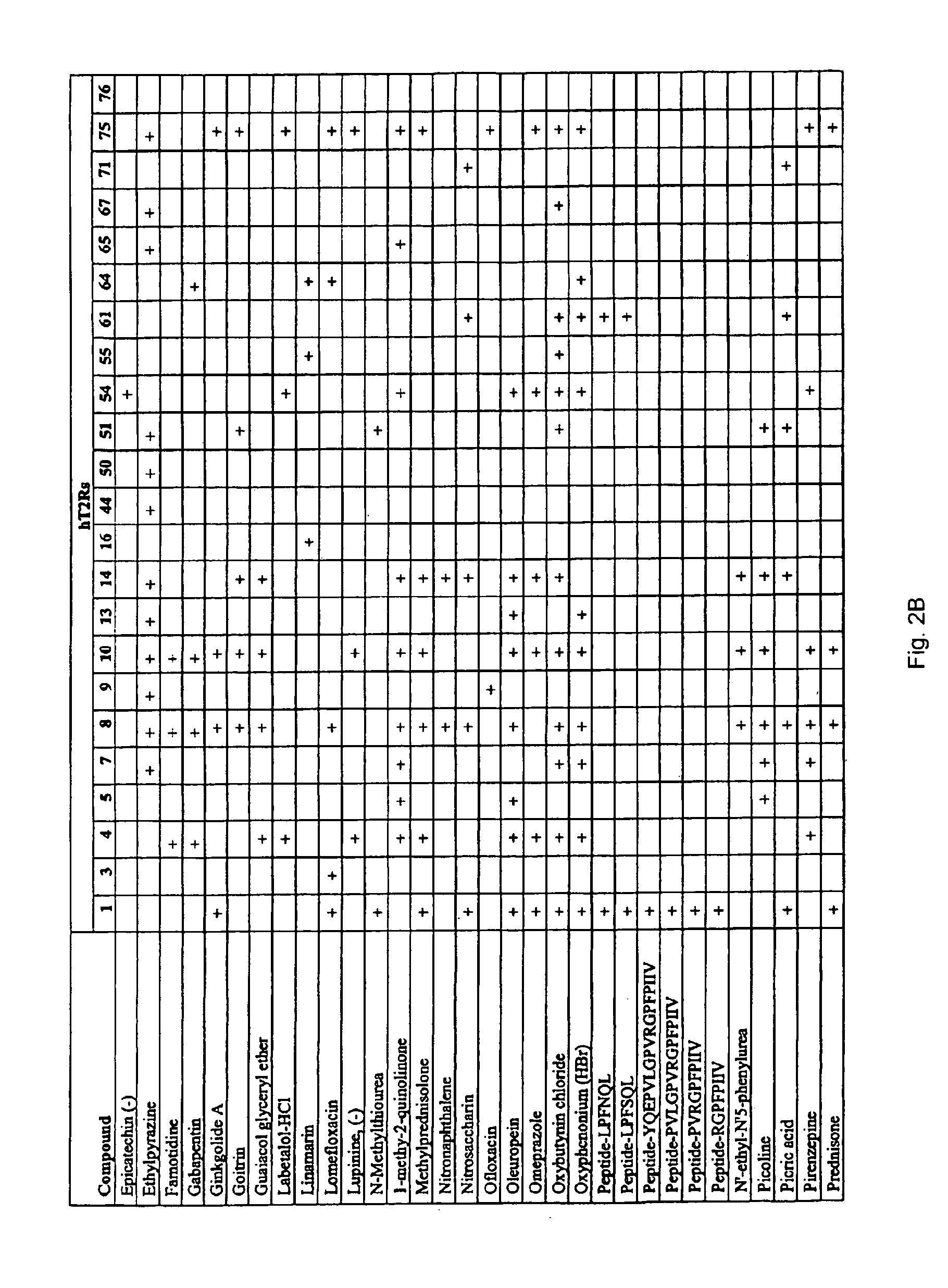
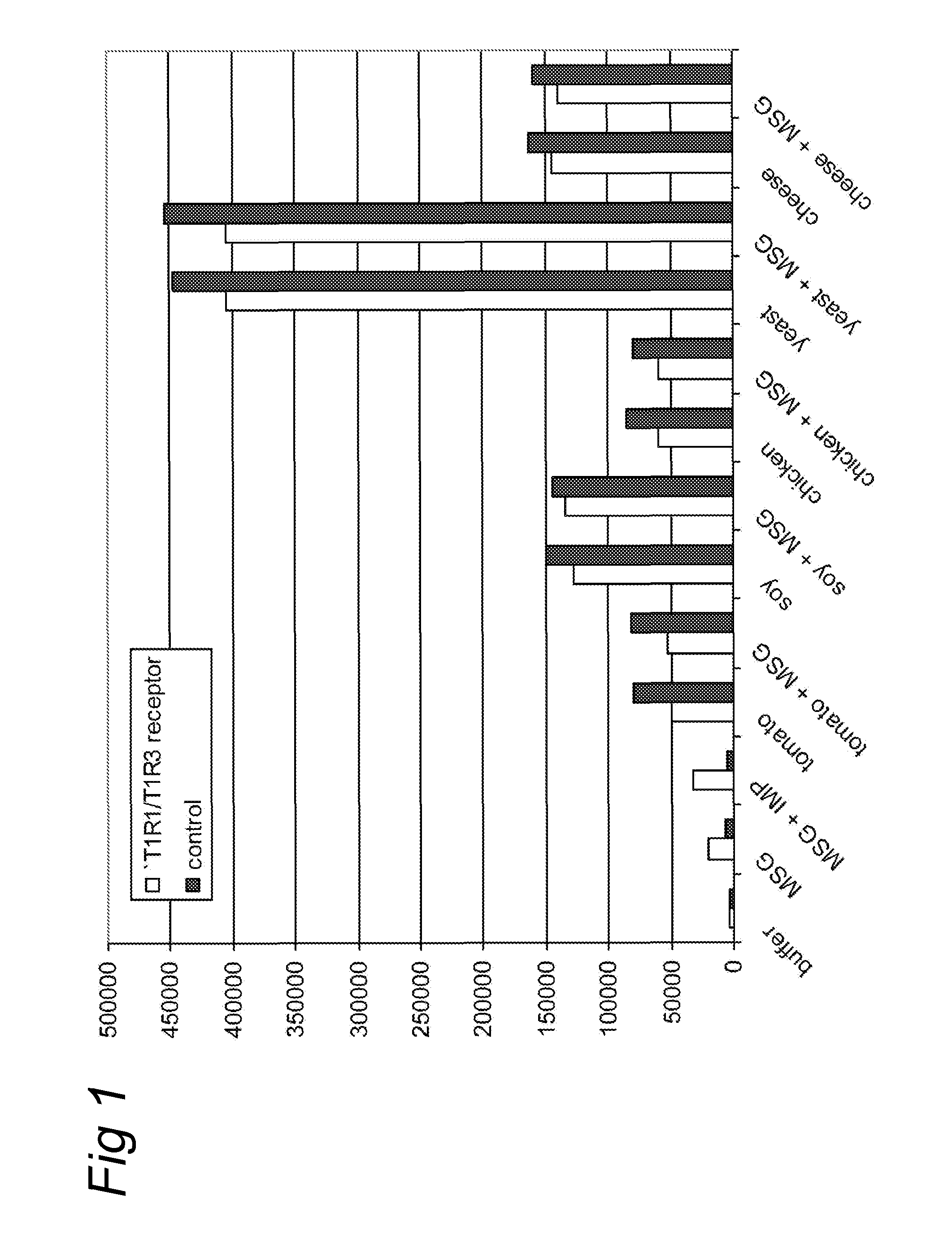
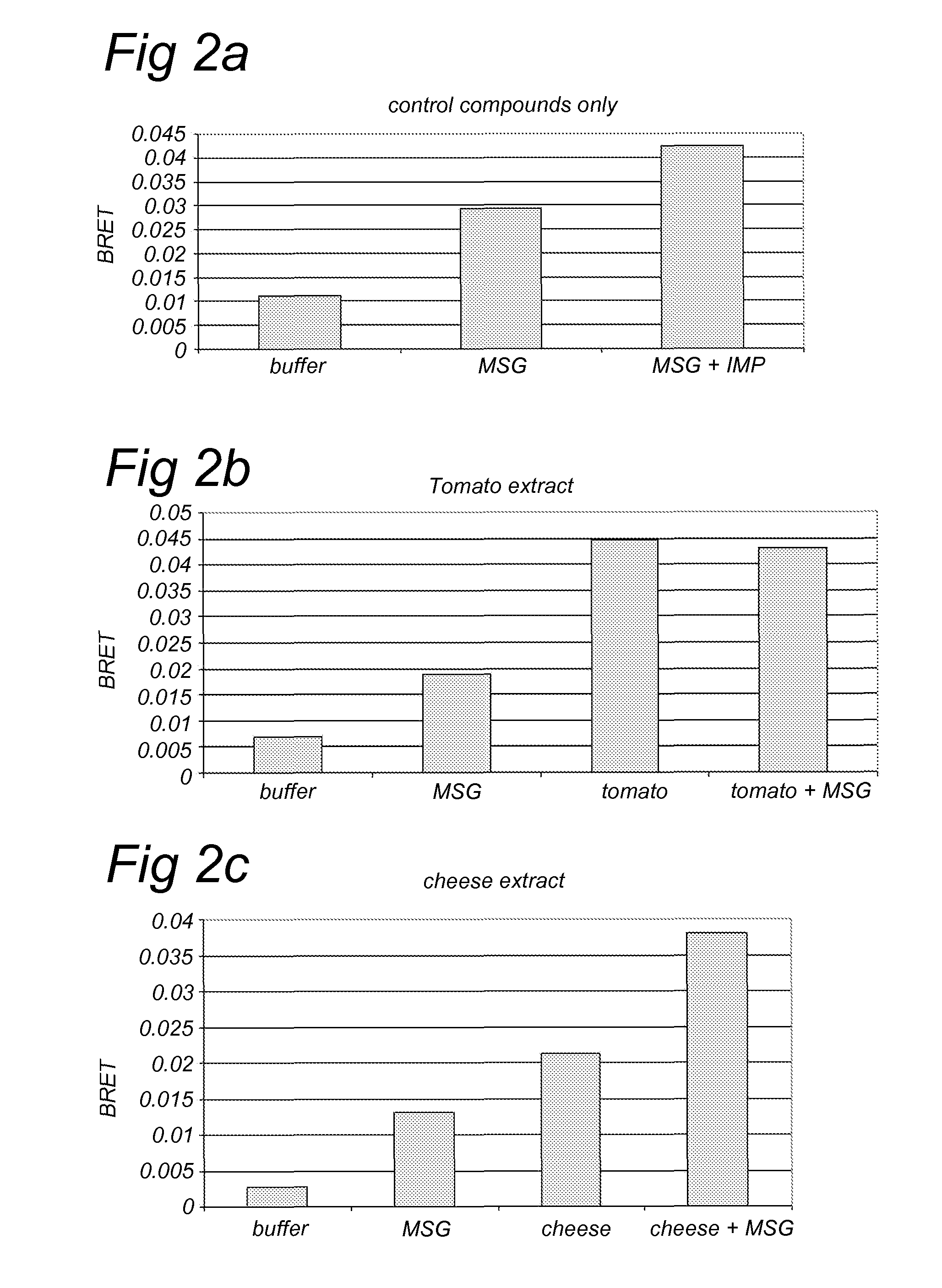
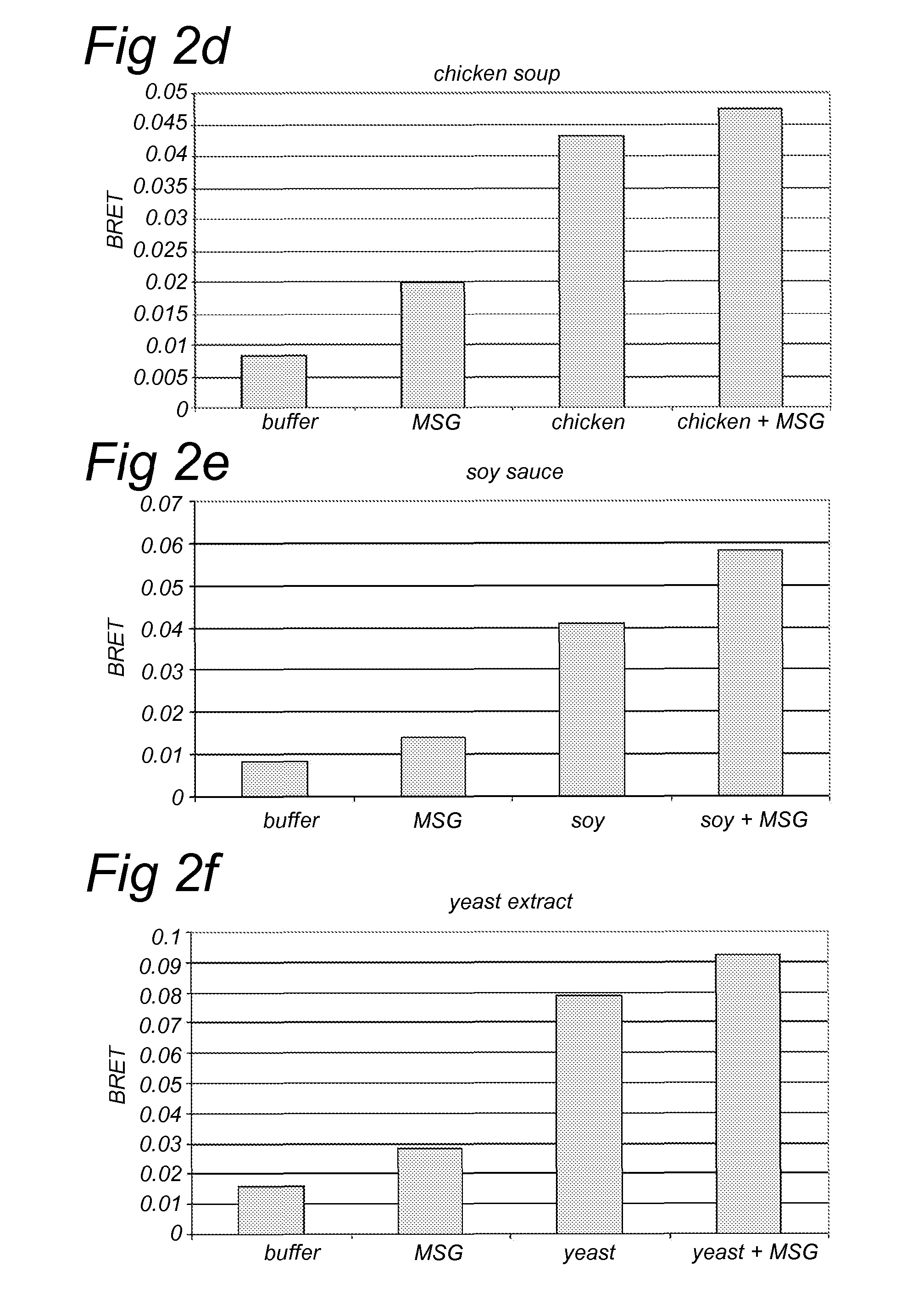
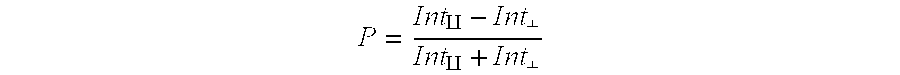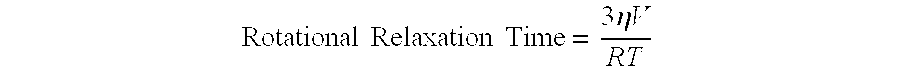Patents
Literature
62 results about "Taste receptor ligand" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
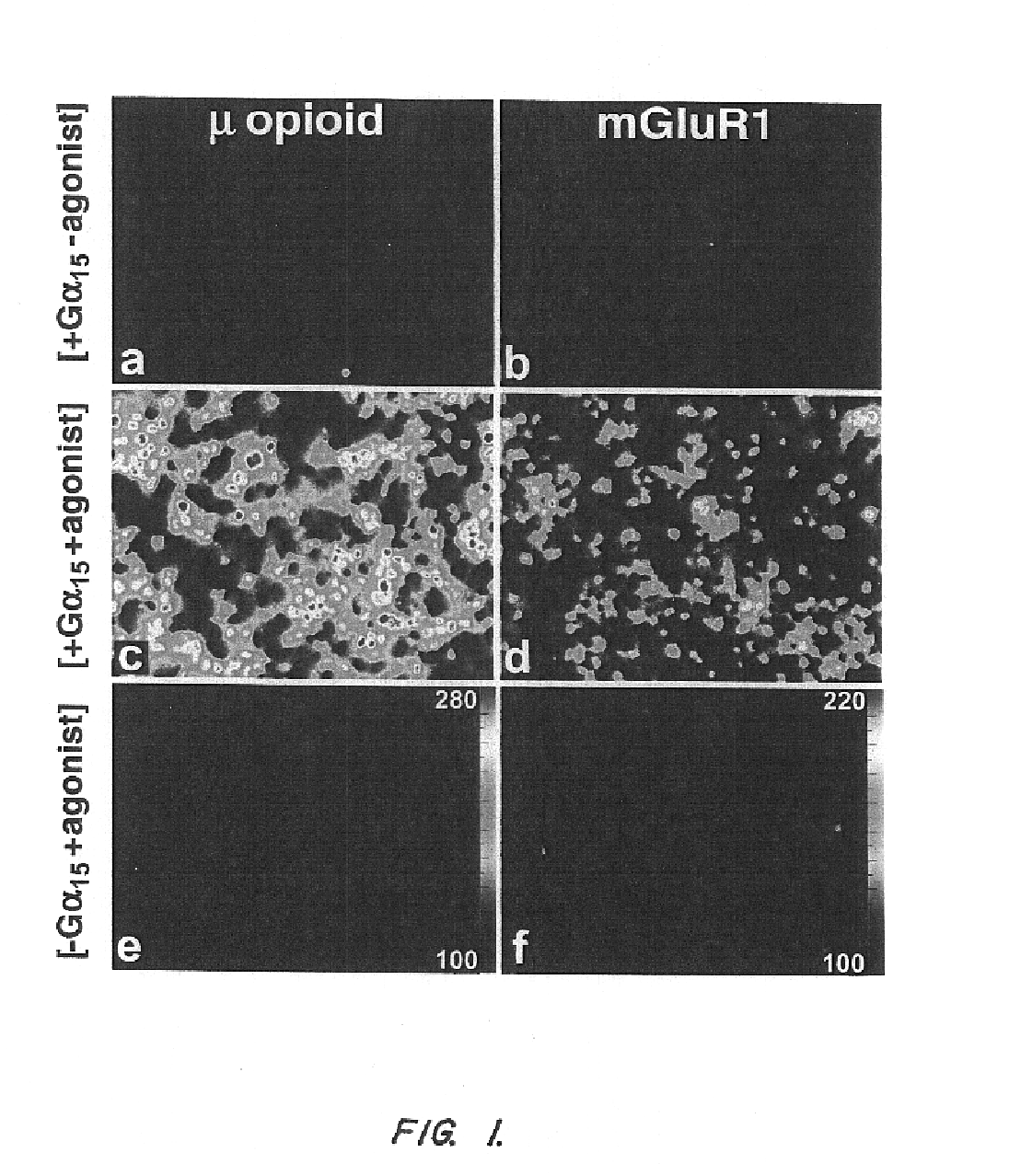
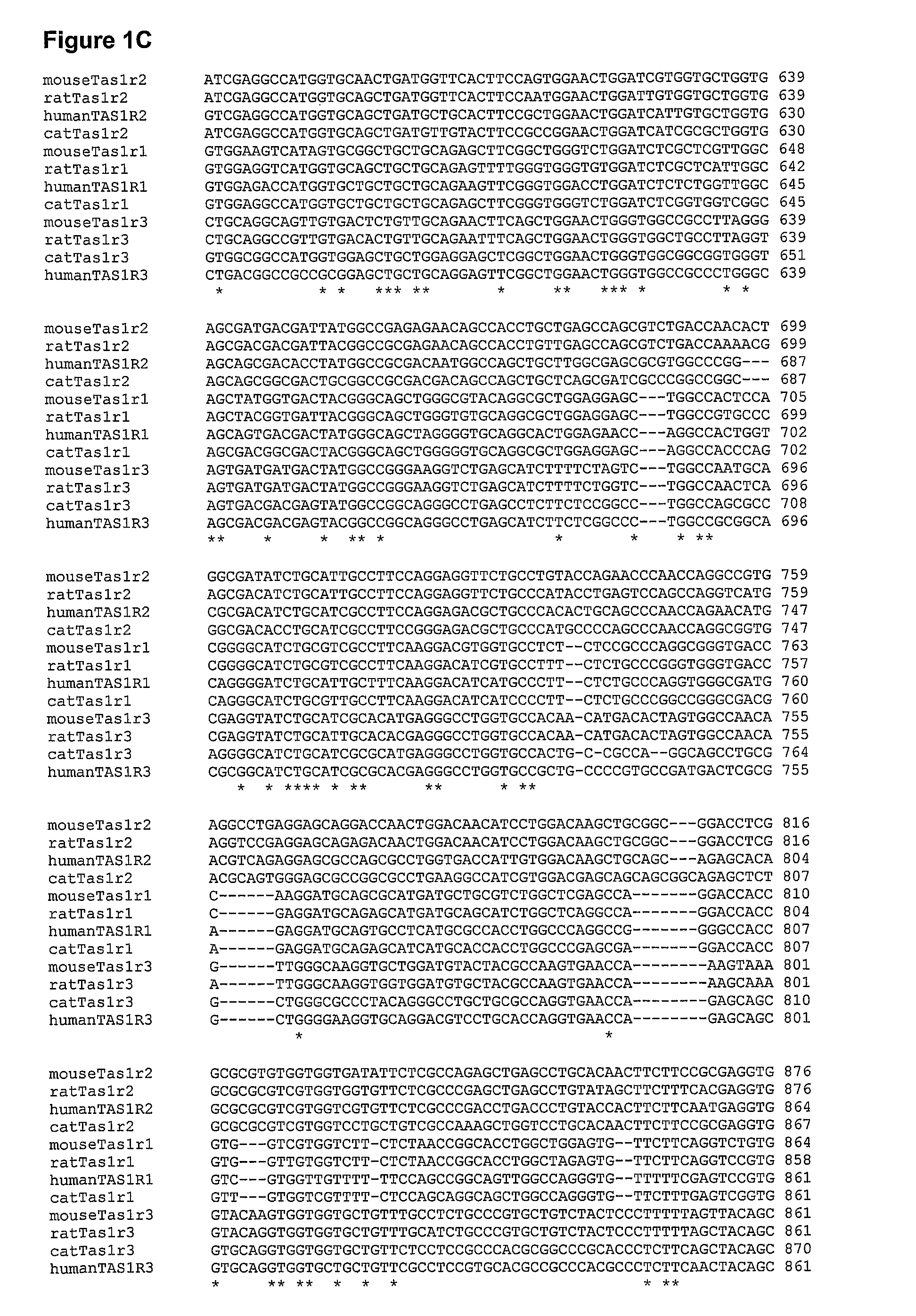
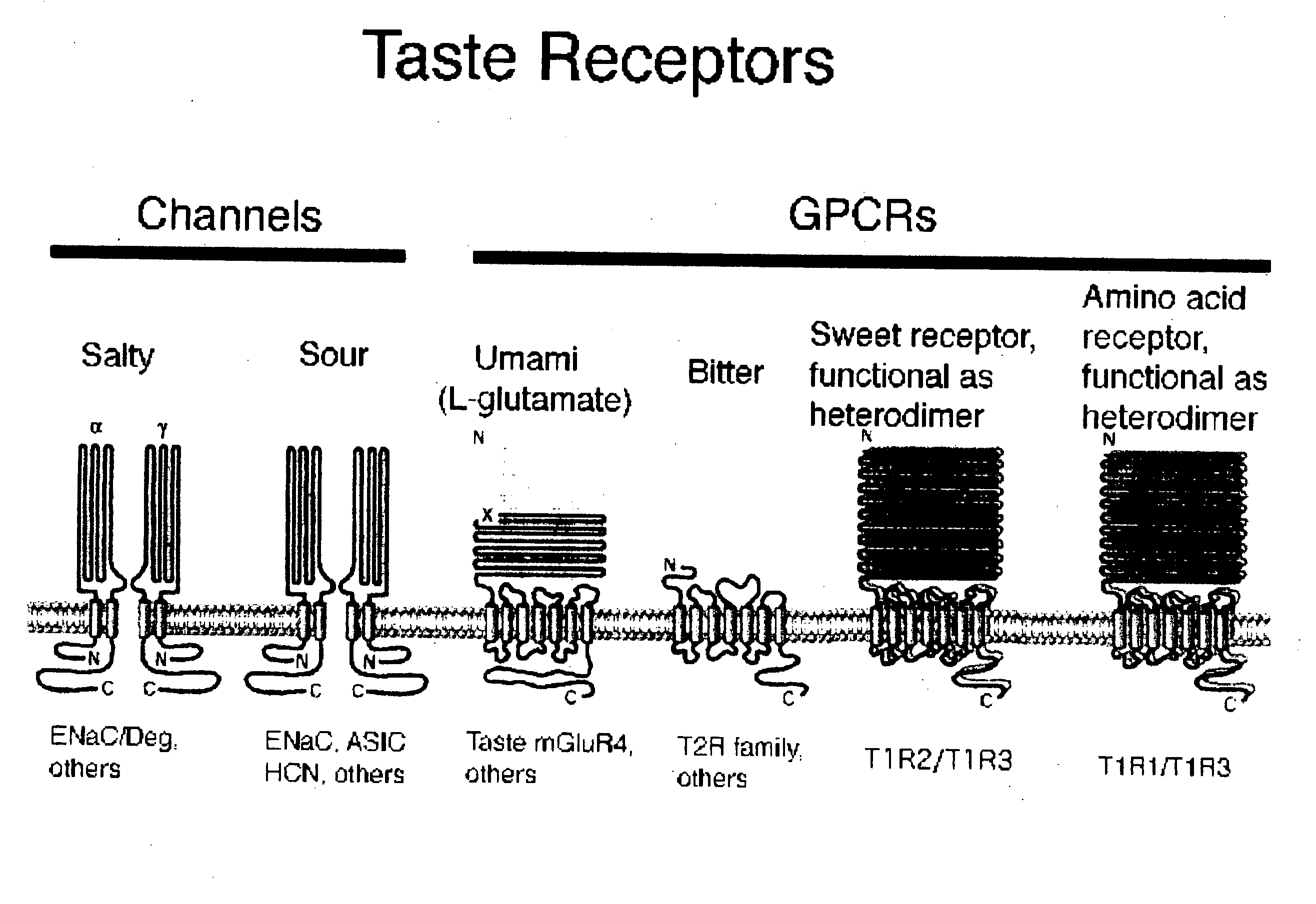
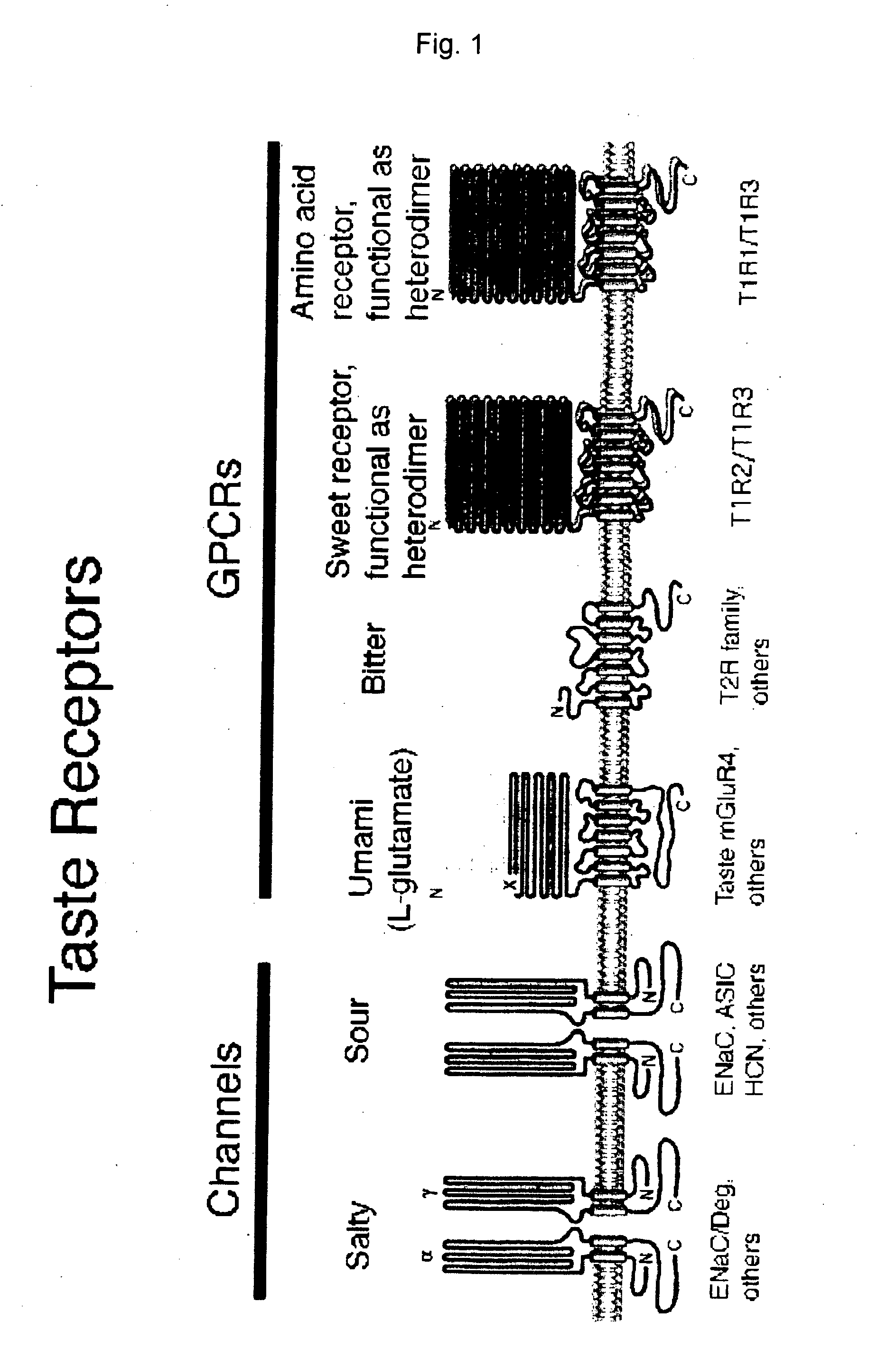
Mechanism of action. The standard bitter, sweet, or umami taste receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor with seven transmembrane domains. Ligand binding at the taste receptors activate second messenger cascades to depolarize the taste cell.
