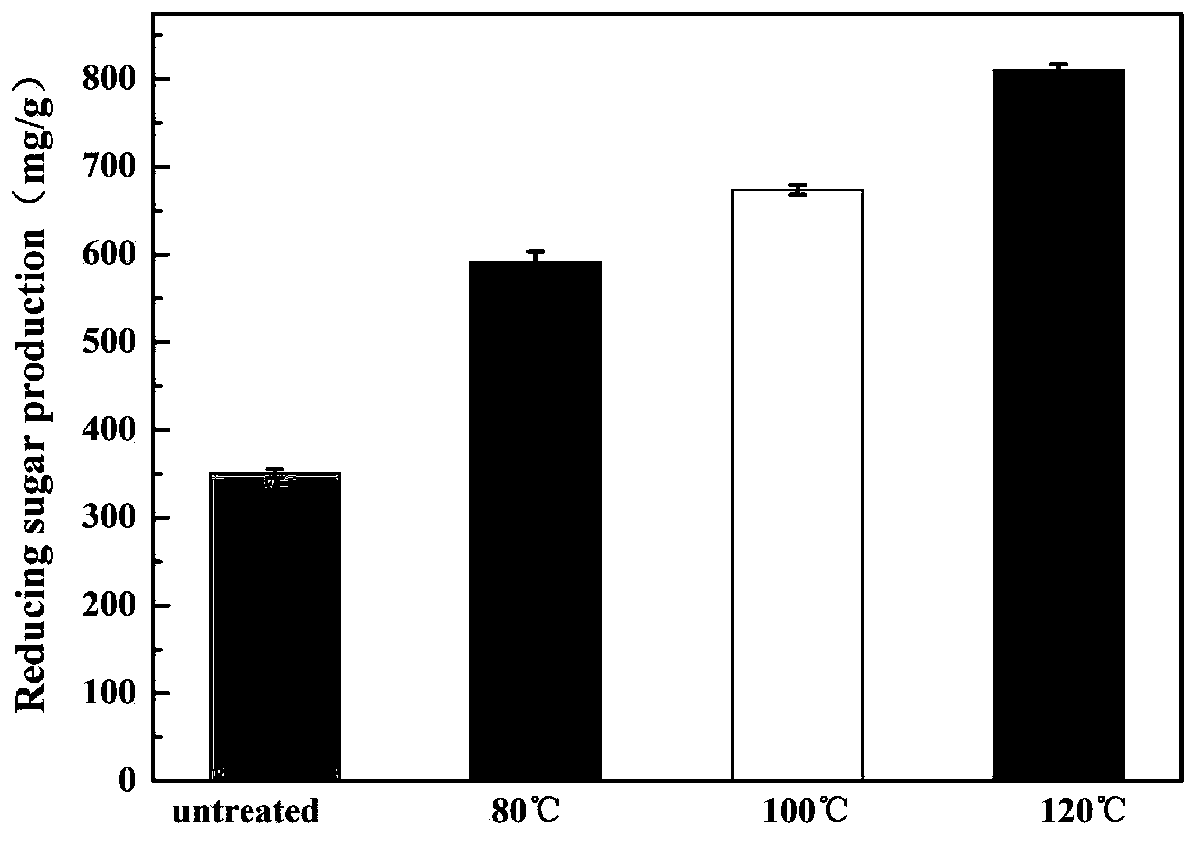
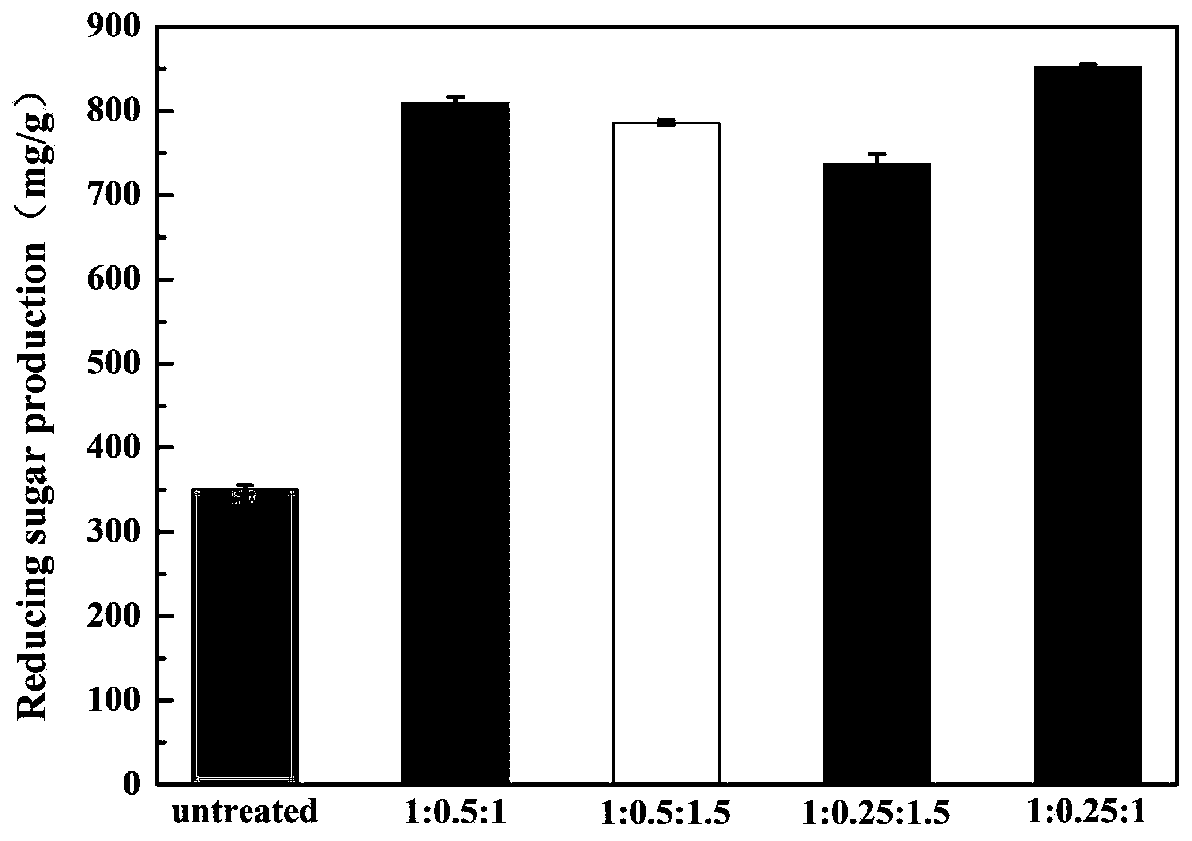
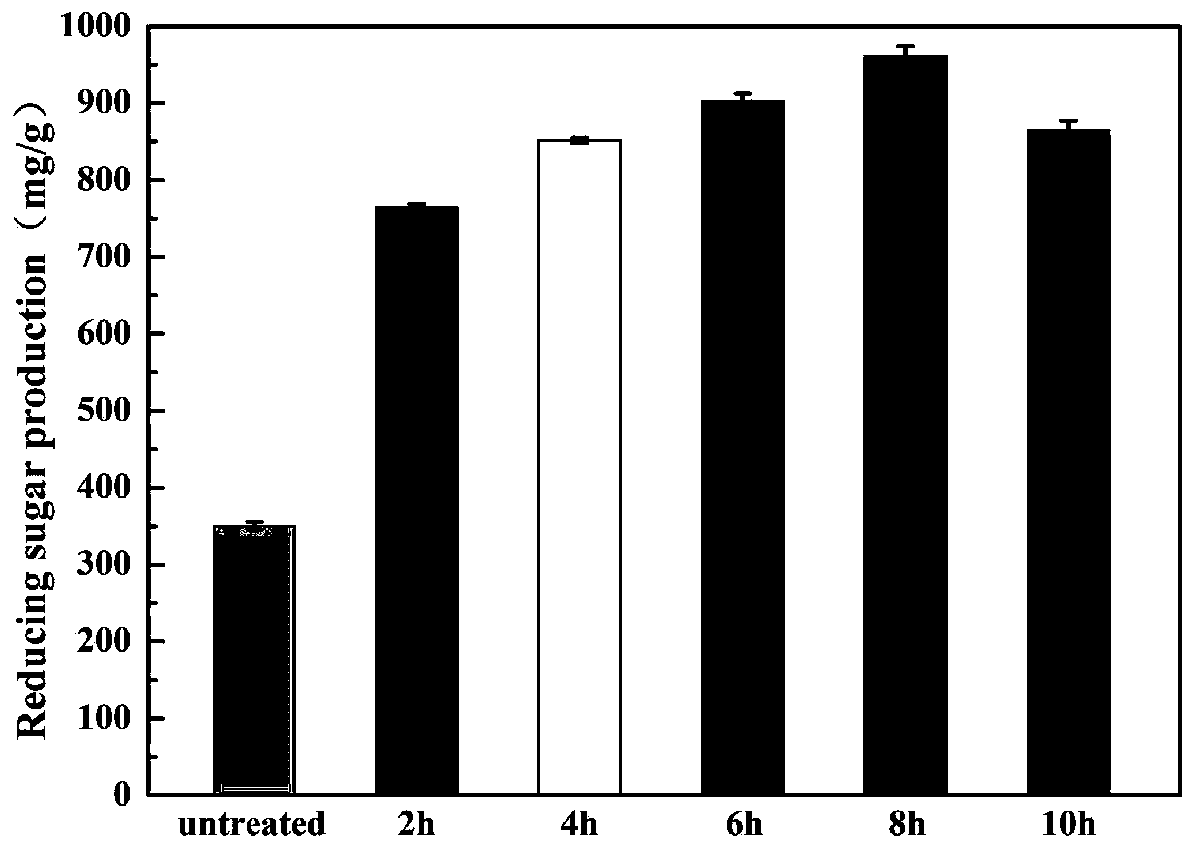
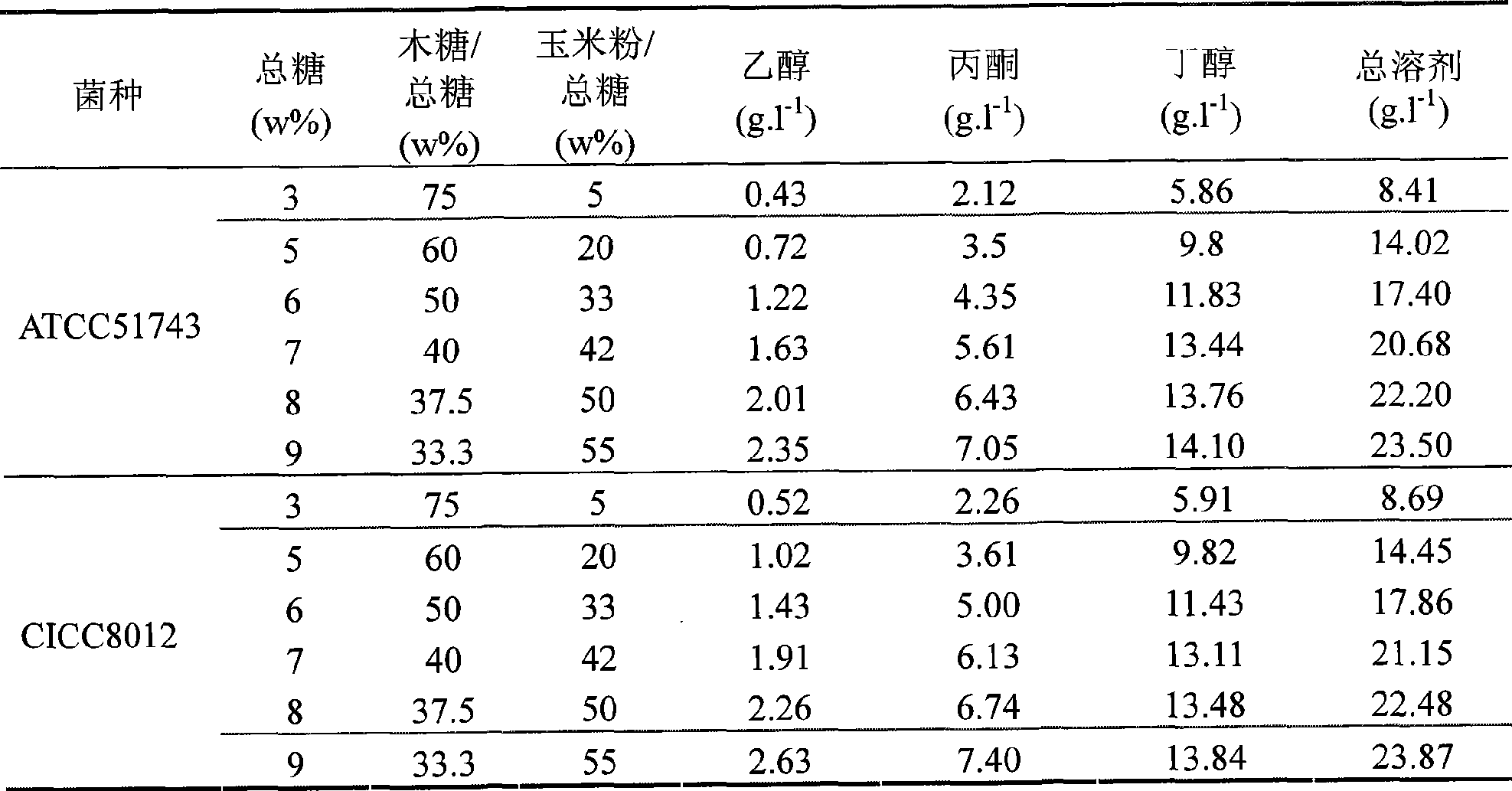
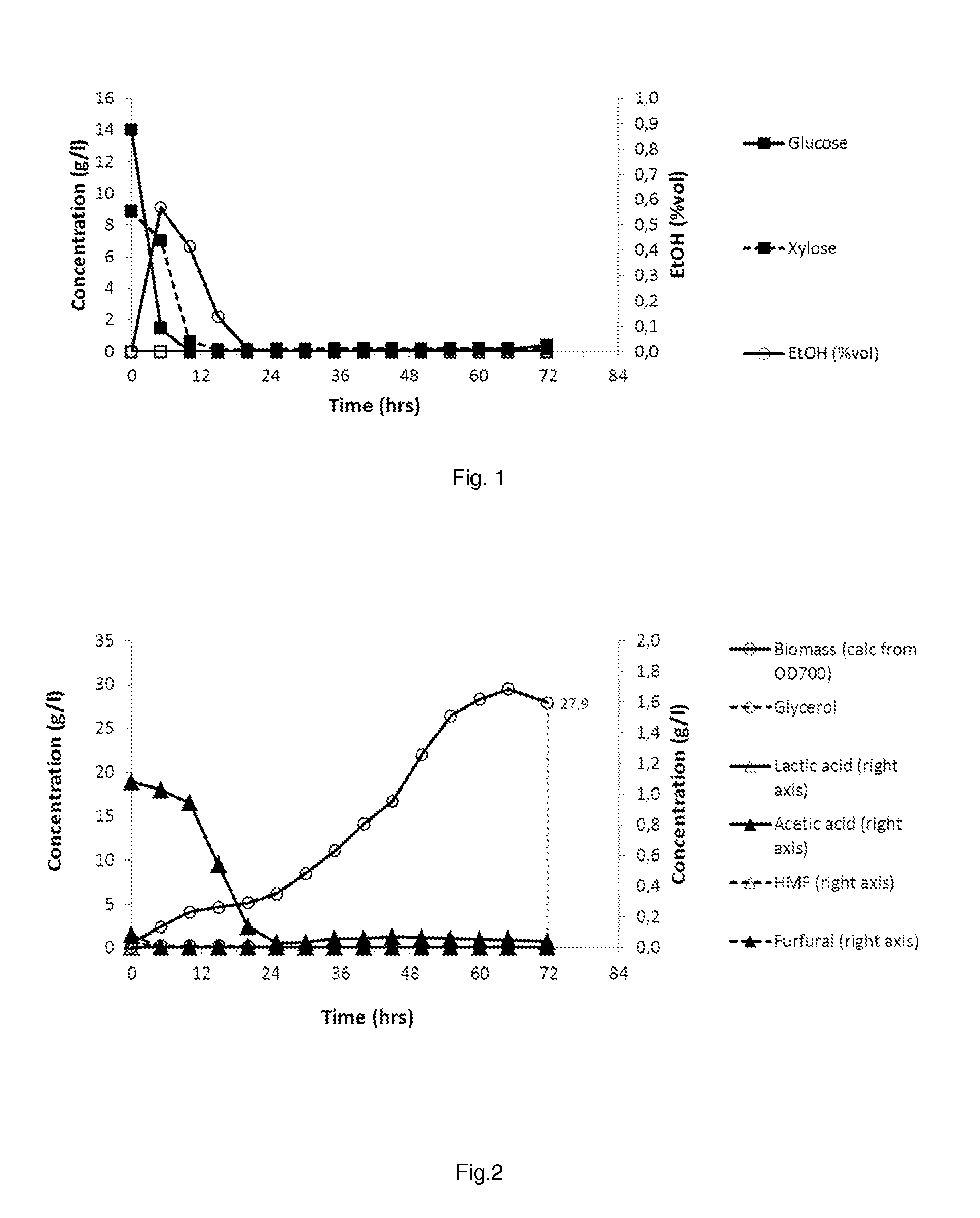
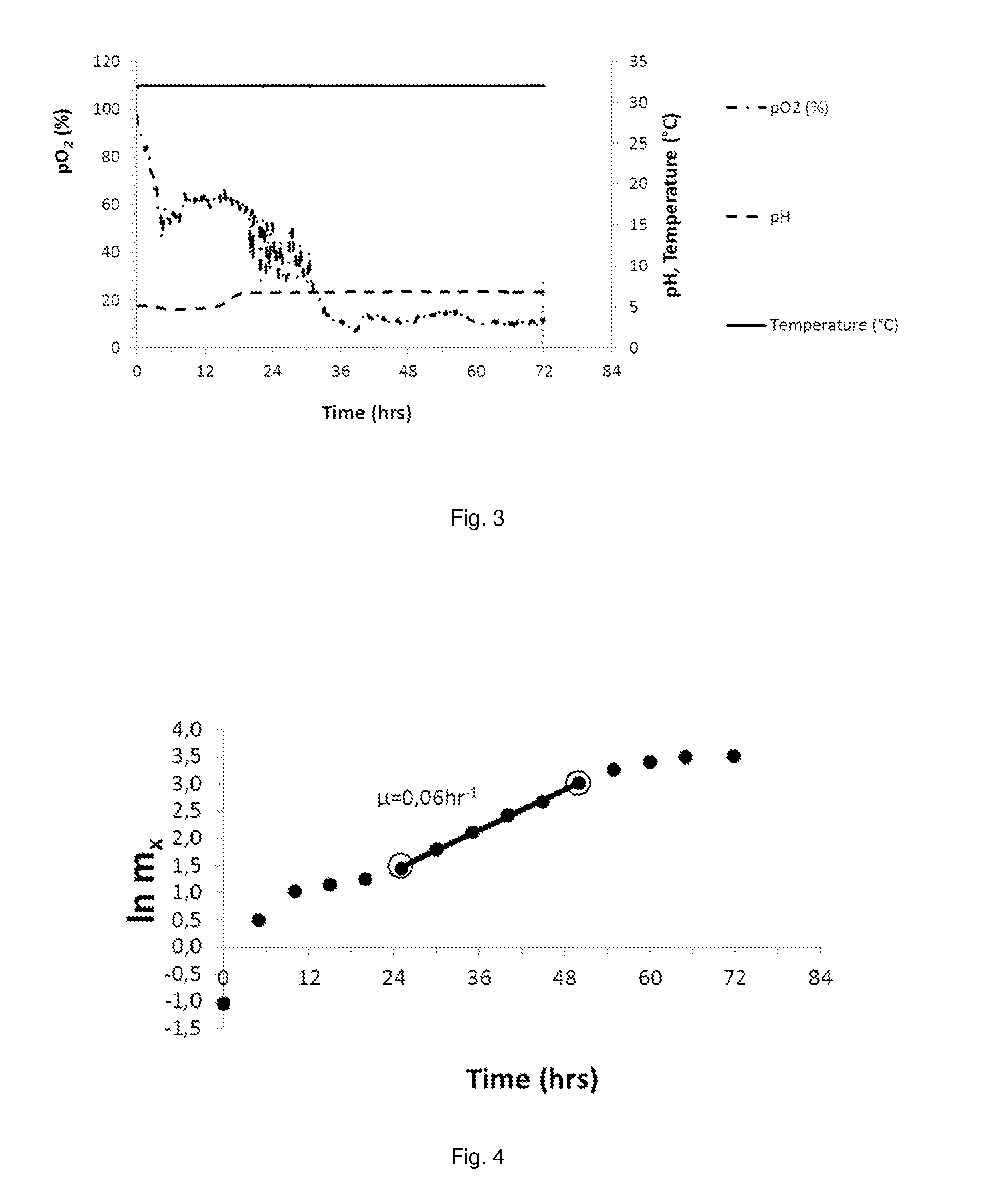
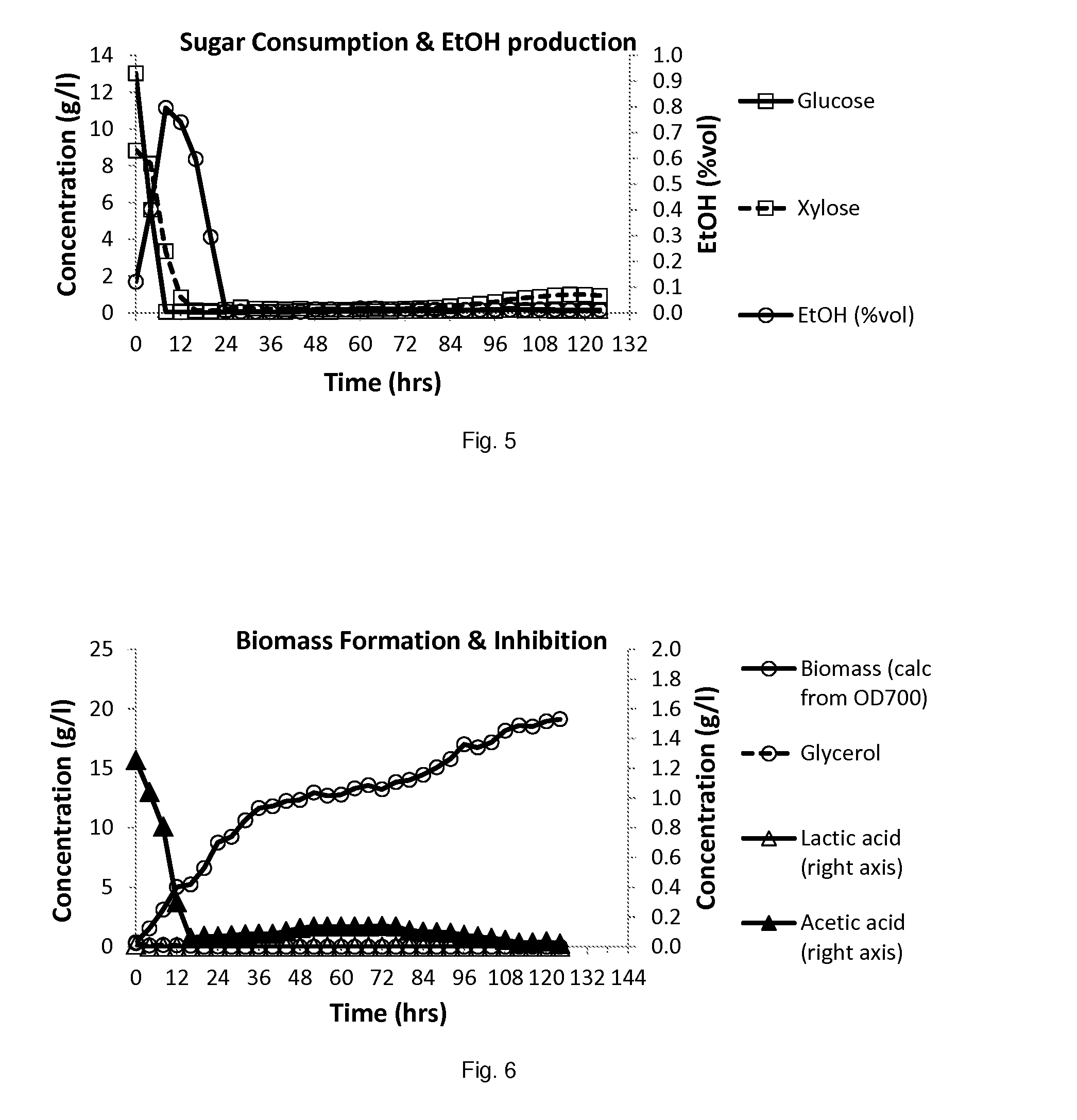
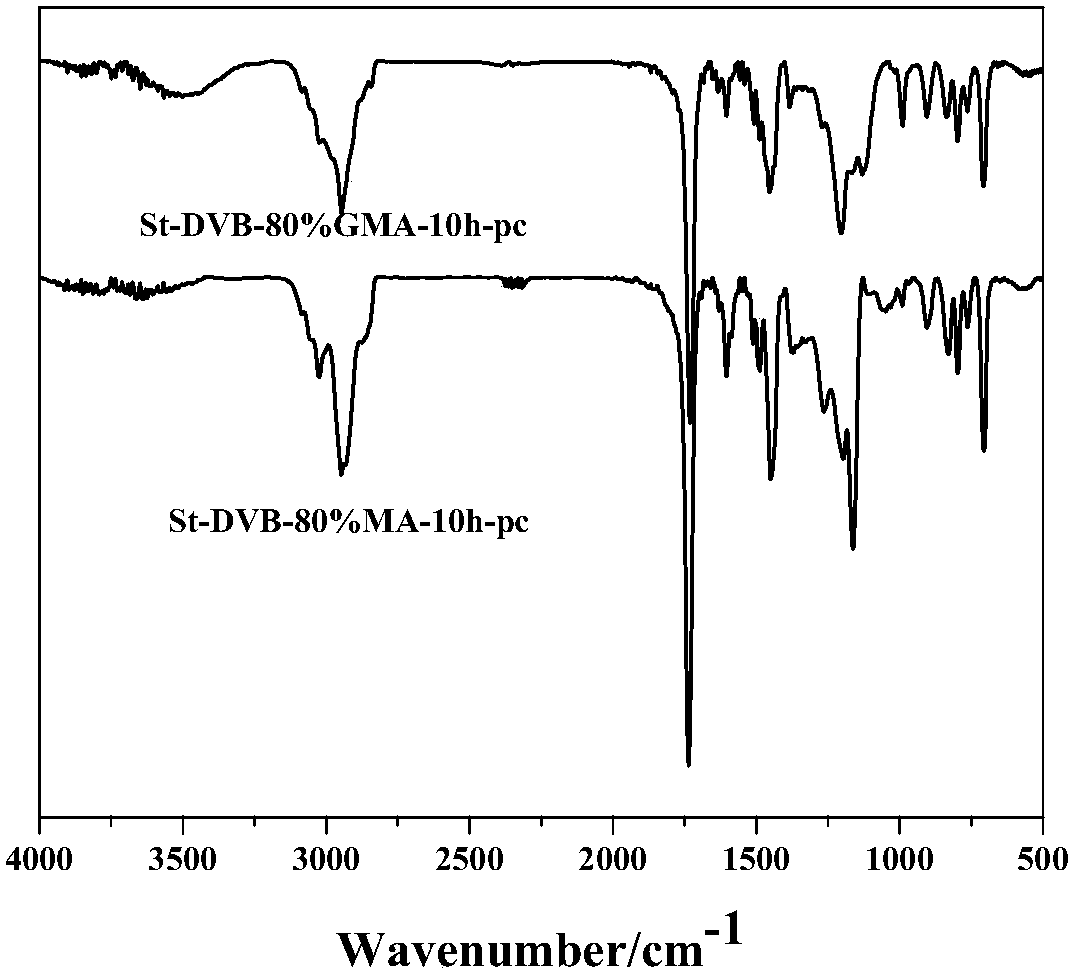
Patents
Literature
164 results about "Lignocellulose hydrolysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
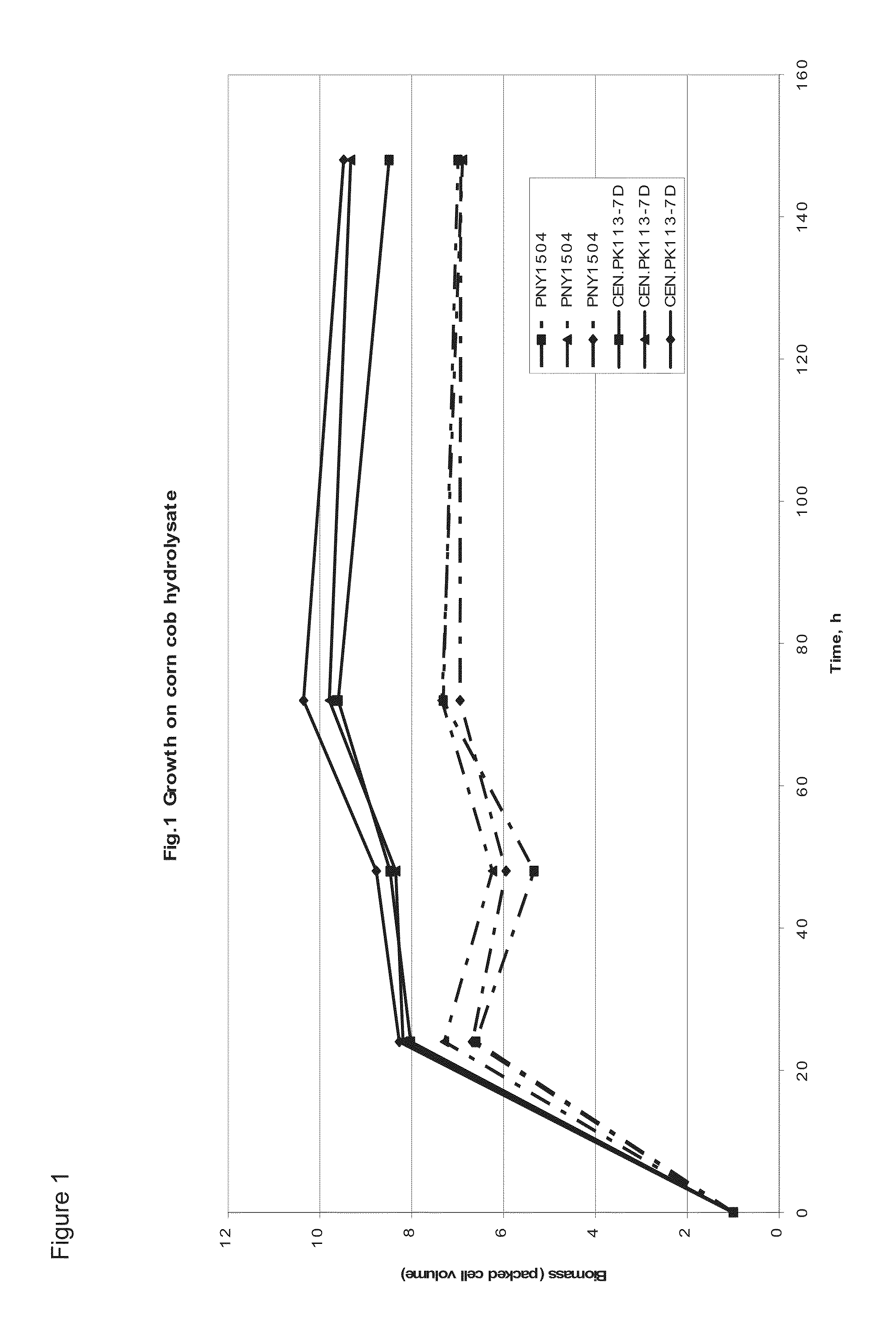
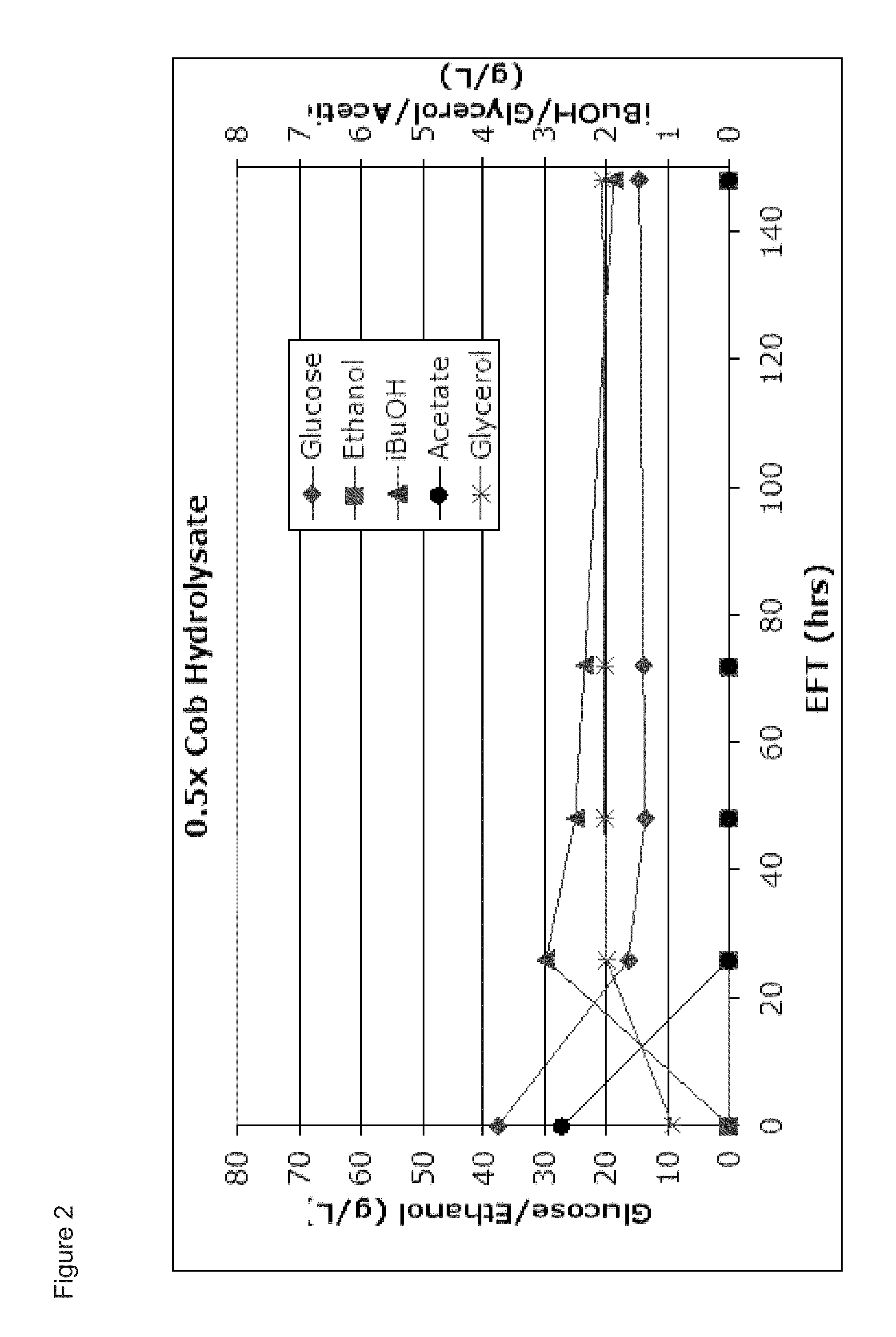
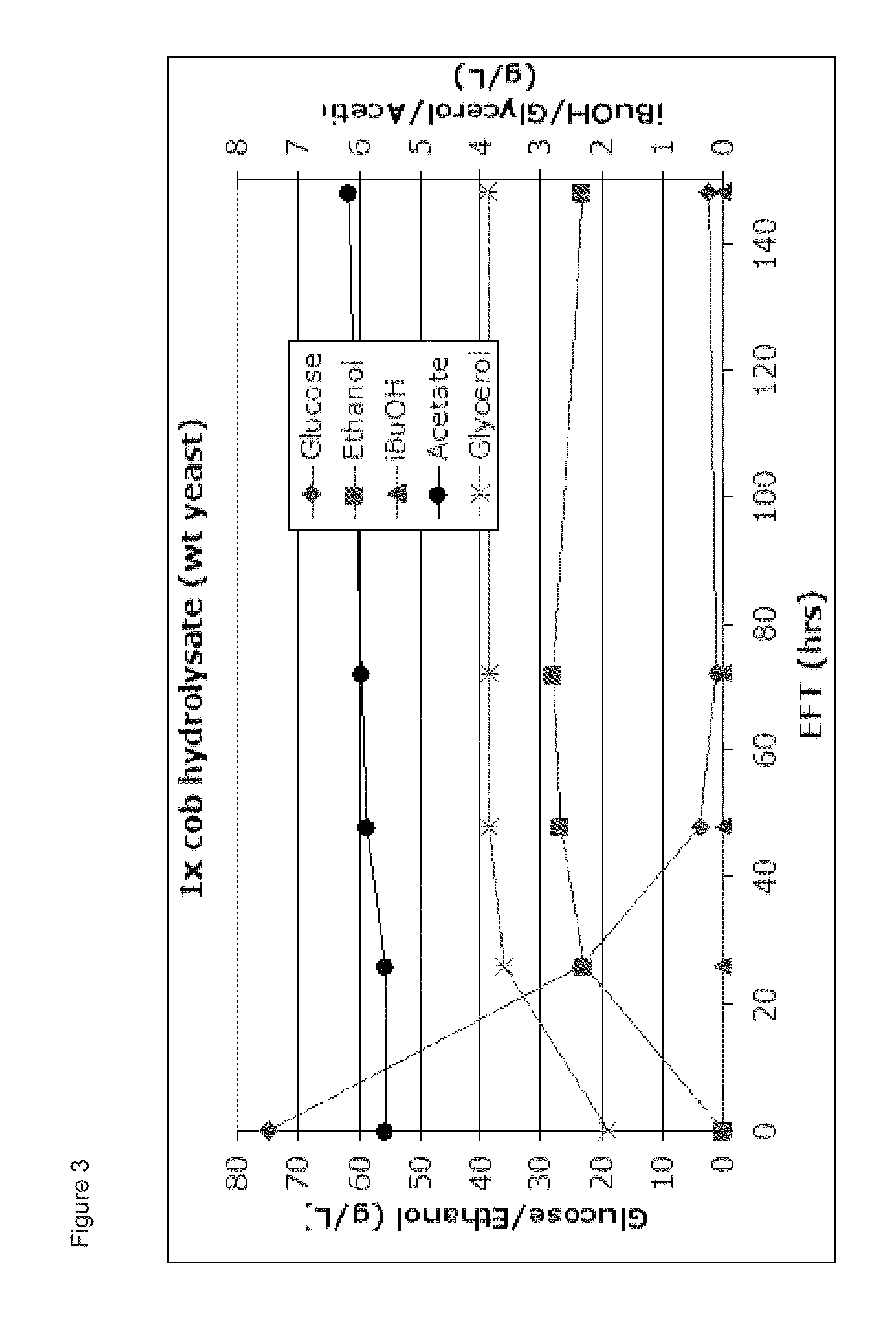
Lignocellulosic hydrolysates as feedstocks for isobutanol fermentation
InactiveUS20130035515A1Improved production of butanolOrganic compound preparationBiofuelsCelluloseIsobutanol
The invention relates generally to the field of industrial microbiology and butanol production from sources of 5-carbon sugars such as lignocellulosic hydrolysates. More specifically, the invention relates to the use of an xylulose or xylulose-5-phosphate-producing enzyme and micro-aerobic or anaerobic conditions to increase butanol production from such sugars and recovery of said butanol through ins situ product recovery methods.
