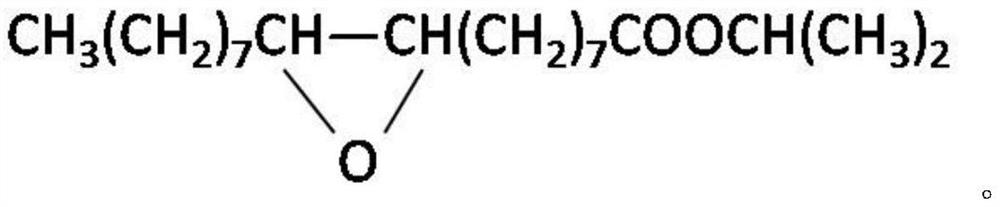Patents
Literature
54 results about "Candida antarctica" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Candida antarctica is a yeast species in the genus Candida. Candida antarctica is a source of industrially important lipases. Immobilized Candida antarctica lipase can be used to catalyze the regioselective acylation of flavonoids or the direct acetylation with phenolic acids.
Biologic deodorant as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103898023AEliminate inhibitionIncrease production intensityFungiBacteriaBacillus licheniformisCandida rugosa
The invention provides a biologic deodorant as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The biologic deodorant is a biologic fermentation liquid of which a microorganism strain is combined with one or more of yeast strains or one or two of bacteria into a mixed bacterium, wherein the yeast strains comprise candida Antarctica lipase and candida rugosa; the bacteria comprise bacillus licheniformis and bacillus subtilis; after microorganism strains are subjected to strain domesticating by using tea seed cake dregs as a sole nitrogen source, a two-stage fermentation process is adopted for fermentation, finally the microorganism strains in a fermentation bacterial liquid are in the dormant state, and the final biologic deodorant is obtained; when the biologic deodorant is used, after water is added and the biologic deodorant is in contact with air, the microorganism strains can continuously grow and generate more enzymes. By adopting the biologic deodorant provided by the invention, organic matters which can generate odor can be fundamentally removed, the degree that a pipeline is blocked by organic matters is reduced or eliminated, and the biologic deodorant can be also used for washing oil-containing or / and protein-containing or / and starch-containing dirt, does not damage any pipeline in a sewer, and is environmental-friendly.
Owner:重庆鸿紫圆光生物科技有限公司
Enzymatically catalyzed method of preparing mono-acylated polyols
The present invention relates to a biocatalytic method of preparing a mono-acylated polyol catalyzed by triacyl-glycerol lipase mutants, as for example derived from Candida antarctica lipase B (CALB); a biocatalytic method of enantioselectively preparing an asymmetric mono-acylated polyol, catalyzed by the same enzyme mutants; as well as the use of a mutated triacylglycerol lipase in a method of preparing mono-acylated polyols. The invention also provides novel mutants, coding sequences thereof, and recombinant microorganisms carrying said coding sequences.
Owner:BASF AG
Method for performing catalytic stereoselective separation on 2,3-diphenylpropionic acid enantiomer by adopting bio-enzyme