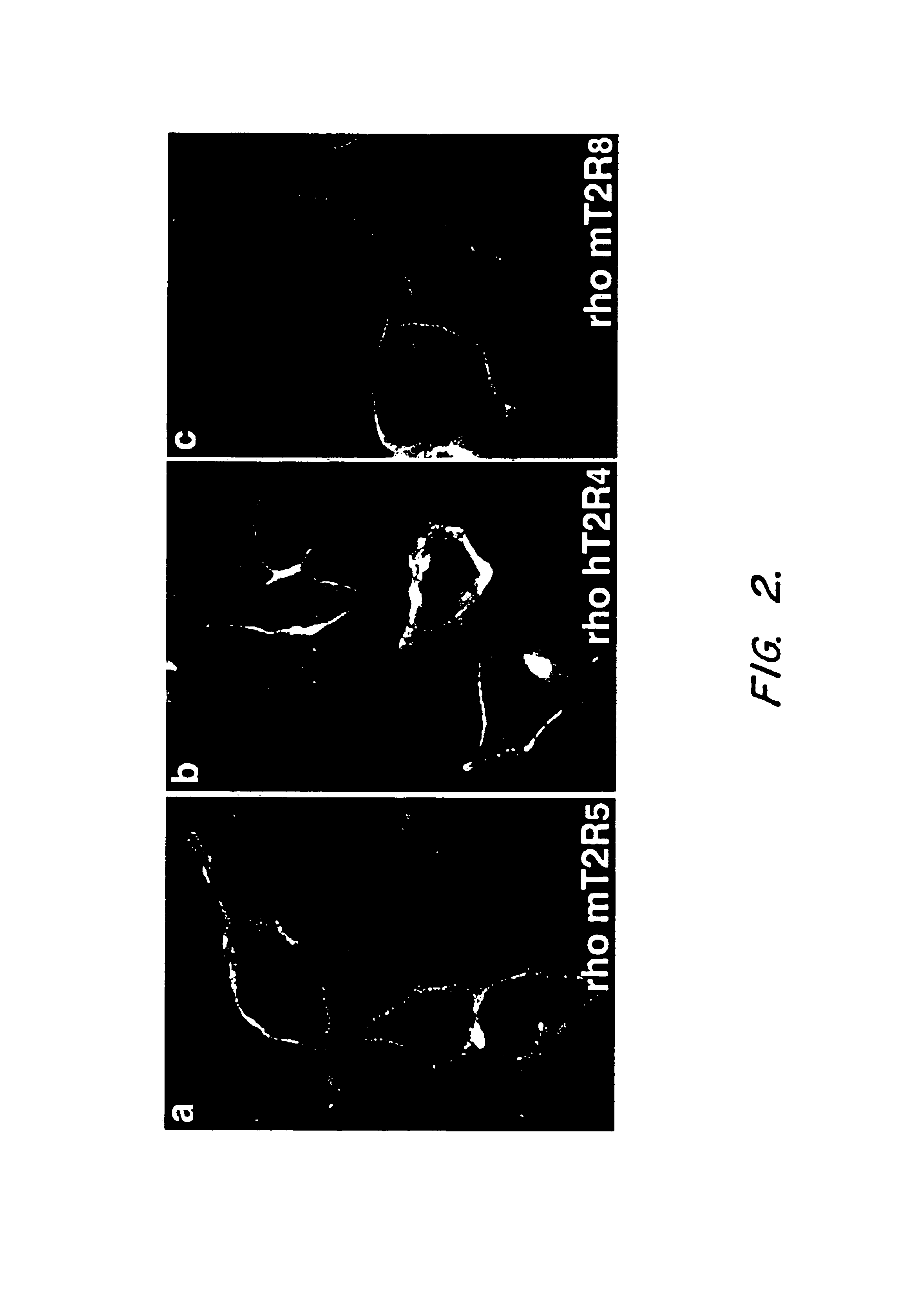
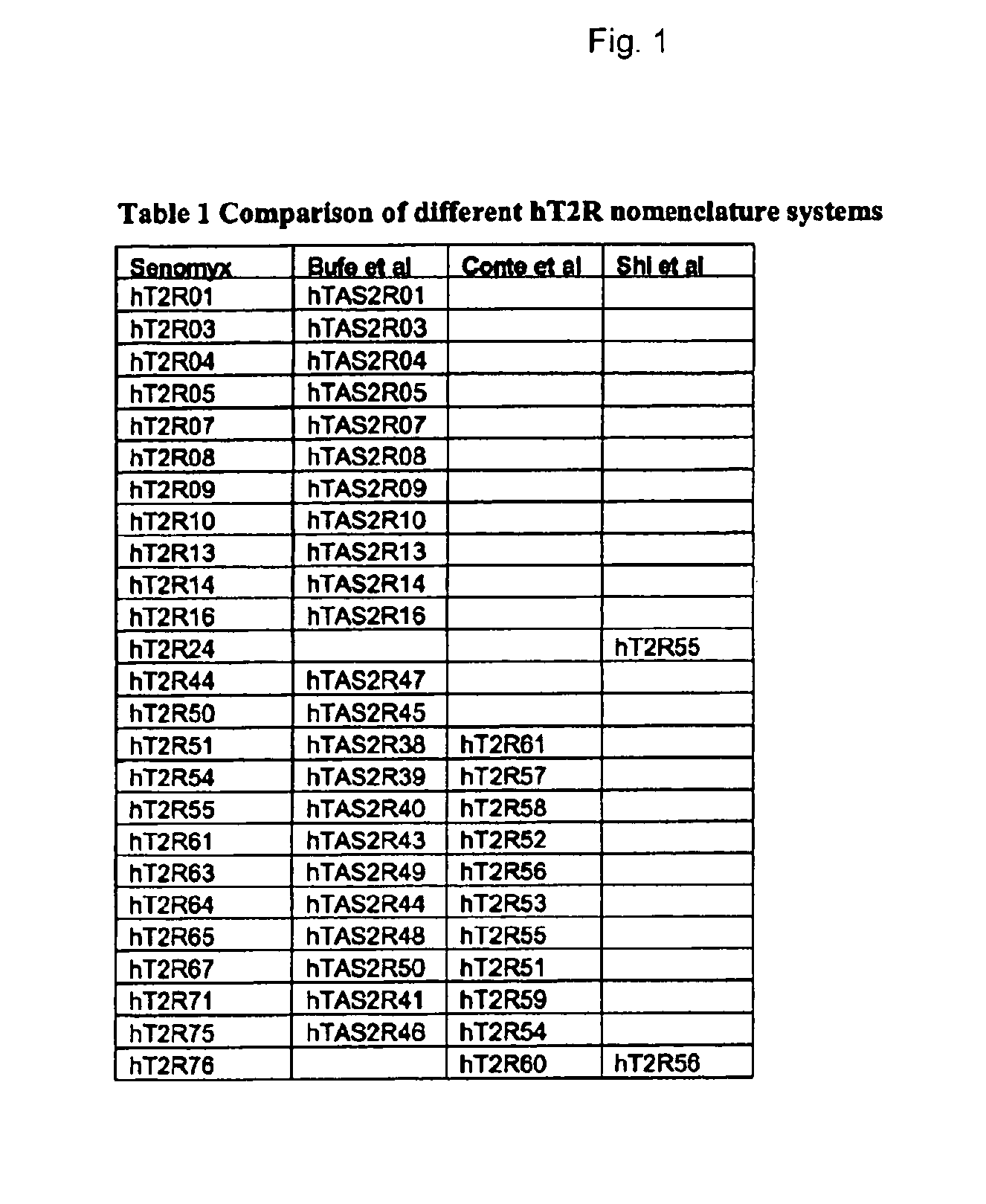
T2R, a novel family of taste receptors
InactiveUS7244584B2Modulated signalCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsBacteriaTaste receptor ligandG protein-coupled receptor
The invention provides nucleic acid and amino acid sequences for a novel family of taste transduction G-protein coupled receptors, antibodies to such receptors, methods of detecting such nucleic acids and receptors, and methods of screening for modulators of taste transduction G-protein coupled receptors.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +2
T1R hetero-oligomeric taste receptor
Newly identified mammalian taste-cell-specific G protein-coupled receptors which function as hetero-oligomeric complexes in the sweet taste transduction pathway, and the genes and cDNA encoding said receptors are described. Specifically, T1R G protein-coupled receptors active in sweet taste signaling as hetero-oligomeric complexes, and the genes and cDNA encoding the same, are described, along with methods for isolating such genes and for isolating and expressing such receptors. Methods for identifying putative taste modulating compounds using such hetero-oligomeric complexes also described, as is a novel surface expression facilitating peptide useful for targeting integral plasma membrane proteins to the surface of a cell.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
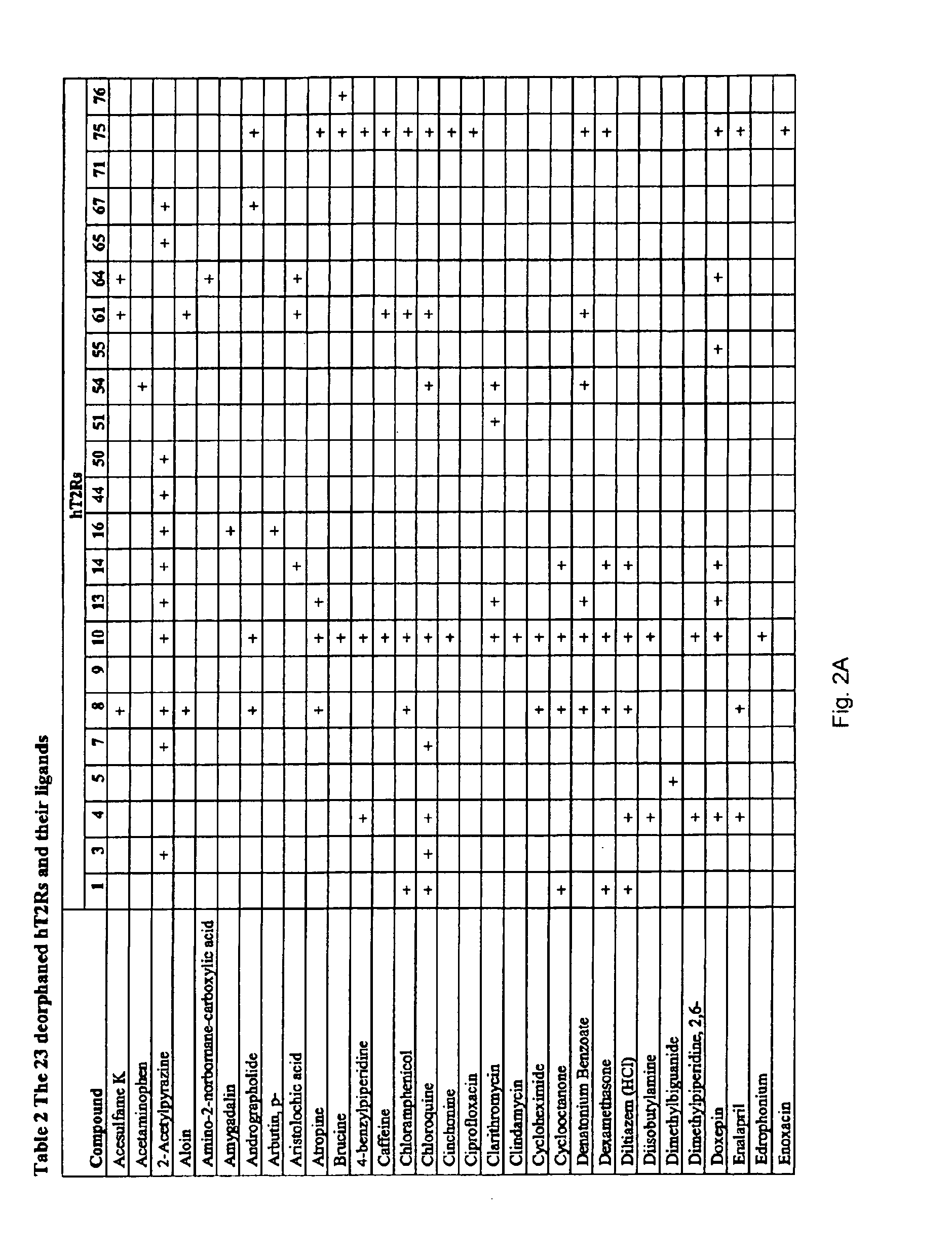
Identification of human T2R receptors that respond to bitter compounds that elicit the bitter taste in compositions, and the use thereof in assays to identify compounds that inhibit (block) bitter taste in compositions and use thereof
ActiveUS20100254916A1Reduce bitternessSuppress bitternessBiocideCosmetic preparationsTaste receptor ligandBitter tastes
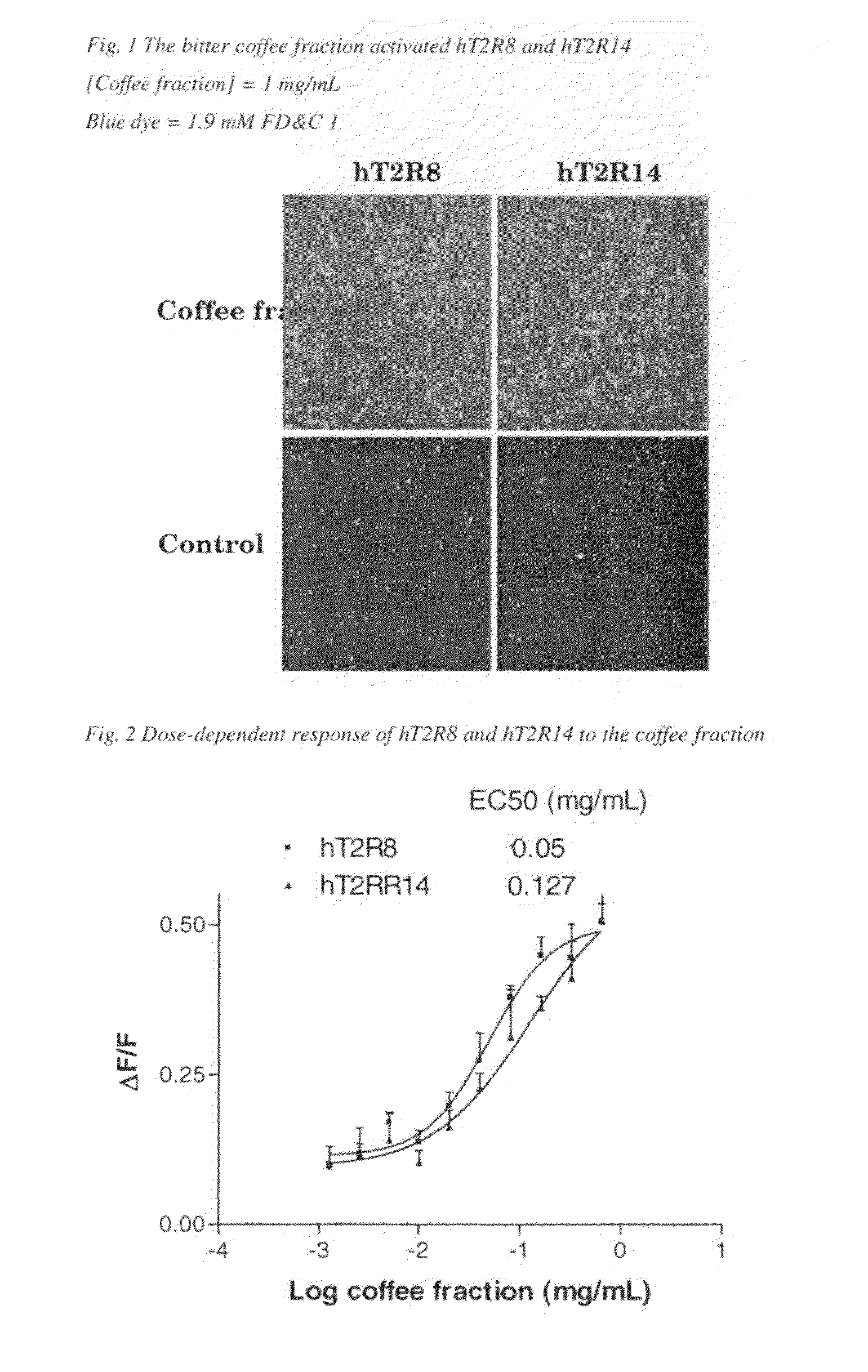
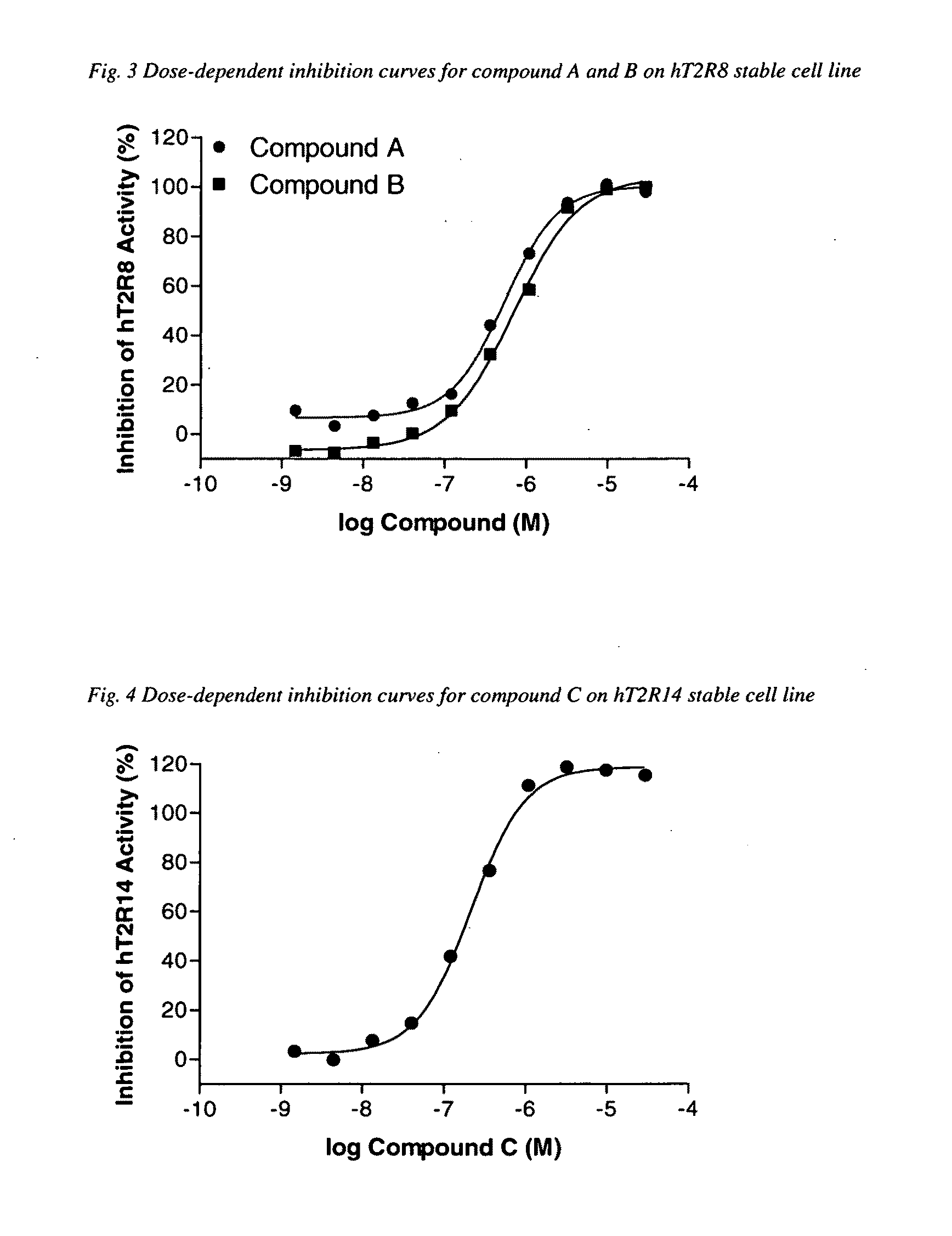
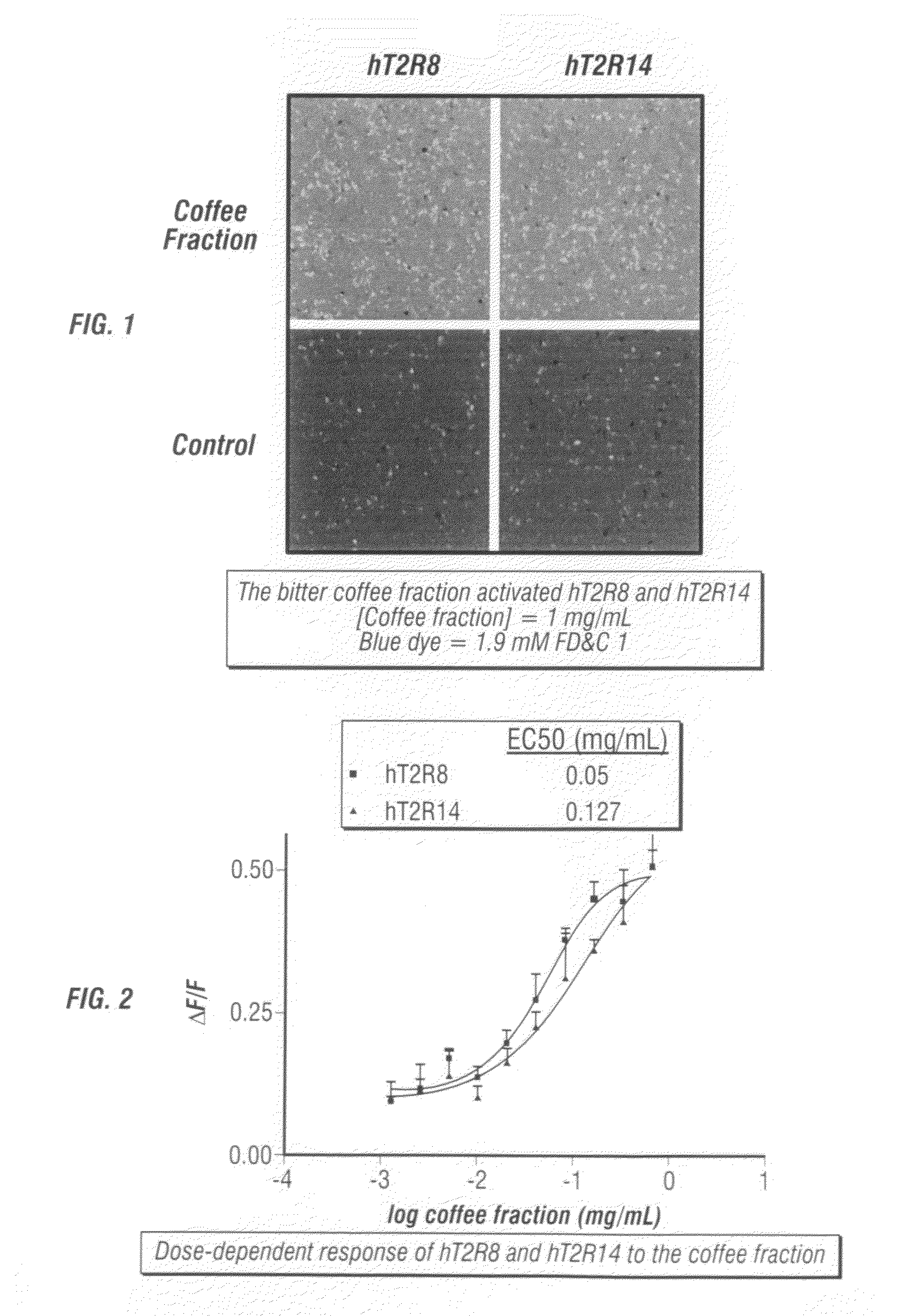
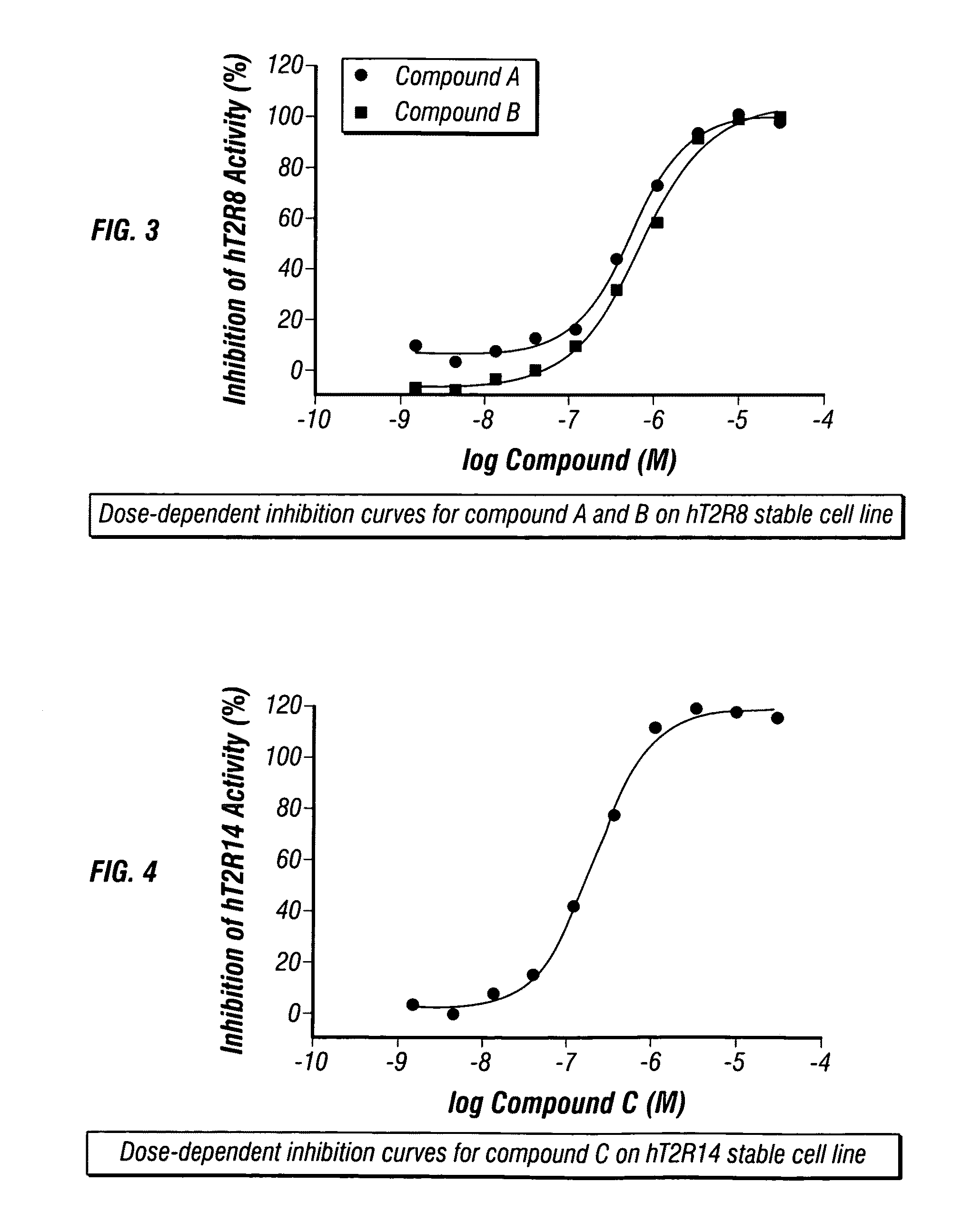
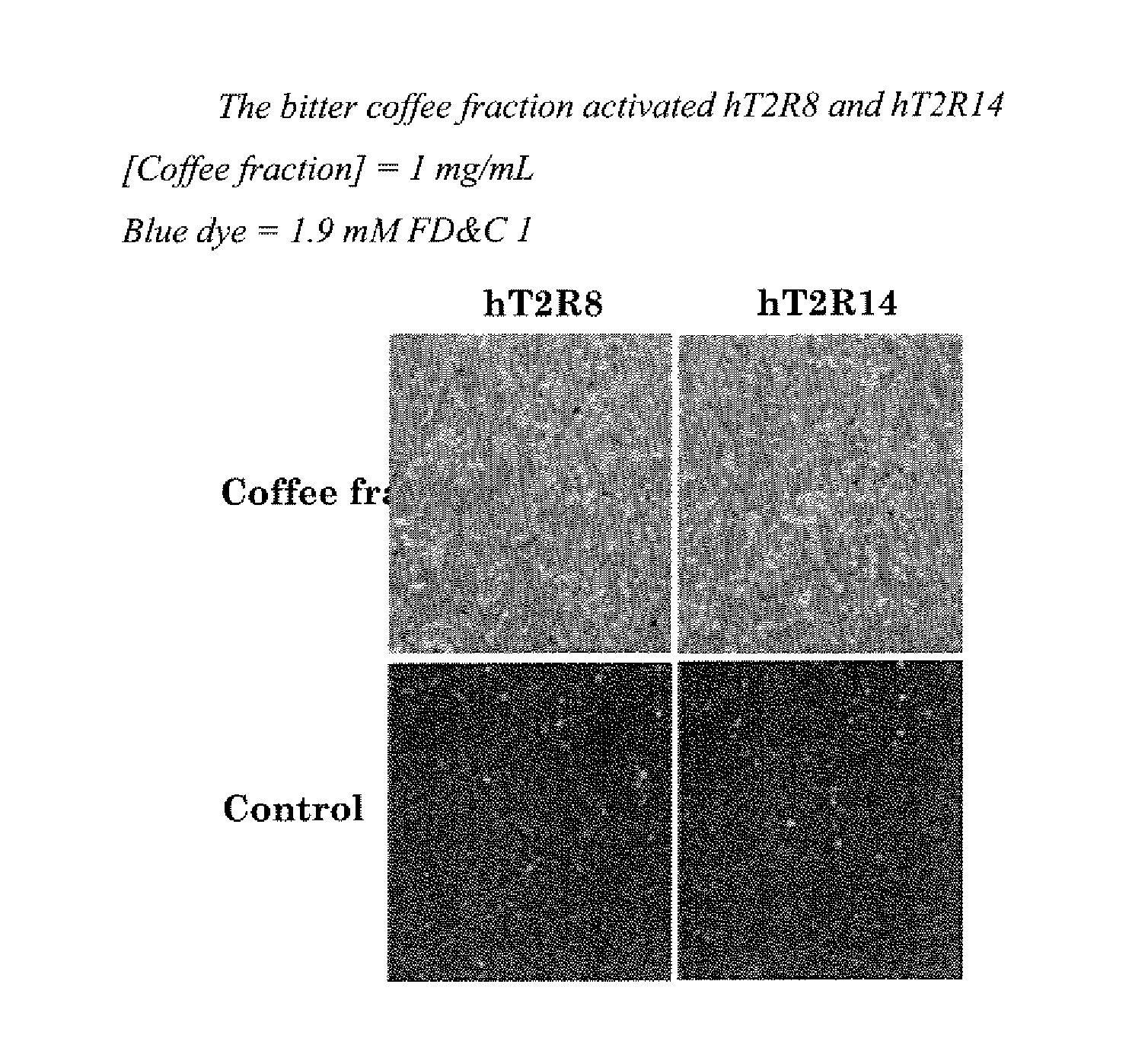
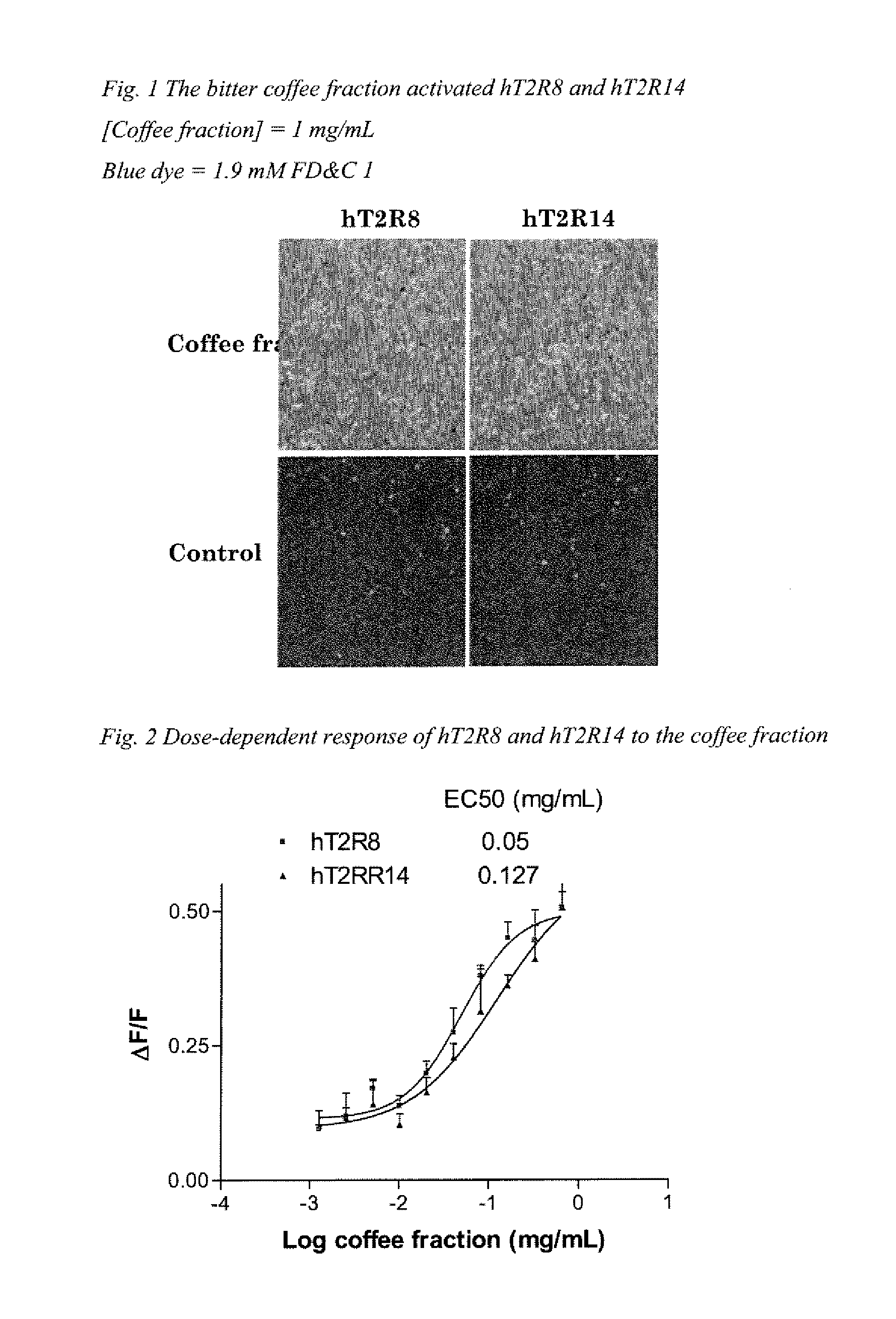
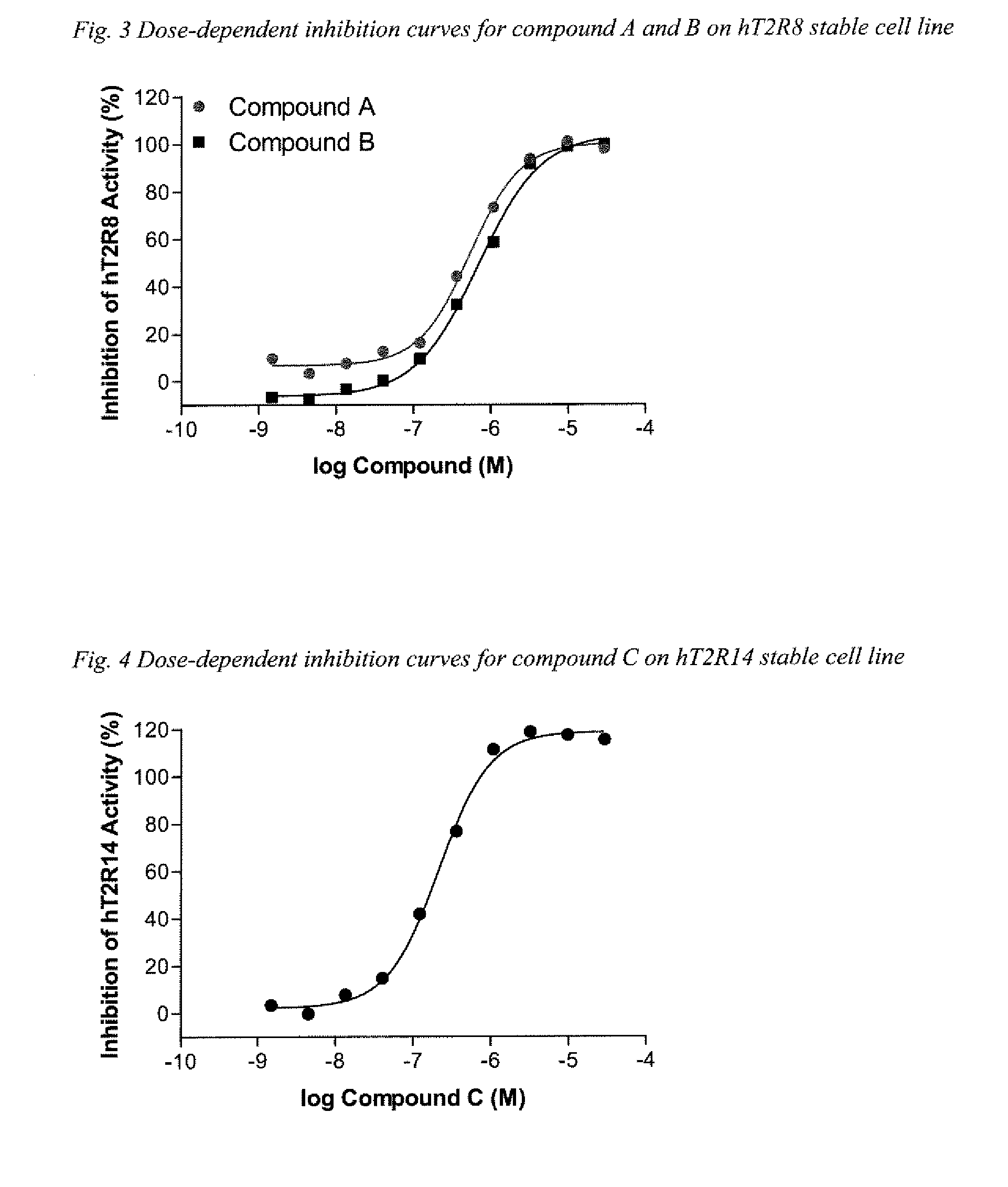
