Polypeptides
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Standard Intestinal Tract Models, Standard Intestinal Stability Assays and Standard Potency Assays
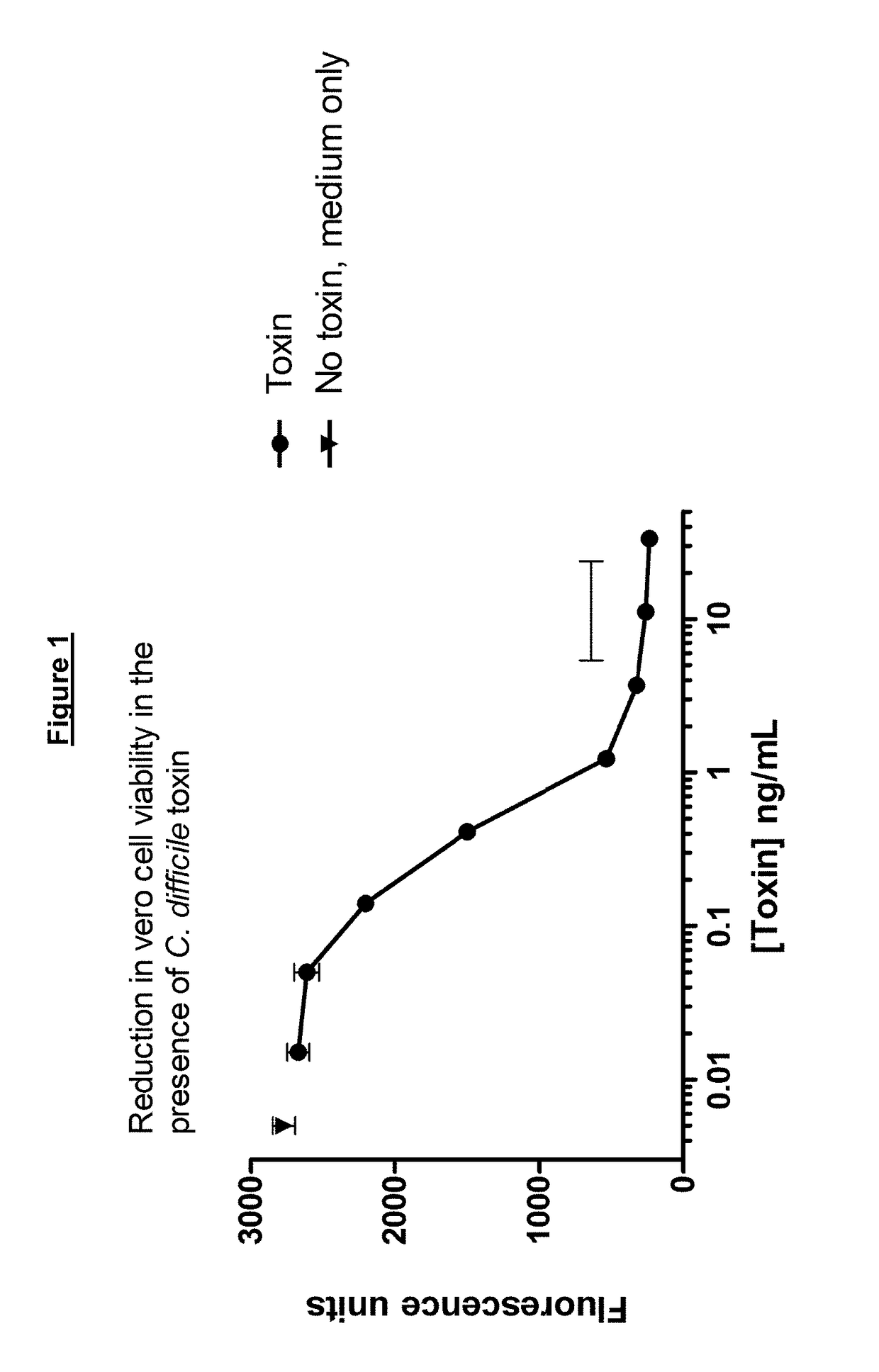
[0258]The intestinal stability and potency of a polypeptide comprising an immunoglobulin chain variable domain can be assayed using the following methods. The methods below refer to
[0259]ICVDs, but are equally applicable to any polypeptide which comprises an ICVD, such as an antibody.
