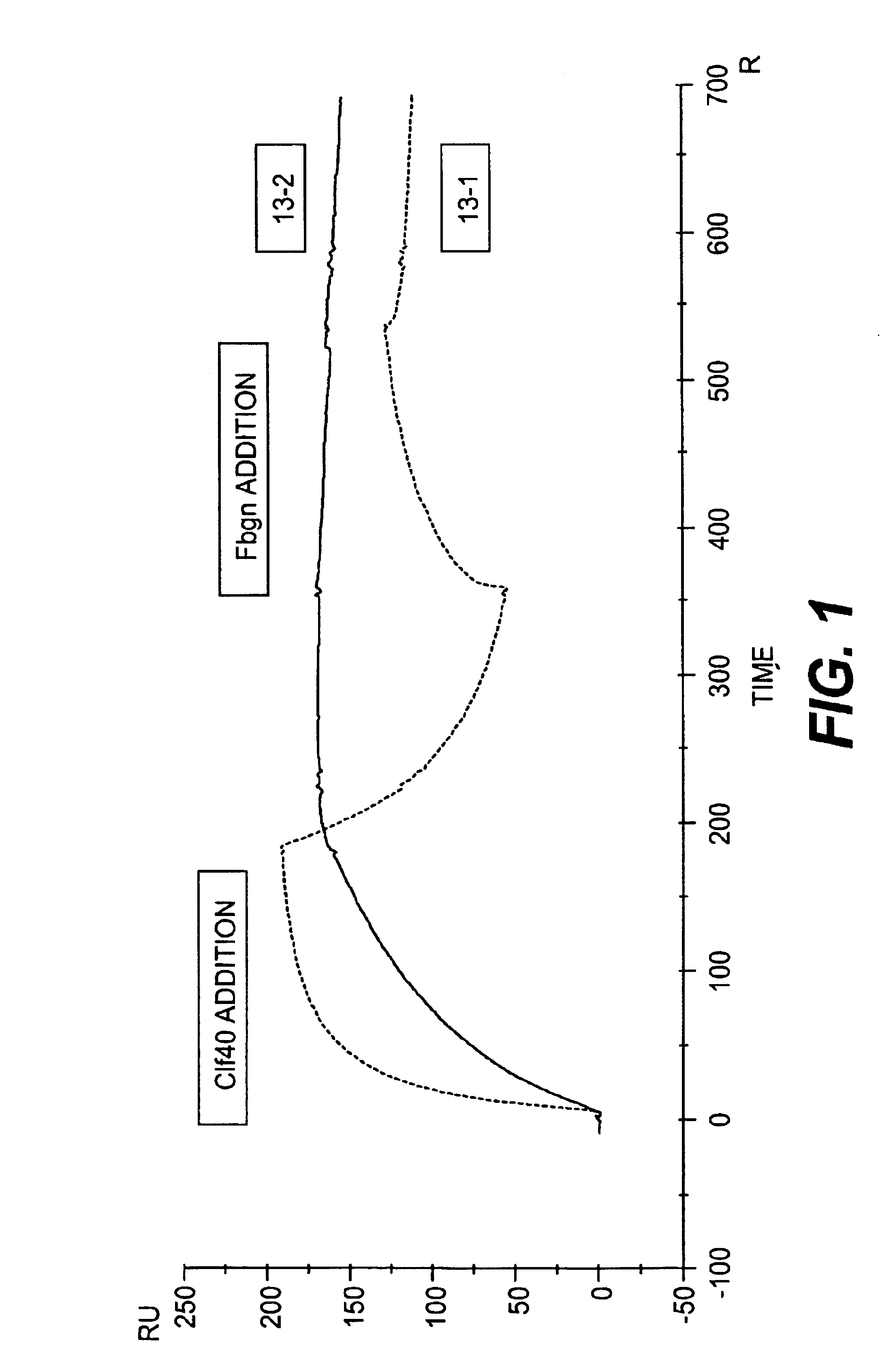
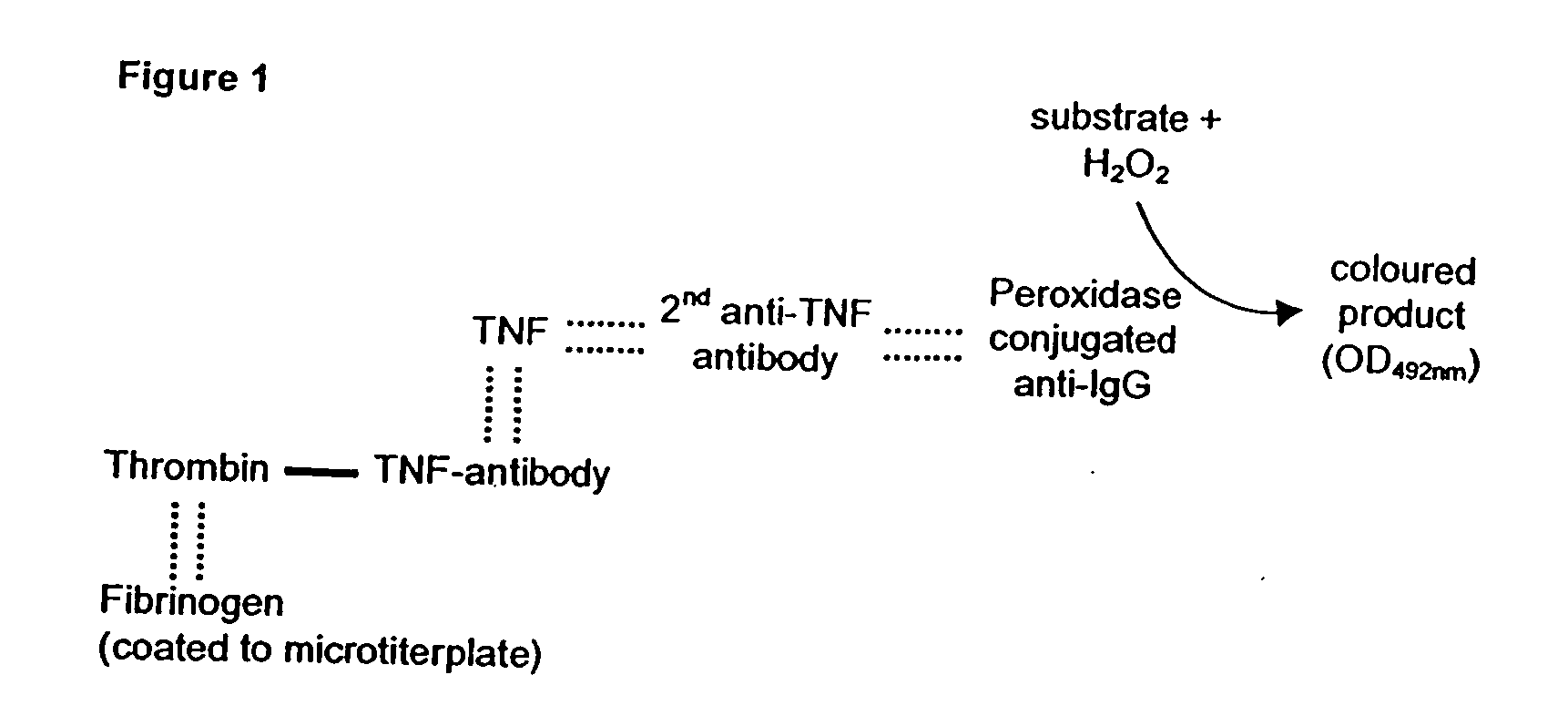
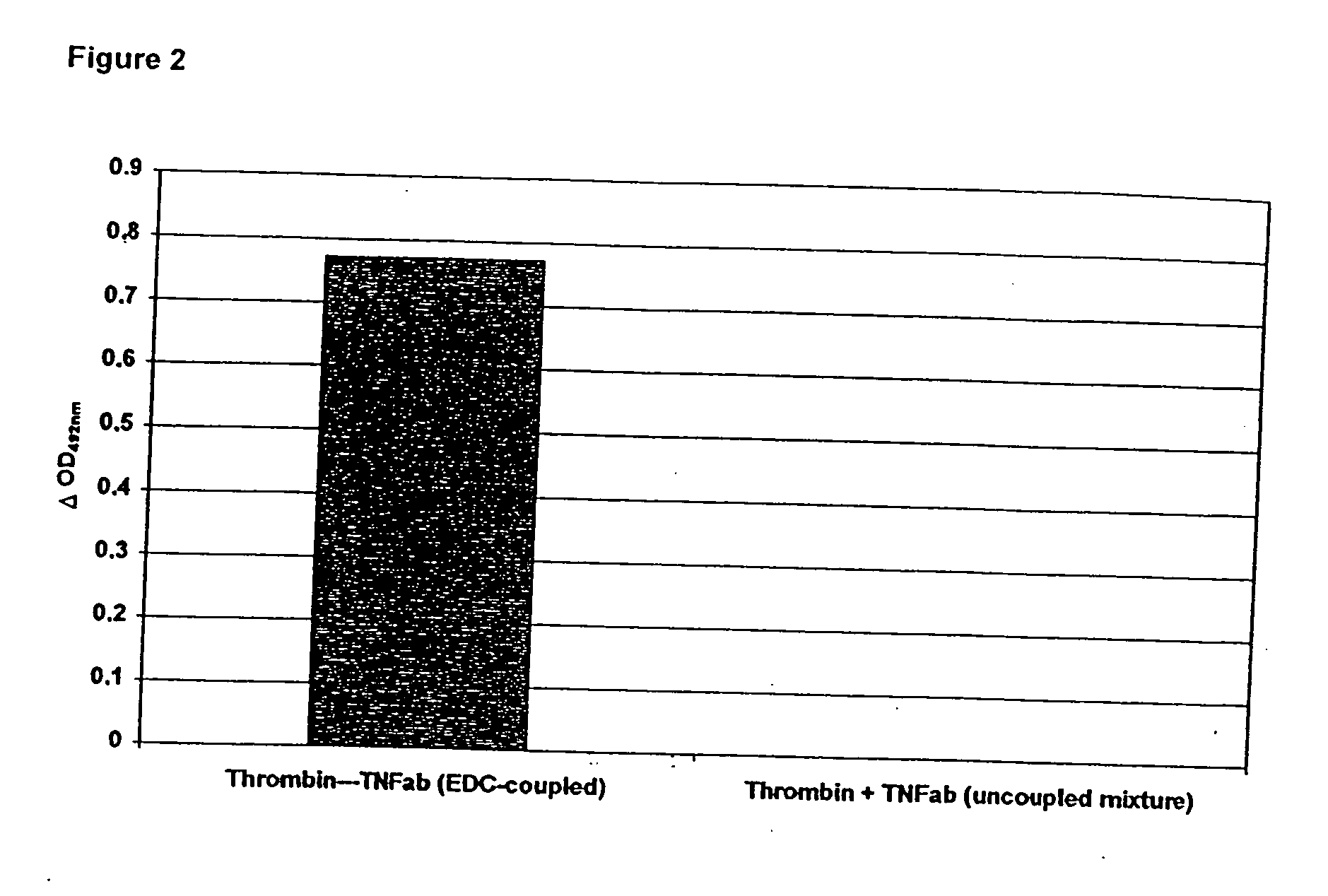
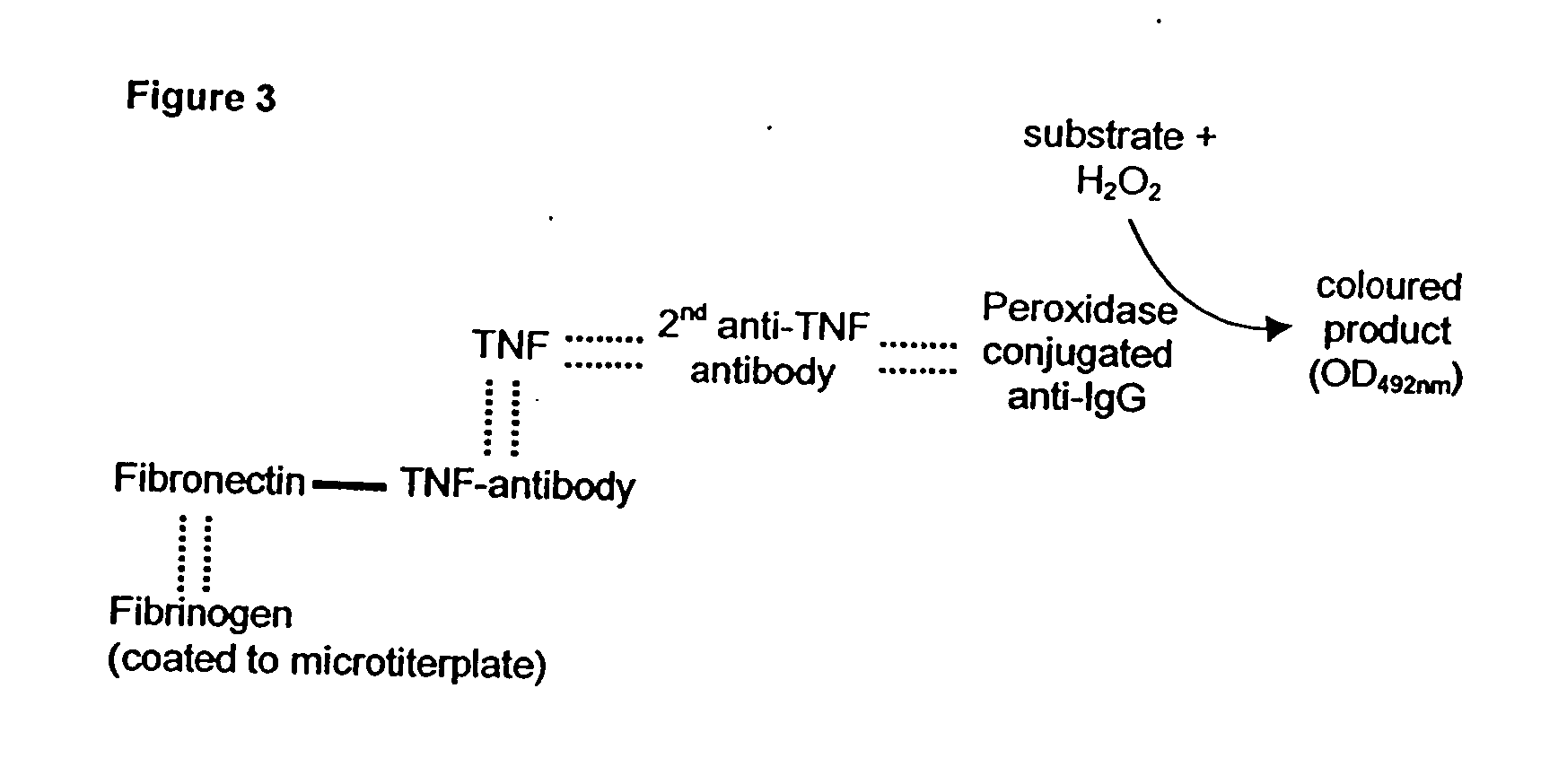
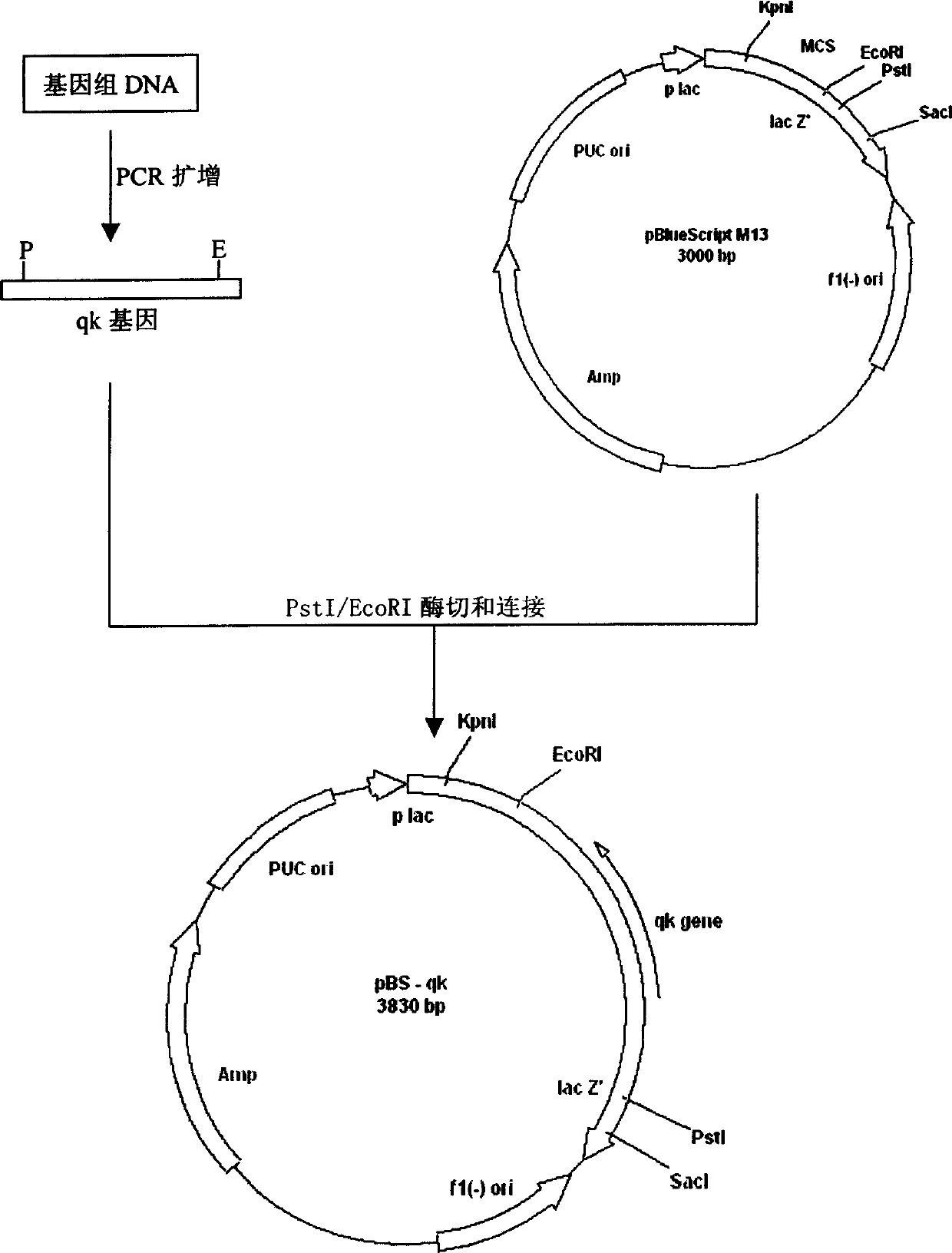
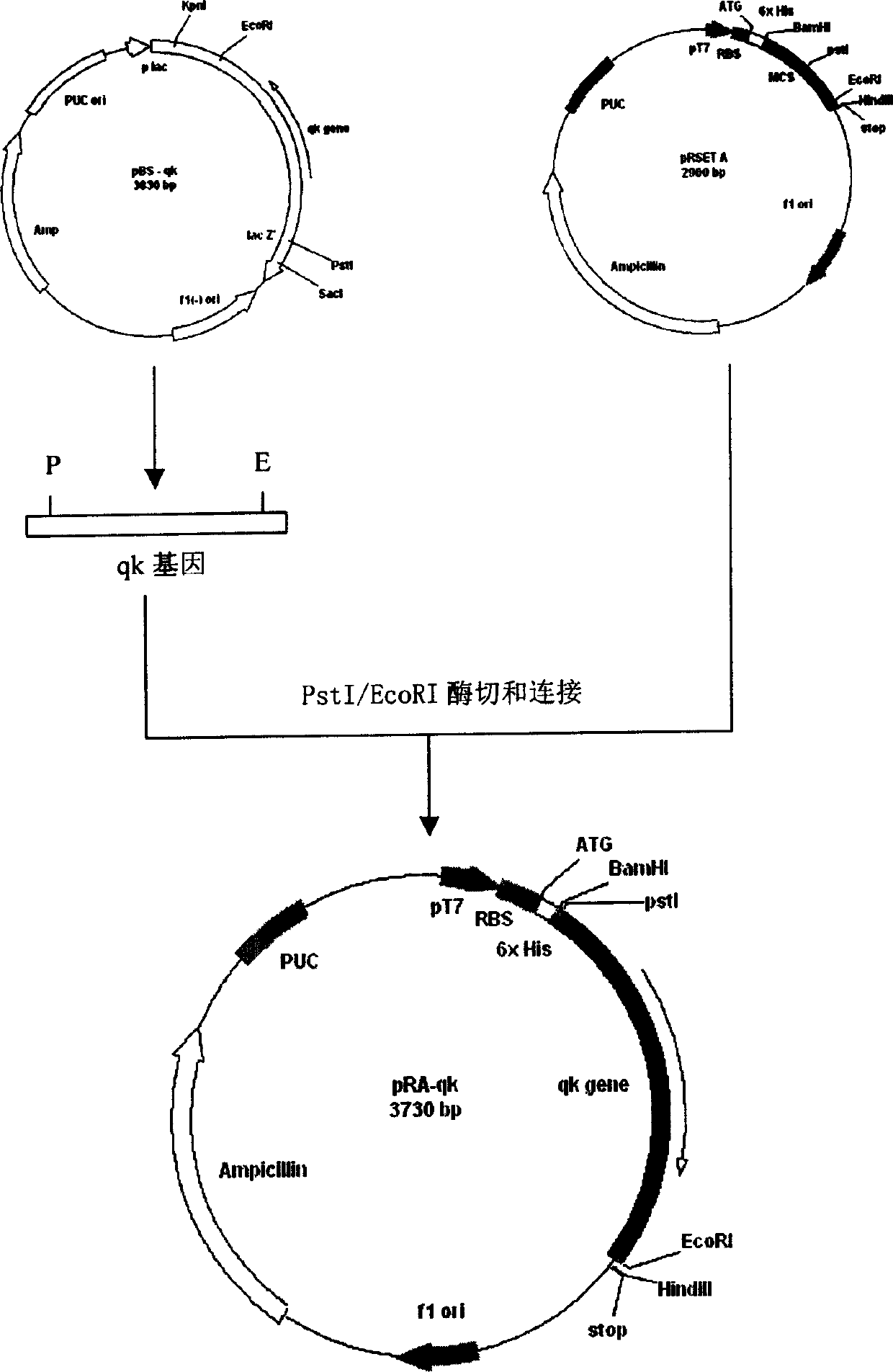
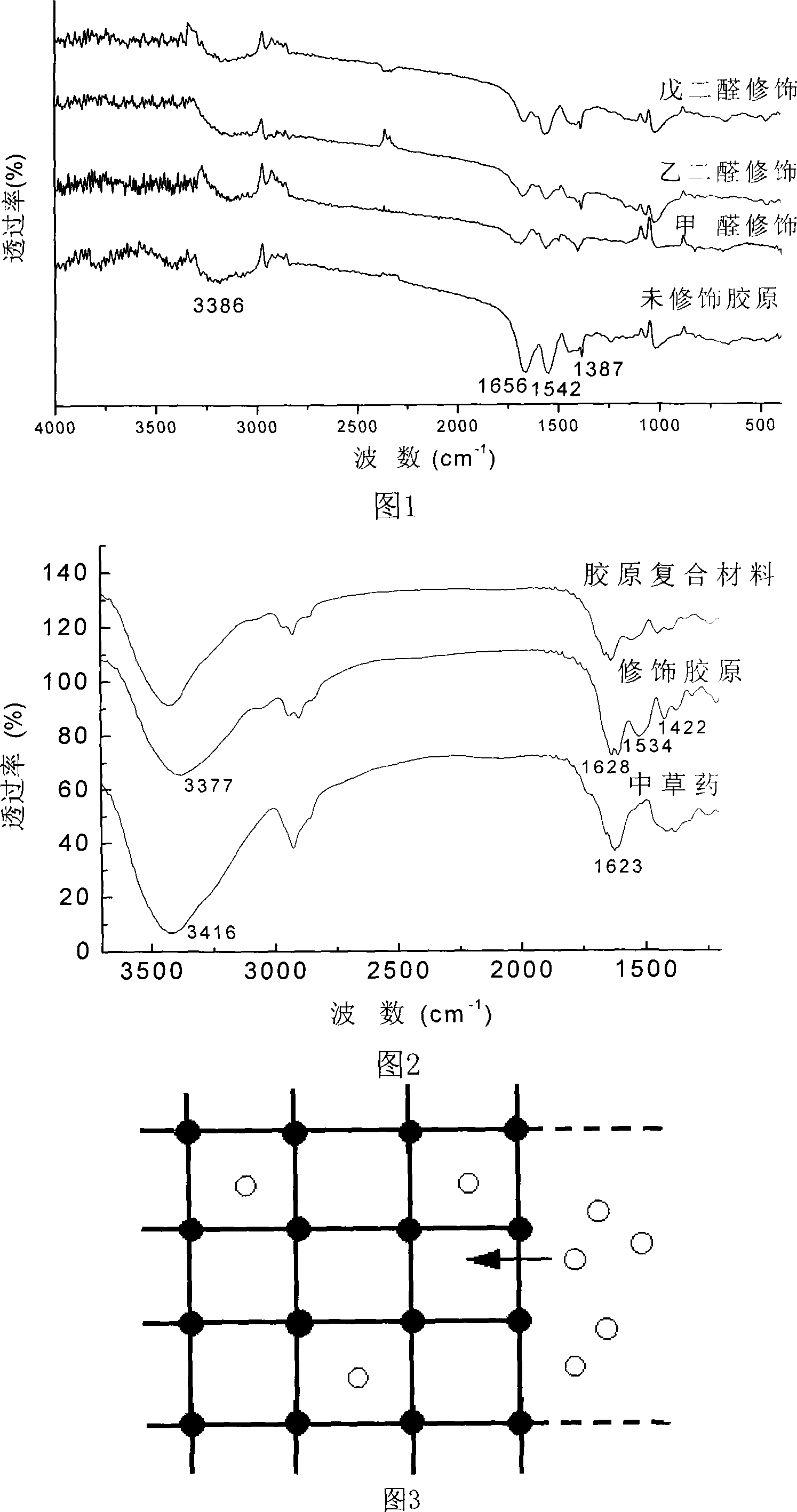
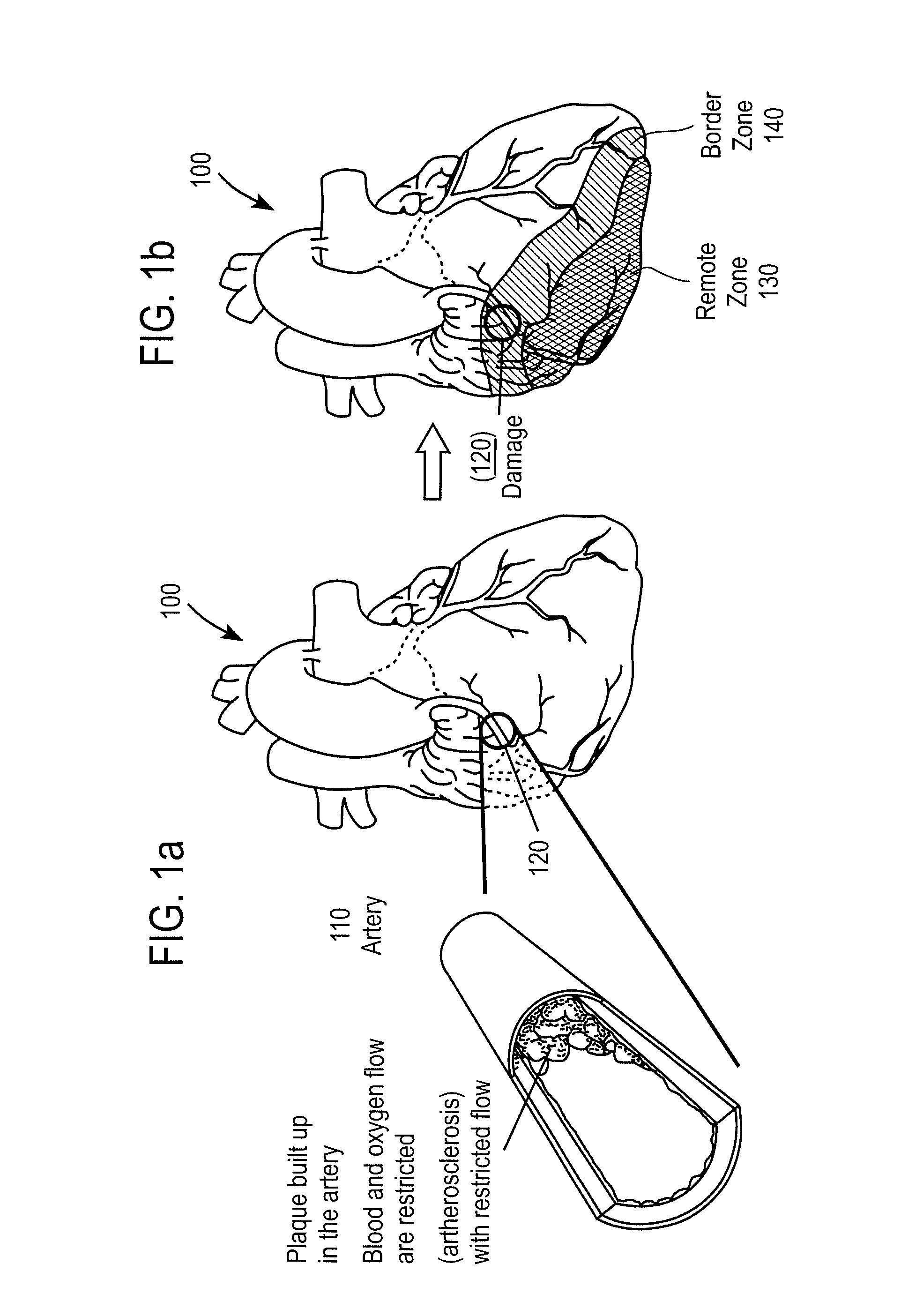
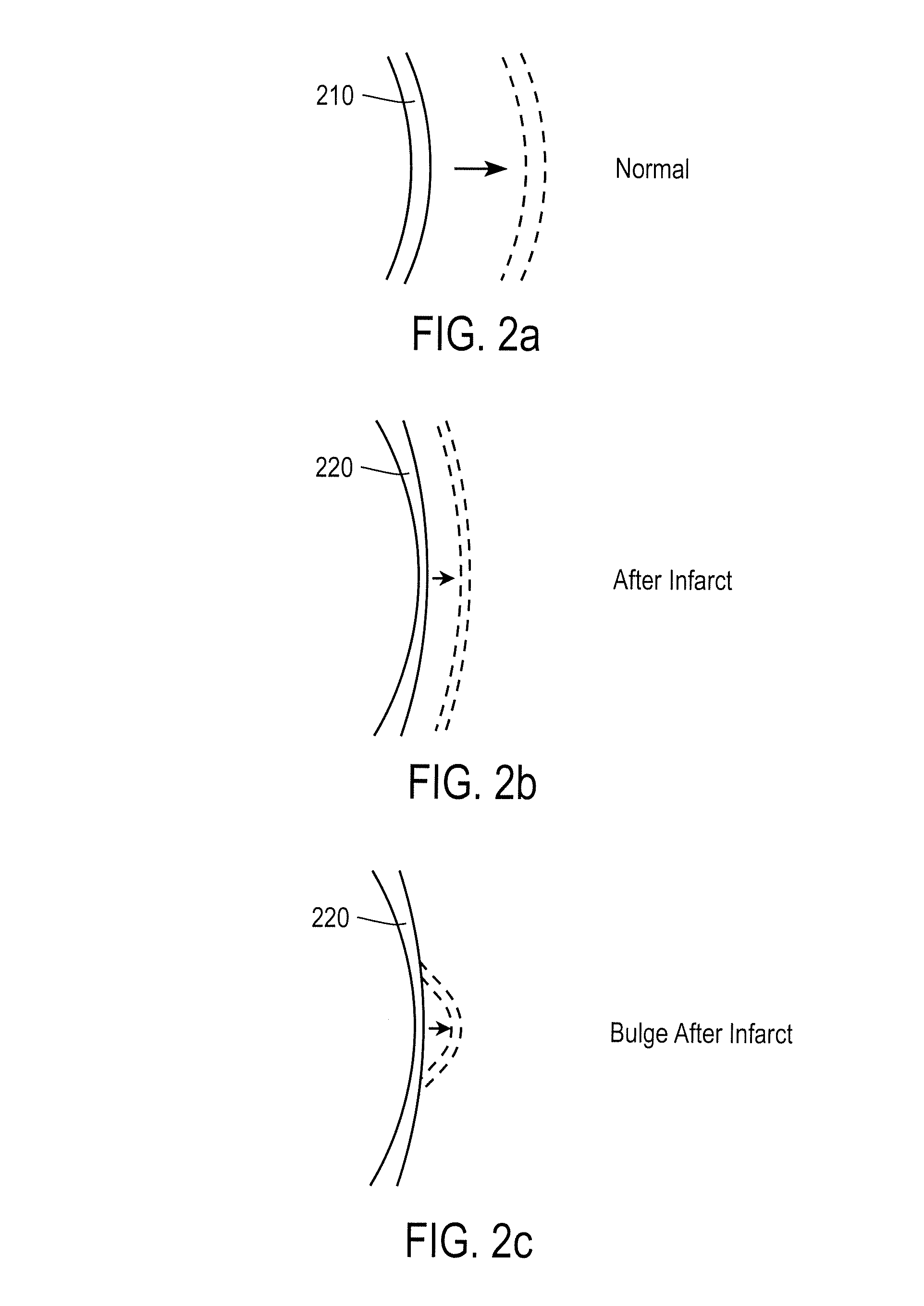
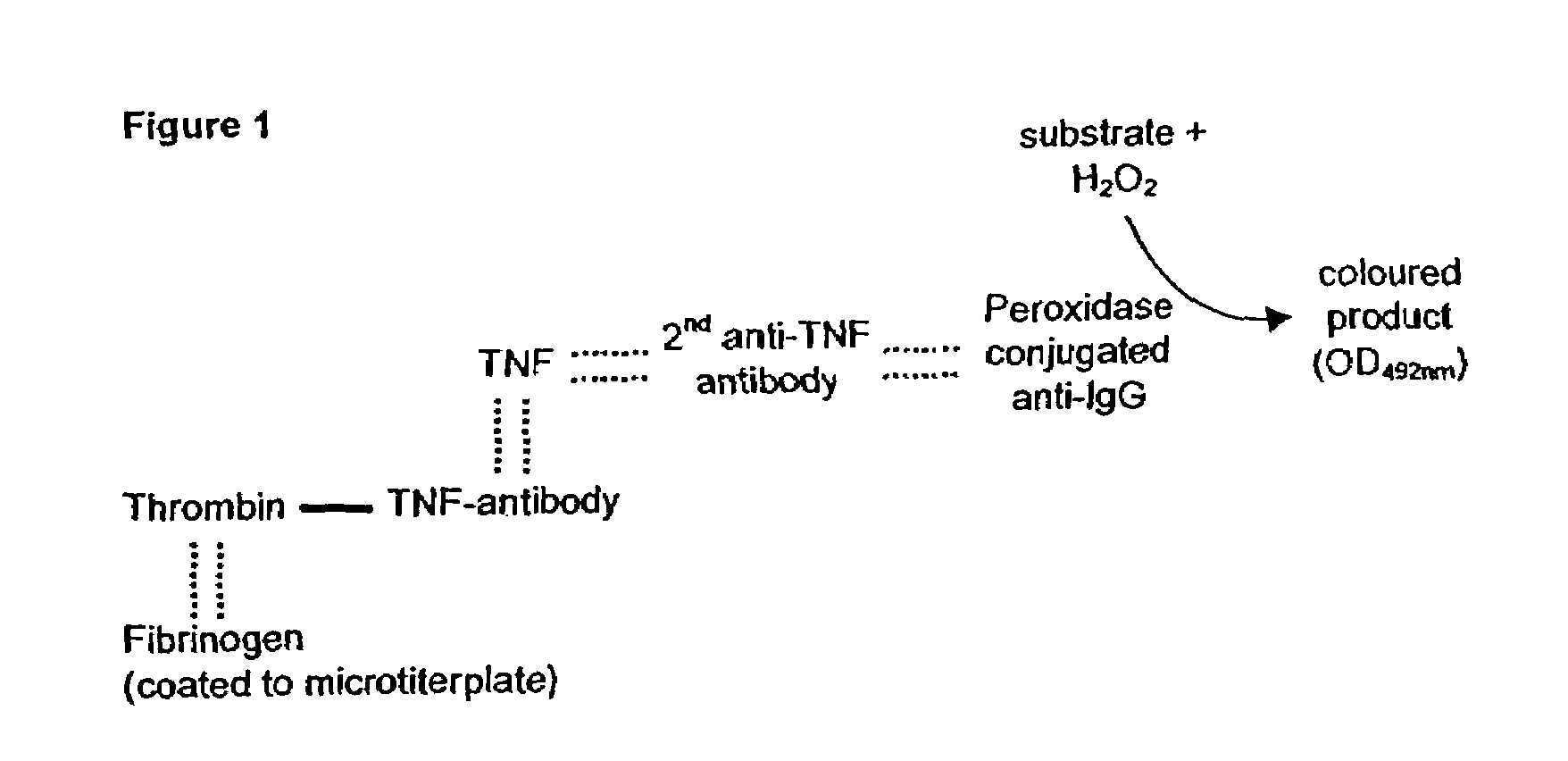
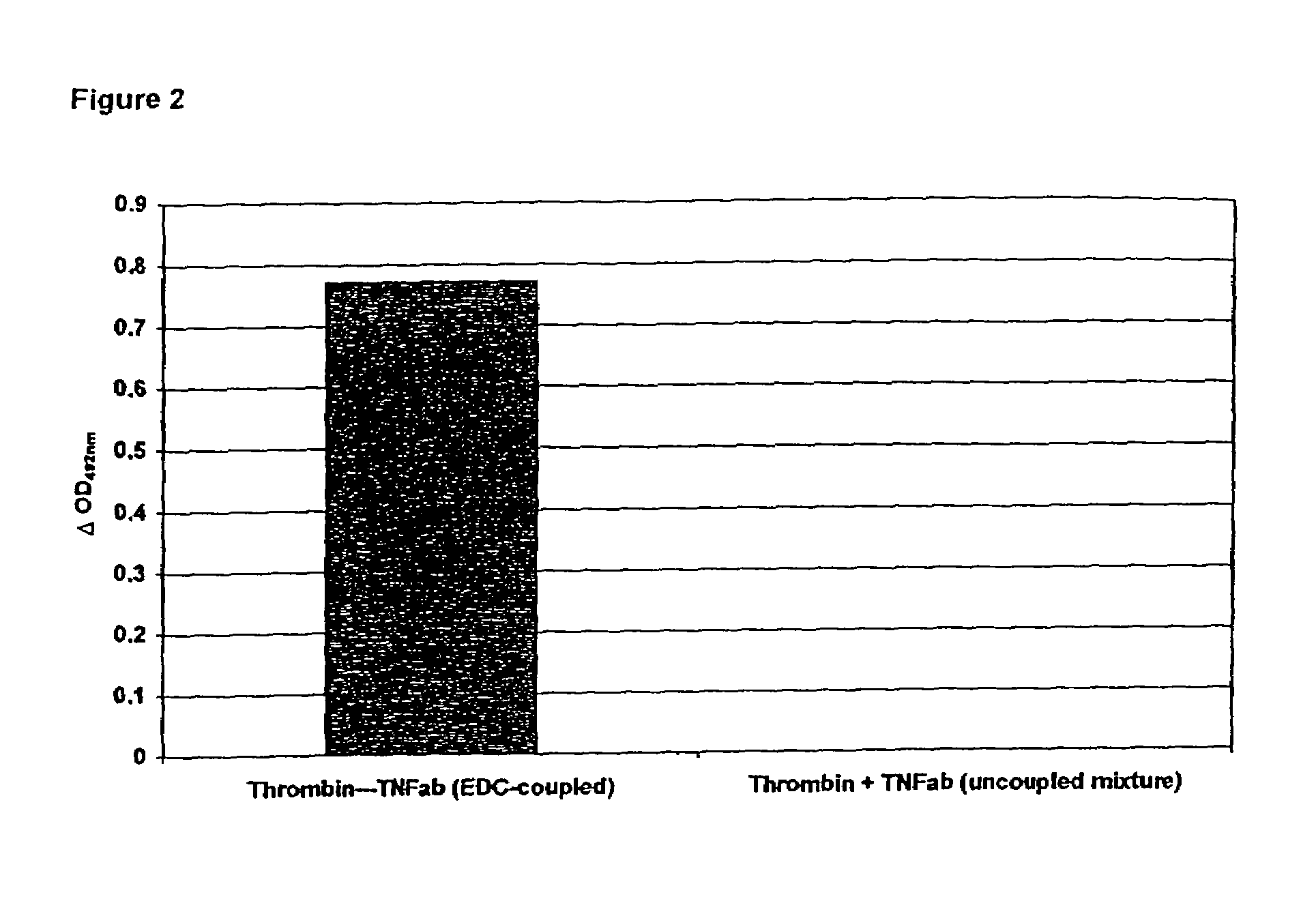
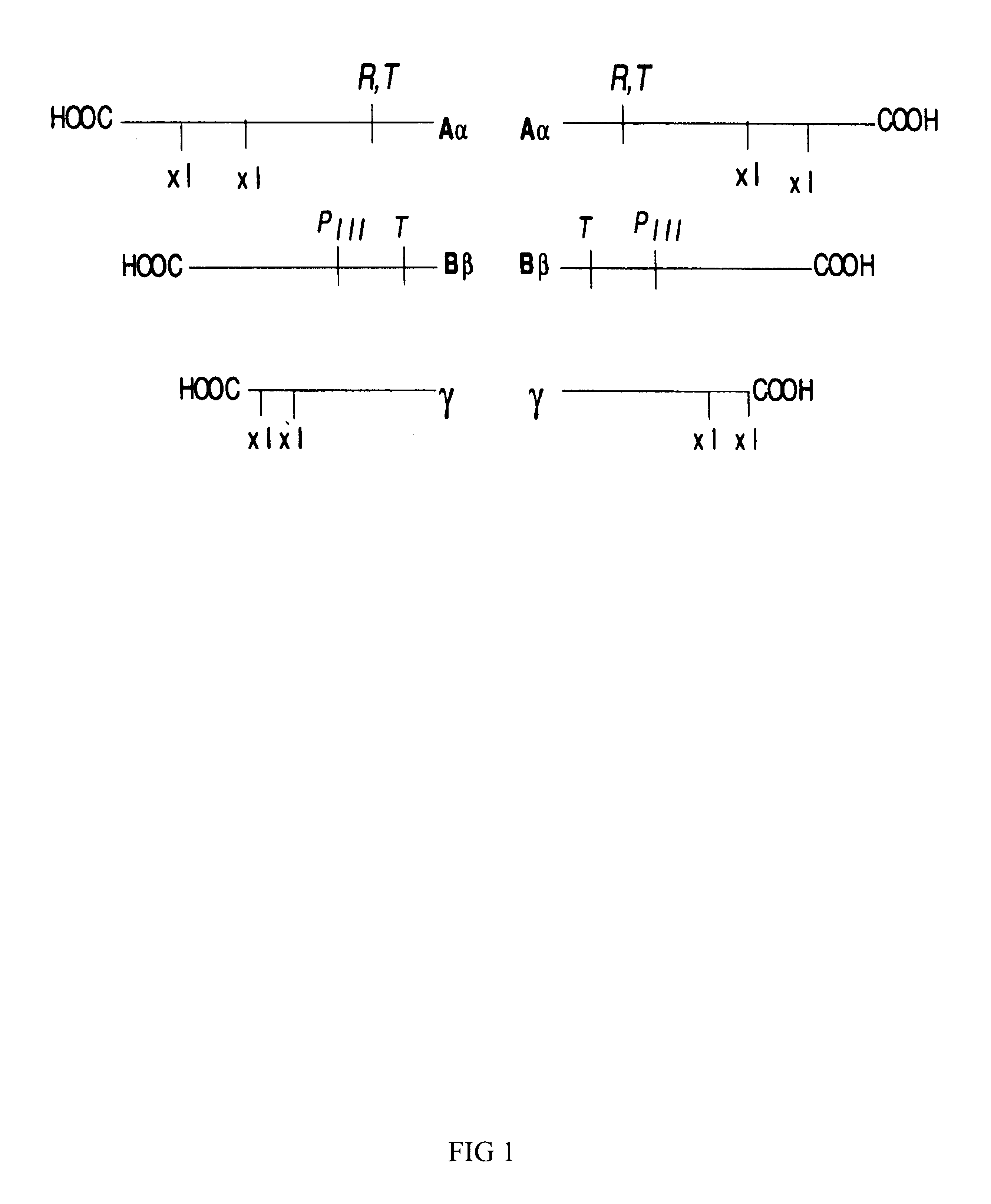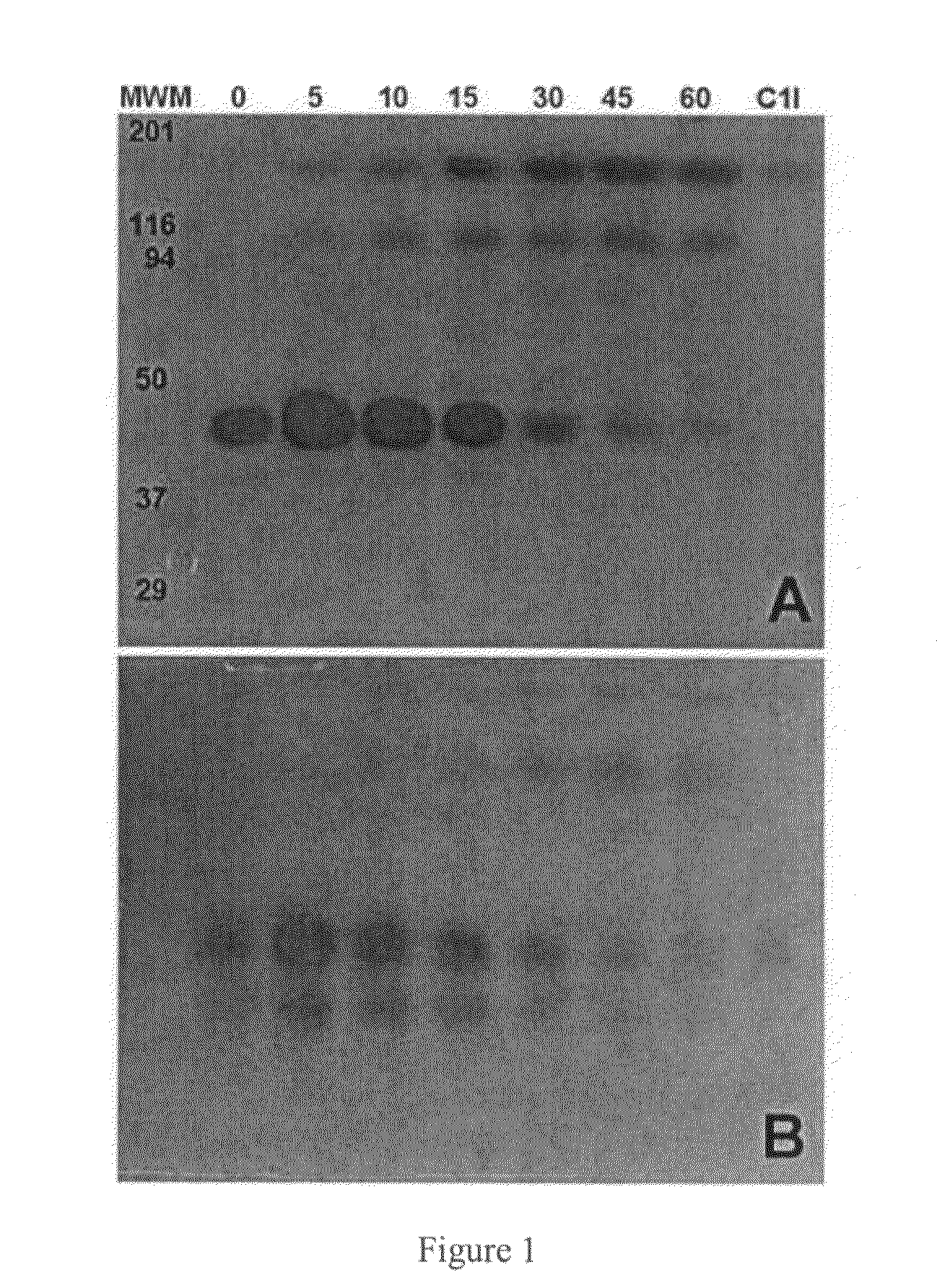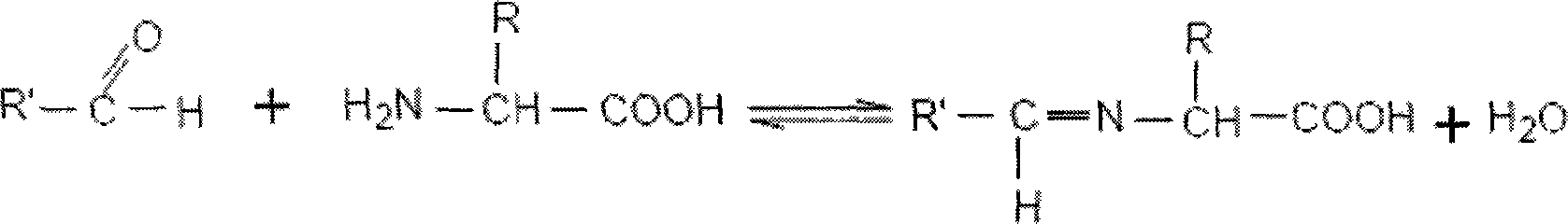Patents
Literature
102 results about "FIBRINOGEN/THROMBIN" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
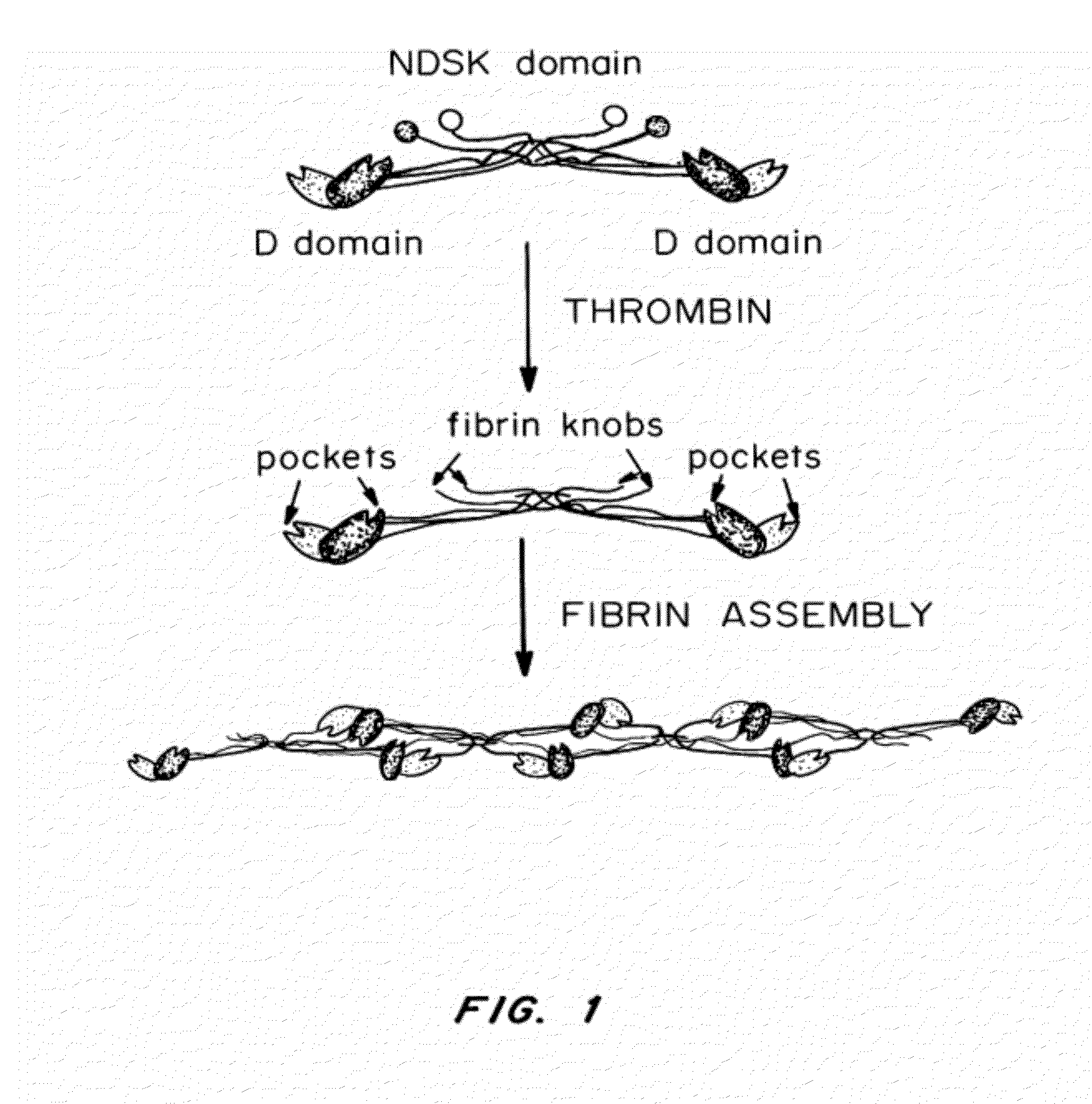
Fibrin (also called Factor Ia) is a fibrous, non-globular protein involved in the clotting of blood. It is formed by the action of the protease thrombin on fibrinogen which causes it to polymerize. The polymerized fibrin together with platelets forms a hemostatic plug or clot over a wound site.
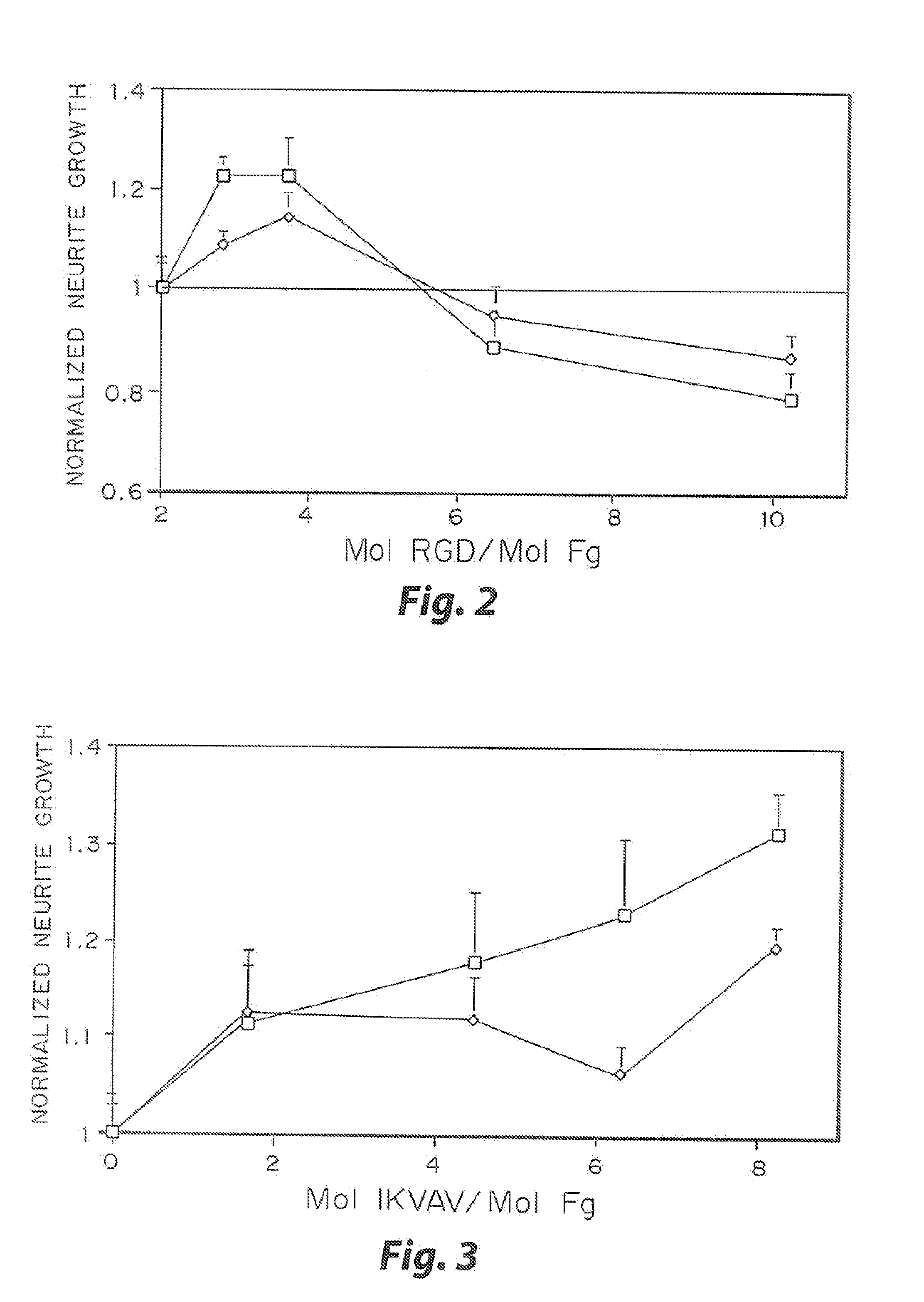
Enzyme-mediated modification of fibrin for tissue engineering