The invention discloses a new chiral separation method of a 2,3-diphenylpropionic acid single enantiomer, i.e., a method for synthesizing the 2,3-diphenylpropionic acid single enantiomer by performing enzyme-catalyzed enantioselective hydrolysis on a 2,3-diphenylpropionic acid enantiomer. 2,3-diphenylpropionate enantiomer is hydrolyzed by utilizing high selectivity and high catalysis efficiency of Candida antarctica lipase A and a solubilization effect of cyclodextrin on a 2,3-diphenylpropionate enantiomer is utilized, so that hydrolysis reaction of the 2,3-diphenylpropionate enantiomer in a phosphate buffering solution is enhanced; the conversion rate of a substrate and the optical purity of a product are respectively up to 44.79 percent and 98.24 percent, and the stereoselectivity E is greater than 276. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the problems of low optical purity, low yield, environment pollution and the like in a general separation technique are overcome; by adopting the method, the high conversion rate and the high selectivity required by hydrolysis of the 2,3-diphenylpropionate enantiomer can be realized, so that the aims of no-toxicity and no-harmlessness of a separation chiral compound, mild reaction conditions, simpleness of equipment, convenience in operation, low cost and the like are fulfilled.
Owner:HUNAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Oligomeric compounds
ActiveUS7947736B2Improve the level ofPrevent cytotoxic damageBiocideOrganic active ingredientsFuranOrganic solvent
Method for the synthesis of a compound of formula H(OCH[CH3]CH2C[O])3—O-A-O—R wherein A is the residue of 1,3-butandiol and R is H or H(OCH[CH3]CH2C[O]3—. The method comprises reacting a cyclic oligomer of (R)-3-hydroxybutyrate consisting of (R)-3-hydroxybutyrate moieties with a 1,3-butandiol in an organic solvent in the presence of Candida antarctica lipase type B in a furan or pyran solvent.
Owner:TDELTAS
Photoluminescent hydrogel
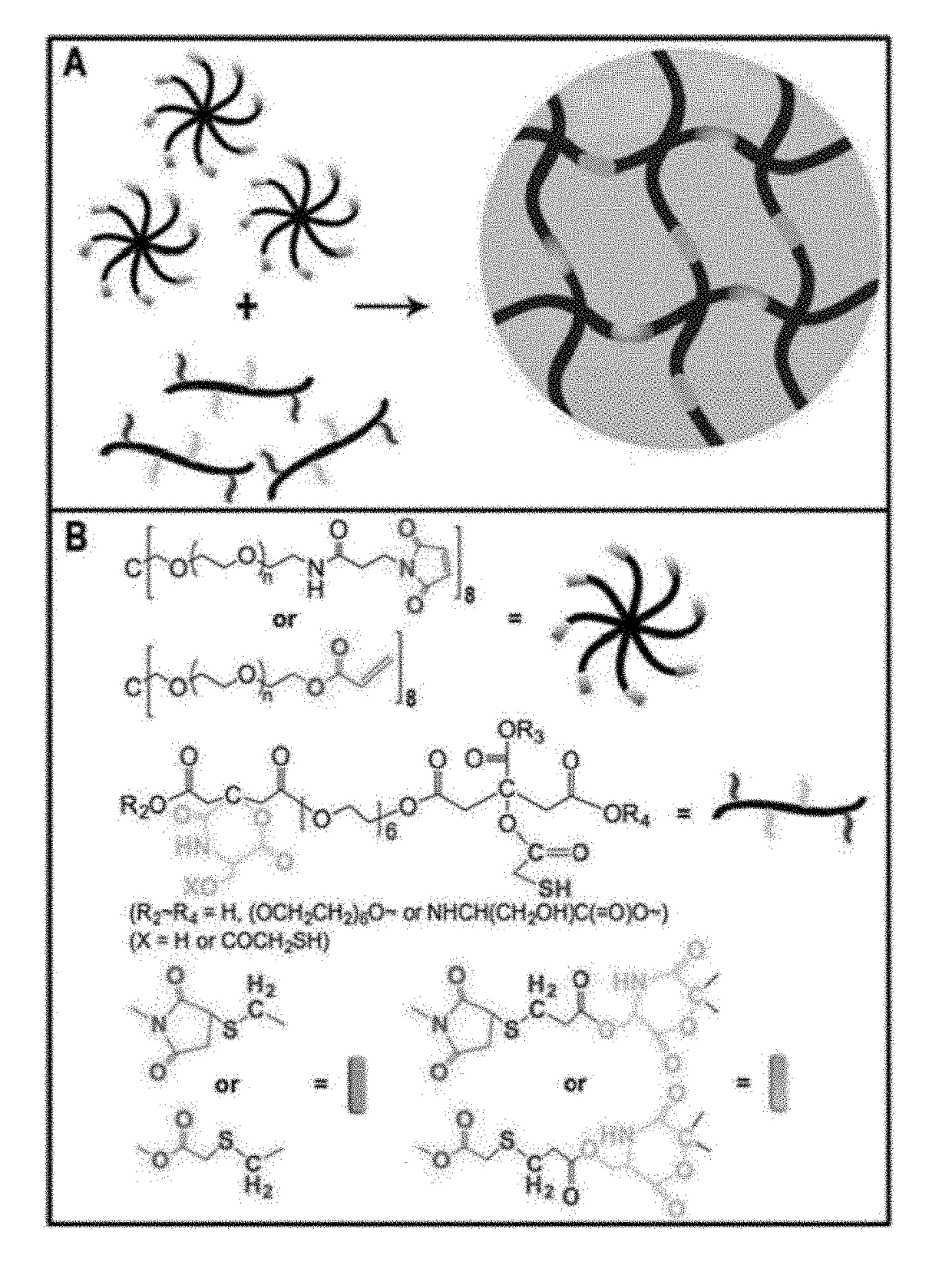
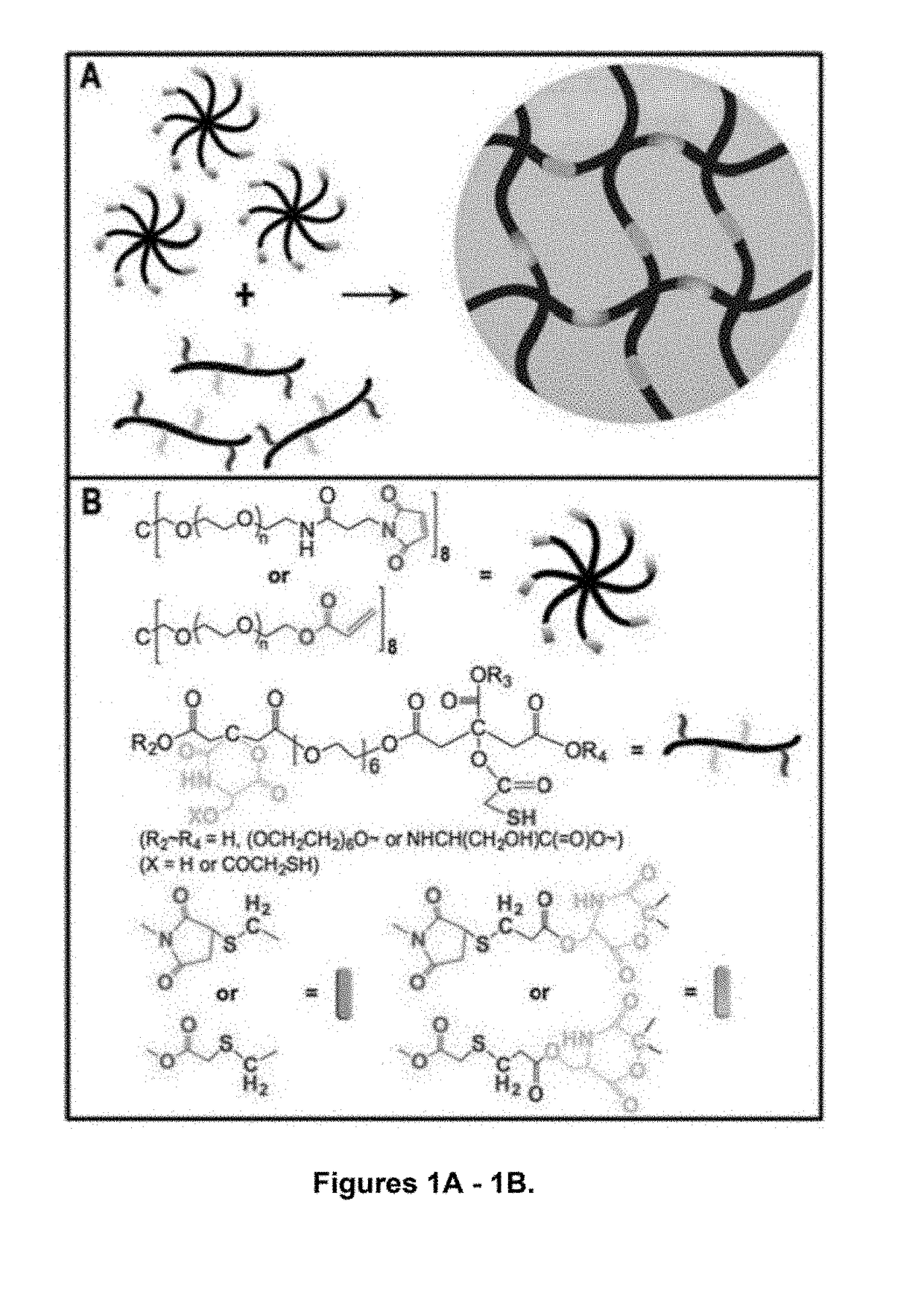
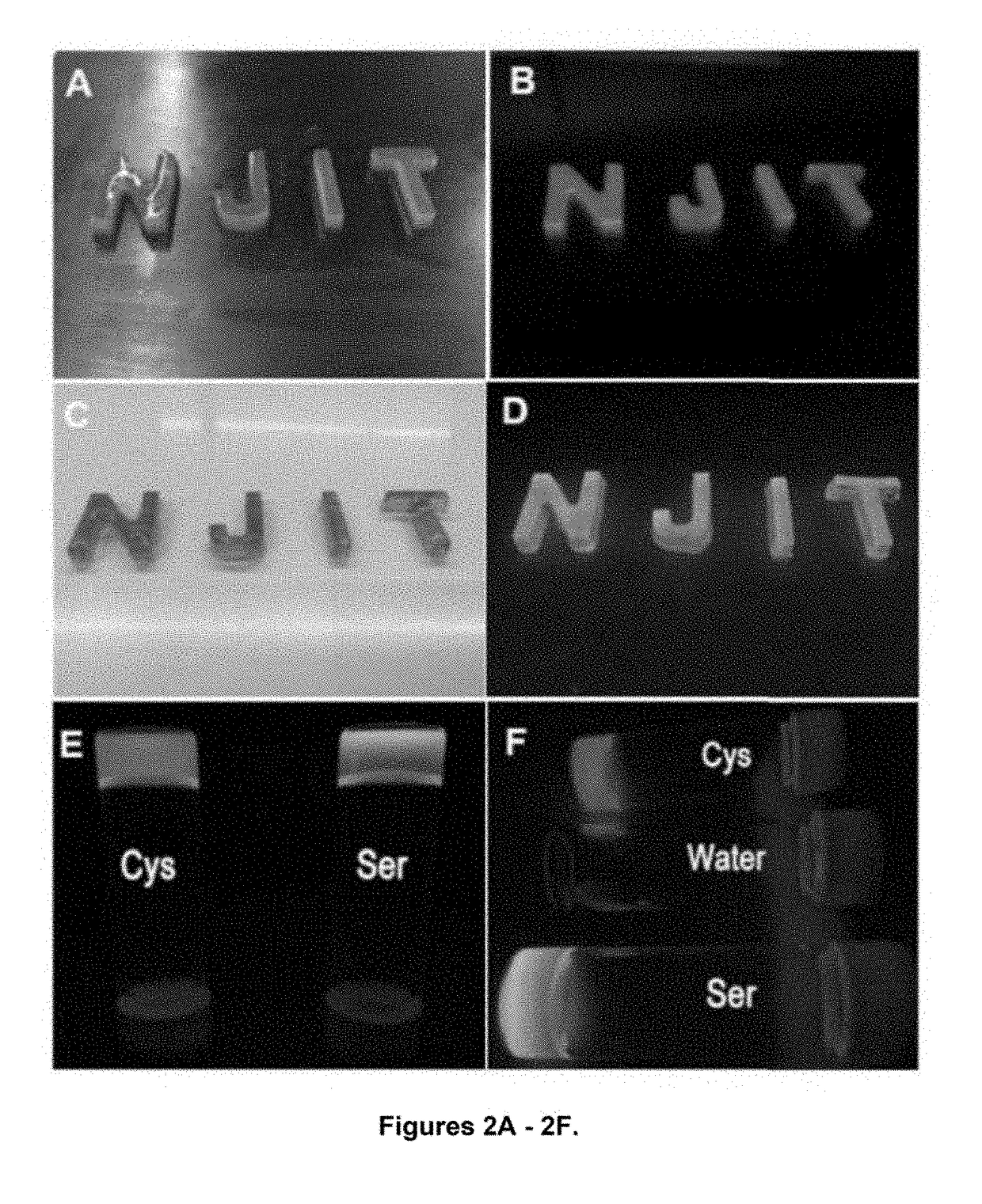
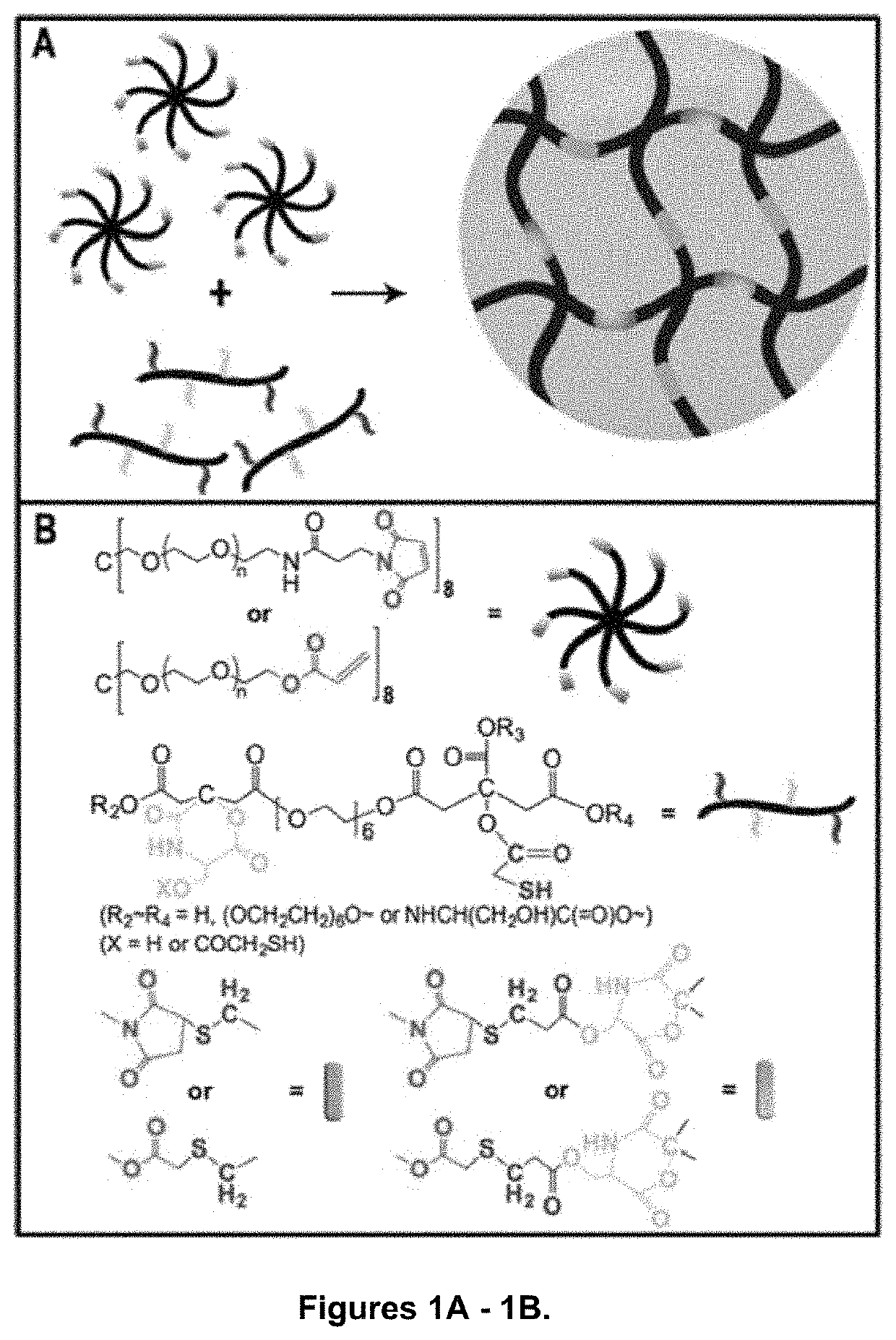
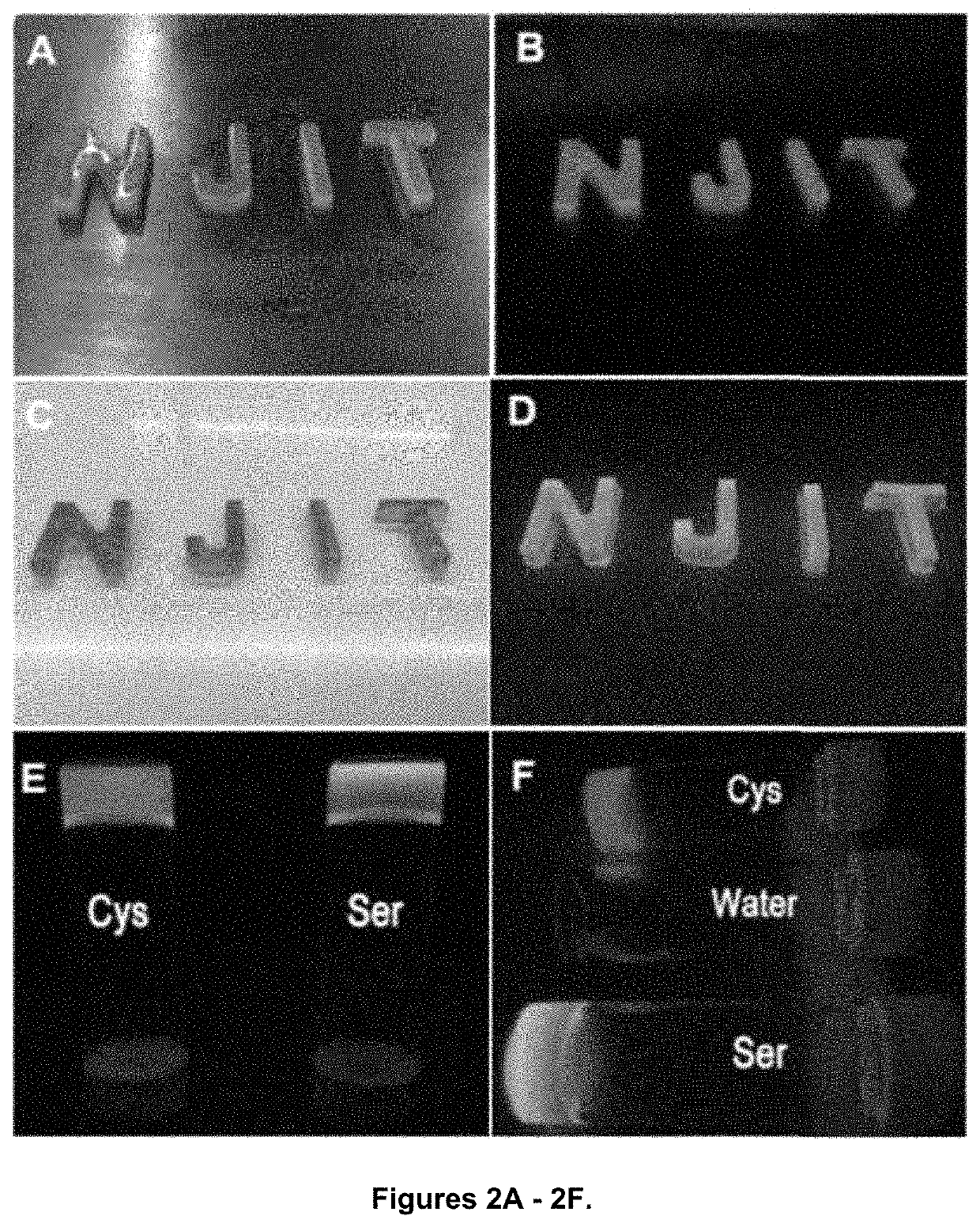
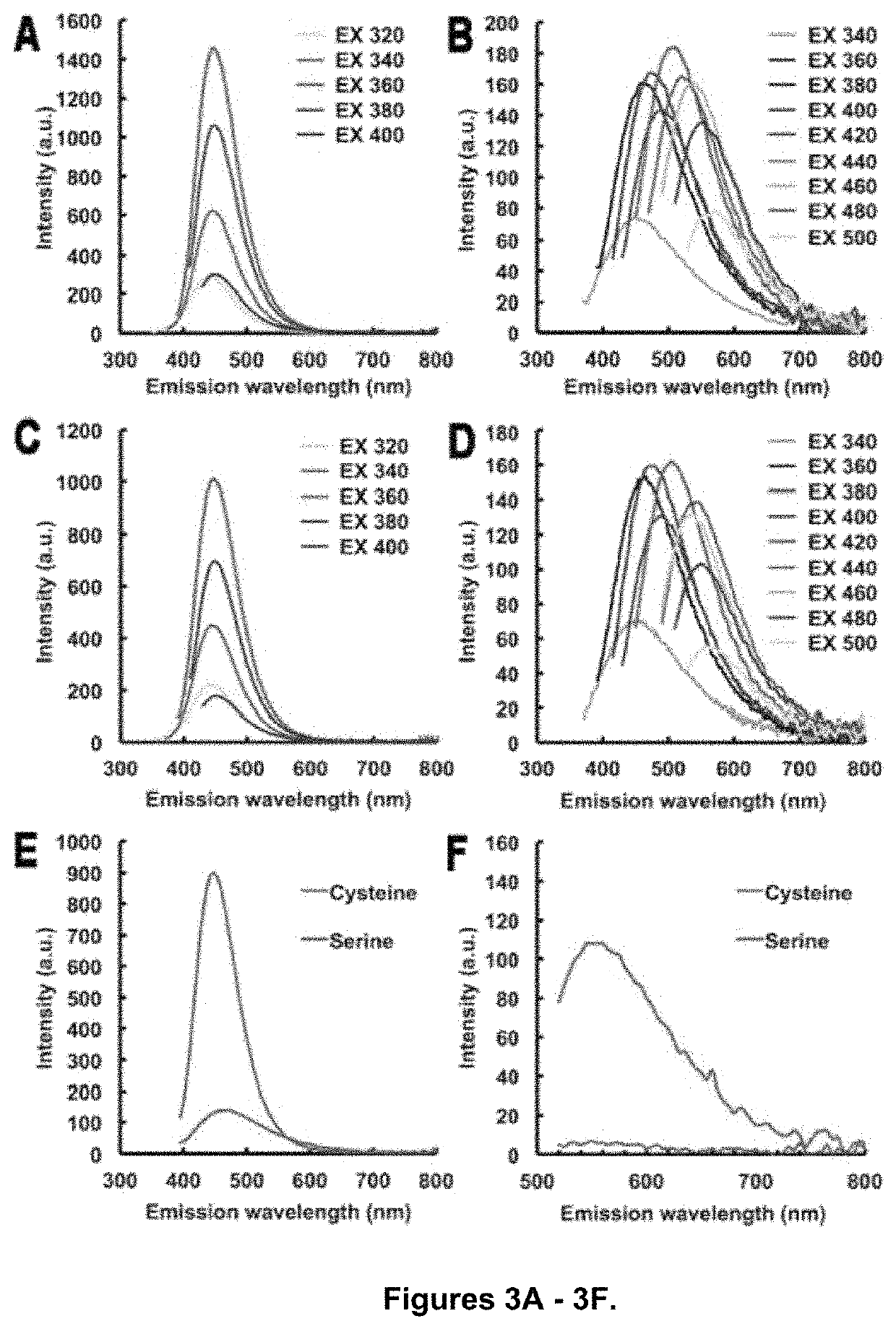
Shown and described is a composition and a method to prepare a dopant-free photoluminescent hydrogel with synthetic polymers are disclosed. The hydrogel can be synthesized in one embodiment by incorporating an amino acid to a citric acid based polyester oligomer followed by multiple cros slinking group functionalization through a transesterification reaction using an enzyme such as Candida Antarctica Lipase B (CALB) as a catalyst. The hydrogels are injectable, degradable, and their mechanical and photoluminescent properties are tunable. An in vivo study shows that the hydrogel emits strong fluorescence under visible light excitation and can completely degrade over time.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Chiral polyester compounds and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109705325ASingle configurationEnvironmentally friendlyMicroorganism based processesFermentationPolyesterTert-Butyloxycarbonyl protecting group
The invention discloses chiral polyester compounds and a preparation method thereof. The chiral polyester compounds have structural units of N-substituted-L-aspartic acid and long-chain fatty diol, and have a structural general formula represented by a formula (I) shown in the description, wherein in the formula (I), a substituent R is benzyloxycarbonyl, t-butyloxycarboryl or benzyl; m = 2, 4, 6or 10; and n represents an integer of 30 to 105; and a substituent of the N-substituted-L-aspartic