[0260]1.1 Standard Intestinal Tract Models
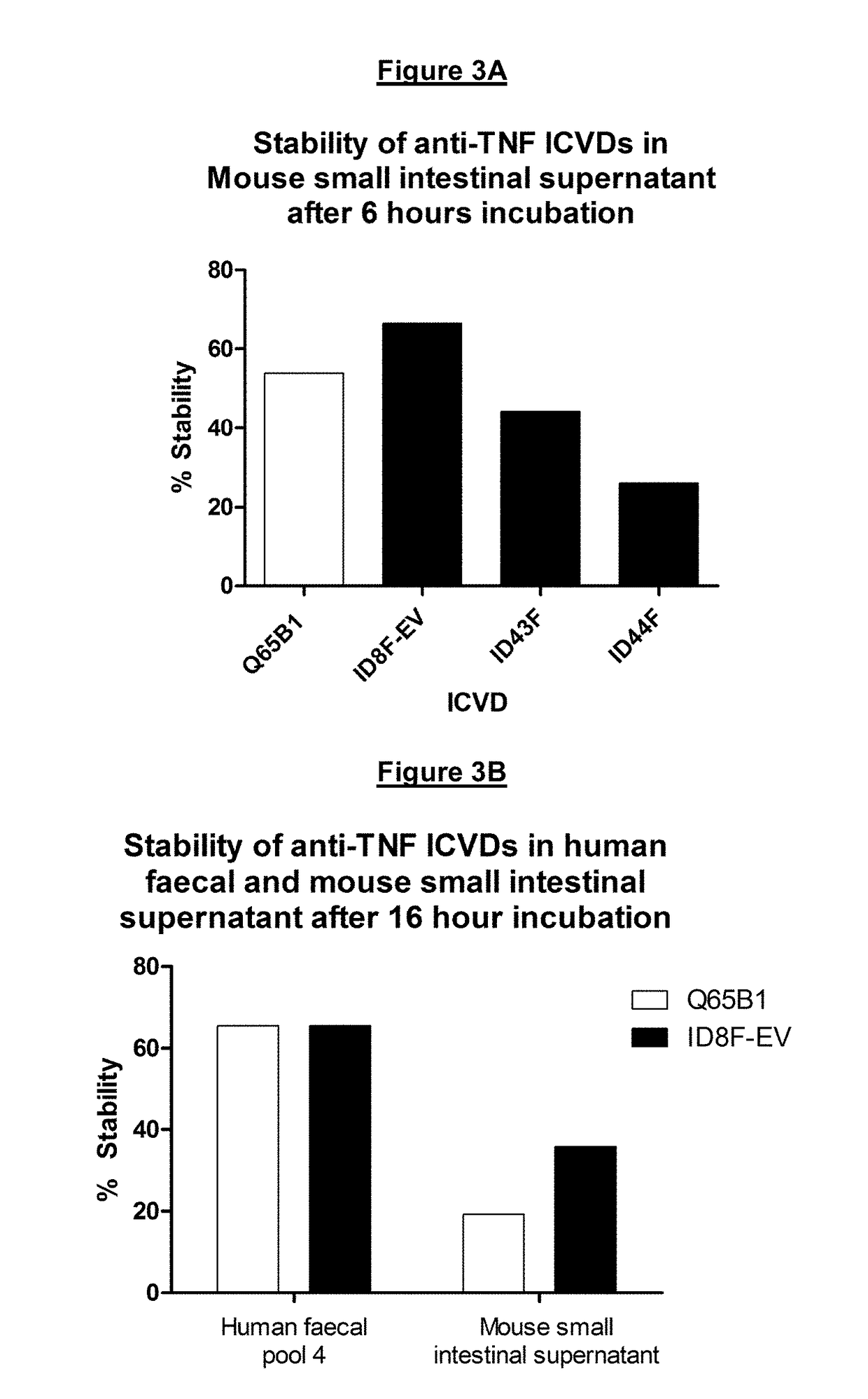
[0261]Ex vivo samples from human faeces and mouse small intestine samples are highly relevant matrices for estimation of stability in the human intestinal tract. Such samples contain native host-produced, and associated microbial-produced, proteases along with any chaotropic agents or surfactants that may influence ICVD stability in the presence of proteases. The enzymatic cleavage sites of at least some proteases present in the small intestine from murine and human origin are well characterised and conserved between the two species. Murine small intestinal supernat...