The invention provides fibrin-based, biocompatible materials useful in promoting cell growth, wound healing, and tissue regeneration. These materials are provided as part of several cell and tissue scaffolding structures that provide particular application for use in wound-healing and tissue regenerating. Methods for preparing these compositions and using them are also disclosed as part of the invention. A variety of peptides may be used in conjunction with the practice of the invention, in particular, the peptide IKVAV, and variants thereof. Generally, the compositions may be described as comprising a protein network (e.g., fibrin) and a peptide having an amino acid sequence that comprises a transglutaminase substrate domain (e.g., a factor XIIIa substrate domain) and a bioactive factor (e.g., a peptide or protein, such as a polypeptide growth factor), the peptide being covalently bound to the protein network. Other applications of the technology include their use on implantable devices (e.g., vascular graphs), tissue and cell scaffolding. Other applications include use in surgical adhesive or sealant, as well as in peripheral nerve regeneration and angiogenesis.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
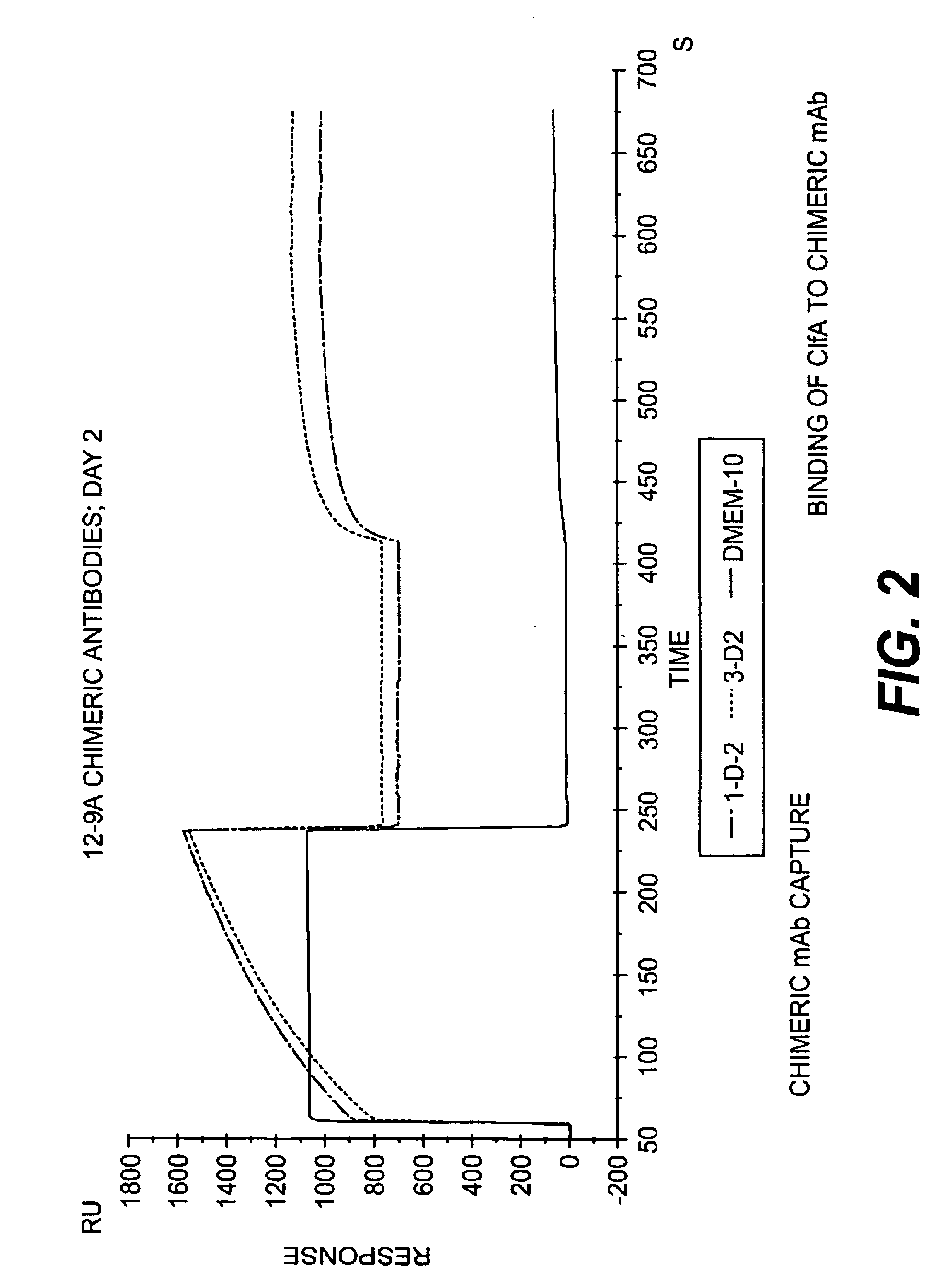
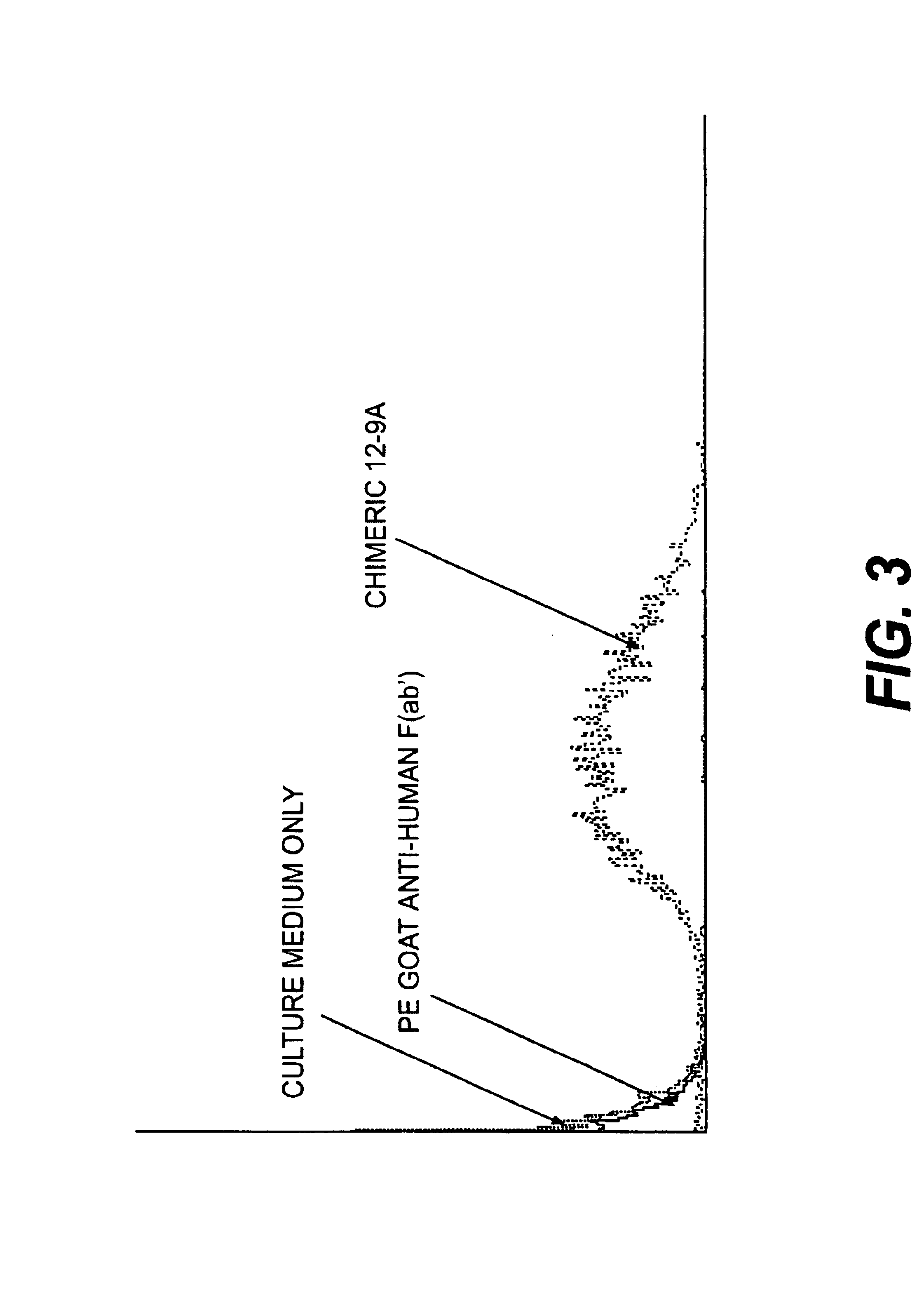
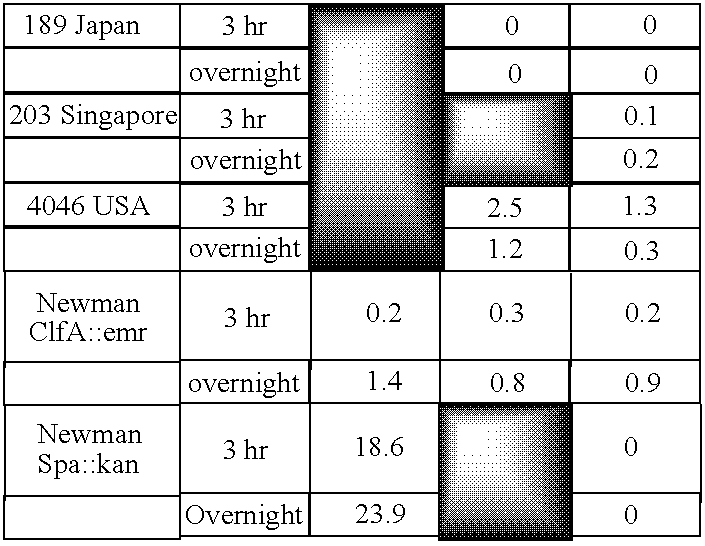
Monoclonal antibodies to the ClfA protein and method of use in treating or preventing infections
InactiveUS6979446B2Avoid stickingInhibiting or impairing the binding of the ClfA proteinAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteroidesStaphylococcus cohnii
Monoclonal antibodies which can bind to the ClfA protein and which are generated from binding subdomains or active fragments of the ClfA protein from Staphylococcus aureus, including the active fragments proteins from its fibrinogen binding domain such as Clf40 protein, the Clf33 protein, or ClfA N3, are provided which can be useful in the treatment and protection against infection from staphylococcal bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus. In addition, medical instruments can be treated using the monoclonal antibodies of the invention in order to reduce or eliminate the possibility of their becoming infected or further spreading the infection. In particular, the antibodies of the present invention are advantageous because they can prevent adherence of the bacteria to host cells by impairing or inhibiting the ability of S. aureus ClfA to bind to fibrinogen or fibrin, and thus can be utilized in methods or treating or preventing staphylococcal inventions.
