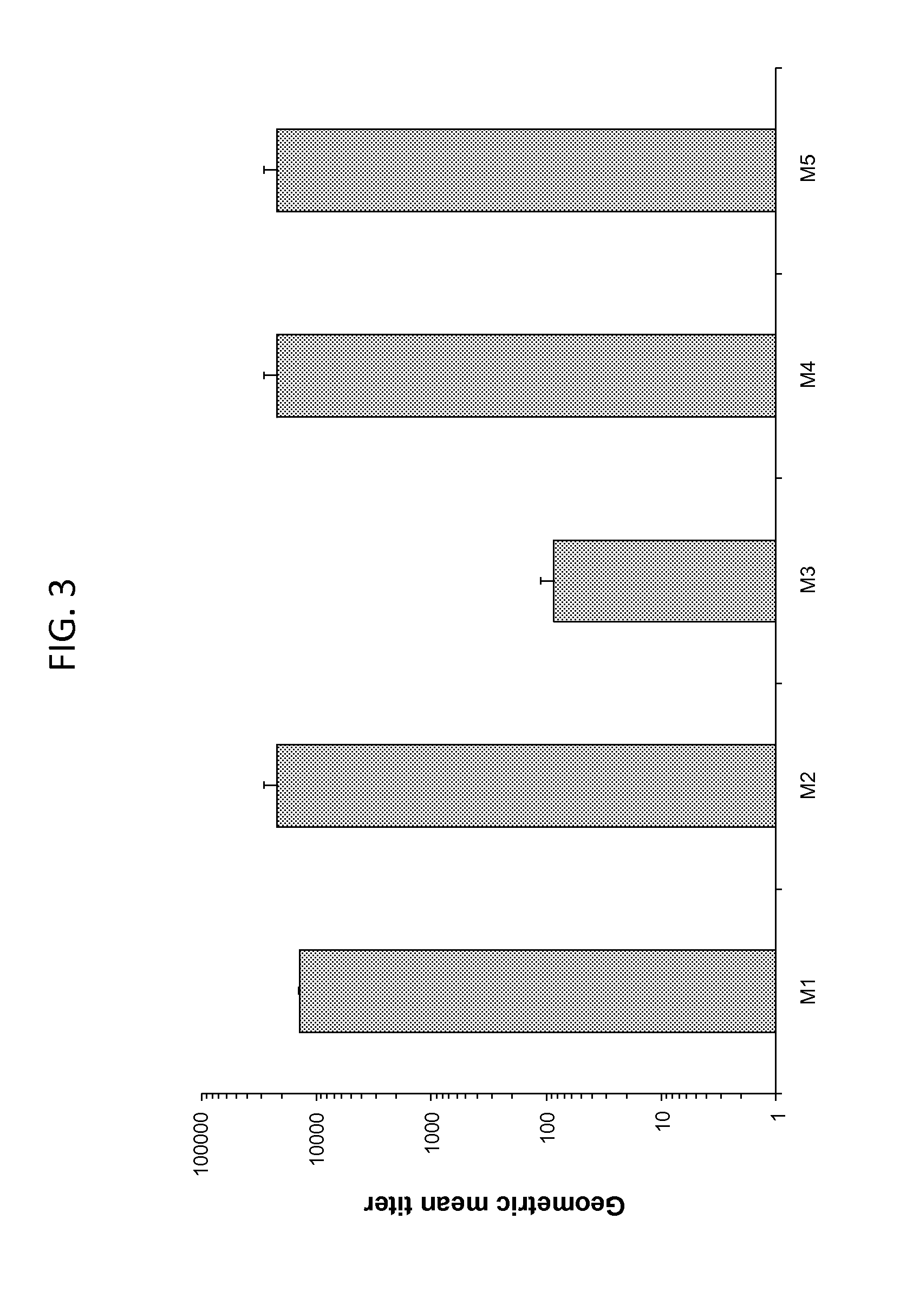
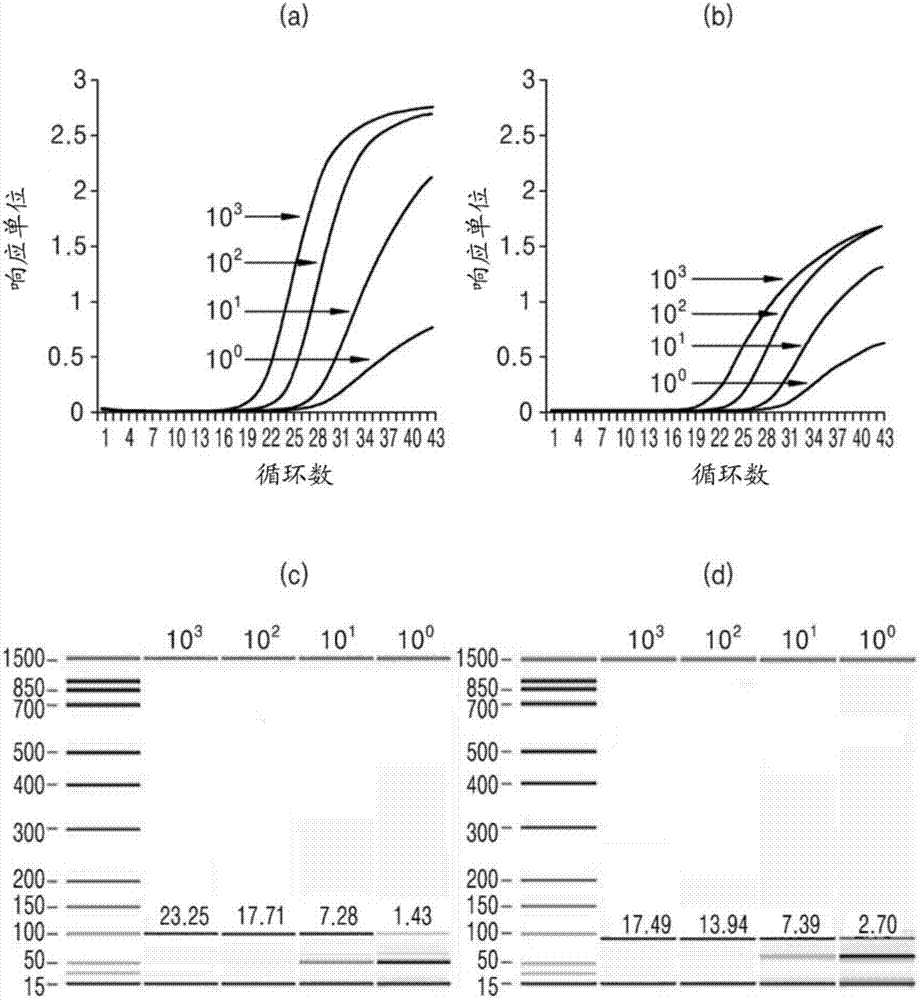
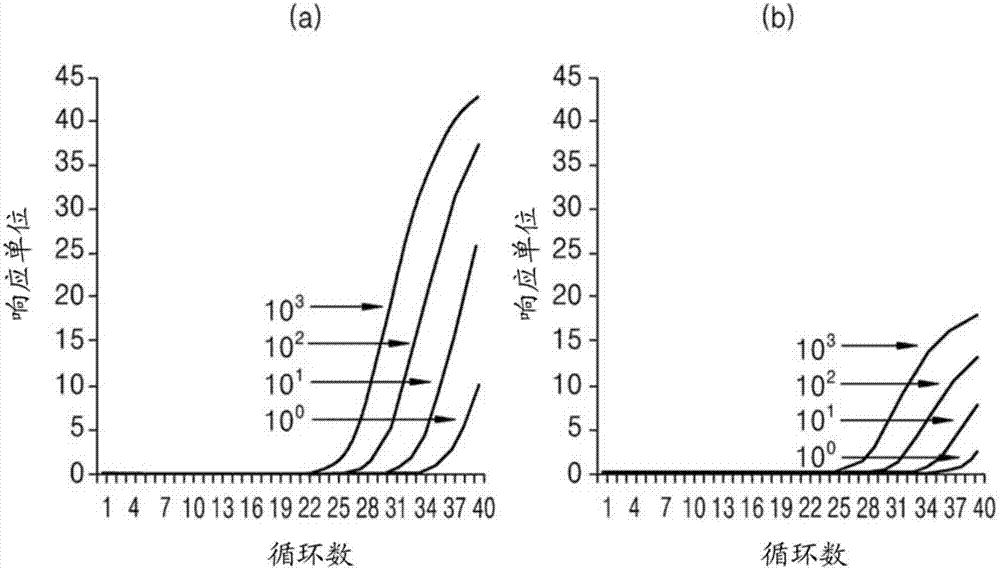
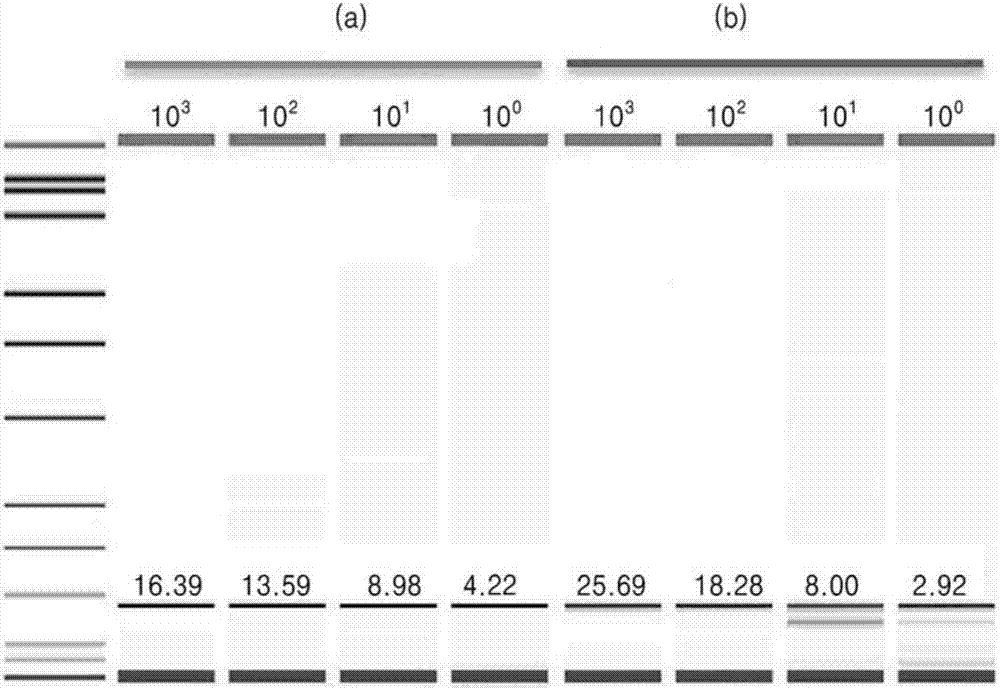
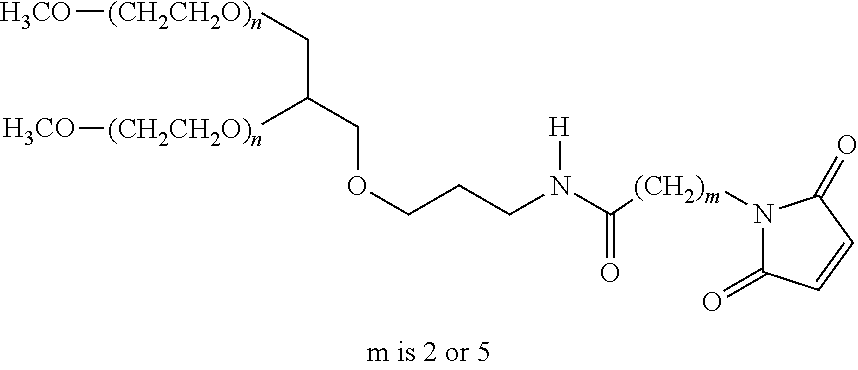
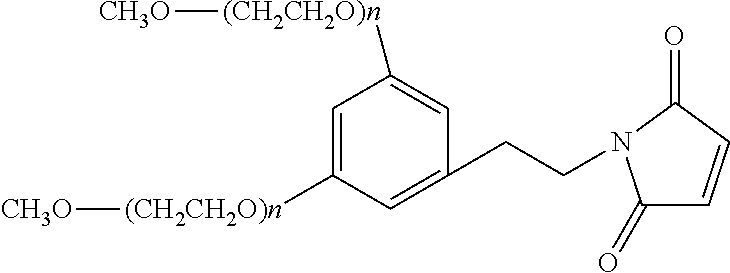
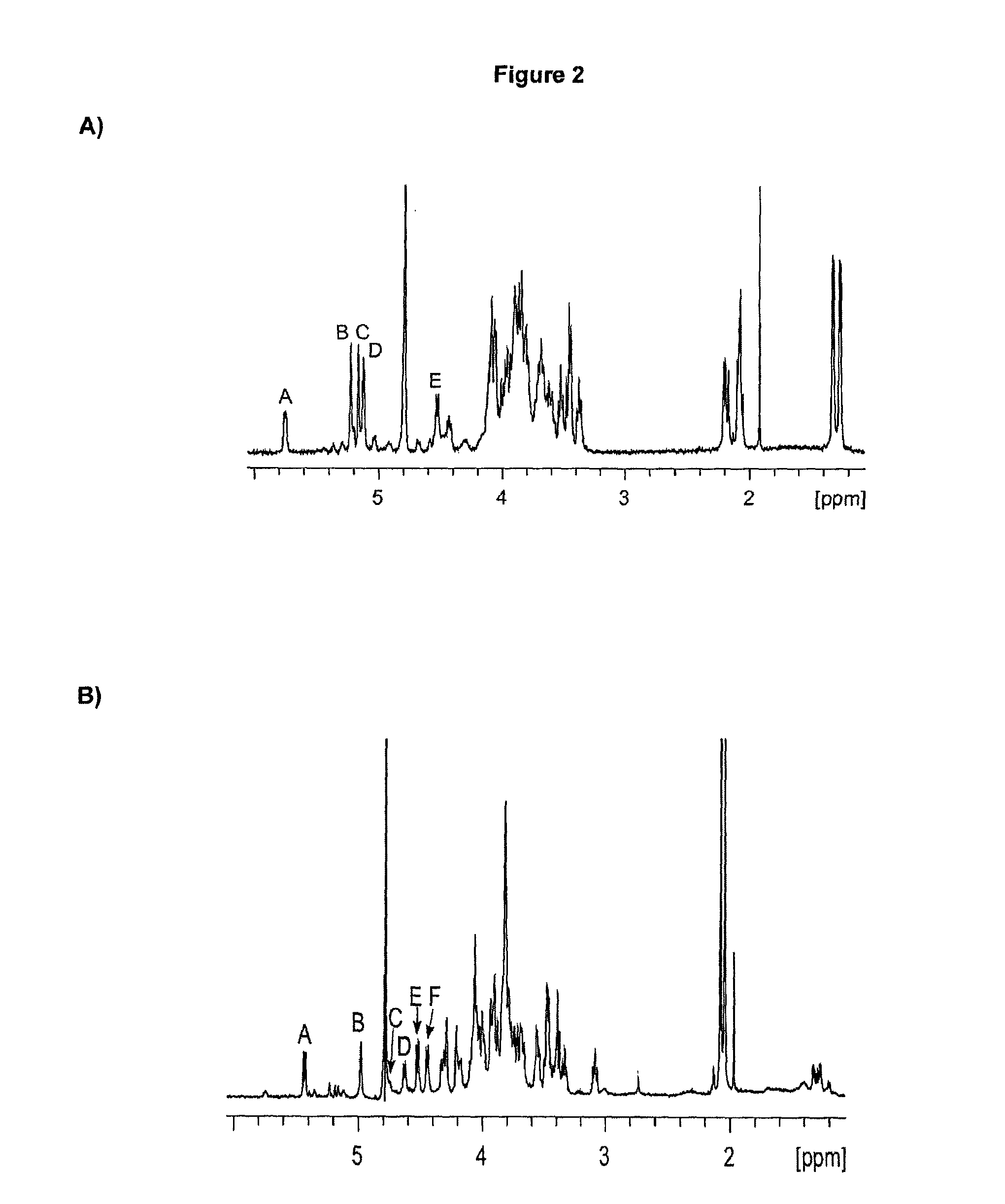
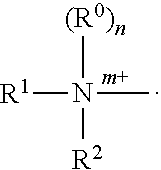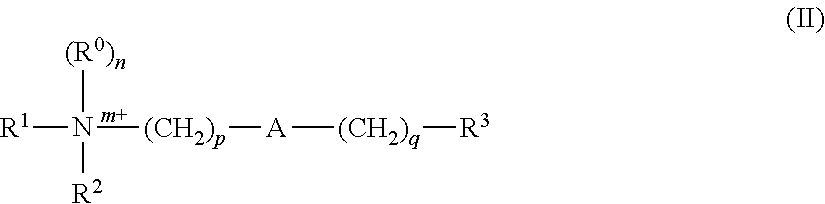Patents
Literature
59 results about "Clostridium difficile toxin A" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
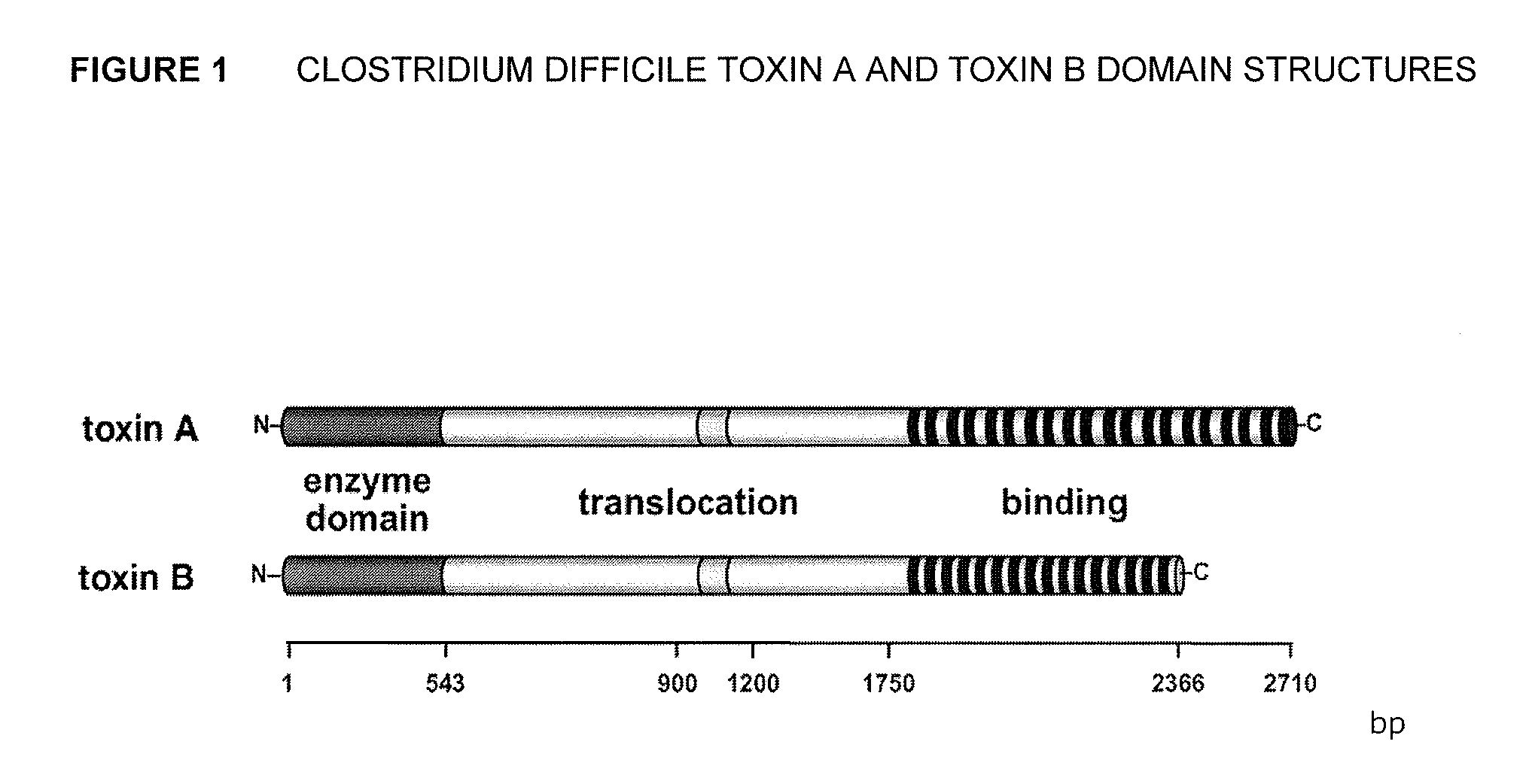
Clostridium difficile toxin A (TcdA) is a toxin generated by Clostridium difficile. It is similar to Clostridium difficile Toxin B. The toxins are the main virulence factors produced by the gram positive, anaerobic, Clostridium difficile bacteria. The toxins function by damaging the intestinal mucosa and cause the symptoms of C. difficile infection, including pseudomembranous colitis.
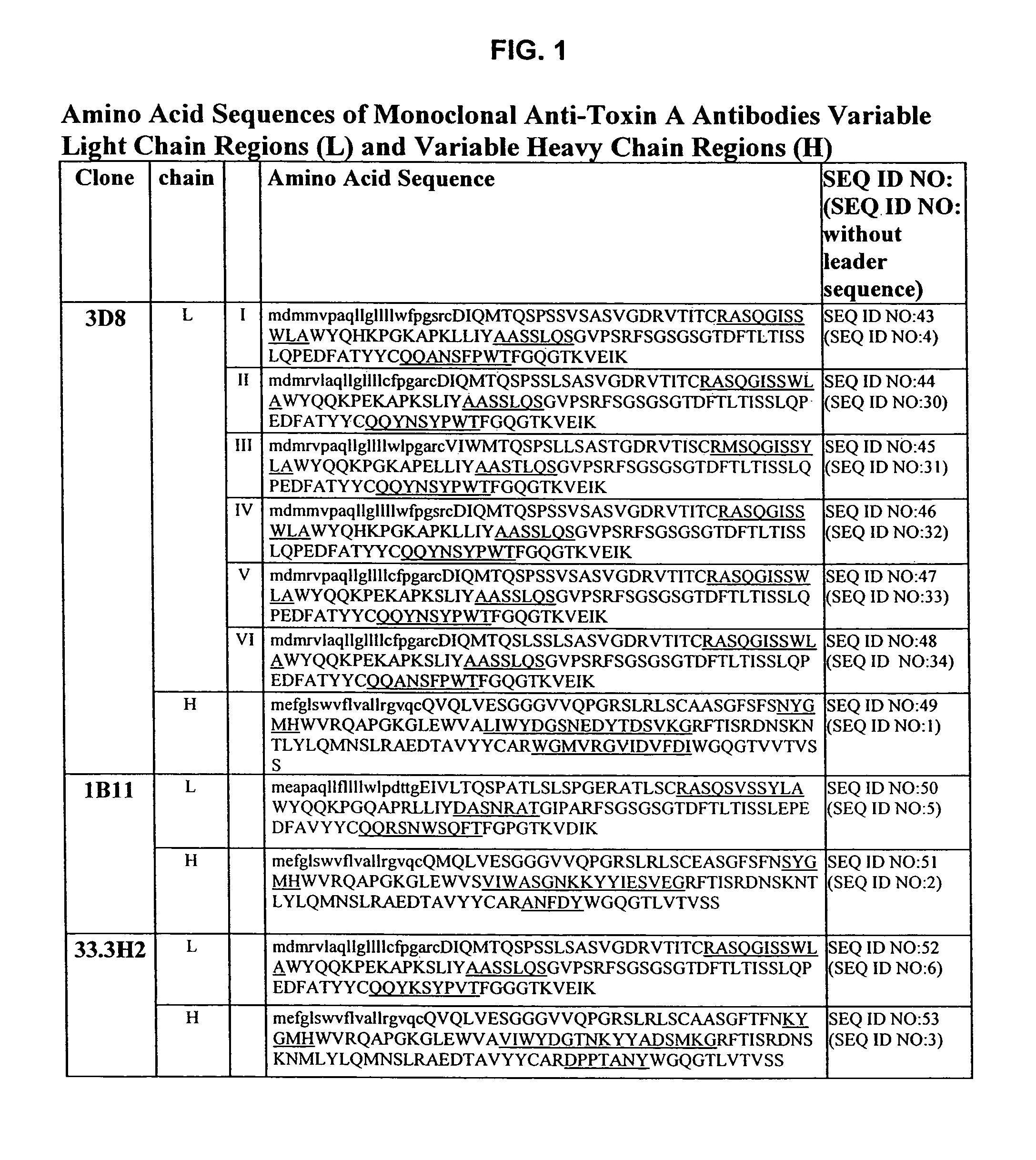
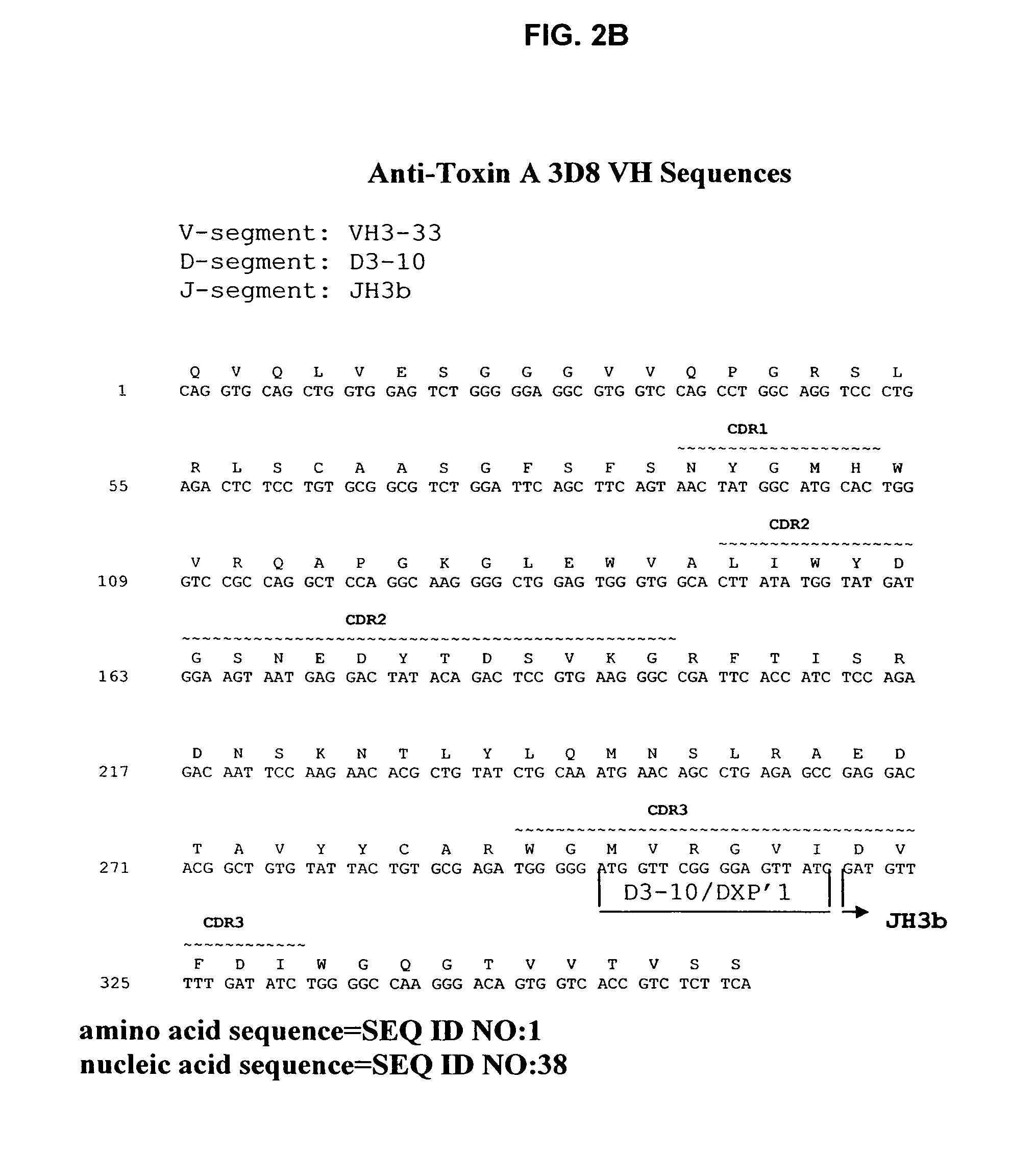
Antibodies against Clostridium difficile toxins and uses thereof
ActiveUS7625559B2High affinityLess immunogenicAntibacterial agentsGenetic material ingredientsClostridium difficile toxin AClostridium difficile (bacteria)
