Patents
Literature
504results about How to "Lower bandgap" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
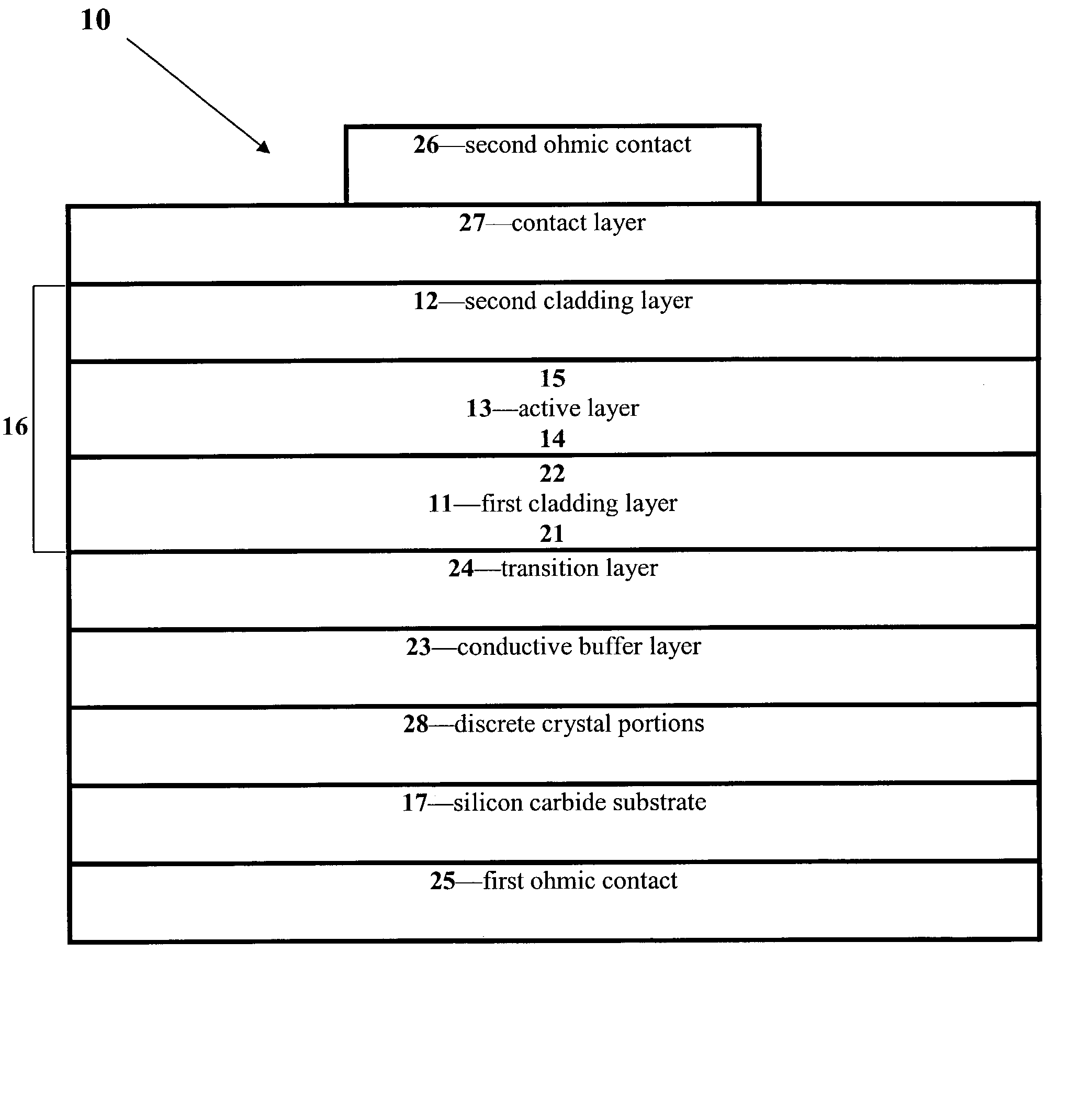
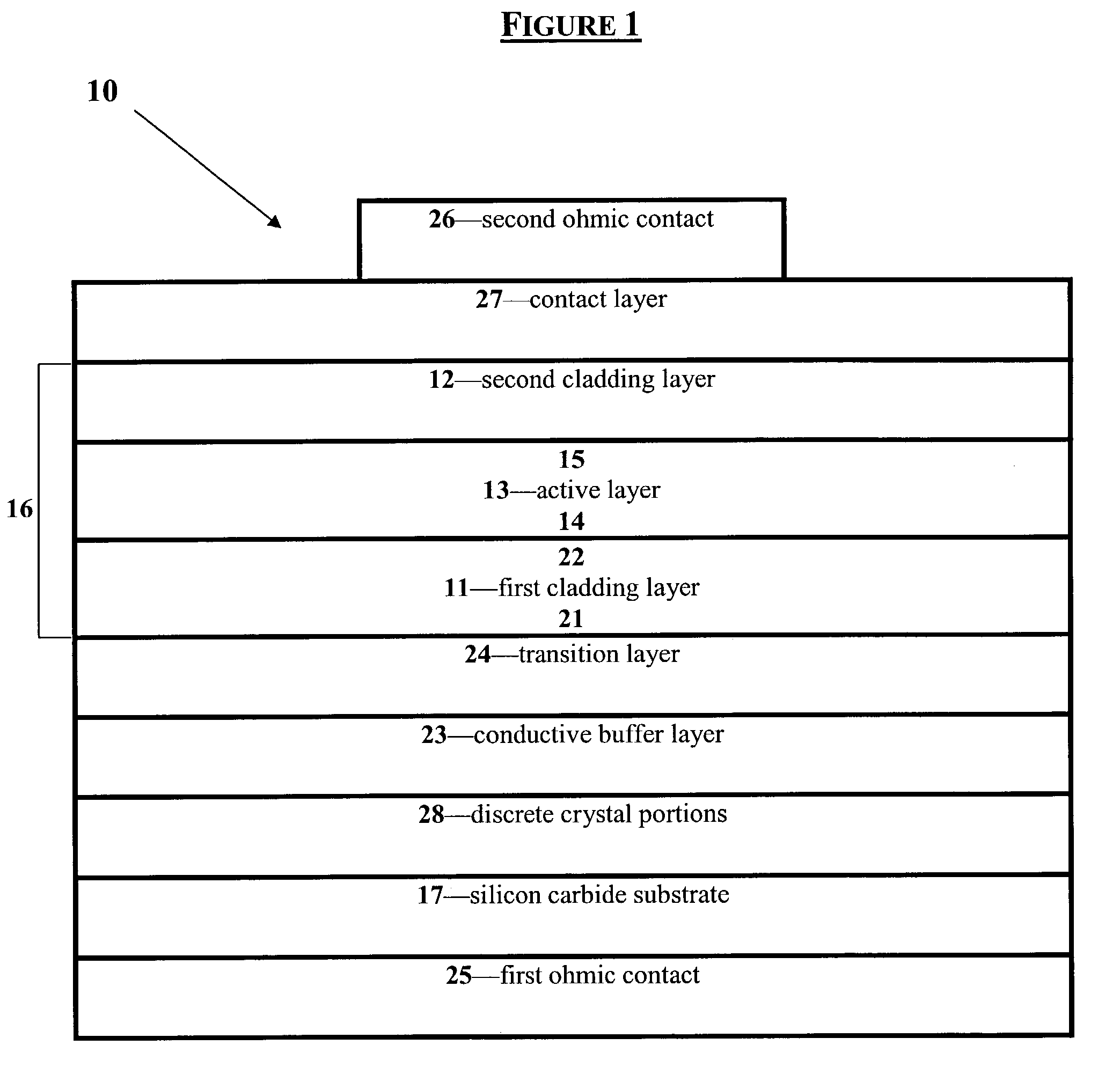
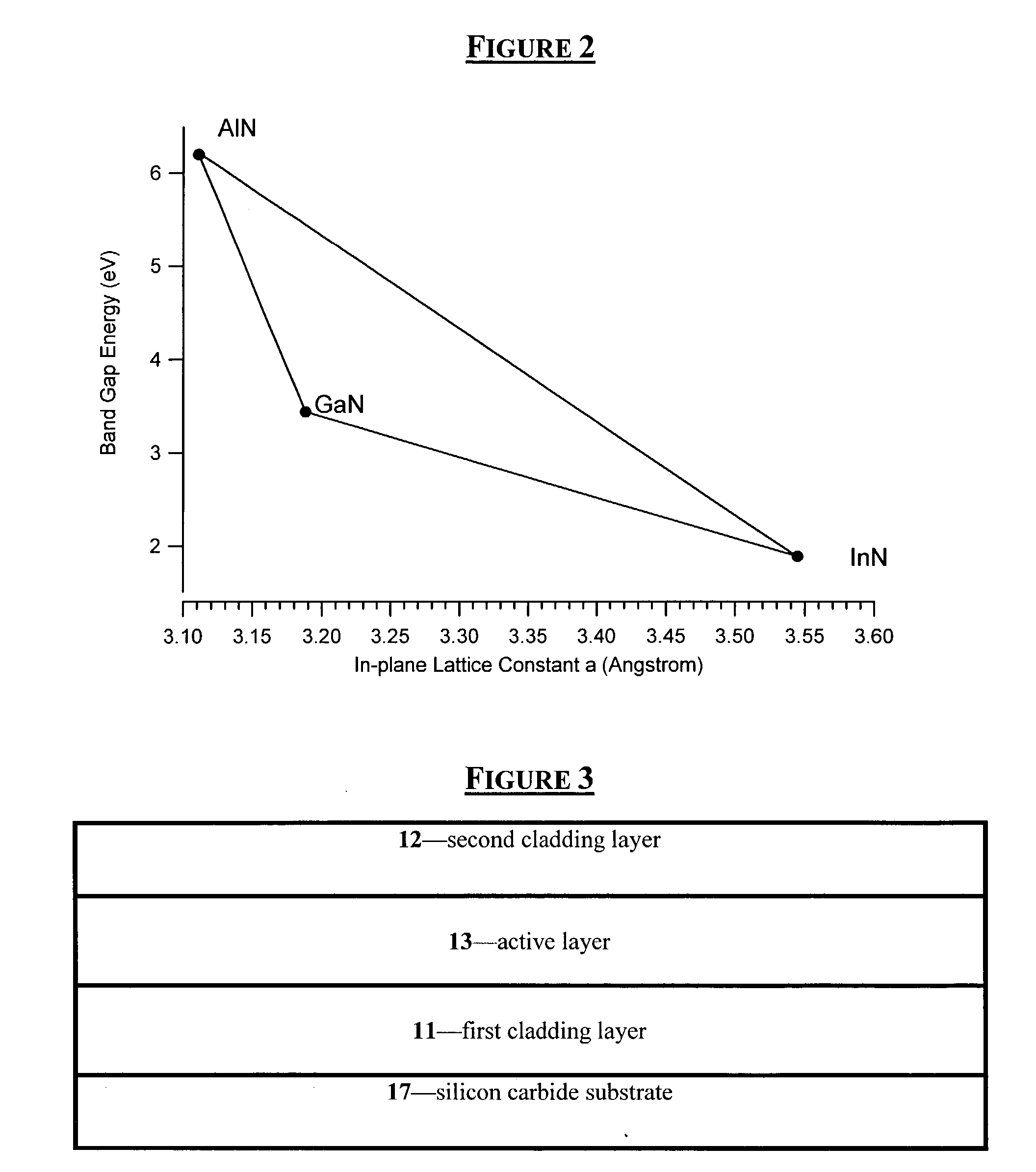
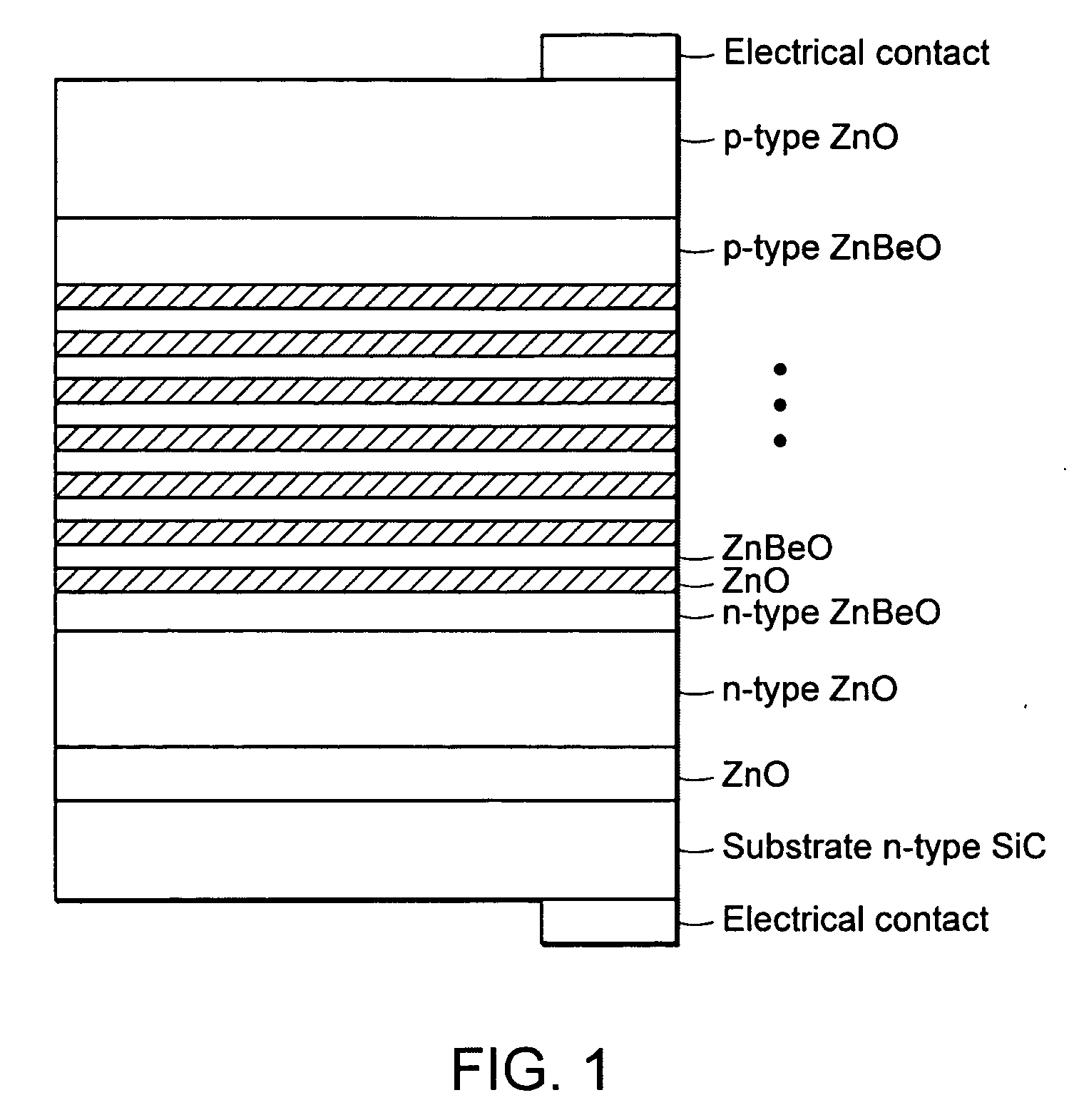
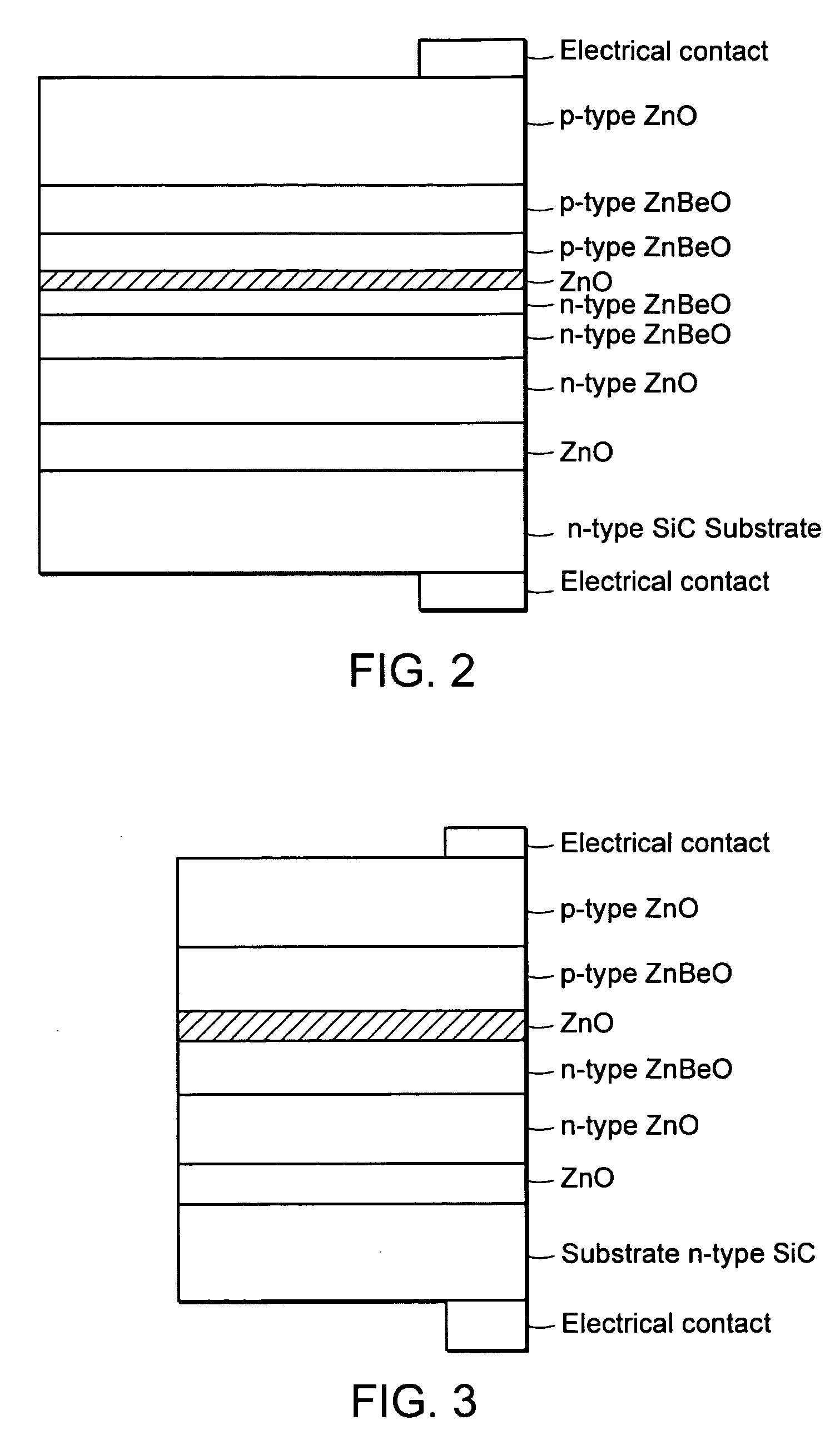
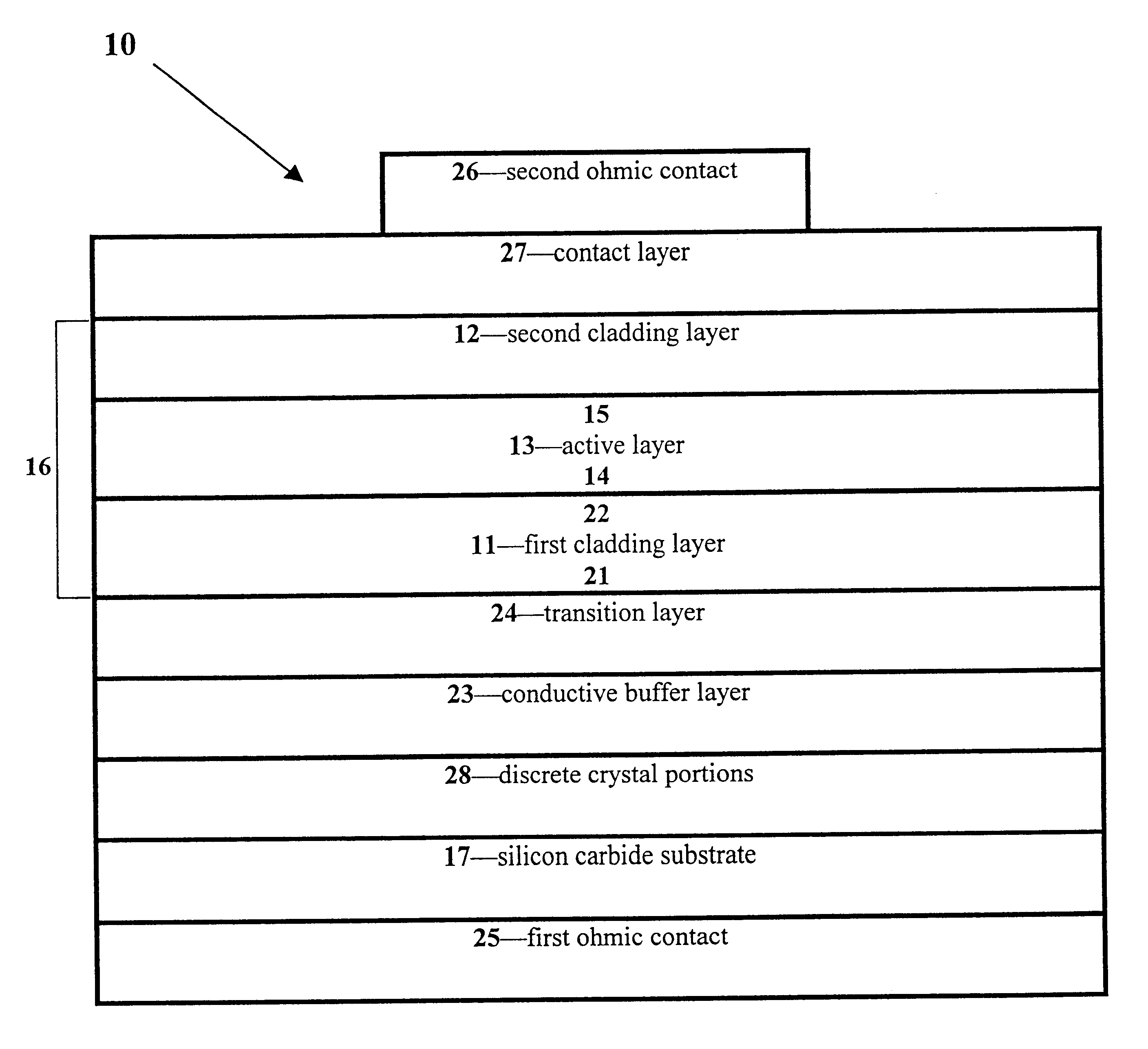
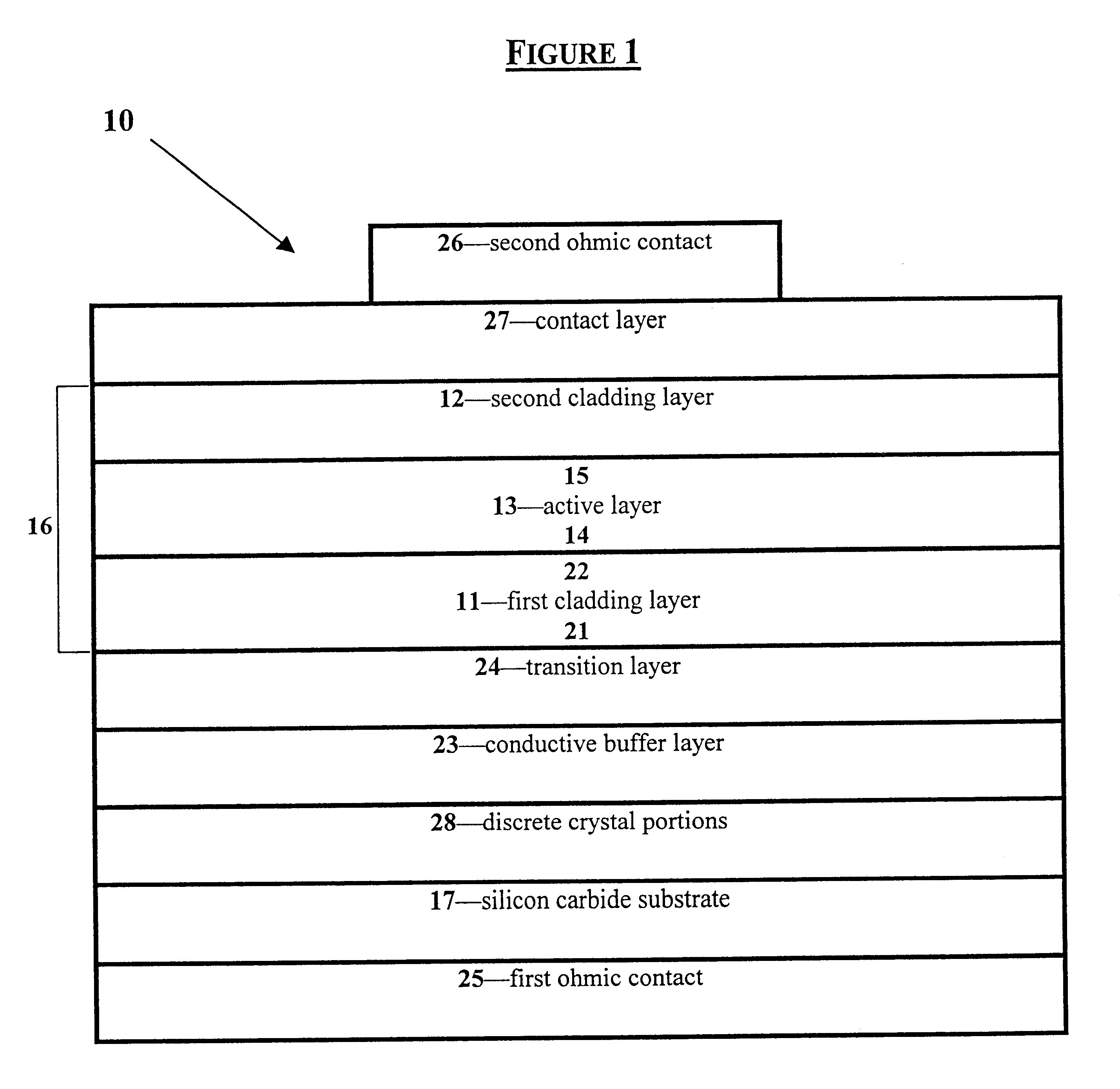
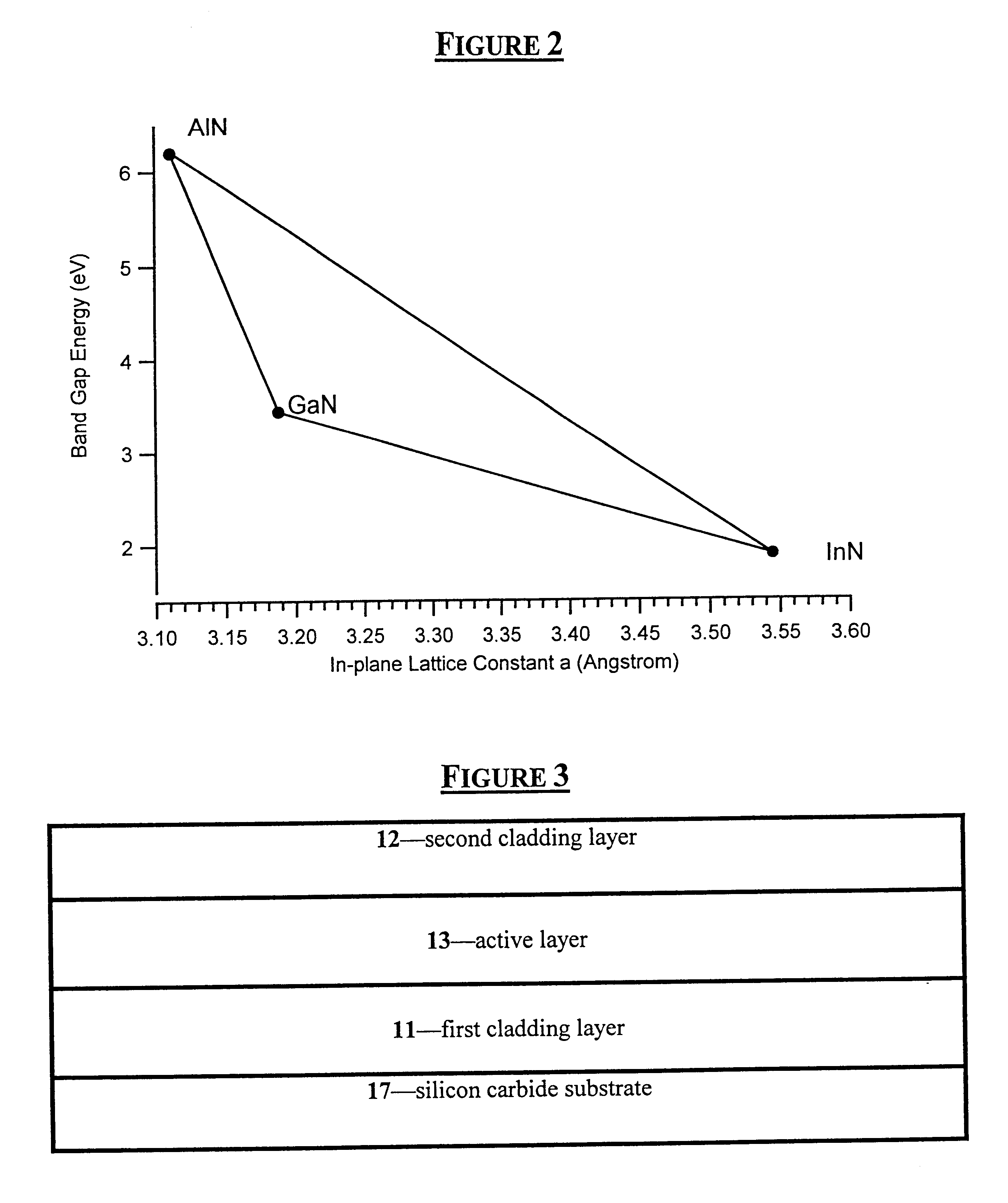
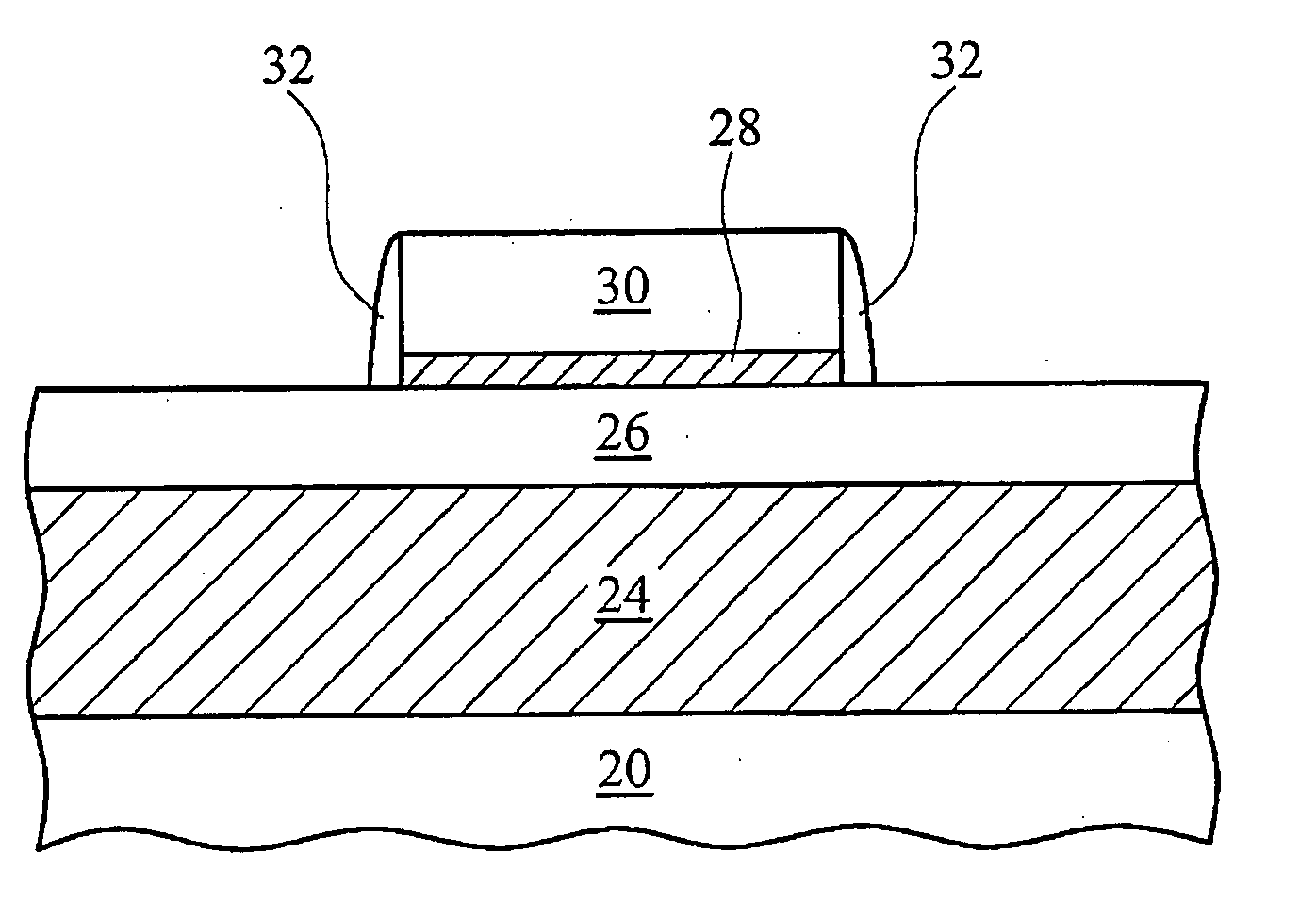
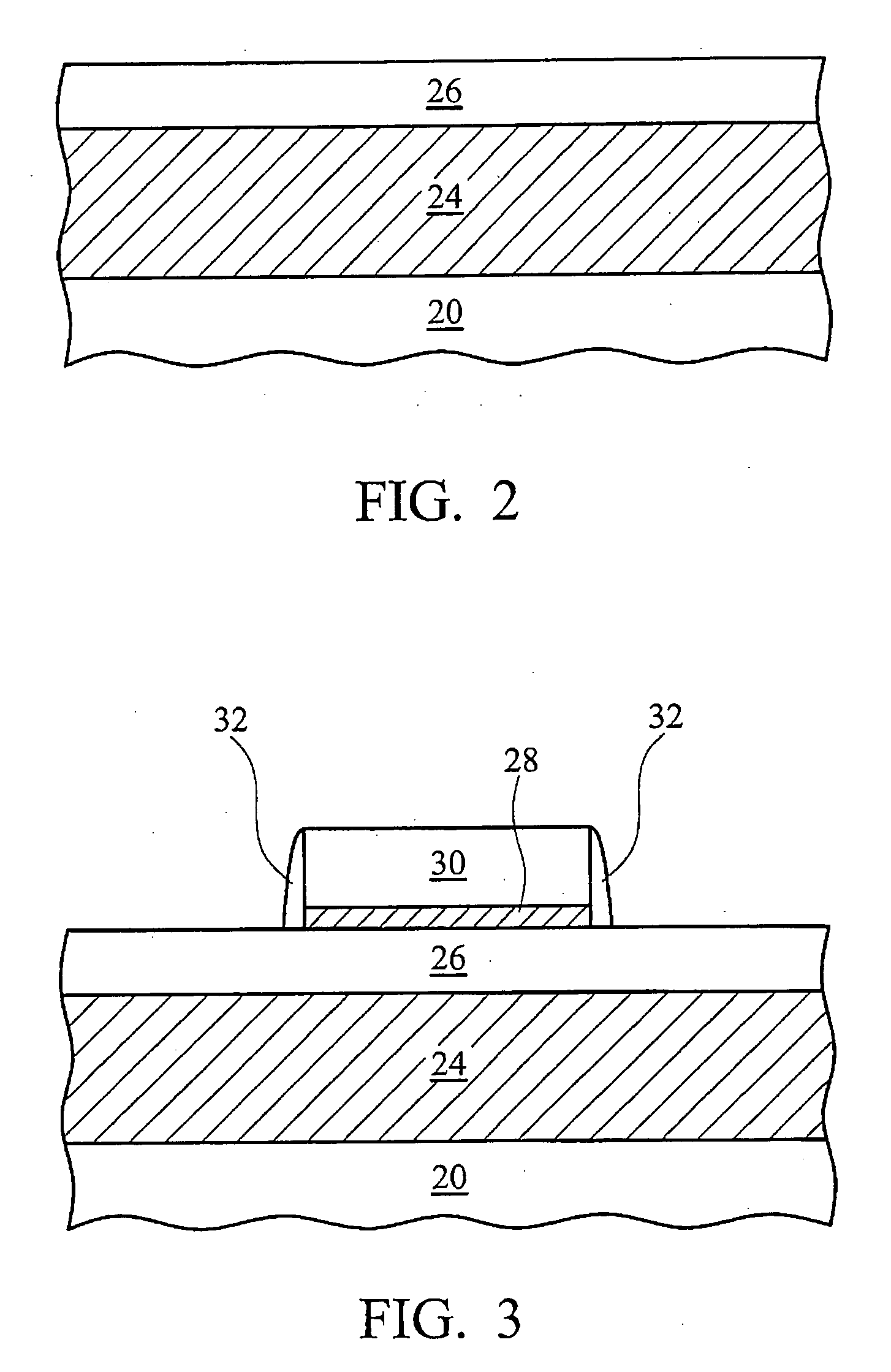
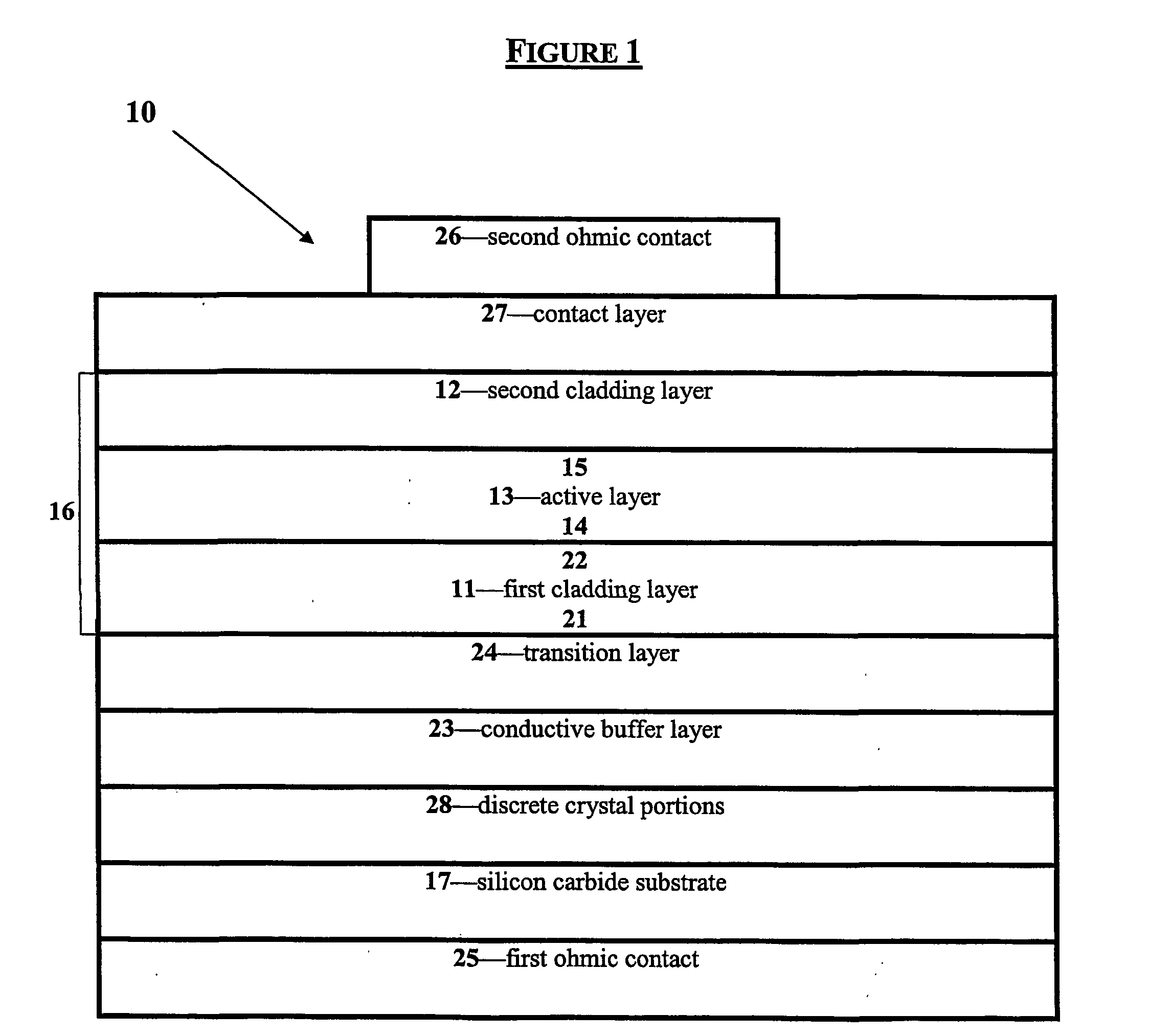
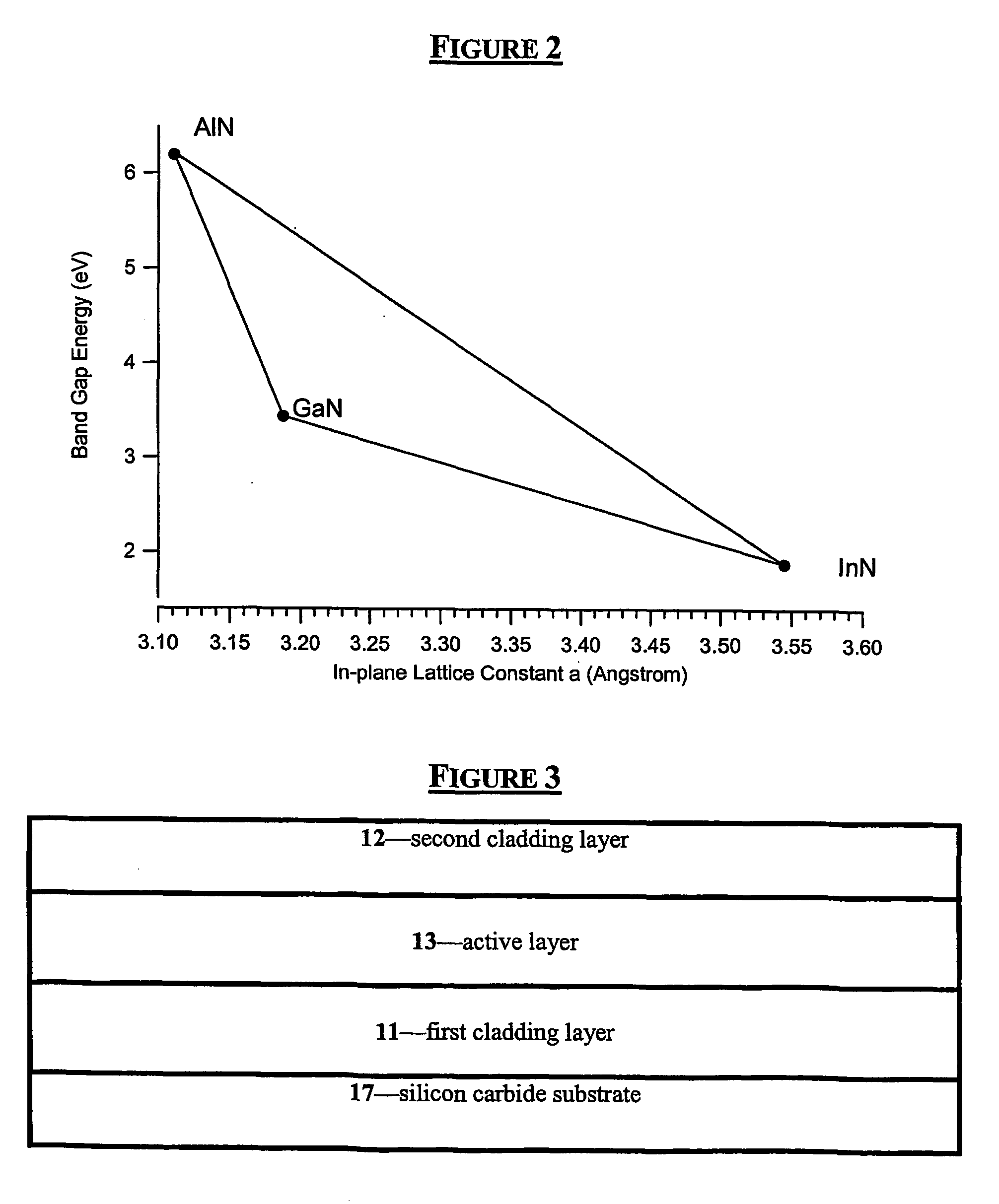
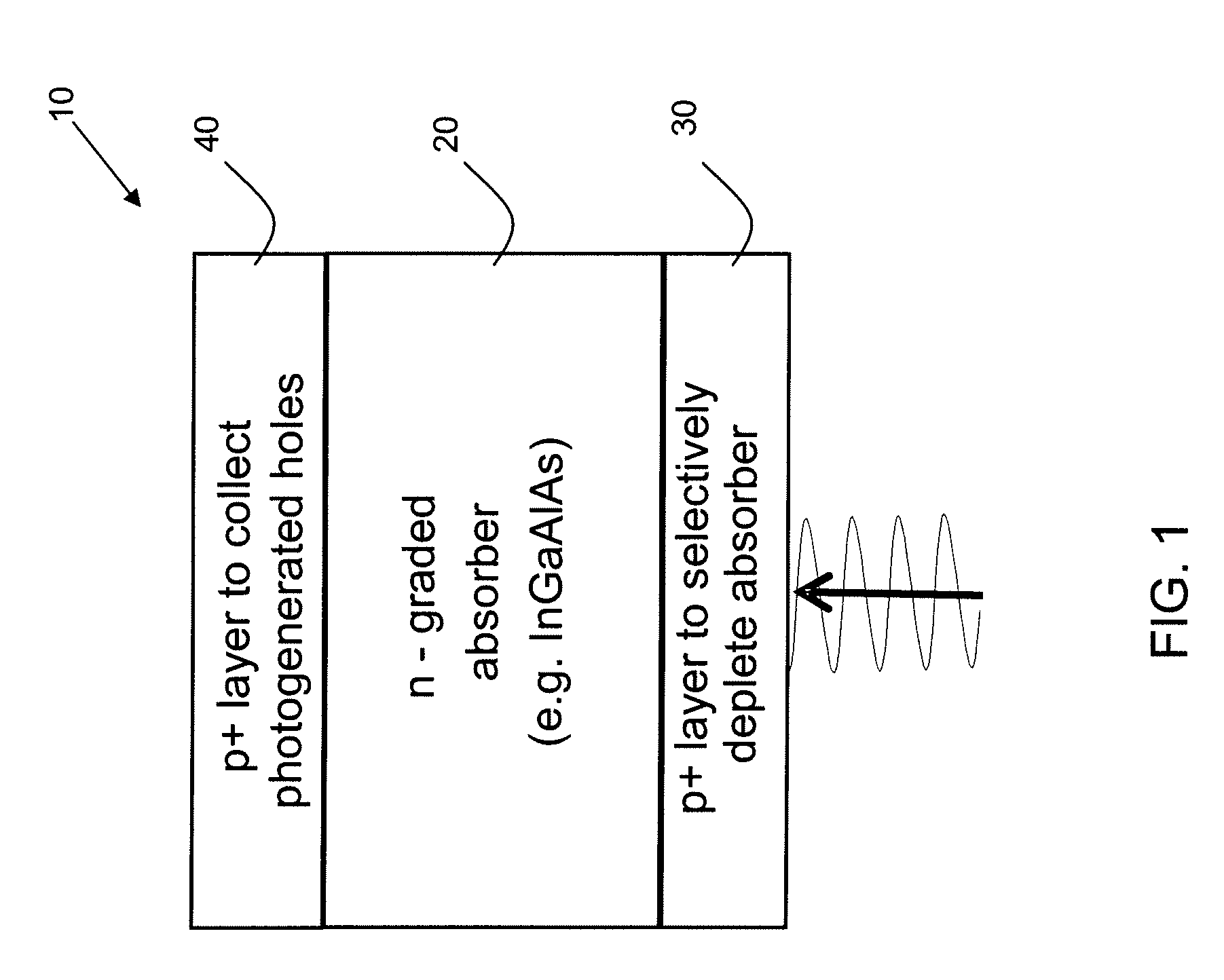
Group III nitride light emitting devices with progressively graded layers
