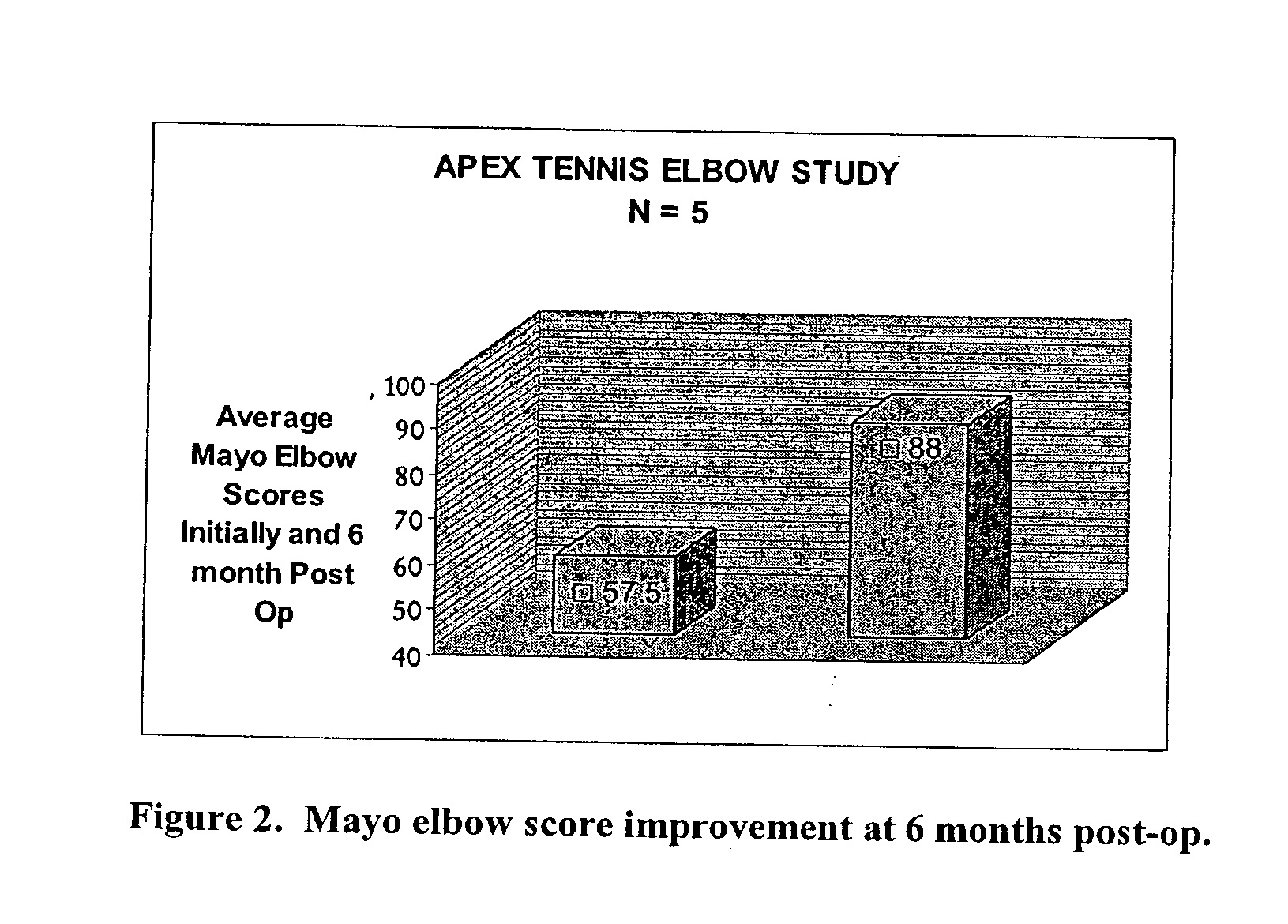
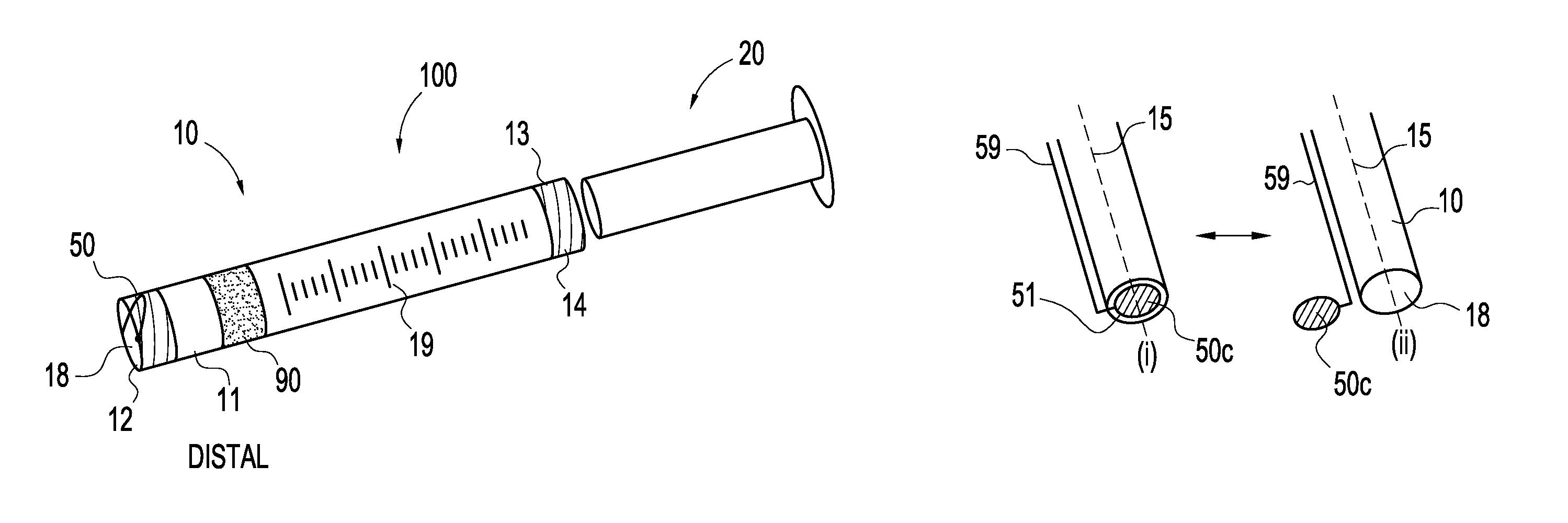
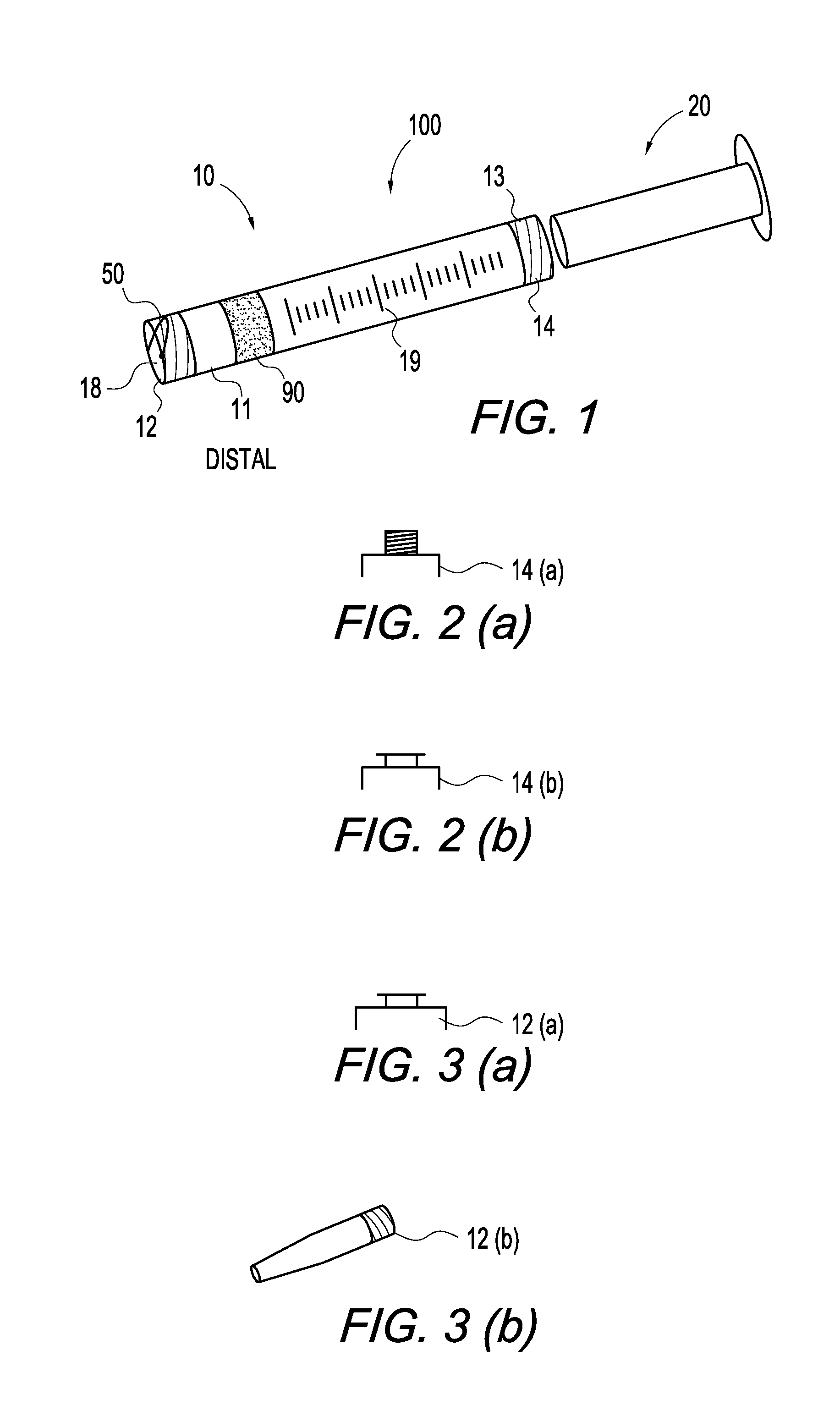
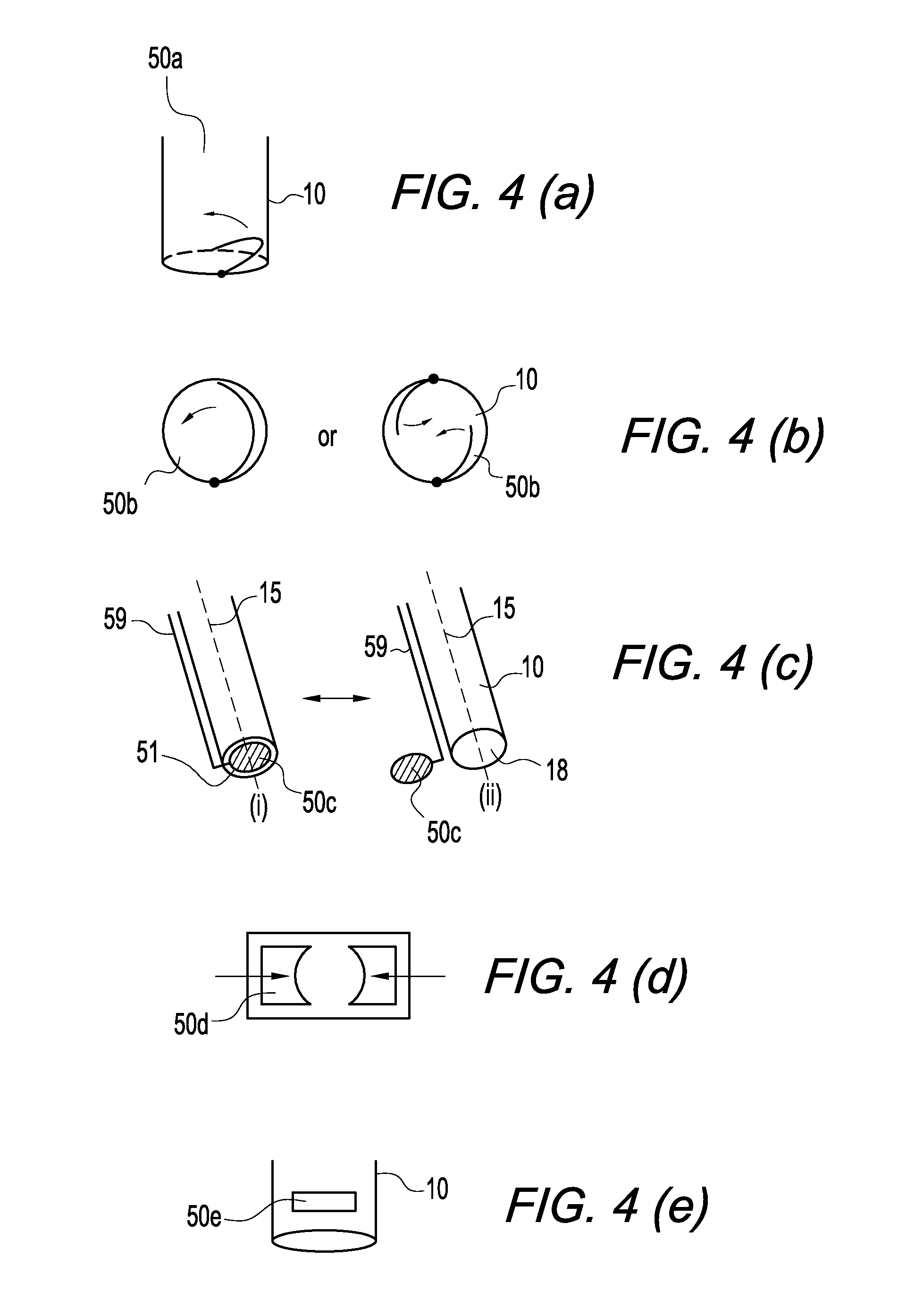
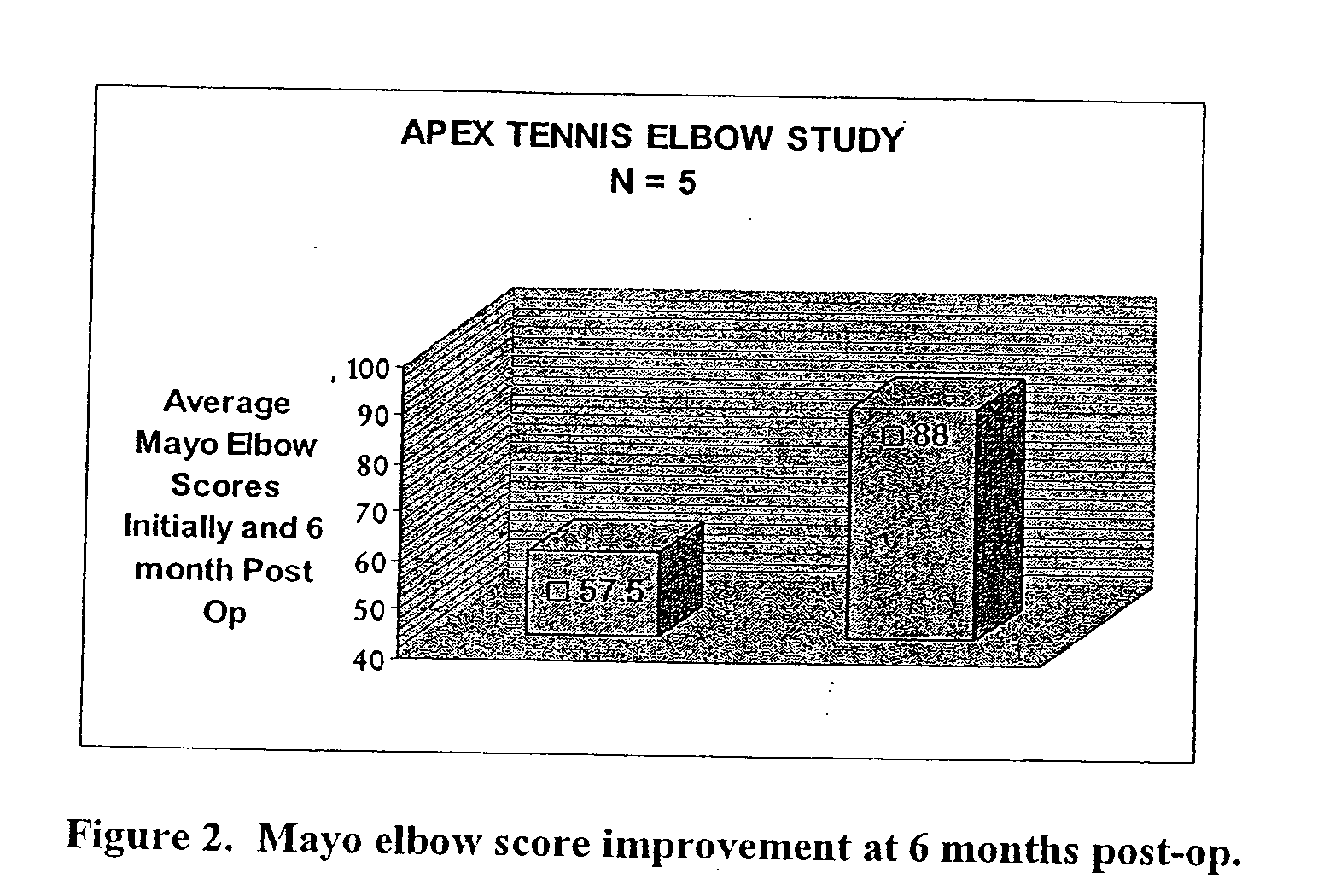
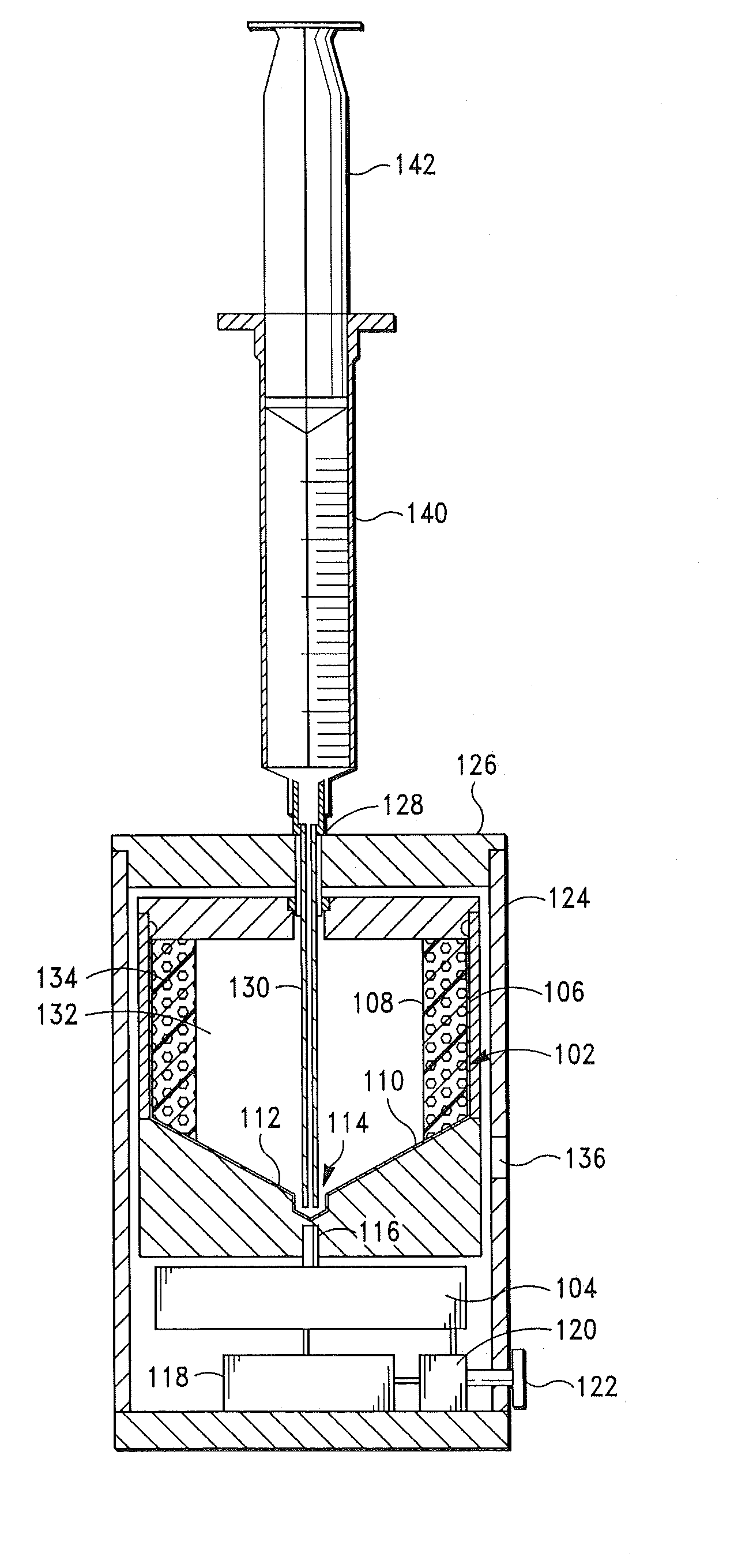
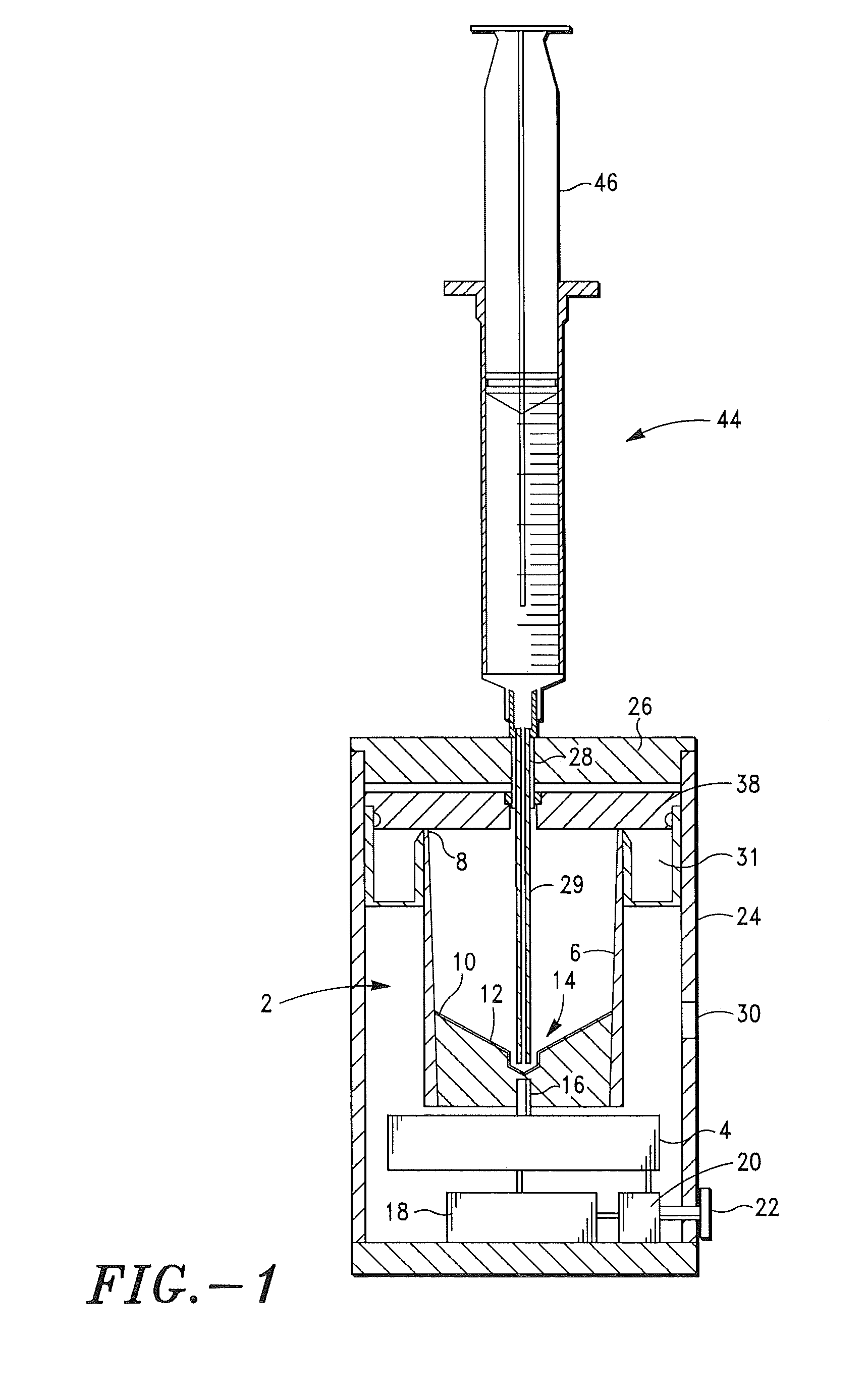
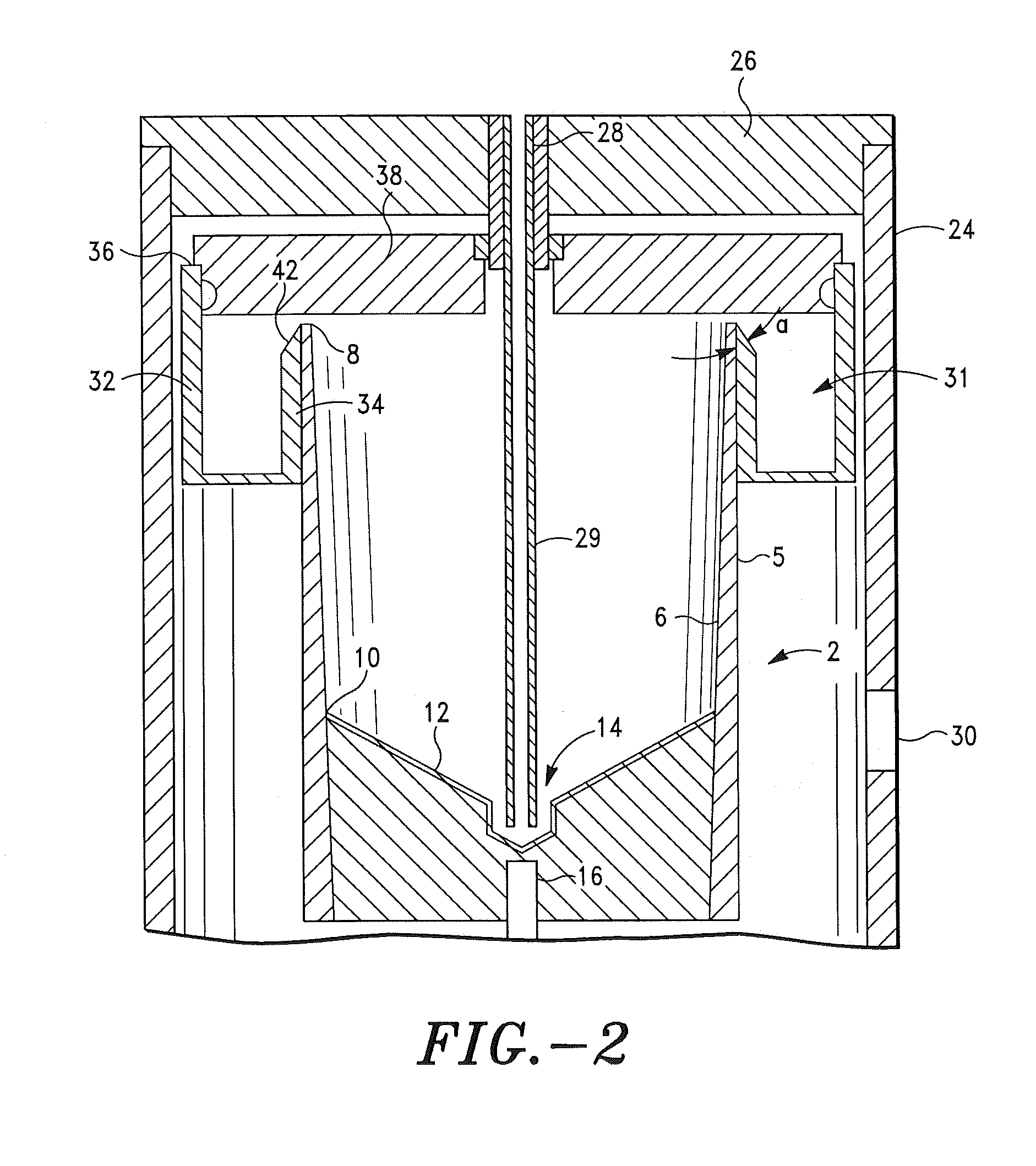
Patents
Literature
351 results about "Platelet-rich plasma" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP), also known as autologous conditioned plasma, is a concentrate of platelet-rich plasma protein derived from whole blood, centrifuged to remove red blood cells. Evidence for benefit is poor as of 2016. The cost per injection is generally $US 500 to 2,000 as of 2019.