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS UNIV OF +2
Amino acid sequences for therapeutic and prophylactic use against diseases due to clostridium difficile toxins
InactiveUS7151159B2Antibacterial agentsFungiClostridium difficile toxin AClostridium difficile (bacteria)
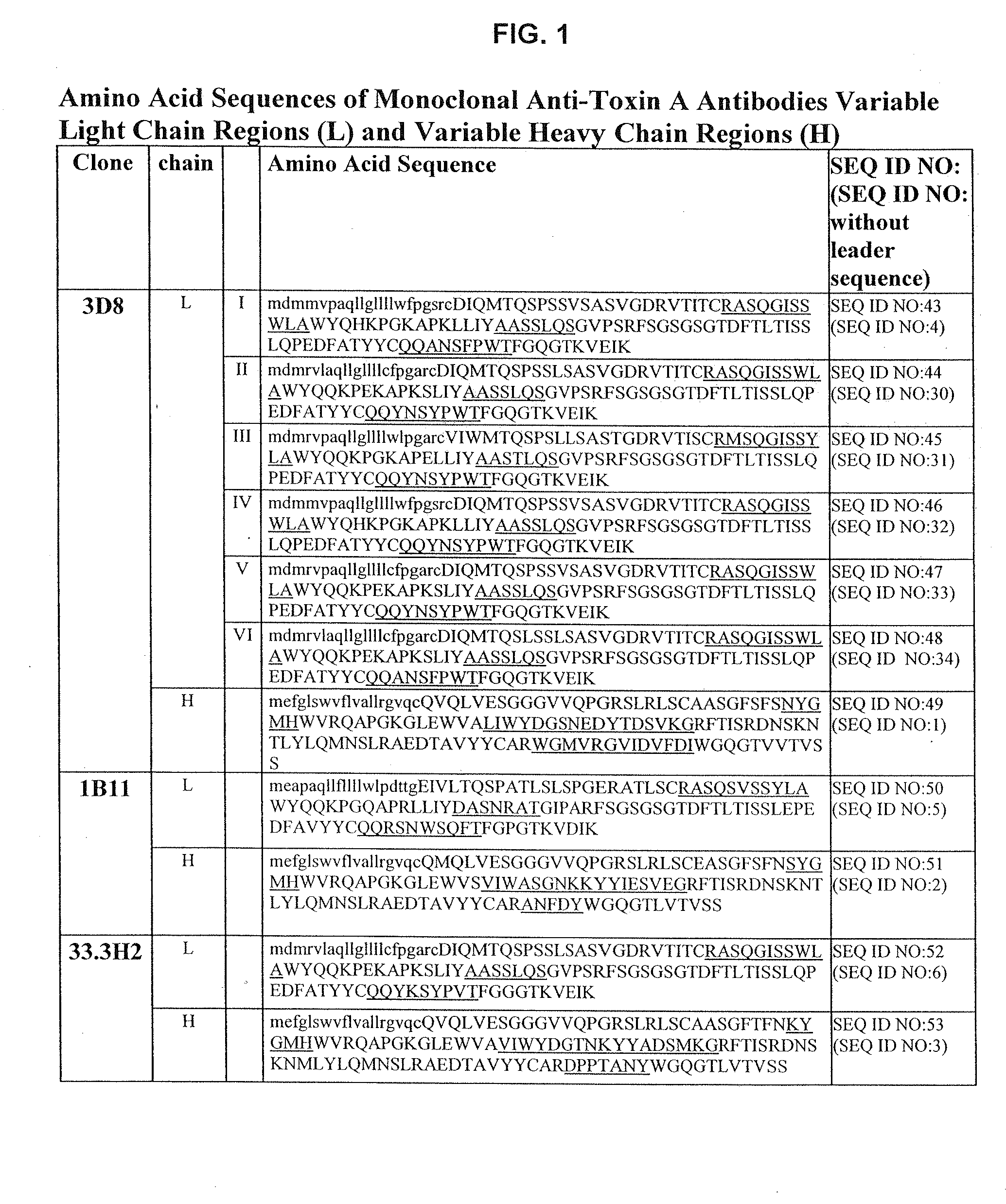
The invention relates to monoclonal antibodies capable of recognizing and neutralizing epitopes from the ligand domain, the translocation domain or the catalytic domain of the enterotoxin (toxin A) and cytotoxin (toxin B) from Clostridium difficile, as well as their production and therapeutic and prophylactic applications to diseases caused by said toxins.
Owner:VON EICHEL STREIBER CHRISTOPH
Synthesis of human secretory IgA for the treatment of Clostridium difficile associated diseases
A composition for treating a subject is provided. The composition includes dimeric or polymeric secretory IgA therapeutic. Formulating agents are mixed with the dimeric or polymeric secretory IgA to yield a dosing form of a capsule, tablet, and a suppository. A process for manufacturing a medicament for the treatment of C. difficile associated disease in a human is also provided wherein dimeric or polymeric IgA is