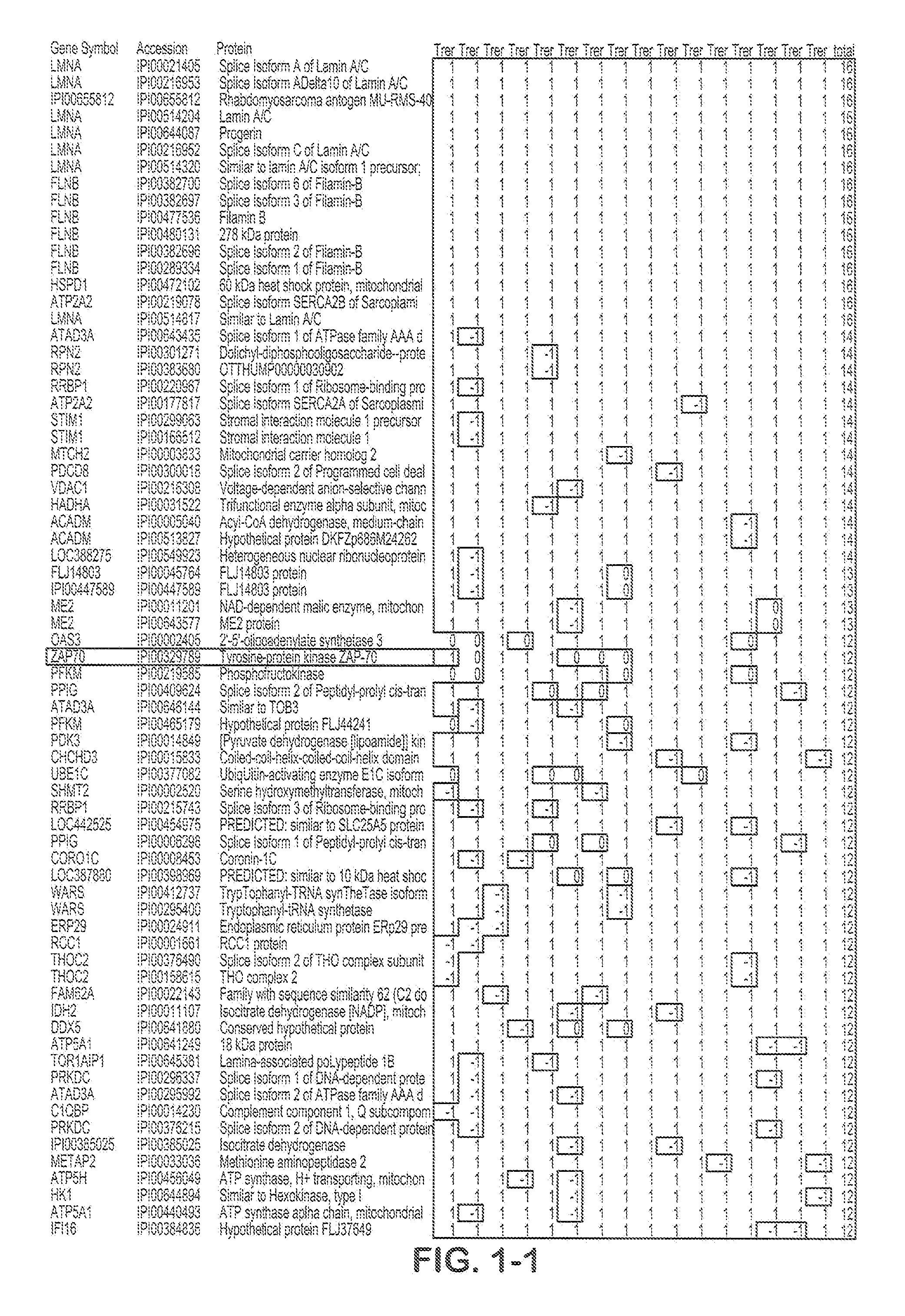
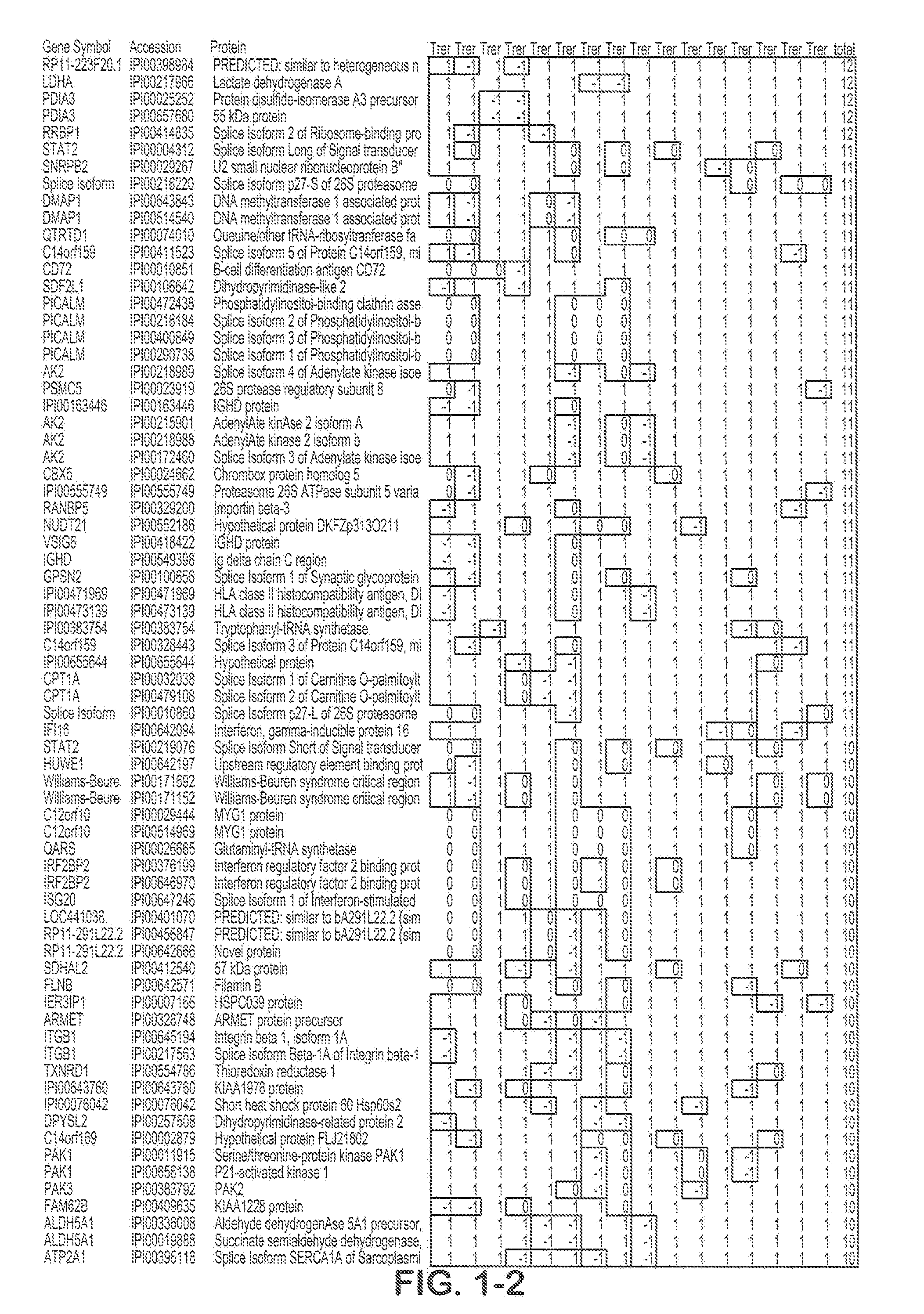
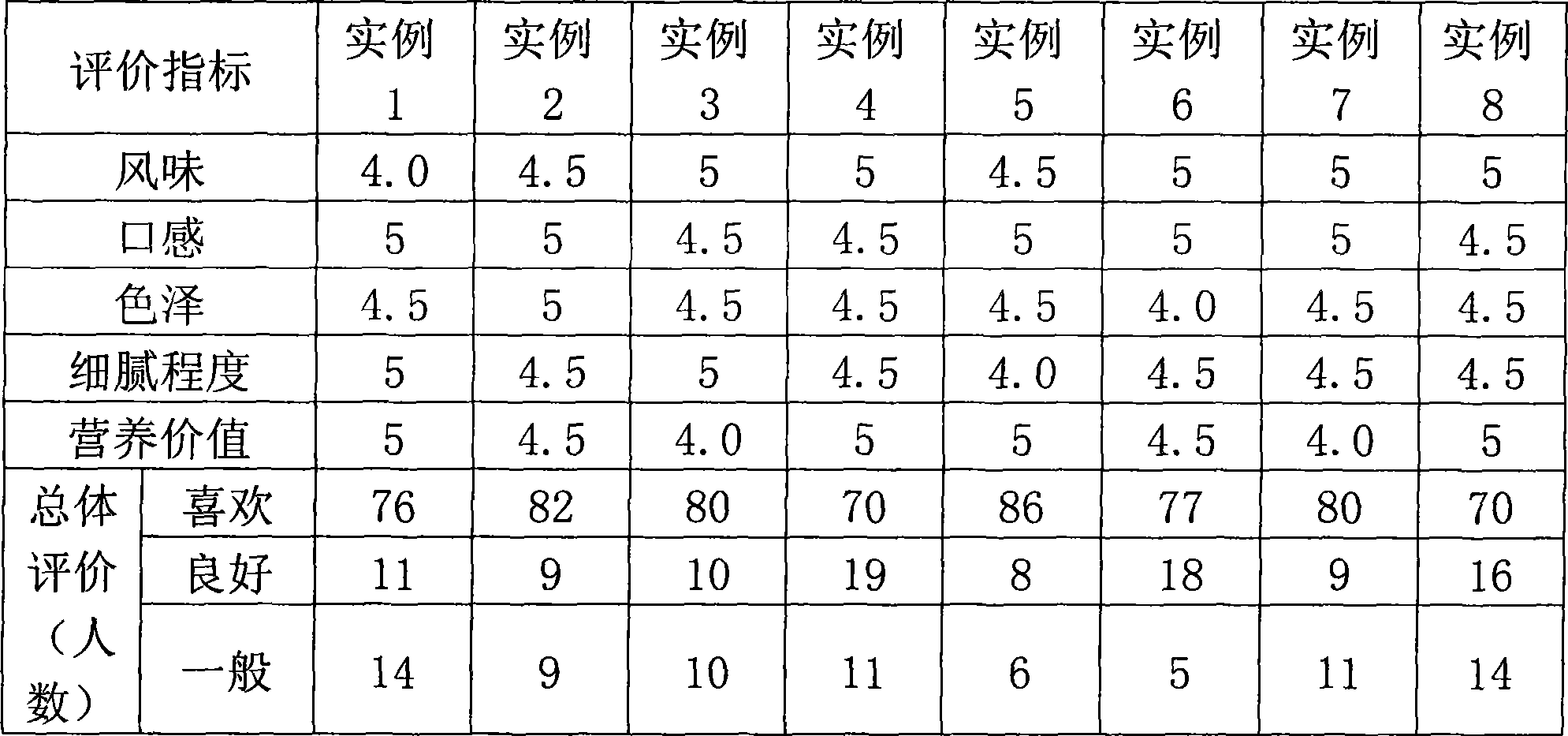
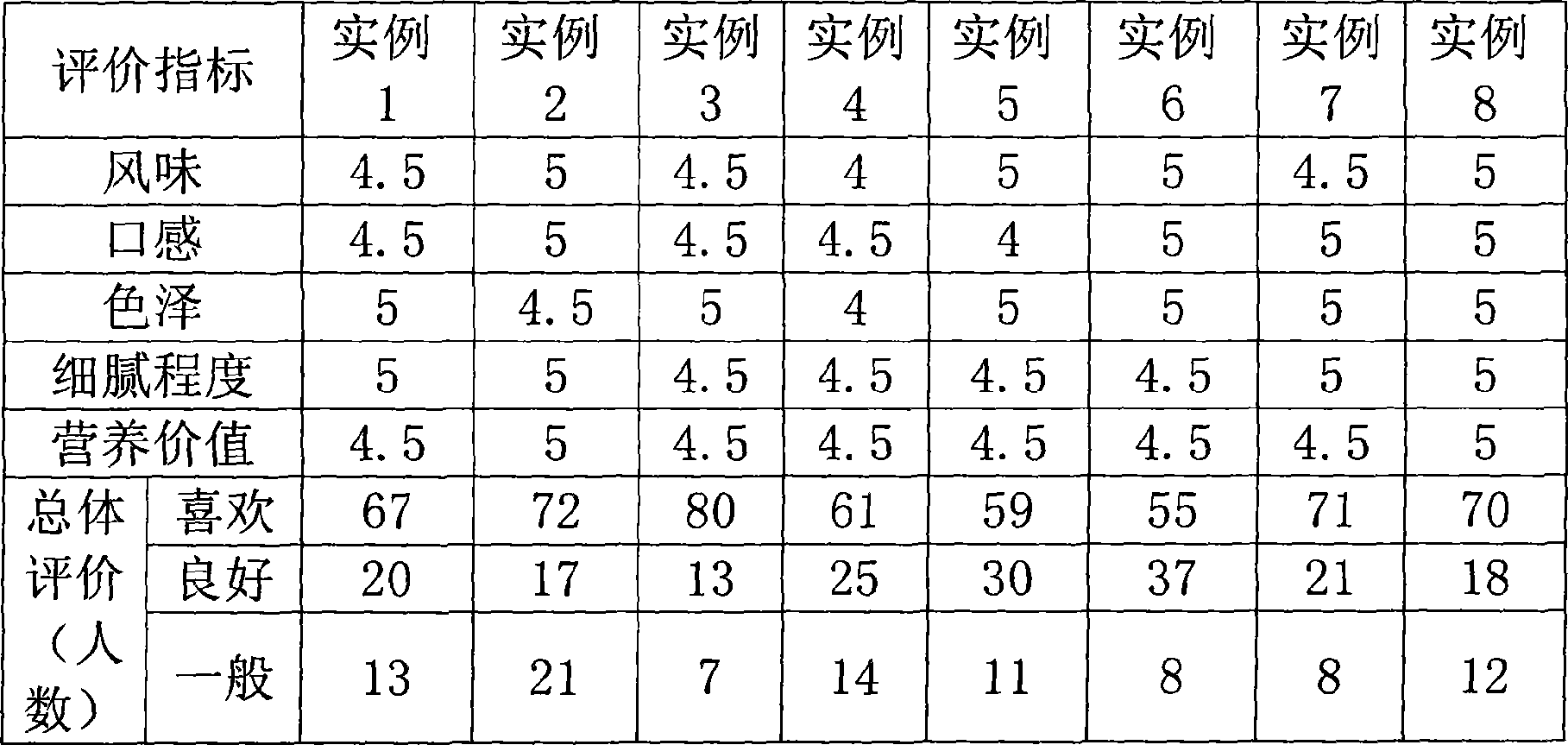
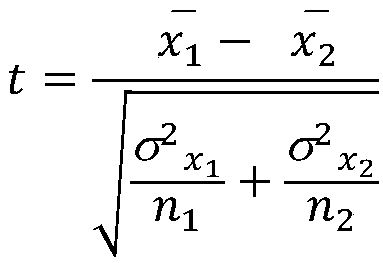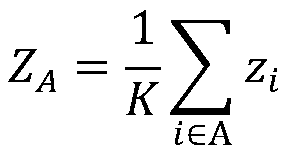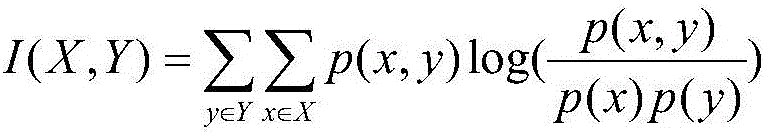Patents
Literature
95 results about "Protein network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
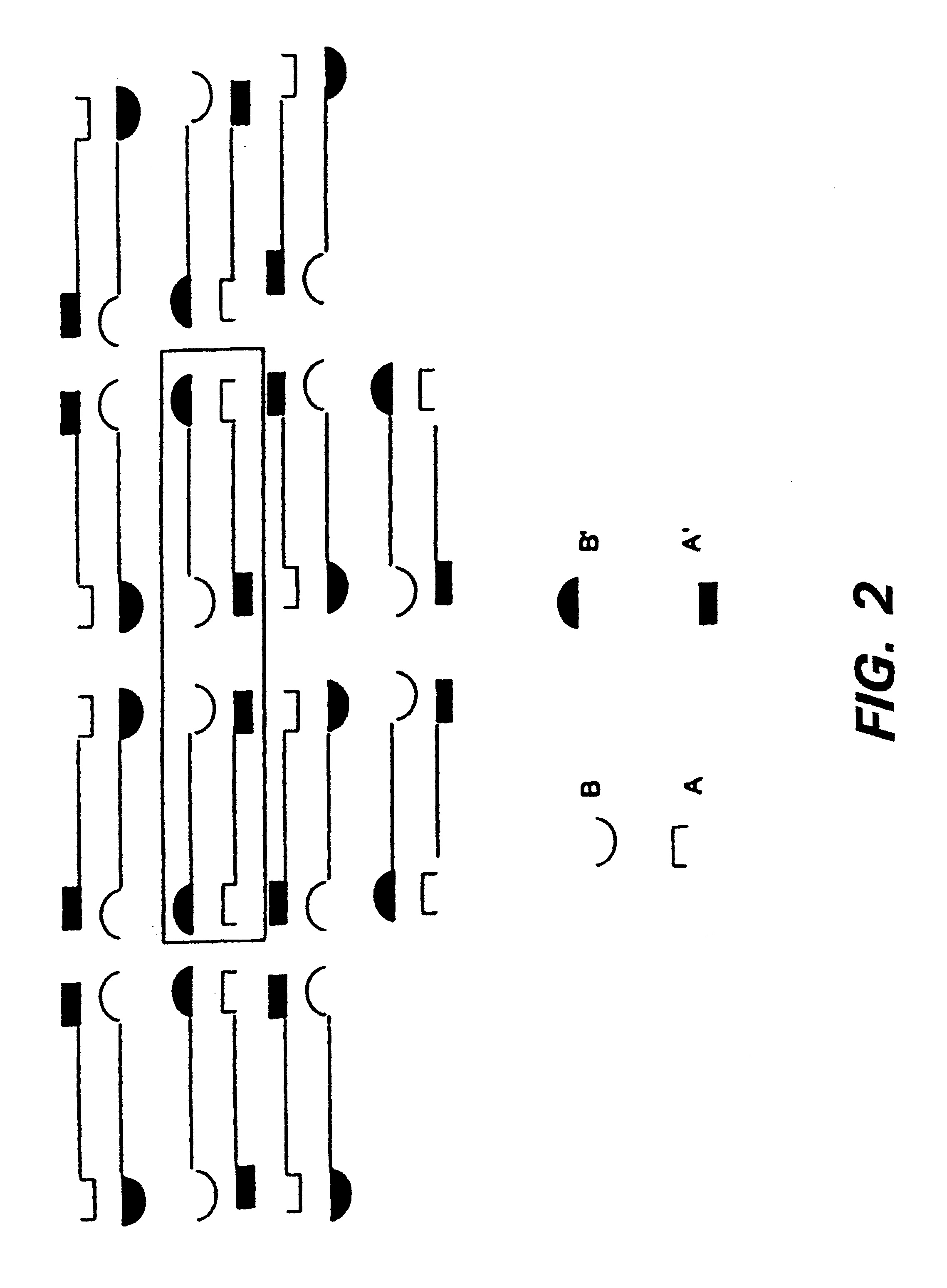
Enzyme-mediated modification of fibrin for tissue engineering
The invention provides fibrin-based, biocompatible materials useful in promoting cell growth, wound healing, and tissue regeneration. These materials are provided as part of several cell and tissue scaffolding structures that provide particular application for use in wound-healing and tissue regenerating. Methods for preparing these compositions and using them are also disclosed as part of the invention. A variety of peptides may be used in conjunction with the practice of the invention, in particular, the peptide IKVAV, and variants thereof. Generally, the compositions may be described as comprising a protein network (e.g., fibrin) and a peptide having an amino acid sequence that comprises a transglutaminase substrate domain (e.g., a factor XIIIa substrate domain) and a bioactive factor (e.g., a peptide or protein, such as a polypeptide growth factor), the peptide being covalently bound to the protein network. Other applications of the technology include their use on implantable devices (e.g., vascular graphs), tissue and cell scaffolding. Other applications include use in surgical adhesive or sealant, as well as in peripheral nerve regeneration and angiogenesis.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
InactiveUS20110190157A1Improve clinical outcomesMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningMolecular classificationHer Disease
A molecular classification procedure based on activity levels of modules in protein networks, wherein the proteins are biomarkers for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and method for use of the subnetworks to distinguish between patients at low or high risk of progression of their disease.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Non-fermentation type sour milk and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to non-fermentation type sour milk and a preparation method thereof. The non-fermentation type sour milk uses fresh cow milk as principal raw material. After being hydrolyzed by milk sugar, the cow milk is pasteurized and concentrated in vacuum to be 40 percent of the original volume. After the cow milk is cooled, probiotic powder is added. The invention has the core that transglutaminase is added at an optimal temperature; under the action of the transglutaminase, milk protein is connected together to form a protein network, thereby a uniform stable gelatin system is easily formed; delta-gluconolactone is then added, and the gelatin system and the delta-gluconolactone are heated at 35-40 DEG C in a water bath way for 2 to 3 hours so that the uniform, stable and exquisite non-fermentation type sour milk like a quark can be obtained. The invention has simple preparing process, no requirement for fermentation, and full utilization of resources. The non-fermentation type sour milk can be used as a base to develop various products, such as corn non-fermentation type sour milk for breakfast, jelly non-fermentation type sour milk, and the like, and can satisfy the requirements of consumers in nutrition, mouthfeel, texture, and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Instant cheese and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to an instant cheese and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps: using full-cream fresh milk as main material, pasteurizing the milk after being hydrolyzed through lactase, and concentrating the full-cream fresh milk to 35-40 percent of the original volume in vacuum. The preparation method of the instant cheese has the