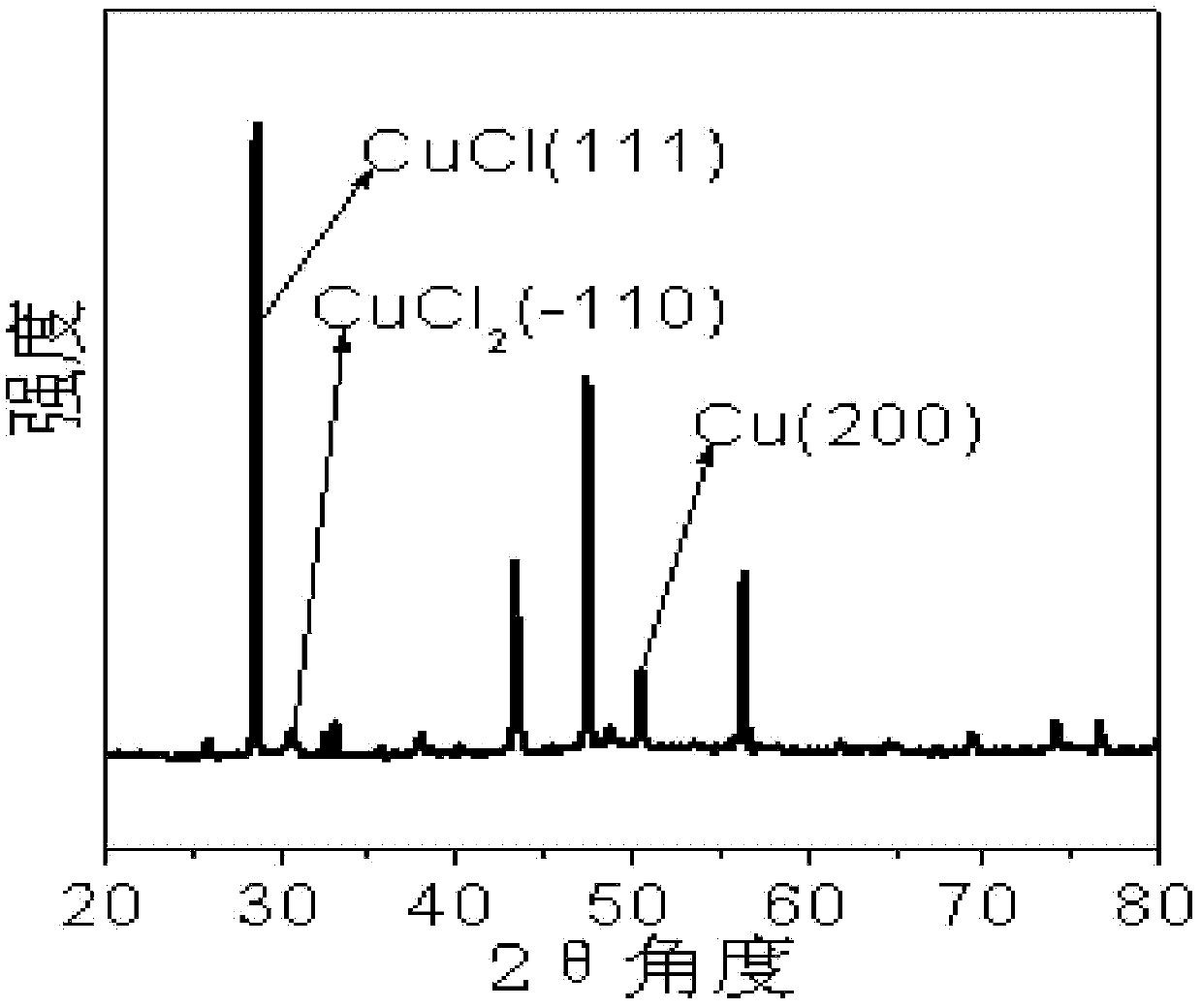
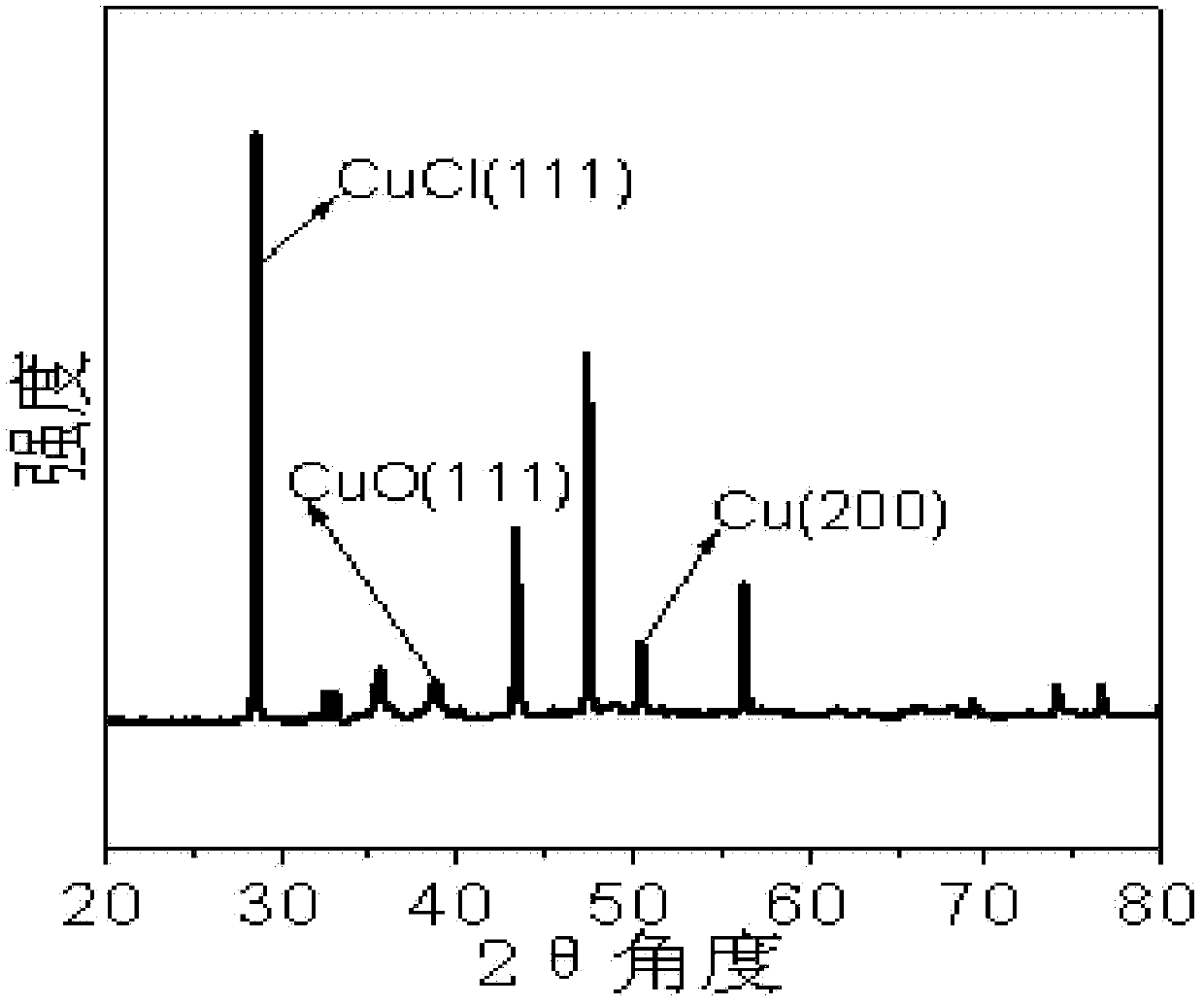
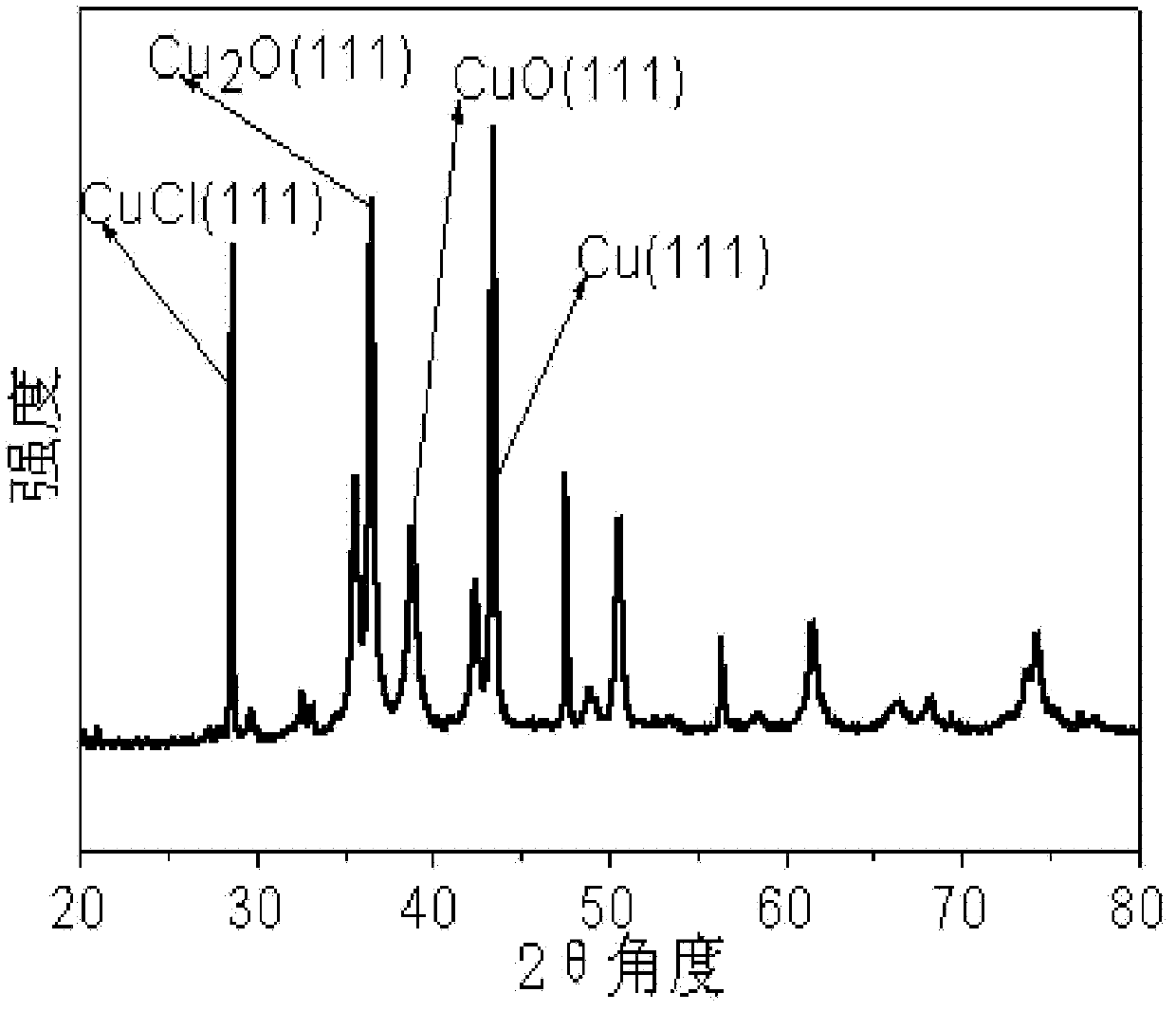
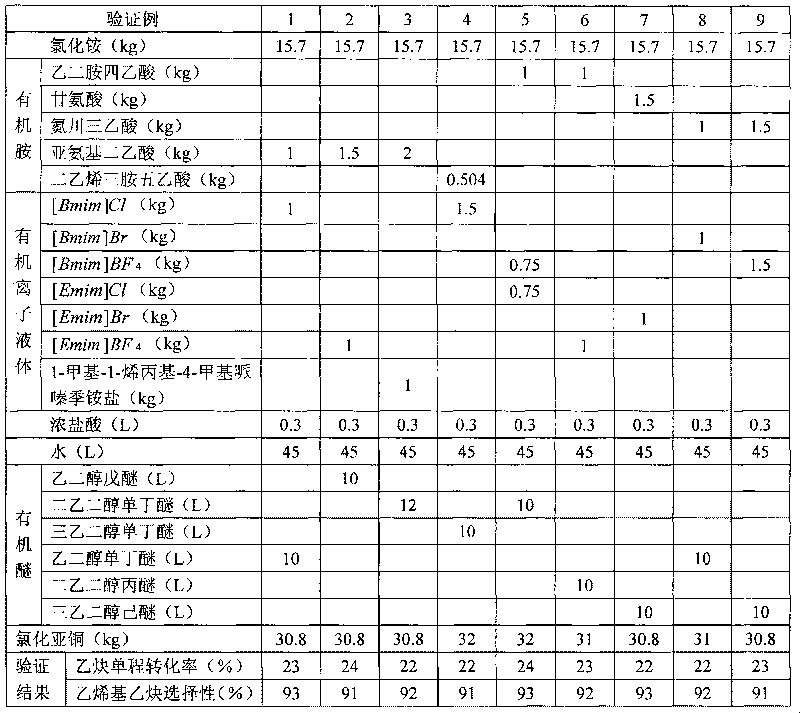
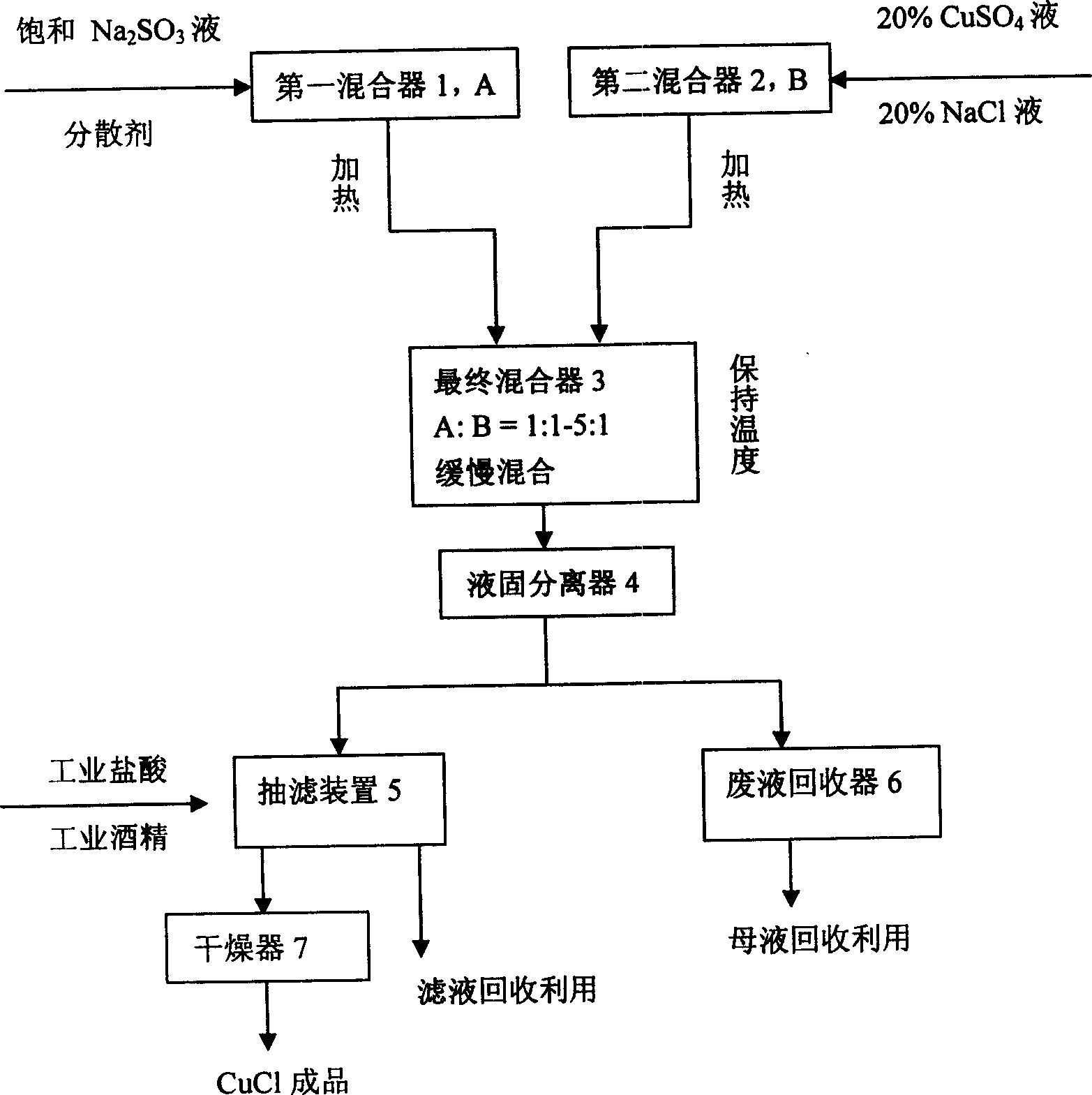
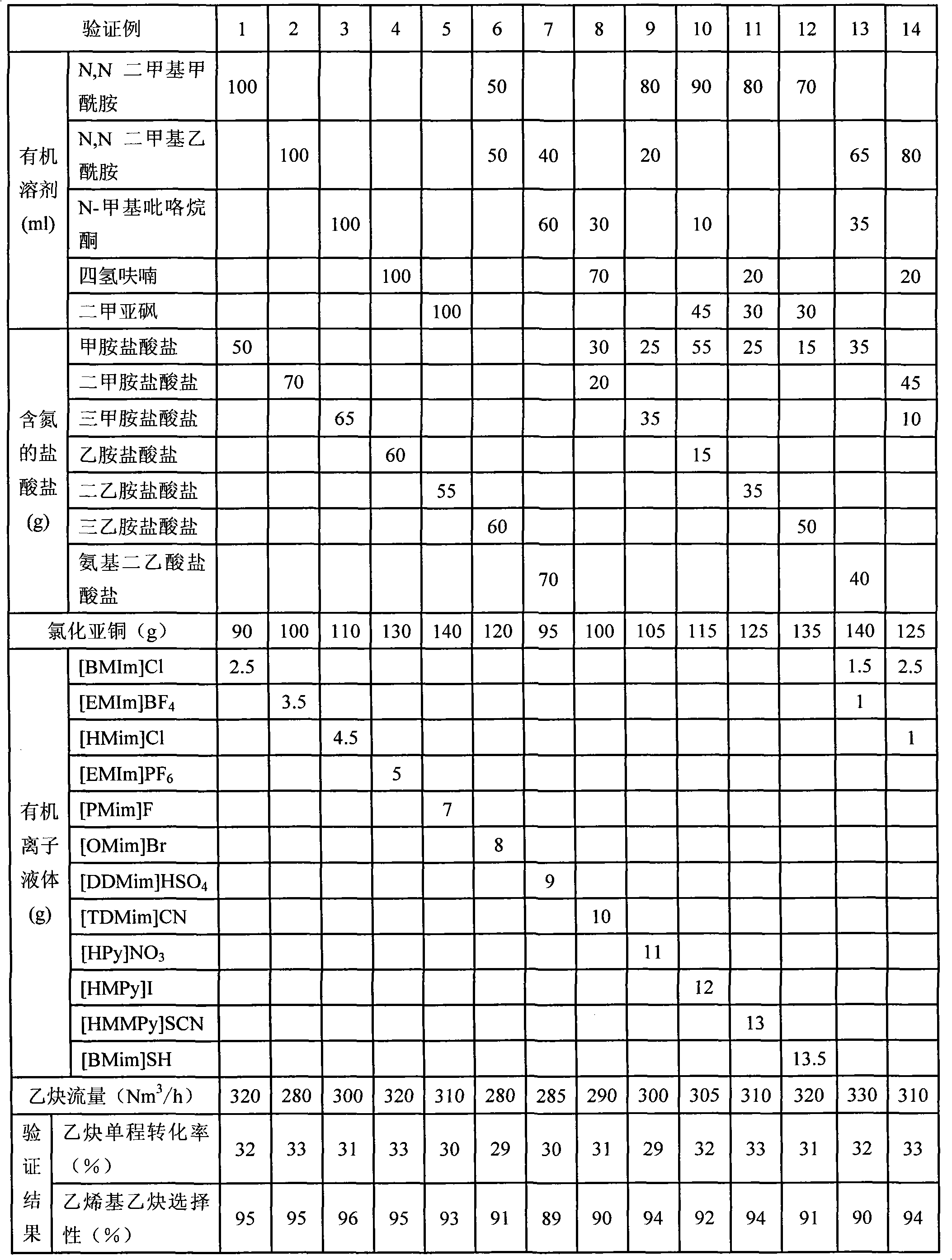
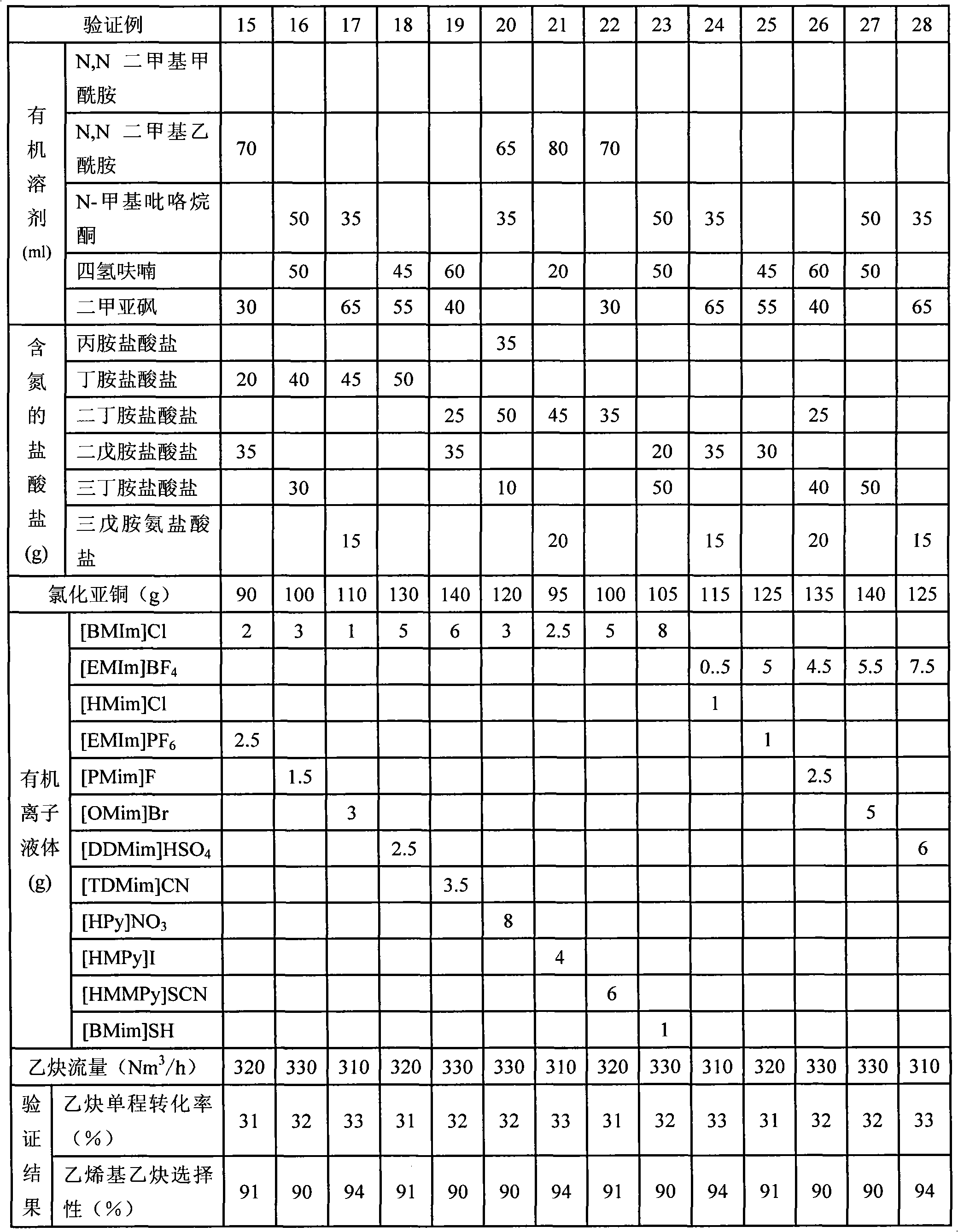
Patents
Literature
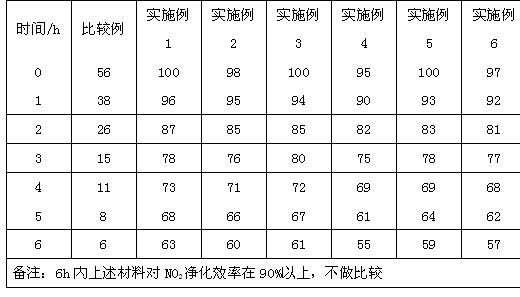
800 results about "Cuprous chloride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Copper(I) chloride, commonly called cuprous chloride, is the lower chloride of copper, with the formula CuCl.The substance is a white solid sparingly soluble in water, but very soluble in concentrated hydrochloric acid. Impure samples appear green due to the presence of copper(II) chloride (CuCl 2).