Owner:INHIBITEX INC
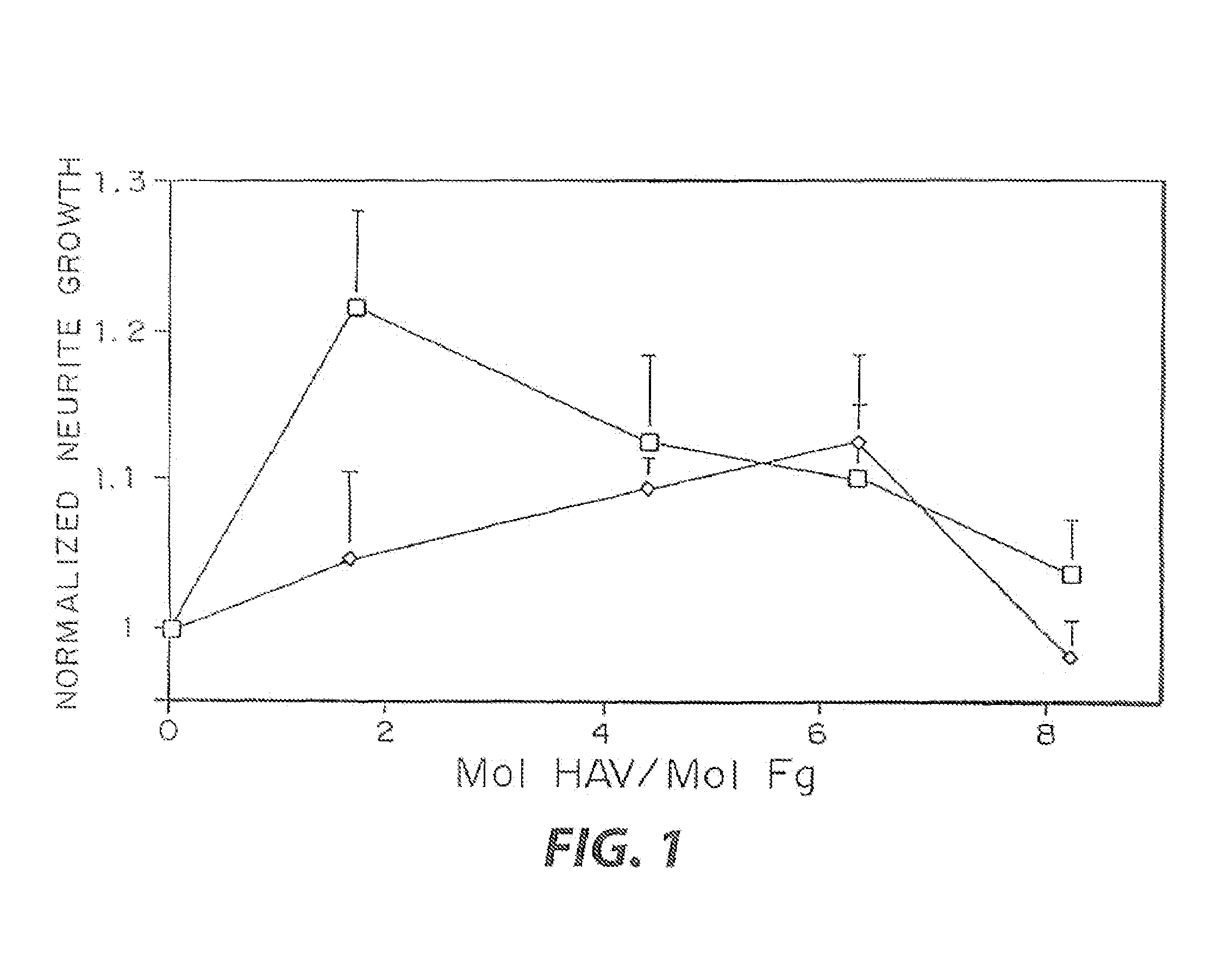
Enzyme-mediated modification of fibrin for tissue engineering: fibrin formulations with peptides
InactiveUS7241730B2Efficacious platformEnhanced andPeptide/protein ingredientsTransferasesCell Surface ProteinsADAMTS Proteins
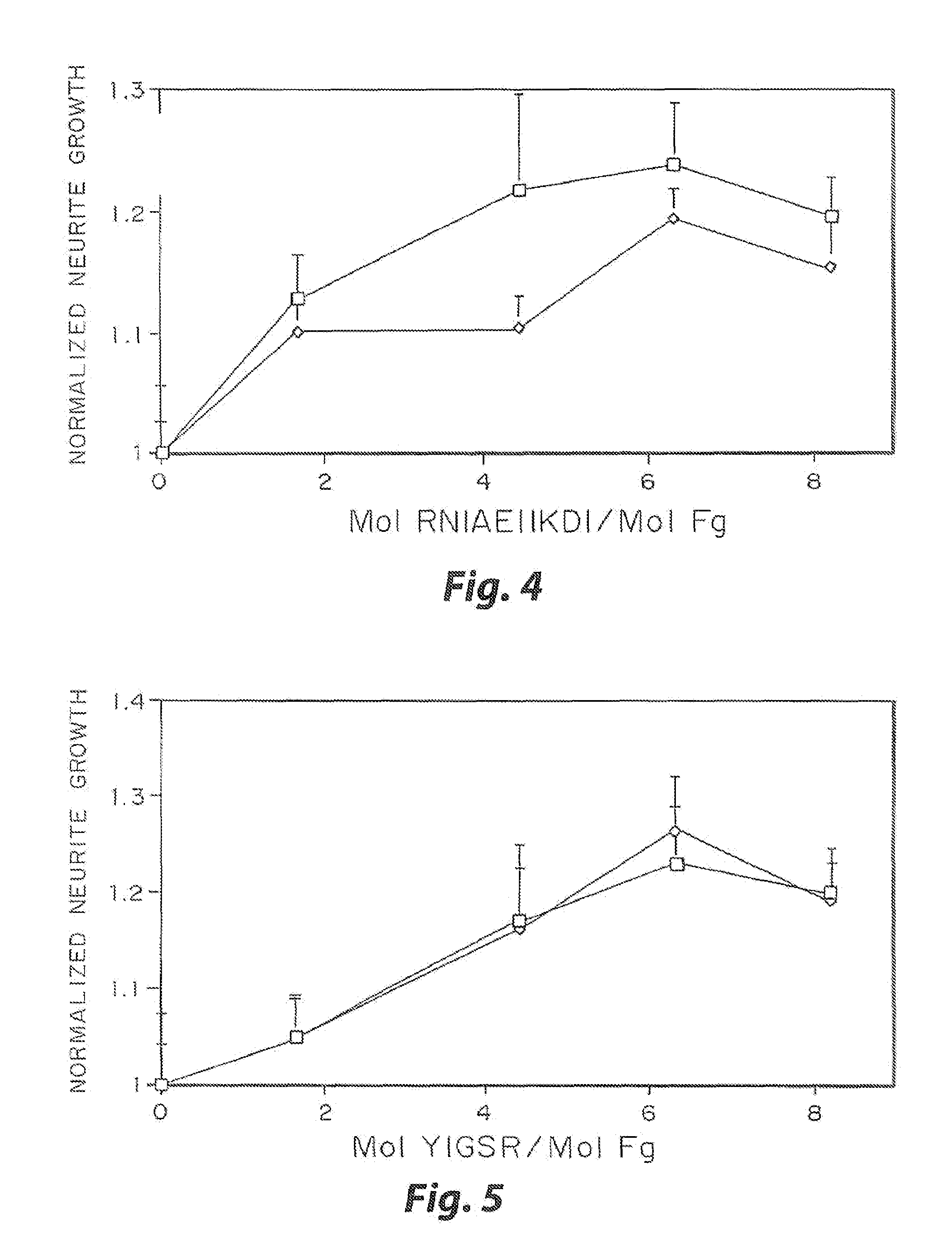
Heparin-binding regions of several proteins, such as neural cell adhesion molecule, fibronectin, laminin, midkine, and anti-thrombin III have been shown to promote neurite extension on two-dimensional surfaces. The effect of heparin-binding peptides on neurite extension through three-dimensional matrices was investigated by culturing embryonic chick dorsal root ganglia (DRG) within fibrin gels containing chemically attached heparin-binding peptide (HBP). The length of neurites within fibrin gels containing cross-linked HBP was increased by more than 70% over extension through fibrin gels containing no peptide. The HBP sequence of antithrombin III was incorporated into the fibrin gel as the C-terminal domain of a bidomian, chimeric peptide; the N-terminal second domain of this peptide contained the ∀2-plasmin inhibitor substrate for Factor XIIIa. Factor XIIIa, a transglutaminase, was used to chemically attach the HBP-containing chimeric peptide to the fibrin gels during polymerization. The amount of HBP cross-linked into the fibrin gels was determined, after degradation by plasmin using gel permeation chromatography, to be approximately 8 moles of peptide per mole fibrinogen. A peptide (HBP), where the cross-linking glutamine was replaced with glycine, showed no increase in extension in comparison with fibrin gels. The additional of heparin to the gel percursors resulted in no increase in neurite extension in comparison with fibrin gels. HBPs promote neurite extension by binding to cell surface proteoglycans on the DRG.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH +1
Hydrogel bioscaffoldings and biomedical device coatings
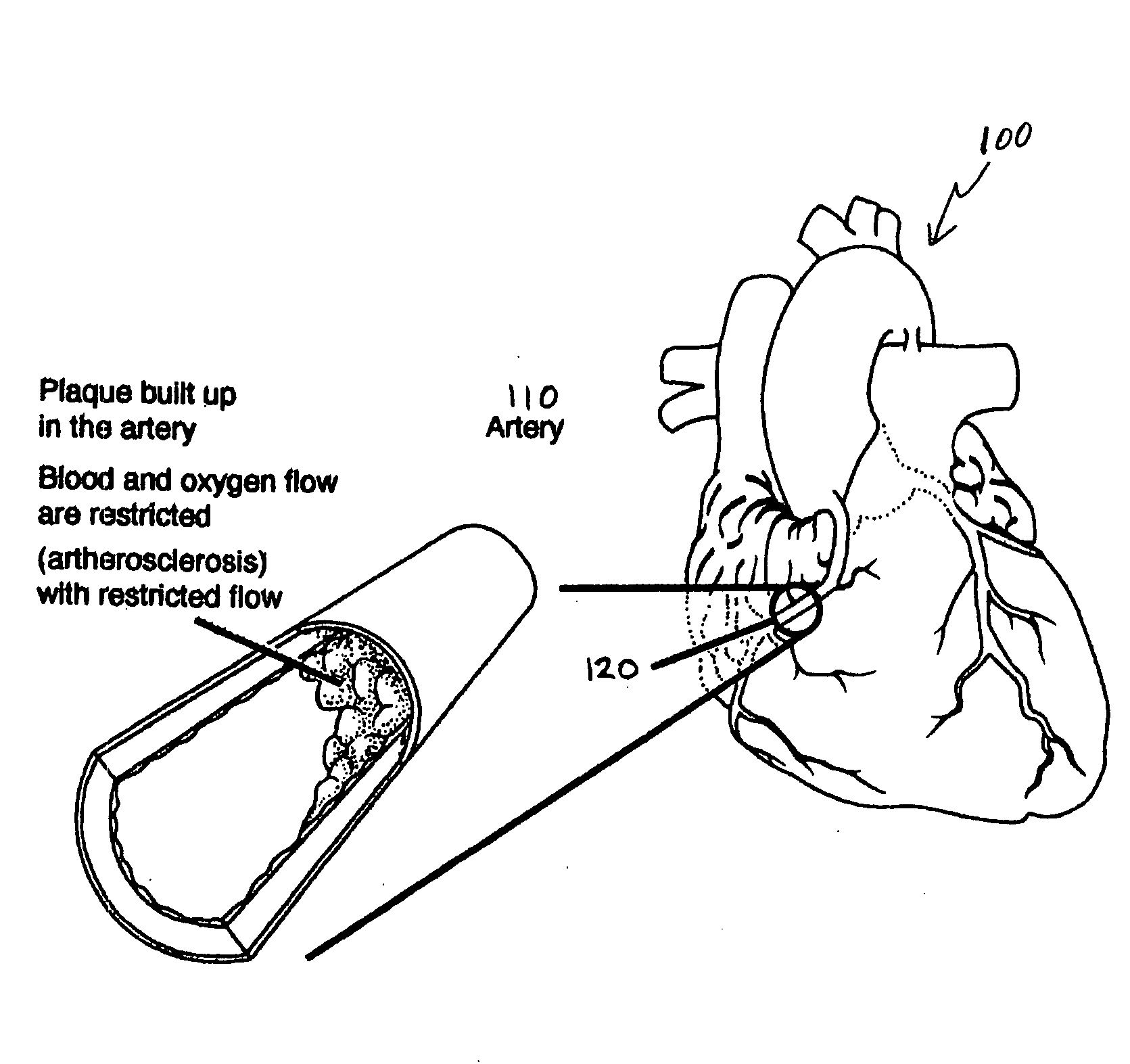
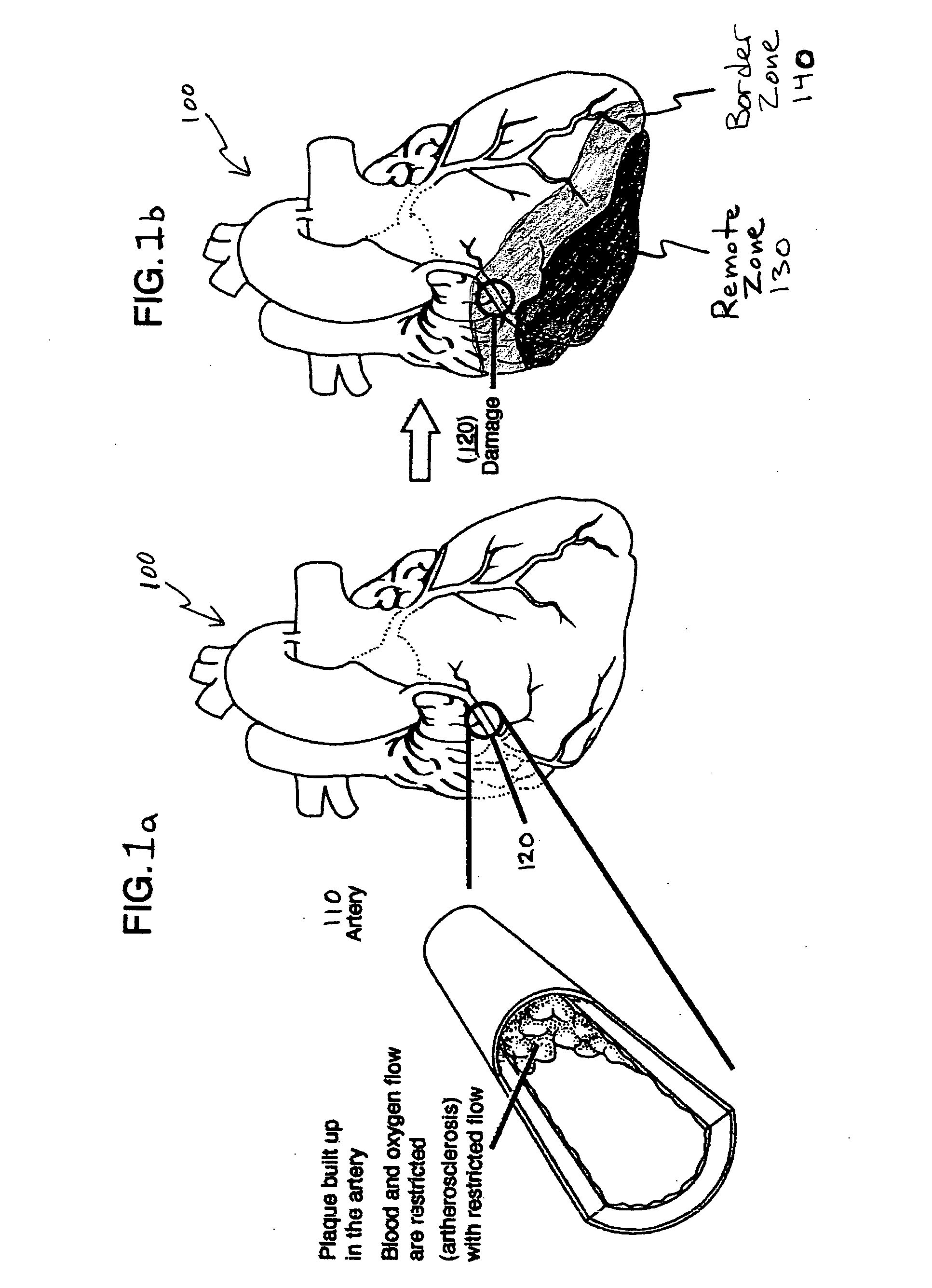
Bioscaffoldings formed of hydrogels that are crosslinked in situ in an infarcted region of the heart (myocardium) by a Michael's addition reaction or by a disulfide bond formed by an oxidative process are described. Each of the bioscaffoldings described includes hyaluronan as one of the hydrogel components and the other component is selected from collagen, collagen-laminin, poly-1-lysine, and fibrin. The bioscaffolding may further include an alginate component. The bioscaffoldings may have biofunctional groups such as angiogenic factors and stem cell homing factors bound to the collagen, collagen-laminin, poly-1-lysine, or fibrinogen hydrogel component. In particular, the biofunctional groups may be PR11, PR39, VEGF, bFGF, a polyarginine / DNA plasmid complex, or a DNA / polyethyleneimine (PEI) complex. Additionally, the hydrogel components may be injected into the infarct region along with stem cells and microspheres containing stem cell homing factors. The bioscaffolding may be formed on a stent or a cardiac medical device.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Suspension comprising fibrinogen, thrombin and alcohol, a method for preparing such a suspension, a method for coating a carrier with such a suspension, a method of drying a coating of a carrier, and a coated collagen sponge
InactiveUS20050214277A1Easy to identifySatisfy fixationSurgical adhesivesFibrinogenFiberMean diameter
A suspension of fibrinogen, thrombin, alcohol and optionally aprotinin is obtained by mixing fibrinogen in alcohol with thrombin in alcohol. The suspension contains fibrinogen and thrombin particles with a Folk Ward mean diameter of 25-100 μm. The thrombin may be human, bovine or recombinant. The fibrinogen may be human or recombinant. A method for coating a carrier, such as a collagen sponge, with the suspension, and a method for drying the coating is disclosed. The coated collagen carrier may be used as a ready-to-use absorbable composition for tissue gluing, tissue sealing and hemostasis wherein the carrier is coated with solidly fixed components of fibrin glue, i.e. fibrinogen and thrombin.
Owner:SCHAUFLER ALFRED
Enzyme-mediated modification of fibrin for tissue engineering: incorporation of proteins
InactiveUS6960452B2Improve fidelityHigh activityPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsDrug biological activityBiology
Owner:ETH ZZURICH +1
Immunoassay of PIVKA-II
InactiveUS6893831B1Immune reactionInhibit enzyme activityImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsPeptide/protein ingredientsSerum igeThrombin activity
The present invention provides an immunoassay for specifically measuring with high sensitivity PIVKA-II in serum or plasma through antigen-antibody reaction by adding an animal serum containing thrombin and / or an antibody reacting with human fibrin-like related substances to the reagents. The immunoassay of the invention comprises the steps of adding thrombin and / or an antibody reacting with human fibrin-like related substances to the reagents, and measuring PIVKA-II in serum or plasma.
Owner:SEKISUI MEDICAL CO LTD
Fibrinogen binding moieties
ActiveUS7041790B2Increased serum half-lifeExtended half-lifeFibrinogenMammal material medical ingredientsBinding peptideFibrinogen binding
Compositions comprising non-naturally occurring fibrinogen binding moieties are described, together with methods of use thereof, e.g., for detecting or isolating fibrinogen molecules in a solution, for blood circulation imaging, and for linking therapeutics or other molecules to fibrinogen. Preferred binding peptides having a high affinity for fibrinogen are particularly disclosed.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Method of thrombolysis by local delivery of reversibly inactivated acidified plasmin
InactiveUS6964764B2Formula stableReduce capacityPeptide/protein ingredientsInorganic non-active ingredientsWhole bodyThrombus
Methods of thrombolysis that allow the use of a fibrinolytic composition comprising reversibly inactivated acidified plasmin and the localized delivery of the plasmin to a vascular thrombotic occlusion are disclosed. Further disclosed is a method for administering a therapeutic dose of a fibrinolytic composition substantially free of plasminogen activator to a human or animal having a vascular thrombotic occlusion. The fibrinolytic composition includes a reversibly inactivated acidified plasmin substantially free of plasminogen activator. Intravascular catheter delivery of the fibrinolytic composition directly into or in the immediate vicinity of the thrombus is disclosed to minimize the systemic degradation of fibrin while retaining the maximum plasmin activity against the thrombus.
Owner:GRIFOLS THERAPEUTICS LLC
Water soluble reactive derivatives of carboxy polysaccharides and fibrinogen conjugates thereof
ActiveUS20100086594A1Inhibit productionHigh yieldAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryTissue repairWater soluble
The present invention provides water-soluble reactive esters of carboxy polysaccharides and derivatives thereof. The reactive carboxy polysaccharide derivatives are useful per se in aqueous solutions or specifically for the formation of water-soluble covalent fibrinogen conjugates. A preferred conjugate is a hyaluronic acid-fibrinogen conjugate and fibrin adhesive, clot or matrix derived from it. Methods of preparation and methods of use in tissue repair and regeneration are also disclosed.
Owner:HEPACORE LTD
Monoclonal antibodies to the ClfA protein and method of use in treating or preventing infections
InactiveUS20050287164A1Avoid stickingInhibiting or impairing the binding of the ClfA proteinAntibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBacteroidesStaphylococcus cohnii
Monoclonal antibodies which can bind to the ClfA protein and which are generated from binding subdomains or active fragments of the ClfA protein from Staphylococcus aureus, including the active fragments proteins from its fibrinogen binding domain such as Clf40 protein, the Clf33 protein, or ClfA N3, are provided which can be useful in the treatment and protection against infection from staphylococcal bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus. In addition, medical instruments can be treated using the monoclonal antibodies of the invention in order to reduce or eliminate the possibility of their becoming infected or further spreading the infection. In particular, the antibodies of the present invention are advantageous because they can prevent adherence of the bacteria to host cells by impairing or inhibiting the ability of S. aureus ClfA to bind to fibrinogen or fibrin, and thus can be utilized in methods or treating or preventing staphylococcal inventions.