modified with secretory component to form a dimeric or polymeric secretory IgA therapeutic. The dimeric or polymeric secretory IgA therapeutic is then mixed with formulating agents to create a capsule, tablet, or suppository dosing form. The therapeutic is amenable to enrobement directly through microencapsulation or the dosing form is coated with an enteric coating. A method of C. difficile treatment with the therapeutic is also provided that is amenable to supplementation with concurrent or prior antibiotic administration.
Owner:SIMON MICHAEL R
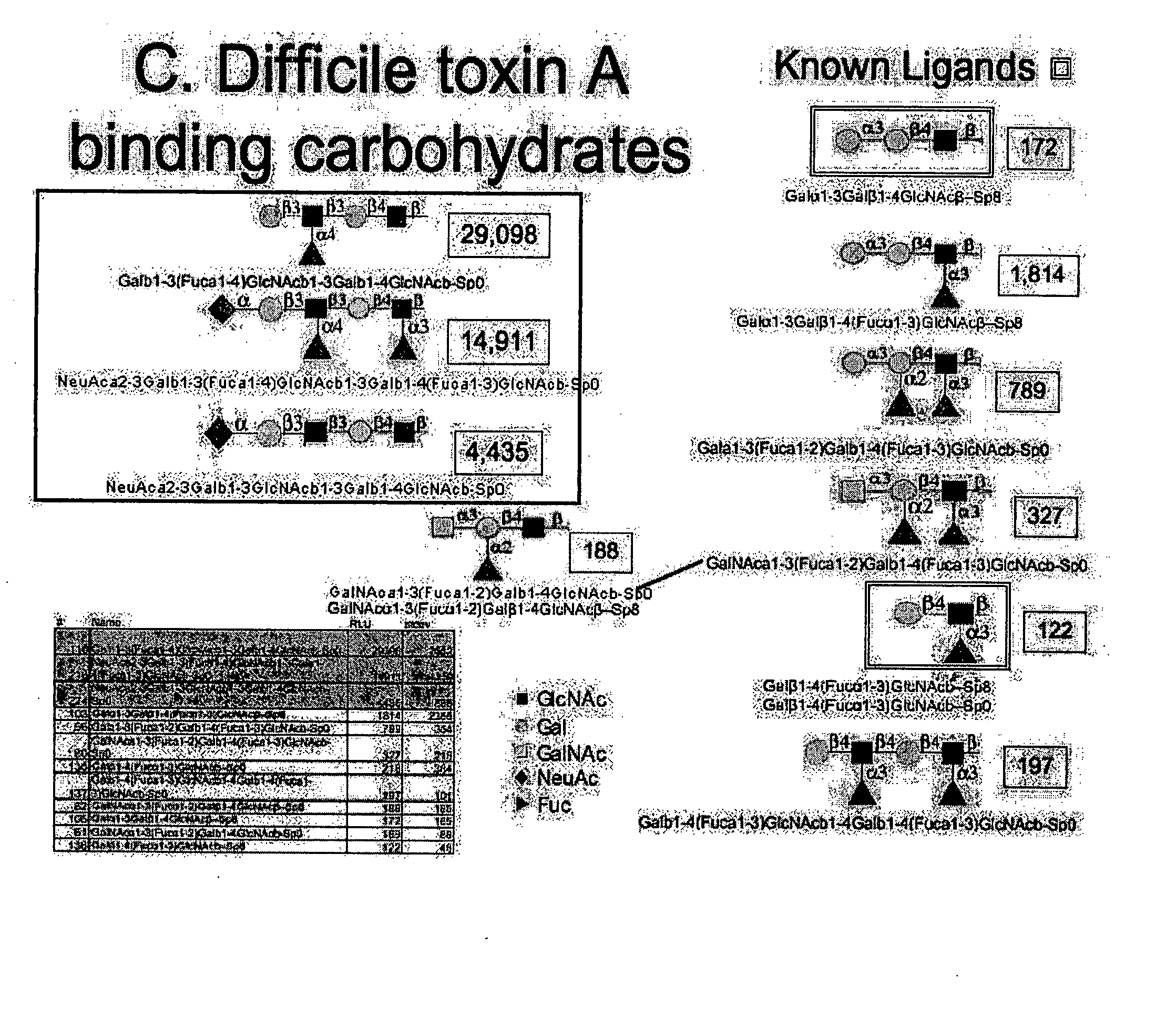
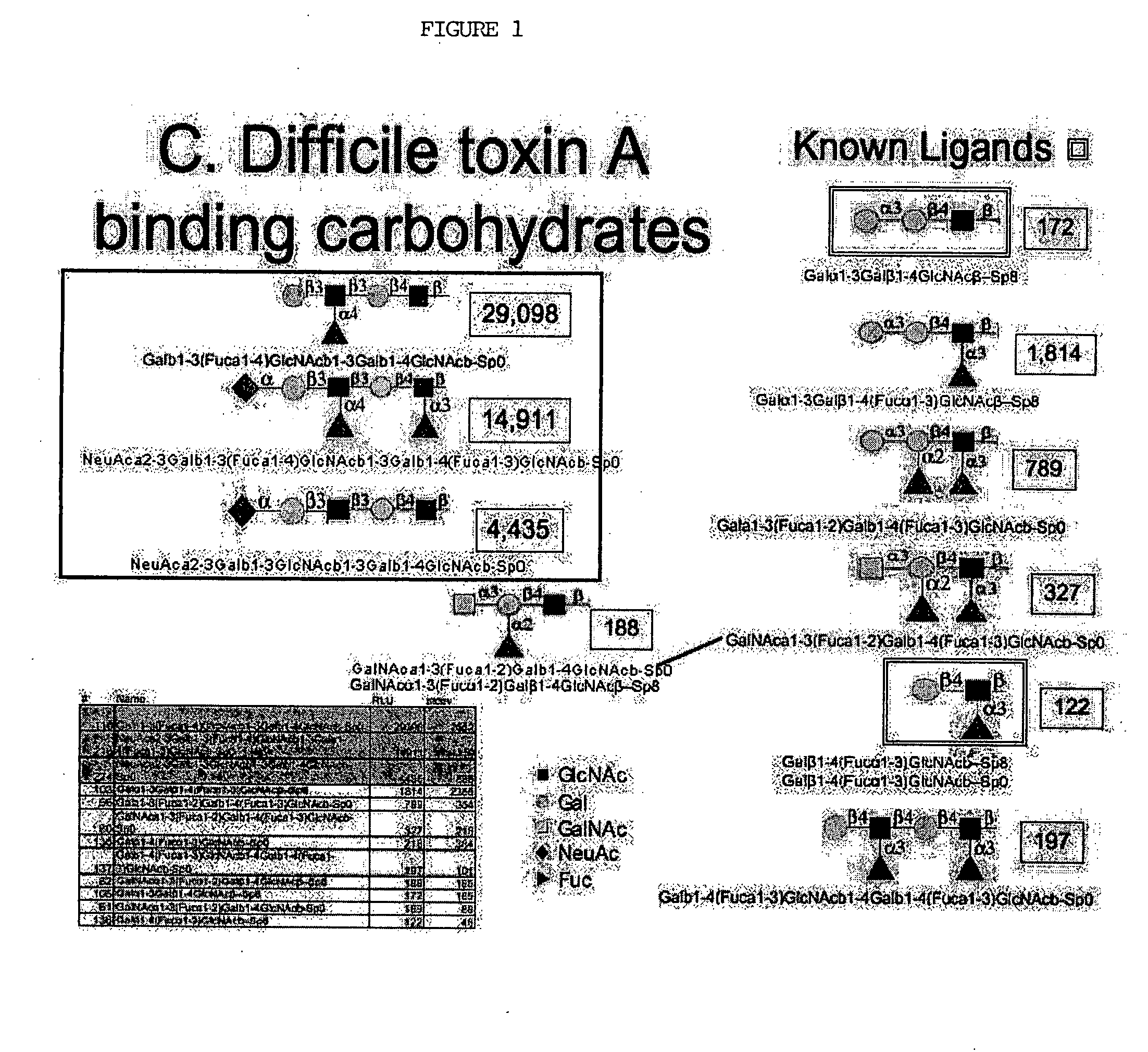
High affinity ligands bind to clostridium difficile toxin A
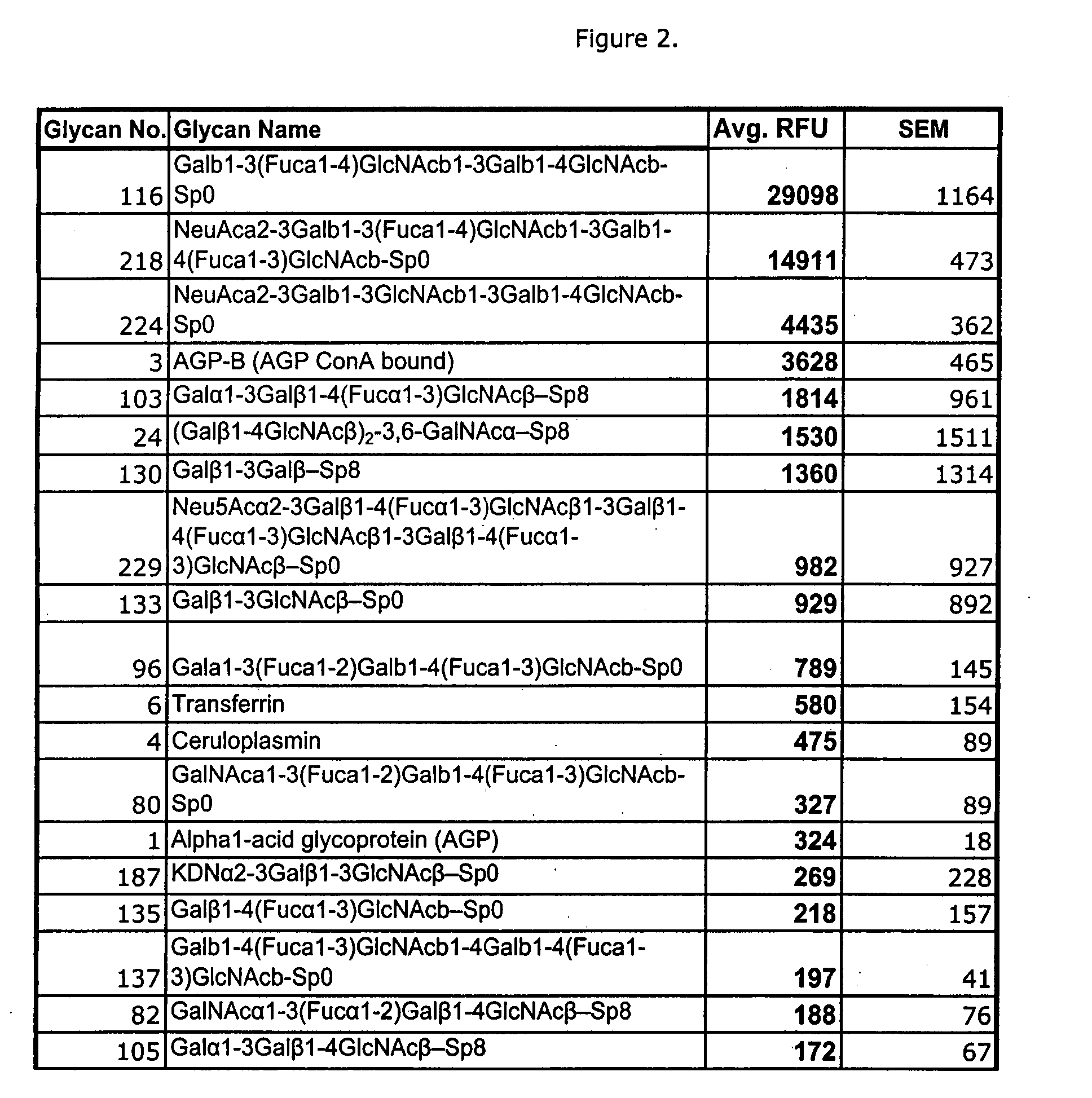
Glycans are identified which have high affinity for C. difficile toxin A. They share one of two saccharide backbones and may have additional side chains. The backbones are galactose-β1-3 N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-β-1-3-galactose-β-1-4-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and galactose-α-1-3-galactose-β-1-4-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine. The ligands may be used therapeutically, prophylactically, and diagnostically.
