MicroRNA-disease association prediction method based on multi-mode stacking automatic coding machine
An automatic encoding machine and prediction method technology, applied in the fields of machine learning and bioinformatics, can solve the problems of no concern about the relationship between miRNA and diseases and other biomolecules, so as to improve prediction accuracy, reduce model complexity, and time complexity low degree of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
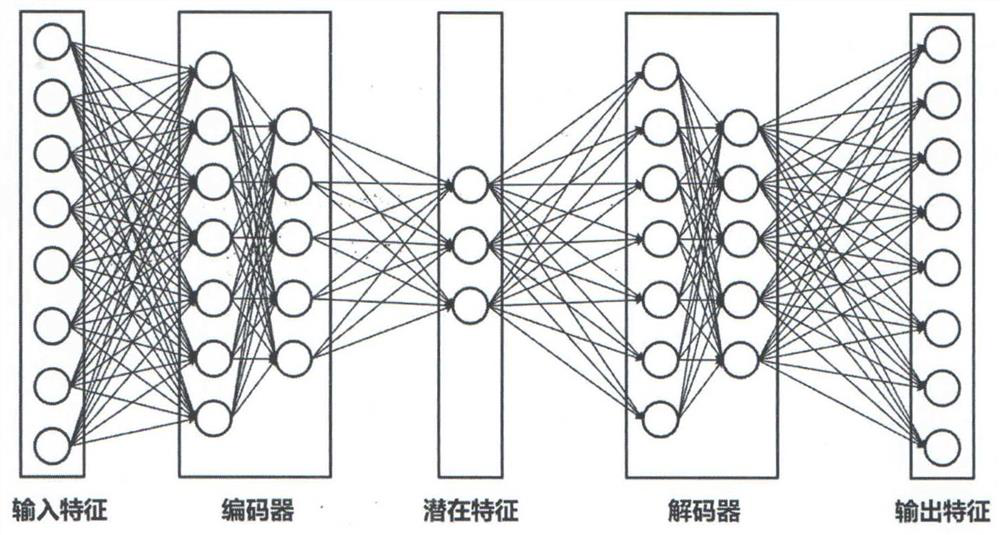
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
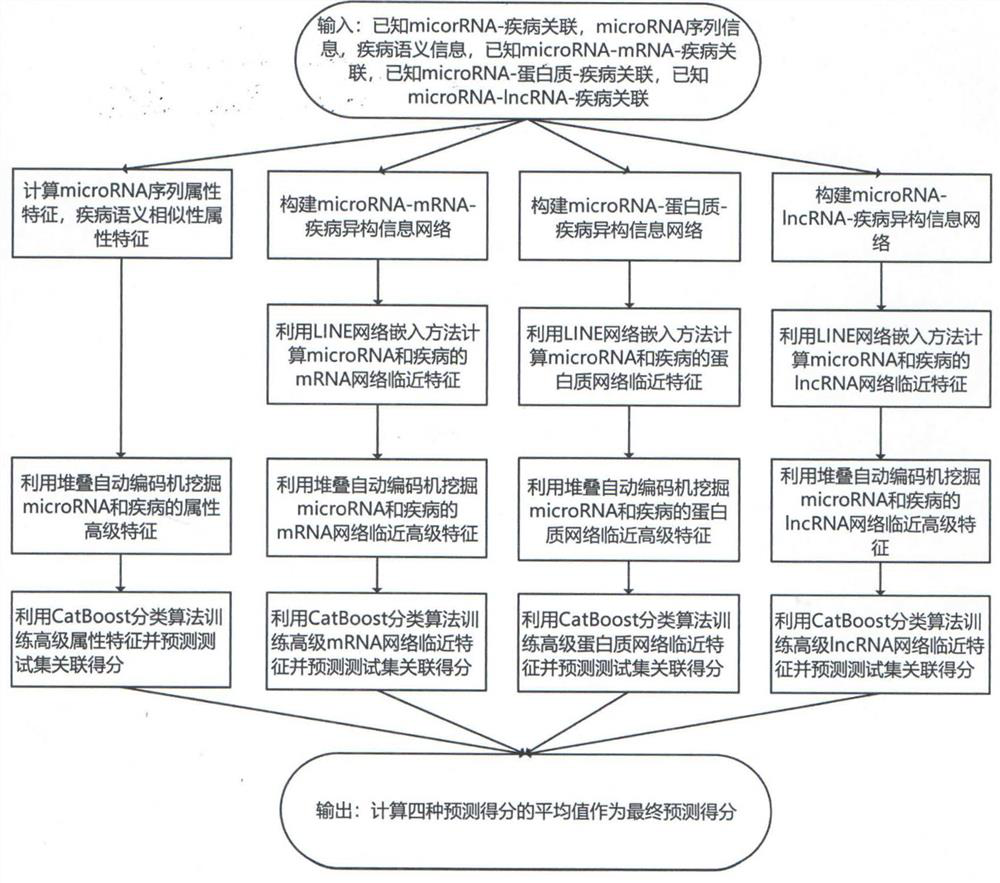
[0085] A kind of microRNA-disease association prediction method based on multimodal stacking autoencoder according to the present invention is carried out according to the following steps:
[0086] a. Selection and establishment of data sets: Based on the Human MicroRNA Disease Database v3.0 database, the known human microRNA and disease association data were obtained; microRNA sequence information was obtained based on the miRbase database; disease subject terms were obtained based on the Medical Subject Heading database; based on the miRTarBase database Obtain known microRNA-protein and microRNA-mRNA association data; obtain known protein-disease and mRNA-disease association data based on DisGeNET database; obtain known microRNA-lncRNA association data based on lncRNASNP2 database; obtain based on lncRNASNP2 and LncRNADisease database Known lncRNA-disease association data;
[0087] b. Generation of microRNA sequence features: the nucleotides based on microRNA are uracil, cyt...
