Method for identifying key module or key node in biomolecular network
A biomolecular network and key module technology, applied in biological systems, evolutionary biology, biostatistics, etc., can solve the problems of lack of quantitative analysis of key modules or key nodes, ignoring influence, ignoring module network topology, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Example 1 Identification and verification of key modules
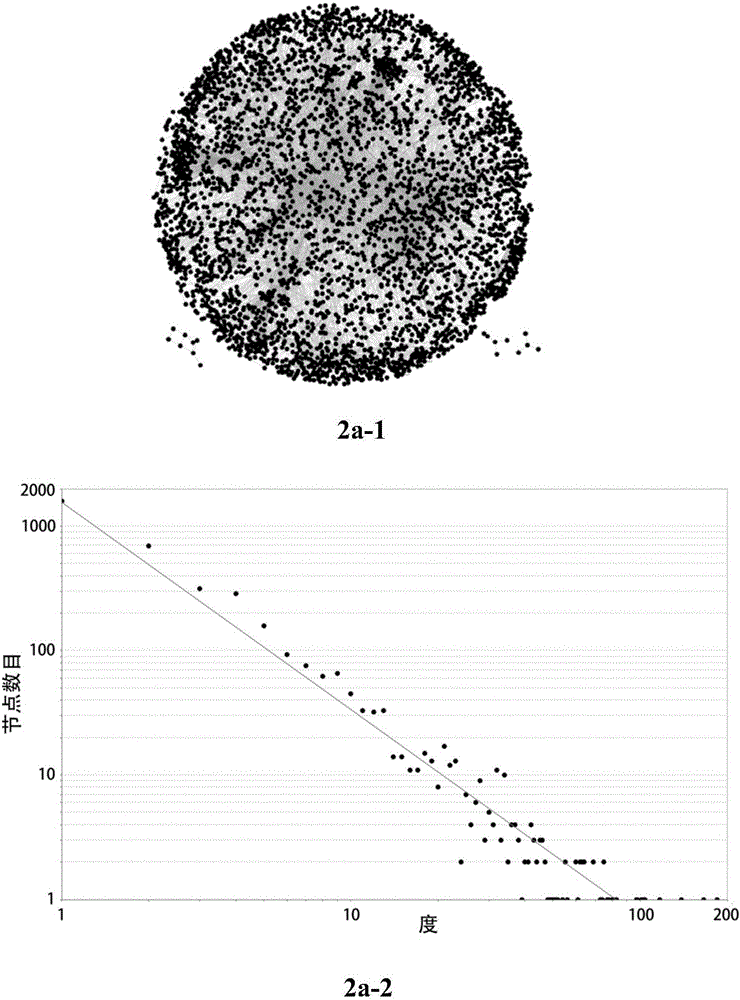
[0060] The protein interaction network of the cerebral ischemia mouse model was intervened by the components of Qingkailing ( figure 2 ; see Zhang Yingying, Identification and comparison of the main modules of the protein network of the Qingkailing multi-component intervention cerebral ischemia model [D], China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, 2014):
[0061] The protein interaction network of the cerebral ischemia model group (Vehicle group) ( figure 2 a-1), consisting of 3750 nodes and 9162 edges;
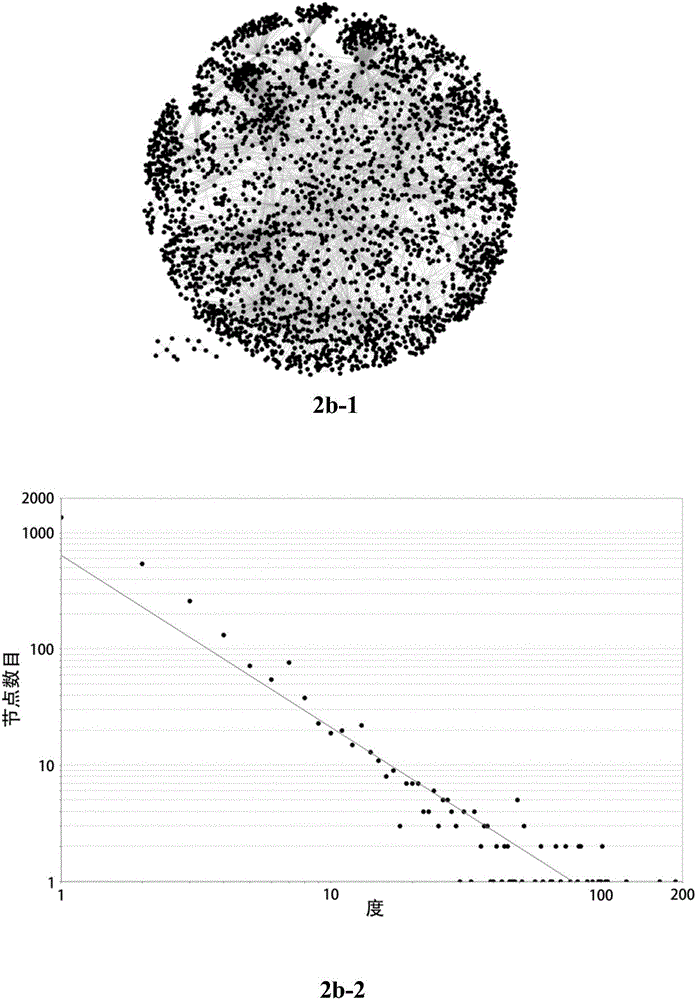
[0062] The protein interaction network of the baicalin group (BA group) ( figure 2 b-1), is the protein interaction network after the drug baicalin intervenes in the cerebral ischemia model, consisting of 2813 nodes and 6217 edges;
[0063] The protein interaction network of the geniposide group (JA group) ( figure 2 c-1), is the protein interaction network after the drug geniposide intervenes in the...