acid is the same as the substituent R in the formula (I). The method provided by the invention adoptsa diester containing a chiral carbon atom and a diol without a chiral carbon atom as raw materials for the first time, and the novel chiral polyester compounds are synthesized under the action of a candida antarctica lipase B catalyst; and the compounds have the advantage of single configuration, are environmentally-friendly biodegradable materials, and have broad application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
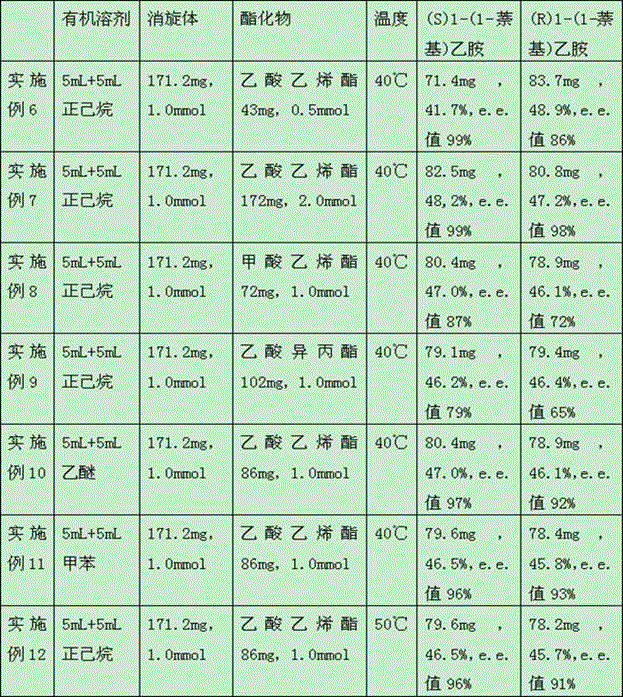
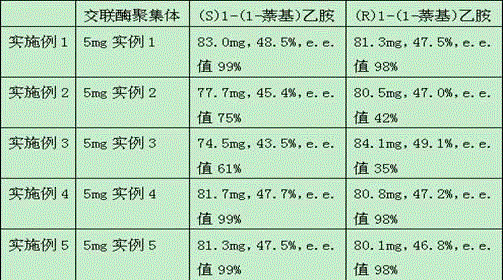
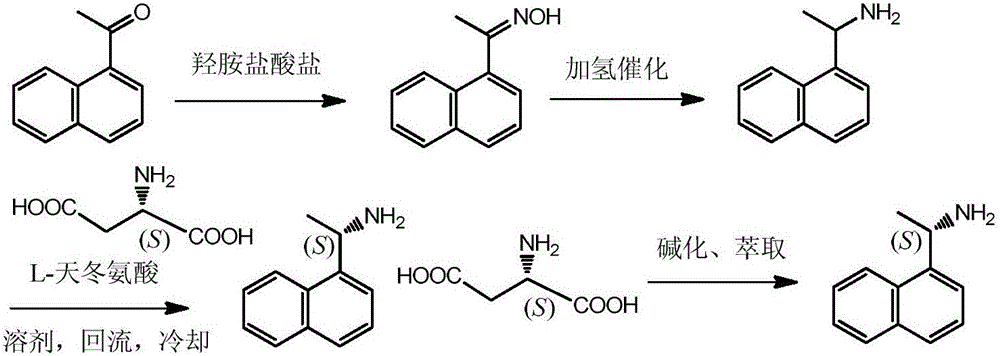
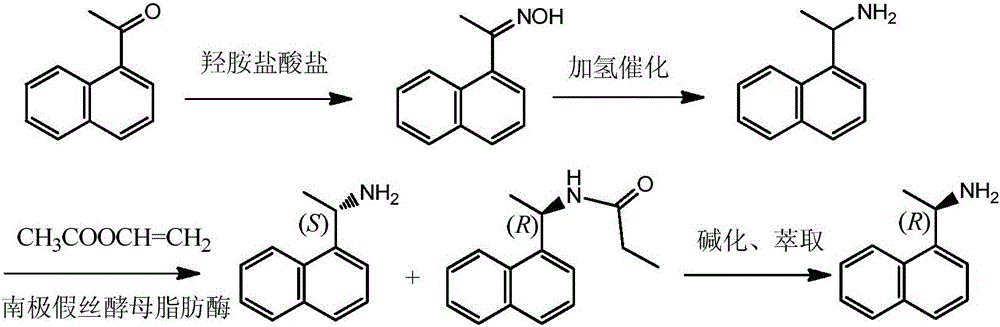
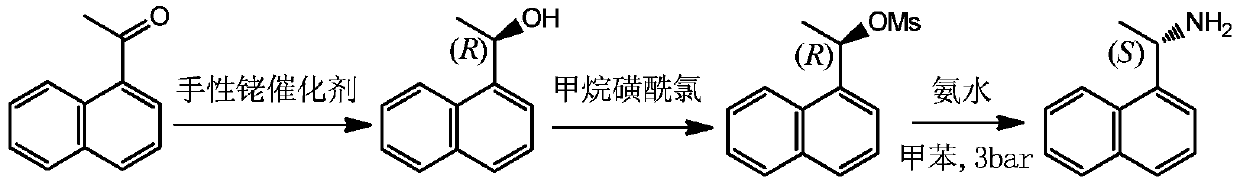
Method for preparing optical pure 1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine through resolution with immobilized enzyme process
InactiveCN104630322AExtended reaction timeStrong operational stabilityFermentationCross-linked enzyme aggregateOrganosolv
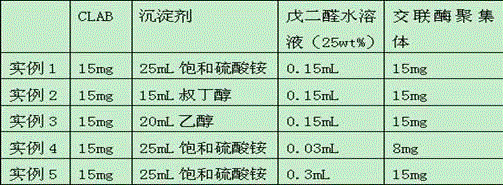
The invention discloses a method for preparing optical pure 1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine through resolution with immobilized enzyme process. The method comprises the following steps of selectively esterifying (R)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine in 1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine racemate, then separating (R)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine esterified compound from (S)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine to obtain (S)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine, and finally hydrolyzing the (R)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine compound to obtain the (R)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine. The catalyst for selective esterification is crosslinked Candida antarctica lipase B aggregate which is prepared through the following steps of dissolving Candida antarctica lipase B in water to obtain enzyme solution, depositing zymoprotein from the enzyme solution with a precipitator, then adding a difunctional crosslinking agent for crosslinking, and drying. The crosslinked enzyme aggregate is high in repeated utilization rate, and has relatively strong operation stability in a pure organic solvent.
Owner:南京普瑞特生物科技有限公司
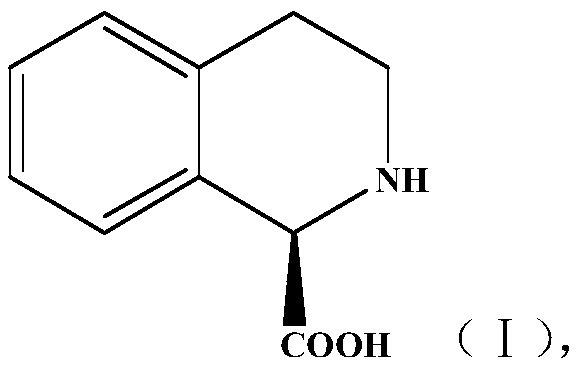
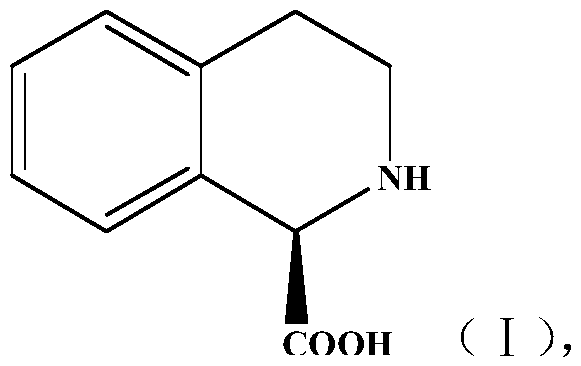
Method for preparing chiral isoquinoline carboxylic acid
PendingCN109897874AEfficient preparationHigh yieldHydrolasesFermentationIsoquinolineCandida antarctica
The invention discloses a method for preparing chiral isoquinoline carboxylic acid (I). The method comprises following steps: racemate of a compound I is subjected to a reaction to produce the compound shown as (I) in an aqueous phase buffer solution and under the catalysis of candida antarctica lipase B, the reaction is required to be always carried out at a preset pH value, and the preset pH value is 7.8-8.2. The method has the characteristics that the reaction condition is mild, stereoselectivity is high, reaction efficiency is high, and the technology is relatively simple and the like andhas industrial application prospects.
