Patents
Literature
573 results about "Femtosecond pulse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
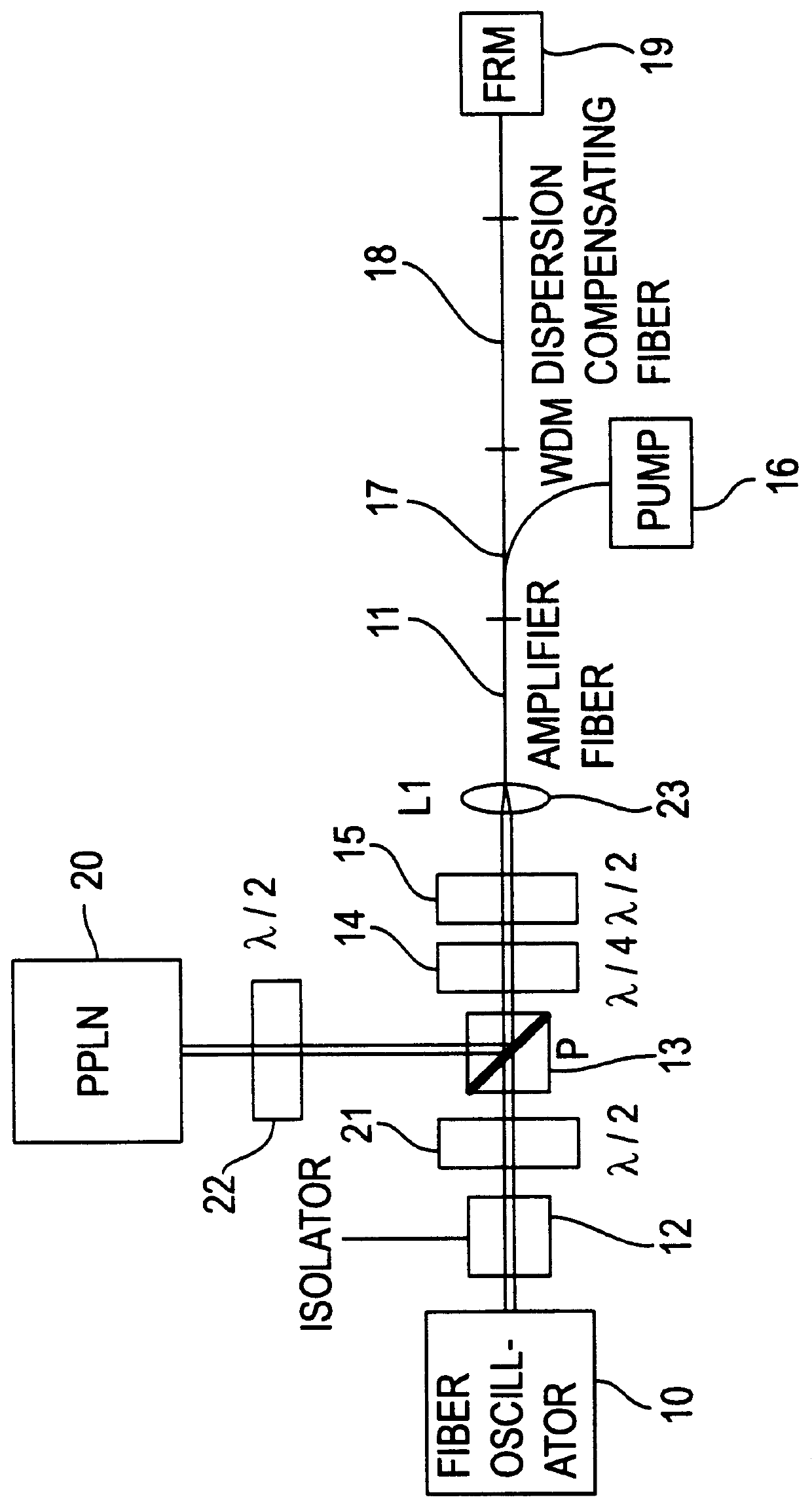
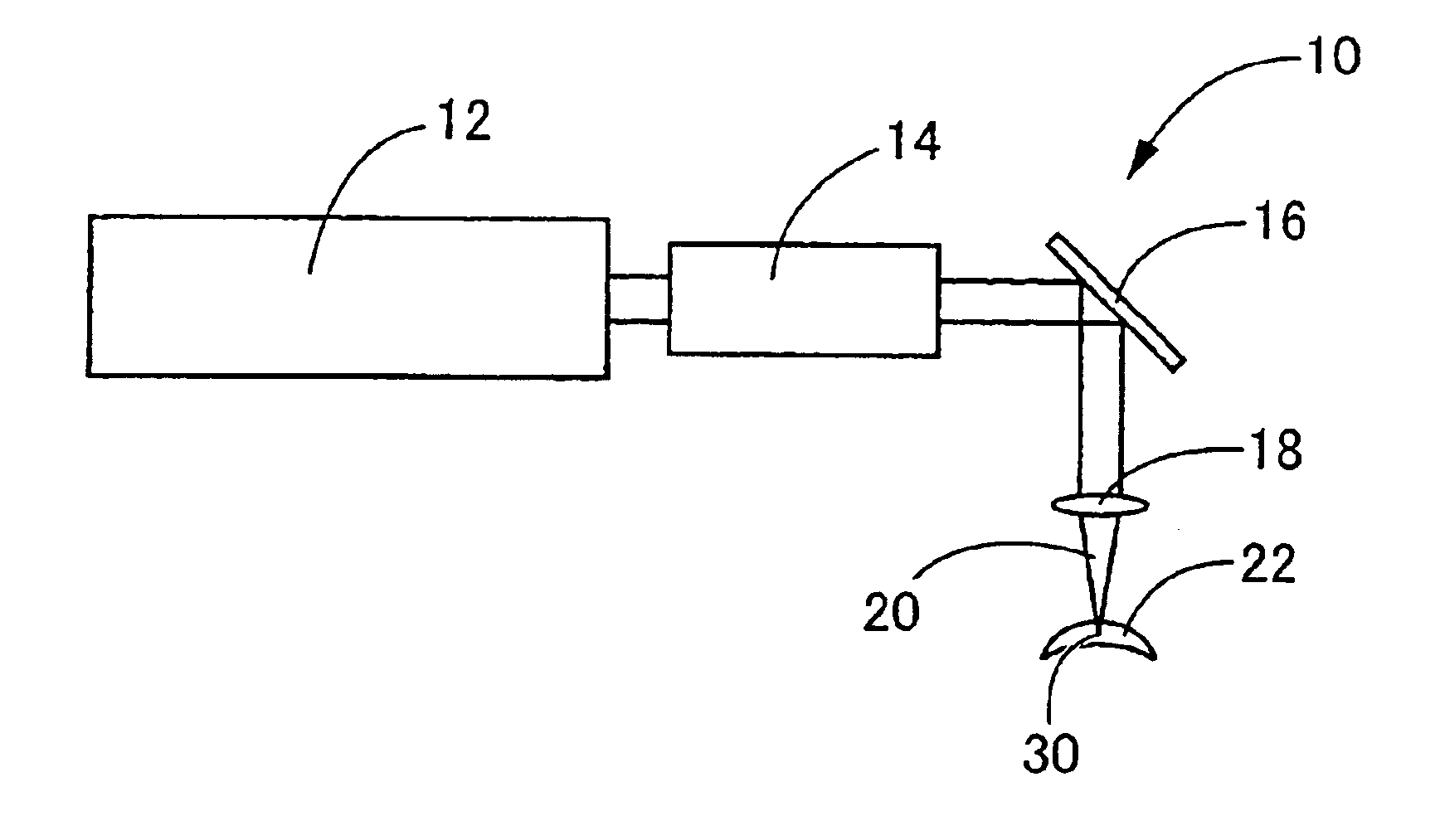
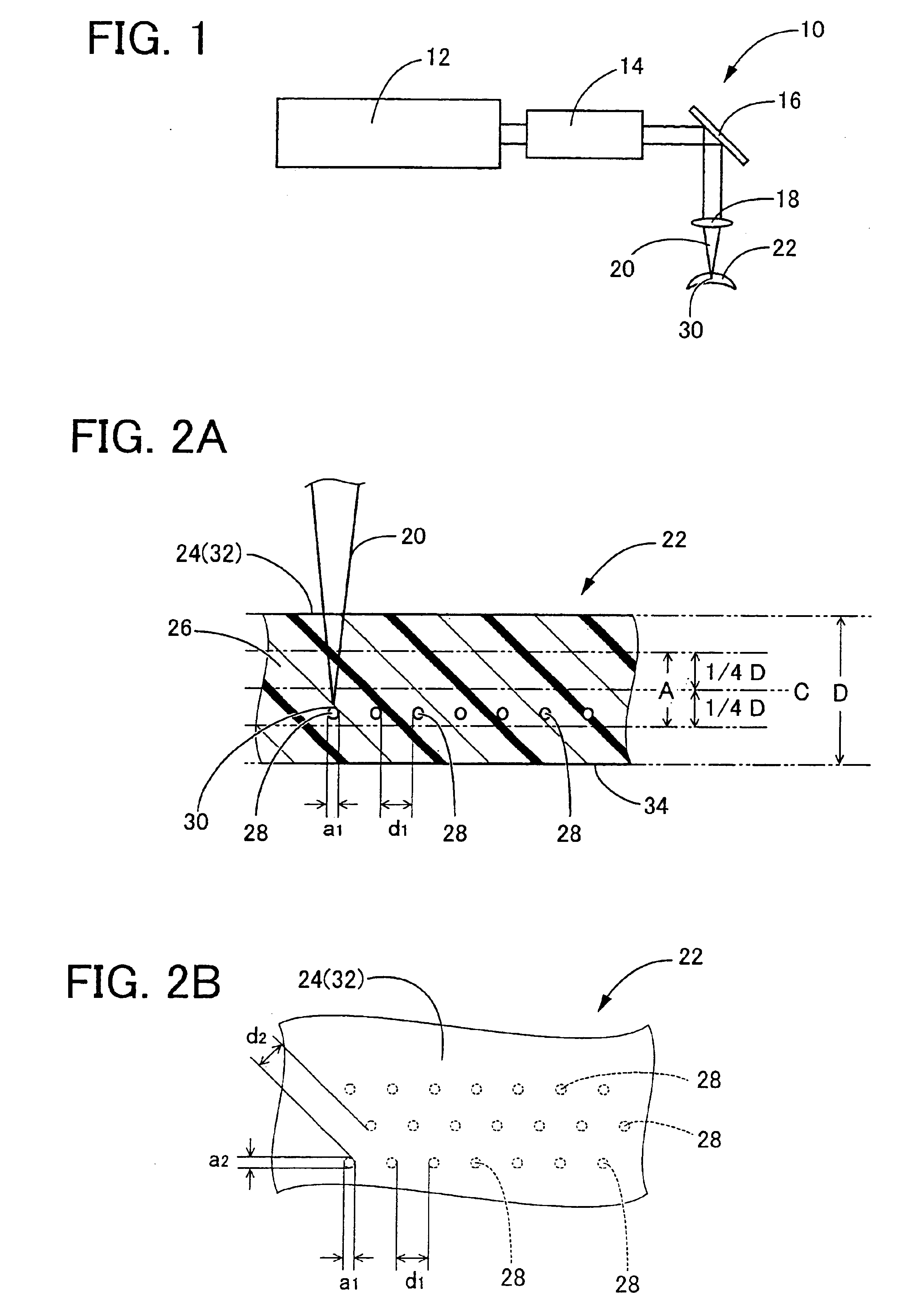
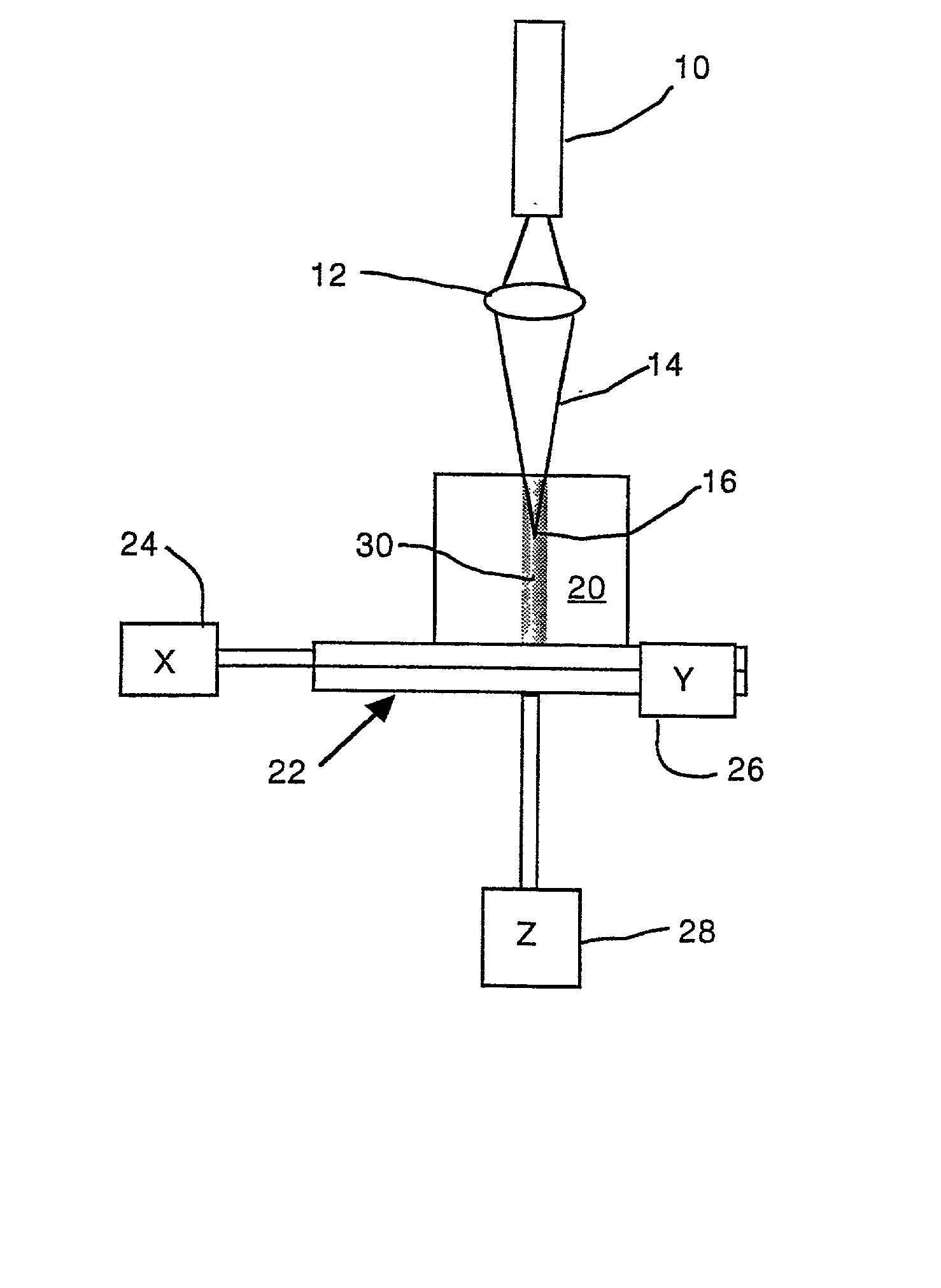
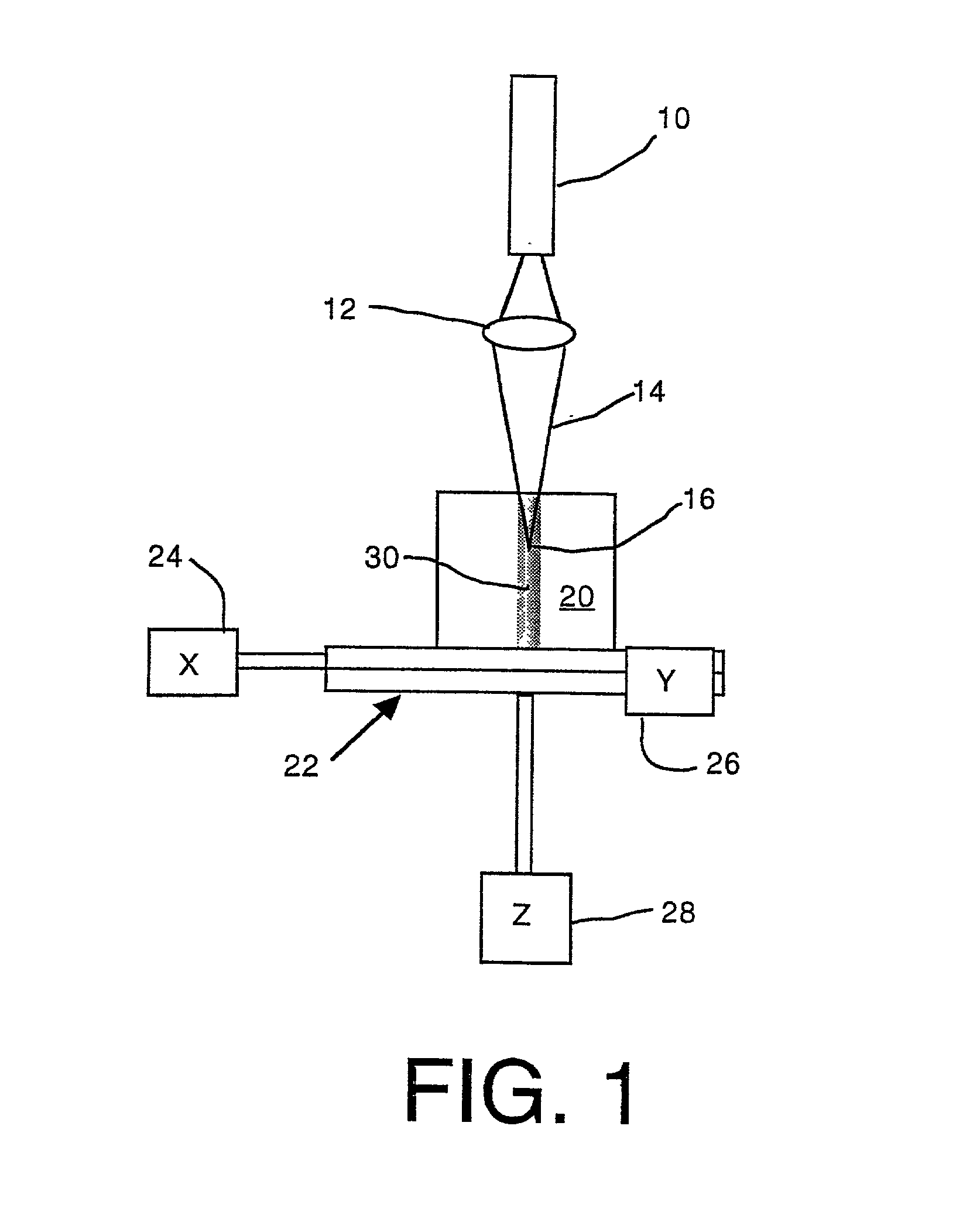
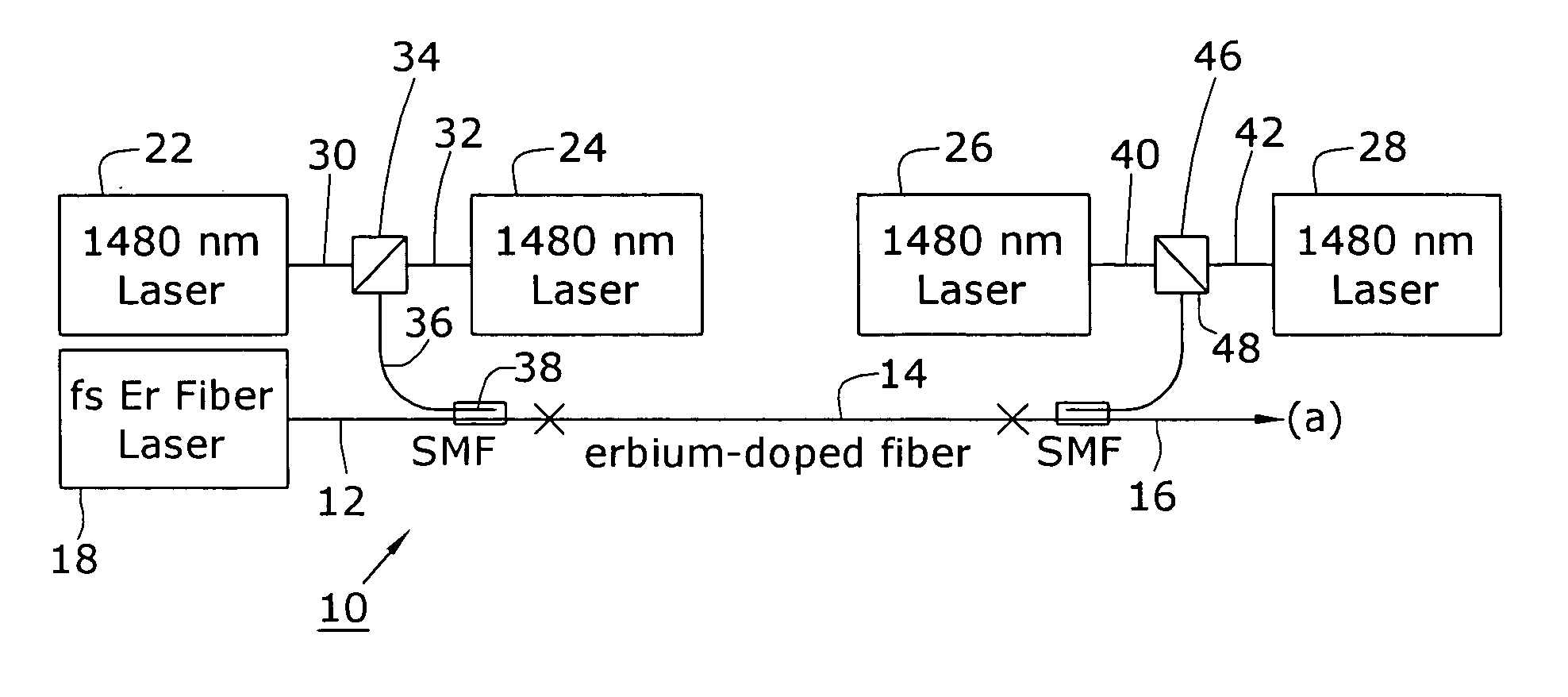
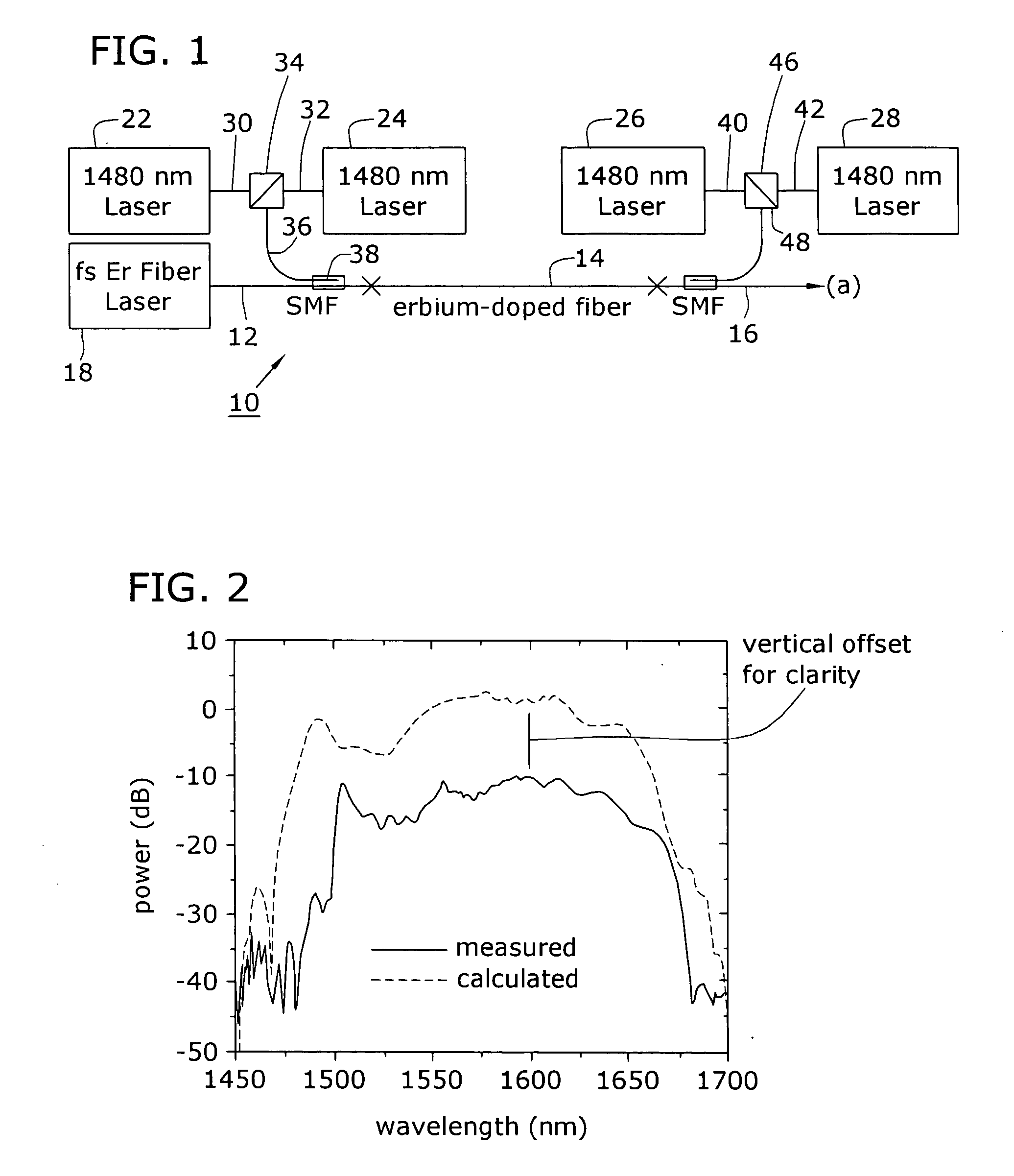
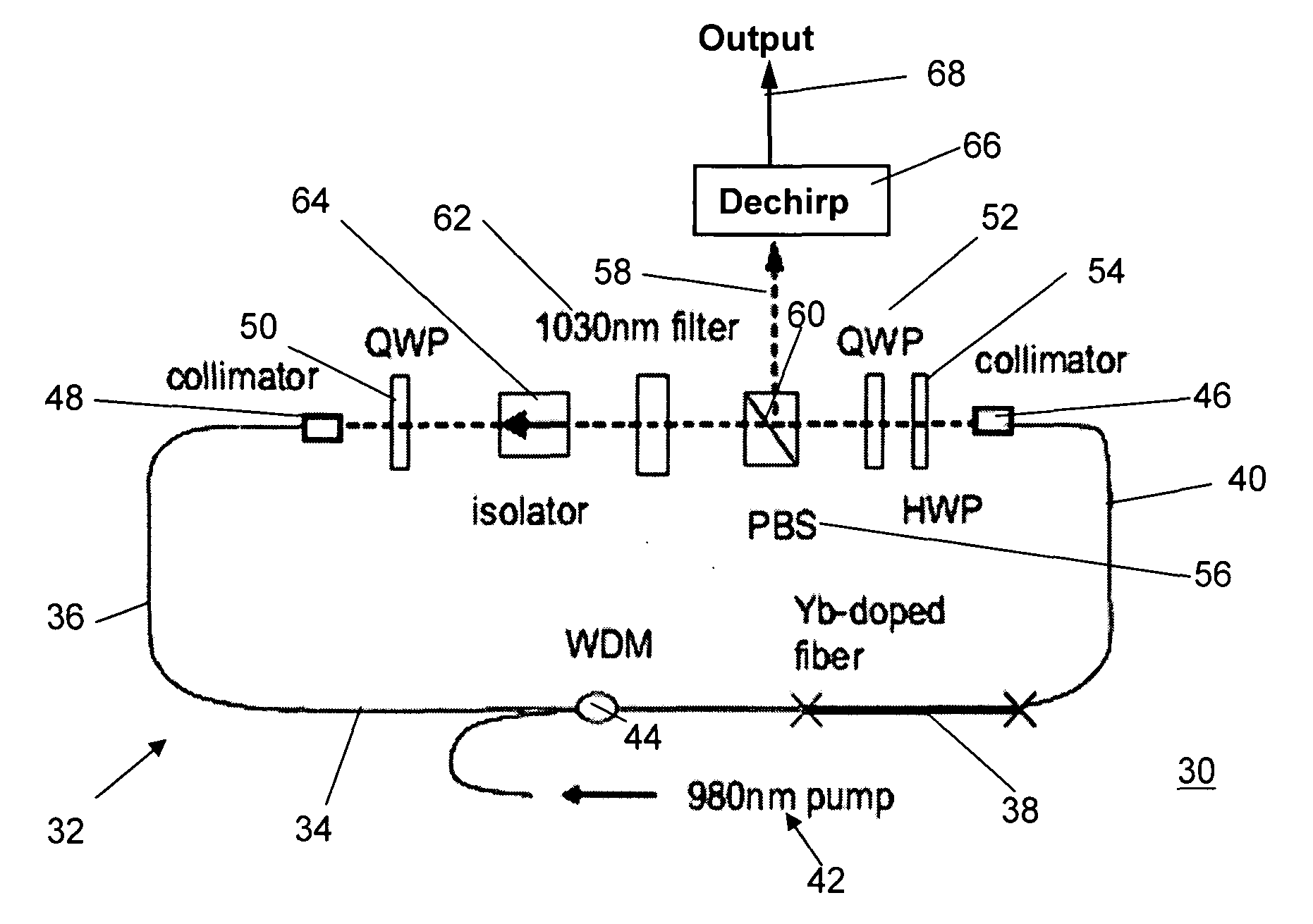
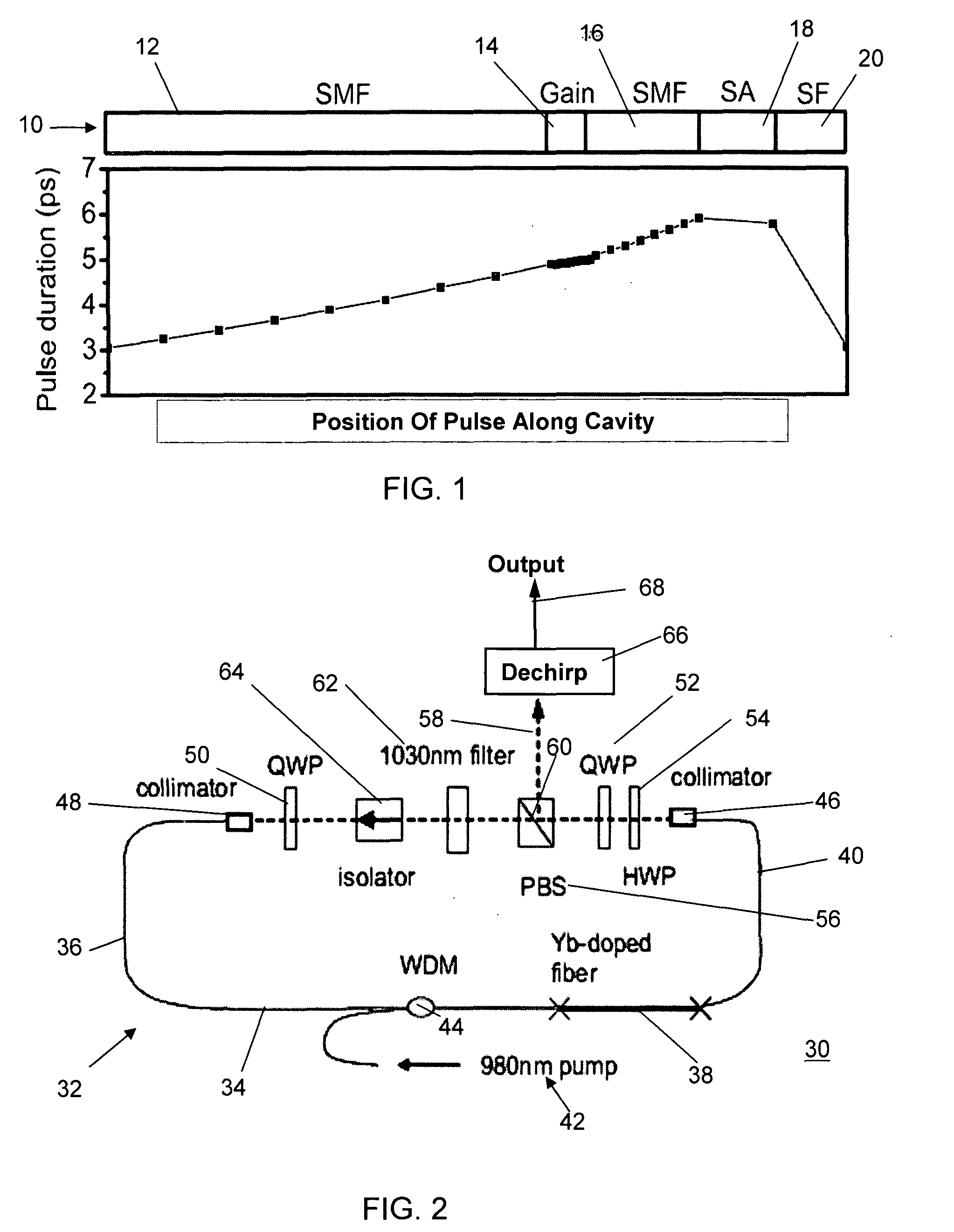
Apparatus and method for the generation of high-power femtosecond pulses from a fiber amplifier
InactiveUS6014249ALong pulse widthLow costLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsFiberDouble-clad fiber
An apparatus generates femtosecond pulses from laser amplifiers by nonlinear frequency conversion. The implementation of nonlinear frequency-conversion allows the design of highly nonlinear amplifiers at a signal wavelength (SW), while still preserving a high-quality pulse at an approximately frequency-doubled wavelength (FDW). Nonlinear frequency-conversion also allows for limited wavelength tuning of the FDW. As an example, the output from a nonlinear fiber amplifier is frequency-converted. By controlling the polarization state in the nonlinear fiber amplifier and by operating in the soliton-supporting dispersion regime of the host glass, an efficient nonlinear pulse compression for the SW is obtained. The generated pulse width is optimized by utilizing soliton compression in the presence of the Raman-self-frequency shift in the nonlinear fiber amplifier at the SW. High-power pulses are obtained by employing fiber amplifiers with large core-diameters. The efficiency