InactiveUS20030164507A1Improve emission efficiencyReduce non-radiative recombinationLaser detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureElectromagnetic spectrum
The present invention is a semiconductor structure for light emitting devices that can emit in the red to ultraviolet portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. The semiconductor structure includes a first cladding layer of a Group III nitride, a second cladding layer of a Group III nitride, and an active layer of a Group III nitride that is positioned between the first and second cladding layers, and whose bandgap is smaller than the respective bandgaps of the first and second cladding layers. The semiconductor structure is characterized by the absence of gallium in one or more of these structural layers.
Owner:CREE INC
Metal oxide semiconductor film structures and methods
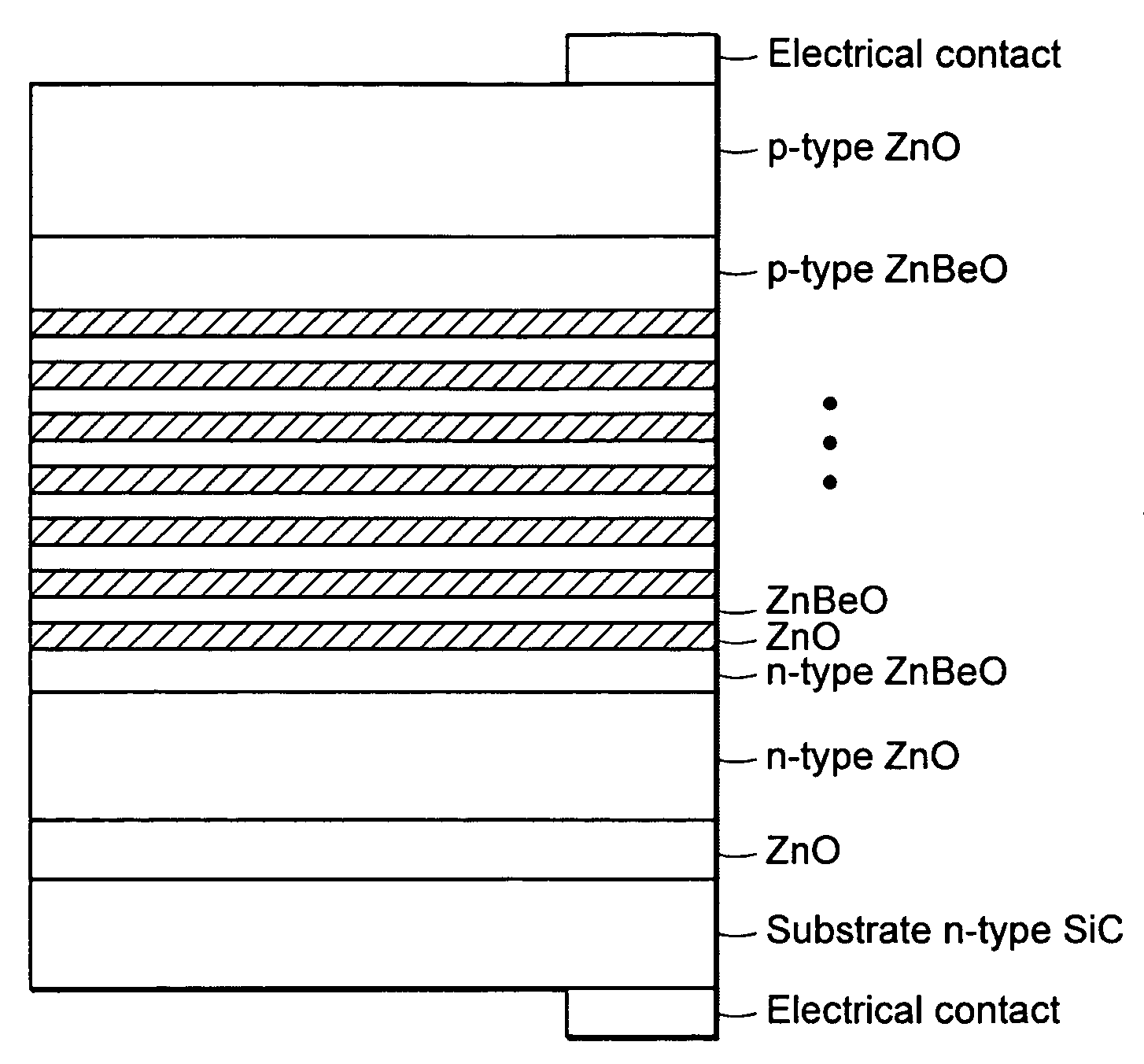
InactiveUS20070126021A1Lower bandgapLaser active region structureNanoopticsDevice materialSemiconductor
Layered and film structures for improving the performance of semiconductor devices include single and multiple quantum wells and double heterostructures and superlattice structures.
Owner:MOXTRONICS
Group III nitride light emitting devices with gallium-free layers
InactiveUS6534797B1Maintain good propertiesImprove emission efficiencyLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersSemiconductor structureElectromagnetic spectrum
The present invention is a semiconductor structure for light emitting devices that can emit in the red to ultraviolet portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. The semiconductor structure includes a first cladding layer of a Group III nitride, a second cladding layer of a Group III nitride, and an active layer of a Group III nitride that is positioned between the first and second cladding layers, and whose bandgap is smaller than the respective bandgaps of the first and second cladding layers. The semiconductor structure is characterized by the absence of gallium in one or more of these structural layers.