The present invention relates to the discovery that specific human taste receptors in the T2R taste receptor family respond to particular bitter compounds present in, e.g., coffee. Also, the invention relates to the discovery of specific compounds and compositions containing that function as bitter taste blockers and the use thereof as bitter taste blockers or flavor modulators in, e.g., coffee and coffee flavored foods, beverages and medicaments. Also, the present invention relates to the discovery of a compound that antagonizes numerous different human T2Rs and the use thereof in assays and as a bitter taste blocker in compositions for ingestion by humans and animals.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
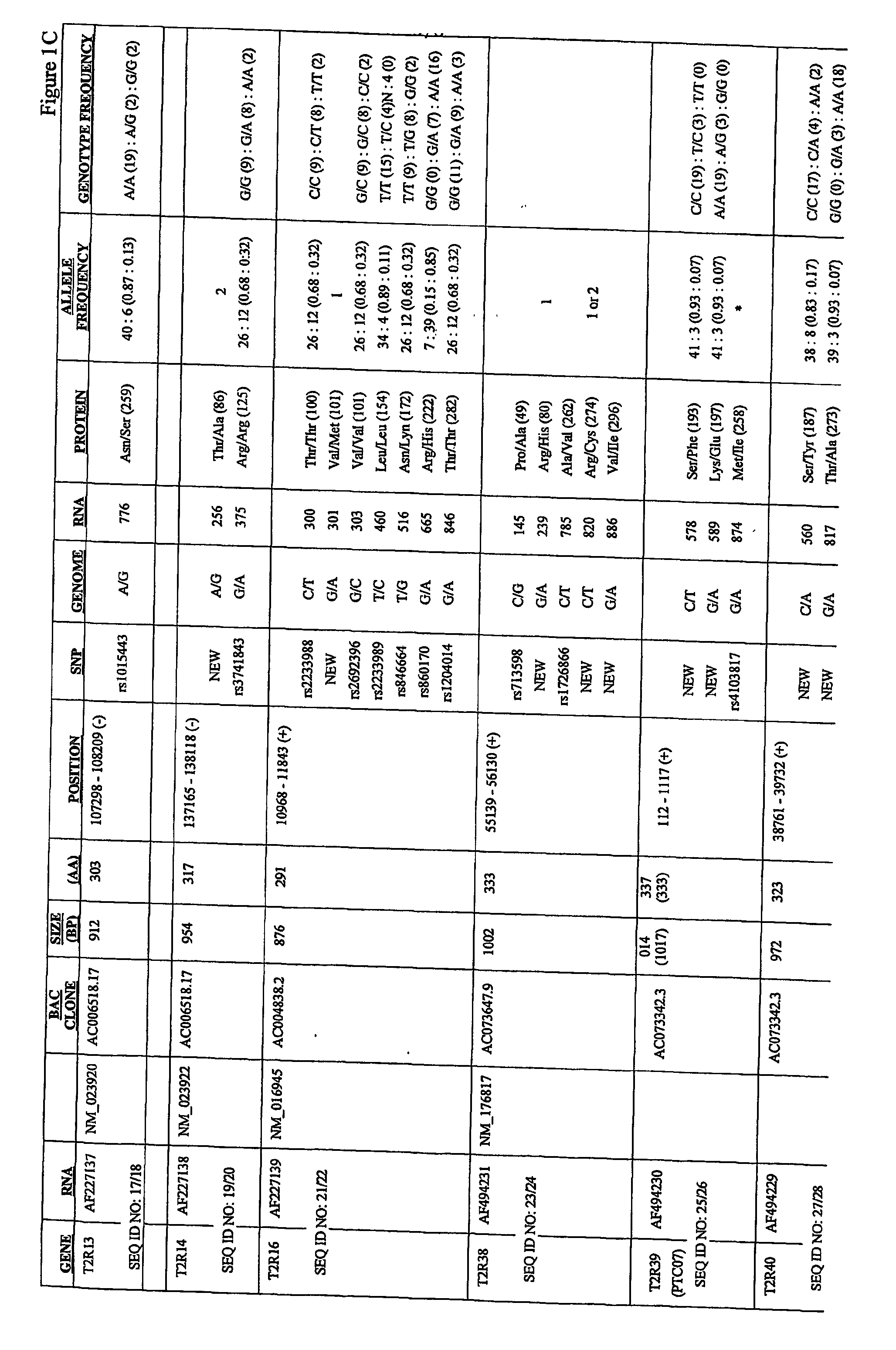
Nucleic acid encoding a haplotype of human T2R receptor hT2R50
InactiveUS7811788B2Suppress bitternessCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsBacteriaTaste receptor ligandBitter tastes
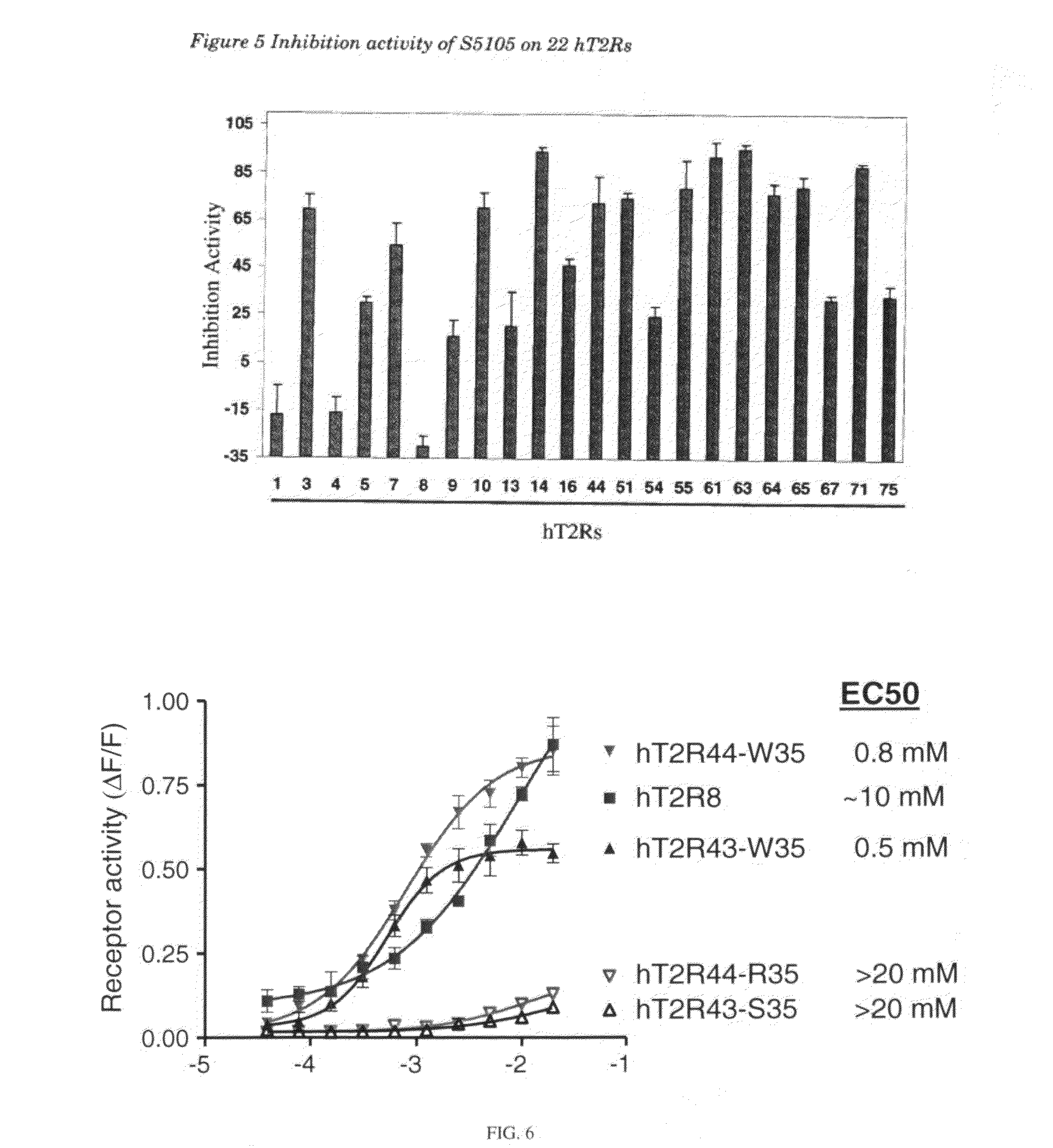
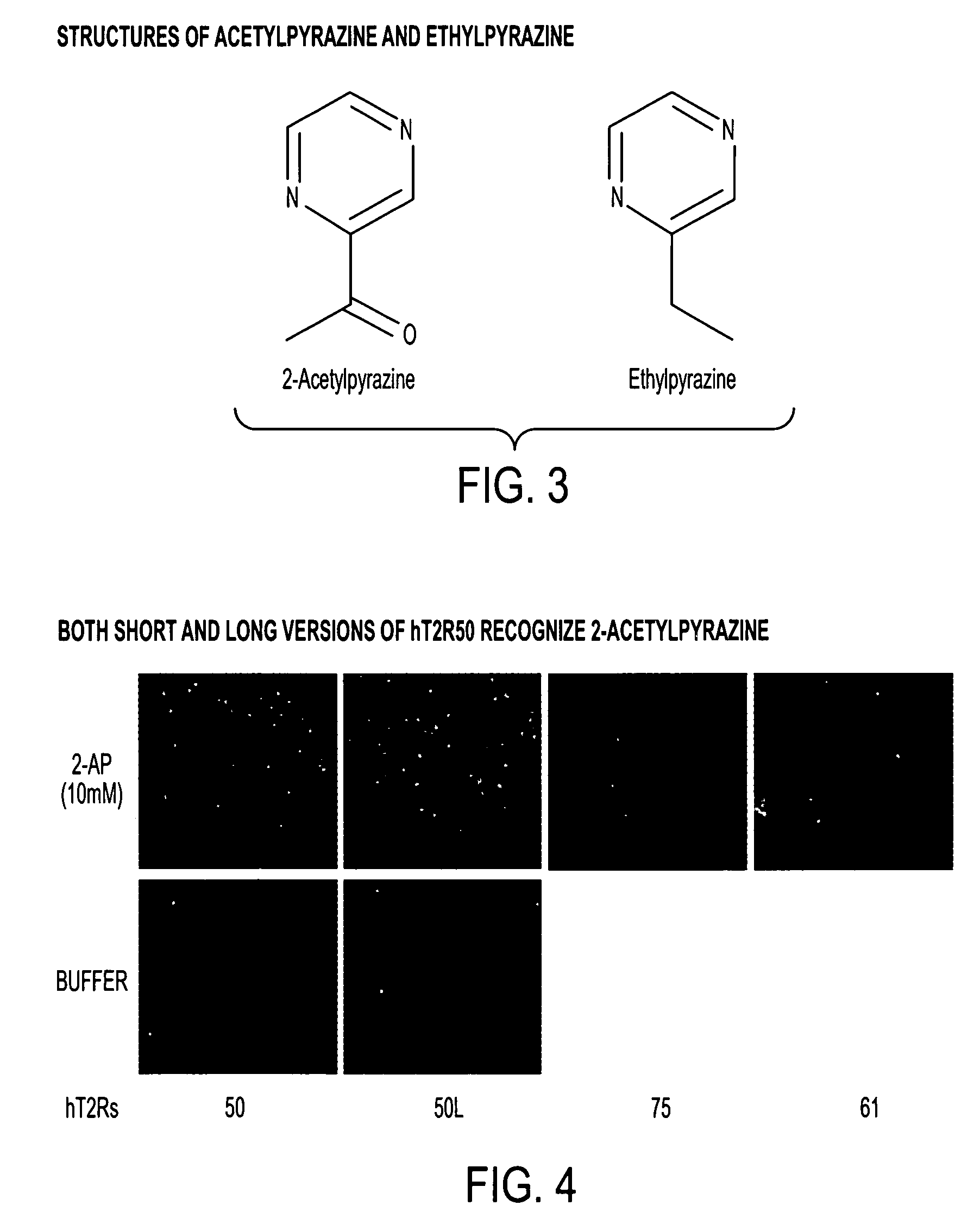
The present invention relates to the discovery of a novel haplotype of the human taste receptor hT2R50 in the T2R taste receptor family that responds to particular bitter ligands, i.e., 2-acetylpyrazine and ethylpyrazine. The present invention also relates to the use of this novel haplotype in assays for identifying ligands that modulate the activation of the hT2R50 taste receptor. These compounds potentially may be used as additives in foods, beverages and medicinals for modifying (blocking) hT2R50-associated bitter taste.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
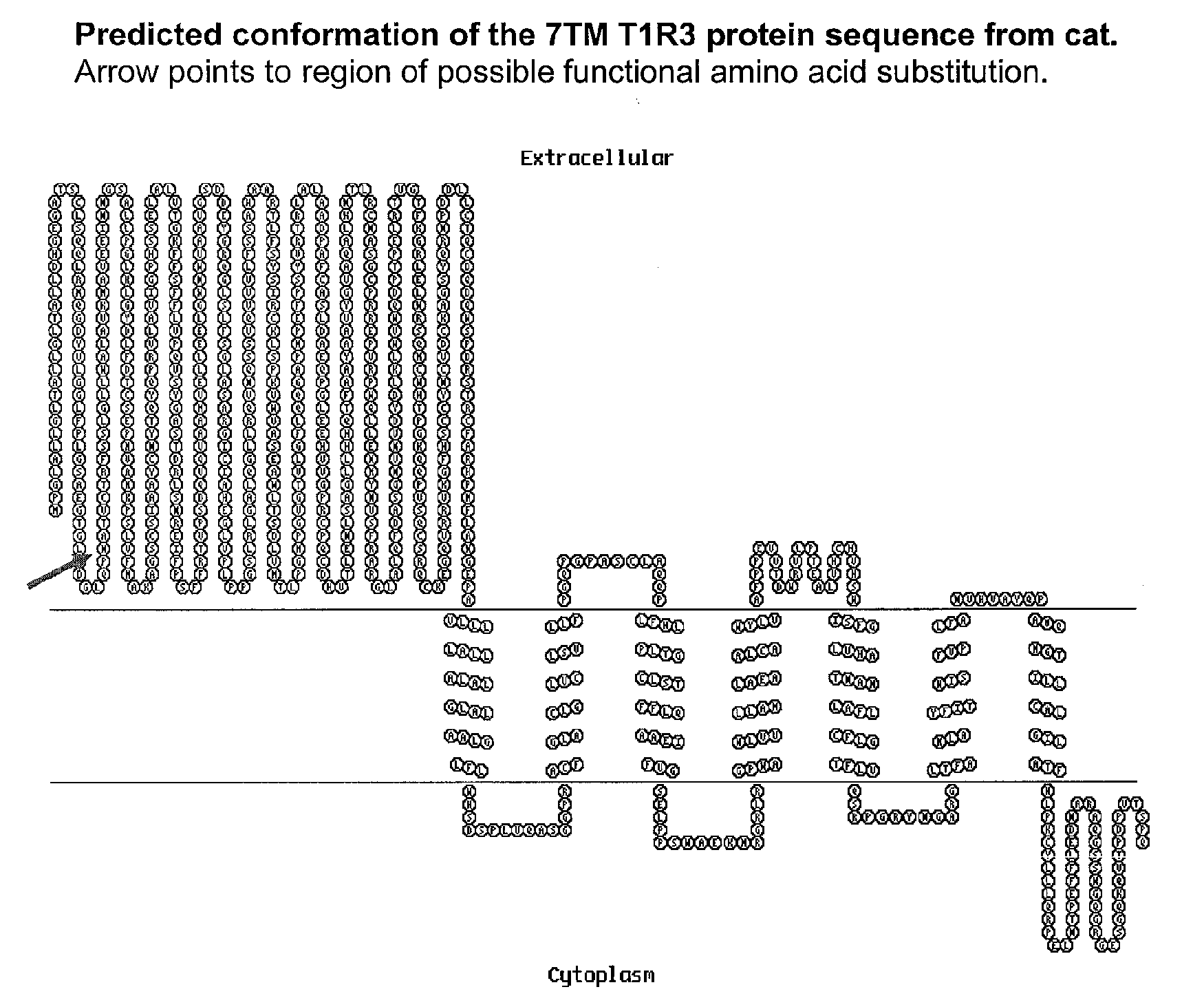
Taste receptors of the T1R family from domestic cat
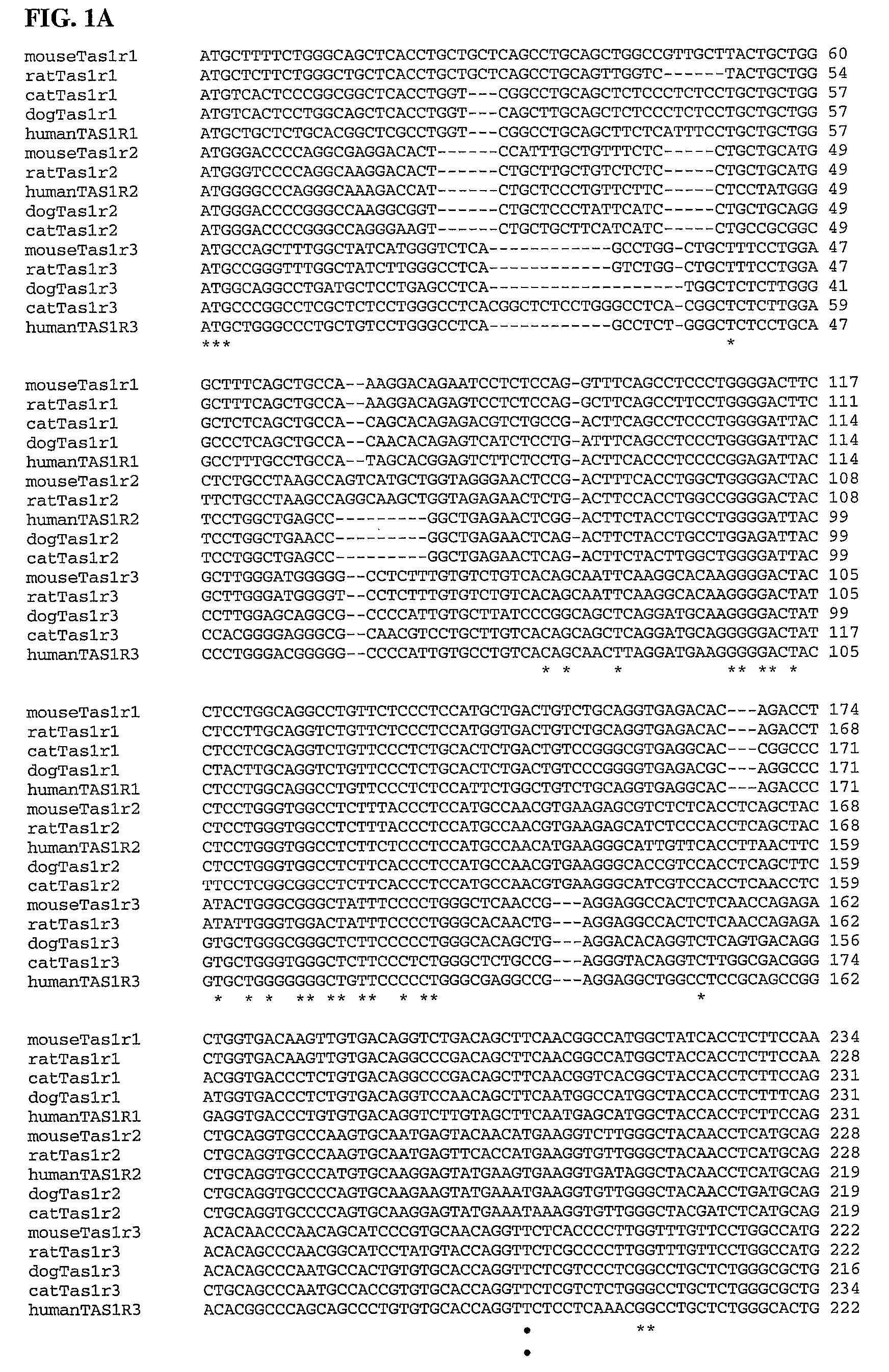
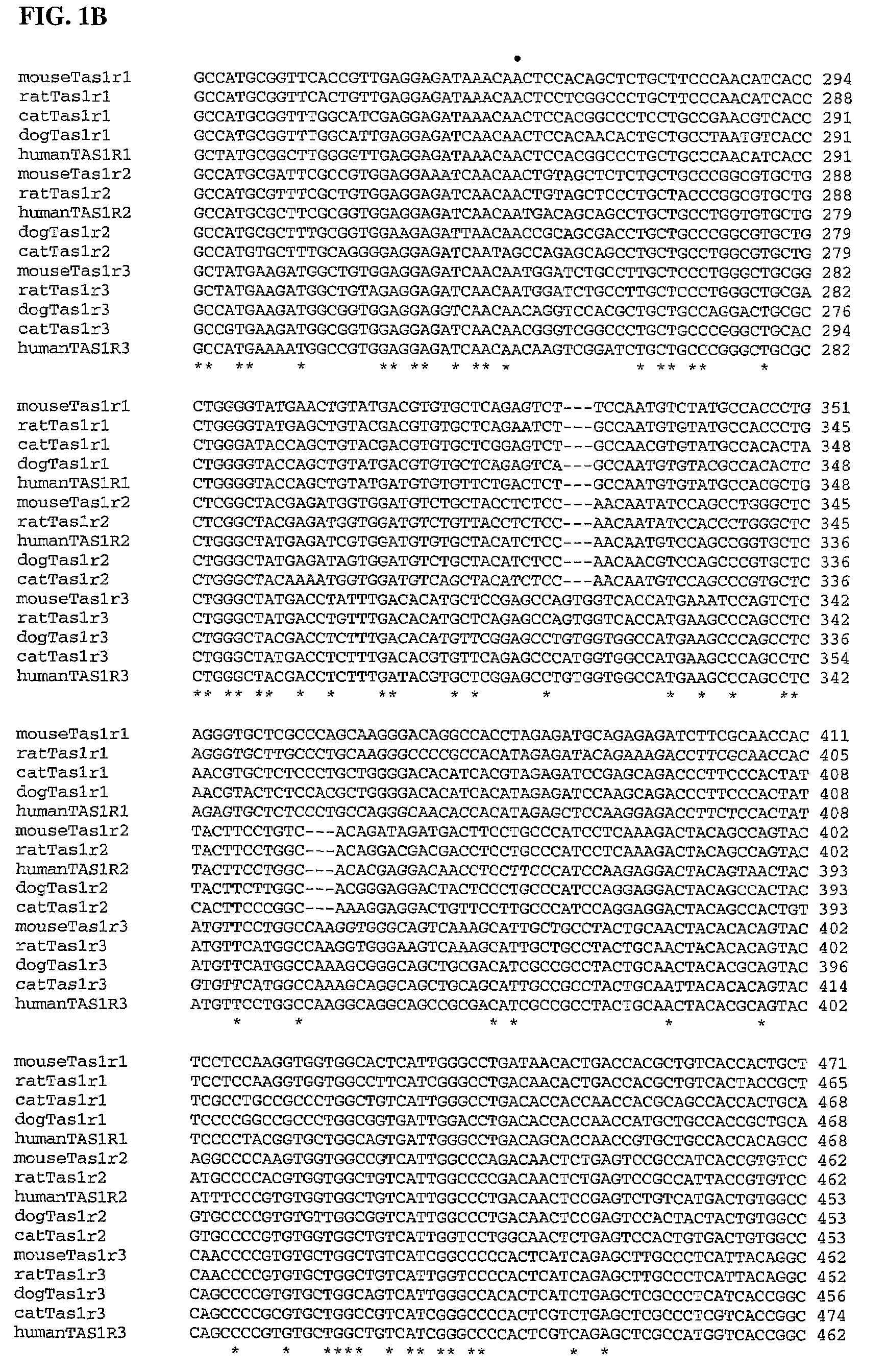
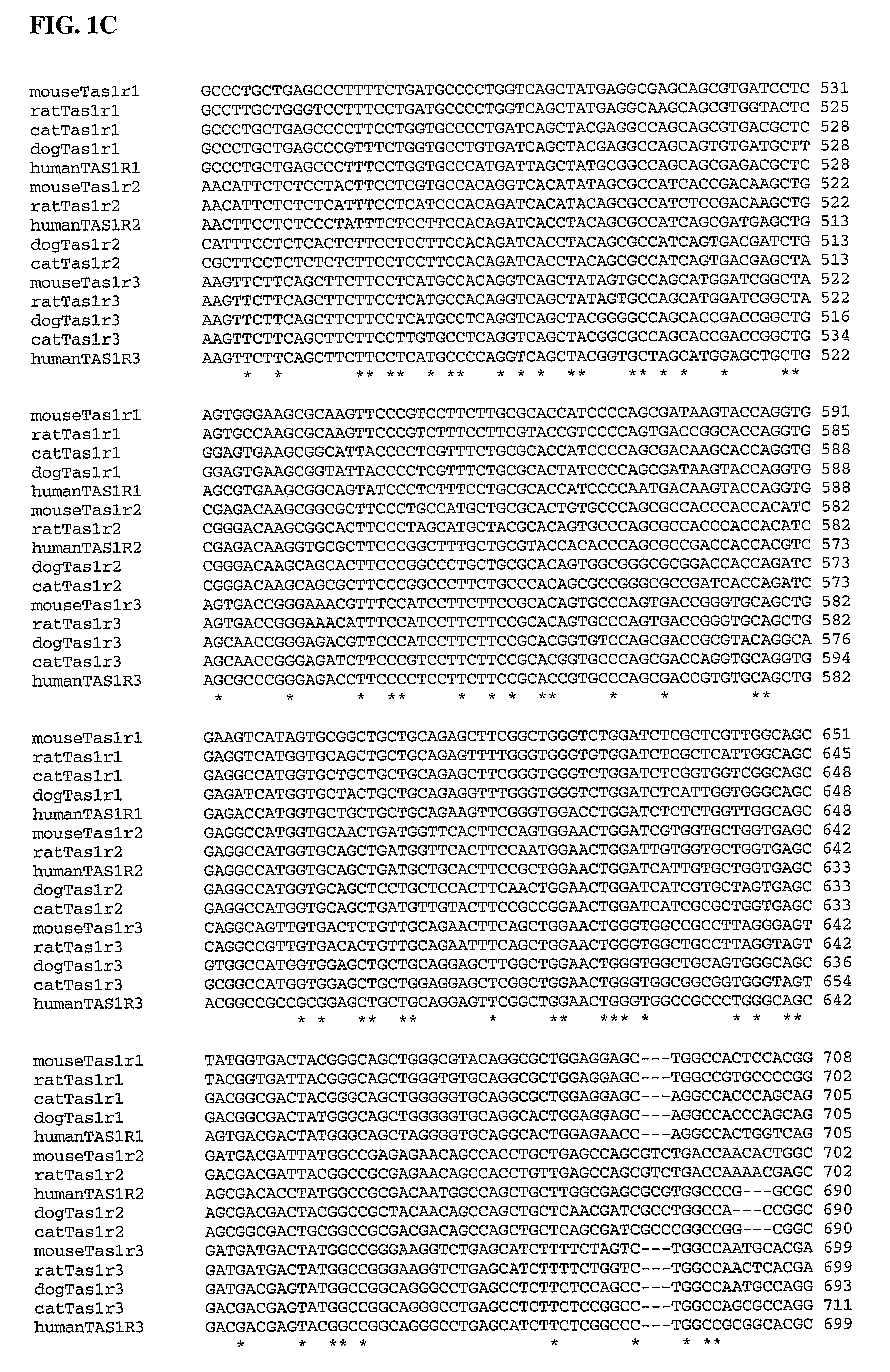
The present invention relates to the discovery of several genes of the domestic cat (Felis catus) associated with taste perception. The invention provides, inter alia, the nucleotide sequence of the feline Tas1r1, Tas1r2, and Tas1r3 receptor genes, the amino acid sequences of the polypeptides encoded thereby, and antibodies to the polypeptides. The present invention also relates to methods for screening for compounds that