Low-mercury catalyst for acetylene hydrochlorination
InactiveCN102380407AEasy to makeLow costPhysical/chemical process catalystsPreparation by halogen halide additionO-Phosphoric AcidPtru catalyst
Disclosed is a low-mercury catalyst for acetylene hydrochlorination. Mercuric chloride is carried on activated carbon. Raw materials comprise, by weight, 100 parts of activated carbon, 4-5 parts of mercuric chloride, 8-10 parts of total essential assistant, 1-5 parts of total non-essential assistant, wherein the essential assistant comprises 2-5 parts of bismuth chloride, 1-5 parts of cerium chloride, 1-5 parts of barium chloride and 2-5 parts of copper chloride; and the non-essential assistant comprises at least one of potassium chloride, phosphoric acid, zinc chloride and cuprous chloride. After being subjected to surface subtraction and drying on acid and oxidizing conditions, activated carbon is in reflux treatment with urea solution; and the catalyst can be prepared by soaking the treated activated carbon with HgC12 dissolved in hydrochloric acid and assistant solution sufficiently after urea is removed by steps of heating, washing the activated carbon with hydrochloric acid and finally drying the same. The carrying capacity of mercuric chloride in the catalyst is lower so that cost for the catalyst is reduced and consumption of mercury resources is decreased. Furthermore, activity and stability of the low-mercury catalyst are much higher than those of the existing high-mercury catalyst, and reforming rate and selectivity of reaction of vinyl chloride can be 99.7% and be higher than 99.8%. Accordingly, the low-mercury catalyst for acetylene hydrochlorination is suitable for industry production and is environment-friendly.
Owner:CHENGDU HUIEN FINE CHEM
Surface modification method for polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) film or polyvinyl chloride (PVC) film
InactiveCN102558595AImprove the effect of graftingImprove controllabilityAtom-transfer radical-polymerizationPolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a surface modification method for a polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) film or a polyvinyl chloride (PVC) film. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: (1) performing vacuum low temperature plasma treatment on the PVDF film or the PVC film at the power of 5 to 100W and the reaction vacuum degree of 2 to 100Pa for 1 to 20 minutes; and (2) mixing a solution which is formed by mixing methanol and deionized water and serves as a solvent, cuprous chloride or cuprous bromide serving as a catalyst, 2,2'-bipyridyl or a derivative thereof serving as a ligand, and sulphobetaine methyl methacrylate or allyl polyethylene glycol serving as a grafting monomer, controlling reaction temperature to 20-100 DEG C, and performing atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) reaction for 1 to 24 hours to obtain a product, wherein the molar ratio of the catalyst to the ligand is 1:(0.5-4), and the molar ratio of the film to the monomer is (100-0.1):1. The methodhas the advantages that: the hydrophilicity and anti-pollution capacity of the film can be improved, environment friendliness is achieved, and operation steps are simple.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Method for preparing copper-titanium dioxide core-shell nanoparticles
InactiveCN102335605ASmall particle sizeMorphological components are adjustableElectrolytic capacitorsCell electrodesPolyethylene glycolSolvent
The invention relates to a method for preparing copper-titanium dioxide core-shell nanoparticles. In the method, cupric ions provided by cuprous chloride are dissolved into ammonia water; an aqueous solution of polyethylene glycol, an aqueous solution of sodium citrate, an aqueous solution of ascorbic acid, a solution of tetrabutyl titanate (absolute ethyl alcohol) and urea are sequentially addedinto the ammonia water; the ammonia water is put into a teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave after the ammonia water is stirred at room temperature; and the nearly-spherical core-shell nanoparticles are prepared through controlling the temperature and the time for the thermal reaction of the mixed solvents. In the method for preparing the copper-titanium dioxide core-shell nanoparticles, the ascorbic acid serves as a reducing agent and is used for reducing the cuprous ions; and the polyethylene glycol serves as a soft template. The method for preparing the copper-titanium dioxide core-shellnanoparticles has the advantages of simple process, environment-friendliness, low cost and the like; the outer layer of each of the prepared copper-titanium dioxide core-shell nanoparticles is anatase titanium dioxide, and the inner layer of each of the prepared copper-titanium dioxide core-shell nanoparticles is cubic-phase copper elementary substance; and the size distribution is even, and the particle size is controllable, thus the copper-titanium dioxide core-shell nanoparticles can be used as the electrode materials and the photocatalyst materials of dye-sensitized solar cells.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
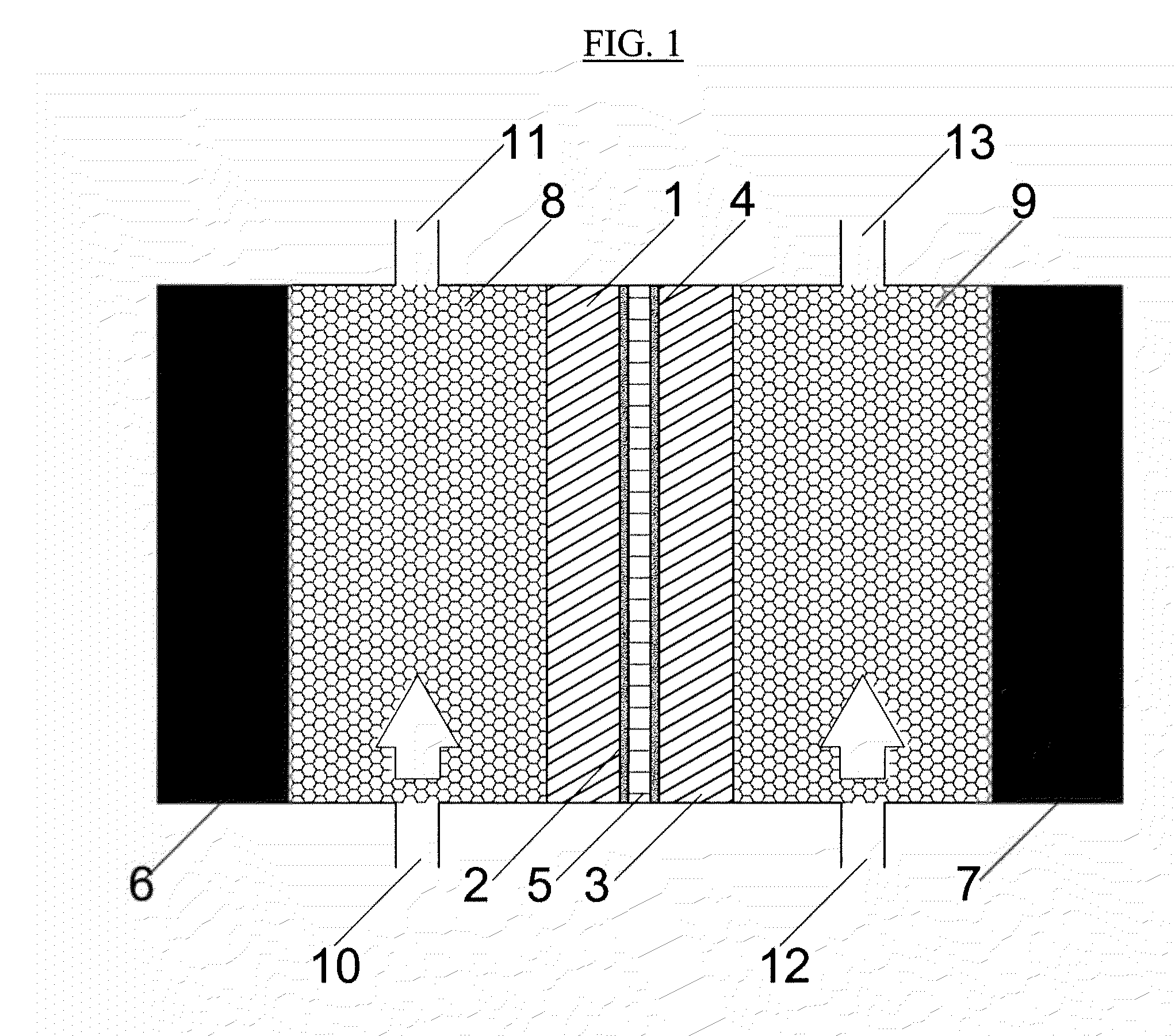
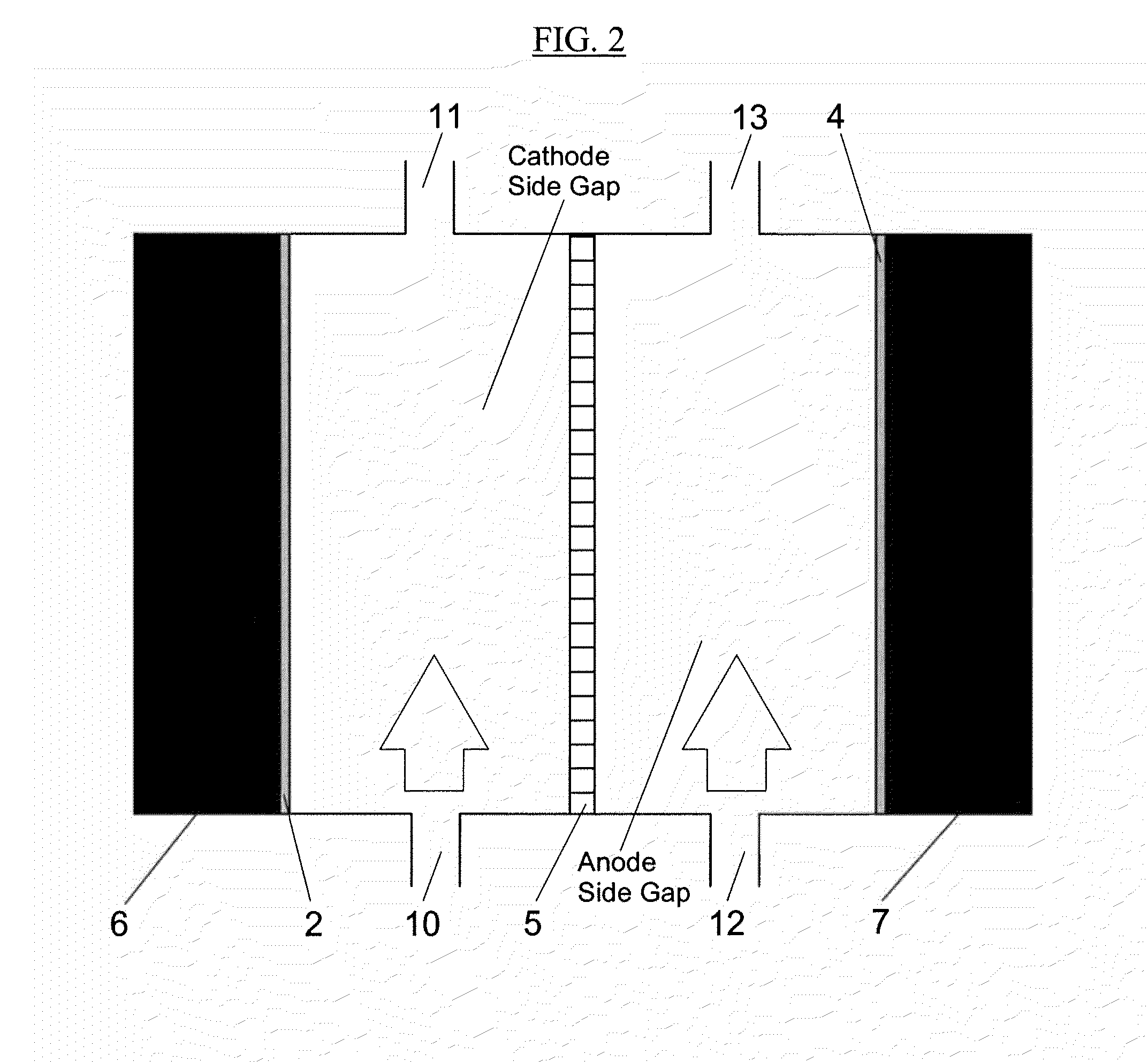
Electrolysis Cell for the Conversion of Cuprous Chloride in Hydrochloric Acid to Cupric Chloride and Hydrogen Gas
The present invention provides an electrochemical cell for producing hydrogen gas and cupric chloride, comprising an anode compartment including an anode disposed in an anolyte, wherein the anolyte is cuprous chloride in hydrochloric acid, a cathode compartment including a cathode, wherein the cathode comprises an electrocatalyst, and a cation exchange membrane disposed between the anode compartment and the cathode compartment.