core points that transglutaminase is added at 35 DEG C, and milk proteins are linked to form a protein network under the action of the transglutaminase, thereby forming a uniform and stable gel system easily. Then, chymosin is added for promoting gel to form , and uniform, stable and delicate instant cheese can be obtained in a water bath for half hour at about 30 DEG C. The invention is simple and easy for operation, and can be used for development of various application products on the theoretical basis, including breakfast cereal cheese, jelly cheese and the like. Moreover, the instant cheese can meet the requirements of consumers for taste, texture, nutrition, and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
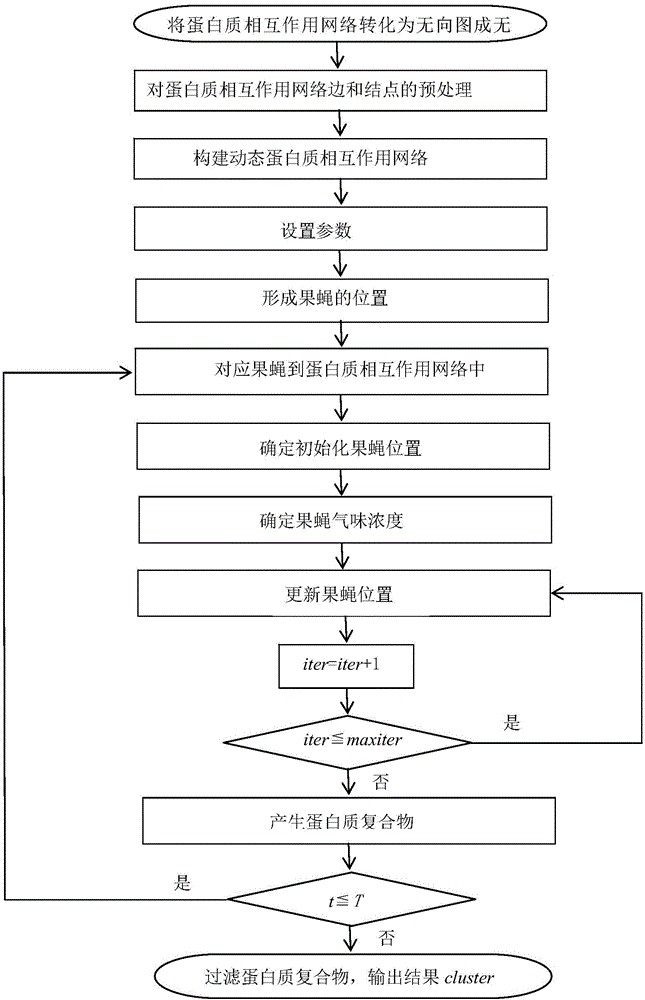
A method of identifying protein compounds by using a fruit fly optimization method
InactiveCN105868582AImprove accuracyRealistically simulate dynamicsProteomicsGenomicsProtein protein interaction networkProtein-protein complex
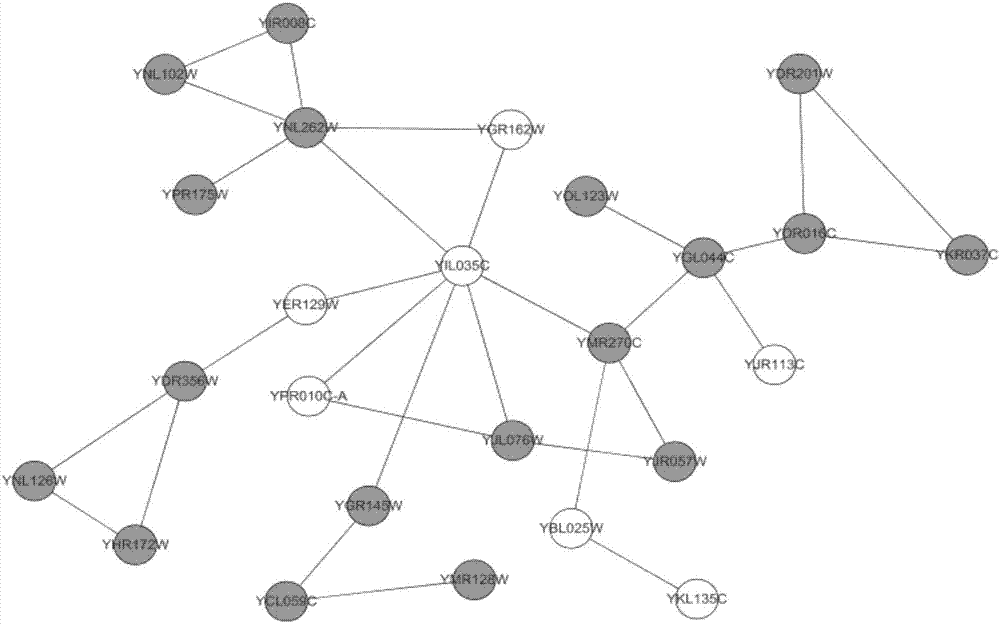
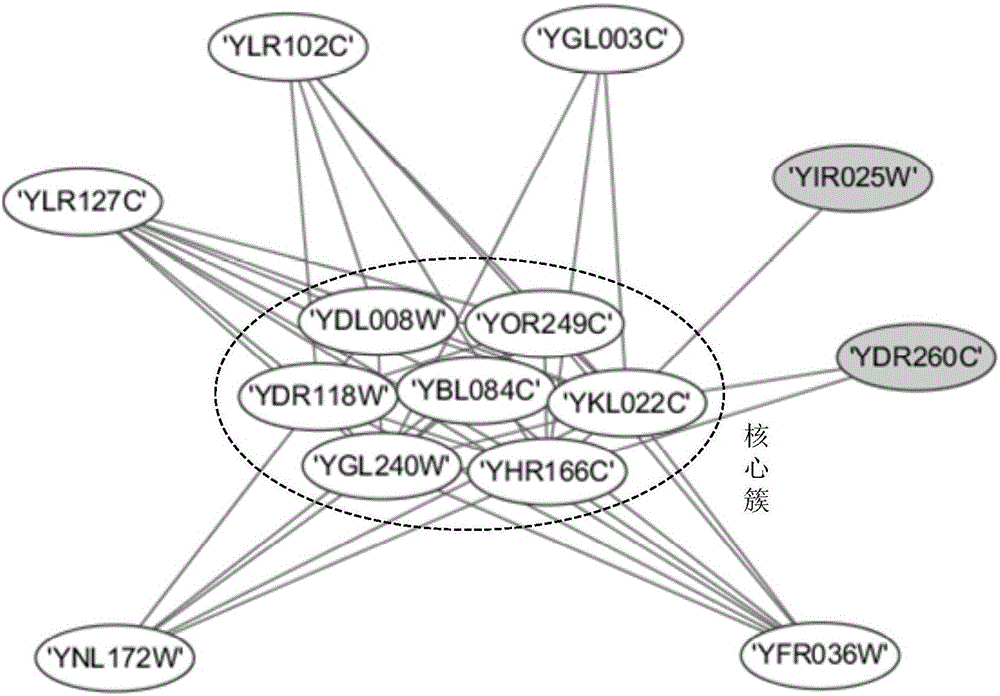
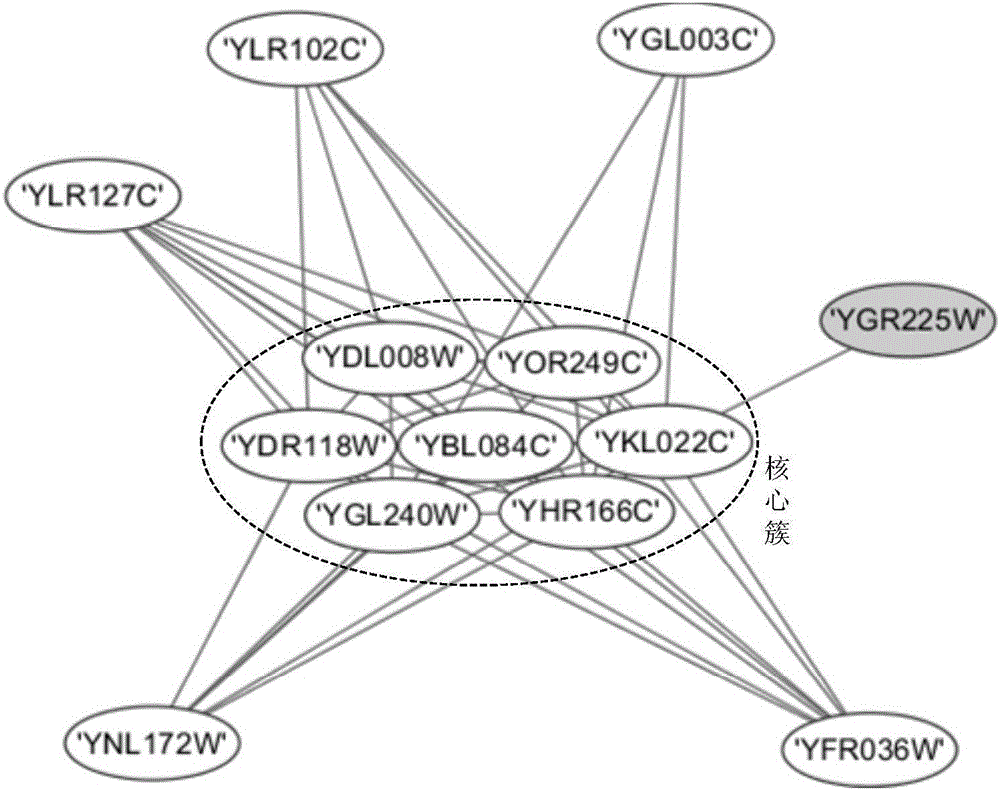
The invention provides a method of identifying protein compounds by using a fruit fly optimization method. The method comprises the steps of converting a protein-protein interaction network into a undirected graph, performing pretreatment on the edges and nodes of the protein-protein interaction network, establishing a dynamic protein-protein interaction network, setting parameters, forming fruit fly positions, matching fruit flies with the protein-protein interaction network, determining initialization fruit fly positions, determining the fruit fly odor concentration, updating the fruit fly positions, generating a protein compound, and filtering the protein compound. The method gives full consideration to the dynamic nature of the protein network, the protein compound inner core-attachment structure and the locality and wholeness of the protein-protein interaction network and can identify protein compounds accurately. The results of simulation experiments show that the performance of the indexes such as the accuracy and the recall ratio are excellent. Compared with other clustering methods, the method, based on the characteristics of the protein network and the protein compounds, realizes the protein compound identification process and improves the protein compound identification accuracy.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Enzyme-mediated modification of fibrin for tissue engineering
The invention provides fibrin-based, biocompatible materials useful in promoting cell growth, wound healing, and tissue regeneration. These materials are provided as part of several cell and tissue scaffolding structures that provide particular application for use in wound-healing and tissue regenerating. Methods for preparing these compositions and using them are also disclosed as part of the invention. A variety of peptides may be used in conjunction with the practice of the invention, in particular, the peptide IKVAV, and variants thereof. Generally, the compositions may be described as comprising a protein network (e.g., fibrin) and a peptide having an amino acid sequence that comprises a transglutaminase substrate domain (e.g., a factor XIIIa substrate domain) and a bioactive factor (e.g., a peptide or protein, such as a polypeptide growth factor), the peptide being covalently bound to the protein network. Other applications of the technology include their use on implantable devices (e.g., vascular graphs), tissue and cell scaffolding. Other applications include use in surgical adhesive or sealant, as well as in peripheral nerve regeneration and angiogenesis.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
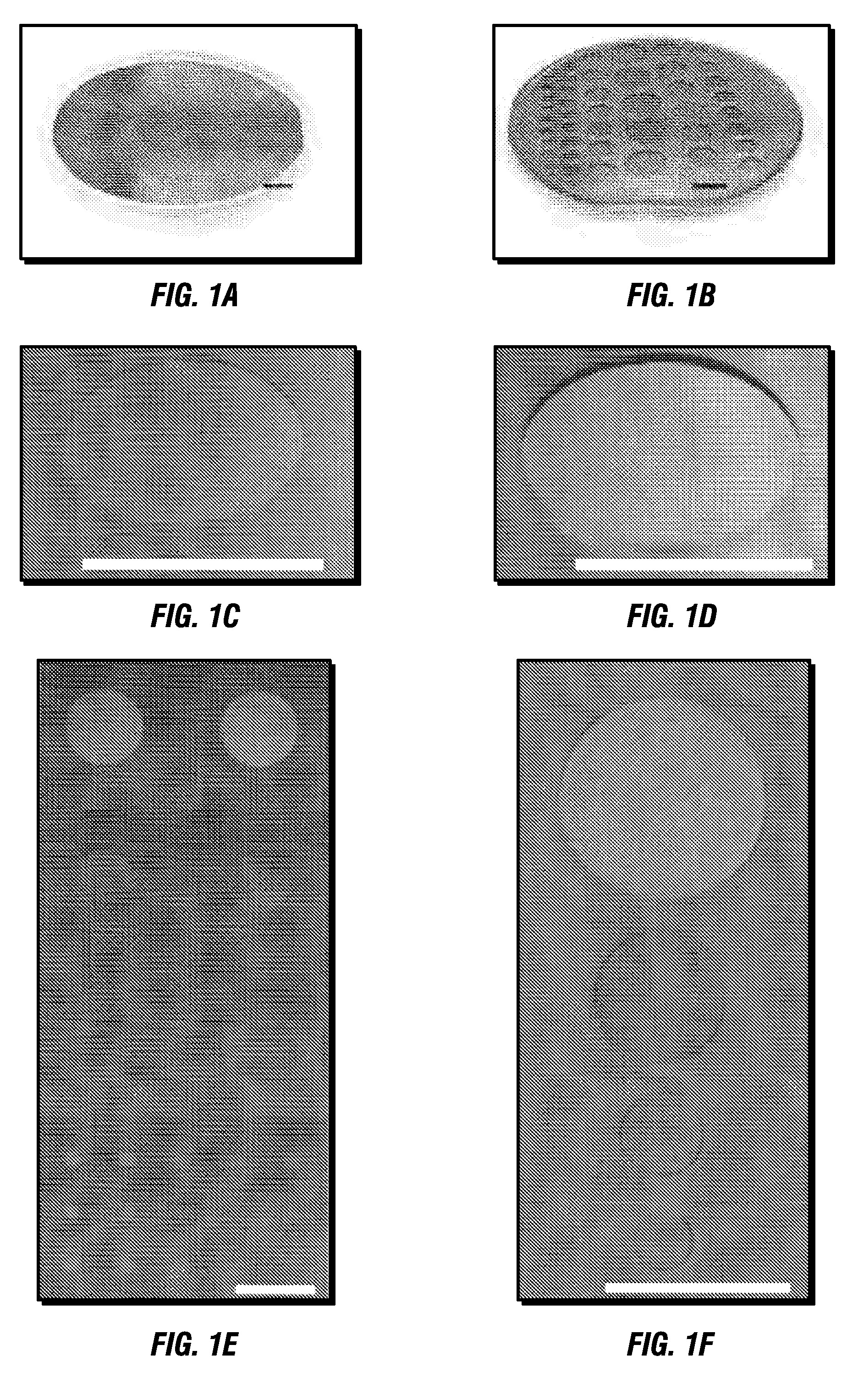
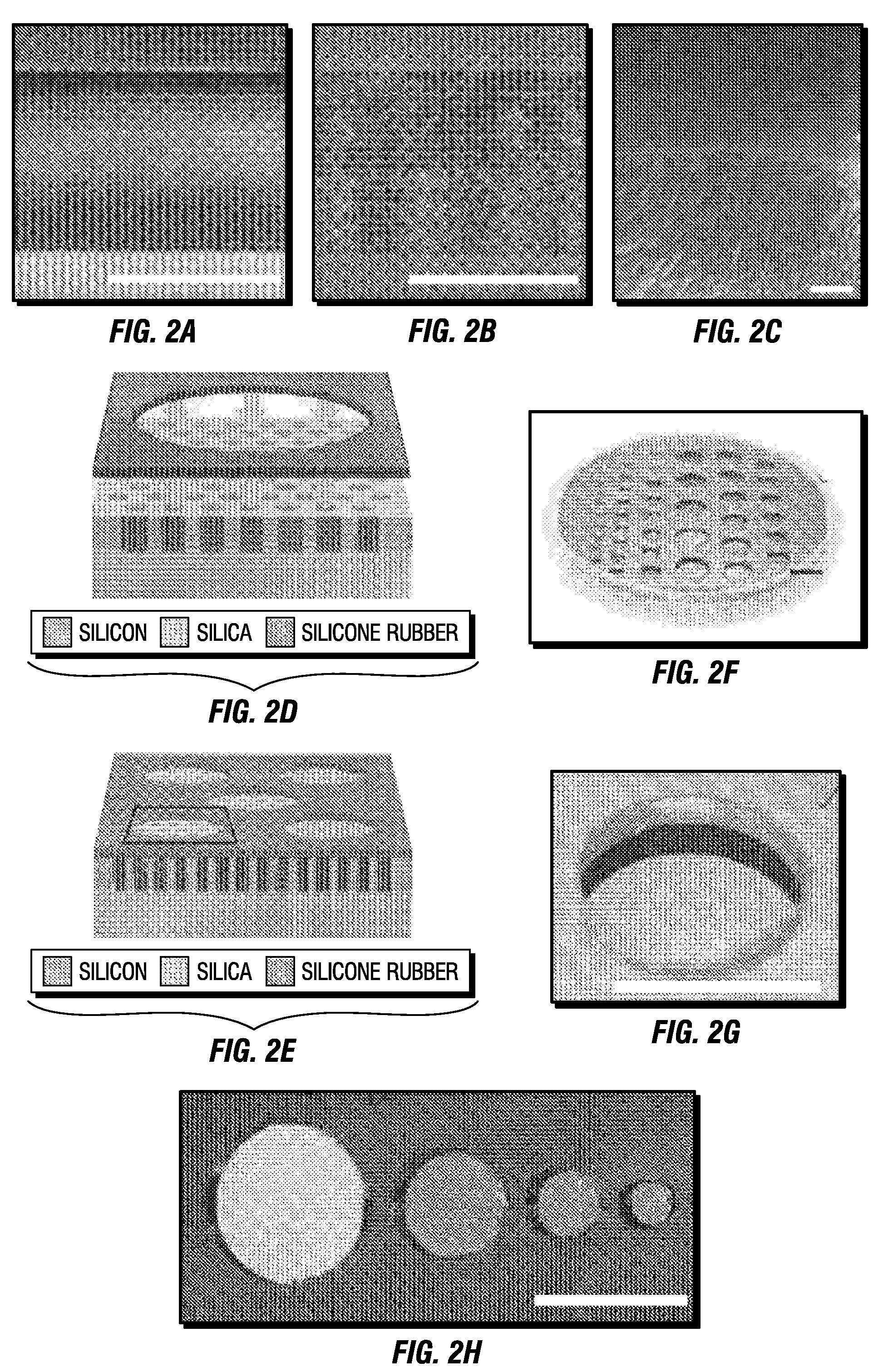
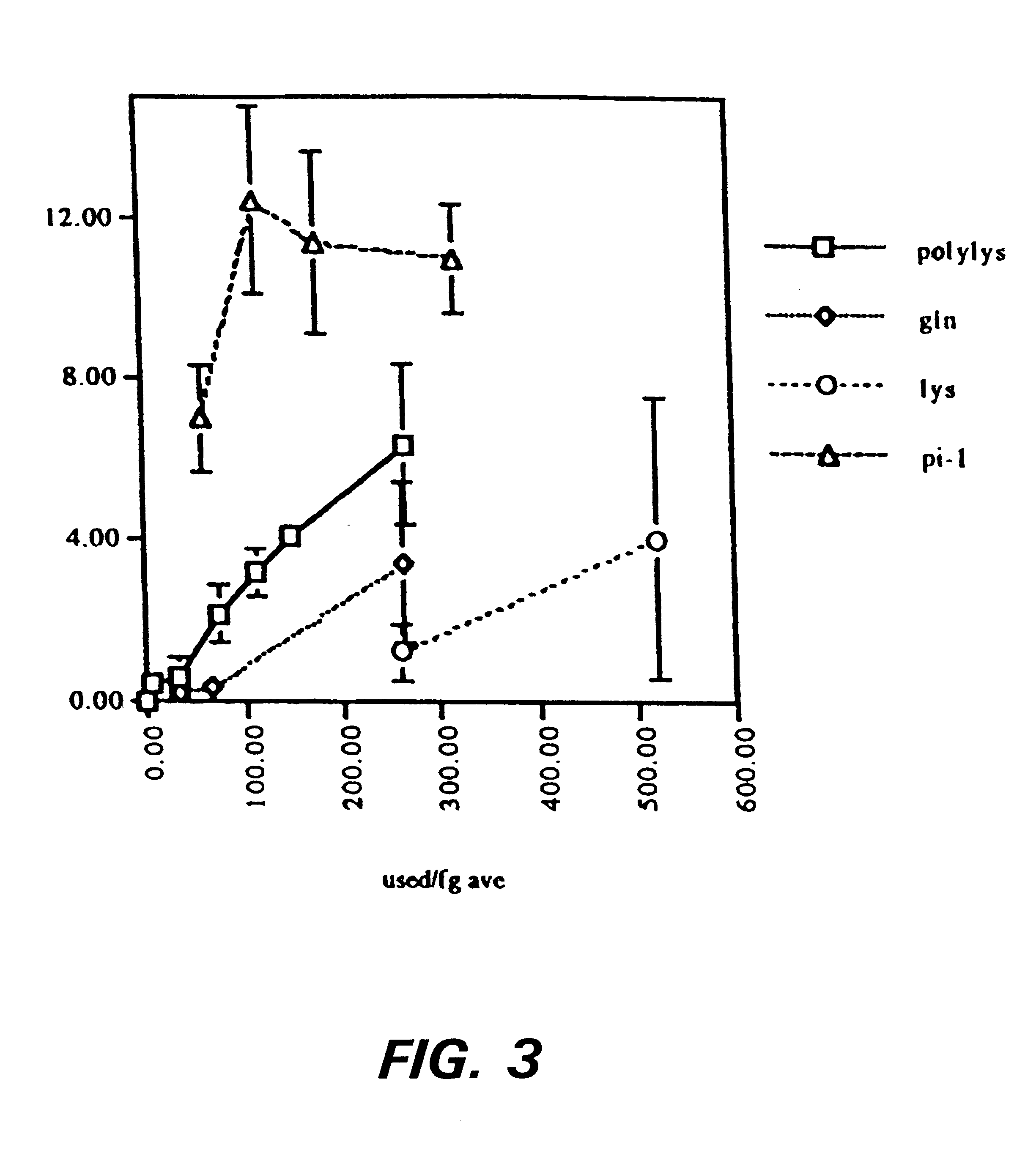
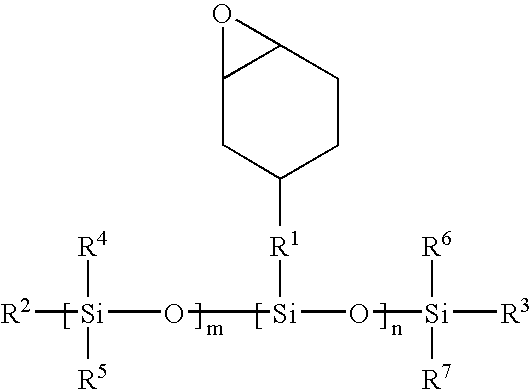
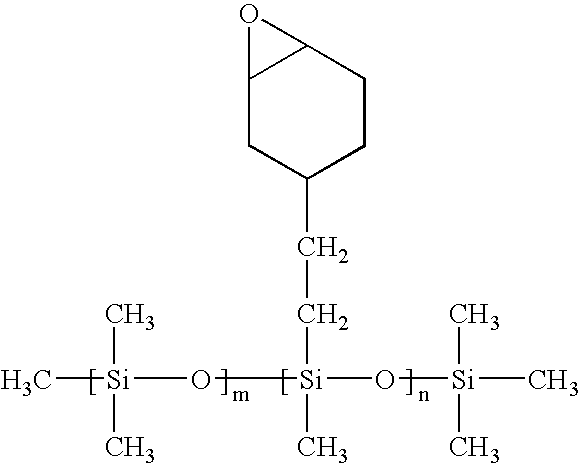
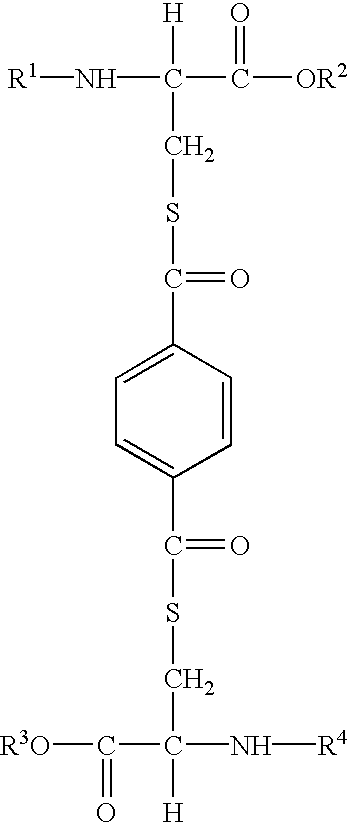