modify the genes' function or activity, the compounds identified by such screens, and mimetics of the identified compounds. The invention further provides methods for modifying the taste preferences, ingestive responses, or general behavior of a mammal, such as a cat, by administering compounds that affect the function or activity of the gene or the polypeptide encoded thereby.
Owner:MONELL CHEM SENSES CENT
Compounds that inhibit (block) bitter taste in composition and use thereof
ActiveUS7939671B2Reduce bitternessInhibition of activationBiocideCosmetic preparationsTaste receptor ligandChemical compound
The present invention relates to the discovery that specific human taste receptors in the T2R taste receptor family respond to particular bitter compounds present in, e.g., coffee. Also, the invention relates to the discovery of specific compounds and compositions containing that function as bitter taste blockers and the use thereof as bitter taste blockers or flavor modulators in, e.g., coffee and coffee flavored foods, beverages and medicaments. Also, the present invention relates to the discovery of a compound that antagonizes numerous different human T2Rs and the use thereof in assays and as a bitter taste blocker in compositions for ingestion by humans and animals.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
Taste receptors of the T1R family from domestic dog
The present invention relates to the discovery of several genes of the domestic dog (Canine familiaris) associated with taste perception. The invention provides, inter alia, the nucleotide sequence of the canine Tas1r1, Tas1r2, and Tas1r3 receptor genes, the amino acid sequences of the polypeptides encoded thereby, and antibodies to the polypeptides. The present invention also relates to methods for screening for compounds that modify the genes' function or activity, the compounds identified by such screens, and mimetics of the identified compounds. The invention further provides methods for modifying the taste preferences, ingestive responses, or general behavior of a mammal such as a dog by administering compounds that affect the function or activity of the gene or the polypeptide encoded thereby.