Owner:BUTAMAXTM ADVANCED BIOFUELS
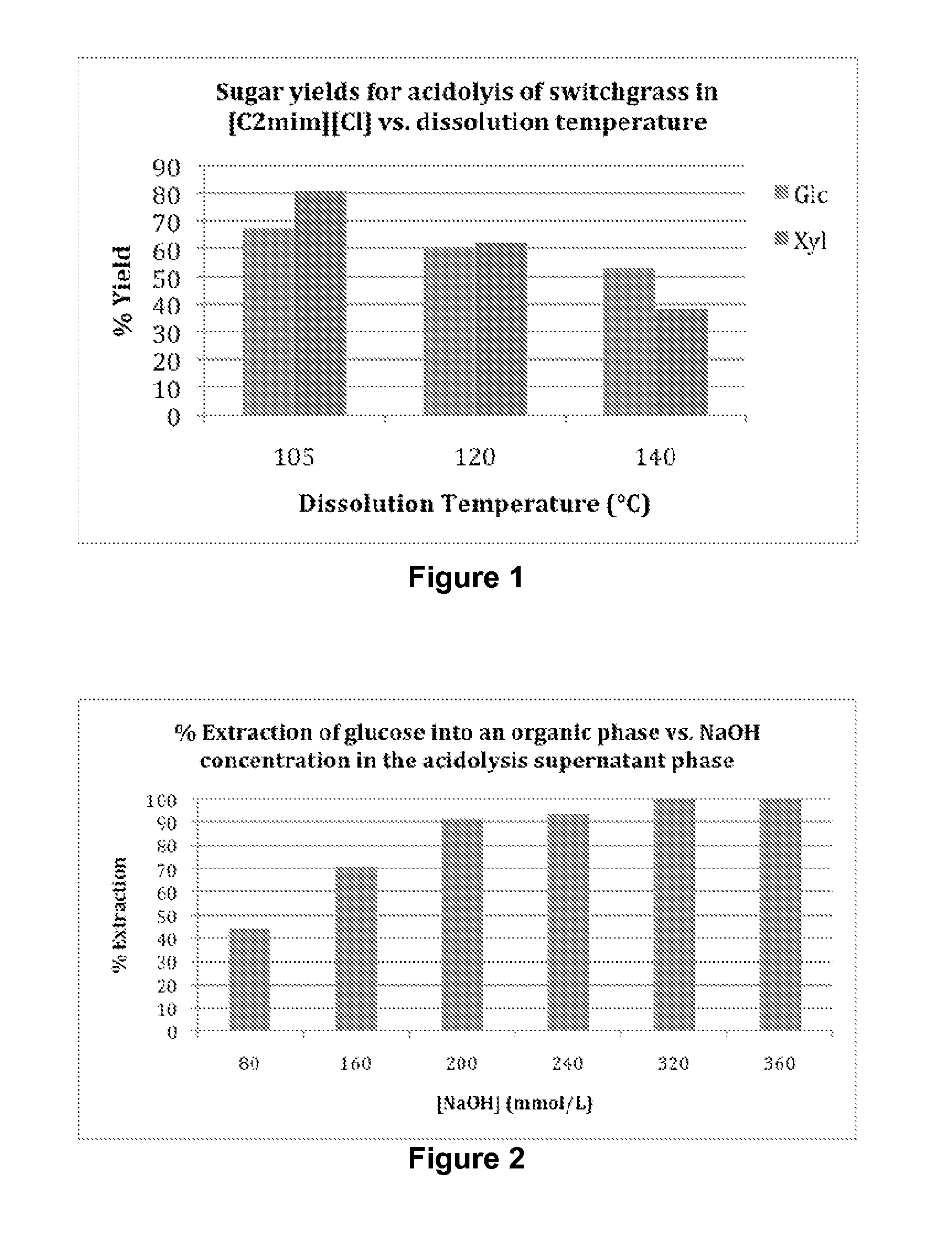
Novel method of acid hydrolysis of biomass and the recovery of sugars thereof by solvent extraction
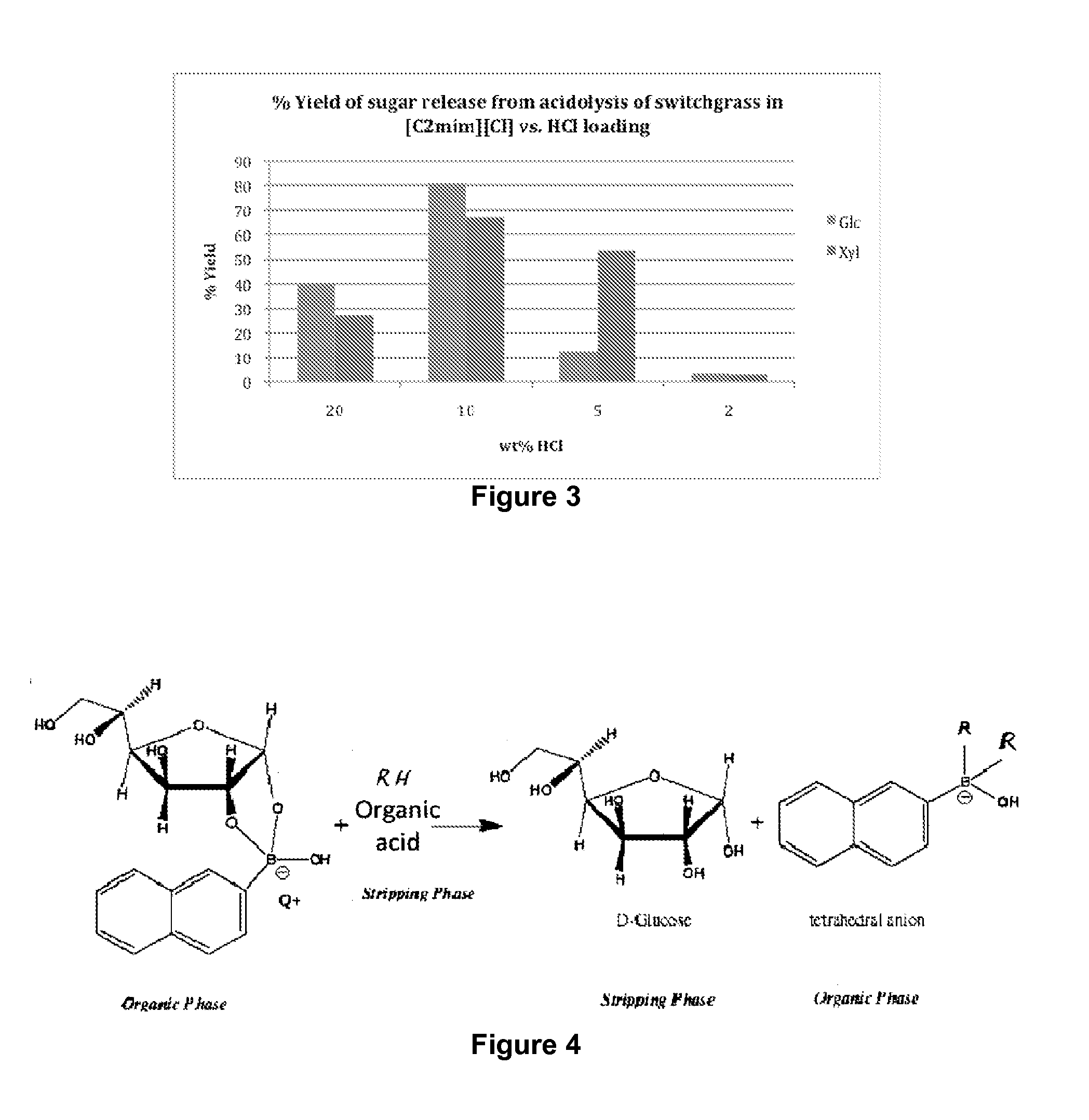
InactiveUS20120301948A1Minimize formationSugar derivativesOther chemical processesOrganic acidAcid hydrolysis
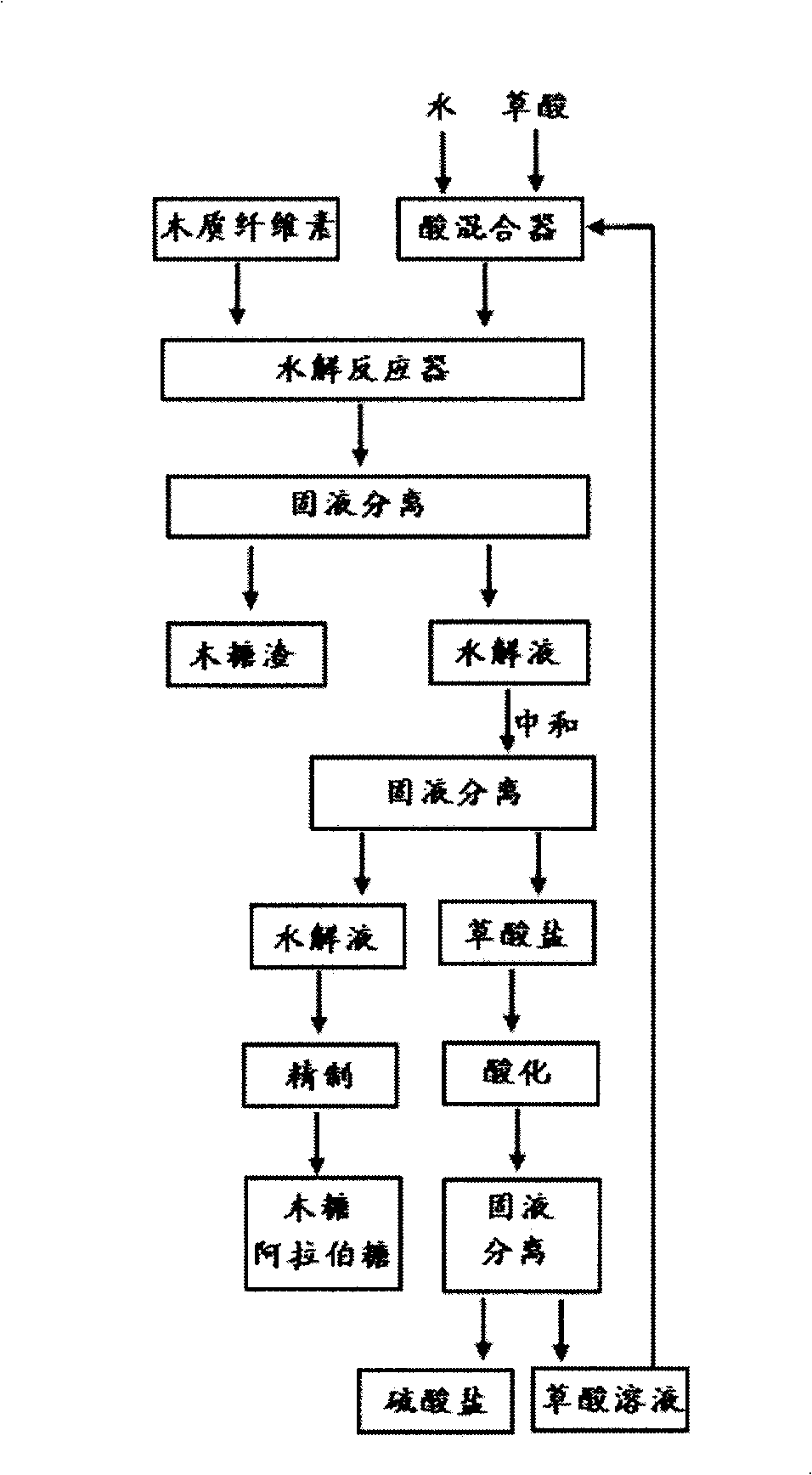
The present invention provides for a method of hydrolyzing a cellulose, hemicellulose, or ligno-cellulose comprising: (a) contacting (i) an ionic liquid (IL) or ionic liquid-aqueous (ILA) phase comprising cellulose, hemicellulose, or ligno-cellulose, or a mixture thereof, and (ii) an acid, such that the cellulose, hemicellulose, or ligno-cellulose is hydrolyzed into sugar, and (b) optionally adding water to the IL or ILA phase wherein the proportion of water in the IL or ILA phase does not exceed about 60% by weight. The present invention also provides for a method of recovering a sugar comprising contacting an IL or ILA phase and an organic phase comprising an organic acid.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Method for preparing xylose and arabinose by hydrolyzing lignocellulose
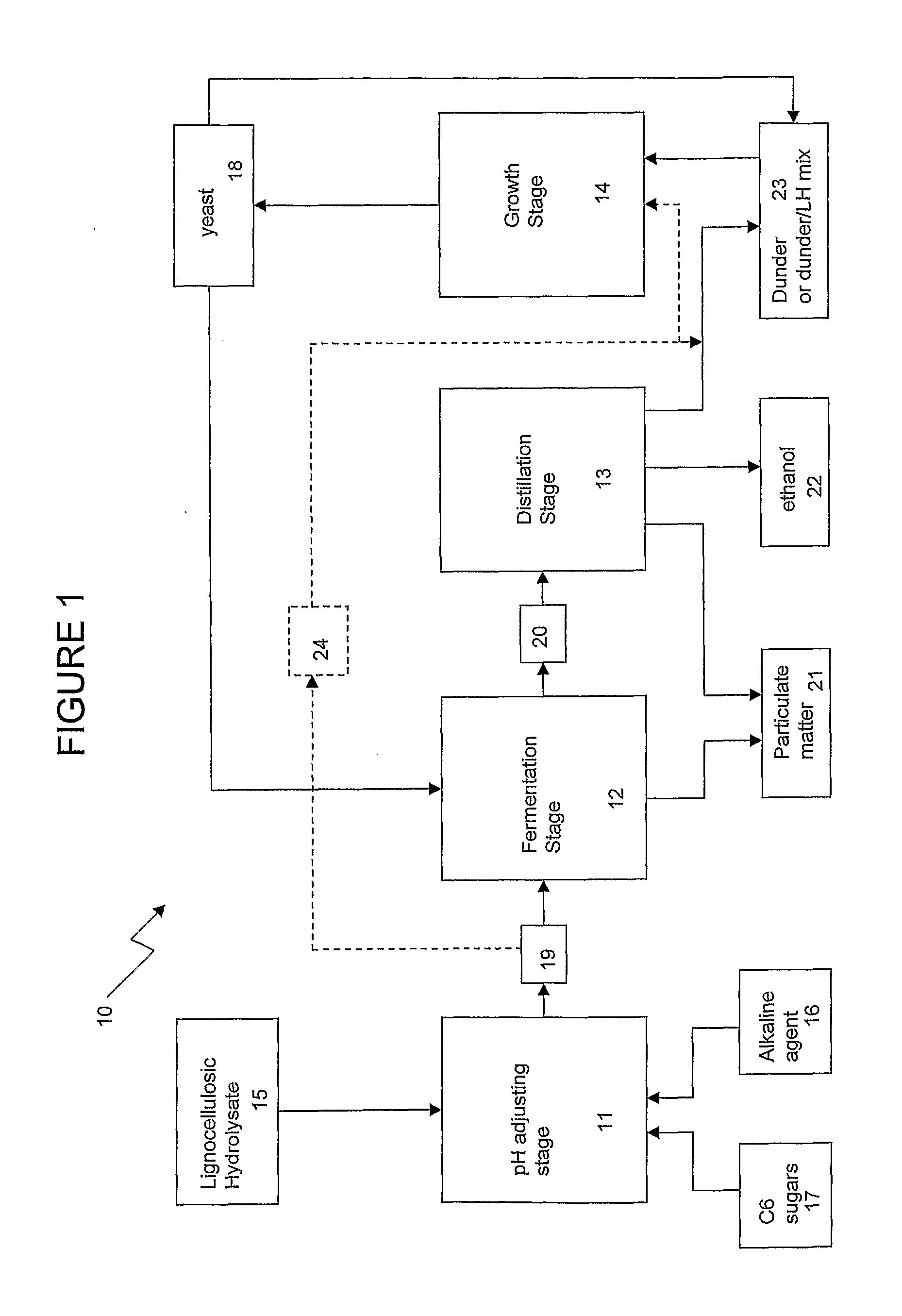
InactiveCN101525355ALess side effectsLess corrosiveSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationHydrolysateBio engineering
The invention discloses a method for preparing xylose and arabinose by hydrolyzing lignocelluloses in the technical field of biological engineering. In the method, aqueous oxalate solution is used for carrying out catalytic hydrolysis on crushed lignocelluloses; lignocelluloses hydrolysate solution and xylose resides are obtained by solid-liquid separation after the reaction; the hydrolysate solution is neutralized to obtain oxalate sediment and obtain solid oxalate by solid-liquid separation again; the oxalate reacts with sulfate in an acidizing tank for regeneration to obtain the aqueous oxalate solution; the oxalate solution is used repeatedly to catalyze next batch of lignocelluloses raw material. The invention uses oxalic acid as organic acid catalyst and has the advantages of high conversion rate, strong selectivity, less side reaction, being capable of recycling, and the like, the oxalic acid can replace regular inorganic acid catalyst, and the invention solves the problem thatthe traditional technology has equipment erosion, evaporating equipment scaling, serious pollution and the like and can be used for hydrolyzing the hemicellulose in lignocelluloses raw material and used for preparing the xylose and the arabinose.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method of producing yeast biomass
InactiveUS20110183394A1Reduces biological oxygen demandReducing chemical and biological oxygen demandFungiBiofuelsCelluloseYeast biomass
The invention relates to use of a substrate comprising C5 compound-containing material, in the growth of Saccharomyces yeast or the production of a product of Saccharomyces yeast, wherein the C5 compound-containing material is: (a) C5 compound-containing material obtained from lignocellulosic hydrolysate; (b) C5 compound-containing material obtained from fermentation of lignocellulosic hydrolysate; or (c) a mixture of (a) and (b). The invention also relates to a method of producing Saccharomyces yeast biomass or a product of Saccharomyces yeast using the substrate, and to methods of producing ethanol comprising incubating Saccharomyces yeast produced by the use or method. The invention further relates to strains of Saccharomyces yeast suitable for the use or methods.
Owner:MICROBIOGEN PTY LTD
Method for producing amber acid by continuous fermentation or semi-continuous fermentation
InactiveCN101302546AIncrease production intensityLess investmentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBatch fermentationSweet sorghum
The invention discloses a method for producing butane diacid through continuous fermentation or semi-continuous fermentation, which belongs to the bioengineering technical field. The invention provides application of Actinobacillus succinogenes in the method for continuously or semi-continuously preparing the butane diacid by utilizing carbohydrate raw materials such as cane molasses, corn starch syrup, Jerusalem artichoke hydrolysis syrup, sweet sorghum straw syrup, and lignocellulose hydrolysis syrup and so on. The method utilizes multi-step continuous fermentation or two-step semi-continuous fermentation, which can improve germ concentration and cell activity and can obtain high butane diacid output and high butane diacid production intensity; the method is easy to realize automatic and continuous operation; compared with batch fermentation, the method can save non-fermentation time such as repeated tank cleaning, sterilization and so on, so the production efficiency can be greatly improved; the semi-continuous fermentation for producing the butane diacid is easier to control fermentation parameters than the continuous fermentation, has high sugar utilization rate, target product yield and target product output, has simple and easy equipment and operation, and is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Magnetic carbon-based solid acid catalyst with core-shell structure and preparation method of magnetic carbon-based solid acid catalyst, as well as application in lignocelluloses saccharification process