Owner:ATOMIC ENERGY OF CANADA LIMITED
Method for preparing temperature-sensitive polyvinylidene fluoride intelligent membrane material and its product
This invention relates to a method for prparing temperature-sensitive polyvinylidene flourine intelligent membrane. The method is: NIPA as grafted monomer, PVDF as macromelocular initiator, cuprous chloride as catalyst,4,4 demethyl 2,2 bipyridine as ligand, using atom transfer free radical process, preparation of temperature-sensitive polyvinylidene flourine intelligent membrane comprising: in reaction kettle, adding 7-13% PVDF(WT%) and solvent N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone,heating to 50 deg. C to make it solve completely; then adding grafted monomer NIPA, its mol ratio with cuprous chloride is 2000:1-2500:1,filling nitrogen gas 30mins. at stirring, and separately adding 0.20-025g ligand 4,4-dimethyl 2,2-bipyridine and 0.04-0.06g catalyst cupous chloride, stirring and heating to 80-120deg.C,constant reaction 19-25 hrs; then washing reaction product using pure water to obtain light brown solid, filtering and 80 C degree drying to obtain finish product.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Preparation method of anthraquinone functionalized polyvinylidene fluoride ultrafiltration membrane
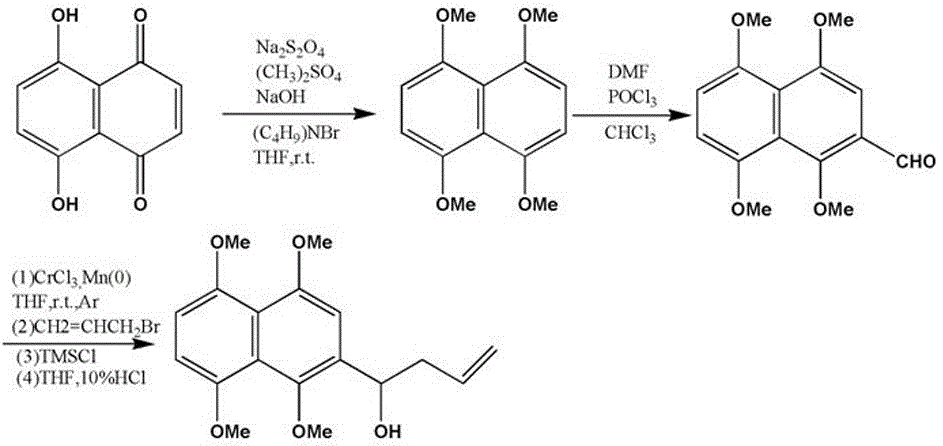
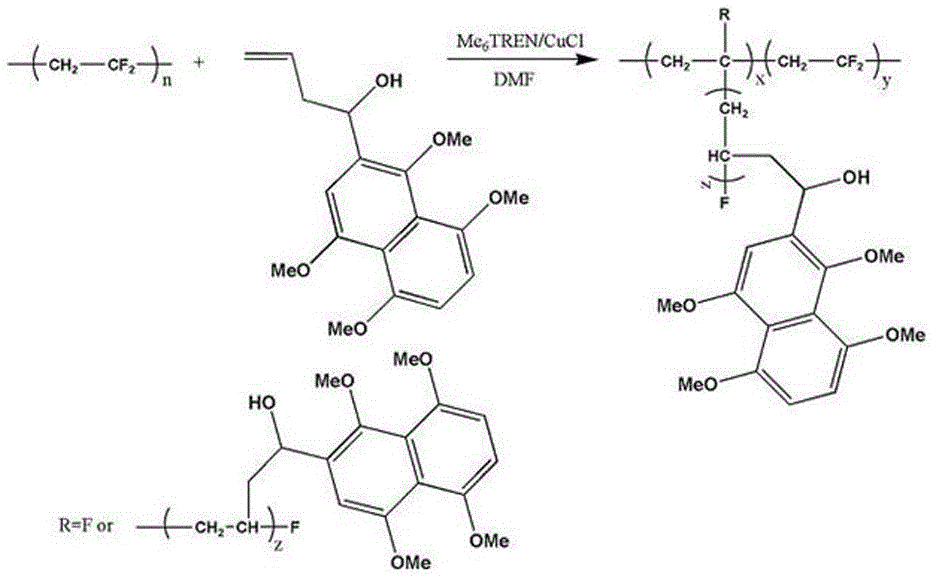
InactiveCN105642127AWon't fall offPromote degradationMembranesWater contaminantsQuinoneUltrafiltration
The invention belongs to the field of preparation of polyvinylidene fluoride ultrafiltration membranes and in particular relates to a preparation method of an anthraquinone functionalized polyvinylidene fluoride ultrafiltration membrane. The preparation method specifically comprises the following steps: (1) synthesizing 2-(1-hydroxy-3-butene)-1,4,5,8-tetramethyl naphthalene; (2) synthesizing a polyvinylidene fluoride-aromatic ethers copolymer: selecting polyvinylidene fluoride as an initiator, the 2-(1-hydroxy-3-butene)-1,4,5,8-tetramethyl naphthalene as a monomer, N,N-dimethyl formamide as a solvent and cuprous chloride / Me6TREN as a catalyst system, and synthesizing the polyvinylidene fluoride-aromatic ethers copolymer through an atom free radical polymerization method; (3) reducing the polyvinylidene fluoride-aromatic ethers copolymer into quinone by using a demethylation oxidization method; and (4) preparing the polymer in the step (3) and the N,N-dimethyl formamide into a film casting solution and scraping to form the membrane. According to the preparation method provided by the invention, anthraquinone molecules fixed on the polyvinylidene fluoride membrane are firm and do not fall off.