Owner:INHIBITEX INC
Peptides for binding fibrinogen and fibrin
ActiveUS20120114682A1Promote healingPromote fibrinolysisFibrinogenSerum albuminCrystallographyFibrin Monomer
Compositions and methods for targeting substances to fibrinogen, fibrin monomers, or fibrin polymers are provided. These compositions and methods generally involve the use of fibrin knob peptides that bind fibrin(ogen), which can be used to detect fibrin(ogen) and modulate fibrin polymerization and fibrinolysis.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Enzyme-mediated modification of fibrin for tissue engineering
The invention provides fibrin-based, biocompatible materials useful in promoting cell growth, wound healing, and tissue regeneration. These materials are provided as part of several cell and tissue scaffolding structures that provide particular application for use in wound-healing and tissue regenerating. Methods for preparing these compositions and using them are also disclosed as part of the invention. A variety of peptides may be used in conjunction with the practice of the invention, in particular, the peptide IKVAV, and variants thereof. Generally, the compositions may be described as comprising a protein network (e.g., fibrin) and a peptide having an amino acid sequence that comprises a transglutaminase substrate domain (e.g., a factor XIIIa substrate domain) and a bioactive factor (e.g., a peptide or protein, such as a polypeptide growth factor), the peptide being covalently bound to the protein network. Other applications of the technology include their use on implantable devices (e.g., vascular graphs), tissue and cell scaffolding. Other applications include use in surgical adhesive or sealant, as well as in peripheral nerve regeneration and angiogenesis.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Hemostatic compositions, devices and methods
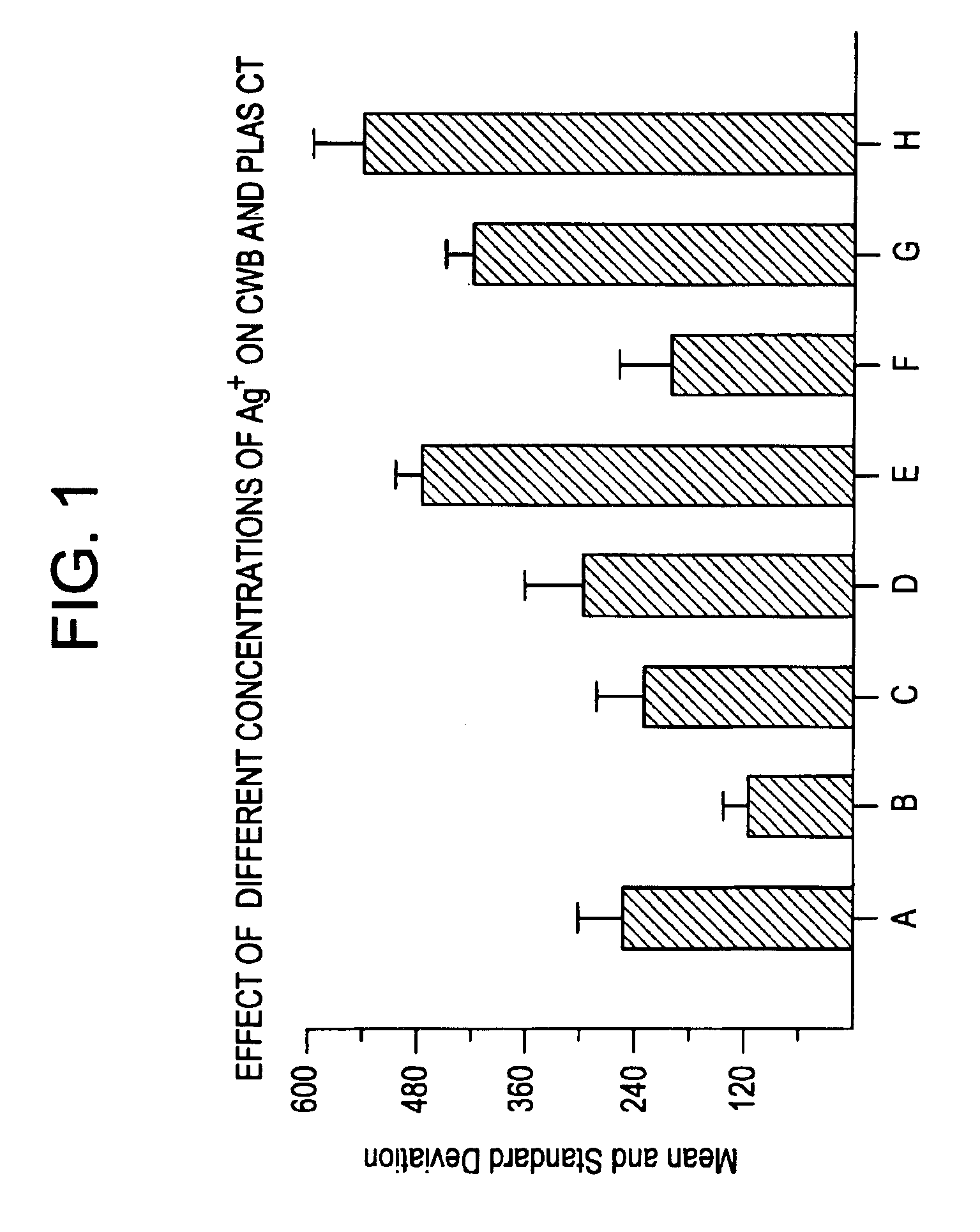
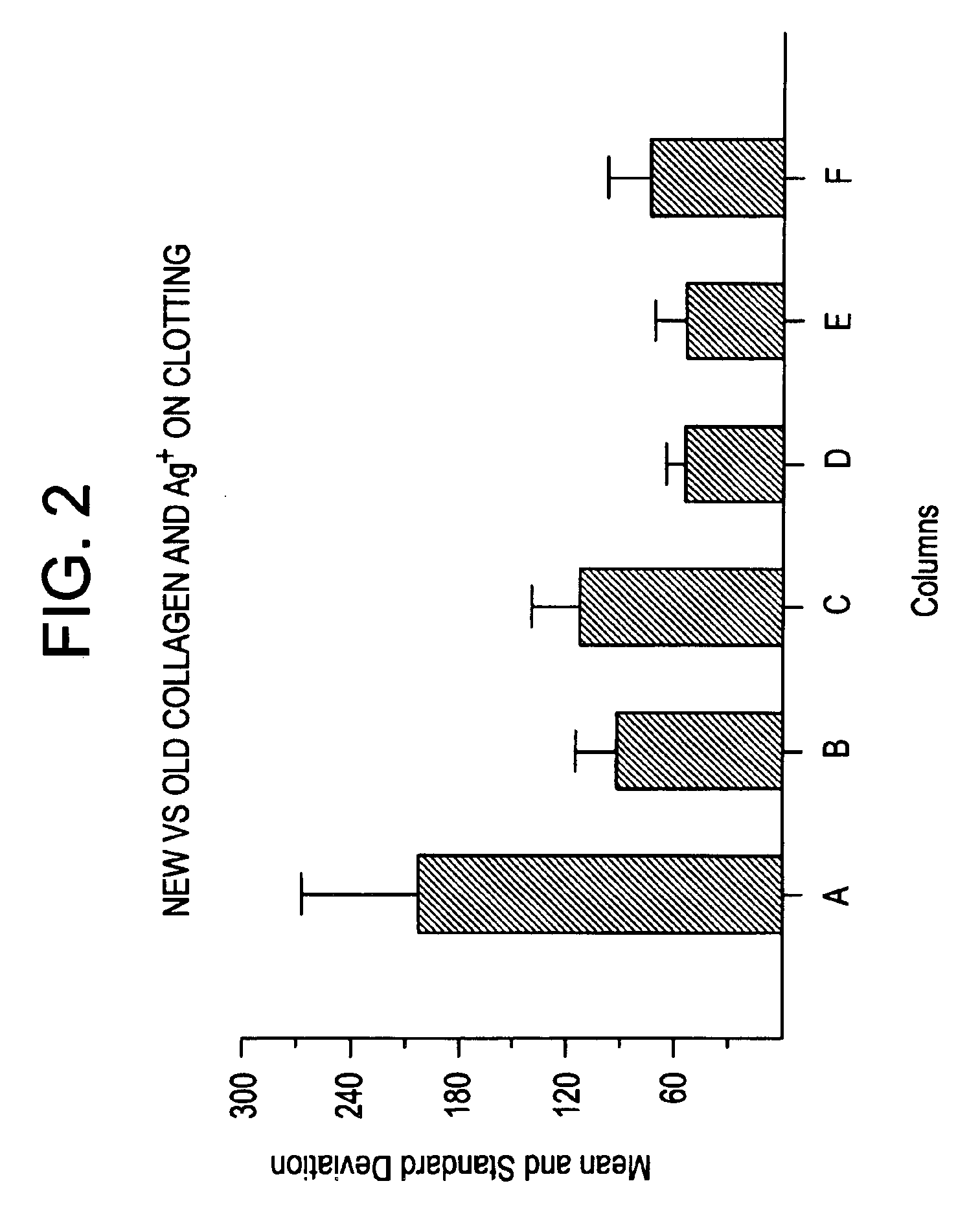
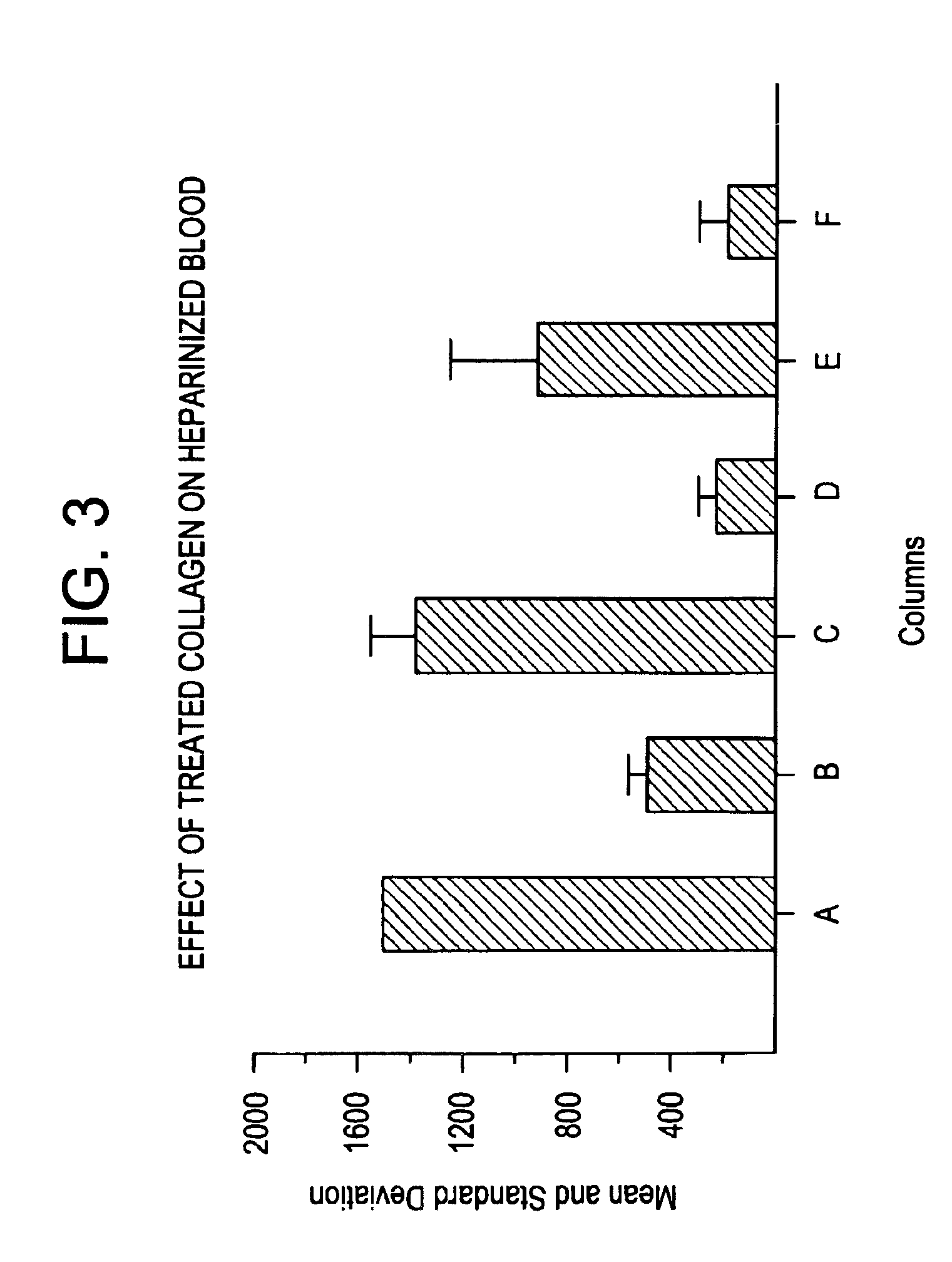
InactiveUS7094428B2Lower Level RequirementsReduce concentrationPowder deliveryFactor VIIFactor VIIaBiopolymer
A hemostatic composition which comprises at least one procoagulant metal ion, such as silver (I) or mercury (II), and at least one procoagulant biopolymer, such as collagen, thrombin, prothrombin, fibrin, fibrinogen, heparinase, Factor VIIa, Factor VIII, Factor IXa, Factor Xa, Factor XII, von Willebrand Factor, a selectin, a procoagulant venom, a plasminogen activator inhibitor, glycoprotein IIb-IIIa, a protease, or plasma. The composition in the form of a paste, dough, glue, liquid, lyophilized powder or foam, may be provided, for application to a wound. A hemostatic device is also described which comprises a hemostatic composition as described above. The device may be in the form of, for example, a plug, bandage, gauze, cloth, tampon, membrane or sponge. Methods are also provided for prophylaxis or treatment of bleeding at a site by application to the site of the composition or device as described.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Fibrous protein hemostatic patch and making method thereof
ActiveCN102178975APlay a protective effectThe main components are stableFibrinogenAbsorbent padsFiberCollagen VI
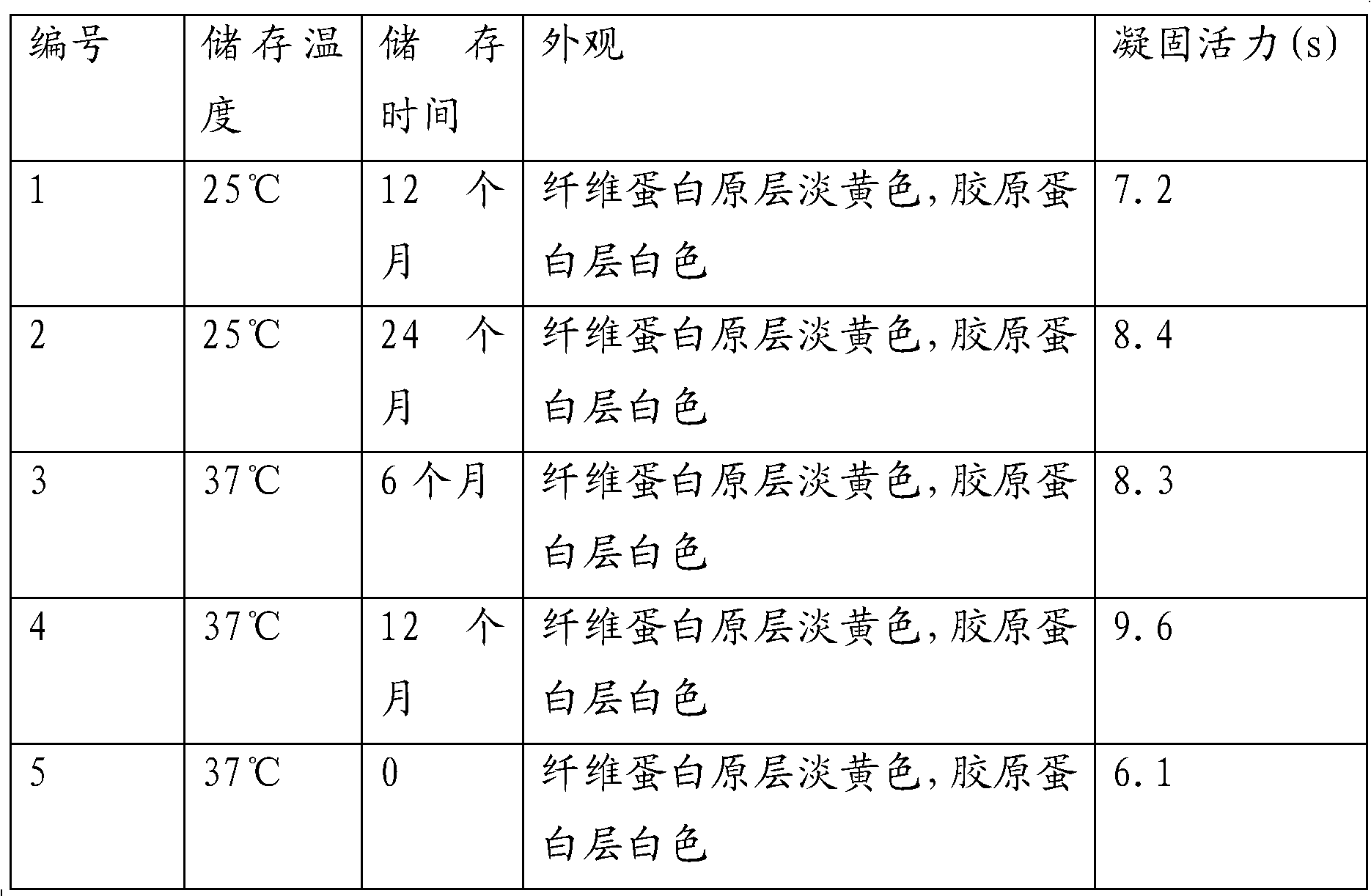
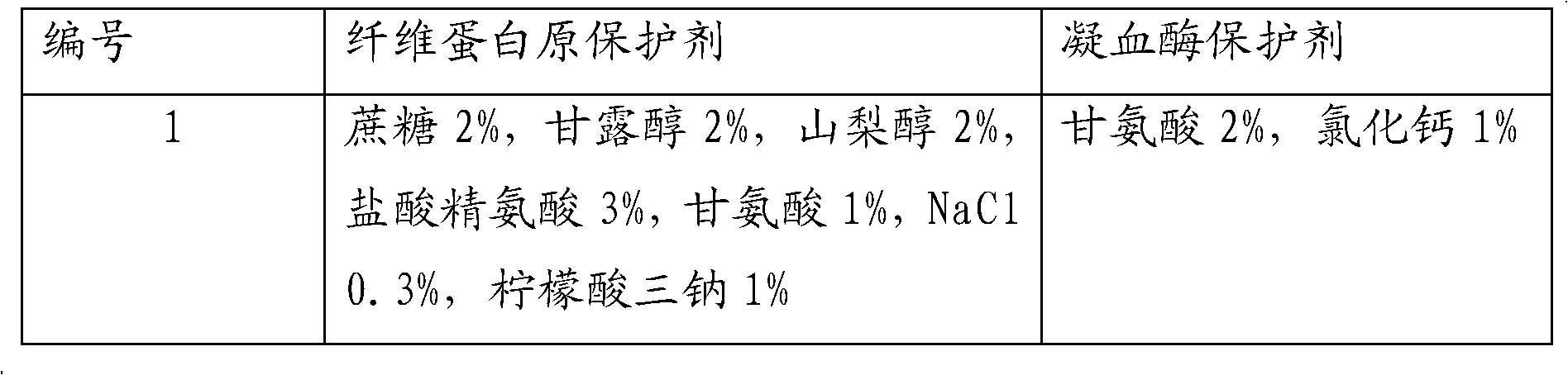
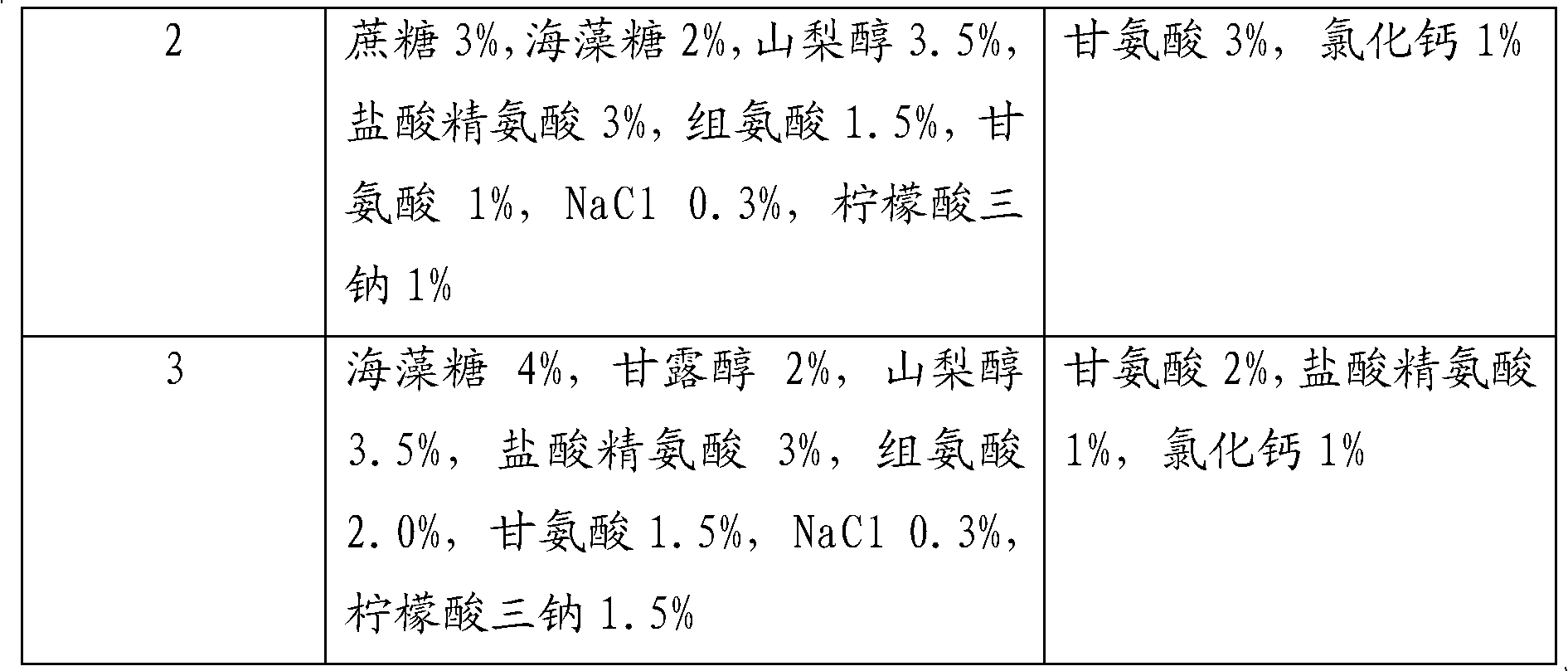
The invention relates to a fibrous protein hemostatic patch capable of being stored at room temperature. The fibrous protein hemostatic patch mainly comprises fibrinogen and thrombin derived from blood of human or mammal, and collagen derived from skin or tendon of the mammal; the fibrous protein hemostatic patch consists of the fibrinogen, the thrombin and the collagen. The fibrinogen and the thrombin are added with a protective agent, so that the fibrous protein hemostatic patch can be stored at room temperature, and has the quality guarantee period of more than 6 months and the longest quality guarantee period of 2 years. The fibrous protein hemostatic patch is suitable for locally stopping bleeding in surgeries and quickly stopping bleeding on occasions such as battlefields and disasters.