ActiveCN106215951AAvoid Oversized SituationsSimple operation processOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsXylose productionCelluloseDepolymerization
The invention relates to a preparation method of a magnetic carbon-based solid acid catalyst with a core-shell structure. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing magnetic particles Fe3O4 by a coprecipitation method, adding a buffer agent and an anionic surfactant into the magnetic particles Fe3O4, modifying the size and the surface characteristic of the magnetic particles Fe3O4 to obtain magnetic powder Fe3O4, then grinding and mixing the magnetic powder Fe3O4 and a biobased material, and performing carbonization at the temperature of 350 to 550 DEG C under an N2 protection atmosphere for 2 to 6 h; grinding and pulverizing a carbonized mixture, adding a sulfonating agent for sulfonation at the temperature of 60 to 160 DEG C for 5 to 15 h to obtain a mixture, and performing adsorption with an external magnet, washing and drying to obtain the magnetic carbon-based solid acid catalyst with the core-shell structure. The preparation process disclosed by the invention is simple in process; the prepared catalyst is high in magnetism, high in activity, easy to recycle, high in stability and high in reusability, and is high in catalysis activity in the reaction of preparing fermentable sugars by catalyzing the depolymerization of a lignocelluloses biomass raw material.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
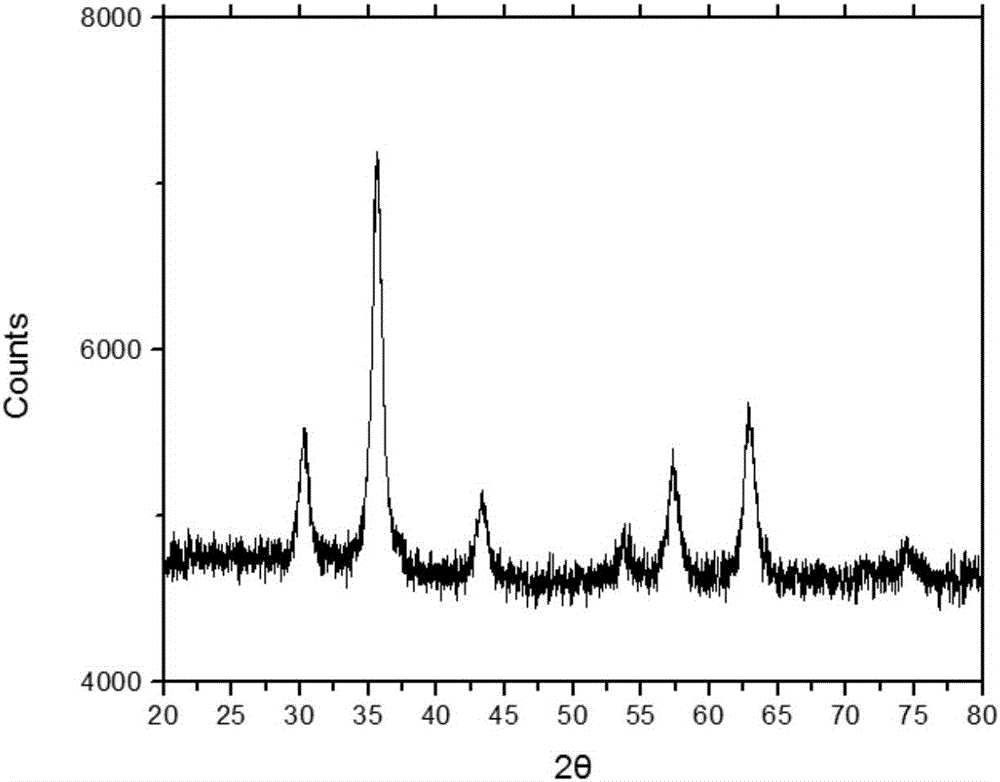
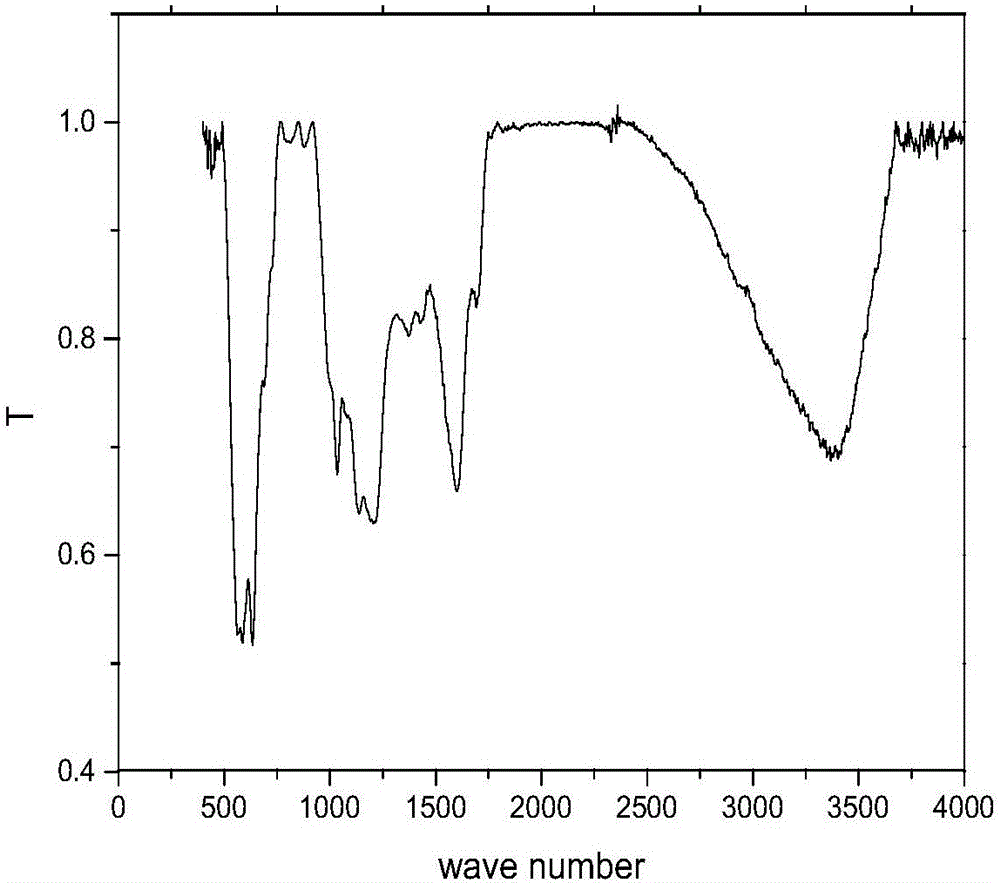
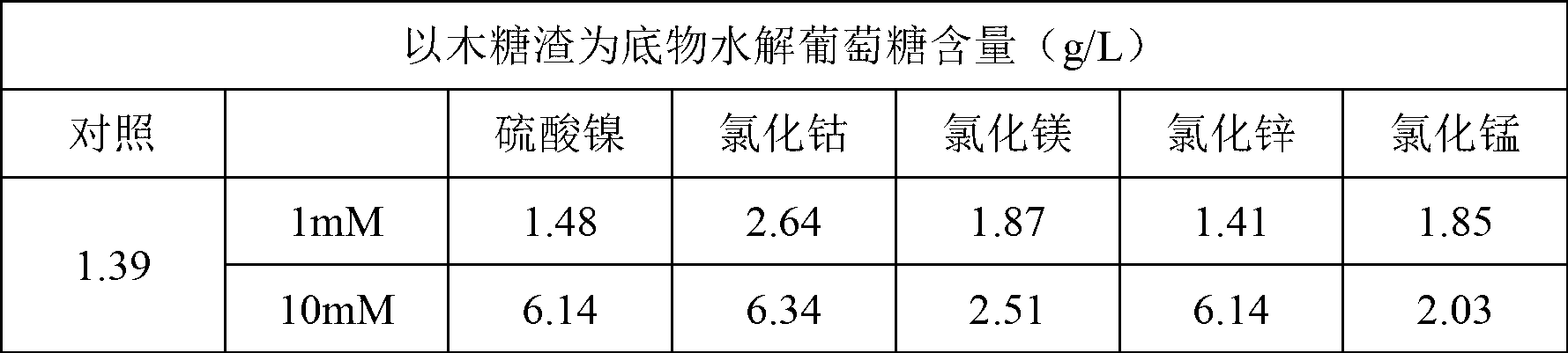
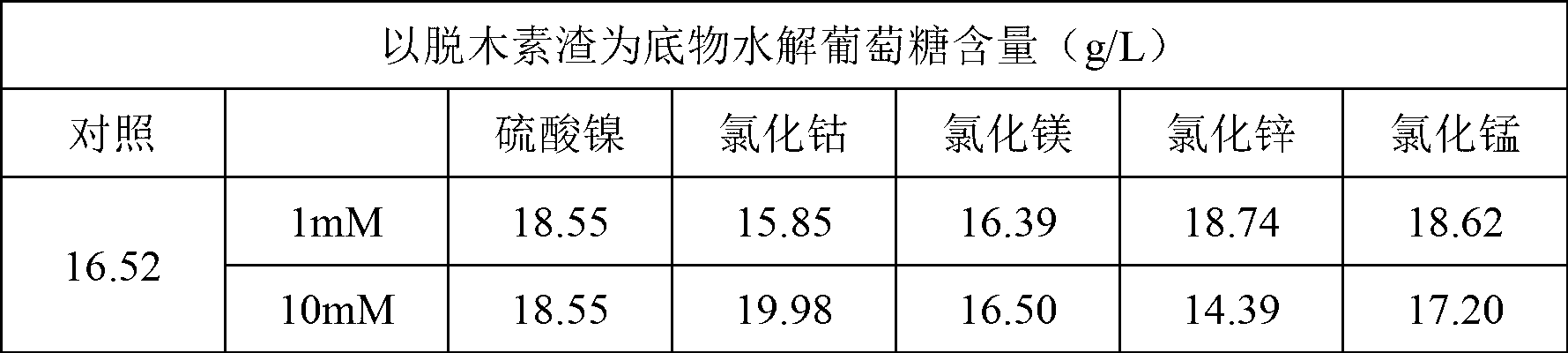
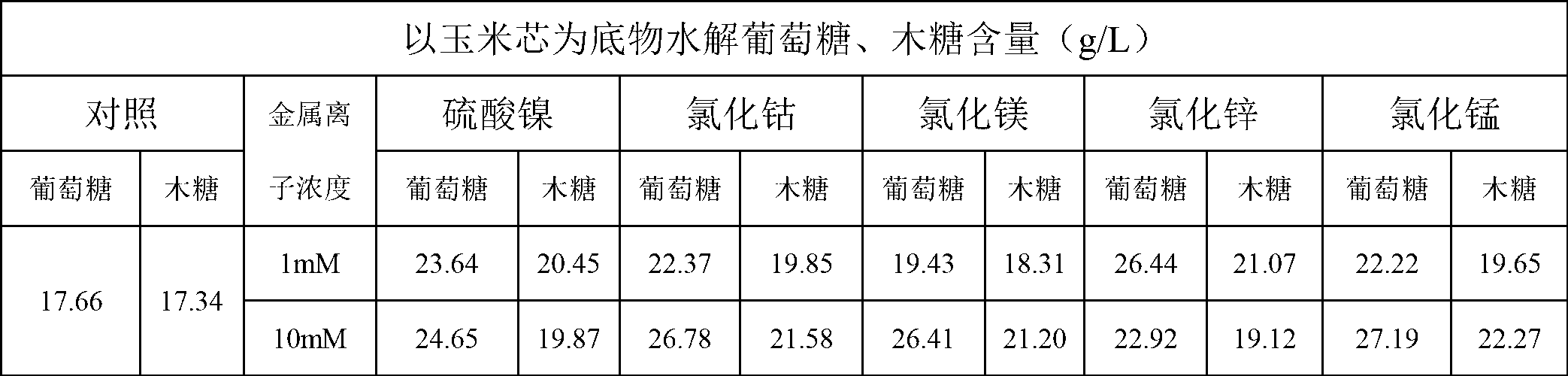
Method for promoting hydrolysis of lignocellulose
The invention discloses a method for promoting hydrolysis of lignocelluloses. According to the method, metal ions such as nickel, cobalt, magnesium, zinc, manganese and the like are added in the processes of saccharifying and hydrolyzing the lignocelluloses so as to improve the enzyme activity of the ligno-cellulase and hemicellulase, thereby further improving the hydrolysis efficiency of the ligno-cellulase. Proved by experiments, the hydrolysis efficiency of glucan can be improved by 4.5 times by adding the metal ions. According to the method, the operation is simple, the metal ions can be recycled, the investment cost is low, the usage range is wide, the pollution does not exist, the hydrolysis efficiency of the cellulose is obviously improved, and the method can be widely applied in the process of hydrolyzing the lignocelluloses and in the fields of manufacturing and developing biomass energy.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +1
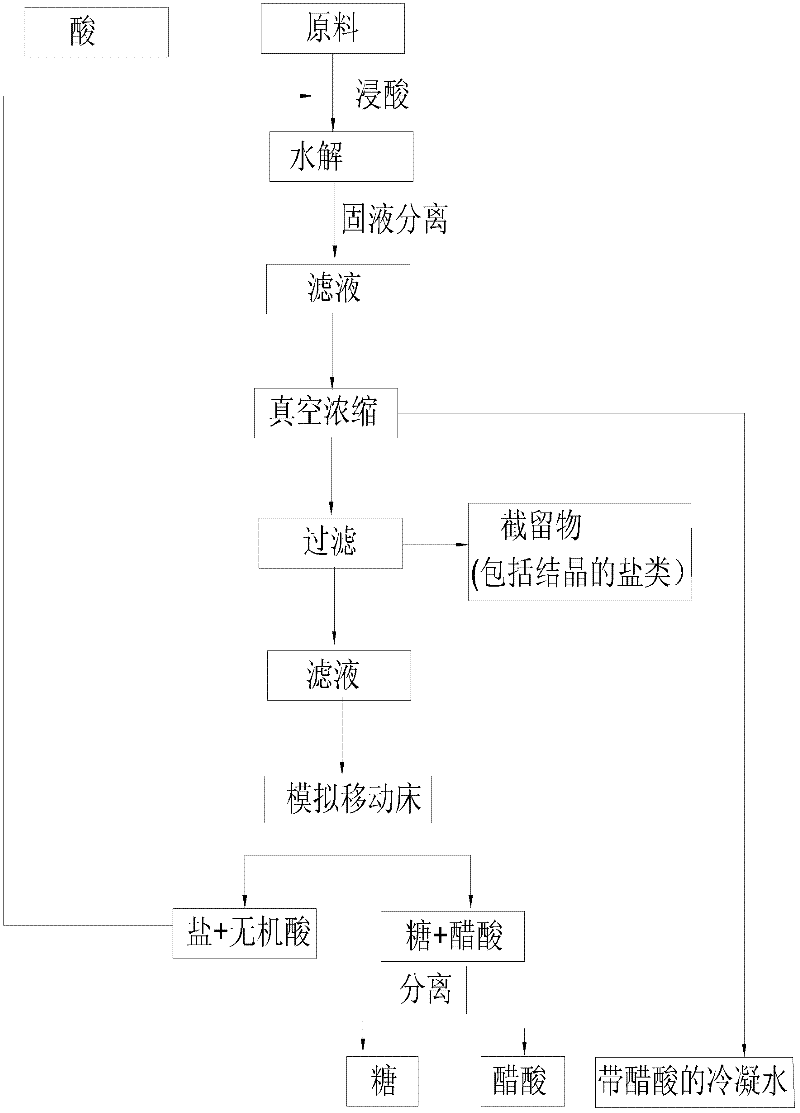
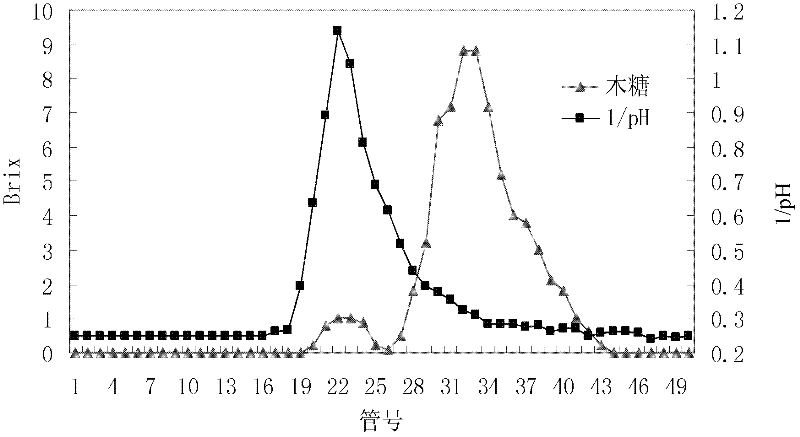
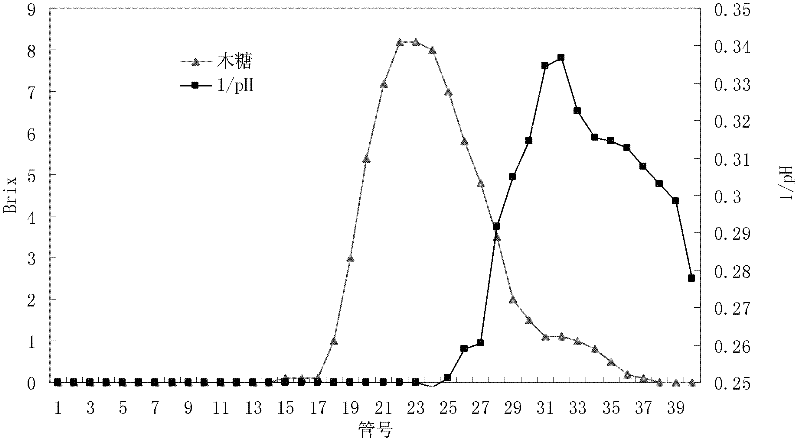
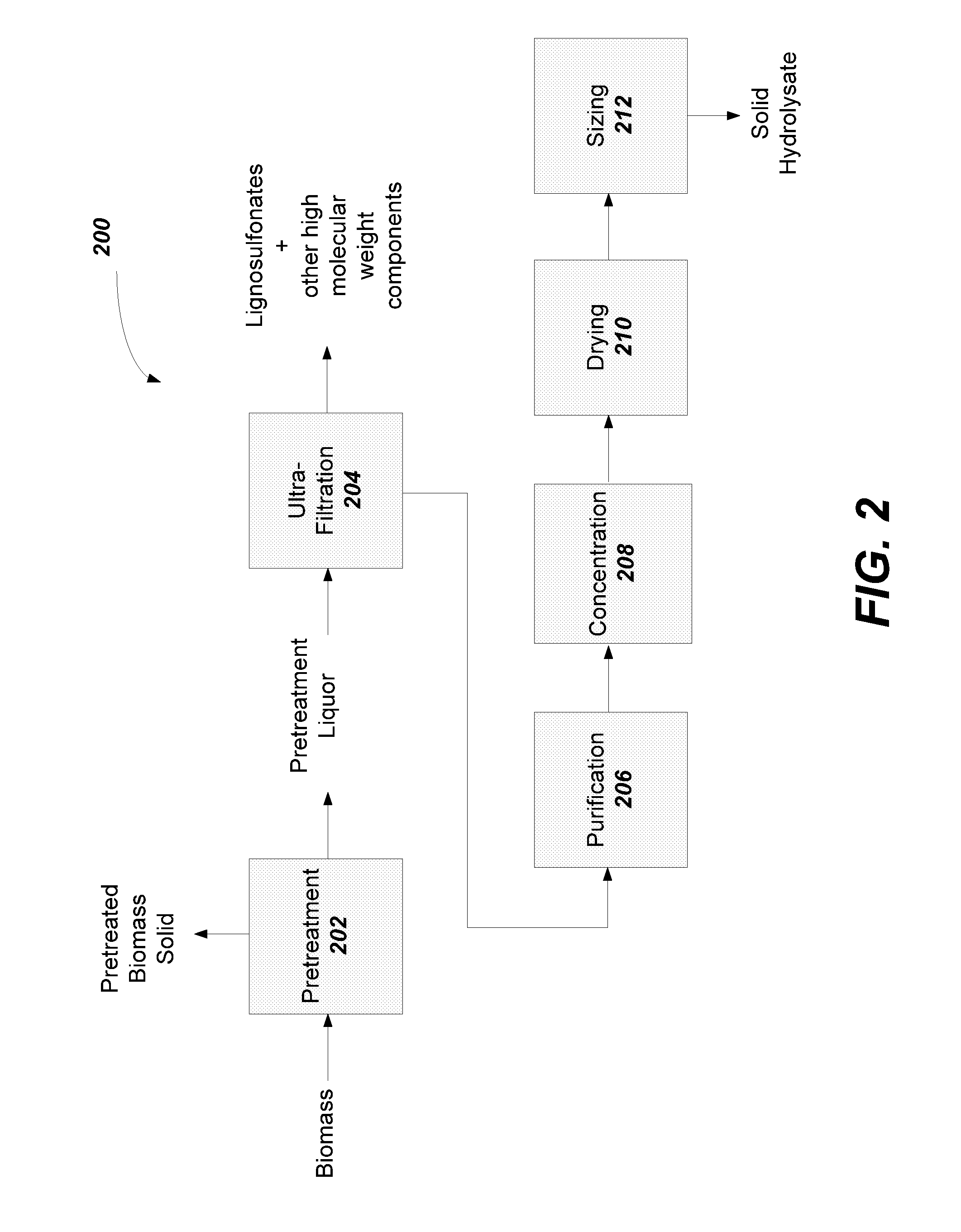
Method for separating sugar, acid and salt of lignocellulose hydrolysate
ActiveCN102600640AIncrease concentrationReduce fermentation costsSugar derivativesSolid sorbent liquid separationHydrolysateSimulated moving bed
The invention discloses a method for separating sugar, acid and salt of lignocellulose hydrolysate. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) utilizing inorganic acid to hydrolyze a hemicellulose part of a lignocellulose raw material, and performing solid-liquid separation, thereby obtaining the lignocellulose hydrolysate; (2) performing vacuum concentration on the lignocellulose hydrolysate, filtering and clearing a concentrate, re-crystallizing filtered remains so as to recycle potassium salt, performing sugar-acid-salt separation on the cleared filtrate, taking pure water as a flow phase to perform sugar-acid separation on the concentrated hydrolysate on a simulated moving bed filled with an H-type cation chromatographic column, and cutting by taking inorganic acid and salt as quick components and sugar and acetic acid as slow components during the separating process; (3) purifying and concentrating the quick component, complementing the concentration of acid by using fresh acid liquor for hydrolysis of the next batch of raw material; and (4) separating acetic acid from the slow component, thereby obtaining purified syrup. The method provided by the invention is used for separating the sugar, acid and salt of the lignocellulose hydrolysate.