of the nonlinear fiber amplifier is optimized by using a double clad fiber (i.e., a fiber with a double-step refractive index profile) and by pumping light directly into the inner core of this fiber. Periodically poled LiNbO3 (PPLN) is used for efficient conversion of the SW to a FDW. The quality of the pulses at the FDW can further be improved by nonlinear frequency conversion of the compressed and Raman-shifted signal pulses at the SW. The use of Raman-shifting further increases the tuning range at the FDW. For applications in confocal microscopy, a special linear fiber amplifier is used.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
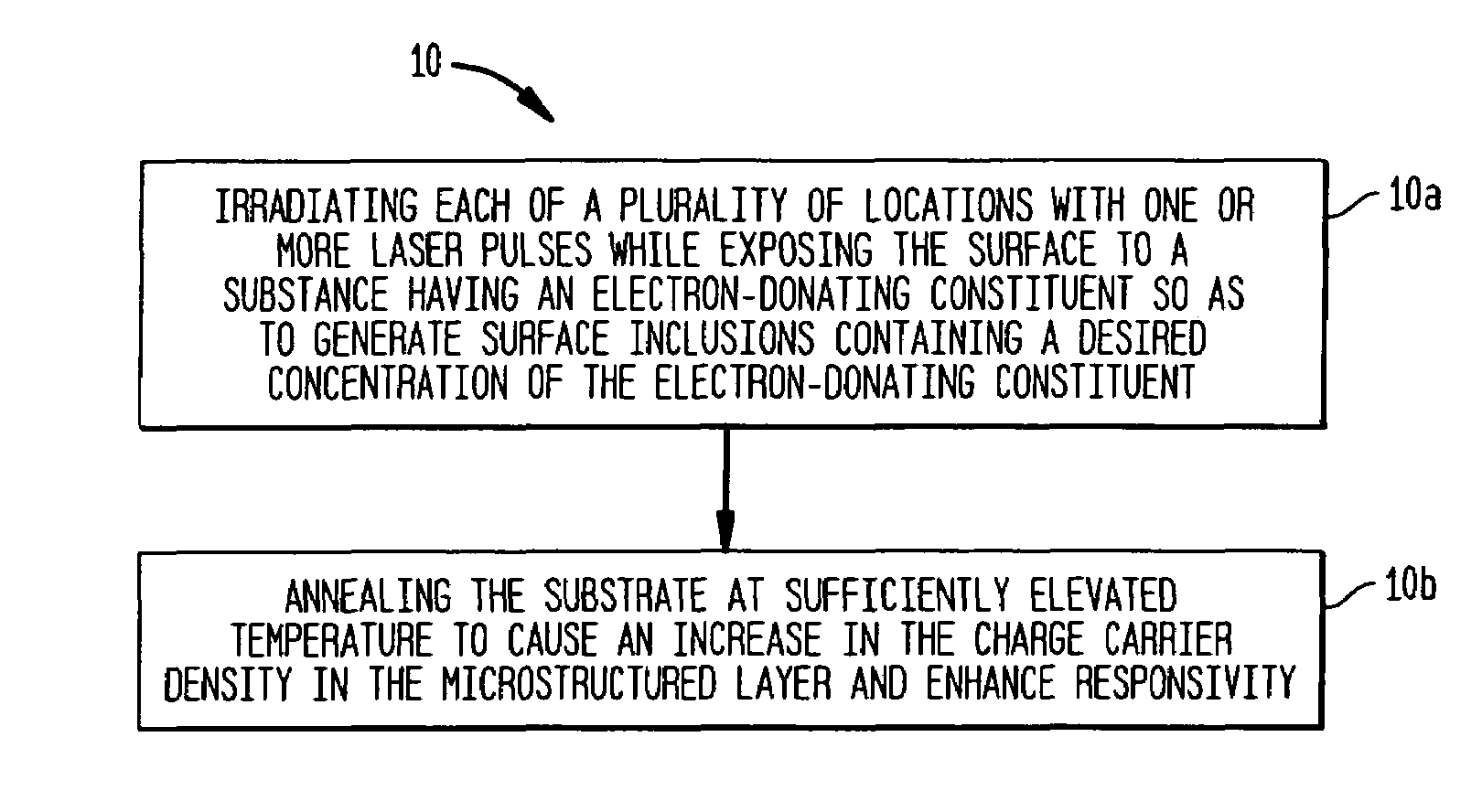
Manufacture of silicon-based devices having disordered sulfur-doped surface layers
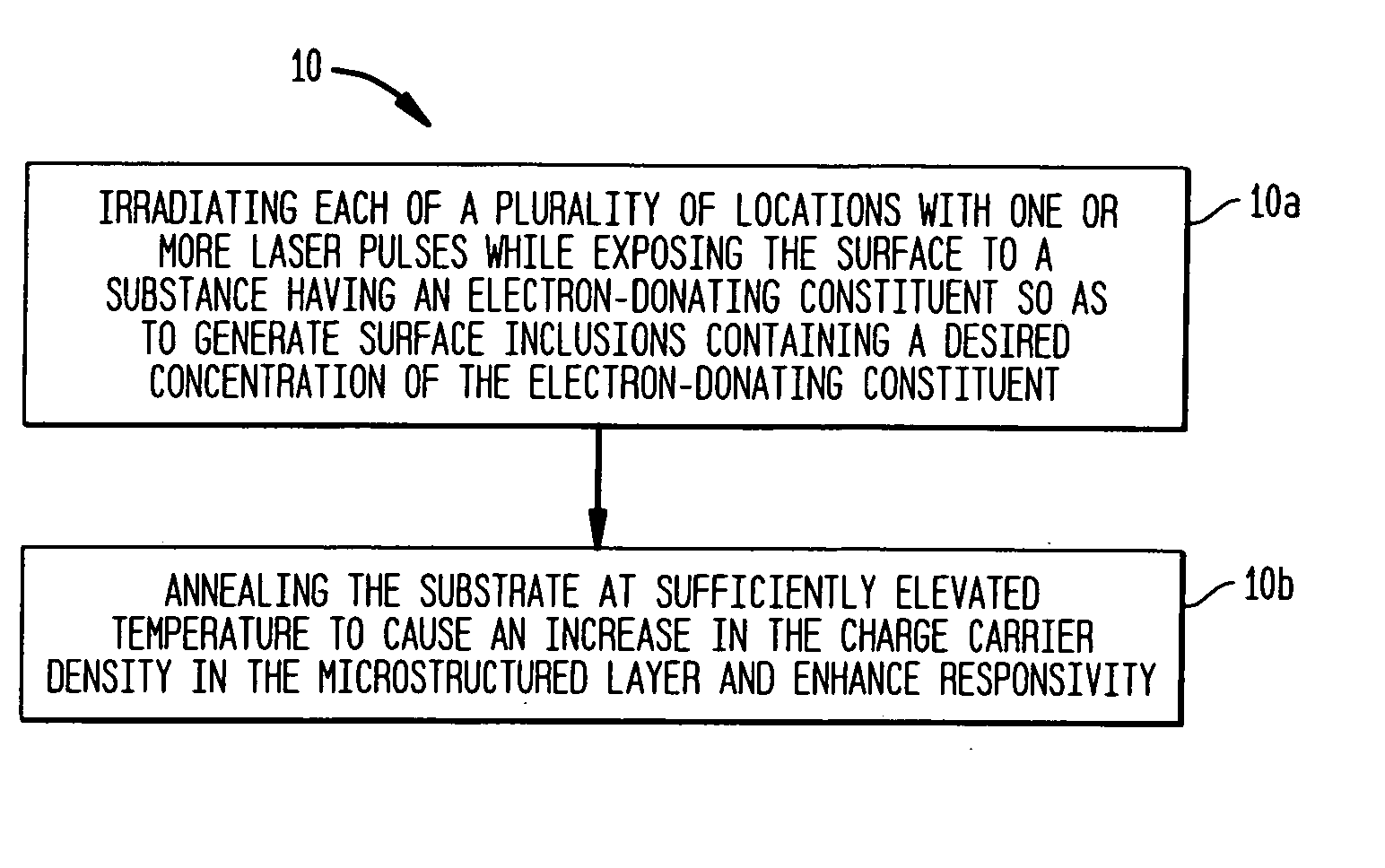
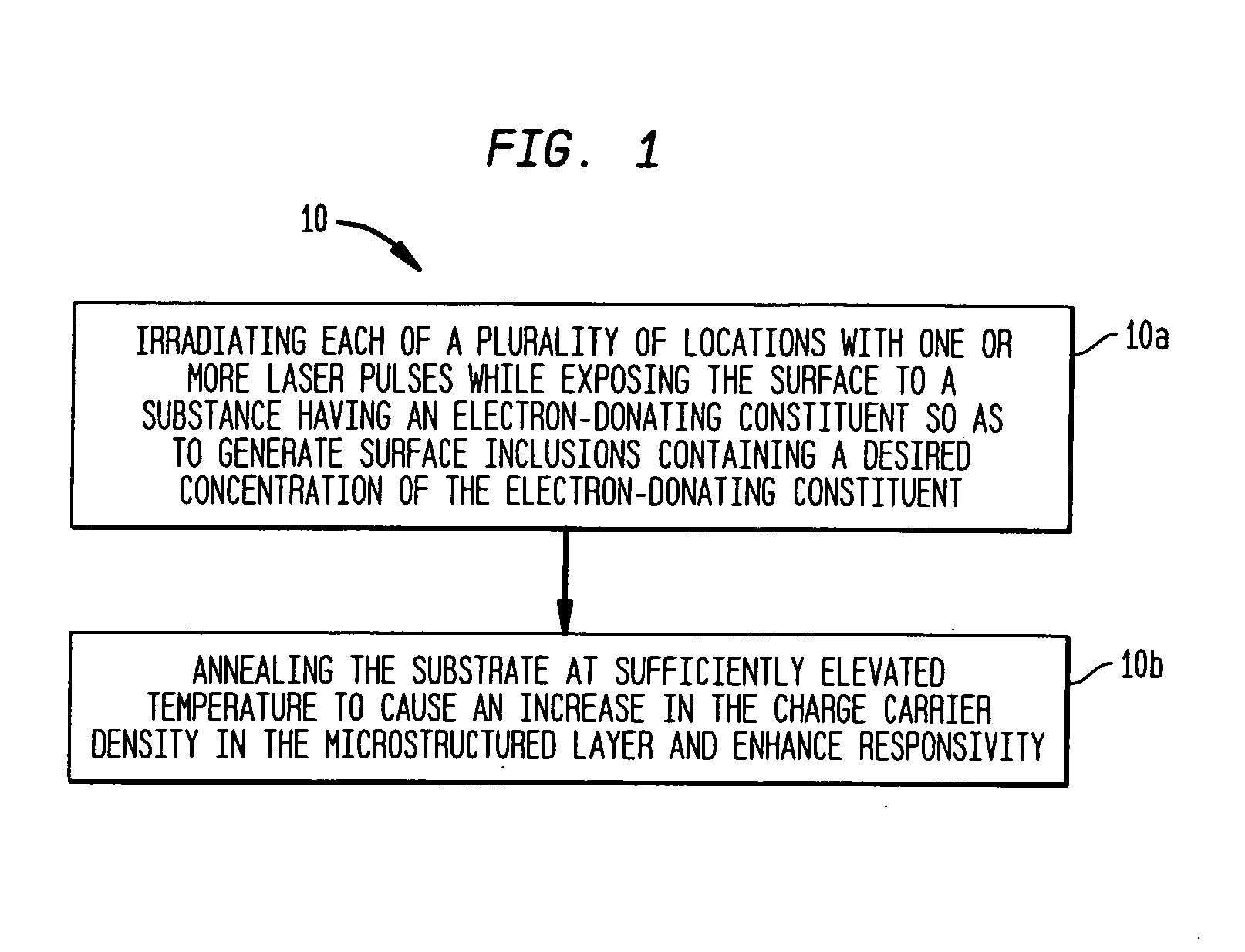
InactiveUS7354792B2Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface layerCharge-carrier density
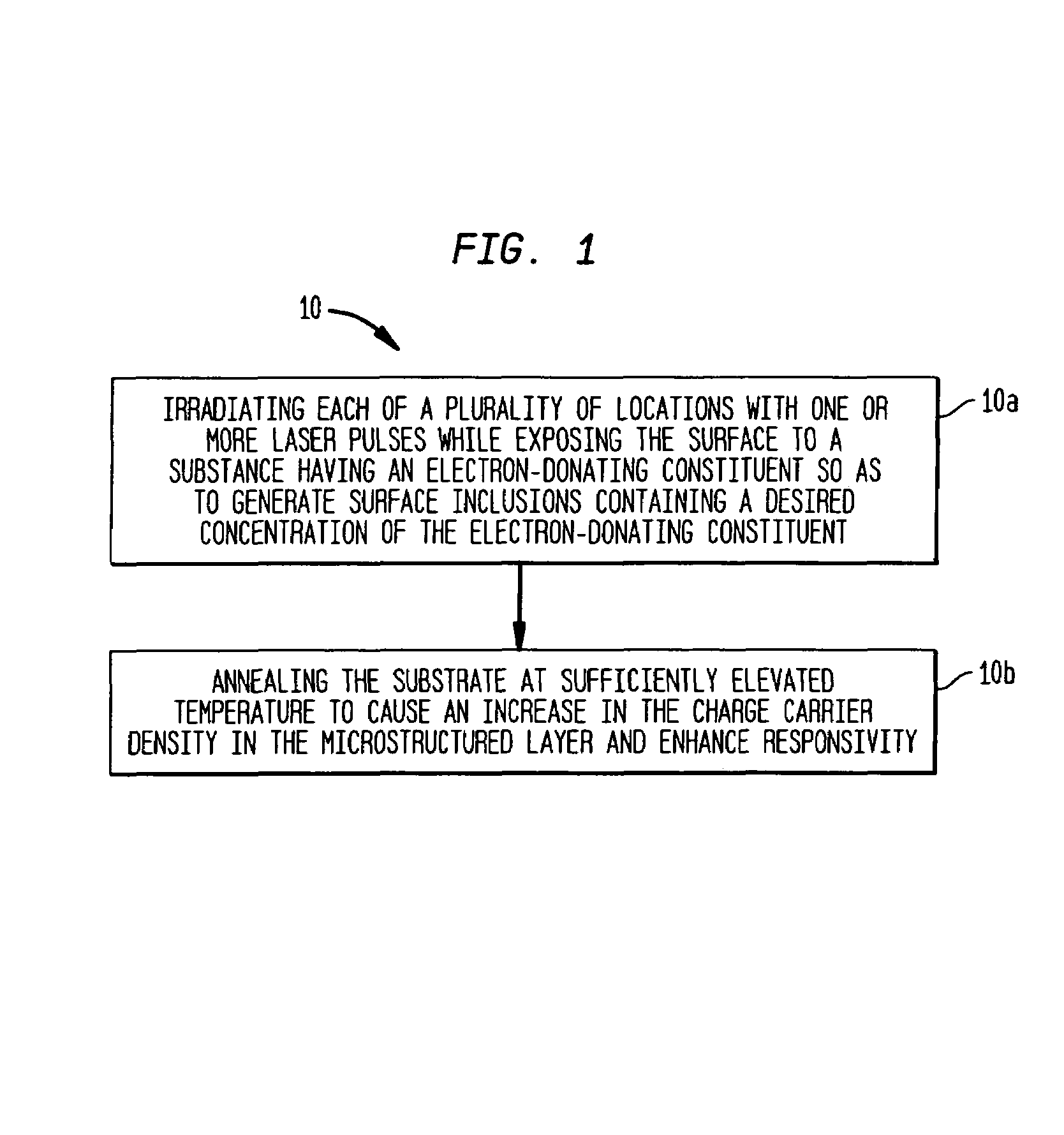
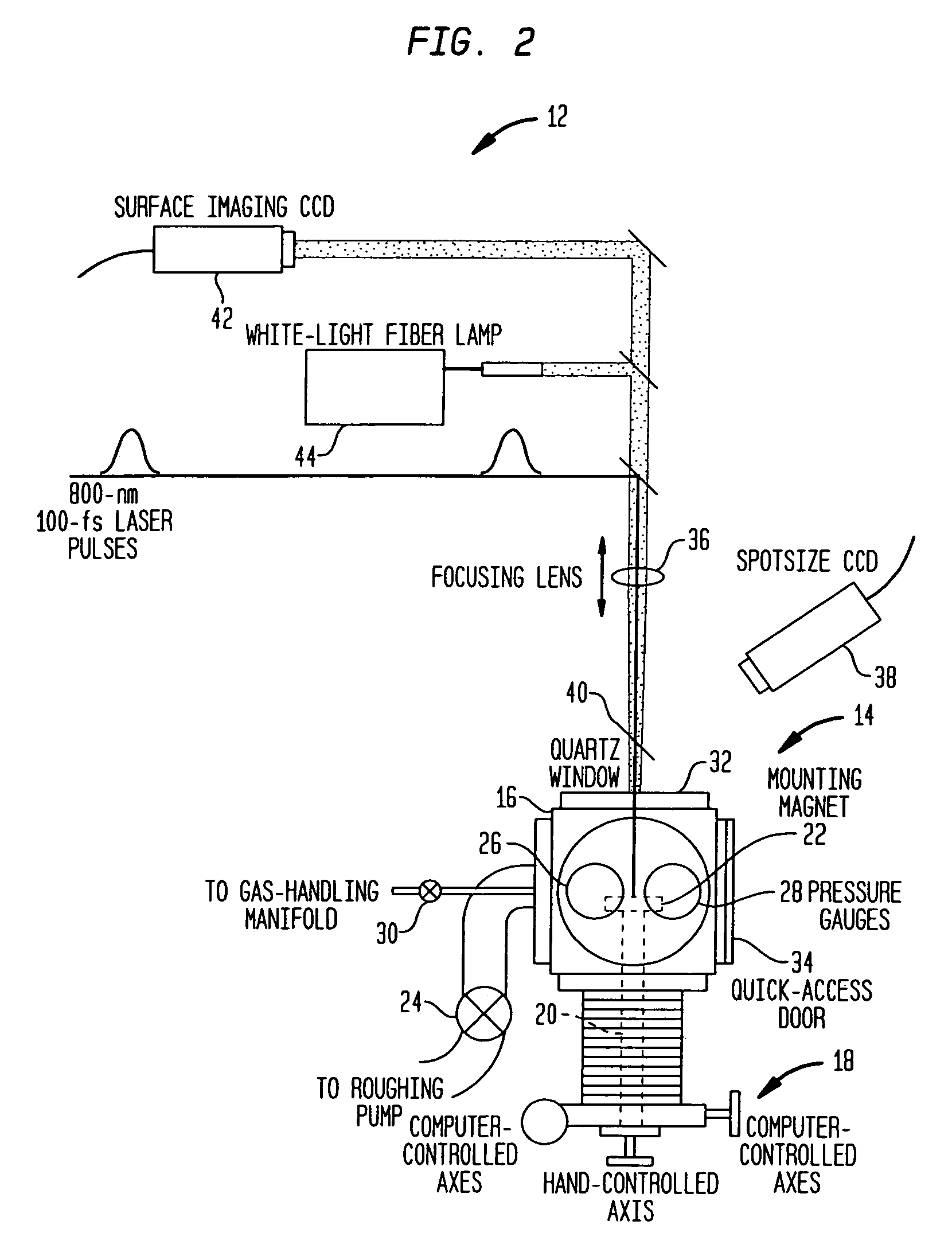
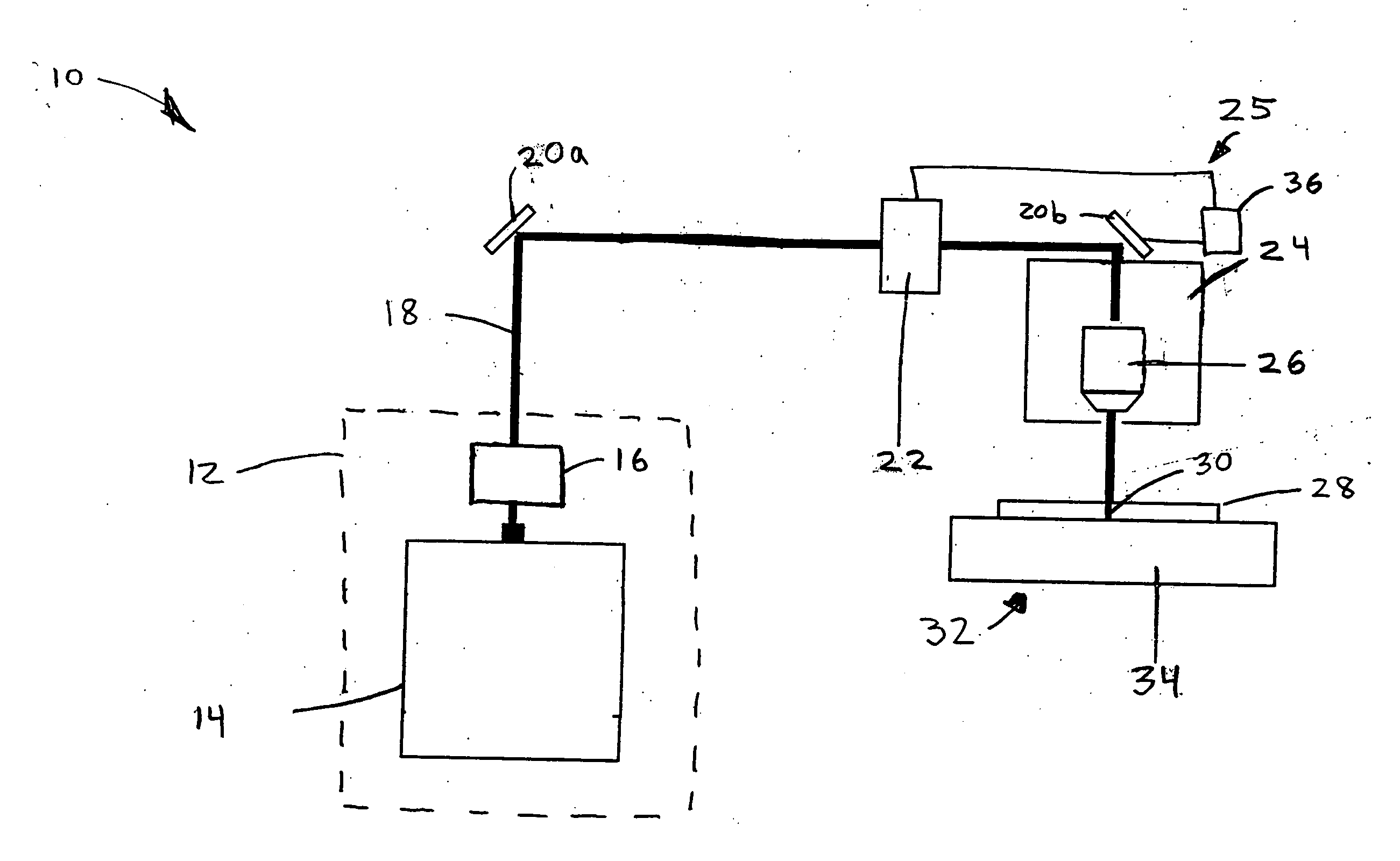
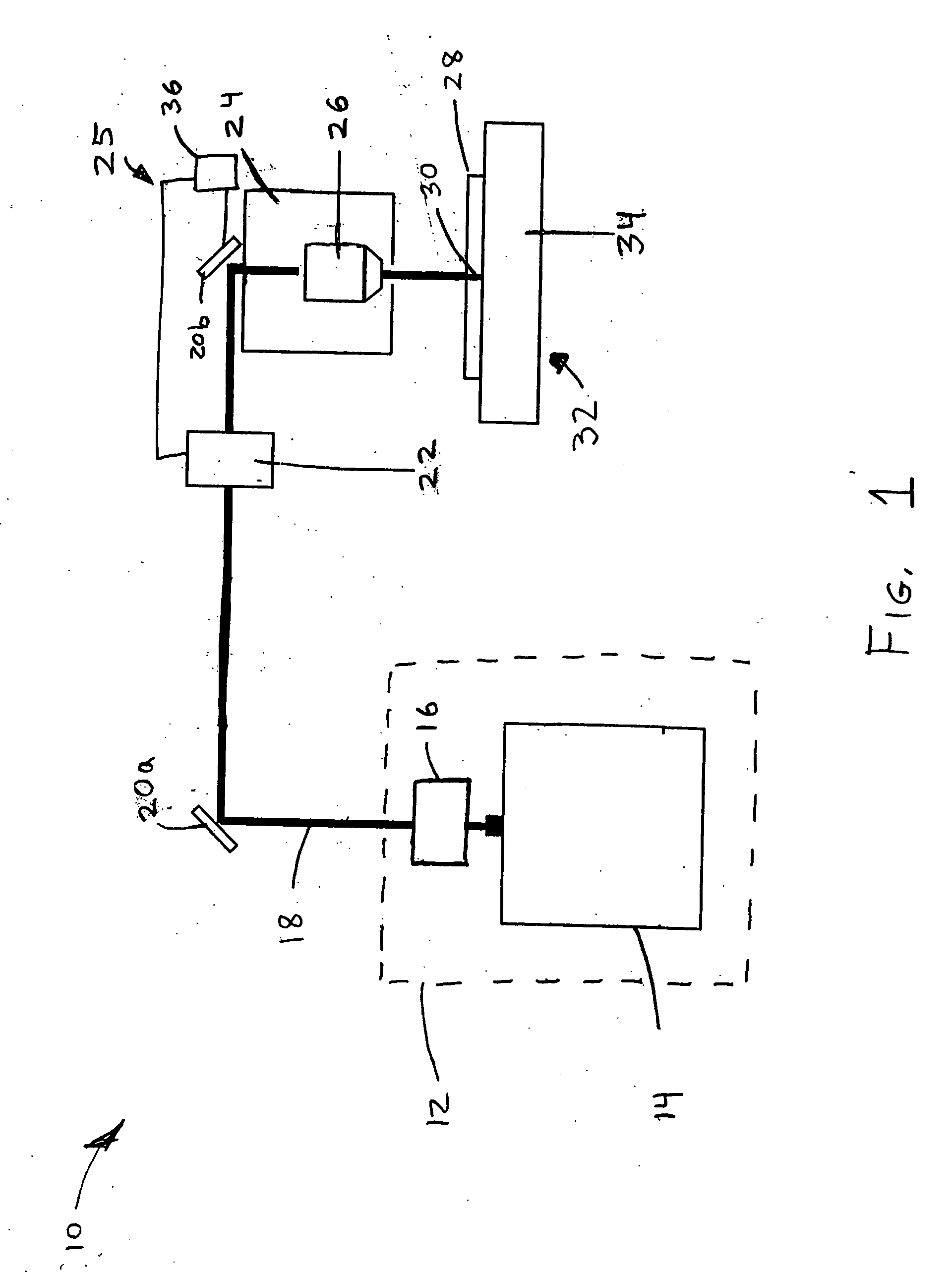
The present invention provides methods of fabricating a radiation-absorbing semiconductor wafer by irradiating at least one surface location of a silicon substrate, e.g., an n-doped crystalline silicon, by a plurality of temporally short laser pulses, e.g., femtosecond pulses, while exposing that location to a substance, e.g., SF6, having an electron-donating constituent so as to generate a substantially disordered surface layer (i.e., a microstructured layer) that incorporates a concentration of that electron-donating constituent, e.g., sulfur. The substrate is also annealed at an elevated temperature and for a duration selected to enhance the charge carrier density in the surface layer. For example, the substrate can be annealed at a temperature in a range of about 700 K to about 900 K.