Owner:CREE INC
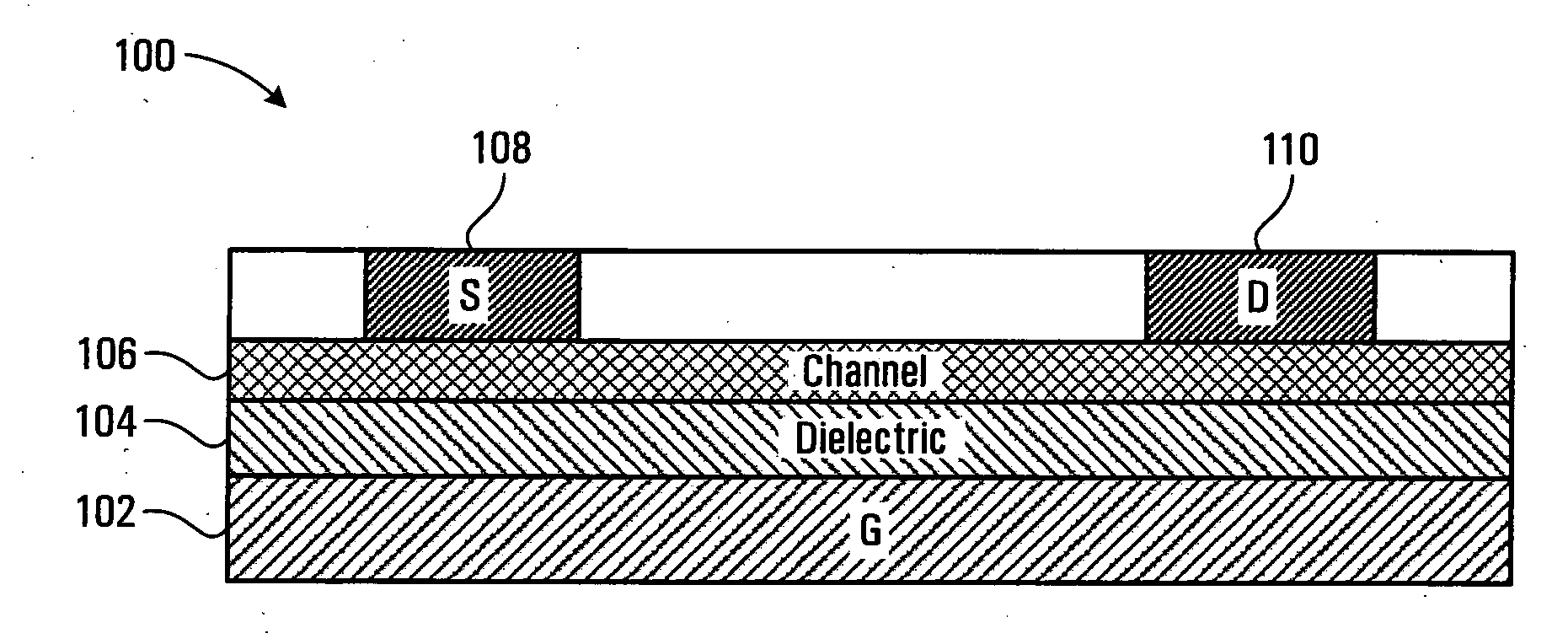
Capacitor-less 1T-DRAM cell with Schottky source and drain
InactiveUS20060125121A1Improve equipment reliabilityLower bandgapTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceGate dielectric
A tunneling injection based Schottky source / drain memory cell comprising: a first semiconductor layer with a first conductivity type overlying an insulating layer, wherein the first semiconductor acts as a body region; a gate dielectric overlying the semiconductor layer; a gate electrode overlying the gate dielectric; a pair of spacers on sides of the gate electrodes; and a first Schottky barrier junction formed on a source region and a second Schottky barrier junction formed on a drain region on opposing sides of the body region. The source and the regions have an overlapping portion with the gate electrode and length of overlapping portion is preferably greater than about 5 Å. Interfacial layers are formed between the first and the second Schottky barrier regions.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
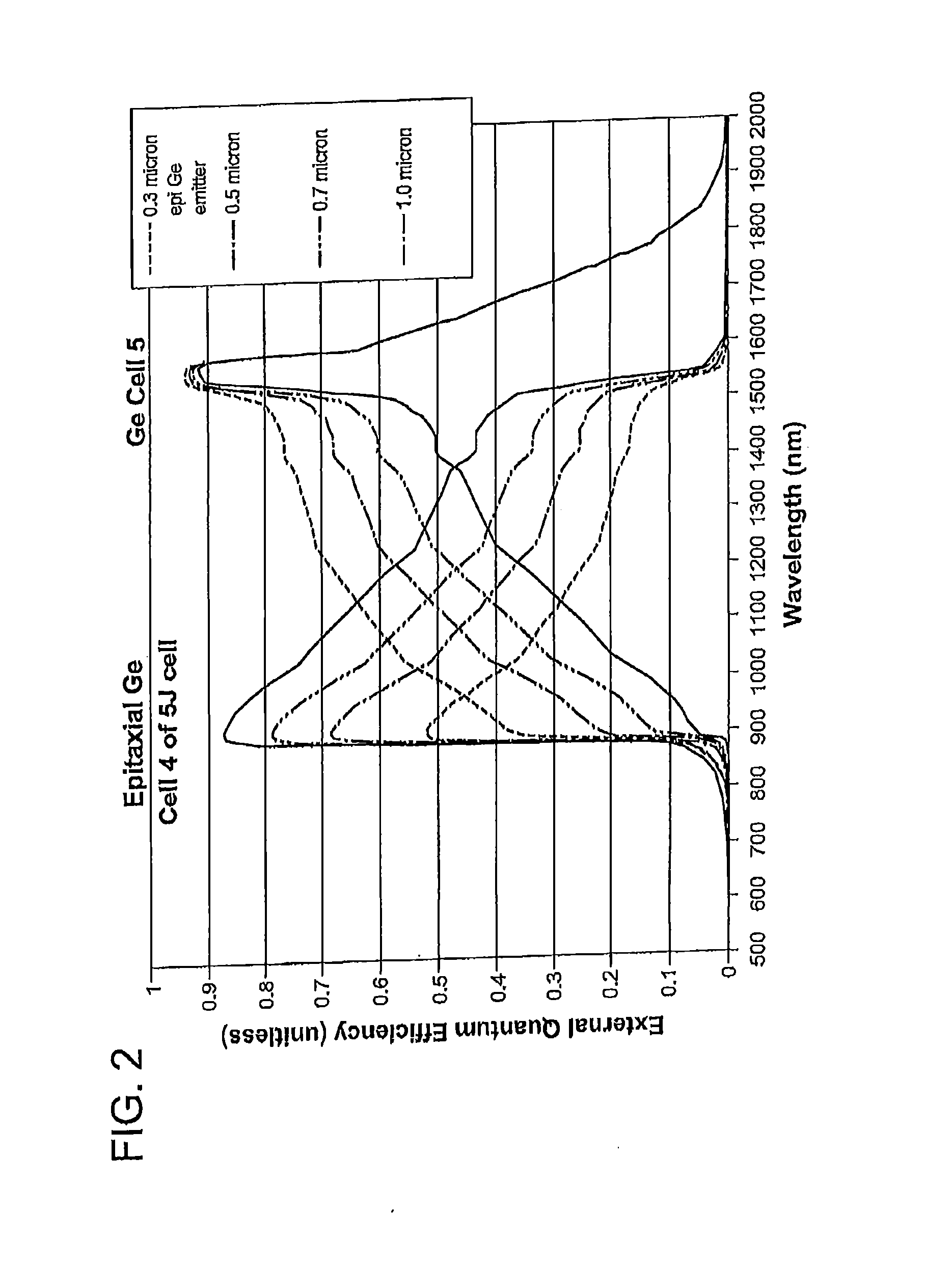
Inverted multijunction solar cells with group iv alloys
InactiveUS20120186641A1Lower bandgapFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsAlloy
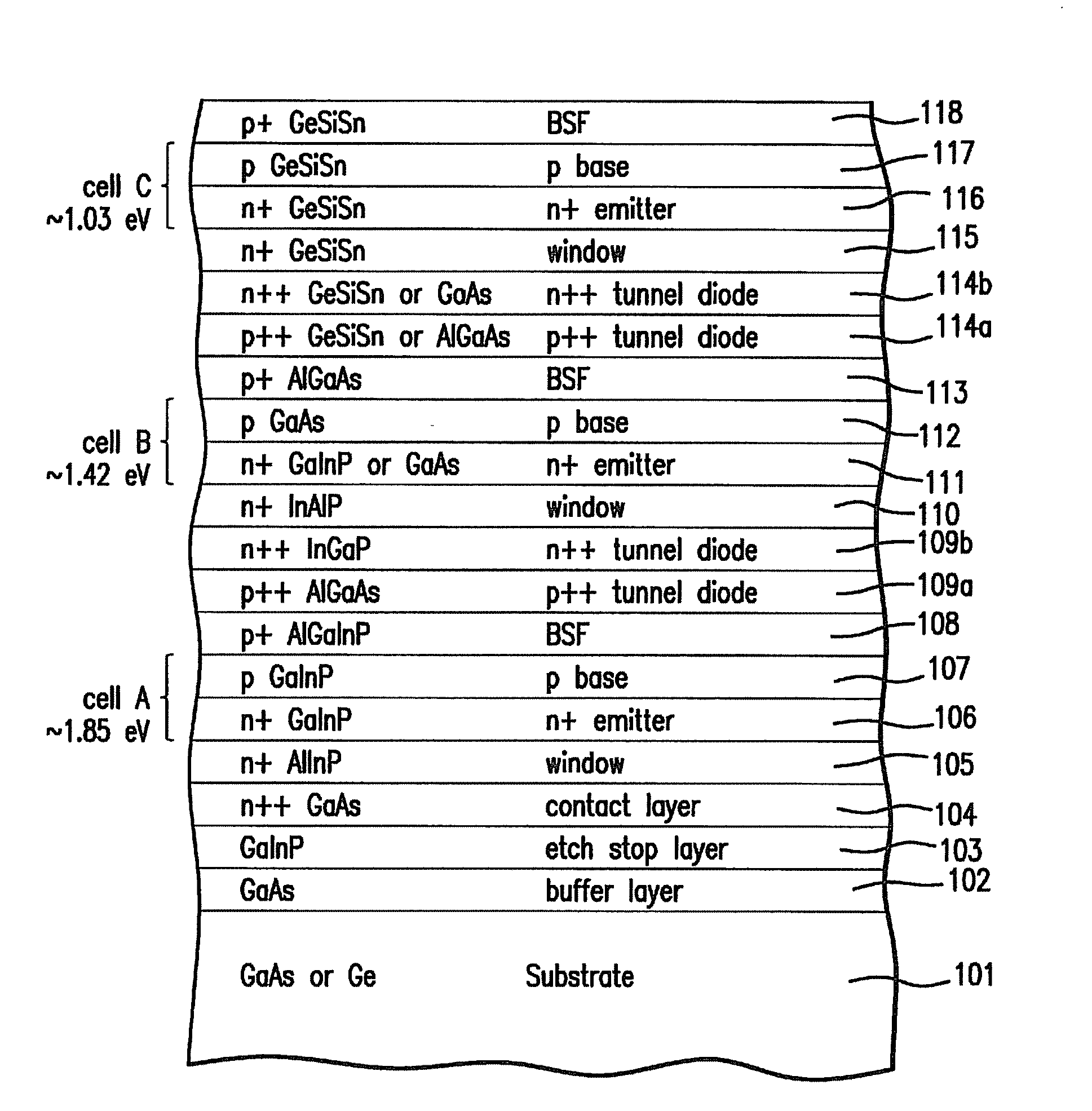
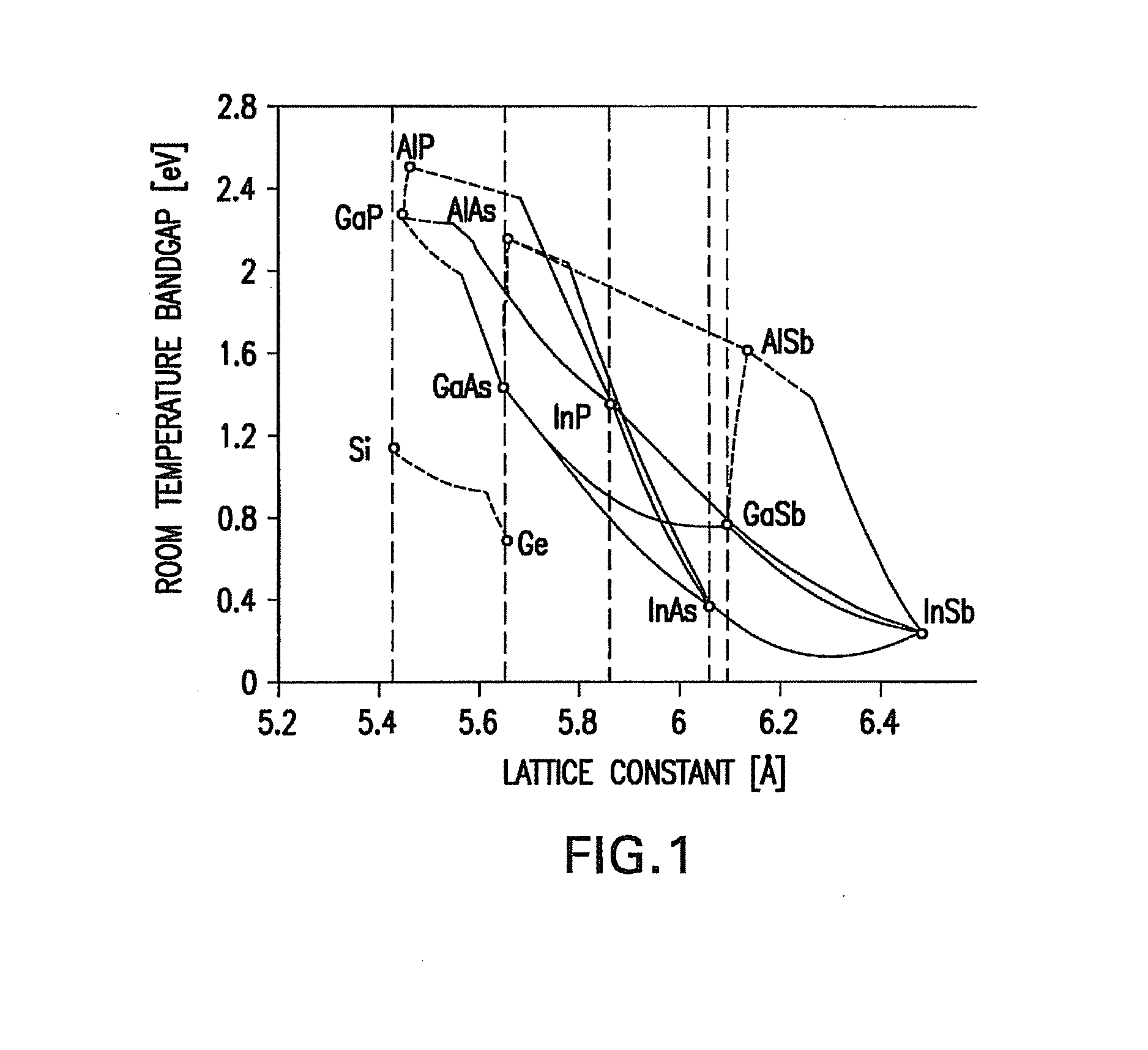
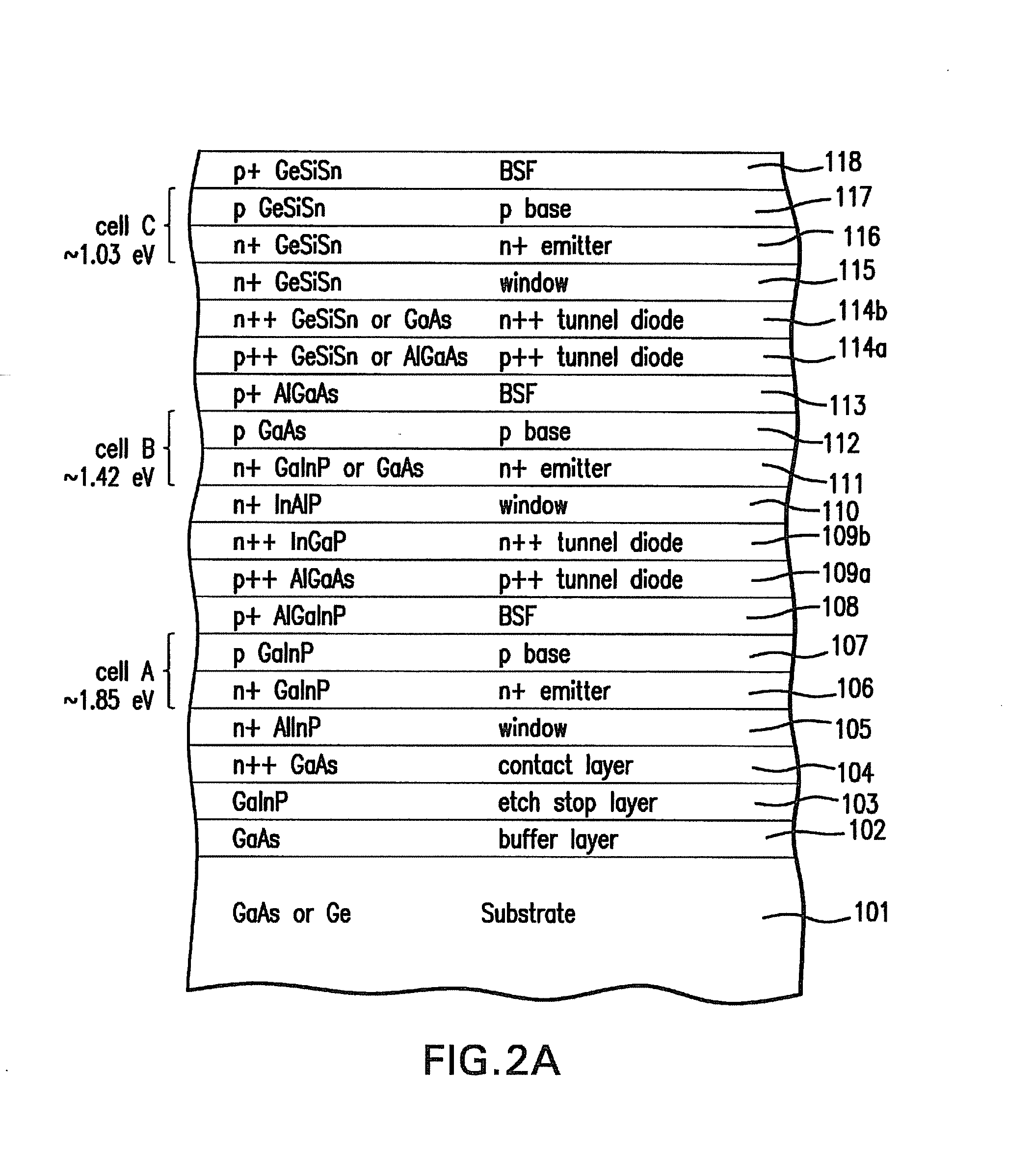
A method of manufacturing a solar cell comprising providing a growth substrate; depositing on said growth substrate a sequence of layers of semiconductor material forming a solar cell, including at least one subcell composed of a group IV alloy such as GeSiSn; and removing the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:SOLAERO TECH CORP
Method for preparing Ag:ZnIn2S4 luminescent quantum dots and photocatalyst
InactiveCN105950140AFully crystallizedGood dispersionMaterial nanotechnologyPhysical/chemical process catalystsFluorescenceZinc Acetate Dihydrate
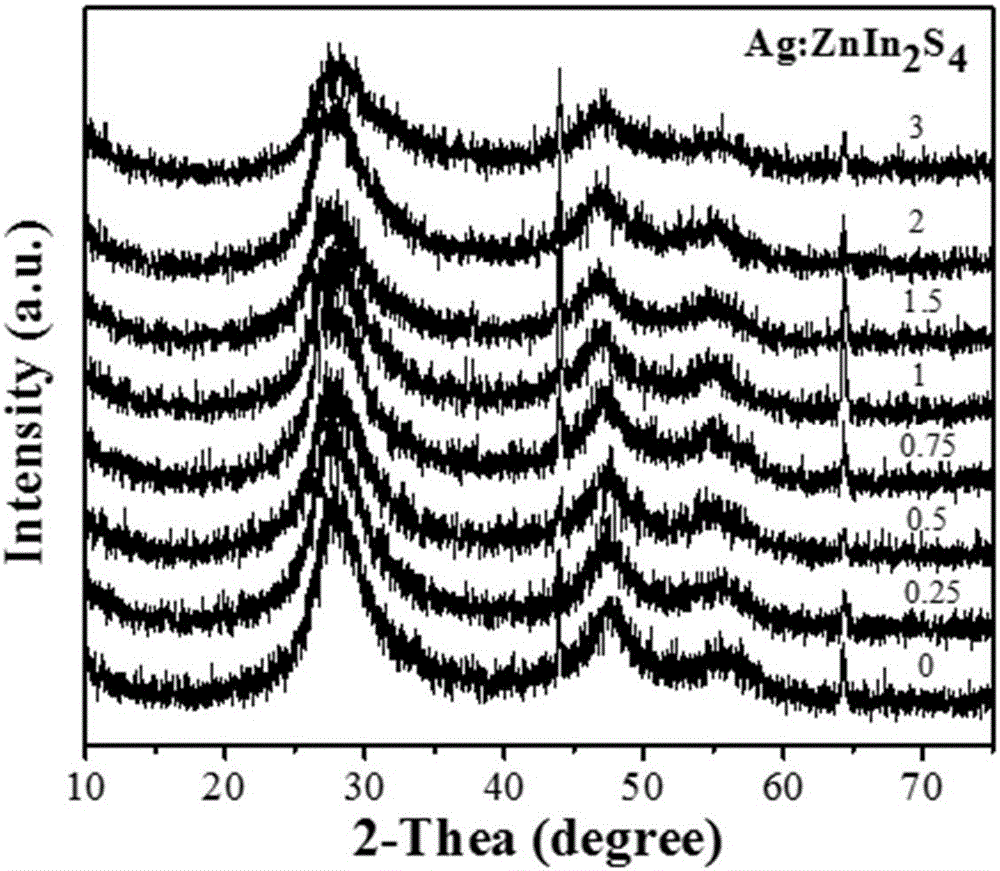
The invention relates to the field of synthesis of nano-materials and particularly relates to a method for synthesizing a series of Ag:ZnIn2S4 luminescent quantum dots by using a simple and rapid hydrothermal method in one step. Fluorescence is adjustable in the range of 460nm to 830nm, the fluorescent life is relatively long, and the luminescent quantum dots can be applied to water-decomposed hydrogen production under visible light. The method comprises the steps of firstly, mixing and dissolving silver nitrate, indium nitrate, zinc acetate dihydrate and L-cysteine in an aqueous solution, adjusting the pH value of the solution to 8.5 by using NaOH, adding thioacetamide into the solution, carrying out ultrasonic stirring, then, carrying out a hydrothermal reaction for 4 hours at the temperature of 110 DEG C, and carrying out centrifugal drying after the reaction ends, thereby obtaining Ag@ZnIn2S4 nanocrystals of different ratios. Proven by a photocatalytic hydrogen production experiment under the visible light, the prepared composite photocatalyst has good photocatalytic activity.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Visible Light Activatable Photocatalyst