Owner:谷创芯生物科技(厦门)有限公司
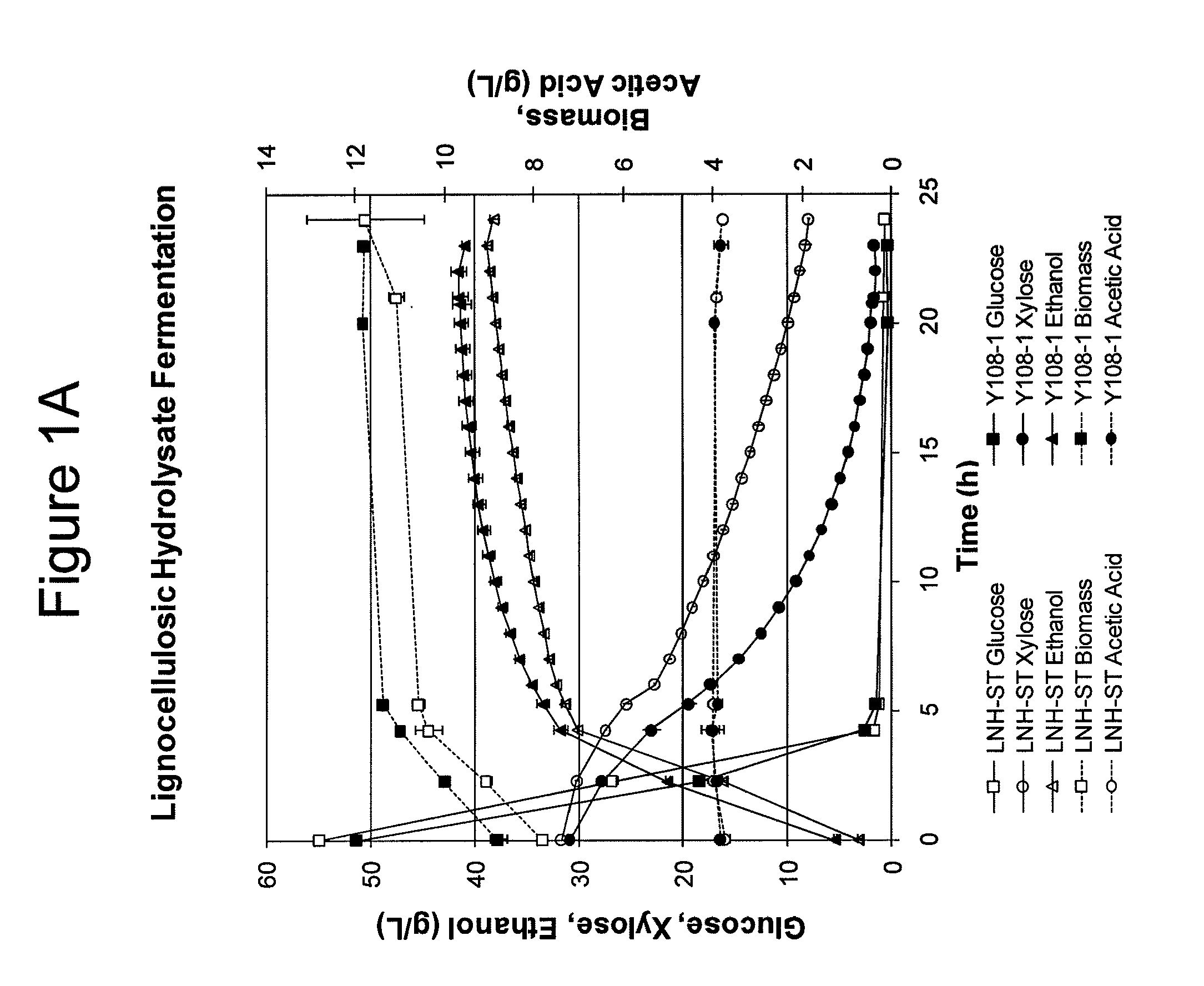
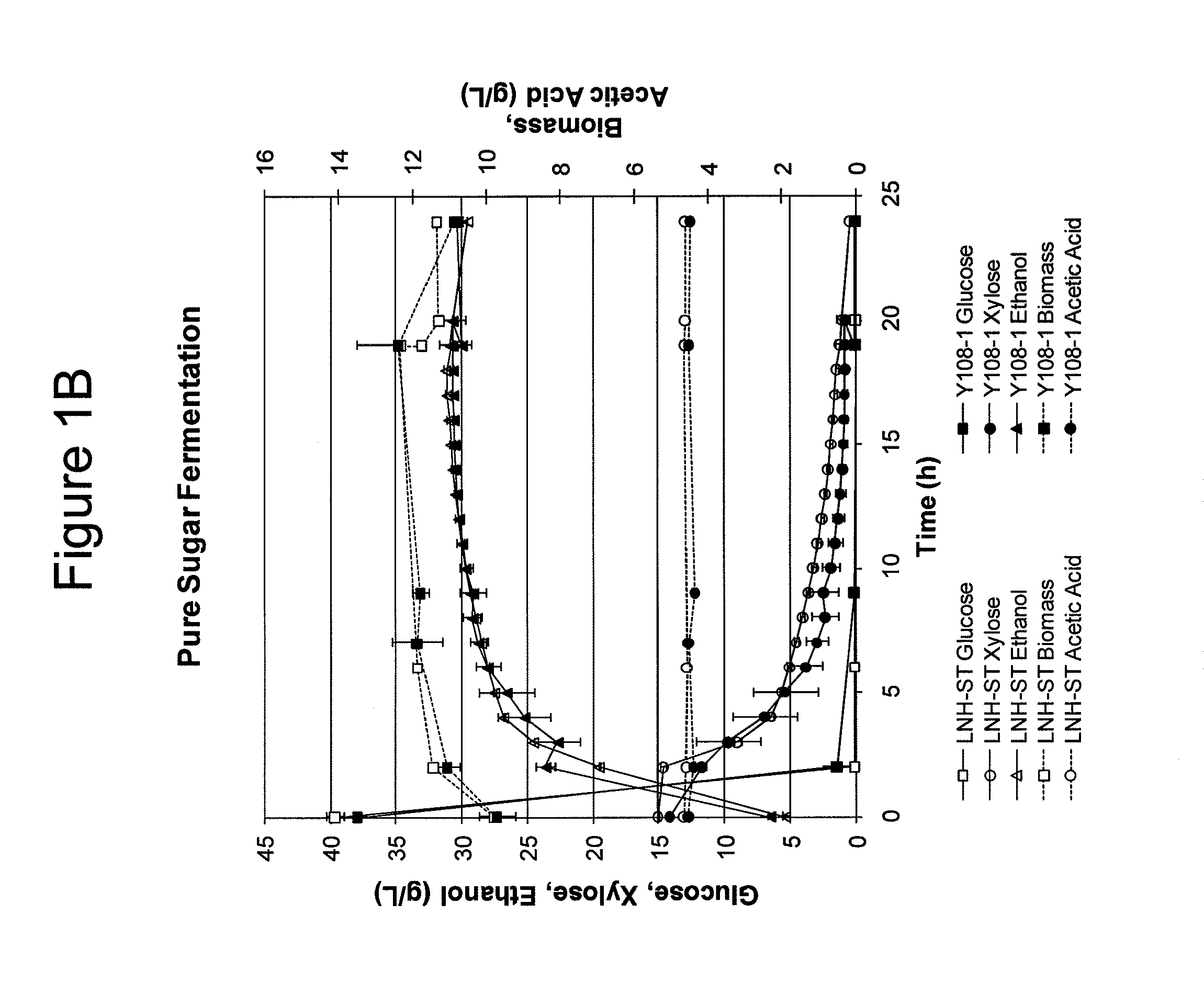
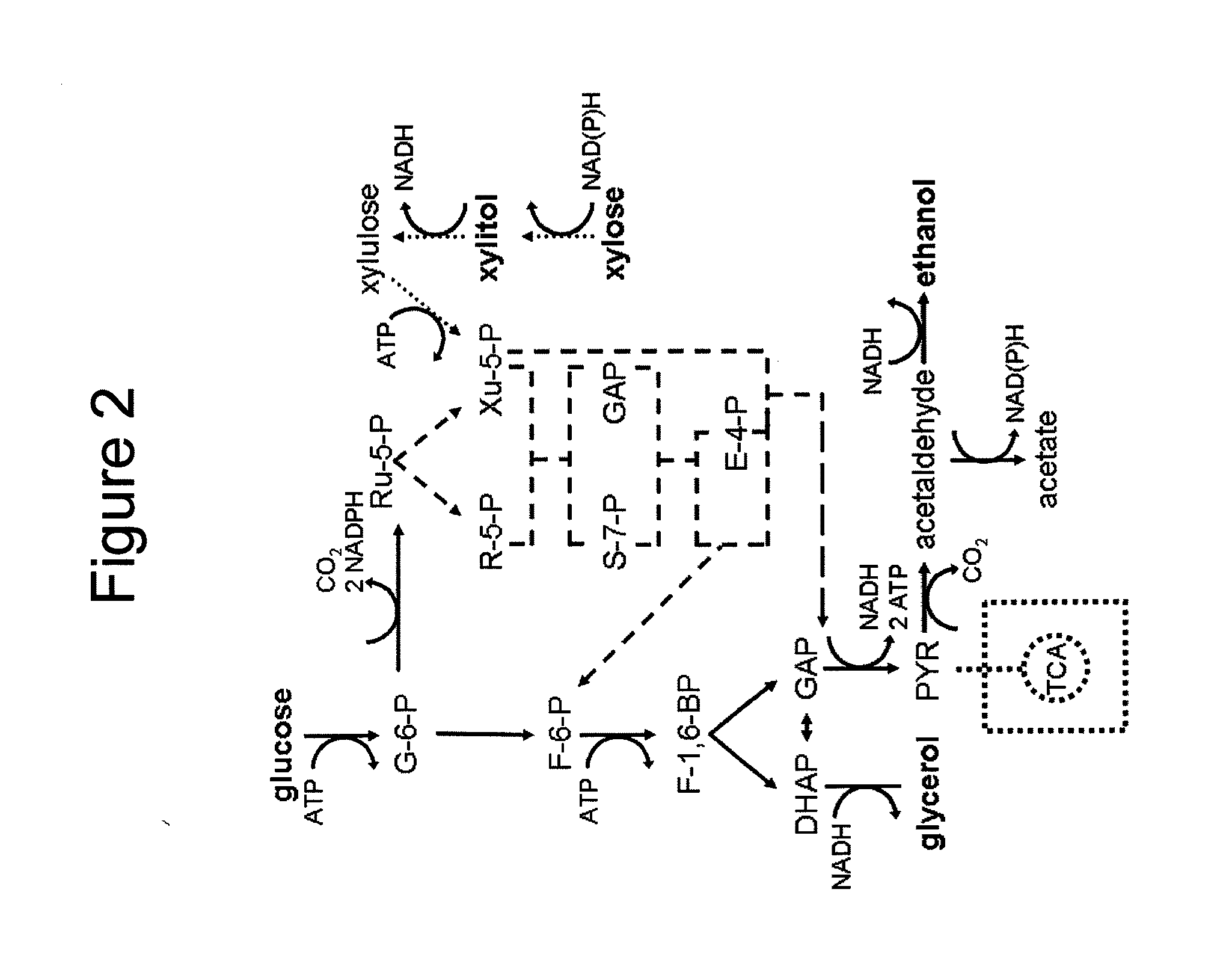
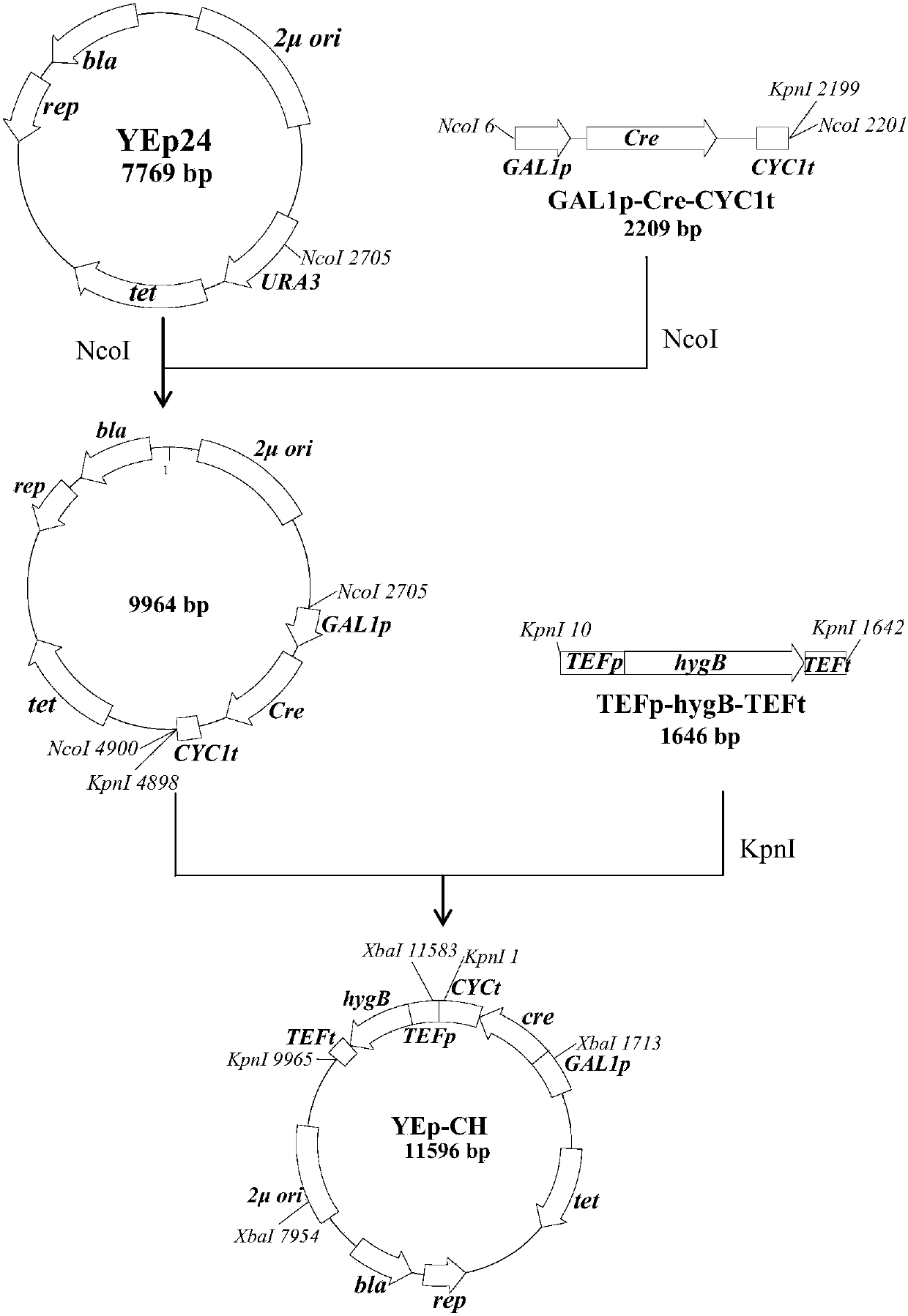
Modified yeast strains exhibiting enhanced fermentation of lignocellulosic hydrolysates
The present invention relates to novel xylose-fermenting yeast strains (for example, yeast of the genus Saccharomyces, e.g., S. cerevisiae) with an enhanced ability to ferment the xylose (and / or another pentose sugar) present in a lignocellulosic hydrolysate to a fermentation product(s) (for example, an alcohol (e.g., ethanol) or a sugar alcohol (e.g., xylitol)).
Owner:IOGEN ENERGY CORP
Fermentable silk spore yeast strains and application for preparing microbial oil thereof
InactiveCN101967452AEfficient accumulationReduce yieldFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses fermentable silk spore yeast strain and a method for preparing microbial oil with lignocellulose hydrolyzate. The method for preparing the yeast strain comprises the following steps of: taking the fermentable silk spore yeast CICC 1368 as the original strains, performing the ultraviolet ray mutagenesis and the composite mutagenesis of the ultraviolet ray and the LiCl, obtaining the high-yield strains by means of fermenting and screening, and naturalizing the obtained strains in the lignocellulose hydrolyzate to finally obtain the oil yeast strain CCTCC M209060 which can effectively accumulate the oil in the lignocellulose hydrolyzate. The strains has high oil yield compared with the original strains, can effectively accumulate the oil in the lignocellulose hydrolyzate which contains the inhibitor with higher concentration, and offers the probability for preparing the microbial oil with low cost, high efficiency and large scale.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for efficiently co-fermenting glucose and xylose and application of recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
ActiveCN105199976AImprove fermentation effectStrong fermentation abilityFungiBiofuelsCelluloseHydrolysate
The invention discloses a recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for efficiently co-fermenting glucose and xylose. The strain is (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) LF1 which is collected with the serial number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.11331 in CGMCC on September 8, 2015. The invention also discloses an application of the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain to ethanol production through fermentation in a mixed sugar culture medium with glucose and xylose as carbon sources or a lignocellulose hydrolysate. Experiments prove that the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain LF1 disclosed by the invention has relatively high glucose and xylose co-fermentation capacity, and after the glucose and the xylose are fermented for 12 hours, the glucose is completely consumed, and meanwhile about 77.6% (33.24gL<-1>) of xylose is utilized, so that the strain LF1 basically has the actual industrialized potential for producing fuel ethanol by fermenting lignocellulose raw materials.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
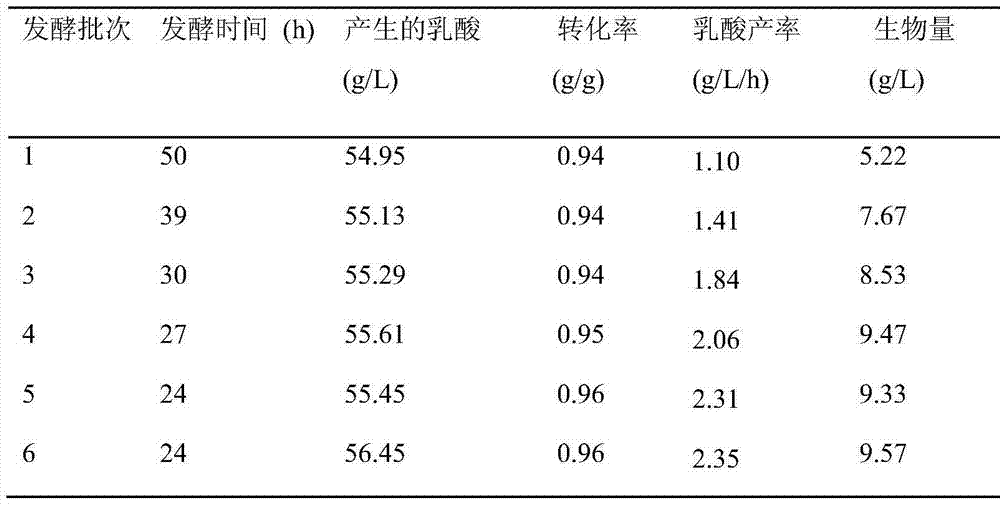
Method for producing lactic acid through continuously fermenting batches of lignocellulose hydrolysate by coupling fermenting and membrane separation
ActiveCN103834696AReduce manufacturing costReduce productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationCelluloseFiltration
The invention discloses a method for producing lactic acid through continuously fermenting batches of lignocellulose hydrolysate by coupling fermenting and membrane separation. According to the method, bacillus coagulans CGMCCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No. 7635 is taken as the fermented culture, and mixed sugar in the lignocellulose hydrolysate is taken as the carbon source. Aiming at the defects in the fermentation process that unsynchronized utilization of hexose and pentose by microorganism results in longer fermentation period and low yield, the invention provides a method for cell recycling and continuous batch fermentation through coupling of membrane separation units and fermentation, and the method comprises steps of activation of culture, seed culture, fermentation cultivation, filtration of ultrafiltration membrane, cell recycling and batch fermentation. By adopting the method, the fermentation period can be effectively shortened, and the utilization efficiency of the mixed carbon source of hexose and pentonse by the thallus is improved. The method has mild operation conditions, has good stability, has general guiding significance in production of biochemical products through fermenting by the microorganism using the mixed sugar in the lignocellulose hydrolysate, and has wide industrial application prospect.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing aromatic aldehyde from lignocellulose hydrolysis residue by two-step process
InactiveCN103059067AHigh reactivityImprove conversion rateOrganic compound preparationLignin derivativesCelluloseFenton reagent
The invention discloses a method for preparing aromatic aldehyde from lignocellulose hydrolysis residue by a two-step process. The method comprises the following steps of: based on the lignocellulose hydrolysis residue as a raw material, degrading lignin by two-step reaction in a reaction kettle to produce an aromatic aldehyde compound, wherein the first reaction step is activating the lignin by utilizing strong oxidability of a fenton reagent in a proper pH range, and the second reaction step is catalytically oxidizing the lignin by using a copper sulfate catalyst and filling an oxidative gas under an alkaline condition to degrade to produce the aromatic aldehyde compound. By adopting the two-step reaction of the activation and the catalytic oxidization, the method has the characteristics that the lignin in the hydrolysis residue is efficiently degraded into the aromatic aldehyde compound, and the addition value of the hydrolysis residue used as the industrial waste is improved.
Owner:HUAIYIN TEACHERS COLLEGE
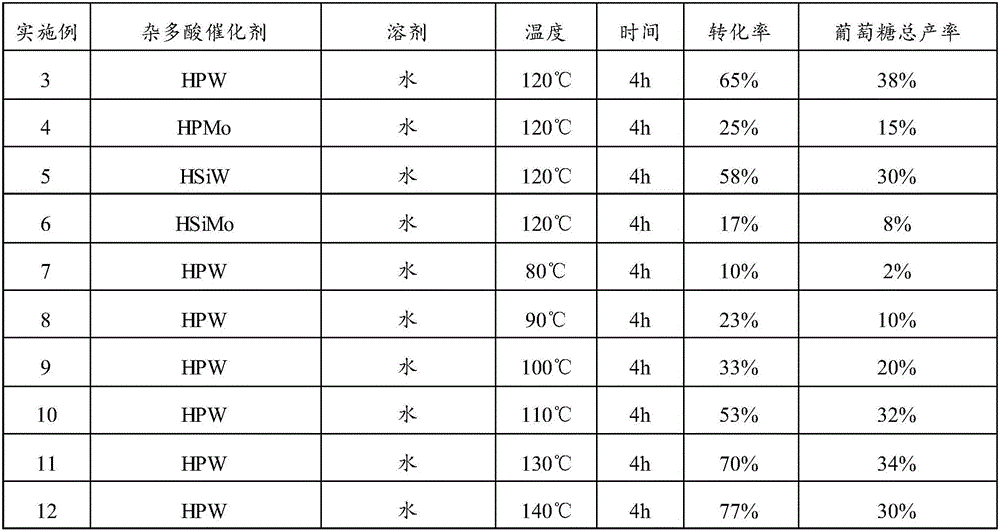
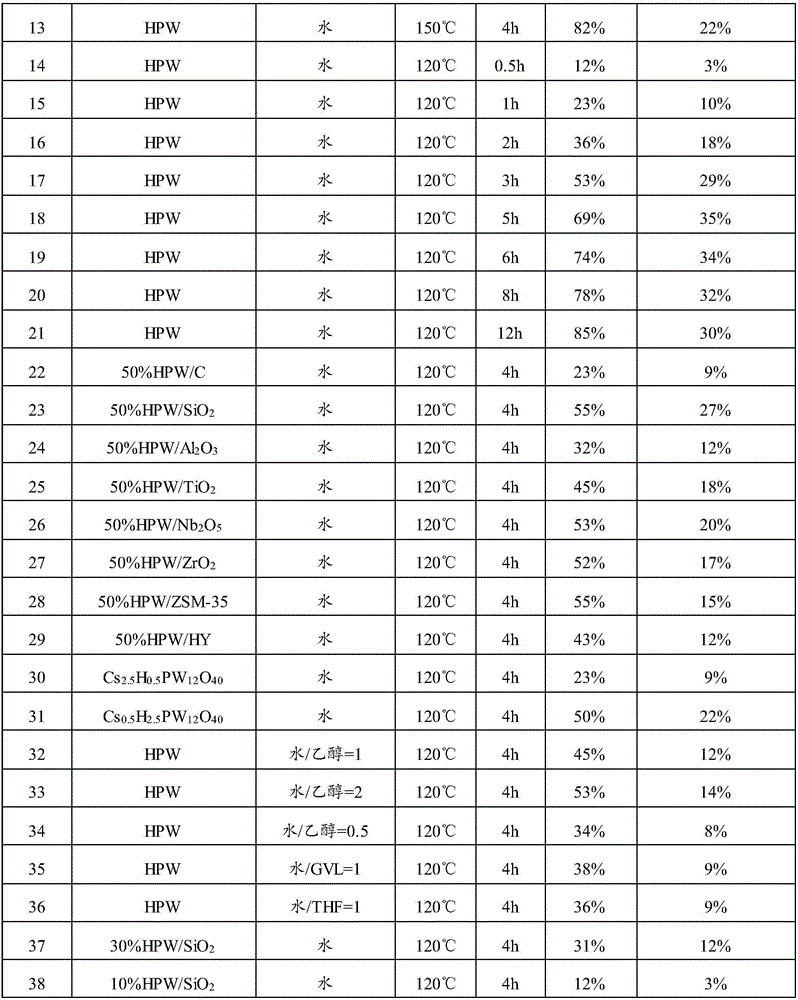
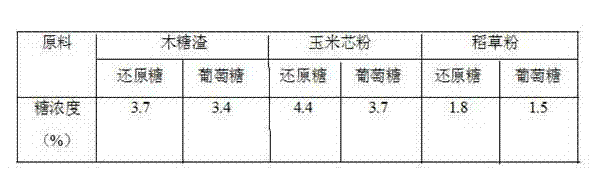
Method for catalyzing hydrolysis of lignocellulose by heteropoly acid
InactiveCN106755611AMild reaction conditionsEasy to operateXylose productionGlucose productionCelluloseHeteropoly acid
The invention provides a method for catalyzing hydrolysis of lignocellulose by heteropoly acid. The method comprises the following steps: mixing plant biomass, a heteropoly acid catalyst and a reaction solvent; carrying out hydrolysis reaction to obtain a hydrolysis product, wherein the hydrolysis product comprises monosaccharides; the heteropoly acid catalyst is one or more of heteropoly acid, heteropoly acid salt and a supported heteropoly acid catalyst; the supported heteropoly acid catalyst comprises a carrier and an active component supported on the carrier; the active component is the heteropoly acid and / or the heteropoly acid salt; the reaction solvent is water or a water-containing mixed solvent. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that the heteropoly acid catalyst is used for catalyzing the hydrolysis of the lignocellulose, the heteropoly acid is strong protonic acid which can be used for catalyzing the hydrolysis of the plant biomass by hydrogenation, and high-selectivity hydrolysis of a glucosidic bond in polysaccharides is catalyzed efficiently to prepare the monosaccharides; the method has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, easiness in operation, adoption of cheap and readily-available catalyst, recyclability, and easiness in scale production.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Trichoderma atroviride strain and application thereof in preparation of cellulase
ActiveCN102925365AIncrease enzyme activityReasonable compositionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention relates to a trichoderma atroviride B-8-1-34 strain capable of highly yielding cellulose and application of the trichoderma atroviride B-8-1-34 strain in the preparation of the cellulose, belonging to the technical field of microorganisms. The trichoderma atroviride B-8-1-34 strain disclosed by the invention has been preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on Aug.10, 2012, with the preservation number of CGMCC No.6390. The trichoderma atroviride B-8-1-34 disclosed by the invention can be used for producing the cellulose by making use of lignocellulose-containing industrial and agricultural wastes in combination of low-cost raw materials such as bran, maize slurry and soybean cake powder through liquid or solid fermentation, has the advantages of short fermentation period, high activity of produced cellulose, reasonable components and high lignocellulose hydrolysis, and provides a novel strain resource to solve the problems on high production cost, low saccharifying efficiency and the like caused by low enzyme activity and unreasonable enzyme components in the utilization of cellulose resources.
