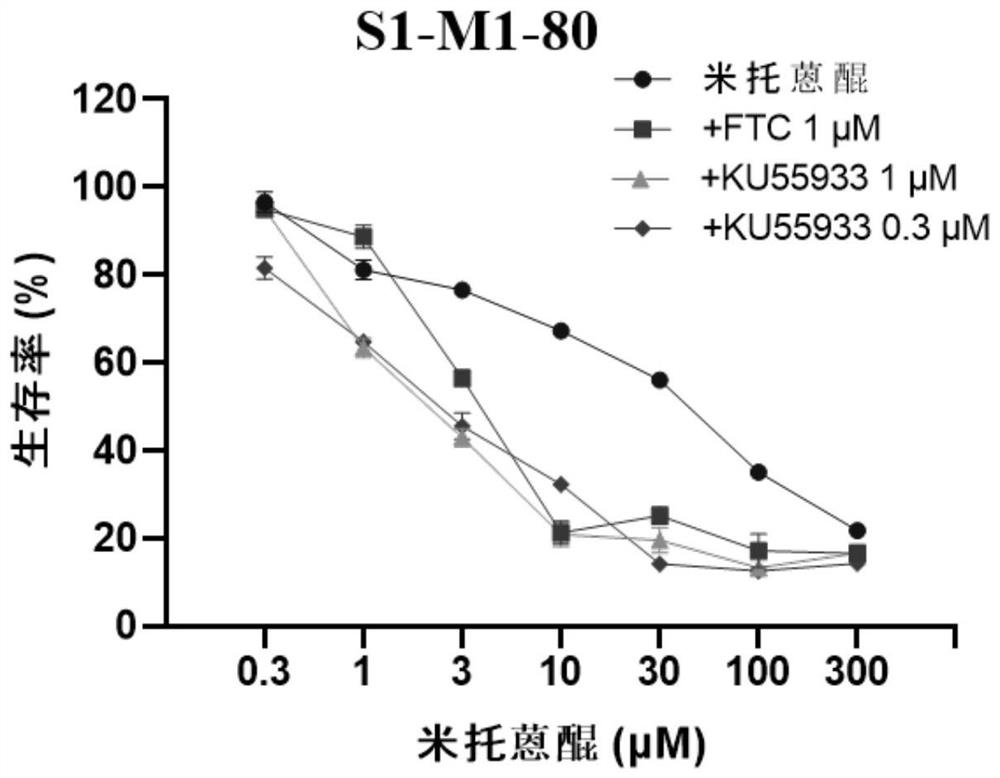
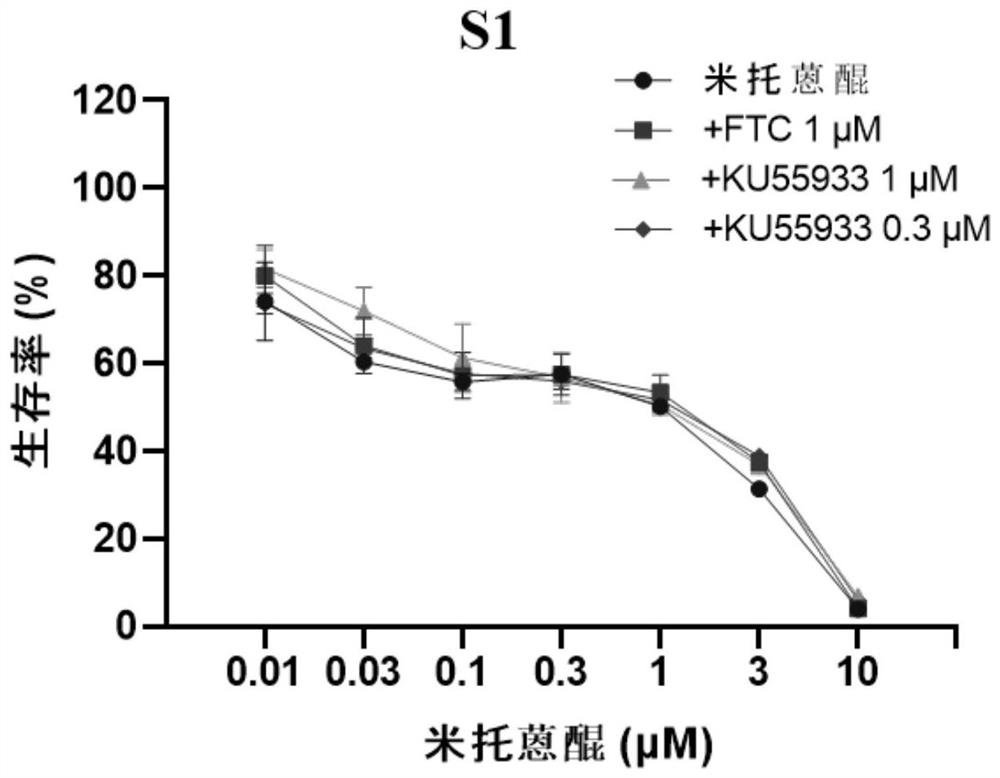
Application of KU55933 in preparation of drugs for reversing multidrug resistance of tumor
ActiveCN112972477AReverse multidrug resistanceRestore sensitivityOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsMembrane TransportersPharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses application of KU55933 in preparation of drugs for reversing multidrug resistance of tumors, and belongs to the technical field of drug application. According to the invention, KU55933 is found to be capable of remarkably