pH CONTROLLED YEAST PROPAGATION
a technology of yeast and controllable growth, applied in the field of yeast propagation process, can solve the problems of yeast growth inhibited by acetic acid and/or sugar degradation products, excess yeast production (129,000 tons of feed yeast) and achieve the effect of avoiding excess production of yeas
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
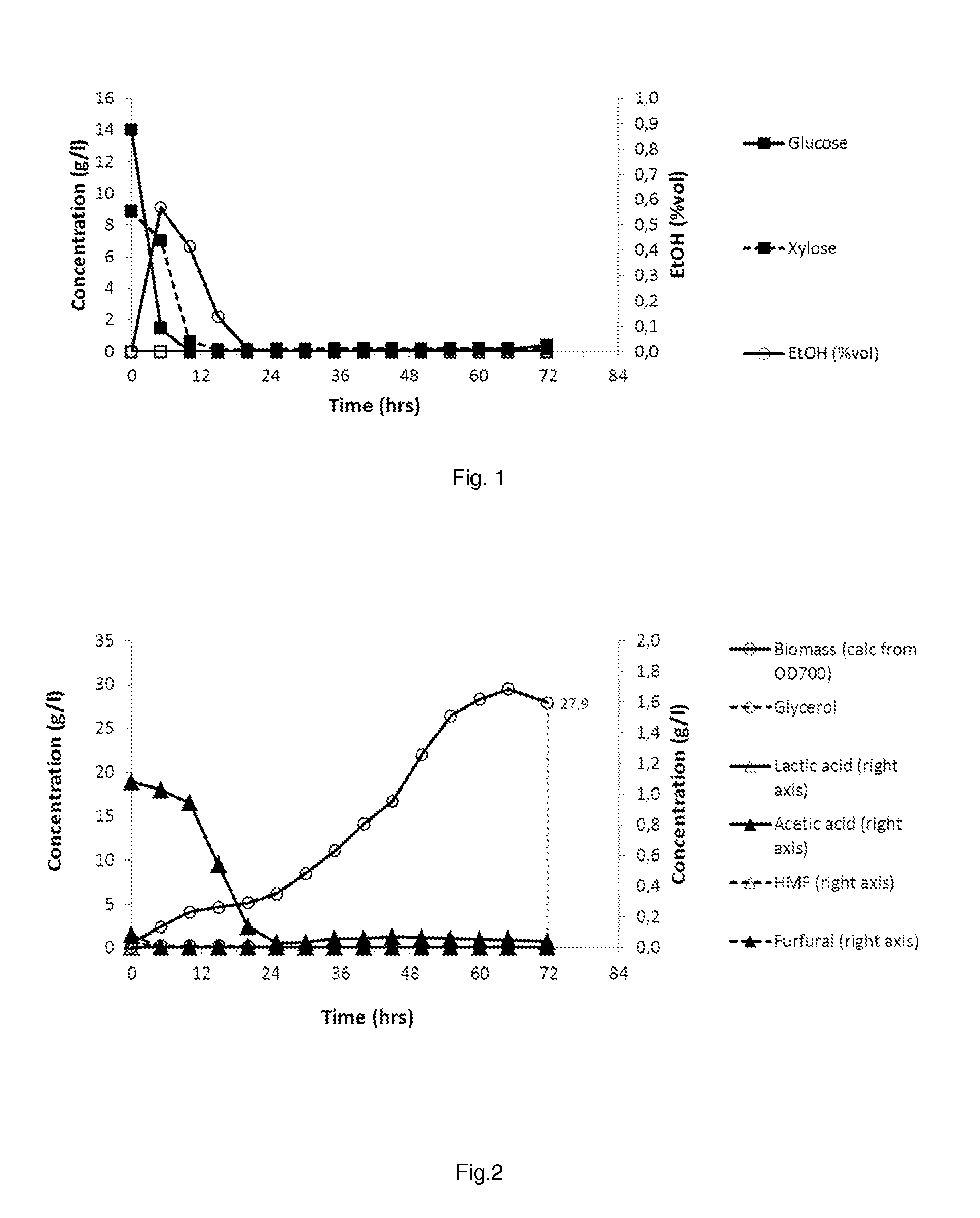
[0092]In example 1, as lignocellulosic hydrolysate, enzymatically hydrolyzed pretreated corn stover (17% dry matter) was used. The composition of the hydrolysate is given in table 1.
