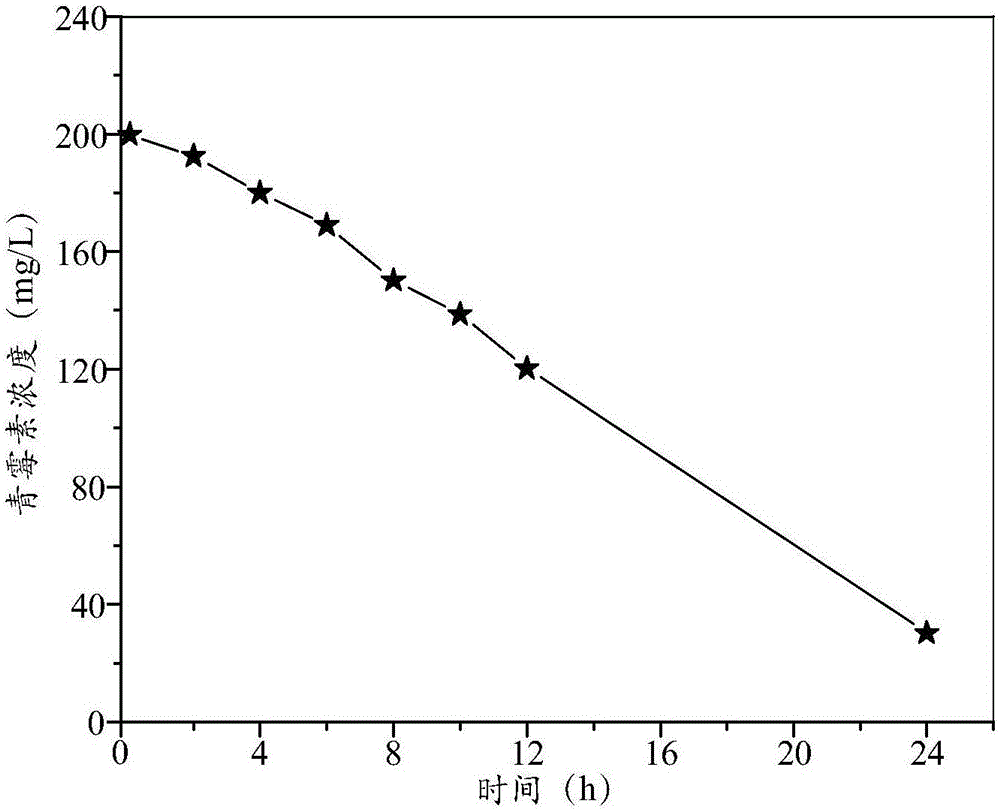
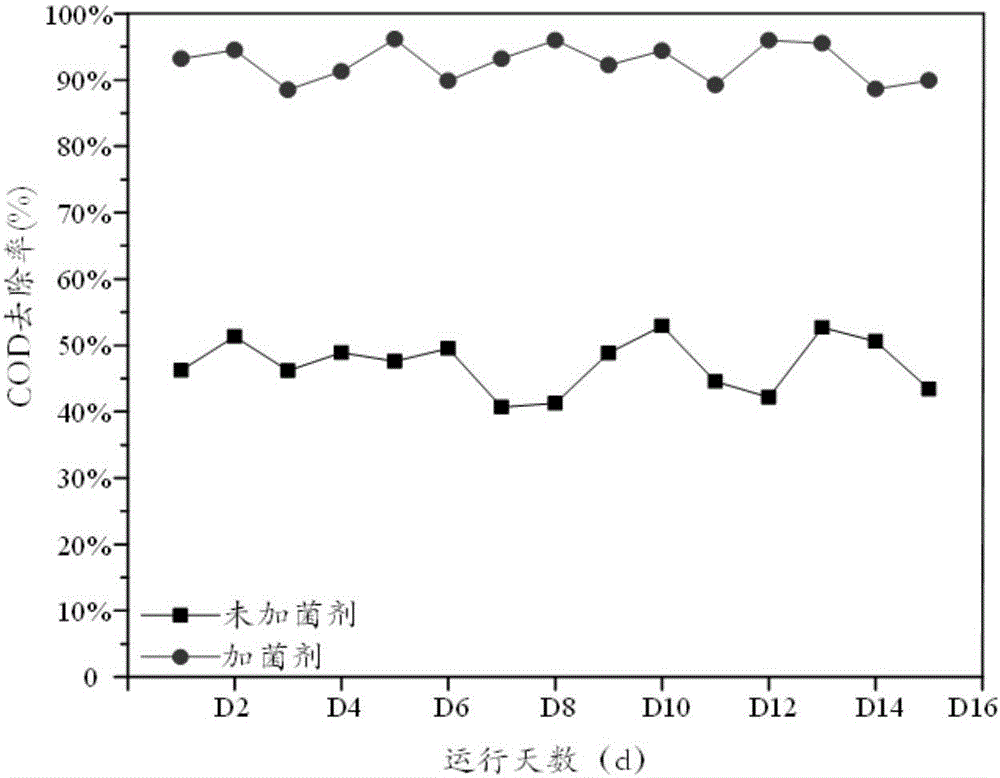
Patents
Literature
112 results about "Antibiotic degradation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
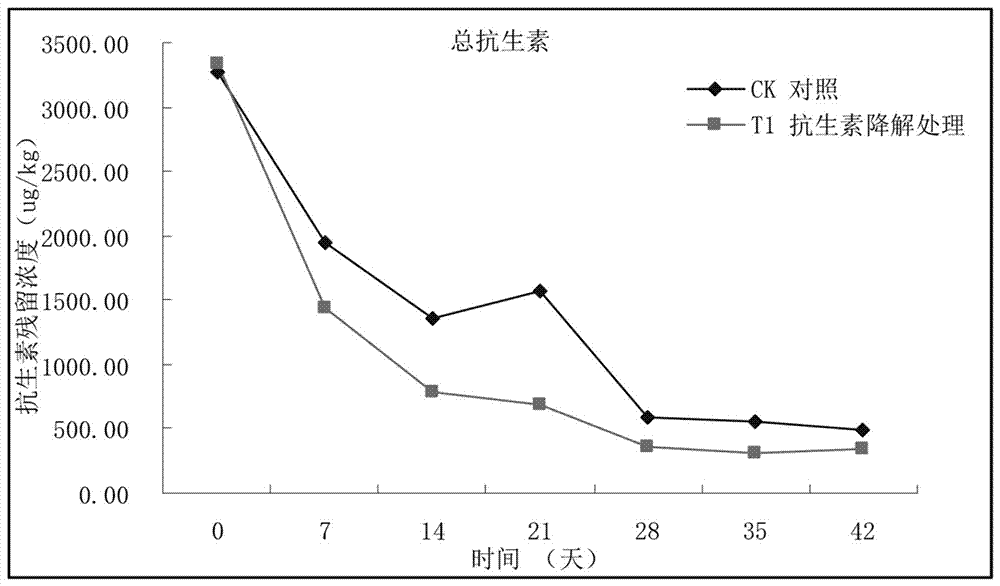
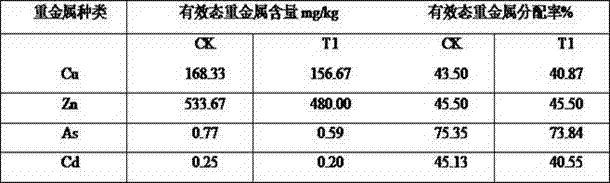
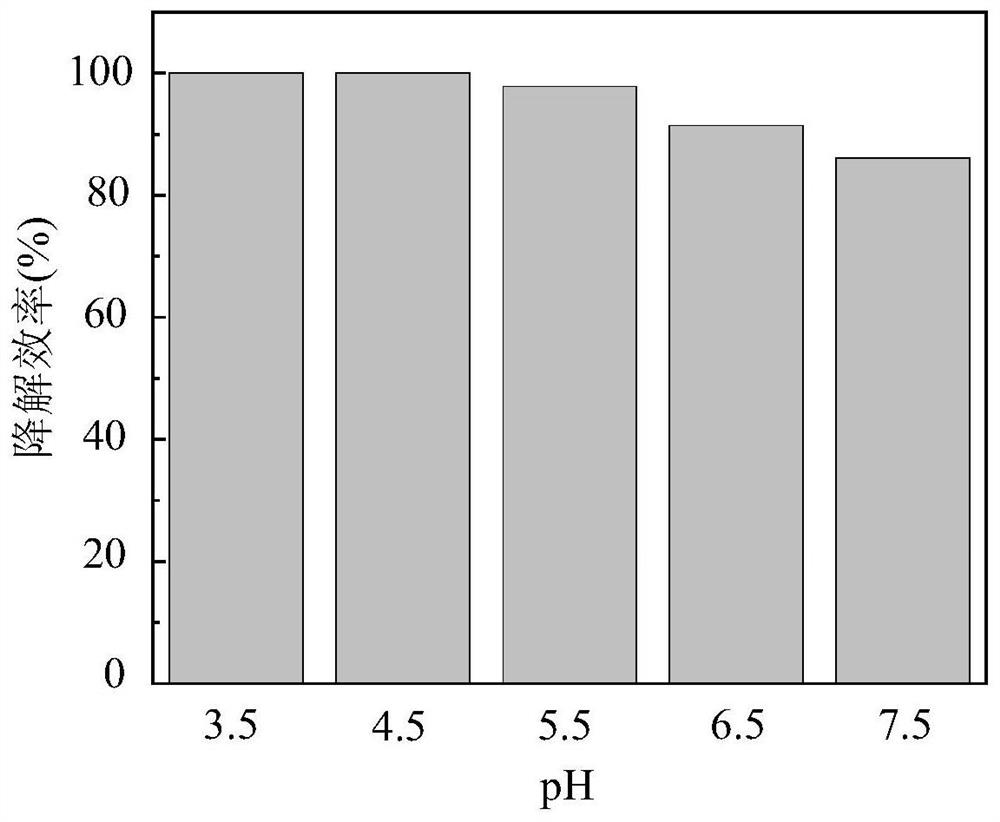
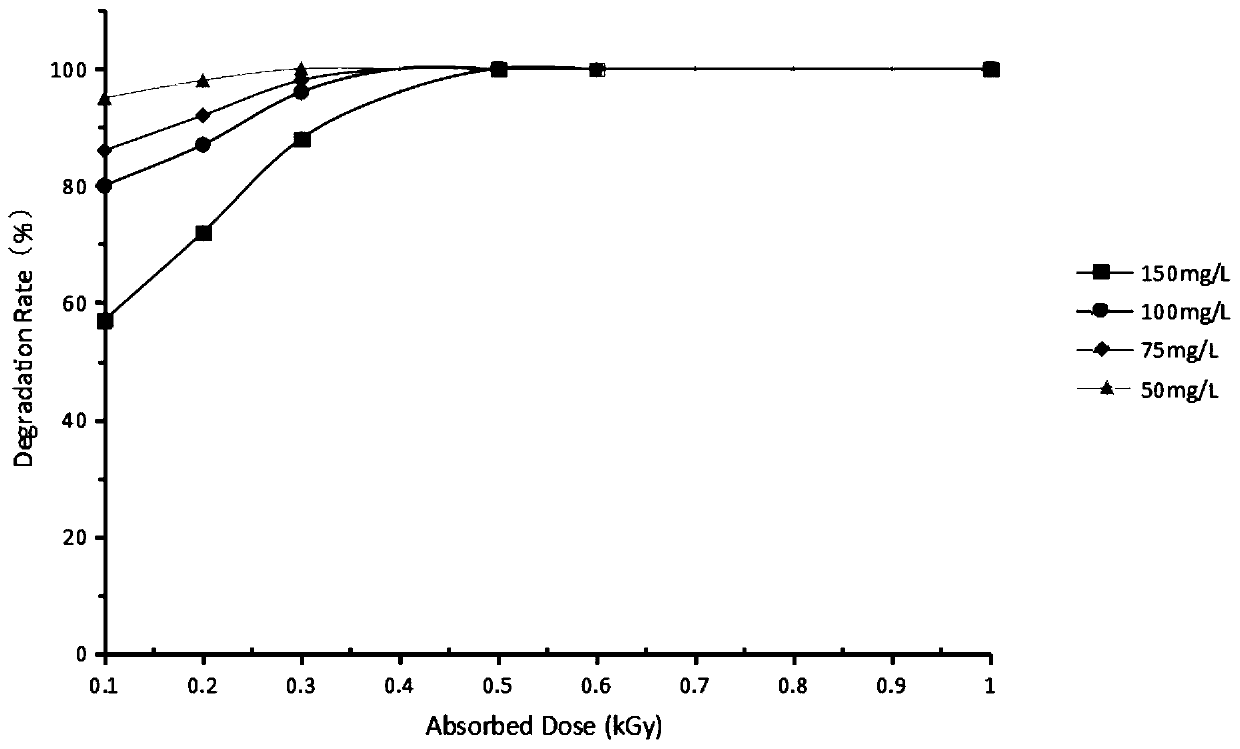
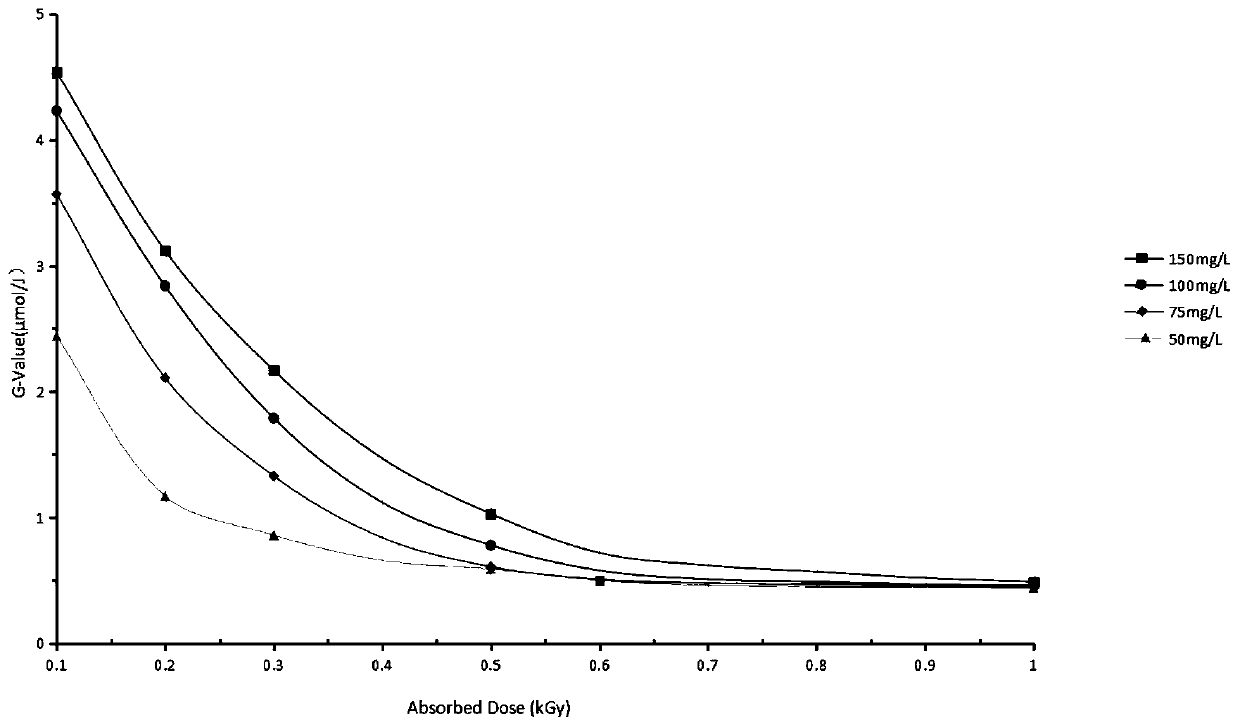
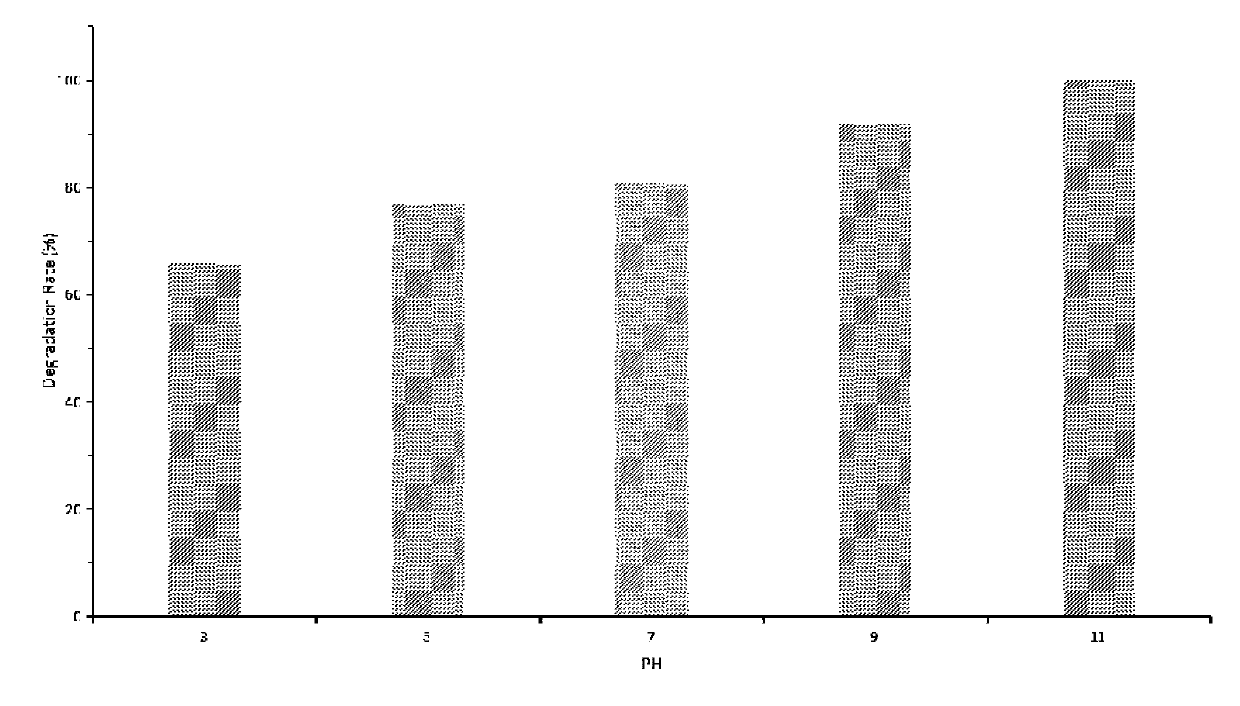
Residual antibiotics in land-applied manure and biosolids present a potential threat to public and ecological health. It remains important to determine antibiotic degradation efficiencies for manure and biosolids waste management practices and to identify conditions that enhance antibiotic degradation.
