Compound bacterium agent for preparing fertilizer
A technology of compound bacterial agents and strains, which is applied in the direction of bacteria, fungi, organic fertilizers, etc., can solve the problems that the level of fertilizer efficiency is not involved, and achieve the effect of solving the problem of reuse, new strain combinations, and improving fertilizer efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Compound bacterial agent: 10% of fermenting cellulophage, 5% of cellulomonas chrysogenum, 4.5% of fibrinolytic butyricum vibrio, Clostridium papyrosolvens 14%, Clostridium cellobiose 8.5%, Clostridium termitidis 4%, Bacillus megaterium 13%, Candida tropicalis 11%, Trichoderma reesei 19%, Phaneroderma chrysosporium 11%.
[0029] Experimental group: add water to dilute the composite bacterial agent composed above, the dilution ratio is 1:5 (weight ratio), then take 500g of the diluted composite bacterial agent and mix it with 3000g of bacterial residue, and then compost and retting to make compost.
[0030] CK group: no compound bacterial agent was added to the edible fungus residue to make fertilizer directly, and other operations were the same as the experimental group.
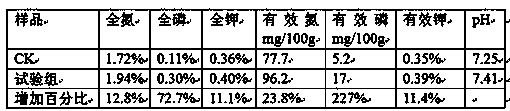
[0031] Compared with the CK group, the improvement of fertilizer efficiency of the experimental group is shown in the table below:
[0032]
Embodiment 2
[0034] Compound bacterial agent: 12% of fermenting cellulophage, 8% of cellulomonas chrysogenum, 7% of cellulolytic butyricum vibrio, Clostridium papyrosolvens 15%, Clostridium cellobiose 5%, Clostridium termitidis 4%, Bacillus megaterium 9%, Candida tropicalis 11%, Trichoderma reesei 15%, Phaneroderma chrysosporium 14%.
[0035] Experimental group: add water to dilute the composite bacterial agent composed above, and the dilution ratio is 1:10 (weight ratio), then take 500g of the diluted composite bacterial agent and 2500g of bacterial residue, and then compost and retting to make compost.
[0036] CK group: no compound bacterial agent was added to the edible fungus residue to make fertilizer directly, and other operations were the same as the experimental group.
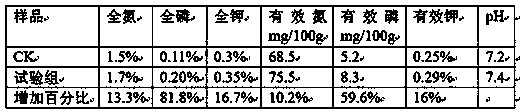
[0037] Compared with the CK group, the improvement of fertilizer efficiency of the experimental group is shown in the table below:
[0038]
Embodiment 3
[0040] Compound bacterial agent: 15% of fermenting cellulophage, 7% of cellulomonas chrysogenum, 8.5% of cellulolytic butyricum vibrio, Clostridium papyrosolvens 18%, Clostridium cellobiose 5%, Clostridium termitidis 1%, Bacillus megaterium 9%, Candida tropicalis 15%, Trichoderma reesei 15%, Phaneroderma chrysosporium 6.5%.
[0041] Experimental group: add water to dilute the composite bacterial agent composed above, the dilution ratio is 1:8 (weight ratio), then take 500g of the diluted composite bacterial agent and 4000g of bacterial residue to mix and compost to make compost.
[0042] CK group: no compound bacterial agent was added to the edible fungus residue to make fertilizer directly, and other operations were the same as the experimental group.
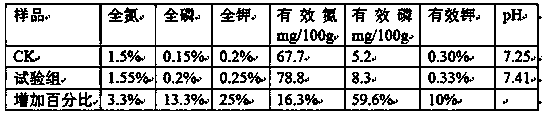
[0043] Compared with the CK group, the improvement of fertilizer efficiency of the experimental group is shown in the table below:
[0044]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com