Owner:TONGLI BIOMEDICAL +1
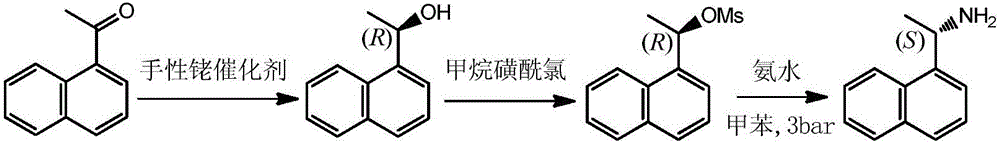
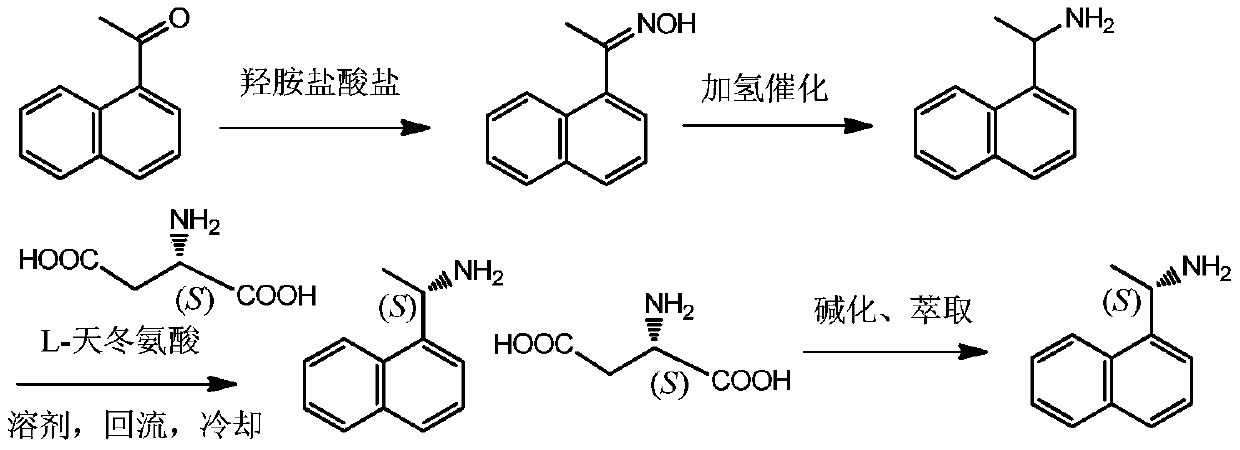
Method for preparing (S)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine by enzymatic resolution
InactiveCN105907833AImprove high temperature resistanceHigh split efficiencyFermentationAcetic acidHydrogen
The invention relates to a method for preparing (S)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine by an enzyme method. According to the method, Candida antarctica lipase B is adsorbed by macroporous resin, and cross-linking is carried out by using glutaraldehyde so as to obtain immobilized Candida antarctica lipase B. The immobilized lipase serves as a catalyst, toluene serves as a solvent, ethyl acetate serves as an acyl donor, (S)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylketoxime is selectively esterified, (R)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine is not esterified, and a racemation reaction is carried out in the presence of a racemation catalyst and hydrogen gas. According to the method, the immobilized Candida antarctica lipase B can be used for completely converting 1-(1-naphthyl)ethylketoxime into (S)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine ethyl ester at a relatively high temperature, and the reaction has the characteristics of short reaction time, high product optical purity, and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
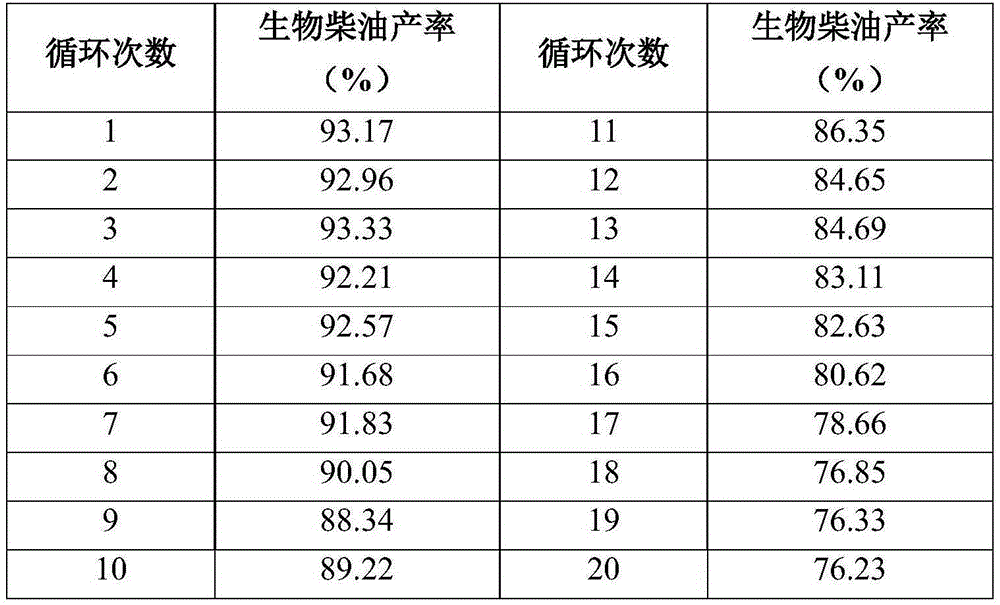
Method for producing biodiesel by utilizing immobilized lipase and adopting static emulsion method
ActiveCN105274157AEasy to exert interface activityHigh catalytic activityChemical industryBiofuelsBiodieselEmulsion
The invention relates to a method for producing biodiesel by utilizing immobilized lipase and adopting a static emulsion method. The method for producing biodiesel by utilizing immobilized lipase and adopting the static emulsion method comprises the following steps: (1) adding polydimethylsiloxane, lipase solution and a platinum catalyst into a reactor, carrying out vacuum magnetic stirring for 0.5-2 hours to obtain emulsion, then adding a dispersing agent into the emulsion to form composite emulsion, under the condition of mechanical stirring, solidifying for forming enzyme-loaded static emulsion silica gel microspheres, and filtering, so that immobilized lipase is obtained; and (2) adding vegetable fat and short chain alcohol into the reactor, then adding normal hexane with the volume 1-4 times that of the vegetable fat and immobilized lipase with the mass 20-30% that of the vegetable fat, and reacting at constant temperature of 20-600 DEG C, so that the biodiesel is obtained, wherein the lipase is candida antarctica lipase B, candida rogusa lipase or burkholderia cepacia lipase. The method for producing biodiesel by utilizing immobilized lipase and adopting the static emulsion method has the advantages of simple preparation technology, mild reaction conditions, no environmental pollution and high catalyst repeated utilization factor and is beneficial to industrial application of production of biodiesel.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for stereoselectively separating carprofen enantiomer through biological enzyme catalysis
The invention introduces a novel chiral separation method for acquiring a carprofen single enantiomer, namely a method for synthesizing the carprofen single enantiomer by stereoselectively hydrolyzing a carprofen enantiomer through biological enzyme catalysis. According to the method, candida Antarctica lipase A is utilized for hydrolyzing the carprofen enantiomer and cyclodextrin in a high selectivity and high catalytic efficiency manner so as to solubilize the carprofen enantiomer, so that the hydrolysis reaction of the carprofen enantiomer in a phosphate buffer solution is accelerated; the conversion rate of a substrate and the optical purity of a product can respectively reach 48.00% and 96.24%, and the stereoselectivity E is more than 145; the problems of low optical purity and yield, environmental pollution and the like in a common separation technique are overcome, and the high conversion rate and the high selectivity of the hydrolysis of the carprofen enantiomer can be realized, so that the purposes that non-toxic, harmless and environment-friendly separation of a chiral compound, reaction conditions are mild, the operation is simple and convenient, the cost is low and the like are achieved.
Owner:HUNAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Lipase mutant with improved heat stability, and construction method thereof
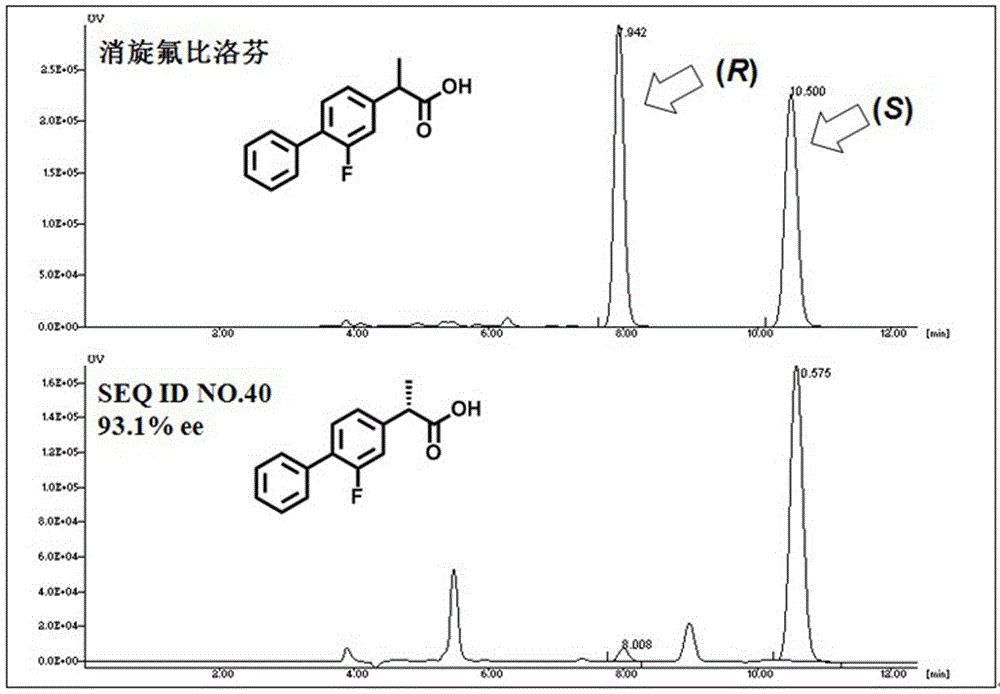
The invention provides a lipase mutant with improved heat stability and a construction method thereof. The lipase mutant with improved heat stability is obtained by subjecting Candida Antarctica lipase B gene to several rounds of fixed point saturation mutagenesis, the Candida Antarctica lipase B having an amino acid residue sequence expressed by SEQ ID No:1, and the lipase mutant having amino acid residue sequences expressed by SEQ ID No:2, SEQ ID No:3 or SEQ ID No:4, each of which consists of 317 amino acids. A method of semi-rational design is utilized in the invention, and a lipase mutantis obtained by subjecting Candida Antarctica lipase B gene to several rounds of fixed point saturation mutagenesis, wherein the mutant includes amino acid mutations D223G, L278M and combination of the two. Expressed by T50<15> and half-life t1 / 2 at the temperature of 48 DEG C respectively, the heat stability of the lipase mutant is improved, and a high actual application value and broad market prospects are also provided.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Preparation method of chemically modified lipase, lipase and application of lipase in synthesis of L-lactide