Innocent treatment method for antibiotic fungi residues
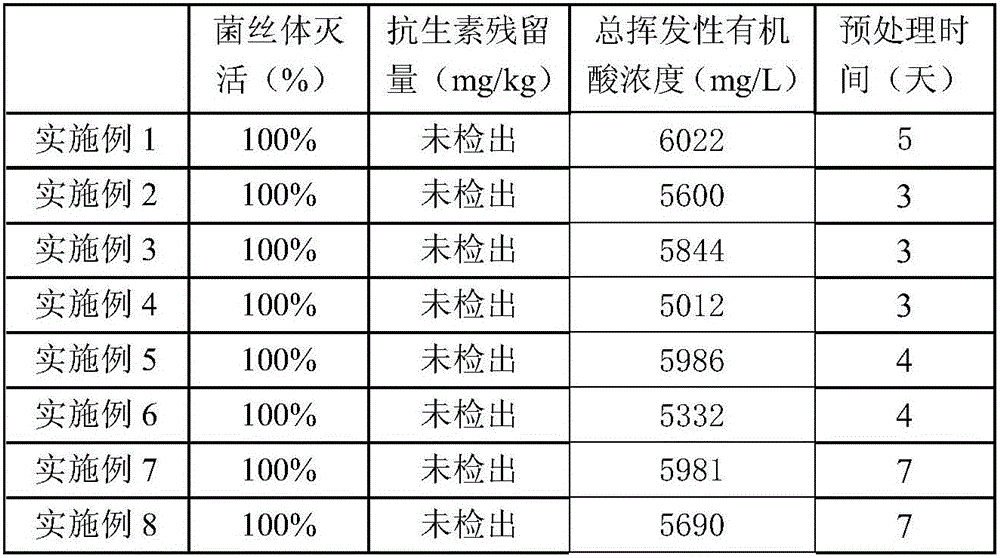
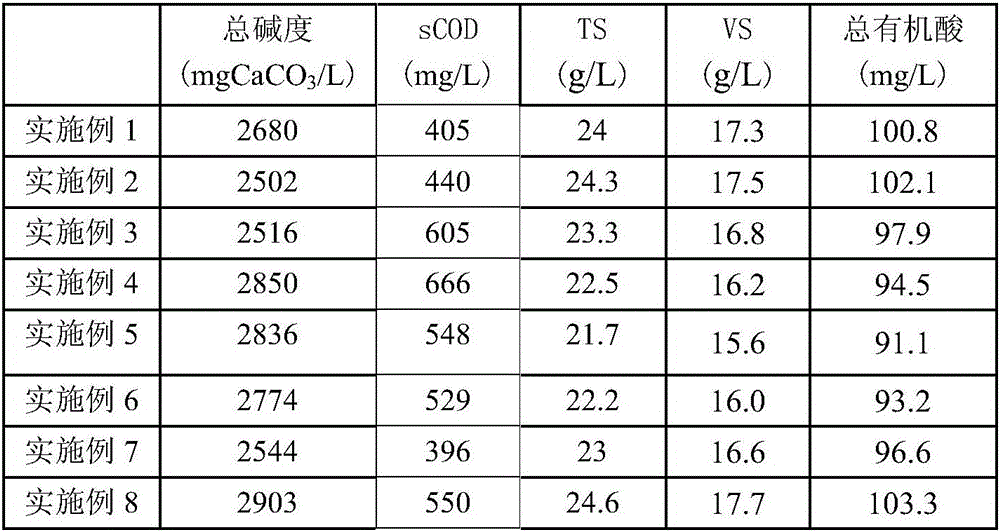
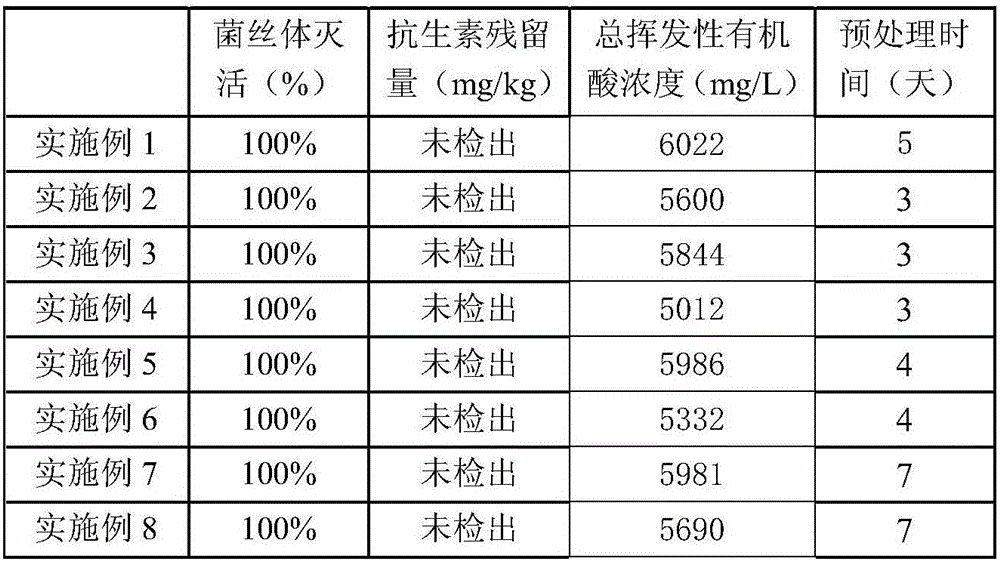
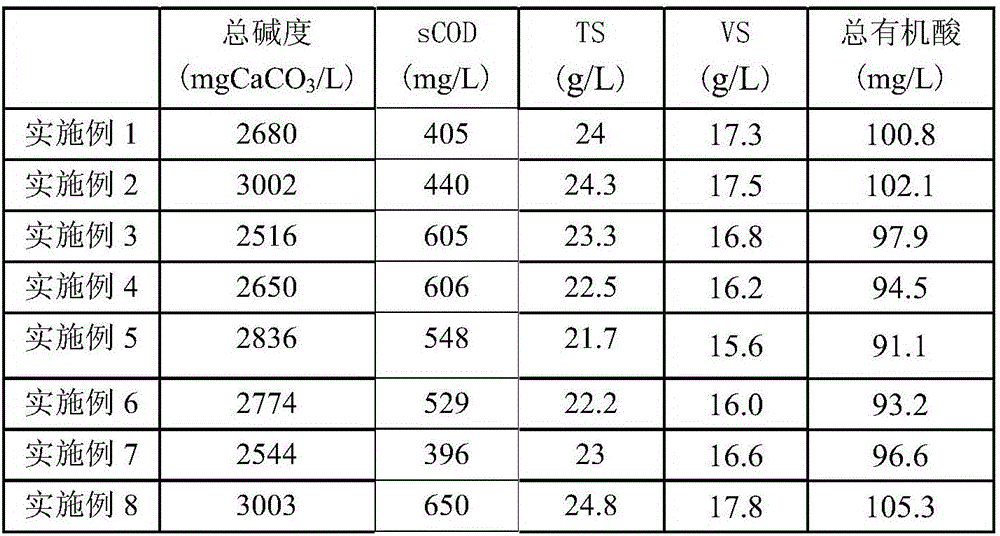
InactiveCN105457968AReasonable useReduce processing costsSolid waste disposalTransportation and packagingMicroorganismAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses an innocent treatment method for antibiotic fungi residues. The innocent treatment method is characterized in that the antibiotic fungi residues are inactivated under conditions with a pH value of 8-11 and a temperature of 90-100 DEG C. According to the method, the fungi residues are inactivated, so that the antibiotics in the antibiotic fungi residues lose activity, and the inactivated fungi residue mycelia comprise microorganism-containing cells, a coagulant aid and residual nutritional ingredients, and can be used for an organic fertilizer or a feed additive. In a treatment process, waste gas is not generated and treatment cost is relatively low, and the treated fungi residues can be reasonably reutilized, so that certain economic benefits can be generated, and therefore, the innocent treatment method has the characteristics of being energy-saving, environmentally-friendly, pollution-free, relatively low in cost and the like.
Owner:邢富斋 +1
Preparation method of clay-perovskite composite material and application thereof
ActiveCN105688918ASmall particle sizeAvoid uneven loadWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsWater bathsChemical industry
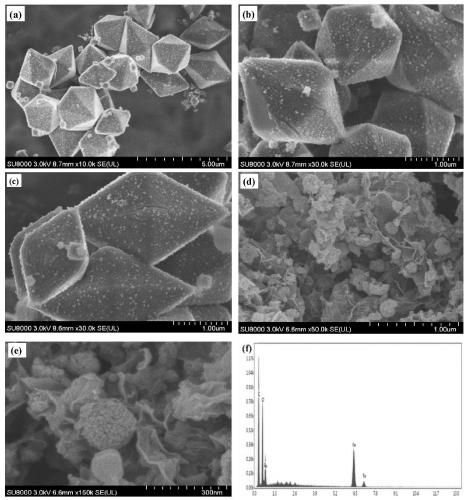
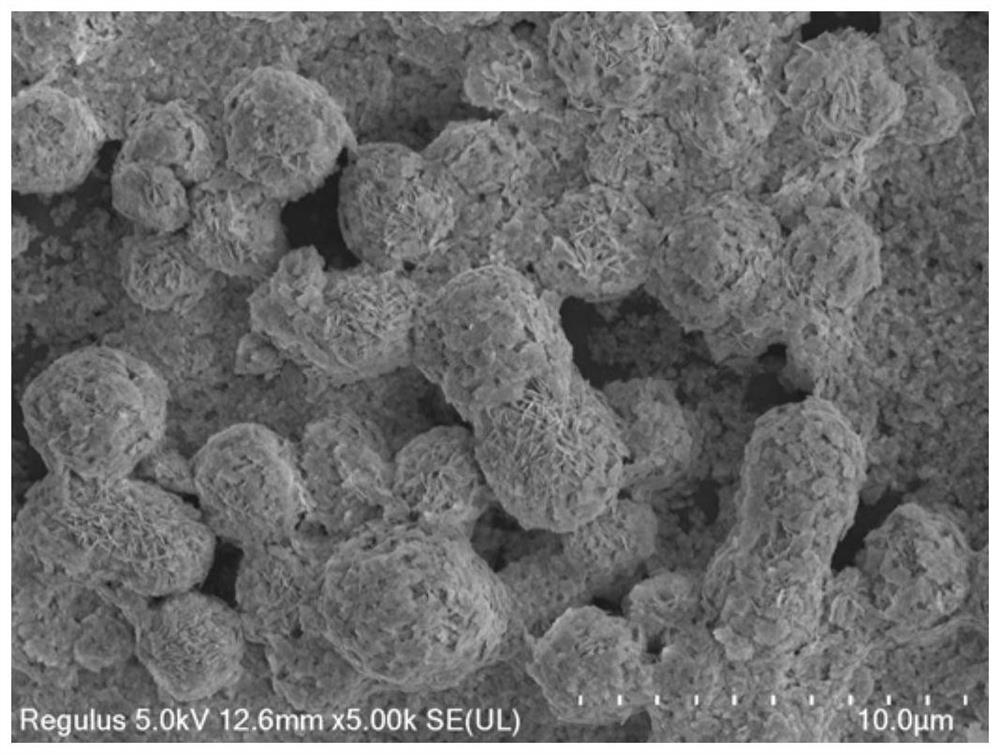
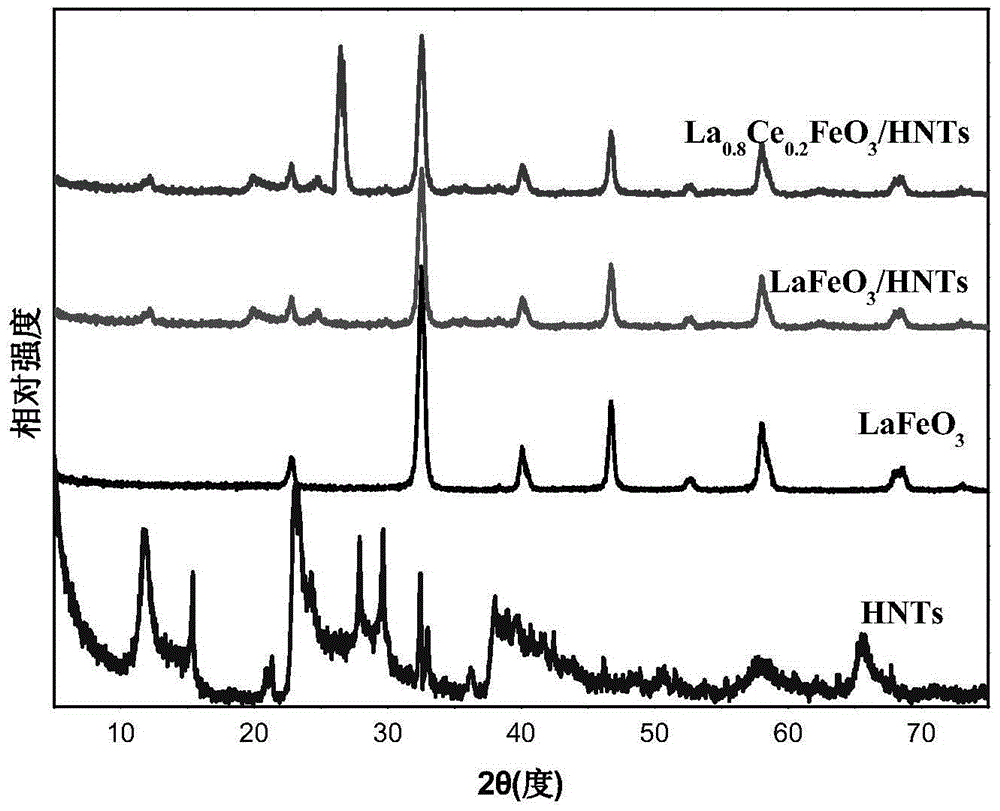
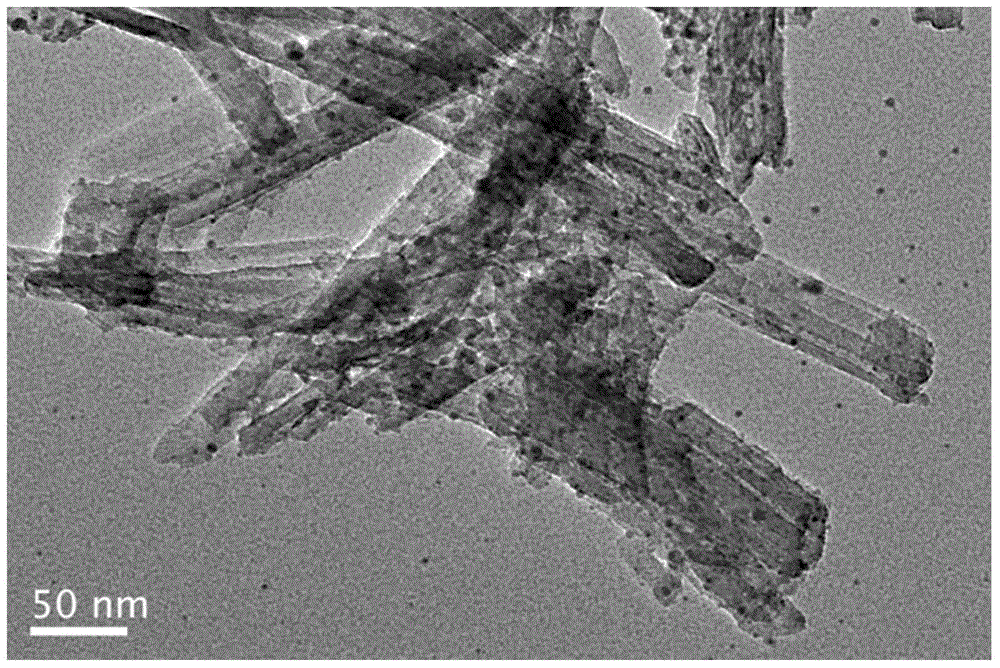
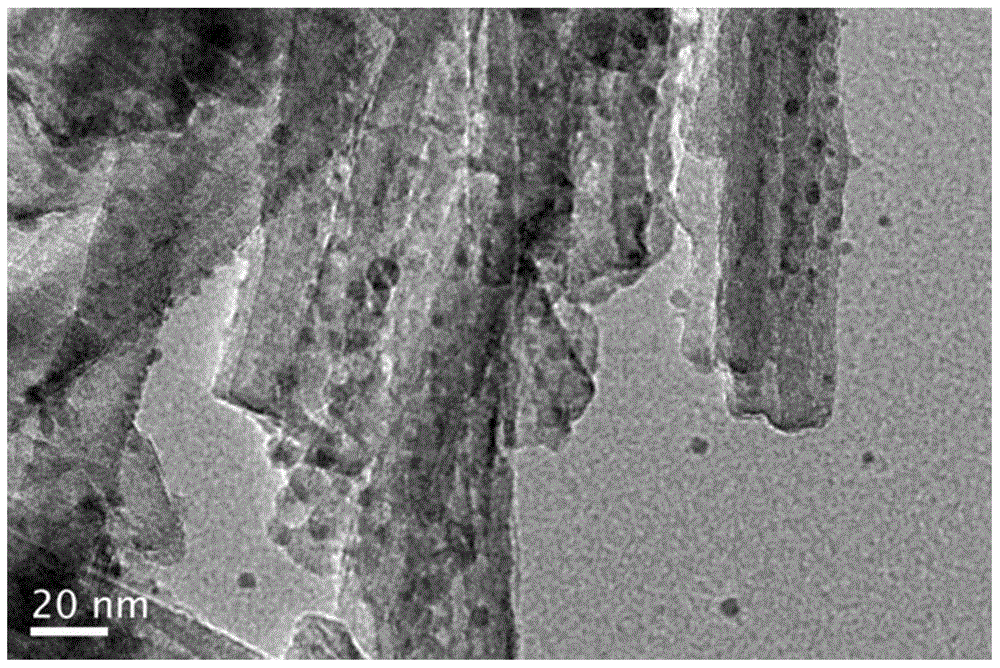
The invention belongs to the field of the energy and chemical industry and particularly relates to a preparation method of a nanometer material using clay as a carrier and using a perovskite type compound as an active component and application of the nanometer material in photocatalytic degradation of antibiotics.Lanthanum nitrate, ferric nitrate, cerous nitrate, citric acid and the clay are added to deionized water and are mixed, then the mixture is transferred to a water bath kettle for evaporation to obtain wet gel, and drying, calcinations and dry grinding are performed to obtain the lanthanum ferrite / clay nano-structure composite material.The antibiotics are subjected to the photocatalytic degradation by adopting the composite material and can be rapidly degraded under visible light by utilizing the high catalytic activity of (cerium doped) lanthanum ferrite.The clay carrier facilitates antibiotic molecular adsorption in the antibiotic degradation process, the antibiotics are in contact with the lanthanum ferrite after being absorbed to the catalyst surface, and antibiotic molecules are decomposed under visible light irradiation to produce other active species.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Method for harmless treatment of ferment antibiotic fungus residues
ActiveCN106480103AReduce risk of recurrenceHigh residue removal rateMicroorganism based processesWaste based fuelSocial benefitsEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a method for harmless treatment of ferment antibiotic fungus residues. The method includes: subjecting the ferment antibiotic fungus residues to ultrahigh-temperature intensive acidogenic fermentation treatment; performing biochemical treatment on the fungus residues subjected to ultrahigh-temperature intensive acidogenic fermentation treatment. Thermophilic hydrolysis acidogenic bacteria are adopted for high-temperature anaerobic acidogenic fermentation treatment of the ferment antibiotic fungus residues, the fungus residues are hydrolyzed and acidized, antibiotic producing strains in the fungus residues are inactivated, residual antibiotics are degraded prior to biochemical treatment, and accordingly harmless treatment and recycling of the antibiotic fungus residues are realized. By adoption of the method, the antibiotic producing strains in the fungus residues subjected to harmless treatment are completely killed, antibiotic residues are avoided, and the fungus residues subjected to biochemical treatment is free of dangers caused by drug-resistant fungi and drug-resistant genes. The method has advantages that efficiency in harmless treatment of the antibiotic fungus residues is improved, environment protection is benefited, hazardous wastes are recycled, and remarkable economic benefits and social benefits are achieved.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Antibiotic degradation mixed bacterial agent and application thereof
ActiveCN108546665ADefine the bacterial compositionSimple preparation processFungiBacteriaAntibiotic degradationPolluted soils
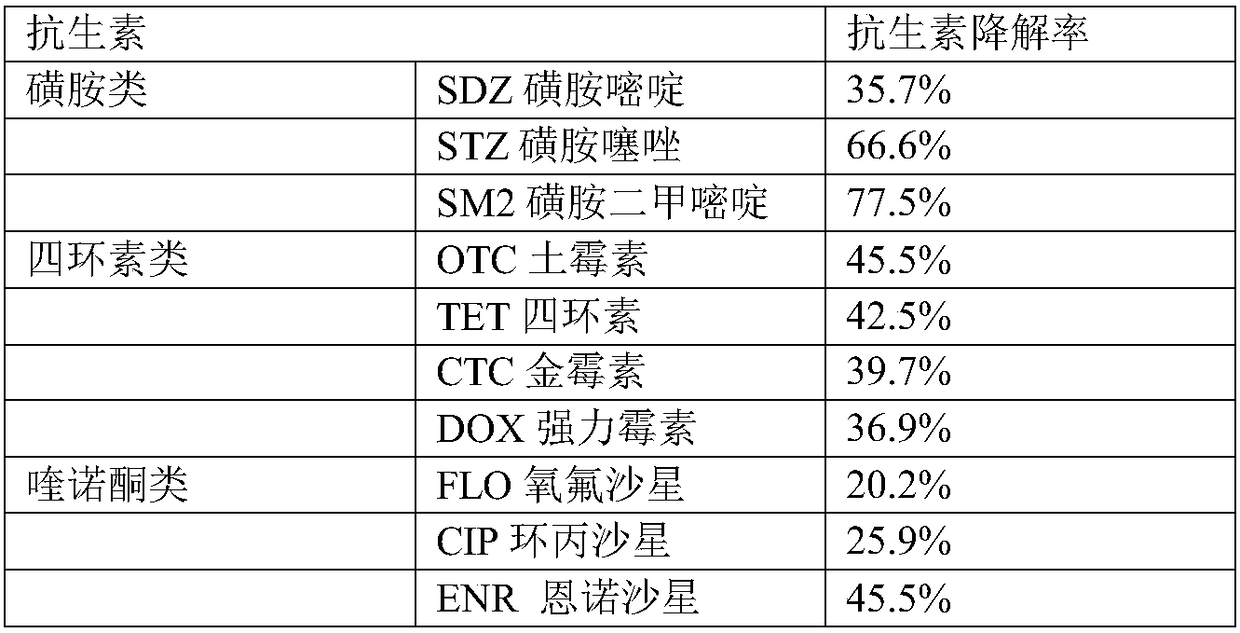
The invention relates to the field of environmental protection, and discloses an antibiotic degradation mixed bacterial agent and application thereof. The mixed bacterial agent is prepared from Arthrobacter sp. and Alcaligenes sp.. The Arthrobacter sp. is tetracycline antibiotic degradation arthrobacterium, and can be used for simultaneously degrading oxytetracycline, tetracycline and aureomycin;the Alcaligenes sp. is sulfanilamide antibiotic degradation bacterium, can be used for degrading sulfadimethoxine, and can tolerate sulfadimidine, sulfadiazine and sulfamonomethoxine. The antibiotic degradation strains and bacterial agents can be used for degradation removal of residue antibiotics in waste such as livestock and poultry excrement; the release of the residue antibiotic in the wasteto the environment can be reduced; meanwhile, the bacterial agent can be applied to the degradation removal of the antibiotic contaminants in the antibiotic polluted soil; when the bacterial agent isused for environmental restoration, good application prospects and environmental benefits are realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Degradation bacteria for sulfonamide antibiotics and application thereof
ActiveCN108611285APromote degradationHarm reductionFungiContaminated soil reclamationEcological environmentAntibiotic Y
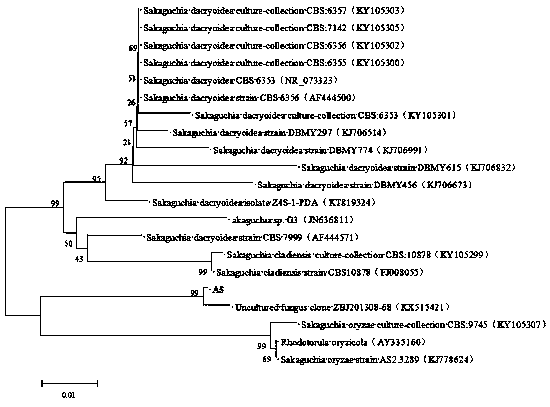
The invention discloses a degradation bacteria for sulfonamide antibiotics and an application thereof, wherein the bacteria is Sakaguchia cladiensis A5 and is preserved in Guangdong Center of Microbial Culture Collection at Jan. 26th, 2018, and is assigned the accession number of GDMCC No.60319. The bacterial strain has great degradation effect on sulfonamide antibiotics such as sulfamerazine, sulfamethoxazole and the like, and can be used for degradation treatment to sulfonamide antibiotics pollution to application objects comprising wastewater, waste residue, water environment, soil and thelike, which contain the sulfonamide antibiotics. The bacterial strain can reduce damage on ecological environmental safety due to the antibiotics, is energy-saving and environment-friendly, and has extensive application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Composting method for rapid degrading veterinary antibiotic and organic fertilizer