Owner:厦门凯茂水处理科技有限公司
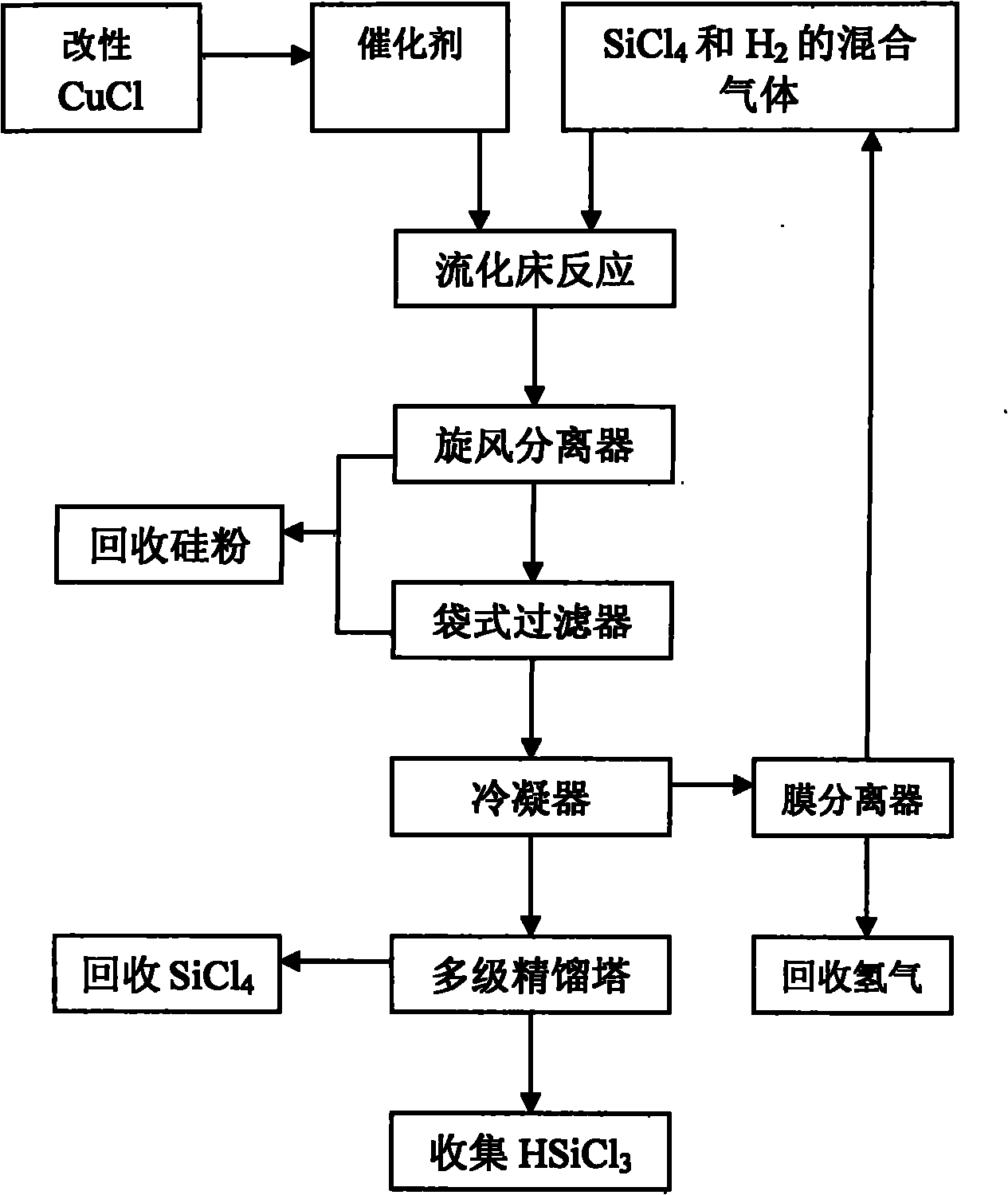
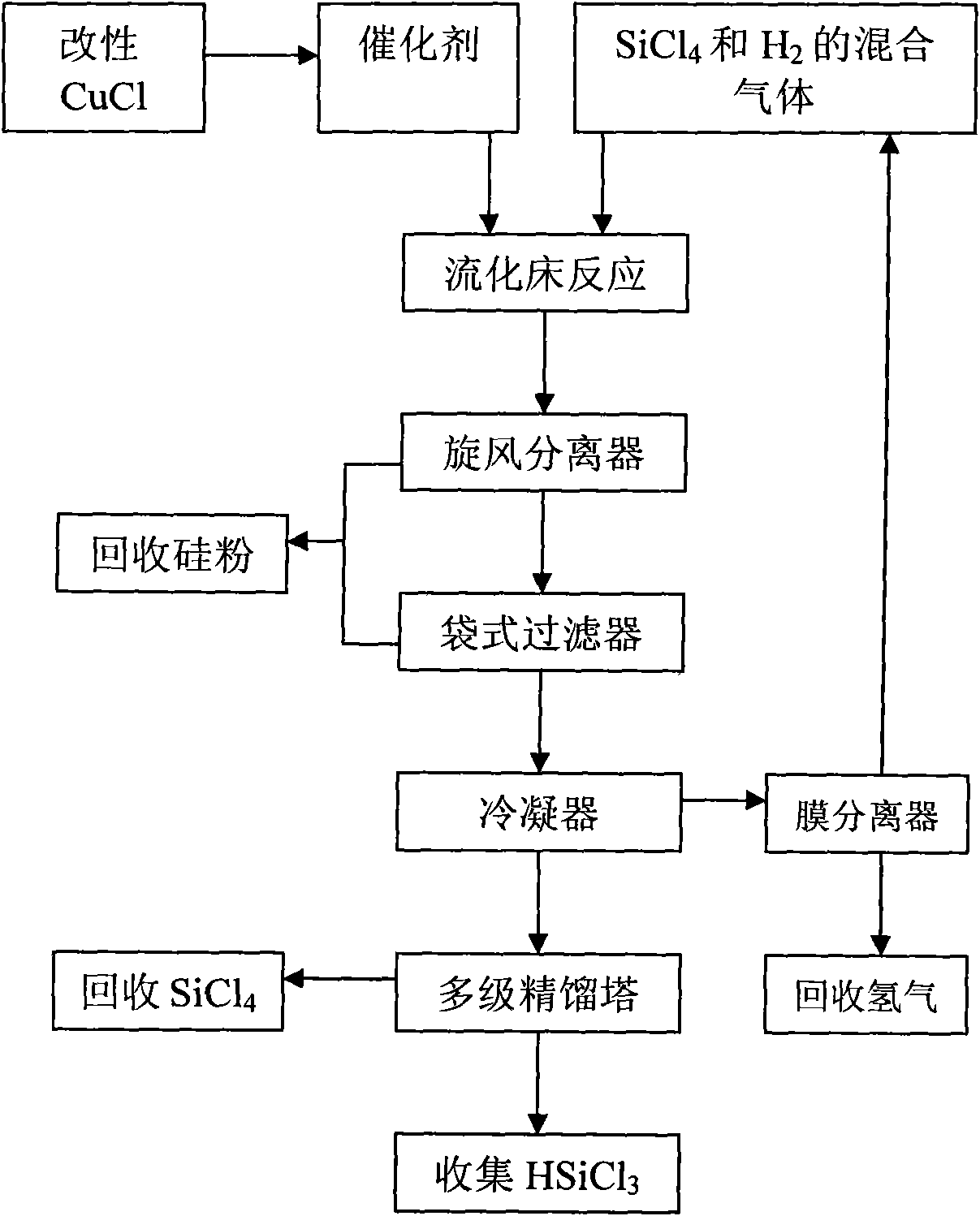
Preparation method and application of catalyst used in hydrogenation of silicon tetrachloride
InactiveCN101816946AHigh catalytic efficiencyHigh yieldSilicon organic compoundsPhysical/chemical process catalystsFiltrationShielding gas
The invention provides a preparation method of a catalyst used in hydrogenation of silicon tetrachloride, which comprises the following steps of: mixing cuprous chloride after pretreatment and silicon powder in an agitated bed reactor, and performing heated reaction on the mixture under a hydrogen condition, wherein the pretreatment refers to putting the cuprous chloride into the silicon tetrachloride, stirring and heating the mixture, and drying the mixture in a shielding gas after filtration. The invention also discloses a method for applying the catalyst in the hydrogenation of the silicon tetrachloride, which comprises the following steps of: premixing the silicon tetrachloride and hydrogen gas to form a gas mixture; adding the gas mixture and the catalyst into a fluidized bed reactor for reaction; and separating a product of trichlorosilane from a reaction tail gas. The catalyst prepared by the method has high catalytic efficiency and greatly improves the yield of the trichlorosilane.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
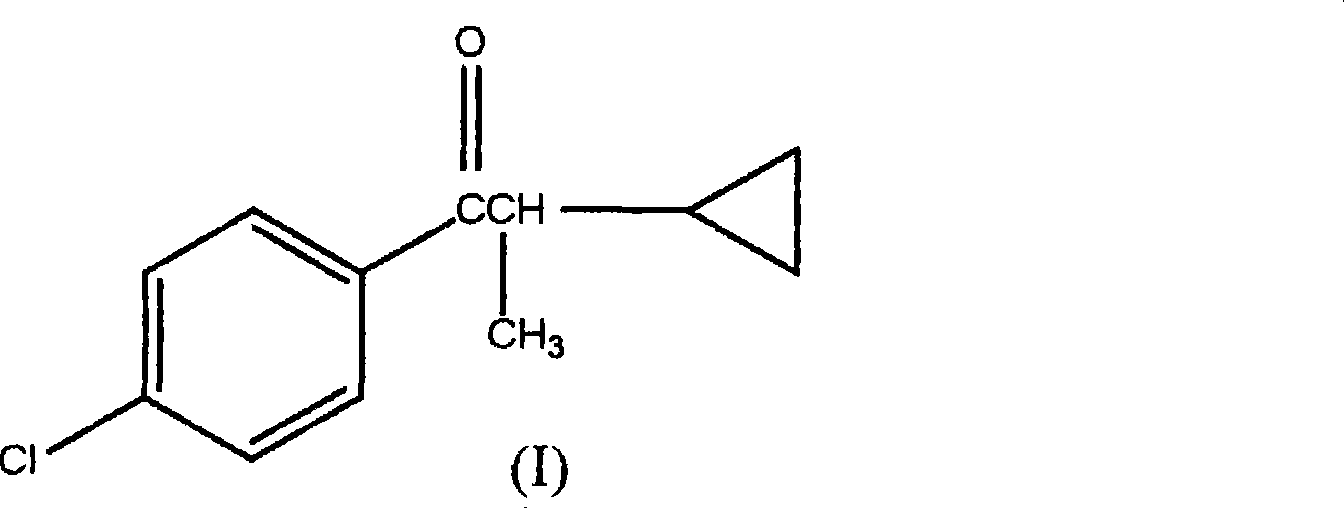
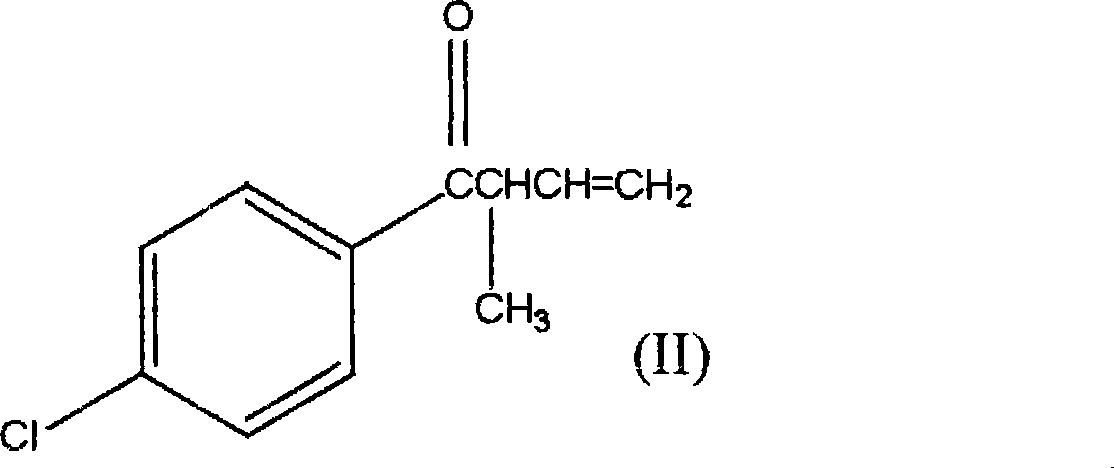
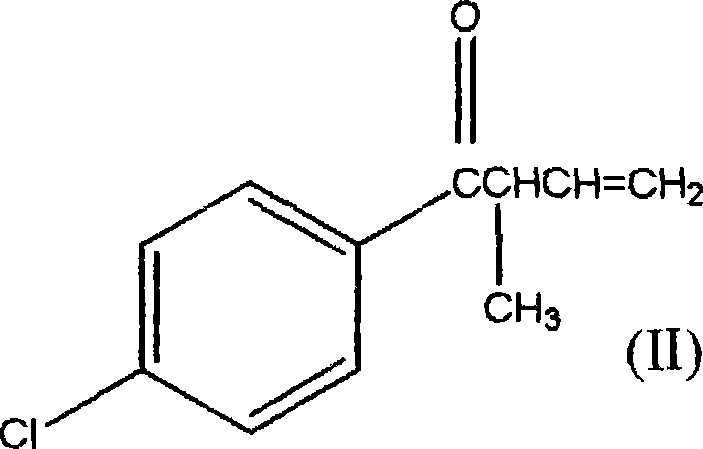
1-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-cyclopropyl-1-acetone and preparation method for intermediate thereof
ActiveCN101125807ALow costImprove responseOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparation by condensationOrganic solventCrotyl chloride
The invention relates to a preparation method of 1-(4-chlorphenyl)-2-cyclopropyl-1- rolactone(I) and cyclopropanation of 1-(4-chlorphenyl)-2-methyl-3-butylene-1-ketone(II); and the 1-(4-chlorphenyl)-2-methyl-3-butylene-1-ketone(II) is produced by the reaction of parachloronitrile, crotyl chloride, zinc powder in tetrahydrofuran and alchlor and alchlor can also not be applied; (II) is reacted with dibromomethane, zinc powder in organic solvent and cuprous chloride to produce 1-(4-chlorphenyl)-2-cyclopropyl-1- rolactone(I). Midbody (II) can not be separated and cleaned in the process of reaction.