Owner:MONELL CHEM SENSES CENT
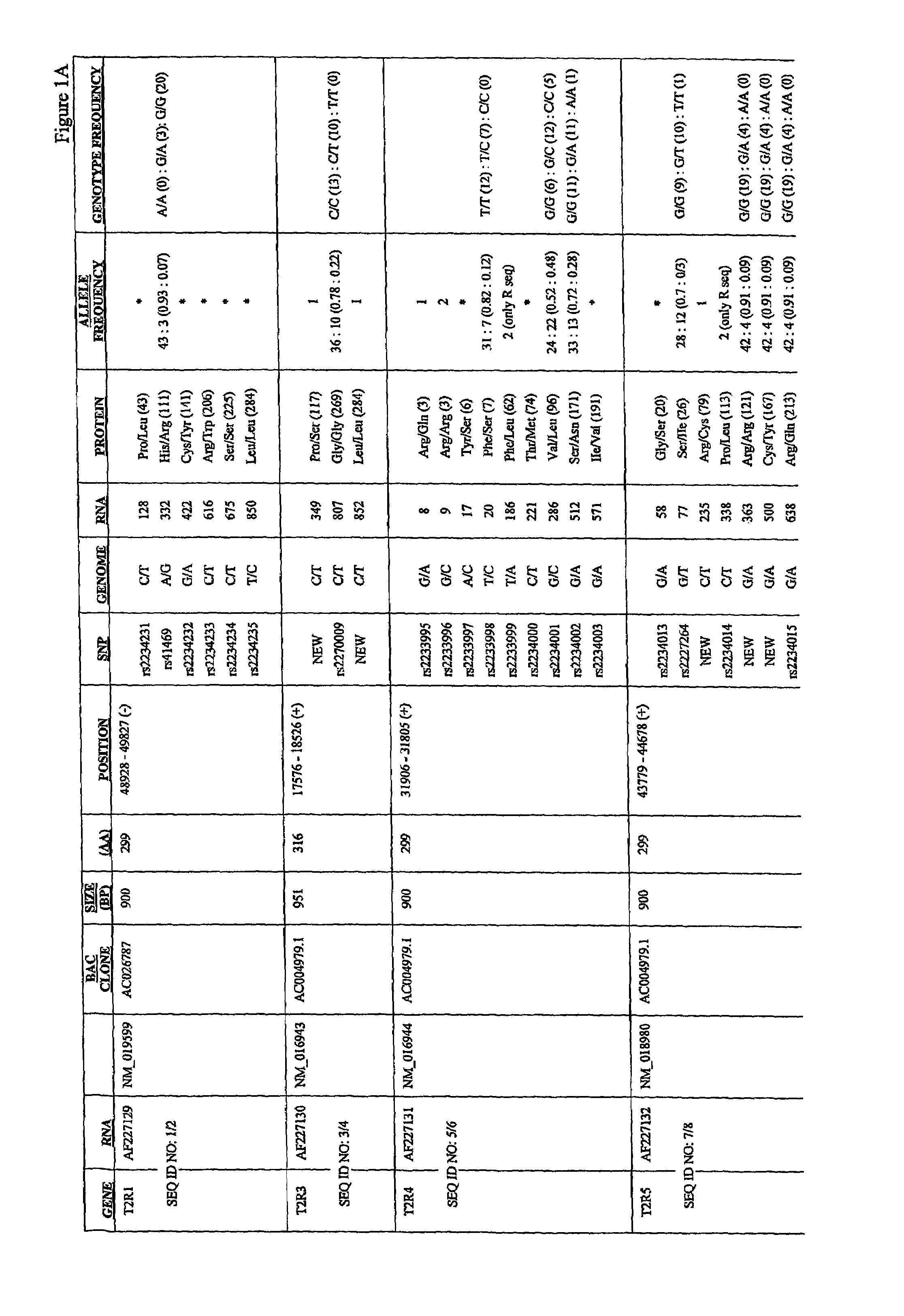
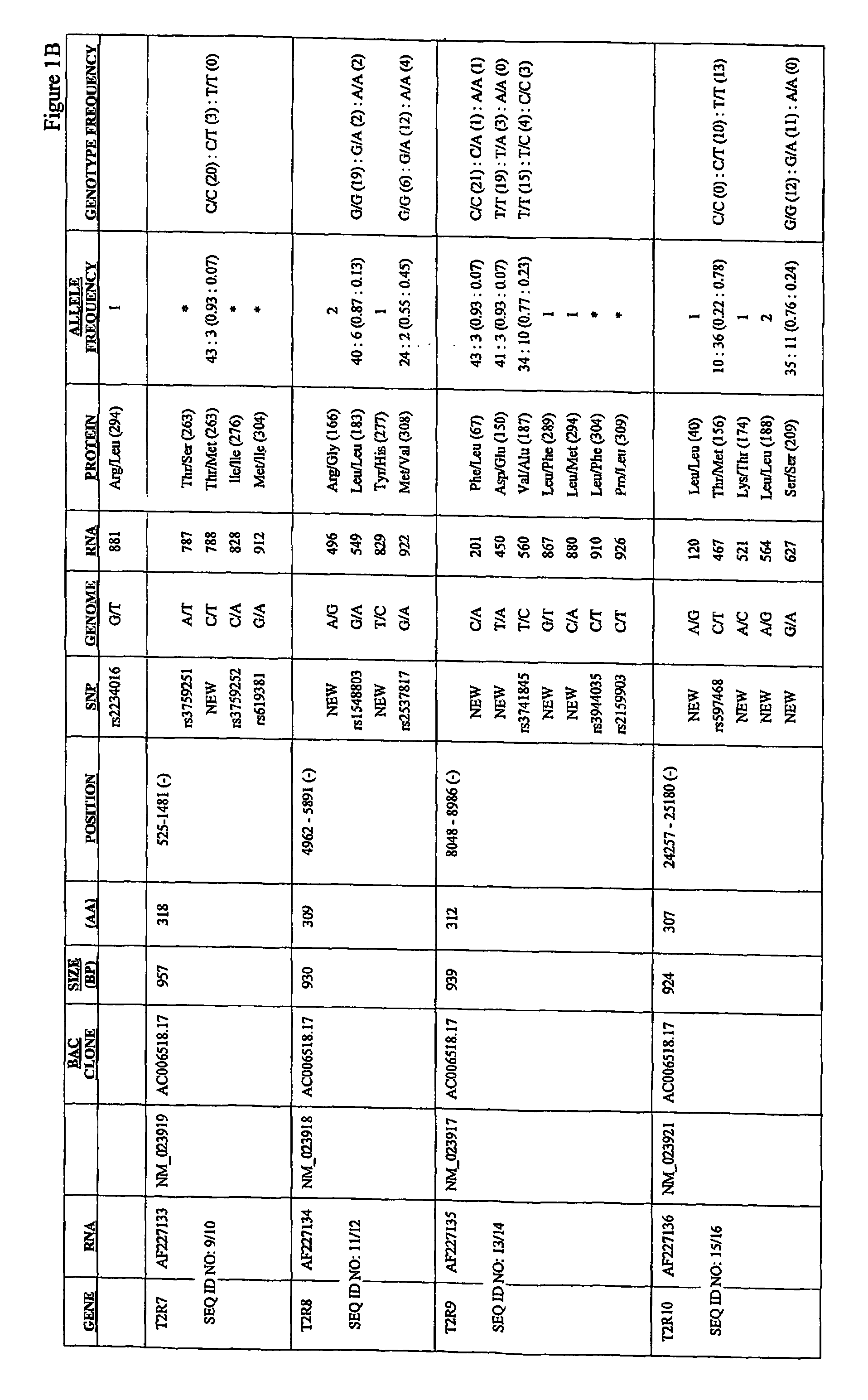
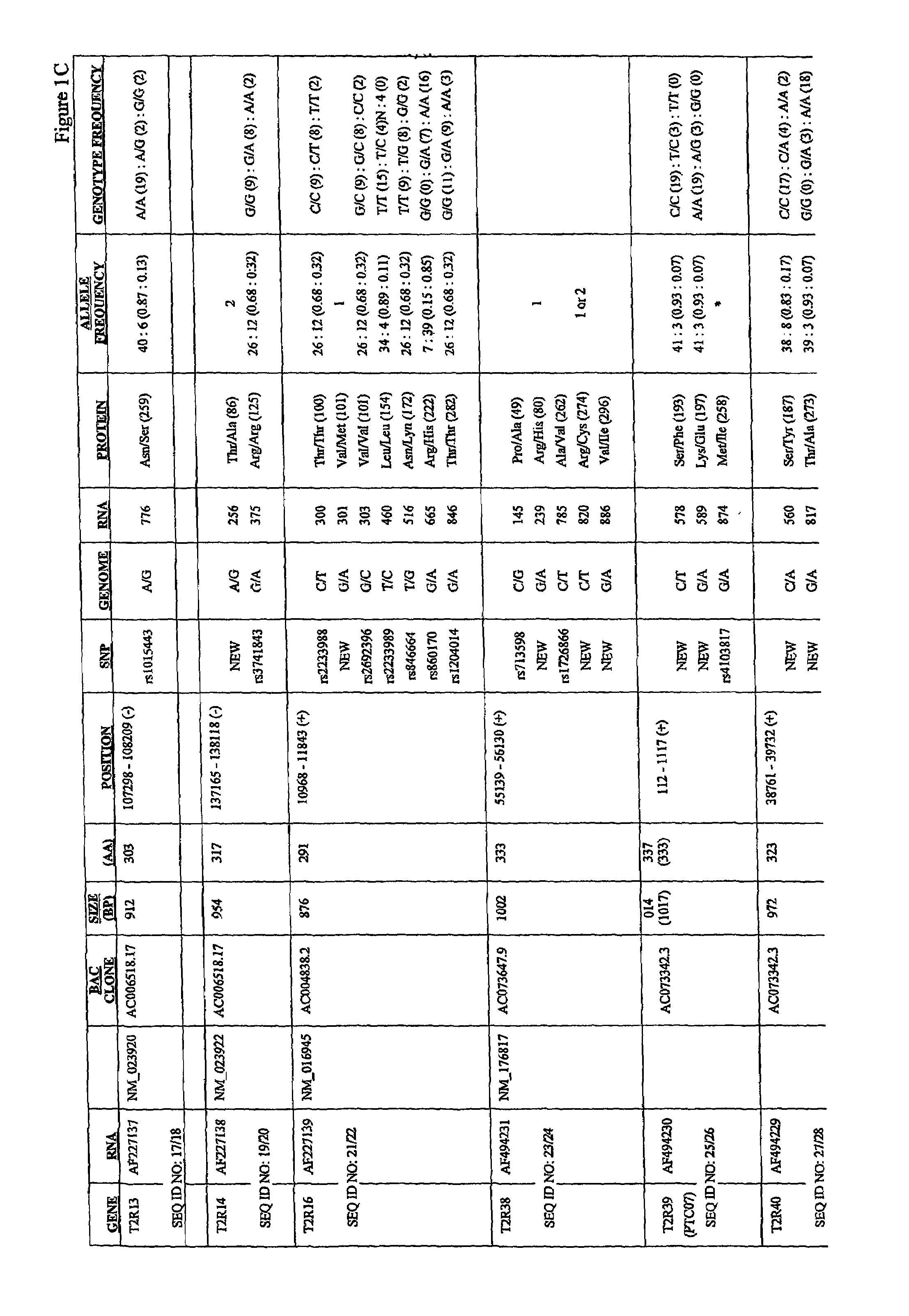
Variants of human taste receptor genes
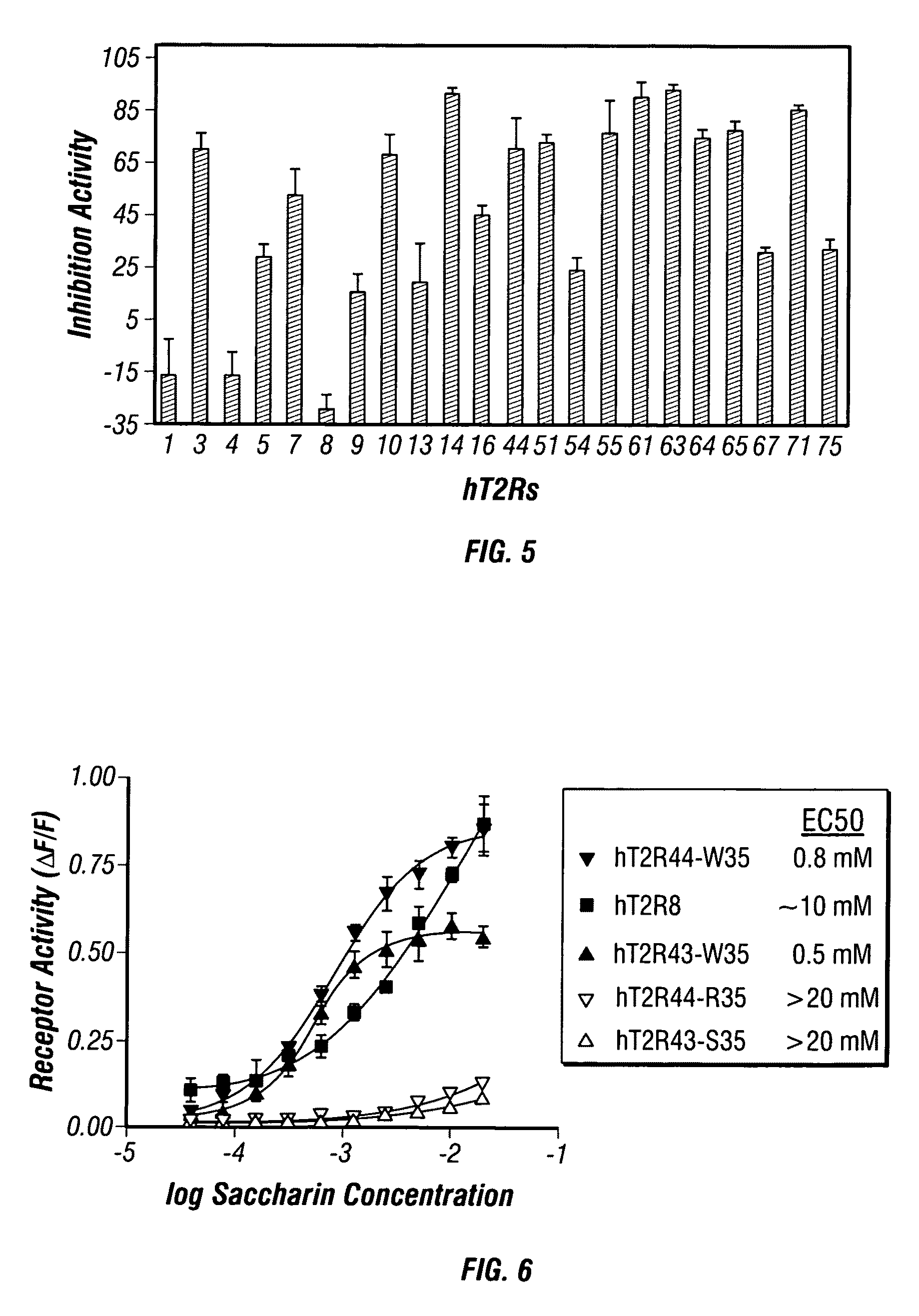
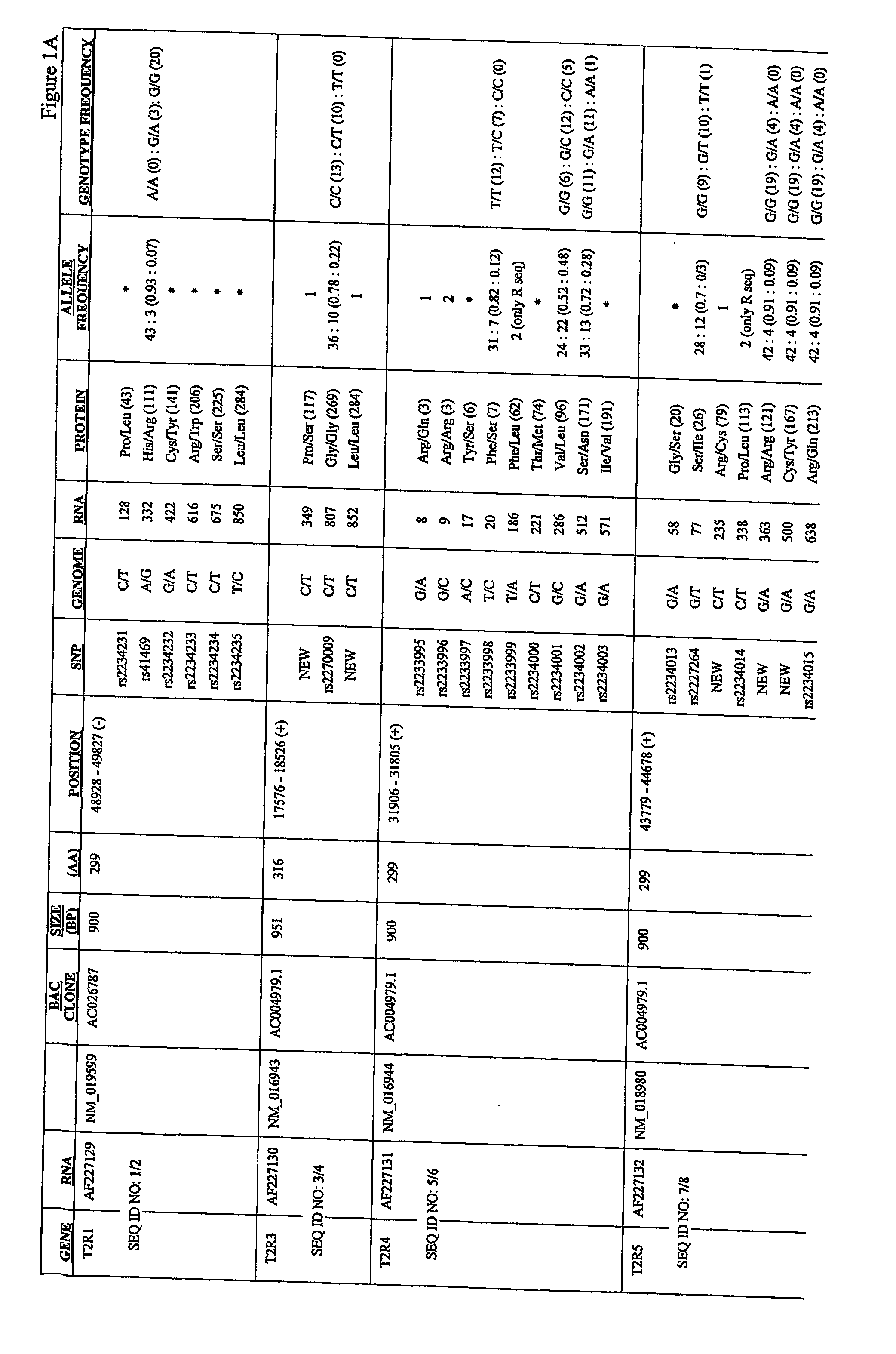
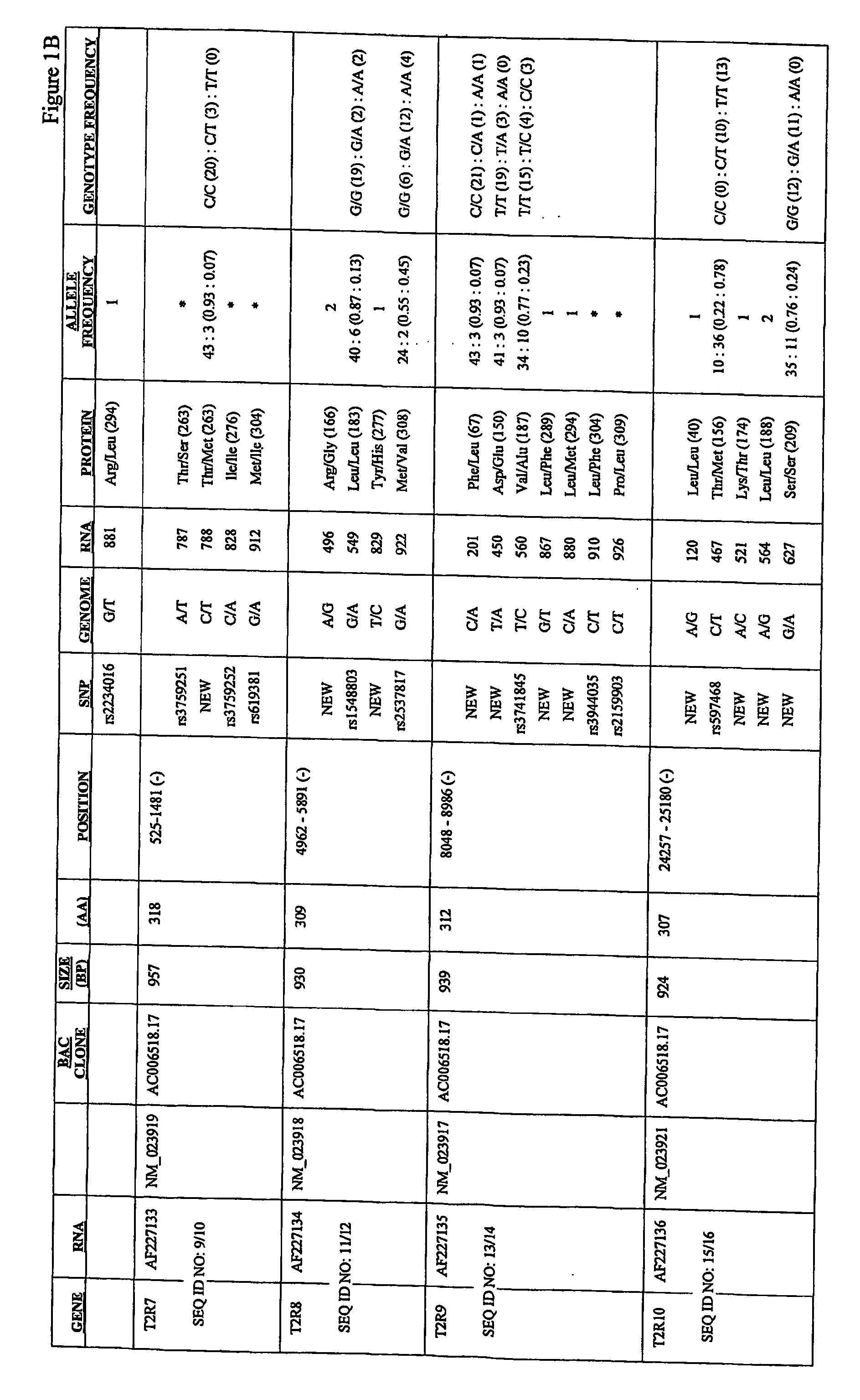
Identified herein are different forms of bitter receptor genes that occur in different humans. These alleles are generated by numerous coding single nucleotide polymorphisms (cSNP's) that occur within the members of the T2R gene family. Some SNP's cause amino acid substitutions, while others introduce chain termination codons, rendering the allele non-functional. Differences in these genes are believed to have a large effect on those individuals' sense of bitter taste, such that these individuals perceive the taste of bitter substances differently than the rest of the population. The ability to assay this allelic information is useful in the development of flavorings and flavor enhancers, as it can be used to define large groups and populations who perceive bitter tastes differently. This in turn allows the taste preferences of these groups to be addressed at the molecular level for the first time.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Identification of bitter ligands that specifically activate human T2R receptors and related assays for identifying human bitter taste modulators
InactiveUS8030008B2Compound screeningCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsTaste receptor ligandAssay
The present invention relates to the discovery that specific human taste receptors in the T2R taste receptor family respond to particular bitter compounds. The invention further relates to the use of these receptors in assays for identifying ligands that modulate the activation of these taste receptors by these bitter ligands and related compounds and which may be used as additives and / or removed from foods, beverages, cosmetics and medicinals in order to modify (block) T2R-associated bitter taste.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
Method for screening a potential modulator compound of a taste receptor
ActiveUS20120276563A1Improve the level ofHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisTaste receptor ligandBiochemistry
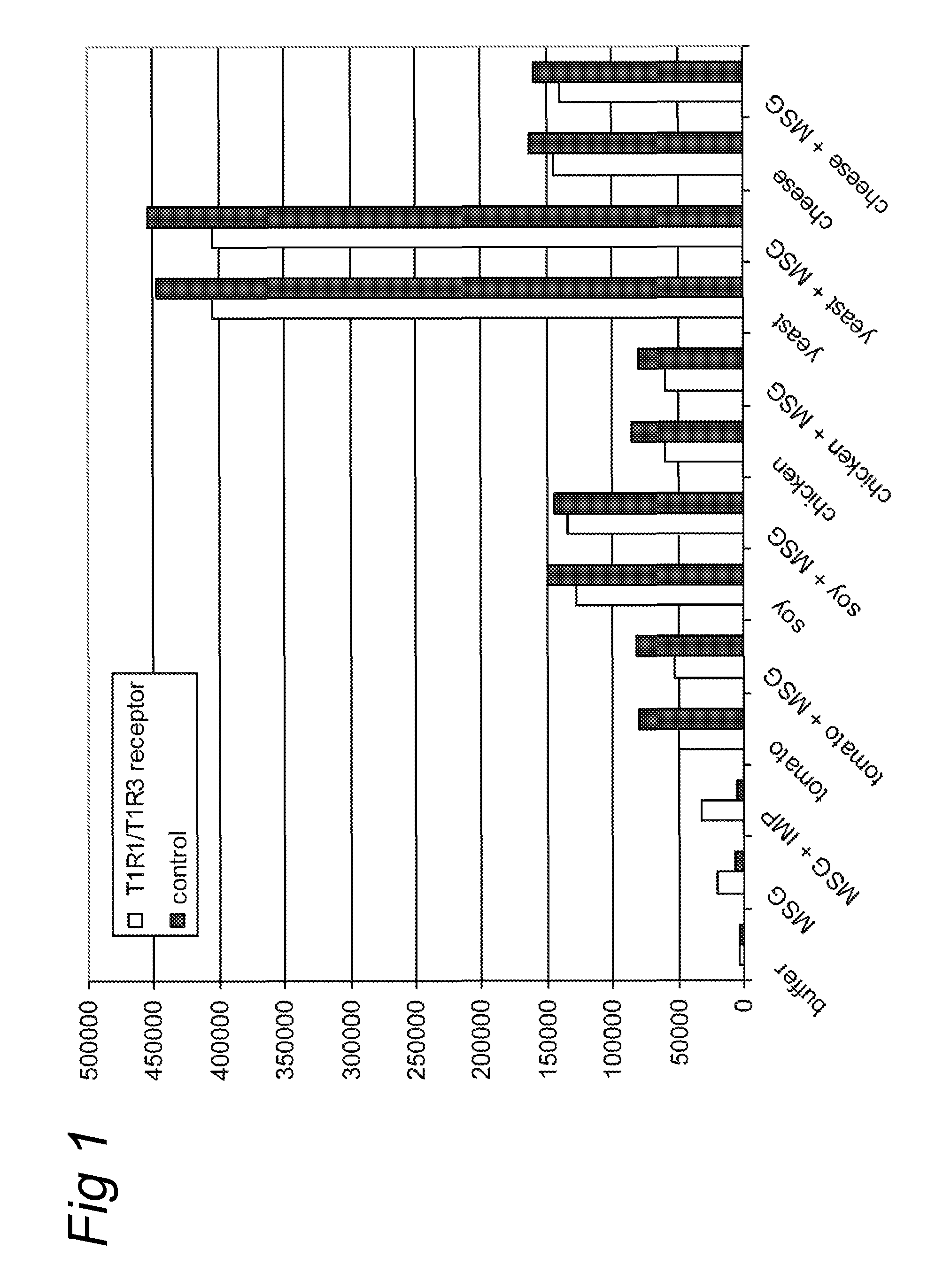
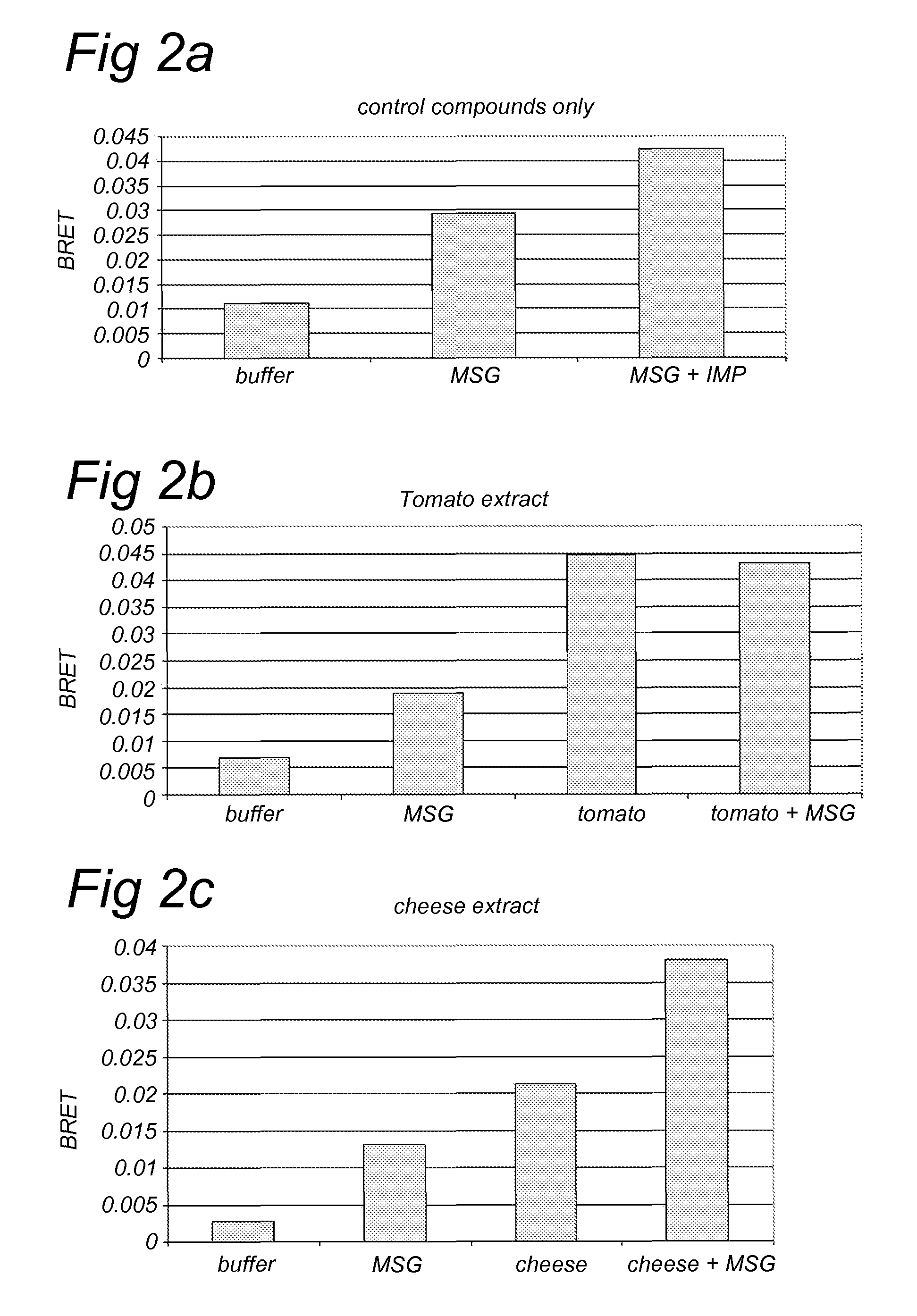
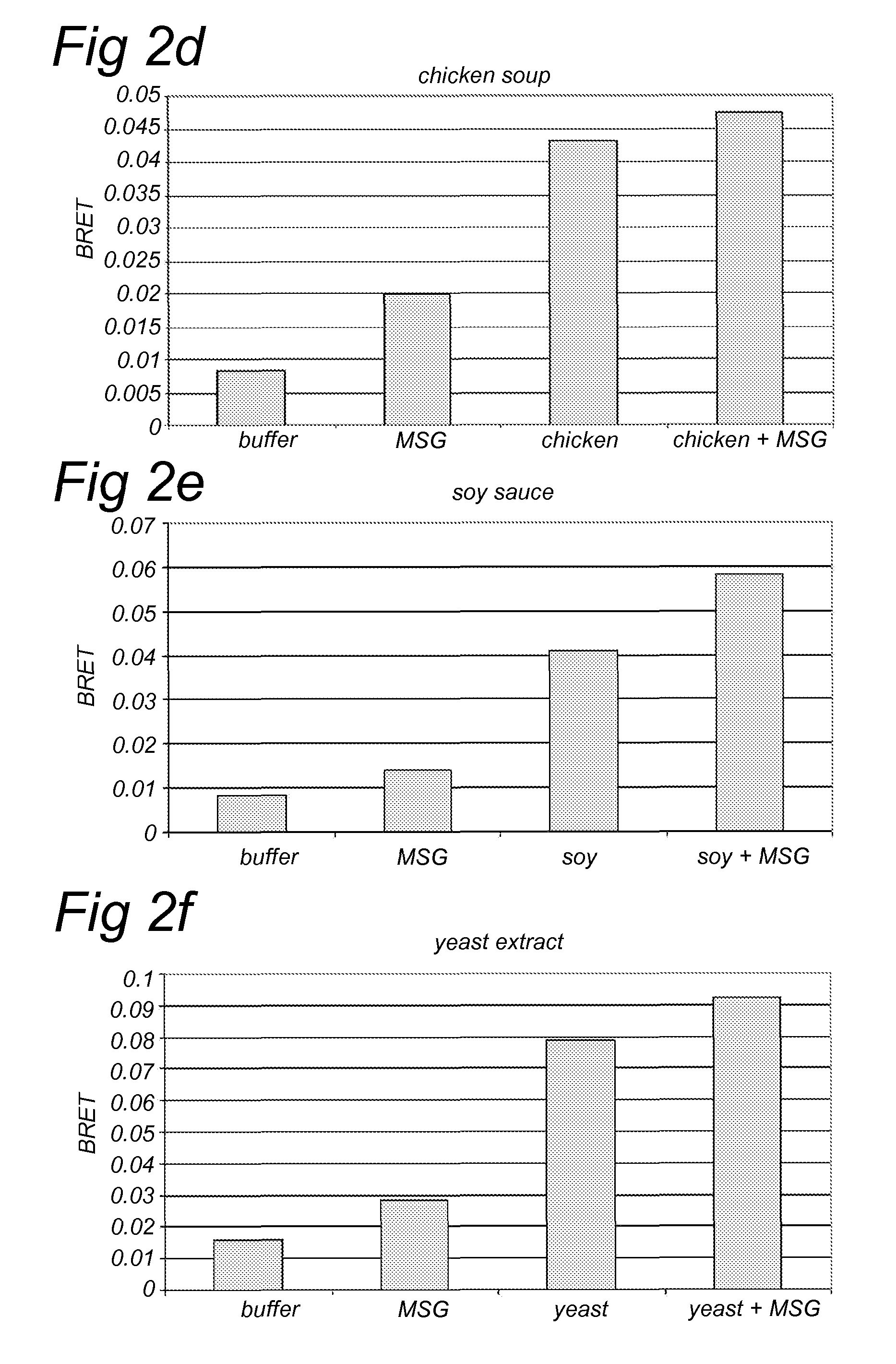
A method for screening a potential modulator compound of a taste receptor wherein use is made of a BRET technique.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
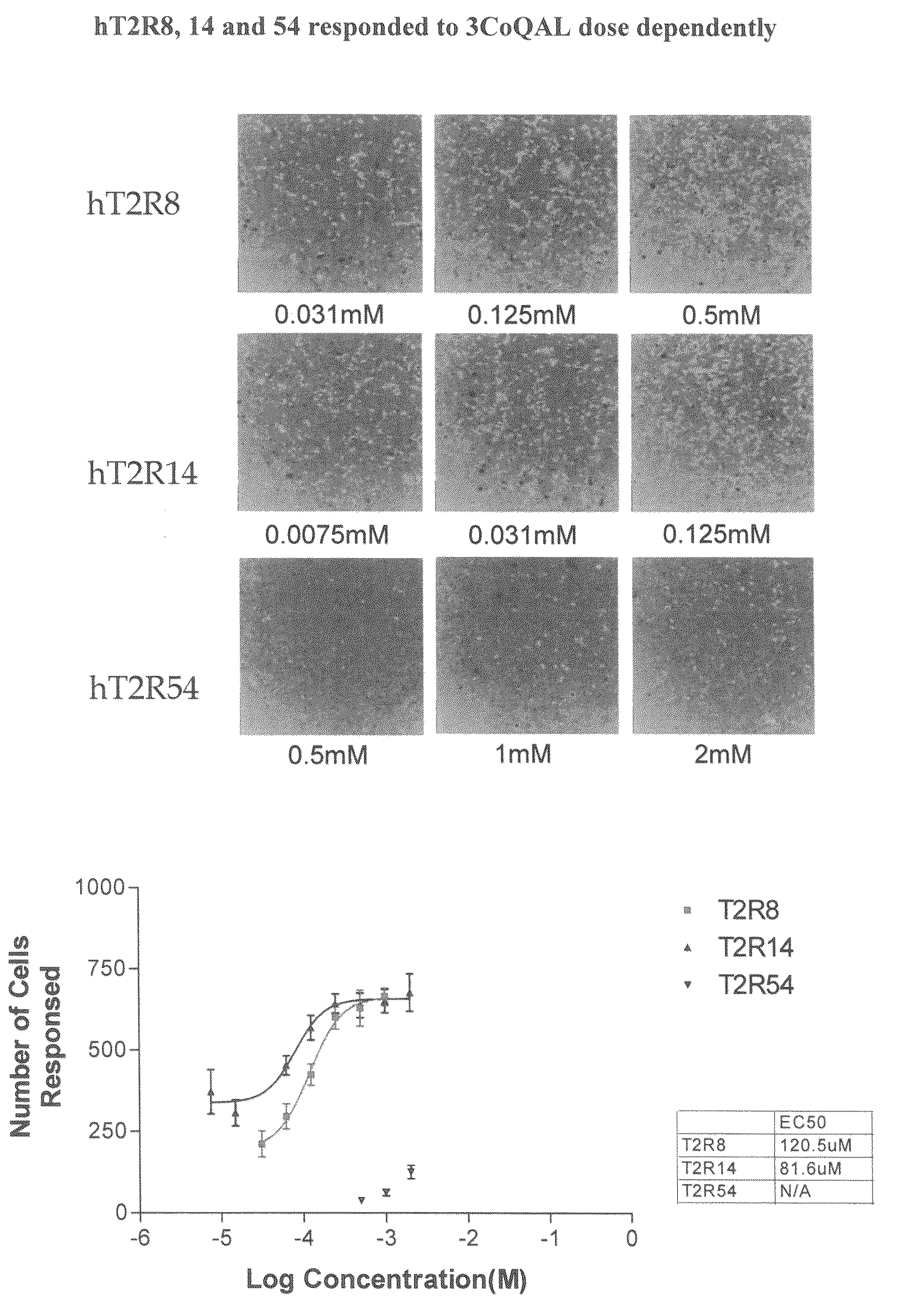
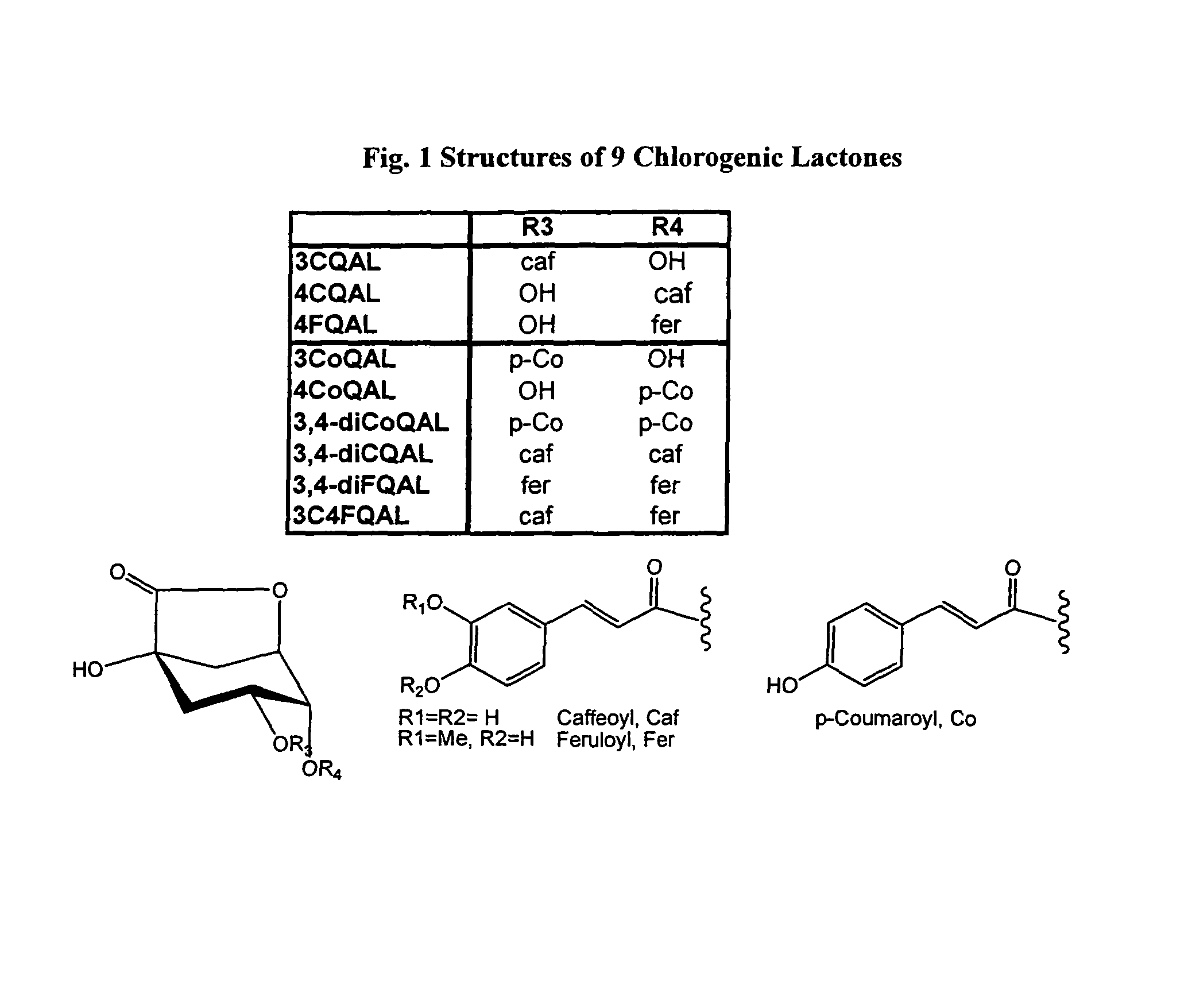
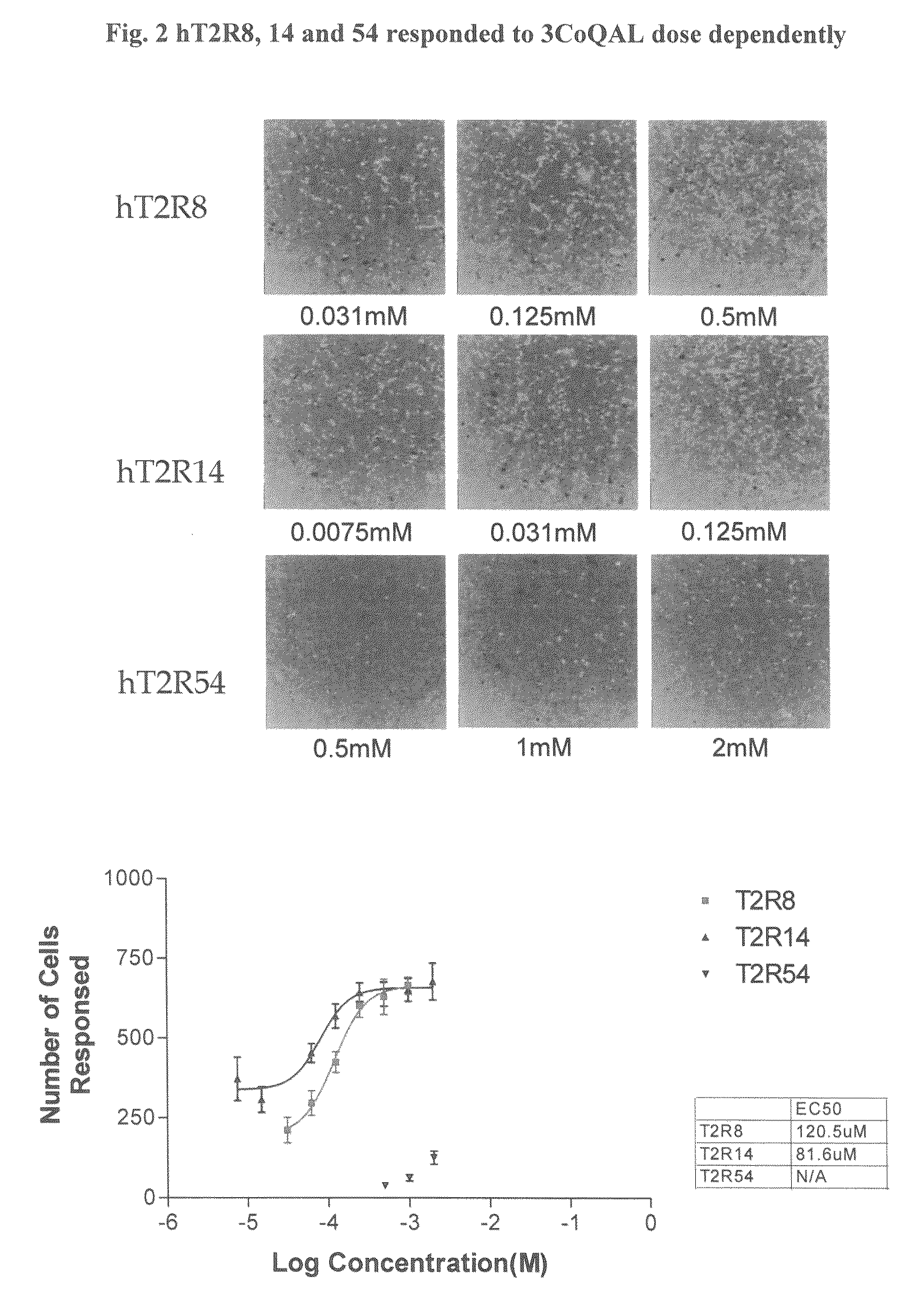
Assays which screen for compounds that modulate bitter taste of chlorogenic lactone compounds
ActiveUS7939276B2Compound screeningCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsTaste receptor ligandBitter tastes
Owner:SENOMYX INC
Processing method of roxburgh rose juice
ActiveCN104544416AStabilizes and strengthens natural qualitiesGuarantee quality stabilityFood scienceAlgluceraseSaccharum
The invention relates to a processing method of roxburgh rose juice. The processing method of the roxburgh rose juice disclosed by the invention is characterized by comprising the following steps: A, draining after cleaning fresh roxburgh roses, which are sufficiently matured and are not decayed and mildewed, and squeezing and filtering through a mechanical squeezing method so as to obtain original roxburgh rose juice; B, adding 20-25 U / L of beta-glucosidase into the roxburgh rose juice, keeping at 45 DEG C for 60-70 min, adding 25-30 U / L of glucose oxidase into the roxburgh rose juice again, and keeping at 35-40 DEG C for 40-50 min; and C, adding 0.03-0.04% of adenylic acid and 0.015-0.020% of sucralose into the processed juice, uniformly mixing, after adjusting by using saccharose till the juice is sour and sweet properly, instantly sterilizing at high temperature, bottling