Methods for producing, films comprising, and methods for using heterogeneous crosslinked protein networks
InactiveUS6989437B2Efficiently formedCosmetic preparationsHydrolysed protein ingredientsProtein networkSilicone
Methods for producing biocompatible heterogeneous proteinaceous networks crosslinked with a heterogeneous crosslinking agent, and novel heterogeneous crosslinked networks. Preferred heterogeneous crosslinking agents are silicone-based.
Owner:KERAPLAST TECH LTD
Methods for producing, films comprising, and methods for using heterogenous crosslinked protein networks
Owner:KERAPLAST TECH LTD
Method for predicting miRNA [micro-RNA (ribonucleic acid)] target proteins of miRNA regulation protein interaction networks
InactiveCN106529203AConvenient researchData visualisationSystems biologyProtein targetProtein insertion
The invention discloses a method for predicting miRNA [micro-RNA (ribonucleic acid)] target proteins of miRNA regulation protein interaction networks. The method includes steps of building three sub-networks including a human protein-protein interaction network on the basis of HIPPIE, a miRNA-target protein network on the basis of mirTARbase and a miRNA-miRNA network on the basis of target protein overlapping structures; combining the three sub-networks with one another according to acquisition numbers of proteins and ID (identification) numbers of miRNA molecules in miRbase databases and building fusion miRNA-target protein association relationship networks; representing miRNA-target protein association features on the basis of guilt-by-association principles, building classification prediction models by the aid of random forest and predicting potential interaction association relationships between miRNA and the target proteins. The method has the advantages that research on many-to-many relationships of the miRNA regulation target proteins can be effectively carried out, and accordingly the method has high application value.
Owner:SYSU CMU SHUNDE INT JOINT RES INST +2
Method of miRNA function recognition based on multi-genomics
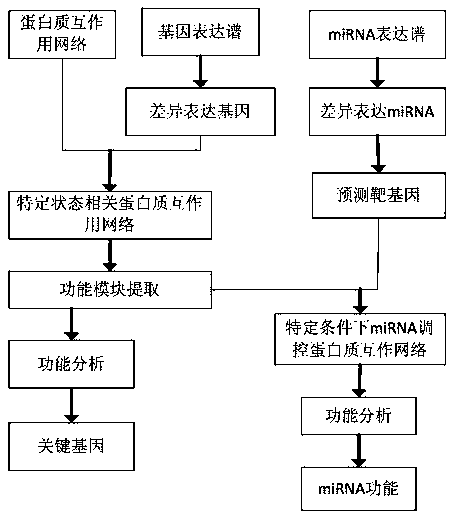
The invention relates to a miRNA function recognition method based on multi-genomics, and relates to a miRNA function recognition method based on multi-genome. The present invention aims to solve theproblem of low accuracy of miRNA function recognition in the prior art. The method of the invention comprises: analyzing differentially expressed genes through gene expression profiles; constructing disease-or drug-related protein networks; selecting functional modules of the constructed protein network related to disease or drug; performing enrichment analysis of the selected functional modules to determine the key genes in the functional modules; analyzing differentially expressed miRNAs by miRNA expression profiles to predict the target genes of differentially expressed miRNAs; performing construction of miRNA-regulated disease-or drug-related protein networks; performing functional enrichment analysis on the nodal genes of the constructed miRNA-regulated disease or drug-related proteinnetwork to identify the function of miRNA. The invention is used in the field of bioinformatics.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY
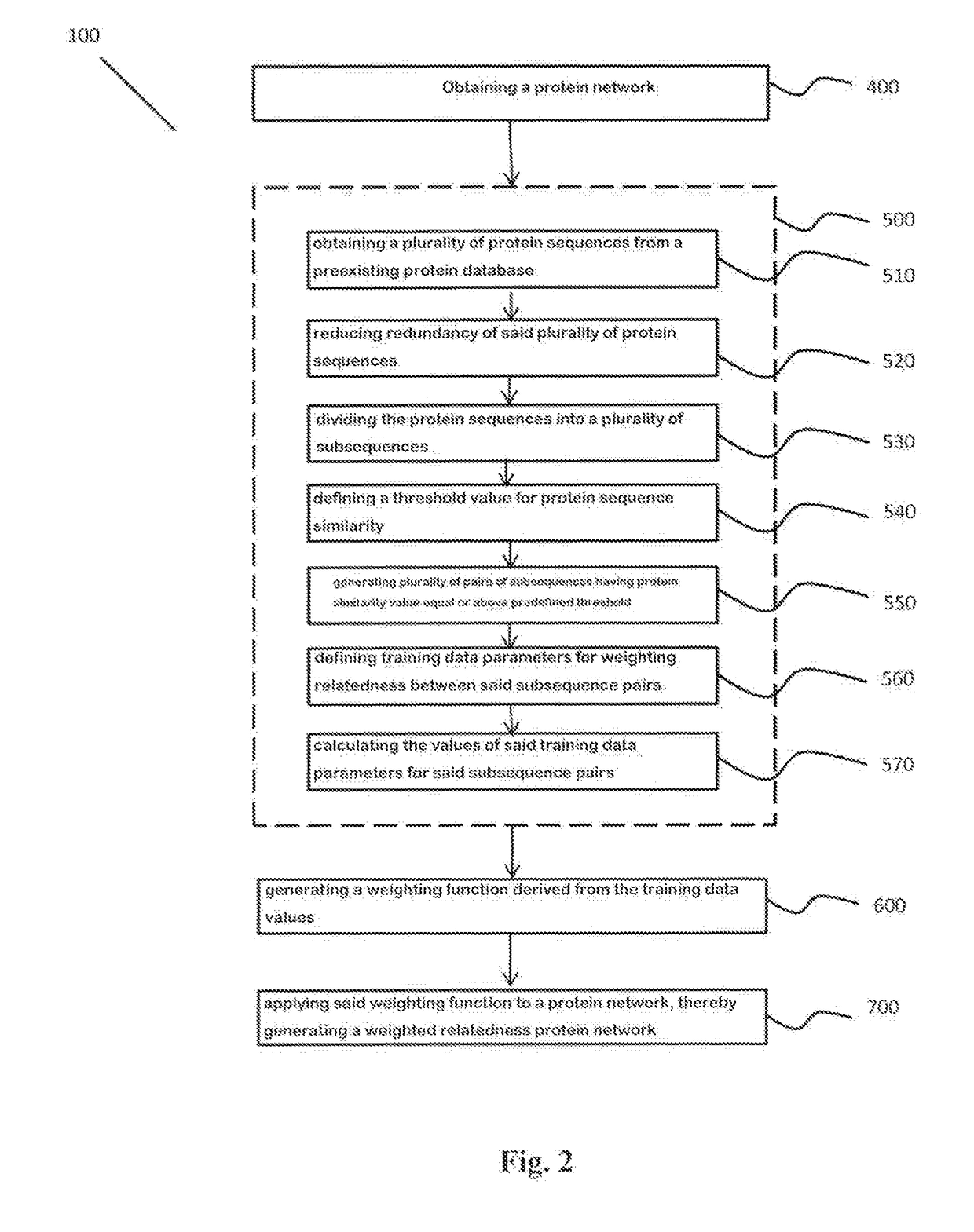
System and method for generating detection of hidden relatedness between proteins via a protein connectivity network
InactiveUS20170098030A1Improve predictive performanceBiostatisticsMachine learningTARP ProteinData value
Systems and methods are for generating a weighted relatedness protein network. The method includes steps of obtaining a protein network; generating training data; generating a weighting function derived from the training data values; and applying the weighting function to a protein network, thereby generating a weighted relatedness protein network. The protein network may be applied for prediction of protein properties by detection of relatedness with annotated sequences.