ActiveCN112695020AHigh yieldIncrease enzyme activityHydrolasesPeptide preparation methodsPoly-L-lactidePolymer science
The invention belongs to the technical field of polylactic acid production, particularly discloses chemically modified lipase for synthesizing L-lactide, and further discloses a preparation method of the lipase. According to the preparation method, epoxy isopropyl oleate is adopted for chemically modifying the lipase B derived from Candida antarctica, such that chemically modified lipase is obtained. The chemically modified lipase is high in enzyme activity, and the yield is remarkably improved when the chemically modified lipase is used for catalyzing to generate L-lactide.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA BIOCHEMICAL CO LTD
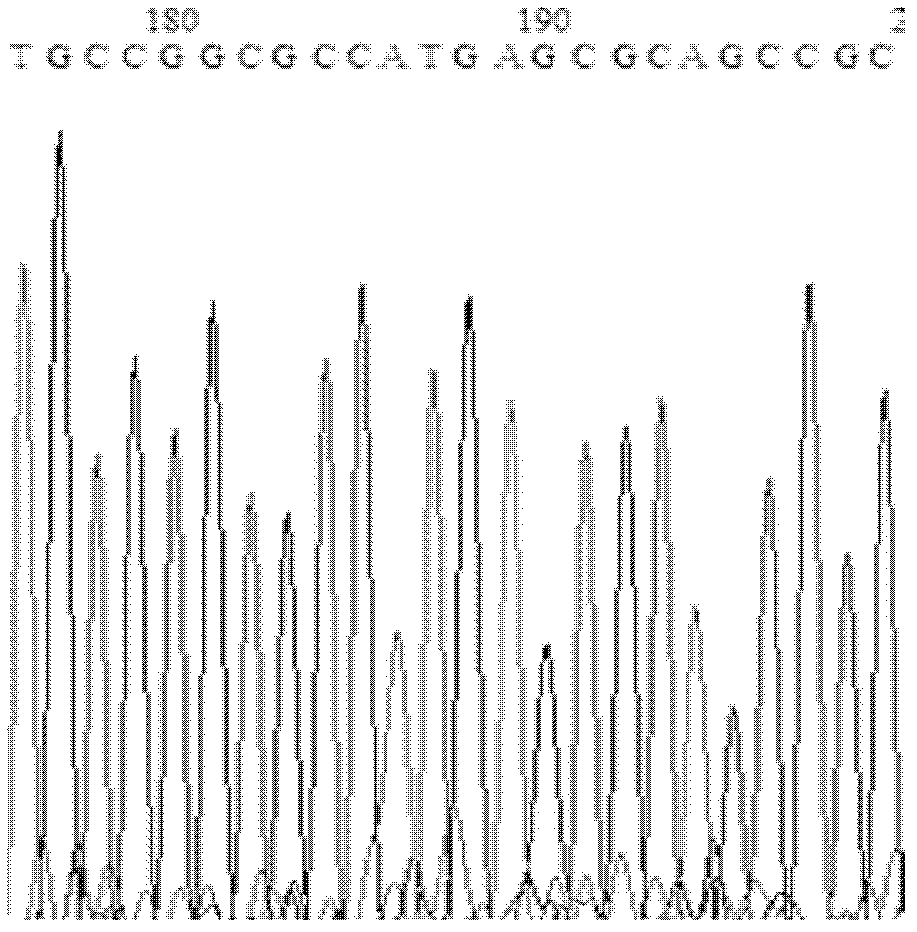
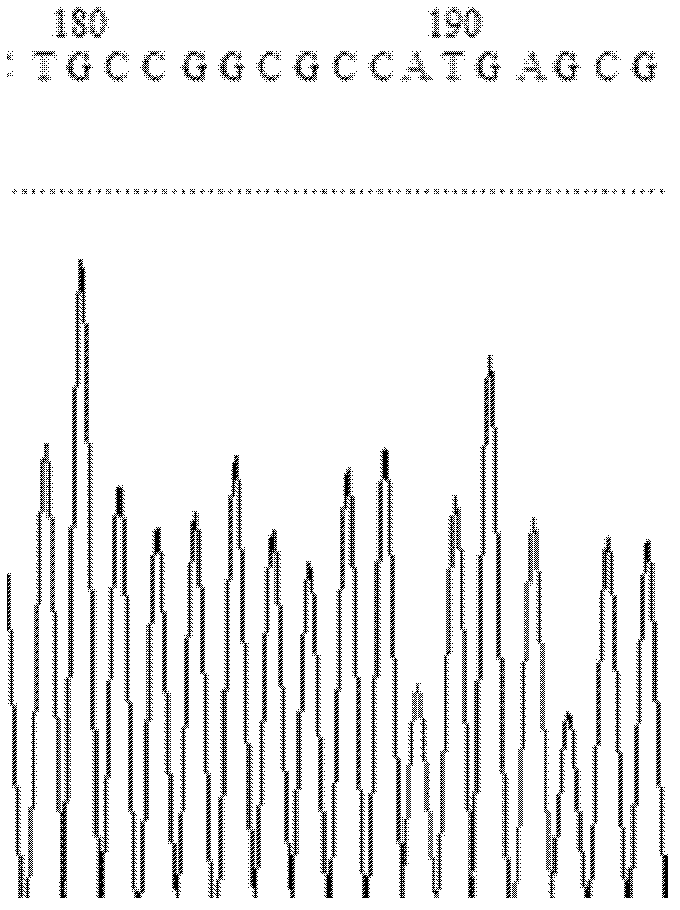
A kind of lipase mutant and its use
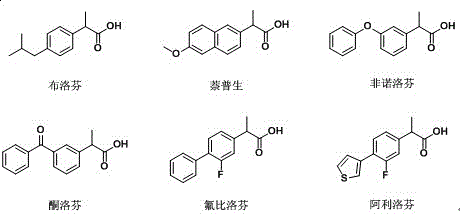
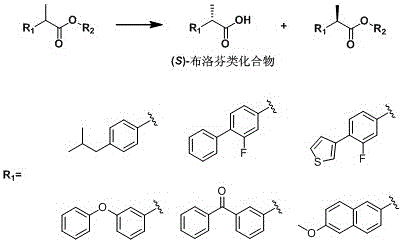
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and relates to a lipase mutant and uses thereof. The mutant is obtained from wild type candida antarctica lipase B (CALB) through mutation. The invention particularly relates to the lipase mutant, a preparing method thereof, and a method of preparing S-configuration ibuprofen type compounds with optical activity through catalysis of hydrolysis of ester derivatives of the ibuprofen type compounds by utilization of the lipase mutant and through kinetic resolution. The wild type candida antarctica lipase B is subjected to mutation to obtain the modified lipase. The lipase is expressed in pichia pastoris engineering bacteria. The lipase comprises an amino acid sequence having at least 85% of identity with the SEQ ID NO.02. The 189 site residue corresponding to the SEQ ID NO.02 of the lipase is an aromatic amino acid residue and the 190 site residue corresponding to the SEQ ID NO.02 of the lipase is a nonpolar amino acid residue. By subjecting the wild type candida antarctica lipase B to mutation, the enantioselectivity of the lipase to the ibuprofen type compounds is improved.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
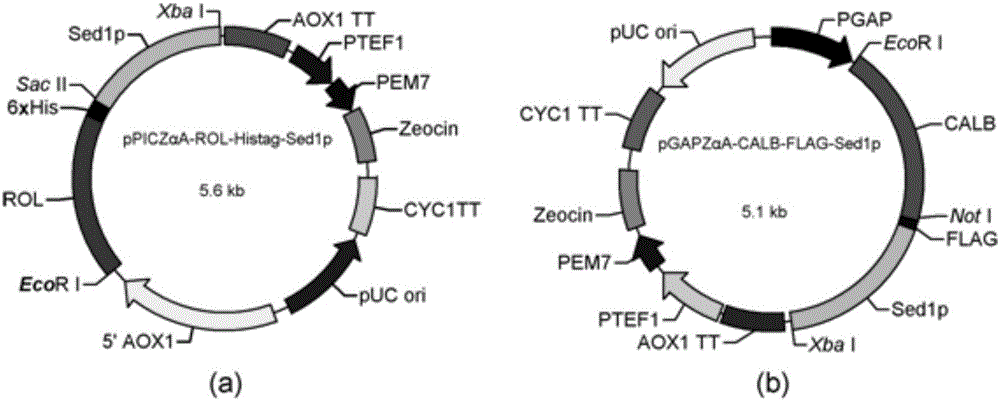
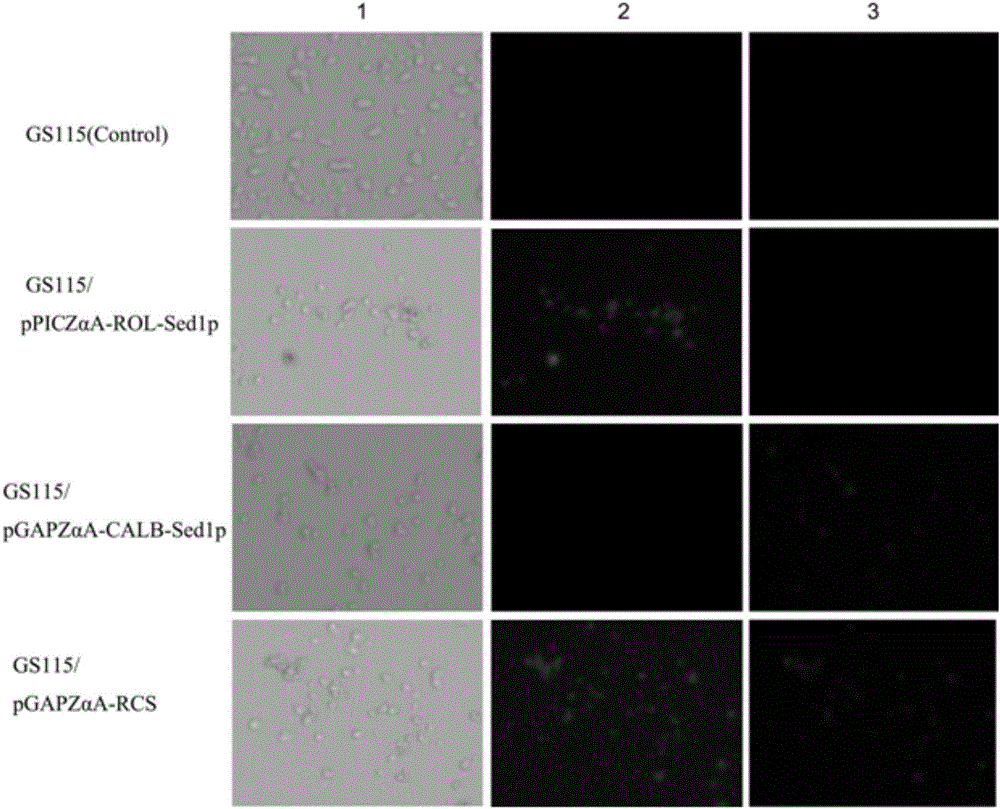
Double-lipase cell surface co-display engineering bacterium, and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN105062909AHigh catalytic efficiencyCatalytic reaction time is shortFungiBiofuelsPichia pastorisDry weight
The invention discloses a double-lipase cell surface co-display engineering bacterium, and a construction method and application thereof. The engineering bacterium is co-displayed on the Pichia pastoris cell surface by using Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell wall protein Sed1p as ankyrin and Rhizopus oryzae lipase and Candida antarctica lipase B as double-lipase target proteins, thereby constructing the double-lipase cell surface co-display recombinant yeast engineering bacterium. The Rhizopus oryzae lipase and Candida antarctica lipase B are co-displayed on the Pichia pastoris cell wall surface to prepare the Rhizopus oryzae lipase / Candida antarctica lipase B cell surface co-display complete cell catalyst. The maximum enzyme activity of the surface co-display complete cell catalyst is 686U / g-cell dry weight, which is respectively 3 times or 2 times of the enzyme activity of the independently displayed Rhizopus oryzae lipase or Candida antarctica lipase B; and the methyl ester yield of the catalytic grease esterification reaction is up to 96%.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
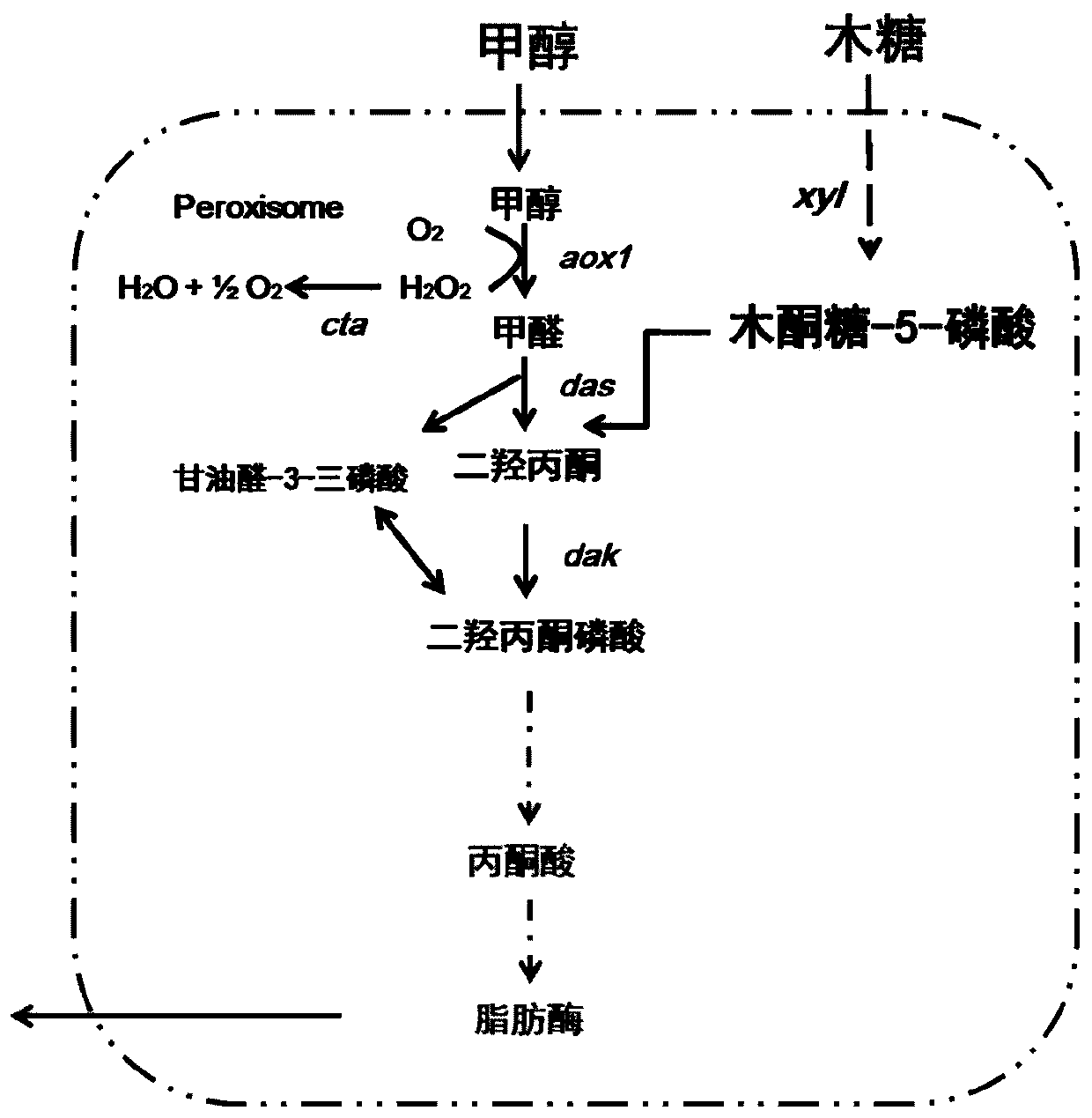
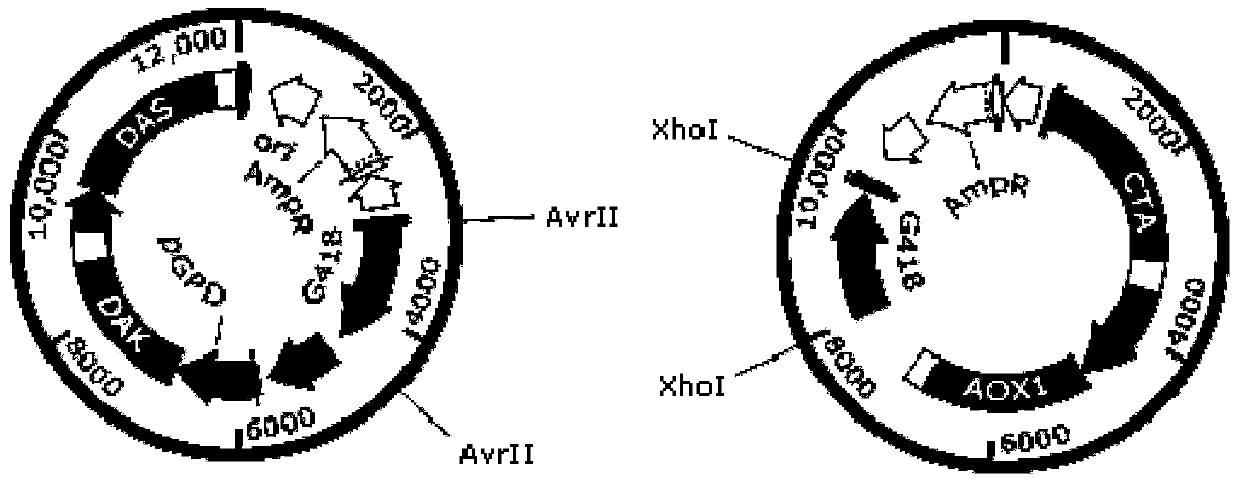
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing lipase by using methanol and xylose co-substrate and application of genetically engineered bacterium
The invention relates to a genetically engineered bacterium for producing lipase by using a methanol and xylose co-substrate and application of the genetically engineered bacterium. A methanol oxidasegene aox1, a dihydroxyacetone synthase gene das, a catalase gene cta and a dihydroxyacetone kinase gene dak are introduced into host bacteria; and the host bacteria are Candida antarctica capable ofproducing the lipase by utilizing xylose. According to the invention, a methanol metabolic pathway is introduced into the Candida antarctica by utilizing a synthetic biology way, so that the Candida antarctica can produce the lipase by taking non-food-grade raw materials, namely the methanol and the xylose, as a co-substrate, the production cost is reduced to a certain extent, and the applicationhas great significance and economic value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Plasmid Vectors For Transformation of Filamentous Fungi
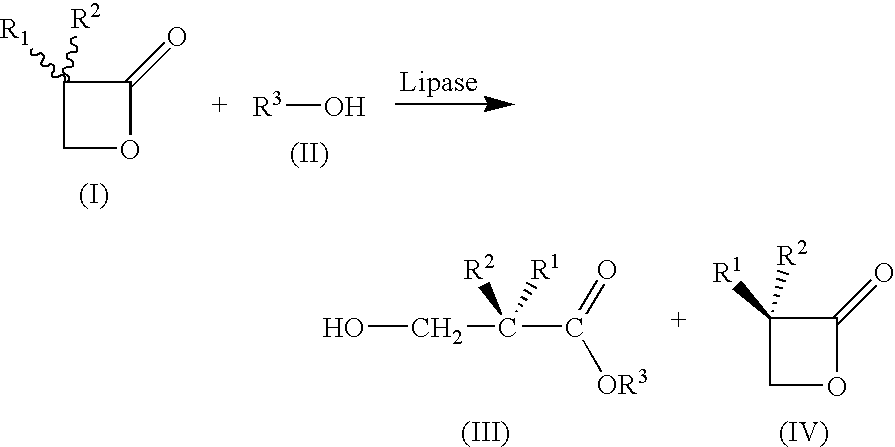
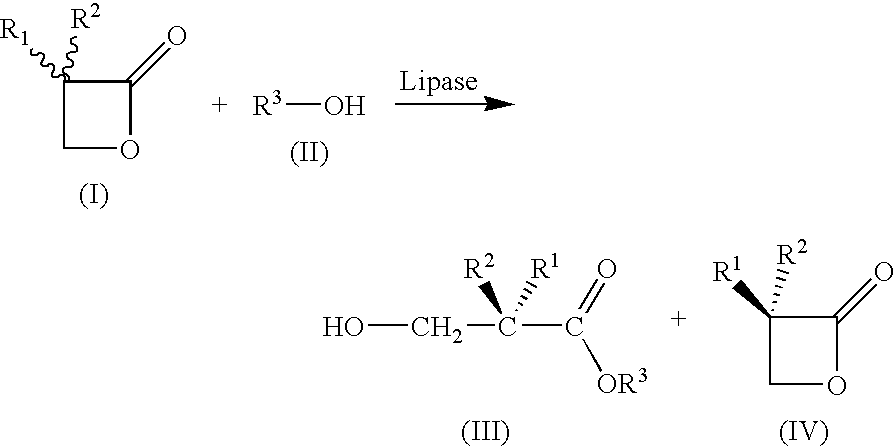
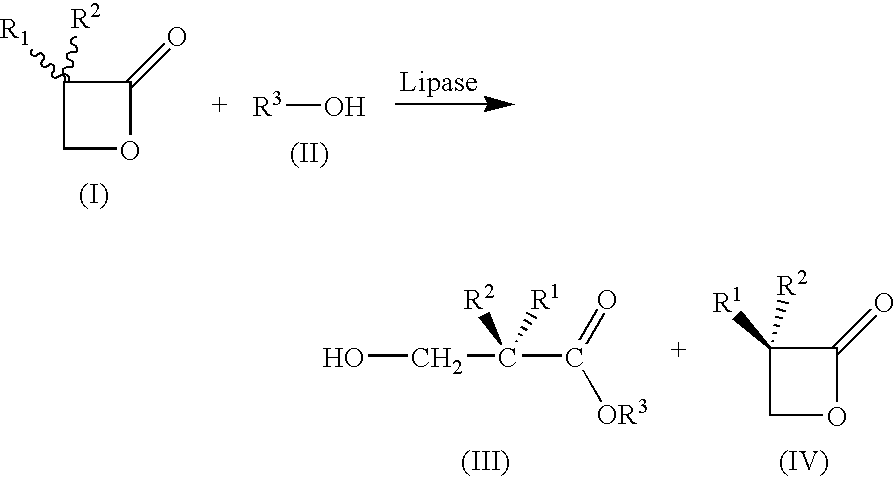
A method for preparing substantially enantiopure 3-hydroxy carboxylic acids or esters of the general formula (III) by reacting racemic oxetan-2-ones of the general formula (I) with compounds R3-OH of the general formula (II) in the presence of a lipase from Candida antartica or Burkholderia plantarii, and separating the resulting products of the formula (III) and (IV) from one anotherwhere the radicals have the following meaning:R1, R2, R3 independently of one another H; C1-C10-substituted or unsubstituted alkyl, substituted or unsubstituted aryl or hetaryl, where R1 and R2 may not simultaneously have the same meaning.