InactiveCN102757280AEfficient degradationImprove qualityBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationFecesLivestock manure
The invention relates to an organic fertilizer and a method for rapid degrading antibiotic in livestock manure. The organic fertilizer is prepared from fertilizer-making base stock, an organic conditioner and antibiotic degrading oxidant, wherein the volume ratio of the fertilizer-making base stock to the organic conditioner is 1 to 1-3, and the weight of the antibiotic degrading oxidant is 0.3-0.5wt% of total weight of the fertilizer-making base stock and the organic conditioner. According to the invention, an aerobic composting process is mainly utilized, and the purposes of thoroughly degrading the veterinary antibiotic in livestock manure and producing excellent organic fertilizer are achieved by regulating the ratio of the filler and adding the oxidant which is easy to degrade the antibiotic.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Composting method capable of efficiently degrading antibiotics in livestock excrements
ActiveCN106866234APromote degradationResidue reductionBio-organic fraction processingExcrement fertilisersFecesMacrolide resistance
The invention discloses a composting method capable of efficiently degrading antibiotics in livestock excrements. Degradation of a plurality of antibiotics, such as sulfonamides, tetracyclines, macrolides and fluoroquinolones, in a compost can be obviously promoted by adding an antibiotic degradation promoter with a specific using amount into a composting raw material and using specific composting steps, and meanwhile, available heavy metal content in the compost is reduced. The antibiotic degradation promoter consists of an activated carbon and an attapulgite, and can also be used with a biological activated carbon comprising the activated carbon and phanerochaete chrysosporium.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
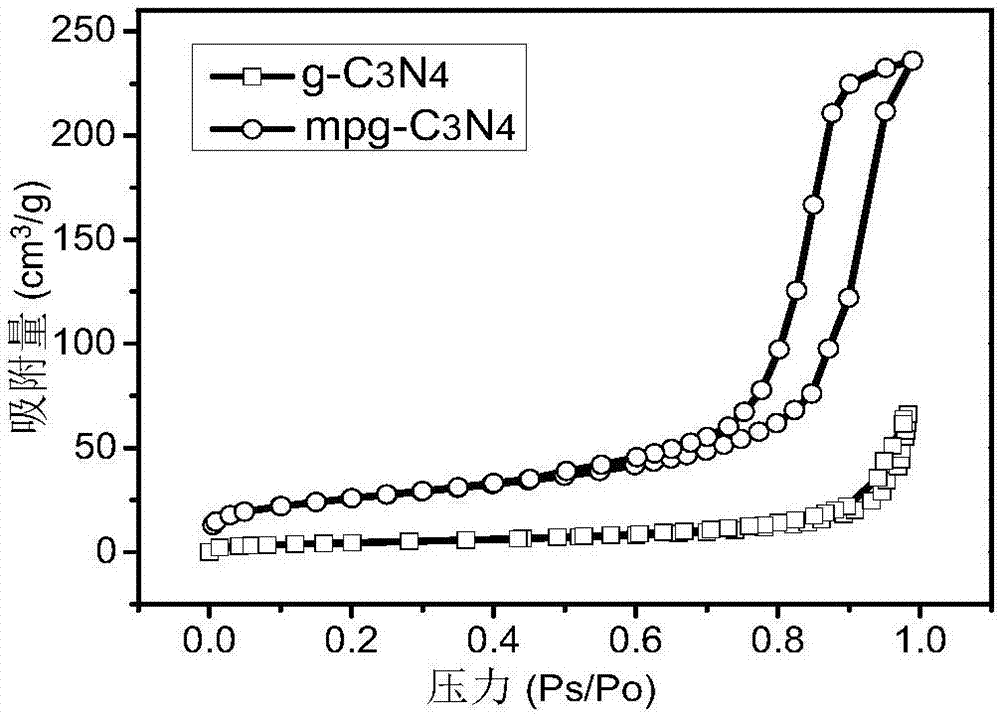
Mpg-C3N4 adsorbing material as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107349901ALarge specific surface areaImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesWater contaminantsHydrogen fluorideMaterial synthesis
The invention discloses a mpg-C3N4 adsorbing material as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The method comprises the steps as follows: cyanamide is added to silica sol and heated to be completely mixed, vacuum drying is performed, an obtained solid is ground and calcined at 450-550 DEG C, a calcined product is added to an ammonium hydrogen fluoride solution, subjected to stirring, suction filtering, washing and vacuum drying, cooled to the room temperature, ground and sieved, and the mpg-C3N4 adsorbing material is obtained. A simple thermal polymerization method is adopted in the method, the material synthesis process is simple and good in repeatability, and mass production can be performed. The obtained mpg-C3N4 has very high specific surface area and can be used as an effective antibiotic adsorbent, the adsorption process is simple, easy to operate, low in energy consumption and high in adsorption capacity, the mpg-C3N4 can be widely applied to the antibiotic degradation field and has higher application prospects and use value.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
In-situ microorganism degradation preparation for soil contaminated by sulfonamide antibiotics, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110616170AImprove buffering effectPromote degradationBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationMagnetic mediaAntibiotic Y
The present invention discloses an in-situ microorganism degradation preparation for soil contaminated by sulfonamide antibiotics, a preparation method and an application thereof. A sulfonamide antibiotic-degrading microorganism solution, an energy supply bacterial solution, a magnetic medium bacterial solution, a surfactant and a fermentation culture medium are mixed to obtain a mixed solution; and fermentation is performed to obtain an in-situ microorganism degradation preparation for soil contaminated by sulfonamide antibiotics. The sulfonamide antibiotic-degrading microorganisms can significantly improve degradation efficiency of microorganisms through accompanying and coupled fermentation of the energy supply bacteria and improve colonization and proliferation ability of the degrading strains in in-situ soil environment; the surfactant and magnetic medium bacteria can help the degradation preparation relieve water tension and antibiotic polarity after the degradation preparationis applied into soil, enhance affinity of sulfonamide antibiotic residues and degrading microorganisms, and accelerate degradation of the sulfonamide antibiotic residues; and the sulfonamide antibiotic-degrading microorganisms can produce laccase and have superior performances of wide oxidation substrates, low energy consumption, high efficiency, environmental friendliness, etc. on the sulfonamideantibiotic degradation.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & ENVIRONMENT GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
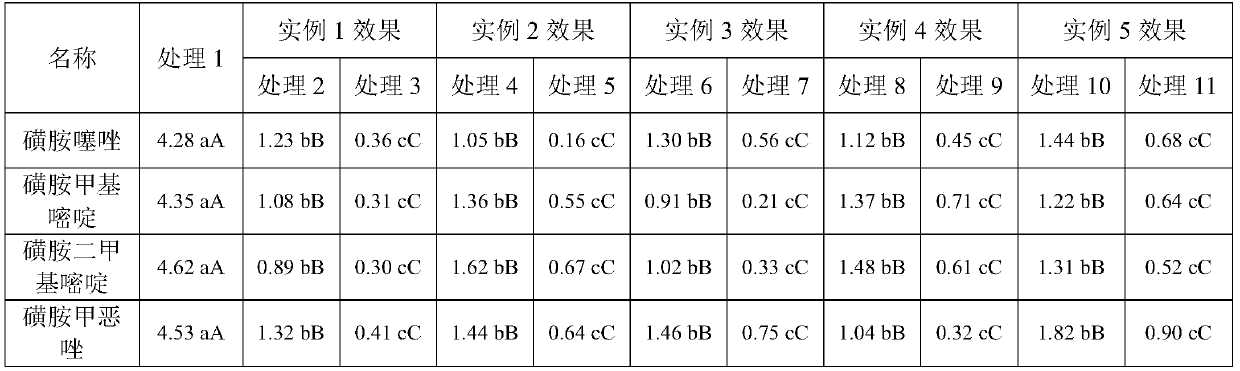
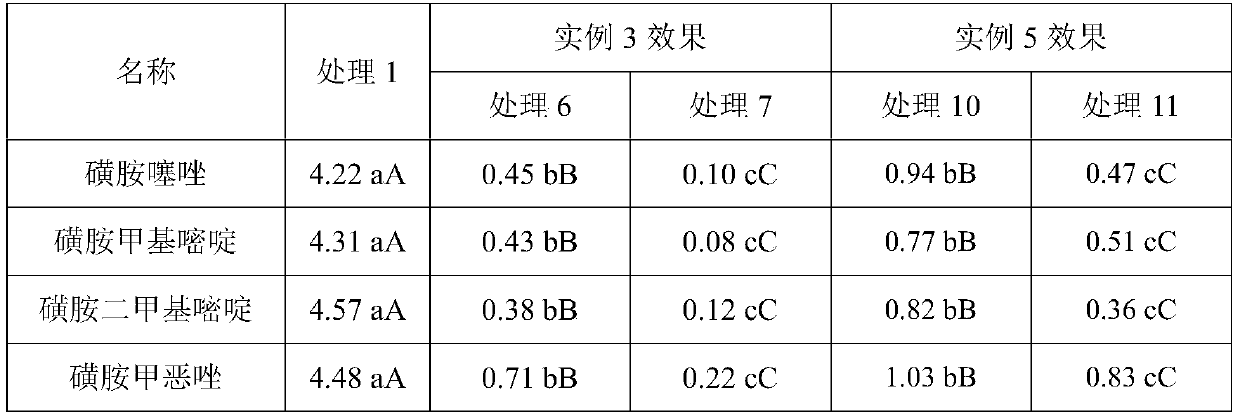
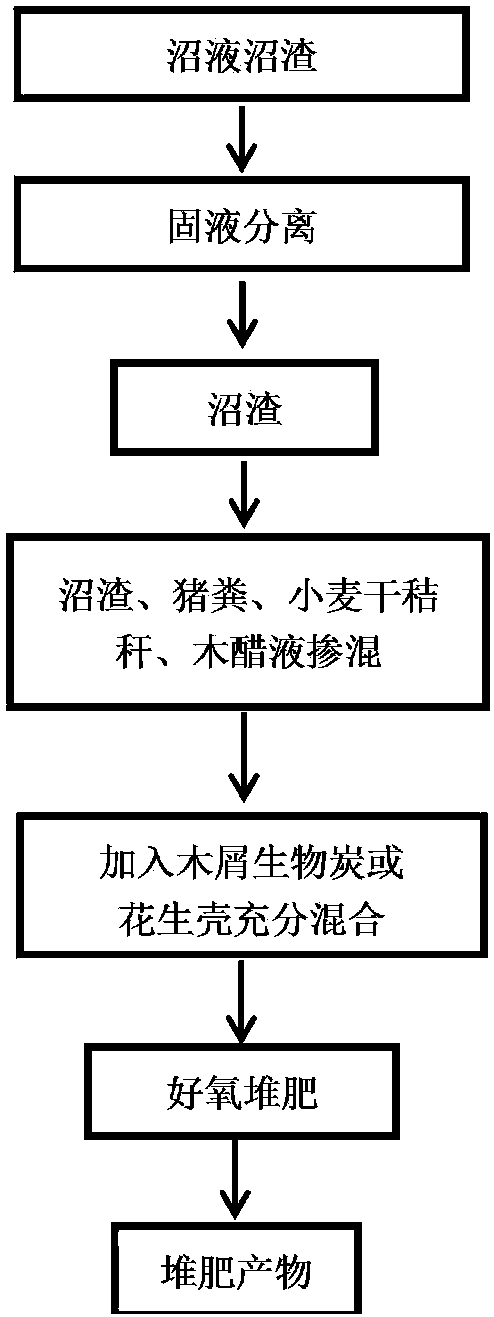
Composting method for adding auxiliary materials to quickly remove tetracycline antibiotics in biogas residue
InactiveCN108456068AImprove composting efficiencyImprove efficiencyBio-organic fraction processingExcrement fertilisersAntibiotic YCompost
The invention discloses a composting method for adding auxiliary materials to quickly remove tetracycline antibiotics in biogas residue. The composting method comprises the following steps: mixing biogas residue with fresh pig manure, wheat dry straws and wood vinegar which is diluted by 500 times according to parts by weight, evenly stirring to obtain mixture, adding charcoal into the mixture, and evenly mixing to obtain composting raw materials, wherein the dry substance ratio of the mixture to the charcoal is (80-100):1; putting the composting raw materials in an aerobic fermentation tank to be subjected to aerobic composting to obtain a composting product of which the antibiotics are removed. According to the composting method, the auxiliary materials can be added to shorten compost body warming time and prolong a high temperature phase, antibiotic degradation in a biogas residue composting process is accelerated, antibiotic residues in the composting product can be lowered, and the subsequent utilization risk of the biogas residues is lowered.