ActiveUS20110028311A1Lower bandgapCost energy efficientMaterial nanotechnologyCatalyst activation/preparationDecompositionPhotochemistry
A visible light activatable mesoporous titanium dioxide photocatalyst having a surface area of from 100 m2 / g to 400 m2 / g. The photocatalyst may have a rate of decomposition greater than 0.005 min−1. The photocatalyst may have a band gap width less than 2.95 eV. The photocatalyst may comprise undoped titanium dioxide or doped titanium dioxide. A hydrothermal process for synthesising a photocatalyst is also described.
Owner:KASTUS TECHNOLOGIES DESIGNATED ACTIVITY COMPANY
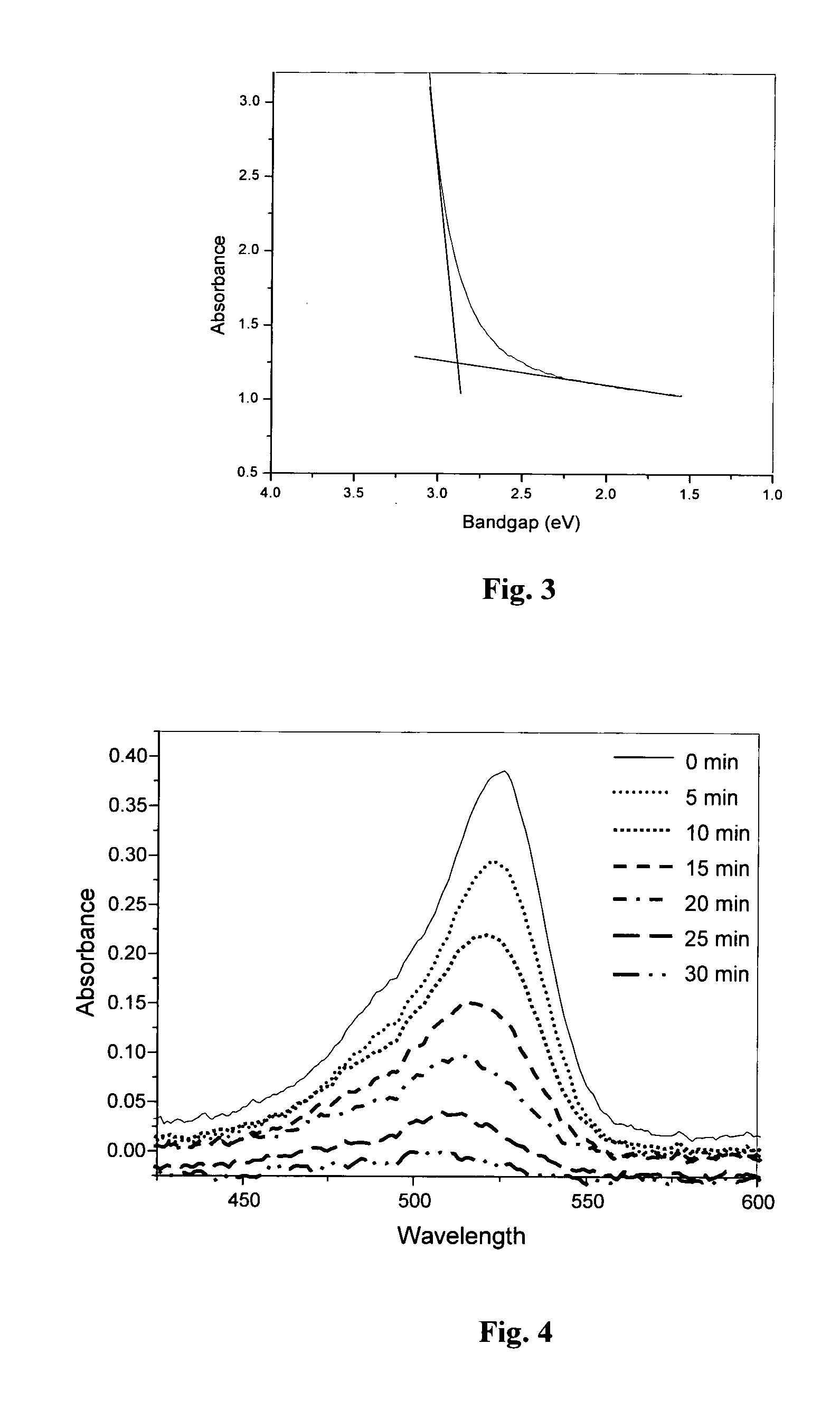
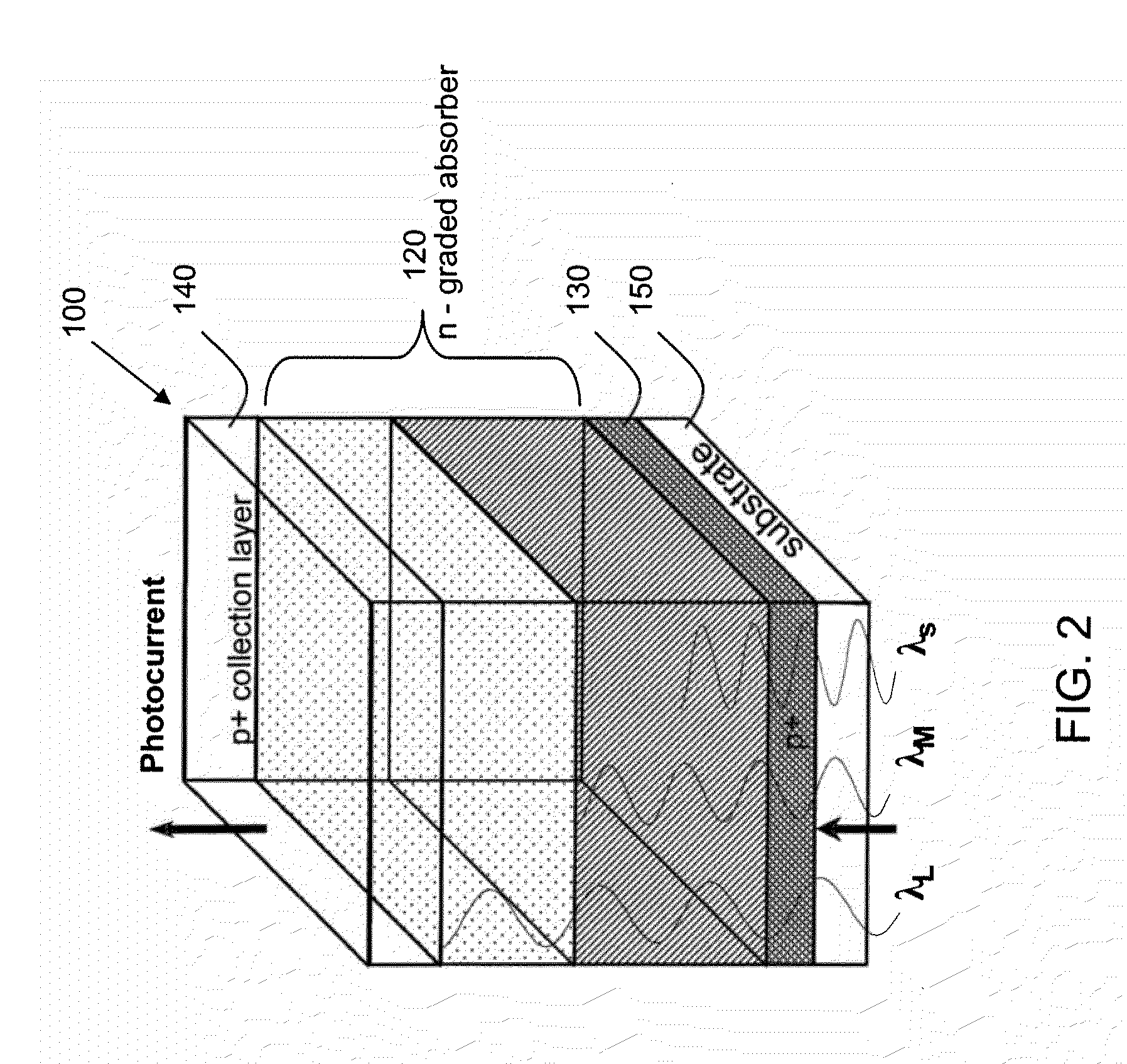
Electronically tunable and reconfigurable hyperspectral photon detector
InactiveUS7800067B1Wavelength agility and tunabilityMinimum powerSpectrum investigationFinal product manufactureTerrainLength wave
Electronically tunable and reconfigurable hyperspectral IR detectors and methods for making the same are presented. In one embodiment, a reconfigurable hyperspectral sensor (or detector) detects radiation from about 0.4 μm to about 2 μm and beyond. This sensor is configured to be compact, and lightweight and offers hyperspectral imaging capability while providing wavelength agility and tunability at the chip-level. That is, the sensor is used to rapidly image across diverse terrain to identify man-made objects and other anomalies in cluttered environments.
Owner:HRL LAB
Conjugated Polymers and Their Use in Optoelectronic Devices
ActiveUS20120186652A1Enhanced light absorptionGood charge transport characteristicNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesSolubilityPhotodetector
Disclosed are certain polymeric compounds and their use as organic semiconductors in organic and hybrid optical, optoelectronic, and / or electronic devices such as photovoltaic cells, light emitting diodes, light emitting transistors, field effect transistors, and photodetectors. The disclosed compounds can provide improved device performance, for example, as measured by power conversion efficiency, fill factor, open circuit voltage, field-effect mobility, on / off current ratios, and / or air stability when used in photovoltaic cells or transistors. The disclosed compounds can have good solubility in common solvents enabling device fabrication via solution processes.