Owner:FUJIAN NANSHENG TECH
Hydrogel bioscaffoldings and biomedical device coatings
Bioscaffoldings formed of hydrogels that are crosslinked in situ in an infarcted region of the heart (myocardium) by a Michael's addition reaction or by a disulfide bond formed by an oxidative process are described. Each of the bioscaffoldings described includes hyaluronan as one of the hydrogel components and the other component is selected from collagen, collagen-laminin, poly-l-lysine, and fibrin. The bioscaffolding may further include an alginate component. The bioscaffoldings may have biofunctional groups such as angiogenic factors and stem cell homing factors bound to the collagen, collagen-laminin, poly-l-lysine, or fibrinogen hydrogel component. In particular, the biofunctional groups may be PR11, PR39, VEGF, bFGF, a polyarginine / DNA plasmid complex, or a DNA / polyethyleneimine (PEI) complex. Additionally, the hydrogel components may be injected into the infarct region along with stem cells and microspheres containing stem cell homing factors. The bioscaffolding may be formed on a stent or a cardiac medical device.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
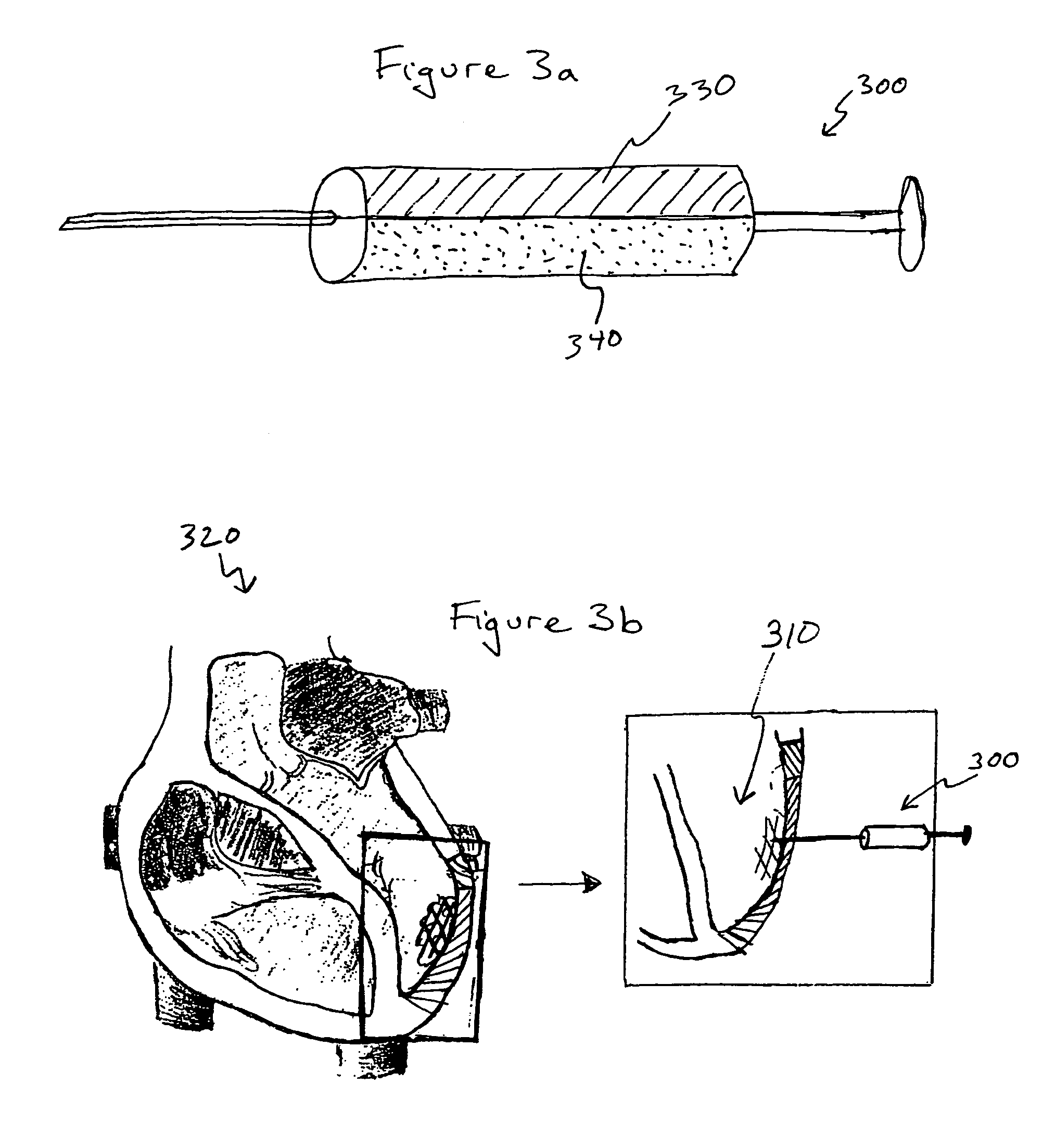
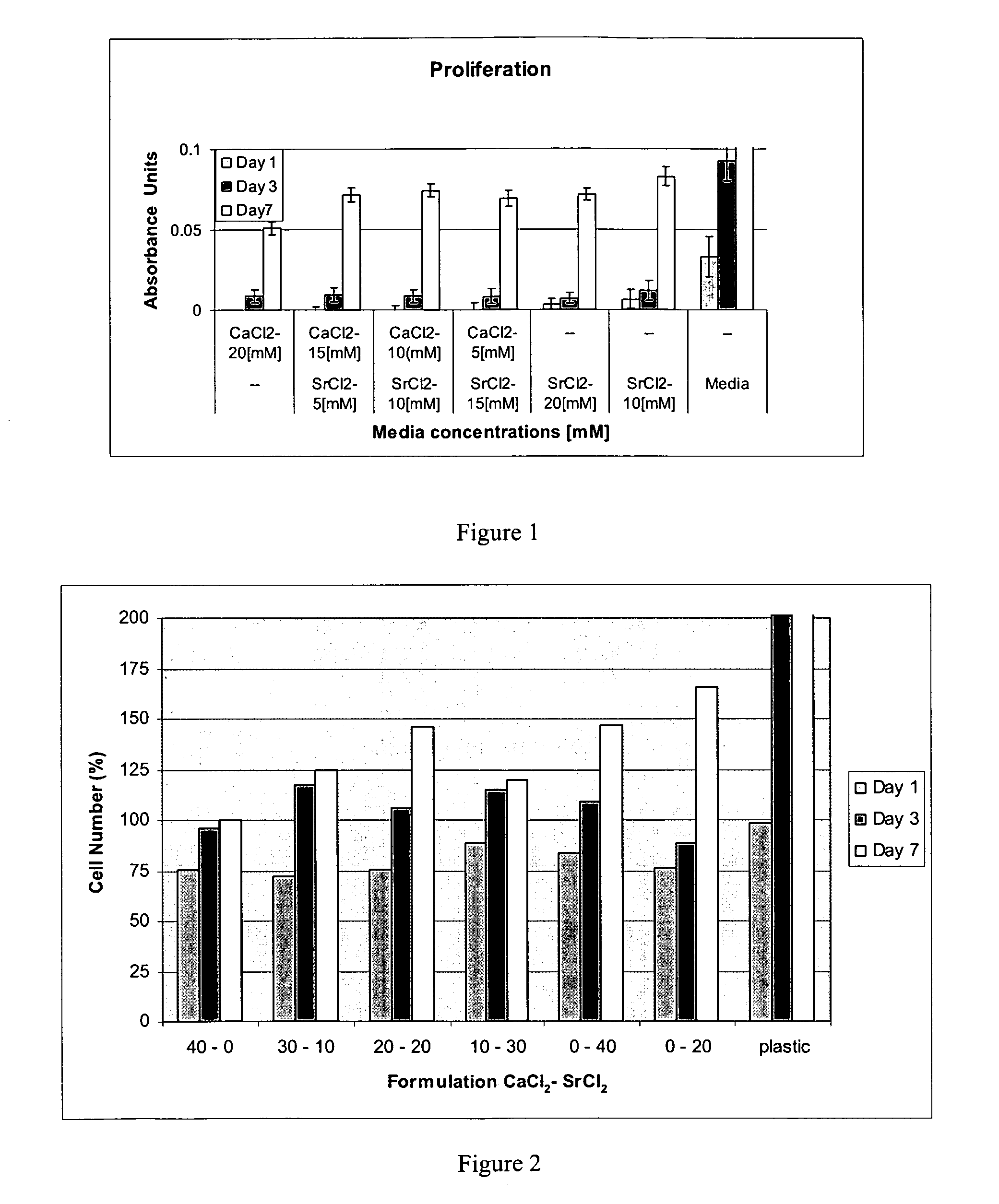
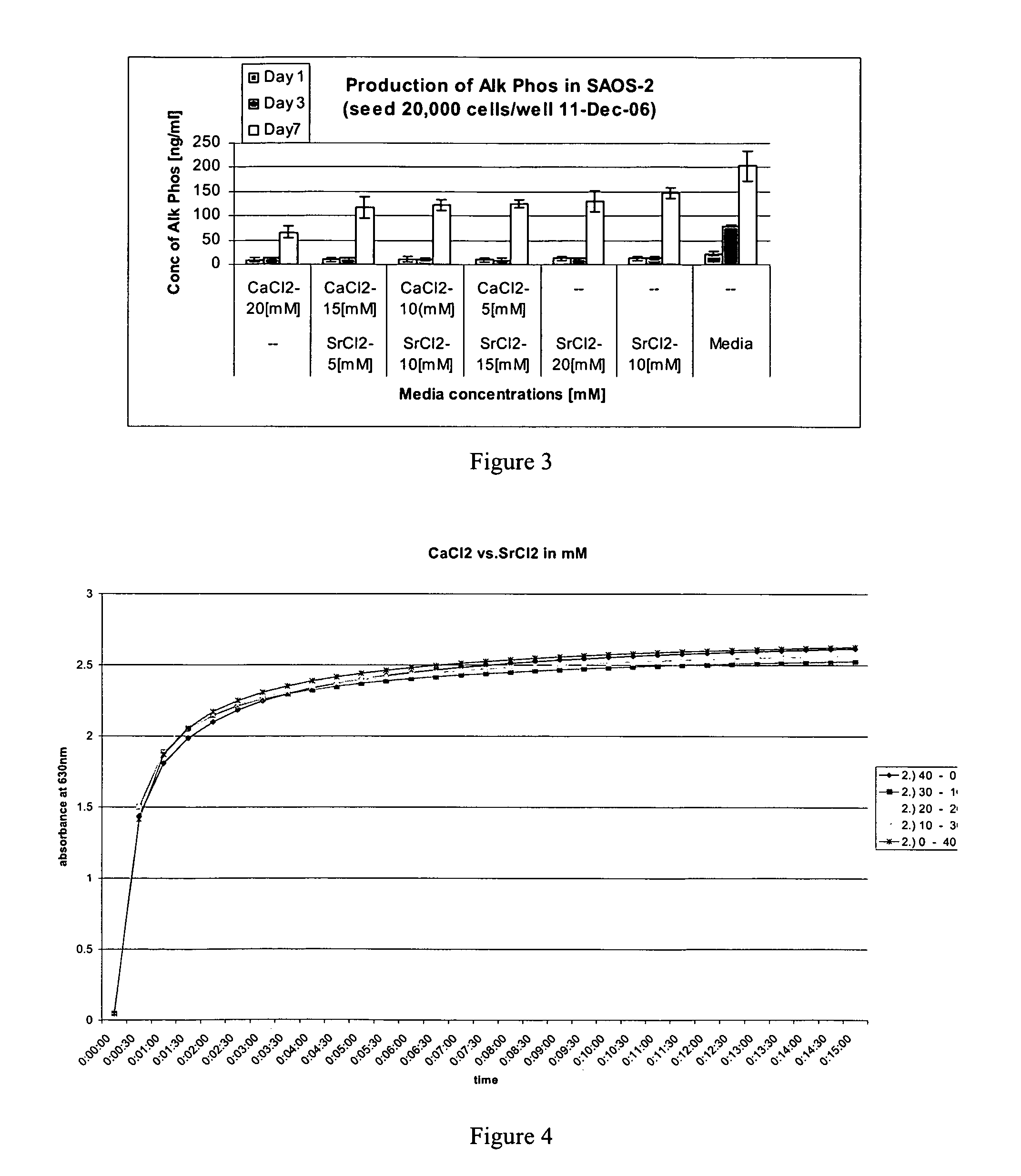
Fibrin Compositions Containing Strontium Compounds
InactiveUS20080260714A1Rate of healingFaster rate of healingPeptide/protein ingredientsInorganic phosphorous active ingredientsParticulatesInorganic compound
A composition for use in bone healing and bone regeneration in the form of a viscoelastic hydrogel gel or liquid formulation comprising fibrinogen, thrombin and an inorganic component comprising a strontium (Sr) containing compound and / or possibly another metal such as a calcium containing compound. The strontium containing compound can be dissolved in the thrombin solutions or added to the clot in crystalline particulate form. Upon mixing the components, gelation takes place to form a matrix. The composition may also comprise an iodine-containing compound which acts as a plasticizer.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
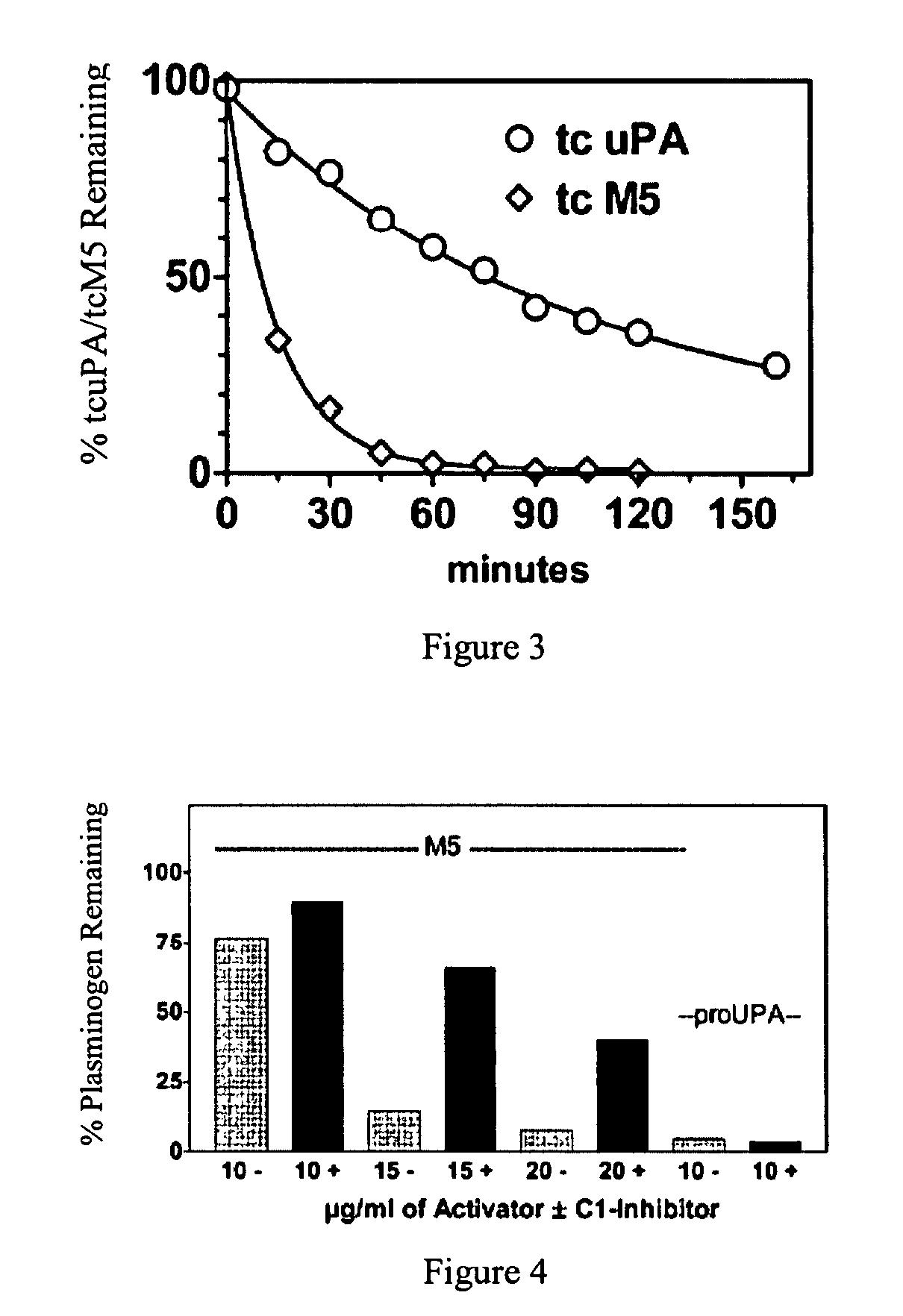
C-1 inhibitor prevents non-specific plasminogen activation by a prourokinase mutant without impeding fibrin-specific fibrinolysis
ActiveUS7837992B2Attenuation of rateHigh dose tolerancePeptide/protein ingredientsBlood disorderC1-inhibitorHigh doses
Owner:THROMBOLYTIC SCI +1
Fibrin-Binding Peptides and Conjugates Thereof
ActiveUS20100158814A1High degreeSuperior fibrin specific bindingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAntibacterial agentsBinding peptideCompanion animal
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
Fibrin/fibrinogen-binding conjugate
InactiveUS20040191261A1Evenly distributedSustained releasePeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsWound healingFibrinogen binding
A fibrin / fibrinogen binding conjugate for forming a depot for the sustained release of a pharmaceutically active substance from a fibrin clot. The conjugate comprises a fibrin / fibrinogen binding moiety bound to a pharmaceutically active substance either directly or via an intervening substance capturing moiety such as an antibody. The conjugate can also be a recombinant fusion protein comprising a fibrin / fibrinogen binding moiety such as VEGF165 C-terminal domain fused to a wound-healing substance such as leptin.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Gene of streptokinase, recombination protein and preparation method
InactiveCN1563378ALow costIncrease fibrinolytic activitySugar derivativesFermentationNucleotideProtein insertion
This invention discloses a thrombolytic zyme gene, a recombination protein and its preparation method relating to a thrombus dissolving material, relating to a source strain of thrombus dissolving gene and two reorganized strains containing said gene. Study shows that the zyme is a new plasmin and its vitality is 41000IUmg computed by the fibrin panel method having the function of anti-damage and suppressing protein oxidation arisen from beam, NaNO2 and H2O2.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
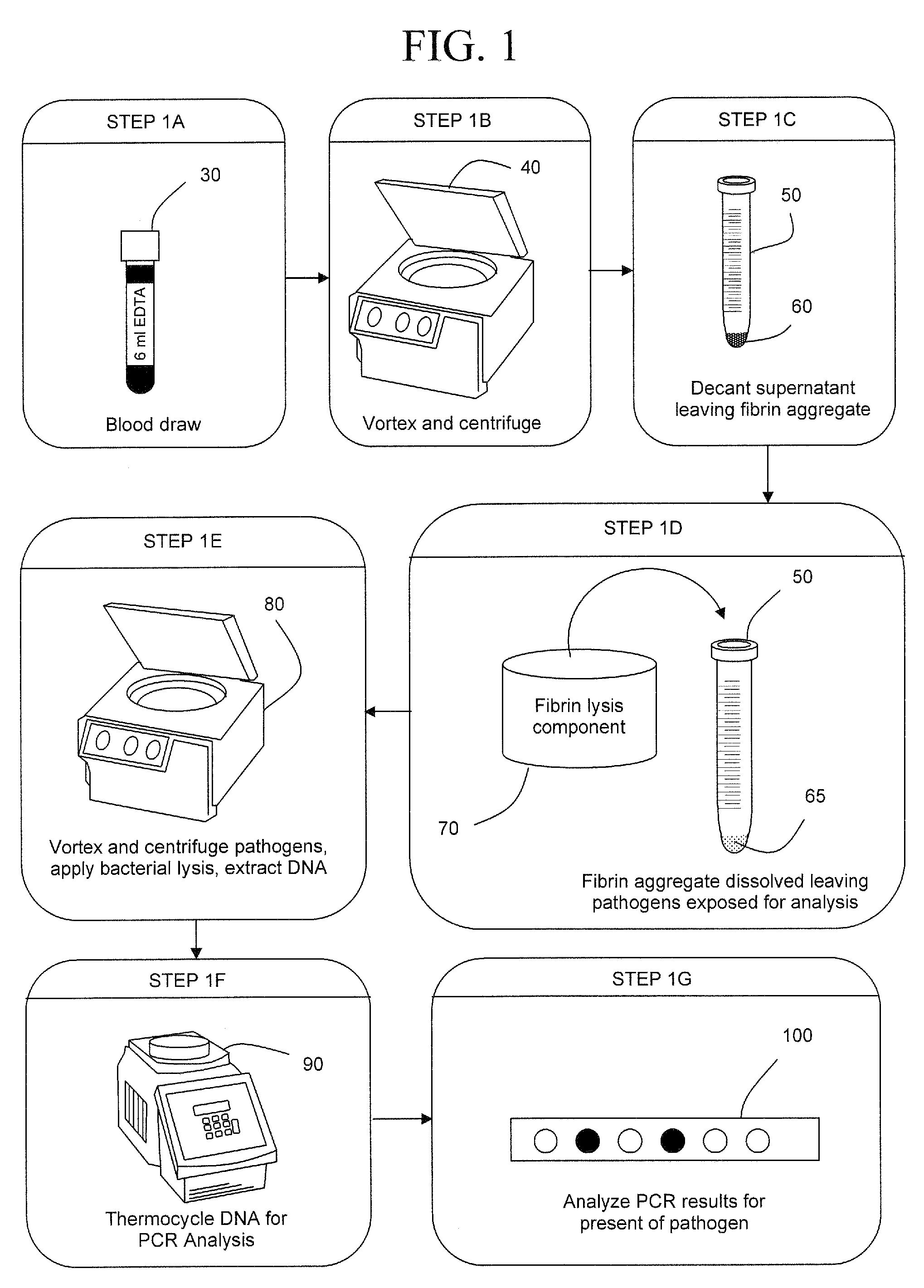
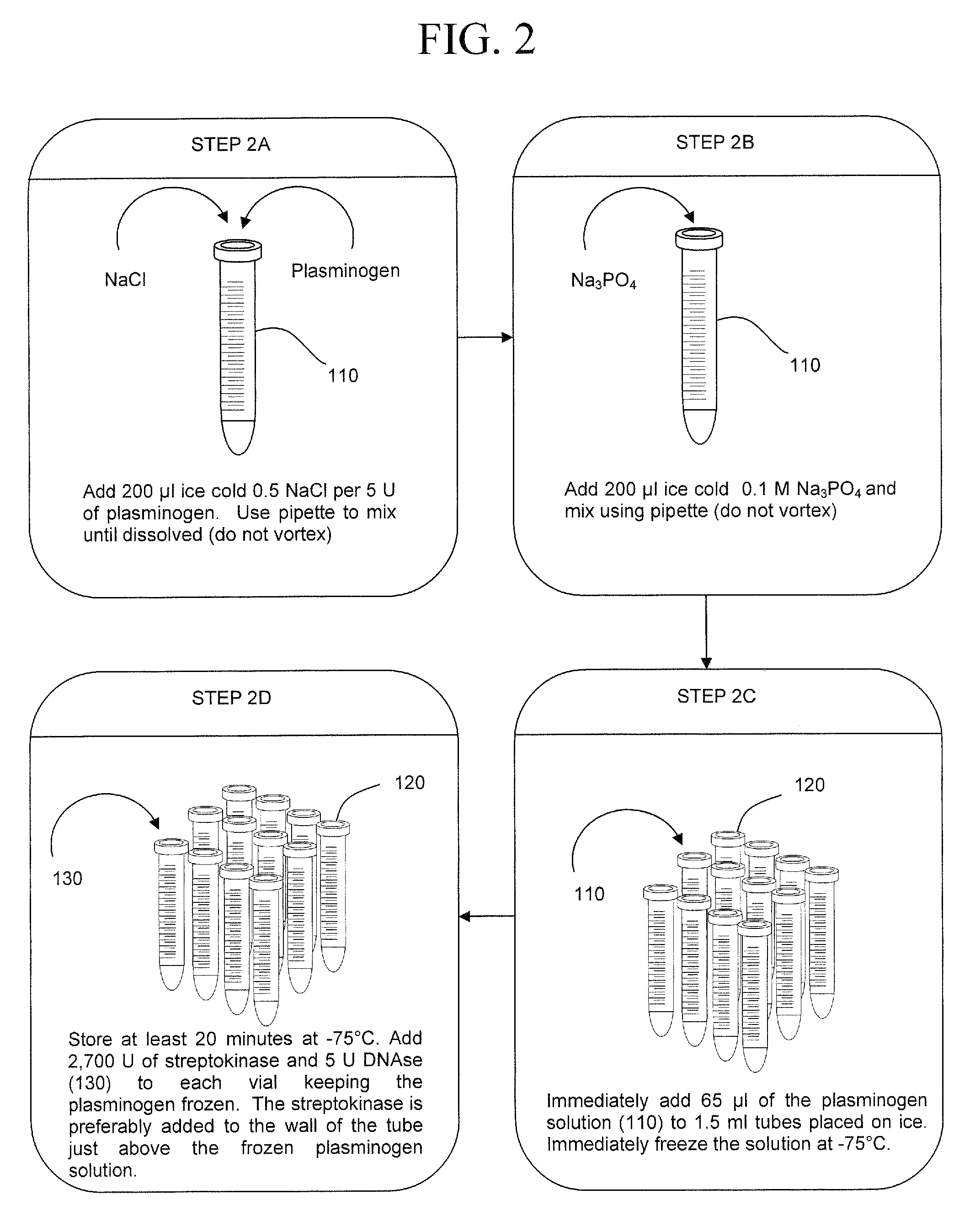
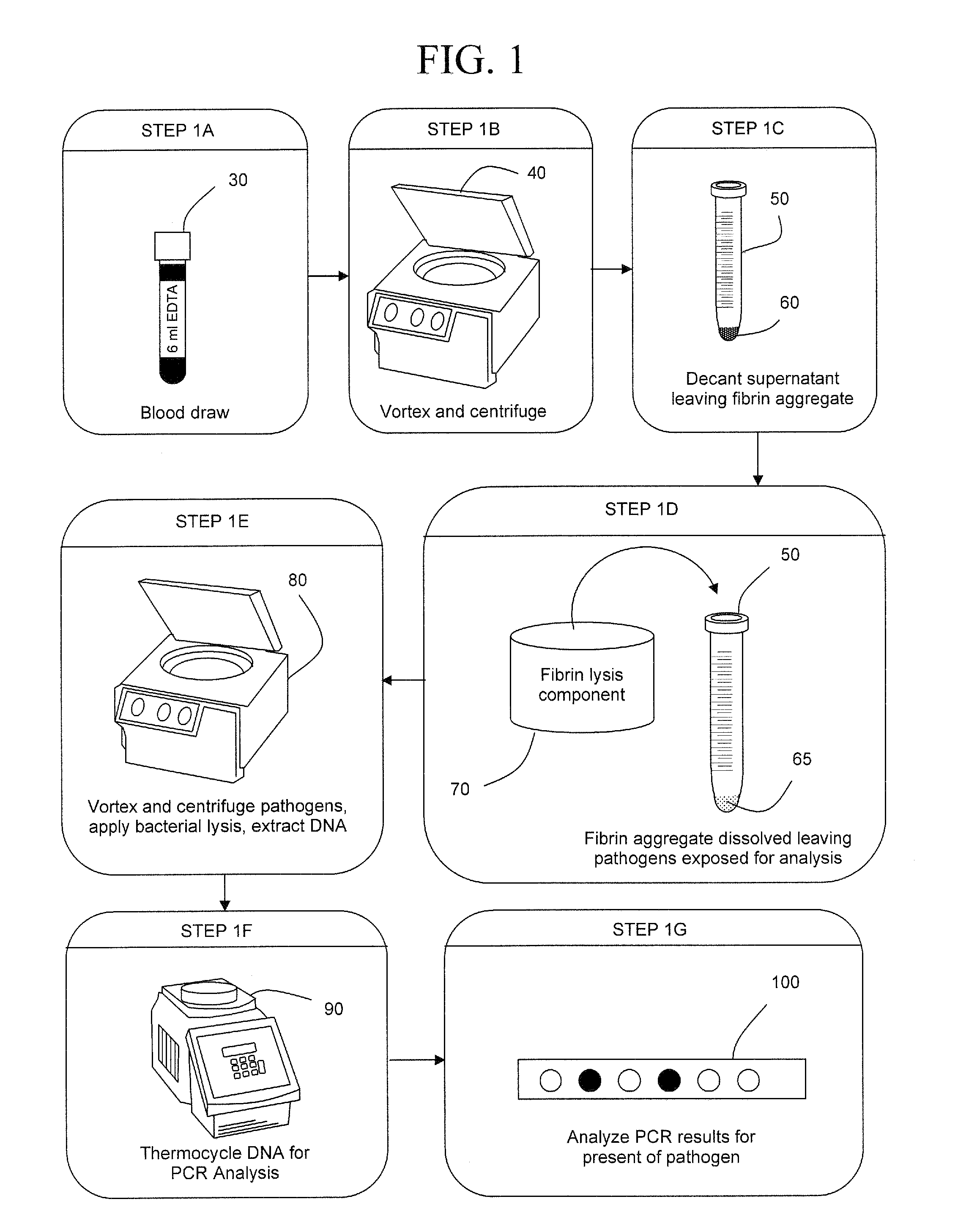
Early detection of pathogens in blood
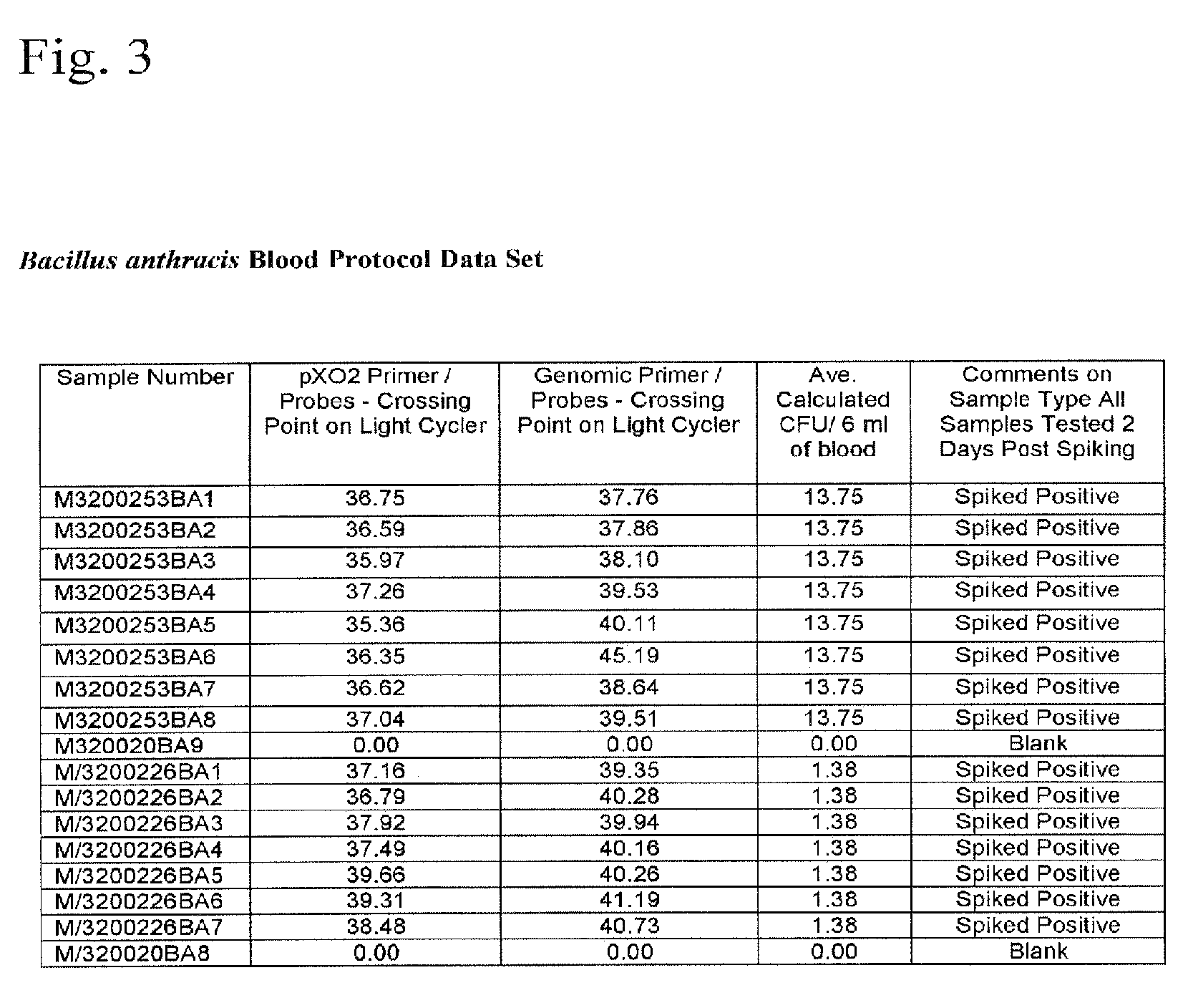
InactiveUS7993870B2Rapid and efficient analysisSmall proportionSugar derivativesHydrolasesZymogenFIBRINOGEN/THROMBIN
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Early Detection of Pathogens in Blood