TABLE 1Composition of the lignocellulosic hydrolysate(HPLC (H-column) analysis)Glucose(g / l)69.8Xylose(g / l)43.4Glycerol(g / l)0.2Formic acid(g / l)0.2Acetic acid(g / l)5.1Ethanol(% vol)0HMF(g / l)0.19Furfural(g / l)0.98Arabinose(g / l)5.2
Fermentation Parameters
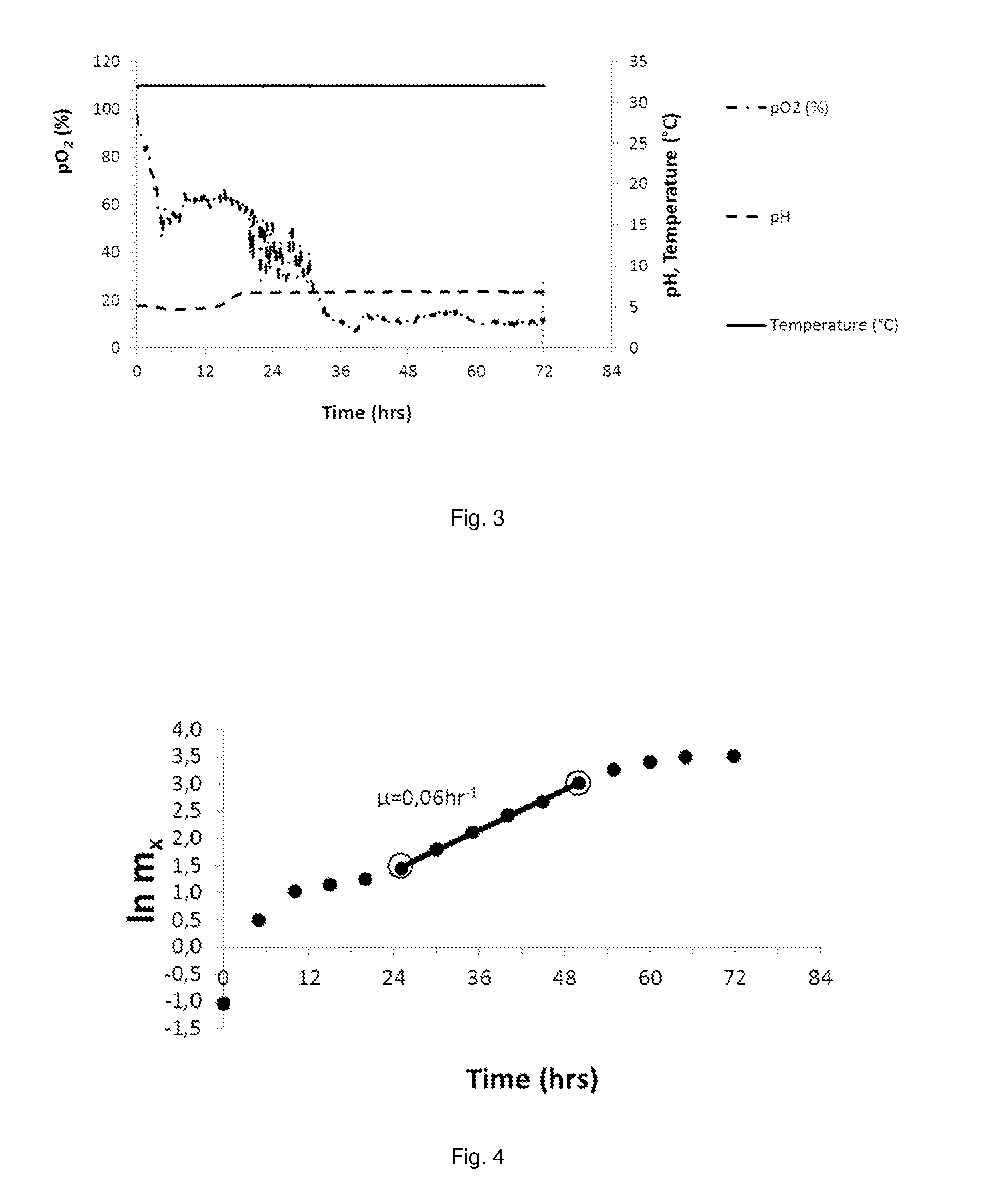
[0093]A fed batch propagation reactor (1500 ml ) was filled with 709 g 5 times diluted lignocellulosic hydrolysate. There was added 0.2 g / l MgSO4, 1.1 g / l (NH4)2SO4, 4.5 g / l urea, 4 ml / l vitamin solution and 4 ml / l trace elements (As in Verduyn et al, 1992, ref. see below). The pH was adjusted to 5 with NH4OH. Temperature was of the fed batch reactor was controlled at 32° C. Dissolved oxygen levels were kept above 9% by aeration at 3 vvm (final volume) in combination with a stirring cascade (controlled between 200-700 rpm). Starting volume of the propagation ex...