Embodiment 2
[0136] In order to better illustrate the effect of the prediction method of the present invention, this prediction method is compared with the most popular random forest model at present, and table 1 has listed this embodiment and the random forest model using the five-fold cross-validation method in HMDDv3. The results generated on the 0 dataset:
[0137] Table 1 is based on the comparison of the present invention and random forest model results based on the HMDD v3.0 data set under the five-fold cross-validation
[0138]
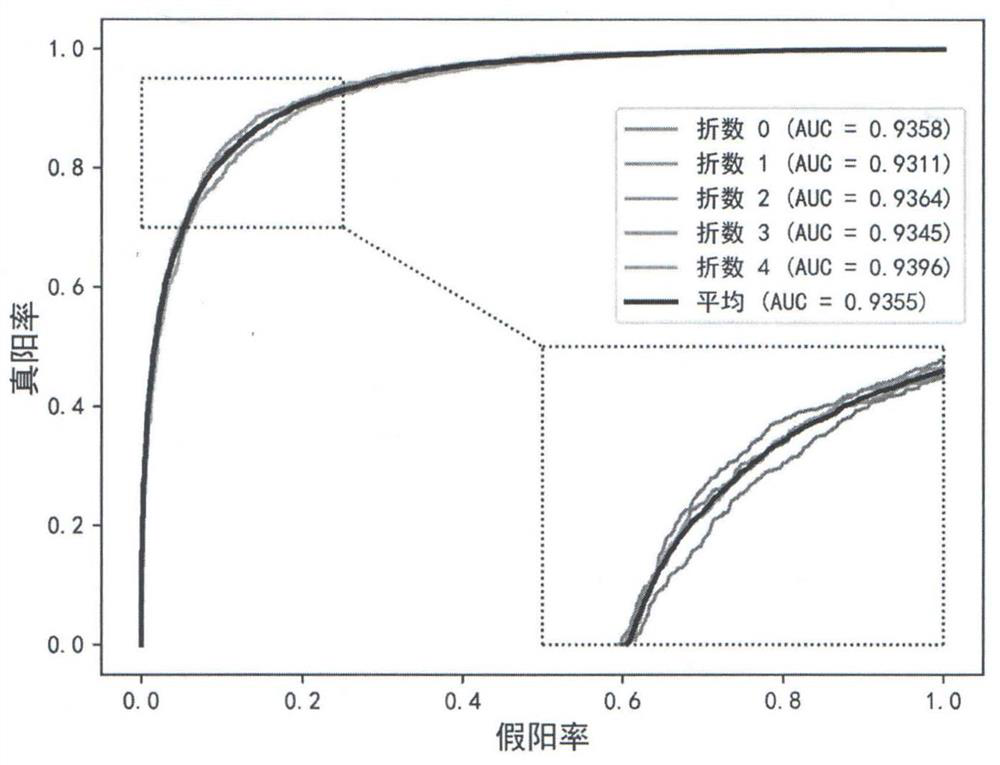
[0139] image 3 and Figure 4The ROC curves generated by the present invention and the random forest model are shown respectively; by comparison, it can be seen that this embodiment has achieved more excellent results in sensitivity rate, specific rate, precision rate, Matthews correlation coefficient, and AUC value. The results are all higher than the random forest method, which shows that the comprehensive performance of the present invention is bet...
Embodiment 3
[0141] In order to further embody the effect of the prediction method of the present invention, this prediction method is compared with the latest calculation model at present, Figure 5 It shows the histogram of the mean AUC comparison between different models and the present invention based on the same HMDD data set under the five-fold cross-validation; With a higher AUC value, the overall performance is better than other models.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com