Owner:OFEK ESHKOLOT RES & DEV
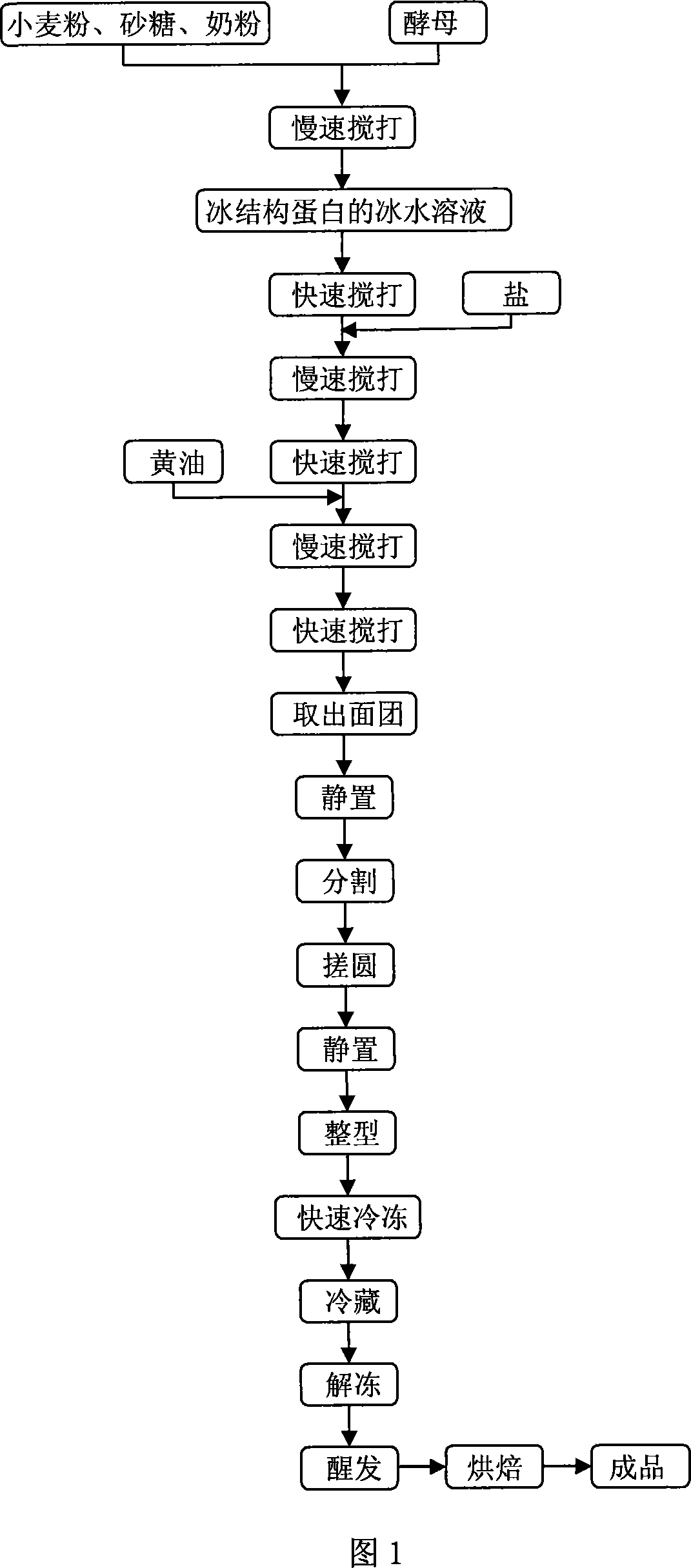
Method for producing freezing dough through the antifreezing zymolysis of ice structure protein
InactiveCN101133751AReduce recrystallizationAvoid growing upDough treatmentPre-baking dough treatmentYeastIce water
The present invention relates to a method for producing frozen dough by using ice-structure protein and utilizing a certain antifreezing fermentation process, belonging to the field of food processing technology. Said production method includes the following steps: adding wheat flour, granulated sugar, milk powder and yeast into a stirring apparatus, slowly beating and uniformly stirring them to obtain their mixture; dissolving ice-structure protein in ice water and adding them into the above-mentioned mixture, beating until the dough is formed into gluten film; adding salt and butter, beating them until the dough is formed into uniform and transparent film, taking out dough, standing still, cutting, rolling, further standing still, shaping and placing the dough into a refrigerator until the dough is completely hardened, sealing and storing; taking out frozen dough and proving so as to obtain the invented finished product.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for recognizing protein network compound based on semantic density
InactiveCN104992078AReduce time complexityShort timeSpecial data processing applicationsData setGene ontology
The invention discloses a method for recognizing a protein network compound based on a semantic density, which is specifically implemented at the steps that all the protein properties in a network data set are searched in a gene ontology base GO as for a protein-protein interaction network data set without a weight; based on searching results, similarity of connected proteins in the network data set is calculated by a semantic similarity calculation method based on gene ontology; according to obtained similarity results, the given protein-protein interaction network data set is converted into an undirected network data set with a weight, wherein nodes represent the proteins, borders stand for interactions among the proteins, and the similarity among the proteins is the weight of the border; and the protein compound can be recognized from a protein-protein interaction network, wherein recognition accuracy is high and time complexity is low.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Leavened products made from non-wheat cereal proteins
InactiveUS20090304861A1Stress resistantProtein composition from fishDough treatmentAdditive ingredientProtein-protein complex
Gluten-free baked products, particularly gluten-free bread products, which exhibit properties comparable those made with wheat flour. Compositions and methods for preparation of gluten-free baked products. A conditioned protein or protein composite which functions to replace gluten in gluten-free flour. The conditioned protein comprises one more non-wheat cereal storage proteins, particularly prolamins, optionally, but preferably in combination with one or more co-proteins which function to facilitate formation and stabilize formation of a protein network, e.g., β-sheet network, that facilitates retention of CO2 for leavening. More specifically, protein composites of zein and or other non-wheat prolamins with co-proteins including casein, elastin or mixtures thereof conditioned at temperatures above the glass transition temperature of the protein mixture provide improved ingredients for preparation of gluten-free breads and other baked products. Sorghum or maize mutant flours with prolamins available for viscoelastic protein formation may also be used.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Combinatorial multidomain mesoporous chips and a method for fractionation, stabilization, and storage of biomolecules
ActiveUS20110065207A1High protein recoveryLow protein amountElectrolysis componentsSamplingFractionationTherapeutic effect
A new fractionation device shows desirable features for exploratory screening and biomarker discovery. The constituent MSCs may be tailored for desired pore sizes and surface properties and for the sequestration and enrichment of extremely low abundant protein and peptides in desired ranges of the mass / charge spectrum. The MSCs are effective in yielding reproducible extracts from complex biological samples as small as 10 μl in a time as short as 30 minutes. They are inexpensive to manufacture, and allow for scaled up production to attain the simultaneous processing of a large number of samples. The MSCs are multiplexed, label-free diagnostic tools with the potential of biological recognition moiety modification for enhanced specificity. The MSCs may store, protect and stabilize biological fluids, enabling the simplified and cost-effective collection and transportation of clinical samples. The MSC-based device may serve as a diagnostic tool to complement histopathology, imaging, and other conventional clinical techniques. The MSCs mediated identification of disease-specific protein signatures may help in the selection of personalized therapeutic combinations, in the real-time assessment of therapeutic efficacy and toxicity, and in the rational modulation of therapy based on the changes in the protein networks associated with the prognosis and the drug resistance of the disease.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
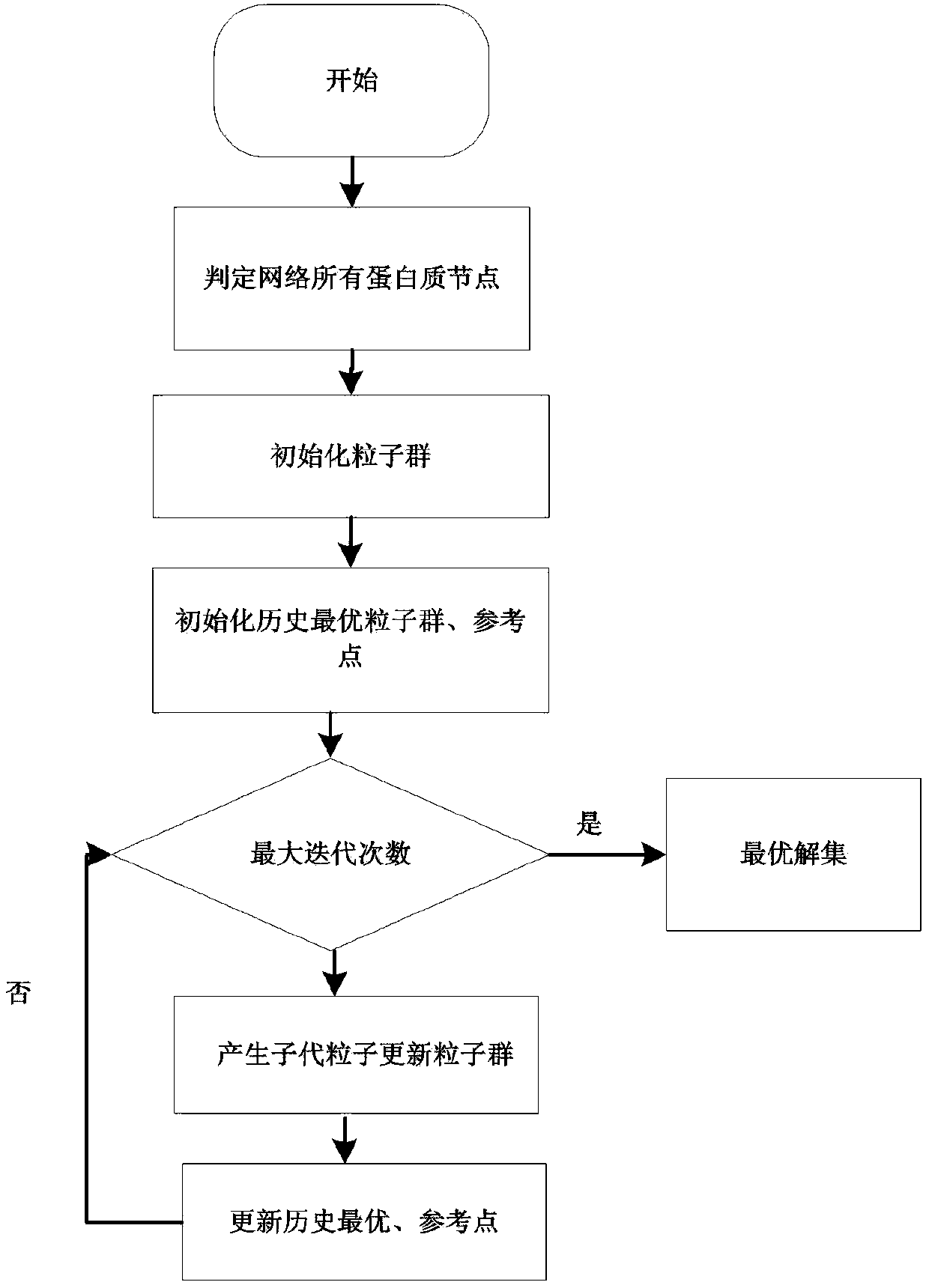
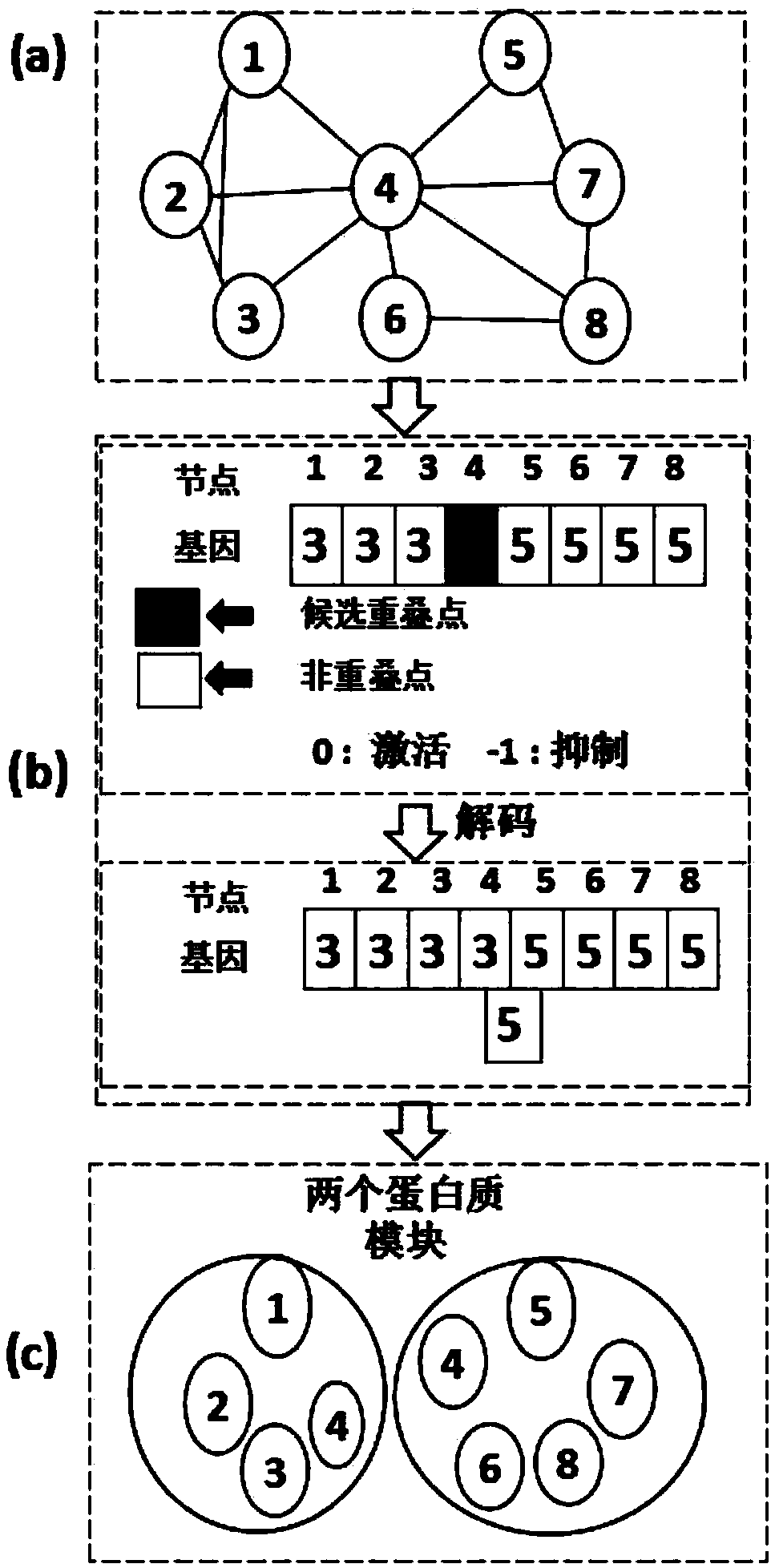
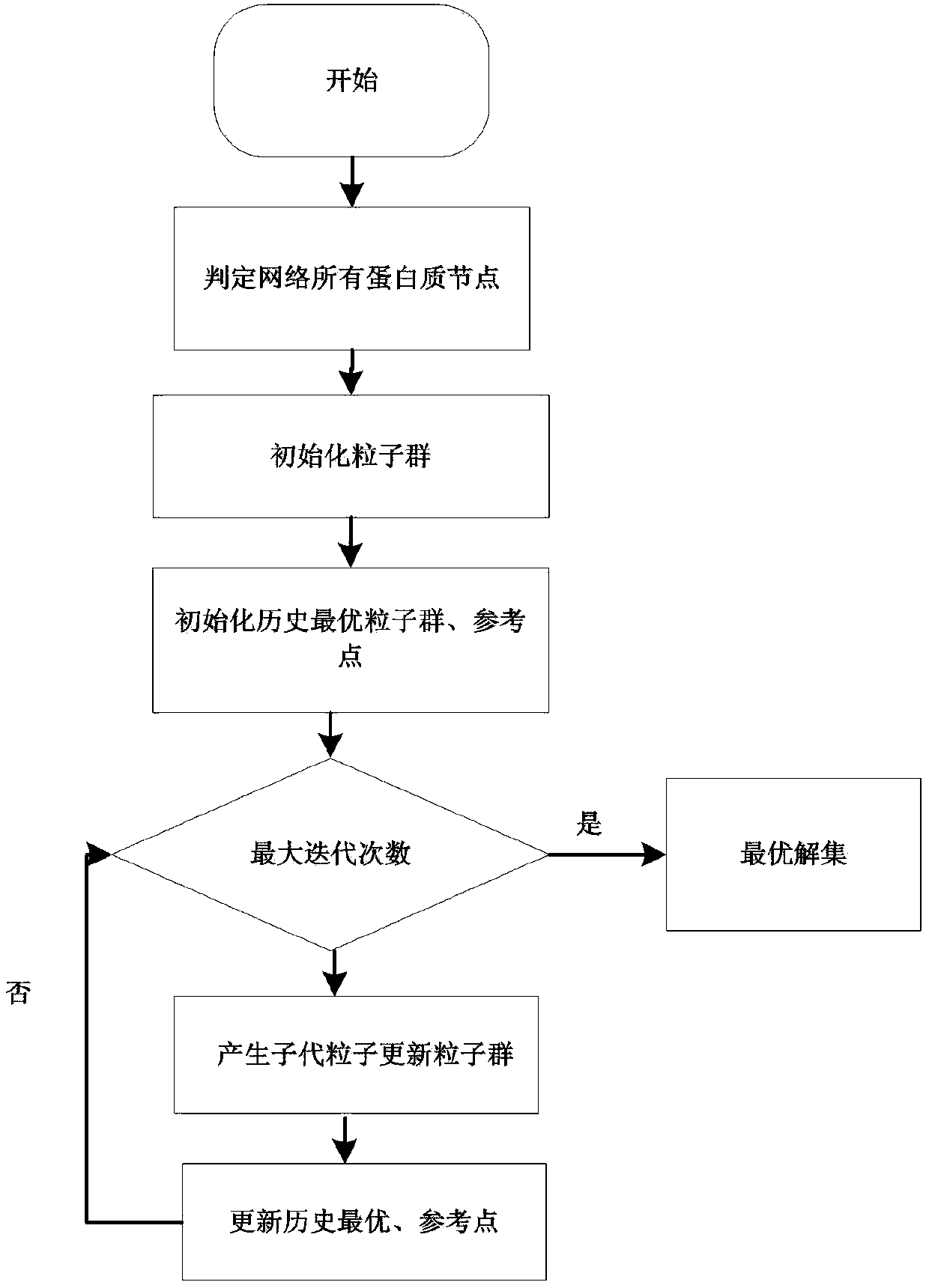
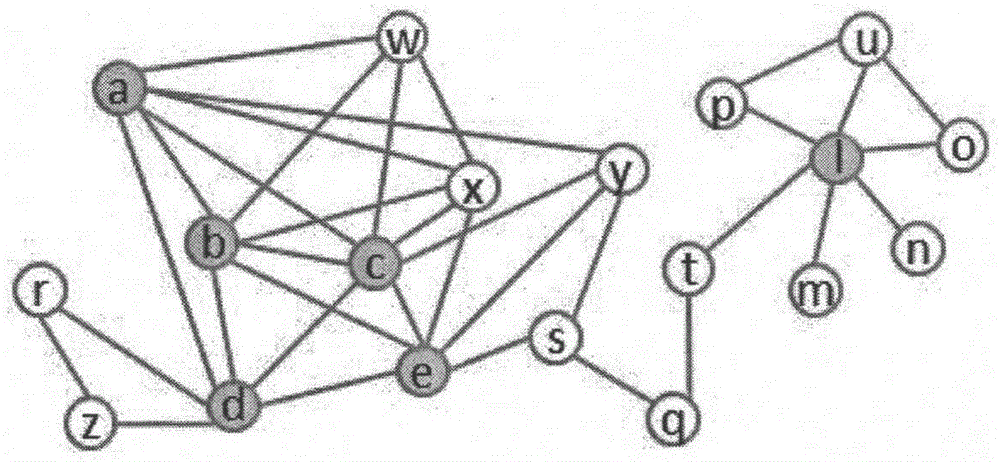
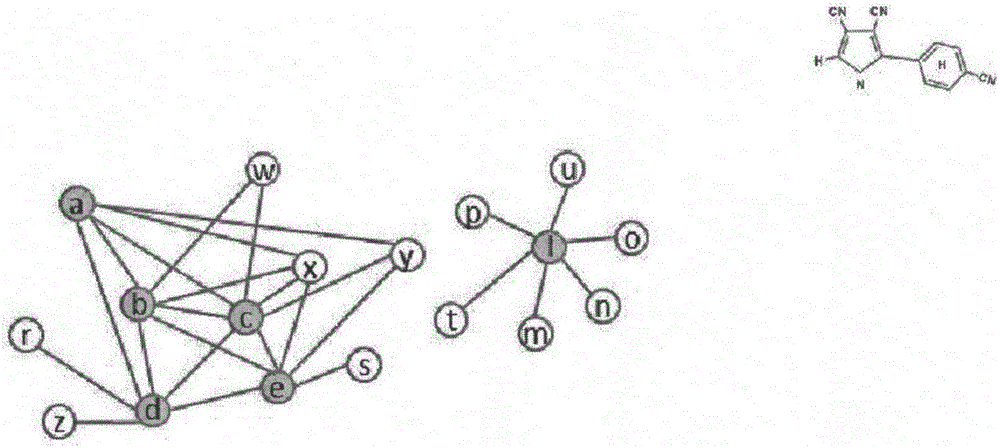
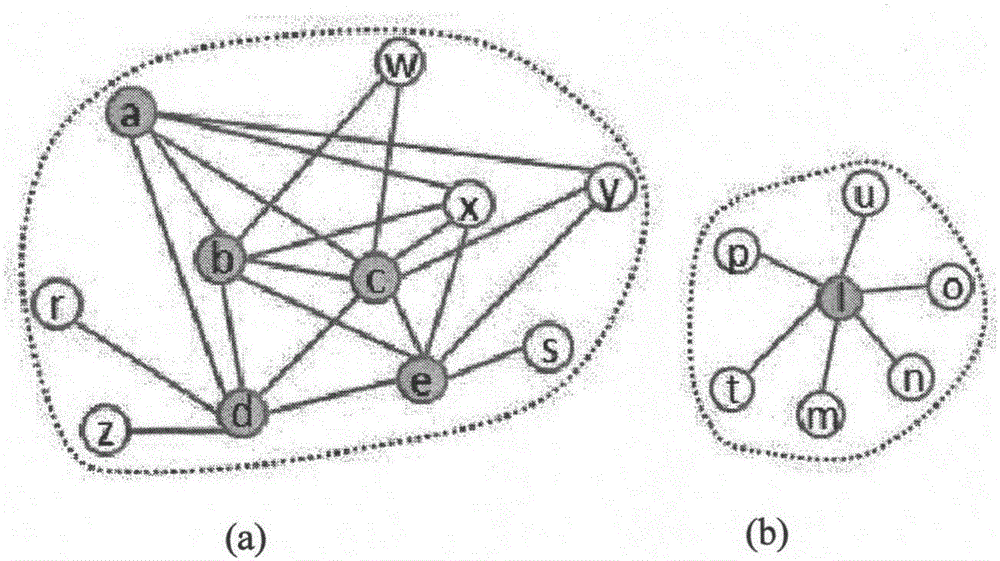
Protein network module mining method based on multi-target optimization
ActiveCN106991295AEasy to divideImprove digging efficiencyProteomicsGenomicsAlgorithmProtein function
The invention discloses a protein function module recognizing method based on a multi-target optimization algorithm. The protein function module recognizing method includes the steps that a network protein node is judged to be a nonoverlapping protein node and a candidate overlapping protein node, the problem of protein network module function mining is solved through hybrid coding, particle swarm initialization and particle swarm evolution. The monotony problem of protein network function module combinations can be solved, multiple module combinations are provided for a user to select, and therefore function module mining accuracy and effectiveness are improved.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Protein composite identifying method based on graph model
The invention provides a protein composite identifying method based on a graph model; a protein interactive network of a given species is regarded as a network drawing =(V, E), wherein V is combining point of protein, and E is set of protein-protein interaction side; the self-connecting side and the repeat side in a network are removed from the set of all sides; the method includes steps of firstly acquiring a nuclear protein vertex set of the protein composite, and then expanding a first-order neighbor of the edge combining point thereof, and forming a graph model; judging its connectivity according to characteristics of the graph model, and finding out all dense subgraphs, namely, protein composite. The method provided by the invention can regard the graph model as the nucleus of the protein composite; through investigating and expanding the first-order neighbor combining point of the graph model, the protein composite is identified; an algorithm provided by the invention is applied to the known yeast protein network; the experimental result indicates that the algorithm can identify multiple protein composites with biological significance, and the algorithm is not sensitive to the input parameter.