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Laser material micromachining with green femtosecond pulses
Various embodiments of a system described herein relate to micromachining materials using ultrashort visible laser pulses. The ultrashort laser pulses may be green and have a wavelength between about 500 to 550 nanometers in some embodiments. Additionally, the pulses may have a pulse duration of less than one picosecond in certain embodiments.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
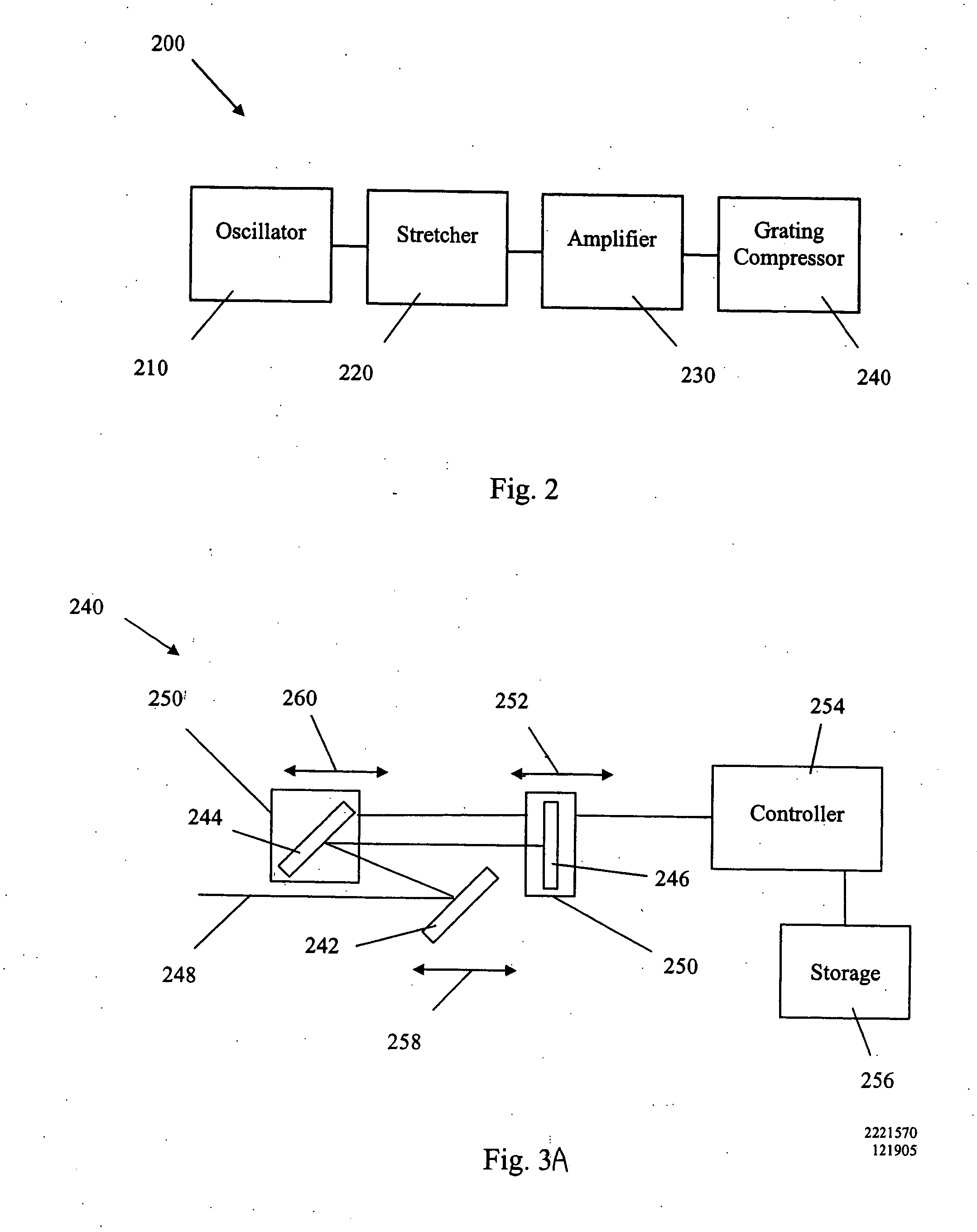
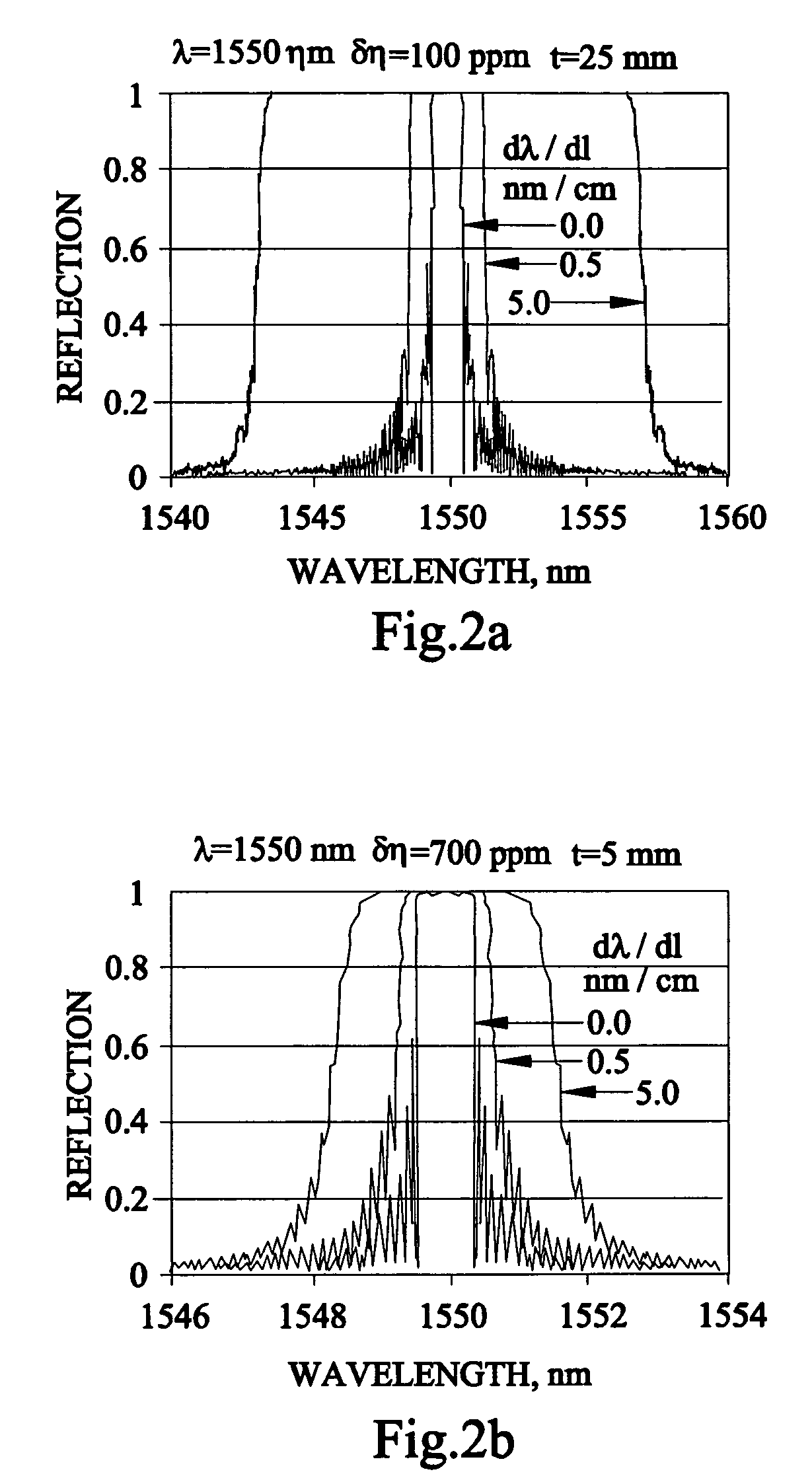
Stretching and compression of laser pulses by means of high efficiency volume diffractive gratings with variable periods in photo-thermo-refractive glass
InactiveUS20060221449A1Eliminate significant beam distortionImprove efficiencyLaser using scattering effectsPhotomechanical apparatusUltrashort laserVolume bragg grating
High efficiency reflective volume Bragg gratings with chirped gratings recorded in photo-thermo-refractive glass having an absolute diffraction efficiency exceeding 95% in transmitting and reflecting modes are used to stretch and / or compress ultrashort laser pulses with high efficiency. Robustness, compactness, thermal and laser stability along with placement of multiple elements in the same space provides femtosecond laser system with high efficiency of stretching and re-compression of femtosecond pulses.
