Compositions and methods for reducing hepatotoxicity associated with drug administration and treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and associated cirrhosis
a technology of hepatotoxicity and drug administration, which is applied in the direction of aerosol delivery, spray delivery, immunological disorders, etc., can solve the problems of hepatocyte death, reduce the usefulness of bioactive agents, and increase the effectiveness of such agents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0202]The following description of experiments conducted are presented to exemplify the present invention. They are by way of example only and are not to be taken the limit the invention in any way.
Materials and Methods
Animals.
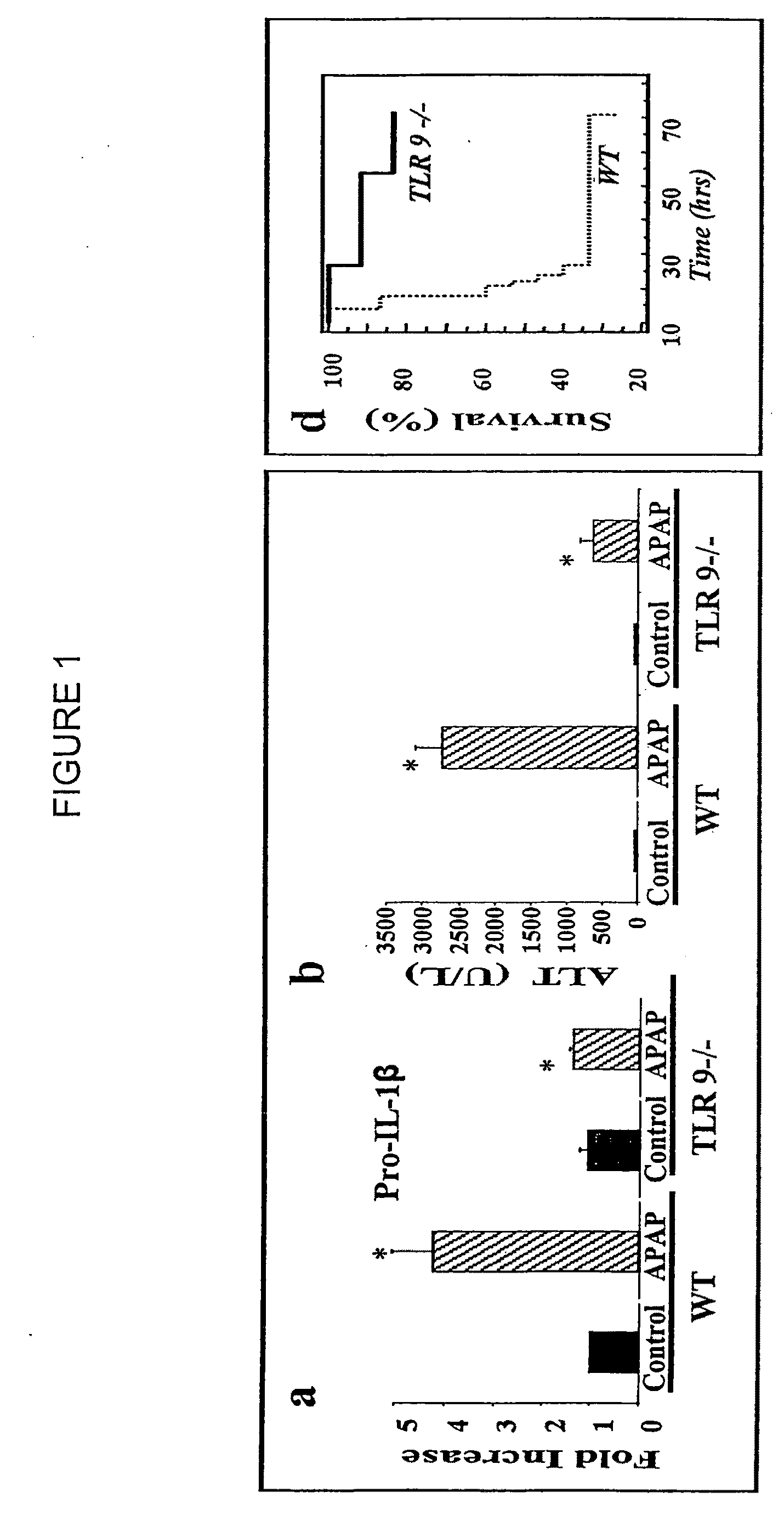
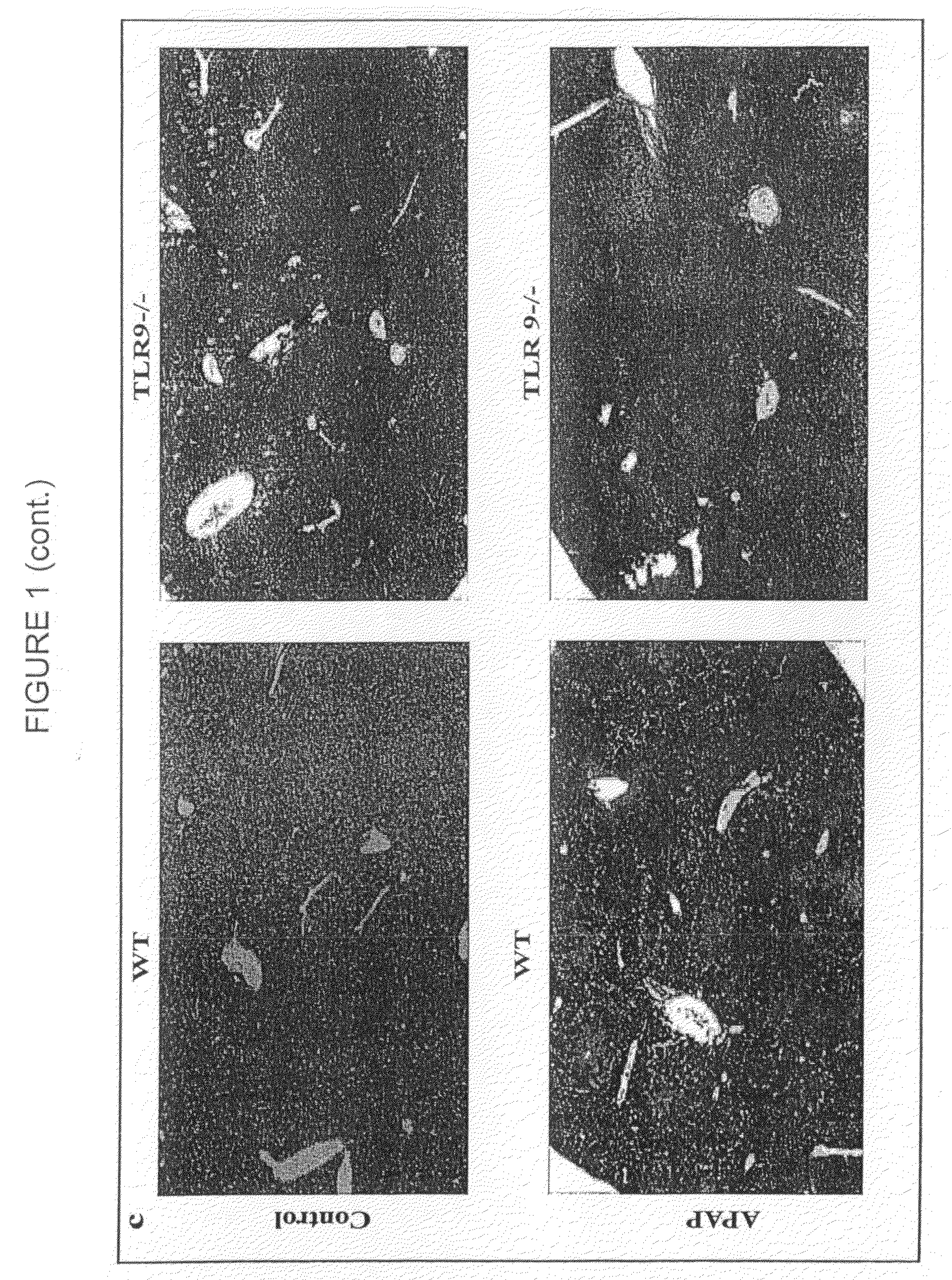
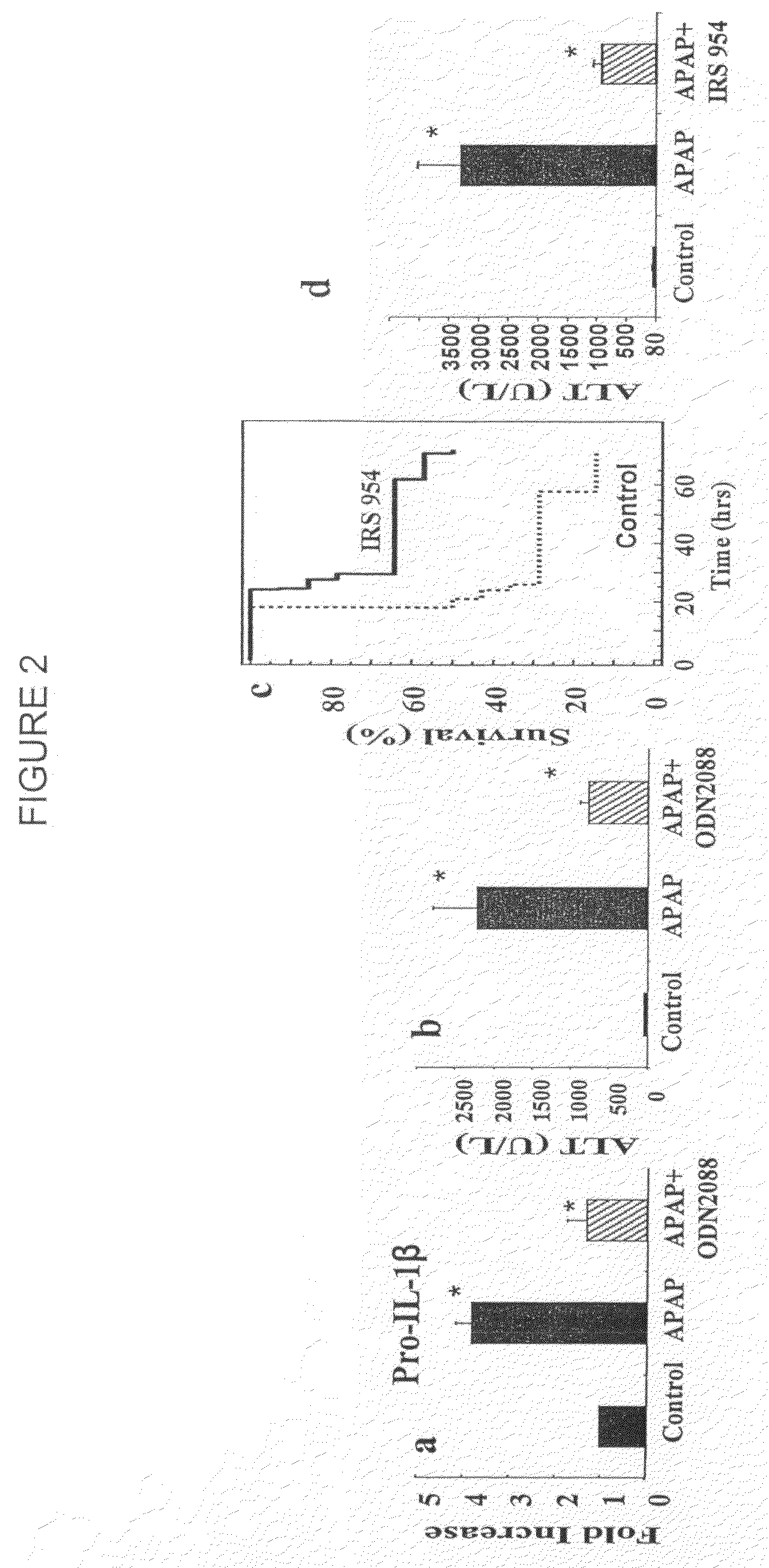
[0203]C57BL / 6 mice were purchased from commercial sources. NALP3 − / −, IL-18 − / − ASC − / −, IPAF − / − and TLR9 − / − mice were backcrossed nine generations onto the C57BL / 6 background. Caspase 1 − / − mice were backcrossed 5-6 generations onto the C57BL / 6 background. These mice have been described previously (39, 40). IL-1β was neutralized in by using the anti-IL-1β antibody from clone B122 (a gift of R. Schreiber, Washington University) at a dose of 0.2 mg / mouse iv twice a day for a total of 48 hours after giving APAP. Control mice received Armenian hamster isotype control antibody. For survival experiments animals were euthanized when they became moribund using criteria of lack of response to stimuli or lack of righting reflex. Animal protocols were approved by the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Therapeutic | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Antimicrobial properties | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com