Owner:DIECKGRAEFE BRIAN
Antibodies against clostridium difficile toxins and uses thereof
ActiveUS20100233181A1High affinityLess immunogenicAntibacterial agentsGenetic material ingredientsClostridium difficile toxin AClostridium difficile (bacteria)
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS UNIV OF +1
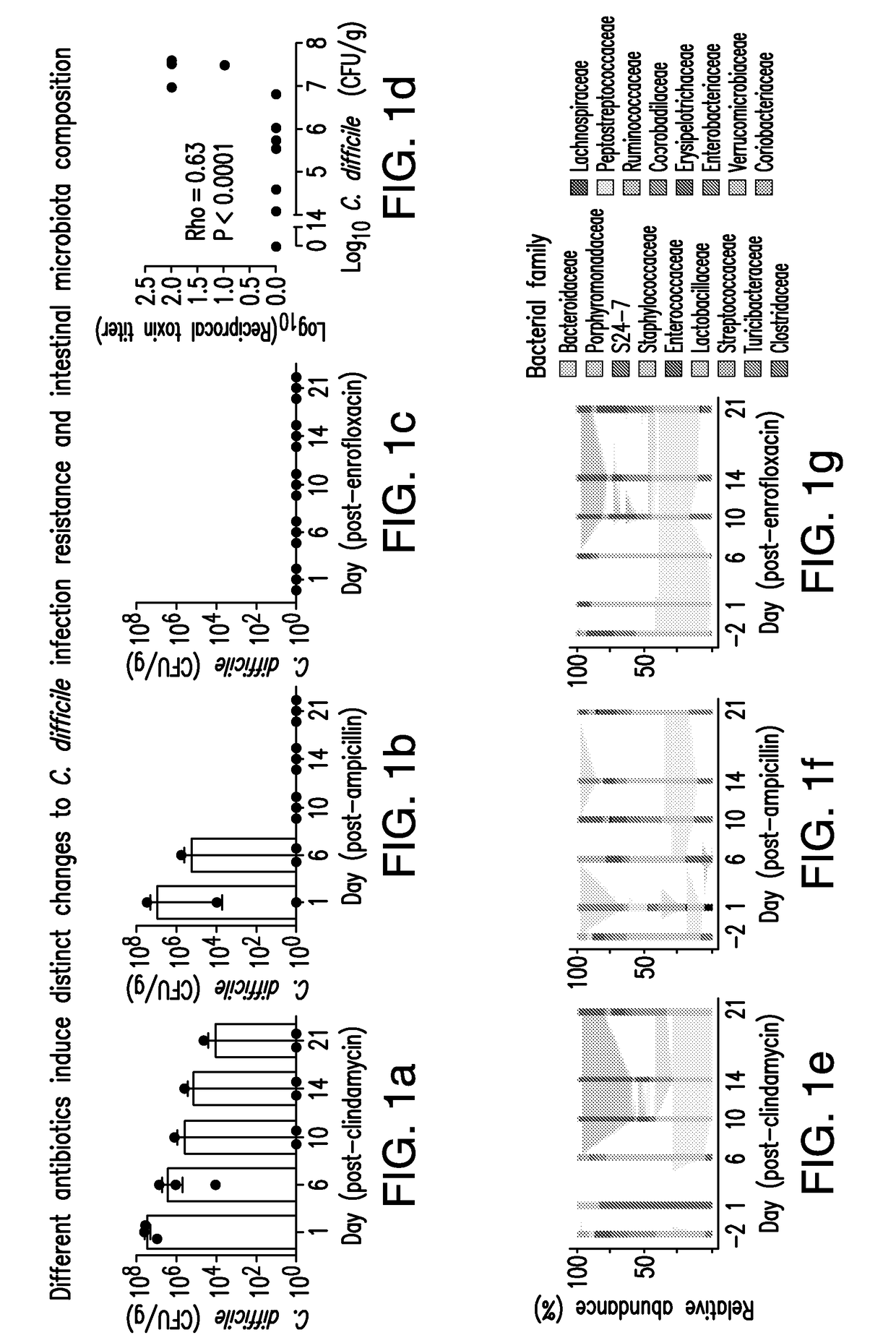
Methods and compositions for reducing clostridium difficile infection
InactiveUS20170087196A1Reduce riskReduce severityPeptide/protein ingredientsBacteria material medical ingredientsClostridial infectionClostridium difficile infections
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for reducing the risk and severity of C. difficile infection. It is based, at least in part, on the discovery that a restricted fraction of the gut microbiota, including the bacterium Clostridium scindens, contributes substantially to resistance against C. difficile infection. Without being bound by any particular theory, it is believed that this is achieved through the biosynthesis of secondary bile acids.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Multivalent live vector vaccine against Clostridium difficile-associated disease
ActiveUS10046040B2Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsDiseaseClostridium difficile toxin A
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
Clostridium difficile exotoxin B amino-terminal gene sequence with optimized codon and nucleic vaccine of clostridium difficile exotoxin B
InactiveCN102181457AOvercome the defect that the protective effect is not strongImprove protectionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsEscherichia coliClostridium difficile toxin A
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedicines and relates to a clostridium difficile exotoxin B amino-terminal gene sequence with optimized codon and a nucleic vaccine of the clostridium difficile exotoxin B. The gene sequence with optimized codon gives consideration to the preferences of the codon in the mammalian cell and the escherichia coli. The related vaccine of the clostridium difficile comprises the exotoxin B amino-terminal gene sequence with optimized codon and a eukaryotic expression vector pJW4303. The clostridium difficile exotoxin B amino-terminal gene sequence with optimized codon not only can be used for constructing the nucleic vaccine, effectively simulates the immune system of the host after immunizing the mammals so that the specific humoral immune response is generated and shows that the specific antibodies have good protective effects in the in vivo and in vitro models, but also is suitable for carrying out prokaryotic expression on the protein in the escherichia coli and lays the foundation for obtaining the protein in quantity.
Owner:王世霞 +3
Butyrogenic bacteria as probiotics to treat clostridium difficile
The subject invention pertains to the use of certain bacterial strains, particularly butyrogenic bacteria, for preparing a composition to treat and / or prevent Clostridium difficile infection. In particular, the invention relates to the use of butyrate-producing anaerobic fermenters of gut commensals in pharmaceutical or food compositions.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Vaccines against clostridium difficile and methods of use
InactiveUS20120020996A1Antibacterial agentsPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSalmonella wienVaccination
Attenuated microorganisms expressing Clostridium difficile antigen(s), and methods of using the same for vaccination of patients are disclosed The invention provides an attenuated microorganism expressing an immunogenic portion of a C difficile Toxin A C-terminal repeat region and / or a C difficile Toxin B C-terminal repeat region The microorganism is an attenuated Salmonella comprising an integrated gene expression cassette that directs the expression of the immunogenic peptide from an in vivo inducible promoter.
Owner:PROKARIUM
Engineered Type IV Pilin of Clostridium difficile
InactiveUS20140227314A1Bacterial antigen ingredientsBiological material analysisAntigenClostridium difficile toxin A
The present invention relates to engineered Clostridium difficile type IV pilin (tfp) genes, type IV pilin proteins which can serve as a diagnostic marker for identification of patients infected with C. difficile, and vaccines comprising type IV pilin proteins, antigenic fragments and variants thereof for therapeutic interventions.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
Composition and kit for detection and analysis of strains of clostridium difficile and method of detecting strains of clostridium difficile by using the same
InactiveCN103484532AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesClostridium difficile toxin AClostridium P
A composition and kit for detecting Clostridium difficile including a primer set for detecting a strain of Clostridium difficile, and a method of detecting Clostridium difficile by using the same.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Methods and compositions for reducing clostridium difficile infection
ActiveUS20190381113A1Lessen risk of and severityReduce riskPeptide/protein ingredientsBacteria material medical ingredientsClostridial infectionBacteroides
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Transcription factor decoys for the treatment and prevention of infections caused by bacteria including clostridium difficile
Decoy nucleic acid sequences comprising a binding site for a target transcription factor, wherein the binding site is not operably linked to a gene, and wherein the transcription factor comprises a regulator of expression of a gene or genes in Clostridium difficile encoding one or more of: (i) a cellular growth factor; (ii) a cellular toxin; (iii) a cellular sporulation factor; (iv) a cellular stress response; and / or (v) a cellular essential gene are described. Uses of the decoys in antibacterial complexes for the treatment of bacterial infections are also described.