Owner:UNIV OF MICHIGAN THE +1
Method and system for spectral analysis of biological materials using stimulated cars
InactiveUS20060066848A1Enhance CARS response signalEasy to analyzeRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringTime delaysSpectral analysis
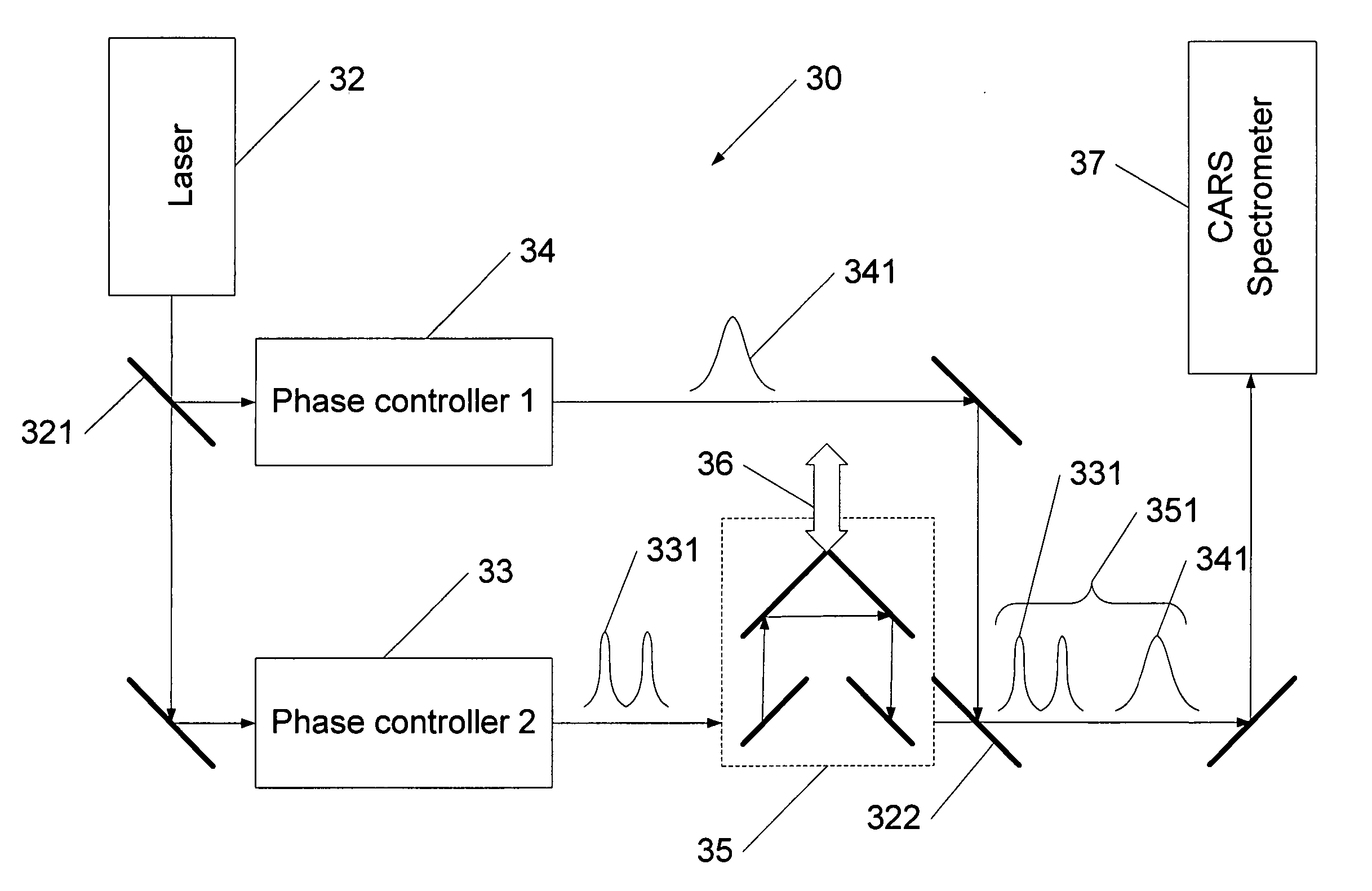
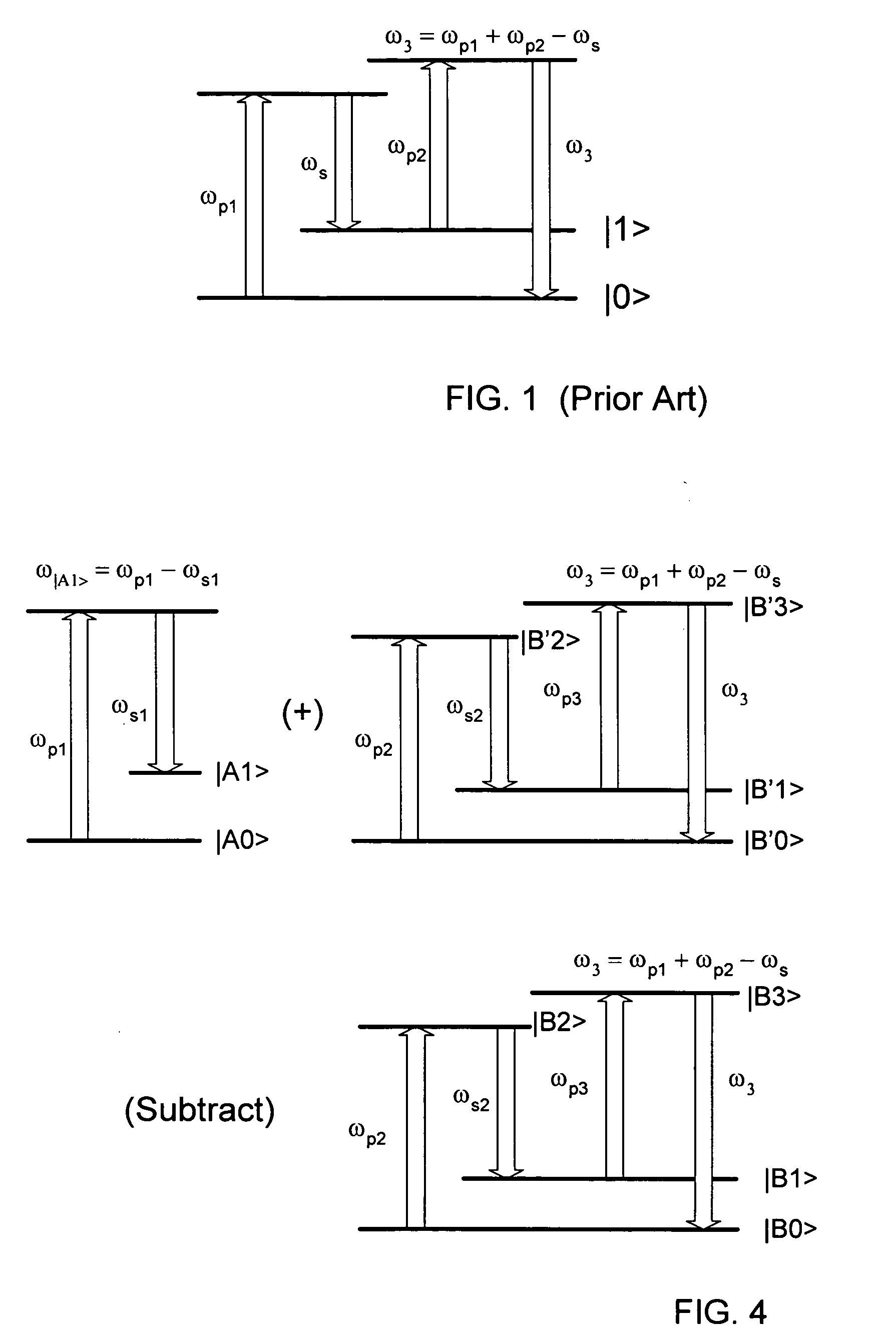
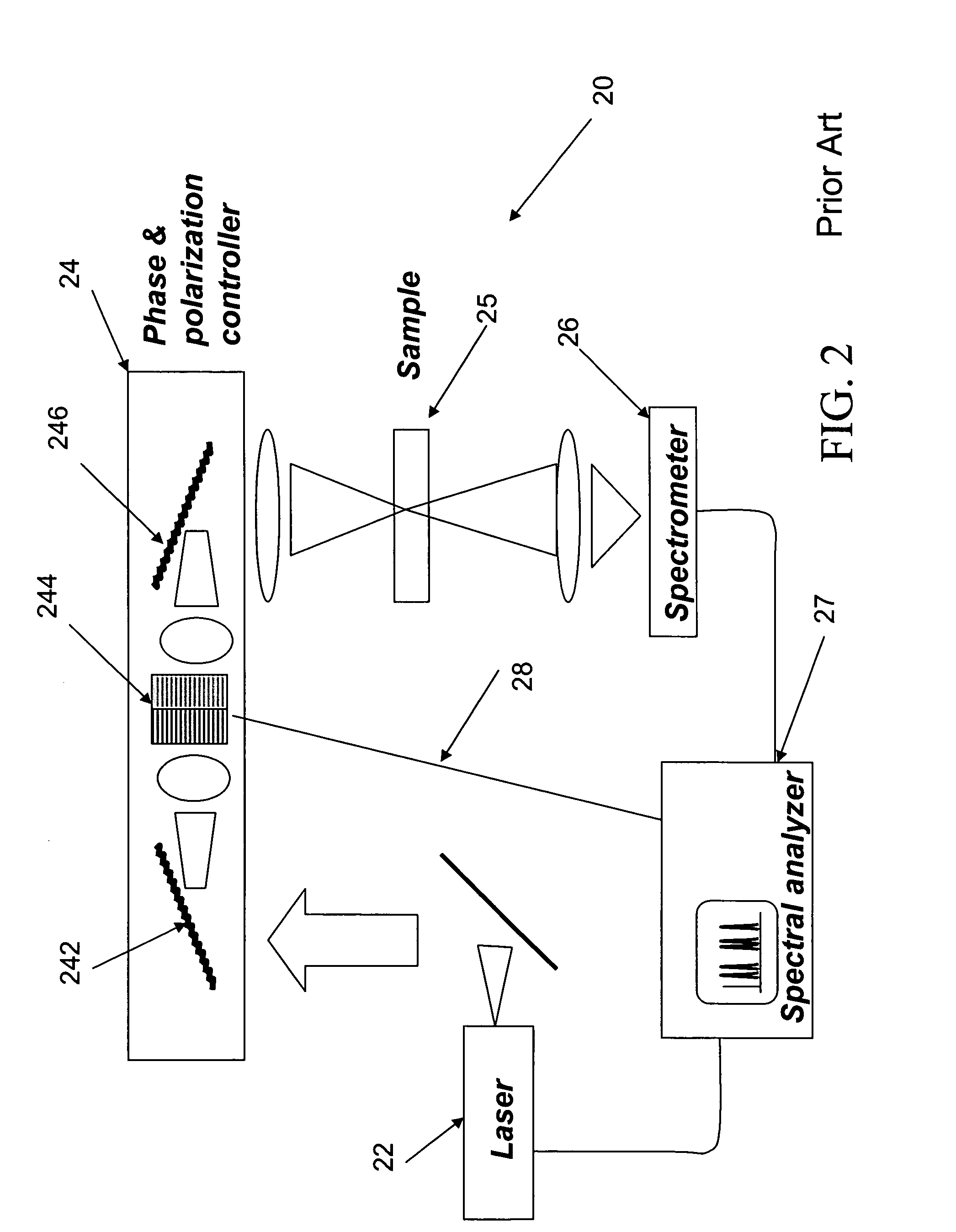
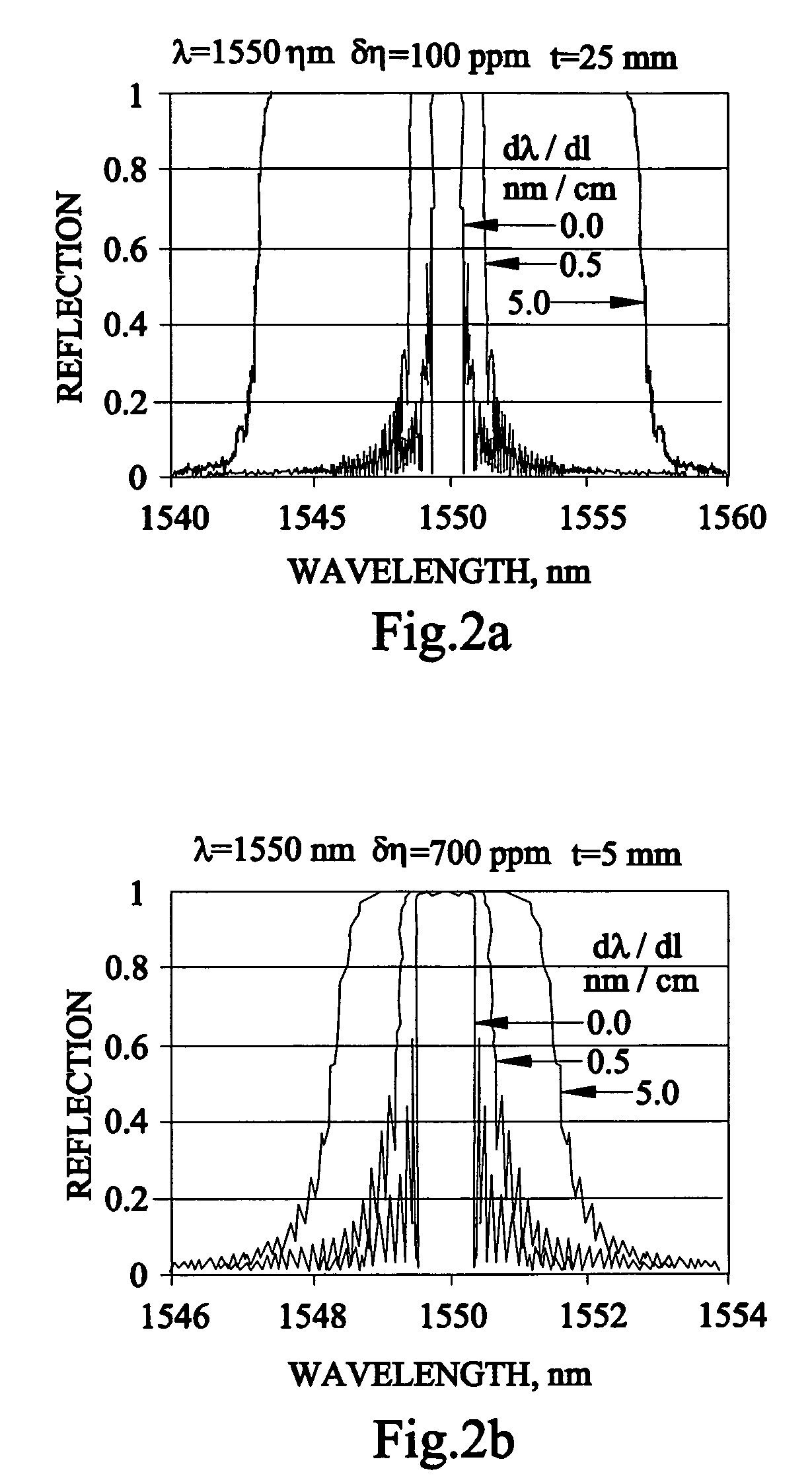
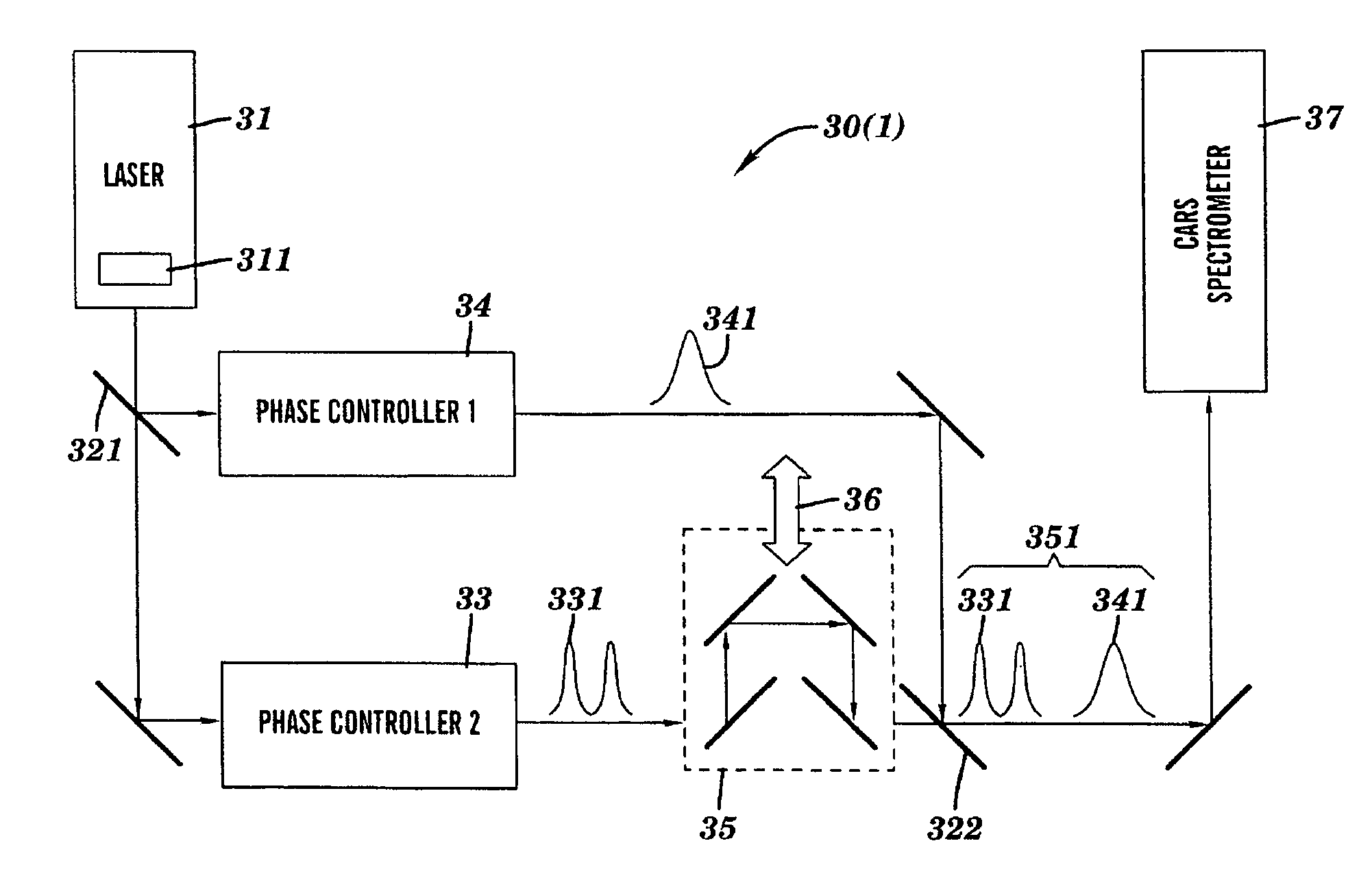
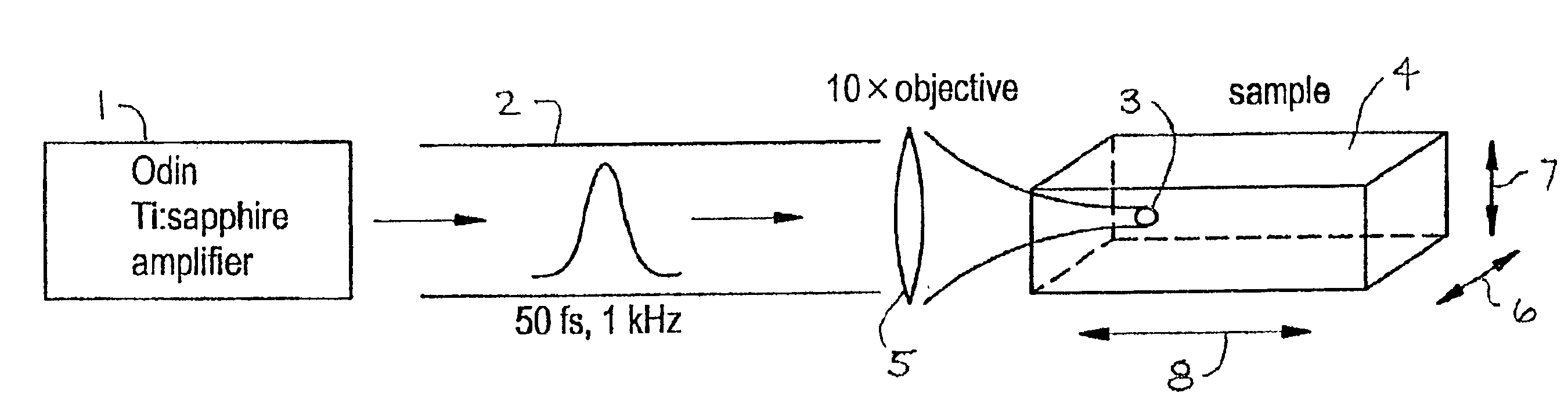
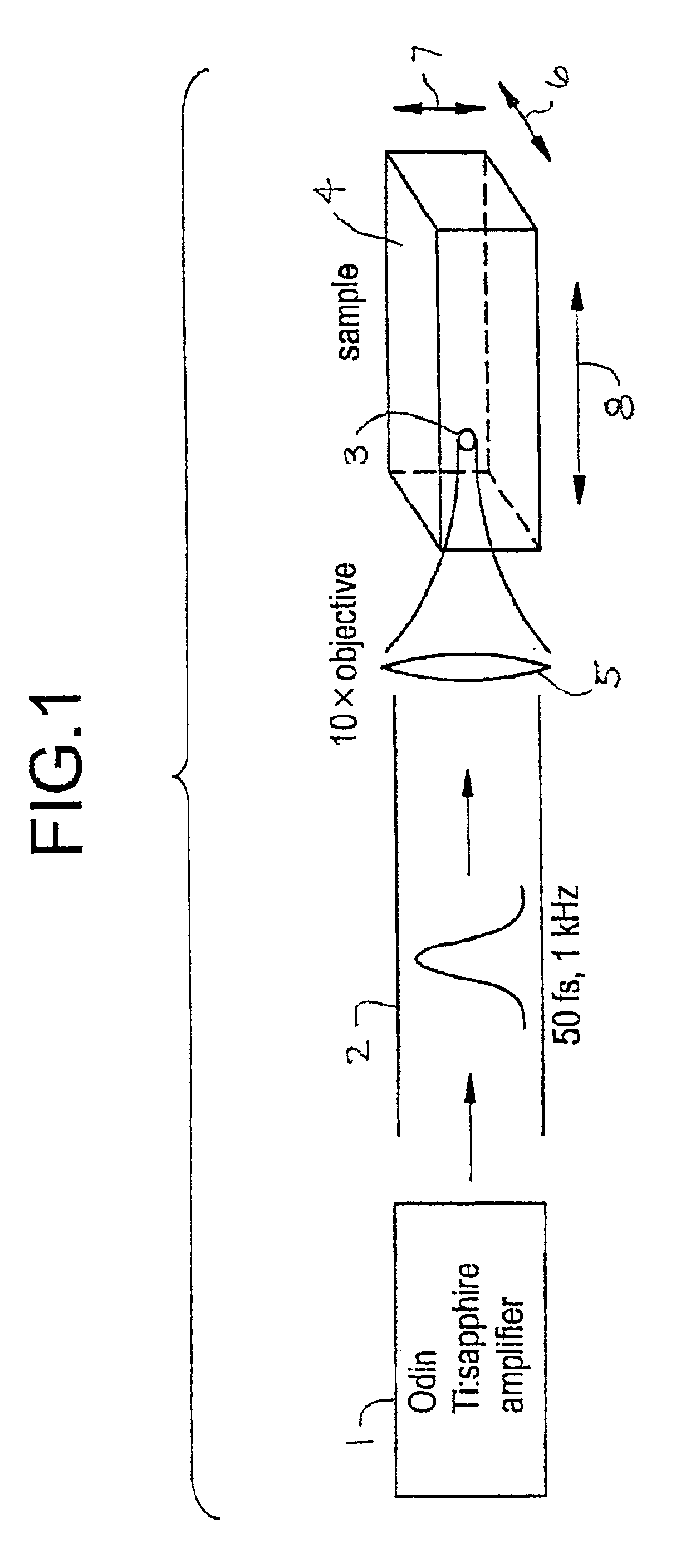
A CARS system and method for probing a Raman signature of a sample are described. A short femtosecond pulse from one or more lasers is split into two pulses, a stimulus pulse and a probe pulse, whereby the probe pulse is time-delayed with respect to the stimulus pulse. Both pulses can be phase- and polarization-modulated. The stimulus pulse excites a vibronic level in the sample and the probe pulse probes molecular Raman transitions in the sample. A difference in the signals with and without excitation can be used to determine on which molecule a bond is most likely located. This will allow an accurate and sensitive determination of the presence of specific molecules in the sample. The system and method can be used to analyze biological samples and to discriminate between molecules having overlapping Raman signatures.
Owner:CHROMAPLEX
Direct writing of optical devices in silica-based glass using femtosecond pulse lasers
InactiveUS20020076655A1Efficient rateHigh sensitivityPhotography auxillary processesRadiation applicationsLight guideRefractive index
The invention relates to methods of writing a light-guiding structure in a bulk glass substrate. The bulk glass substrate is preferably made from a soft silica-based material having an annealing point less than about 1380°K. A pulsed laser beam is focused within the substrate while the focus is translated relative to the substrate along a scan path at a scan speed effective to induce an increase in the refractive index of the material along the scan path. Substantially no laser-induced physical damage of the material is incurred along the scan path. Various optical devices can be made using this method.
Owner:CORNING INC
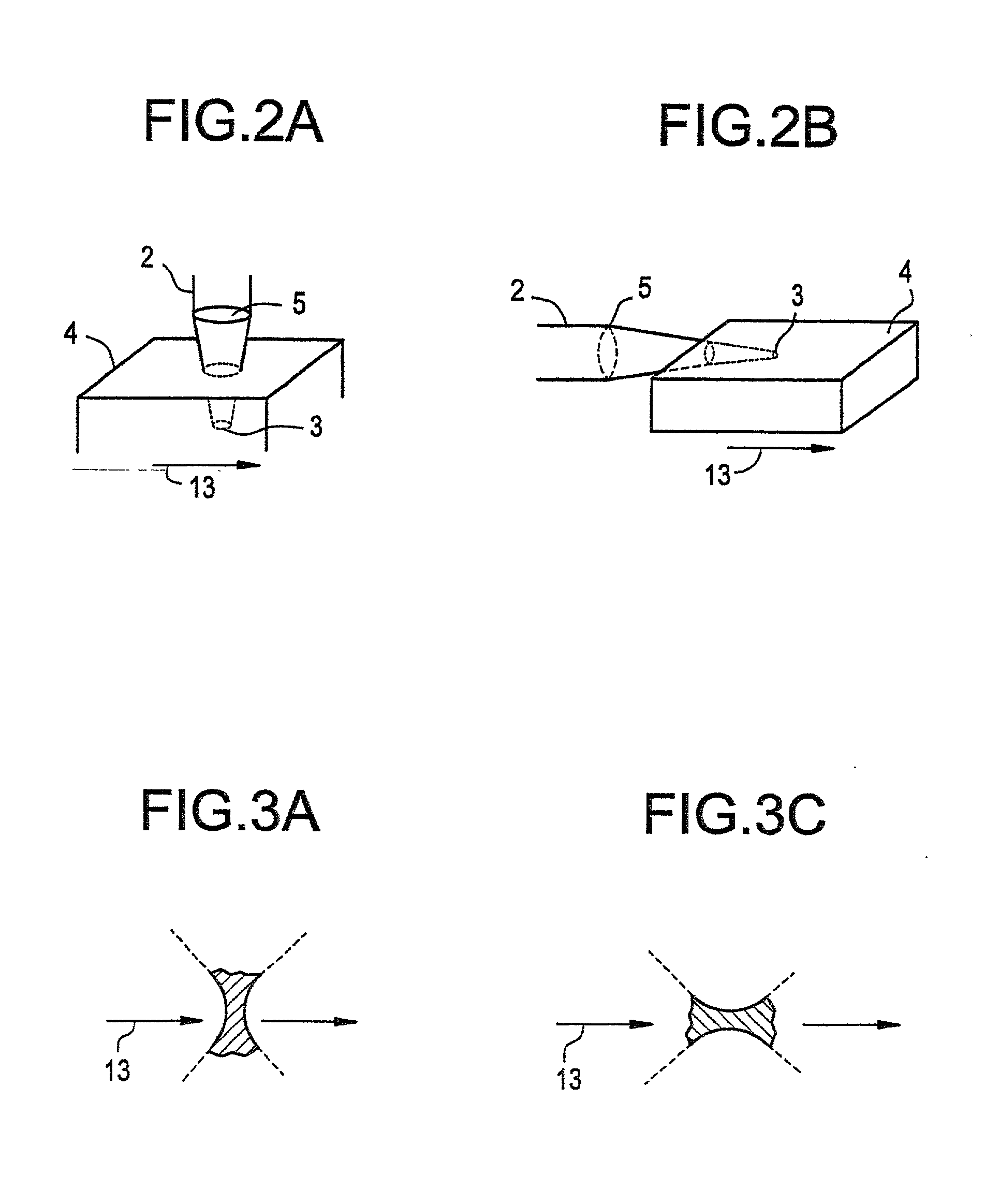
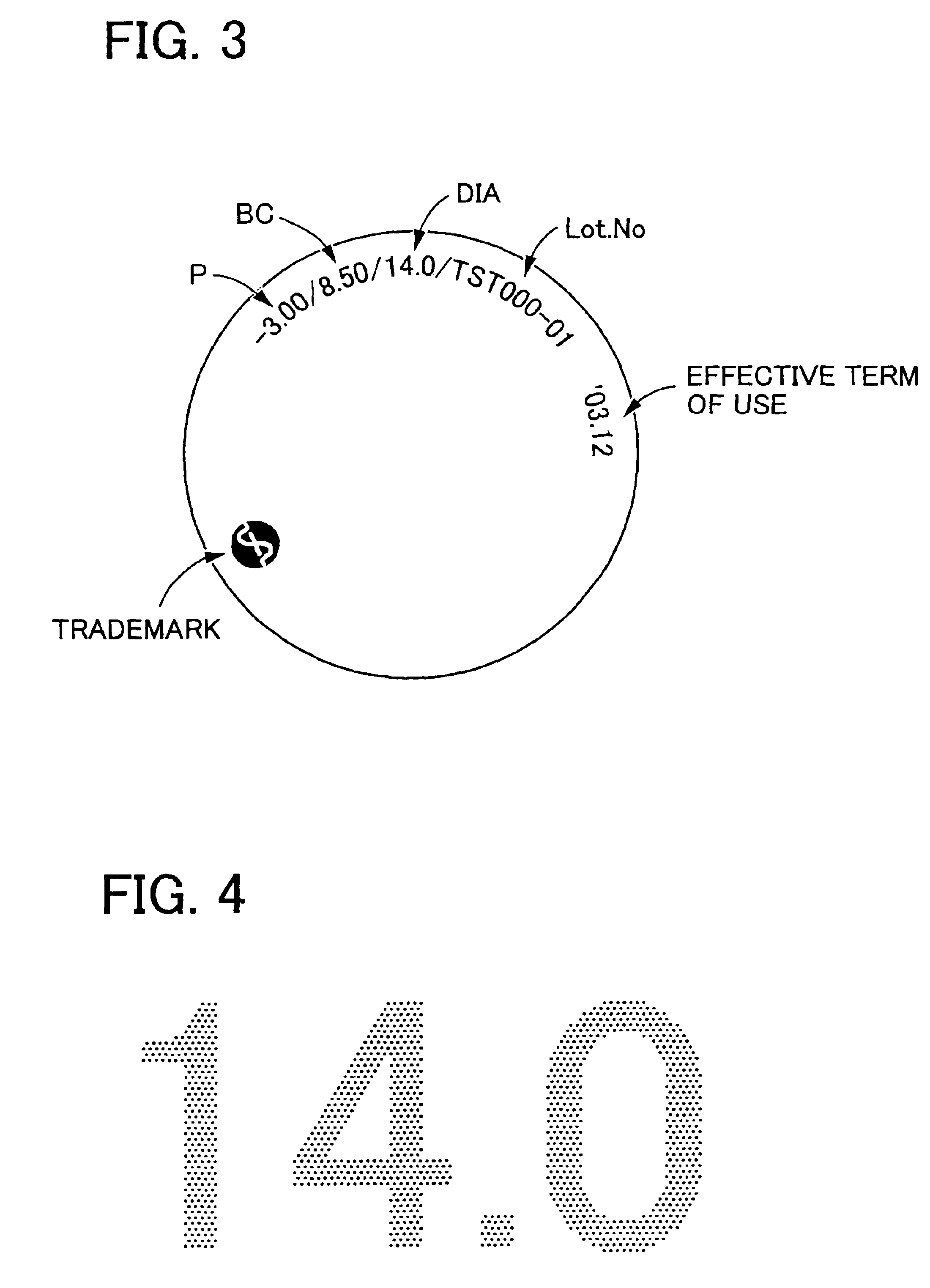
Method of marking ophhalmic lens by using laser radiation of femtosecond pulse width
InactiveUS6857744B2Easy to readEasy to recognizeDuplicating/marking methodsEye diagnosticsLens plateLaser
A method of marking an ophthalmic lens, including a step of irradiating the ophthalmic lens formed of a resin material with a laser radiation of a femtosecond pulse width, such that the laser radiation is condensed at each of at least one predetermined spot within the ophthalmic lens, to form a whitened portion at the each of the at least one predetermined spot, for thereby providing the ophthalmic lens with a marking.
