Method for pre-processing corn stalks through physical-chemical-biological method
A biological pretreatment and corn stalk technology, applied in the field of biochemistry, can solve the problems of long biological treatment cycle, environmental pollution, high energy consumption, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the utilization efficiency, simple process and simple equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Embodiment 1: Pretreat corn stalks according to the following steps
[0023] (1) Corn stalks are crushed through a pulverizer first, and then passed through a 40-mesh sieve;
[0024] (2) Treat the crushed corn stalks with a NaOH solution with a mass concentration of 1.0%, with a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:10, filter at 100°C for 1 hour, wash the filter residue with water to neutrality, and dry it to a constant weight as a fermentation substrate;
[0025] (3) First prepare every 10mL containing FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O0.0005g, MnSO 4 ·7H 2 O0.0016g, ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O0.0014g, CoCl 2 .0.002g of trace element mixed solution; secondly prepare nutrient solution, the mass percent concentration of each component in the nutrient solution is: (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 1%, KH 2 PO 4 0.3%, MgSO 4 0.05%, CaCl 2 0.05%, the rest is water; then prepare the mixed solution, which is prepared by adding 1mL of trace element mixed solution to every 100mL of nutrient solution; add the mixed solution to...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Example 2: Steps (1), (2) are the same as in Example 1; the preparation of the mixed solution in step (3) is the same as in Example 1; add and mix to the fermentation substrate in step (2) according to the material-to-liquid ratio of 1:2.25 liquid, adjust the pH to 5.5, and sterilize at 121°C for 20 minutes to obtain a solid-state fermentation medium; 6The Phanerochaete chrysosporium spore suspension of each / mL was inserted into the solid-state fermentation medium with an inoculum size of 10% by mass, and fermented for 10 days; 6 Trichoderma viride spore suspension per mL was cultured at 28°C for 4 days to obtain the pretreated product.
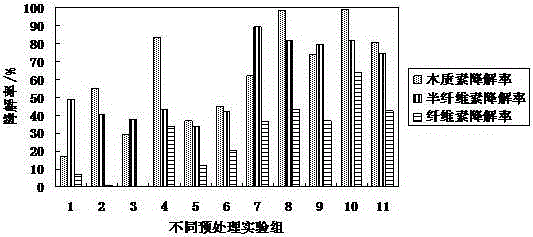
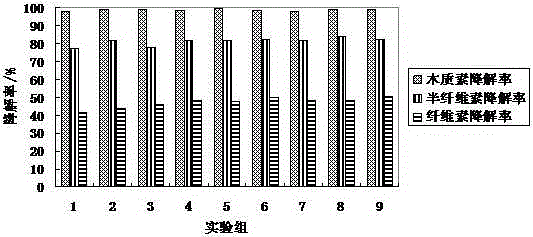
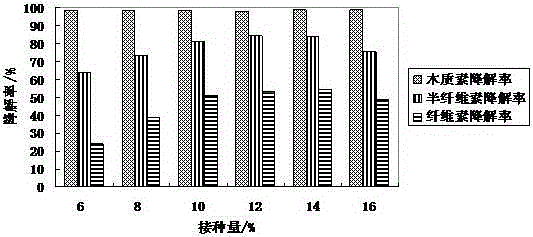
[0028] Such as figure 2 As shown in group 1, the degradation rates of lignin, hemicellulose and cellulose in the straw were 98.1%, 77.1% and 41.6%, respectively.
Embodiment 3
[0029] Example 3: Steps (1), (2) are the same as in Example 1; the preparation of the mixed solution in step (3) is the same as in Example 1; add and mix to the fermentation substrate in step (2) according to the material-to-liquid ratio of 1:2.25 liquid, adjust the pH to 5.5, and sterilize at 121°C for 20 minutes to obtain a solid-state fermentation medium; 6 The Phanerochaete chrysosporium spore suspension of each / mL was inserted into the solid-state fermentation medium with an inoculum size of 10% by mass, and fermented for 10 days; 6 pcs / mL Trichoderma asperelloides The spore suspension was cultured at 28°C for 4 days to obtain the pretreated product.
[0030] Such as figure 2 As shown in group 2, the degradation rates of lignin, hemicellulose and cellulose in the straw were 98.8%, 81.7% and 44.2%, respectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com