Composition and method for the repair and regeneration of cartilage and other tissues
InactiveUS7148209B2Add supportImprove coagulation/solidificationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthRepair tissue
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Method and apparatus for preparing platelet rich plasma and concentrates thereof
ActiveUS20060175242A1Shaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersTransportation and packagingFiberRed blood cell
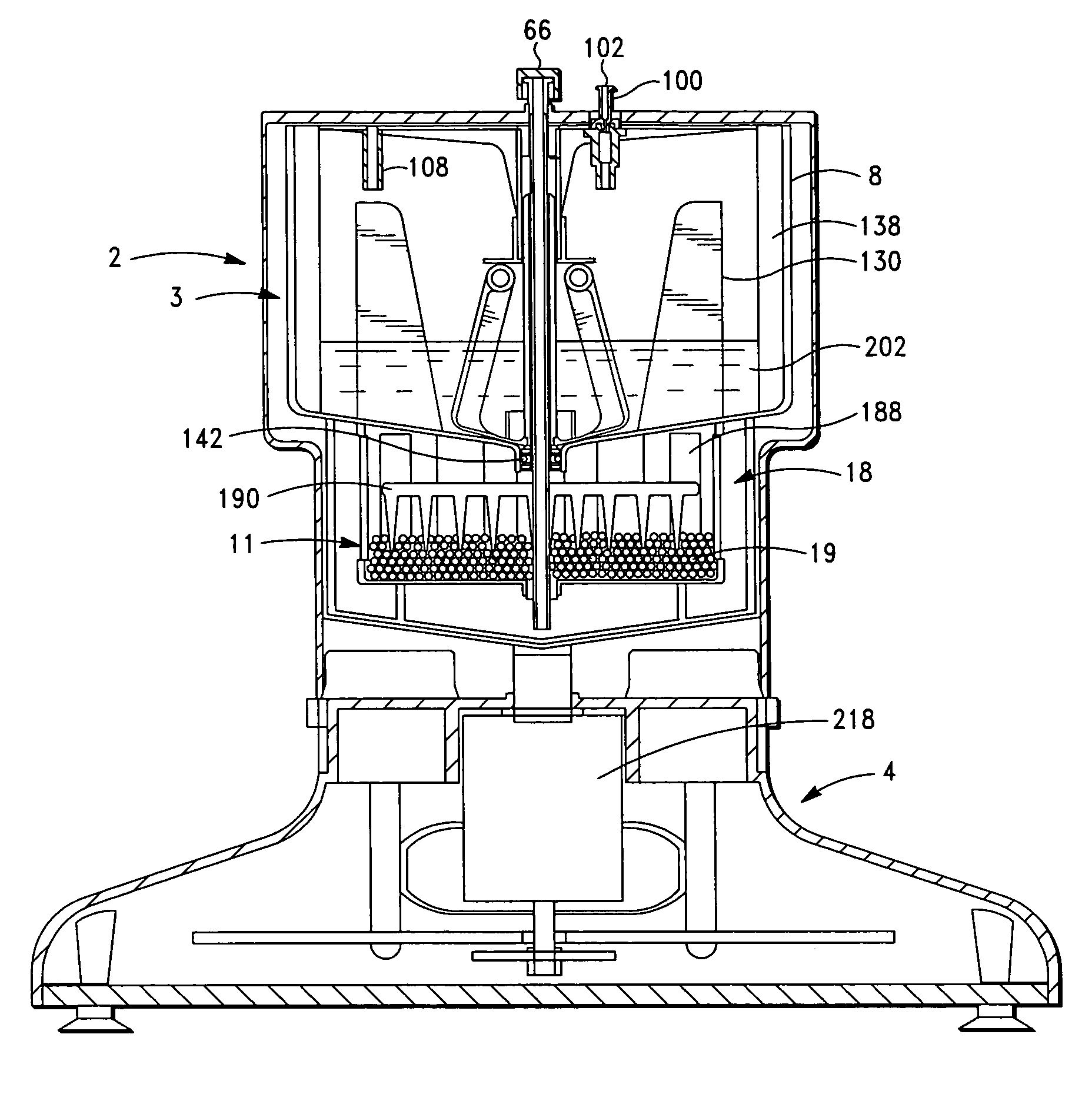
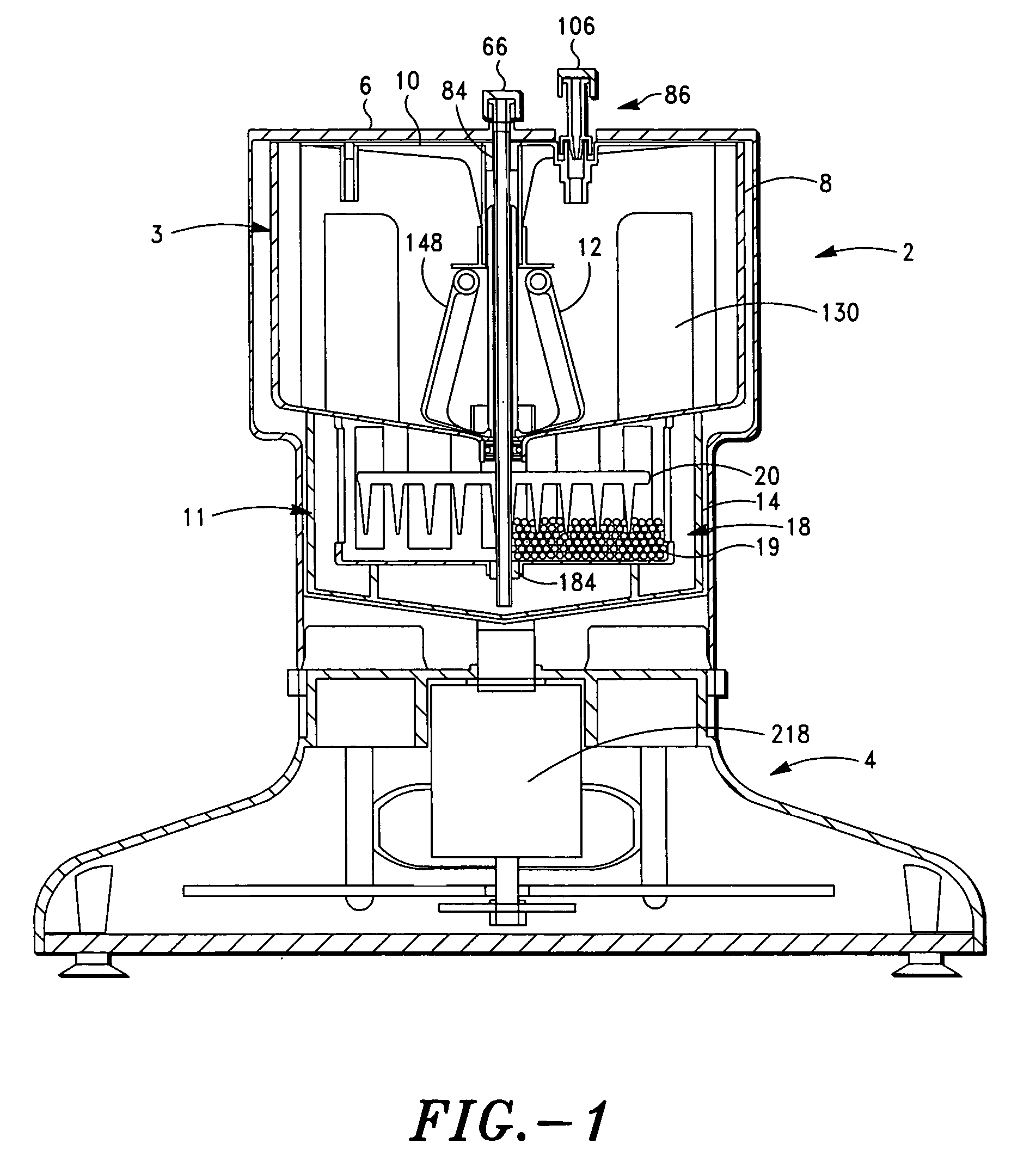
The PRP separator-concentrator of this invention is suitable for office use or emergency use for trauma victims. The PRP separator comprises a motorized centrifugal separation assembly, and a concentrator assembly. The centrifugal separator assembly comprises a centrifugal drum separator that includes an erythrocyte capture module and a motor having a drive axis connected to the centrifugal drum separator. The concentrator assembly comprises a water-removal module for preparing PRP concentrate. The centrifugal drum separator has an erythrocyte trap. The water removal module can be a syringe device with water absorbing beads or it can be a pump-hollow fiber cartridge assembly. The hollow fibers are membranes with pores that allow the flow of water through the fiber membrane while excluding flow of clotting factors useful for sealing and adhering tissue and growth factors helpful for healing while avoiding activation of platelets and disruption of any trace erythrocytes present in the PRP.
Owner:HANUMAN +1
Method and apparatus for preparing platelet rich plasma and concentrates thereof
ActiveUS7708152B2Shaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersTransportation and packagingFiberRed blood cell
The PRP separator-concentrator of this invention is suitable for office use or emergency use for trauma victims. The PRP separator comprises a motorized centrifugal separation assembly, and a concentrator assembly. The centrifugal separator assembly comprises a centrifugal drum separator that includes an erythrocyte capture module and a motor having a drive axis connected to the centrifugal drum separator. The concentrator assembly comprises a water-removal module for preparing PRP concentrate. The centrifugal drum separator has an erythrocyte trap. The water removal module can be a syringe device with water absorbing beads or it can be a pump-hollow fiber cartridge assembly. The hollow fibers are membranes with pores that allow the flow of water through the fiber membrane while excluding flow of clotting factors useful for sealing and adhering tissue and growth factors helpful for healing while avoiding activation of platelets and disruption of any trace erythrocytes present in the PRP.
Owner:HANUMAN +1
Composition and method for the repair and regeneration of cartilage and other tissues
InactiveUS20060029578A1Add supportImprove coagulation/solidificationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthRepair tissue
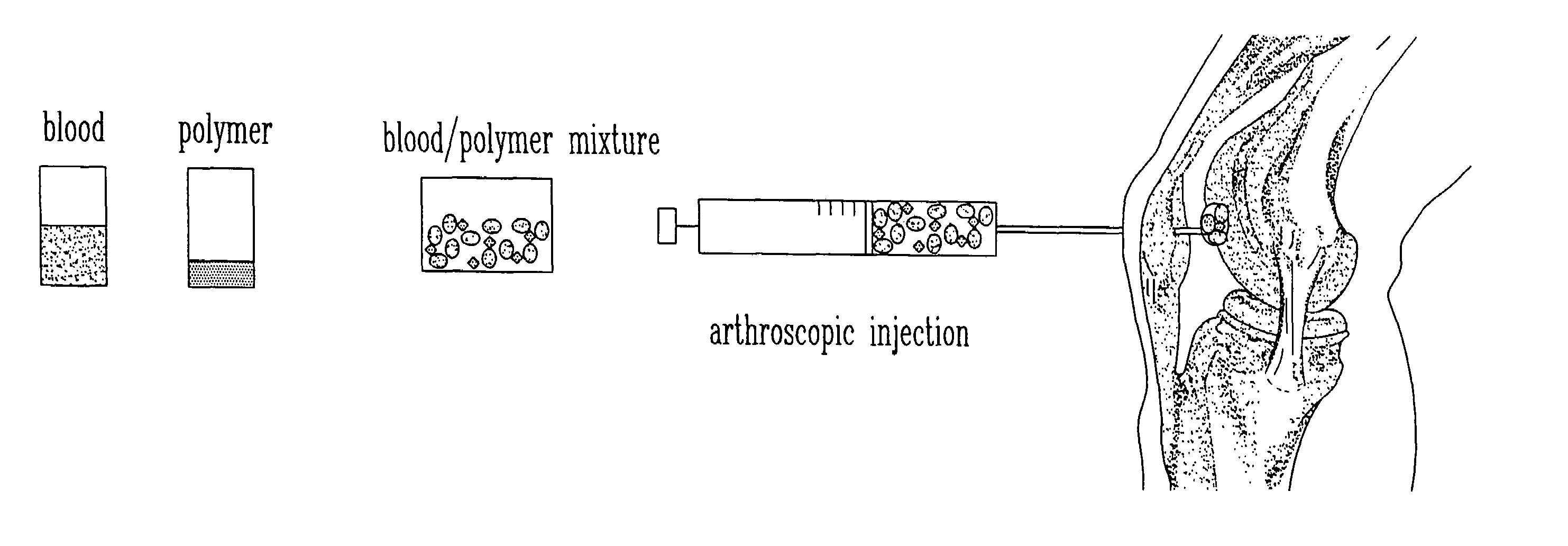
The present invention relates to a new method for repairing human or animal tissues such as cartilage, meniscus, ligament, tendon, bone, skin, cornea, periodontal tissues, abscesses, resected tumors, and ulcers. The method comprises the step of introducing into the tissue a temperature-dependent polymer gel composition such that the composition adhere to the tissue and promote support for cell proliferation for repairing the tissue. Other than a polymer, the composition preferably comprises a blood component such as whole blood, processed blood, venous blood, arterial blood, blood from bone, blood from bone-marrow, bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, placenta blood, erythrocytes, leukocytes, monocytes, platelets, fibrinogen, thrombin and platelet rich plasma. The present invention also relates to a new composition to be used with the method of the present invention.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Apparatus and method for preparing platelet rich plasma and concentrates thereof
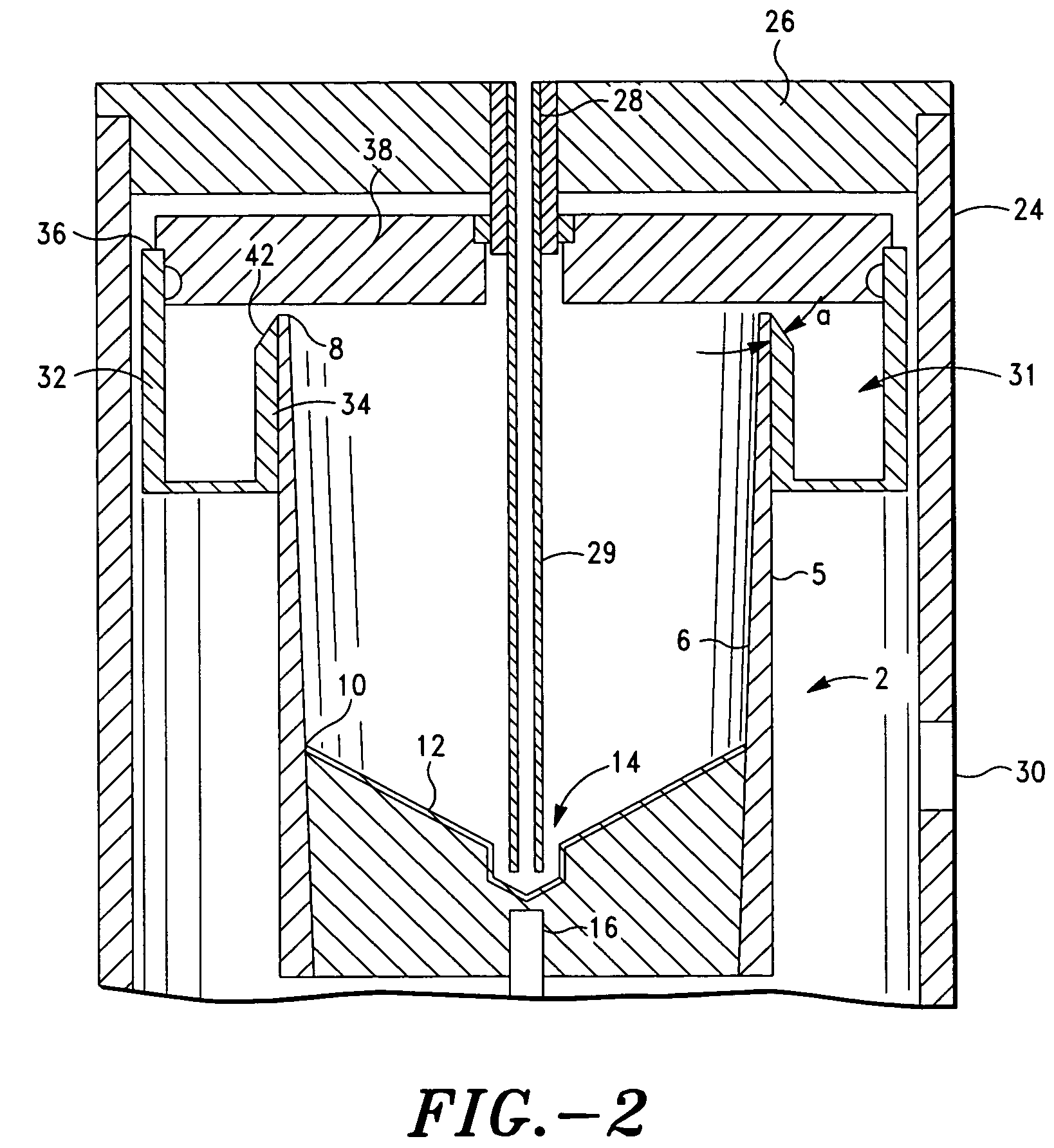
ActiveUS20060175244A1Increase in platelet levelAvoid assemblyRotary centrifugesMedical devicesRed blood cellEngineering
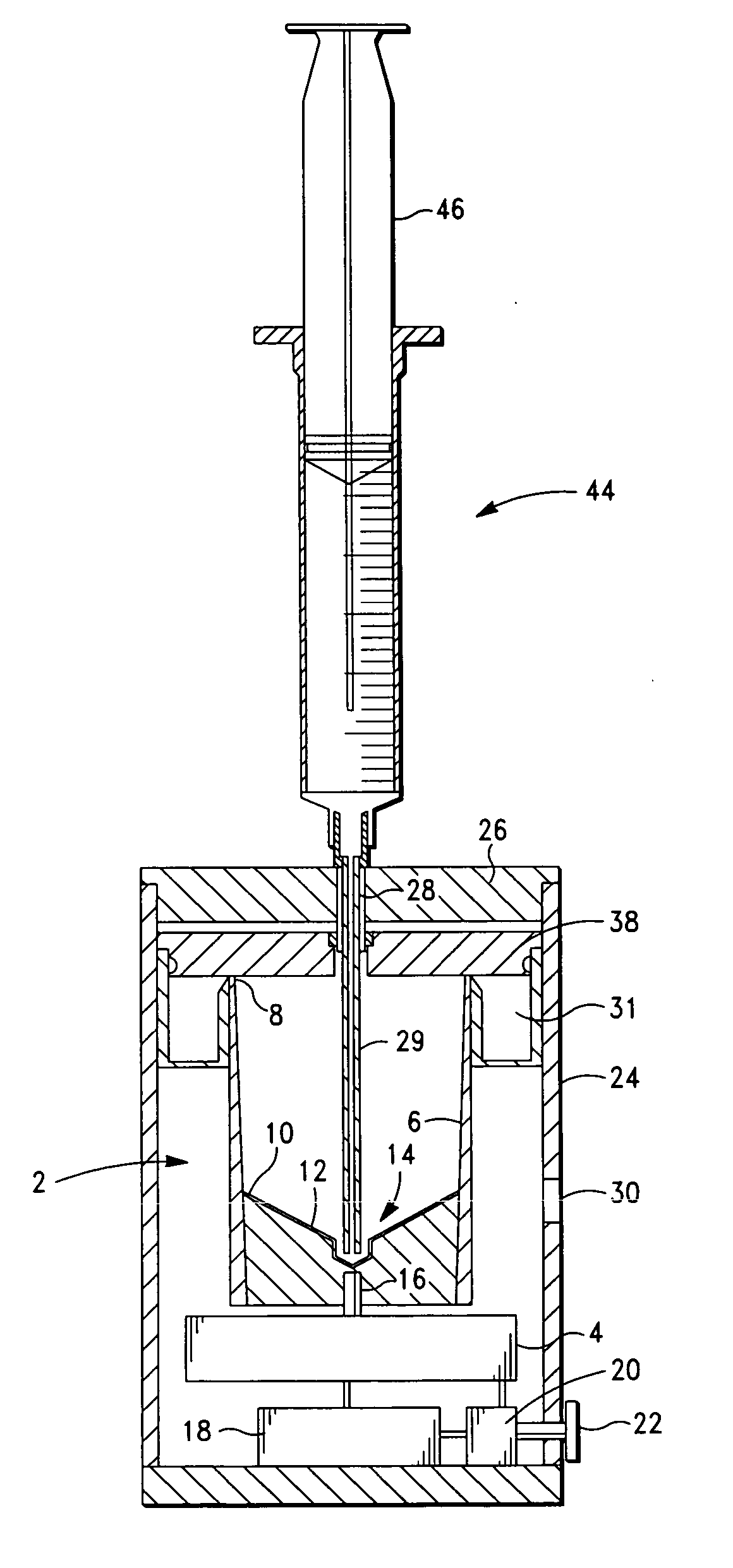
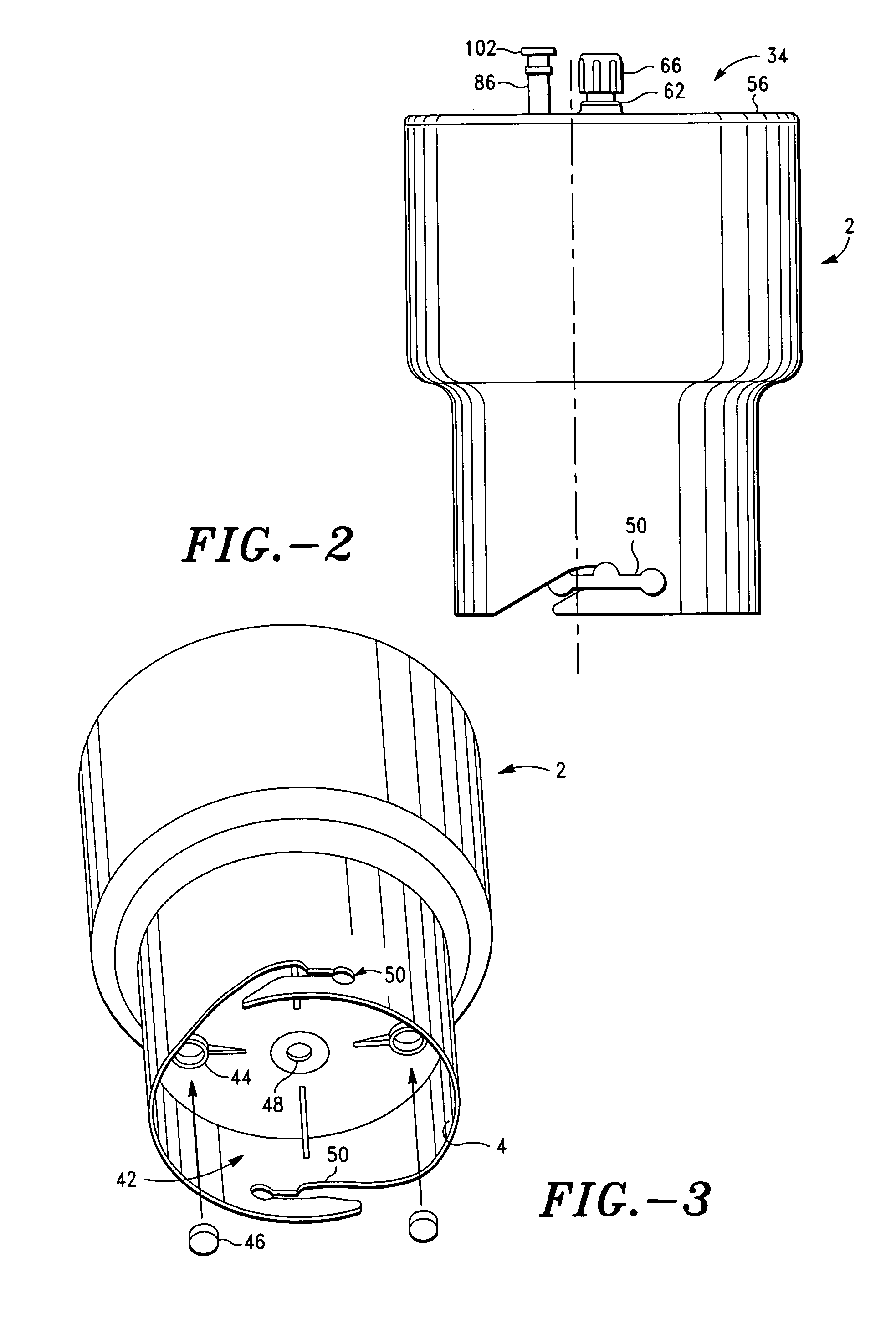
A PRP separator-concentrator comprising a housing, a separation assembly, and a concentration assembly. The concentration assembly has a concentration sump. An axially concentric rigid stationary outlet tube is secured to the housing and extends through the separation assembly to the sump. The separation assembly is attached to and positioned above the concentration assembly to form a combined separator-concentrator assemblage that is rotatable about the outlet tube. The separation assembly includes a separation chamber lined with a depth filter having pores and passageways that are sized to receive and entrap erythrocytes during centrifuging. The concentration chamber has a floor for supporting desiccated beads and a wall with at least one opening closed with a screen. The concentrator can have a distribution of upright screen supports, the upright screen supports having an inner surface and an outer surface, the cylindrical screen being supported on the outer surface of the upright screen supports. A stationary bead rake can be secured to the stationary tube and extend outward therefrom, the rake having distal ends that are spaced at a distance from the upright screen supports. The rake can comprise a longitudinal body, the center of which is secured to the rigid outlet tube. The separator-concentrator includes a valve assembly connecting the separation chamber and the concentration chamber. PRP concentrate is produced by contacting PRP with desiccated beads while the beads are stirred with a stationary rake, and rotating the concentration chamber at centrifugal speeds to separate PRP concentrate from the beads.