Owner:MENICON CO LTD
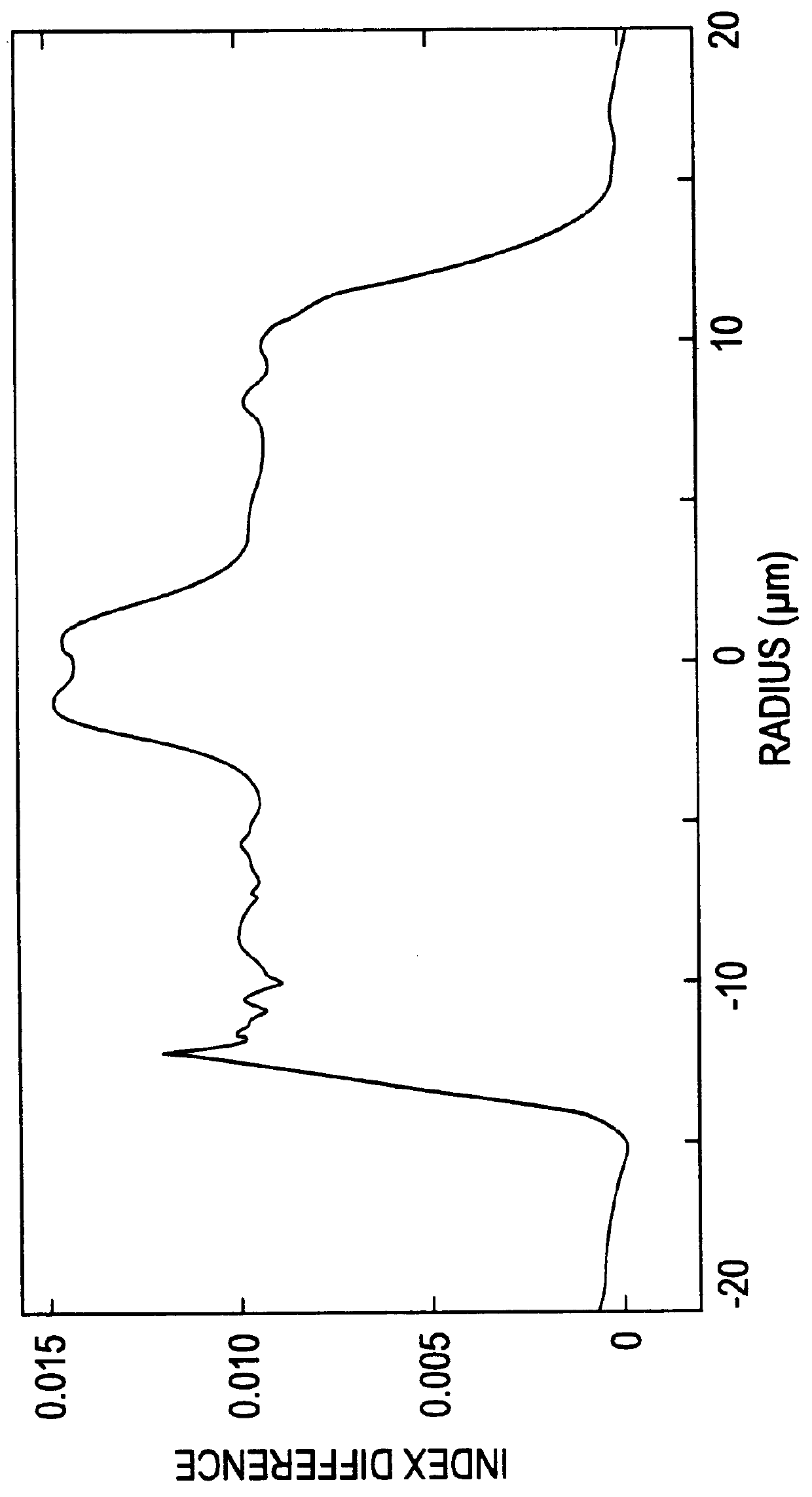
Manipulating the size of waveguides written into substrates using femtosecond laser pulses
InactiveUS20030099452A1Control over the refractive index profile of the waveguidesPhotomechanical apparatusCoupling light guidesFemto second laserLight beam
Waveguides produced in bulk glass using femtosecond pulsed lasers have diameters and refractive index profiles that are manipulated by additional motions or beams. For example, spot focuses of the femtosecond pulsed lasers trace overlapping or widened tracks by superimposing additional relative motions between the spot focuses and the bulk glass. Additional femtosecond pulsed beams can also be used to produced widened waveguides.
Owner:CORNING INC
Manufacture of silicon-based devices having disordered sulfur-doped surface layers
InactiveUS20080044943A1Increase carrier densityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface layerSulfur
The present invention provides methods of fabricating a radiation-absorbing semiconductor wafer by irradiating at least one surface location of a silicon substrate, e.g., an n-doped crystalline silicon, by a plurality of temporally short laser pulses, e.g., femtosecond pulses, while exposing that location to a substance, e.g., SF6, having an electron-donating constituent so as to generate a substantially disordered surface layer (i.e., a microstructured layer) that incorporates a concentration of that electron-donating constituent, e.g., sulfur. The substrate is also annealed at an elevated temperature and for a duration selected to enhance the charge carrier density in the surface layer. For example, the substrate can be annealed at a temperature in a range of about 700 K to about 900 K.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
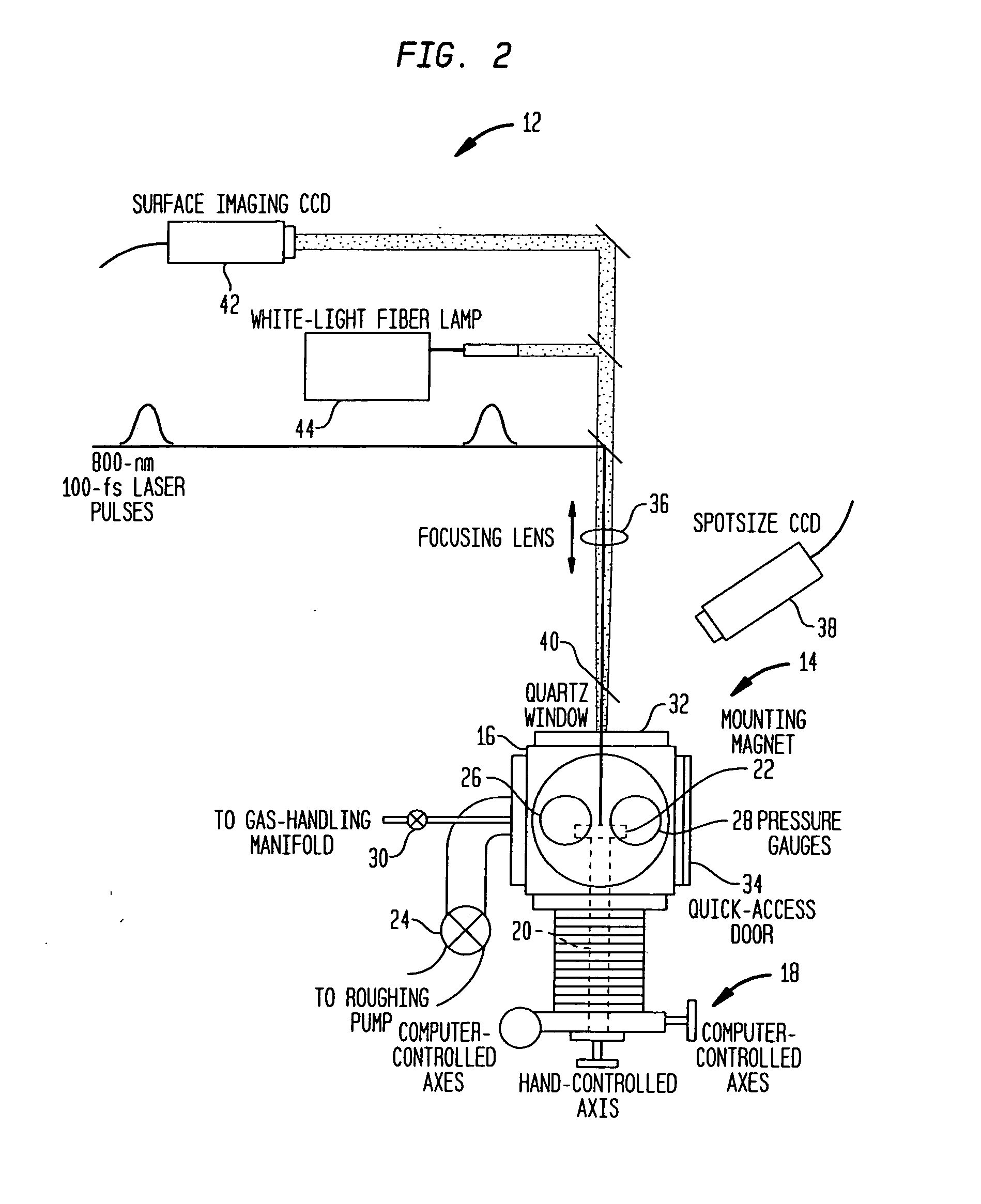
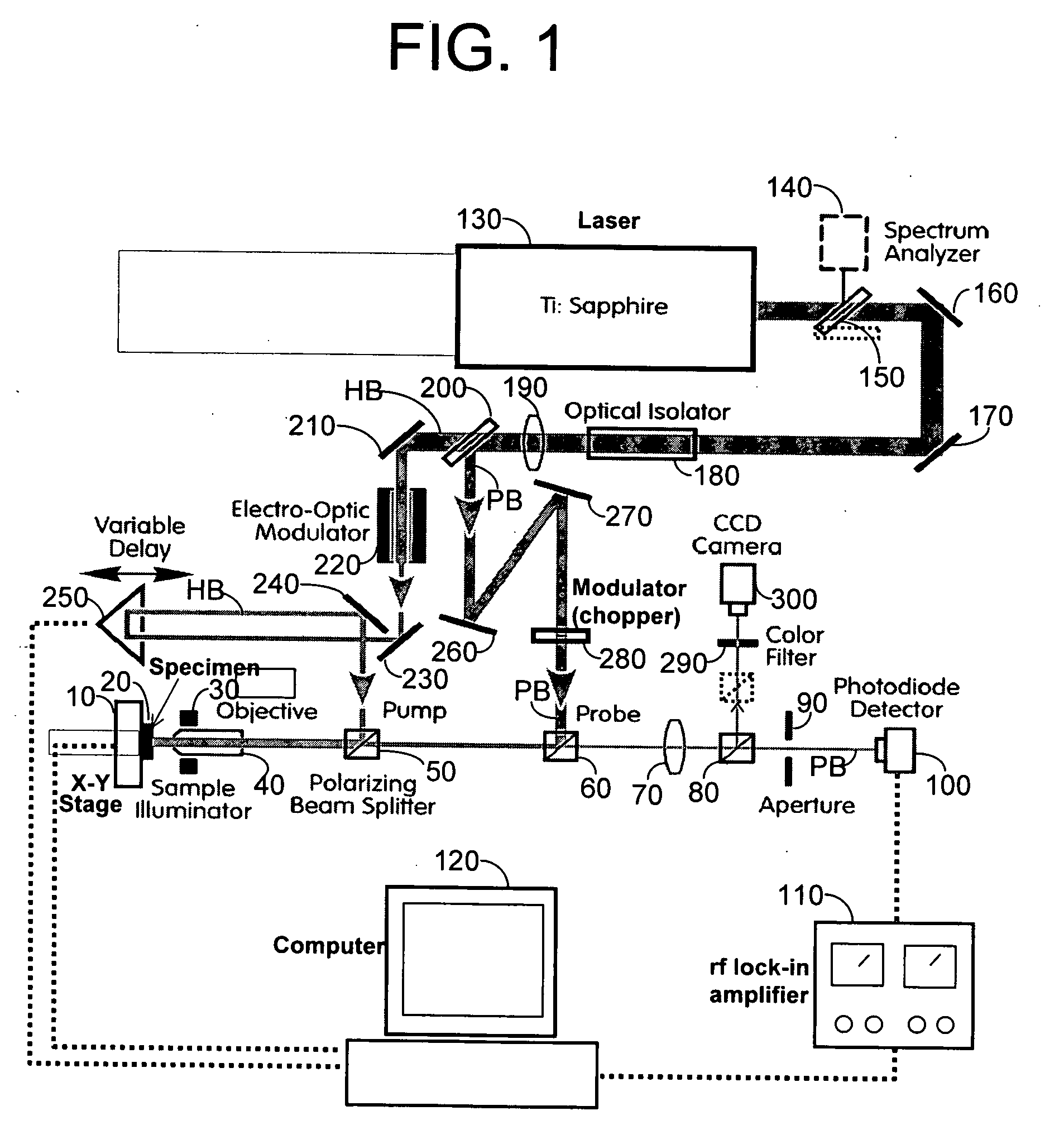
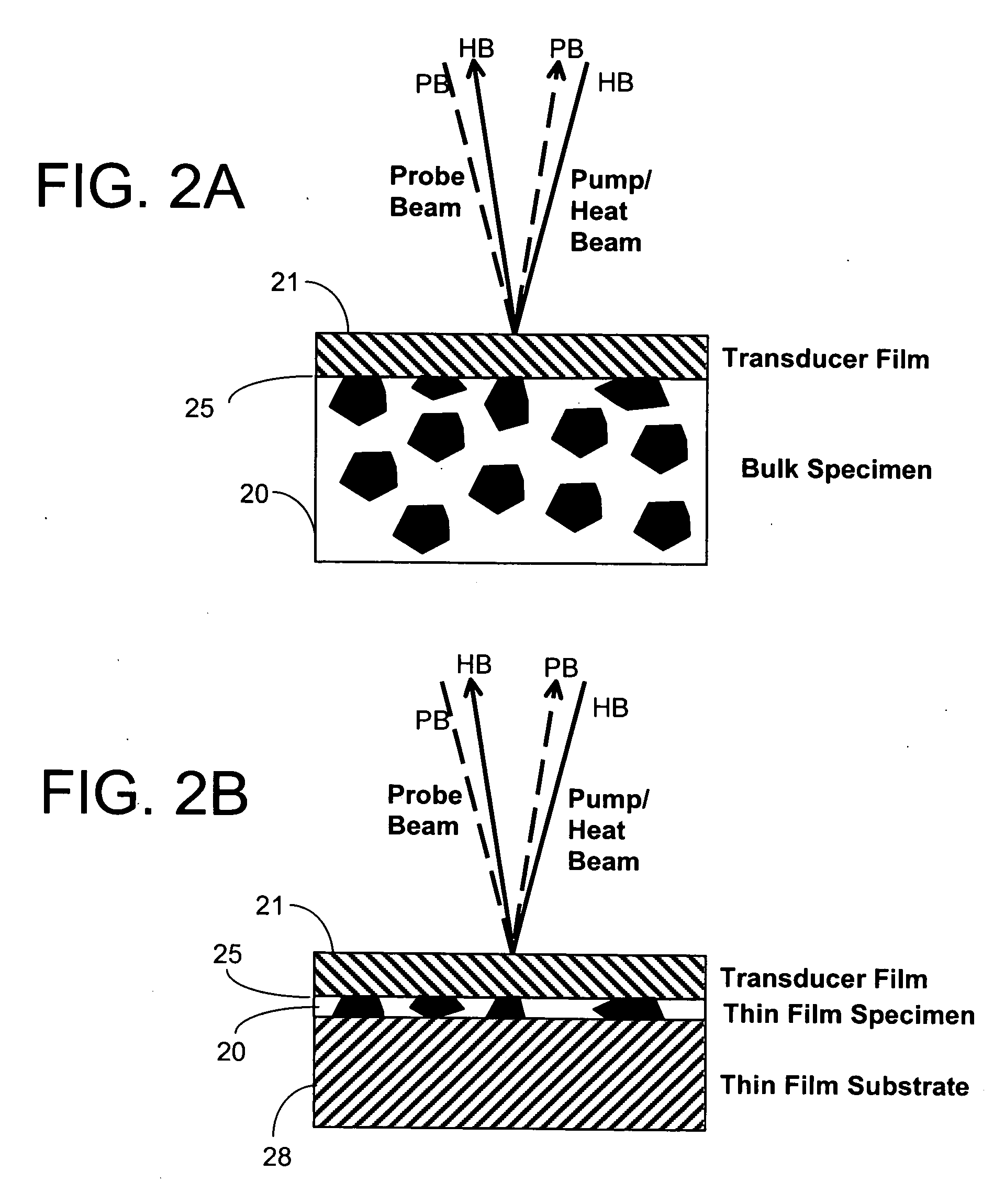
Apparatus and method for measuring thermal conductivity
InactiveUS20060222043A1Increase heightLow thermal conductivityThermometer detailsMaterial thermal conductivityFemtosecond pulsed laserPump probe
An apparatus and method for measuring and mapping thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity at micrometer scale resolution. The apparatus and method utilize a mode-locked femtosecond pulsed laser in a pump-probe configuration to analyze time-domain thermoreflectance of a specimen to evaluate its thermal conductivity in micro-scale, so that, if desired, an image of thermal conductivity distribution of micro-scale regions may be obtained therefrom. A multi-layer, complete three-dimensional model that takes into account the entire three-dimensional heat flow in cylindrical coordinates enables micro-scale measurements to be made at an accuracy of about 90% of well-accepted values.