Owner:ACADEMY OF PLANNING & DESIGNING OF THE MINIST OF AGRI
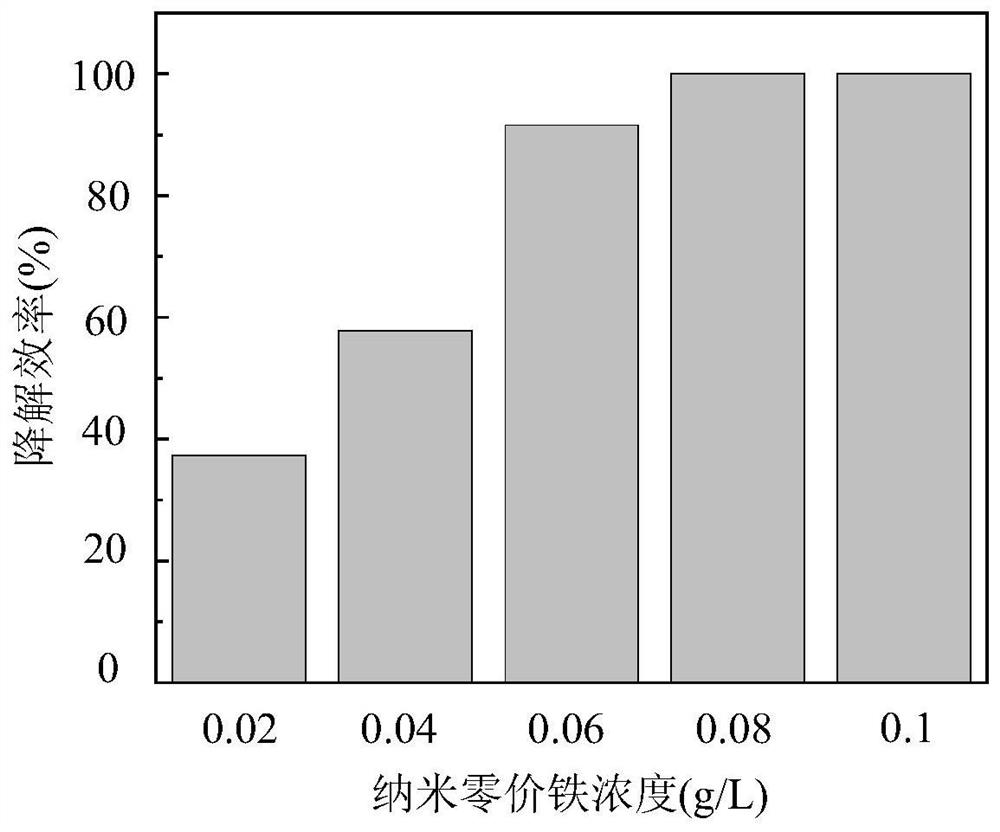
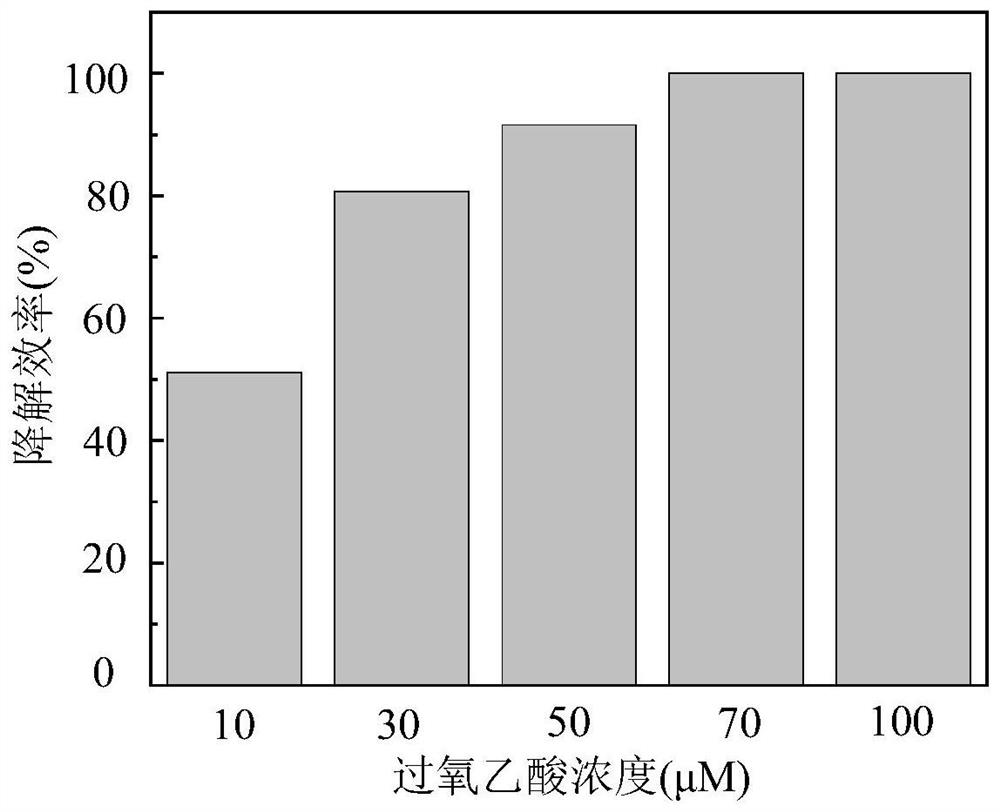
Method for degrading antibiotics in water by activating peracetic acid through zero-valent metal
ActiveCN112723518AImprove activation efficiencyReduce utilization costWater contaminantsEnergy based wastewater treatmentMicrobiologyHydroxyl radical
The invention discloses a method for degrading antibiotics in water by activating peracetic acid through zero-valent metal. According to the method, peracetic acid which is high in oxidation-reduction potential, widely applied to the disinfection field and few in by-products is selected as a precursor for generating hydroxyl radicals, and the peracetic acid is activated by the zero-valent metal to generate strong oxidizing free radicals so as to degrade antibiotics in the water body. The method comprises the following specific steps: adding a proper amount of a strong oxidant, namely the peroxyacetic acid into a to-be-treated water body containing antibiotics, then adding the zero-valent metal with a concentration of 0.02 g / L-0.1 g / L as an activating agent, adjusting the pH value of a reaction solution to 3-9, and carrying out uniform stirring and reacting at room temperature for 30 minutes so as to oxidize and degrade the antibiotics. The zero-valent metal used in the method has the advantages of being low in cost, high in activation efficiency, easy to recycle and the like, the peracetic acid can be completely activated within 30 min, and high antibiotic degradation efficiency is achieved, so the method is a novel antibiotic degradation technology which is rapid, efficient and environmentally friendly.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
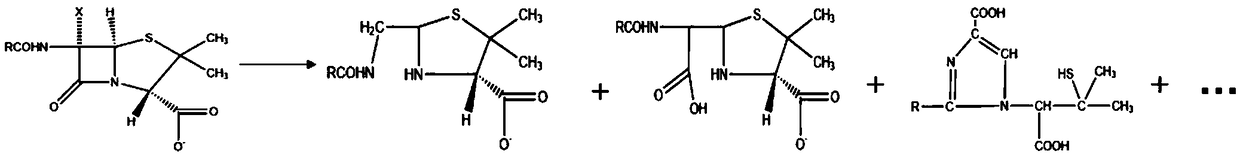
Method for removing residual penicillin antibiotics in biological medicine waste residues
ActiveCN108653971AFast and efficient removal processEasy to transportChemical protectionSlurryAntibiotic Y
The invention relates to a method for removing residual penicillin antibiotics in biological medicine waste residues. The method comprises the following steps that (1) an activating agent is added into the biological medicine waste residues containing the penicillin antibiotics, size mixing and dispersing are carried out, then waste residue slurry is obtained; and (2) a catalyst and an oxidizing agent are added into the waste residue slurry obtained in the step (1), and after the degradation reaction, the residual penicillin antibiotics in the biological medicine waste residues is removed. Compared with the prior art, the residual antibiotics can be rapidly and efficiently removed by 99% and more by the method, moreover, the penicillin antibiotics is degraded into other substances which are non-toxic and have no pesticide effect, the obtained waste residues are solid, is convenient to store and transport, and can be applied to production of fertilizers and soil conditioners, the development concept of green coordination and sustainable development is met, and the requirements of energy conservation and environmental protection advocated by China are met.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES INST OF CHEM IND
Device for degrading antibiotics by adopting photocatalysis-assisted enhanced biological anode
ActiveCN112125390AImprove degradation efficiencyIncrease production capacityTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesBiological treatment apparatusPtru catalystBiology
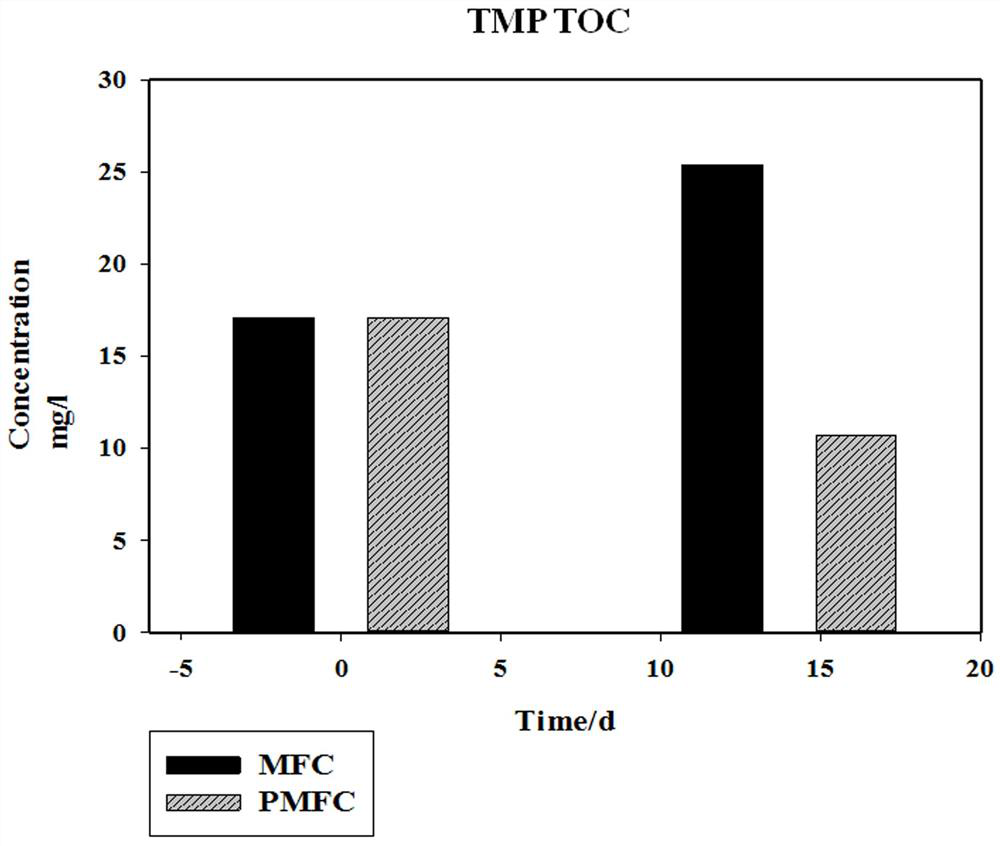
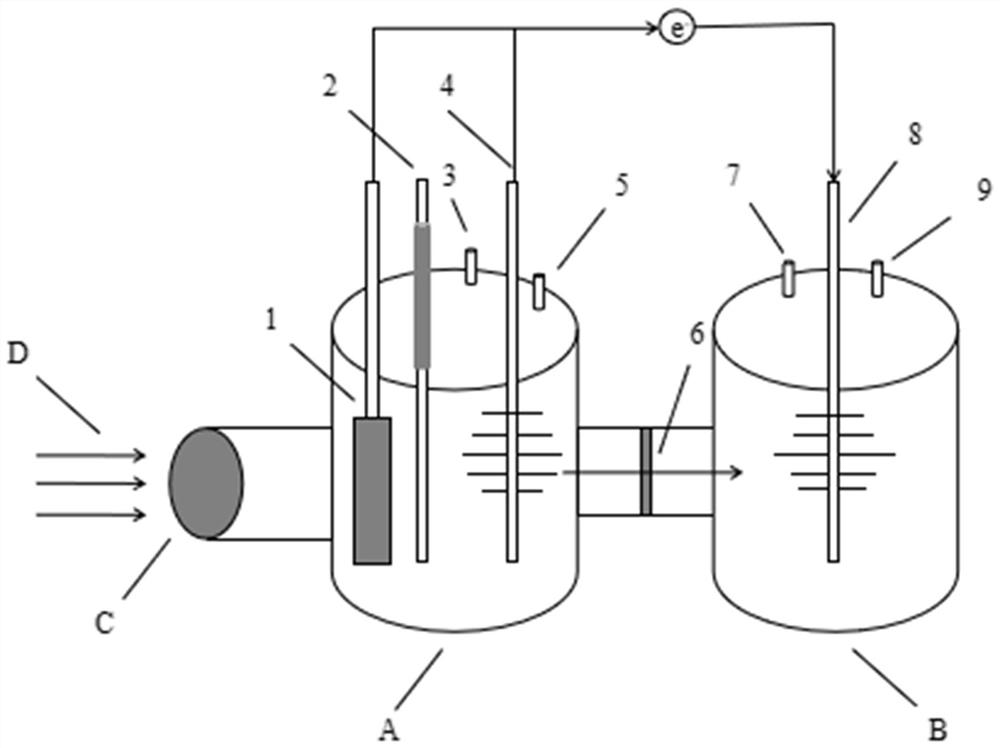
The invention provides a photoelectrocatalysis and microbial fuel cell coupling system for treating antibiotics, and belongs to the technical field of difficult-to-degrade pollutant treatment and energy recovery and utilization. An electrogenesis biological anode of a microbial fuel cell (MFC) is coupled with a photoelectrocatalysis anode to form a coupled electrogenesis catalytic degradation antibiotic system; a photocatalysis anode of the system is of a net structure with a nickel net loaded with a hydrothermal TiO2 catalyst; the biological anode of the system is a carbon brush loaded with electrogenesis microorganisms; and a cathode of the system is a common carbon brush; the cathode and the anode are separated by an ion exchange membrane. The effect of the system in the degradation ofdifficult-to-degrade antibiotics by an anode is obviously superior to that of a traditional microbial fuel cell or a photoelectrocatalysis system; and degradation reaction of the traditional microbialfuel cell is carried out under the condition of the absence of light. According to the advantages of the device, the MFC system and the photocatalysis system are coupled, the problems that an existing MFC is low in degradation efficiency and low in power generation can be solved, and the degradation efficiency of the antibiotics is higher, and the degradation of the antibiotics is more thorough.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Graphitized mesoporous carbon-TiO2 composite photocatalytic material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108654586AIncrease the areaLarge mesoporous structurePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationNanoparticleTio2 nanoparticles
The invention relates to a graphitized mesoporous carbon-TiO2 composite photocatalytic material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The graphitized mesoporous carbon-TiO2 composite photocatalytic material is prepared by taking resorcinol-formaldehyde as a carbon source and titanium trichloride as a titanium source through simple hydrothermal and calcining treatment under an acidic condition. The photocatalytic material comprises uniformly dispersed TiO2 nanoparticles and laminated graphitized mesoporous carbon, and shows up efficient adsorption-photocatalytic synergistic effect in the aspect of antibiotic degradation. The preparation method is simple in process and low in cost; furthermore, the prepared composite photocatalytic material is environmentally friendly andhas wide application prospect in the field of water treatment.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for degrading antibiotics in livestock manure
InactiveCN109354351ACompletely degradedNo secondary pollutionSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningFungiLivestock manureFeces
The invention discloses a method for degrading antibiotics in livestock manure. The method includes the steps: firstly, fermenting and degrading the antibiotics in the livestock manure for the first time by resistant bacillus pumilus, sphingomonas xenophaga, Aspergillus niger and trichoderma viride; secondly, further degrading the antibiotics into small molecule substances by the aid of algae decomposing agents and an infrared radiation technology; finally, inactivating microorganisms at high temperature generated by secondary fermentation. According to the method, the antibiotics in the livestock manure can be effectively degraded into small molecule non-toxic substances, worm eggs in the manure can be killed, harm of the antibiotics in the livestock manure to environments is fundamentally avoided, the livestock manure subjected to secondary fermentation can be prepared into organic fertilizers and recycled, and waste is turned into wealth.