Owner:BIOMET BIOLOGICS +1
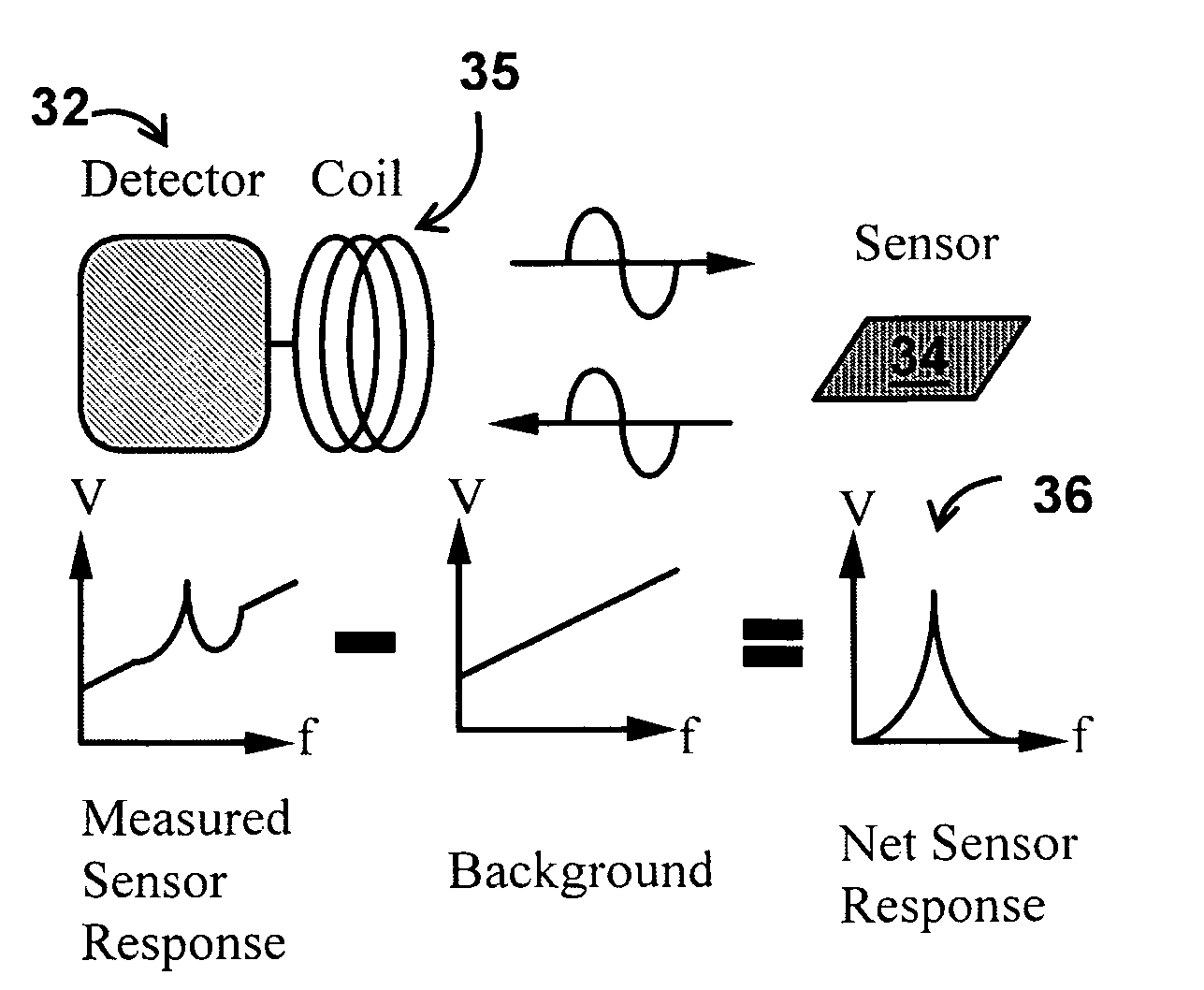
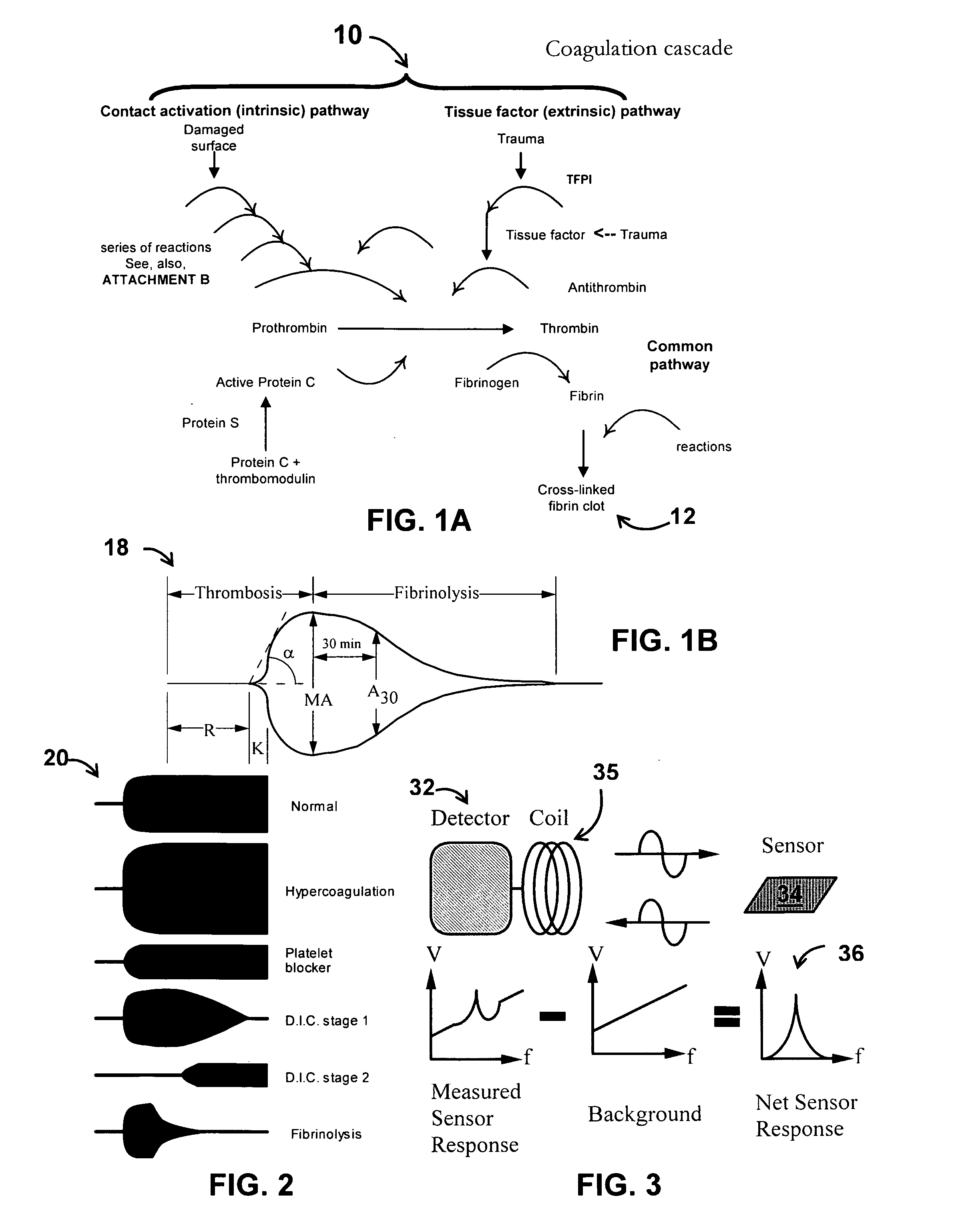
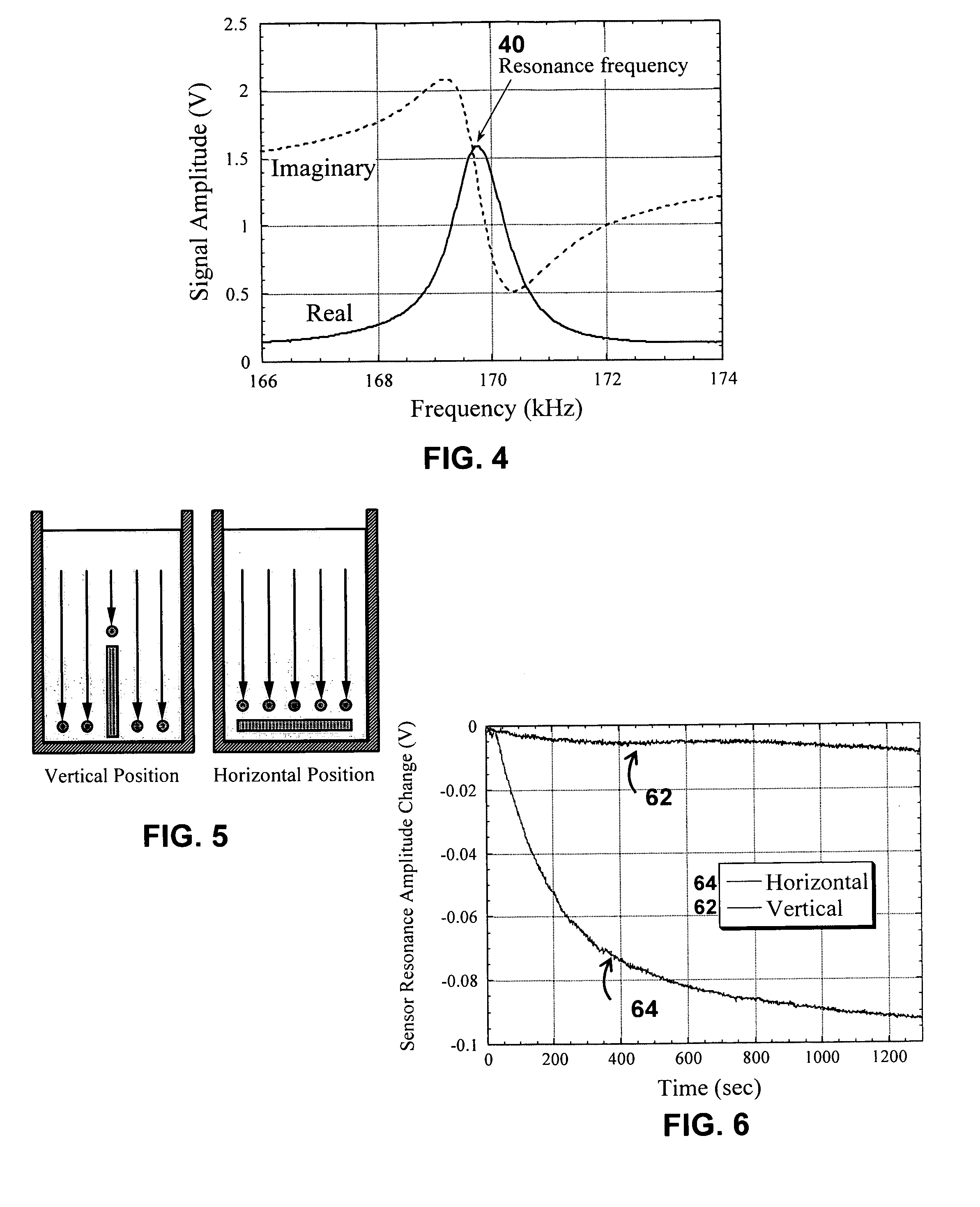
System/unit and method employing a plurality of magnetoelastic sensor elements for automatically quantifying parameters of whole blood and platelet-rich plasma
InactiveUS20080261261A1Quantifying platelet-fibrin clot strengthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsClot formationBlood plasma
A system / analyzer-unit and method / platform—using information obtained from at least one, adapted for a plurality of, magnetoelastic sensor elements in contact with one or more samples comprising blood from a patient—for automatically quantifying one or more parameters of the patient's blood. Information obtained from emissions measured from each of the sensor elements is uniquely processed to determine a quantification about the patient's blood, such as, quantifying platelet aggregation to determine platelet contribution toward clot formation; quantifying fibrin network contribution toward clot formation; quantifying platelet-fibrin clot interactions; quantifying kinetics of thrombin clot generation; quantifying platelet-fibrin clot strength; and so on. Structural aspects of the analyzer-unit include: a cartridge having at least one bay within which a sensor element is positioned; each bay in fluid communication with both (a) an entry port for injecting a first blood sample composed of blood taken from the patient (human or other mammal), and (b) a gas vent through which air displaced by injecting the first blood sample into the bay.
Owner:KMG2 SENSORS CORP
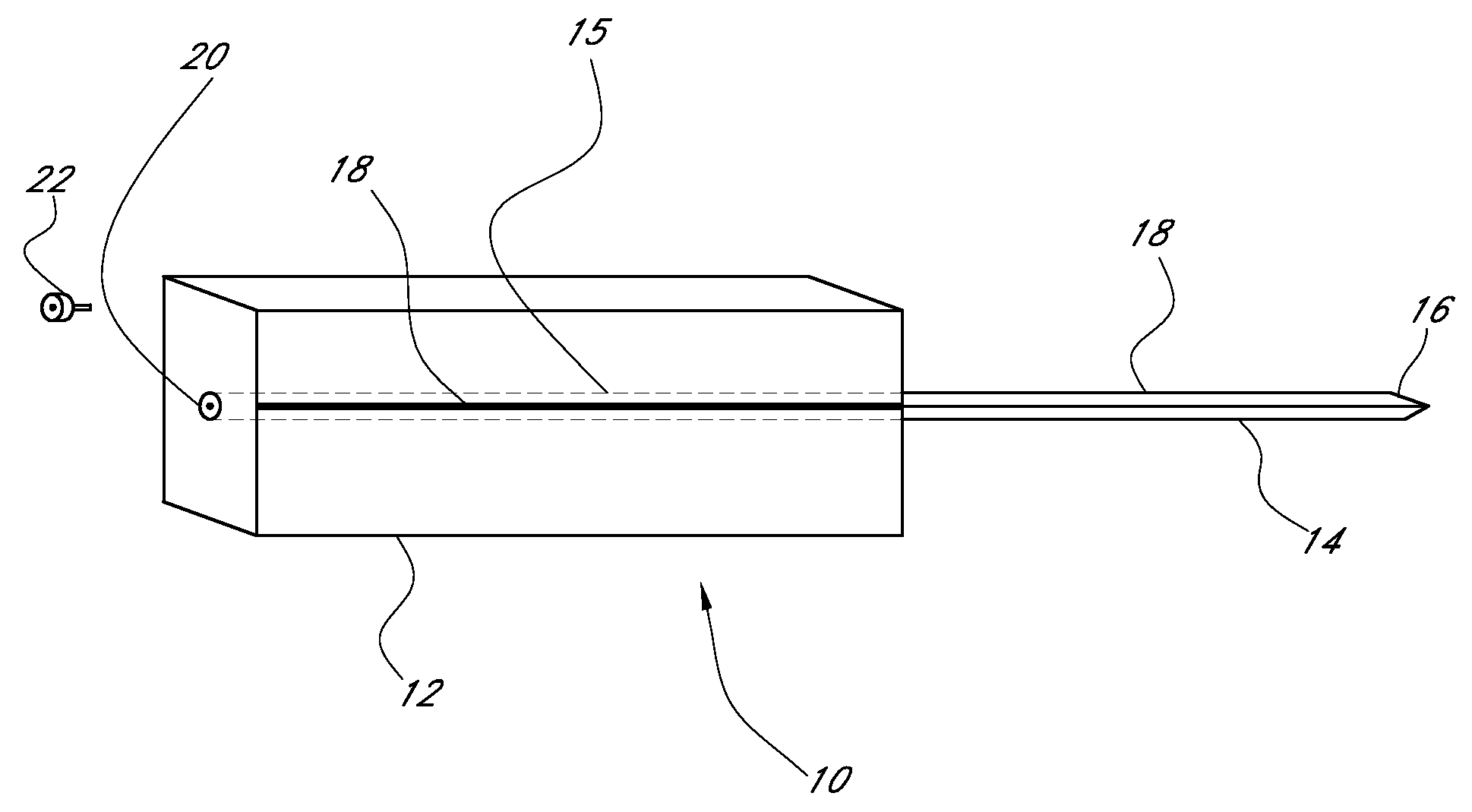
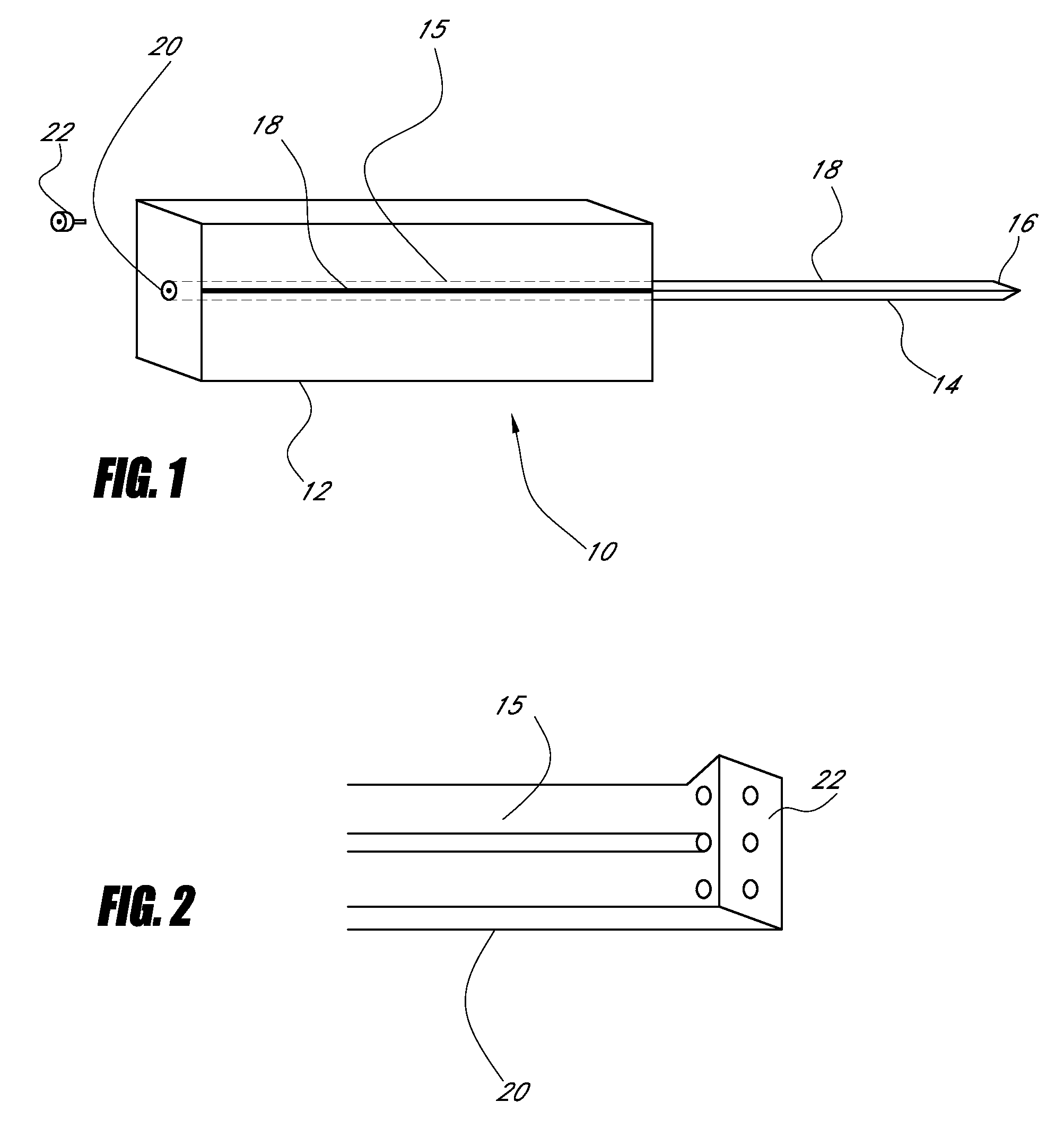
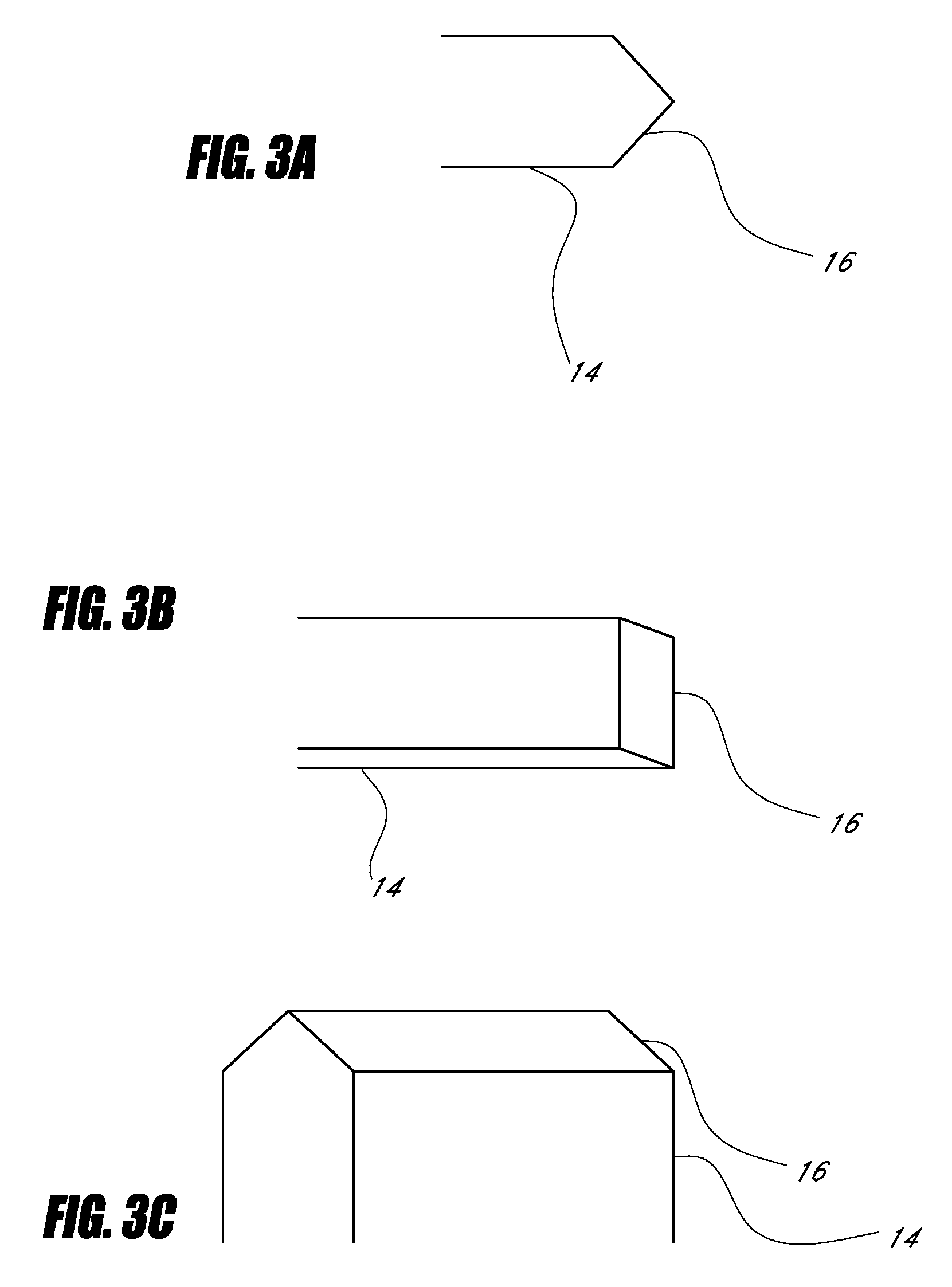
Device for cartilage repair
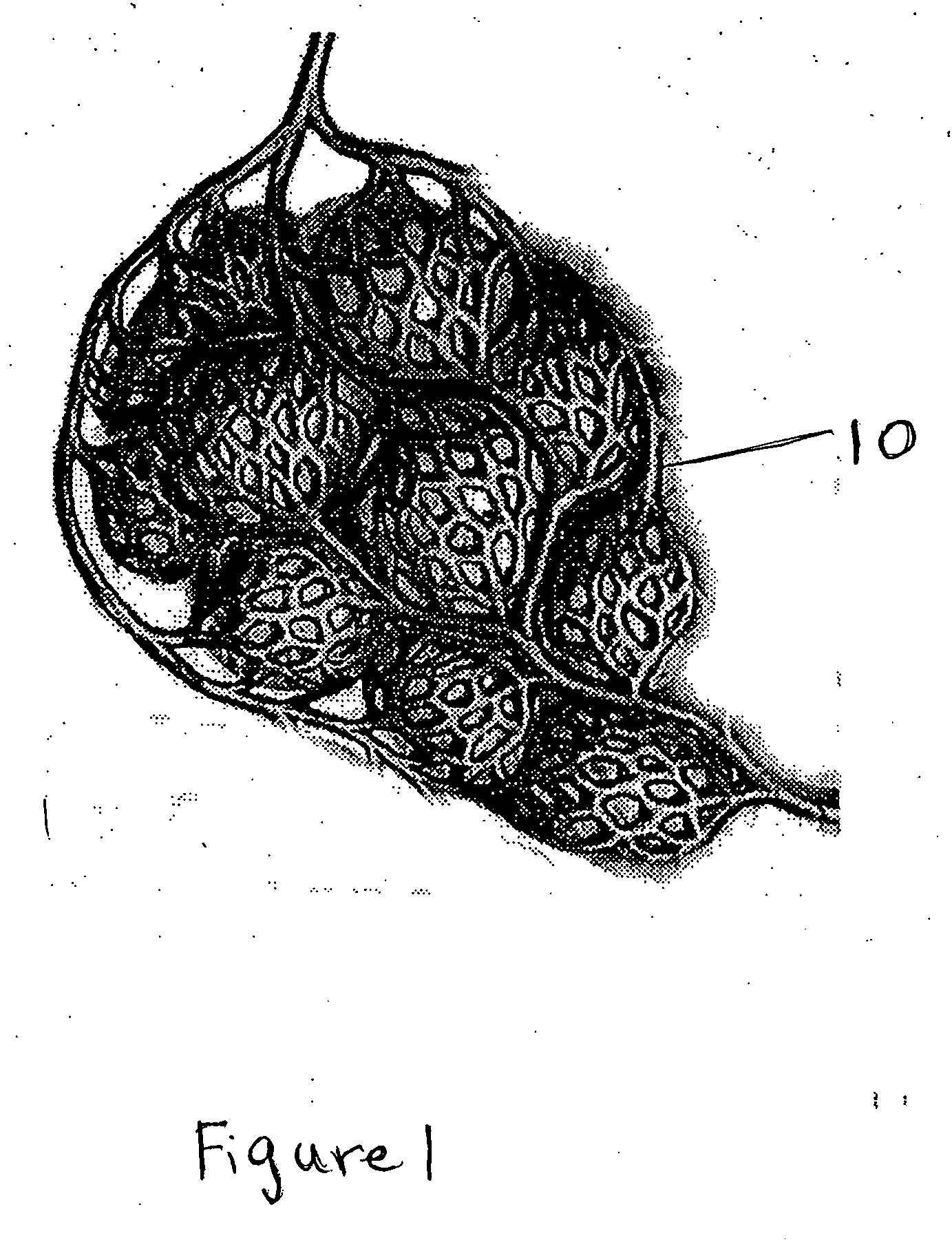
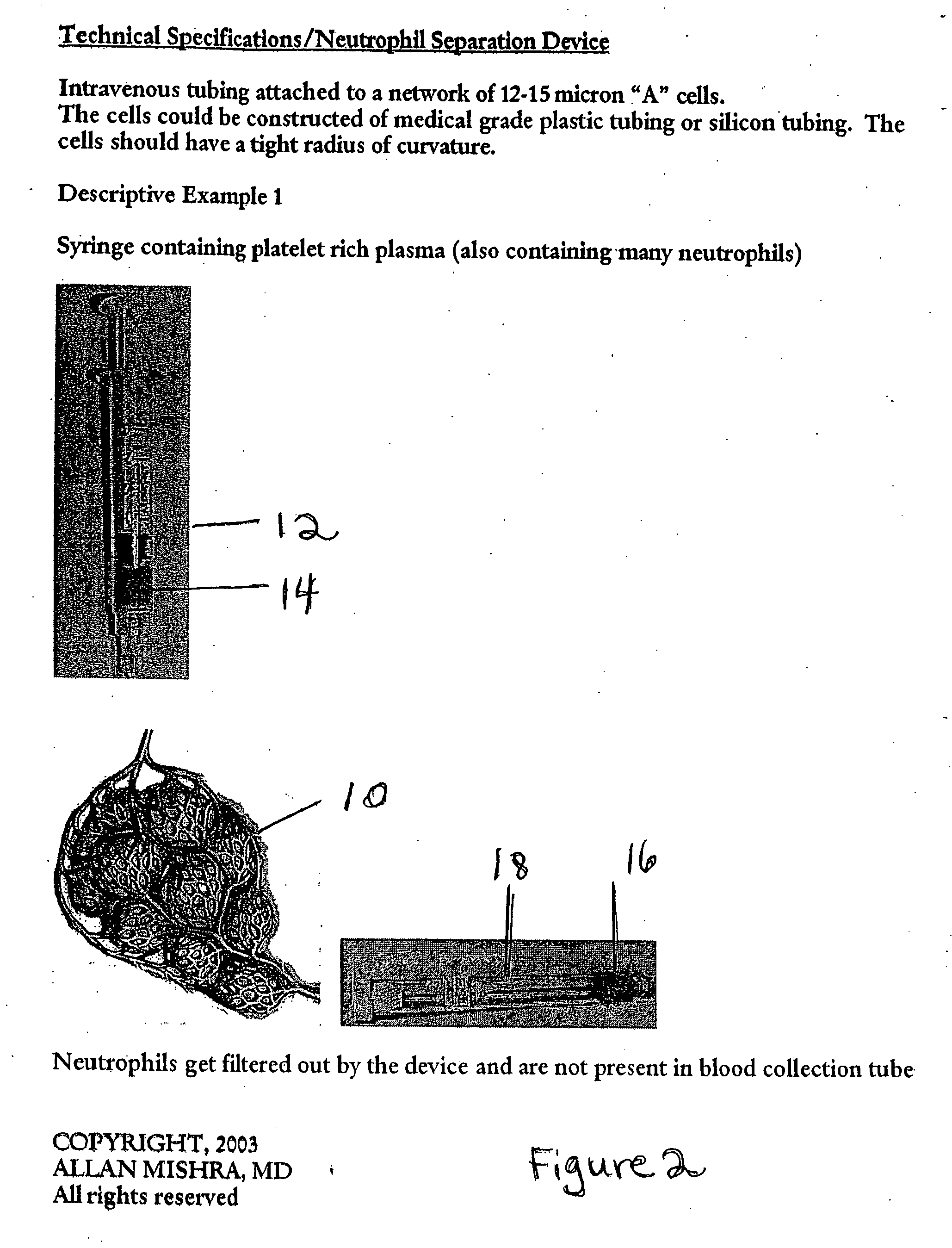
A surgical awl is disclosed for tissue repair. The surgical awl includes an internal lumen through which bioactive substances, such as platelet-rich plasma, may be delivered to a site of tissue or organ disease or dysfunction. In particular, the surgical awl is useful as a microfracture awl for cartilage repair augmented by delivery of platelet-rich plasma through the lumen of the device.