reversing tumor multidrug resistance mediated by membrane transporter for the first time, so that ABCG2 high-expression cells recover sensitivity to anti-cancer drugs. The drugs for reversing the multidrug resistance of the tumors can contain KU55933, anti-cancer medicines, carriers and auxiliary agents, can be prepared into a tablet, a particle, a capsule, an oral liquid or an injection form, and can be used for treating and controlling resistant tumors.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
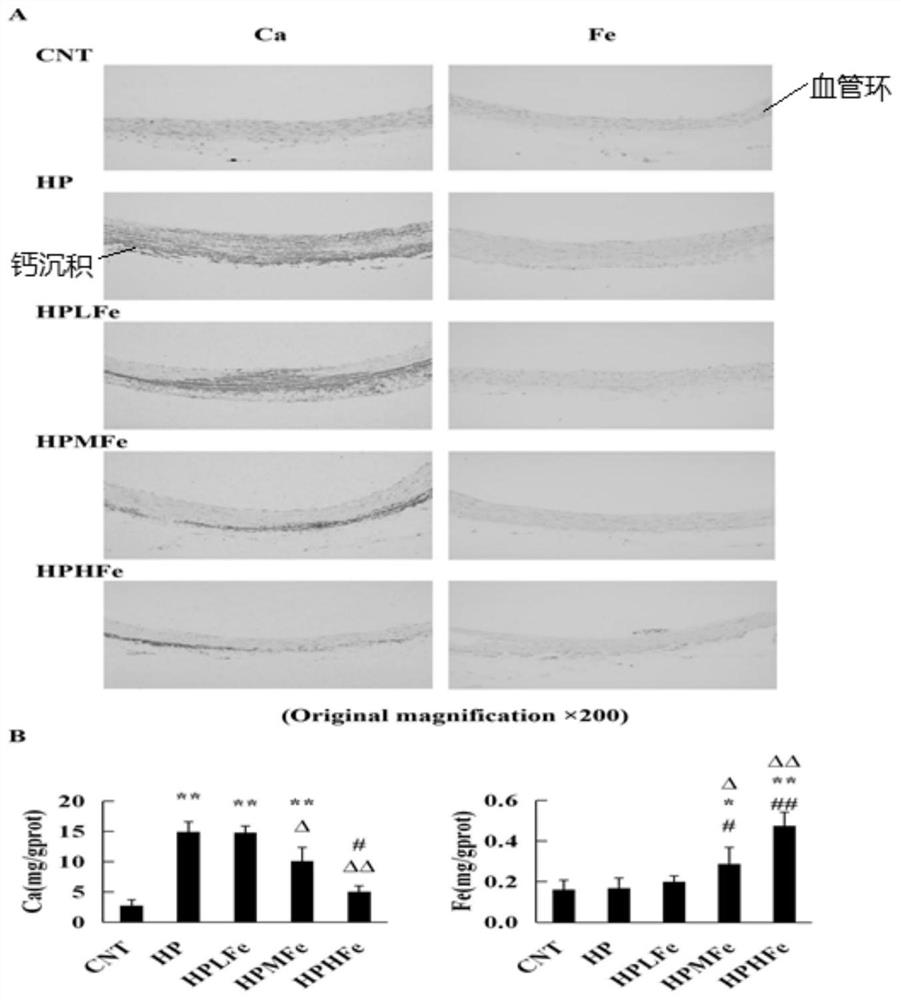
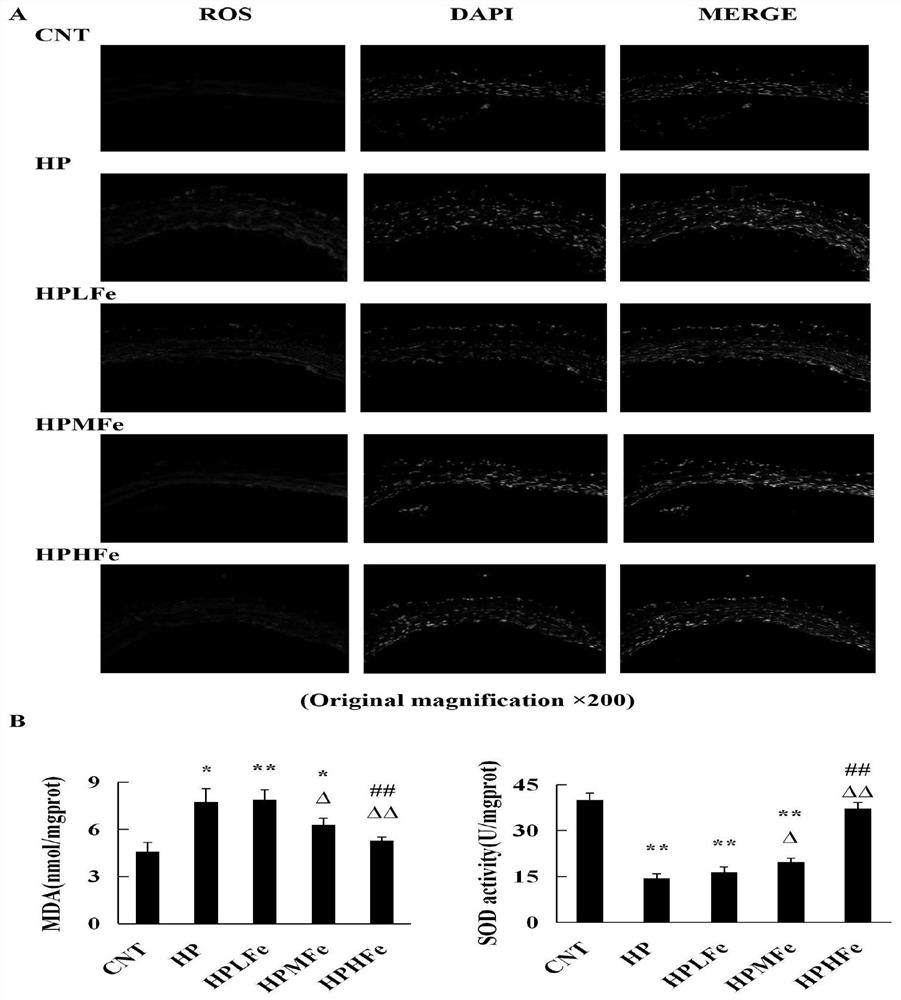