example 2
Substitution of a Lysine Residue with Alanine, Histidine or Glutamine in CDR2 of an Anti-TNF-alpha ICVD
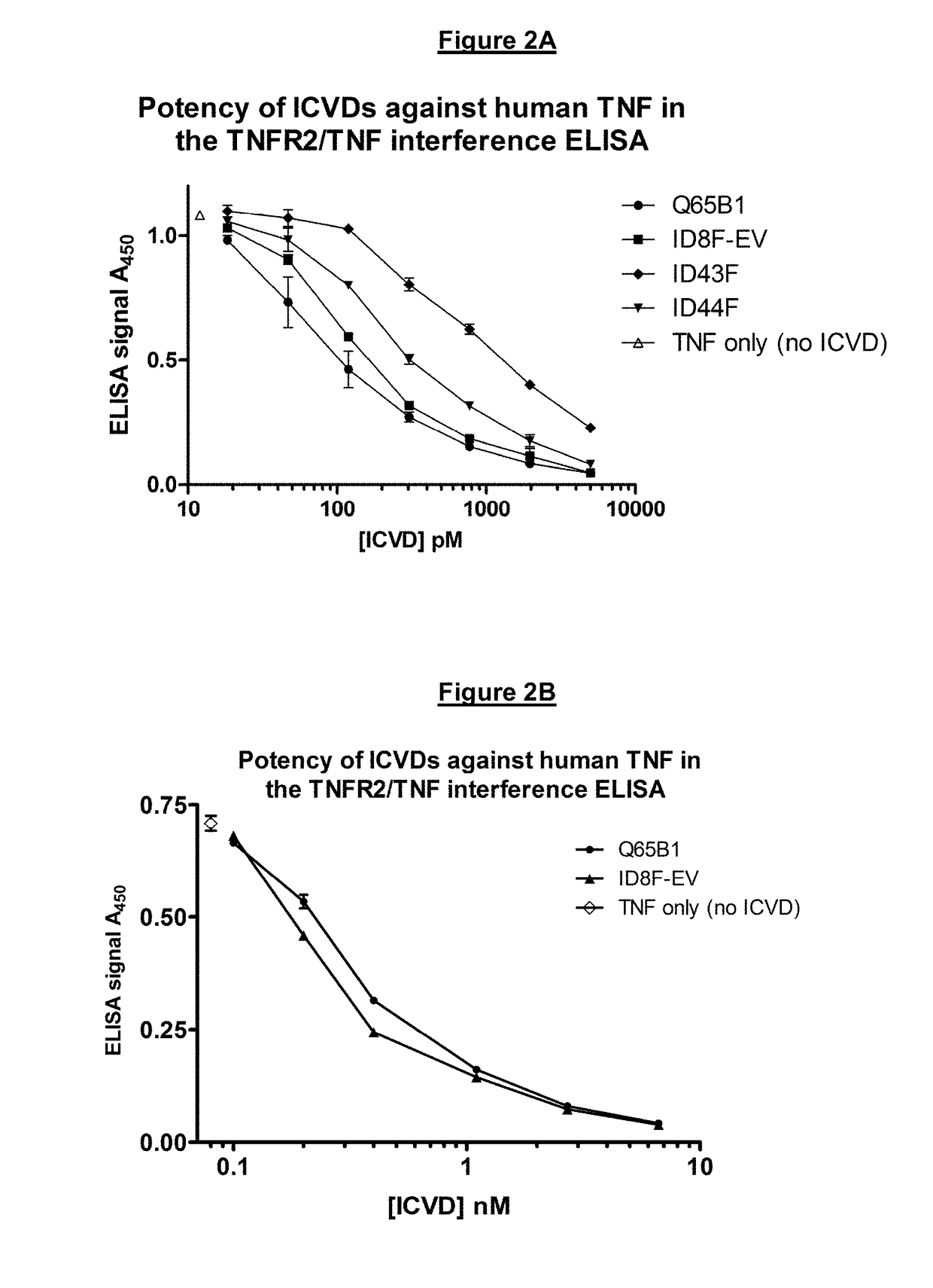
[0525]Q65B1 is an anti-TNF-alpha ICVD isolated, cloned and purified from a llama immunised with soluble human recombinant TNF-alpha. Residue K59 of the Q65B1 polypeptide sequence was substituted with alanine, histidine or glutamine and the impact of each substitution on intestinal tract stability and potency was tested.
[0526]DNA encoding each ICVD was cloned into vector pMEK222, expressed, and purified from the periplasm of E. coli (either by Talon or Nickel NTA column). All ICVDs tested here carry an identical C-terminal Flag-His6 tag.
[0527]Residue K59 resides in CDR2 of Q65B1. Q65B1 with a K59A substitution is labelled “ID43F”, Q65B1 with a K59H substitution is labelled “ID8F-EV”, and Q65B1 with a K59Q substitution is labelled “ID44F”.
[0528]2.1.1 Potency—Standard TNFR2 / TNF Interference ELISA Assay—Experiment 1
[0529]Dose-response curves of each ICVD were generated using the Standa...
example 3
Substitution of a Lysine Residue with a Histidine Residue in both CDR2 and CDR3 of an anti-TNF-alpha ICVD
[0543]Both residues K59 and K101 of Q65B1 were substituted with histidine (making “ID34F”). Residue K59 resides in CDR2 of Q65B1 and residue K101 resides in CDR3 of Q65B1. DNA encoding ID34F was cloned and expressed in yeast.
[0544]Q65B1 substituted with a K59H residue (as in Example 2) was produced again, having the same sequence as ID8F-EV described above. However, on this occasion DNA encoding this ICVD was cloned and expressed in yeast (therefore lacking the C-terminal Flag-His6 tag) and is therefore labelled “ID32F” in this example.
[0545]3.1 Potency—Standard TNFR2 / TNF Interference ELISA Assay
[0546]Dose-response curves of each ICVD were generated using the Standard TNFR2 / TNF Interference ELISA Assay. A concentration range of 0-3 nM was used (FIG. 4).
[0547]3.2.1 Intestinal stability—Standard Mouse Small Intestinal Supernatant Intestinal Tract Model
[0548]ICVDs were digested for ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com