High-enantiomer selectivity epoxide hydrolase and gene coded thereby
A technology of epoxides and hydrolytic enzymes, which is applied in the fields of hydrolytic enzymes, plant genetic improvement, genetic engineering, etc., and can solve problems such as inability to meet large-scale industrial applications, high prices, and limited scope of substrate action
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
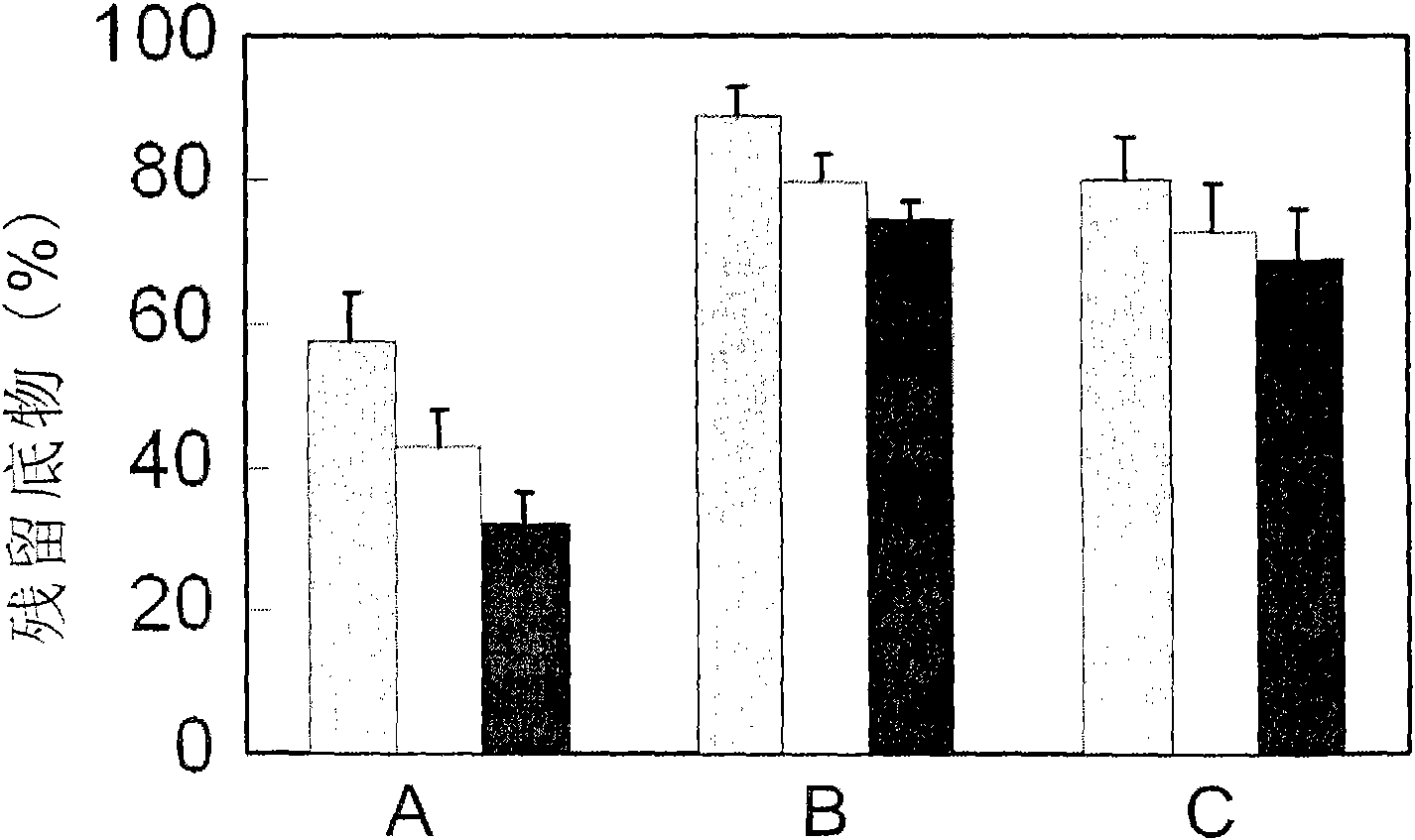
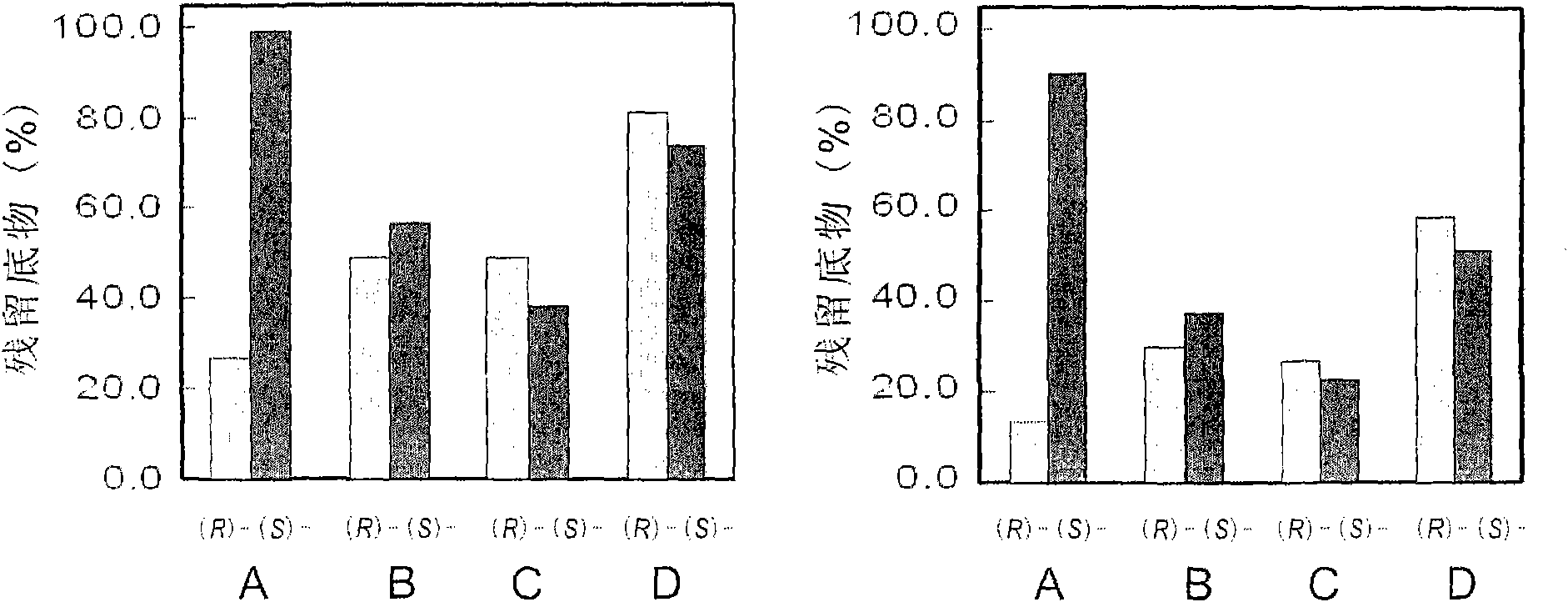
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0014] Example 1: Cloning of the sequence of the epoxide hydrolase PchEHA coding region from P.chrysosporium
[0015]Cultivation and RNA extraction of P.chrysosporium BKM-F1767: Inoculate P.chrysosporium BKM-F1767 on a PDA plate and culture at 38°C for 5 days. After a large number of conidia are formed on the plate, use 0.1% sterile Tween- 20 solution to wash the spores from the plate, vortex to disperse and filter with gauze. Centrifuge the filtrate at 4000rpm for 5min, wash twice with sterile water, resuspend the spores, and adjust the concentration to A 600 ≈1.0. Inoculate 3ml of the prepared spore suspension into 50mL of Kirk low-nitrogen medium, respectively, and inoculate it with oxygen at 39°C, set up 3 parallel samples, and collect the mycelium by filtration at 48h and 72h after cultivation For the extraction of total cellular RNA. The total RNA of P. chrysosporium was extracted using TRIZOL kit (Invitrogen Company), and the operation steps were carried out accordin...
Embodiment 2
[0020] Embodiment 2: Construction of epoxide hydrolase PchEHA expression vector
[0021] Plasmid pTEHA was double digested with BamH I and Hind III, and the coding region fragment of the epoxide PchEHA was recovered after agarose electrophoresis detection, and pET-28a(+) (Novagen) was digested with BamH I and Hind III Gel recovery was carried out to prepare the carrier. Ligate the coding region fragment of recovered epoxide PchEHA with the prepared pET-28a(+) vector, transform the ligation product into E.coliJM109, select positive clones and extract the plasmid, and perform agarose gel electrophoresis detection on the plasmid, and after electrophoresis The detection confirmed that the plasmid containing the inserted fragment was identified by restriction digestion with BamH I and Hind III. Thus, the expression plasmid containing PchEHA was obtained, and it was named pET28EHA.