Owner:RAYNERGY TEK INC
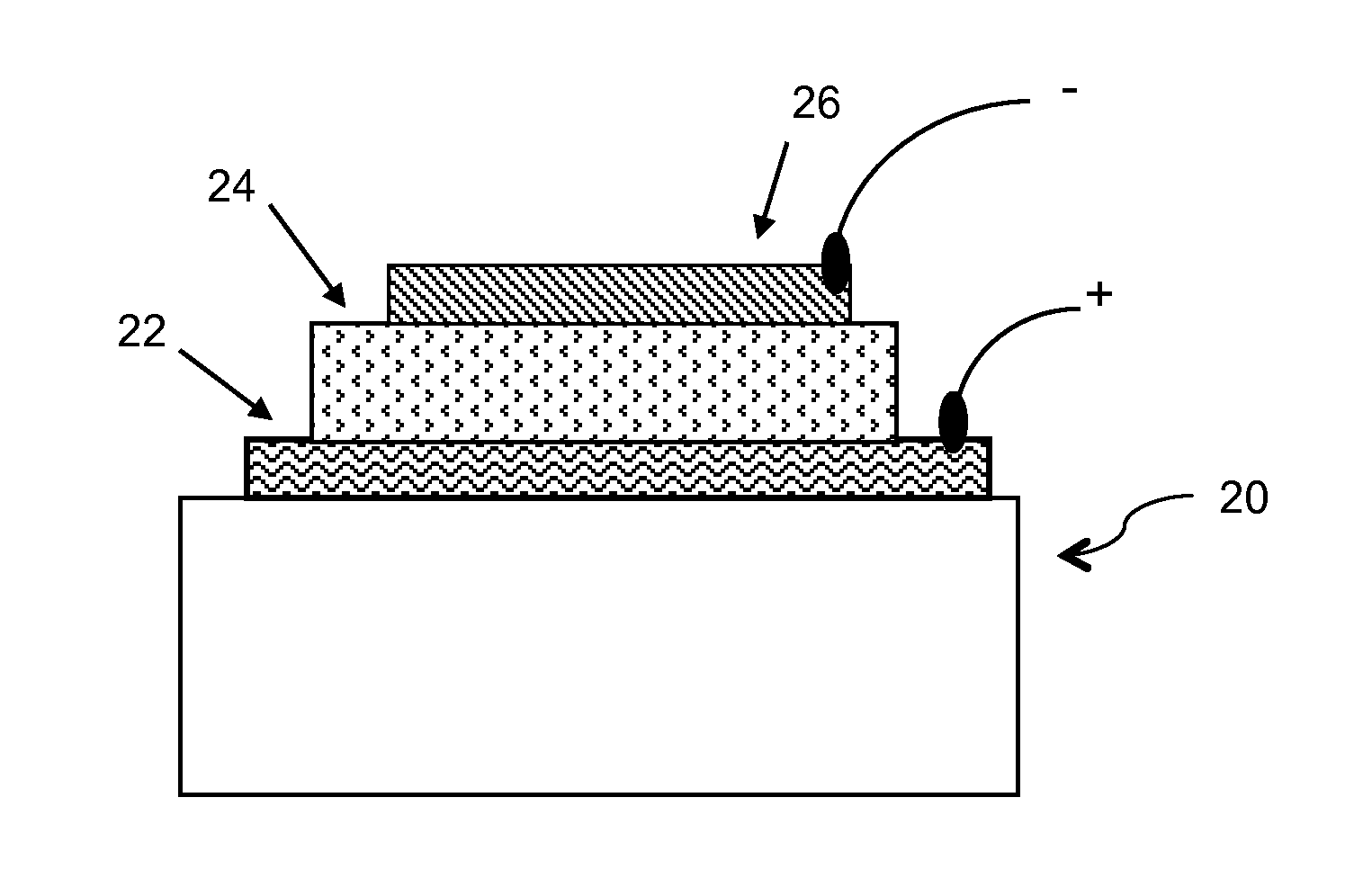
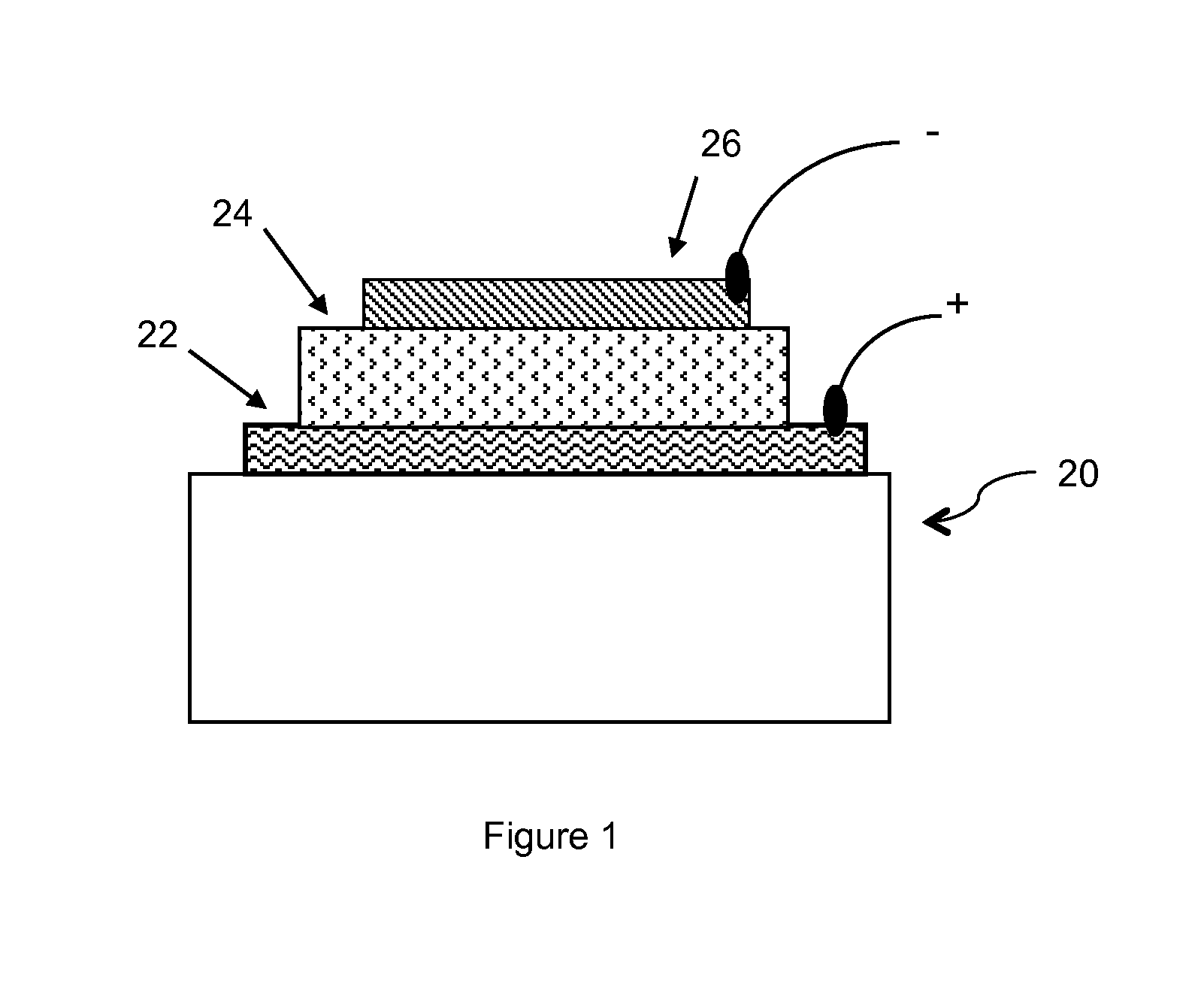
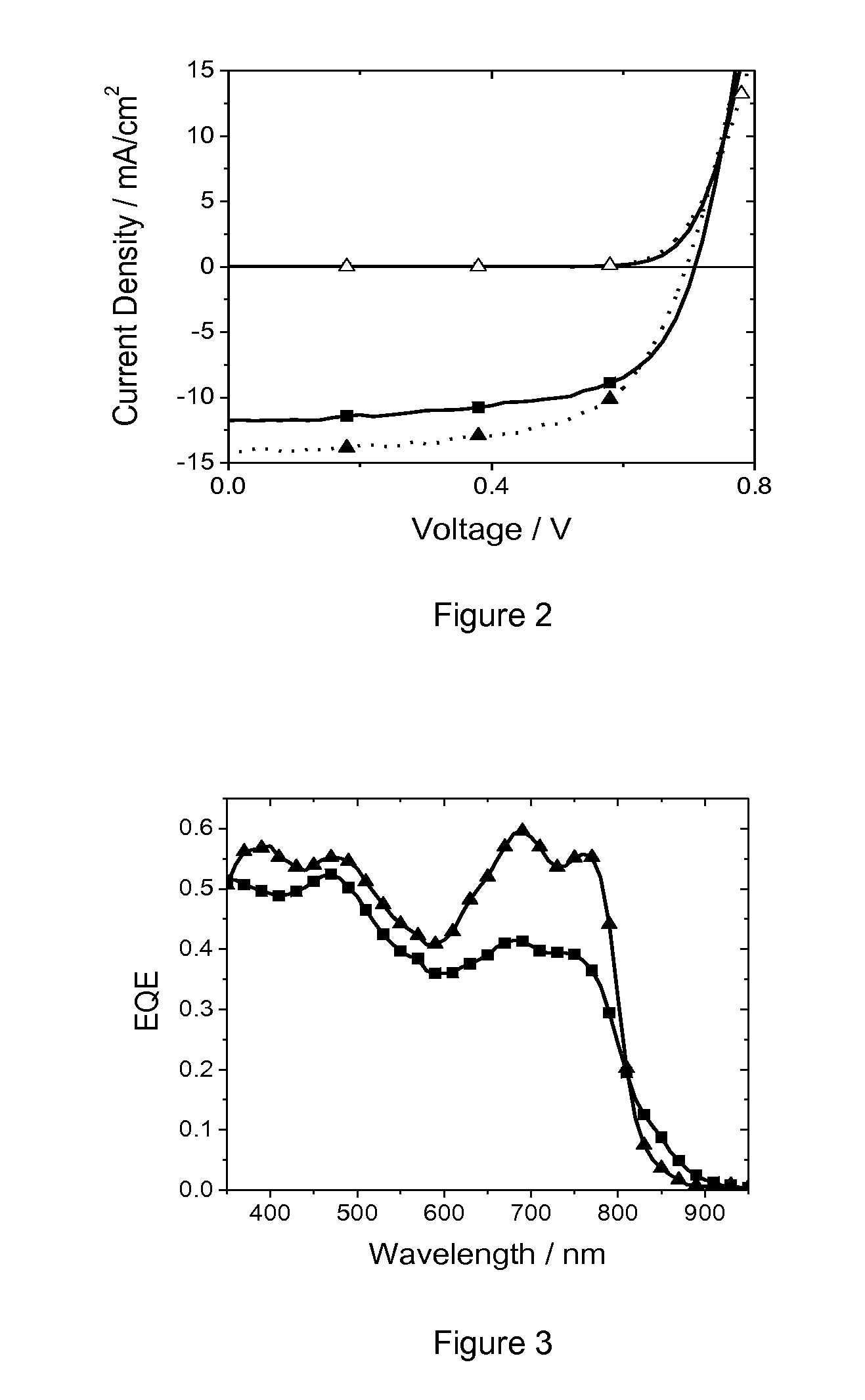
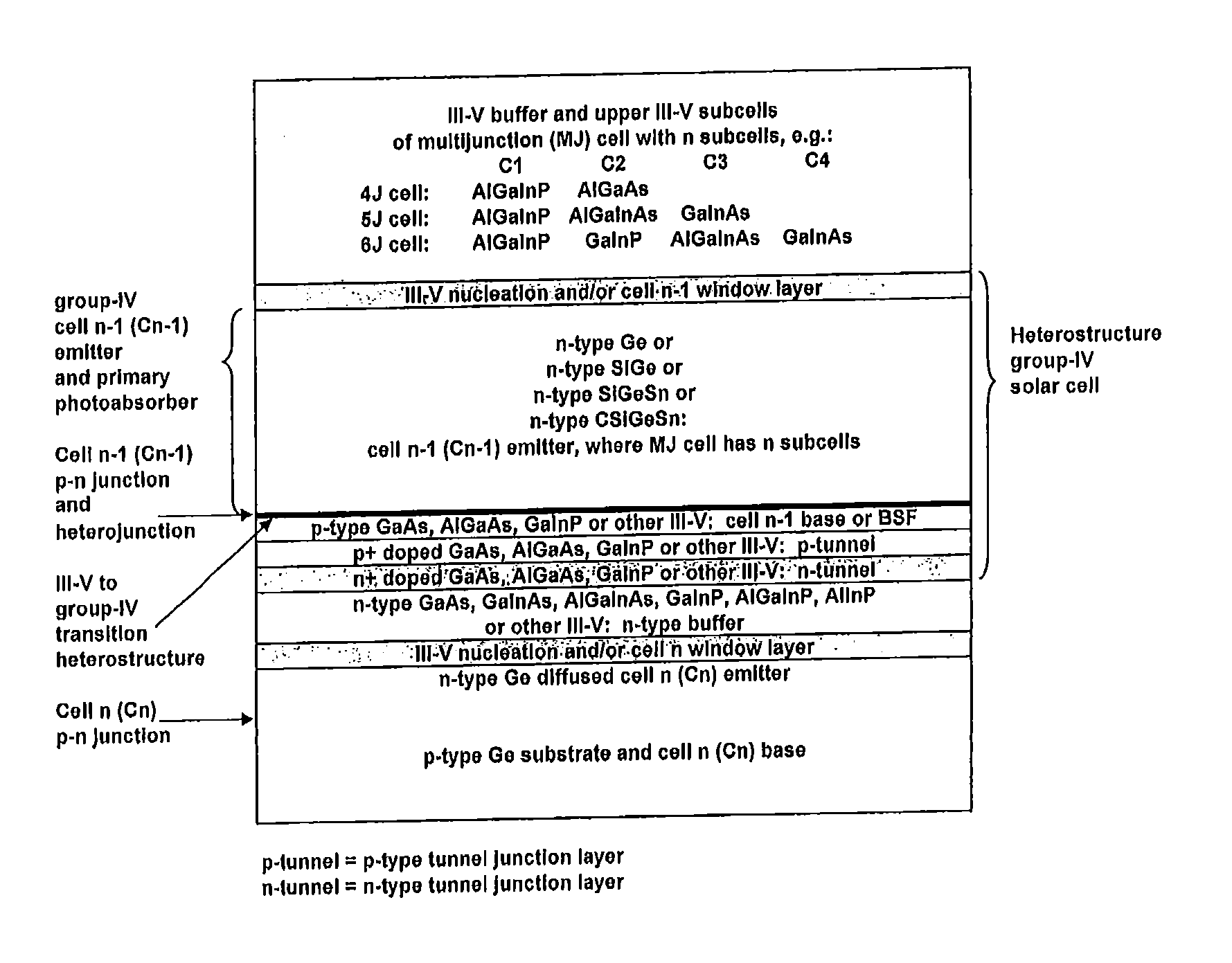
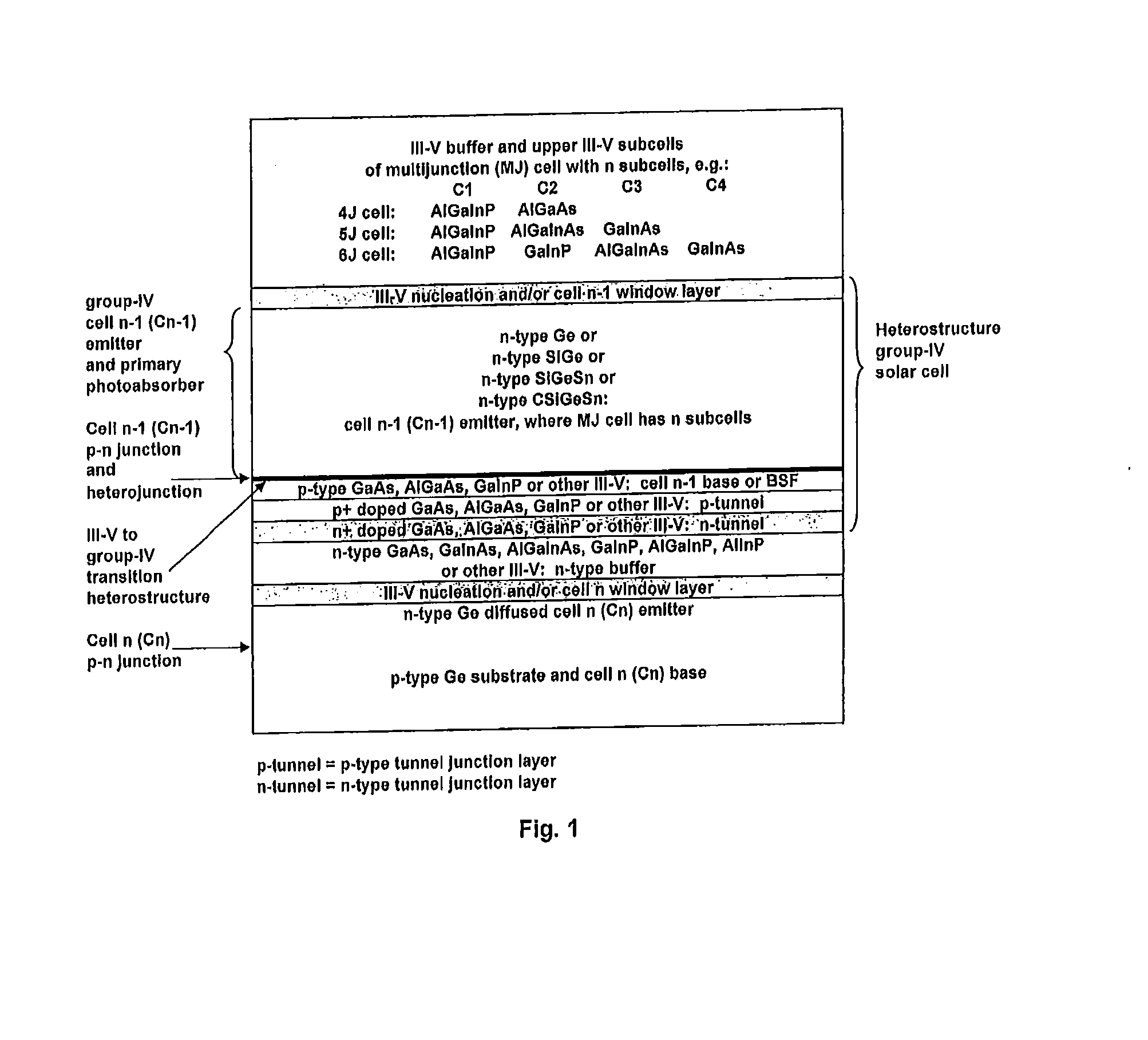
GROUP-IV SOLAR CELL STRUCTURE USING GROUP-IV or III-V HETEROSTRUCTURES
ActiveUS20140076386A1Lower bandgapIncreasing photogeneratedFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductorMultijunction photovoltaic cell
Device structures, apparatuses, and methods are disclosed for photovoltaic cells that may be a single junction or multijunction solar cells, with at least one layer comprising a group-IV semiconductor in which part of the cell comprises a second layer comprising a III-V semiconductor or group-IV semiconductor having a different composition than the group-IV semiconductor of the first layer, such that a heterostructure is formed between the first and second layers.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
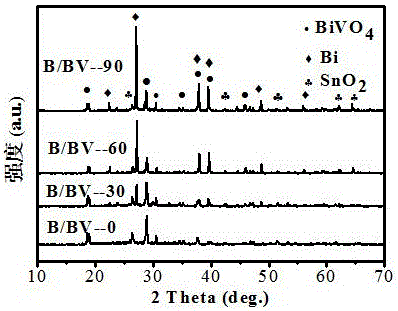
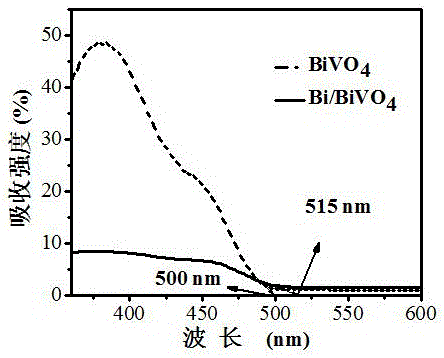
Method for preparing Bi/BiVO4 composite photoanode material by photodeposition
ActiveCN106498372ALower bandgapImprove photoelectrochemical performanceEnergy inputLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingElectron holeAlcohol