Owner:SHANGHAI DIANJI UNIV
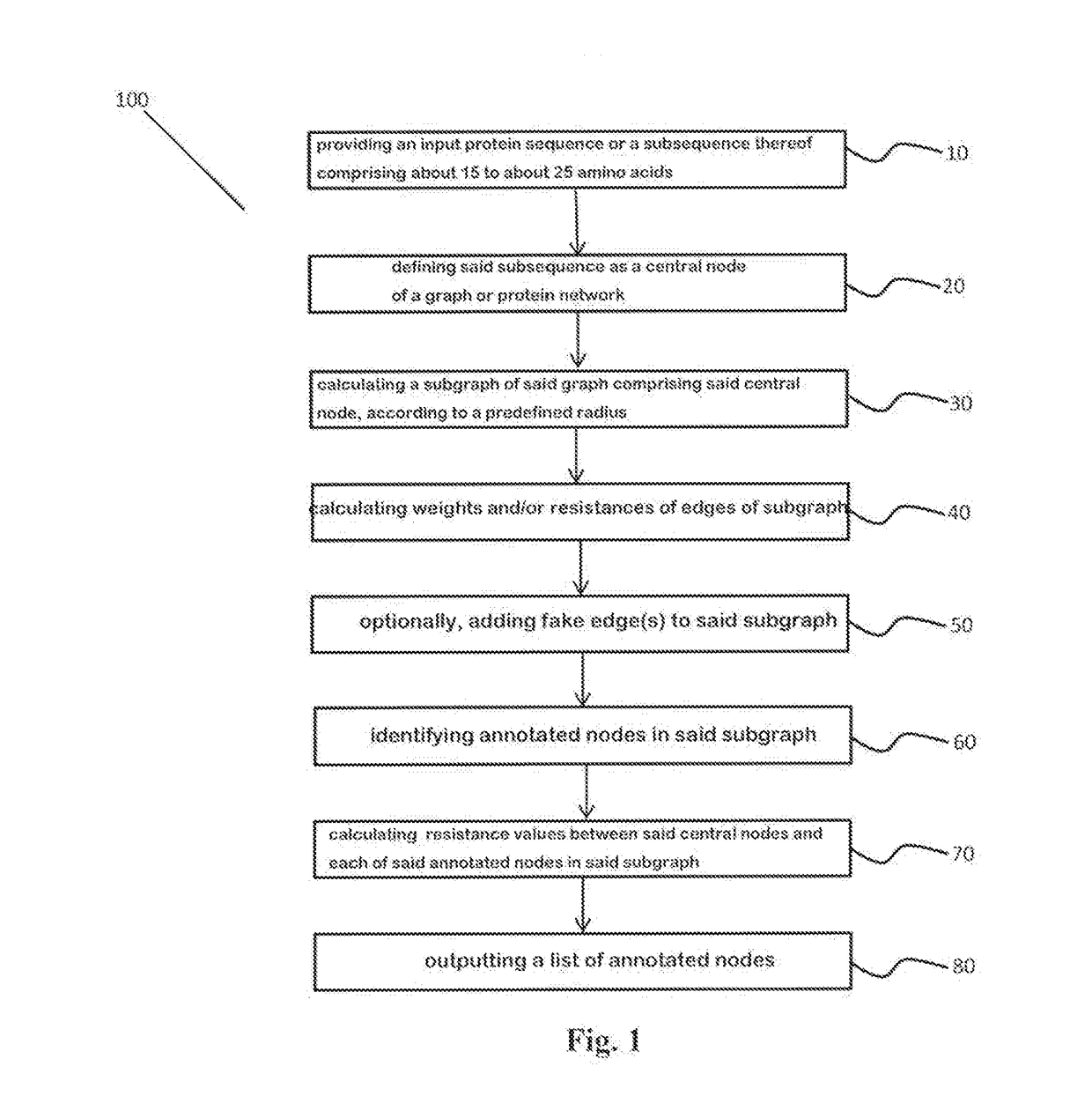
Protein design method and system
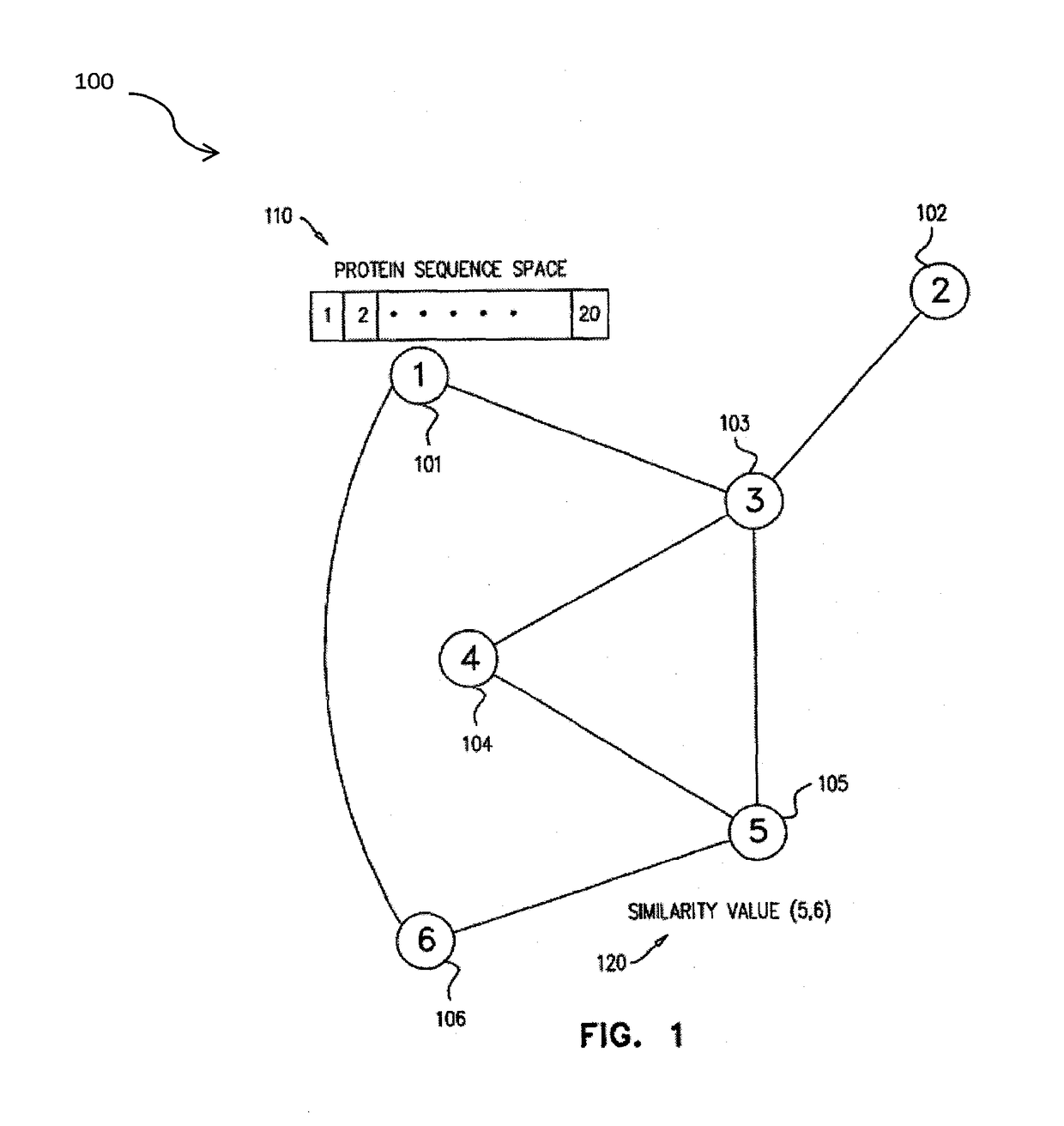
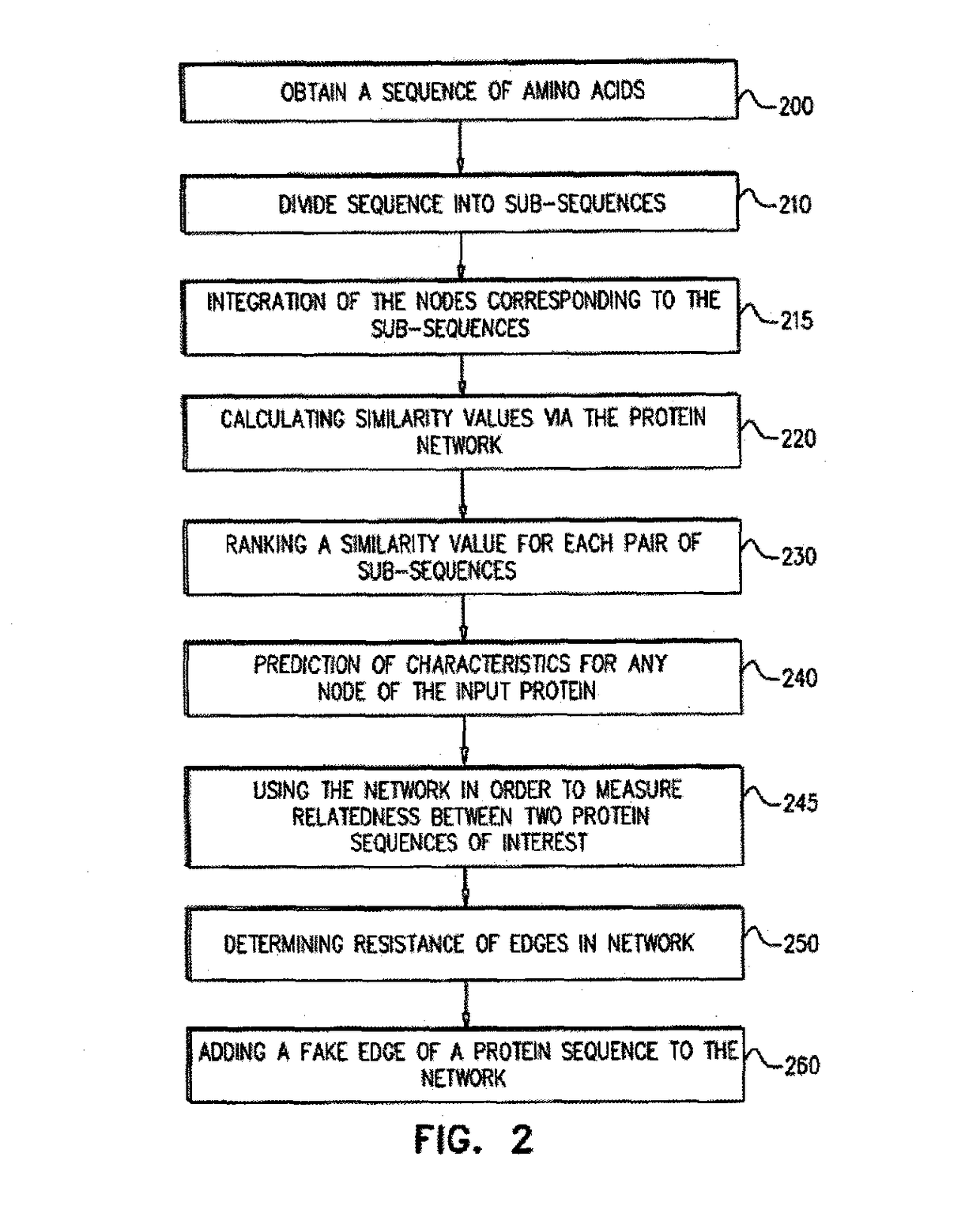
A method for annotating a protein sequence or a subsequence thereof includes the steps of providing an input protein sequence or a subsequence thereof. The subsequence is defined as a central node of a graph or protein network. A subgraph of the graph is calculated including the central node, according to a predefined radius and weights and / or resistances of edges of the subgraph are also calculated. Annotated nodes in the subgraph are identified. Resistance values between the central nodes and each of the annotated nodes in the subgraph are calculated and a list of annotated nodes is outputted. Each of the annotated nodes has a characteristic calculated resistance value to the central node of the input protein sequence.