Owner:CAHILL DAVID GERARD
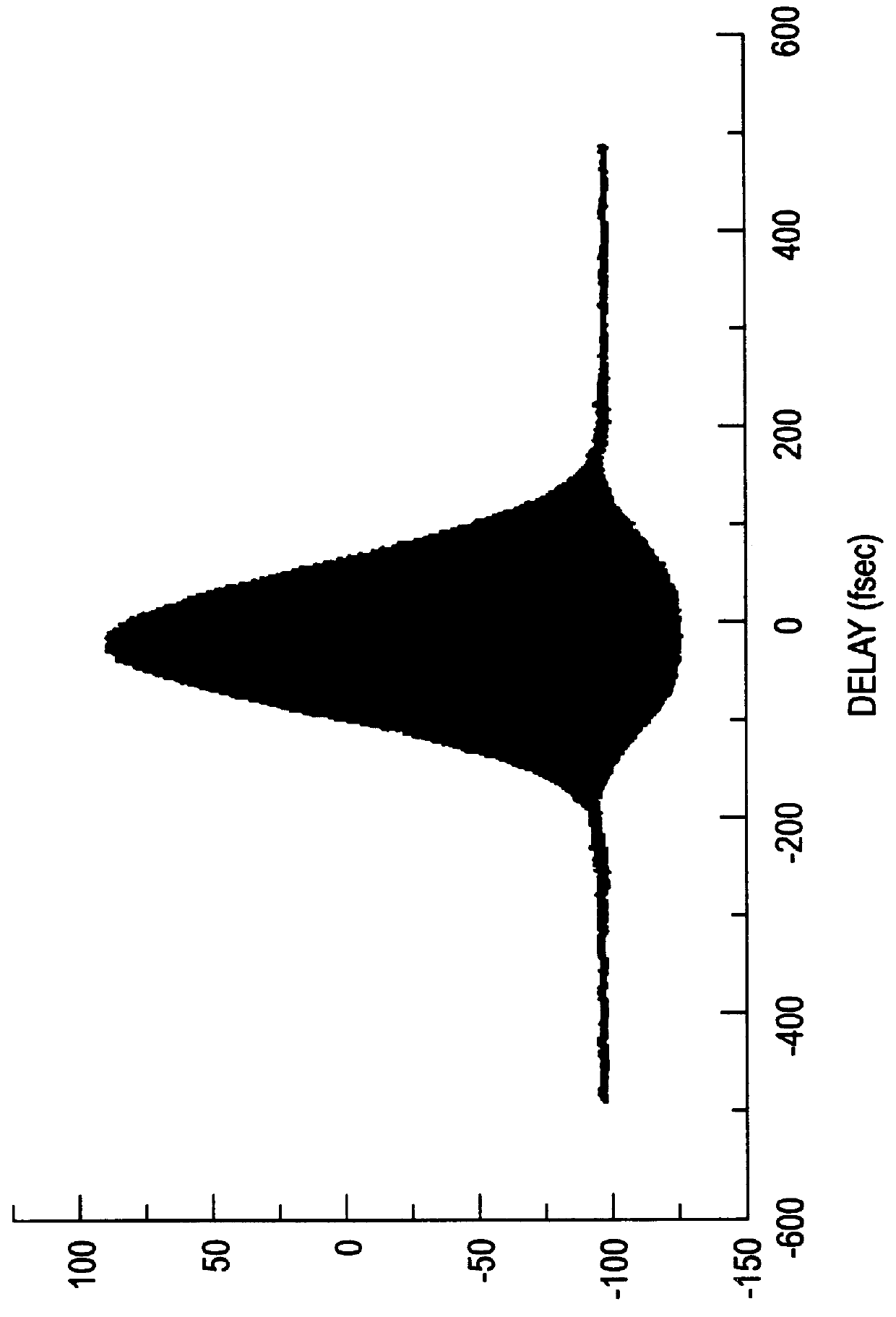
Fiber amplifier for generating femtosecond pulses in single mode fiber
ActiveUS6990270B2Efficient compressionLaser using scattering effectsCoupling light guidesAudio power amplifierHigh energy
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Nano-femtosecond dual-laser composite machining system
InactiveCN102059451AHigh precisionHigh nanosecond laser processing efficiencyLaser beam welding apparatusOptical elementsMicro nanoNuclear fusion
The invention relates to a nano-femtosecond dual-laser composite machining system. The system comprises a femtosecond laser, a nanosecond laser, a synchronous control circuit, an illuminating light source, a semi-transparent semi-reflecting mirror, a first dichroscope, a second dichroscope, a focusing lens and a charge coupled device (CCD) image detector, wherein the synchronous control circuit controls laser pulse output of the femtosecond laser and the nanosecond laser, and accurately adjusts relative time of nanosecond pulse and femtosecond pulse in the aspect of time to synchronize leading edges of the two pulses; the illuminating light source is positioned on one side of the semi-transparent semi-reflecting mirror, and the second dichroscope, the first dichroscope and the focusing lens are coaxially arranged on the other side of the semi-transparent semi-reflecting mirror in turn and are positioned on a straight line together with the illuminating light source; and the CCD image detector is positioned at the tail end of a reflecting light path of the semi-transparent semi-reflecting mirror. Through the system, the advantages of high femtosecond laser machining accuracy and high nanosecond laser machining efficiency are simultaneously integrated, and high-accuracy and high-efficiency micro-nano machining is realized; and the system can be widely applied to the fields such as high-accuracy machining of aviation and aerospace key parts, microstructure machining of a laser fusion ignition target, microstructure machining of a microsensor and the like.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
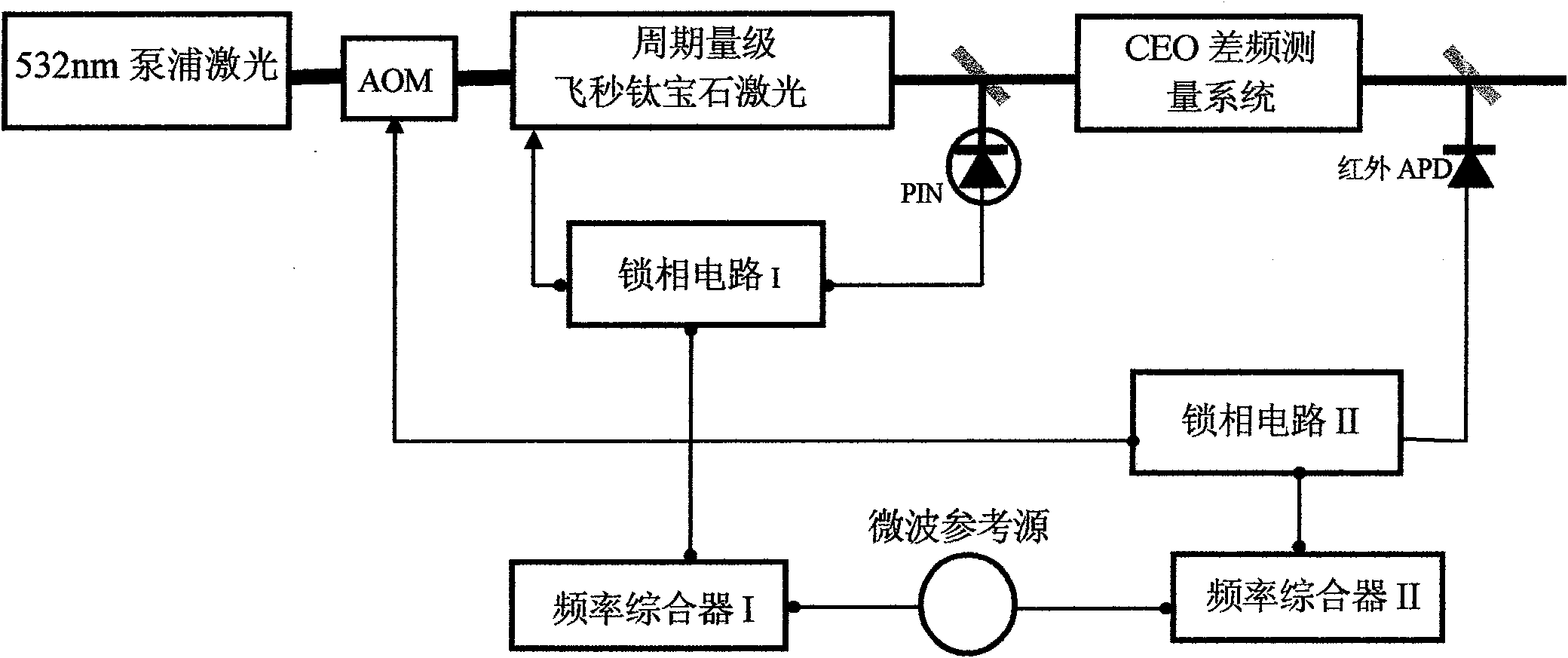
Single optical frequency comb with high stability and high repetition frequency
InactiveCN101846861AImprove stabilityLong lock timeActive medium materialNon-linear opticsPhase noiseFrequency measurements
The invention discloses manufacturing method and equipment of a single optical frequency comb with high stability and high repetition frequency. The method comprises the following specific steps of: outputting femtosecond pulses with high repetition frequency, wide spectrum and pulse width less than 7 fs by using a cycle-grade femtosecond titanium sapphire oscillator; carrying out beat measurement of the CEO of the femtosecond pulses by using a single nonlinear crystal; and simultaneously locking repetition frequency and CEO frequency to a stable external microwave reference source by using a circuit feedback technology. The equipment comprises the cycle-grade femtosecond titanium sapphire oscillator, the single nonlinear crystal beat measurement fceo device and a feedback circuit device controlled on the basis of the phase lock principle. The invention has the characteristics of compact equipment structure, long locking time, high usable output power, small phase noise and the like, and is mainly applied to the scientific researches of absolute optical frequency measurement, optical clock composition, atto-second production and the like.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
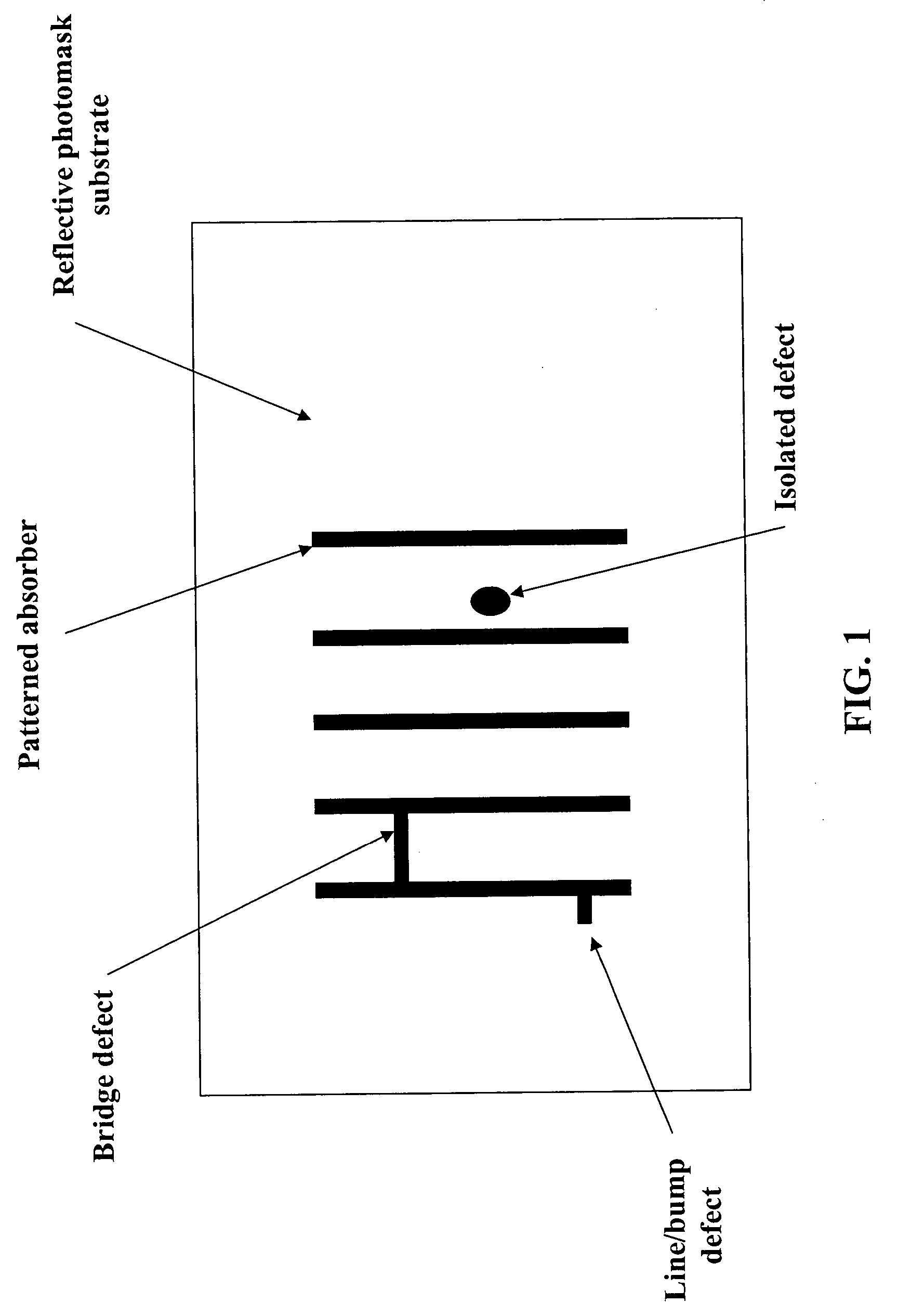
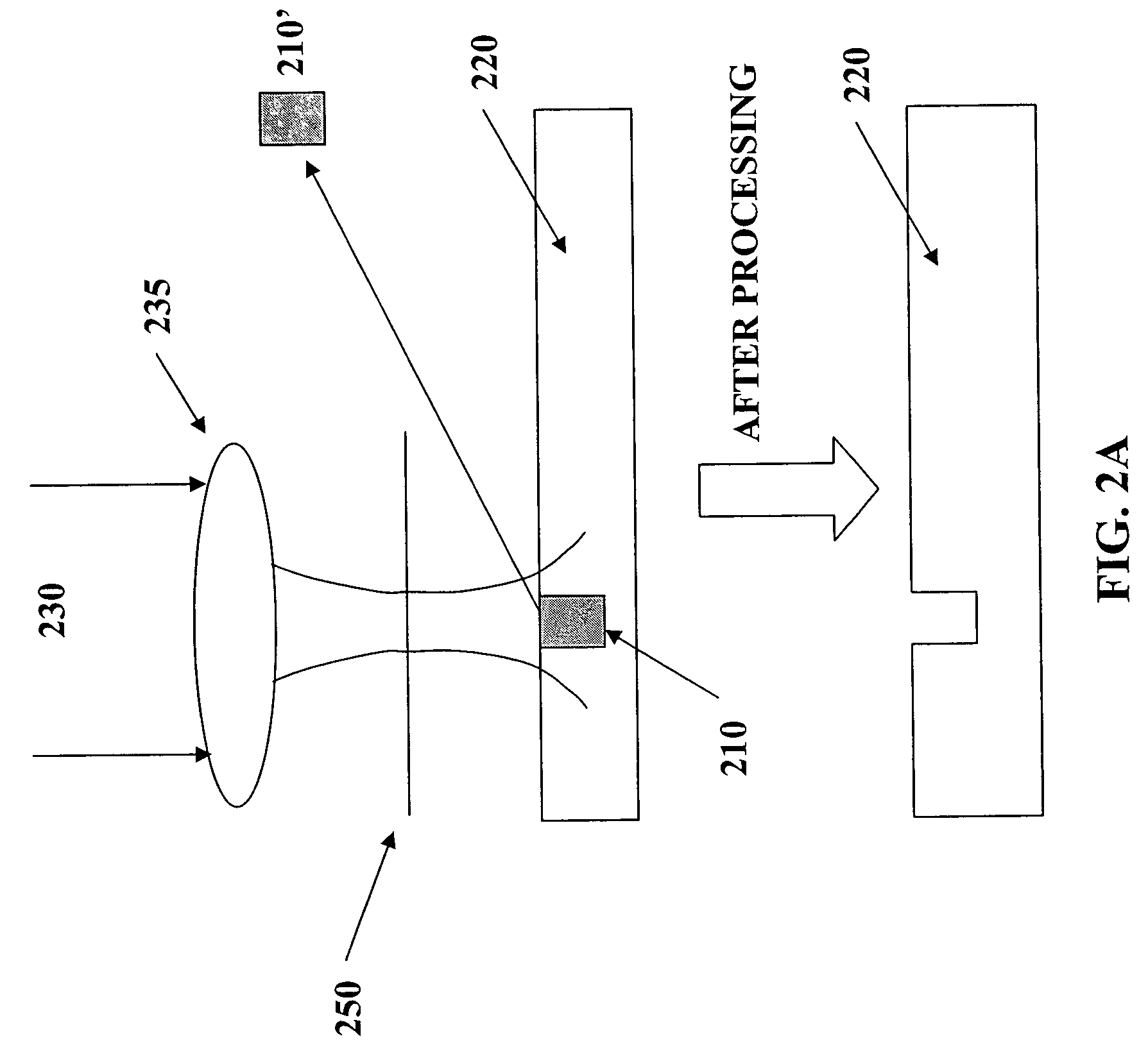
Method and apparatus for repair of reflective photomasks
A method of selectively ablating an undesired material from a substrate includes providing a substrate with two regions; providing laser pulses; tuning a wavelength of the laser pulses to match a desired wavelength characteristic of a material and directing the tuned laser pulses onto the substrate; and controlling a pulse duration, wavelength, or both, of the laser pulses to ablate the undesired material without damaging the substrate or any adjacent material. In another embodiment, an apparatus for repairing a defect on a reflective photomask includes a femtosecond pulse width laser; a harmonic conversion cell; a filter for passing a selected EUV harmonic of the laser light; a lens arrangement configured to direct the selected EUV harmonic of the laser light onto the photomask; and a control unit connected to the laser to control an ablation of the defect on the reflective photomask.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Tattoo Removal and Other Dermatological Treatments using Multi-Photon Processing
ActiveUS20090149843A1Reduce the amount requiredDiagnosticsCavity massageElectromagnetic pulseFocal volume
A system and method for providing multi-photon processing treatment to a patient. A localized, multi-photon processing event is initiated within a vicinity of an unwanted pigment in order to remove the pigment. The multi-photon processing event requires a relatively low energy, but very intense, pulse of light. The low amount of energy per pulse allows ablation of the material to be highly localized, with negligible thermal damage to surrounding material. The multi-photon event may be initiated by focusing a suitable electromagnetic pulse, such as a 2 mJ laser pulse having a 100 to 300 femtoseconds pulse duration, into a focal volume small enough that the intensity exceeds 1011 Watts / cm2. A suitably configured Ti:Sapphire solid state laser may provide such pulses at 1-10 kHz. By repeating the multi-photon processing event along the location of a tattoo, the tattoo may be removed with no damage to the surrounding tissue.
Owner:SMITS ALEXANDER +1
Light frequency reference fiber femtosecond light frequency comb with tunable broadband repetition frequency
InactiveCN105826804AConstant working temperatureContinuously adjustable repetition rateActive medium shape and constructionFemto second laserErbium doping
The invention relates to a light frequency reference fiber femtosecond light frequency comb with tunable broadband repetition frequency. The comb comprises a hybrid-locking-based erbium-doped fiber femtosecond laser device with tunable broadband repetition frequency, a reference laser locking system based on piezoelectric ceramic, a reference laser locking system based on a pumping current, a computer control system and a temperature control system, wherein the erbium-doped fiber femtosecond laser device is an annular chamber structure and is internally added with an electric control optical delay wire, and the repetition frequency of the laser device can realize continuous tunable broadband. For realizing light frequency reference femtosecond pulse output, rapid and slow piezoelectric ceramics and the pumping current are employed to cooperatively control beat frequency of the femtosecond laser device and two reference laser devices, the rapid piezoelectric ceramics fixing structure which is easy to use is designed, and a temperature control box is further designed to acquire stable beat frequency; the light frequency reference fiber femtosecond light frequency comb has advantages of light frequency reference output, tunable broadband repetition frequency, good stability and small size and further has application potential in the industrial environment.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for improving machining efficiency of micro-channel preparation through femtosecond laser
InactiveCN102601529AImprove processing efficiencyImprove production efficiencyLaser beam welding apparatusFemtosecond pulsed laserPolarizer
The invention relates to a method for improving the machining efficiency of micro-channel preparation through femtosecond laser, which belongs to the technical field of femtosecond laser application. The method includes the steps: firstly, generating the femtosecond pulse laser by the aid of a femtosecond laser system, adjusting energy by means of combination of a half wave plate and a polarizing film and modulating the femtosecond laser into femtosecond interval pulse sequence by the aid of a pulse shaper; secondly, reflecting the pulse sequence laser obtained in the first step to an objective lens for focusing through a reflector, realizing imaging by the aid of a CCD (charge coupled device) and a lighting source, moving a six-dimensional precision electric control platform and positioning a laser focus on the lower surface of a sample horizontally placed on the six-dimensional precision electric control platform; and thirdly, controlling the six-dimensional precision electric control platform to move along a laser propagation direction by the aid of a computer to machine a micro-channel on the sample. As the femtosecond laser is modulated into the femtosecond interval pulse sequence by the aid of the pulse shaper, the micro-channel preparation efficiency is improved. Moreover, introduction of a vibration source is omitted, so that controllability of precision machining cannot be reduced.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering spectrum detection and microimaging system and method
InactiveCN106226284ARapid Simultaneous ImagingSimple structureRaman scatteringMicro imagingBandpass filtering