Owner:PROCARTA BIOSYST
Neutralising antibodies to the major exotoxins tcda and tcdb of clostridium difficile
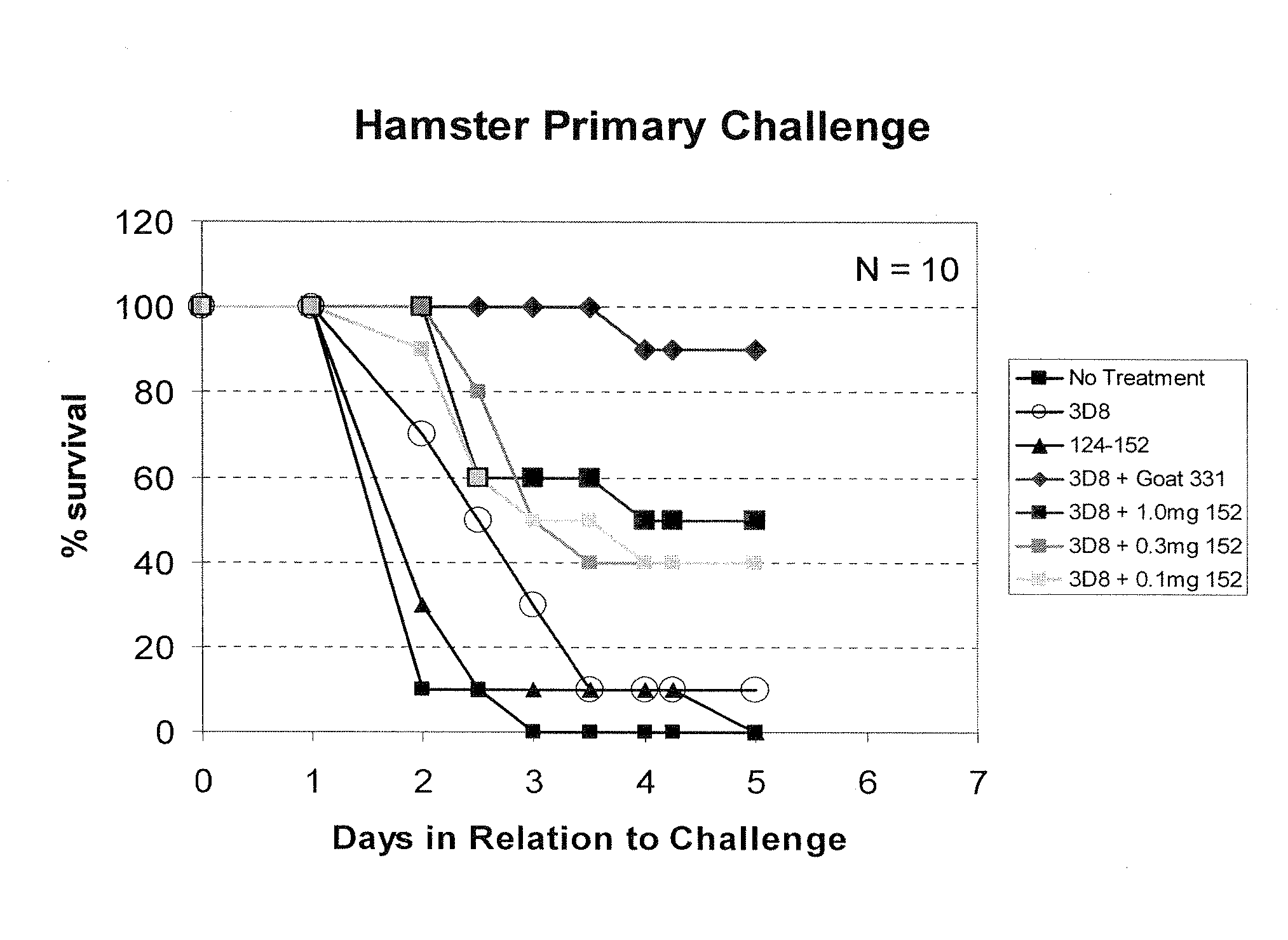
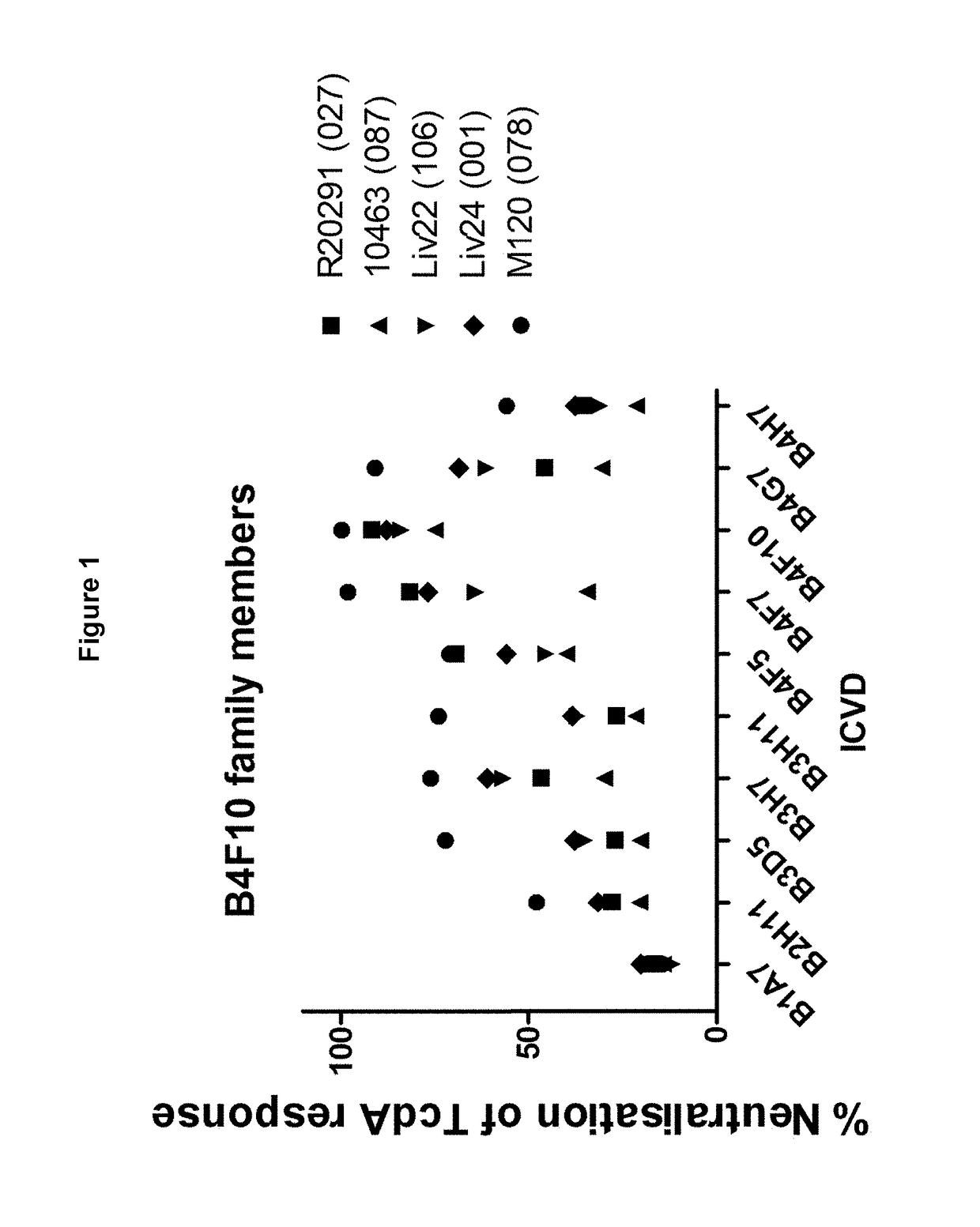
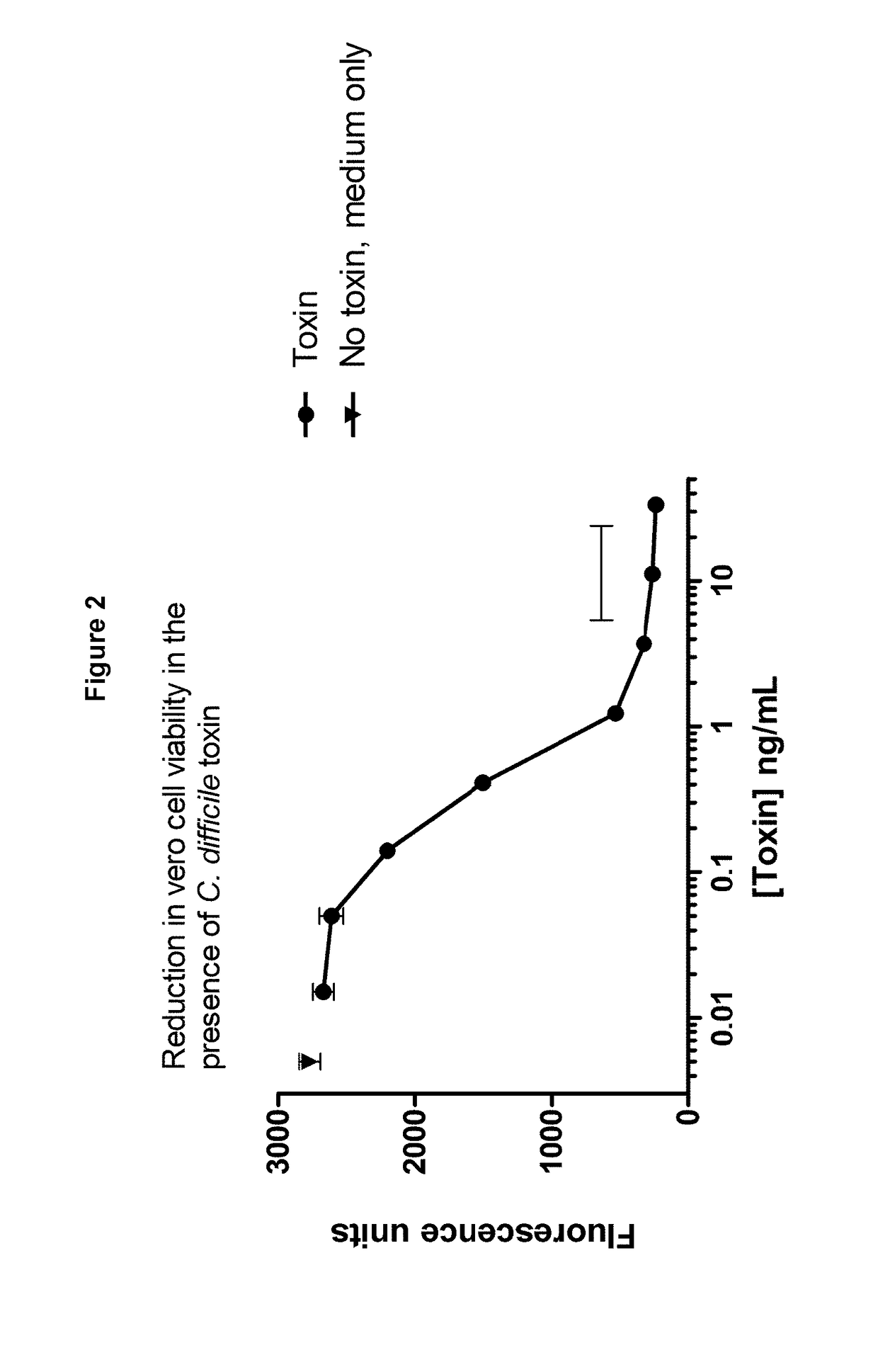
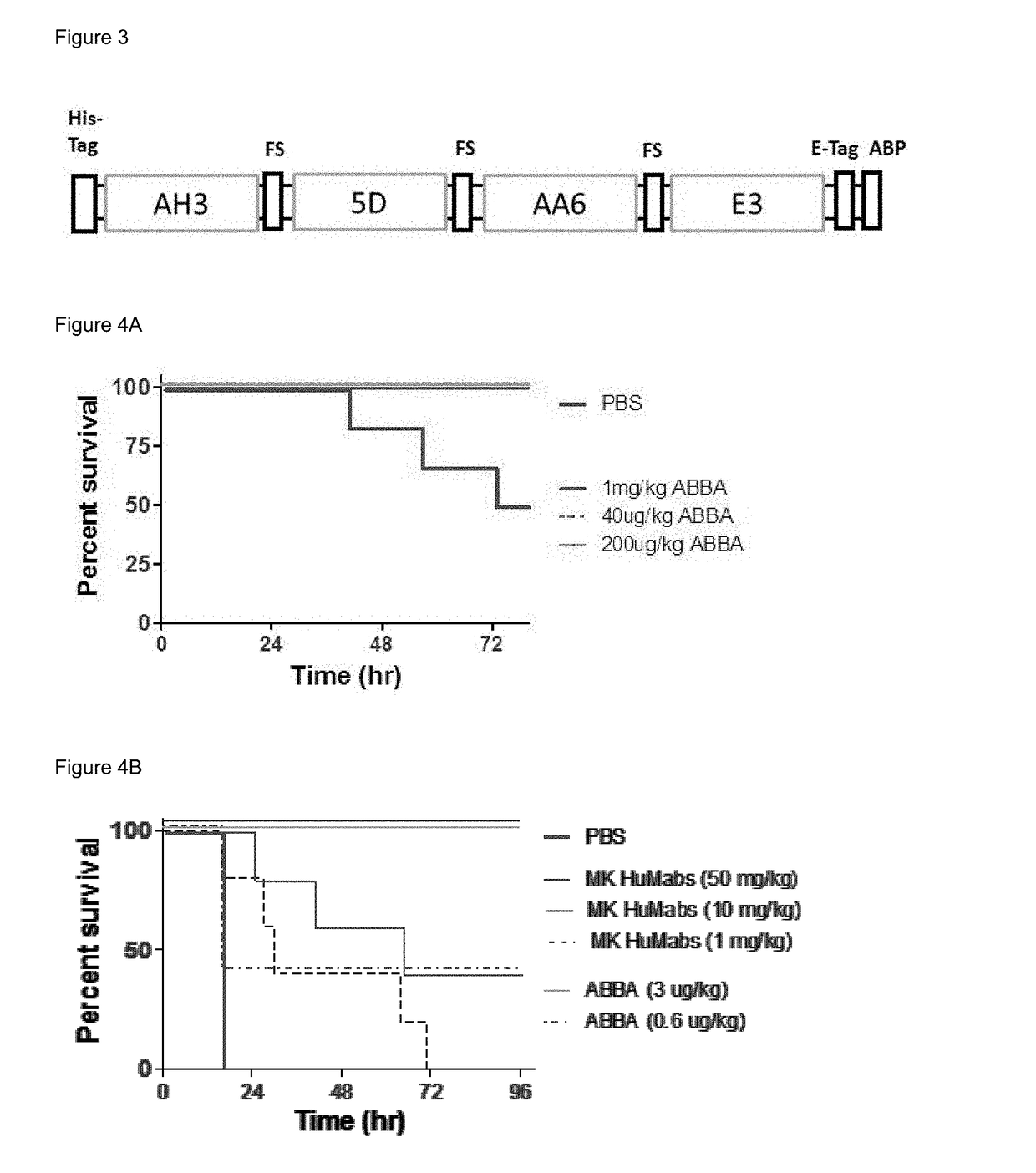
ActiveUS20140348844A1Improve performanceSignificant and positive impact on survivalAntibacterial agentsLibrary screeningNeutralising antibodyClostridium difficile toxin A
This present invention describes the derivation and selection of antibodies capable of neutralising the major exotoxins; TcdA and TcdB of Clostridium difficile. The invention also describes novel neutralisation and antigen binding properties of individual Mabs and mixtures thereof.
Owner:UCB PHARMA SRL
LAMP detection method of clostridium difficile binary toxin and special primers and kit for LAMP detection method
InactiveCN104328206AEasy identification of resultsEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDiseaseClostridium difficile toxin A
The invention discloses an LAMP detection method of clostridium difficile binary toxin and special primers and kit for the LAMP detection method. The LAMP detection method comprises the following steps: designing the primers according to specificity conserved genes cdtA and cdtB of clostridium difficile, performing LAMP amplification under the guide of the obtained primers by taking the genome DNA of a sample to be tested as a template, and further rapidly and quantitatively detecting whether the sample to be tested carries the clostridium difficile binary toxin according to the color change of reaction liquid or the turbidity change of the reaction liquid. By adopting the LAMP detection method, clostridium difficile cdtA or / and cdtB can be independently or simultaneously detected, rapid, convenient, synchronous, efficient, high-specificity and high-sensitivity detection under an isothermal condition can be achieved without complex instruments, a novel technical platform can be provided for clostridium difficile binary toxin detection and toxin classification, clinical diagnosis and treatment can be instructed, fulminant diffusion of clostridium difficile high-toxicity strains can be prevented, the method can be used for screening and detecting the clostridium difficile binary toxin in primary medical treatment and public health departments and disease prevention and control centers and has a wide market prospect and relatively great economic and social benefits.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
Polypeptide comprising an immunoglobulin chain variable domain which binds to clostridium difficile toxin a
InactiveUS20180100009A1High potency against TcdAResistance to degradationImmunoglobulins against bacteriaDepsipeptidesClostridial toxinClostridium difficile toxin A
There is provided inter alia a polypeptide comprising an immunoglobulin chain variable domain which binds to Clostridium difficile toxin A.