Owner:MISHRA ALLAN
Compositions and minimally invasive methods for treating incomplete tissue repair
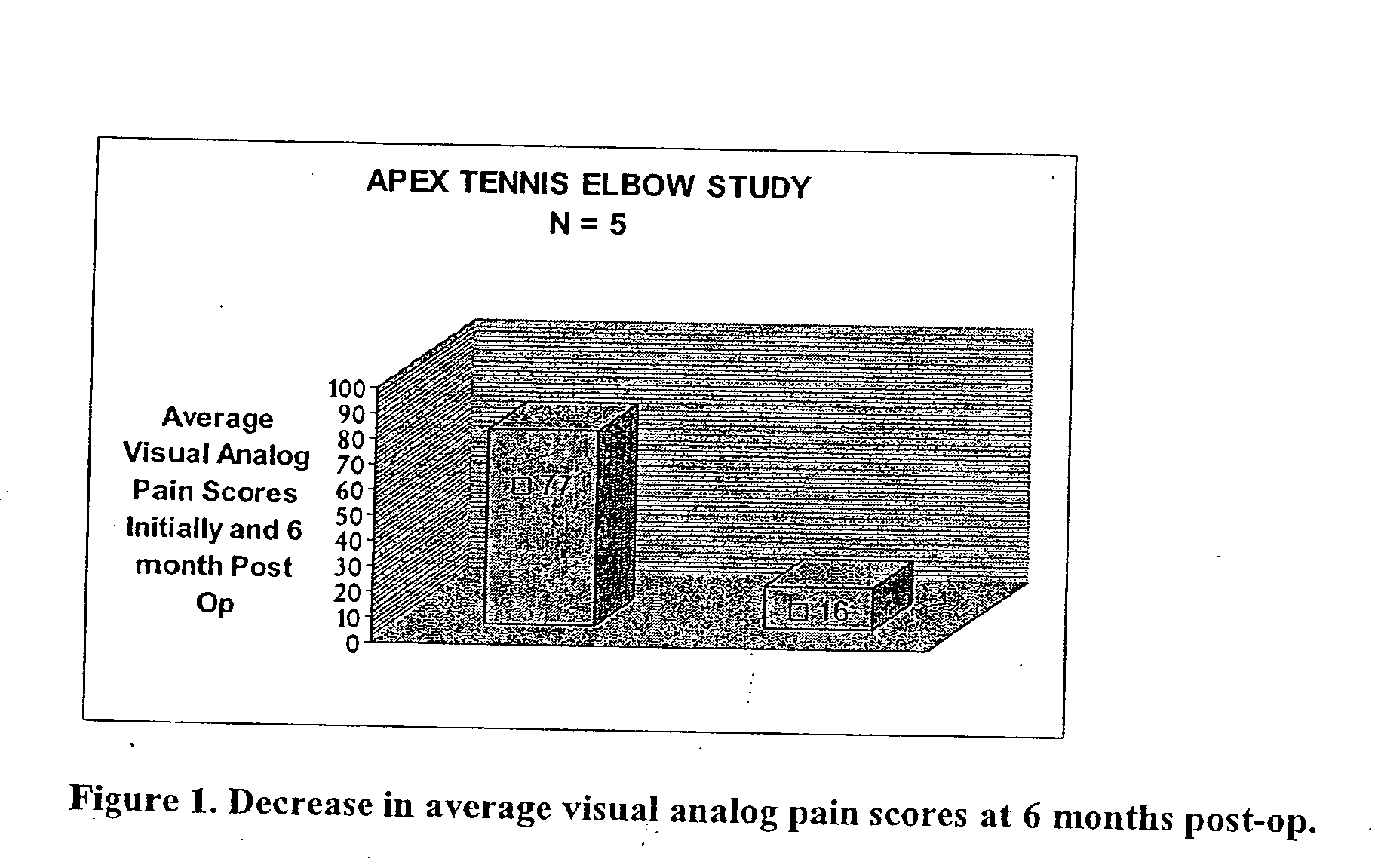
ActiveUS20050100536A1Extended storage timeCause effectsBiocideOrganic active ingredientsEpicondylitisTissue repair
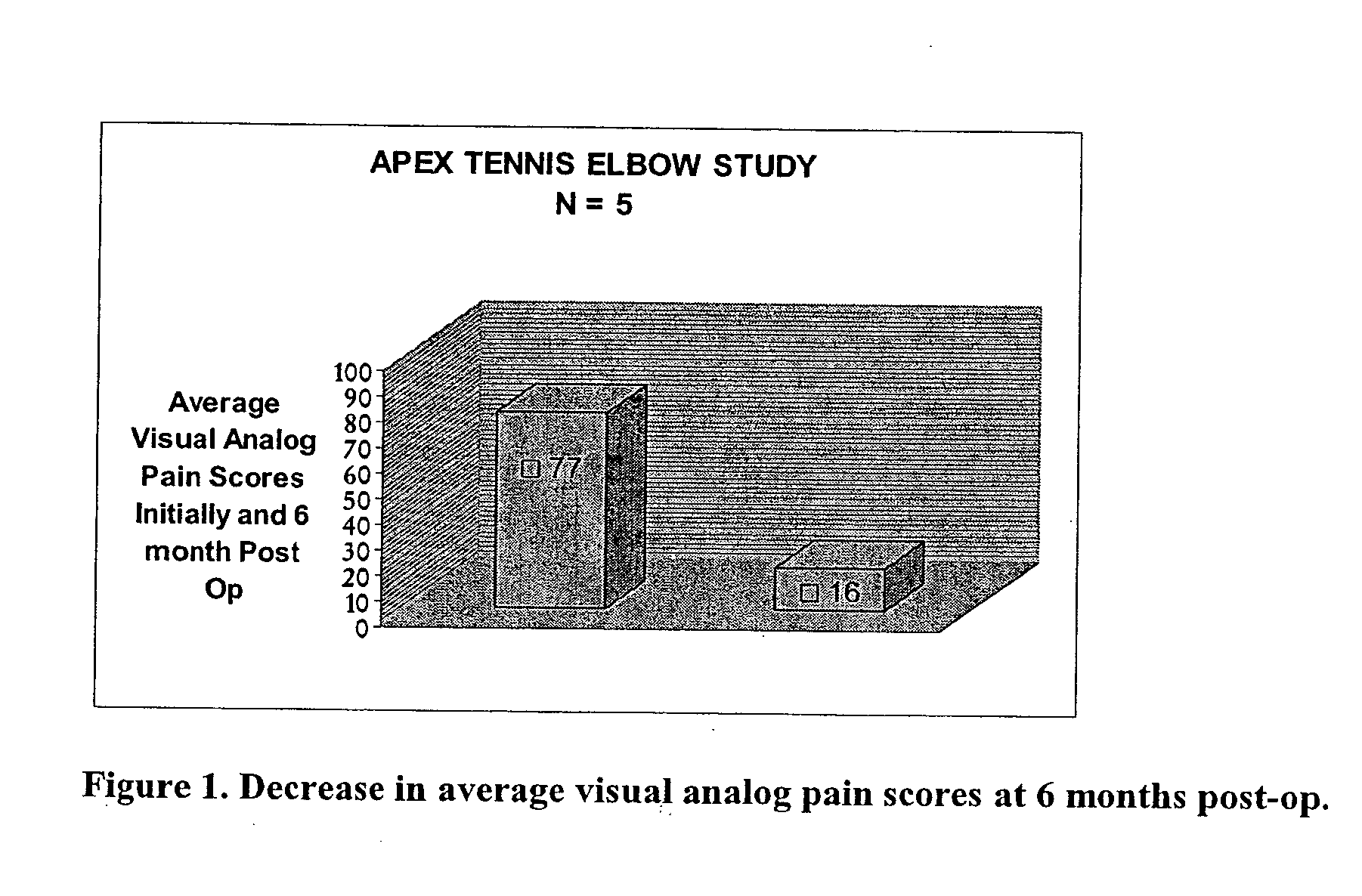
Methods are described for using compositions containing platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of a variety of tissue lesions. Particularly, delivery of platelet-rich plasma to connective tissue is described. The described method and compositions have been shown to provide both pain relief and improved mobility in treatment of lateral epicondylitis.
Owner:BLUE ENGINE BIOLOGICS LLC
Bone void filling tube and shear mechanism
Owner:ARTHREX
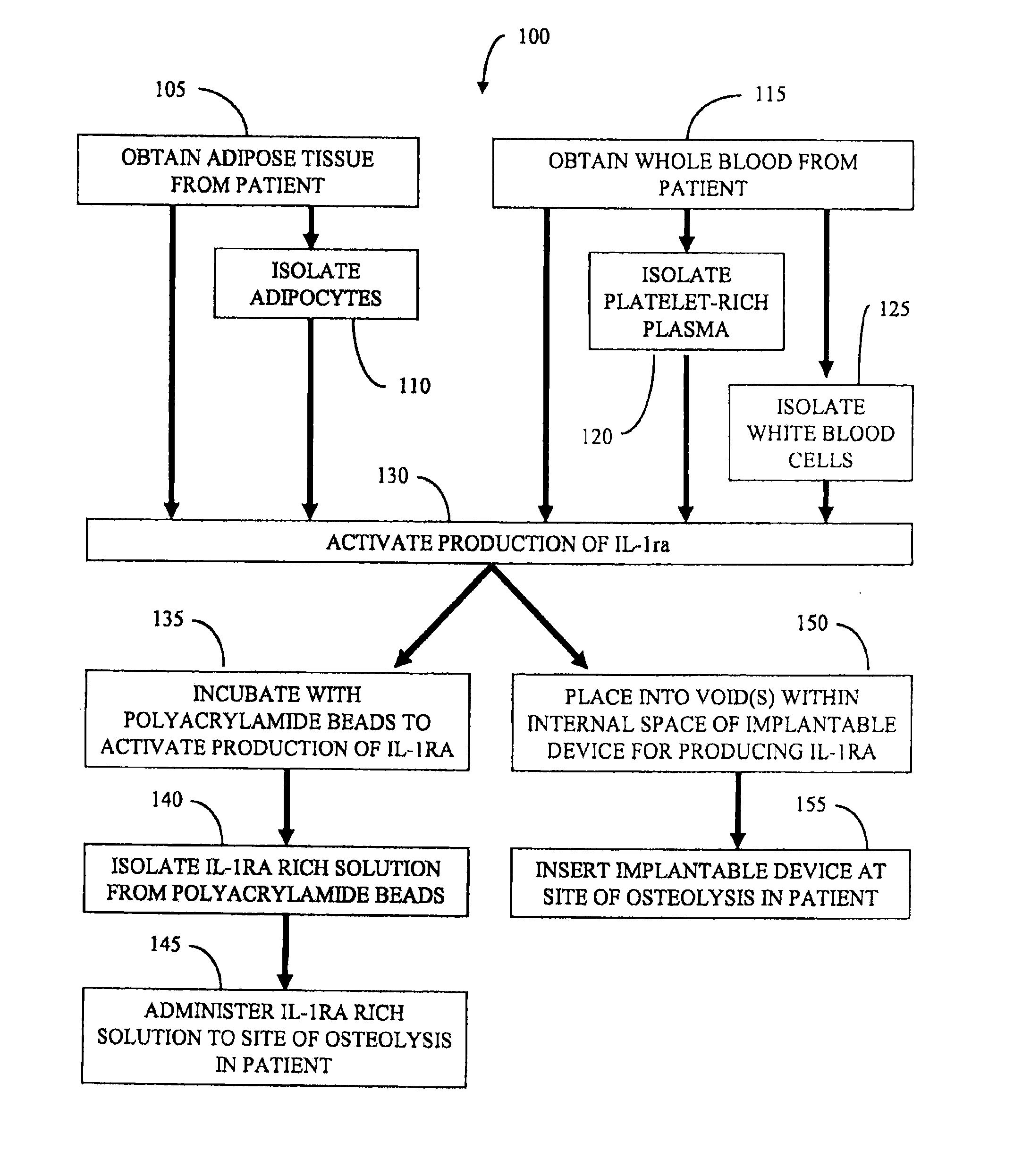
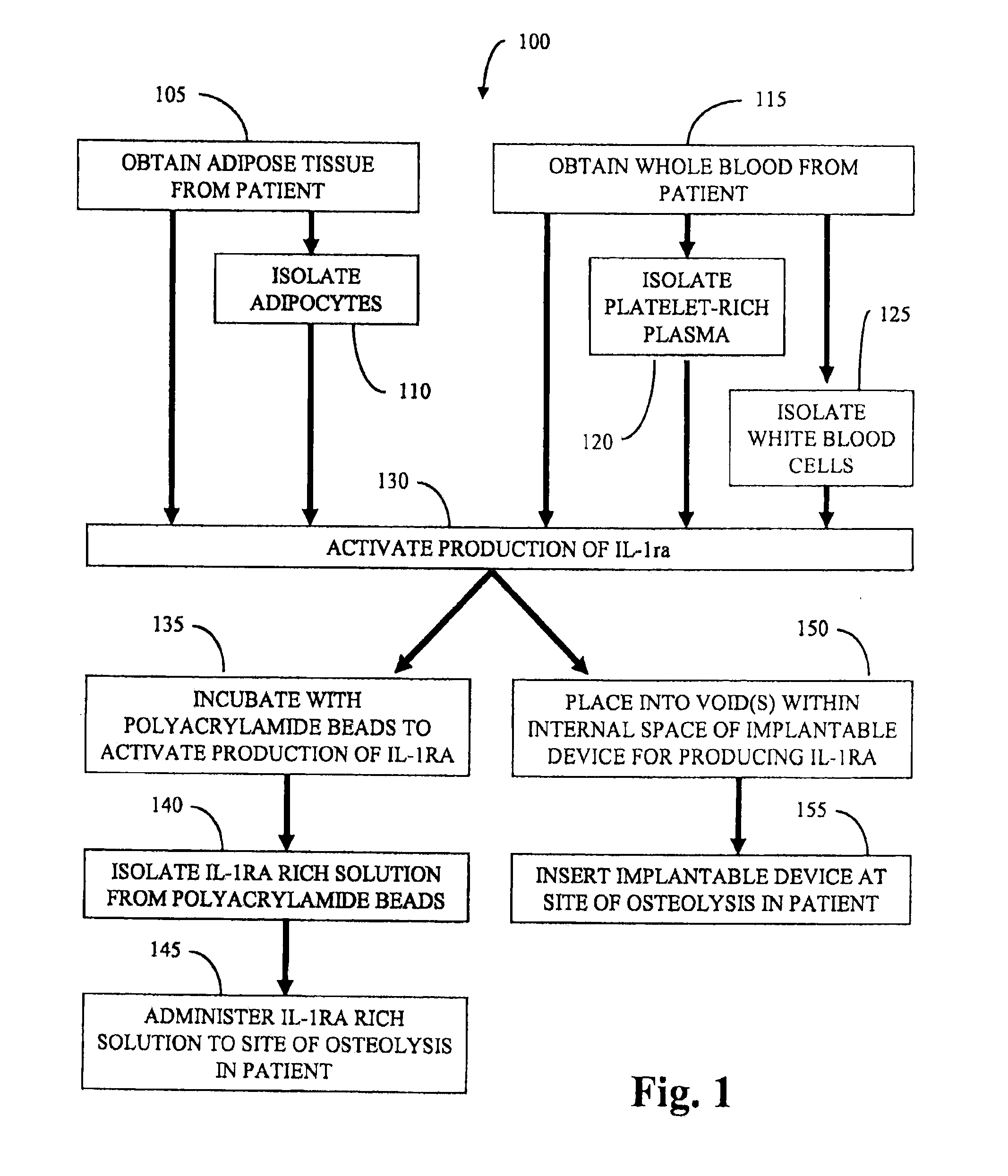
Osteolysis treatment
InactiveUS20110052561A1Reduce inflammationShorten the progressPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderWhite blood cellImplanted device
Methods and treatments for osteolysis employing interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra). Activating production of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist includes incubating adipose tissue, adipocytes, whole blood, platelet rich plasma, and / or isolated white blood cells with polyacrylamide beads to produce a solution rich in interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Activating the production of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist includes using an implantable device loaded with adipose tissue, adipocytes, whole blood, platelet rich plasma, and / or isolated white blood cells. Methods for treating osteolysis at the site of an artificial joint in a patient include administering and / or inserting the solution rich in interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and / or the implantable device, respectively.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Compositions and minimally invasive methods for treating dysfunction of cardiac muscle
ActiveUS20060263407A1Cause effectsExtended storage timeOrganic active ingredientsBiocideEpicondylitisConnective tissue fiber
Methods are described for using compositions containing platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of a variety of tissue lesions. Particularly, delivery of platelet-rich plasma to connective tissue is described. The described method and compositions have been shown to provide both pain relief and improved mobility in treatment of lateral epicondylitis.
Owner:BLUE ENGINE BIOLOGICS LLC
Method And Apparatus For Preparing Platelet Rich Plasma And Concentrates Thereof
ActiveUS20100206798A1Shaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersTransportation and packagingHollow fibreFiber
The PRP separator-concentrator of this invention is suitable for office use or emergency use for trauma victims. The PRP separator comprises a motorized centrifugal separation assembly, and a concentrator assembly. The centrifugal separator assembly comprises a centrifugal drum separator that includes an erythrocyte capture module and a motor having a drive axis connected to the centrifugal drum separator. The concentrator assembly comprises a water-removal module for preparing PRP concentrate. The centrifugal drum separator has an erythrocyte trap. The water removal module can be a syringe device with water absorbing beads or it can be a pump-hollow fiber cartridge assembly. The hollow fibers are membranes with pores that allow the flow of water through the fiber membrane while excluding flow of clotting factors useful for sealing and adhering tissue and growth factors helpful for healing while avoiding activation of platelets and disruption of any trace erythrocytes present in the PRP.
Owner:HANUMAN +1
Semi-synthetic platelet gel and method for the preparation thereof
A semi-synthetic platelet gel comprising a platelet-rich plasma, at least one platelet activator, and a biocompatible polymer selected from the group comprising carbomers, polyalkylene glycols, poloxamers, polyesters, polyethers, polyanhydrides, polyacrylates, polyvinyl acetates, polyvinyl pyrrolidones, polysaccharides, and derivatives thereof. A method for preparing a semi-synthetic platelet gel comprising the steps of (a) mixing a platelet-rich plasma with at least one platelet activator, and, before the start of clot formation, (b) adding the mixture thus obtained to a biocompatible polymer selected from the group comprising carbomers, polyalkylene glycols, poloxamers, polyesters, polyethers, polyanhydrides, polyacrylates, polyvinyl acetates, polyvinyl pyrrolidones, polysaccharides, and derivatives thereof.
Owner:LECTIO PHARMAENTWICKLUNGS UND VERW
Apparatus and method for preparing platelet rich plasma and concentrates thereof
ActiveUS7824559B2Increase in platelet levelAvoid assemblyRotary centrifugesMedical devicesEngineeringBlood plasma
A PRP separator-concentrator comprising a housing, a separation assembly, and a concentration assembly. The concentration assembly has a concentration sump. An axially concentric rigid stationary outlet tube is secured to the housing and extends through the separation assembly to the sump. The separation assembly is attached to and positioned above the concentration assembly to form a combined separator-concentrator assemblage that is rotatable about the outlet tube. The separation assembly includes a separation chamber lined with a depth filter having pores and passageways that are sized to receive and entrap erythrocytes during centrifuging. The concentration chamber has a floor for supporting desiccated beads and a wall with at least one opening closed with a screen. The concentrator can have a distribution of upright screen supports, the upright screen supports having an inner surface and an outer surface, the cylindrical screen being supported on the outer surface of the upright screen supports. A stationary bead rake can be secured to the stationary tube and extend outward therefrom, the rake having distal ends that are spaced at a distance from the upright screen supports. The rake can comprise a longitudinal body, the center of which is secured to the rigid outlet tube. The separator-concentrator includes a valve assembly connecting the separation chamber and the concentration chamber. PRP concentrate is produced by contacting PRP with desiccated beads while the beads are stirred with a stationary rake, and rotating the concentration chamber at centrifugal speeds to separate PRP concentrate from the beads.
Owner:BIOMET BIOLOGICS +1
Apparatus for sequestering platelet rich plasma
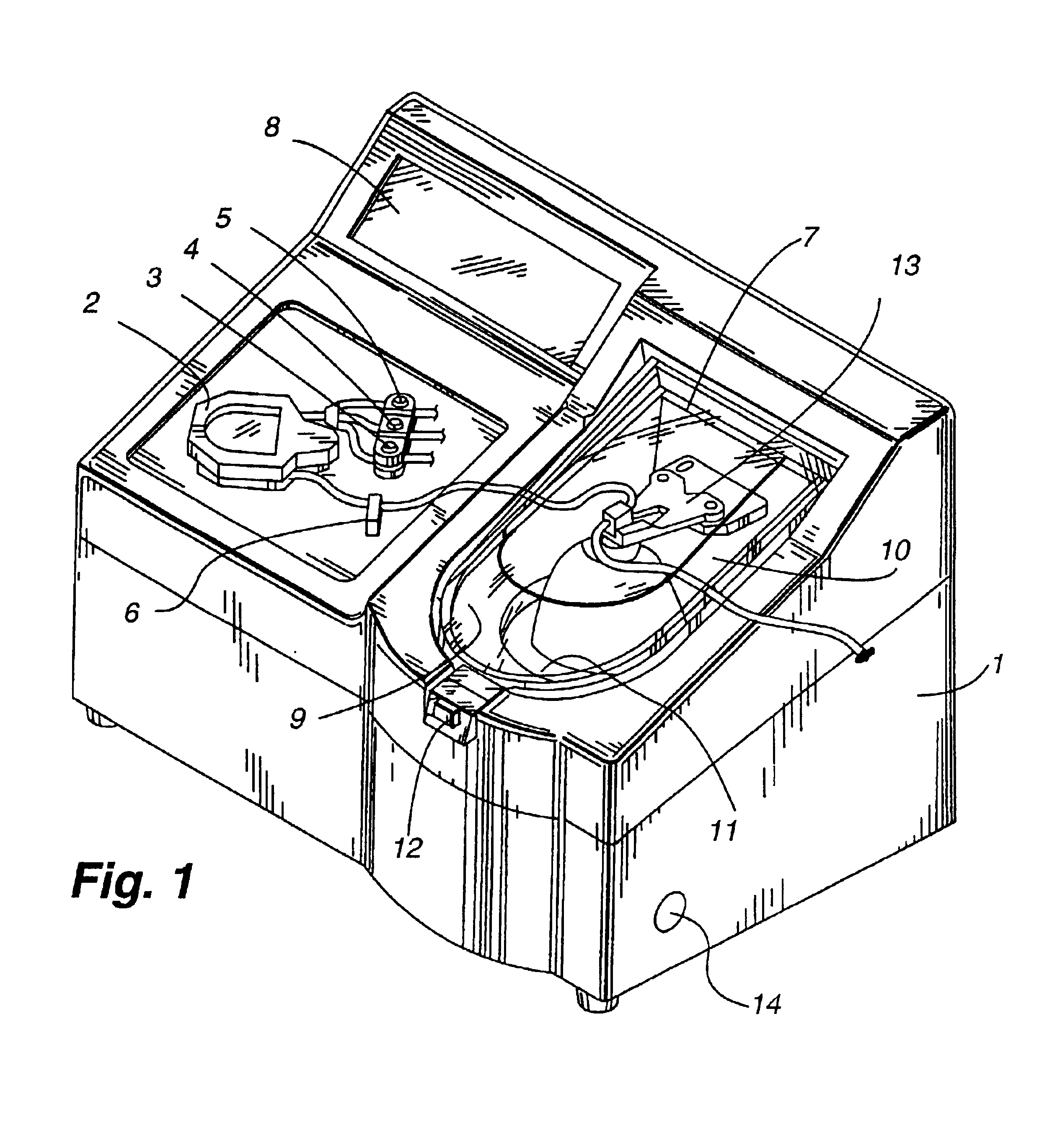
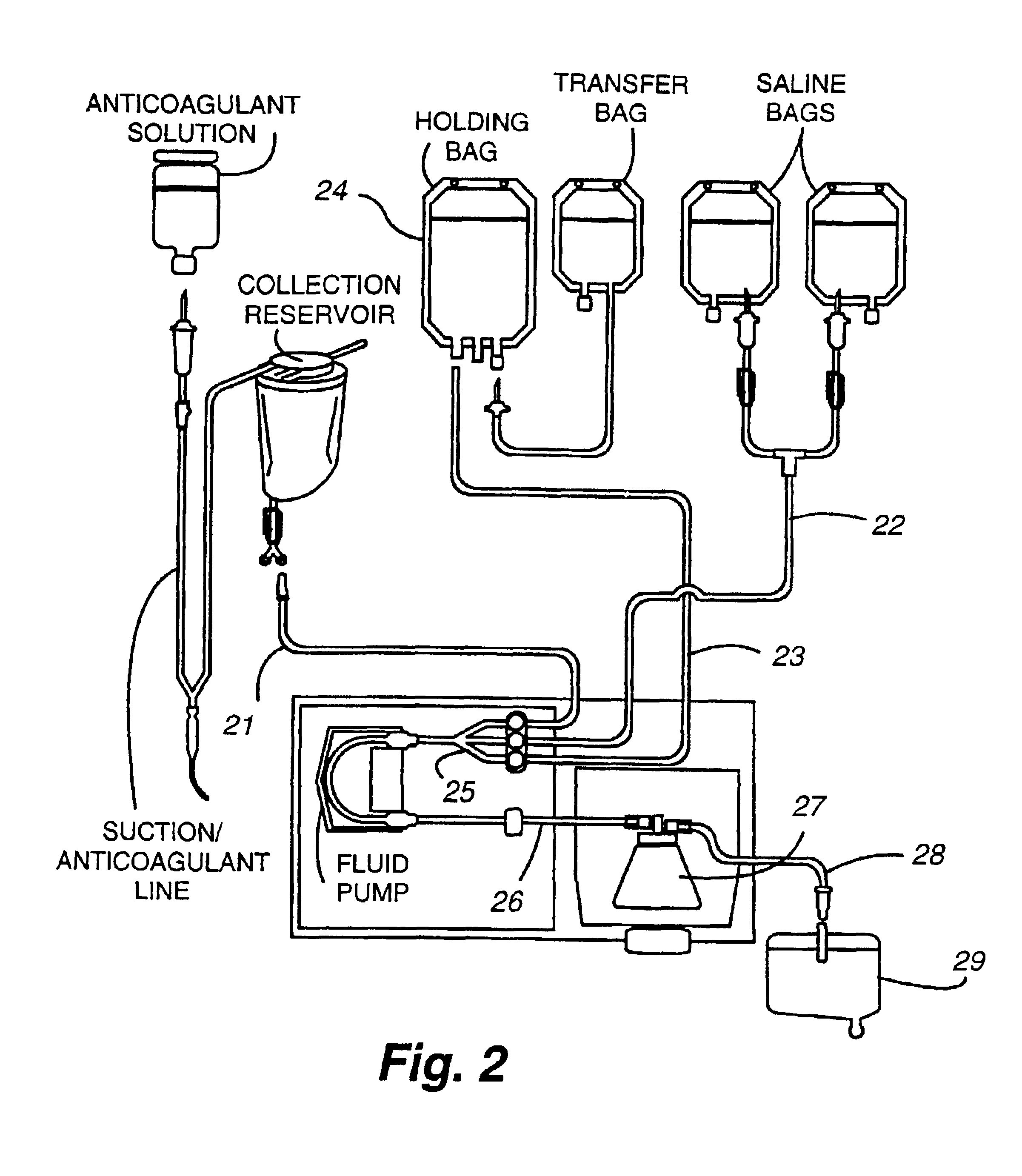
InactiveUS6855119B2Improve efficiencyWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationOther blood circulation devicesLow speedSpins
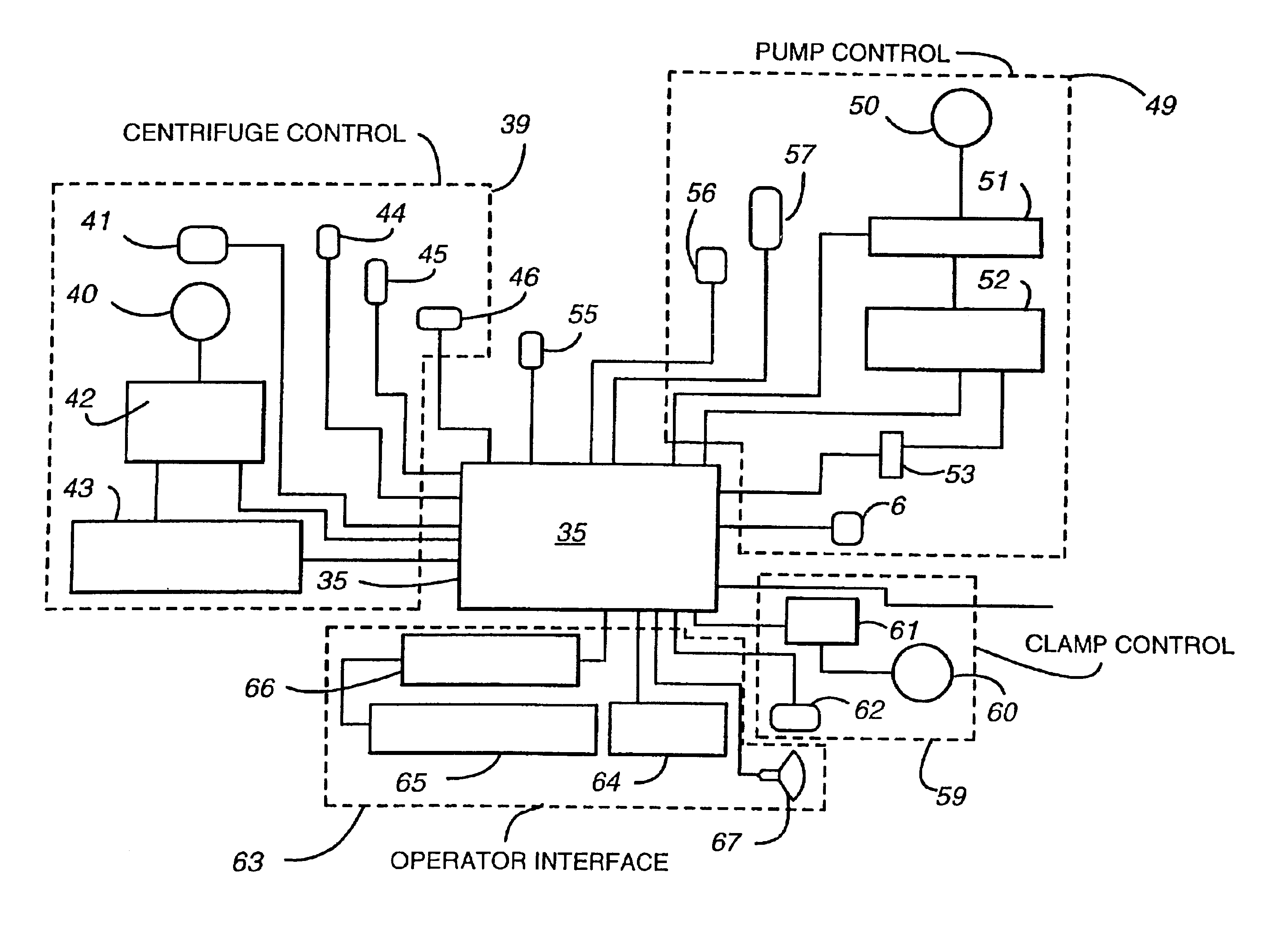
A blood separation system is fully mechanized to collect blood from a patient, separate waste portions of the blood, wash the blood, and redirect the usable portions to a device for reinjecting the usable portions into the patient. The system provides screen displays with detailed setup instructions and instructs the operator at the appropriate times to do certain manual steps. Apparatus for sequestration of platelet rich plasma spins at a high speed sufficient to separate solid cells from the blood sample and then spins at a lower speed for a predetermined time to allow platelets to elute from the solid cells.