The invention relates to the field of optics, and provides a coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering spectrum detection and microimaging system which comprises a femtosecond pulse laser device, a beam divider, a pohotonic crystal fiber, a narrow bandpass filter, a delay unit, a beam combiner and a detector, wherein the beam divider is used for dividing femtosecond pulse laser into a first light beam and a second light beam; the pohotonic crystal fiber is used for pumping the first light beam to output super-continuum spectrum laser of which the pulse width is picosecond grade as Stokes light; the narrow bandpass filter is used for filtering the second light beam to increase the pulse width to be approximate to that of the super-continuum spectrum laser as pumping light and detection light; the delay unit is used for synchronizing the stokes light, the pumping light and the detection light; the beam combiner is used for combining the Stokes light, the pumping light and the detection light into a third light beam; the detector is used for detecting a correlated anti-Stokes Raman scattered spectrum. By adopting the coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering spectrum detection and microimaging system, simultaneous imaging of multiple chemical bands can be rapidly achieved, a super-continuum spectrum light source is lowly required, a complete CARS (Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering) spectrum can be obtained, the light beam utilization efficiency can be maximized, and the spectral resolution of CARS imaging can be improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Fiber amplifier for generating femtosecond pulses in single mode fiber
ActiveUS20050175280A1Efficient compressionLaser using scattering effectsCoupling light guidesAudio power amplifierHigh energy
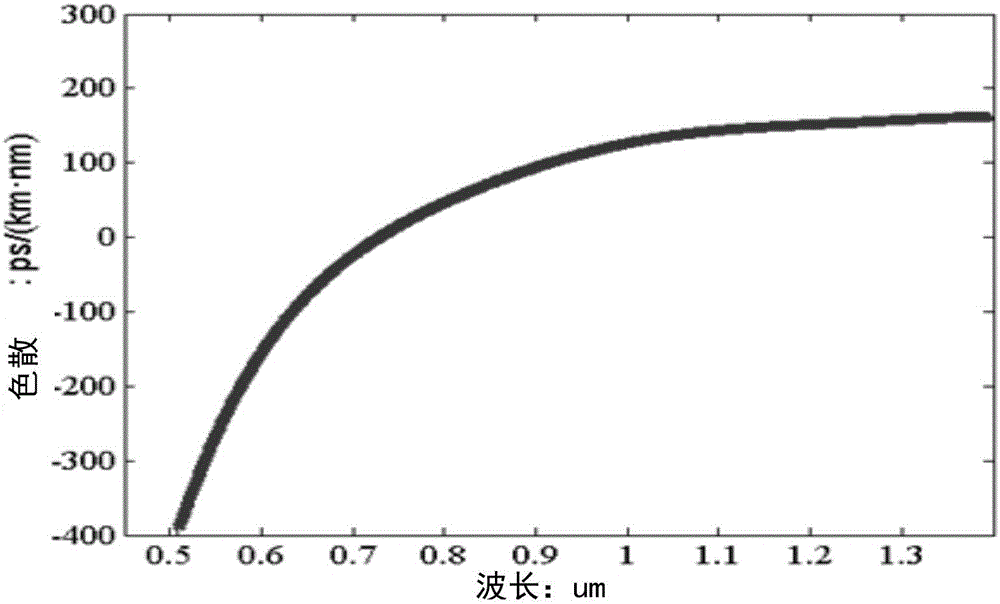
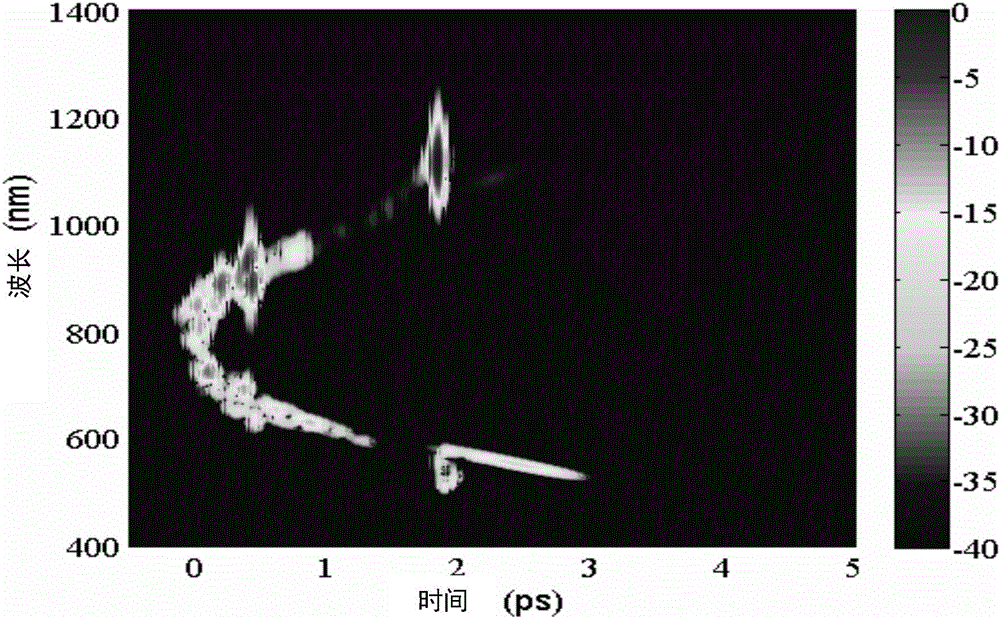
A source of high-power femtosecond optical pulses comprises a combination of a relatively short rare-earth doped fiber amplifier (e.g., less than five meters) with a first section of single mode fiber (or other dispersive element) disposed at the input of the amplifier to “pre-chirp” the output from a femtosecond pulse source, and a second section of single mode fiber fused to the output of the fiber amplifier to provide compression to the amplified pulses generated by the fiber amplifier. The rare-earth doped fiber amplifier is formed to comprise a normal dispersion, which when combined with self-phase modulation and distributed gain leads to a regime in amplifiers defined as “self-similar propagation”. In this regime of operation, the fiber amplifier generates high energy pulses with a parabolic shape (the parabolic shape defined as a function of time). These pulses also exhibit a strong linear chirp, where the linear nature of the chirp leads to efficient compression of the pulses.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Fiber assembly for all-fiber delivery of high energy femtosecond pulses
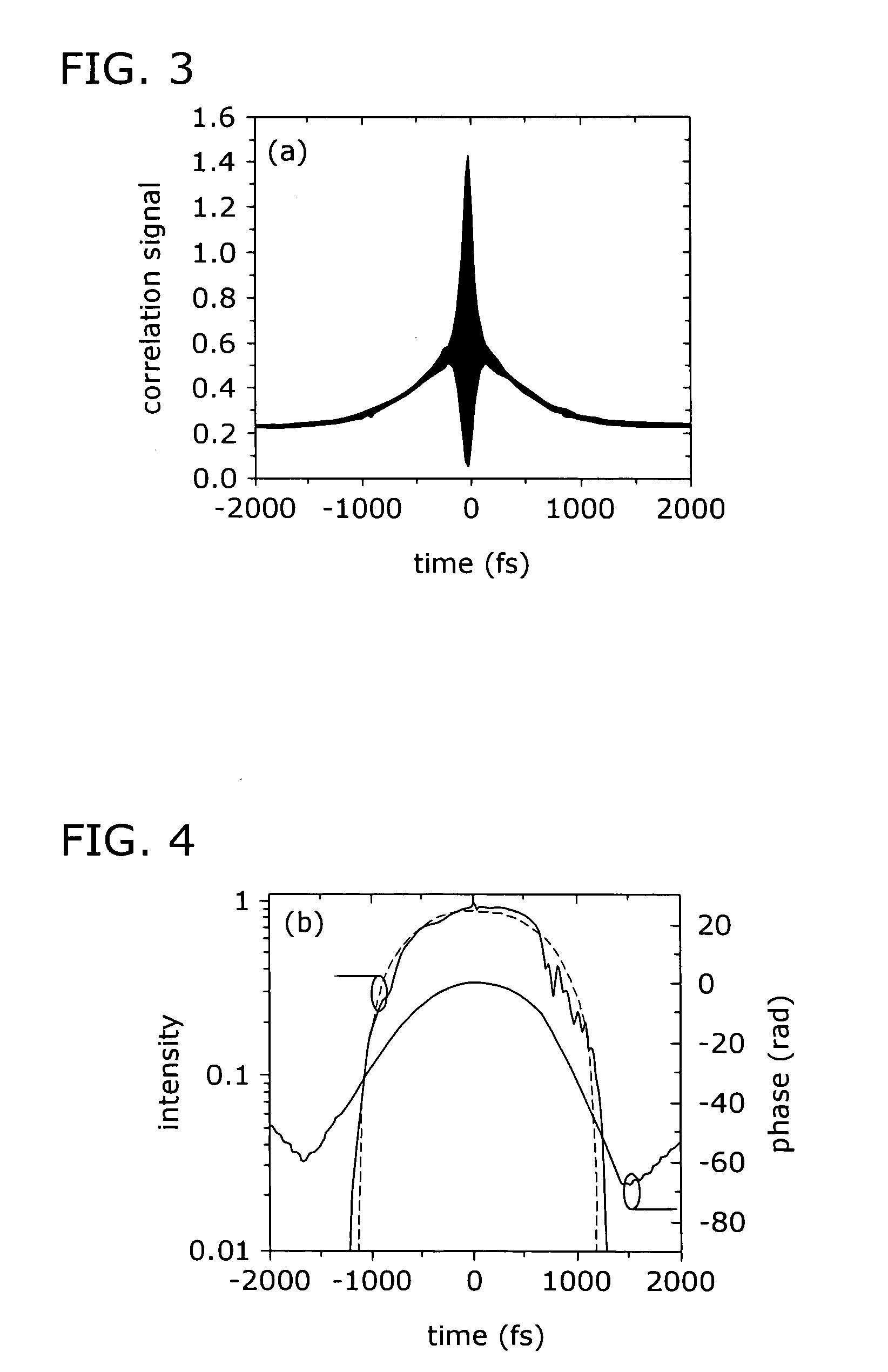
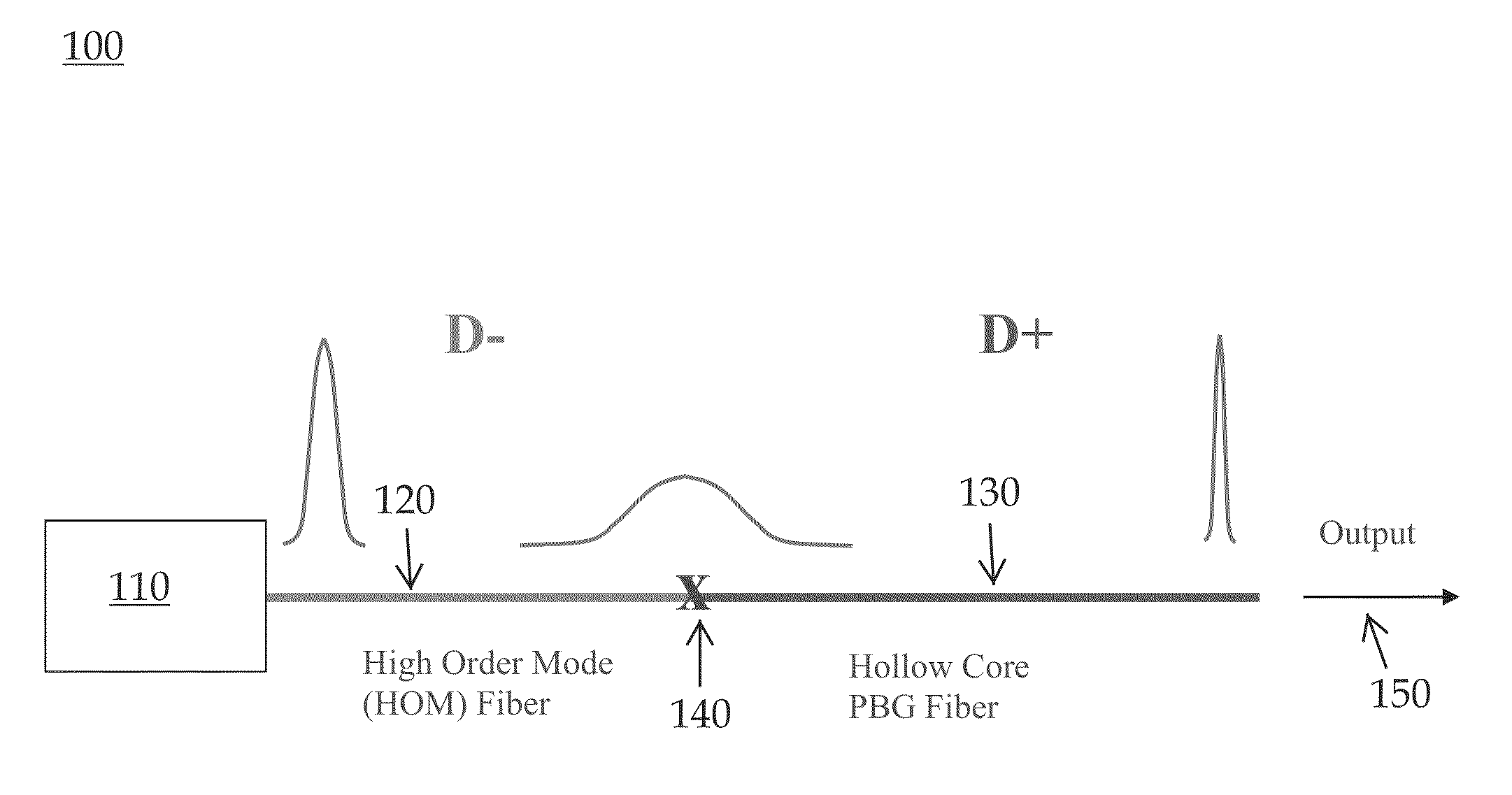
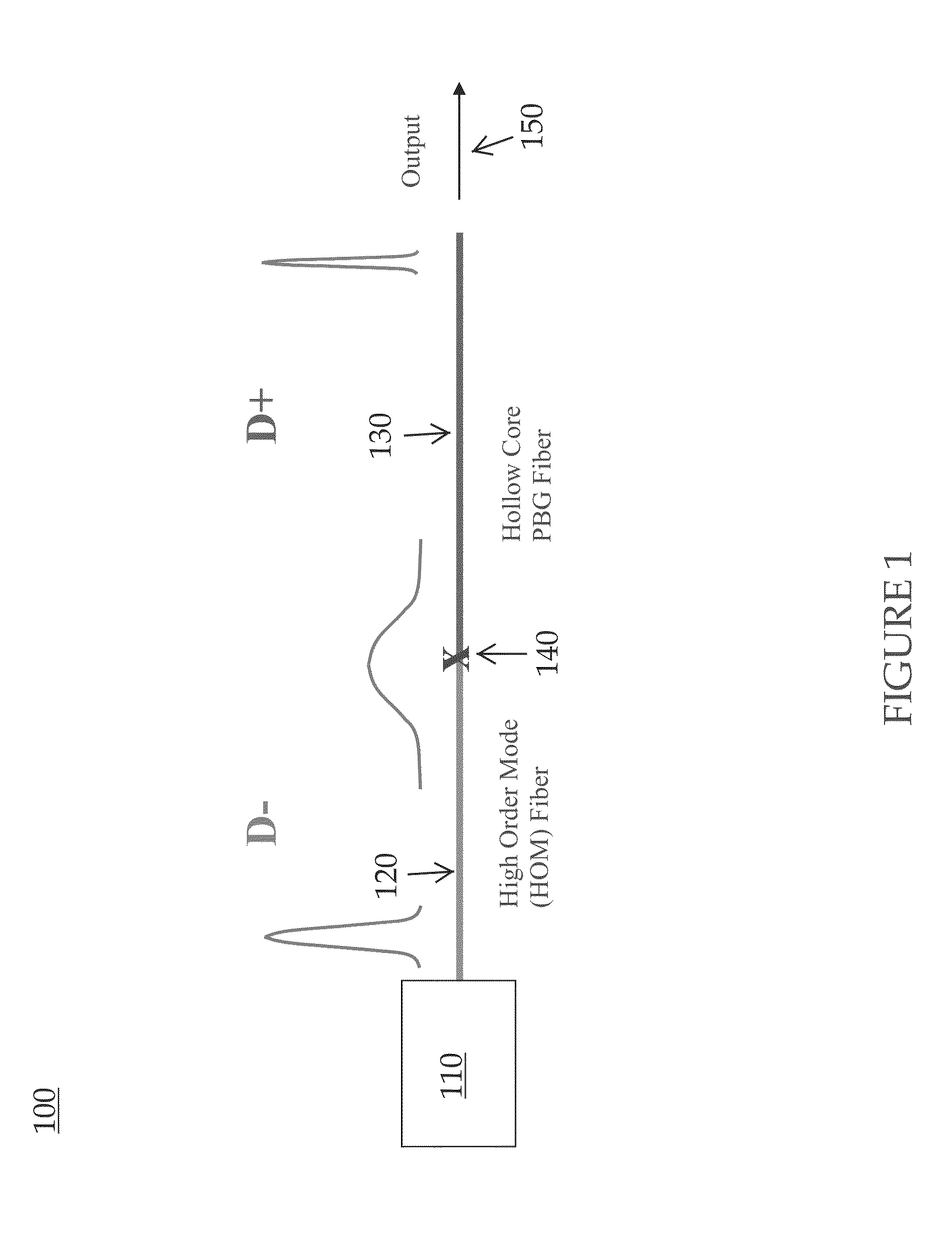
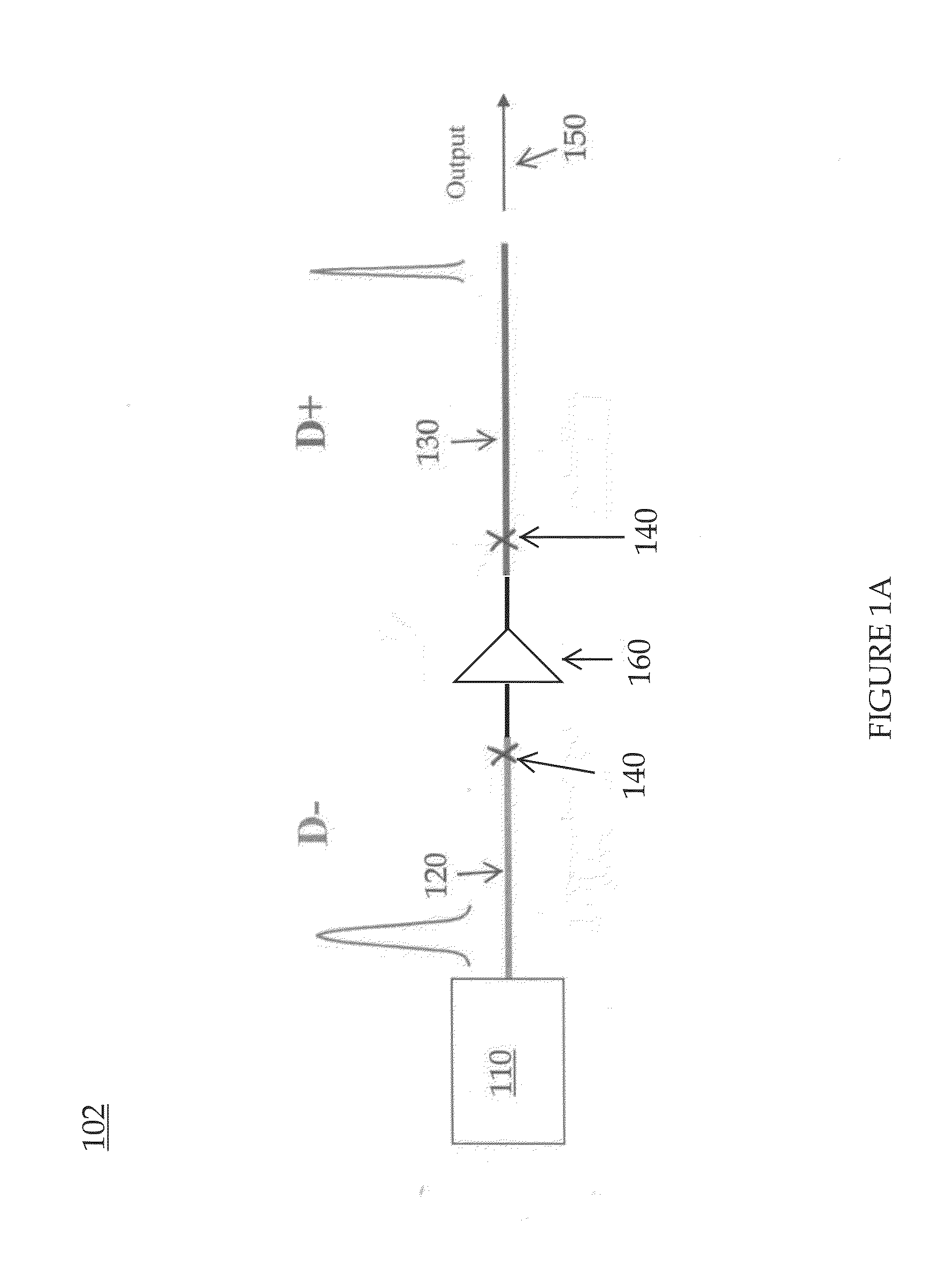
InactiveUS20130038923A1Improving dispersion managementLaser detailsFibre transmissionPhotonic bandgapHigh energy
Embodiments of the present invention are generally related to a fiber assembly, for example, in a chirped pulse amplification system, for all-fiber delivery of high energy femtosecond pulses. More specifically, embodiments of the present invention relate to a system and method for improving dispersion management when using hollow core photonic bandgap fibers for pulse compression. In one embodiment of the present invention, a fiber assembly comprises: an optical laser oscillator; a first fiber section for stretching the pulses from the laser oscillator, the first fiber section comprising a high order mode fiber; and a second fiber section for compressing the stretched pulses, connected to the first fiber section via a splice, the second fiber section comprising a hollow core photonic bandgap fiber; wherein the fiber assembly outputs a pulse compression at less than 200 fs.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
All-Normal-Dispersion Femtosecond Fiber Laser
ActiveUS20100220751A1Easy to adjustLaser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionMode locked fiber laserOptoelectronics
A modelocked fiber laser is designed to have strong pulse-shaping based on spectral filtering of a highly-chirped pulse in the laser cavity. The laser generates femtosecond pulses without a dispersive delay line or anomalous dispersion in the cavity.
Owner:CORNELL CENT FOR TECH ENTERPRISE & COMMLIZATION CCTEC
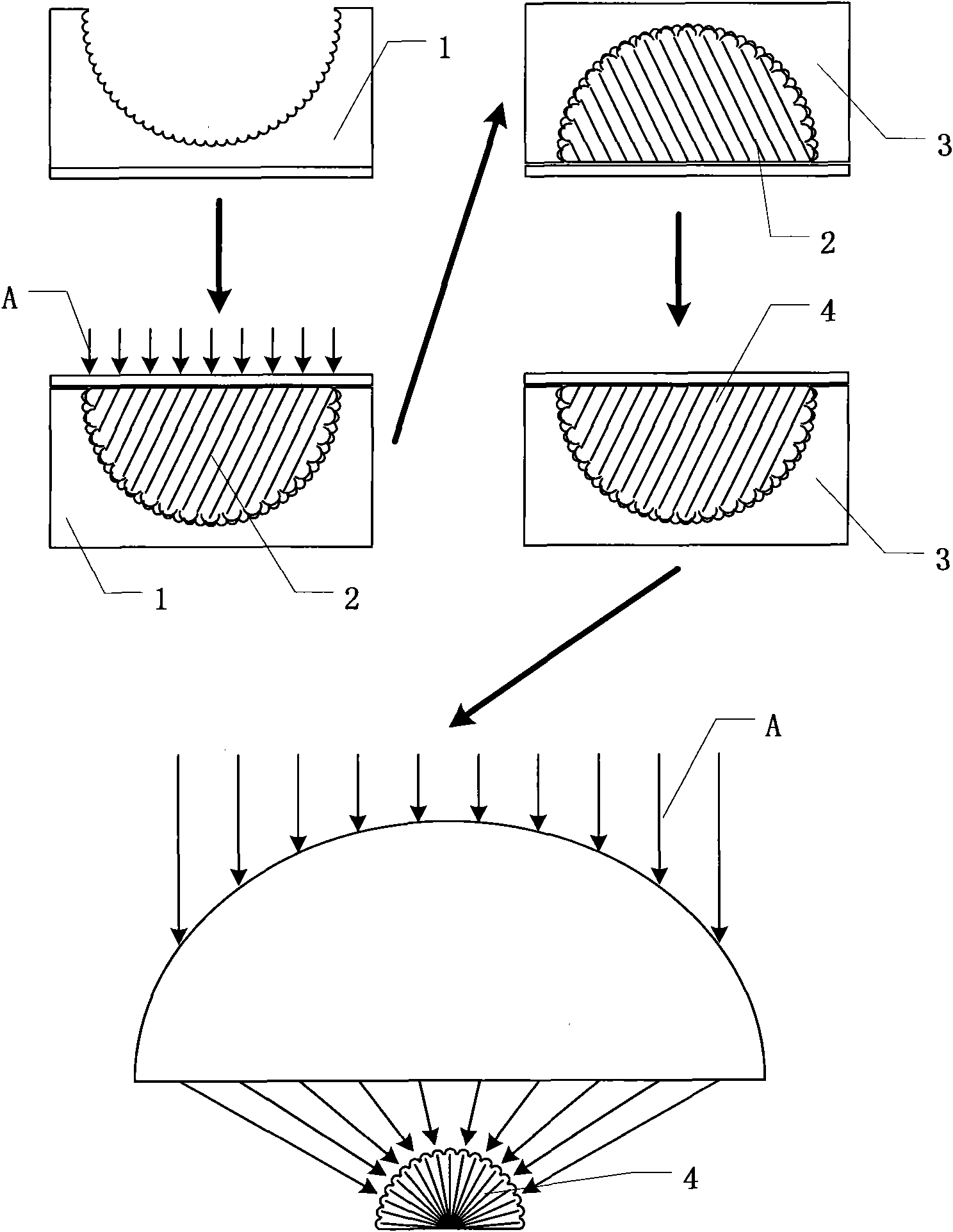
Method for manufacturing artificial bionic compound eyes
InactiveCN101672937AImprove machining accuracyOvercome light scattering effectPhotomechanical apparatusOptical articlesHigh volume manufacturingUltraviolet lights
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing artificial bionic compound eyes, comprising the steps of: firstly using femtosecond pulse bi-photon polymerization method to manufacture an inversioncurved surface micro lens mold; using ultraviolet nano impressing to manufacture into a three-dimensional curved surface micro lens template; then manufacturing an elastic mold on the three-dimensional curved surface micro lens template; sequentially accommodating photosensitive resin in the elastic mold, heating for baking into a photosensitive polymer mold with opposite polarity; and finally using the lens to focus ultraviolet lights and right irradiate to the photosensitive polymer mold placed on a substrate, manufacturing a light transmission channel by self-writing waveguide method, andmanufacturing into an artificial bionic compound eye. The invention overcomes limit of photoetching technology in aspect of three-dimensional micro-processing, improves processing precision of micro lens, can effectively reduce manufacture cost, enhance mass production capacity, and further promote application of artificial compound eyes in medical science, industry, military and other fields.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
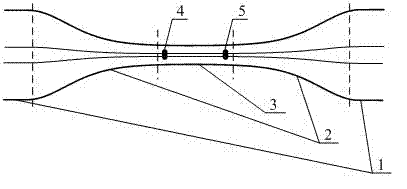
Optical fiber fused taper-based intrinsic Fabry-Perot device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102508337ASmall sizeHigh sensitivityCoupling light guidesConverting sensor output opticallyFemto second laserRefractive index
The invention provides an optical fiber fused taper-based intrinsic Fabry-Perot device and a manufacturing method thereof. The optical fiber fused taper-based intrinsic Fabry-Perot device comprises an optical fiber fused taper, wherein a first optical fiber internal reflection mirror and a second optical fiber internal reflection mirror are arranged in the optical fused fiber taper and radially change the reflection faces formed by reflection rates at the fiber core respectively along the interior of the optical fiber taper waist through femtosecond pulse laser. The diameter of the optical fiber fused taper is 10 to 50 microns; the distance between the first and second optical fiber internal reflection mirrors is 50 to 6000 microns. The device combines the high sensitivity characteristicscaused by a strong evanescent field of the optical fiber fused taper and easy detection characteristics of resonance peak shift for sensing of a Fabry-Perot cavity and enhances the sensitivity, response speed and reliability of an optical fiber sensor. The manufacturing method of the device is to etch the Fabry-Perot cavity by femtosecond pulse laser after adopting optical fiber biconical taper. Moreover, the device provided by the invention is simple and stable in structure, low in cost and high in repeatability and has the advantages of easy for batch processing of the device and the like. The device and method provided by the invention have broad application prospect in miniaturized and high-sensitive sensing areas.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Stretching and compression of laser pulses by means of high efficiency volume diffractive gratings with variable periods in photo-thermo-refractive glass
InactiveUS7424185B2High damage thresholdIncrease powerLaser using scattering effectsPhotomechanical apparatusFemto second laserUltrashort laser
High efficiency reflective volume Bragg gratings with chirped gratings recorded in photo-thermo-refractive glass having an absolute diffraction efficiency exceeding 95% in transmitting and reflecting modes are used to stretch and / or compress ultrashort laser pulses with high efficiency. Robustness, compactness, thermal and laser stability along with placement of multiple elements in the same space provides femtosecond laser system with high efficiency of stretching and re-compression of femtosecond pulses.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
Method and system for spectral analysis of biological materials using stimulated cars
InactiveUS7289203B2Easy to analyzeEnhanced response signalRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringBiological materialsSpectral analysis
A CARS system and method for probing a Raman signature of a sample are described. A short femtosecond pulse from one or more lasers is split into two pulses, a stimulus pulse and a probe pulse, whereby the probe pulse is time-delayed with respect to the stimulus pulse. Both pulses can be phase- and polarization-modulated. The stimulus pulse excites a vibronic level in the sample and the probe pulse probes molecular Raman transitions in the sample. A difference in the signals with and without excitation can be used to determine on which molecule a bond is most likely located. This will allow an accurate and sensitive determination of the presence of specific molecules in the sample. The system and method can be used to analyze biological samples and to discriminate between molecules having overlapping Raman signatures.