Owner:陈先锐
High-efficiency aerobic composting inoculant for livestock and poultry manure and method for aerobic composting thereof
ActiveCN110029073AReduce contentDrain controlFungiBio-organic fraction processingBacillus licheniformisFeces
The invention discloses a high-efficiency aerobic composting inoculant for livestock and poultry manure and a method for aerobic composting thereof. The inoculant is composed of the following bacterial species by following volume proportion: the ratio of Bacillus licheniformis: Phanerochaete chrysosporium: Aspergillus niger is 1:4 to 5:5-6. The aerobic composting comprises the following steps: S1.adding agricultural and forestry waste to the manure of livestock and poultry, adjusting the C / N of livestock manure to 28-30 and the water content being 55%-60%; and S2. adding a sugar source to thelivestock and poultry manure regulated in S1, then adding the above-mentioned inoculant, and uniformly mixing the materials and performing the aerobic composting. After aerobic composting, the degradation of antibiotics in livestock manure is significant, and the content of available heavy metals and resistance genes in livestock manure is greatly reduced, and nitrogen loss is effectively controlled, so that the inoculant has great application prospects.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Mixed microbial agent for degrading sulfonamide antibiotics in sewage and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111057670APromote degradationEfficient degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a mixed microbial agent for degrading sulfonamide antibiotics in sewage and a preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of environmental microorganisms. The mixed microbial agent for degrading sulfonamide antibiotics in sewage is formed by mixing arthrobacter sp. YL1 and pseudomonas sp. YL2 in a volume ratio of 1: (2-3). The mixed microbial agent is used for treating sulfonamide antibiotics in sewage or degrading organic matters in sewage. The arthrobacter sp. YL1 and the pseudomonas sp. YL2 are separated from each other in the invention can use sulfonamide antibiotics as a unique carbon source for growth and can realize rapid and efficient degradation of the sulfonamide antibiotics; and compared with a single strain, the double-strain interaction microbial agent system has higher removal efficiency, more thorough removal amount and a more stable community structure in the process of practical application, and is very criticalto biological treatment of sulfonamide antibiotics in water. The mixed microbial agent of the invention is applied to the field of antibiotic degradation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Pretreatment method of ferment antibiotic fungi residues
ActiveCN106480104AImprove metabolic activityAccelerated hydrolysis and acidificationWaste based fuelFermentationHigh concentrationMicroorganism
The invention discloses a pretreatment method of ferment antibiotic fungi residues. The pretreatment method comprises ultrahigh temperature reinforced acidogenic fermentation treatment of the ferment antibiotic fungi residues. Thermophilic hydrolysis acid-forming bacteria are used for performing high temperature anaerobic digestion treatment on the ferment antibiotic fungi residues, so that the fungi residues are hydrolyzed and acidified, antibiotic producing bacteria in the fungi residues are inactivated, and retained antibiotics are degraded. The fungi residues pretreated through the method can be directly subjected to subsequent biochemical treatment after being subjected to antibiotic removal. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the antibiotic producing bacteria can be completely killed, the antibiotics in the fungi residues can be removed, inhibition of high-concentration antibiotics to microorganisms is reduced, the difficulty in treatment of the fungi residues based on the subsequent biochemical method is reduced, generation of drug-resistant fungi and drug-resistant genes in the subsequent biochemical treatment is reduced, the harmless treatment efficiency of the antibiotic fungi residues is improved, and environmental protection is facilitated.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
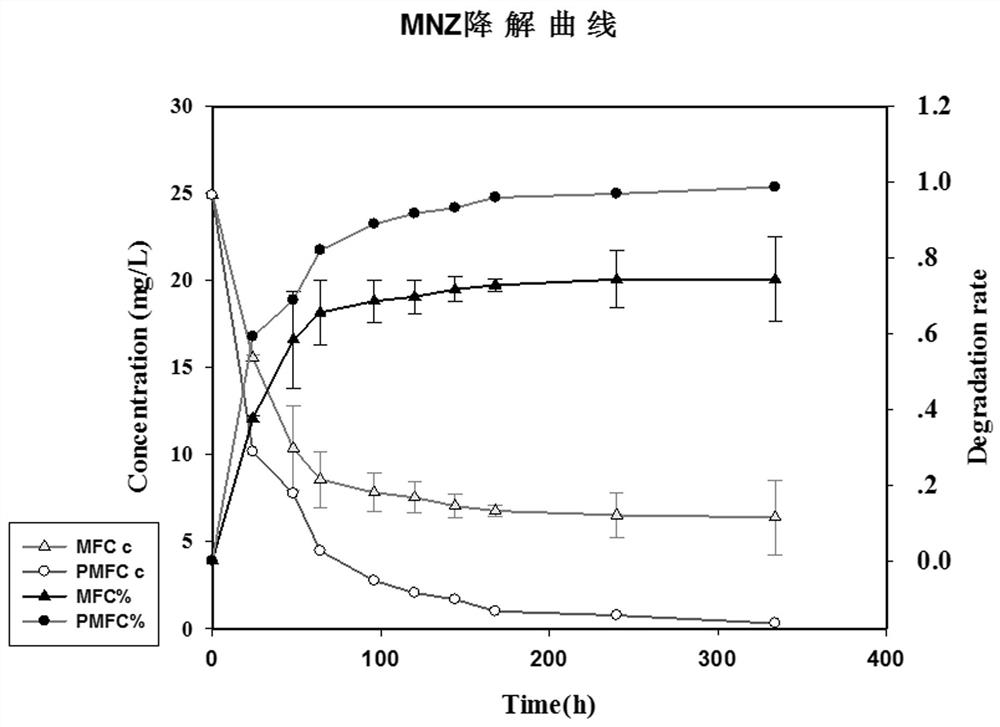
Method for rapidly culturing anaerobic granular sludge applicable to pharmaceutical wastewater treatment
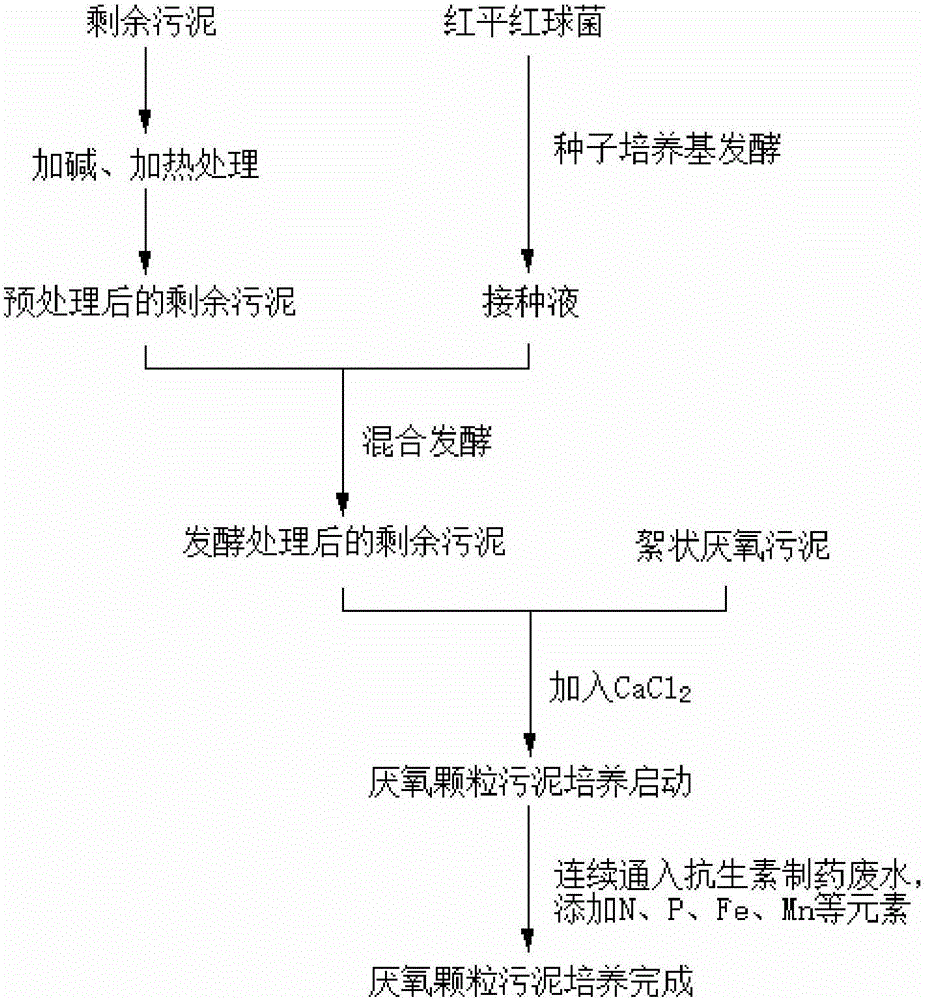
ActiveCN105948243APromote degradationEmission reductionTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesBiological sludge treatmentAnaerobic reactorFermentation
The invention discloses a method for rapidly culturing anaerobic granular sludge applicable to pharmaceutical wastewater treatment. The method specifically comprises the following steps: according to the method disclosed by the invention, performing fermentation treatment on residual sludge by adopting a mode of feeding microbial preparations, putting the treated sludge into an anaerobic reactor, mixing with anaerobic flocculent sludge to culture, and feeding nutrient elements such as N, P, Fe and Mn in the culture process, thereby obtaining the anaerobic granular sludge after about 71-98 days. The anaerobic granular sludge formation time can be greatly shortened. In addition, the anaerobic granular sludge prepared by using the method can be adopted to treat pharmaceutical wastewater of antibiotics, and has a relatively high COD removal rate and a good antibiotic degradation effect.