Owner:VHSQUARED +1
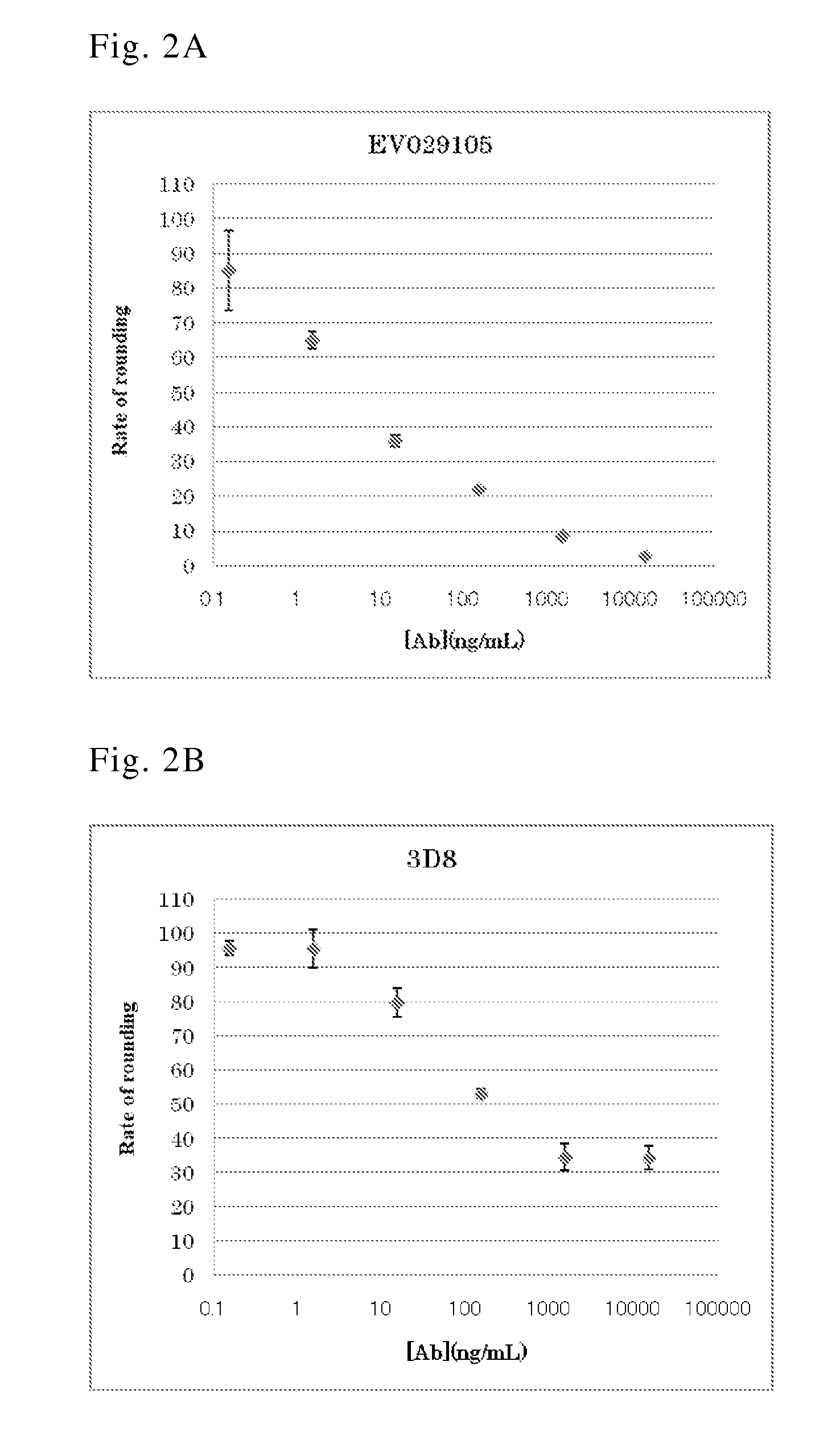
Human antibody specific to toxin produced from clostridium difficile, or antigen-binding fragment thereof
InactiveUS20150259402A1Low immunogenicityAnimal cellsBacterial antigen ingredientsClostridial infectionAntigen Binding Fragment
The present invention provides novel human-derived monoclonal antibodies specifically binding to toxins produced by Clostridium difficile (toxin A and toxin B), respectively, and having excellent neutralizing activity, and antigen-binding fragments thereof. The present invention also provides a pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of Clostridium difficile infection comprising any of the antibodies or antigen-binding fragments thereof.
Owner:EVEC
Clostridium Difficile Toxins a and/or B Antigen and Epitope Antibody, and Pharmaceutical Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20180022784A1Bacterial antigen ingredientsHybrid immunoglobulinsEpitopePassive Immunotherapy
It is described a Clostridium difficile (C-difficile) toxins A and / or B as a target for therapy, including passive immunotherapy, and particularly prevention of C-difficile intoxication in human or other animals. It is also described a polypeptide comprising a portion of C-difficile toxins A and / or B sequence being an epitope for anti-toxins A and / or B antibody. It disclosed a method for generating a neutralizing antibody directed against C-difficile toxins A and / or B. It is also provided a novel formulation that combines key toxins A and / or B epitope antibodies, located in three key domains of toxins A and / or B, for neutralisation of the toxins A and / or B, at any stage of toxins A and / or B intoxication related to C-difficile infection. The novel formulation of toxins A and / or B epitope antibodies are useful in immunotherapy, for 10 therapeutic and / or prophylactic mediation of C-difficile intoxication.
Owner:IMMUNE BIOSOLUTIONS INC
Polysaccharide immunogens from Clostridium difficile
ActiveUS8597663B2Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMedicineClostridium difficile toxin A
The application relates to Clostridium difficile cell surface polysaccharides, compositions comprising Clostridium difficile cell surface polysaccharides, and includes kits, methods and uses thereof.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH
Mono-specific polyclonal antibodies and methods for detecting Clostridium difficile Toxin A
InactiveUS7179611B2High sensitivityProduct can be usedImmunoglobulins against bacteriaPeptide preparation methodsClostridial toxinImmobilized Antibodies
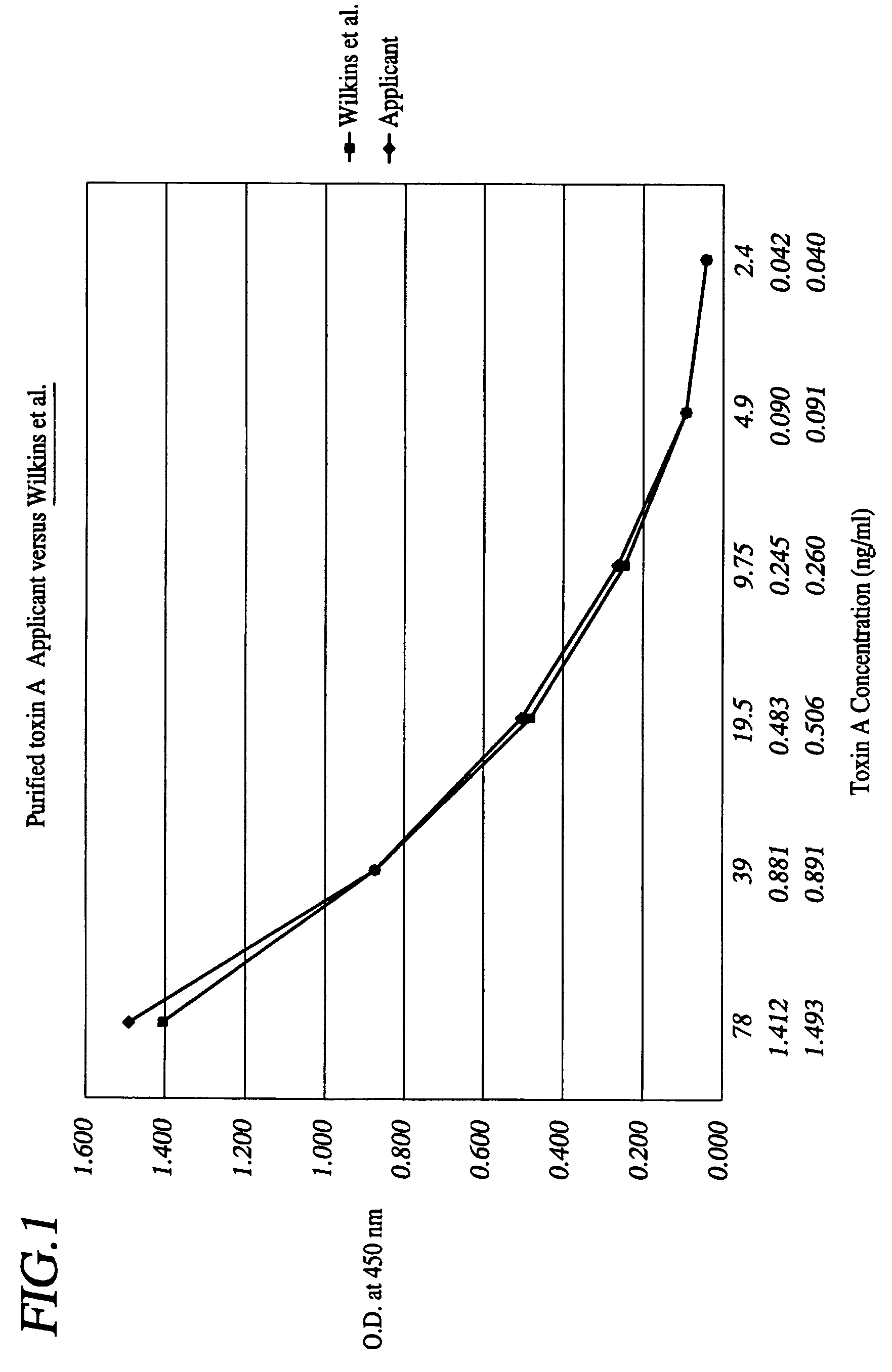
A method is provided for the purification of Clostridium difficile Toxin A antigen comprising reacting impure Toxin A with immobilized mono-specific polyclonal antibodies. The polyclonal antibodies are coupled to a hydrazide group containing matrix such as hydrazide activated agarose gel. The immobilized antibody is specific for Toxin A and will greatly purify Toxin A from a Toxin A containing solution. Antibodies raised to Toxin A purified according to the method are of higher activity than antibodies produced from prior art purified Toxin A.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON LEE LAB
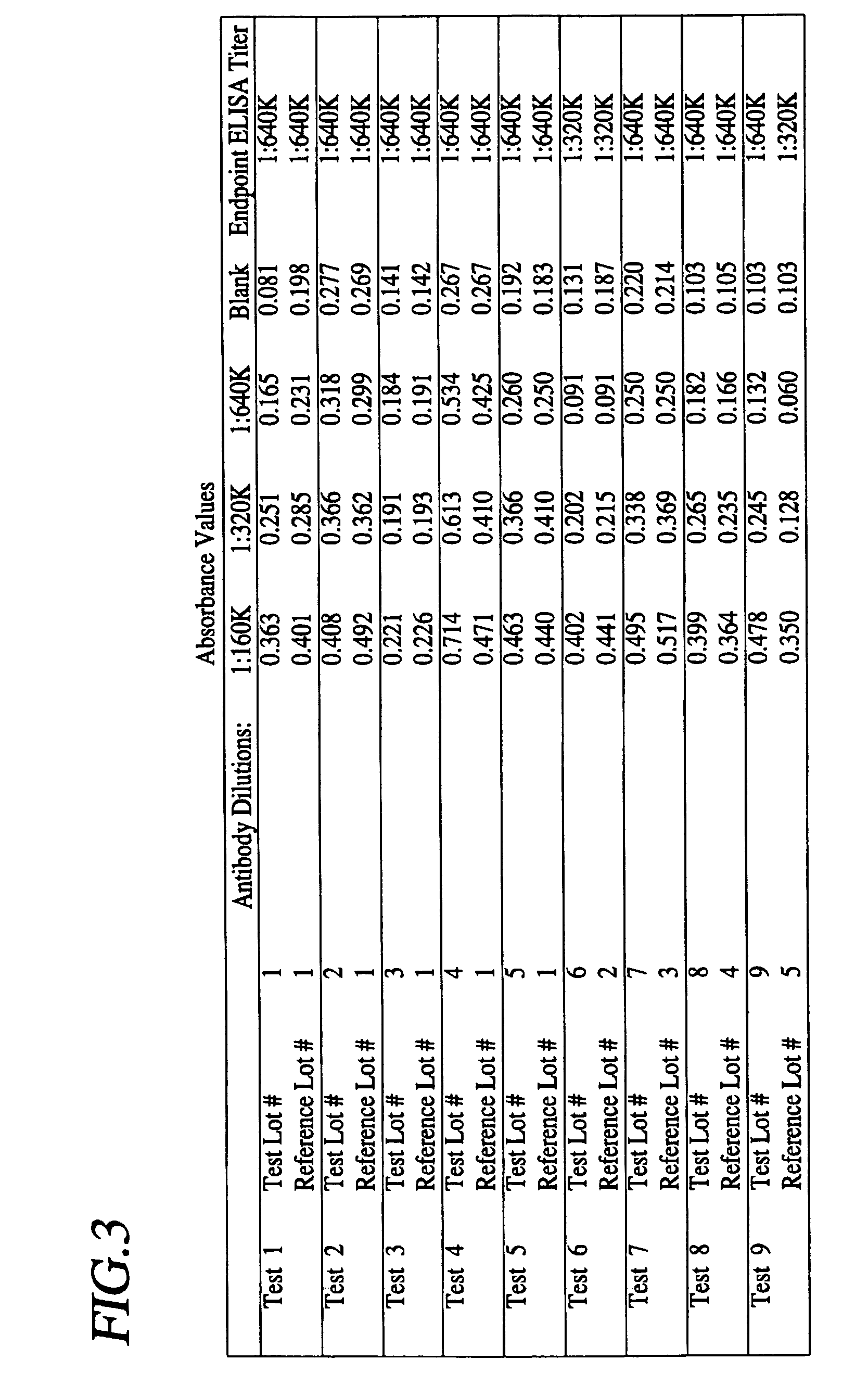
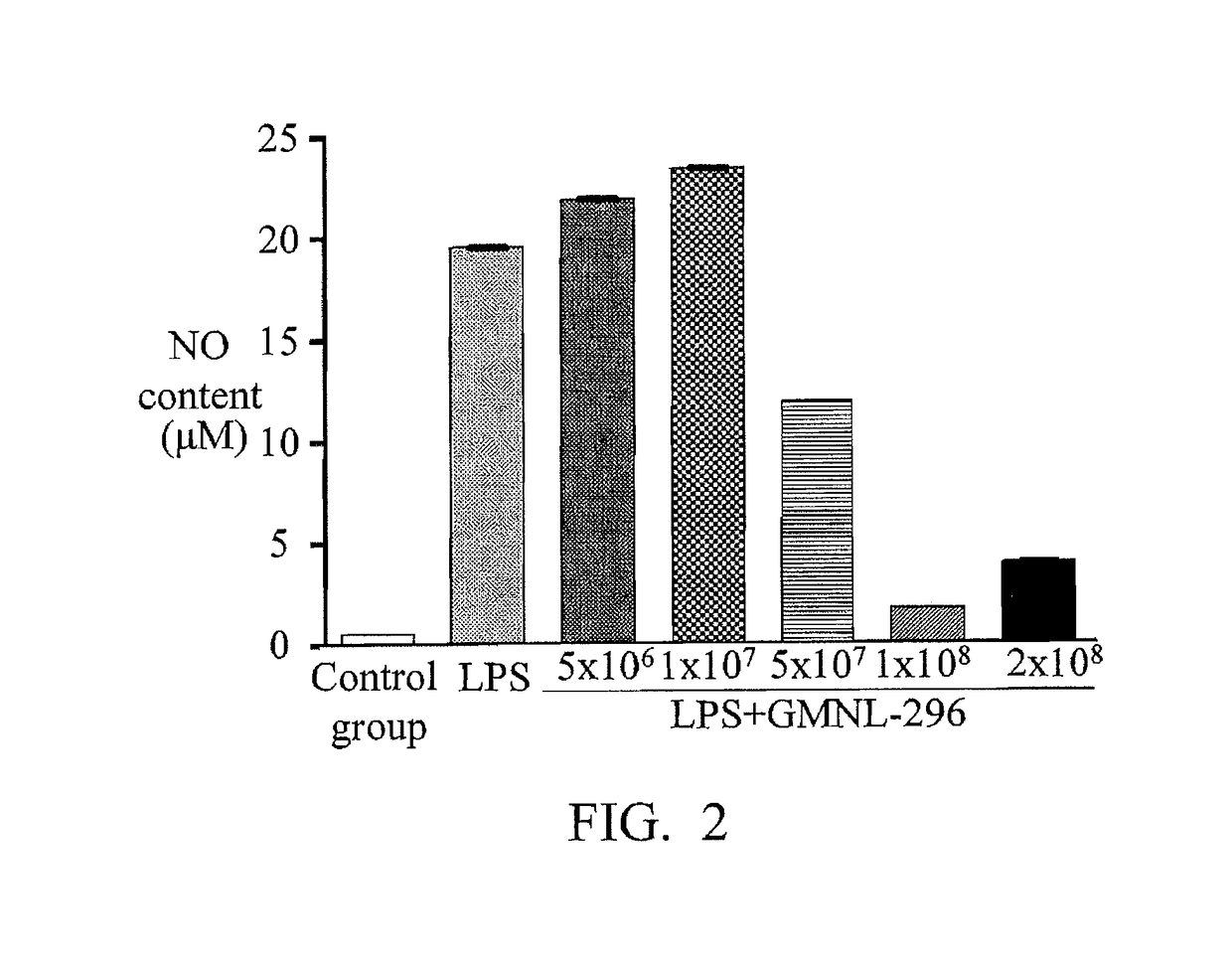
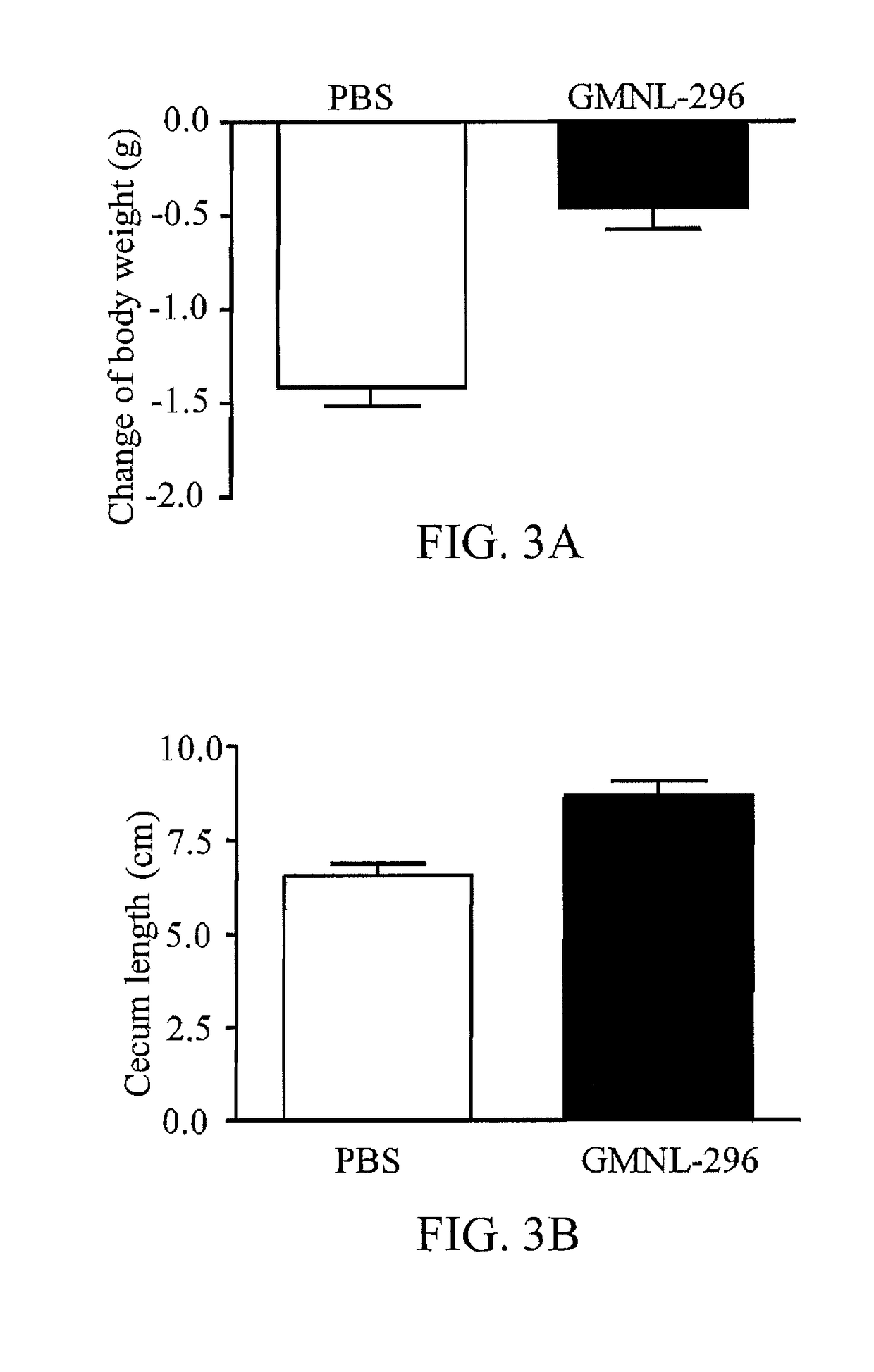
Composition and use of lactobacillus fermentum gmnl-296 to produce composition for improving symptoms of clostridium difficile infection
ActiveUS20180050072A1Symptoms improvedGood for weight lossAntibacterial agentsBacteriaClostridium difficile infectionsLactobacillus fermentum
A composition of Lactobacillus fermentum GMNL-296 and a use of Lactobacillus fermentum GMNL-296 for producing a composition to improve the infection symptoms of Clostridium difficile are provided. The Lactobacillus fermentum GMNL-296 is to promote the expression of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 and Treg cell related transcription factors, so that the infection symptoms of weight loss and intestinal abnormalities are improved.
Owner:GENMONT BIOTECH
Codon-Optimized Dna Molecules Encoding the Receptor Binding Domains of Clostridium Difficile Toxins A and B, and Methods of Use Thereof
InactiveUS20100278868A1Increase dosageReduce riskAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsHuman DNA sequencingClostridium difficile infections