and cooling, wherein the sucralose is added after being dissolved in clear water. The roxburgh rose juice disclosed in the invention is processed under the mild conditions by using a biologic enzymatic technology, so that natural quality of juice is stabilized and strengthened; the sensory characteristics of the roxburgh rose juice are improved by utilizing influence of a substrate to human-body taste receptors; the processing method of the roxburgh rose juice is simple and feasible, high-efficiency and safe; and furthermore, the nutritional components in the roxburgh rose juice are effectively reserved.
Owner:贵州初好农业科技开发有限公司
Compounds that inhibit (BLOCK) bitter taste in composition and use thereof
ActiveUS20120088796A1Reduce bitternessSalicyclic acid active ingredientsBiocideTaste receptor ligandBitter tastes
The present invention relates to the discovery that specific human taste receptors in the T2R taste receptor family respond to particular bitter compounds present in, e.g., coffee. Also, the invention relates to the discovery of specific compounds and compositions containing that function as bitter taste blockers and the use thereof as bitter taste blockers or flavor modulators in, e.g., coffee and coffee flavored foods, beverages and medicaments. Also, the present invention relates to the discovery of a compound that antagonizes numerous different human T2Rs and the use thereof in assays and as a bitter taste blocker in compositions for ingestion by humans and animals.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
Variants of human taste receptor genes
Identified herein are different forms of bitter receptor genes that occur in different humans. These alleles are generated by numerous coding single nucleotide polymorphisms (cSNP's) that occur within the members of the T2R gene family. Some SNP's cause amino acid substitutions, while others introduce chain termination codons, rendering the allele non-functional. Differences in these genes are believed to have a large effect on those individuals' sense of bitter taste, such that these individuals perceive the taste of bitter substances differently than the rest of the population. The ability to assay this allelic information is useful in the development of flavorings and flavor enhancers, as it can be used to define large groups and populations who perceive bitter tastes differently. This in turn allows the taste preferences of these groups to be addressed at the molecular level for the first time.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Model Taste Cells and Methods of Use for Identifying Modulators of Taste Sensation
InactiveUS20080026416A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisTaste receptor ligandEnteroendocrine cell
The present invention provides model taste cells that naturally or recombinantly express taste receptors and relevant cellular proteins and / or molecules useful for taste signal transduction. The present invention further provides methods of use for these model taste cells for screening for compounds that modulate sweet and / or other taste signal transduction. Compositions comprising the compounds / modulators identified using the model taste cells are also provided. In preferred embodiments, the model taste cells are derived from human HuTu-80 enteroendocrine cells, and derivative cells thereof.
Owner:THE COCA-COLA CO
Appetite control compositions and methods of use
Appetite control compositions comprise Gymnema sylvestre and an expectorant. In some embodiments, the appetite control compositions contain from about 3 mg to about 50 mg of gymnemic acid (an extract of Gymnema sylvestre), from about 10 mg to about 80 mg of glycyrrhizin (an extract of Glycyrrhiza glabra), high impact flavor, and a sweetening agent in a non-traditional dosage form. A non-traditional dosage form provides for the topical application of medicaments to the tissues of the mouth and tongue, more specifically, to the sweetness taste receptors of the tongue. By delivering gymnemic acid to the sweetness receptors of the tongue, the sensation of sweetness is blocked, thereby providing appetite control.