Owner:OFEK ESHKOLOT RES & DEV
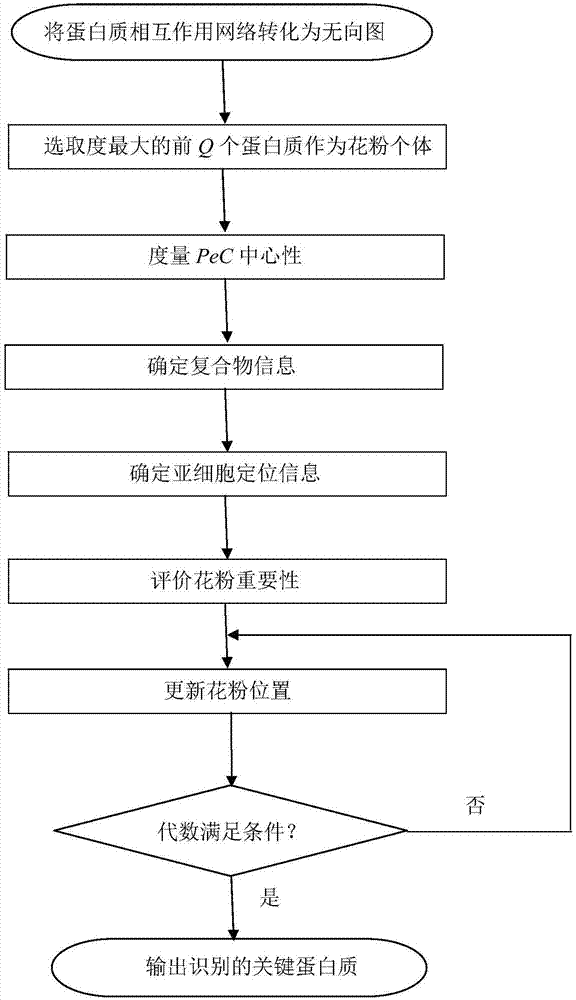
Method for identifying key protein by adopting improved flower pollination algorithm
ActiveCN107885971AImprove accuracyUnderstanding Growth Regulatory ProcessesSystems biologySpecial data processing applicationsUndirected graphPollen
The invention discloses a method for identifying a key protein by adopting an improved flower pollination algorithm. A protein-protein interaction network is converted into an undirected graph, previous Q proteins having the largest choice degree serve as pollen individuals, the PeC centrality is measured, compound information is determined, subcellular localization information is determined, pollen significance is evaluated, a pollen position is updated, and an identified key protein is output. The topological attributes of the protein network are considered and the biological characteristicsof the protein network are fused during evaluation of the pollen significance, and the key protein can be accurately identified. A simulation experiment result shows that the index properties such asaccuracy, specificity and sensitivity are more excellent. Compared with other key protein identifying methods, the key protein identifying process is achieved by combining with the topological attributes and biological characteristics of the protein network, and the key protein identifying accuracy is improved.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
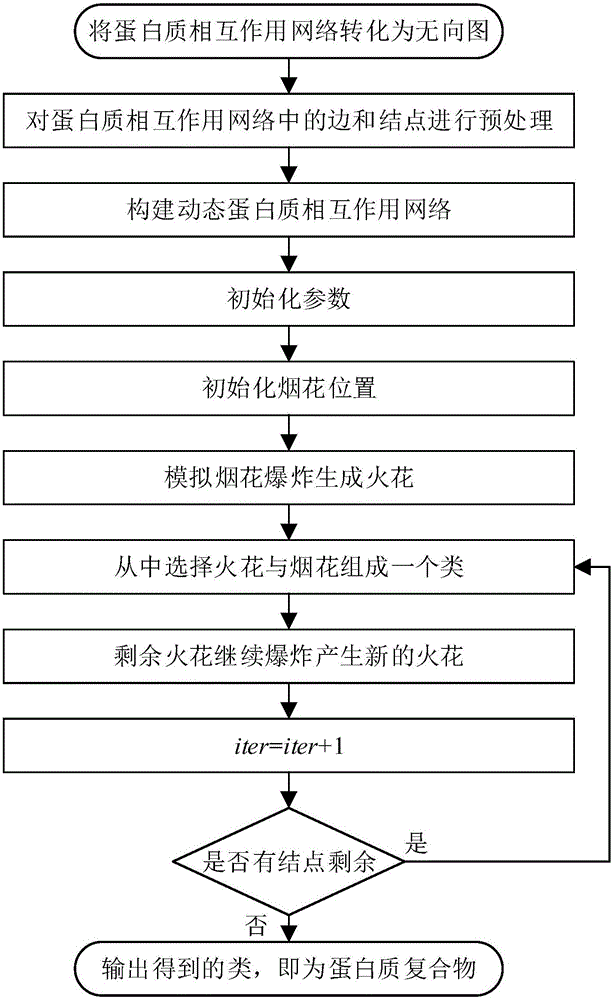
Method of adopting firework algorithm to recognize protein complex
InactiveCN106228036AImprove accuracyEfficient identificationBiostatisticsSpecial data processing applicationsAccessory structureFireworks
The invention provides a method of adopting a firework algorithm to recognize a protein complex. The method includes following steps: converting a protein interaction network into an undirected graph; pre-treating sides and nodes of the protein interaction network; building a dynamic protein interaction network; setting parameters; initializing positions of fireworks; simulating firework explosion to generate spark; selecting part of good points from the spark to serve as fireworks, wherein all fireworks form a class; filtering undesirable classes; outputting a finally-acquired class. The method takes dynamic nature of a protein network and locality and globality of a core-accessory structure inside the protein complex and the protein interaction network into consideration, and the protein complex can be recognized accurately. Simulation experiment results show that performance of indexes like accuracy and recall ratio is excellent. Compared with other clustering methods, the method has the advantages that characteristics of the protein interaction network and the protein complex are combined to recognize the protein complex, and recognition accuracy of the protein complex is improved.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
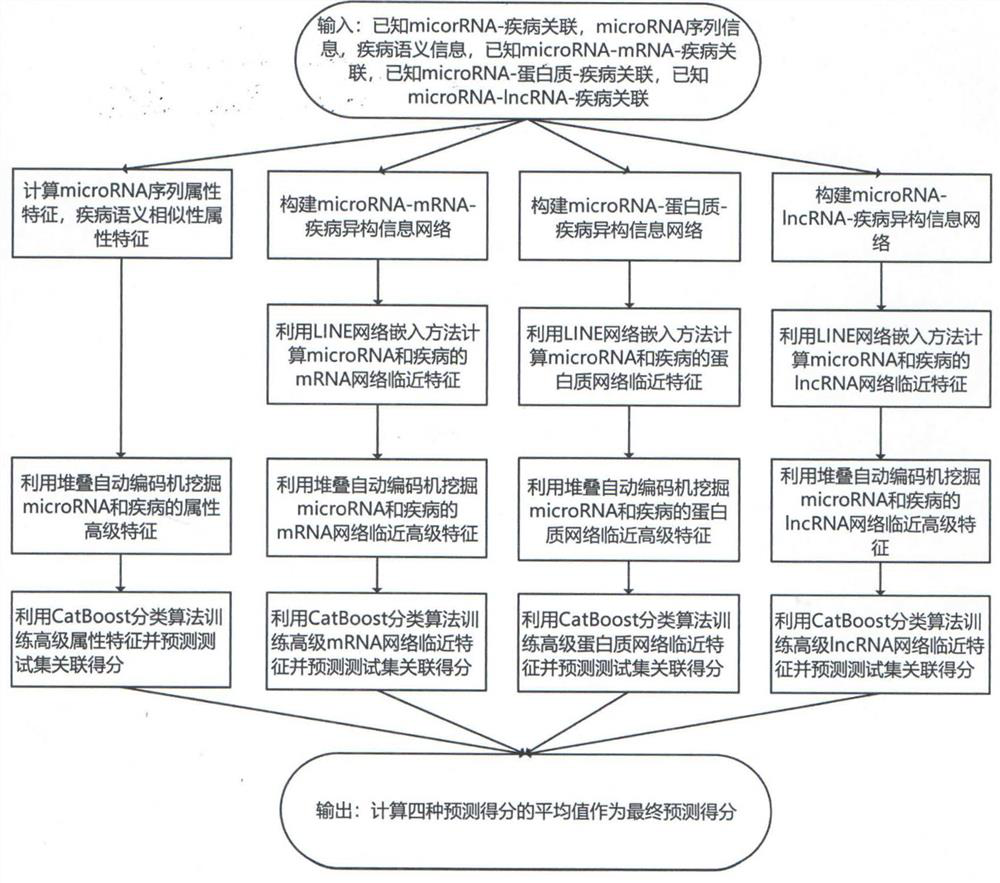
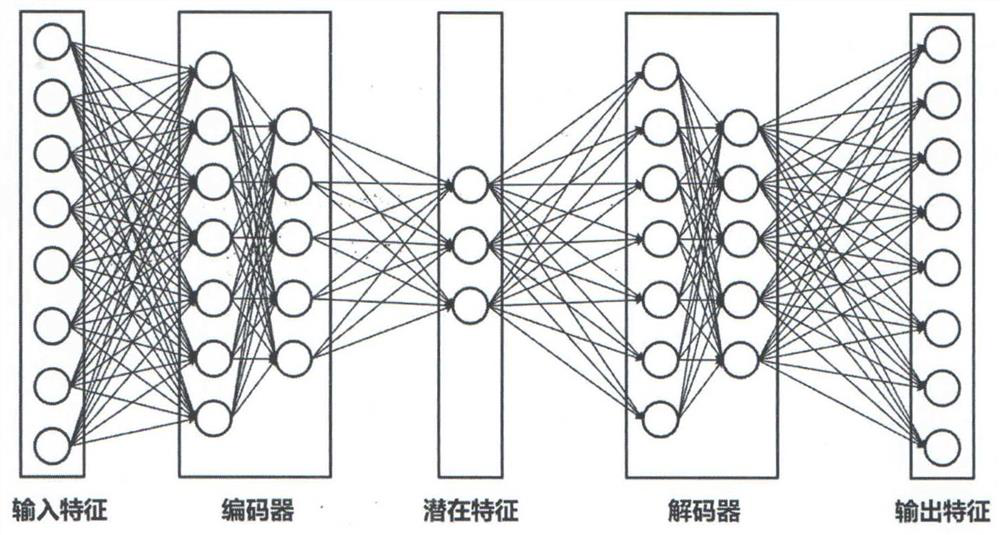
MicroRNA-disease association prediction method based on multi-mode stacking automatic coding machine
ActiveCN112837753AEfficient forecastingReduce complexityBiostatisticsCharacter and pattern recognitionMicroRNAPrediction score
The invention discloses a microRNA-disease association prediction method based on a multi-mode stacking automatic coding machine. The method comprises: forming microRNA sequence features and disease semantic similarity features; constructing a microRNA-protein-disease network, a microRNA-mRNA-disease network and a microRNA-lncRNA-disease network, and respectively obtaining network adjacent characteristics between microRNA and protein, between disease and protein, between mRNA and lncRNA and between disease and lncRNA by using a LINE network embedding method; mining, by using a multi-mode stacking automatic coding machine, the advanced abstract features of four features (self attribute features, protein network adjacent features, mRNA network adjacent features and lncRNA network adjacent features) of microRNA and diseases, thereby reducing the time complexity of a model and improving the prediction accuracy of the model; and training and predicting the processed features by using a CatBoost classifier, and taking an average value of prediction scores of the four features as a final prediction score. According to the method, the problems of high time consumption and high cost of a traditional biological experiment method are solved, so that a better classification effect is achieved, and the potential incidence relation between microRNA and diseases is predicted with higher accuracy.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Key protein identification method in network based on dynamic weighting interaction
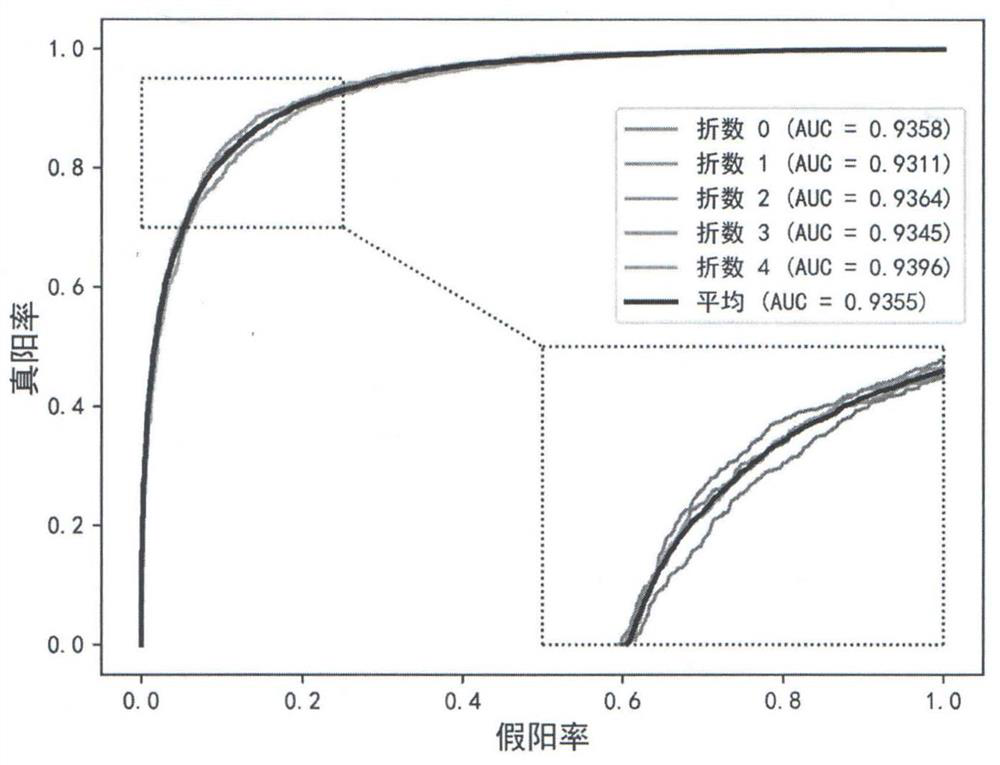
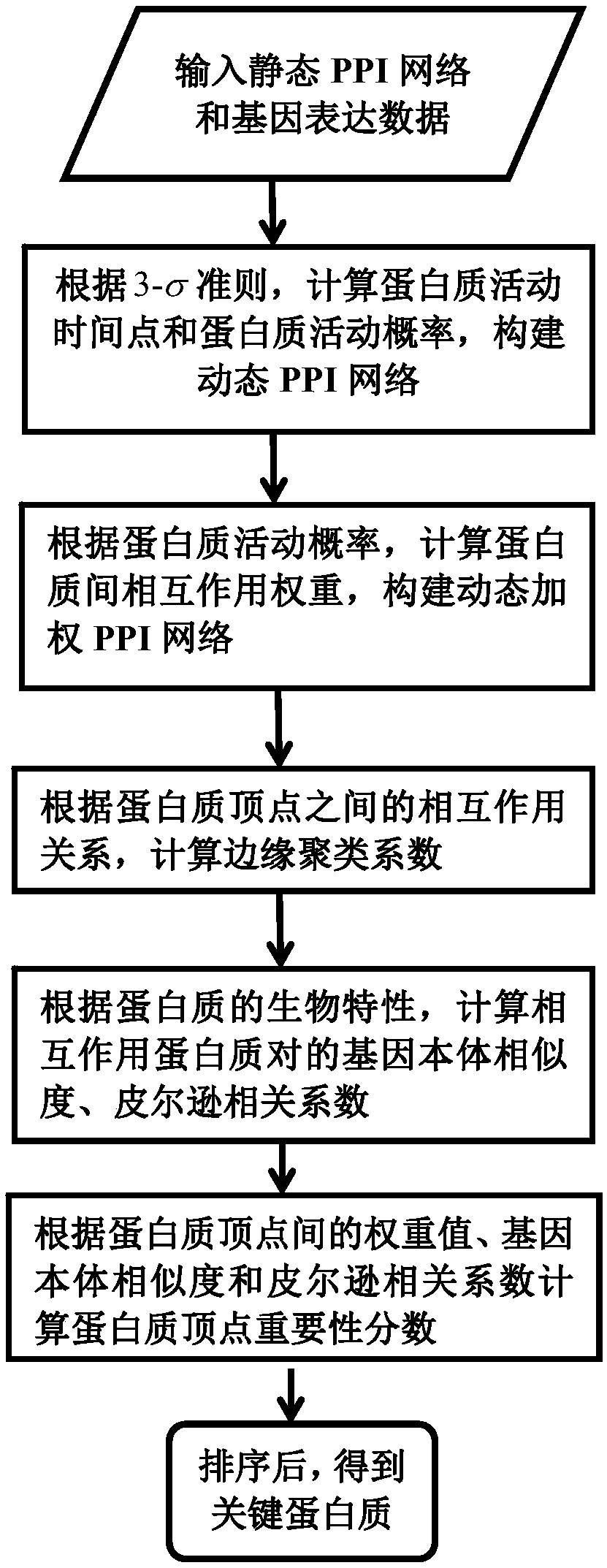
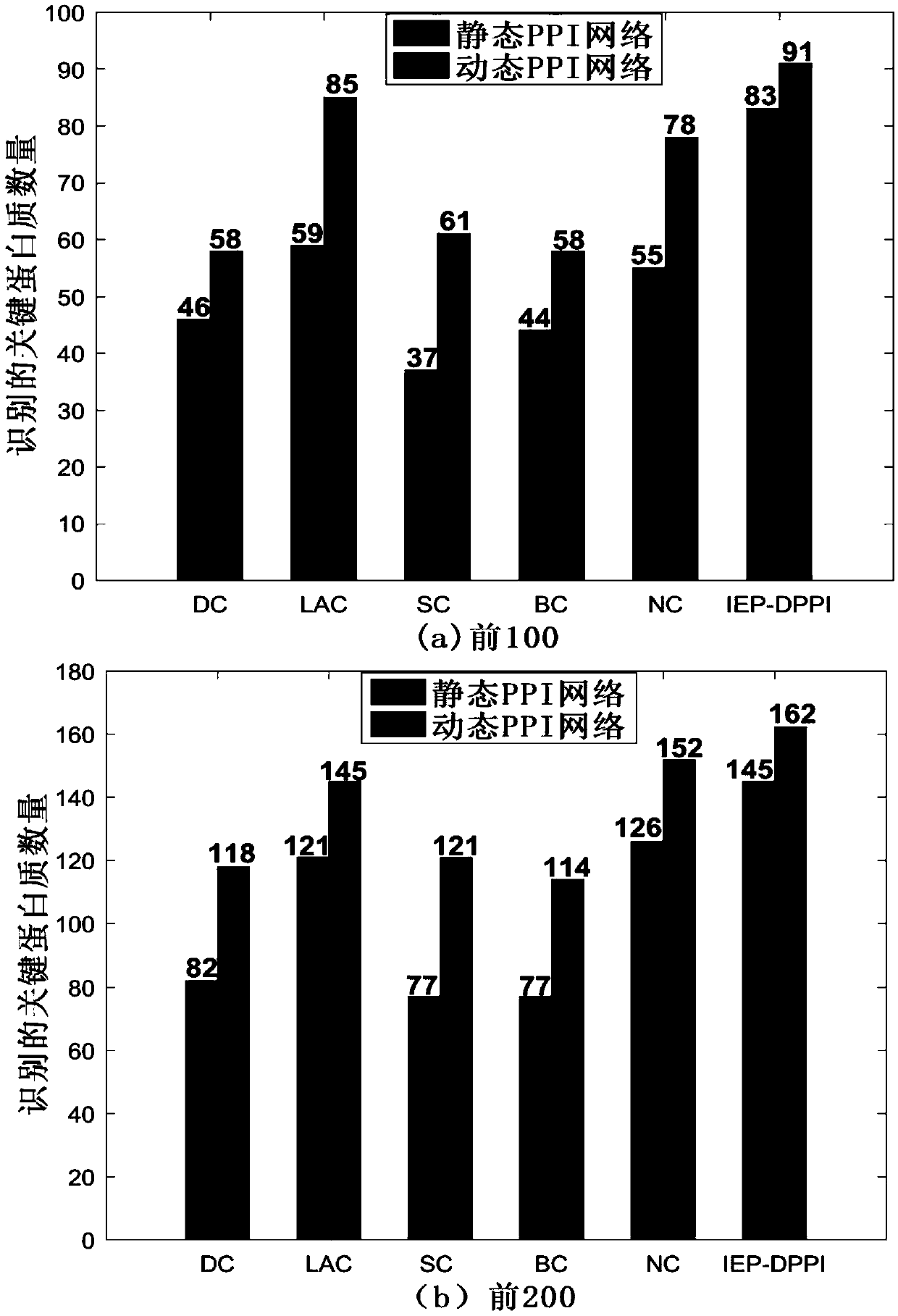
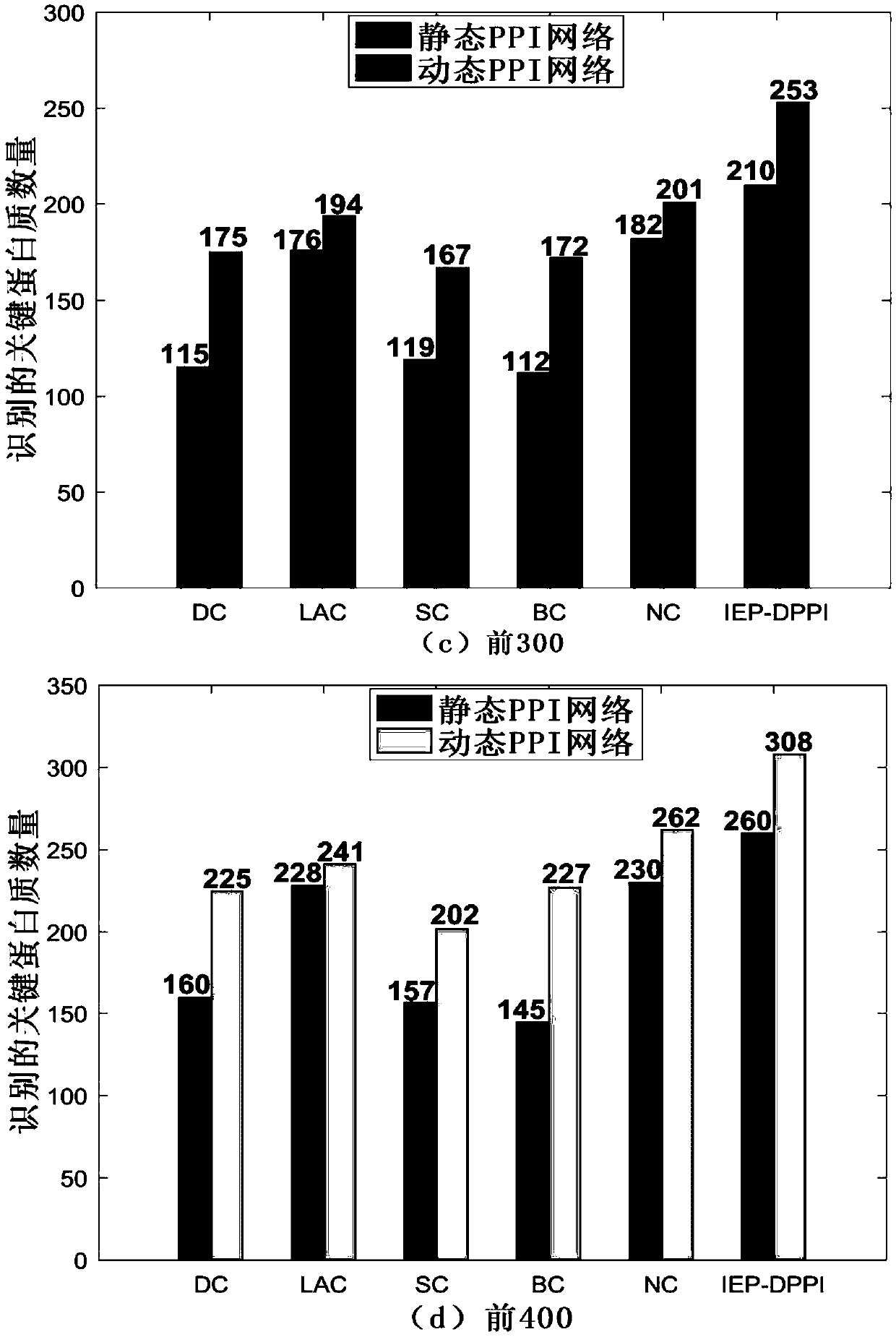
PendingCN109686402AOvercome incompletenessImprove accuracyBiostatisticsProteomicsCorrelation coefficientGene ontology
The invention discloses a key protein identification method use principle in a network based on dynamic weighting interaction. A key protein identification method comprises the steps of calculating aprotein activity time point and a protein activity probability, constructing a dynamic PPI network, then calculating a protein interaction weight according to the protein activity probability, and constructing a dynamic weighted PPI network; based on the established dynamic weighted PPI network, according to the topological characteristic and biological attribute of the protein network, calculating an edge clustering coefficient, a gene body similarity and a Pearson correlation coefficient between the interaction protein pairs; afterwards, obtaining an importance score, and performing arrangement according to the score value from largest to lowest, and outputting k proteins which correspond with the scores as a final result. The method according to the invention improves key protein identification efficiency and expands application range and practicability of the technique in a bioinformation field.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Indeterminate PPI network function module mining method based on fuzzy spectral clustering
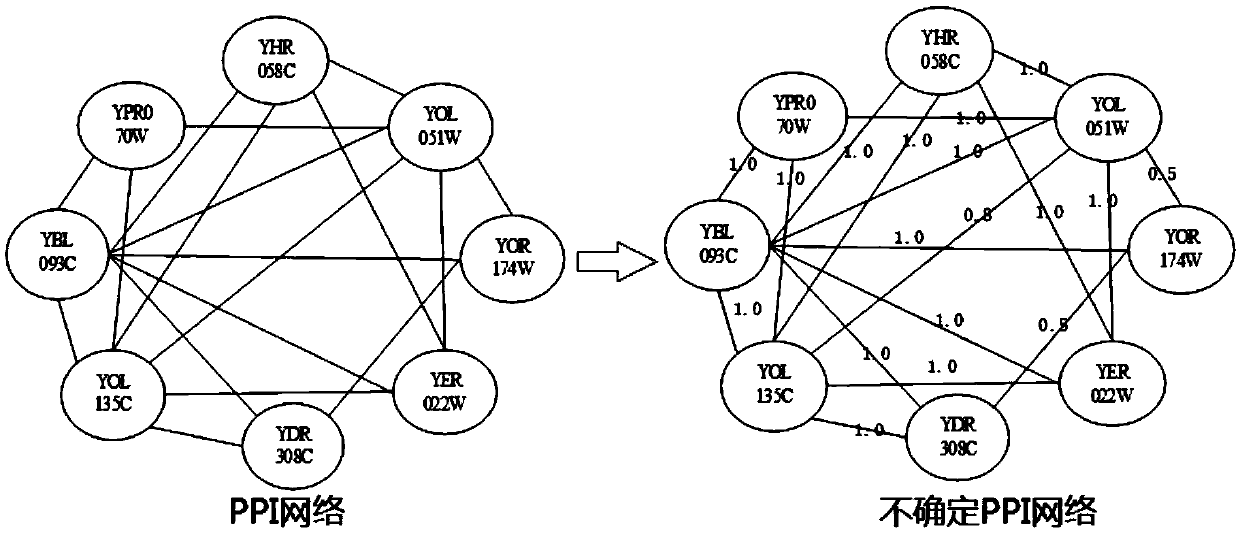
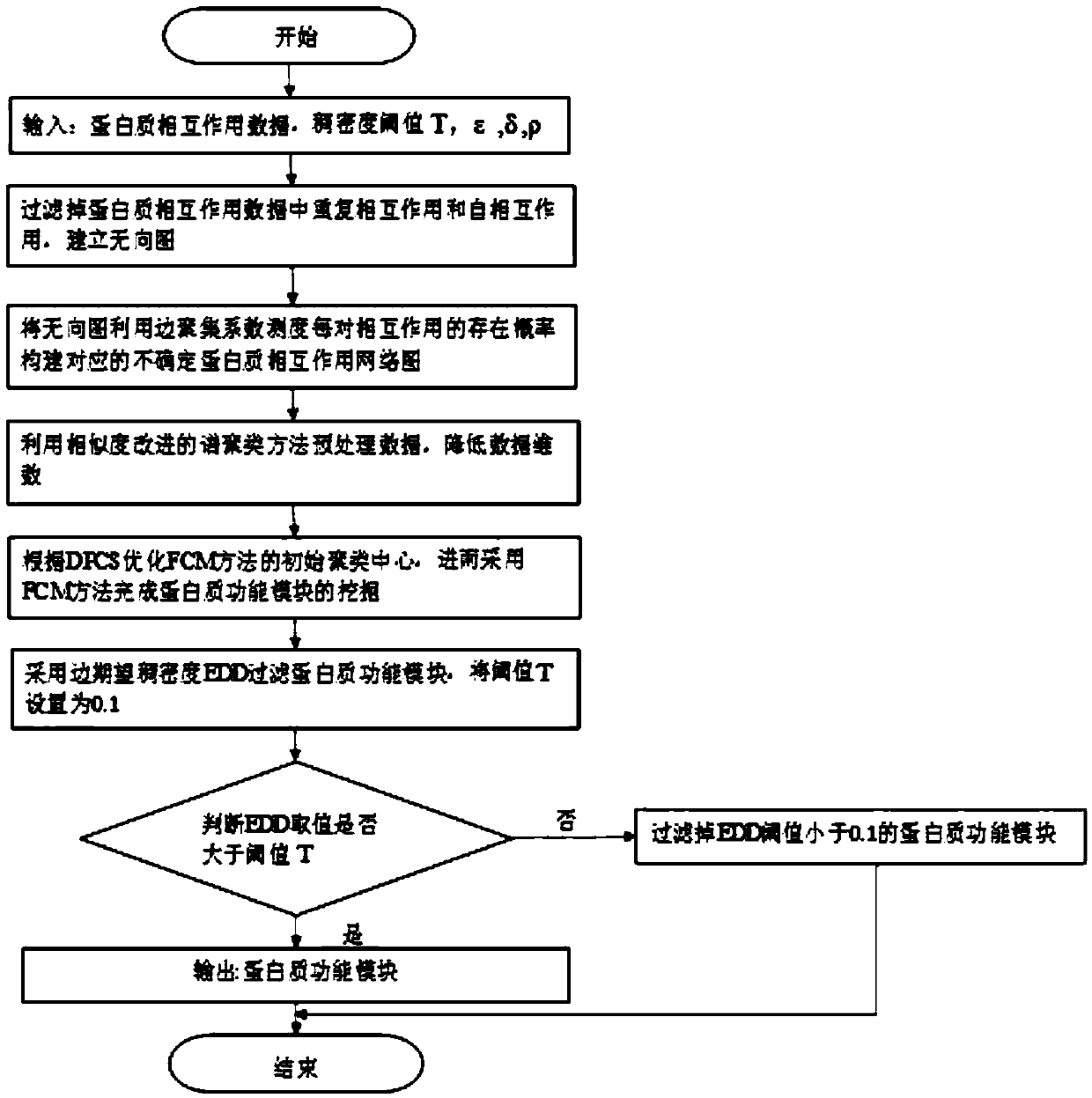