Owner:常州沃富斯农化有限公司 +2
Method for synthesizing copper-indium-selenium nanocrystalline
InactiveCN101698472ANo pollution in the processImprove reaction efficiencySelenium/tellurium compundsNitrogen gasSolvent
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing copper-indium-selenium nanocrystalline and relates to a solar cell material. The invention provides a method for synthesizing copper-indium-selenium nanocrystalline with simple technological steps. The method comprises the following steps: mixing dodecyl mercaptan and oleyl amine to obtain a mixed solvent; adding an elementary substance selenium, and dispersing to obtain an evenly dispersed elementary substance solution; adding cuprous chloride and indium chloride into an oleic acid-octadecylene mixed solvent, heating while stirring, vacuumizing, so that the vacuum degree of the system is lower than -0.1 MPa, and introducing nitrogen to obtain an oleic acid-octadecylene composition of cupric salts and indium salts in the nitrogen atmosphere, wherein the oleic acid-octadecylene composition of cupric salts and indium salts is a light-brown transparent solution; and injecting the prepared selenium solution into the oleic acid-octadecylene composition of cupric salts and indium salts, heating to carry out the reaction, centrifugating to obtain a precipitate, and respectively washing the precipitate with methenyl chloride and ethanol at least once to obtain the copper-indium-selenium nanocrystalline.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Preparation method of Cu-Zn-In-S quantum dot luminescent thin film
ActiveCN103589427AEasy to operateSynthetic temperature is mildLuminescent compositionsFluorescence spectraAdhesive
The invention discloses a preparation method of a Cu-Zn-In-S quantum dot luminescent thin film. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) adding cuprous chloride, indium chloride, zinc salt, a capping agent and a surface coating agent to a non-polar high boiling point organic solvent so as to obtain a Cu, In and Zn mixed precursor solution, stirring and heating under the atmosphere of nitrogen or inert gas so as to form a clear transparent solution; (2) adding an oleylamine solution of sulfur to the clear transparent solution obtained in the step (1), and heating for reacting so as to prepare a Cu-Zn-In-S quantum dot solution; (3) separating so as to obtain Cu-Zn-In-S quantum dots; (4) mixing the prepared Cu-Zn-In-S quantum dots with a component A of an LED (Light Emitting Diode) pouring sealant; (5) uniformly mixing a component B of the LED pouring sealant with a mixture obtained in the step (4), removing air bubbles, then coating a product on a glass substrate, and curing at a room temperature so as to obtain the Cu-Zn-In-S quantum dot luminescent thin film. The fluorescence spectra of the Cu-Zn-In-S quantum dot luminescent thin film prepared by the method can be adjusted. The Cu-Zn-In-S quantum dot luminescent thin film has the excellent fluorescence property of the Cu-Zn-In-S quantum dots and the good machining property of an organic silicon adhesive AB.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
Olefin-alkane separating adsorbent and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103007885ALarge adsorption capacityHigh selectivity of adsorption separationOther chemical processesCombustible gas purificationAlkanePorous carbon
The invention belongs to the field of chemical separation and discloses an olefin-alkane separating adsorbent, a preparation method thereof and an application of the olefin-alkane separating adsorbent in olefin-alkane separation. The olefin-alkane separating adsorbent takes porous carbon with a high specific surface area and ordered pore passages as an adsorbent carrier, and cuprous chloride as an active component, wherein the loading amount of univalent copper is 2-12 mmol in per gram of the carrier; the cuprous chloride and the porous carbon are fully ground and thermally treated in an inert atmosphere to prepare the olefin-alkane separating adsorbent. The olefin-alkane separating adsorbent contacts olefin and alkane so as to separate the olefin from the alkane by an adsorption method. The olefin-alkane separating adsorbent is easy to prepare and good in adsorption effect and can still maintain a relatively good adsorption effect after adsorption regeneration.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
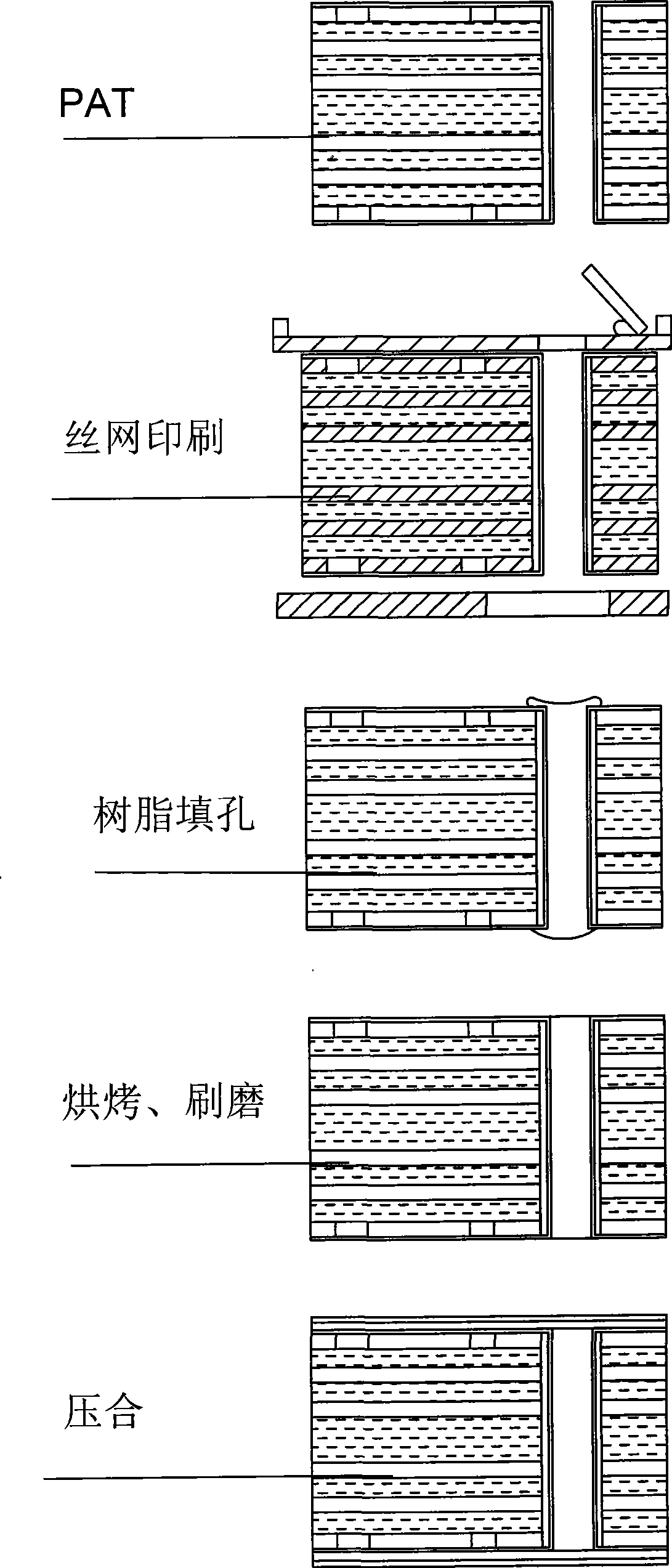
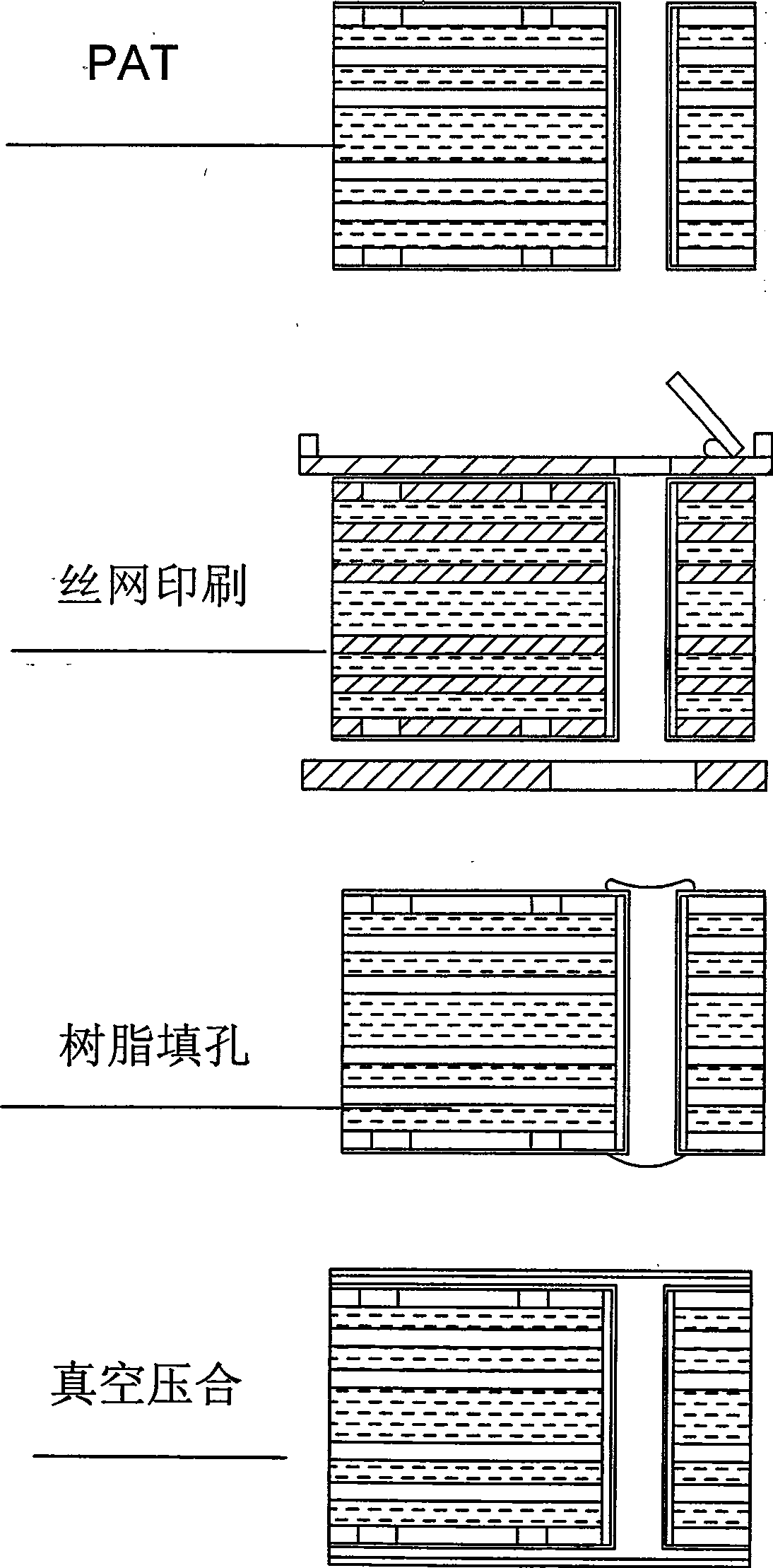
Process for blind hole, buried hole, and filled hole of multi-layered high density interconnected printed circuit board
InactiveCN101478862AShorten production timeShorten production hoursMultilayer circuit manufacturePrinted element electric connection formationScreen printingHigh density
The invention relates to a blind hole, buried hole, and porefilling craft for a multi-layer high-density interconnect printed circuit board, which is characterized in that the blind hole, buried hole, and porefilling craft for a multi-layer high-density interconnect printed circuit board firstly generates even brick red or black oxide layer on the copper surface of a printed circuit board provided with bores utilizing liquid medicine; with roughness of the generated oxide layer, the oxide layer can be closely connected with an adhesive tablet and can avoid an influence on reliability of the product from the surface of pig copper and cuprous chloride formed by a pressing high temperature reaction; then a traditional screen printing is carried out. The craft is characterized in that resin is filled into an appointed hole and laminating of the adhesive tablet is carried out within a time limit, then a vacuum compressing craft is carried out. The blind hole, buried hole, and porefilling craft for a multi-layer high-density interconnect printed circuit board can shorten the production labor hour and improve productivity.
Owner:HONGYUAN TECH HANGZHOU
Cooper base catalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103316702AHigh selectivityImprove conversion rateGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsPhysical/chemical process catalystsCopper chlorideCuprous chloride
The present invention relates to a copper base catalyst, which comprises a catalyst main body and a co-catalyst, wherein the catalyst main body comprises copper powder and / or a copper powder oxide, cuprous chloride and copper chloride. The copper base catalyst preparation method comprises: adopting a formula amount of copper powder and / or a copper powder oxide, cuprous chloride, copper chloride and a co-catalyst as raw materials, and carrying out mixing or mixing grinding. According to the present invention, the cooper base catalyst has high selectivity and a high conversion rate in the field of organic silicon monomer synthesis, the preparation method has characteristics of simple operation and simple process, and large-scale production is easily achieved.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Improved water system nieuwland catalyst and application method thereof
InactiveCN101733150AImprove conversion rateHigh selectivityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrocarbonsVinylacetyleneEther
The invention relates to an improved water system nieuwland catalyst and an application method thereof. The catalyst comprises cuprous chloride, ammonium chloride and aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid in a nieuwland catalytic system, and also comprises organic amine, organic ion liquid and organic ether. In the specific preparation step, the addition sequence of the cuprous chloride, the ammonium chloride and the hydrochloric acid is adjusted, and the organic amine, the organic ion liquid and the organic ether are sequentially added into the mixture. The catalyst improves the performance of the conventional nieuwland catalyst, and can improve the conversion per pass of acetylene and the selectivity of vinyl acetylene simultaneously in a process of preparing the vinyl acetylene by applying the nieuwland catalyst; and the organic amine, the organic ion liquid and the organic ether are less in dosage and can be recycled, and thus the improved water system nieuwland catalyst has the advantages of low cost, simple method, high efficiency and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Lead-free primary explosive composition and method of preparation
ActiveUS7833330B2Group 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsConductive materialSubject matterCuprous salt
Embodiments of the present subject matter provide a compound and material that may be used as a lead-free primary explosive. An embodiment of the present subject matter provides the compound copper(I) nitrotetrazolate. Certain embodiments of the present subject matter provide methods for preparing lead-free primary explosives. The method includes: providing cuprous salt; providing water; providing 5-nitrotetrazolate salt; combining the cuprous salt, water and 5-nitrotetrazolate salt to form a mixture; and heating the mixture. The method may also include providing cuprous chloride and providing sodium 5-nitrotetrazolate. Certain embodiments of the present subject matter also provide methods for preparing copper(I) nitrotetrazolate. The method includes: providing cuprous salt; providing water; providing 5-nitrotetrazolate salt; combining the cuprous salt, water and 5-nitrotetrazolate salt to form a mixture; and heating the mixture. The method may also include providing cuprous chloride and providing sodium 5-nitrotetrazolate.