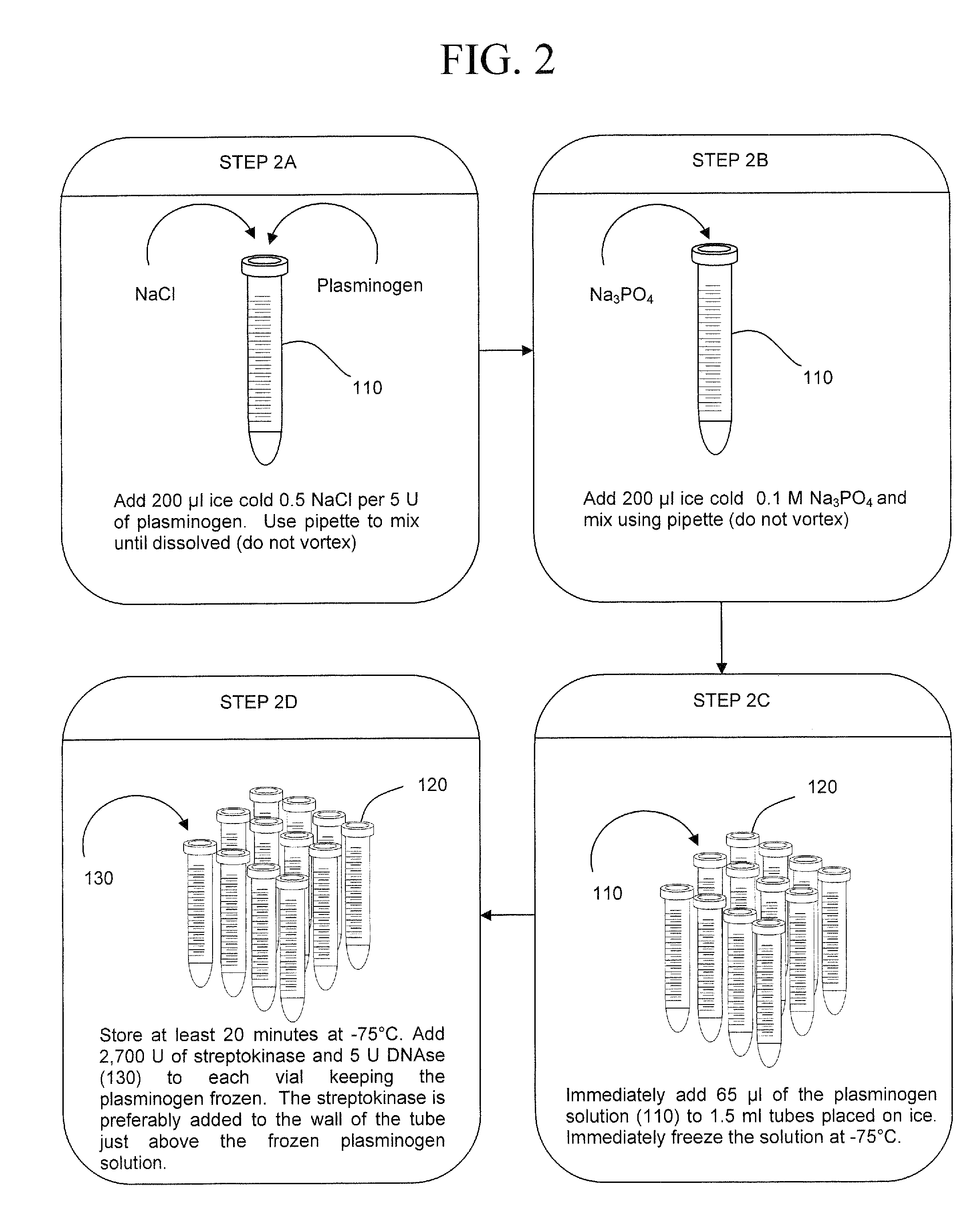
InactiveUS20090305383A1Rapid and efficient analysisSmall proportionSugar derivativesHydrolasesZymogenLysis
The present invention is a method of extracting infectious pathogens from a volume of blood including the steps of creating a fibrin aggregate confining the pathogens and introducing a fibrin lysis reagent to expose the pathogens for analysis. The fibrin lysis reagent is preferably composed of plasminogen and streptokinase frozen in coincident relation until the fibrin lysis reagent is needed whereby streptokinase enzymatically reacts with plasminogen to form plasmin upon thawing. The plasminogen is suspended in an aqueous salt solution prior to freezing including NaCl and Na3PO4.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Preparing method of compound collagen hemostatic material
InactiveCN101224311AImprove actual functionsGood hemostatic effectAbsorbent padsBandagesFiberDrugs solution
A preparing method of complex collagen hemostatic material belongs to the field of medical biomaterials. Hemostatic time is the standard for evaluating the quality of hemostatic materials; therefore, increasing the hemostatic properties of collagen material is still the key point of research and development. The invention firstly uses aldehydes to do chemical modification to soluble collagen, thus making into modified collagen web, and as the water affinity of the collagen is improved, the hemostatic property is improved. Furthermore, Chinese herbal medicine that can catalyze soluble fibrin in plasma into dissoluble fibrin is chosen to prepare into solution; the wed of the modified collagen is immerged in the medical solution completely. Owning to the molecular bond of modified collagen and the herbal, the diffusion and permeability, drug molecules can enter the three-screw structure of the collagen, thus forming the complex collagen hemostatic material. The material has obvious improvement on the basis of modification in both normal coagulation and abnormal coagulation, and the hemostatic time is 45 seconds to 60 seconds, and the material is superior to medical collagen hemostatic materials in board and to similar medical collagen hemostatic materials in Japan.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Hydrogel bioscaffoldings and biomedical device coatings
Bioscaffoldings formed of hydrogels that are crosslinked in situ in an infarcted region of the heart (myocardium) by a Michael's addition reaction or by a disulfide bond formed by an oxidative process are described. Each of the bioscaffoldings described includes hyaluronan as one of the hydrogel components and the other component is selected from collagen, collagen-laminin, poly-1-lysine, and fibrin. The bioscaffolding may further include an alginate component. The bioscaffoldings may have biofunctional groups such as angiogenic factors and stem cell homing factors bound to the collagen, collagen-laminin, poly-1-lysine, or fibrinogen hydrogel component. In particular, the biofunctional groups may be PR11, PR39, VEGF, bFGF, a polyarginine / DNA plasmid complex, or a DNA / polyethyleneimine (PEI) complex. Additionally, the hydrogel components may be injected into the infarct region along with stem cells and microspheres containing stem cell homing factors. The bioscaffolding may be formed on a stent or a cardiac medical device.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Preparation method of pig blood fibrin polypeptide powder
ActiveCN102125164AHigh in peptidesSmall molecular weightAnimal feeding stuffProtease preparationAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to a method for producing fibrin polypeptide powder (pig blood fibrin polypeptide powder) via hydrolyzing blood clots of pig blood. In the processes of collecting, storing and processing pig blood, the principal component of the blood clots generated via blood clotting is fibrin; and separation and cutting, enzymolysis via proteinase preparation, enzyme deactivation, filtration and drying via atomizing are carried out on the blood clots, thus, the pig blood fibrin polypeptide powder is obtained. By means of the technical scheme provided by the invention, fibrin polypeptide is produced via the enzymolysis of the blood clots; when the fibrin polypeptide is used as a feed additive, the pollution is reduced and the green environmental protection requirements are met; andwhen the fibrin polypeptide is used as an excellent animal protein source, the digestibility of the protein is improved and the trend of the upgrading of the current enterprise technologies is met.