Embodiment 3
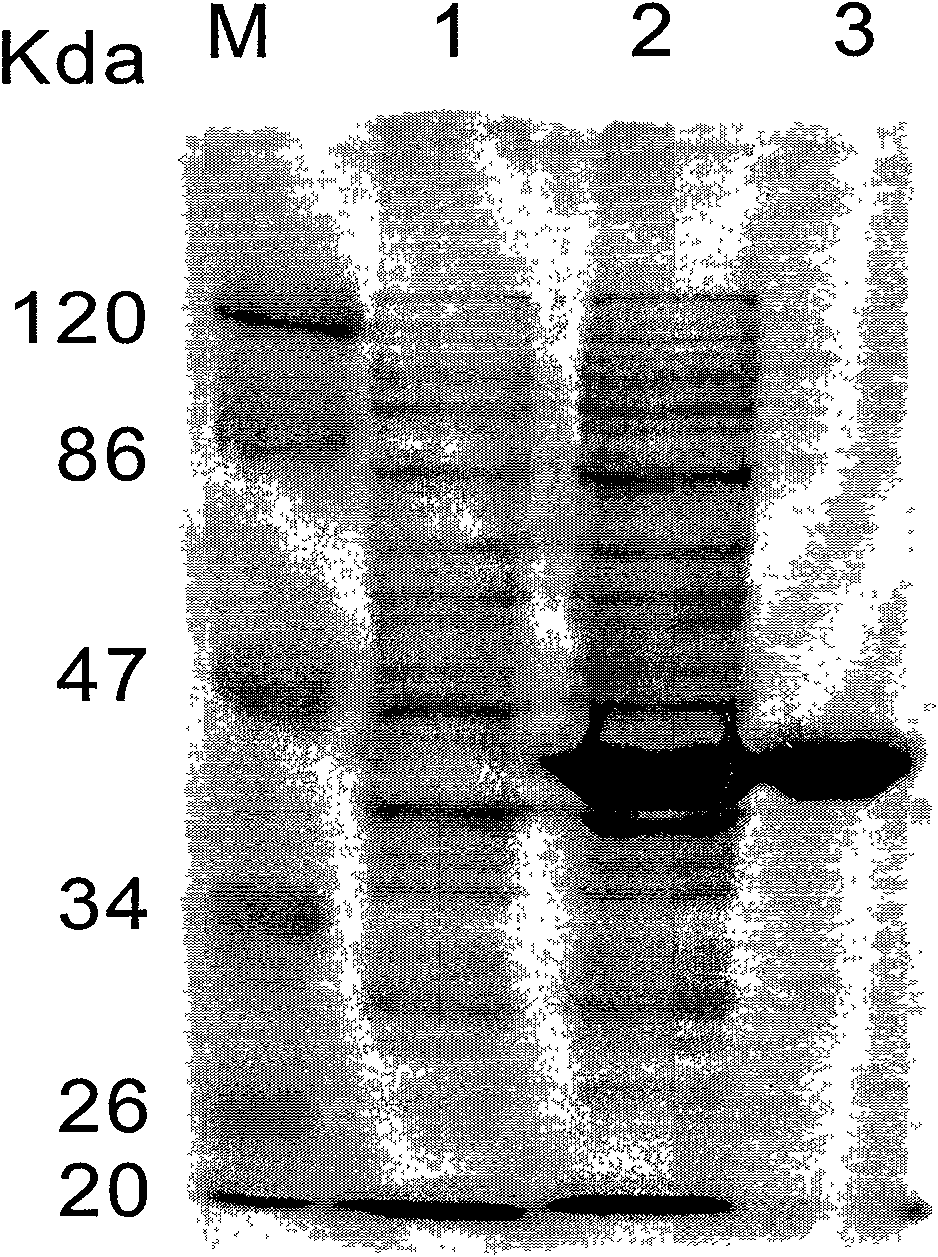
[0022] Example 3: Expression and purification of epoxide hydrolase PchEHA in Escherichia coli
[0023] The recombinant expression plasmid pET28EHA was transformed into E.coli BL21(DE3) competent cells to obtain the genetically engineered strain E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET28EHA expressing the recombinase, and after overnight culture, a single colony was picked to induce expression. The induced expression operation refers to the PET System operation manual. The specific steps are: inoculate a single colony of E.coli BL21(DE3) containing pE28EHA in 3ml LB liquid medium (containing 50μg / ml kanamycin), and cultivate overnight at 37°C with shaking at 220r / min; take 2.5ml The culture solution (1%) was inserted into 250ml of new LB liquid medium (8 bottles were inoculated, 2L in total), at 37°C; 220r / min shaking culture to OD 600 About 0.5; add 0.5mM IPTG, induce expression at 18°C; after culturing for 16-20h, centrifuge for 10 minutes (4000r / min) to collect the bacteria, and resuspend the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com