ActiveCN109545275AInstrumentsMolecular structuresSpectral clustering algorithmProtein Interaction Networks
The invention discloses an indeterminate PPI network function module mining method based on fuzzy spectral clustering. The method comprises the following steps: removing repeated interaction and self-interaction in protein-protein interaction data, measuring the interaction of each group by using an edge clustering coefficient, and constructing an indeterminate protein-protein interaction networkchart; improving the similarity measure of the spectral clustering algorithm by using popular distance and the topological properties of the protein network, and further adopting the spectral clustering algorithm to complete preprocessing on protein-protein interaction data; selecting an initial clustering center by using a DPCS strategy, based on the initial clustering center, using a fuzzy C-mean value algorithm to constantly update a clustering center and degree of membership, and then realizing the mining of a protein-protein interaction function module; filtering the mined protein-proteininteraction function module by using the edge expected density of an edge clustering coefficient fused by expected density; and outputting and predicting the mined protein-protein interaction function module.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Monoclonal antibody of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate oxidase and application thereof
ActiveCN107266576AHigh affinityStrong specificityImmunoglobulins against enzymesMaterial analysisDevelopmental stageProtein target
The invention discloses a monoclonal antibody of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate oxidase. A heavy chain variable region sequence of the monoclonal antibody contains an amino acid sequence of CDR shown as SEQ ID NO. 2, 4, and 6; and a light chain variable region sequence of the monoclonal antibody contains an amino acid sequence of CDR shown as SEQ ID NO. 9, 11, and 13. A polypeptide of the enzyme is used as an immunogen to immunize a mouse to obtain lymphocyte, a fusion cell is prepared by a hybridoma cell fusion technique, and a cell strain which can generate high affinity and high specificity and is used for detecting and identifying the enzyme is obtained. The monoclonal antibody of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate oxidase can be used for detecting the content change of the 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate oxidase in different developmental stages of fruits. The monoclonal antibody disclosed by the invention provides a tool for targeted protein study, so that deeper study on protein expression changes and protein network maps of different plant types, different strains or different development stages is realized.
Owner:艾比玛特医药科技(上海)有限公司
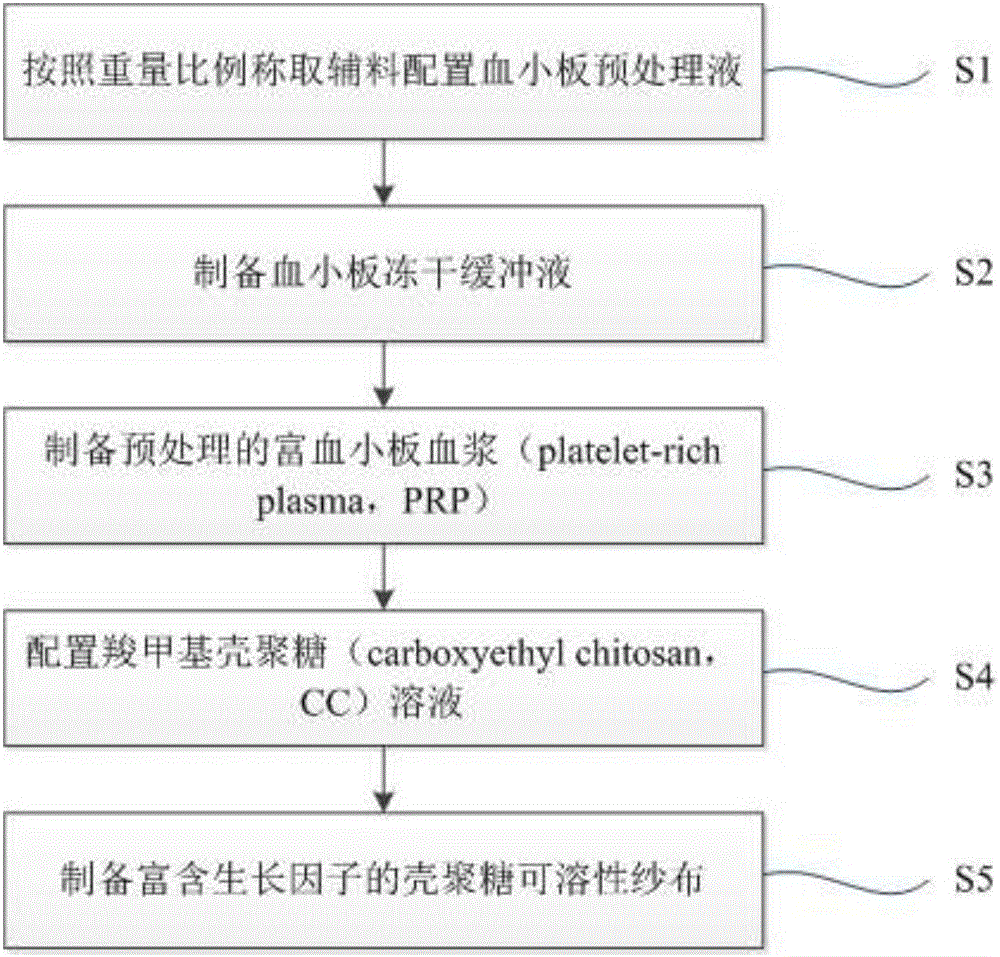
Method for preparing chitosan soluble gauze rich in growth factors
InactiveCN106729955AGrowth inhibitionPromote repairPharmaceutical delivery mechanismBandagesTissue repairSide effect
The invention discloses a method for preparing chitosan soluble gauze rich in growth factors. The method comprises the steps of S1, weighing auxiliary materials according to a weight ratio to prepare blood platelet pretreatment liquid; S2, preparing blood platelet freeze-dried buffer solution; S3, preparing pretreated blood platelet rich plasma; S4, preparing carboxymethyl chitosan solution; and S5, preparing the chitosan soluble gauze rich in growth factors. After chitosan is gelated, the blood platelet rich plasma is added to obtain the chitosan soluble gauze rich in growth factors, pore diameter is 130-160 [mu]m, a large number of growth factors and abundant fibrous protein networks are contained and can be absorbed by the human body easily, no toxic and side effects can be caused, growth of various bacteria and fungi can be restrained, more structure space is provided for cell growth, in-vivo and in-vitro release of various growth factors can be achieved, tissue repair and vascular remodeling can be achieved easily, antibacterial performance is excellent, and the chitosan soluble gauze is a novel medical and biologically hemostatic material with high cost performance.
Owner:GUANGZHOU GENERAL HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MILITARY COMMAND
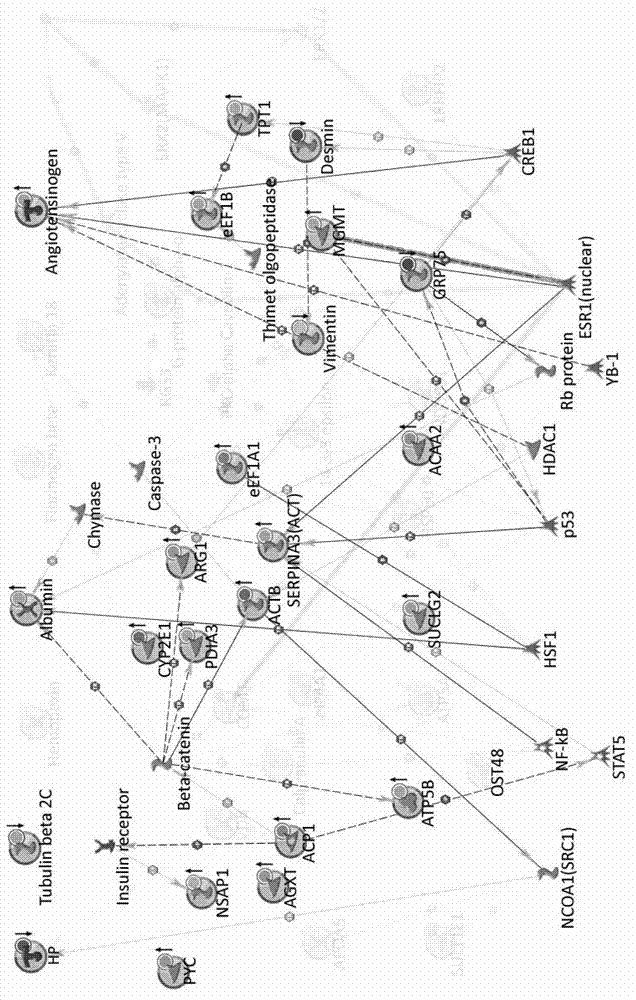
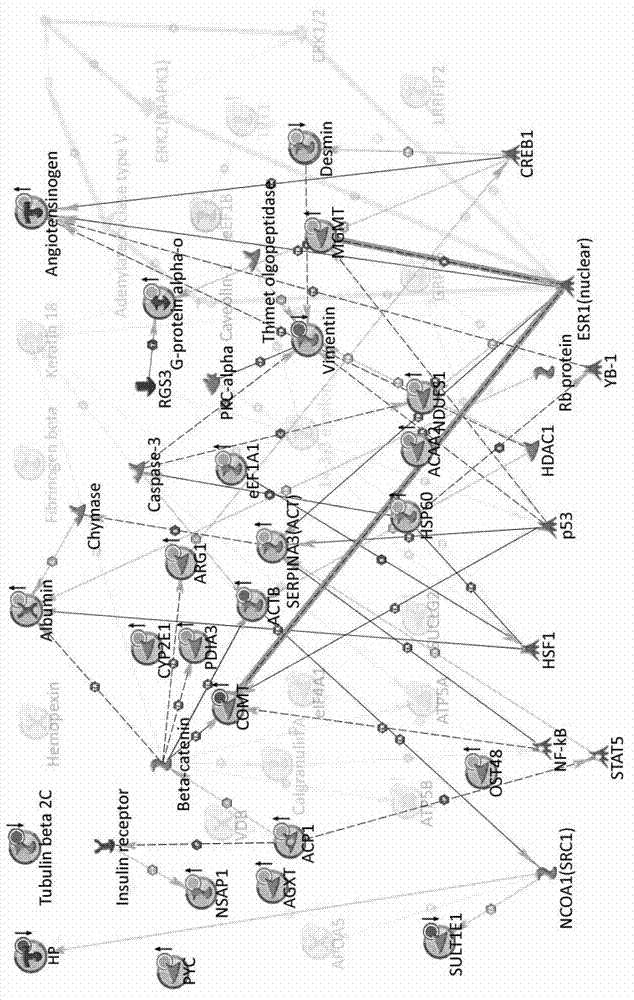
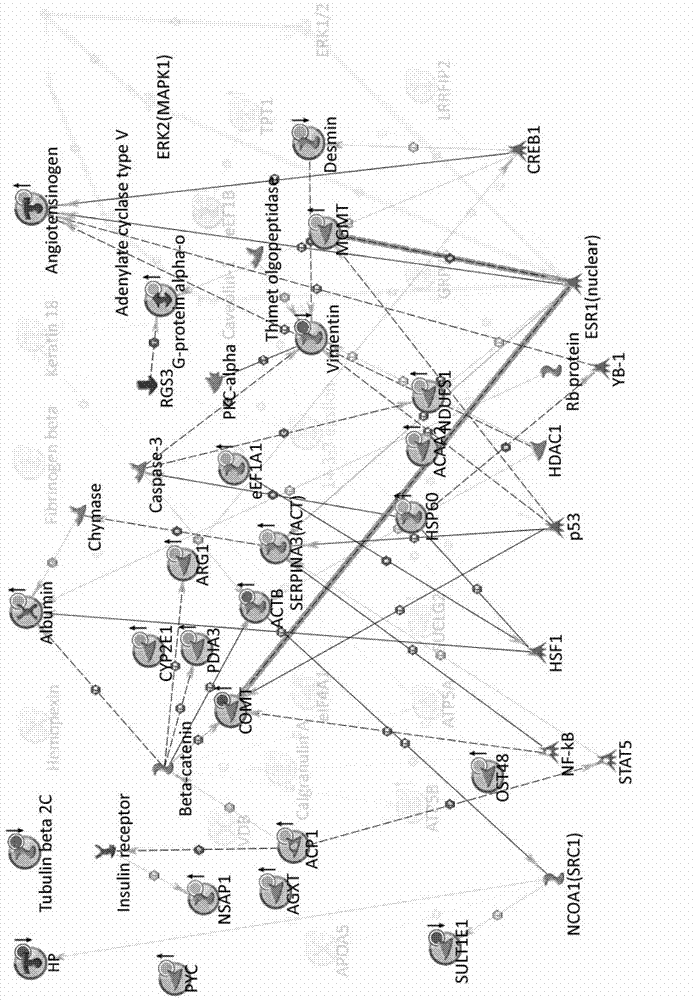
Method for constructing novel visual dynamic protein network reflecting proteome changes
The invention discloses a method for constructing a novel visual dynamic protein network reflecting proteome changes, which comprises the steps of: (1) correcting the expression quantity numerical value of a differential protein in a dynamic proteomic research at each time point: S=(Vtest-Vcontrol) / Vcontrol; (2) uploading an inlet number of a protein database and an S numerical value to a MetaCore network analyzing server and drawing an original protein network map; (3) adjusting the positions of nodes superposed in the original protein network map; (4) activating n data documents sequentially to obtain n network maps with protein expression information at time points, respectively; (5) organizing the network maps in form of flash documents through a time shaft to form a dynamic network map; and (6) adding a cell contour and a popup information frame to the dynamic network map. The method has a significant application value to displaying and researching proteome changes in various biological processes.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for screening tumor protein markers on basis of multilayer complex network
ActiveCN106407742AScreening method is simpleSimple methodBiostatisticsProteomicsNODALCancers diagnosis
The invention provides a method for screening tumor protein markers on the basis of a multilayer complex network. According to the method, node betweennesses of a random forest mode and of a complex network are combined to provide a new visual angle to discover the tumor pathogenic factors and diagnosis markers. Through bioinformatics and mathematic statistical analysis, the correlation of multilayer protein network data is established and a screening method which is more convenient and higher in correctness is disclosed, so that more valuable reference is provided or the cancer diagnosis and drug discovery.