Owner:CRAVE BUSTERS
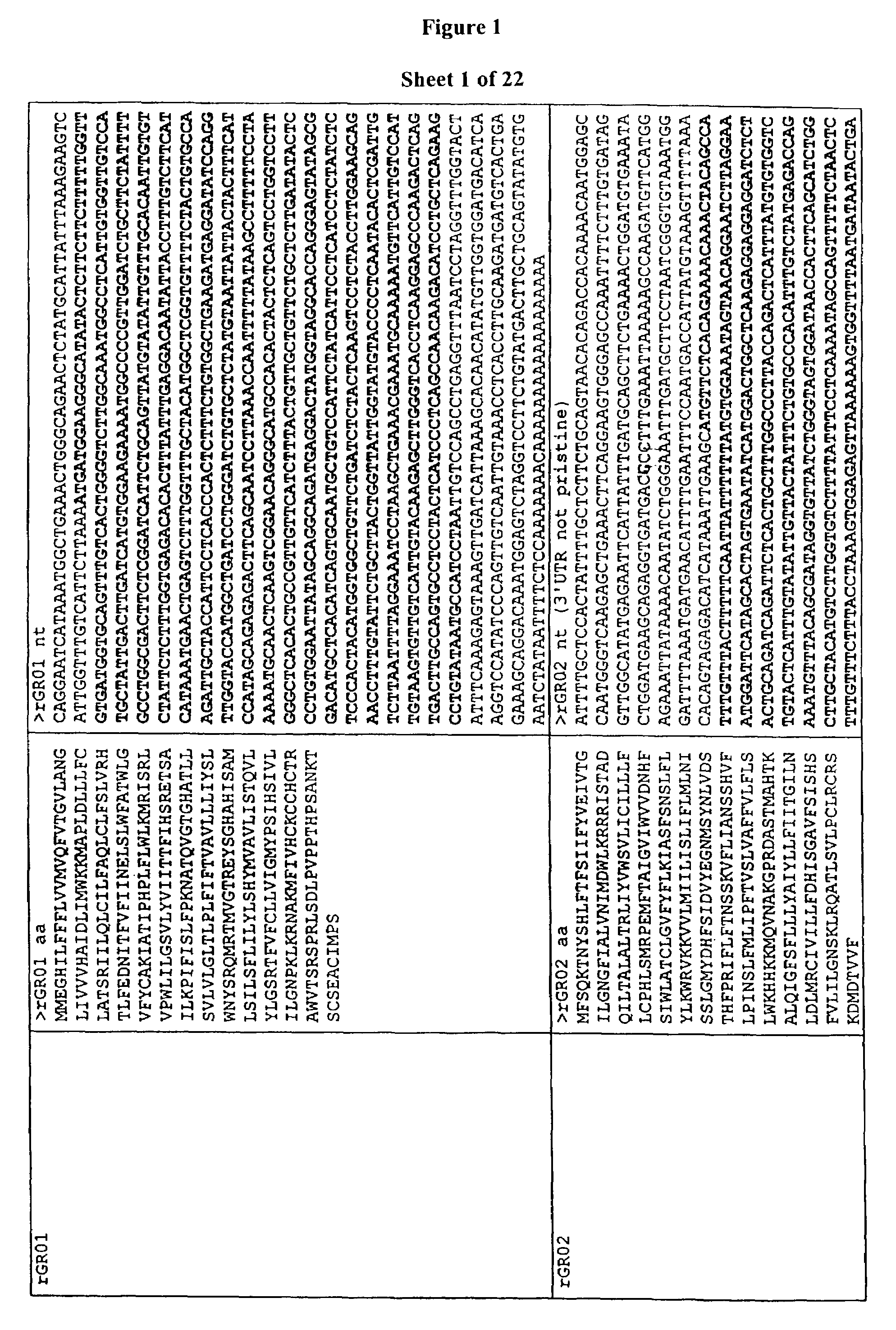
Nucleic acids encoding T2R of taste receptors
InactiveUS7452694B2Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesTaste receptor ligandG protein-coupled receptor
The invention provides isolated nucleic acid and amino acid sequences of taste cell specific G-protein coupled receptors, antibodies to such receptors, methods of detecting such nucleic acids and receptors, and methods of screening for modulators of taste cell specific G-protein coupled receptors.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
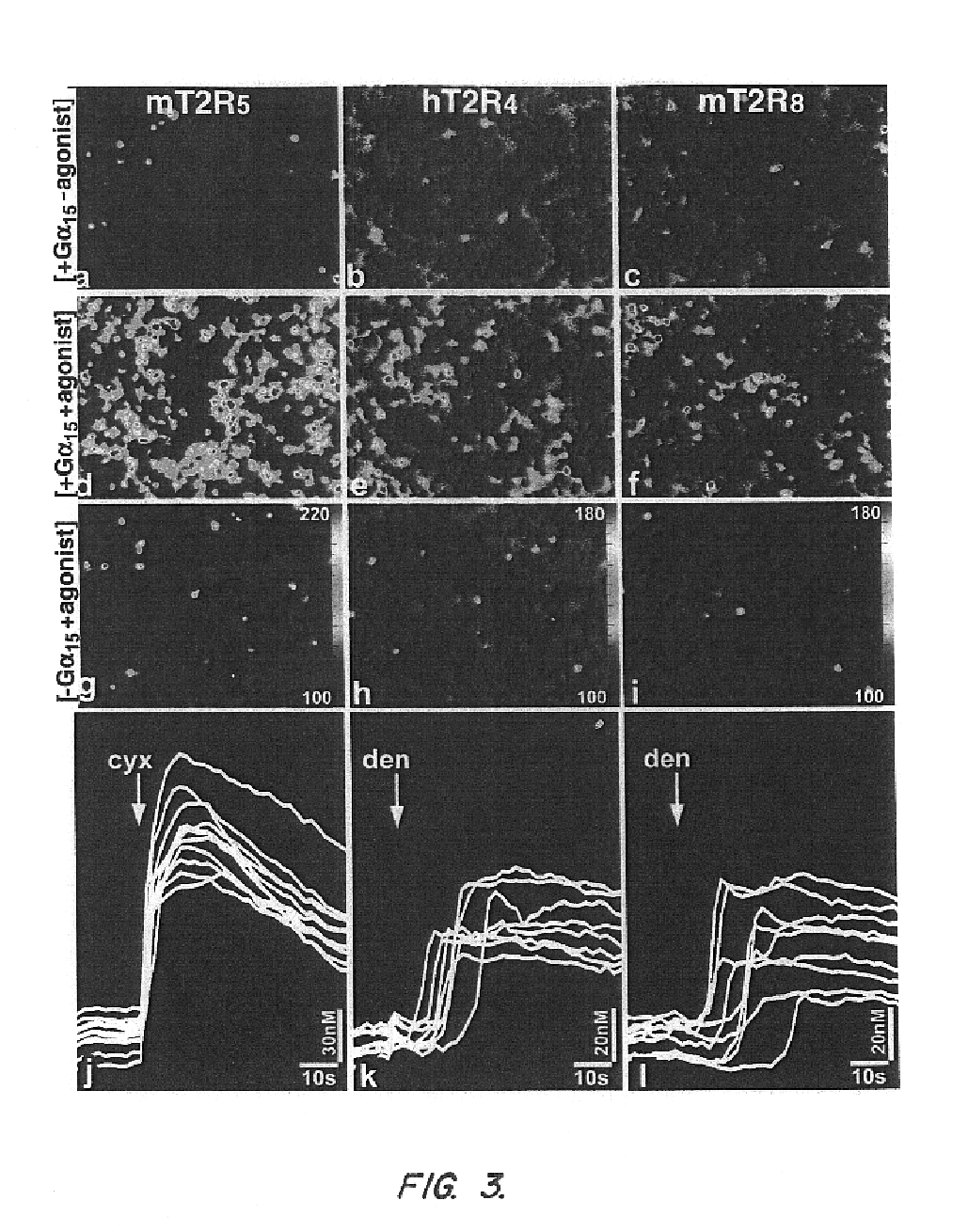
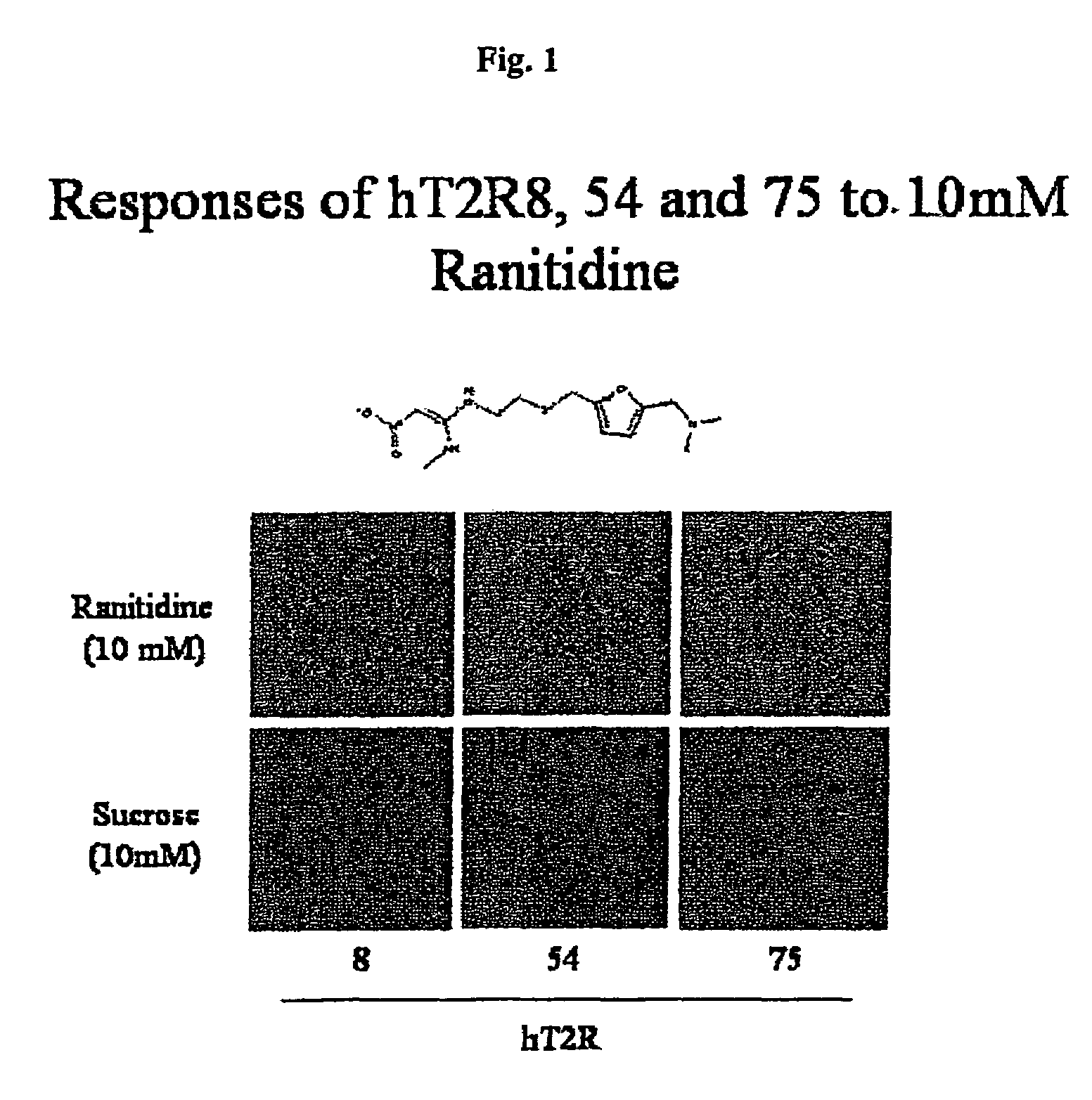
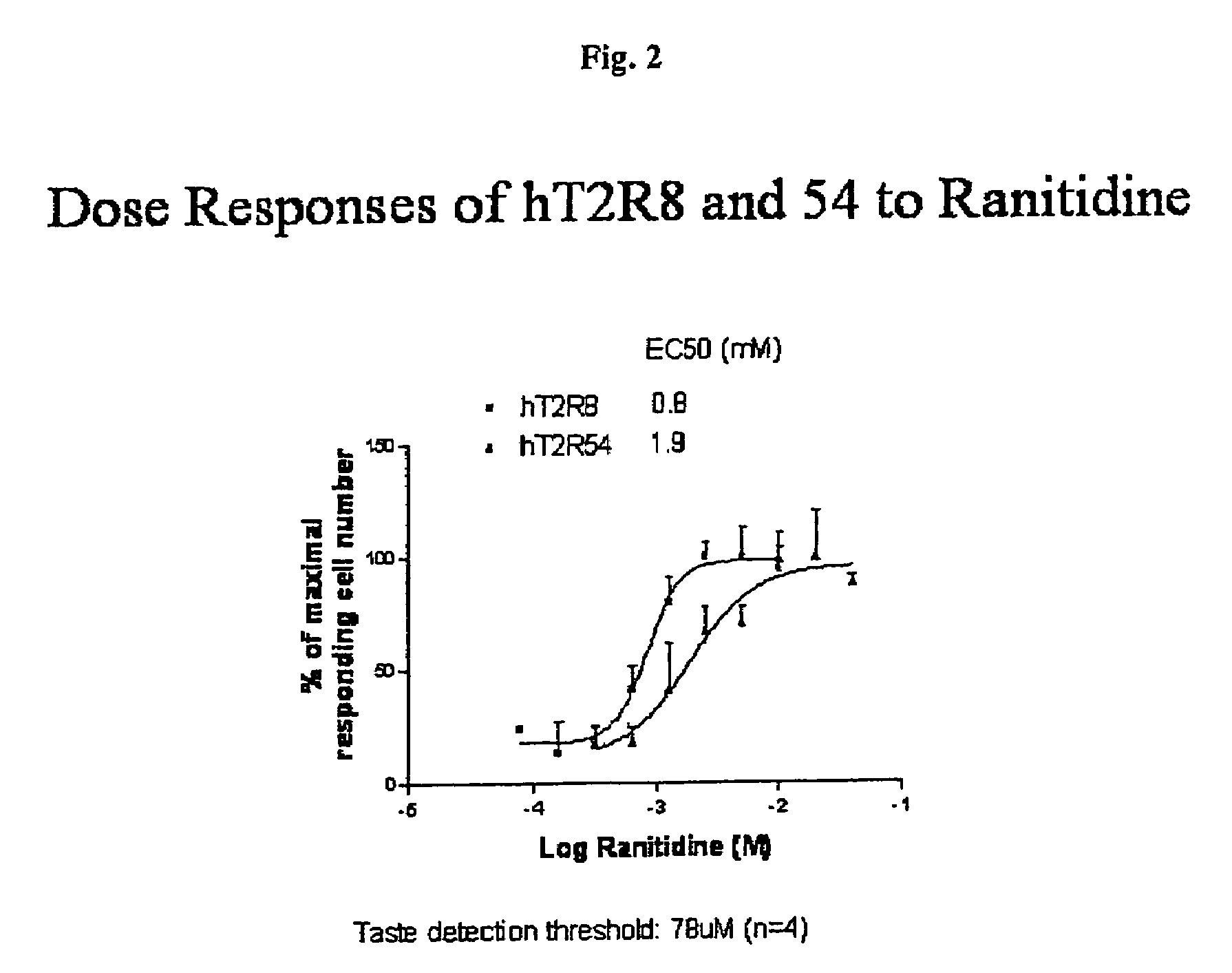
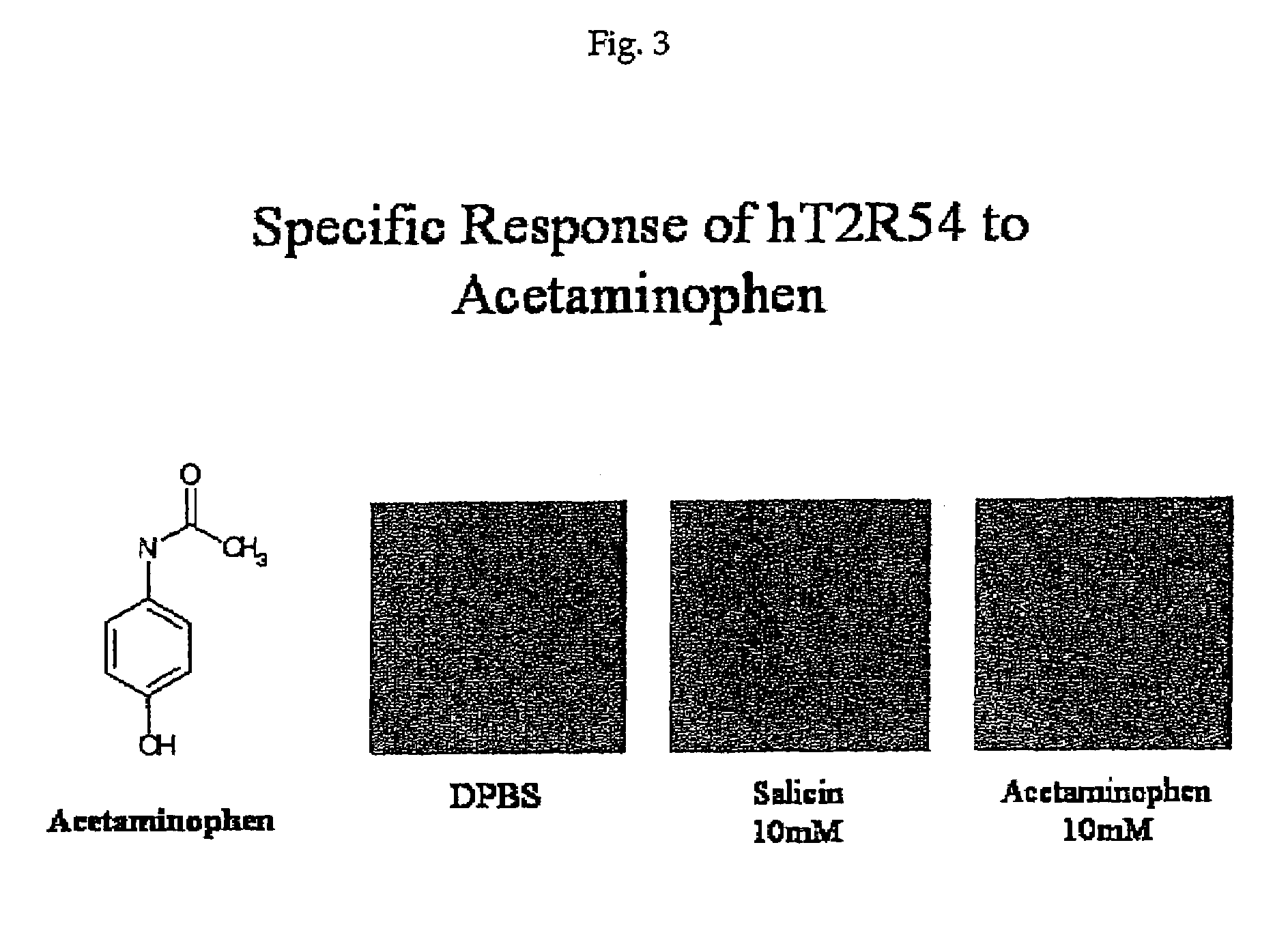
Human T2R receptors for acetaminophen ranitidine, strychnine and denatomium and related assays for identifying human bitter taste modulators
ActiveUS7407765B2Compound screeningCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsTaste receptor ligandRanitidine
The present invention relates to the discovery that specific human taste receptors in the T2R taste receptor family respond to particular bitter ligands, i.e., acetaminophen, ranitidine, strychnine and denatonium. The present invention further relates to the use of these receptors in assays for identifying ligands that modulate the activation of these taste receptors and which may be used as additives in foods, beverages and medicinals for modifying (blocking) T2R-associated bitter taste.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
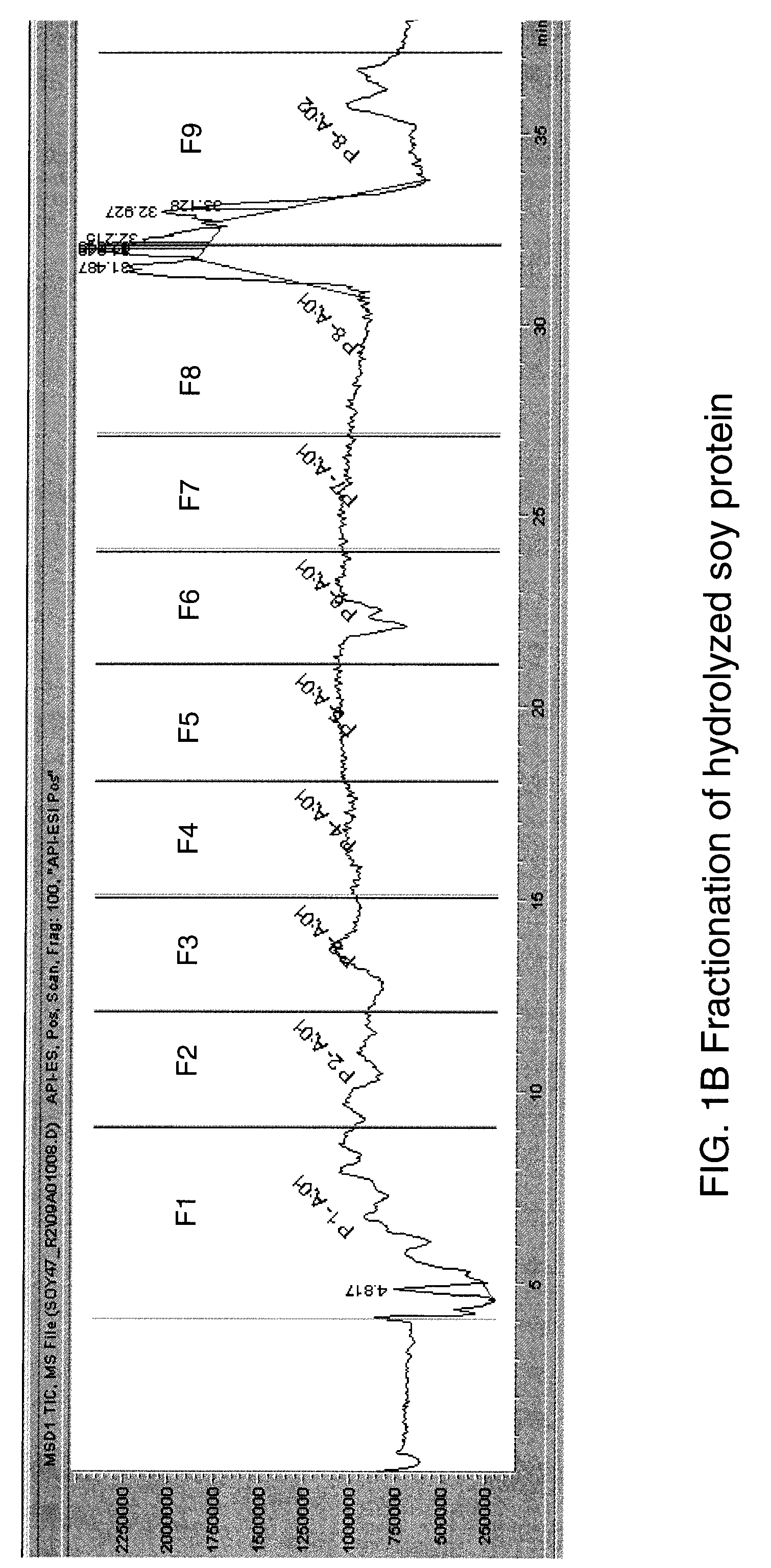
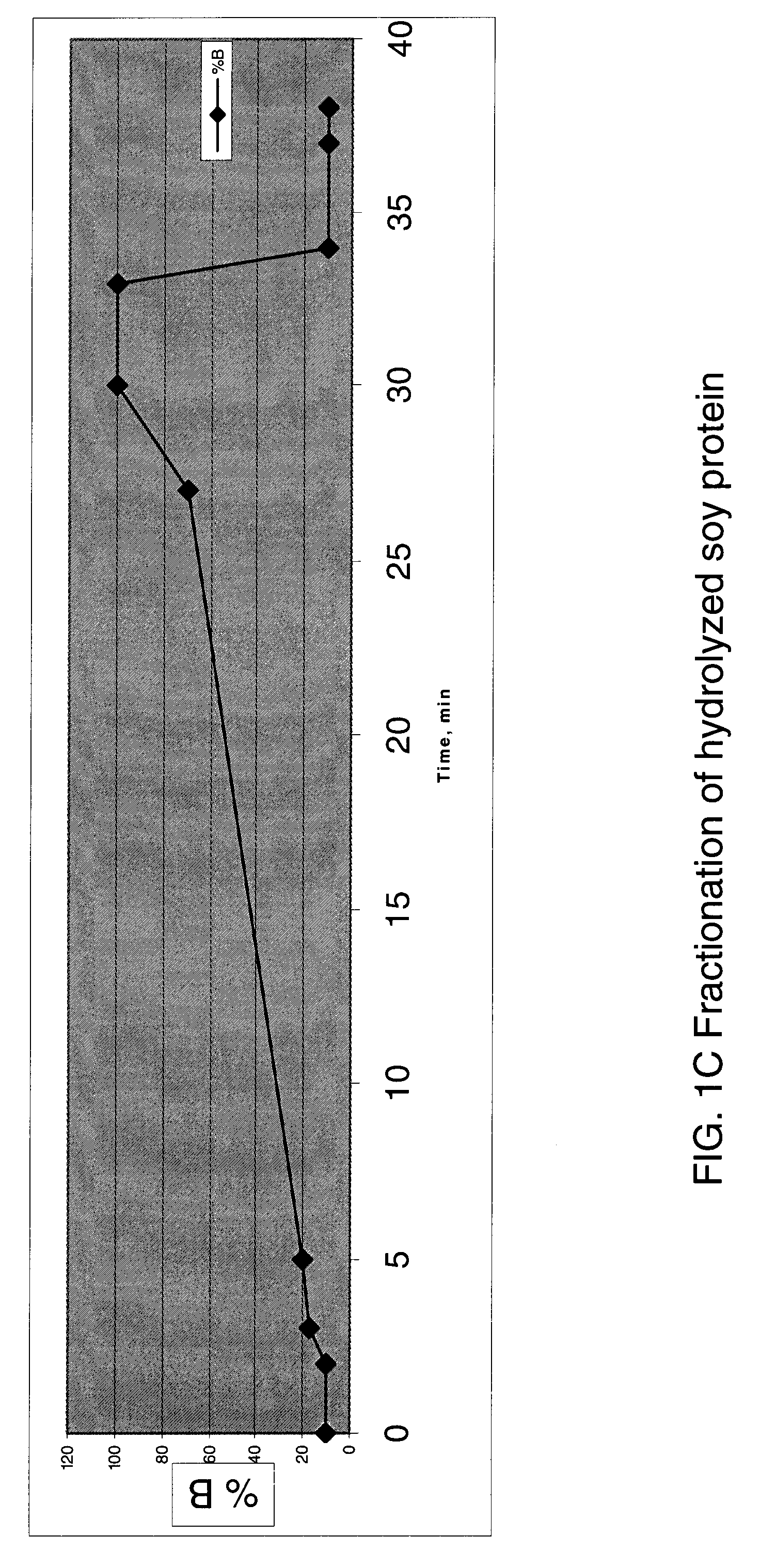
Identification of bitter receptors for hydrolyzed soy protein
InactiveUS7794959B2Effect serum cholesterol levelBiocideCompound screeningTaste receptor ligandT2R receptors
The present invention relates to the discovery that specific human taste receptors in the T2R taste receptor family respond to particular bitter compounds present in hydrolyzed soy protein derived materials. The invention further relates to the use of these T2R receptors in assays for identifying ligands that modulate the activation of these taste receptors by specific bitter ligands present in hydrolyzed soy protein materials and derivatives thereof and related compounds. These compounds may be used as additives and / or removed from soy-based foods, beverages, cosmetics and medicinals in order to modify (block) T2R-associated bitter taste elicited by bitter ligands present in hydrolyzed soy protein materials. Also these T2R ligands potentially may be used as therapeutics to treat and modulate hT2R1 or hT2R67 associated gastrointestinal and metabolic functions such as serum cholesterol levels as well as treat gastrointestinal and metabolic diseases such as eating disorders, food sensing, food absorption, obesity, diabetes, Crohn's disease, celiac disease, et al.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
Edible oral strip or wafer dosage form containing ion exchange resin for taste masking
ActiveUS20170136078A1Good dispersionGood film formingOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticTaste receptor ligandIon exchange
An edible oral film strip dosage form containing an unpalatable basic active pharmaceutical ingredient and an ion exchange resin as a primary taste masking agent, along with an optional acidic agent and further optionally containing one or more secondary taste masking agents is provided. The edible oral film strip dosage matrix is formed from at least one water soluble or miscible polymer(s). The optional secondary taste masking ingredients include one or more of flavoring agent(s), sweetener(s), cooling sensation agent(s), and taste receptor blocker(s). Methods for preparing the inventive edible oral film strip dosage forms are disclosed, as well as their method of administration.