Owner:ARTERIOCYTE MEDICAL SYST
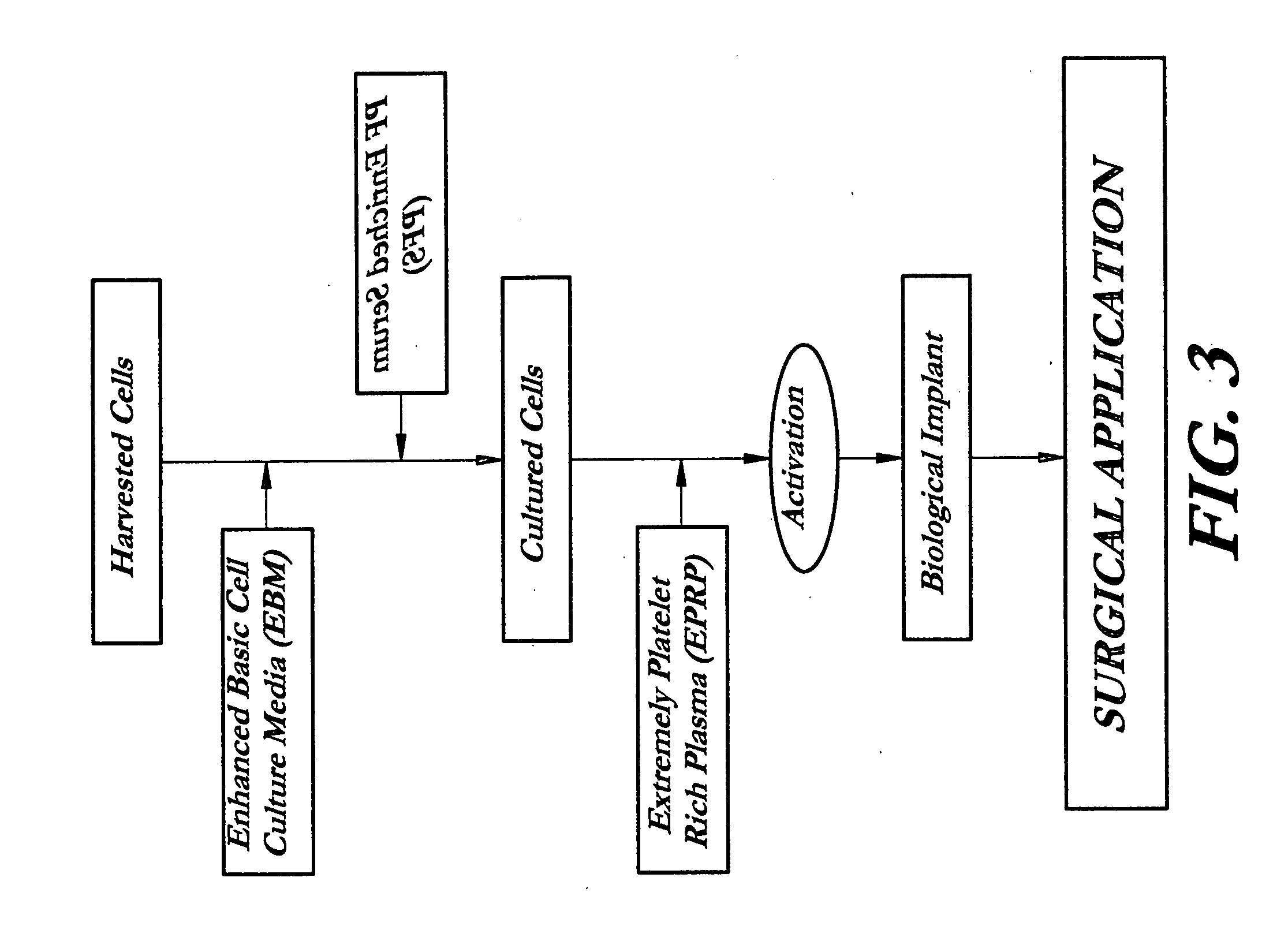
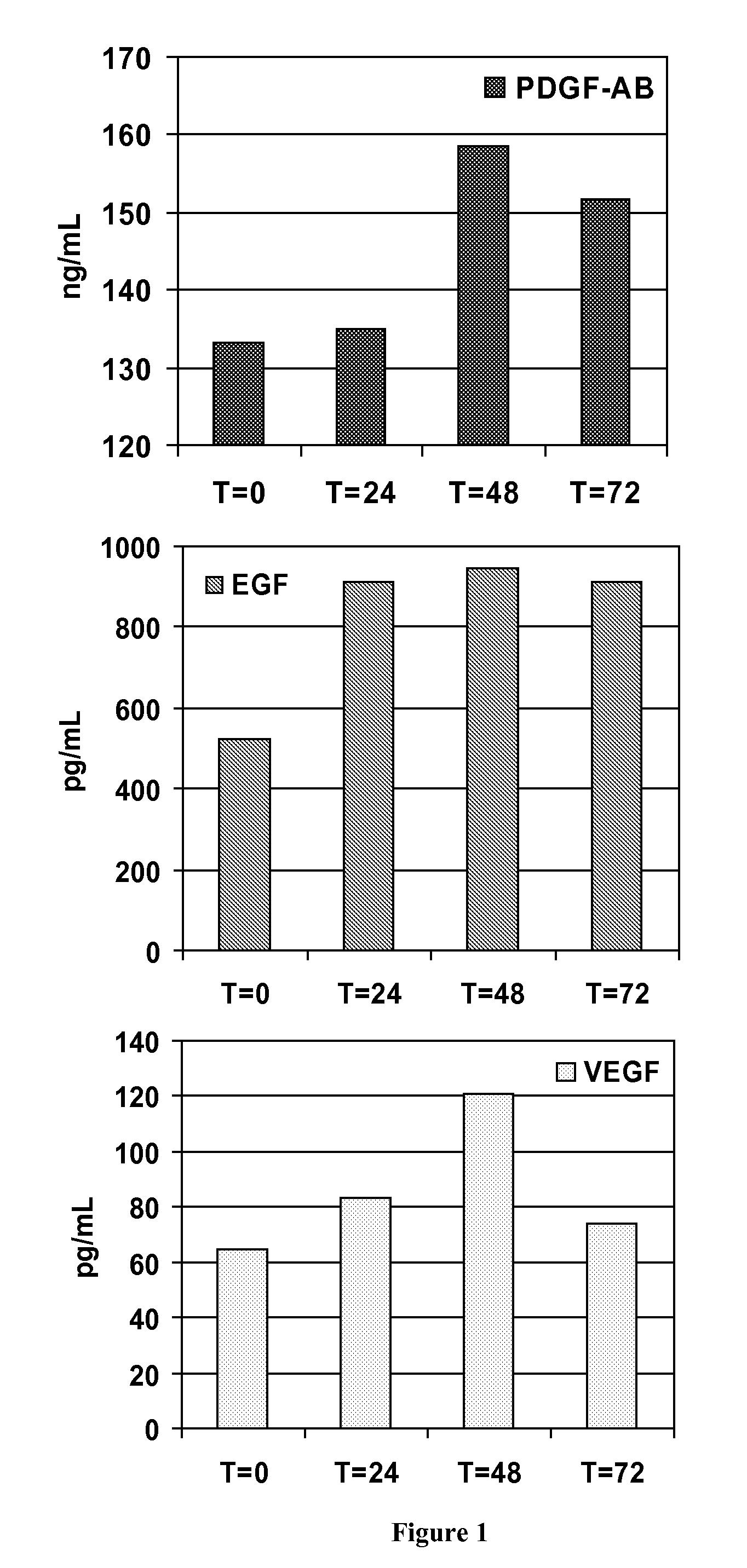
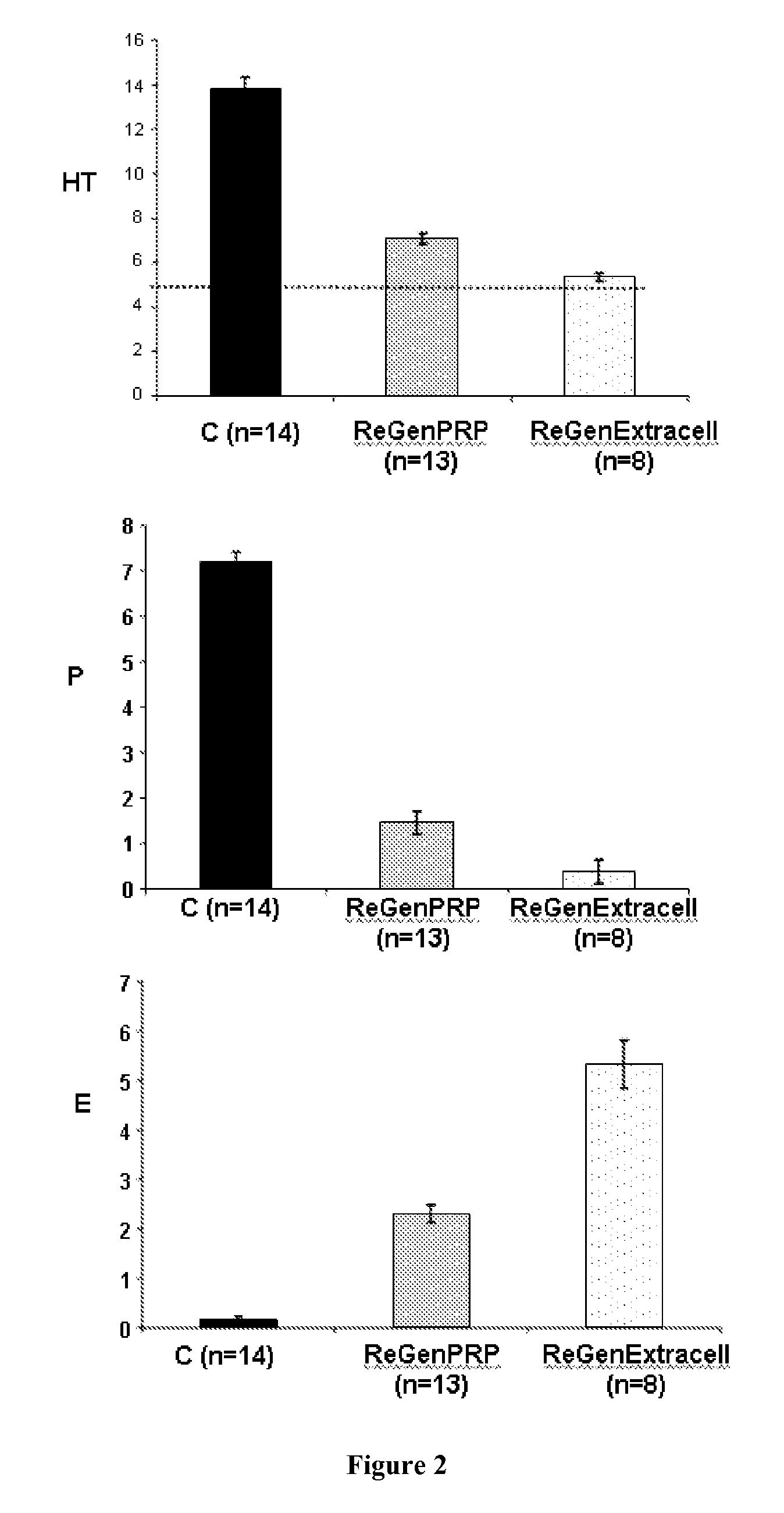
Composition and procedure for tissue creation, regeneration and repair by a cell-bearing biological implant enriched with platelet concentrate and supplements
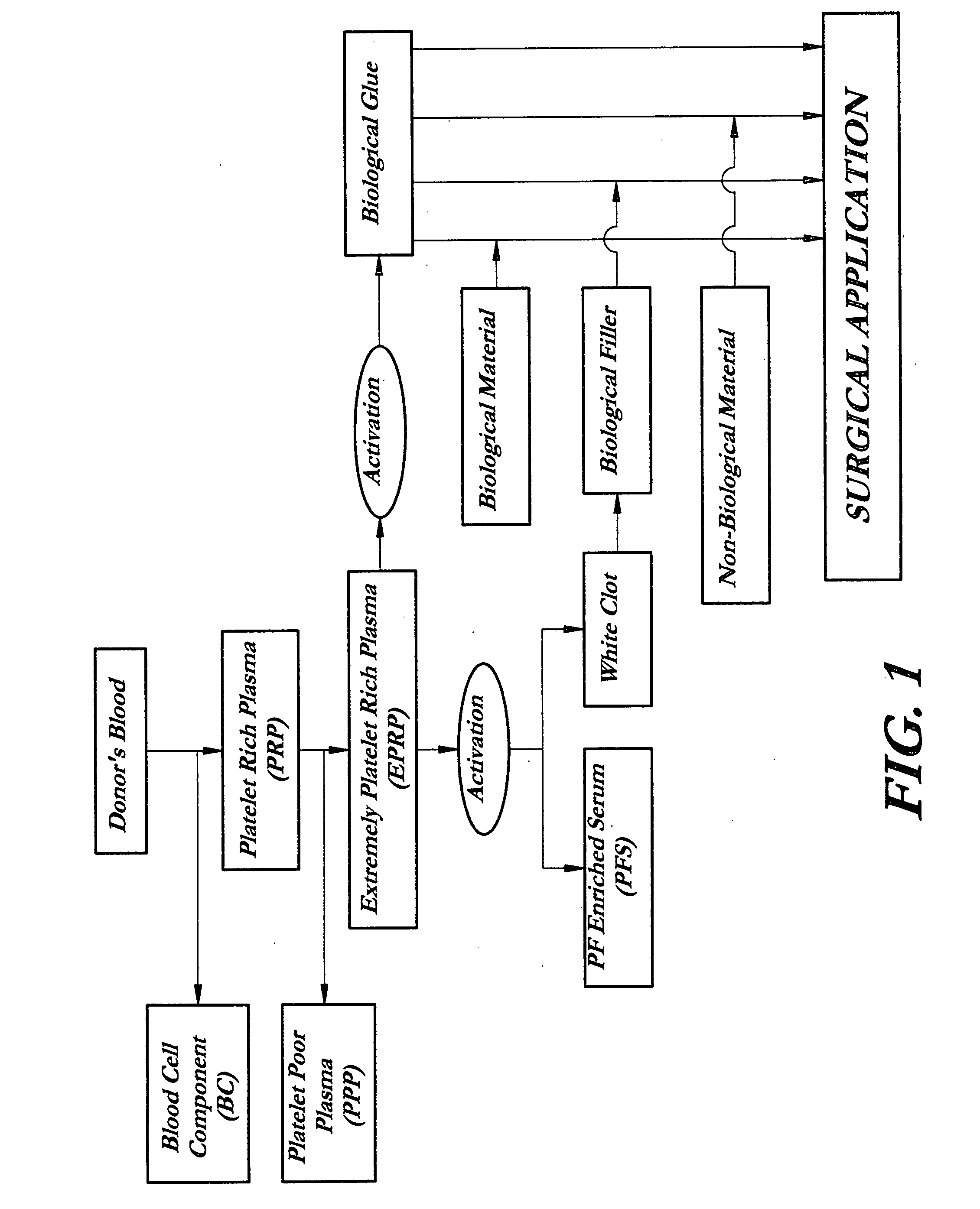
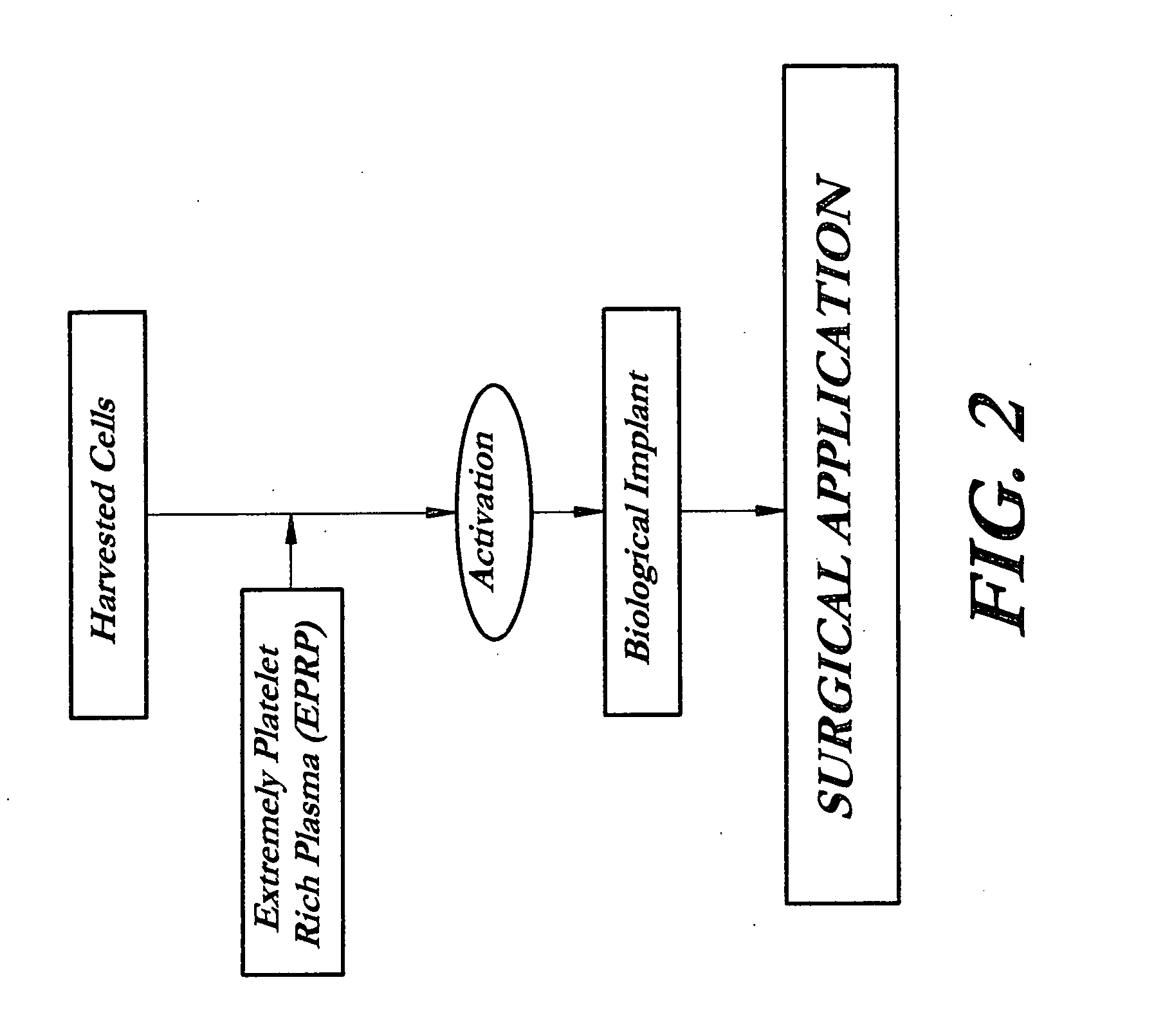
InactiveUS20070141036A1Fill the voidIncrease the number of cellsBiocideCulture processThrombusIn vivo
A composition and method for enhancing tissue growth, regeneration, and repair includes a Biological Glue formed by extraction of an Extremely Platelet Rich Plasma (EPRP) derived from whole blood, and subsequent activation and clotting. The Biological Glue may be utilized alone to fill defects or may be used as an adhesive agent for other biological and non-biological materials. These materials may include processed thrombus derived from the activation of EPRP. Additionally, the Extremely Platelet Rich Plasma may be impregnated with directly harvested or cultured cells, including stem cells, or other materials, prior to activation, to form a Biological Implant that may be implanted in vivo. A Platelet Factor Enriched Serum (PFS) derived from the activation of the Extremely Platelet Rich Plasma (EPRP) may be added to the cell cultures in preparation of a Biological Implant, in order to provide additional growth factors that speed the development of the cell cultures.
Owner:GORROCHATEGUI BARRUETA ALBERTO
Cell Preparations for Extemporaneous Use, Useful for Healing and Rejuvenation In Vivo
The present invention relates to new plasma or new platelet-rich plasma preparations, new cell dissociation methods, new cell associations or compositions, a method of preparation thereof, a use thereof, devices for the preparation thereof and preparations containing such a platelet-rich plasma preparation and cell associations or compositions. Specifically, the invention provides compositions comprising plasma or platelet-rich plasma alone or in combination with cell preparations for use in tissue regeneration and bone regeneration and pain reduction.