Owner:PACIFIC SCI ENERGETIC MATERIALS
Method for producing cuprous chloride form deposed copper chloride fluid of etching board
A process for preparing cuprous chloride from the used etching liquid of copper chloride includes adding copper oxide to said used etching liquid, filtering, heating the clear solution, stirring while filling SO2 gas, cooling, filtering to obtain crystals, washing with diluted hydrochloric acid and then with alcohol, and drying.
Owner:RUANSHI CHEM WUJIANG CITY
Cuprous chloride-modified honeycomb activated carbon adsorbing material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102000547AHigh conversion and adsorption rate of NOxHigh conversion adsorption rateOther chemical processesDispersed particle separationActivated carbonNitrogen oxides
The invention discloses a method for preparing cuprous chloride-modified honeycomb activated carbon for absorbing nitric oxides (NOx less than or equal to 50ppm) with high efficiency normal temperature and normal pressure. In the invention, two times of isovolumetric impregnation are adopted for modifying honeycomb activated carbon. Firstly, cuprous chloride mixed solution using an amine-containing solvent is used as a modifier, and the cuprous chloride mixed solution is loaded on a carrier by isovolumetric impregnation; and secondly, the carrier is dried, and oxidizing activation is performed by isovolumetric impregnation with a strong oxidant solution. The honeycomb activated carbon has the characteristics of high NOx conversion and absorption efficiency, high absorption capacity, low cost, simple preparation process and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT FORNANOTECH
Method for removing fluorine and chlorine from zinc electrolyte
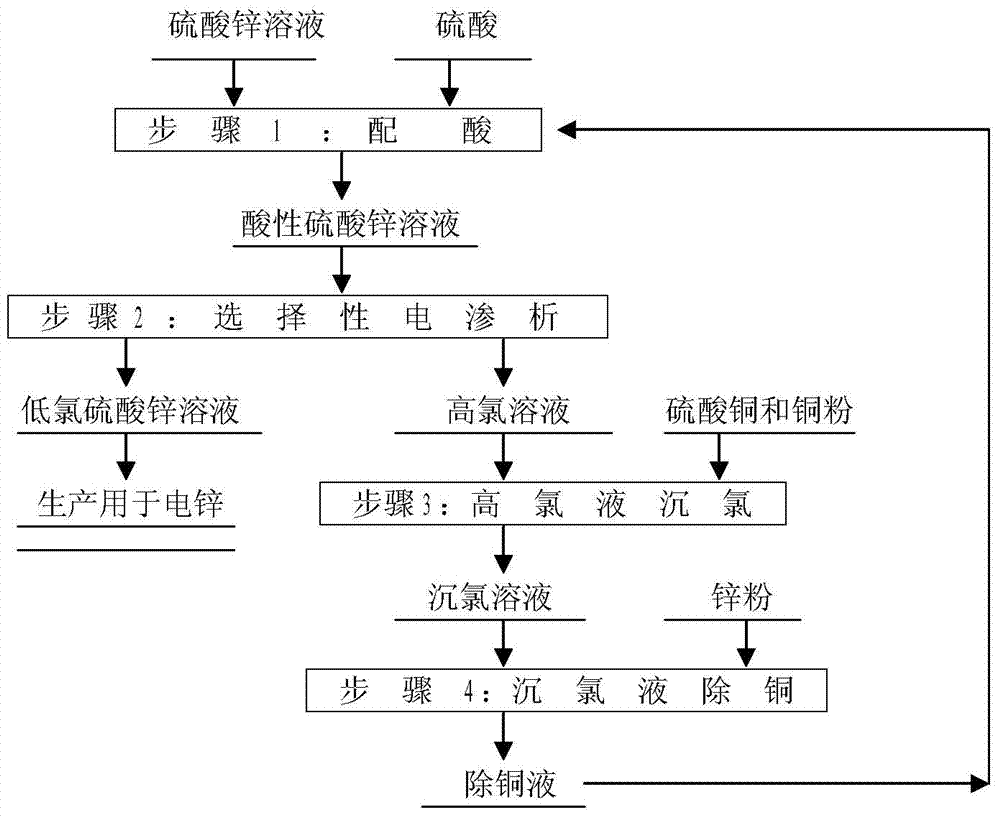
InactiveCN109487082AAvoid harmReduce fluorine contentElectrolysis componentsPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysisHydrometallurgy
The invention discloses a method for removing fluorine and chlorine from a zinc electrolyte, and belongs to the technical field of zinc smelting. According to the method, zinc-containing smoke dust generated in a zinc hydrometallurgy process is leached by using a zinc electrolysis waste liquid, sulfuric acid in the zinc electrolysis waste liquid is used as a leaching agent of zinc in the smoke dust, meanwhile steam is adopted for heating, and the zinc electrolysis waste liquid is used for leaching the zinc-containing smoke dust; and the zinc, the fluorine and the chlorine enter a leaching solution, a step-by-step precipitation method is adopted, the zinc in the solution is precipitated and returns to a zinc smelting system, the fluorine and the chlorine are converted into calcium fluorideand cuprous chloride to be precipitated and removed, the fluorine content in the zinc electrolyte can be reduced to 50 mg / L or below through a certain period of treatment, then the chlorine content isreduced to 200 mg / L or below, and the damage of the fluorine and the chlorine to zinc electrolysis is effectively avoided. The method has the characteristics of being low in cost, high in efficiencyand high in adaptability.
Owner:GRIMAT ENG INST CO LTD
Dechlorination method of zinc sulfate solution
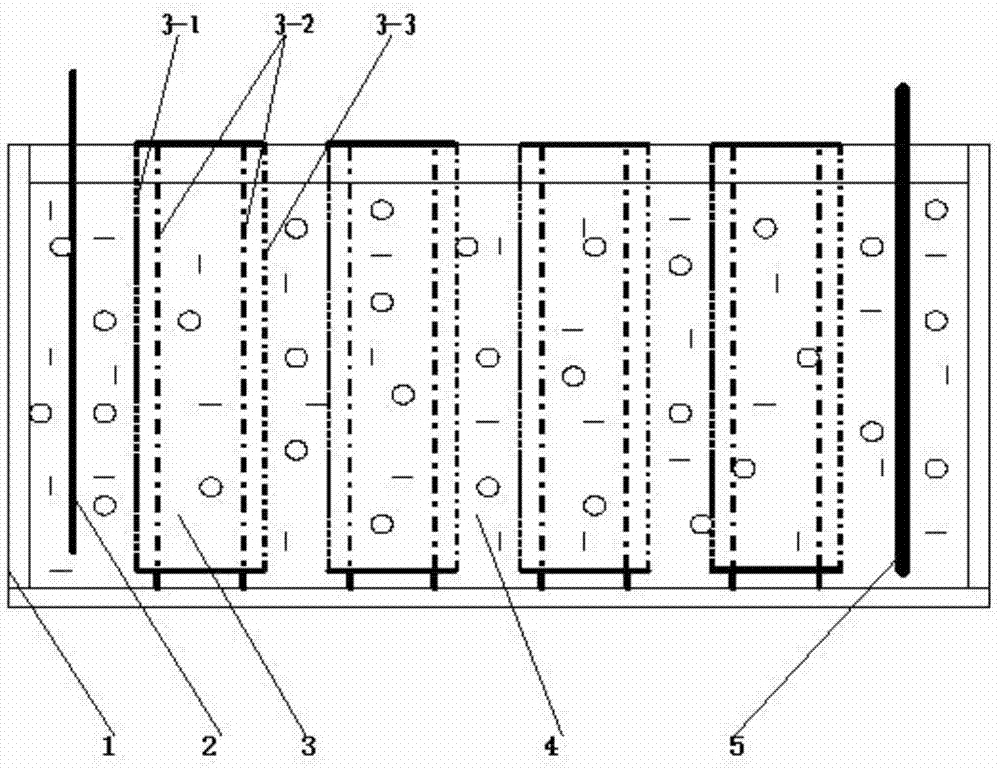
InactiveCN103572051AHigh efficiency removalExpand sourceProcess efficiency improvementEthyl ChlorideCuprous chloride
The invention discloses a dechlorination method of a zinc sulfate solution, which comprises the steps that sulfuric acid is added to a zinc sulfate solution containing 100-150g / L zinc and 0.5-5.0g / L chlorine; an acid solution with the sulfuric acid concentration of 20-75g / L is obtained; the acid solution is subjected to selective electrodialysis in four diaphragm electrolytic cells at a room temperature and at the current density of 50-200A / m<2>; a low-chlorine solution containing 0.1-0.3g / L chlorine and a high-chlorine solution containing 5-20g / L chlorine are obtained; the low-chlorine solution is used for producing electric zinc; the high-chlorine solution is subjected to chlorine precipitation by a cuprous chloride method; a chlorine precipitation solution containing 0.4-1.0g / L chlorine is obtained; zinc powder is added to the chlorine precipitation solution for replacing and removing copper; a copper removal solution containing 0.4-1.0g / L chlorine is produced; the copper removal solution is returned for acid addition, and subjected to the selective electrodialysis. With the adoption of the method, chloride ions in the zinc sulfate solution can be removed at low cost and high efficiency.
Owner:吴鋆
Chemical algae removing method
InactiveCN101475229AShort termWon't breakWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processEutrophicationAlgaecide
The invention relates to a chemical algae-removing method belonging to the field of environmental protection, in particular to a chemical method for removing algae in the water of lakes and reservoirs with algae outbreak, particularly blue-green algae outbreak caused by water eutrophication. The method comprises the following steps that: composite algaecide consisting of a reagent A and a reagent B is prepared; potassium permanganate is ground and prepared to be an aqueous solution, namely the reagent A; acid-soluble cuprous chloride is prepared from cuprous chloride, concentrated hydrochloric acid with the mass percentage of 37 percent and water according to the proportion of 0.03g:0.5mL:100mL; aluminum chloride and sodium chloride are made into aqueous solutions respectively; the reagent B is prepared from the acid-soluble cuprous chloride, an aqueous solution of aluminum chloride and an aqueous solution of sodium chloride; the reagent A and the reagent B are stored separately; and the reagent A and the reagent B are used to be mixed on site so as to form the composite algaecide to be added. The method has the advantages of convenient operation, economical efficiency, practicability and capability of inactivating algal cells in a short time without destroying cell bodies, is characterized in safety and high efficiency, can effectively inhibit algae outbreak, and can obtain remarkable social and economic benefit.