Owner:BASF AG
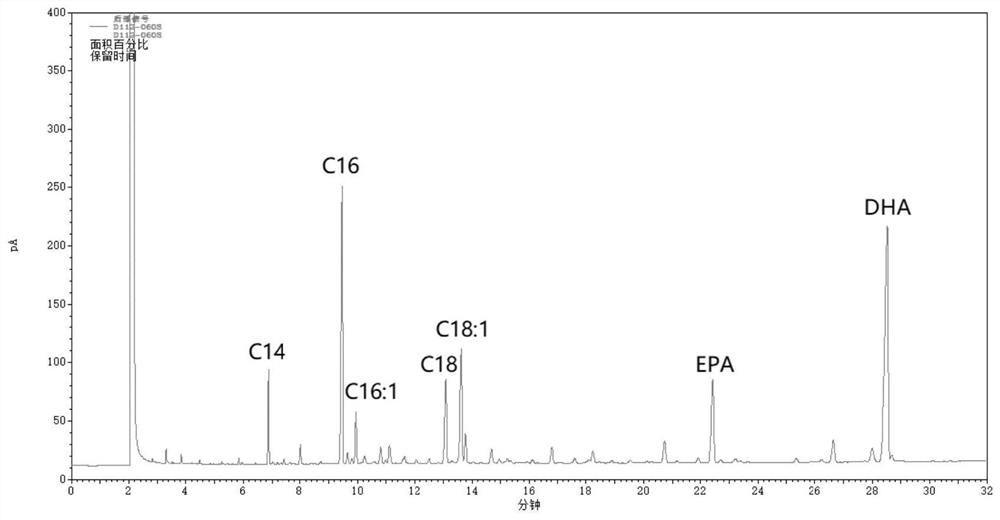
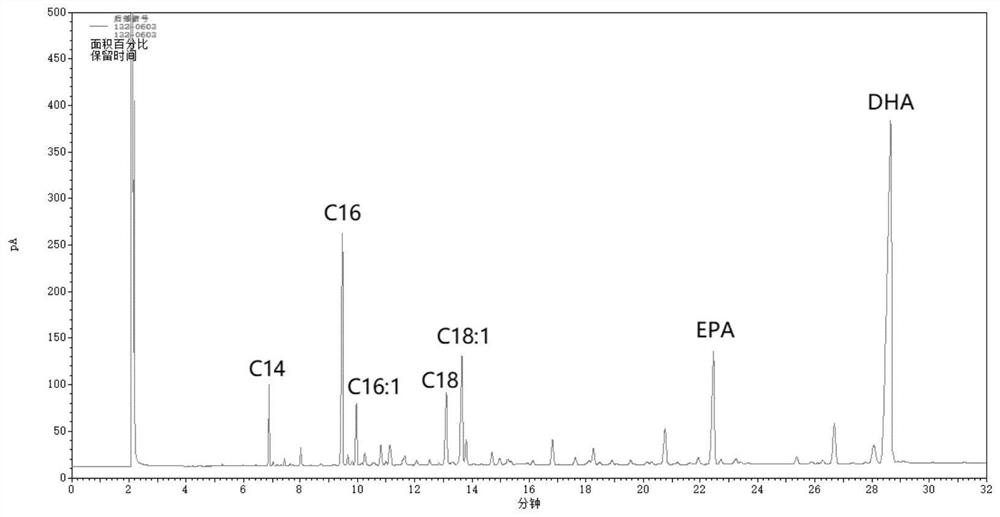
A kind of method for enriching n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid by enzymatic method
ActiveCN112592939BIncrease the rate of hydrolysisEnrichment reachedFermentationCandida antarcticaCatalytic hydrolysis
The invention discloses a method for enriching n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids by an enzymatic method, and belongs to the field of oil and fat deep processing. The method of the invention comprises: taking oil, water (alcohol) solution and lipase to react in a reactor, wherein the lipase includes one or more lipases derived from Candida cylindracea and lipase Candida antarctica lipase A, And the order of adding lipase is not fixed. At present, the content of saturated and monounsaturated fatty acids in the glycerides obtained by enzymatic catalytic hydrolysis or alcoholysis enrichment PUFA reaction is still relatively high; The monounsaturated fatty acid has specificity, and further reduces the non-PUFA fatty acid content in the glyceride product, thereby obtaining a glyceride product with a higher content of PUFA.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for enriching n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids by enzymic method
ActiveCN112592939AIncrease the rate of hydrolysisEnrichment reachedFermentationFatty acids.polyunsaturatedCandida antarctica
The invention discloses a method for enriching n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids by an enzymic method, and belongs to the field of grease deep processing. The method disclosed by the invention comprisesthe steps that: grease, a water (alcohol) solution and lipase are taken to react in a reactor, wherein the lipase comprises one or more kinds of lipase from Candida cylindracea and lipase Candida antarctica lipase A; and the adding sequence of the lipase is uncertain. At present, the content of saturated and monounsaturated fatty acids in glyceride obtained by enzymatic catalytic hydrolysis or alcoholysis PUFA enrichment reaction is still high; two kinds of lipase from different sources are selected and have specificity in hydrolysis or alcoholysis of saturated fatty acids and monounsaturatedfatty acids in the invention; the fatty acid content of non-PUFA in a glyceride product is further reduced; and therefore, the glyceride product with higher PUFA content is obtained.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for preparing DAG by enzymolysis of TAG
ActiveCN104711298AReaction raw materials are cheapLow costFermentationCandida antarcticaTG - Triglyceride
The invention relates to a method for preparing DAG by enzymolysis of TAG, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of DAG. The method comprises the step of adding ethanol or / and metal ions into TAG, water and candida Antarctica lipase A to form a hydrolyzed system. According to the method, through the added metal ions, the activity of the candida Antarctica lipase A can be remarkably improved, and the hydrolysis rate of TAG is increased; ethanol and the metal ions are added at the same time, the 2-site selection tendency of the candida Antarctica lipase A for TAG can be improved, reaction time can be shortened, the hydrolysis rate is increased, and amplitude is further increased; therefore, ethanol plays the effect of promoting the metal ions to increase the hydrolysis rate.
Owner:浙江天顺生态农业开发有限公司
Photoluminescent hydrogel
ActiveUS10653802B2Easy to trackStrong emitted fluorescenceHydrolasesAerosol deliveryAmino acid bindingPolyester
Shown and described is a composition and a method to prepare a dopant-free photoluminescent hydrogel with synthetic polymers are disclosed. The hydrogel can be synthesized in one embodiment by incorporating an amino acid to a citric acid based polyester oligomer followed by multiple crosslinking group functionalization through a transesterification reaction using an enzyme such as Candida antarctica Lipase B (CALB) as a catalyst. The hydrogels are injectable, degradable, and their mechanical and photoluminescent properties are tunable. An in vivo study shows that the hydrogel emits strong fluorescence under visible light excitation and can completely degrade over time.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparing 1,3-diglyceride through enzymolysis
InactiveCN104630296AReaction raw materials are cheapLow costFermentationCandida antarcticaDiglyceride
The invention relates to a method for preparing 1,3-diglyceride through enzymolysis, and belongs to the technical field of 1,3-diglyceride. The method comprises the step of adding ethanol or / and chelating agent in TAG, water and Candida antarctica lipase A to form a hydrolysis system. According to the method, the chelating agent is added in the TAG hydrolysis system to remove metal ion (mainly from the TAG), thereby reducing the inhibiting effect of the metal ion to the enzyme activity and improving the hydrolysis rate; after ethanol and the chelating agent are simultaneously added, not only is the selection tendency of the Candida antarctica lipase A to 2 position of the TAG improved and the reaction time shortened, but also the improvement range of the hydrolysis speed is further increased; therefore, ethanol plays the effect of promoting the chelating agent to improve the hydrolysis speed.
Owner:HANGZHOU DUOHAI TECH
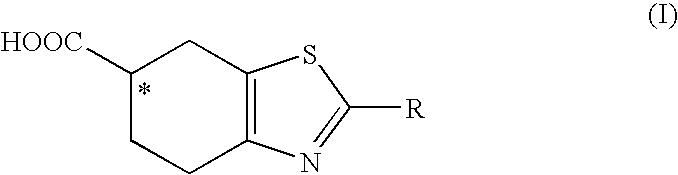
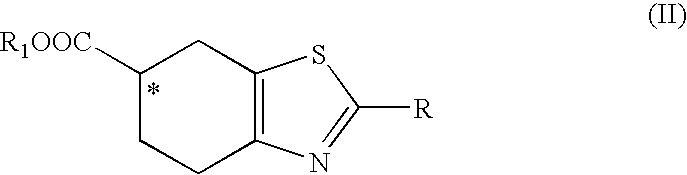
Synthesis of intermediates for the preparation of pramipexol
A process for the preparation of an acid of formula (I), as the individual (R) enantiomer or (S), or a salt thereofwherein R is a protected amino group; and the asterisk * denotes the stereogenic carbon atom, comprising contacting an ester of formula (II), as mixture of (R,S) enantiomers, or a salt thereof,wherein R1 is straight or branched C1-C6 alkyl, optionally substituted with phenyl; (the asterisk * and R defined above), with a lipase from Candida antarctica, under conditions effective to obtain a mixture comprising an acid of formula (I), as the individual (R) enantiomer, and an ester of formula (II), as the individual (S) enantiomer; the subsequent hydrolysis of the latter to obtain an acid of formula (I), as the individual (S) enantiomer; and, if desired, the conversion of an acid of formula (I), either as the (R) or (S) enantiomer, to a salt thereof.