example 2
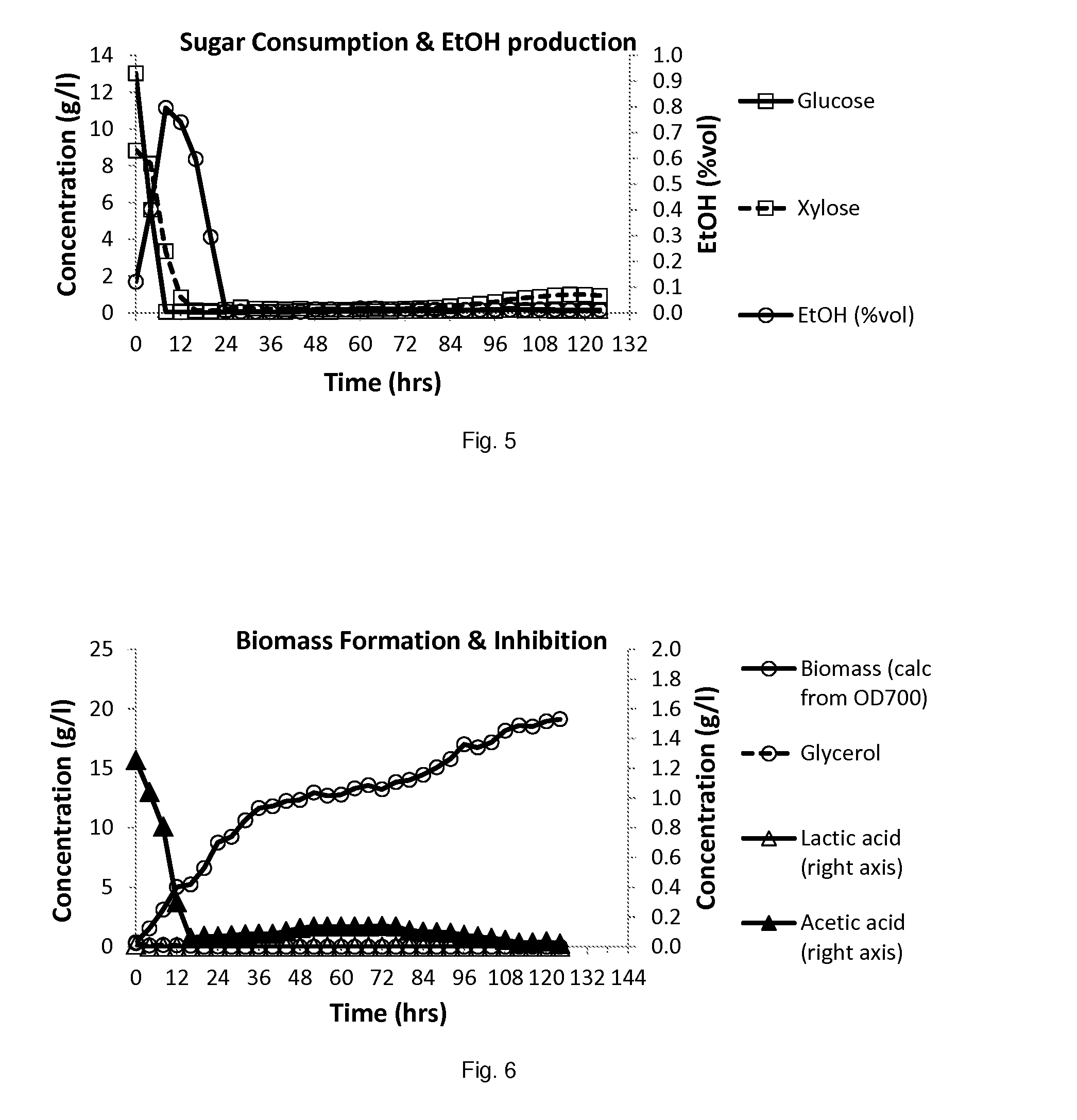
[0098]In example 2, as lignocellulosic hydrolysate, enzymatically hydrolyzed pretreated corn stover (17% dry matter) was used. The composition of the hydrolysate is given in table 2.
TABLE 2Composition of the lignocellulosic hydrolysate(HPLC (H-column) analysis)Glucose(g / l)68.2Xylose(g / l)44.8Glycerol(g / l)0.0Formic acid(g / l)0.3Acetic acid(g / l)5.2Ethanol(% vol)0HMF(g / l)0.18Furfural(g / l)1.02Arabinose(g / l)5.2
Fermentation Parameters
[0099]A fed batch propagation reactor (1500 ml) was filled with 709 g 5 times diluted lignocellulosic hydrolysate. There was added 0.2 g / l MgSO4, 1.1 g / l KH2PO4, 4.5 g / l urea, 4 ml / l vitamin solution and 4 ml / l trace elements (As in Verduyn et al, 1992, ref. see below). The pH was of the hydrolysate (4.3) was not adjusted after enzymatic hydrolysis. Temperature was of the fed batch reactor was controlled at 32° C. Dissolved oxygen levels were kept above 9% by aeration at 3 vvm (final volume) in combination with a stirring cascade (controlled between 200-700 rpm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com