Owner:郑州运维生物技术有限公司
Pretreatment method capable of improving saccharification efficiency of lignocellulose
ActiveCN110760552AImprove enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification efficiencyLow equipment requirementsPulping with organic solventsFermentationCelluloseGlycerol
The invention discloses a pretreatment method capable of improving saccharification efficiency of lignocellulose. According to the method, ethanedioic acid, choline chloride and glycerol are added towater for reaction to obtain a modified deep-eutectic solvent (DES), and a lignocellulose raw material is pretreated with the modified DES. The method can realize pretreatment of the lignocellulose under a lower-temperature condition, is more beneficial to improvement of the saccharification efficiency of the lignocellulose and can substantially increase the total quantity of carbohydrates released in a lignocellulose hydrolytic process.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Method for producing acetone-butanol by co-fermentation of pentoses and hexose
ActiveCN101440381AEnsure safetyRealize comprehensive utilizationMicroorganism based processesFermentationCelluloseLiquid fuel
The invention provides a method for producing acetone butanol by jointly fermenting pentose and hexose. The method comprises the following steps: the pentose and the hexose are mixed, the weight of the pentose against the total weight of the mixture is between 5 and 75 percent, the mixture is added with a nitrogen source or a phosphorus source to obtain a raw material, and the raw material is subjected to cooking sterilization to obtain cooking mash; the cooking mash is cooled to a temperature of below 42 DEG C and injected with strains and fermented; and the fermented solution is filtered, distilled and rectified to obtain final acetone, butanol and ethanol products. By the invention, the method which effectively utilizes the joint fermentation of the pentose and the hexose to produce the acetone butanol is obtained. According to local conditions, lignocellulose is utilized to hydrolyze pentose and the hexose for joint fermentation to produce the acetone butanol, thereby realizing waste reutilization, facilitating environmental protection, promoting diversification of energy structure in China, ensuring safety of liquid fuel in China and having positive significance on improving creativity and research capability in the field of preparing biomass liquid fuel in China.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Grafted solid acid catalyst, preparation method thereof and application of grafted solid acid catalyst in saccharification process of lignocellulose
ActiveCN106345491AImprove stabilityActivity unchangedOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsXylose productionCelluloseBiomass carbon
The invention relates to a grafted solid acid catalyst. A preparation method of the grafted solid acid catalyst comprises the following steps: taking lignocelluloses biomass carbon-based material as a raw material, taking a sulfonating agent as an active molecule, and carrying out carbonization reaction for 1-36 hours at the temperature of 120-240 DEG C, wherein the mass ratio of the raw material and the sulfonating agent is 1 / 10-10; standing black solid obtained by carbonization at high temperature, drying to obtain black solid which is a rough carbon-based solid acid catalyst; and mixing the rough carbon-based solid acid catalyst with an oxidizing agent according to the solid-liquid ratio of 1 / 10-0-1 / 10, reacting for 0.5-3 hours at the temperature of 50-60 DEG C, after reaction, filtering and separating to obtain black solid, and washing and drying the black solid to obtain the grafted carbon-based solid acid catalyst. Cellulose-based glucose is used as the raw material of the catalyst, the structural characteristics of the raw material are similar to the structural characteristics of the raw material of lignocelluloses biomass, therefore, catalyzing effect is excellent, and the catalyzing effect of the grafted solid acid catalyst is similar to the catalyzing effect of liquid acid.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Virus-free in situ and alcohol fermentation method of composite bacteria for lignocellulose hydrolysis product
The present invention relates to an in-situ detoxification ethanol fermentation method of lignocellulose hydrolysate, which respectively inoculates Y5 and CBS6054 into fermentation culture medium containing dilute acid lignocellulose hydrolysate to carry out in-situ detoxification alcoholic fermentation. The method can efficiently metabolize glucose and xylose in the dilute acid lignocellulose hydrolysate to produce ethanol, and rapidly metabolize furfural and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. The yield of ethanol is 0.44g / g, reaching 87.5 percent of the theoretical value. Moreover, any detoxification processing is not needed, the requirement on equipment is low, the operation is convenient, and the cost is low.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
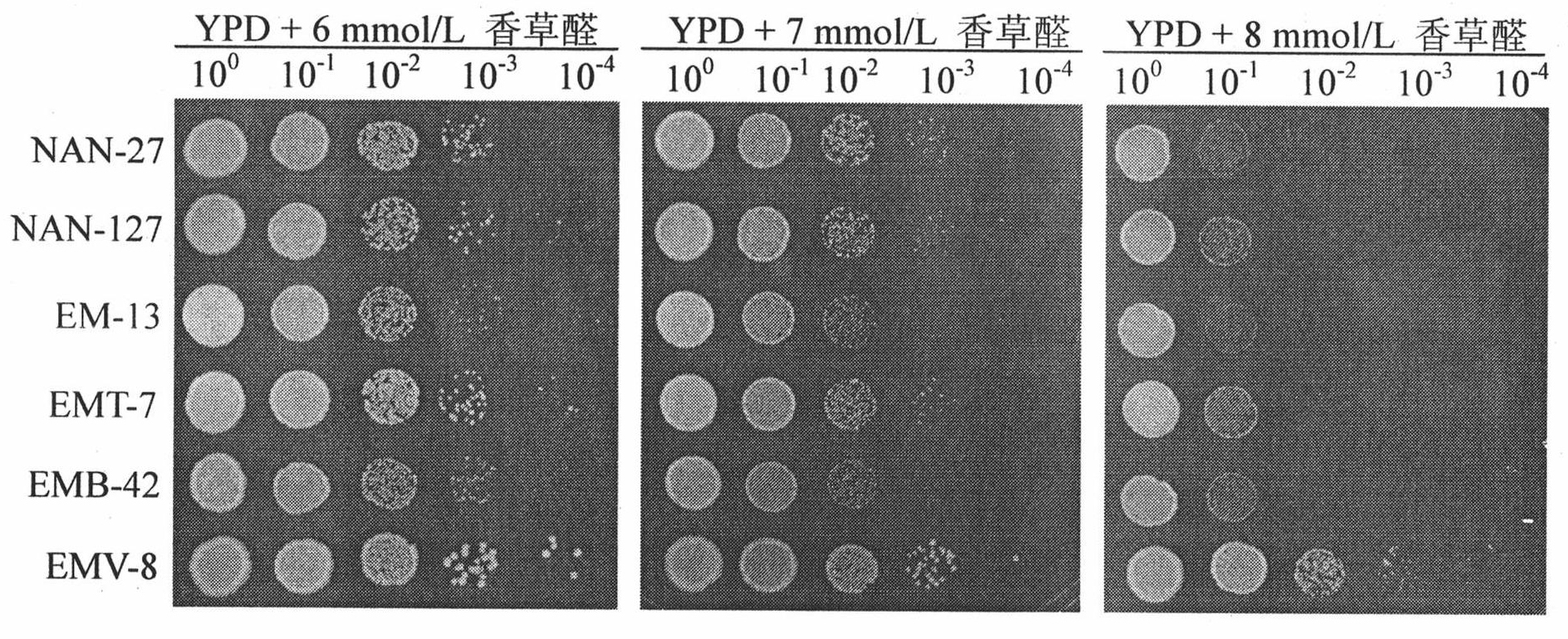
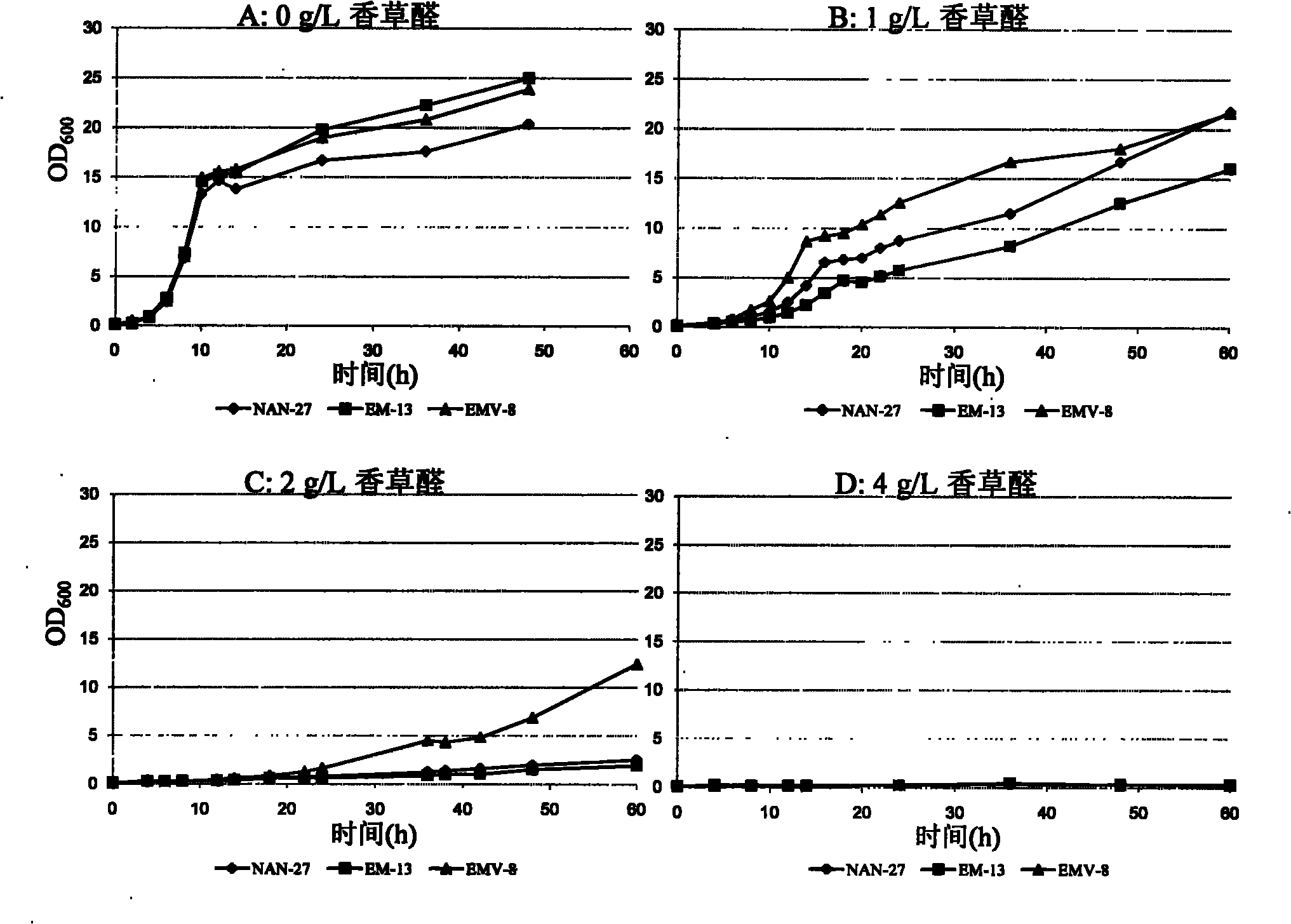
Vanillin-tolerant saccharomyces cerevisiae
InactiveCN101928675AShortened growth lagImprove toleranceFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCellulose
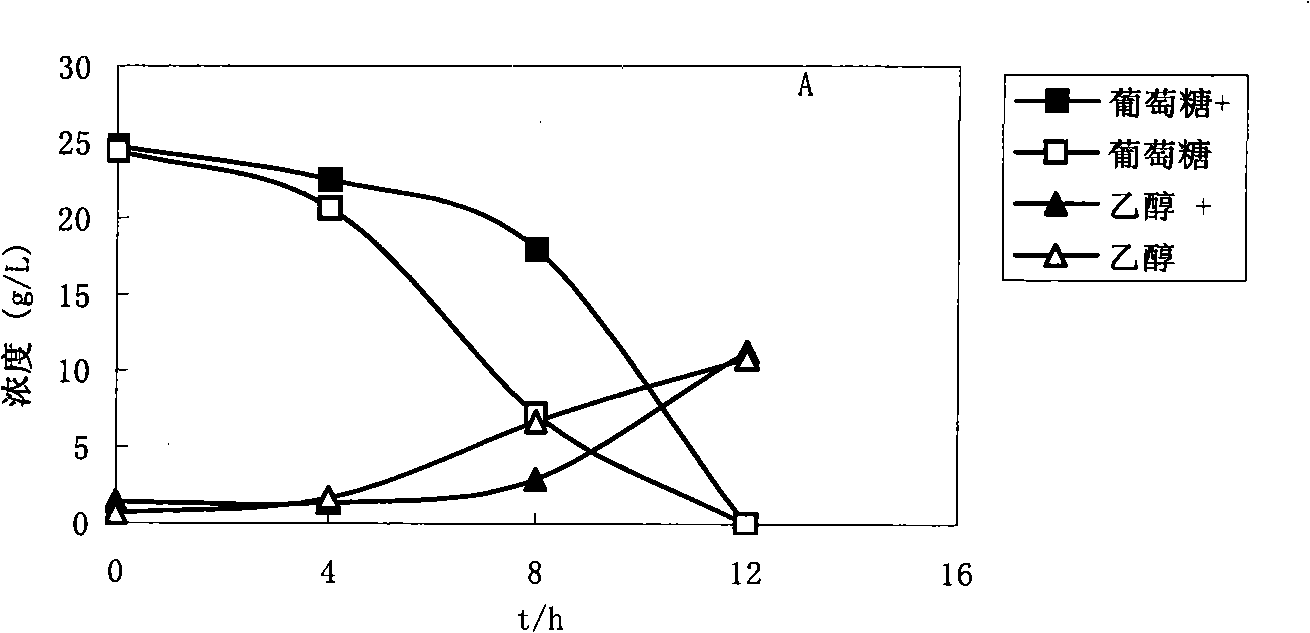
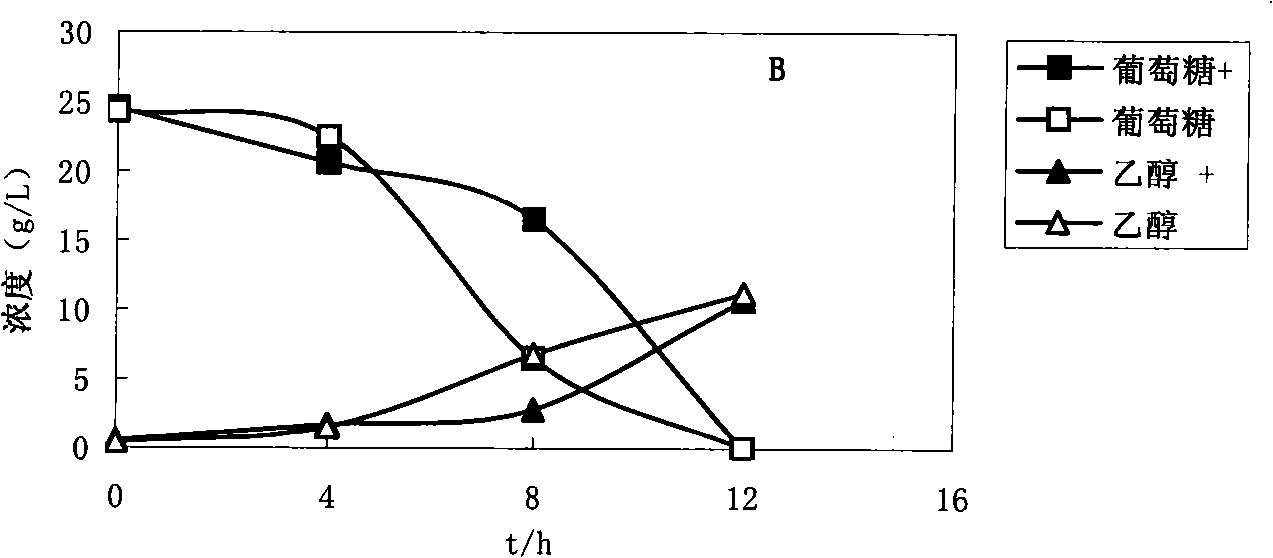
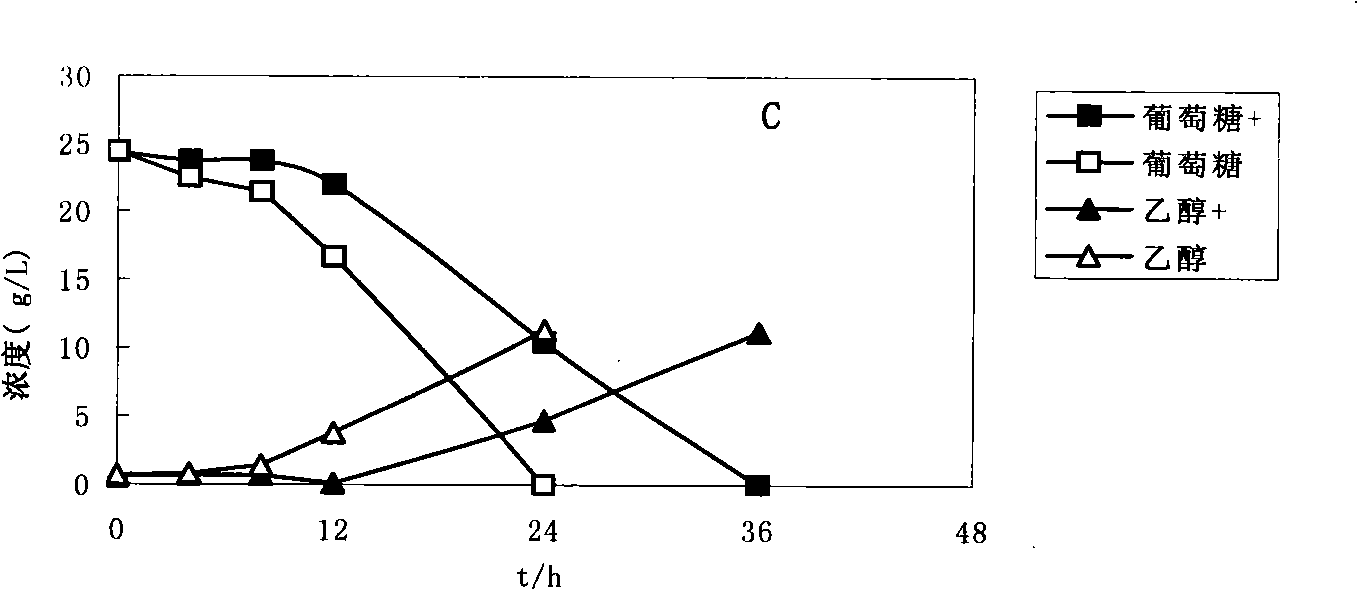
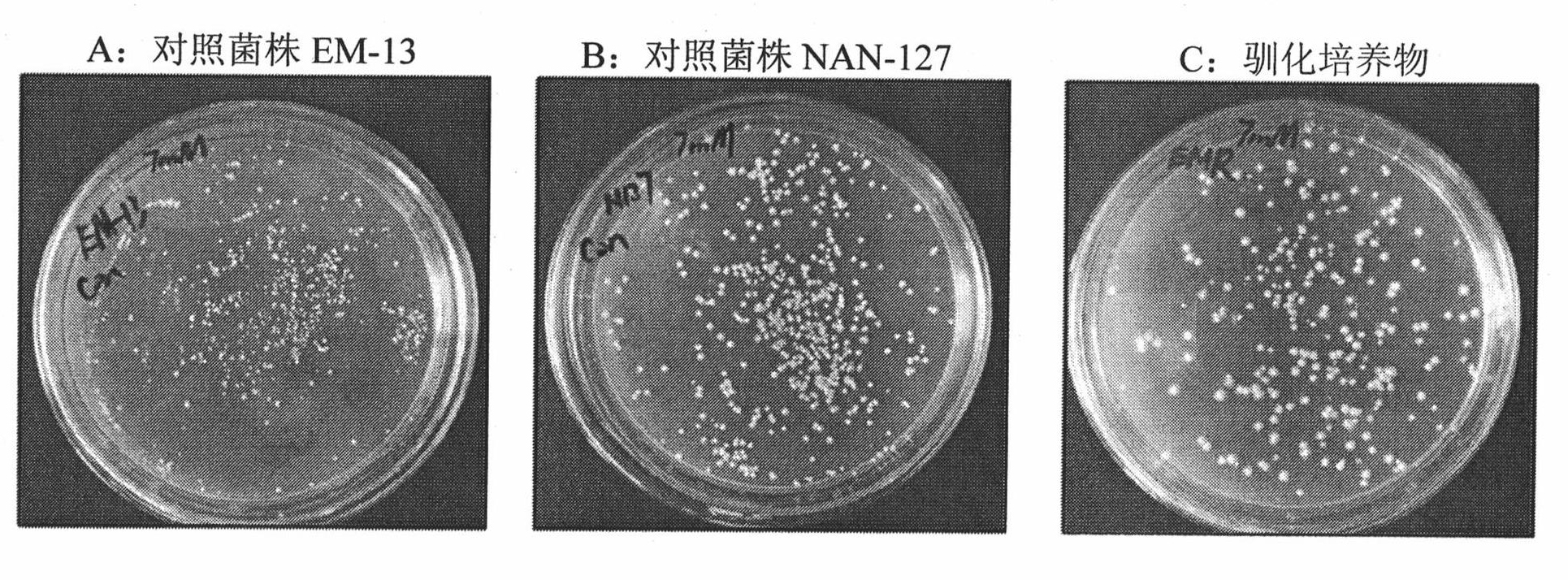