Owner:成都天屹生物科技有限公司
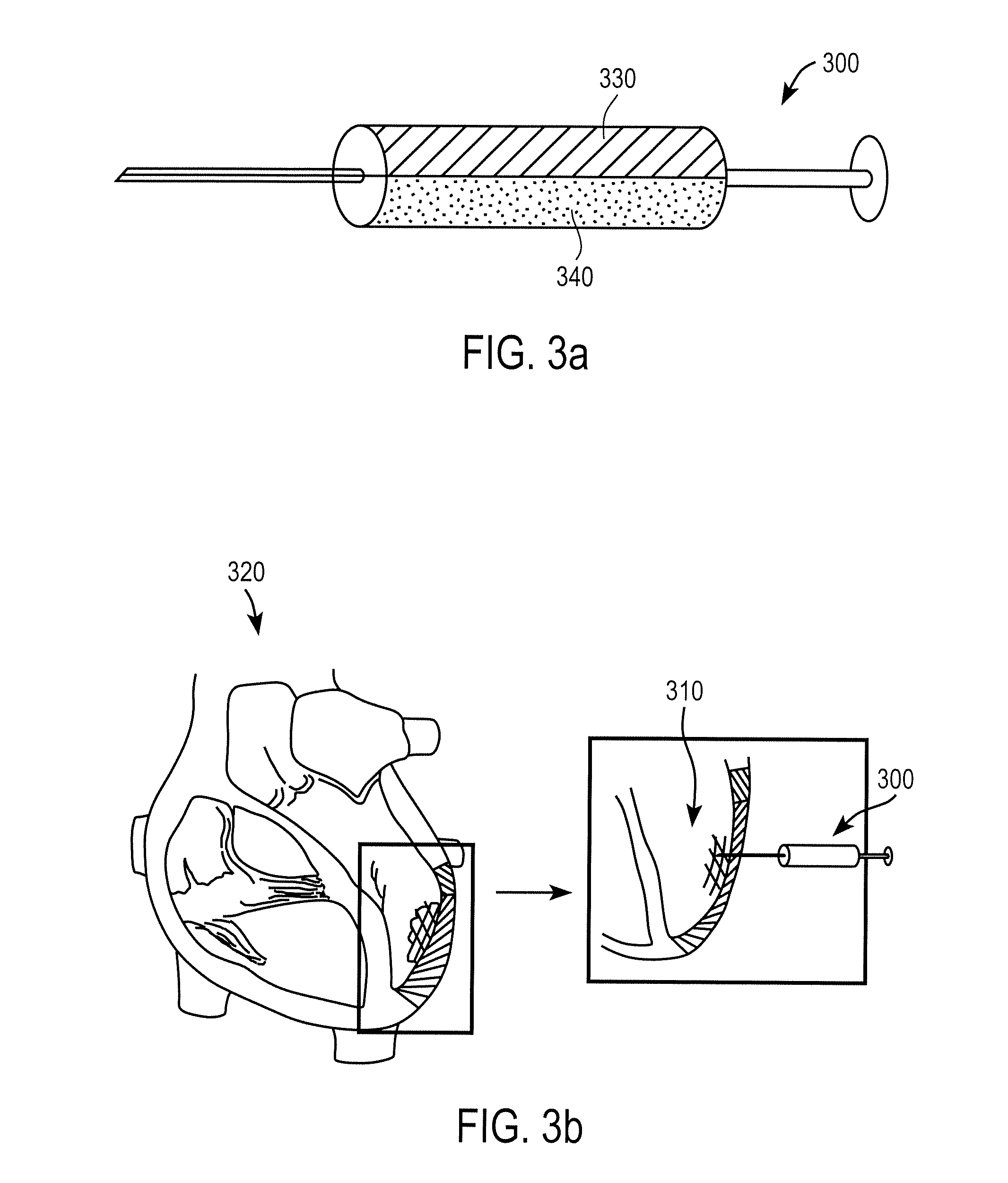
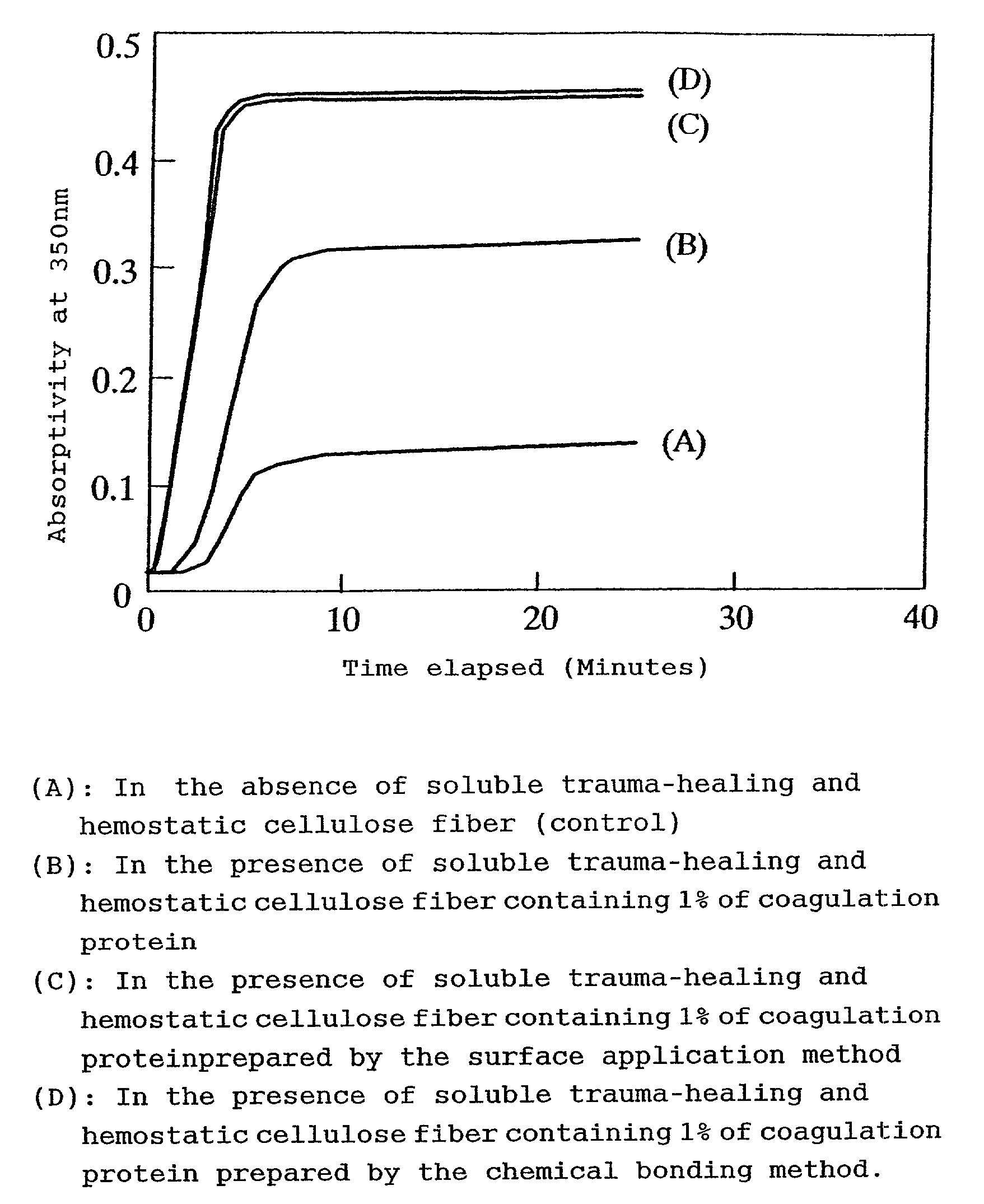
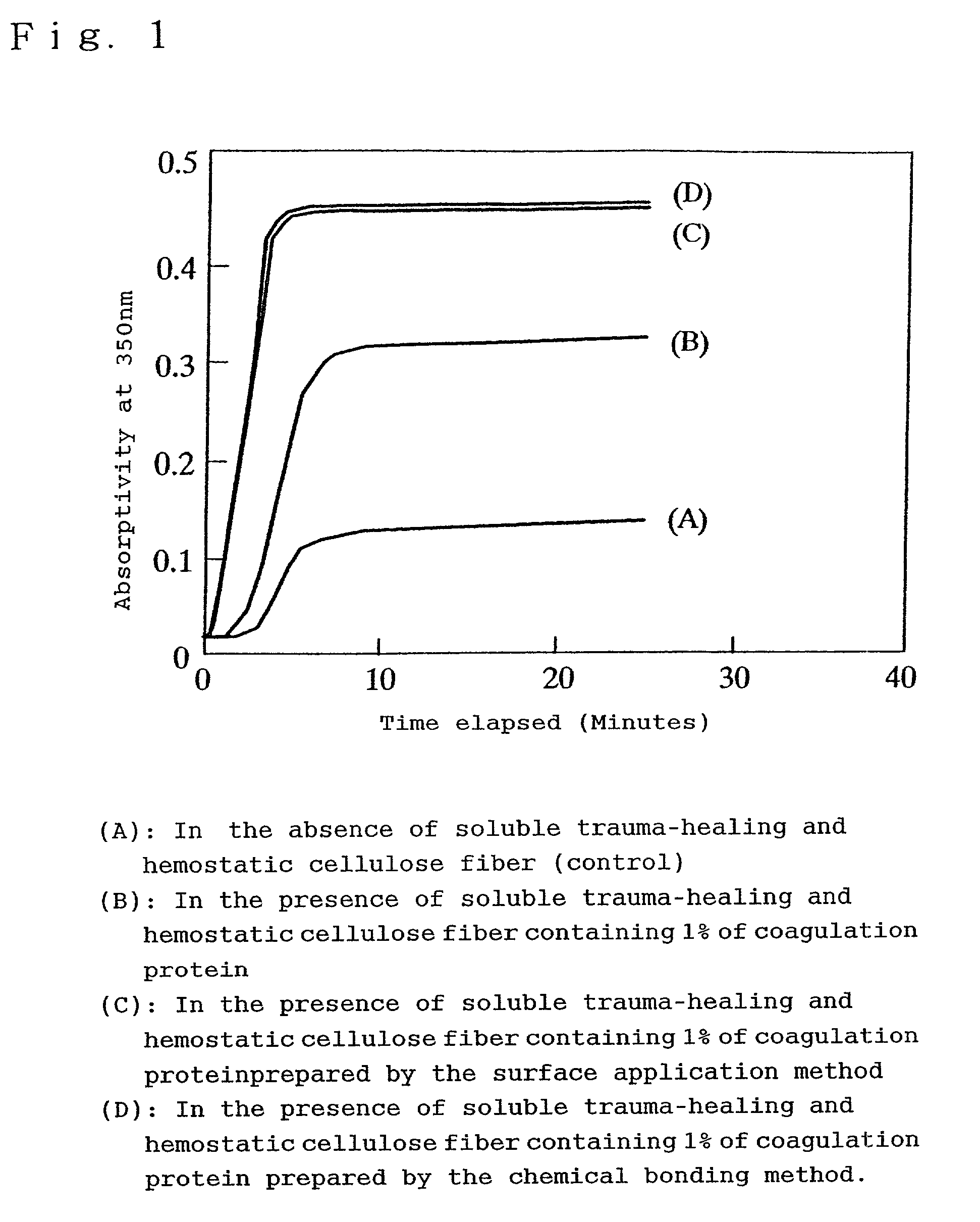
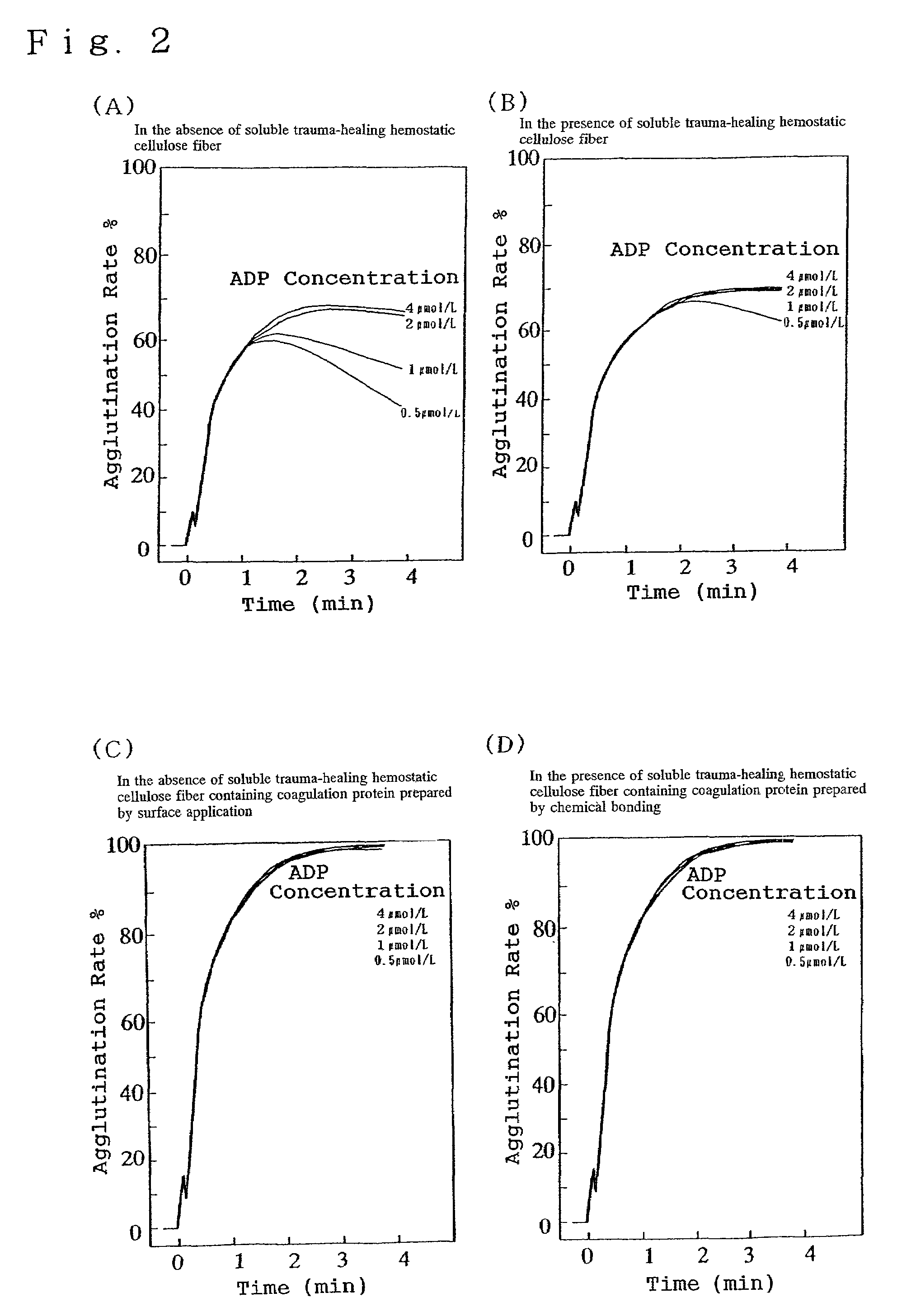
Hemostatic soluble cellulose fibers containing coagulating protein for treating wound and process for producing the same
InactiveUS7351422B2Accelerates agglutinationEasy adhesionOrganic active ingredientsFibrinogenChemical LinkageCell adhesion
Proposed is a novel soluble trauma-healing and hemostatic cellulose fiber capable of absorbing and readily dissolving hemorrhaging trauma loci when applied thereto and of promoting the hemostatic action of blood platelets and fibrin and cell adhesion to the trauma site. The coagulation protein-containing soluble trauma-healing and hemostatic cellulose fiber is produced in that after treatment of a natural or regenerated cellulose fiber with an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution, said fiber is carboxymethylated by reaction with a monochloro acetic acid solution for a given time (hours) in such a manner that the degree of partial substitution of the glucose units constituting the cellulose molecule (etherification degree) is 0.5-less than 1.0% and that, furthermore, the coagulation proteins fibrinogen, thrombin, and coagulation factor XIII are imparted by surface application or chemical bonding.
Owner:HOGY MEDICAL CO LTD
Nerve regeneration gel as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107970438AAvoid Oxidative DamageInhibitory reactivityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderNervous systemCuticle
The invention discloses a nerve regeneration gel as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The matrix of the nerve regeneration gel is formed by fibrinogen, thrombin, laminin and fibronectin; the nerve regeneration gel contains procyanidine, sonic hedgehog, an epidermal growth factor, neurenergen-3 and a vascular endothelial growth factor. In-vitro test and animal test show that thegel is capable of accelerating neuron regeneration and neurite extension and repairing the injured nerve tissue. The matrix of the gel comprises fibrin, laminin and fibronectin and is capable of reducing formation of cavities and accelerating adhesion and proliferation of endogenous neural stem cells; the procyanidine in the gel is capable of resisting oxidation and inhibiting inflammation; the sonic hedgehog, the epidermal growth factor and the neurenergen-3 are capable of accelerating proliferation of the stem cells and differentiation to neurons of the stem cells; the vascular endothelialgrowth factor is capable of accelerating generation of blood vessels. The gel can be formed in situ on injured parts and can be used for treating nervous system injury.
Owner:镇江市中西医结合医院
Fibrin/fibrinogen-binding conjugate
InactiveUS7091325B2Evenly distributedOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsWound healingFibrinogen binding
A fibrin / fibrinogen binding conjugate for forming a depot for the sustained release of a pharmaceutically active substance from a fibrin clot. The conjugate comprises a fibrin / fibrinogen binding moiety bound to a pharmaceutically active substance either directly or via an intervening substance capturing moiety such as an antibody. The conjugate can also be a recombinant fusion protein comprising a fibrin / fibrinogen binding moiety such as VEGF165 C-terminal domain fused to a wound-healing substance such as leptin.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
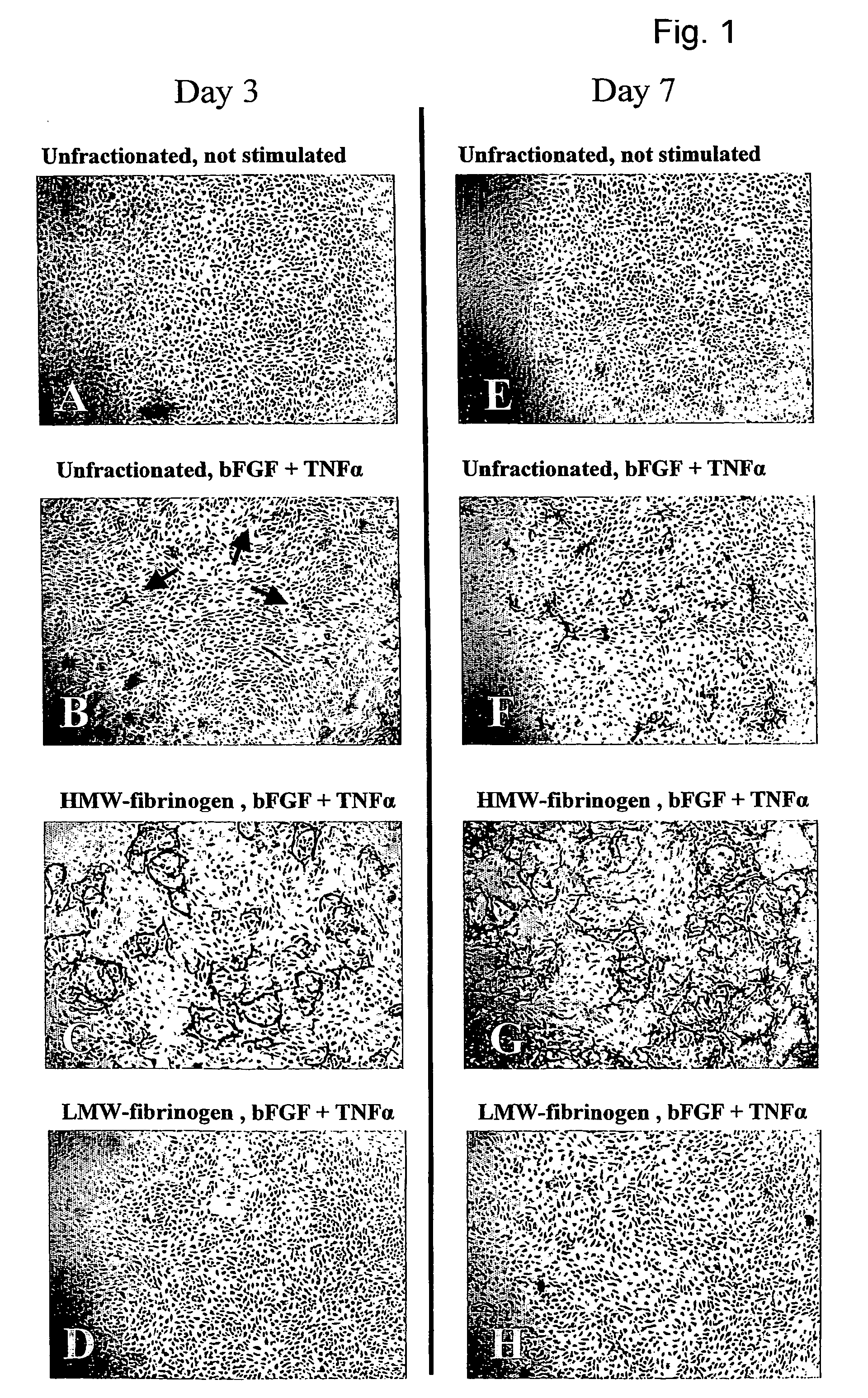
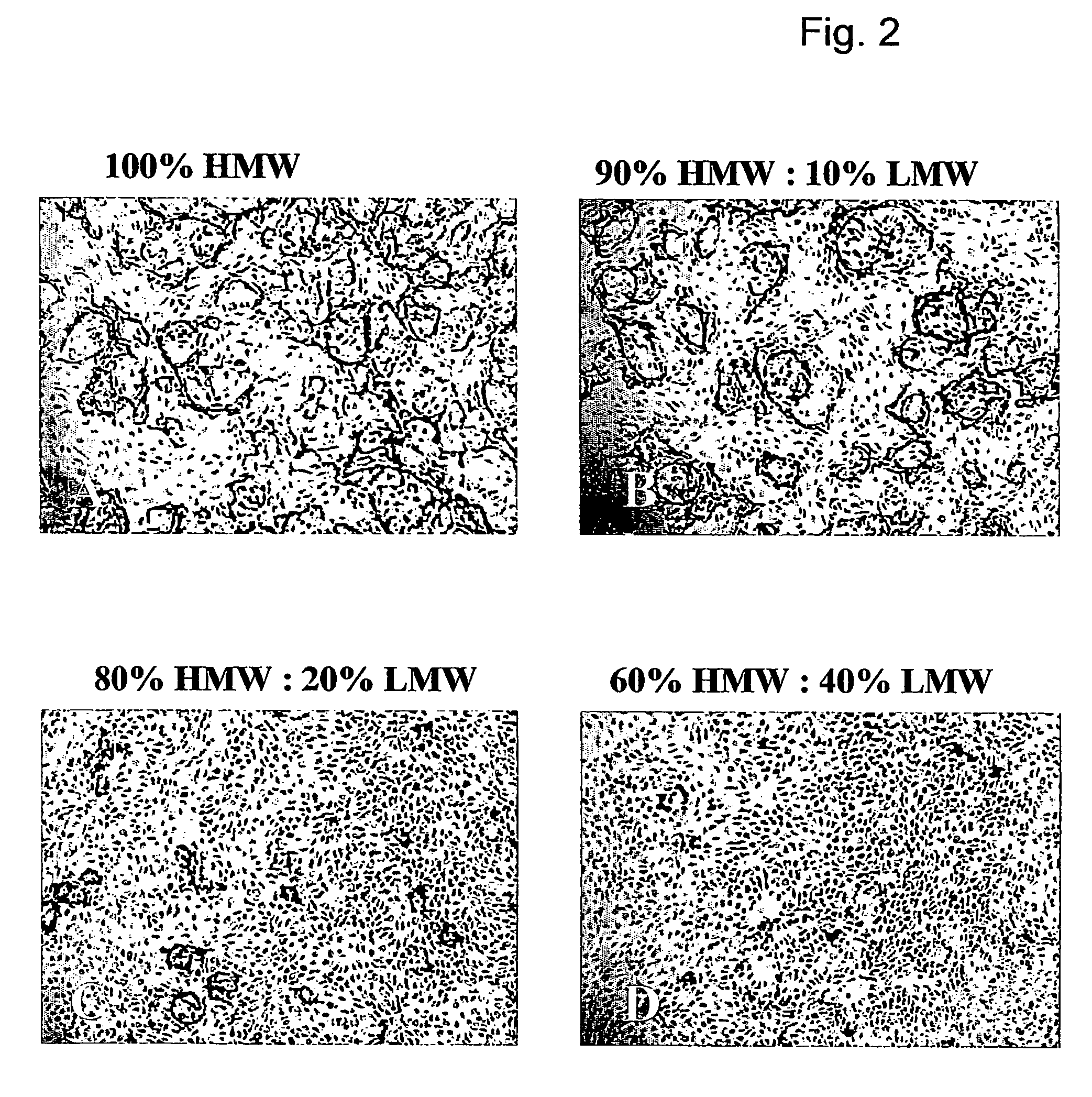
Method for the acceleration or deceleration of angiogenesis using fibrin matrix formed from increased or decreased HMW/LMW fibrinogen ratio
ActiveUS7867519B2Reduced cell and vessel ingrowthIncreased cell and vessel ingrowthFibrinogenSurgical adhesivesFiberScar tissue
A method for modifying the properties of a fibrin matrix relative to growth and ingrowth of cells, wherein for forming the fibrin matrix a fibrinogen is used consisting of a selected fibrinogen variant or a fibrinogen enriched or depleted in a selected fibrinogen variant. In particular, the use of high-molecular weight (HMW) fibrinogen leads to a fibrin having accelerated angiogenesis properties, while the use of low-molecular weight (LMW and / or LMW′) fibrinogen leads to fibrin having decelerated angiogenesis properties. The use of HMW fibrinogen when setting up angiogenesis tests results in that the tests require less time. Fibrin sealants on the basis of HMW fibrinogen can be used for burns, to promote wound healing or to inhibit scar tissue. Fibrin sealants on the basis of LMW or LMW′ fibrinogen are useful to inhibit adhesions and tumor growth, for instance after surgical operations.
Owner:NEDERLANDSE ORG VOOR TOEGEPAST NATUURWETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK TNO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com