Owner:CHROMAPLEX
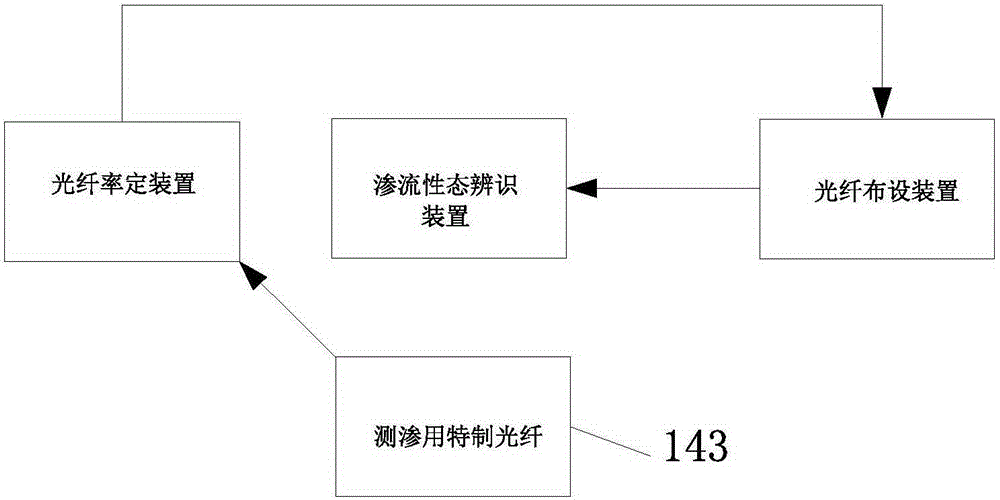
Hydraulic structure seepage property distributed optical fiber sensing integrated system and method
ActiveCN105181362AAchieve warmingImprove visibilityThermometers using physical/chemical changesMountingsImage resolutionHigh spatial resolution
The invention discloses a hydraulic structure seepage property distributed optical fiber sensing integrated system and a method. The system comprises a special optical fiber for seepage measurement, an optical fiber calibration device, an optical fiber laying device, and a seepage property identification device. After the optical fiber calibration device calibrates the special optical fiber for seepage measurement on site, the special optical fiber for seepage measurement is laid and tested with the aid of the optical fiber laying device, and the special optical fiber for seepage measurement is connected to the seepage property identification device for information collection, processing and analysis after successful test. By adopting the system and the method, a long optical fiber can be calibrated efficiently, and the bending curvature of the long optical fiber can be controlled and measured reliably. By combining the special optical fiber for seepage measurement with a self-controlled heat source and a seepage property identification technology based on femtosecond pulse, the seepage property of a hydraulic structure can be sensed with high precision and high spatial resolution, at high sensing speed and at long distance.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
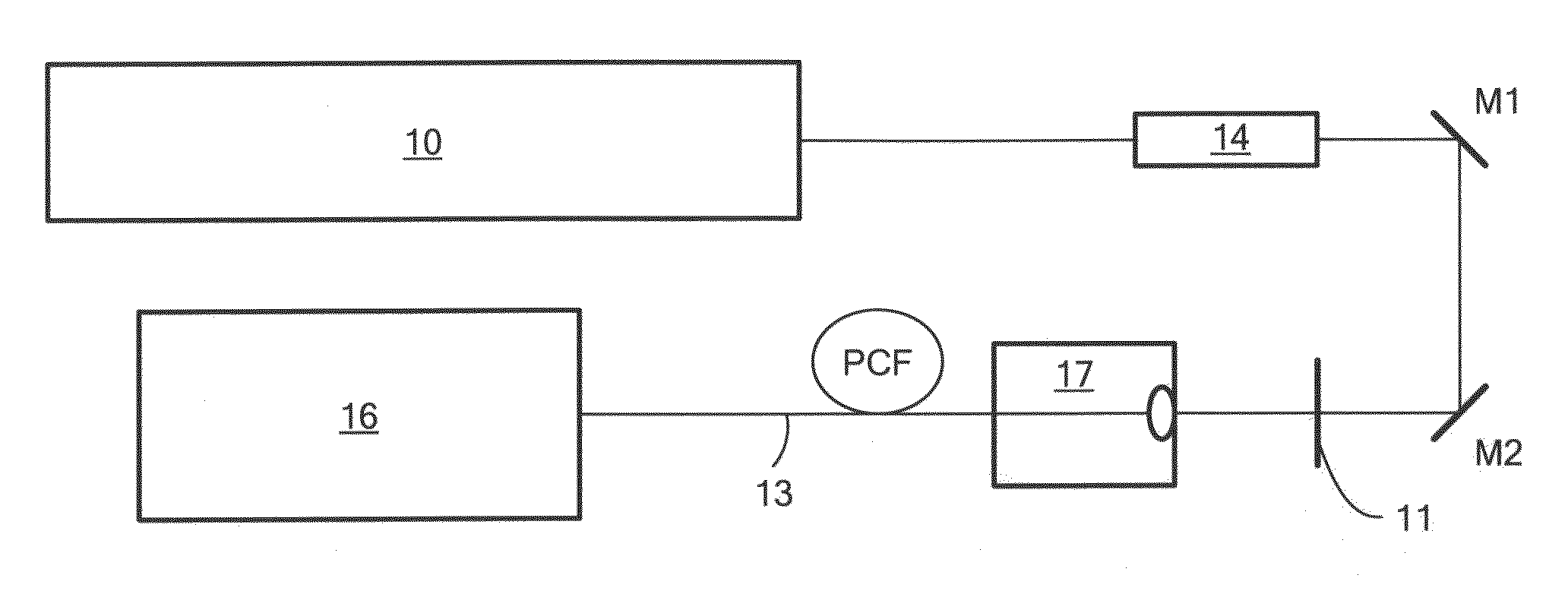
Optical frequency up-conversion of femtosecond pulses into targeted single bands in the visible and ultraviolet
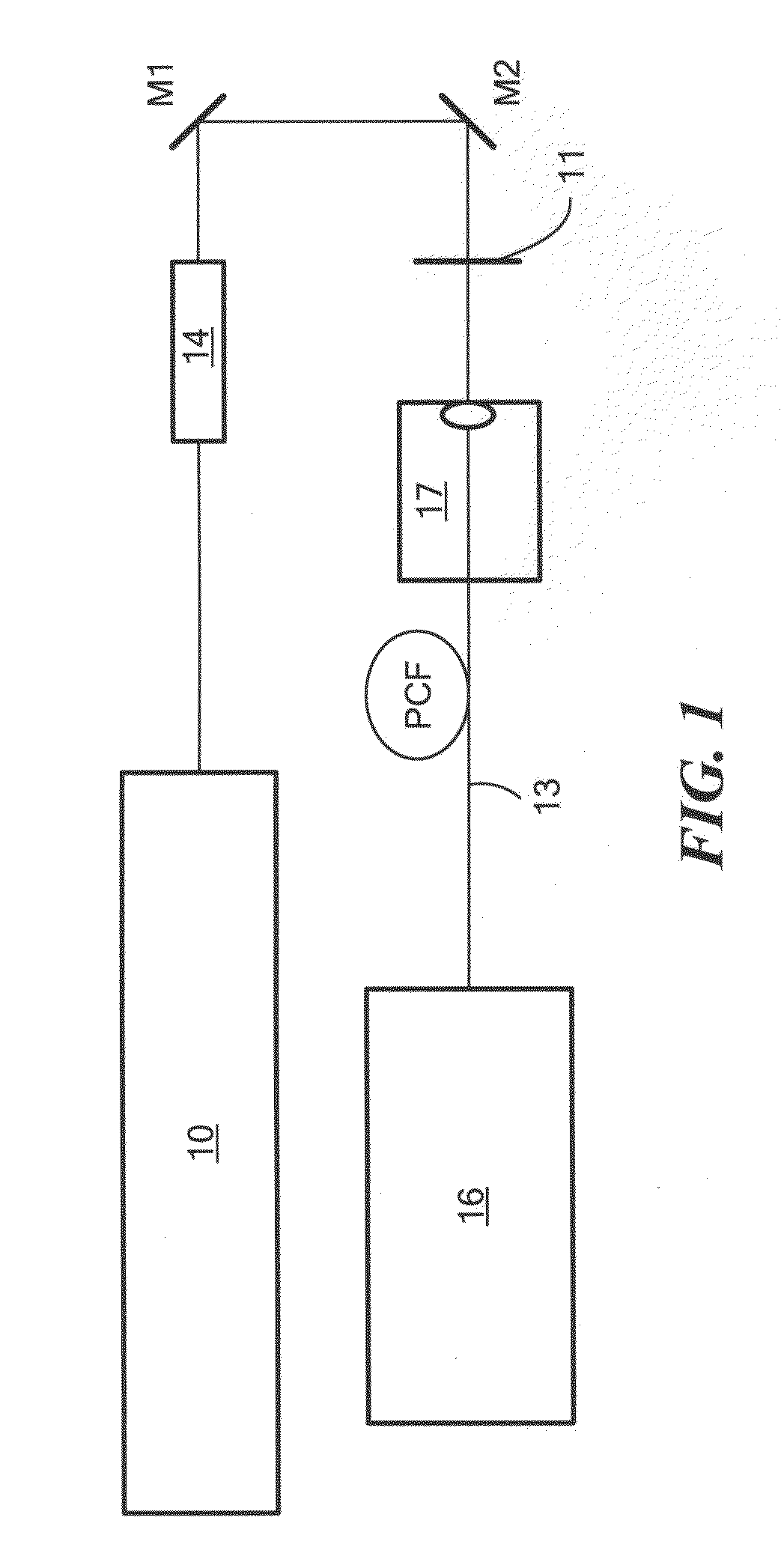
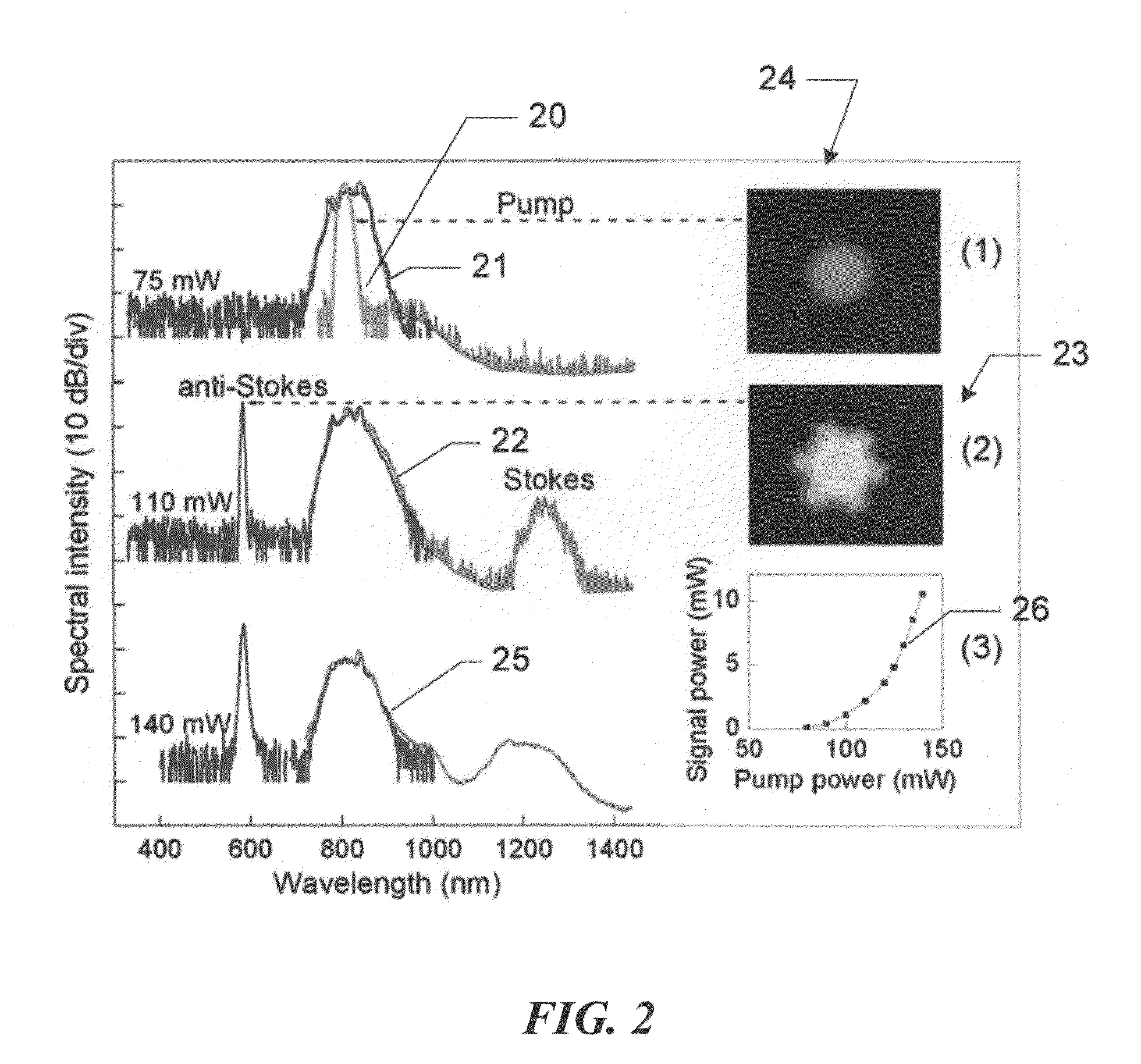
An apparatus and methods for generating a substantially supercontinuum-free widely-tunable multimilliwatt source of radiation characterized by a narrowband line profile. The apparatus and methods employ nonlinear optical mechanisms in a nonlinear photonic crystal fiber (PCF) by detuning the wavelength of a pump laser to a significant extent relative to the zero-dispersion wavelength (ZDW) of the PCF. Optical phenomena employed for the selective up-conversion in the PCF include, but are not limited to, four-wave mixing and Cherenkov radiation. Tunability is achieved by varying pump wavelength and power and by substituting different types of PCFs characterized by specified dispersion properties.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Direct writing of optical devices in silica-based glass using femtosecond pulse lasers
InactiveUS6977137B2Efficient rateHigh sensitivityPhotography auxillary processesRadiation applicationsLight guideRefractive index
The invention relates to methods of writing a light-guiding structure in a bulk glass substrate. The bulk glass substrate is preferably made from a soft silica-based material having an annealing point less than about 1380° K. A pulsed laser beam is focused within the substrate while the focus is translated relative to the substrate along a scan path at a scan speed effective to induce an increase in the refractive index of the material along the scan path. Substantially no laser-induced physical damage of the material is incurred along the scan path. Various optical devices can be made using this method.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method of direct Coulomb explosion in laser ablation of semiconductor structures
InactiveUS7759607B2Generate efficientlyReduce ablationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesSemiconductor materialsMaterial removal
A new technique and Method of Direct Coulomb Explosion in Laser Ablation of Semiconductor Structures in semiconductor materials is disclosed. The Method of Direct Coulomb Explosion in Laser Ablation of Semiconductor Structures provides activation of the “Coulomb explosion” mechanism in a manner which does not invoke or require the conventional avalanche photoionization mechanism, but rather utilizes direct interband absorption to generate the Coulomb explosion threshold charge densities. This approach minimizes the laser intensity necessary for material removal and provides optimal machining quality. The technique generally comprises use of a femtosecond pulsed laser to rapidly evacuate electrons from a near surface region of a semiconductor or dielectric structure, and wherein the wavelength of the laser beam is chosen such that interband optical absorption dominates the carrier production throughout the laser pulse. The further application of a strong electric field to the semiconductor or dielectric structure provides enhancement of the absorption coefficient through a field induced redshift of the optical absorption. The use of this electric field controlled optical absorption is available in all semiconductor materials and allows precise control of the ablation rate. When used in conjunction with nanoscale semiconductor or dielectric structures, the application of a strong electric field provides for laser ablation on sub-micron lateral scales.
Owner:OPTICAL ANALYTICS
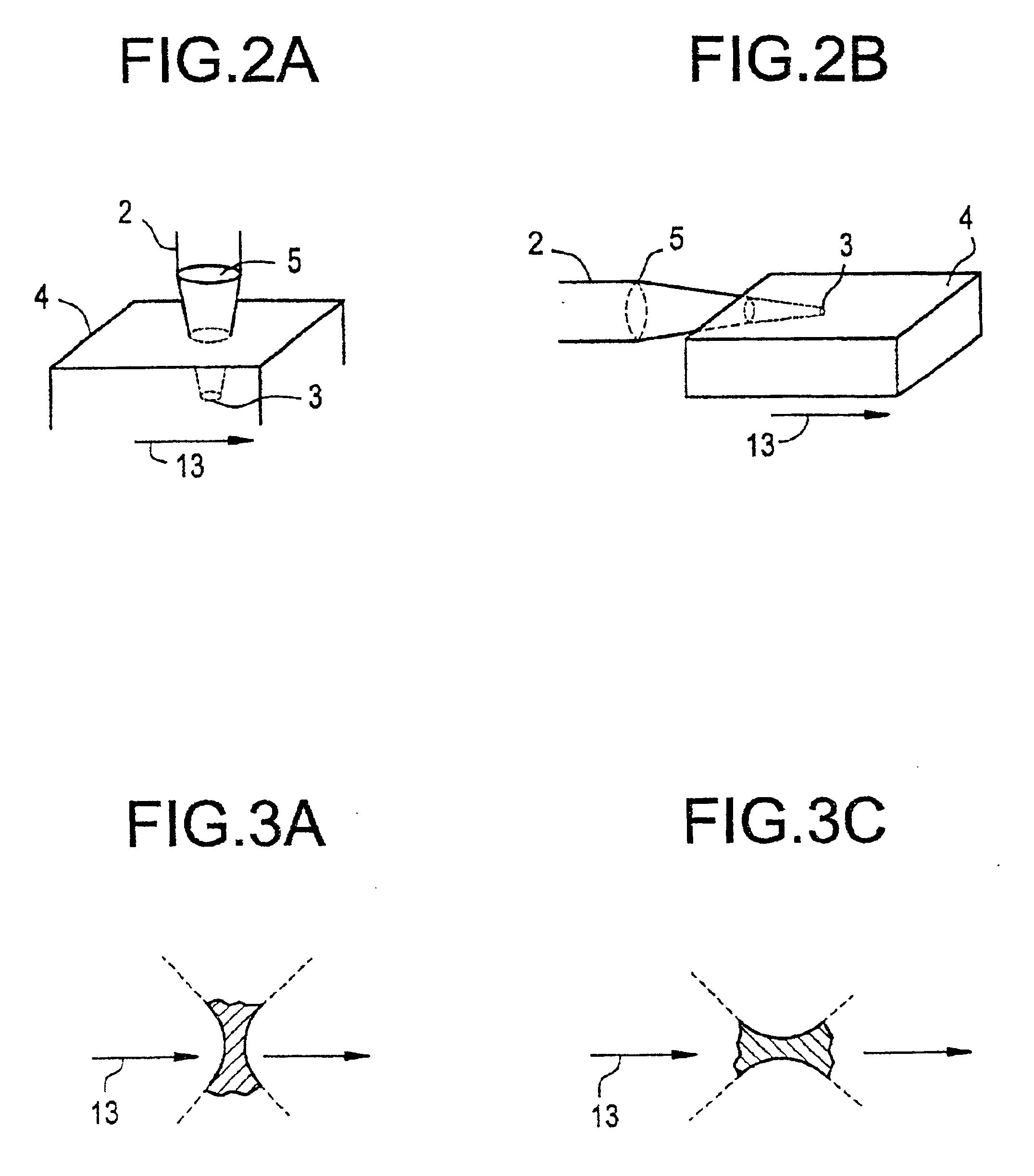
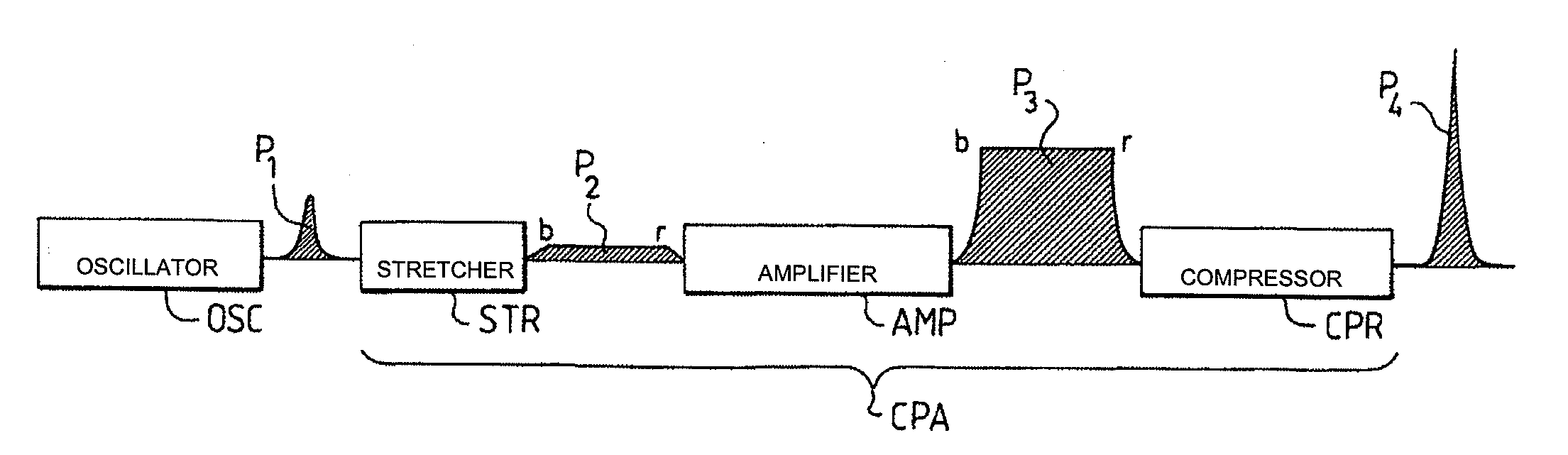
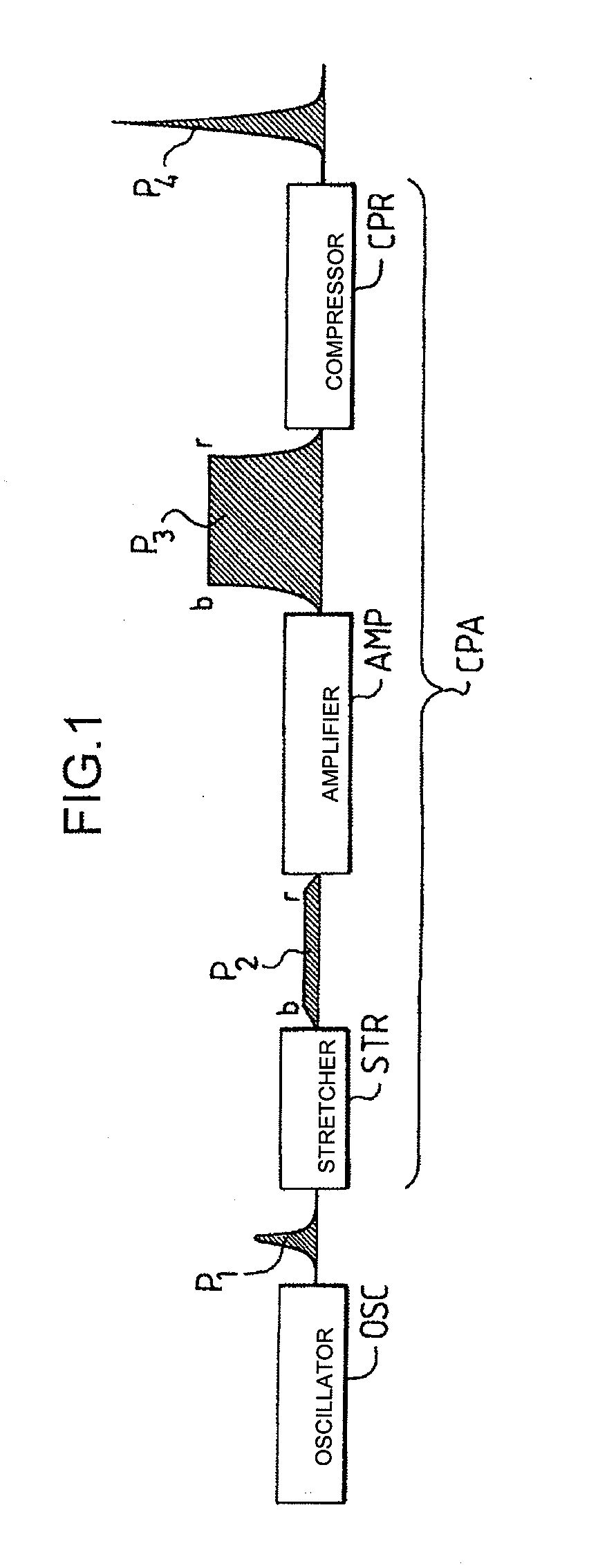
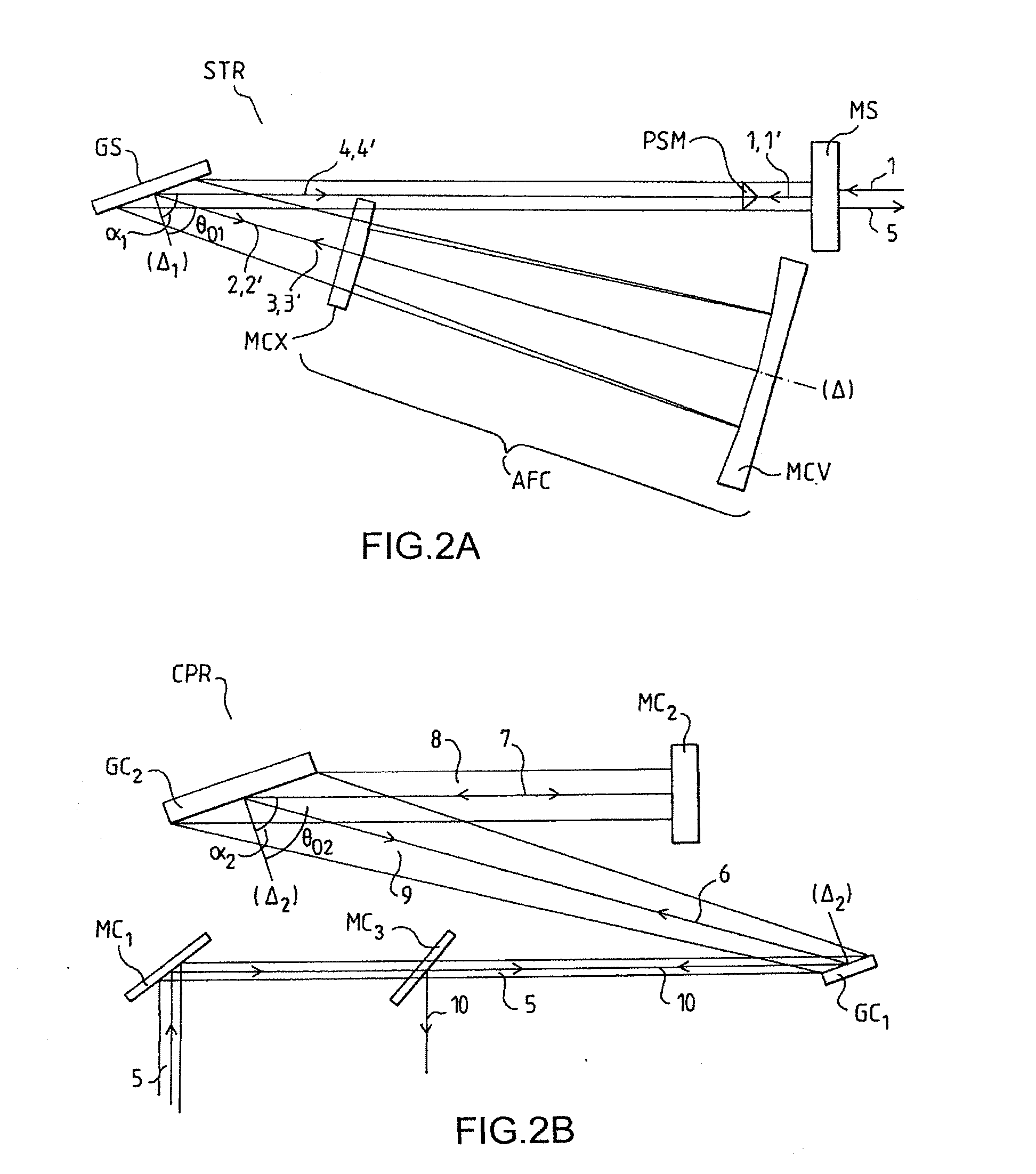
Amplifier Chain for Generating Ultrashort Different Width Light Pulses
The present invention relates to an amplifier chain for generating ultrashort light pulses of different pulse durations and applies in particular to amplifier chains suitable for amplifying picosecond and femtosecond pulses. The amplifier chain comprising a stretcher with at least one entry dispersive element of the grating type and intended to temporally stretch an incident pulse, an amplifying medium designed to amplify said stretched pulse, a compressor with at least one entry dispersive element substantially identical to that of the stretcher, designed to temporally compress said amplified pulse. According to the invention, the stretcher and the compressor include means for moving the dispersive elements between first and second positions, in such a way that the angle of incidence in a first position is equal to the angle of diffraction in the second position, and vice versa, allowing two degrees of stretch of the chain to be defined, each adapted to the amplification of pulses of different durations.
Owner:THALES SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com