Owner:赵毅
Combinatorial multidomain mesoporous chips and a method for fractionation, stabilization, and storage of biomolecules
A new fractionation device shows desirable features for exploratory screening and biomarker discovery. The constituent MSCs may be tailored for desired pore sizes and surface properties and for the sequestration and enrichment of extremely low abundant protein and peptides in desired ranges of the mass / charge spectrum. The MSCs are effective in yielding reproducible extracts from complex biological samples as small as 10 μl in a time as short as 30 minutes. They are inexpensive to manufacture, and allow for scaled up production to attain the simultaneous processing of a large number of samples. The MSCs are multiplexed, label-free diagnostic tools with the potential of biological recognition moiety modification for enhanced specificity. The MSCs may store, protect and stabilize biological fluids, enabling the simplified and cost-effective collection and transportation of clinical samples. The MSC-based device may serve as a diagnostic tool to complement histopathology, imaging, and other conventional clinical techniques. The MSCs mediated identification of disease-specific protein signatures may help in the selection of personalized therapeutic combinations, in the real-time assessment of therapeutic efficacy and toxicity, and in the rational modulation of therapy based on the changes in the protein networks associated with the prognosis and the drug resistance of the disease.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
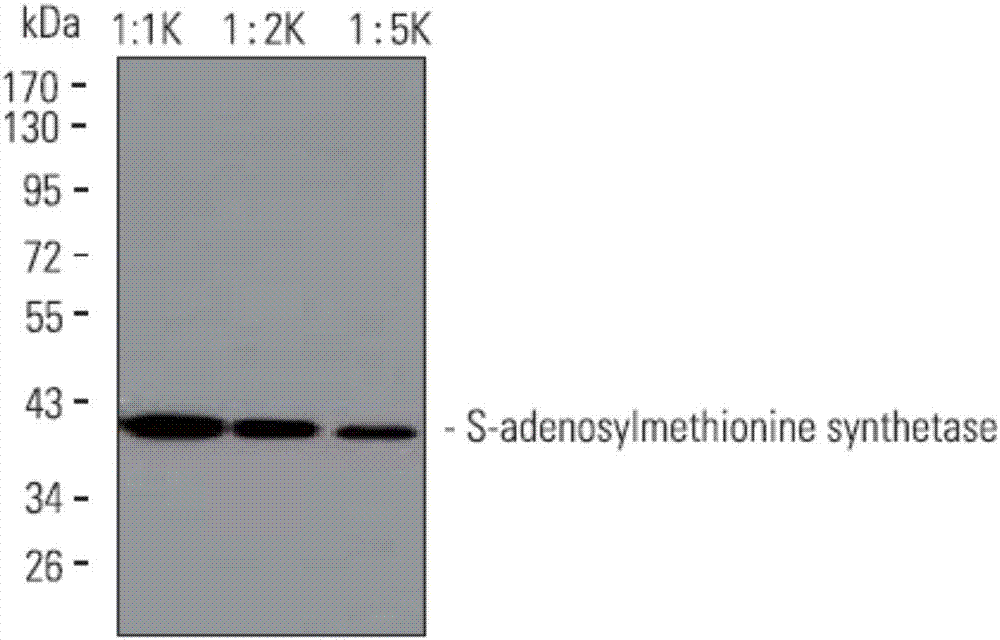
Monoclonal antibody of S-adenosylmethionine synthetase and application thereof
ActiveCN107383199AHigh affinityStrong specificityBiological material analysisImmunoglobulins against enzymesProtein targetDeep level
The invention discloses a monoclonal antibody of S-adenosylmethionine synthetase. A heavy chain variable region sequence of the monoclonal antibody contains CDR amino acid sequences shown by SEQ ID NO.2, 4 and 6; a light chain variable region sequence contains CDR amino acid sequences shown by SEQ ID NO.9, 11 and 13. The polypeptide of the enzyme is used as an immunogen for immunizing a mouse to obtain lymphocyte; a hybridoma fusion technology is used for preparing fusion cells; a cell strain capable of detecting and identifying the S-adenosylmethionine synthetase at high affinity and high specificity is obtained. The monoclonal antibody can be used for detecting the content of S-adenosylmethionine synthetase in bodies of animals and plants. The monoclonal antibody provides a targeted protein study tool, so that the deep level study of protein network atlas and the protein expression change on different plant types, different strains or different development periods can be realized.
Owner:艾比玛特医药科技(上海)有限公司
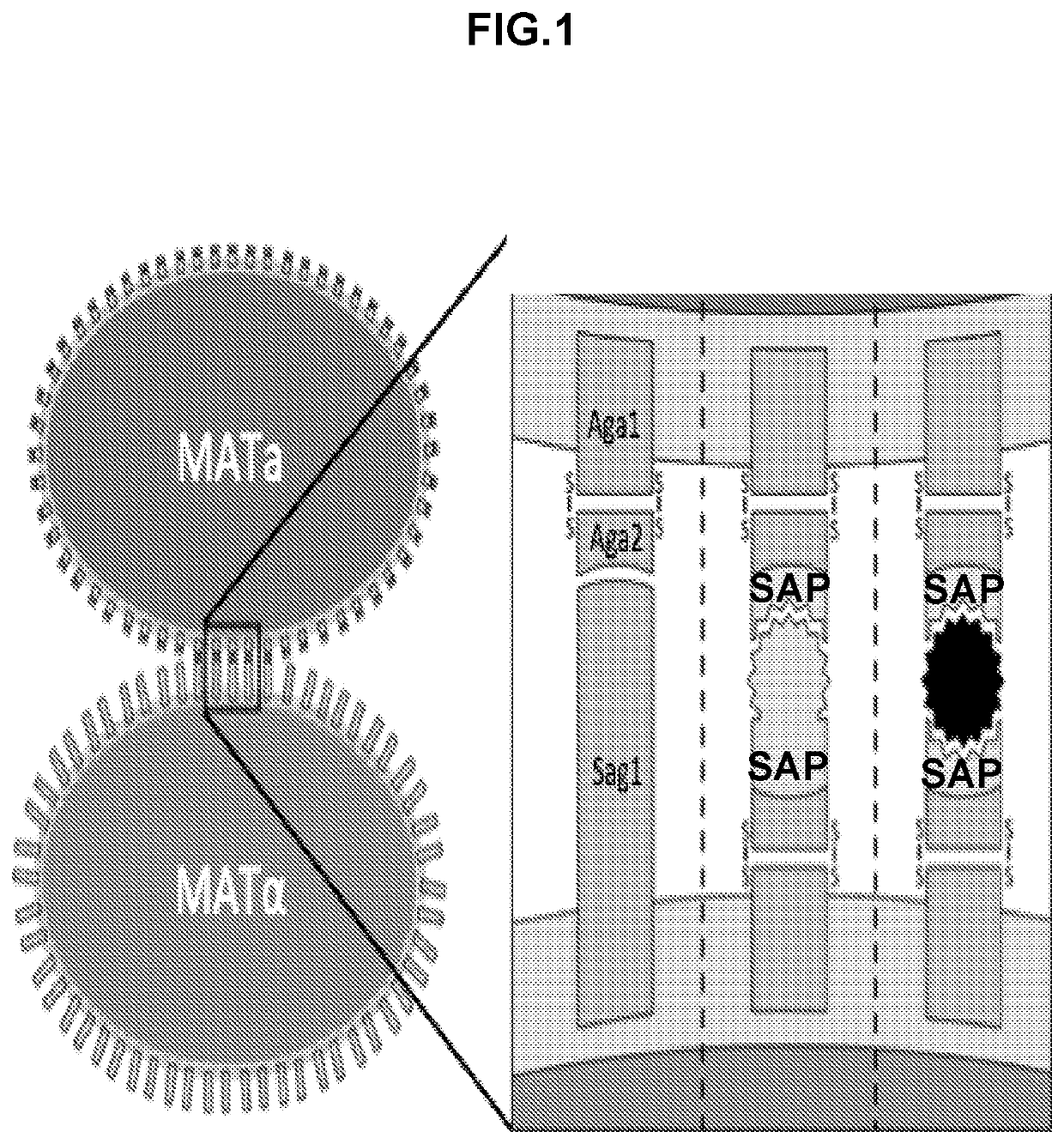
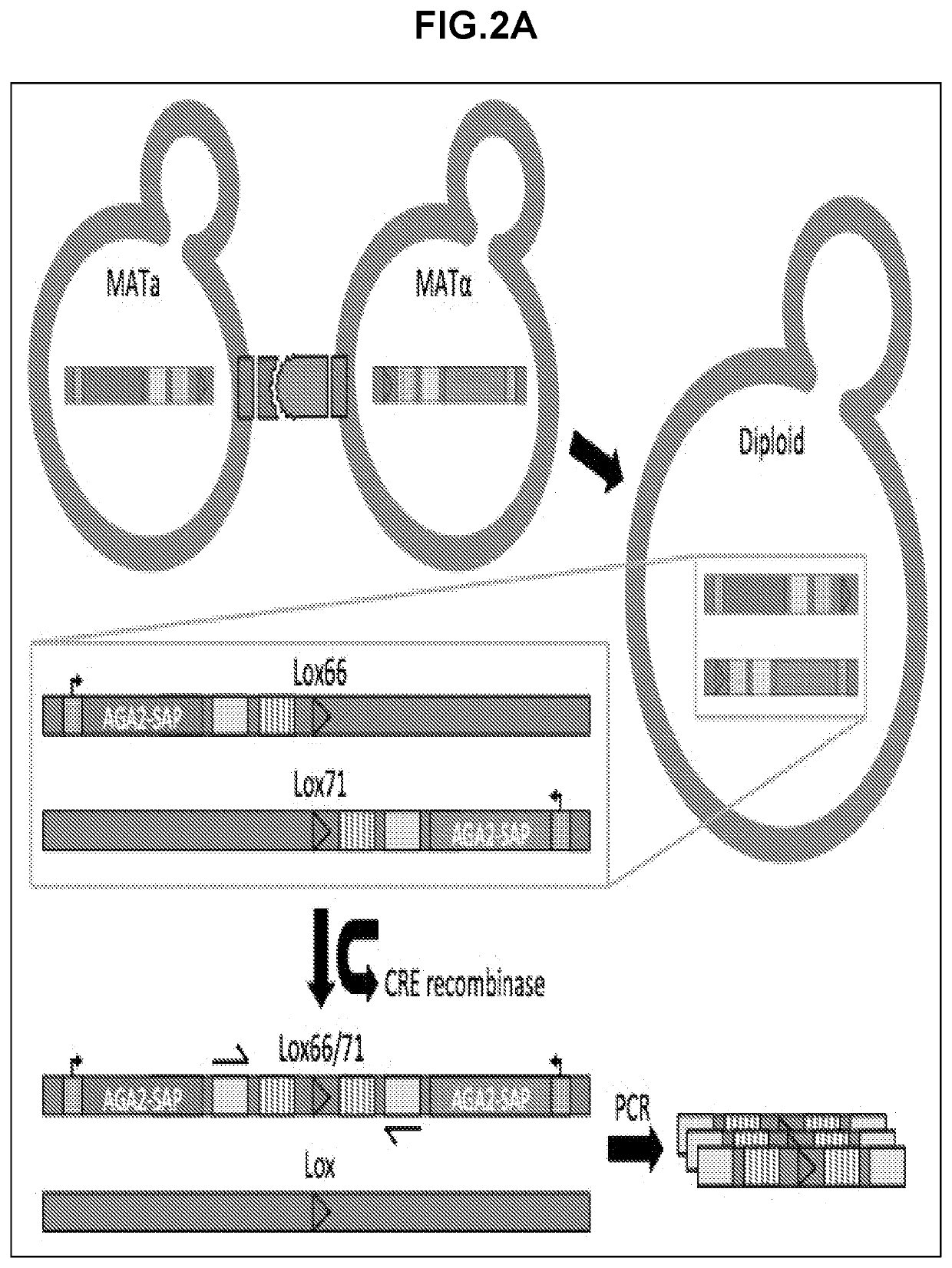
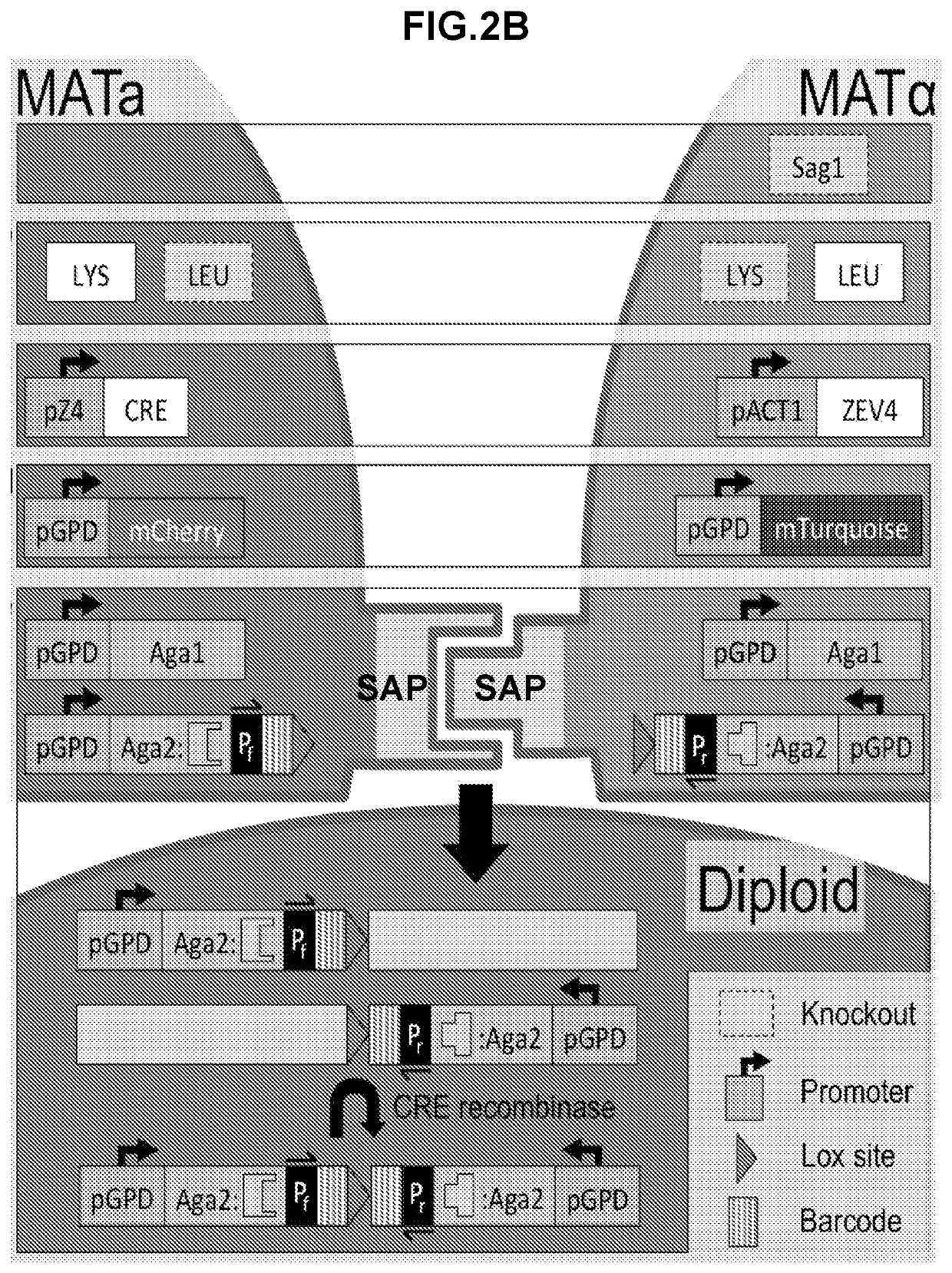
High throughput protein-protein interaction screening in yeast liquid culture
ActiveUS20210054365A1Microbiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsCellular functions
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the high throughput screening of protein-protein interactions in yeast liquid culture. Protein fusions non-native to yeast may be expressed to replace endogenous sexual agglutination proteins and mediate library-by-library interrogation of protein interactions. The methods and compositions of the invention can be utilized for the characterization of protein interaction networks in high throughput for both binding affinity and specificity, which is crucial for understanding cellular functions, screening therapeutic candidates, and evaluating engineered protein networks.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
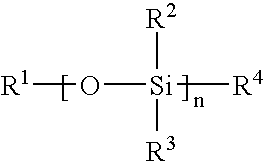
![Method for predicting miRNA [micro-RNA (ribonucleic acid)] target proteins of miRNA regulation protein interaction networks Method for predicting miRNA [micro-RNA (ribonucleic acid)] target proteins of miRNA regulation protein interaction networks](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/2ceb1e3a-4328-4313-b6c3-95d3a50590fe/DEST_PATH_IMAGE001.png)
![Method for predicting miRNA [micro-RNA (ribonucleic acid)] target proteins of miRNA regulation protein interaction networks Method for predicting miRNA [micro-RNA (ribonucleic acid)] target proteins of miRNA regulation protein interaction networks](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/2ceb1e3a-4328-4313-b6c3-95d3a50590fe/DEST_PATH_IMAGE002.png)
![Method for predicting miRNA [micro-RNA (ribonucleic acid)] target proteins of miRNA regulation protein interaction networks Method for predicting miRNA [micro-RNA (ribonucleic acid)] target proteins of miRNA regulation protein interaction networks](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/2ceb1e3a-4328-4313-b6c3-95d3a50590fe/DEST_PATH_IMAGE003.png)