Owner:DIPHARMA FRANCIS
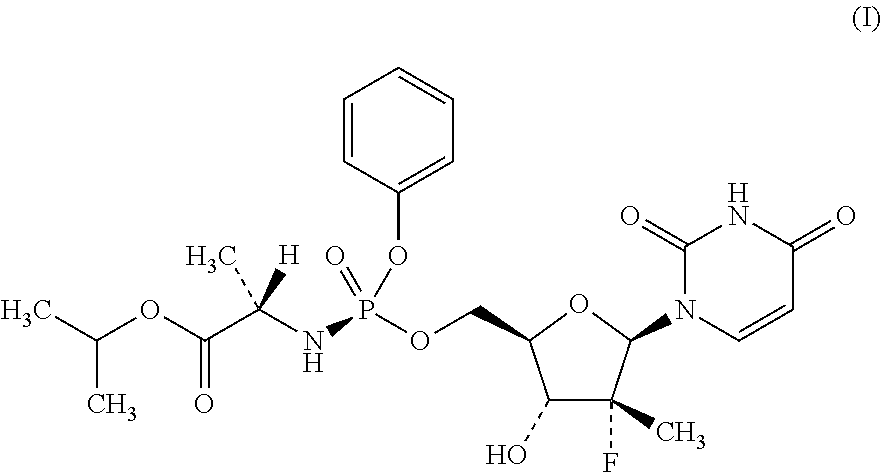
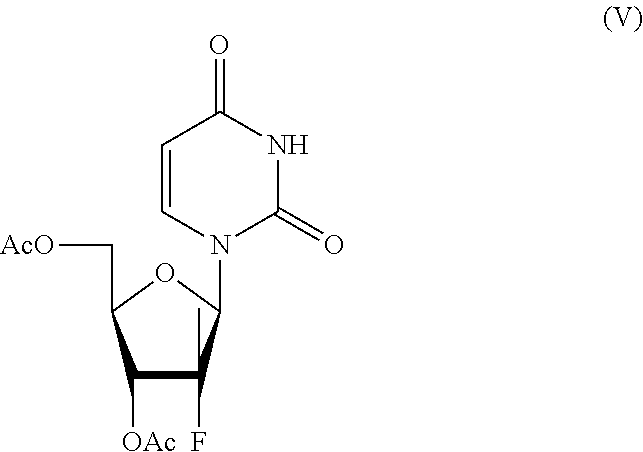
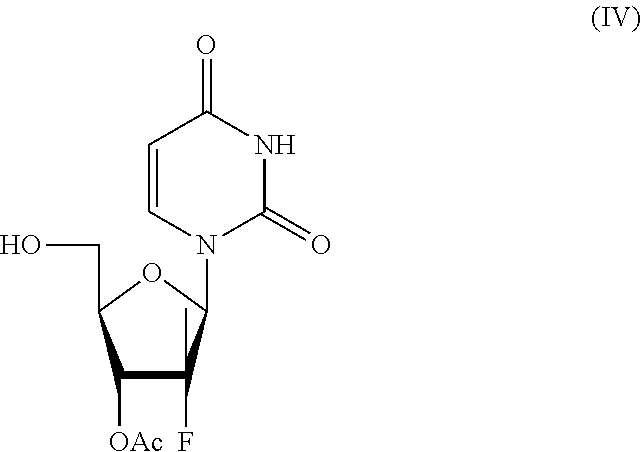
Process for the preparation of sofosbuvir
Owner:HC PHARMA
Immobilized enzyme for oriented catalysis of esterification reaction and preparation method and application of immobilized enzyme
PendingCN111394345AEasy to prepareIncrease enzyme activityHydrolasesOn/in organic carrierFreeze-dryingCandida antarctica
The invention belongs to the technical field of biochemical engineering and in particular discloses an immobilized enzyme for oriented catalysis of an esterification reaction and a preparation methodand application of the immobilized enzyme. The method comprises the following steps: mixing candida antarctica lipase with an HEPES (hydroxyethyl piperazin ethanesulfonic) buffer so as to obtain an HEPES-lipase liquid; and mixing the obtained HEPES-lipase liquid with GMP (guanine nucleotide) or AMP (adenine nucleotide) mother liquor so as to obtain a mixed solution, further uniformly mixing the mixed solution with metal ions, performing filtering, and performing freeze drying, so as to obtain the immobilized enzyme. The immobilized enzyme preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple, and the obtained immobilized enzyme is high in enzyme activity, is capable of effectively catalyzing the esterification reaction, in addition, is good in repeated utilization, but cannot catalyze alcoholysis reactions, has an oriented catalysis property, that is, is capable of catalyzing the esterification reaction but not alcoholysis reactions, and thus has very good application prospects.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
Preparation method of enzyme-loaded xerogel monolithic column catalytic filler
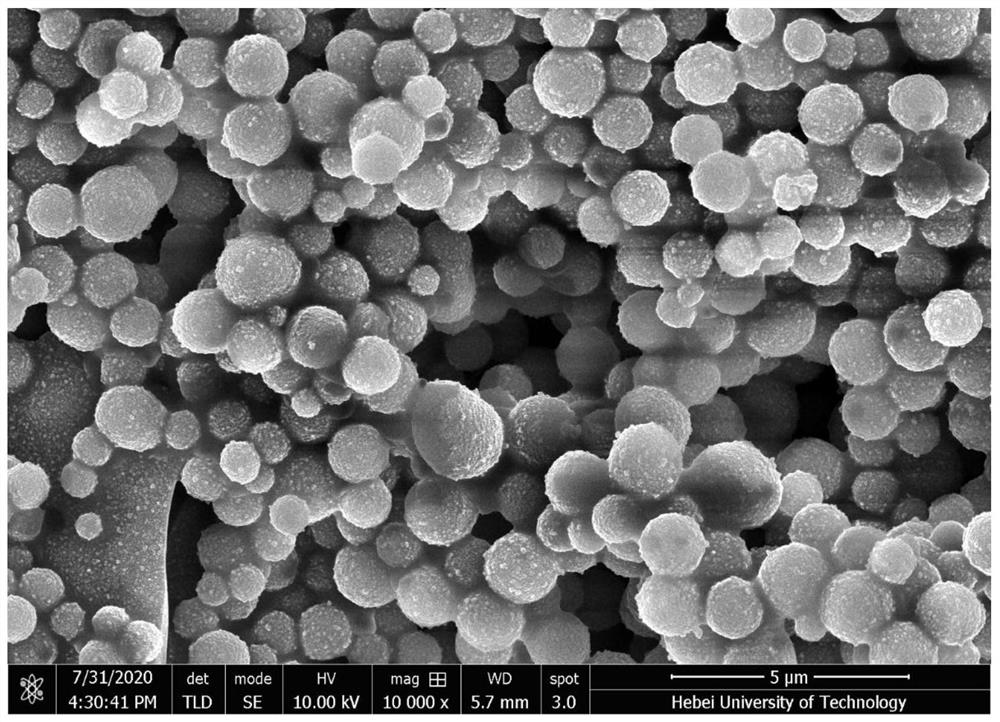
ActiveCN112760314AHigh activityGood choiceHydrolasesOn/in organic carrierCandida antarcticaHydrolysis
The invention relates to a preparation method of an enzyme-loaded xerogel monolithic column catalytic filler. The method comprises the following steps of embedding Candida antarctica lipase B through a sol-gel method, taking organosilicon as a precursor, carrying out hydrolysis and condensation polymerization, and carrying out normal-pressure drying by using a cylindrical mold to prepare the cylindrical enzyme-loaded xerogel monolithic column catalytic filler. In the obtained enzyme-loaded xerogel monolithic column catalytic filler, xerogel has a silicon network structure, enzyme is embedded in the xerogel, and the enzyme-loaded xerogel monolithic column catalytic filler has the advantages of complete catalysis, no surface crack, high mechanical strength and the like.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
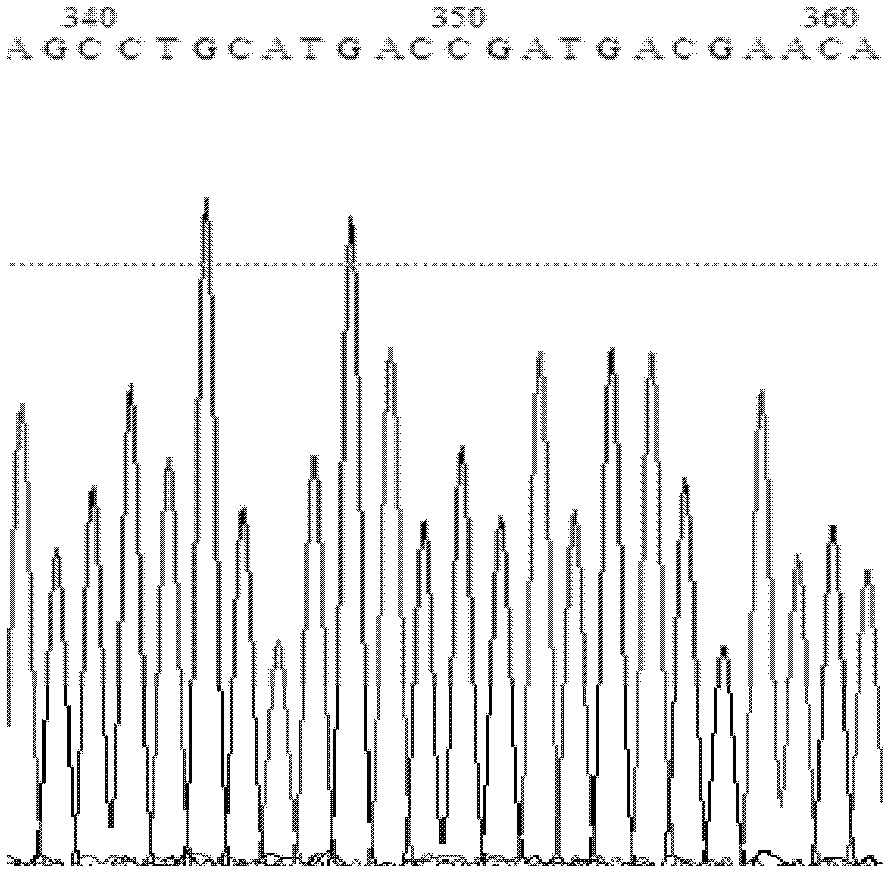
Method for producing candida antarctica lipase B and specific DNA molecule used by method
ActiveCN112410361AIncrease productionHigh purityBacteriaHydrolasesInclusion bodiesProkaryotic expression
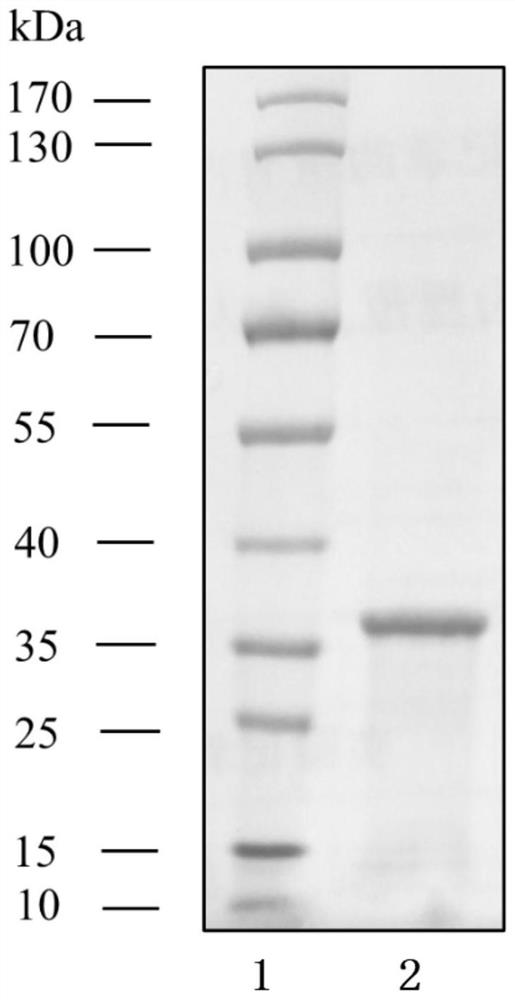