Embodiment 2
[0078] Example 2 Identification and verification of key modules
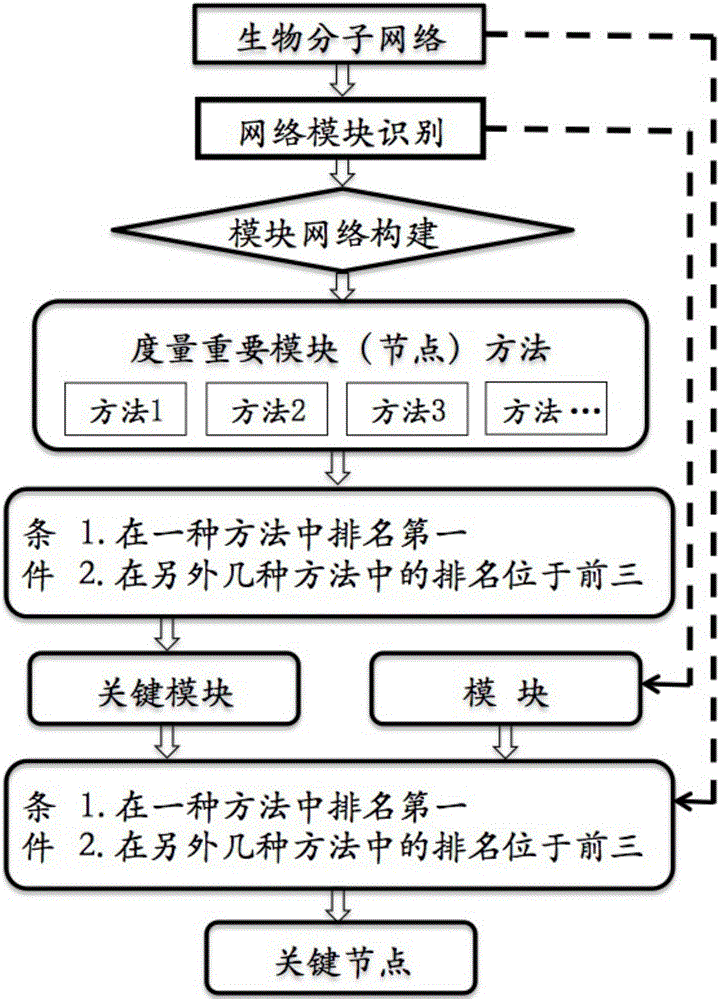
[0079] For the three protein interaction networks (Vehicle group, BA group, and JA group) in Example 1, an unweighted modular interaction network was constructed in step 2 to identify key networks and pharmacological drivers.
[0080] The process is as follows.
[0081] Step 1, use the MCODE method to identify the modules of each network.
[0082] In step 2, an unweighted module interaction network is constructed based on the component dependencies between modules.
[0083] Step 3, select degree centrality, betweenness centrality and page level three measurement methods to identify key modules from a variety of methods for measuring the importance of nodes, wherein the key modules meet the following conditions to be determined as key modules: According to the The method of measuring the importance of nodes is calculated, and the obtained values are arranged in descending order (A) ranks first in one metho...
Embodiment 3
[0093] Example 3 Identification and validation of key nodes, i.e. pharmacological drivers
[0094] Using the key module M of the geniposide group protein interaction network identified in Example 1 JA-1 , using degree centrality, betweenness centrality and page level three measurement methods to identify the key nodes in this key module, that is, pharmacological drivers, where the key nodes can be determined as key nodes only if they meet the following conditions: according to the importance of the measured nodes Calculated by the most accurate method, the obtained values are arranged in descending order (A) ranks first in one method, (B) ranks in the top three in other methods.
[0095] The key module M in the protein interaction network of the geniposide group JA-1 It was found that the primary results of the three methods were consistent, all of which were Il6, see Table 8.
[0096] Table 8: Key module M of geniposide group JA-1 Identification results of key nodes i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com