Owner:REGENLAB USA LLC
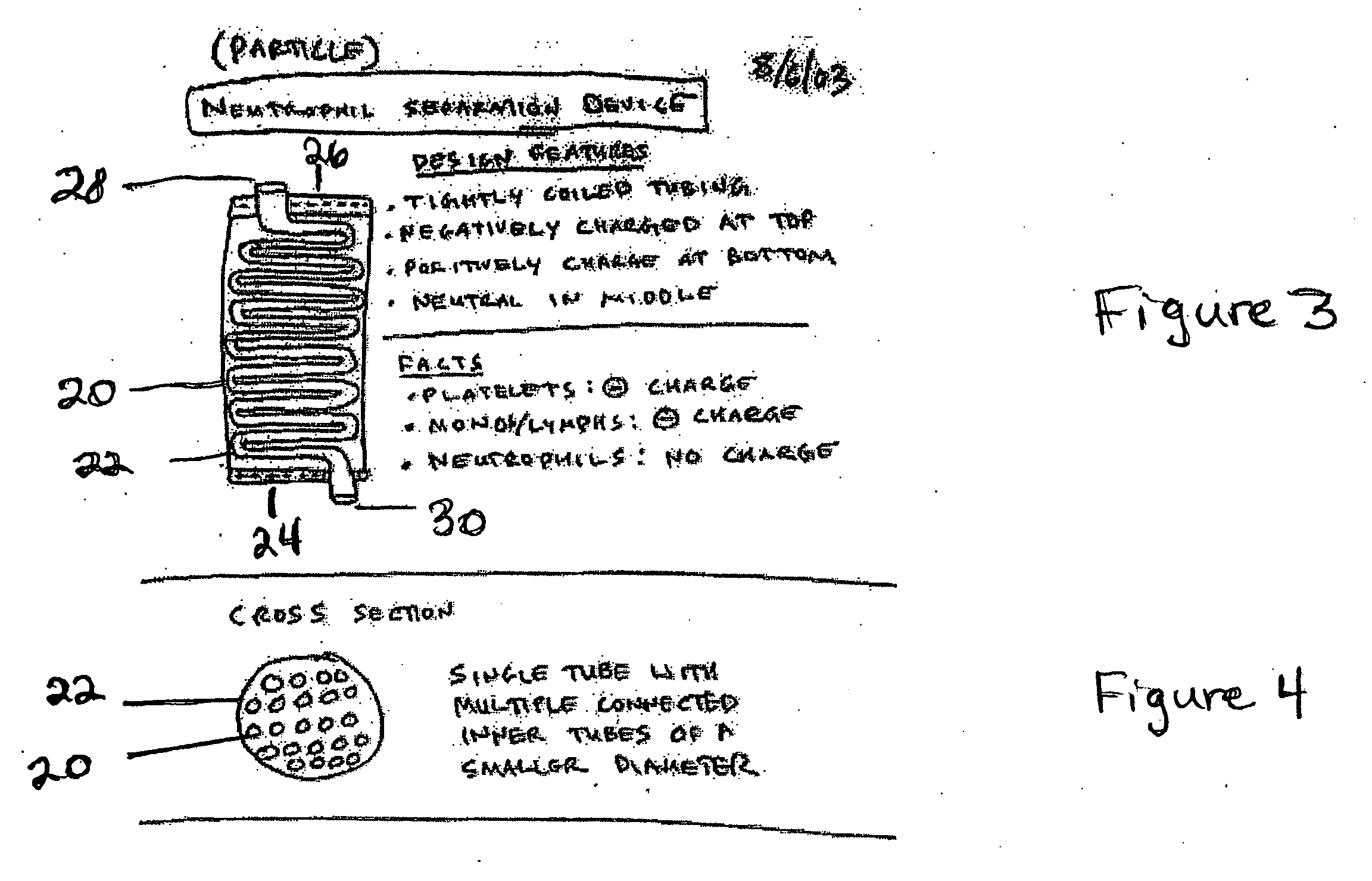
Particle/cell separation device and compositions
ActiveUS20060127382A1Extended storage timeCause effectsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiocideGranular cellNeutrophil granulocyte
Owner:BLUE ENGINE BIOLOGICS LLC
Device and method for detecting the coagulation functions of global, especially primary hemostasis
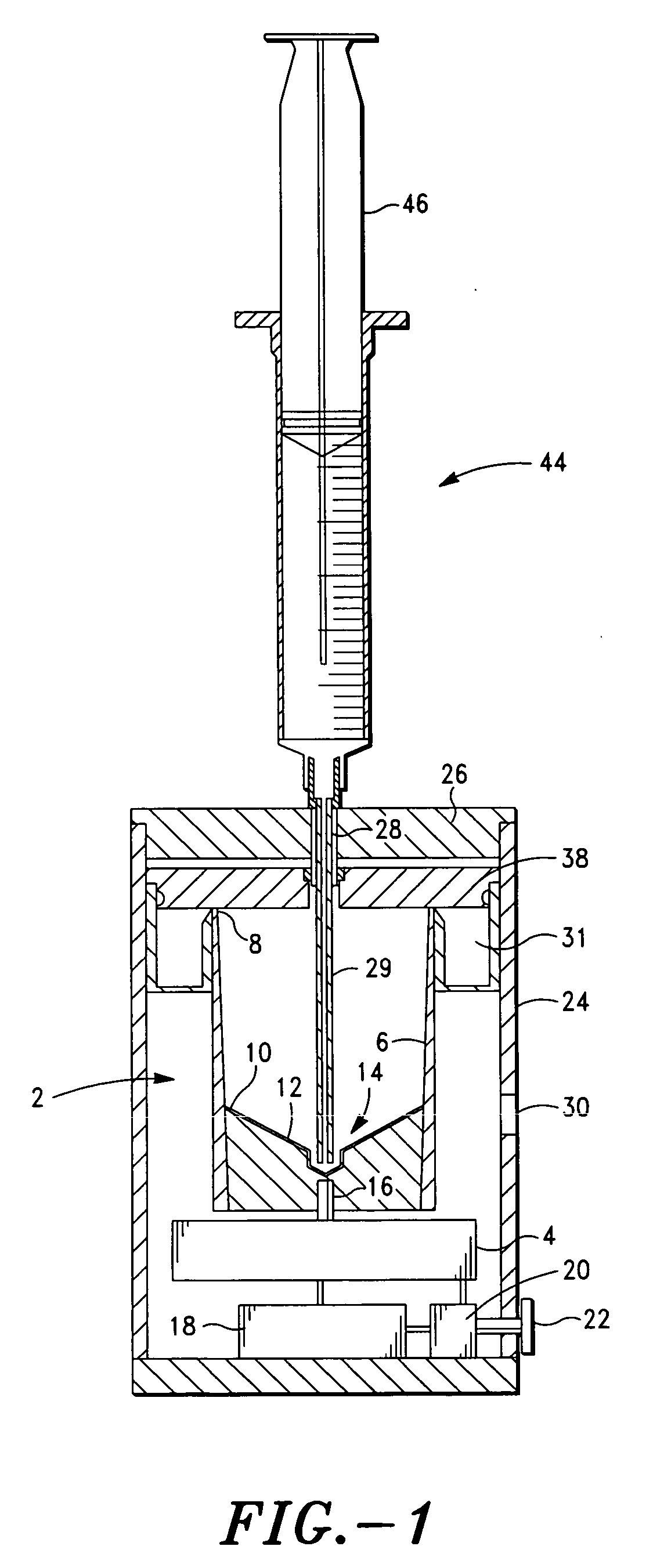
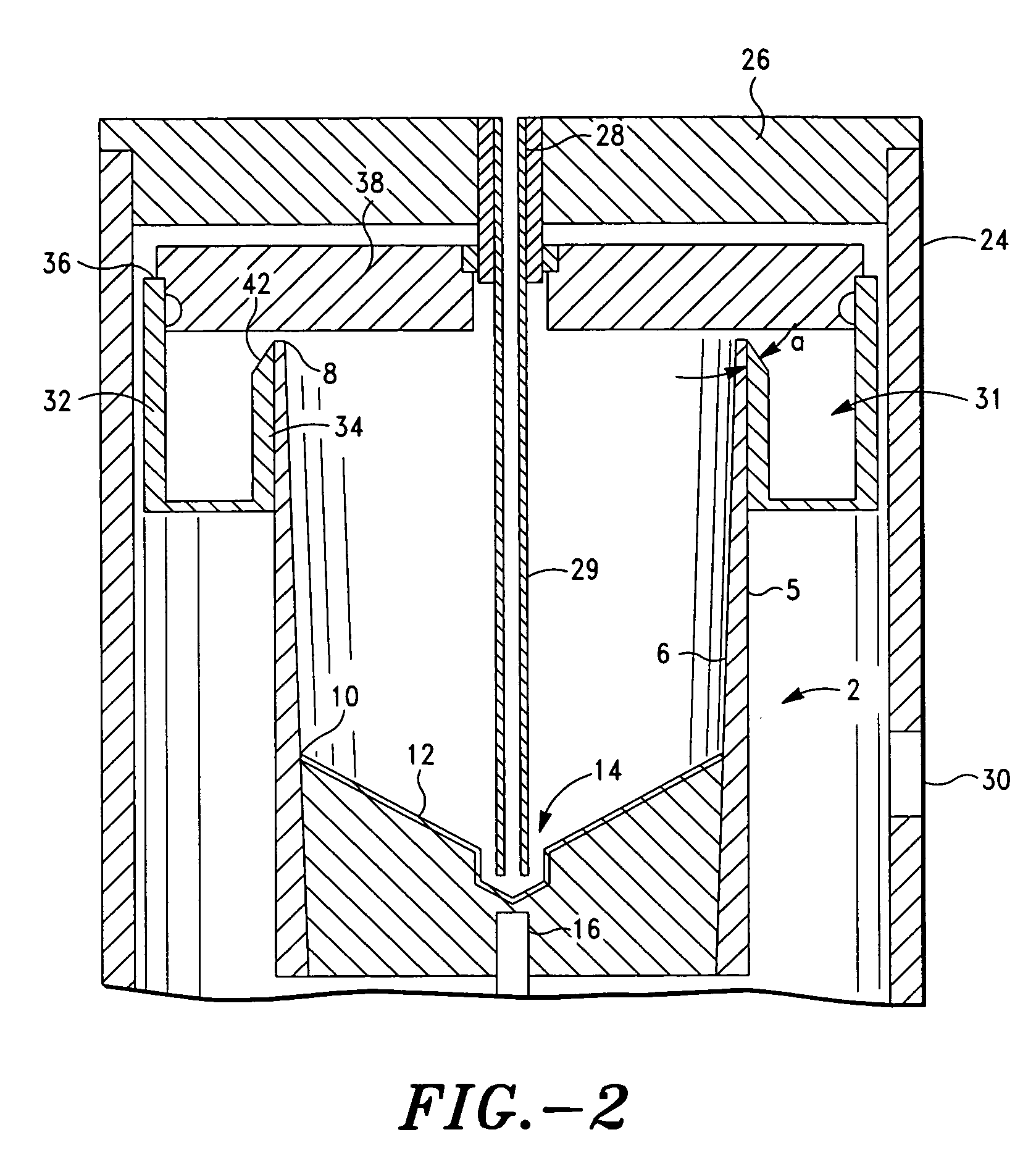
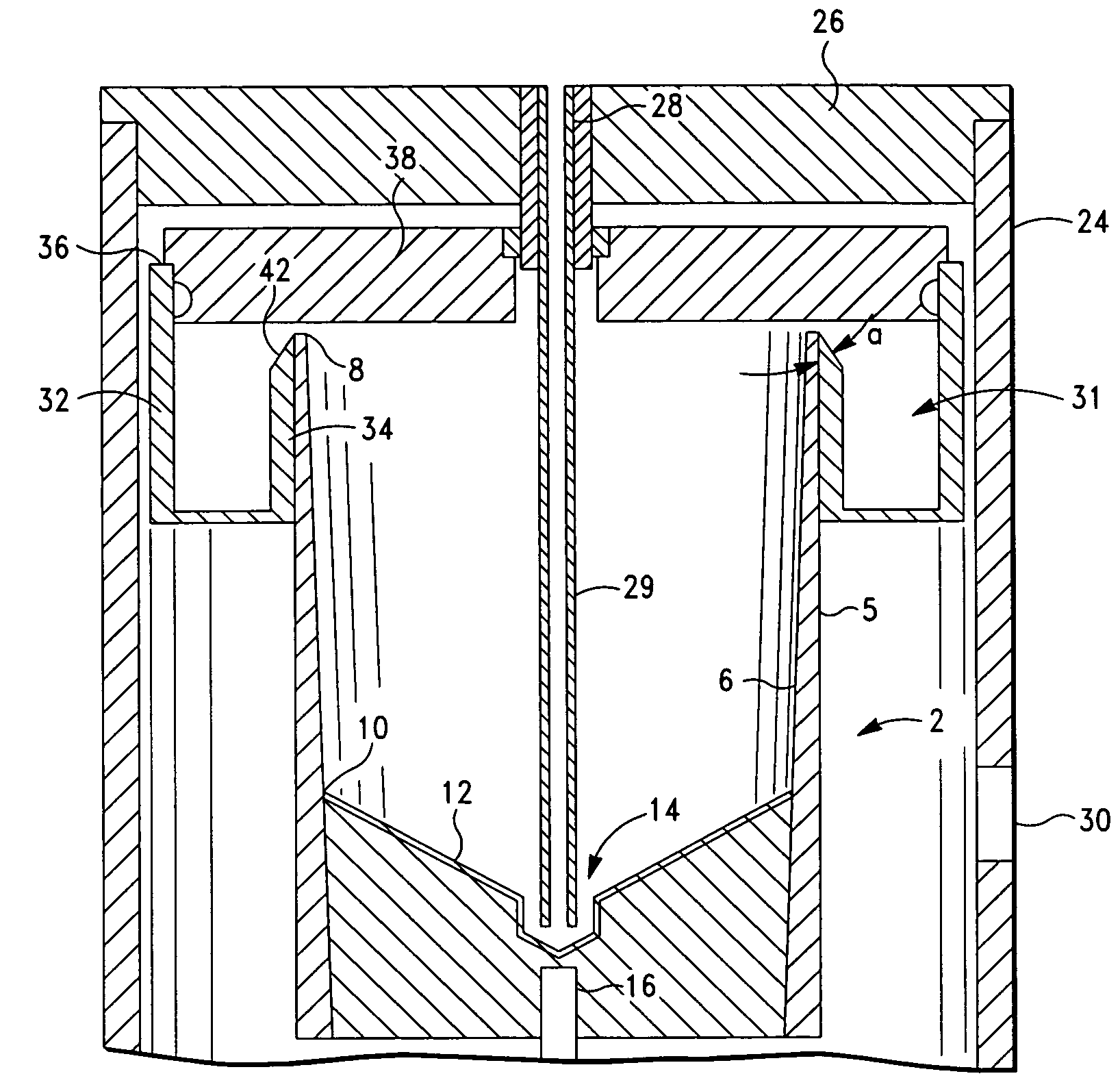
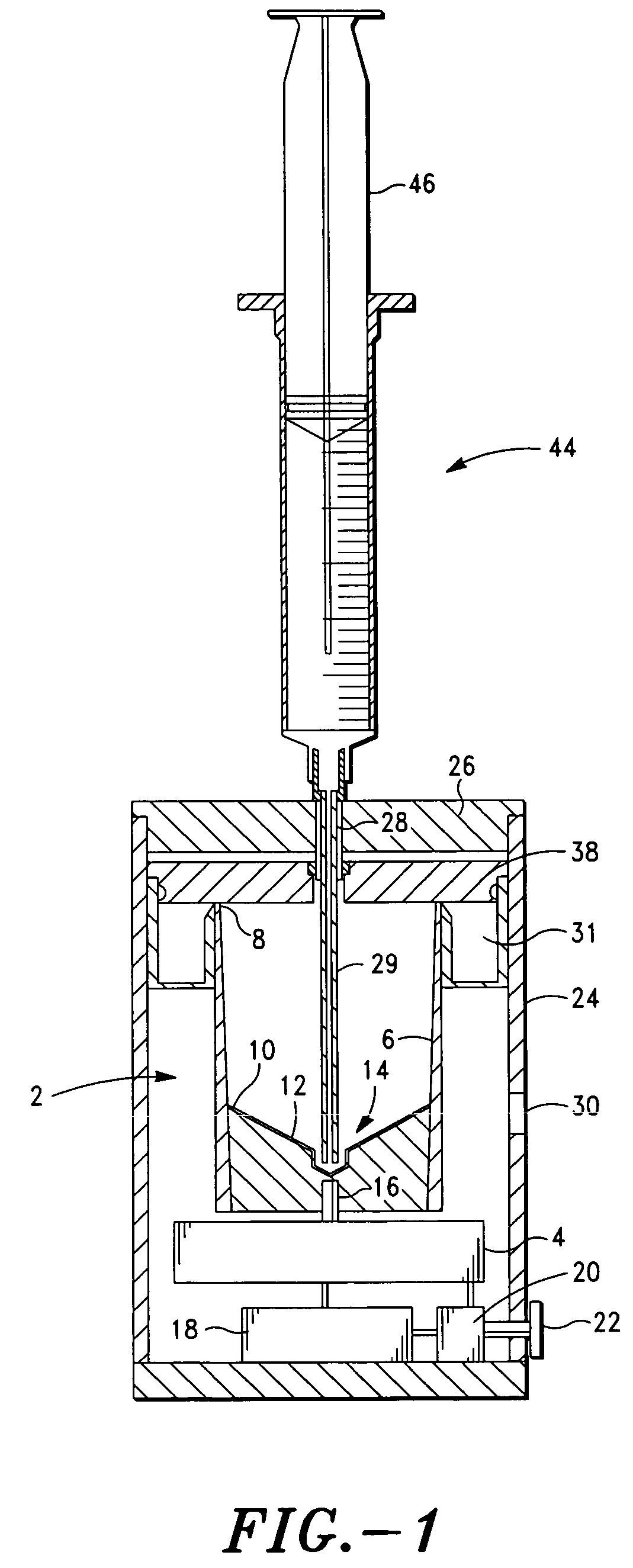
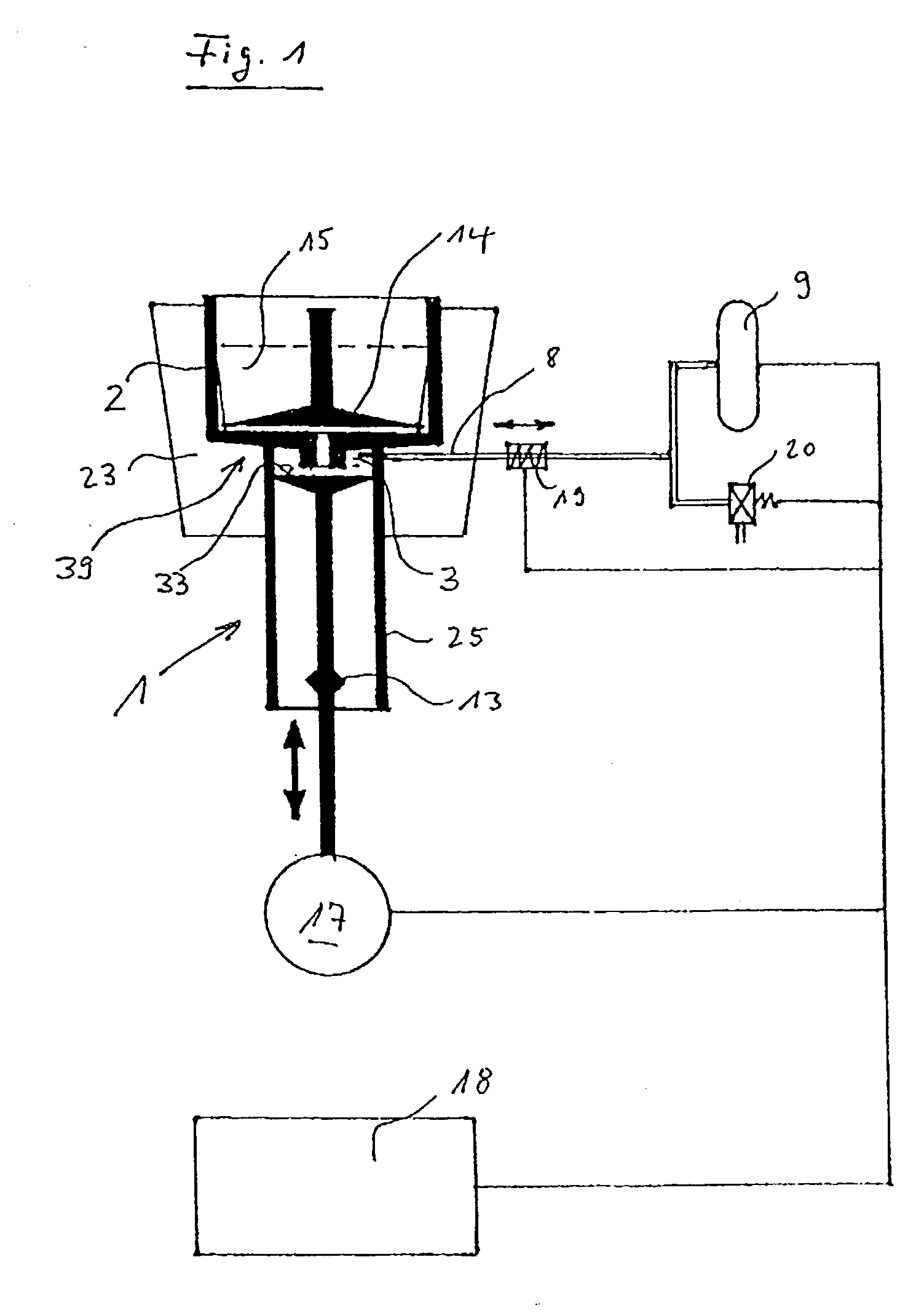
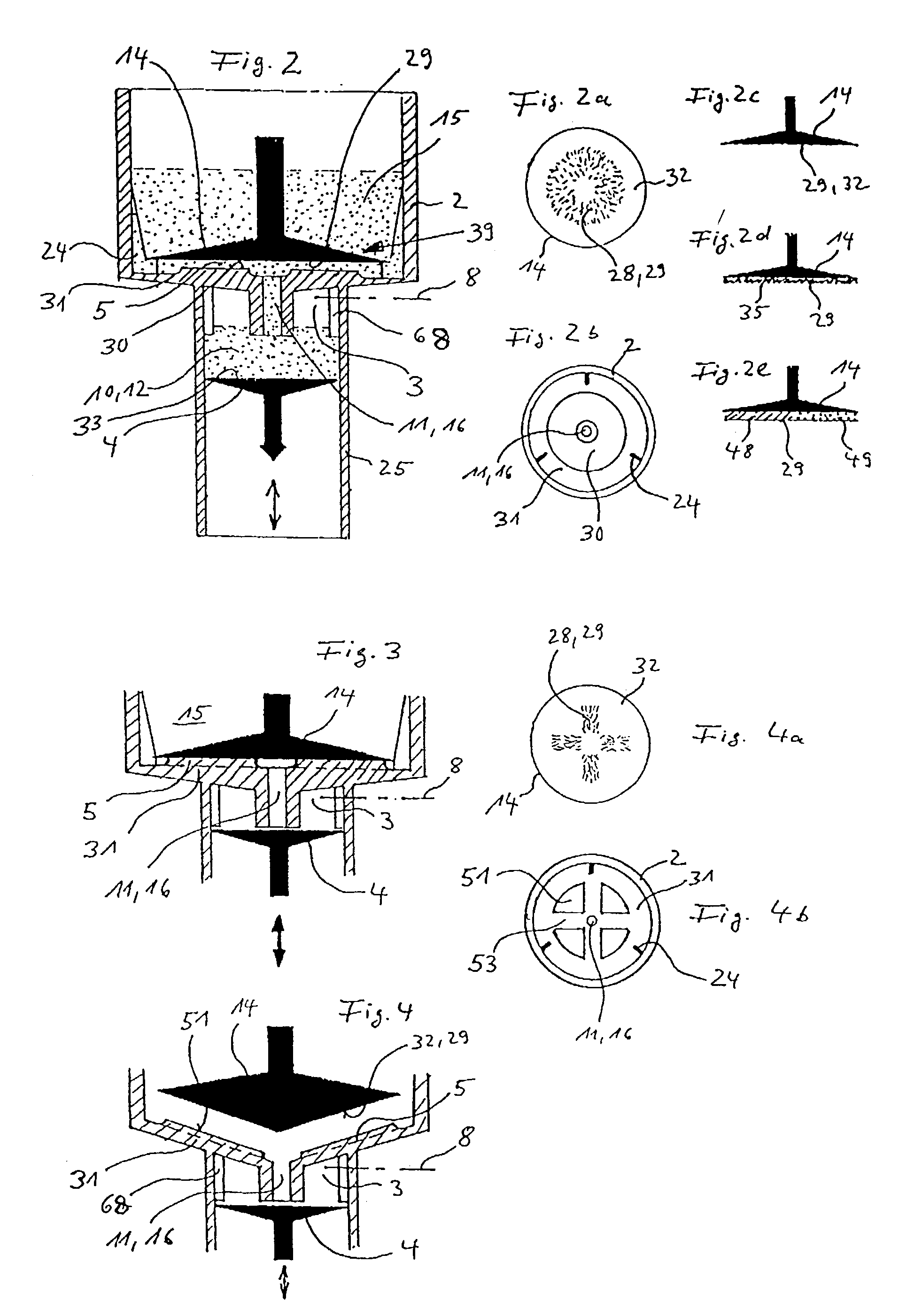
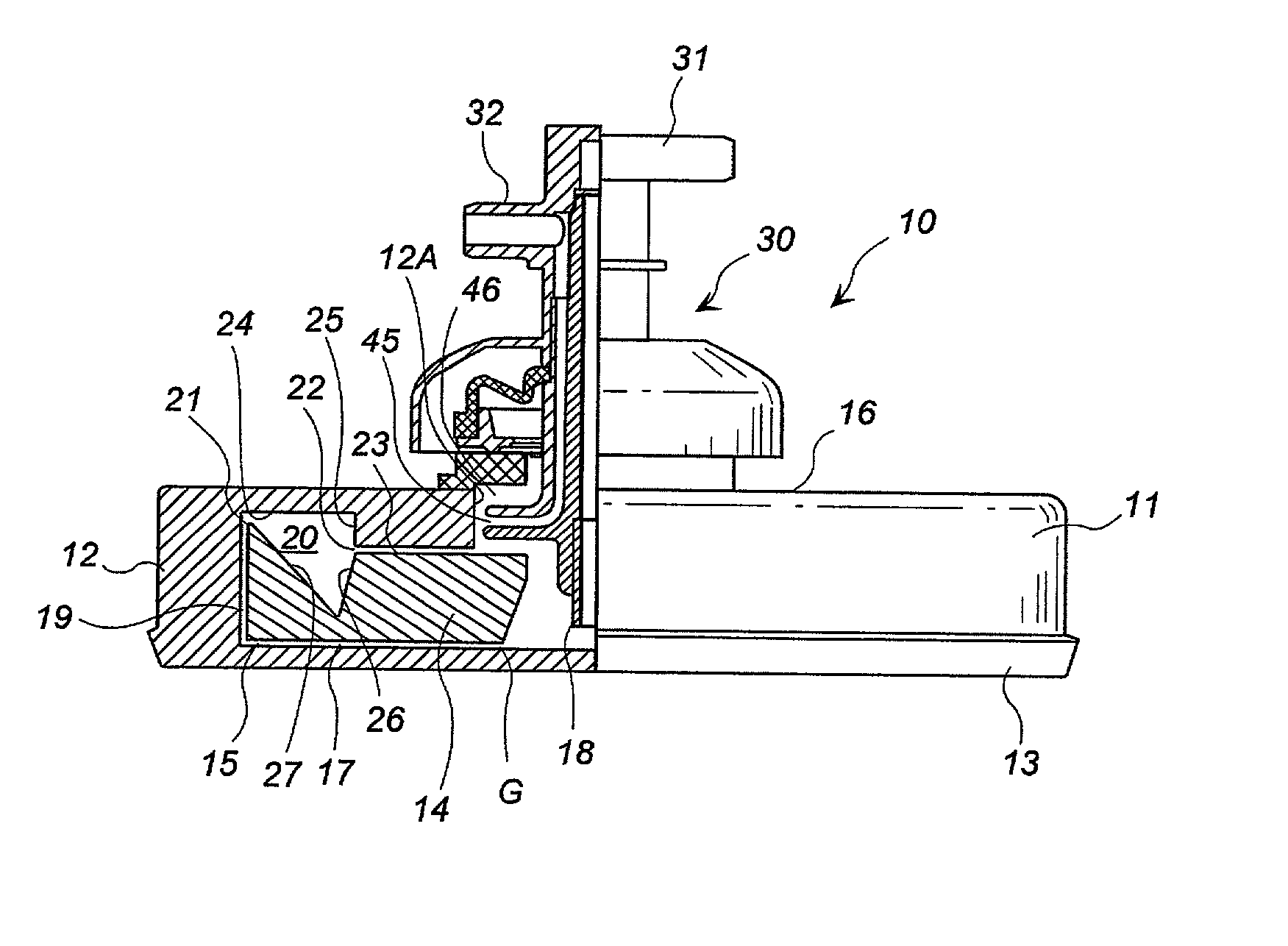
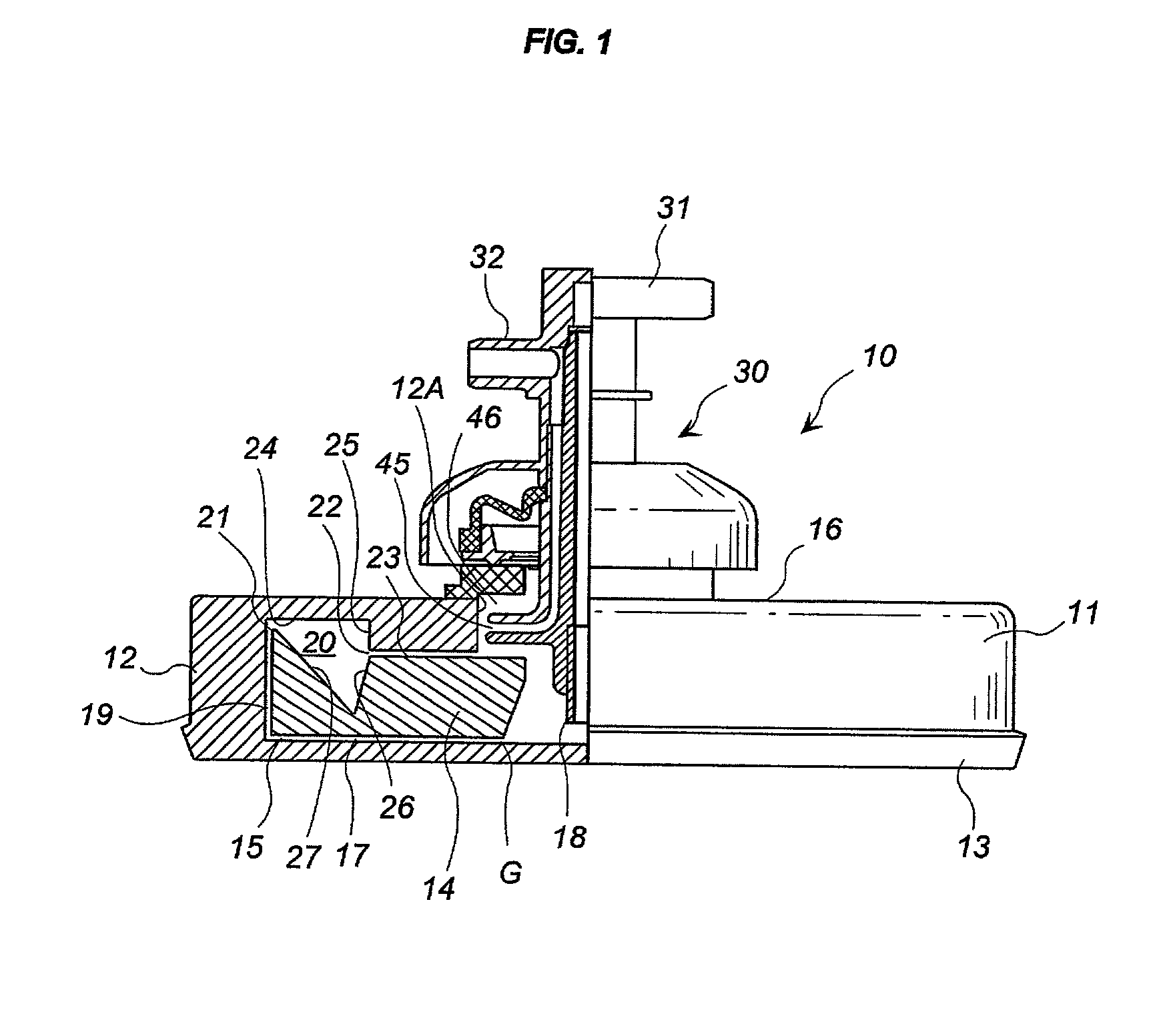
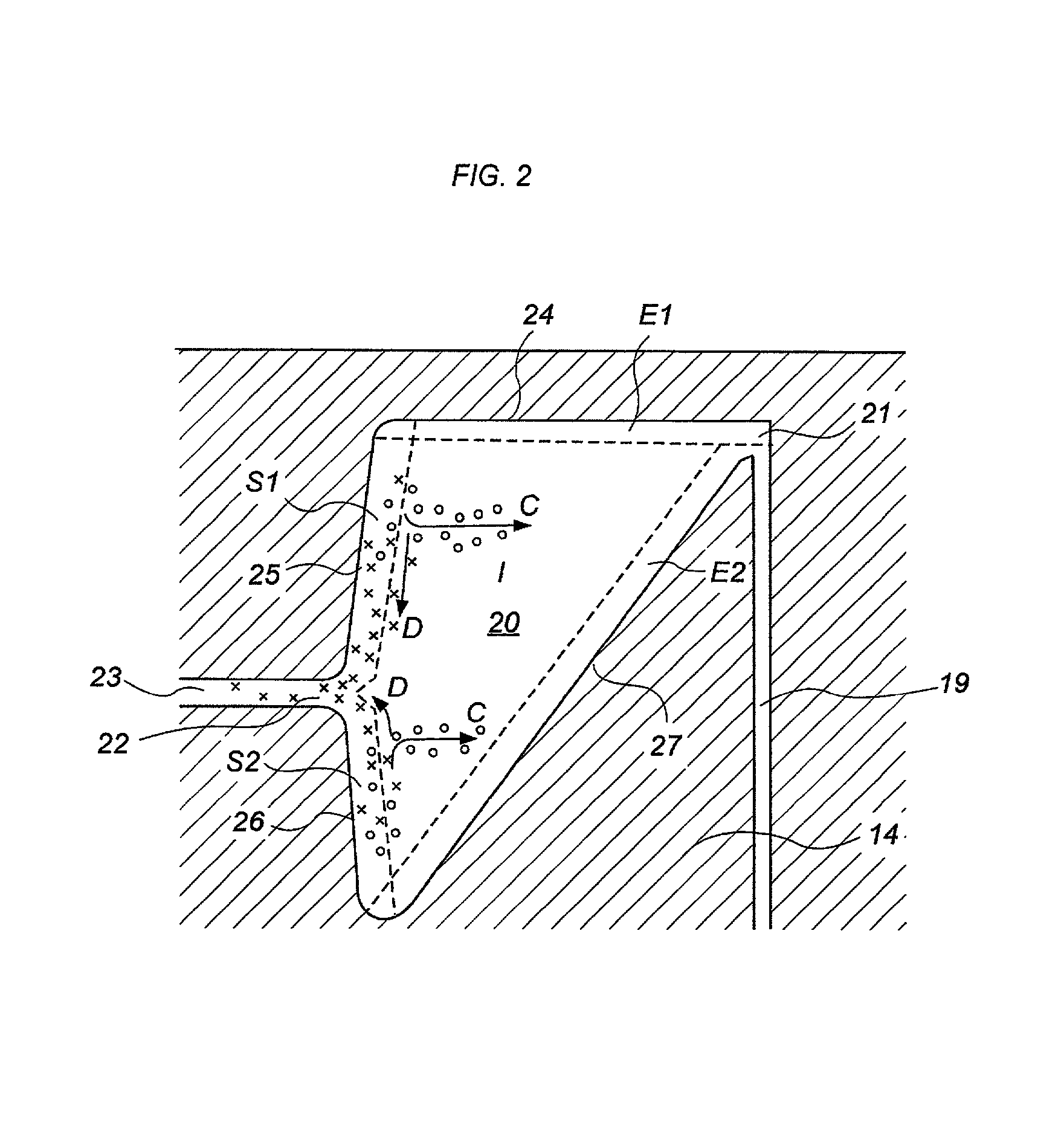
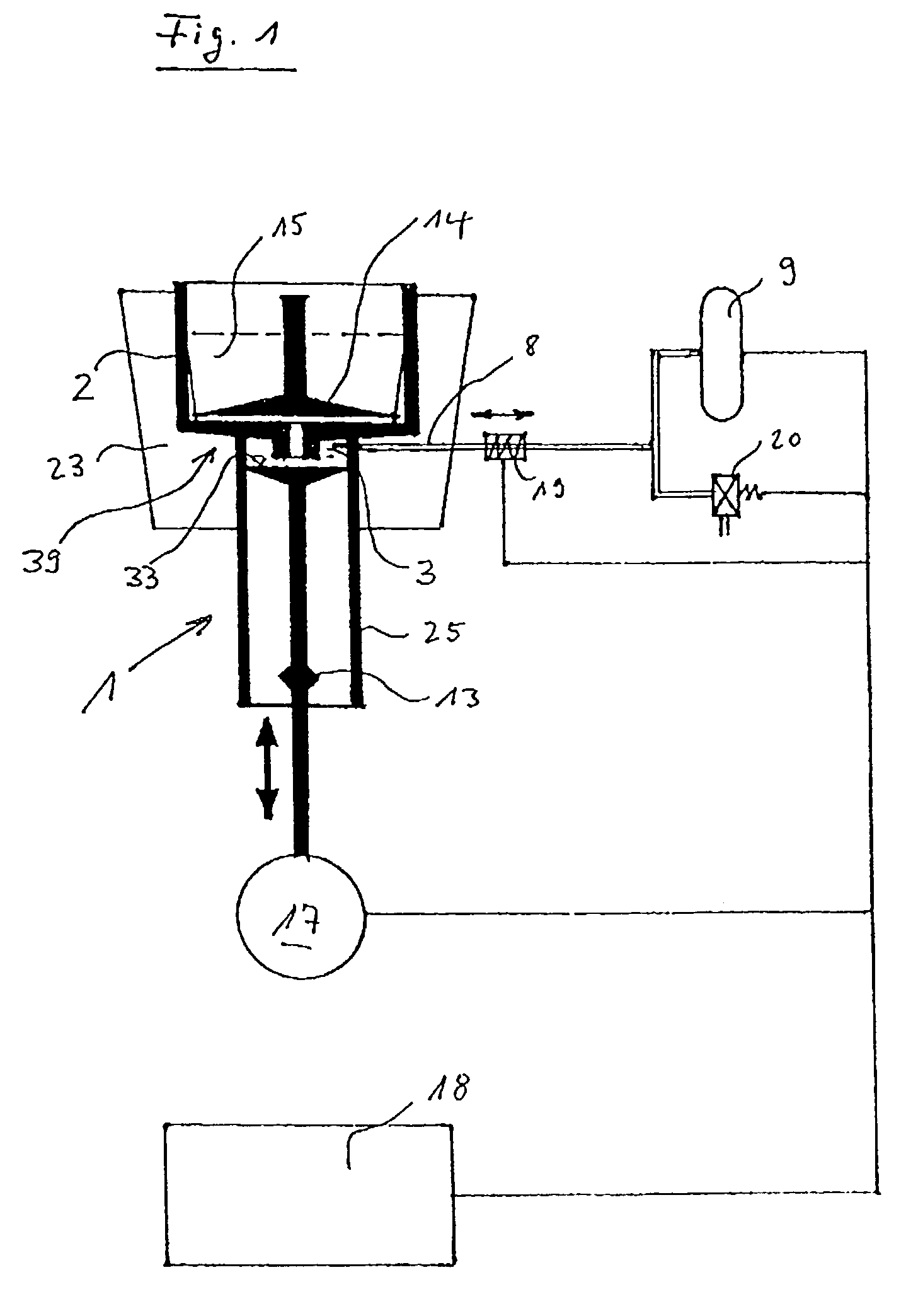
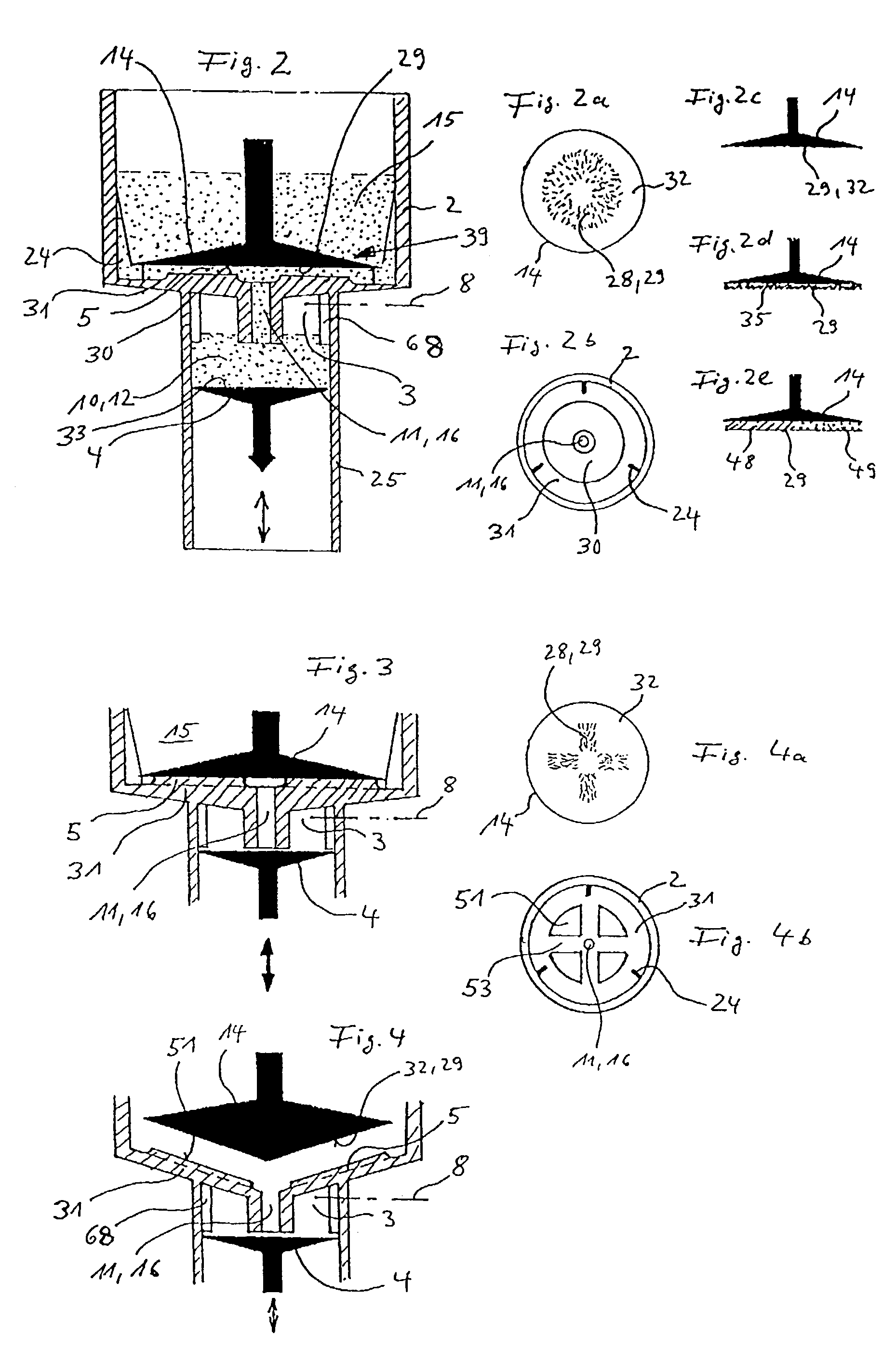
InactiveUS20030130596A1Effect of viscosity can be correctedRealize automatic adjustmentUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringPiston cylinderPlatelet-rich plasma
The invention relates to a method and to a device for examining the properties of the global, in particular the primary, hemostasis functions in whole blood or platelet-rich plasma, comprising a storage chamber (15) for the blood to be examined, a reaction device (39) having at least one flow path (5, 16) via which the blood to be examined is transported for carrying out certain reactions, a conveyor device (1) which conveys a volumetric flow for the transport of the blood through the reaction device (39), thereby generating a conveyor pressure, a pressure gauge (8, 9) which in a blood-free pressure gauge chamber (3) measures changes in the conveyor pressure which appear depending on the reactions of the blood to be examined which have taken place in the reaction device (39), a blood collection chamber (10) for collecting the blood transported through the reaction device (39), the conveyor pressure in a pressure-sealed working chamber (12) being generated by a piston-cylinder system (1), a working surface (33) of the piston (4) forming a boundary of the working chamber (12), and the working chamber (12) being formed by the blood collection chamber (10) and the blood-free pressure gauge chamber (3). According to the method of the invention, the volumetric flow is preferably adjusted, depending on the measured pressure of the volumetric flow, in such a way that the shear rate or the shear force, whose action in the reaction opening causes blood components, in particular thrombocytes, to deposit, follows a predetermined characteristic curve and in particular is held constant.
Owner:FREIHERR VON DER GOLTZ VOLKER
Centrifuge bowl for separating particles
InactiveUS20020142909A1Settling fastEasy to separateRotary centrifugesBiological testingWhite blood cellVolumetric Mass Density