In one aspect, the invention provides a DNA molecule. The DNA molecule includes a nucleotide sequence that encodes the receptor-binding domain of Clostridium difficile toxin A or toxin B in which at least about 10% of the in-frame codons for each amino acid residue has a higher percentage use in the human genome than the corresponding in-frame codons of C. difficile toxin A or toxin B having a known sequence. Methods for generating antibodies to Clostridium difficile toxin A or toxin B, methods for reducing the risk of a C. difficile infection, and methods for treating a C. difficile are also provided.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY +1
Live bacterial vaccine for controlling intestinal infection caused by clostridium difficile, preparation method thereof and application thereof
InactiveCN102743746AEasy to takeEasy to storeAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsClostridial toxinClostridium difficile toxin A
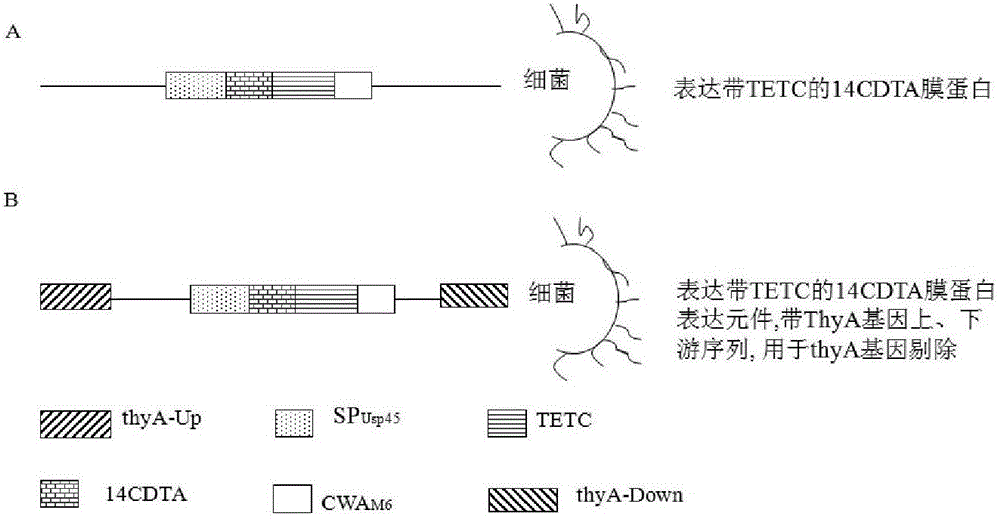
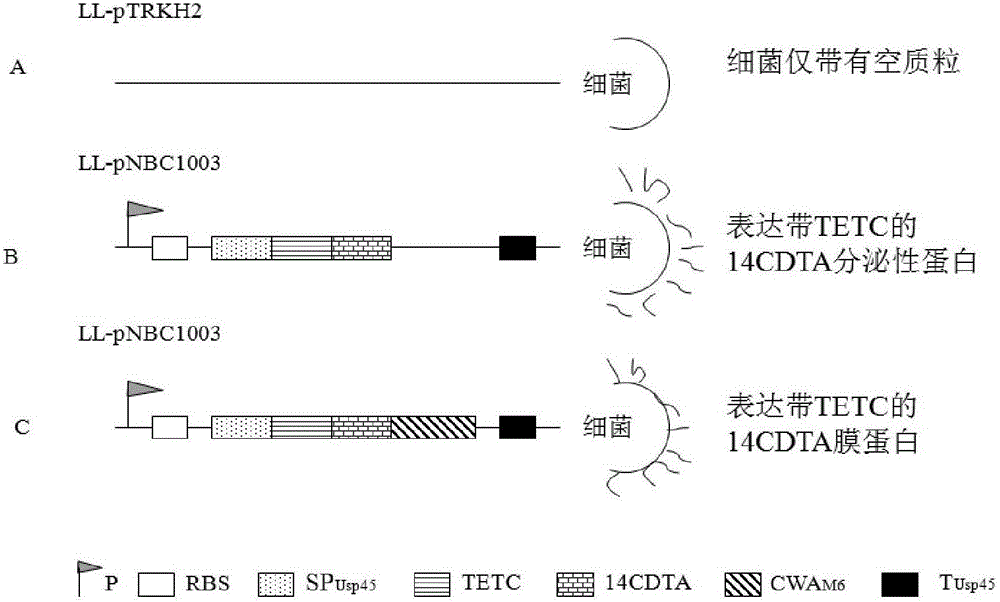
The invention discloses a live bacterial vaccine for controlling intestinal infection caused by positive clostridium difficile of clostridium difficile toxin A, wherein the vaccine contains thymidylate synthetase ThyA gene defective recombined lactic streptococci; and tests of the vaccine verify that the vaccine is safe and effective. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the live bacterial vaccine, and a use of the live bacterial vaccine in the preparation of medicines for controlling the intestinal infection caused by the positive clostridium difficile of the clostridium difficile toxin A.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV (GUANGZHOU RESPIRATORY CENT) +1
Tetra-specific, octameric binding agents and antibodies against clostridium difficile toxin a and toxin b for treatment of c. difficile infection
ActiveUS20180244760A1Promote cloningEasy to produceAntibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsClostridial toxinClostridium difficile toxin B
Novel, antibody-based binding agents derived from human and camelid immunoglobulins are described. These binding agents recognize and bind with specificity to Clostridium difficile toxin A and / or toxin B and in some cases exhibit toxin neutralizing activity. These binding agents can be used to treat or prevent primary and recurrent CDI. The binding agents include camelid VHH peptide monomers, linked groups of VHH peptide monomers, VHH peptide monomers joined to antibody Fc domains, and VHH peptide monomers joined to IgG antibodies.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Thuricin cd, an antimicrobial for specifically targeting clostridium difficile
The present invention relates to a new bacteriocin, to microbial strains which can produce it and to uses of the bacteriocin and the strains. The bacteriocin is effective against Clostridium difficile and Listeria monocytogenes amongst other organisms.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE CORK NAT UNIV OF IRELAND CORK +1
Antibodies for prevention and treatment of diseases caused by clostridium difficile
InactiveUS9815889B2Increase productionRapid immune responseOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaDiseaseClostridium difficile toxin A
The present invention relates to an antibody having specificity for an immunogenic determinant consisting of the pentasaccharide repeating unit of the Clostridium difficile glycopolymer PS-I: α-L-Rhap-(1→3)-β-D-Glcp-(1→4)-[α-L-Rhap-(1→3)]-α-D-Glcp-(1→2)-α-D-Glcp or a fragment thereof. Said antibody is able to prevent and treat diseases caused by C. difficile. The present invention further pertains to a method of treating or preventing a disease caused by the pathogen Clostridium difficile, which comprises administering to a subject said antibody or a vaccine composition comprising said antibody.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Method of prevention and treatment of clostridium difficile infection
InactiveUS20160250151A1Reduce the numberPrevention of declineAntibacterial agentsDigestive systemMicroorganismClostridium difficile infections
This invention relates to prophylactic and / or therapeutic application of microorganism species that are, for example, administered orally as delayed release formulation designed to release its microbial content to the distal small intestine and / or colon in high quantities and density, which is a “normalized” approach to repopulate the colonic flora as a method of prevention and / or treatment of, for example, Clostridium difficile colitis.