Owner:浙江微技环境修复工程有限公司
Application of novel MIL-53(Fe) based catalyst in removal of antibiotics in water
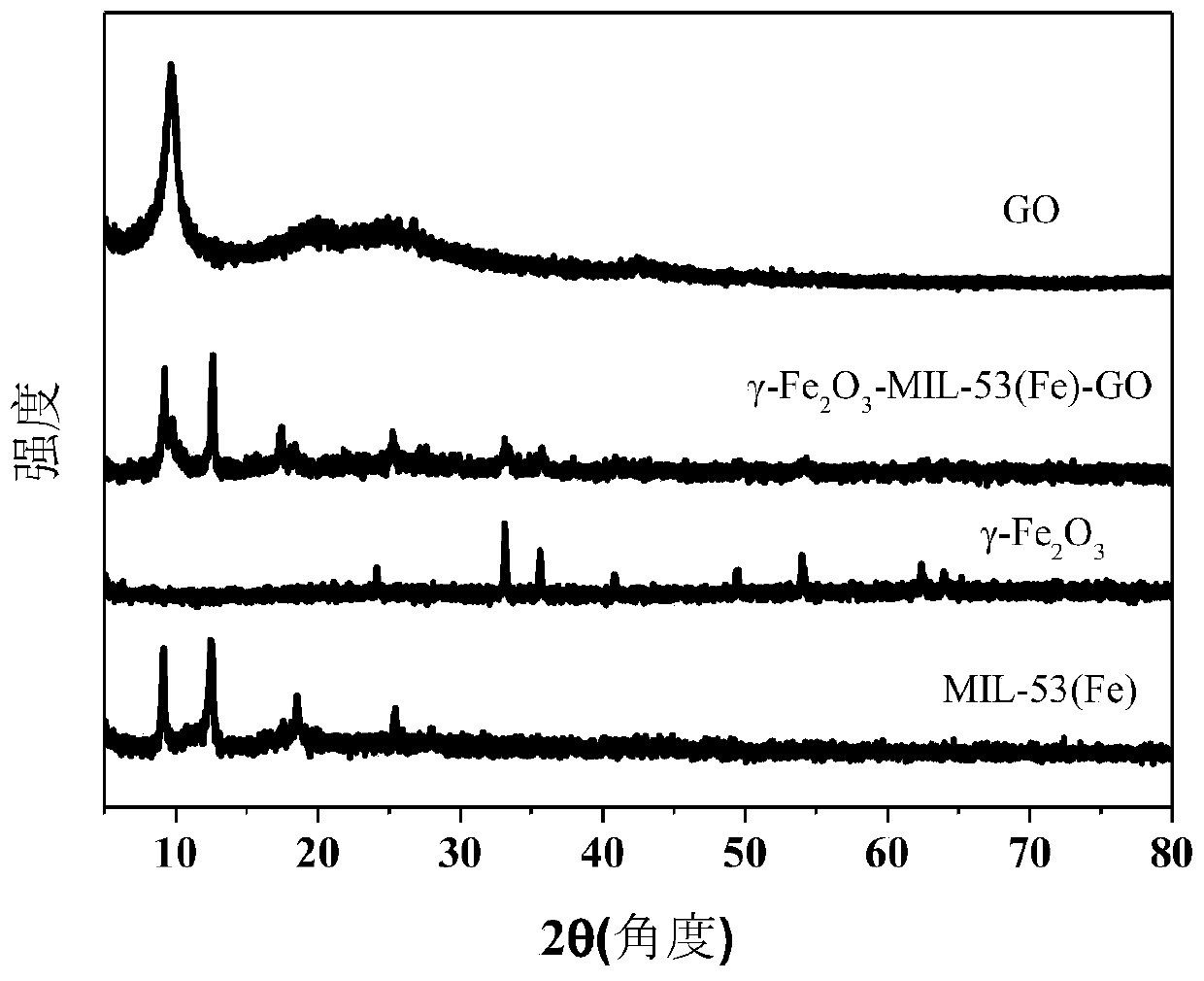
InactiveCN111151303AEnhanced light absorptionHigh recovery rateWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsPtru catalystCrystallinity
The invention discloses design and preparation of an MIL-53(Fe) based catalyst and application of the catalyst in removal of antibiotics in water. The catalyst is synthesized through an in-situ pyrolysis method and a hydrothermal method. The efficient degradation of antibiotics is realized. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: magnetic gamma-Fe2O3 ultrafine particles areuniformly distributed in an MIL-53(Fe) regular octahedron pore structure to form a micro heterojunction; then, layered graphene oxide (GO) with high conductivity enables MIL-53(Fe) with high crystallinity to be dispersed on the surface of the layered graphene oxide (GO), and finally, the gamma-Fe2O3-MIL-53(Fe)-GO composite photocatalyst is synthesized. The catalyst is applied to degradation of antibiotics in water under a certain condition; compared with other composite catalysts taking MIL-53(Fe) as a main body, the composite catalyst gamma-Fe2O3-MIL-53(Fe)-GO has the advantages of high degradation efficiency on antibiotics in water, large photo-response range, low cost, short degradation period and high material reusability in the process of degrading antibiotic wastewater. Therefore, the composite material prepared by the method can be widely applied to removal of antibiotics in water, and has a high application value and industrial prospect.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Immobilized laccase and preparation method thereof, and application of immobilized laccase in antibiotic degradation
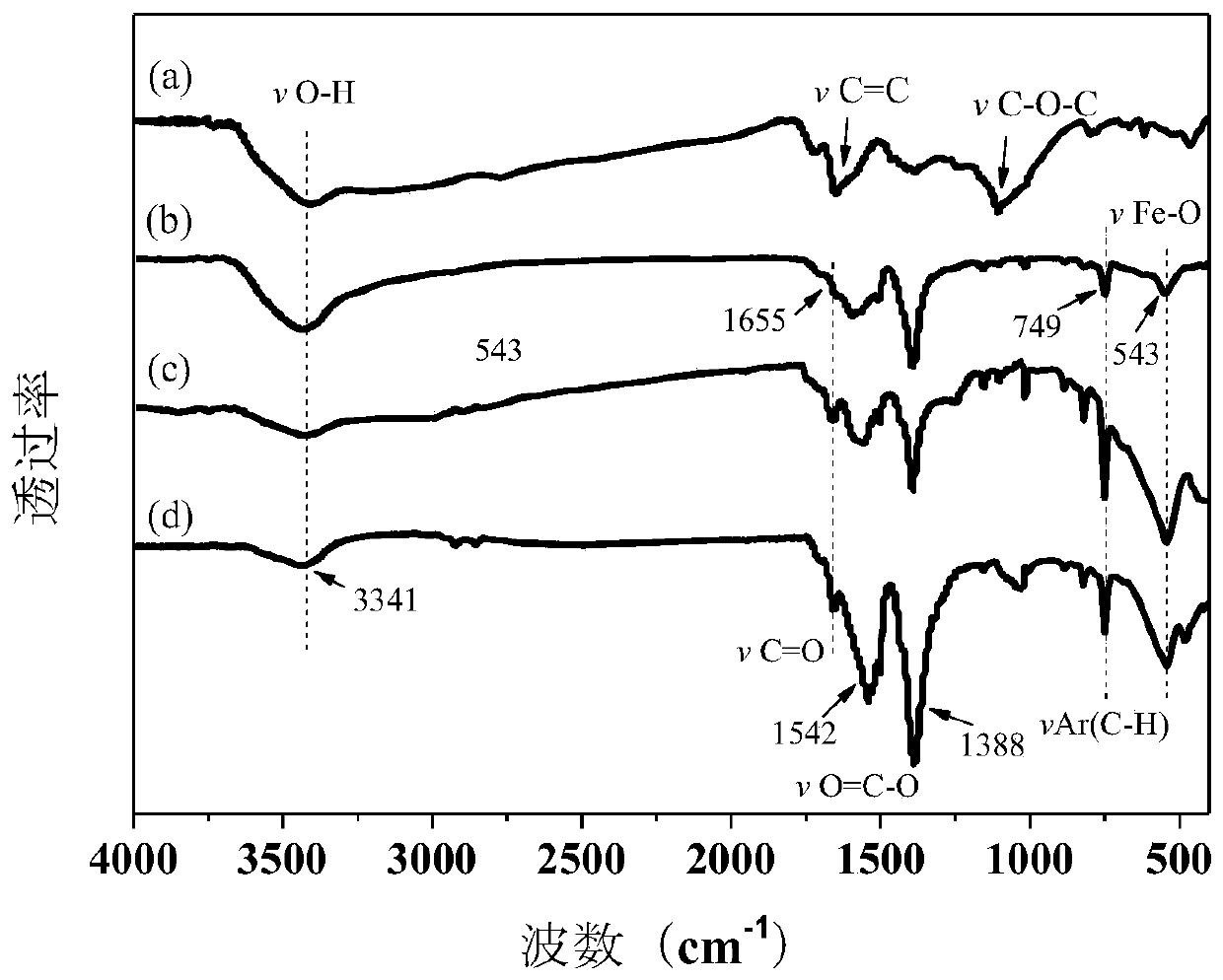
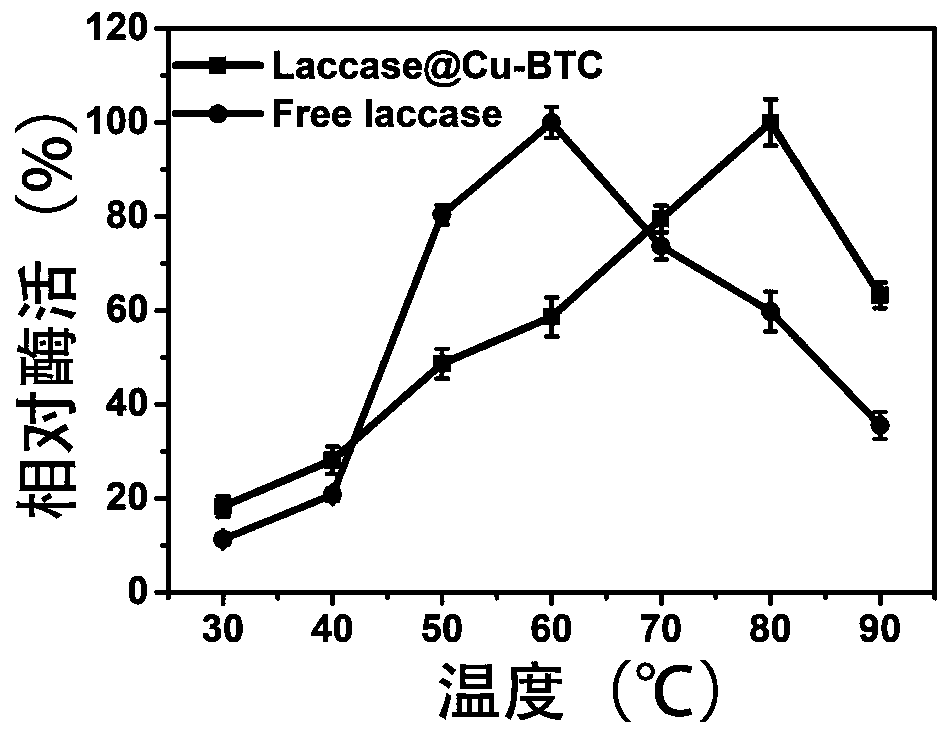
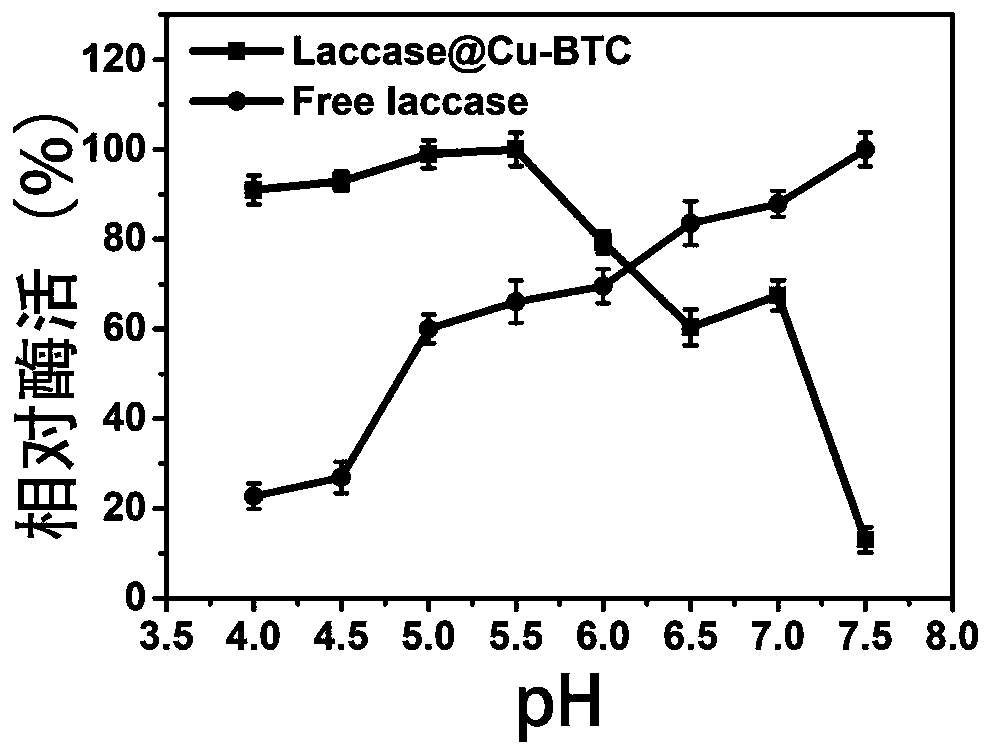
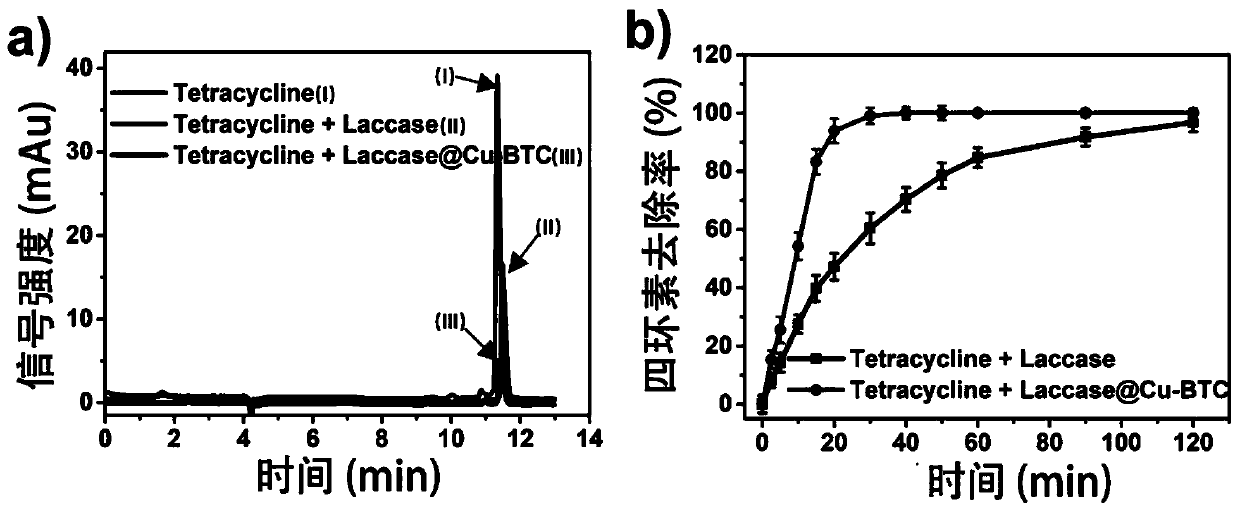
PendingCN111019933AAchieve removalAvoid destructionOxidoreductasesOn/in organic carrierAmpicillinCu2 ions
The invention discloses immobilized laccase and a preparation method thereof, and application of the immobilized laccase in antibiotic degradation. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding laccase into a solution containing copper ions, carrying out uniform mixing, then adding a trimesic acid solution, carrying out uniform mixing, performing centrifuging to remove a supernatant, conducting cleaning with a cleaning solution, and carrying out drying in vacuum to obtain the immobilized laccase. The method is simple to operate; the laccase can be coated in a carrier; and an organic framework structure provides shell protection for the laccase, and damage to the structure of the laccase due to external factors such as friction and shearing force in the use process is avoided. According to the invention, reduction in enzyme activity avoided, and the enzyme activity is greatly improved (the enzyme activity of the immobilized laccase obtained by the immobilization method is1.5-30 times of the activity of equivalent free laccase). The immobilized laccase disclosed by the invention has efficient catalytic degradation capability on antibiotics such as tetracycline, ampicillin, tetracycline derivatives and derivatives of ampicillin, can achieve an effect close to complete degradation in an extremely short time, and is good in reusability and free of secondary pollution.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Degradation method for sulfadimidine in water
InactiveCN110171863ASimple preparation processLow costWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsNitrogen gasElectron
The invention discloses a degradation method for sulfadimidine in water. Biochar made from a biomass raw material is used as a raw material, by loading TiO2, a composite biochar material is prepared,and by utilizing a thermal processing technology, the composite biochar material is converted into a biochar adsorption material; then, with assistance of electron beam irradiation, the synthesized biochar adsorption material is utilized for efficiently degrading the sulfadimidine in a solution, and through irradiation, active free radicals are generated, and the high reduction performance is achieved; the free radicals react with groups and carbon rings of the sulfadimidine, and finally, non-toxic carbon dioxide, nitrogen and water molecules are generated. According to the method, by adding the biochar adsorption material, efficient antibiotic degradation is achieved under the low radiation condition, the electron beam irradiation has a good degradation effect on the sulfadimidine, the demand of the first order kinetics is met, and R is greater than 0.99. The prepared biochar adsorption material has good recycling performance, and the method has the advantages of short consumed degradation time, high recycling performance, low cost and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
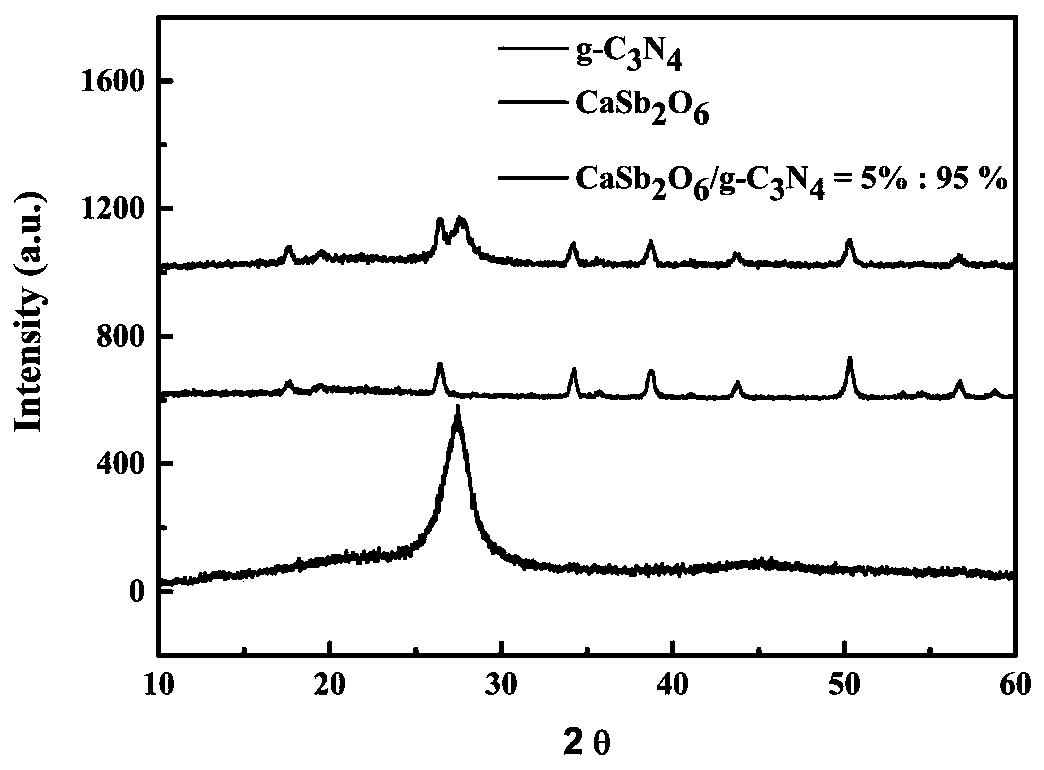
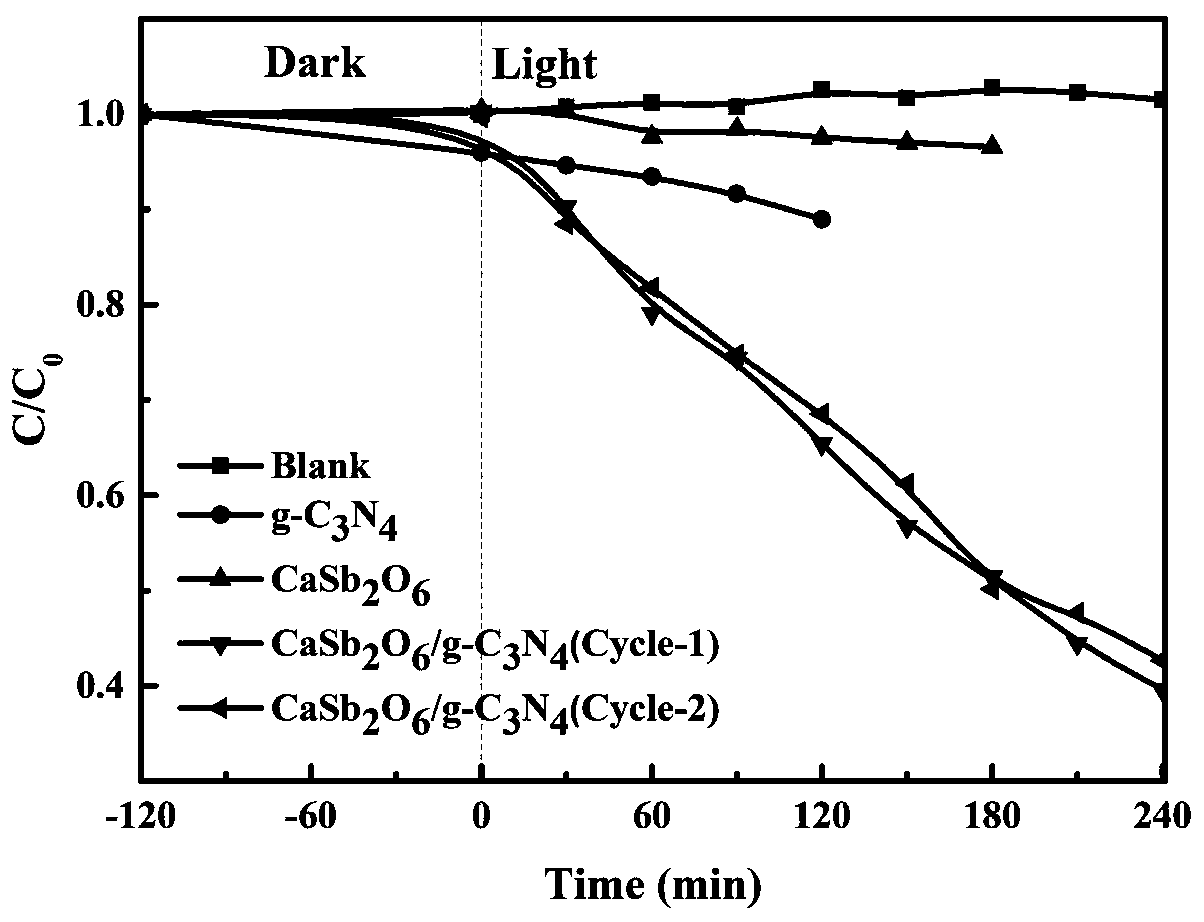
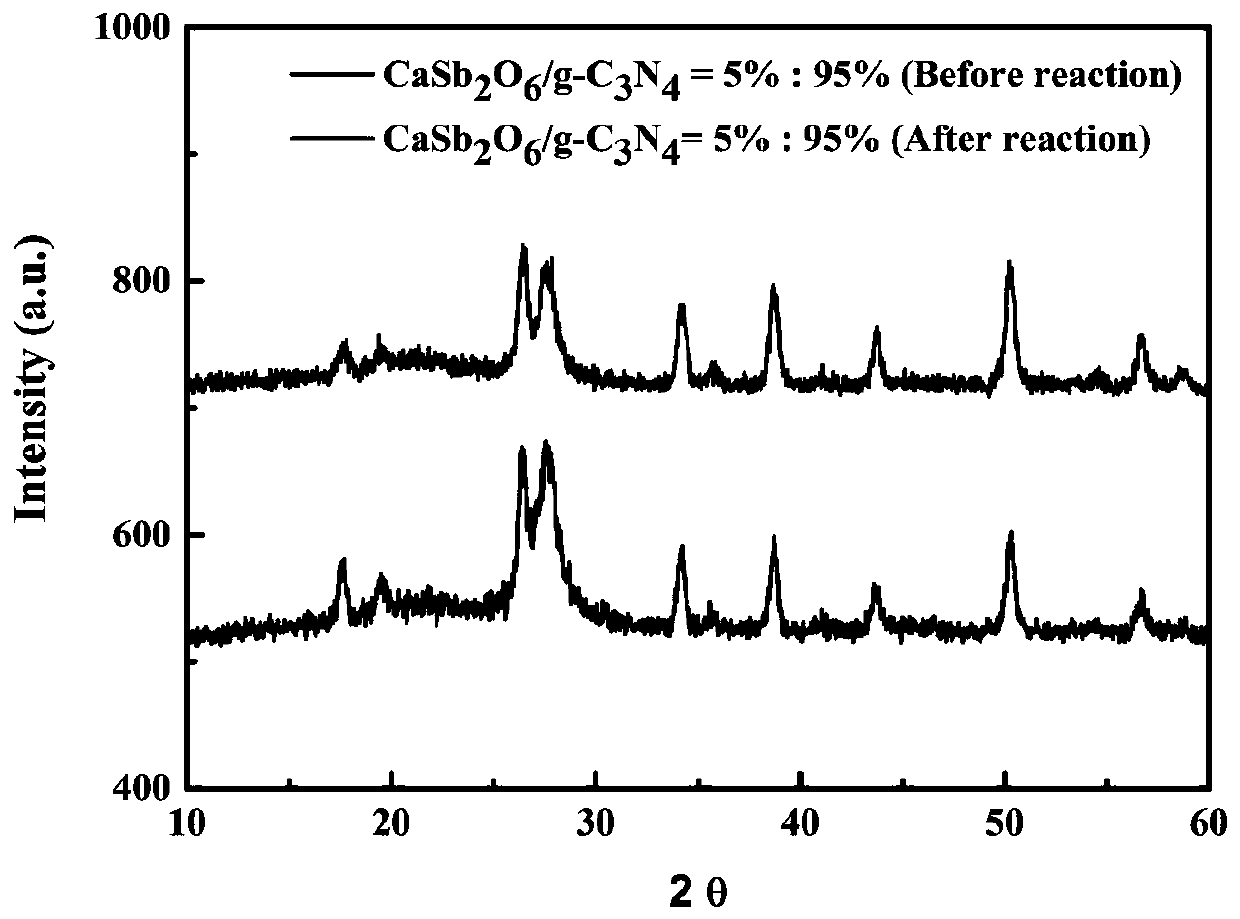
Preparation method and application of heterojunction photocatalyst CaSb2O6/g-C3N4
ActiveCN110075905AGood catalytic degradation effectEase of environmental protectionPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationHeterojunctionRoom temperature