Owner:LTS LOHMANN THERAPIE-SYST AG
Receptor fingerprinting, sensory perception, and biosensors of chemical sensants
ActiveUS7374878B2ConfidenceEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisTaste receptor ligandNucleotide
The use of sensory G protein-coupled receptors that recognize chemical sensants, parti-cularly those involving olfactory and taste receptors; polypeptide fragments and mutants thereof; classes of such receptors; polynucleotides encoding such receptors, fragments and mutants thereof, and representatives of receptor classes; genetic vectors including such polynucleotides; and cells and non-human organisms engineered to express such receptor complexes, fragments and mutants of an olfactory or taste receptor, and representatives of receptor classes to simulate sensory perception of odorants and tastants is described. The use of such products as a biosensor or a component thereof to detect, identify, measure, or otherwise process the event of binding between the receptor and its cognate ligand (i.e., chemical sensant) is also described. The invention has application, for example, in the design and formulation of odorant and tastant compositions.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
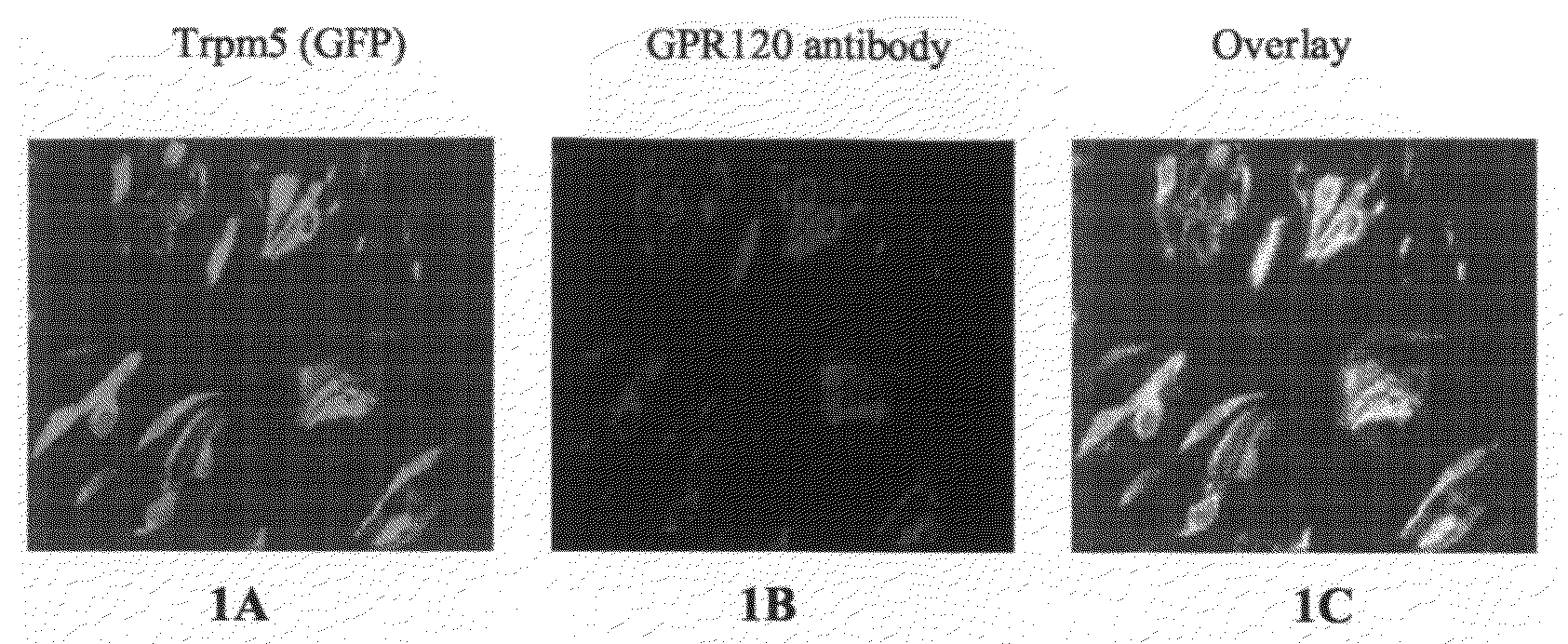
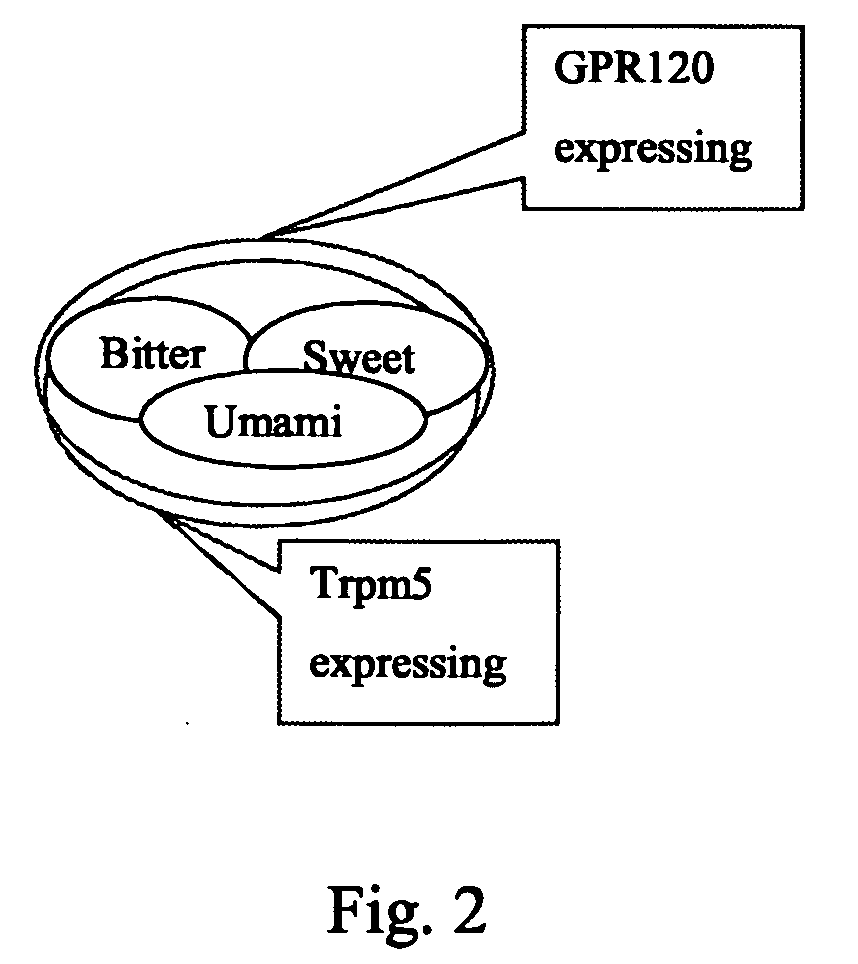
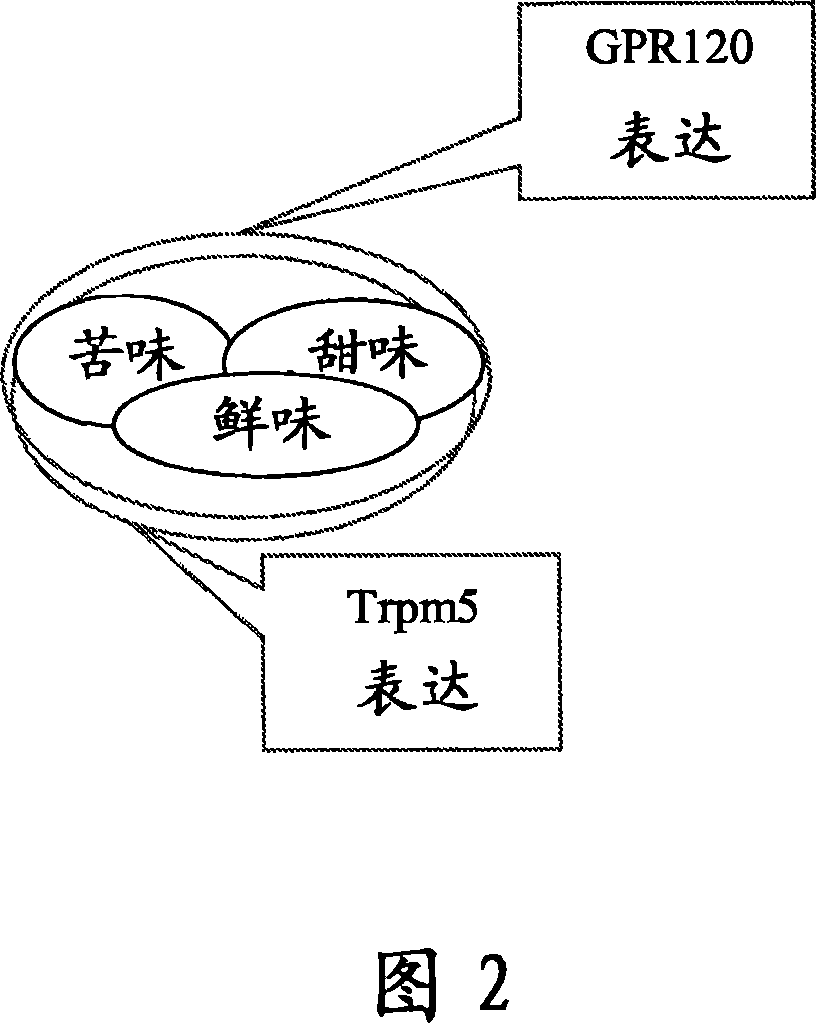
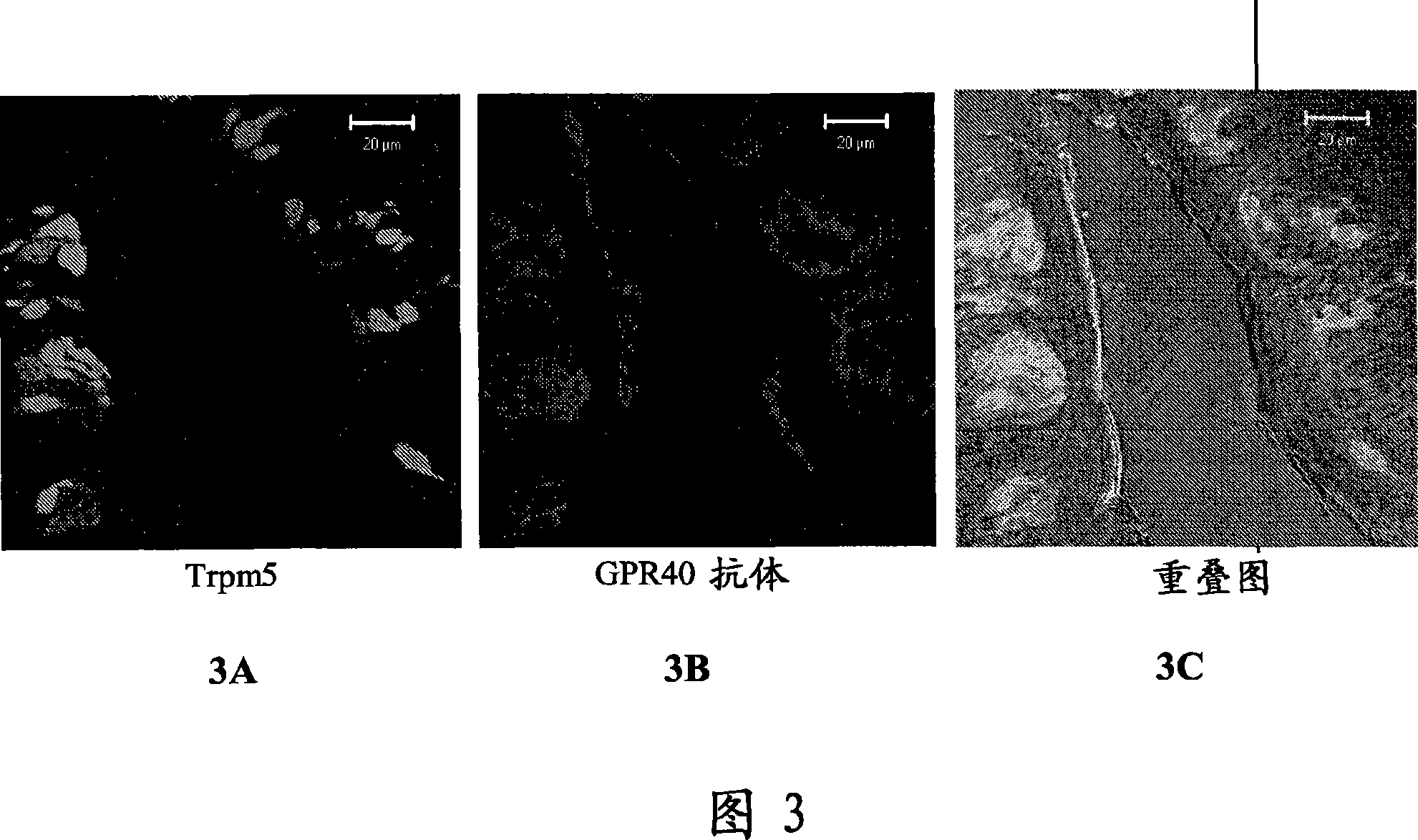
Fat Taste Receptors and Their Methods of Use
InactiveUS20080299270A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMicrobiological testing/measurementTaste receptor ligandGPR120
Fat taste receptors and methods for using the receptors to screen compounds that mimic fat taste are disclosed. The receptors can include G-protein coupled receptor proteins, such as GPR40 or GPR120. New methods for preparing foods are also disclosed that involve testing compounds in the assay system and then incorporating into foods the identified nonfat compounds that have the taste of fat.
Owner:NESTEC SA
Human type i taste receptor subunit 3 modulators and methods of using same
Methods and compositions are provided for modulating the activity of human type I taste receptor subunit 3 (hT1R3). Such materials and methods are useful for the screening and preparation of compositions and methods for the treatment of carbohydrate and lipid metabolic diseases and disorders.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Fat taste receptors and their methods of use
Fat taste receptors and methods for using the receptors to screen compounds that mimic fat taste are disclosed. The receptors can include G-protein coupled receptor proteins, such as GPR40 or GPR120. New methods for preparing foods are also disclosed that involve testing compounds in the assay system and then incorporating into foods the identified nonfat compounds that have the taste of fat.
Owner:NESTEC SA
Model taste cells and methods of use for identifying modulators of taste sensation
InactiveCN101495508ACell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsBiological material analysisTaste receptor ligandEnteroendocrine cell
The present invention provides model taste cells that naturally or recombinant Iy express taste receptors and relevant cellular proteins and / or molecules useful for taste signal transduction. The present invention further provides methods of use for these model taste cells for screening for compounds that modulate sweet and / or other taste signal transduction. Compositions comprising the compounds / modulators identified using the model taste cells are also provided. In preferred embodiments, the model taste cells are derived from human HuTu-80 enteroendocrine cells, and derivative cells thereof.
Owner:THE COCA COLA CO
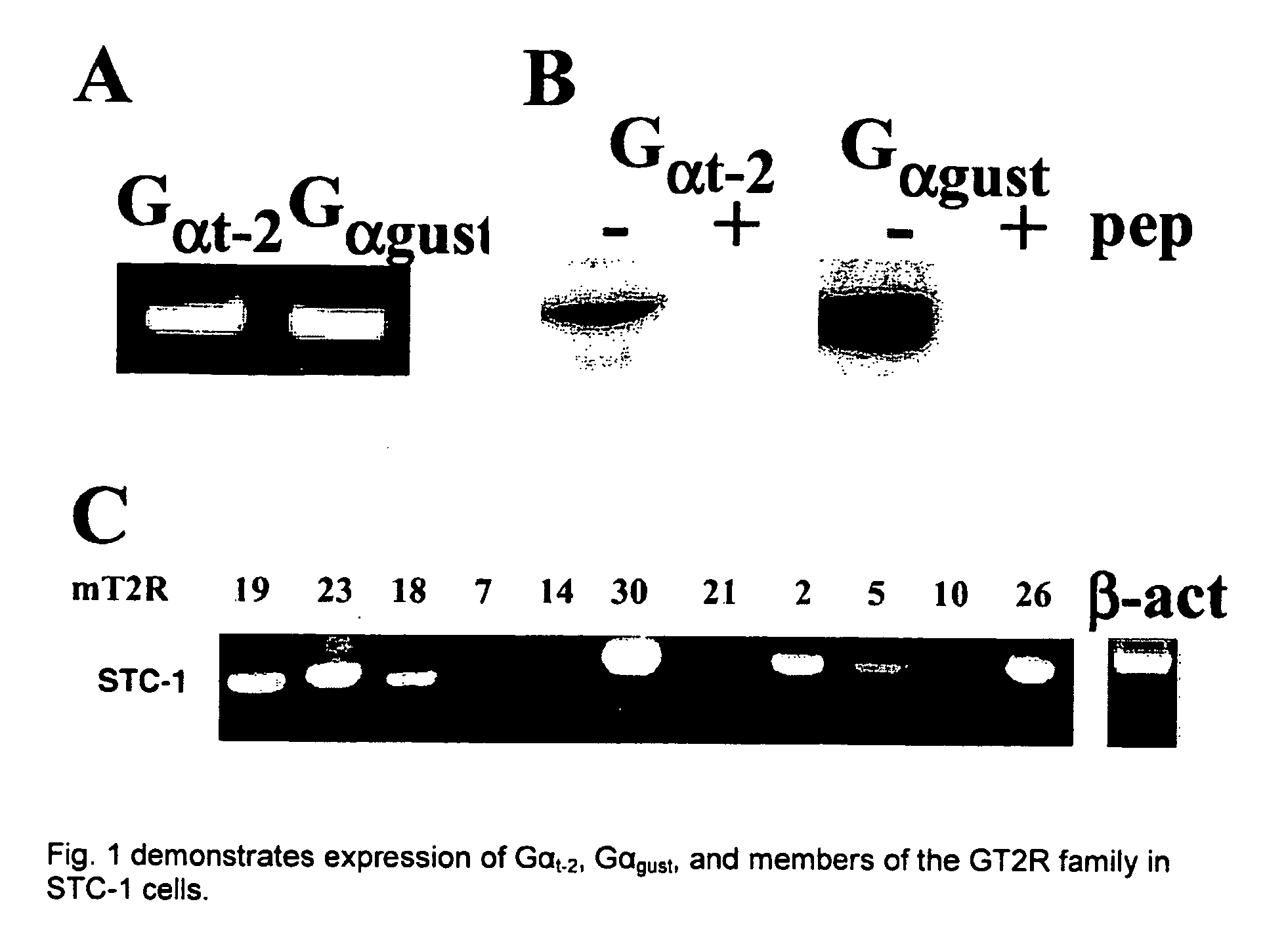
Gastrointestinal chemosensory receptors
InactiveUS20070059688A1Compound screeningApoptosis detectionTaste receptor ligandEnteroendocrine cell
This invention provides isolated nucleic acid and amino acid sequences of gastrointestinal endocrine cell specific G-protein coupled receptors, methods of detecting such receptors, and methods of screening for ligands of such receptors. Furthermore, this invention demonstrates that SrC-1 enteroendocrine cells express multiple bitter taste receptors as well as a-subunits of G proteins that mediate taste signal transduction and respond to bitter taste compounds initiating changes in intracellular calcium concentration. Given that at present there are no cultured cell model system to determine the functional effects of taste receptor-mediated signaling, our findings identify STC-1 cells as a cell model for studying taste-mediated signal transduction.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Novel Test Method For Taste Abnormality
InactiveUS20080145842A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesTaste receptor ligandDysgeusia
A method for testing dysgeusia, which is characterized in that it comprises amplifying at least a portion of a gene encoding a taste receptor belonging to the THTR family and a gene encoding a taste receptor belonging to the T2R family collected from a sample derived from the oral cavity; a primer used for the above amplification; and a kit used for the above test.
Owner:NIHON UNIVERSITY
Method for screening a potential modulator compound of a taste receptor
ActiveUS8795977B2Improve the level ofHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisTaste receptor ligandChemistry
A method for screening a potential modulator compound of a taste receptor wherein use is made of a BRET technique.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Taste Receptors Of The T1R Family From Domestic Cat
The present invention relates to the discovery of several genes of the domestic cat (Felis catus) associated with taste perception. The invention provides, inter alia, the nucleotide sequence of the feline Tas1r1, Tas1r2, and Tas1r3 receptor genes, the amino acid sequences of the polypeptides encoded thereby, and antibodies to the polypeptides. The present invention also relates to methods for screening for compounds that modify the genes' function or activity, the compounds identified by such screens, and mimetics of the identified compounds. The invention further provides methods for modifying the taste preferences, ingestive responses, or general behavior of a mammal, such as a cat, by administering compounds that affect the function or activity of the gene or the polypeptide encoded thereby.
Owner:MONELL CHEM SENSES CENT
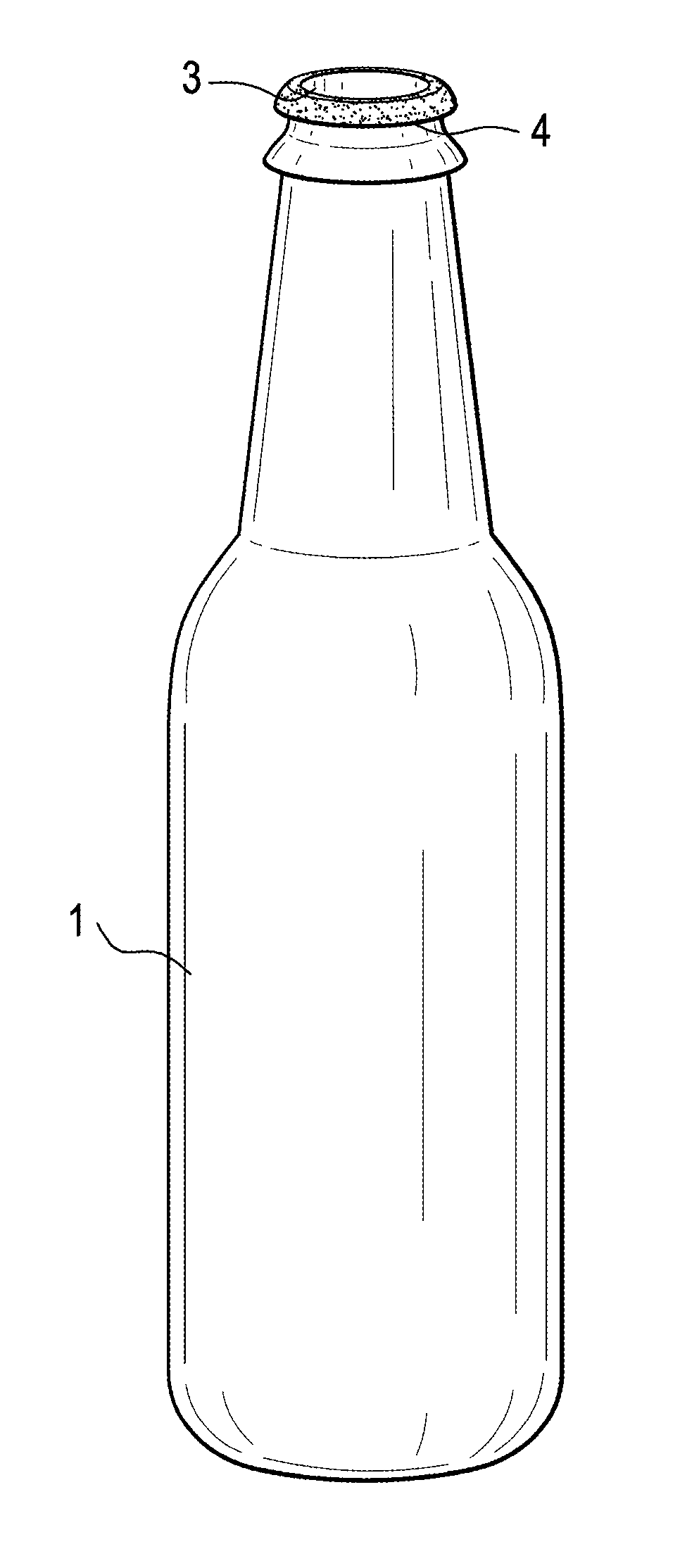
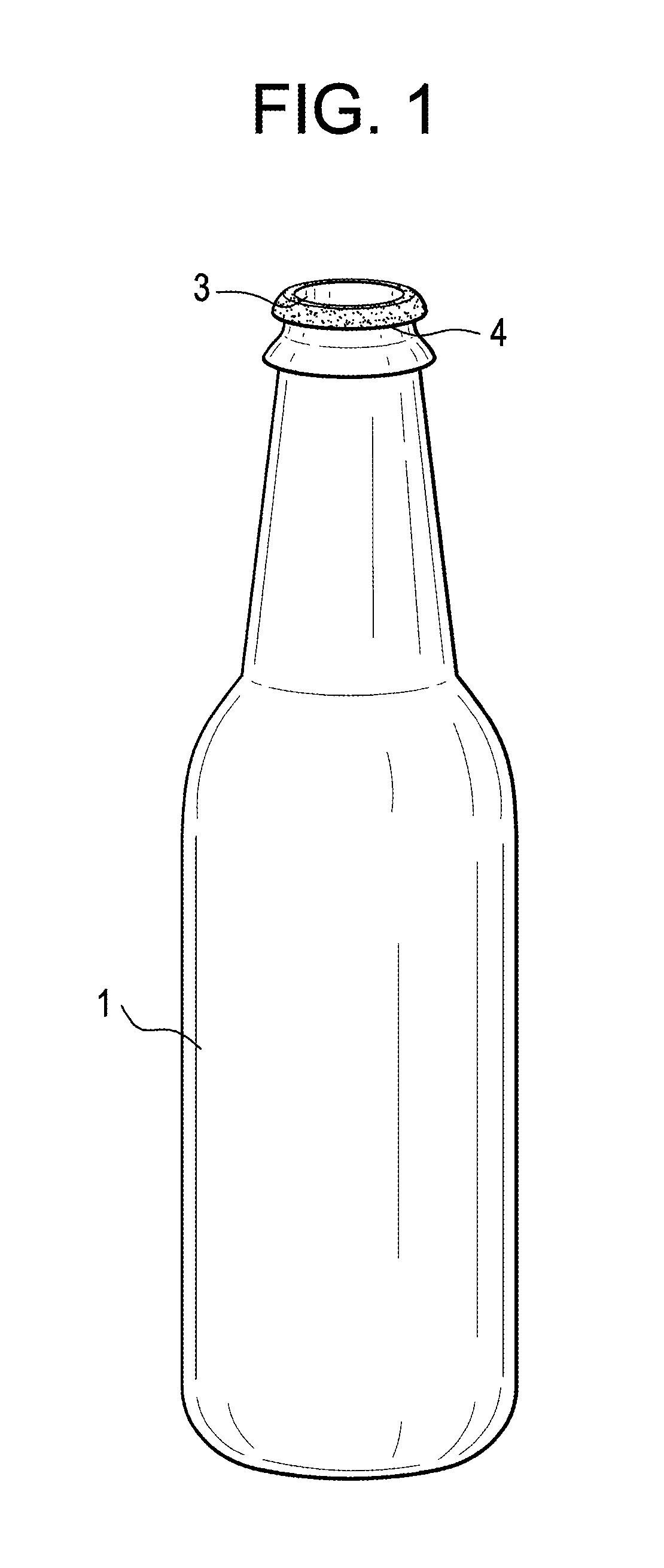
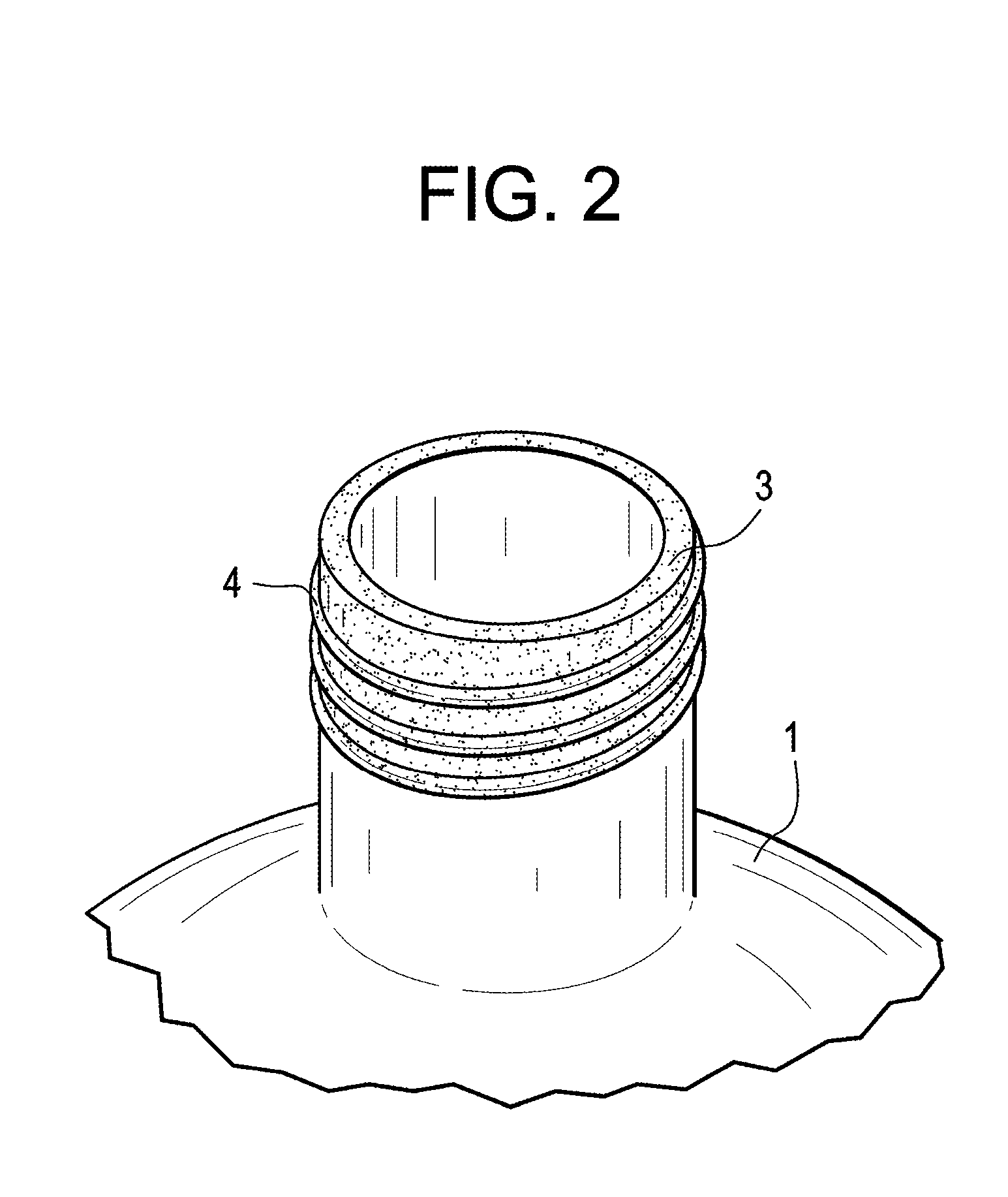
Container With Taste Sensation Enhancement Delivery
InactiveUS20120294989A1Preserve flavor potencyGreat tasteFlexible coversWrappersTaste receptor ligandHuman mouth
The present invention relates to a container for a beverage provided with an edible flavor enhancement coating for release upon opening of a beverage by coming in connect with the liquids in the human mouth. More particularly, the present invention relates to a container with the portion being placed in the mouth for drinking provided with a water-soluble an edible flavor enhancement coating that dissolves by coming in contact with liquids in the human mouth or beverage to be drunk only upon opening of the beverage container, in such a way so as to stimulate the taste receptors immediately prior to and during the drinking or pouring of the contents within the beverage container.
Owner:PICOLLI RICHARD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com