The invention discloses a method for producing candida antarctica lipase B and a specific DNA molecule used by the method. The nucleotide sequence of the specific DNA molecule is shown as SEQ ID NO: 3. Experiments prove that the recombinant plasmid pET30a-CALB is used for prokaryotic expression of the CALB inclusion body, and then renaturation is performed to obtain the CALB protein with high purity (more than 95%) and high activity; the enzyme activity of CALB protein obtained from 1L culture solution is about 21252U, and the specific activity is about 253U / mg, which is far higher than that of the CALB protein prepared by the existing literature. Therefore, the method provided by the invention can improve the yield of the CALB remarkably, the production process is simple, and the method can be applied to actual production The invention has important application value.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Hybrid material comprising a protein matrix and copper nanoparticles therein, process for preparing the same and use thereof
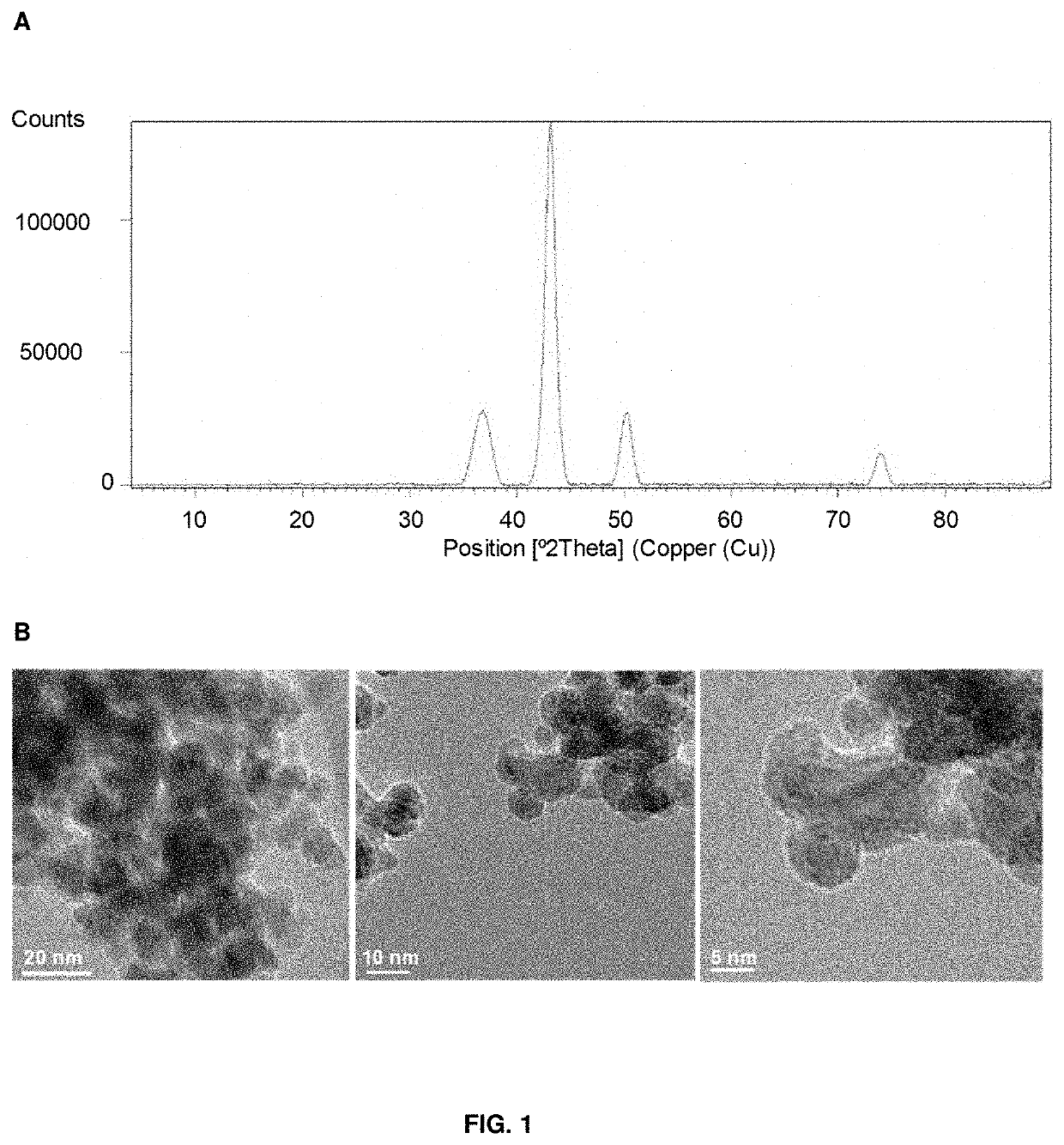
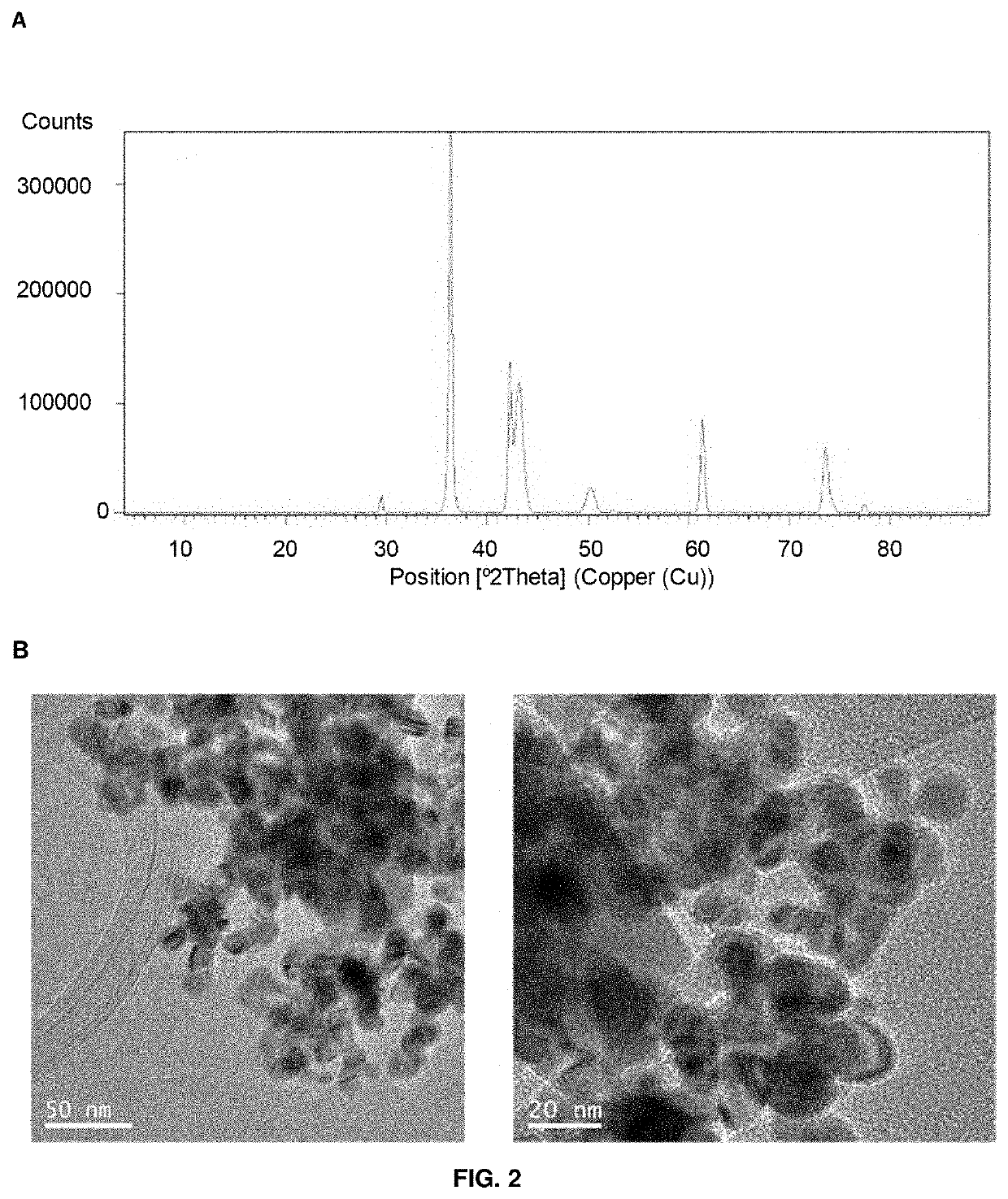
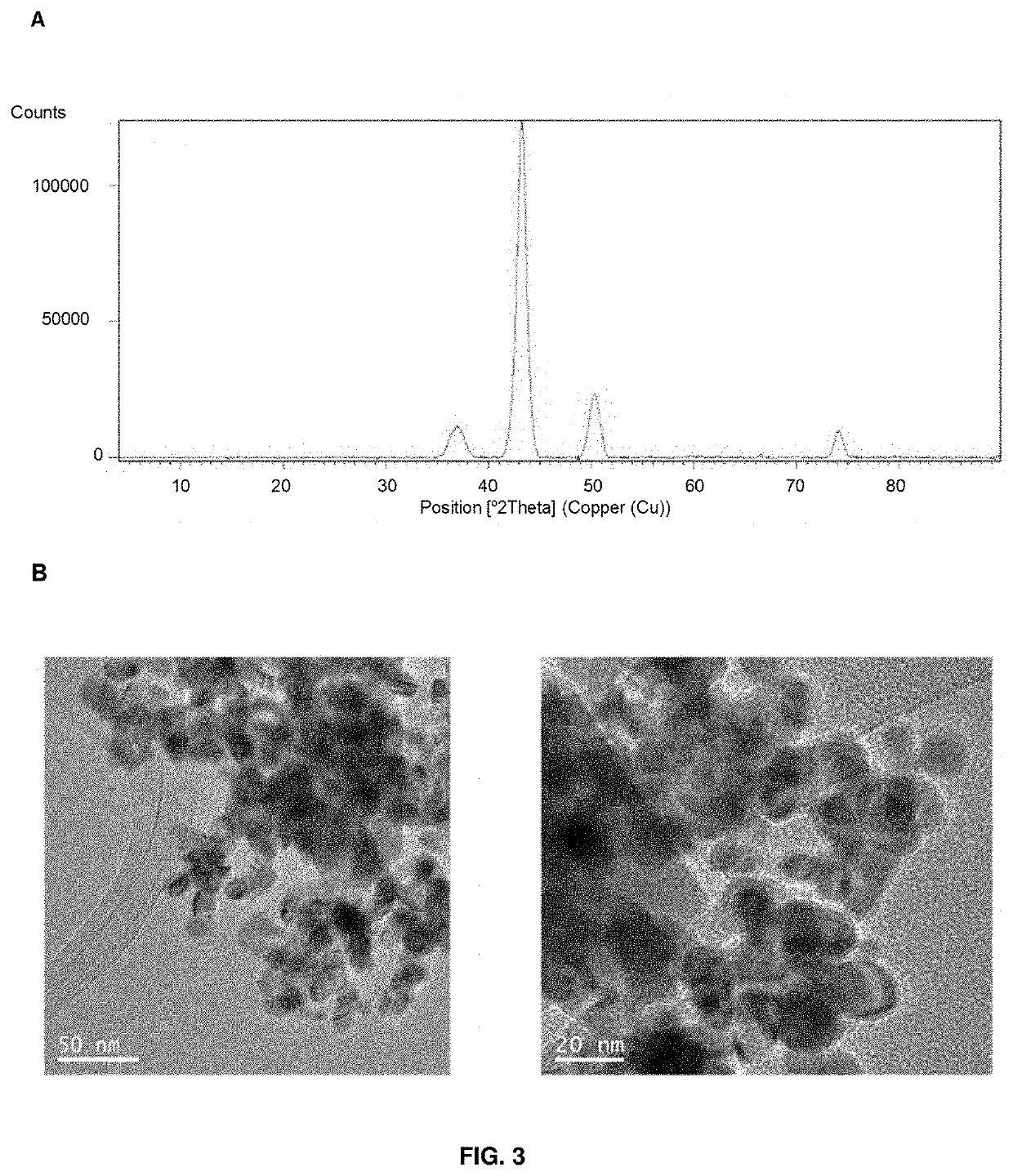
PendingUS20220258143A1High activityLarge capacityHydrolasesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsM-aminophenolNitrobenzene
The present invention relates a hybrid material comprising: a protein matrix comprising the lipase B from Candida antarctica and nanoparticles of copper species selected from: Cu (0), Cu2O Cu3(PO4)2 or any combination thereof, having their larger dimension between 3 and 15 nm. The material was prepared by the use of an enzyme in a buffer solution and a copper salt at room temperature. The material shows excellent catalase-like activity, excellent catalytic capacity in the degradation of organic pollutants, like Bisphenol A, and in the reduction of 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC) +1
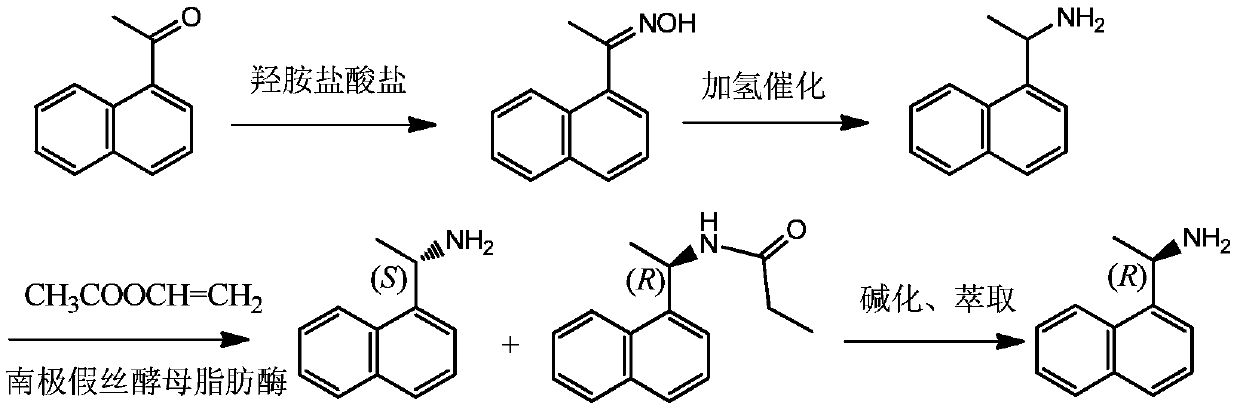
A method for enzymatic resolution and preparation of (s)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine
InactiveCN105907833BImprove high temperature resistanceHigh split efficiencyFermentationPtru catalystAcyl group
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
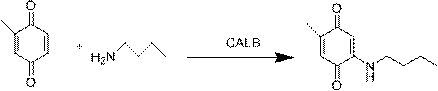
Method for preparing methylbutylamine p-benzoquinone through lipase catalysis
The invention discloses a method for preparing methylbutylamine p-benzoquinone through lipase catalysis. The method is characterized by comprising a step of catalyzing butyl amine to react with methylp-benzoquinone by using immobilized candida antarctica lipase, thereby obtaining 2-methyl-5-methylbutylamine p-benzoquinone. The 2-methyl-5-methylbutylamine p-benzoquinone is prepared by using an enzyme catalysis method, because of high spatial selectivity of an enzyme, difficulties that a chemical synthesis process is poor in selectivity and hard in product separation can be avoided, and the method is an environmental-friendly efficient synthesis method.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com