The invention discloses a preparation method of a heterojunction photocatalyst CaSb2O6 / g-C3N4 and an application of the heterojunction photocatalyst CaSb2O6 / g-C3N4 in degradation of antibiotics undervisible light. The method comprises the following steps: preparing CaSb2O6 and g-C3N4 respectively with a solid state sintering method, then, mixing the CaSb2O6 and g-C3N4, adding a certain amount ofabsolute ethyl alcohol, performing mixing and grinding for 30 min, performing sintering at the constant temperature of 480 DEG C in a muffle furnace for 2 h, and naturally cooling a product to room temperature to obtain the heterojunction CaSb2O6 / g-C3N4 photocatalyst. The heterojunction CaSb2O6 / g-C3N4 photocatalyst prepared with the method has good photocatalytic effects in degradation of antibiotic tetracycline and has stable photocatalytic properties.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF EDUCATION +1
Composite photocatalyst, and preparation method and application of composite photocatalyst
ActiveCN108654671AImprove conductivityImprove photocatalytic activityPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationBismuth oxybromideBlack phosphorus
The invention discloses a composite photocatalyst, and a preparation method and the application of the composite photocatalyst. The preparation method of the composite catalyst comprises the steps ofdissolving bismuth salt in a solvent, adding carbonized nitrogen for uniform dispersion, adding bromide for dispersion, putting in a high-pressure reaction kettle for reaction, and adding a dispersingliquid of black phosphorus at last for stirring and reaction to form the nanosheet composite photocatalyst having bismuth oxybromide growing on carbonized nitrogen and dispersed with black phosphorusparticles. The preparation method is simple, and the prepared composite photocatalyst has better application prospects in antibiotic degradation.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for pretreating wastewater obtained from antibiotic production
ActiveCN106986434ALower titerEffective destructionWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsHigh concentrationMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method for pretreating wastewater obtained from antibiotic production. The method comprises the following steps: adding a solid base to wastewater obtained from antibiotic production, and hydrolyzing the residual antibiotics in the wastewater obtained from antibiotic production under the action of the solid base. The method provided by the invention has high antibiotic degradation efficiency and low antibiotic residue, and the biological toxicity of the wastewater obtained from antibiotic production is significantly reduced. The antibiotic wastewater pretreated by the method provided by the invention can be directly subjected to the subsequent biochemical treatment. The method provided by the invention can completely remove the antibiotics in the antibiotic wastewater, reduce the inhibition of the high concentration antibiotics to microorganisms, reduce the difficulty of the subsequent biochemical treatment of the antibiotic wastewater, and reduce the production of drug-resistant bacteria and drug-resistant genes in the subsequent biochemical treatment.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Tetracycline antibiotics degrading arthrobacterium and application thereof
ActiveCN108707559APromote degradationReduce residual concentrationBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationBacterial strainArthrobacter sp.
The invention relates to the field of environment protection, and discloses a tetracycline antibiotics degrading arthrobacterium and application thereof. The classification name of the tetracycline antibiotics degrading arthrobacterium is Arthrobacter sp.. The Arthrobacter sp. is tetracycline antibiotics degrading arthrobacterium, can effectively degrade various tetracycline antibiotics, has the best oxytetracycline degrading effect, and has the good degrading effect for tetracycline and aureomycin. The bacterial strain OTC-16 can grow under the pH of 6.0-9.0 and under the temperature of 20-35DEG C, the application range is wide, and the tetracycline antibiotics degrading arthrobacterium can be used for repairing tetracycline antibiotics pollution.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
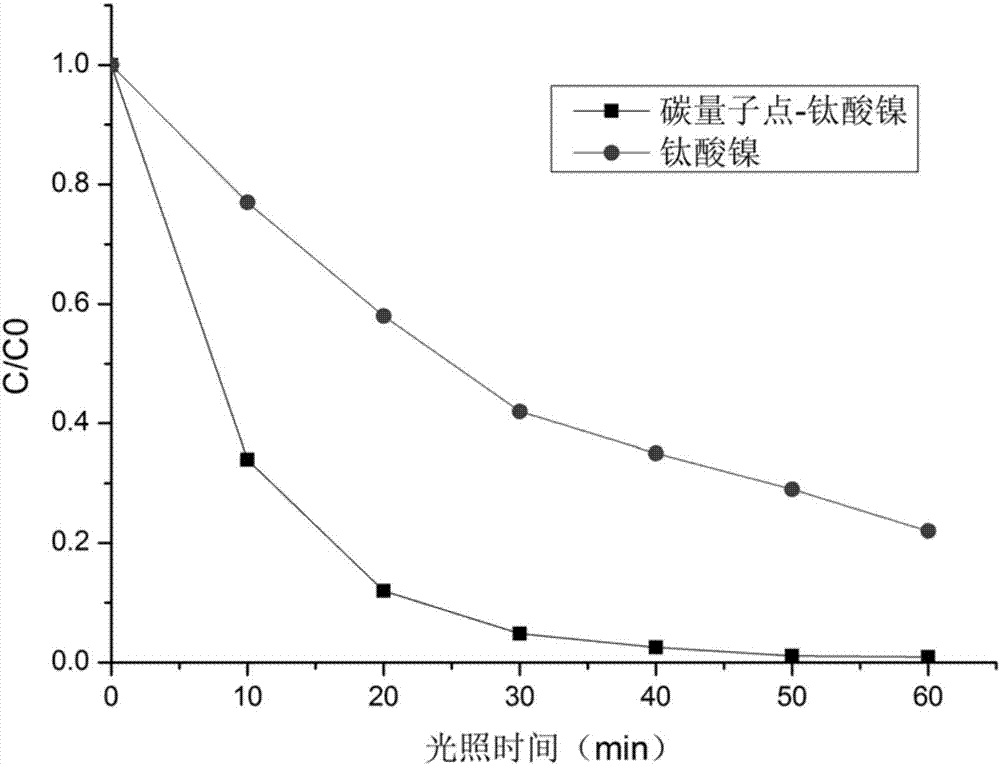
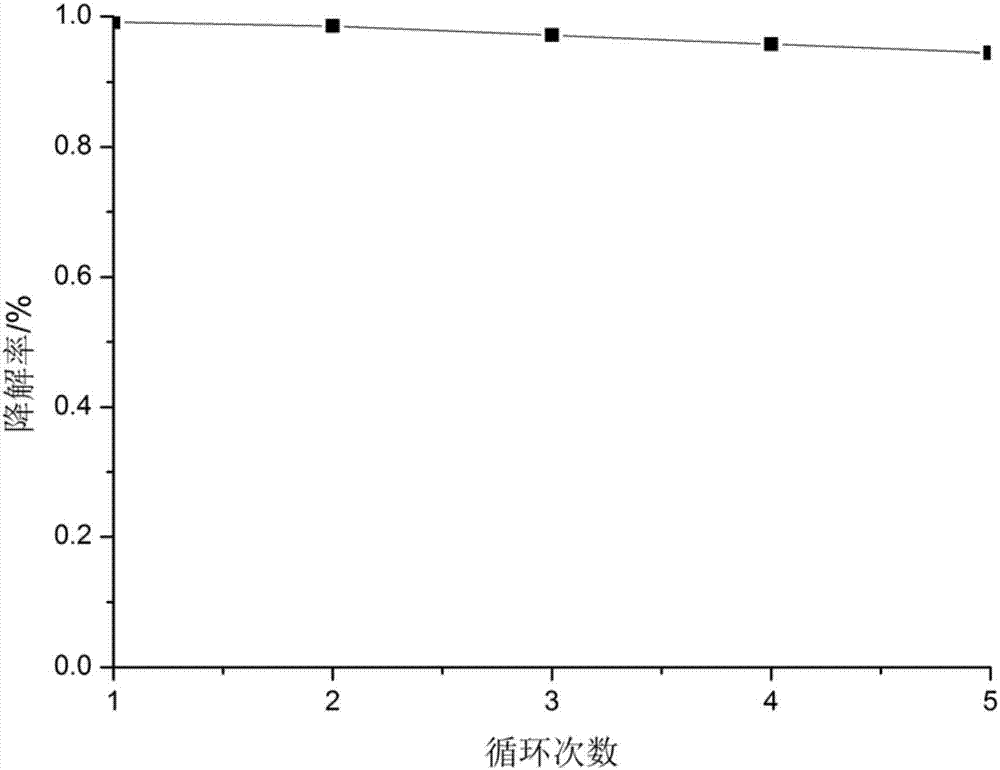
Carbon quantum dot-nickel titanate compounded degradation agent for degrading antibiotics and preparation method of carbon quantum dot-nickel titanate compounded degradation agent
ActiveCN107029725ASmall sizeInhibit synthesisWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsAntibiotic YMaterials science
The invention discloses a carbon quantum dot-nickel titanate compounded degradation agent for degrading antibiotics and a preparation method of the carbon quantum dot-nickel titanate compounded degradation agent. The preparation method comprises the steps that 1, nickel acetate, tetrabutyl titanate and sodium citrate are added into an organic solvent, the materials are mixed to be uniform, and a nickel titanate precursor solution is obtained; 2, ethidene diamine is added into the water solution of glucose, reacting is carried out at the temperature of 140 DEG C to 220 DEG after the materials are stirred to be uniform, the time ranges from 3 h to 8 h, and a carbon quantum dot solution is obtained; 3, the nickel titanate precursor solution obtained in the step 1 and the carbon quantum dot solution obtained in the step 2 are mixed, a hydrothermal reaction is carried out at the temperature of 120 DEG C to 150 DEG C after the materials are stirred to be uniform, the time ranges from 18 h to 24 h, centrifugation is carried out after the reaction is completed, sediment products are subjected to aftertreatment, and the carbon quantum dot-nickel titanate compounded degradation agent is obtained. The preparation method is simple in process and low in cost, and the prepared carbon quantum dot-nickel titanate compounded degradation agent is high in degradation efficiency on antibiotics and good in photocatalysis stability.