A novel centrifuge bowl for processing particles suspended in a fluid is disclosed. The centrifuge bowl includes an annular cavity concentrically located about the rotation axis for suitably separating particles of similar densities but of different diameters. The cavity is preferably configured to have an annular cross sectional area, which is parallel to the rotation axis, that increases from a centrifugal side of the cavity toward a centripetal side of the cavity. This configuration allows to generate an almost rigidly rotating field upon rotation of the centrifuge bowl, which field helps to uniformly disperse Coriolis force throughout the circumference of the cavity to avoid turbulent mixing of the particles. In an alternative embodiment, the cavity is surrounded by an outer cavity for separating particles according to density before processing them through the inner cavity. This construction is particularly suitable for processing whole blood to harvest platelet-rich-plasma with reduced level of white blood cell contamination.
Owner:HAEMONETICS
Method of culturing cells
InactiveUS20070122906A1Extended storage timeMaintain their viabilityCulture processCell culture mediaCulture cellBlood component
A blood component such as platelets are concentrated from the blood. The concentrate such as platelet-rich plasma is used in a cell culture medium to grow and proliferate cells. The cells may be from the same person from which the blood concentrate is obtained. The cells grown in the culture medium may be used to treat a patient which may be the same patient from which the blood was extracted and / or the cells were obtained.
Owner:MISHRA ALLAN
Device and method for detecting the coagulation functions of global, especially primary hemostasis
InactiveUS7223365B2Low cost of measurementSimple and low-maintenance techniqueUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsBlood plasmaPlasma rich platelet
A method and a device are provided for examining the properties of the global, in particular the primary, hemostasis functions in whole blood or platelet-rich plasma. A volumetric blood flow is preferably adjusted, depending on the measured pressure of the volumetric flow, so that the shear rate or the shear force, whose action in the reaction opening causes blood components, in particular thrombocytes, to deposit, follows a predetermined characteristic curve and in particular is held constant.
Owner:FREIHERR VON DER GOLTZ VOLKER
Use of platelet rich plasma composition in the treatment of cardiac conduction abnormalities
InactiveUS20100112081A1Sufficient amountPowder deliveryDispersion deliveryBlood plasmaPlasma rich platelet
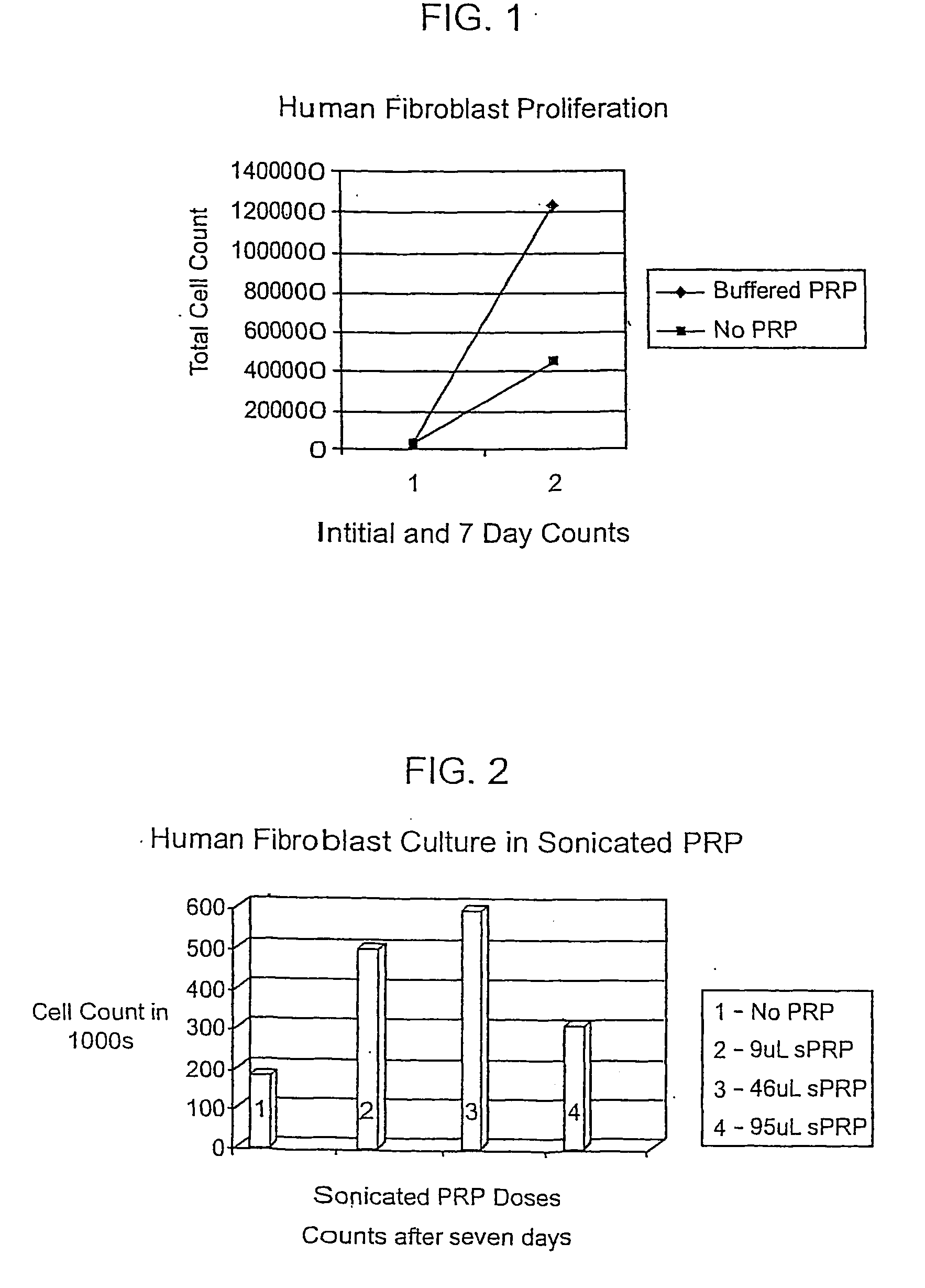
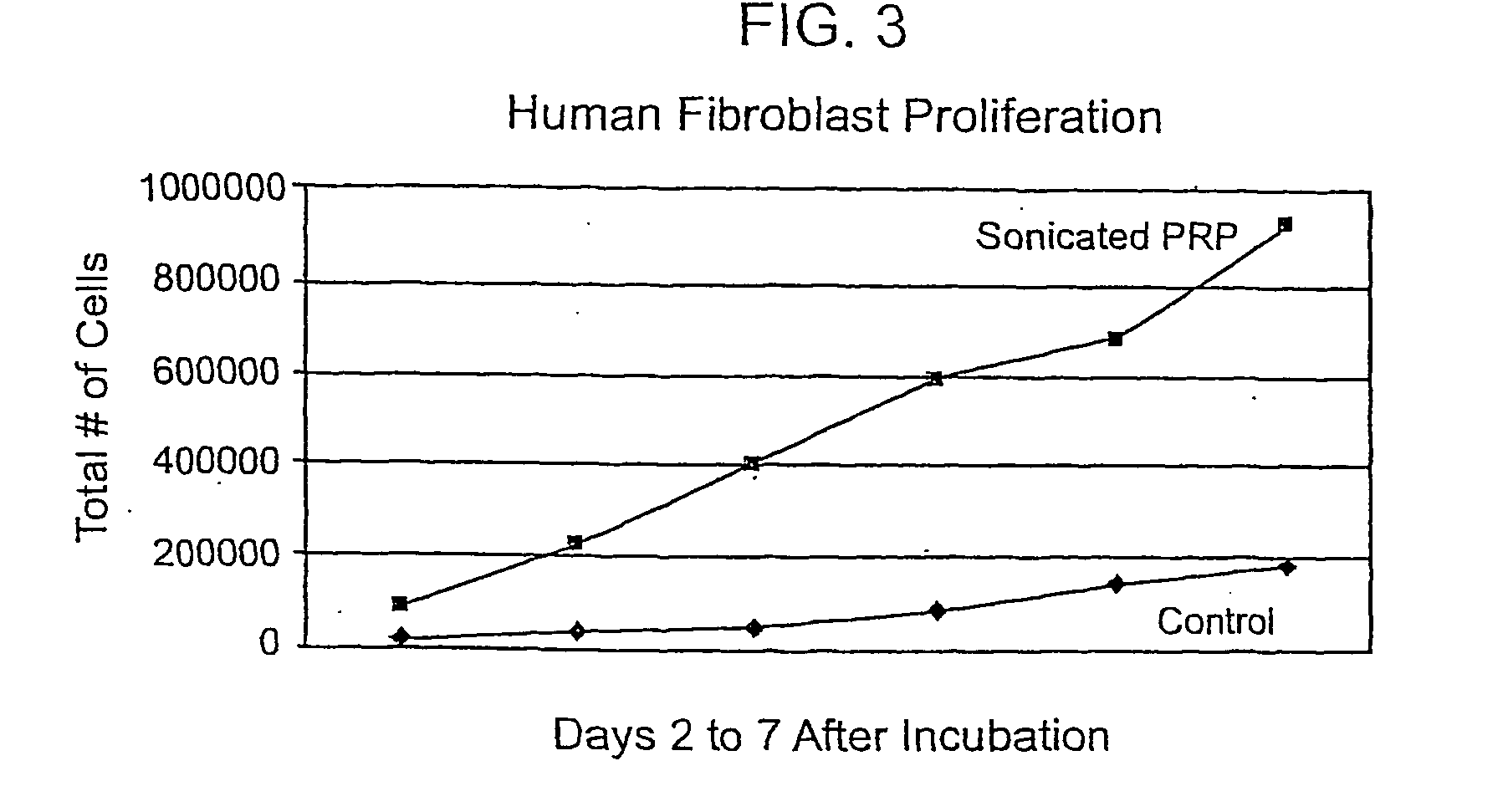
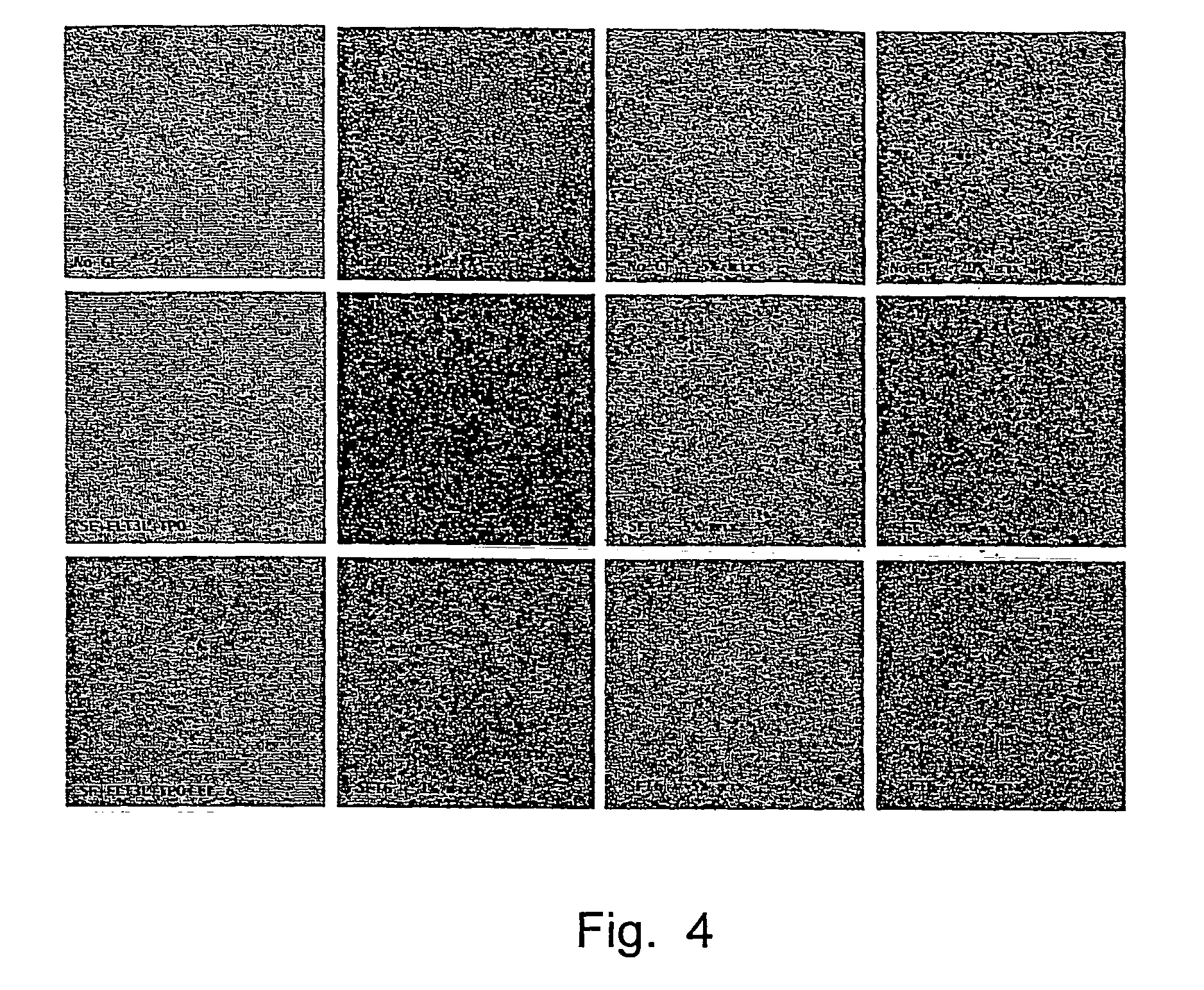
Methods and kits for treating a cardiac arrhythmia using a platelet rich plasma (PRP) composition are provided. Any type of arrhythmia may be treated using the PRP composition. The PRP composition may comprise PRP developed using blood collected from a patient suffering the cardiac arrhythmia. The PRP composition may be buffered to a physiological pH and may include one or more anti-arrhythmic agents, anti-coagulants, or other drugs. The PRP composition may be delivered using a nebulizer, minimally invasively, or surgically. In some embodiments, the PRP composition may be coated on one or more medical devices. The PRP composition may be delivered to an identified portion of the electrical conduction system of the heart affected and / or causing the arrhythmia to occur.