Owner:CHENGDU DUCHENG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION CO LTD
Production process for comprehensively recovering valuable metal of copper, cobalt and iron alloy
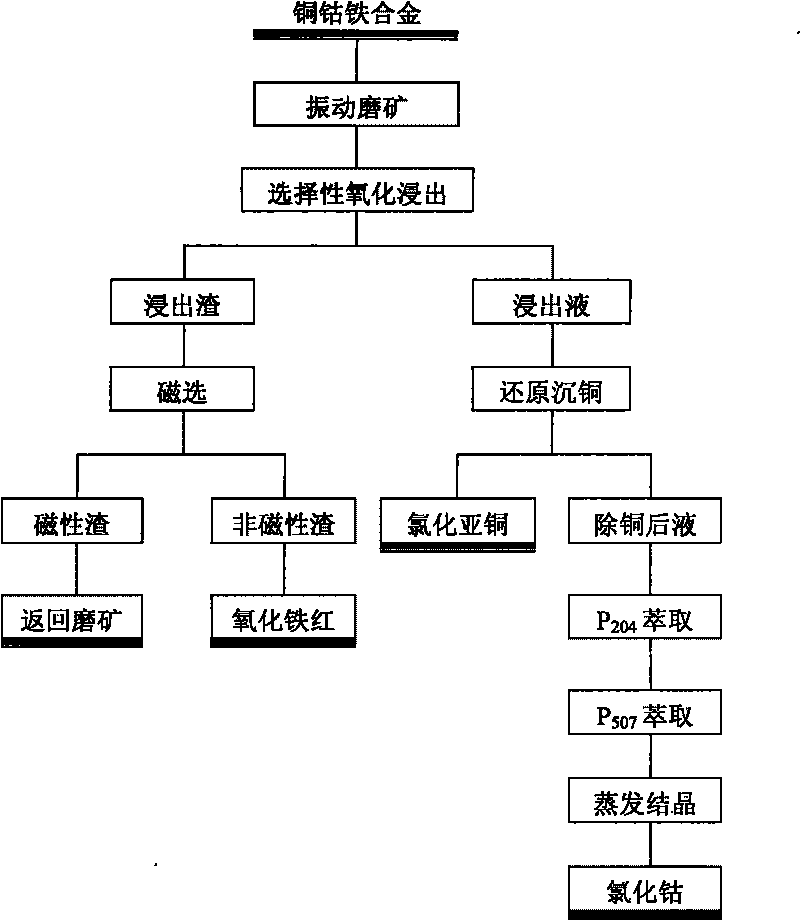
InactiveCN101717862AReduce energy consumptionWide range of reaction initial temperatureProcess efficiency improvementAlloyHydrometallurgy
The invention relates to a production process for comprehensively recovering valuable metal of copper, cobalt and iron alloy, belonging to the technical field of hydrometallurgy and comprising the steps of: preparing fine alloy powder with the mesh of -100 by vibrating, grinding, screening and grading the copper, cobalt and iron alloy; adding water to the fine alloy powder to stir; then adding a required theoretical quantity of fluorine ions F-; adding inorganic acid to react for 1.5 hours; slowly adding oxidant solution; stirring for 1.5 hours at the continuous temperature of larger than 85 DEG C after adding the oxidant solution; separating solid from the solution; adding a reducer whose use quantity is 1.05 times of the theoretical quantity to the obtained filtrate; stirring at normal temperature; reacting for 2 hours; obtaining cuprous chloride and pre-extraction solution after filtering; and finally carrying out P204 extraction and P507 extraction on the pre-extraction solution; and evaporating and crystallizing to obtain cobalt chloride. The production process has the advantages of environmental-friendly performance, simple operation, high efficiency, energy saving and suitability for industrial production.
Owner:HUNAN KAITONG METAL
Preparation method of high activity cuprous chloride catalyst used for organic silicon monomer synthesis
A coprous chloride catalyst used for preparing organosilicon monomer with high activity, selectivity and output rate is prepared through reduction reaction for reducing the mixed solution of Cu and Cl ions by SO3 solution while adding disperser for controlling the granularity and form of product, liquid-solid separation, acid washing, alcohol washing, filtering washing and drying.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Catalyst for preparing vinyl acetylene and application method thereof
InactiveCN101786022AIncrease conversion rate per passImprove conversion rateOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrocarbonsVinylacetyleneOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a catalyst for preparing vinyl acetylene and an application method thereof; the components of the catalyst include cuprous chloride, water, organic solvent, organic amine salt and organic ionic liquid. The application method includes steps that: under deoxygenation condition, the organic amine salt is dissolved in the solution of the organic solvent; and then cuprous chloride and organic ionic liquid are added to the solution; acetylene gas is introduced while the temperature is maintained constantly to produce vinyl acetylene. The invention improves the performance of an acetylene dimerization catalytic system, also increases the conversion per pass of acetylene and vinyl acetylene selectivity, produces less byproduct during reaction, greatly reduces the content of acetylene high polymer and accordingly reduces the separation difficulty and the production cost.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Novel growth method of two-dimensional organic polymer through two-dimensional crystal surface catalysis
ActiveCN107936261AUniform thicknessShape is easy to controlCopper chloridesCopper foilTwo dimensional crystal
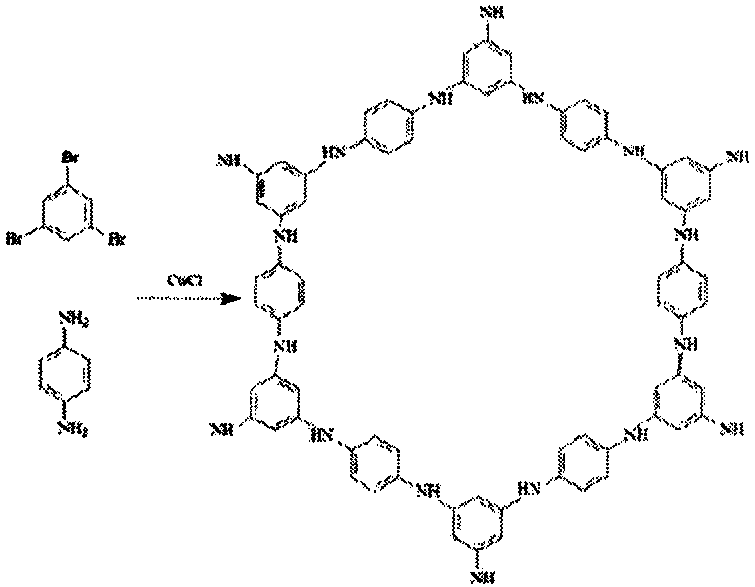
The invention provides a novel growth method of a two-dimensional organic polymer through two-dimensional crystal surface catalysis. A solid-liquid interface rapid preparation method is adopted to directly prepare a two-dimensional cuprous chloride nano-crystal material which has template and catalysis effects on a copper foil substrate; 1,3,5-tribromobenzene and p-phenylenediamine are used as monomer molecules; polymerization reaction is directly carried out on the surface of a two-dimensional cuprous chloride nano-crystal which is used as a catalyst, so as to obtain the two-dimensional organic polymer. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the two-dimensional organic polymer is prepared from specific monomers by utilizing surface-catalyzed reaction and two-dimensional organic polymerization reaction types are widened.
Owner:射阳县新港污水处理有限公司
Method for preparing activated rubber crumb by catalysis and activation reaction
InactiveCN101381476AImprove dynamic performanceEasy to usePlastic recyclingPolymer sciencePlasticizer
The invention provides a method for preparing activated rubber powder by catalytic reaction and activating reaction, and relates to a method for comprehensive utilization of waste and scrap rubber. Compared with the production of regenerated rubber, the method reduces processes of desulfurizing, kneading and refining, thereby avoiding secondary pollution to the environment. The prepared activated rubber powder has excellent compatibility with matrix rubber, and improves the physical and mechanical properties of the product. The formulation comprises the following compositions in weight portion: 100 portions of 30 to 40 meshes of waste rubber powder, 8 to 17 portions of plasticizer-dipentene, 5 to 8 portions of dusting agent-pottery clay, 0.2 to 0.5 portion of catalyst-cuprous chloride, 7 to 1.0 portion of promoting agent-polyalkylphenol disulfide, and 1 to 2.5 portions of dispersing agent-ethanol. The method comprises the following steps: placing the 30 to 40 meshes of waste rubber powder into a high-speed stirring reactor, and heating the waste rubber powder to the temperature of between 80 and 100 DEG C; adding the plasticizer, the dusting agent, the catalyst, the promoting agent and the dispersing agent into the reactor sequentially for reacting for 10 to 20 minutes at a temperature of between 80 and 120 DEG C, and cooling and discharging to produce the activated rubber powder. The prepared activated rubber powder can be used in rubber industry and building industry.
Owner:TIANJIN RUBBER IND RES INST
Static pressure hydrothermal and hydrolytic preparing technology for cuprous chloride crystal
A process for preparing the cuprous chloride crystal by static-pressure hydrothermal hydrolysis includes such steps as dissolving copper sulfate and sodium chloride in solvent, regulating its acidity, adding excessive red copper powder, boiling while reflux reaction, adding hydrochloric acid to dissolve generated cuprous chloride crystals, filtering to remove residual copper powder, adding water heating to 105-150 deg.c in sealed state, static-pressure hydrothermal hydrolyzing, filtering, washing and drying.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Water heating reduction method preparing process for cuprous chloride
InactiveCN101070181ANo emissionsSimple preparation processCopper chloridesCopper chlorideCuprous chloride
The invention is a kind of preparation craft of copper chloride crystal by hydrothermal reduction method, confect bluestone and sodium chloride into mixed water solution, transmit them into pressure and resistant autoclave, add reducer of formaldehyde which then is heated to temperature of 130 degree C-170 degree C closely, make them react for 3-12 hours by hydrothermal reduction method and form copper chloride crystal, cool it and then filter, absterge and dry the filtered crystal according to general method, then get product wanted. In the course of preparing copper chloride crystal in the invention, it uses formaldehyde as reducer, liquor and formaldehyde reducer reacts in the close autoclave directly by hydrothermal reduction method, form product wanted of copper chloride crystal for one step. The preparation craft is simple and easy to control, save water and energy, there is no harmful gas and liquid to discharge, the mother liquor filtered copper chloride crystal can be used circulatoryly after being disposalled, and it has double superiority of environmental protection and energy-conservation.
Owner:YANCHENG TEACHERS UNIV
Acetylene copolymer nonaqueous system catalyst and method for preparing vinyl acetylene
InactiveCN101940953AImprove stabilityHigh activityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrocarbonsVinylacetyleneNitrogenous heterocyclic compound
The invention relates to an acetylene copolymer nonaqueous system catalyst and a method for preparing vinyl acetylene. The catalyst comprises cuprous chloride, organic ether, organic ion liquid, organic amine hydrochlorides, organic pentatomic or hexahydric nitrogen heterocyclic ring compounds, and N,N-dimethyl formamide. In the process of preparing vinyl acetylene, the cuprous chloride is added after other components are thoroughly mixed. The catalyst improves the properties of the prior Nieuland catalyst, and can keep the conversion per pass of the acetylene to be constant, obviously enhance the selectivity of the target product vinyl acetylene and the single-pass conversion rate of acetylene at the same time; and since the amounts of organic pentatomic or hexahydric nitrogen heterocyclic ring compounds, and organic ion liquid is small, and all the components can be recycled, so that the invention also has the advantages of low cost, simple method, high efficiency and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Preparation method for 3,4'dichloro diaryl ether
InactiveCN102516044ARaise the ratioSimple wayOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationDiphenyl etherPtru catalyst
A preparation method for 3,4'dichloro diaryl ether is disclosed, which comprises the following steps of: (1) preparation for potassium alkoxide or sodium alkoxide; (2) preparation for potassium p-chlorophenolate; (3) preparation for active cuprous chloride; and (4) preparation for 3,4'dichloro diaryl ether. The preparation method has the following advantages that: side reactions are greatly reduced, reaction speed is fast, the pollution caused by the volatilization of benzene solvents is reduced, the utilization rate of equipment and the like are increased, the quality of product is improved, as well as yield and chilling efficiency are increased by using p-chlorophenol waterless salifying process, using newly-prepared catalyst, optimizing the ratio and pouring method of materials, and protecting by inert gas.
Owner:HUBEI XINGHUO CHEM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com