The invention discloses vanillin-tolerant saccharomyces cerevisiae. The strain is named as saccharomyces cerevisiae EMV-8 and collected in CGMCC on July 16th, 2010 with a collection number CGMCC No.4012. The strain is obtained by domesticating saccharomyces cerevisiae EM-13 in a YEPD liquid culture medium prepared from corn straw steam blackout extraction solution of different concentrations and screening; compared with the original strain EM-13, the strain can consume all glucose faster and has high ethanol yield when cultured in the YEPD liquid culture medium containing 1g / L of vanillin,; when cultured in the YEPD liquid culture medium containing 2g / L of vanillin, the strain has the growth delay period shortened by about 20 hours compared with the original strain; and the strain has good application value for further breeding the inhibitor tolerant saccharomyces cerevisiae in lignocellulose hydrolysis solution, and meanwhile has certain theoretical value for researching the phenolic compound tolerance mechanism of the saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
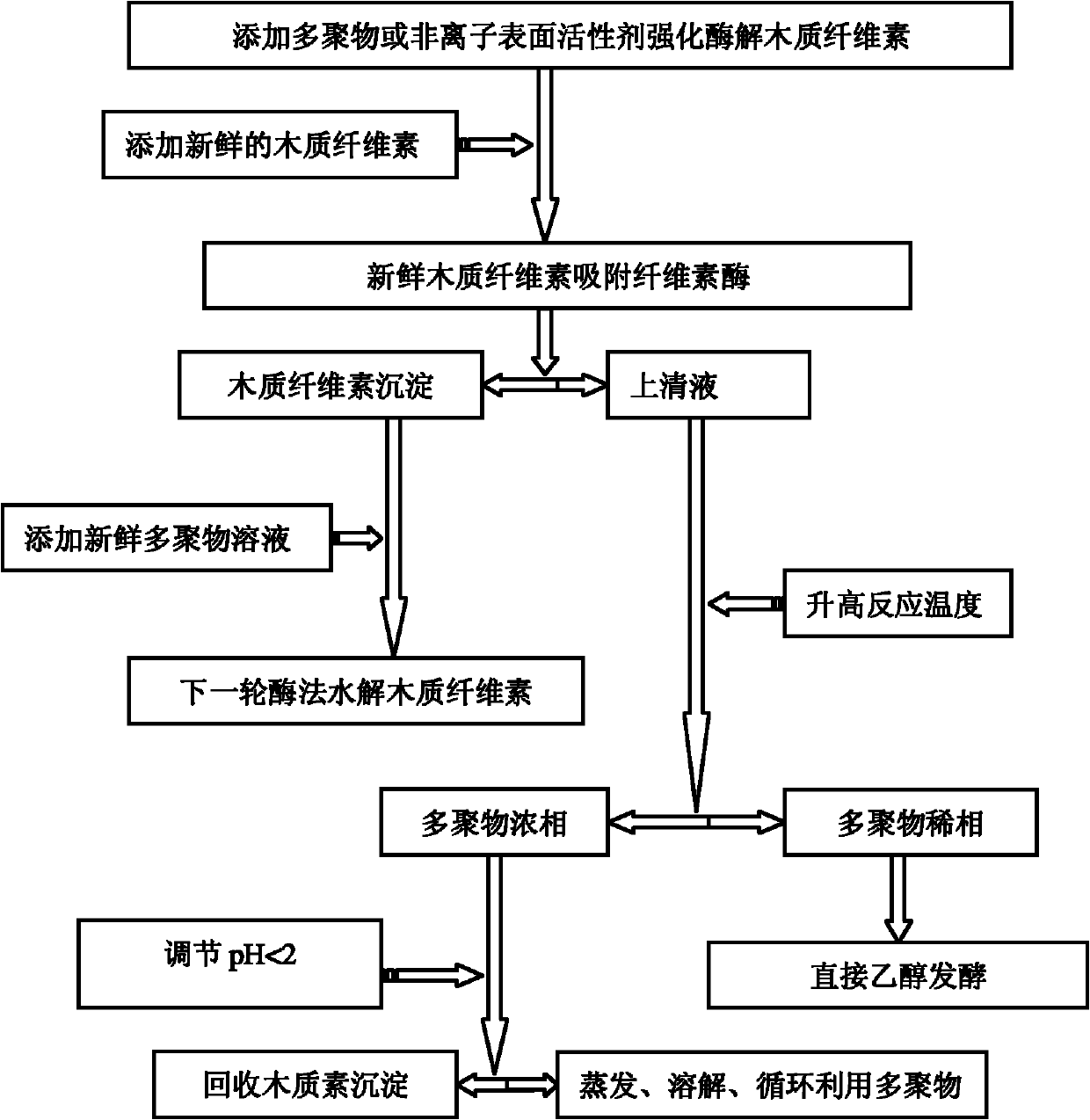
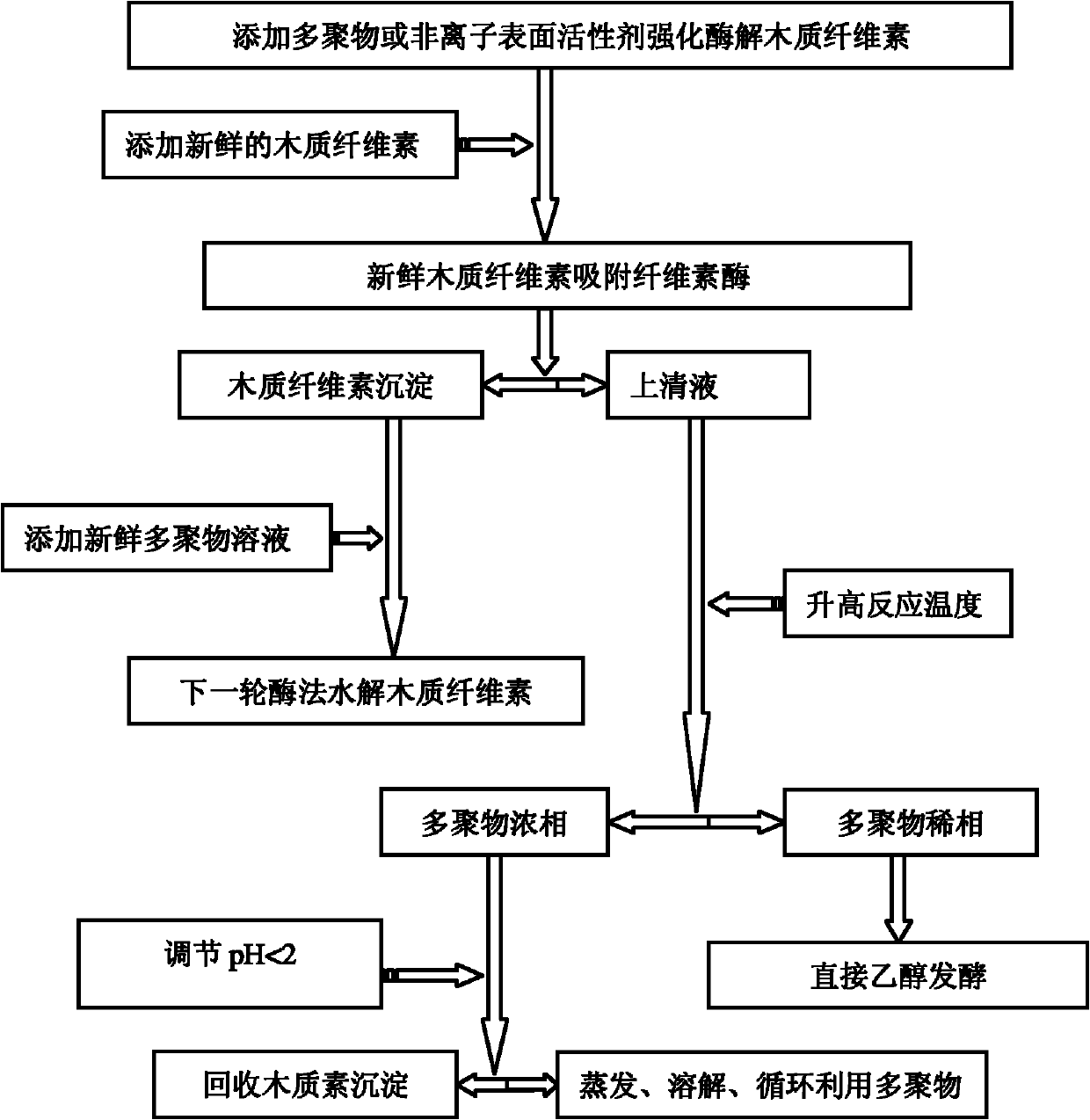
Extraction method of cellulase for improving hydrolysis of lignocellulose
InactiveCN101906450AExtraction achievedAchieve precipitationBiofuelsFermentationD-GlucoseGlucose polymers
The invention provides an extraction method of cellulose for improving the hydrolysis of lignocellulose, relating to the technical filed of biochemistry. In the process of enzyming lignocellulose, polymer or nonionic surfactant capable of being separated are added to selectively extract the lignocellulose so as to improve the hydrolysis efficiency of the lignocellulose by the cellulose, thus further separating the lignocellulose and the cellulose so as to realize recovery and reutilization of added polymer or nonionic surfactant and obtain byproduct lignocellulose; and meanwhile, hydrolyzed glucose solution can be directly used for sugar fermentation process in the next step. The method realizes the deposition of lignocellulose and obtains byproduct lignocellulose, copolymer L64 is recovered and recycled, and lignocellulose is recovered to hydrolyze lignocellulose for the next cycle.
Owner:GEOTHINK ECOTECH SHANGHAI
pH CONTROLLED YEAST PROPAGATION
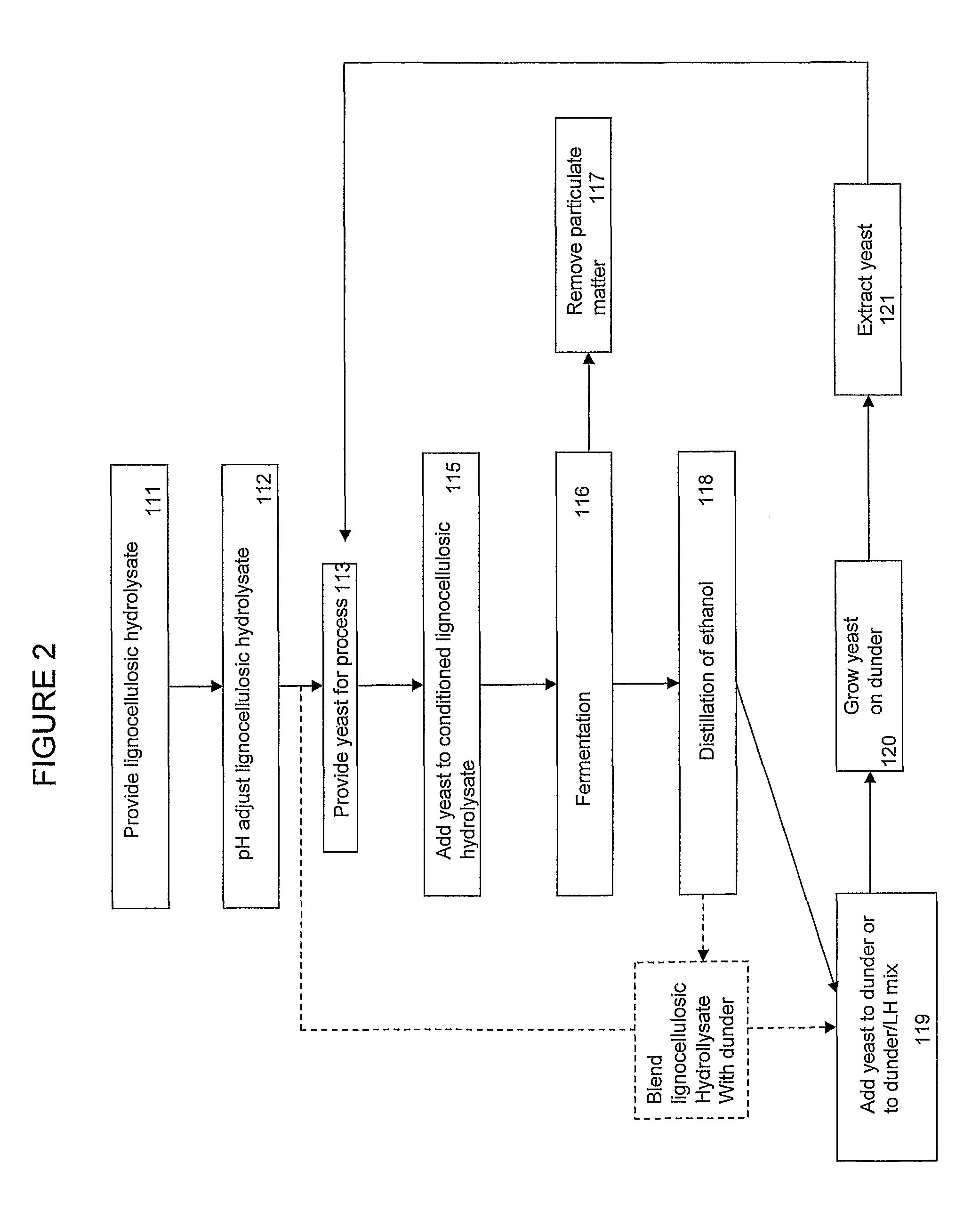
InactiveUS20150252319A1Avoids excess productionImprove performanceFungiBiofuelsCelluloseBiotechnology
The invention relates to a process for the aerobic propagation of yeast wherein the yeast is grown in a reactor, comprising the following steps:a) filling the reactor with carbon source and an initial yeast population,b) optionally growing the initial yeast population in the reactor in batch mode,c) measuring the pH in the reactor,d) adding lignocellulosic hydrolysate to the reactor in fed batch mode at a rate to set the pH in the reactor at a predetermined value,ande) after sufficient propagation, isolation of yeast from the reactor.The invention further relates to yeast propagated according to that propagation process and to a process for the production of fermentation product wherein sugar comprising hexose and pentose is anaerobically fermented to fermentation product with the propagated yeast.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
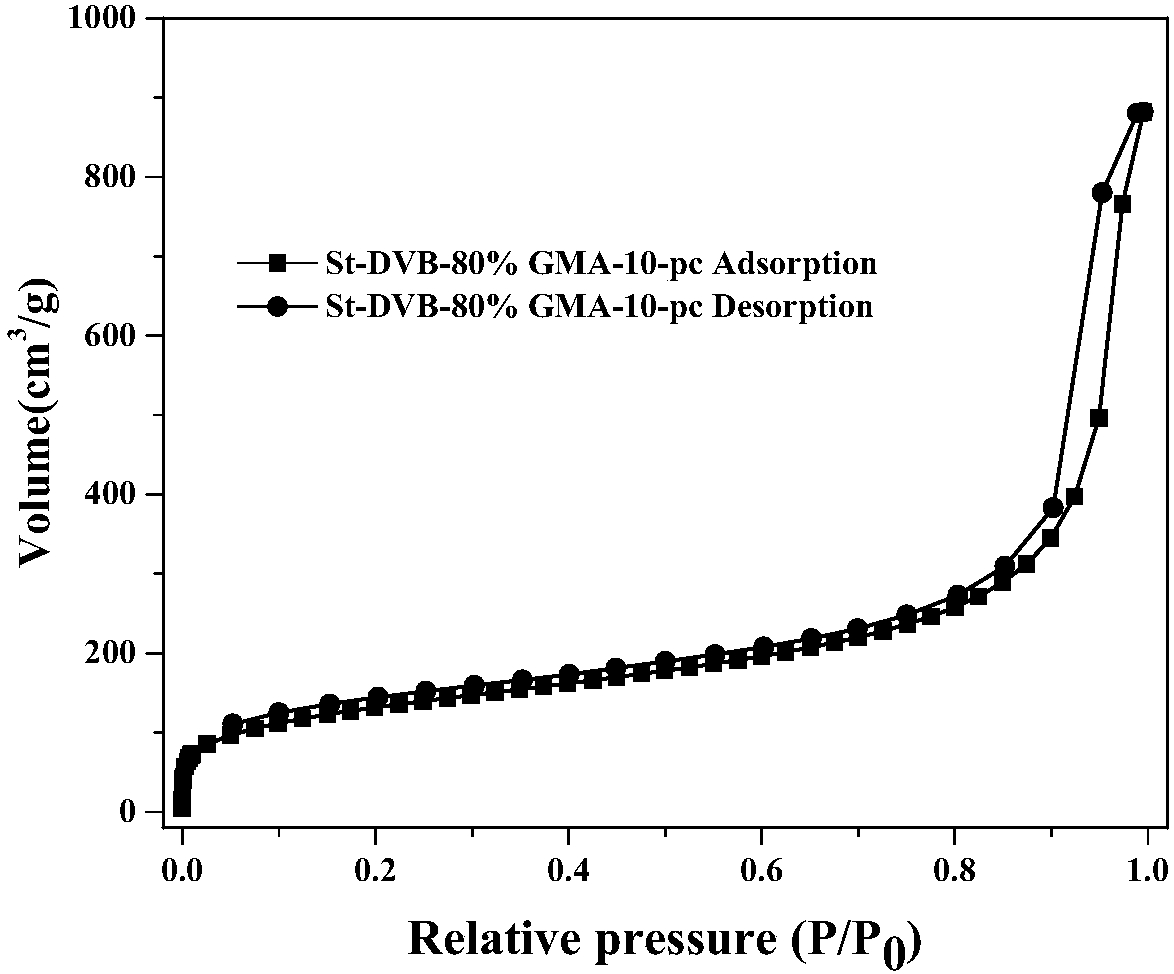
Modified styrene adsorption resin, preparation method of modified styrene adsorption resin and application of modified styrene adsorption resin to refining of lignocellulose hydrolysate
ActiveCN108355626AImprove hydrophilicityImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesCross-linkCellulose
The invention provides modified styrene adsorption resin, a preparation method of the modified styrene adsorption resin and application of the modified styrene adsorption resin to refining of lignocellulose hydrolysate. The preparation method of the modified styrene adsorption resin comprises the following steps: sequentially adding an acrylate monomer, a styrene monomer, a cross-linking agent, aninitiating agent a pore-forming agent to an aqueous solution containing a dispersing agent, and performing suspension polymerization reaction to obtain precursor resin; and performing Friedel-Craftsreaction on the precursor resin under the action of Lewis acid as a catalyst to obtain the modified styrene adsorption resin. By modifying the acrylate unit in the styrene adsorption resin, the acrylate unit contains an ester group which can form intermolecular hydrogen bonding with water molecules, thereby greatly improving the hydrophilicity of the modified styrene adsorption resin and being favorable for adsorbing hydrophilic fermentation inhibitors in the lignocellulose hydrolysate.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
COD degradation agent for removing sulfamide from industrial wastewater
ActiveCN102070237AChange hueNo secondary pollutionWater/sewage treatment by oxidationAmylaseCellulose
The invention discloses a chemical oxygen demand (COD) degradation agent for removing sulfamide from industrial wastewater in the field of environment sewage treatment. The degradation agent is formed by compounding the following components in percentage by mass: 70 to 85 percent of inorganic strong oxidant, 1 to 5 percent of catalyst and 10 to 29 percent of genetic engineering bacteria enzyme, wherein the inorganic strong oxidant is one or two of sodium chlorate, potassium ferrite, ammonium persulfate and sodium bismuthate; the catalyst is one of nickel oxide, copper oxide, titanium oxide and lead oxide; the genetic engineering bacteria enzyme is one or two of cyclic amide hydrolase, lignocellulose hydrolase, protein hydrolase, organic phosphorus hydrolase and amylase; and the wastewater is added with 1 to 5 percent of degradation agent and continuously stirred, so that the concentration of the sulfamide in the wastewater is reduced to below 0.5mg / L from 1,000mg / L, and the removal rate is more than 99.9 percent. The degradation agent is easy to use and cannot produce secondary pollution; raw materials are readily available; and precipitates are not produced.