Owner:BIOPARADOX
Microchip and blood monitoring device
ActiveUS20100267066A1Efficient preparationStir wellBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBlood plasmaPlasma rich platelet
A microchip comprising therein a first channel which allows inflow of a first liquid selected from whole blood, platelet-rich plasma and a drug-treated liquid thereof, a second channel connected to the first channel, which allows inflow of a second liquid containing an agent that is reactive with the first liquid, and a merged channel extended from the connection portion of the first channel with the second channel, wherein, in the merged channel, a stirring section having a stirring bar for mixing the first liquid with the second liquid is provided; and a blood monitoring device using the same.
Owner:FUJIMORI KOGYO CO LTD
Lyophilized platelet rich plasma for the use in wound healing (chronic or acute) and bone or tissue grafts or repair
InactiveUS20050191286A1Simple compositionPrevent flow awayBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsWhite blood cellAntibiotic Y
This invention relates to an improved Lyophilized platelet rich plasma used to make a platelet gel wound healant, and methods of preparation and use thereof for healing wounds are disclosed. The improved wound healant comprises therapeutically effective amounts of activated growth factors, platelet ghost, plasma (know as the plasma back bone), white blood cells with optional none, one or more additional anti-oxidant such as vitamin A and / or C and / or E, and / or none one or more antibiotics and / or GHK-Cu (produced by ProCyte Inc.)
Owner:WALKER MACKIE J JR
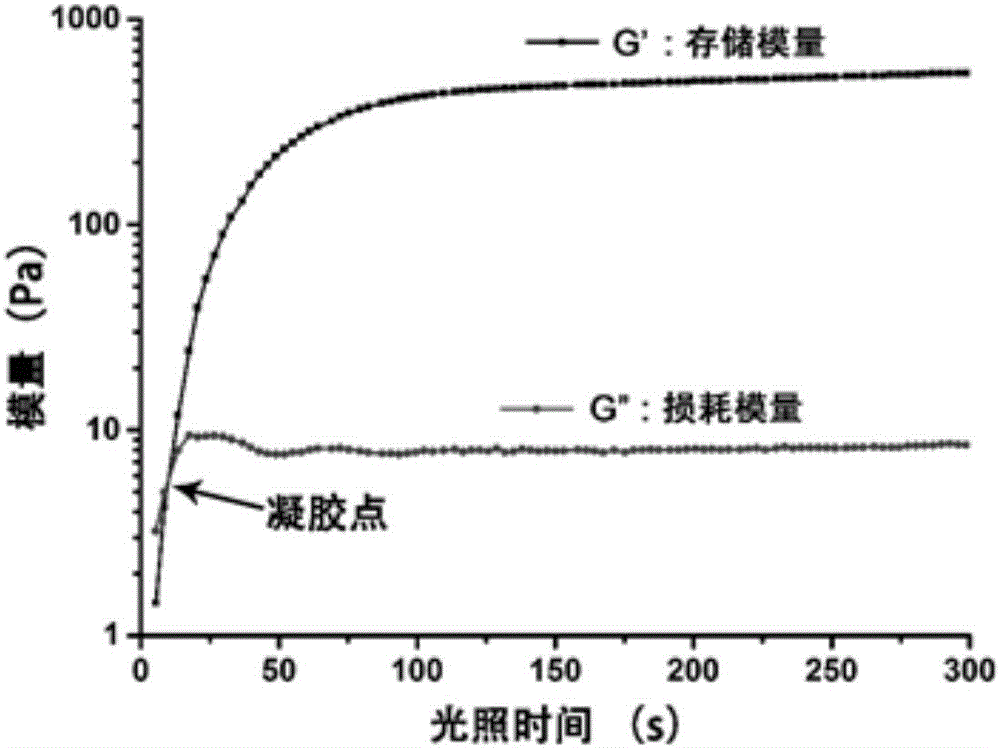
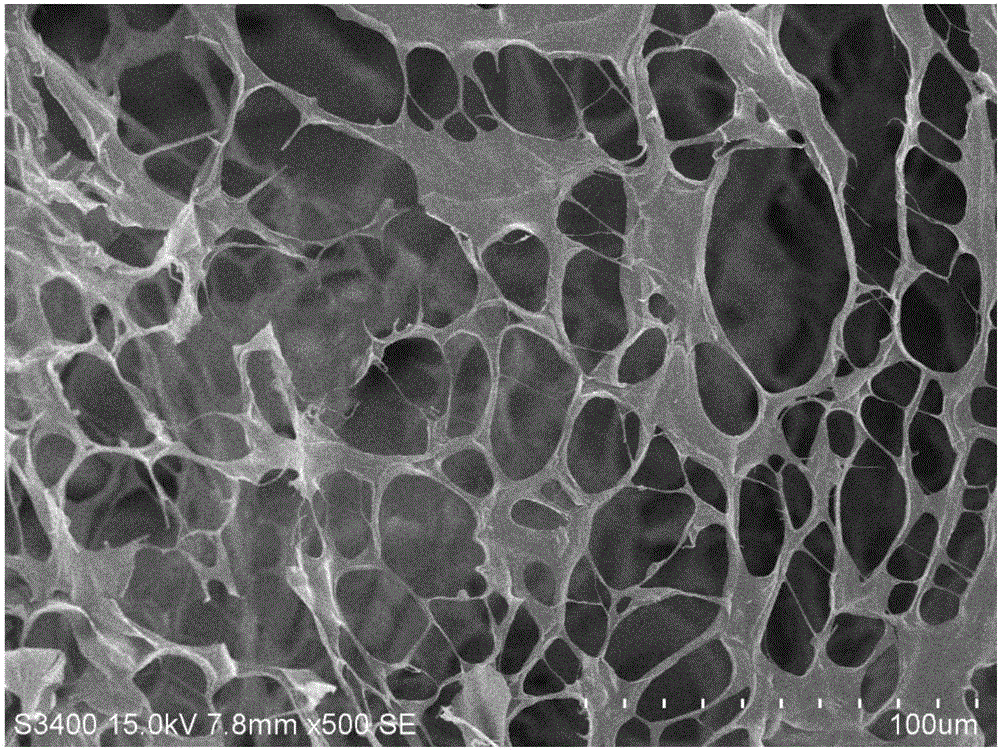
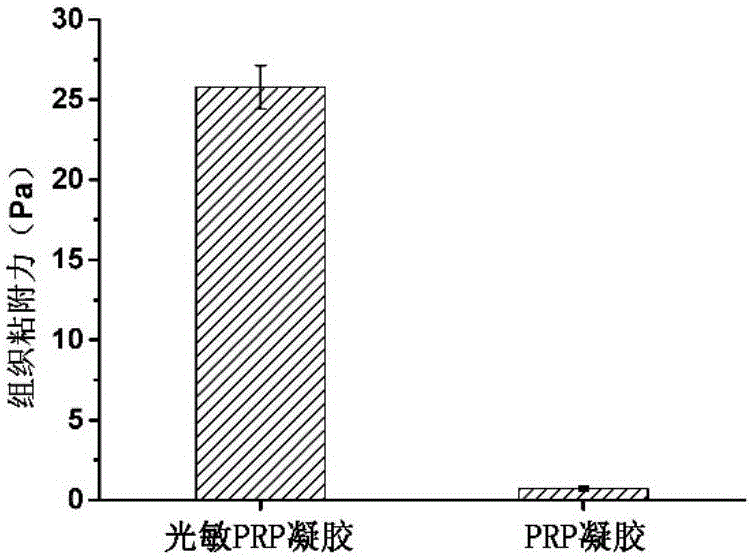
Photosensitive PRP (platelet-rich plasma) gel and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106822183ATightly boundSeamless integrationSurgical adhesivesAerosol deliveryChemical reactionBlood plasma
The invention relates to a photosensitive PRP (platelet-rich plasma) gel and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of mixing a biocompatible medium solution of a macromolecule modified by an o-nitrobenzyl photo response group and an extracted PRP according to a certain ratio, so as to form a gel precursor solution; then, radiating the gel precursor solution by light, and enabling the o-nitrobenzyl group in the macromolecule modified by the o-nitrobenzyl photo response group to generate photochemical reaction under the excitation action of a light source, so as to produce an aldehyde functional group; generating coupling reaction with amino distributed at the surface of the protein in the PRP to form an imine bond, so as to realize the preparation of the photosensitive PRP gel. Compared with the prior art, the photosensitive PRP gel prepared by the method has the advantages that the internal cell factors can be slowly released, and the tight and seamless bonding between the PRP gel and wounds is realized.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN GUANGHE MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Microchip and blood monitoring device
ActiveCN101874208AGenerate efficientlyEfficient determinationFlow mixersTransportation and packagingMedicineBlood plasma
A microchip which comprises therein a first channel for the inflow of a first liquid selected from among whole blood, platelet-rich plasma or a liquid prepared by treating the same with a chemical, a second channel connected to the first channel for the inflow of a second liquid containing a chemical capable of reacting with the first liquid as described above, and a confluence channel extended from the connection section of the first channel with the second channel, characterized in that a stirring section provided with a stirrer for mixing the above-described first liquid with the above-described second liquid is provided in the confluence channel as described above, and a blood monitoring device using the microchip.
Owner:FUJIMORI KOGYO CO LTD
Injected bone repairing material and its prepn and application
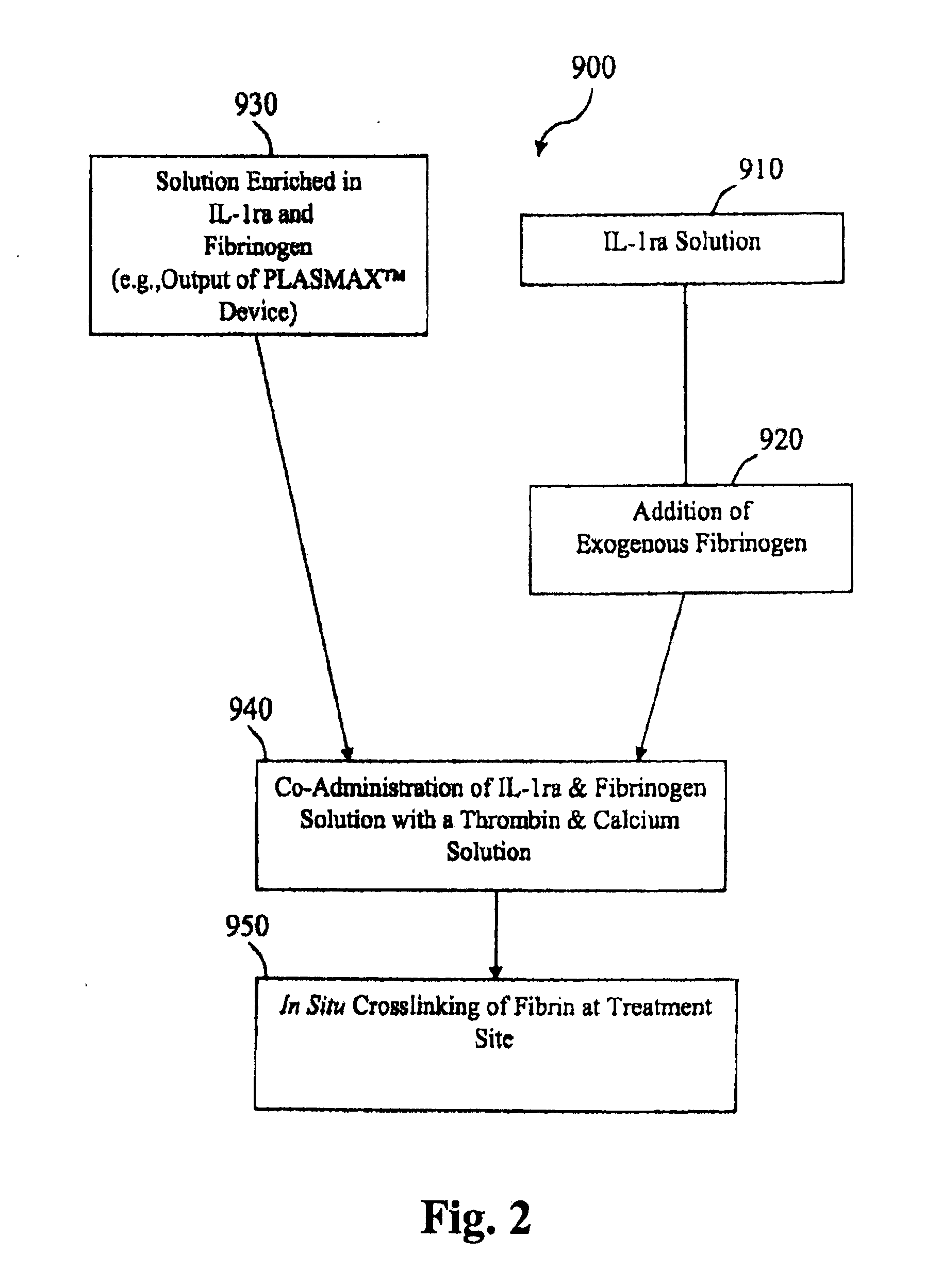
InactiveCN1846789ABiologically activeClosed woundPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderFiberBlood plasma
The present invention discloses one kind of injected bone repairing material and its preparation and application. The injected bone repairing material consists of solution I and solution II, the solution I is the mixture of platelet rich plasma (PRP) and 80-100 mg / ml concentration fibrinogen solution in the ratio of 1 to 3-6; and the solution II is solution mixture of calcium chloride in 40 mmol / ml concentration and thrombin in 400-1000 U / ml concentration. When the injected bone repairing material is used, solution I and solution II in the volume ratio of 1-9 are sucked with two syringes and injected into body to form gel with high adhesive force, with PRP accounting for 10-30 vol%. The injected bone repairing material is used in preparing implant for treating bone defect and bone nonunion and promoting fracture healing.
Owner:NAN FANG HOSPITAL
Method for preparing platelet-rich plasma
InactiveUS20050170327A1High activitySimply and conveniently acquireNervous disorderMedical devicesBlood collectionDefinite period
An object of this invention is to provide platelet-rich plasma having high activity easily and at low cost. The object is achieved by a method for preparing platelet-rich plasma comprising a step of adding a water-soluble polymer compound to whole blood obtained by blood collection. For example, by adding poly-L-glutamic acid to whole blood and allowing the mixture to stand still for a definite period, it is possible to obtain platelet-rich plasma having high activity that contains blood plasma components containing much fibrinogen in addition to platelets in the supernatant and blood cell components including white blood cells. This invention also includes the platelet-rich plasma and the use thereof as well as a kit for preparing platelet-rich plasma.
Owner:SUMIDA EMI
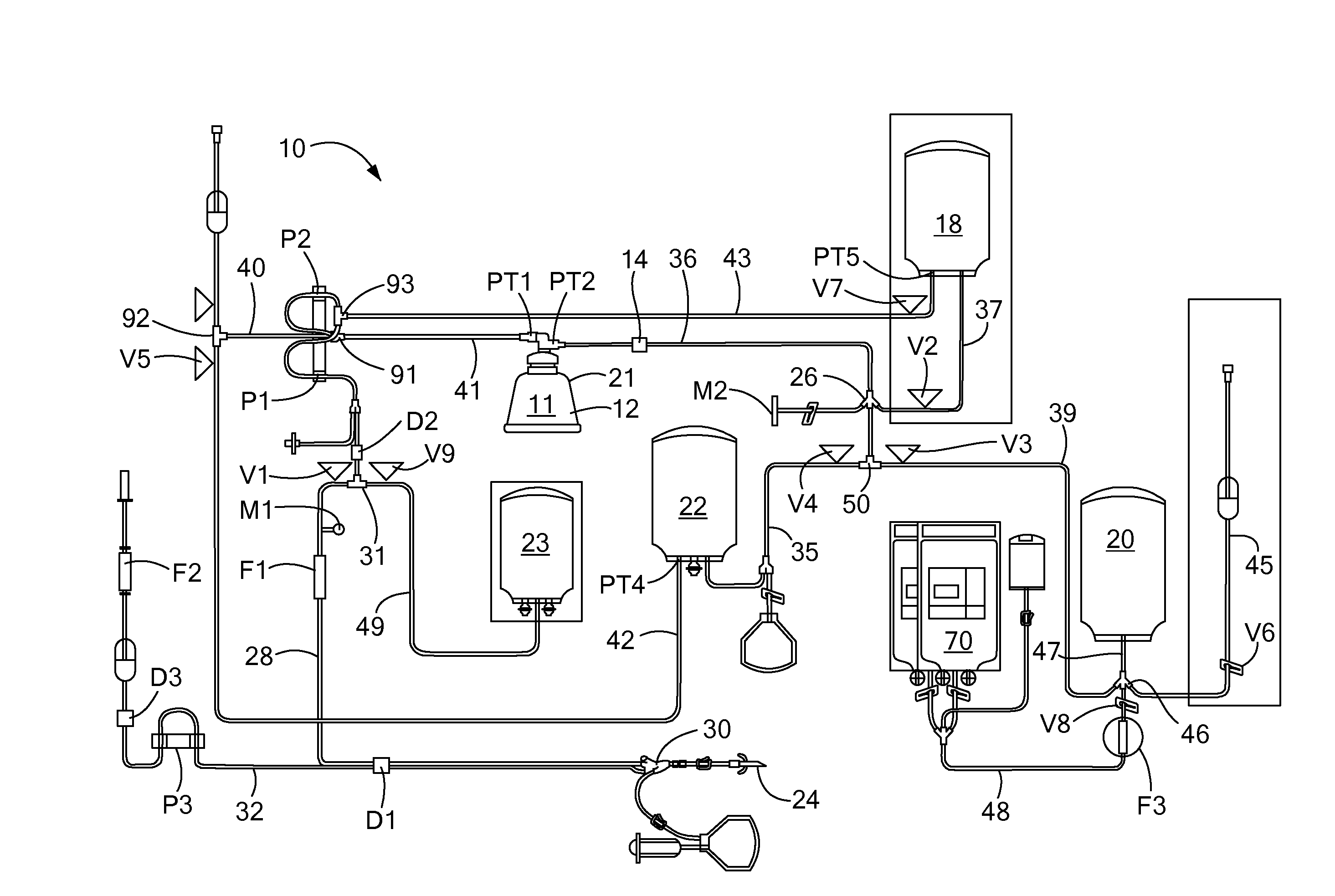
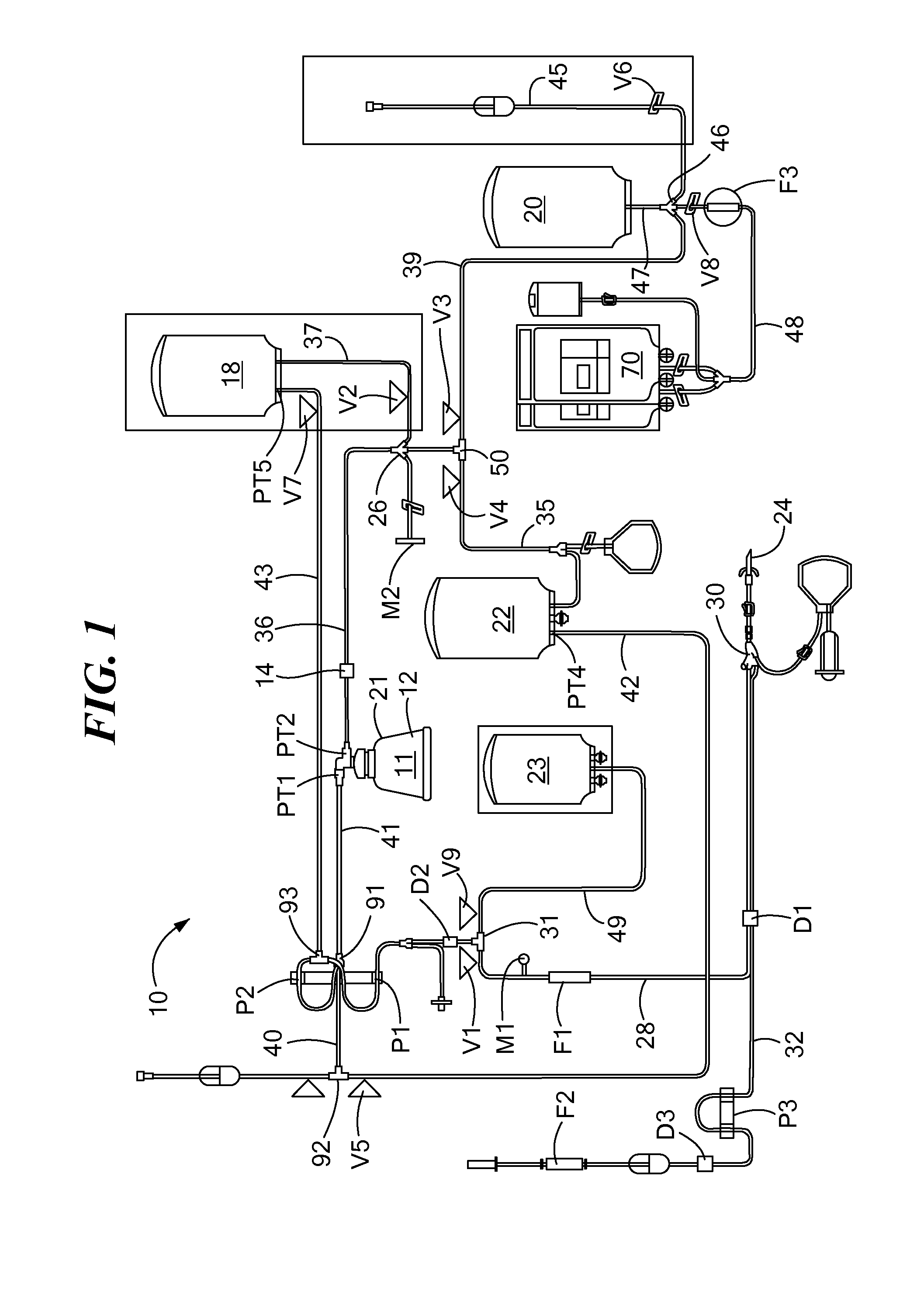
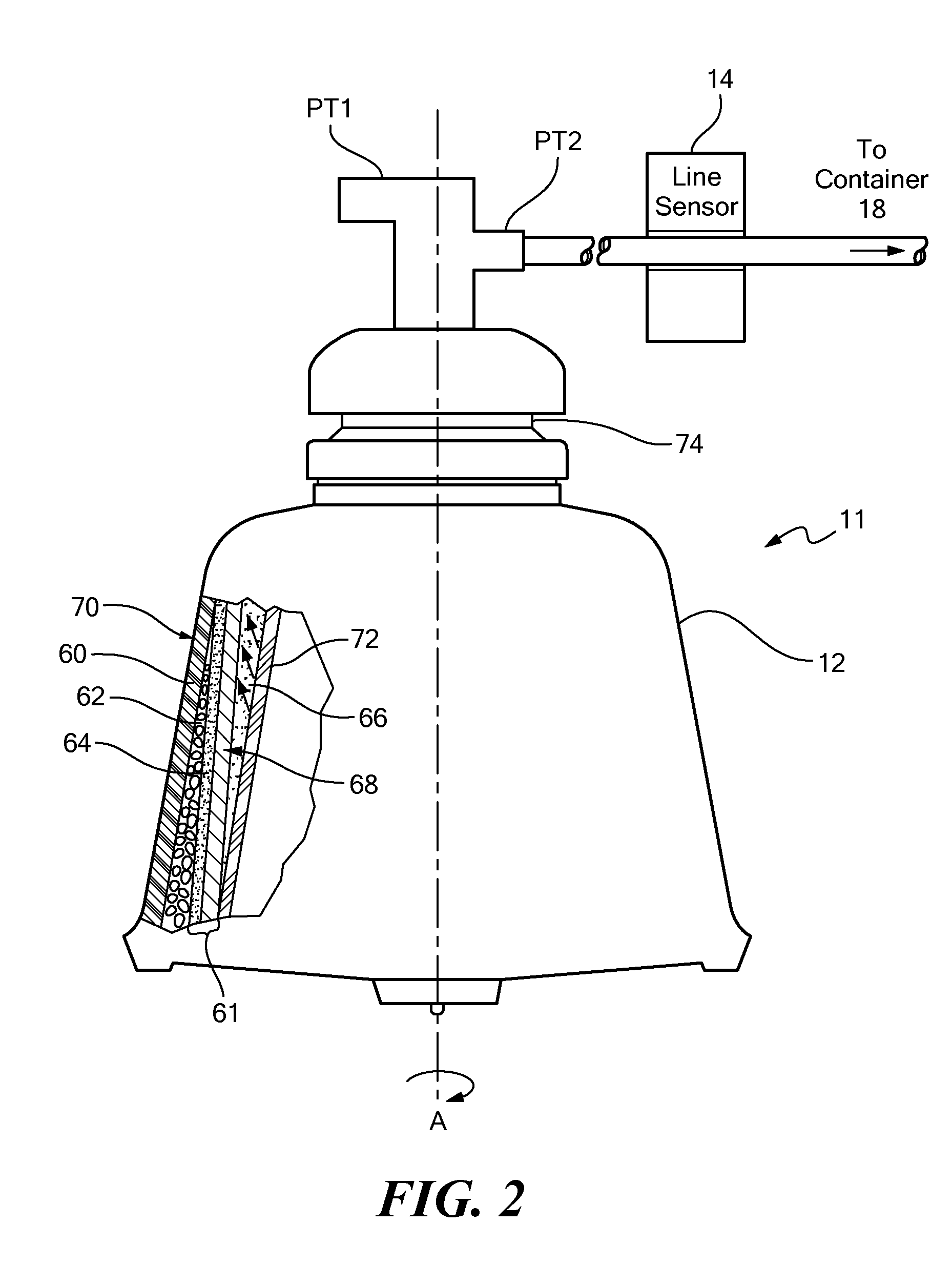
System and Method for the Re-Anticoagulation of Platelet Rich Plasma
A method for the re-anticoagulation of platelet rich plasma in a blood apheresis system includes priming the blood apheresis system with anticoagulant, such that a volume of anticoagulant is transferred to a PRP container. The method may then transfer the anticoagulant within the PRP container to a red blood cell container, and collect a volume of platelet rich plasma within the PRP container. The platelet rich plasma may be collected in a plurality of cycles. Between collection cycles, the method may transfer a portion of the volume of anticoagulant from the red blood cell container to the PRP container.
Owner:HAEMONETICS
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com