Owner:BOCHENEK WIESLAW J +1
Fluorescent PCR detection method for clostridium difficile toxin genes, as well as primer and kit of fluorescent PCR detection method
ActiveCN105039516AStrong specificityModerate lengthMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFluorescenceClostridium difficile toxin A
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene detection, and specifically relates to a fluorescent PCR detection method for clostridium difficile toxin genes, as well as a primer and a kit of the fluorescent PCR detection method. The primer has good corresponding specificity, proper length and efficiency in transcription, and can not form a secondary structure, the primer contains complementation of not more than four continuous four basic groups; the testing coincidence rate obtained by adopting the primer is 98.6%, and the detection sensitivity can achieve 100copies / mL. According to the detection method, clostridium difficile DNA in a specimen, such as an excrement specimen, can be easily and conveniently extracted, and the genes of clostridium difficile toxins A and B are detected; the specific amplification primer and a fluorescence probe are adopted, so that the detection sensitivity and the specificity are greatly improved, the defect of insufficient specificity existing in an antibody and a cultivation detection method is overcome, and the problem of misdetection is also solved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL (GUANGZHOU DIGESTIVE DISEASE CENT GUANGZHOU FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH) +1
Use of small molecules for the treatment of clostridium difficile toxicity
InactiveUS20170128420A1Antibacterial agentsMicrobiological testing/measurement3-phenylpropylamineClostridium difficile infections
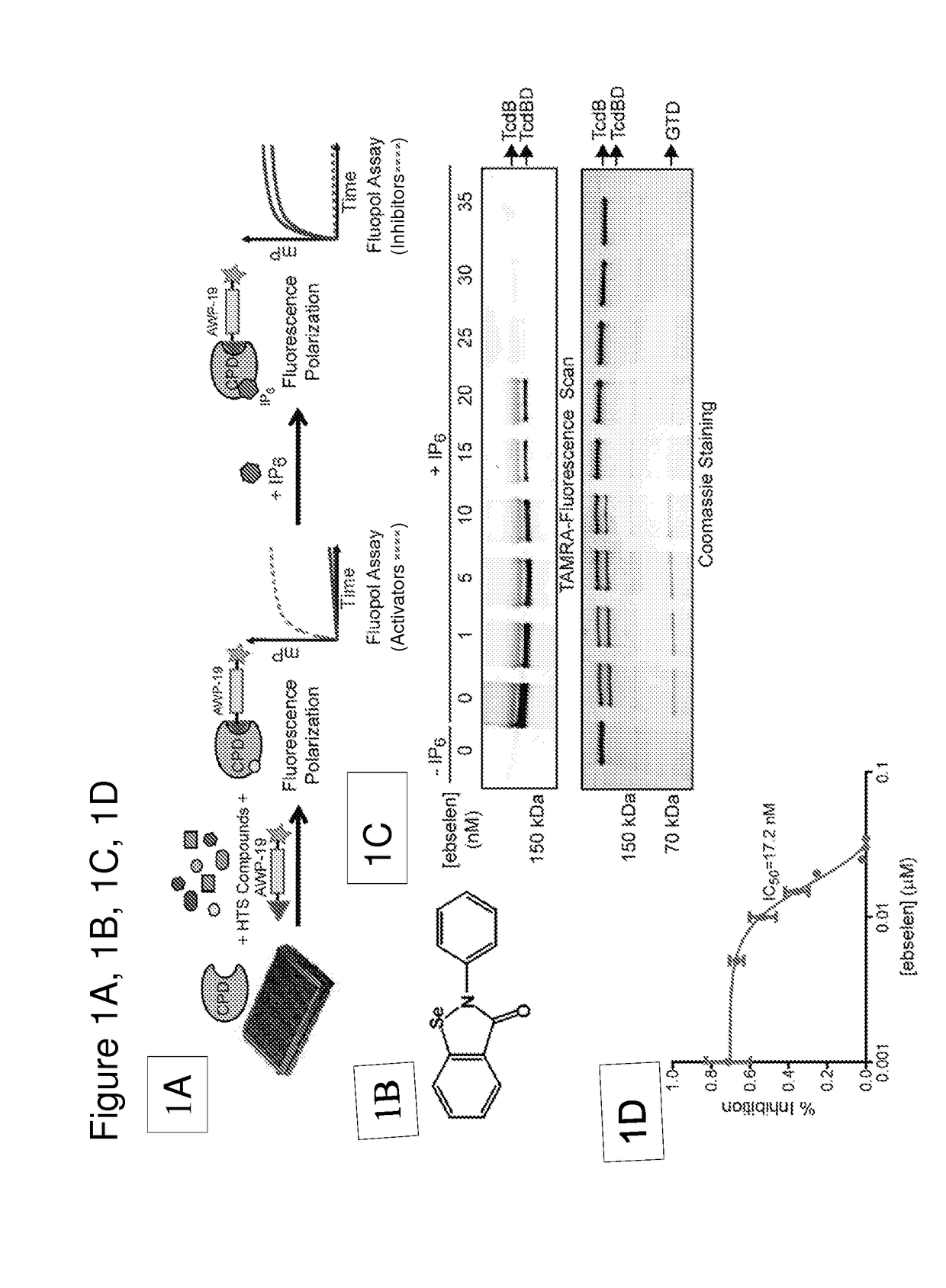
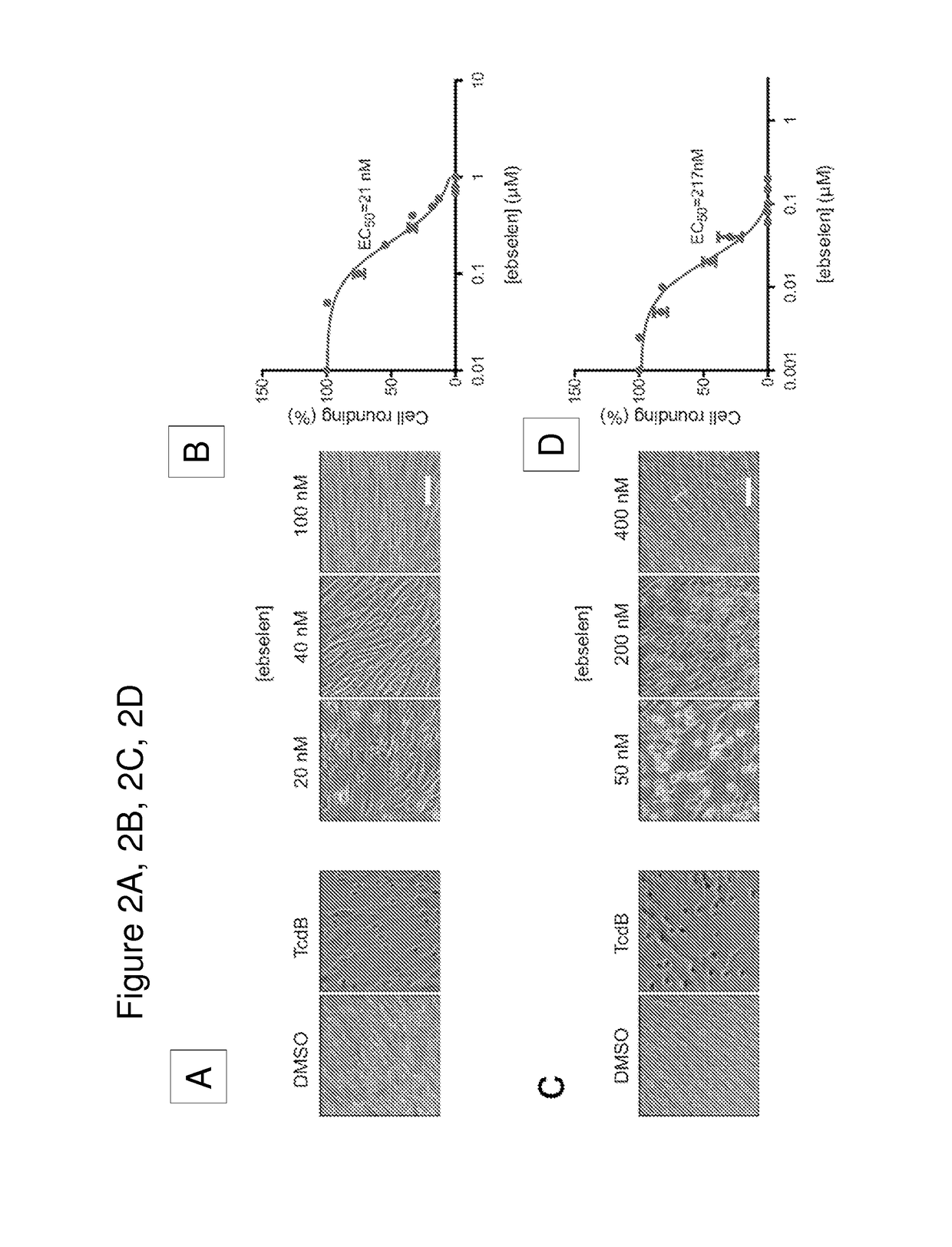
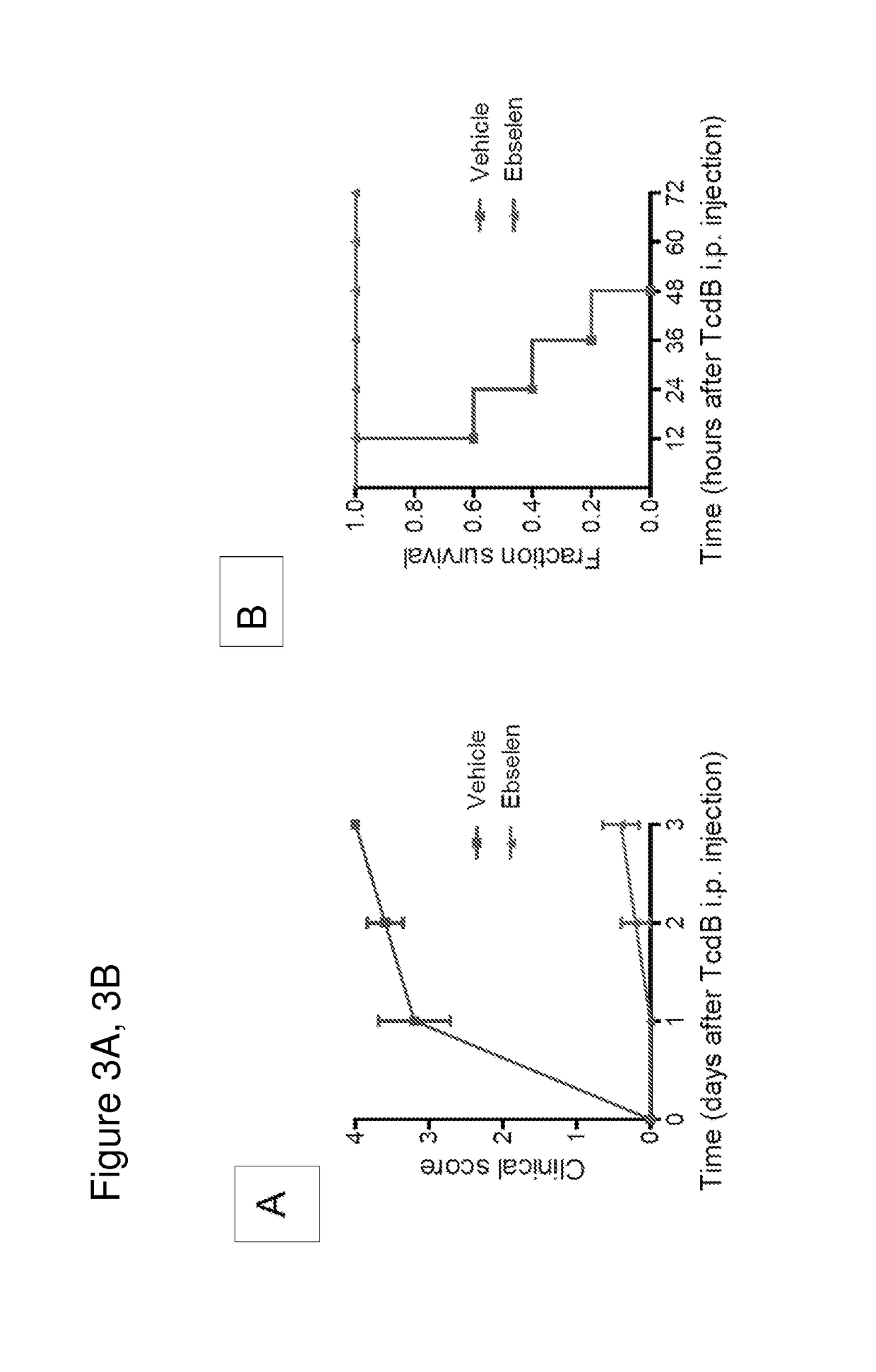
Disclosed are methods and compositions for reducing toxicity associated with infection by Clostridium difficile by inhibiting Clostridium difficile toxin B (TcdB) and / or toxin A (TcdA). Such compounds include ebselen compounds, namely ebselen and its salts, ebselen functional analogues and ebselen structural analogues, as well as certain amide derivatives. This includes Formula I, e.g. 1-methyl-3-phenylpropylamine, Formula II, e.g., 2,2′-diselane-1,2-diylbis[N-(2,4-difluorophenyl)benzamide]; and Formula III, e.g. 2-(2-methoxy-5-methylphenyl)-1, 2-benzoselenazol-3-one. The present compositions may be comprised in a colon-retentive formulation that increases residence of and / or release of the compound in the area where the infection is active.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com