Owner:溧阳常大技术转移中心有限公司
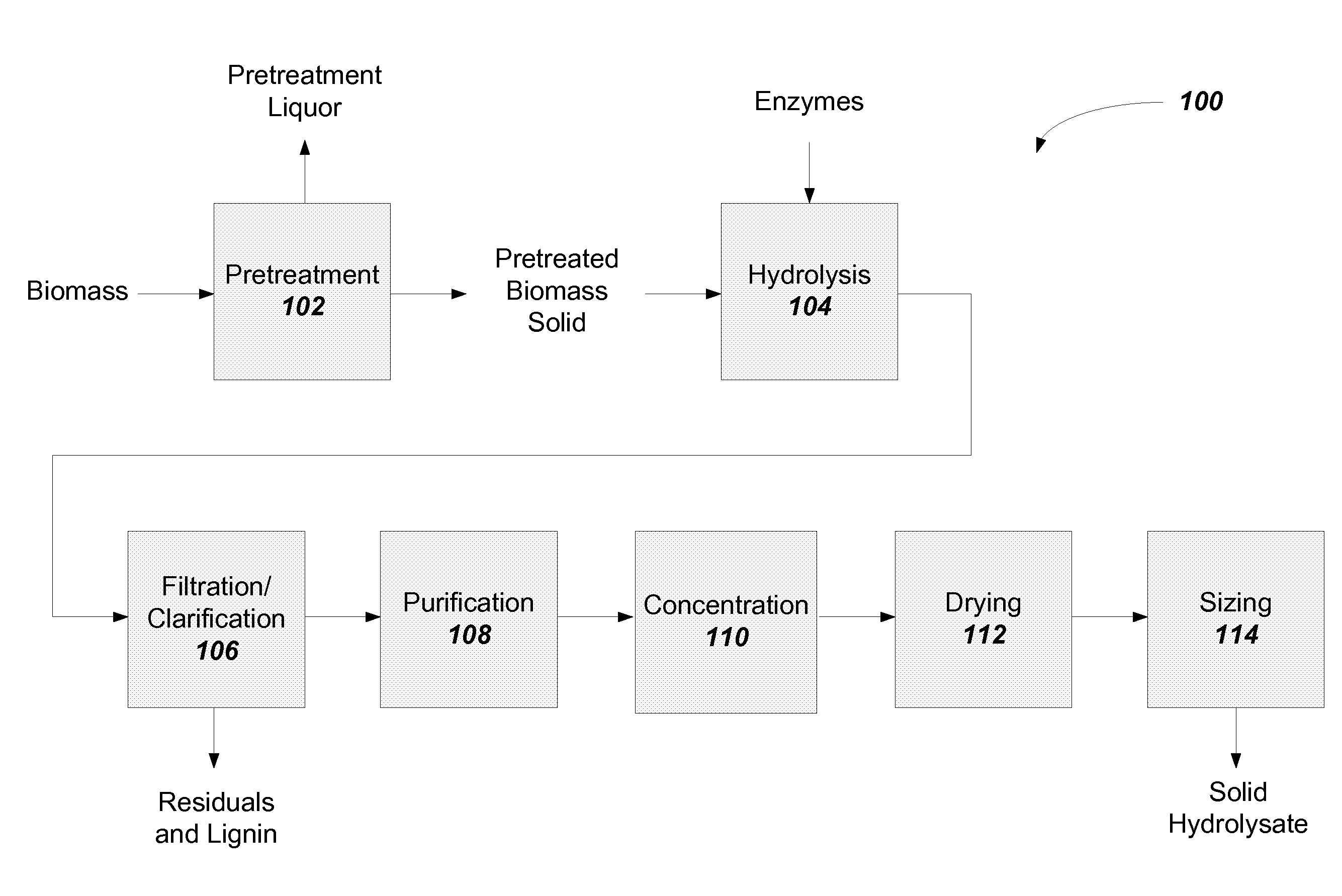
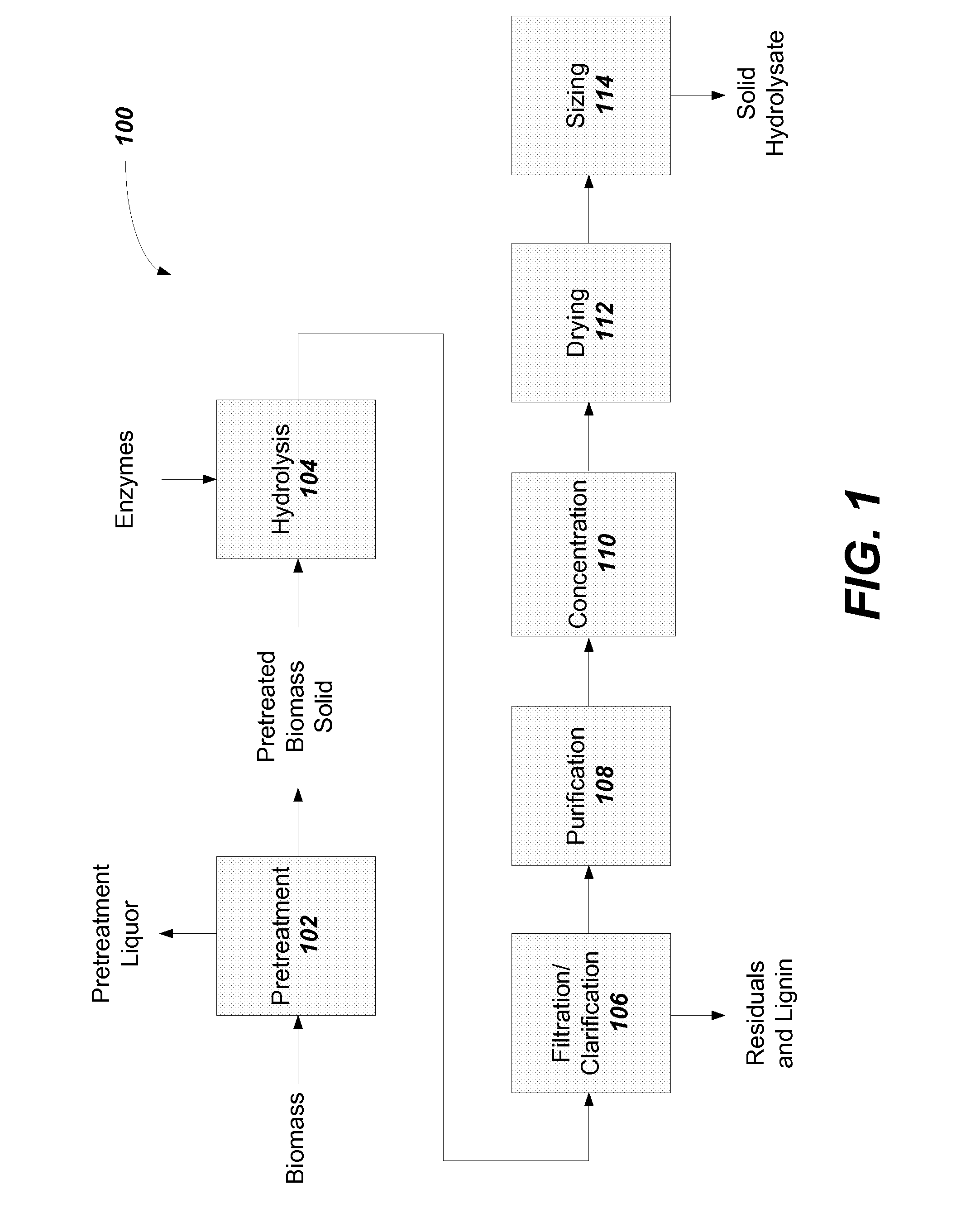
Solid lignocellulosic hydrolysate and methods to prepare a solid lignocellulosic hydrolysate
InactiveUS20130118483A1High in sugarIncrease in sizeSugar productsPretreatment with acid reacting compoundsCelluloseSolubility
The present disclosure provides a solid lignocellulosic hydrolysate and methods to prepare the solid lignocellulosic hydrolysate from a woody biomass or an herbaceous biomass. The solid lignocellulosic hydrolysate may be used in the production of biofuels, bioproducts, and food products. The solid lignocellulosic hydrolysate allows for ease of storage, ease of transportation and handling of the solid lignocellulosic hydrolysate, and ease of use in biological or fermentation processes or chemical processes for the production of biofuel, bioproducts, chemicals and food products due to the bulk handling characteristics (e.g., solubility and rate of dissolution) of the solid lignocellulosic hydrolysate.
Owner:WEYERHAEUSER NR CO
Production method for microbial oil
ActiveCN102634549AEasy to operateThe fermentation process is simpleMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicrobial oilHydrolysate
The invention discloses a production method for microbial oil. In the invention, oil yeast is obtained by domesticating the yeast, the domestication method is simple to operate, the oil yield coefficient of the domesticated oil yeast in lignocellulose hydrolysate is 13-20% which is higher than that of before the domestication processing by 20%-30%, the domesticated oil yeast is inoculated into the lignocellulose hydrolysate for fermentation, then thallus in the fermentation liquor is collected and broken, extracted by an organic solvent, and then the organic solvent is removed so as to obtain the microbial oil. In the method, the lignocellulose hydrolysate is not required for detoxification and the other treatment, only simple pretreatment is conducted on the lignocellulose acid hydrolysate, no nitrogen source and trace elements are added in the lignocellulose hydrolysate, and after yeast strains are inoculated, the microbial oil can be obtained by efficiently using different saccharide materials and fermenting lignocellulose hydrolysate; and the fermentation process is simple, and the cost is low.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing microbial oil by fermenting corn stalk hydrolysate
InactiveCN102719499AReduce or inhibit fermentation inhibitorsPromote fermentationBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismMicrobial oil
The invention relates to a method for producing a microbial oil by fermenting corn stalk hydrolysate. The method comprises the following steps: (1) hydrolyzing corn stalks with acid to obtain the corn stalk hydrolysate; (2) adding Ca(OH)2 into the hydrolysate, regulating the pH to 10 to 11, centrifuging the solution for 10 to 20 min at a speed of 3,800 r / min, taking the supernatant, regulating the pH back to 6.0 with phosphoric acid, centrifuging the solution for 10 to 20 min at a speed of 3,800 r / min, taking the supernatant, sterilizing and filtering the supernatant, and regulating the pH of the obtained filtrate with NaOH to 6.0; (3)fermenting and cultivating oleaginous microorganism; and (4)crushing and extracting the dried bacteria in step (3) to obtain the microbial oil. According to the method for producing the microbial oil, the corn stalks are hydrolyzed by dilute sulphuric acid to obtain lignocellulosic hydrolysate, which is detoxified by Ca(OH)2 to effectively reduce or inhibit the fermentation inhibitor in the hydrolysate, so as to promote the fermentation of the microorganism and obtain a large amount of microbial oils which can be further transformed into biodiesel.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Activity expression and application of thermobifida fusca xylose isomerase in wine brewing yeast
The invention discloses a method for extraction of xylose isomerases by taking brown hot crack loving spore fungus as sources and the activity expression and application of the brown hot crack loving spore fungi xylose isomerases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The molecule weight of the brown hot crack loving spore fungi xylose isomerases is 43 kilodaltons; the most suitable reaction temperature of the xylose isomerases is 80 to 85 DEG C; and the most suitable reaction pH of the xylose isomerases is 7.0. The xylose isomerases can convert xyloses into xyluloses under normal biochemical reaction conditions; genes of the xylose isomerases can be recombined into the Saccharomyces cerevisiae in which the activity expression is realized, and the xyloses or other carbon sources such as lignocellulose hydrolysate and so on can be utilized for production of various fermentation products such as alcohols and so on. The method utilizes the genetic engineering means to expand substrates which are converted by the alcohols and has important theoretical significance and application value on full utilization of lignocellulose resources.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Bacillus coagulans strain and integrated process for producing lactic acid by using same through synchronous saccharification and fermentation of lignocellulose
The invention relates to a Bacillus coagulans strain and an integrated process for producing lactic acid by using the same through synchronous saccharification and fermentation of lignocellulose, belonging to the field of biochemical engineering. According to the invention, lactic acid is produced by using the Bacillus coagulans CGMCC No.7635 strain separated from soil through bioconversion of lignocellulose. The method provided by the invention has the following advantages: the strain has a high-temperature fermentation characteristic, has high tolerance to fermentation inhibitor in lignocellulose hydrolysis liquid and can efficiently produce lactic acid from hexose, pentaglucose and cellobiose. According to the process provided by the invention, raw materials can be pretreated by using the Bacillus coagulans CGMCC No.7635 strain; lignocellulose acidolysis liquid fermentation and cellulose saccharification fermentation processes are integrated; and steps of solid-liquid separation and raw material liquid detoxification are omitted. Thus, the method can simplify the operating process, save the equipment investment, improve the fermentation efficiency and realize the high-valued application of lignocellulose, thereby having important industrial application prospects.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of increasing yield of lignocellulose substrate hydrolase
InactiveCN106434735AEfficient expressionHigh activityMicroorganism based processesNucleic acid vectorHeterologousPichia pastoris
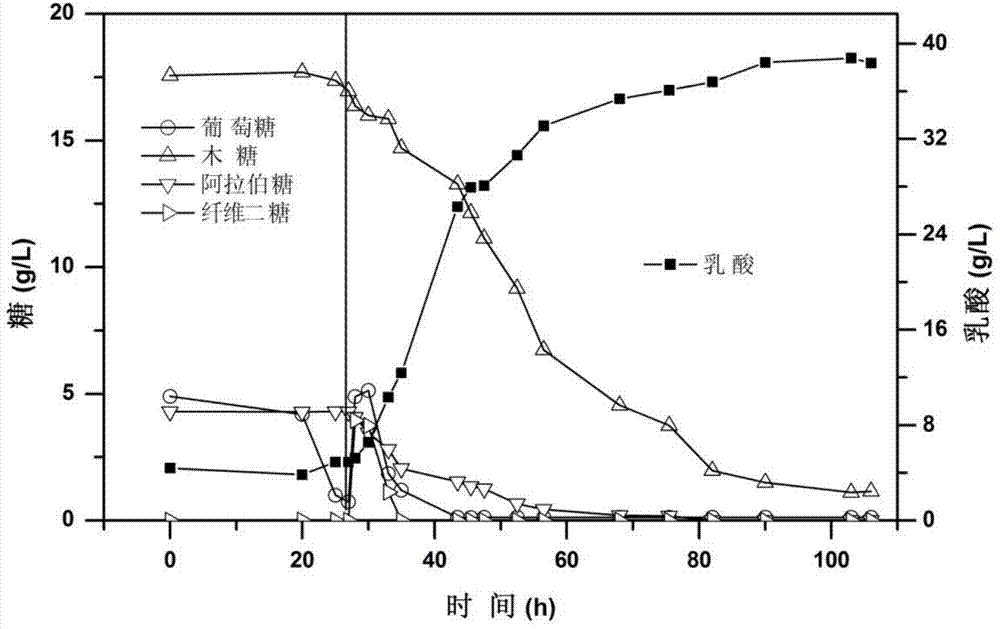
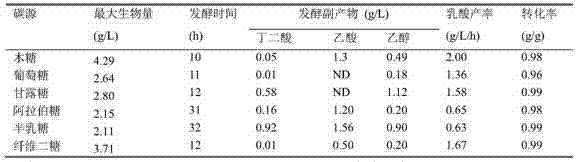
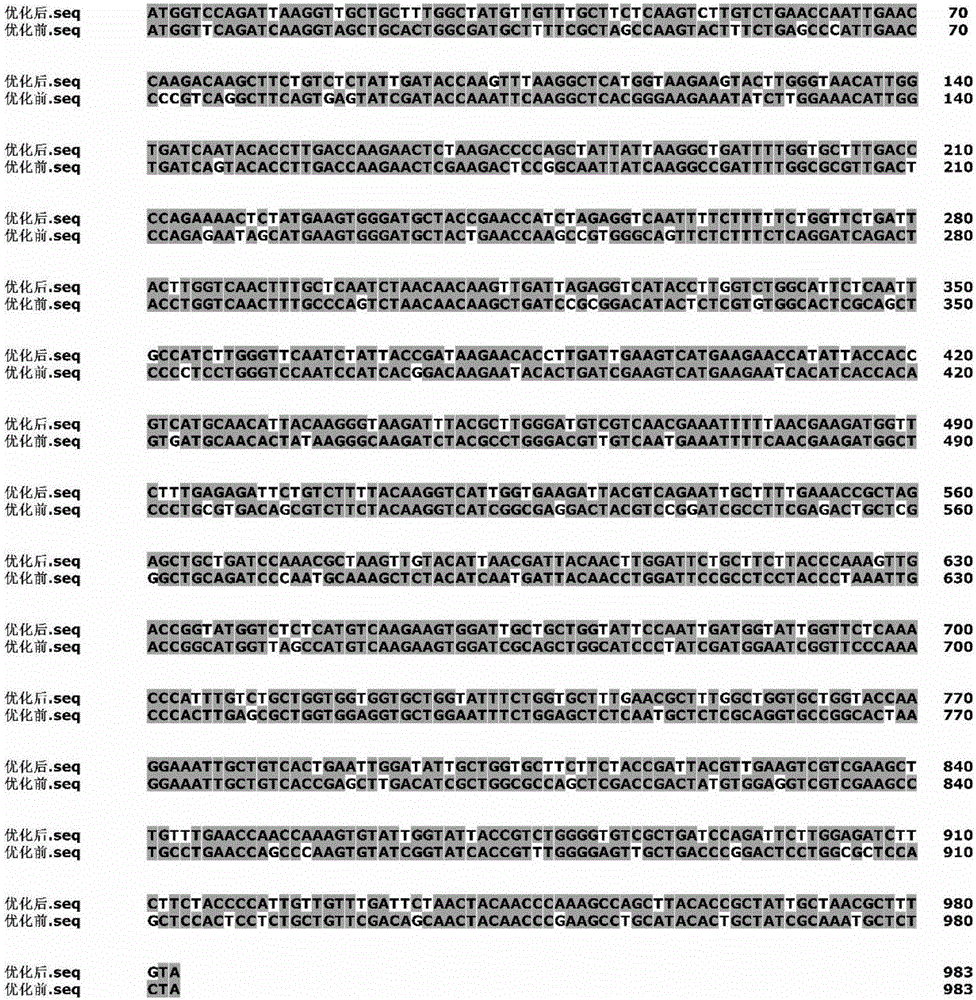
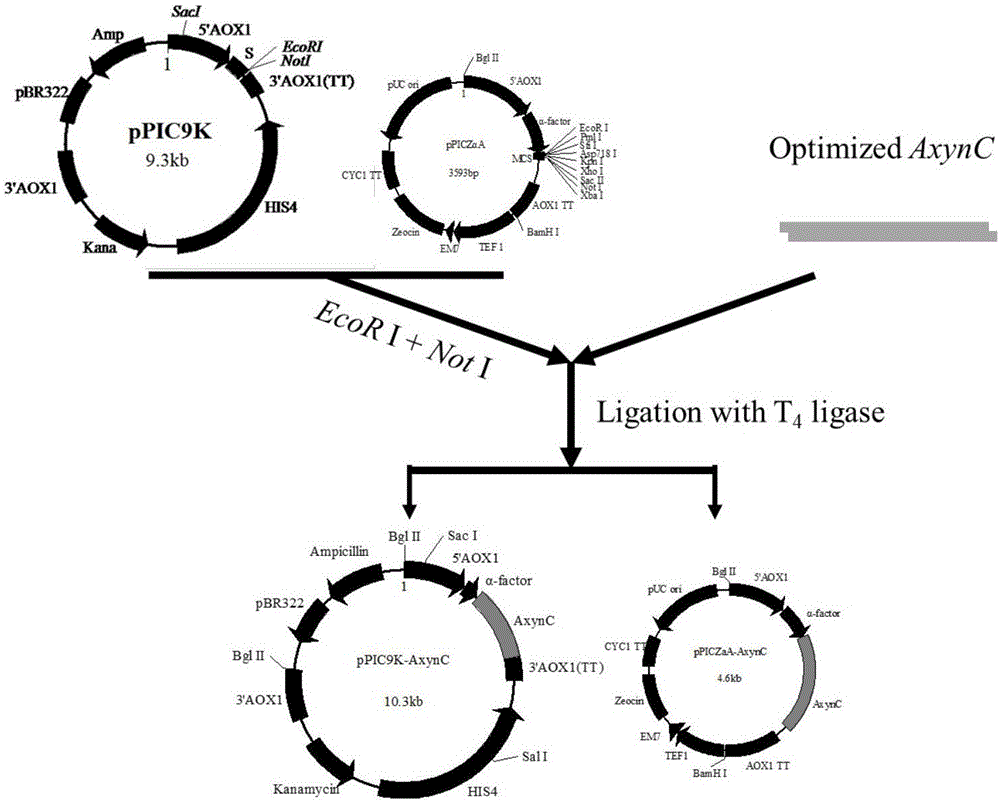
The invention discloses provides a method of increasing heterologous expression quantity of hemicellulase, cellulase or lignocellulose hydrolysis assistance zymoprotein in pichia pastoris. An xylanase (XynC) gene from Aspergillus niger is subjected to codon optimization according to pichia pastoris codon preference characteristics, and an optimized nucleotide sequence (AxynC) is artificially synthesized, and constructs and recombines expression vectors pPIC9K-AxynC and pPICZ alpha A-AxynC. Recombined pichia pastoris of high yield xylanase is constructed by a two-step shock conversion method. That is to say, linearized pPIC9K-AxynC converts the pichia pastoris GS115 to obtain a strain with better enzyme producing ability. The high enzyme activity is subjected to second shock conversion as a host bacterium, and the linearized pPICZ alpha A-AxynC is shocked to convert the strain to obtain double-plasmid recombined pichia pastoris of the high yield xylanase. Tests show that the codon optimized xylanase gene can be expressed successfully in the pichia pastoris, the high yield xylanase recombinant bacterium constructed by a two-step shock conversion method can stably and efficiently produce the xylanase, the flask level enzyme activity reaches 410U / mL, and a protein content in a fermentated supernate reaches 0.37mg / mL.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com