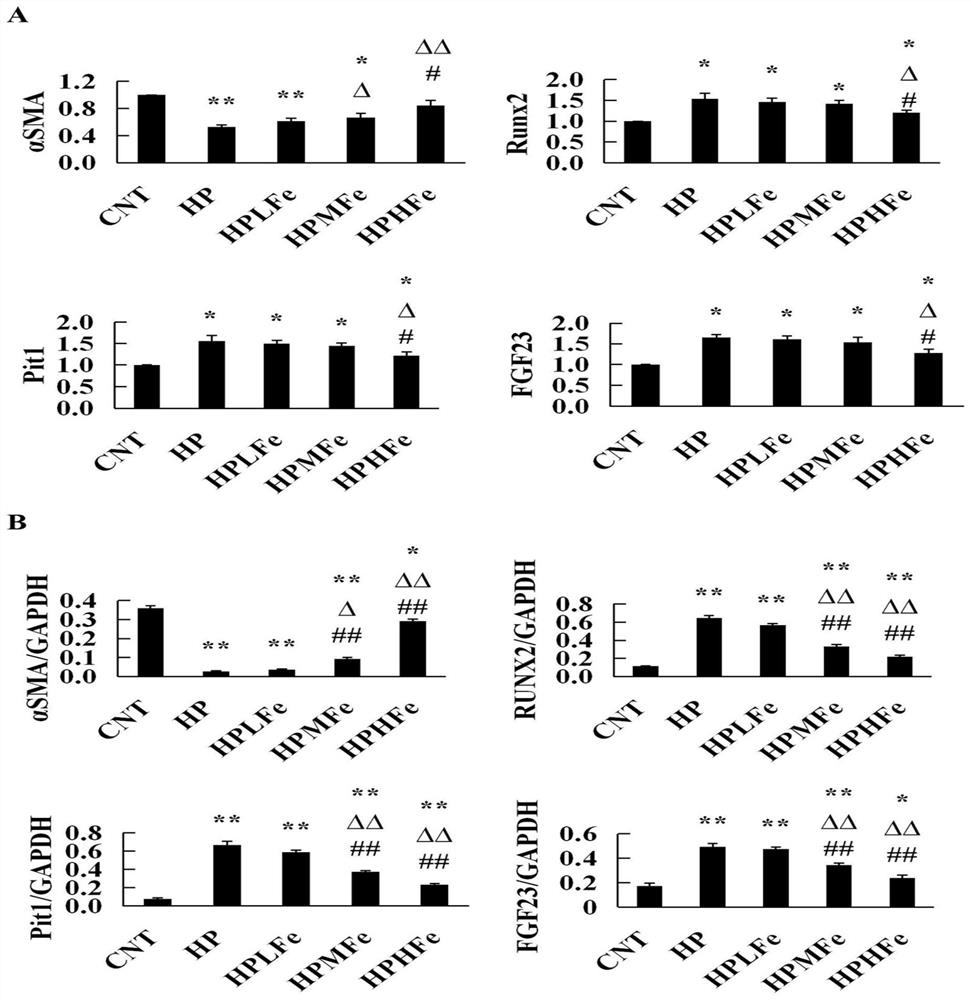
Application of iron sucrose to preparation of drug for treating angiosteosis induced by hyperphosphatemia
ActiveCN111773247AReduce incidenceProlong lifeOrganic active ingredientsHeavy metal active ingredientsMembrane TransportersHyperphosphoremia
The invention belongs to the technical field of angiosteosis treatment and particularly relates to an application of iron sucrose to preparation of a drug for treating angiosteosis induced by hyperphosphatemia. Hyperphosphatemia causes an oxidative stress injury in a vascular smooth muscle cell to induce phenotypic transformation from the vascular smooth muscle cell into an osteoblast and to finally develop into angiosteosis. In experiments of the invention, it is found that the iron sucrose can interfere with the transmembrane transport of inorganic phosphorus in blood, inhibit the expressionof a phosphorus transmembrane transporter and antagonize the oxidative stress injury induced by the hyperphosphatemia, so as to play a role in treating, relieving or inhibiting the angiosteosis induced by the hyperphosphatemia.
Owner:荆门市第一人民医院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com