Owner:HUNAN VAUBAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
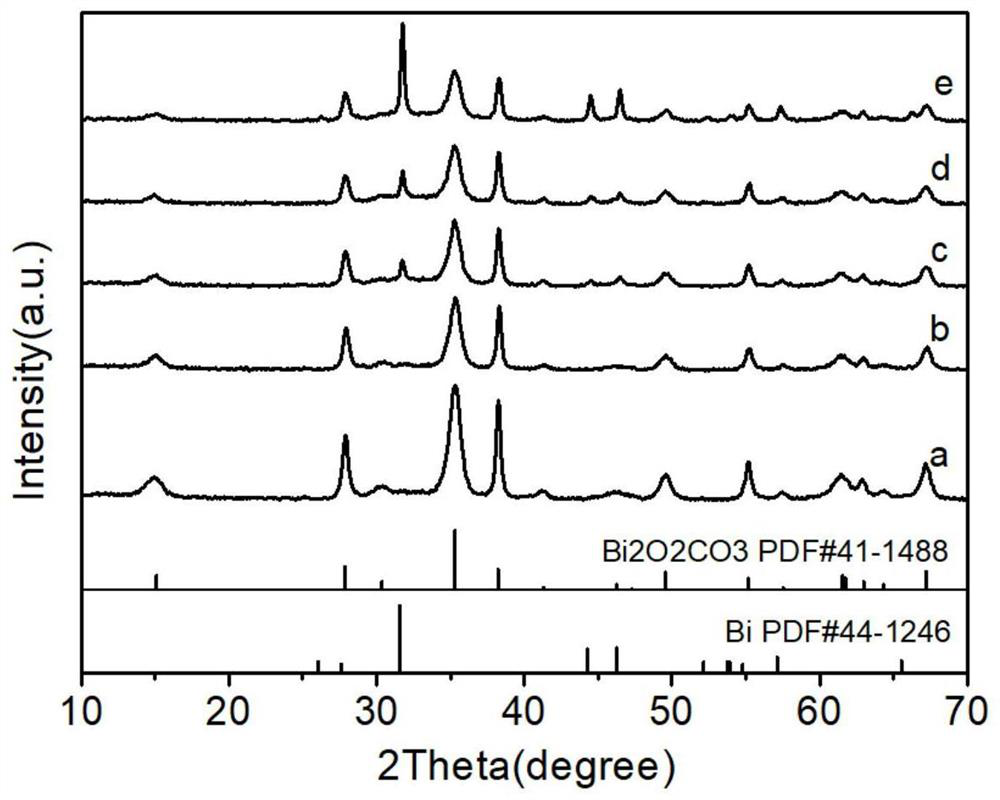
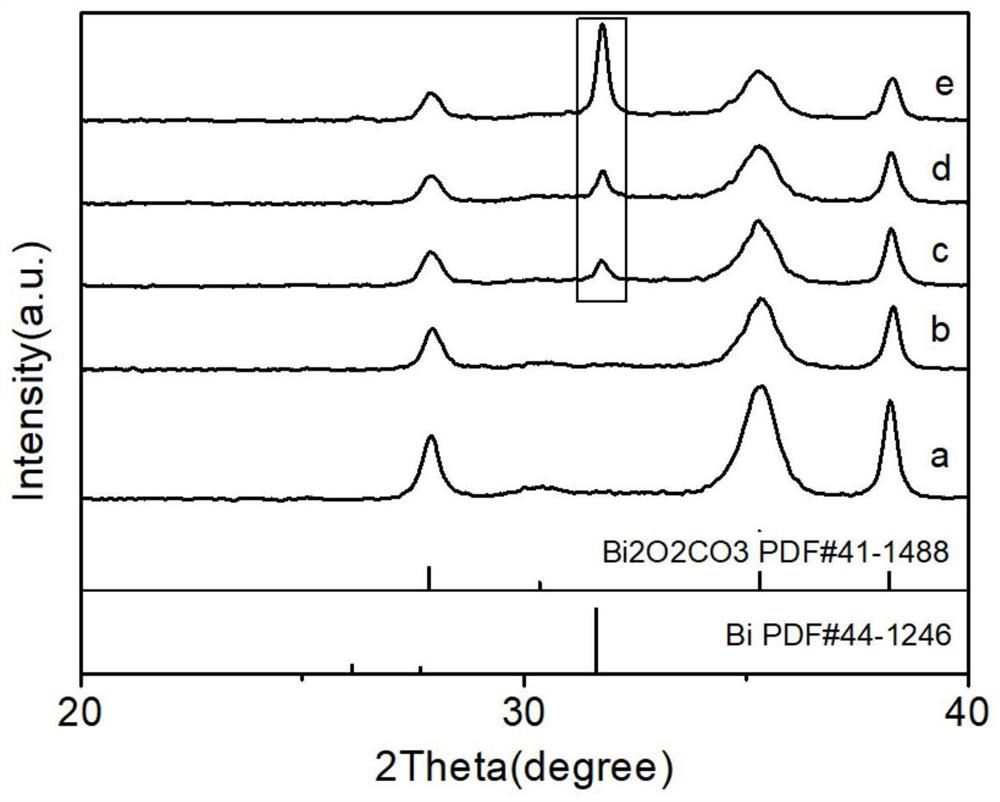
Bismuth-bismuthyl carbonate composite photocatalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN113600174ALower bandgapEasy to getWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsPhoto catalysisTetracycline
The invention provides a bismuth-bismuthyl carbonate composite photocatalyst and a preparation method and application thereof, the preparation method comprises the following steps: step 1, dispersing nano flower-ball-shaped Bi2O2CO3 powder and NaBH4 in deionized water according to a molar ratio of (0.25-7.5): (1-3) to obtain a precursor solution A, and dispersing flaky Bi2O2CO3 powder and NaBH4 in deionized water according to a molar ratio of (0.5-7.5): (1-3), so as to obtain a precursor solution B; and step 2, uniformly mixing the precursor solution A or the precursor solution B, then filtering to obtain a mixed solution, and sequentially washing and drying the obtained filter cake to obtain the nano flower-ball-shaped or sheet-shaped bismuth-bismuthyl carbonate composite photocatalyst, which can realize efficient degradation of tetracycline under visible light and near-infrared light, and has a good application prospect in antibiotic degradation.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for rapid detection of drug resistant gene New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase in bacteria
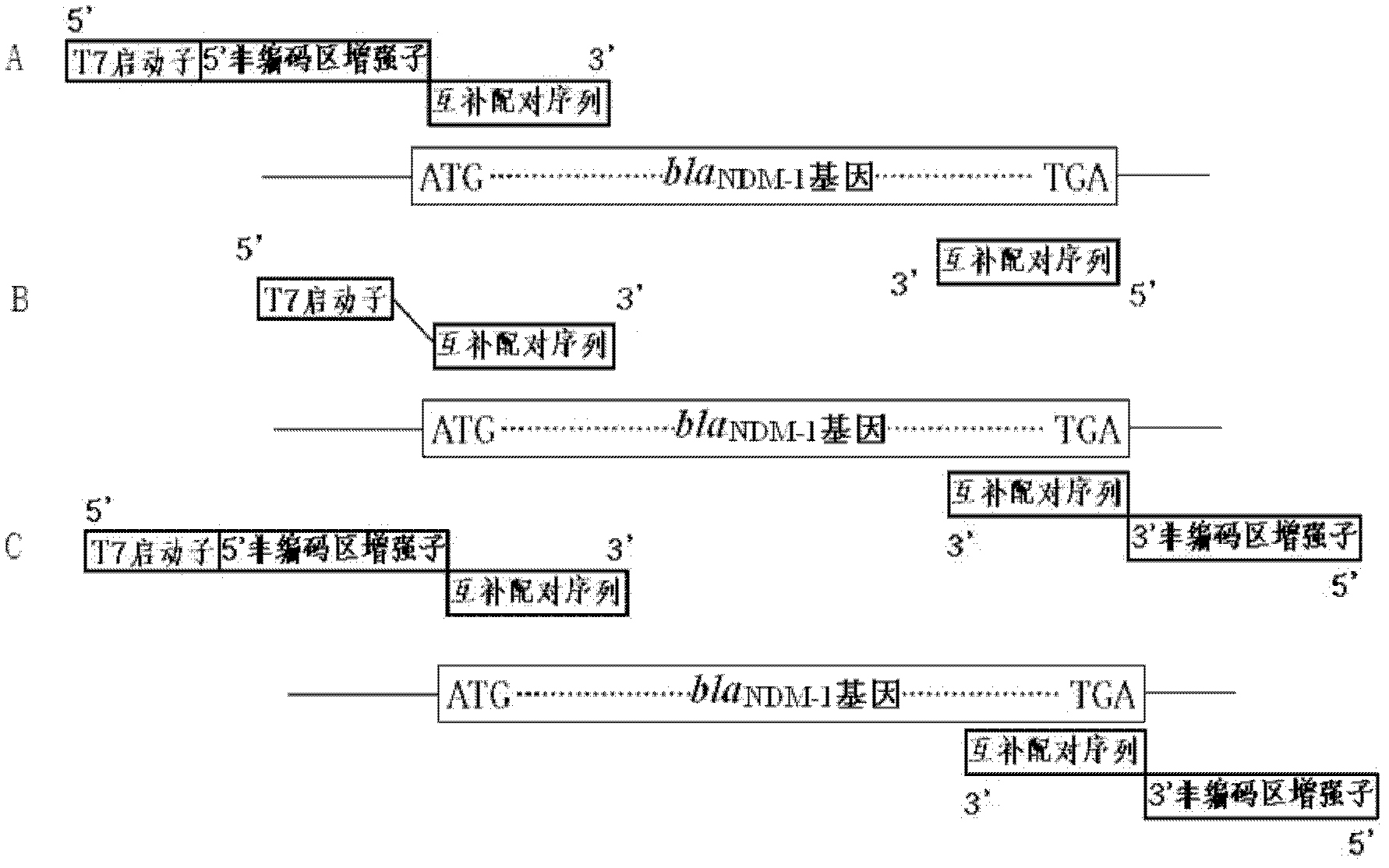
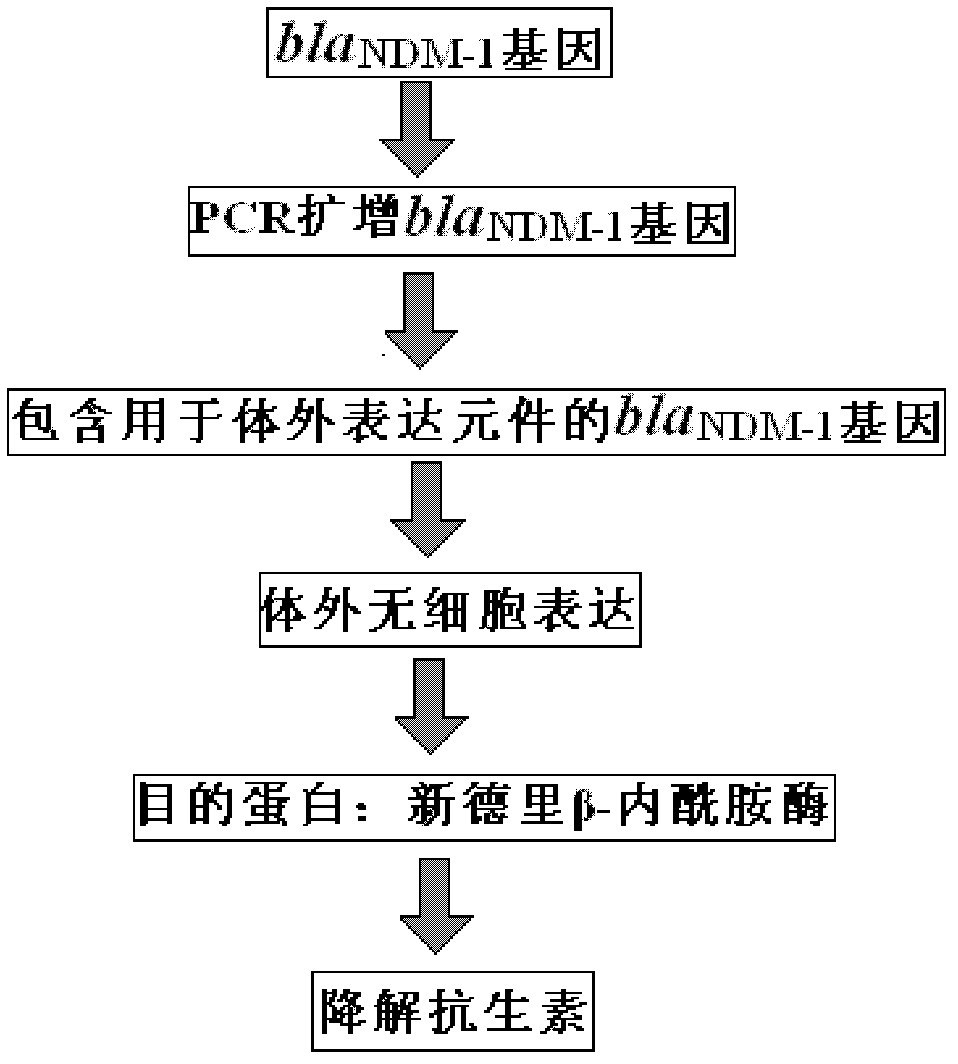
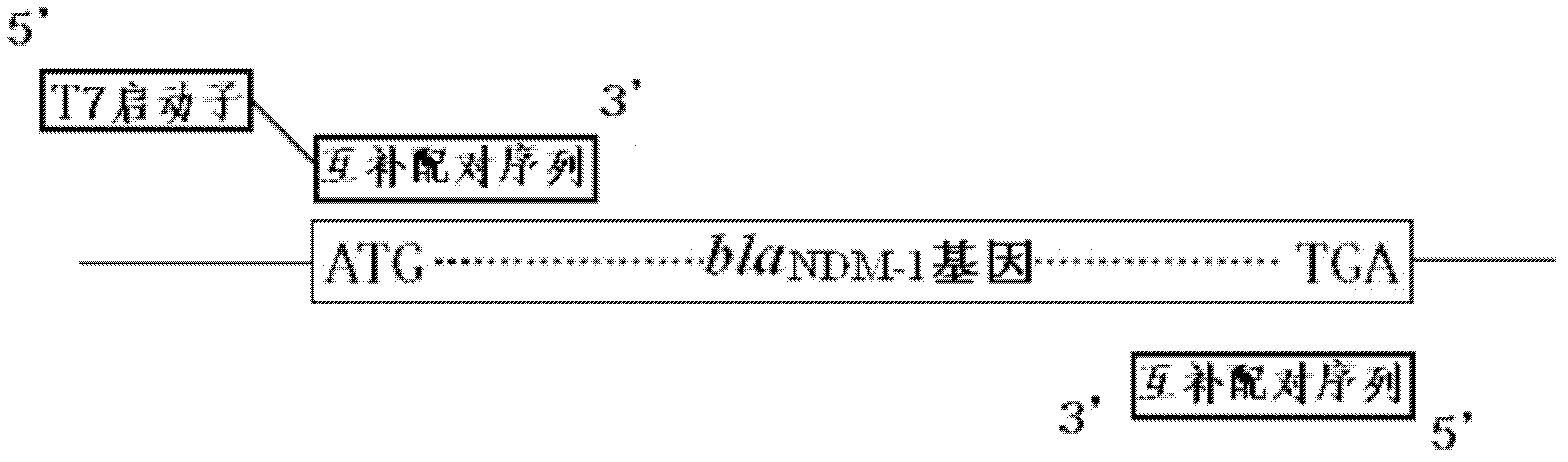
The invention discloses a method for rapid detection of a drug resistant gene New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase (NDM-1) in bacteria, comprising the steps of: A. cracking or extracting DNA in bacteria to be detected so as to be used as a template of PCR (polymerase chain reaction); B. designing PCR primers and amplifying a full-length New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase gene; C. condensing the amplified blaNDM-1 gene segment and quantifying; D. expressing blaNDM-1 enzyme with a wheat germ cell-free expression system; E. determining the activity of the expressed NDM-1 in degrading antibiotics. In the invention, the detection and characterization of the drug resistant gene New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase in bacteria are realized by a pair of PCR primers and the determination of antibiotic degradation activity. Meanwhile, a primer sequence for amplifying the full-length blaNDM-1 gene and for expressing NDM-1 by the wheat germ cell-free expression system is disclosed. With feasibility, high sensitivity and simple operation, the method of the invention can be used for rapid detection. With a pair of PCR primers and by determination of antibiotic degradation activity, the detection and characterization of the drug resistant gene New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase in bacteria come true.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
High-efficiency antibiotic wastewater treatment agent and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106434467AGuaranteed treatment effectImprove securityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAntibiotic YSodium sulfate
The invention discloses a high-efficiency antibiotic wastewater treatment agent and a preparation method and application thereof. The high-efficiency treatment agent comprises the following steps that 1, mixed liquid in an aeration tank of a domestic sewage treatment plant is taken, a proper amount of glass beads is added, and then standing is performed; 2, supernate is taken, gradient dilution is performed, flat plate coating is conducted on a solid culture medium containing sodium chloride or sodium sulfate, and salt-tolerant strains are screened out; 3, reagent resistance of the screened salt-tolerant strains is analyzed; 4, the cultured strains having high reagent resistance are inoculated to a salt-containing liquid culture medium in an independent or mixed mode for culture, and the antibiotic high-efficiency degradable fungicide can be obtained. The preparation method is very simple, easy to operate and high in safety, no antibiotic is used in the fungicide production process, and the obtained fungicide can be used for high-efficiency antibiotic degradation and can be applied to high-efficiency antibiotic wastewater treatment.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com