The invention discloses a method for preparing a Bi / BiVO4 composite photoanode material by photodeposition. The method comprises the following steps: soaking a BiVO4 electrode in an ethylene glycol / water mixed solution of Bi(NO3)3 5H2O, and illuminating to uniformly generate a layer of an ash black film on the surface of the BiVO4 electrode; and washing with ethyl alcohol to obtain a Bi / BiVO4 composite photoanode. According to the method, metal Bi particles are successfully loaded on a multihole BiVO4 thin film in a simple photo-reduction process; furthermore, introduction of the metal Bi particles enlarges an absorption range of bismuth vanadate to visible light; meanwhile, electrons in the metal Bi particles are transferred onto a BiVO4 conduction band to increase the concentration of current carriers; and a hole in the BiVO4 surface in a pure Na2SO4 solution oxidizes part of the metal Bi nano particles, so that separation of electron-hole pairs is effectively promoted, and the photoelectric chemical decomposition performance of water is improved.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
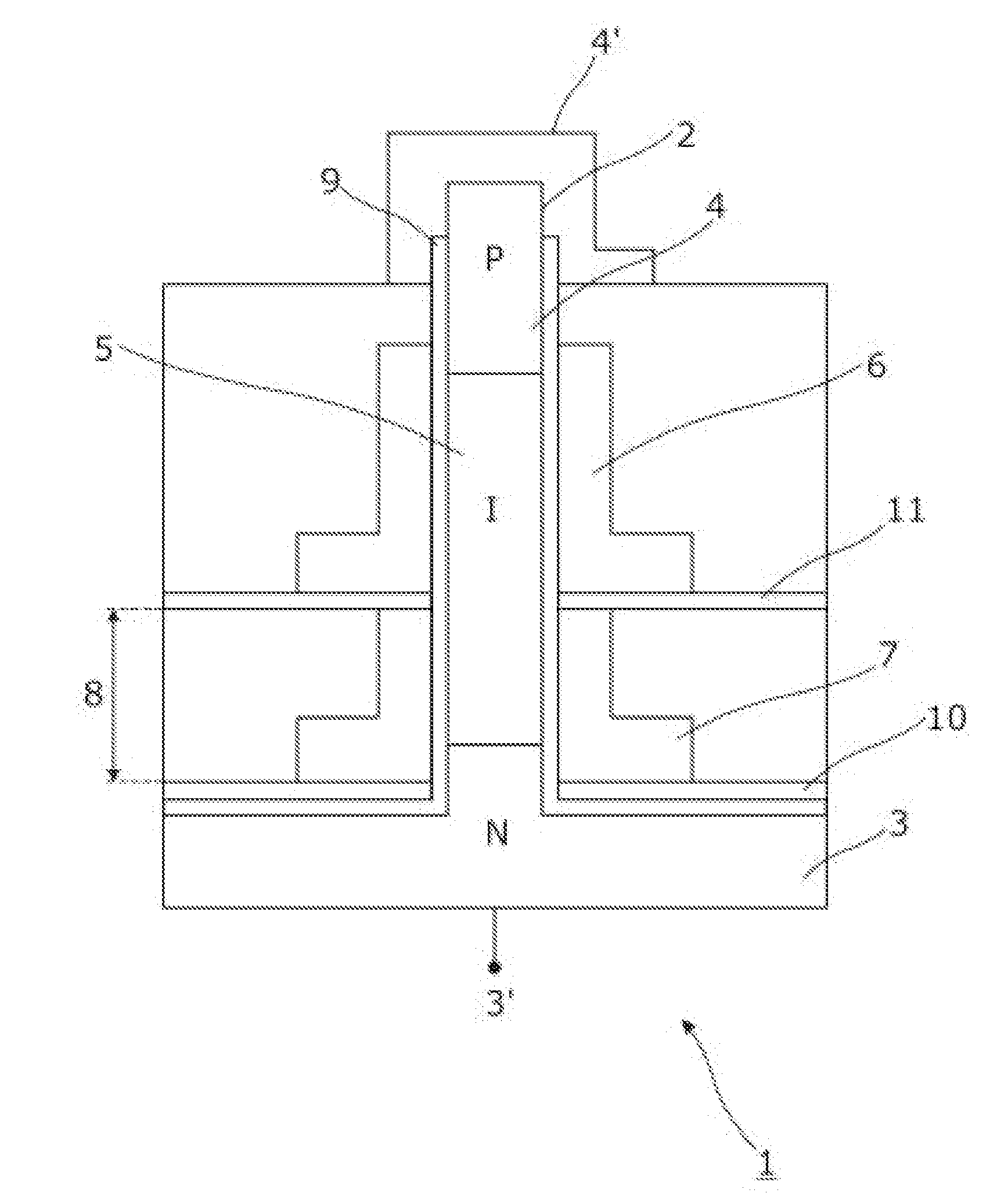
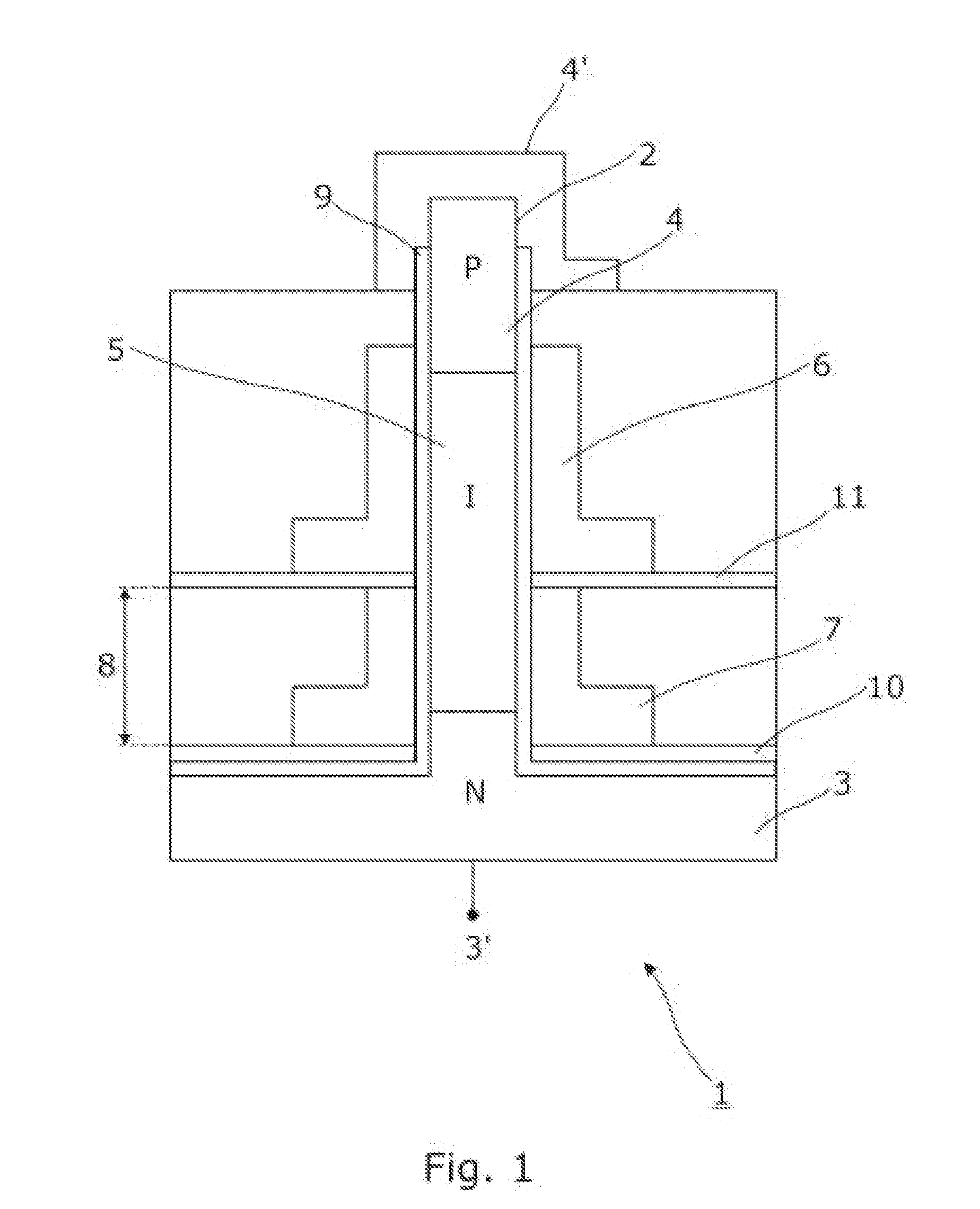
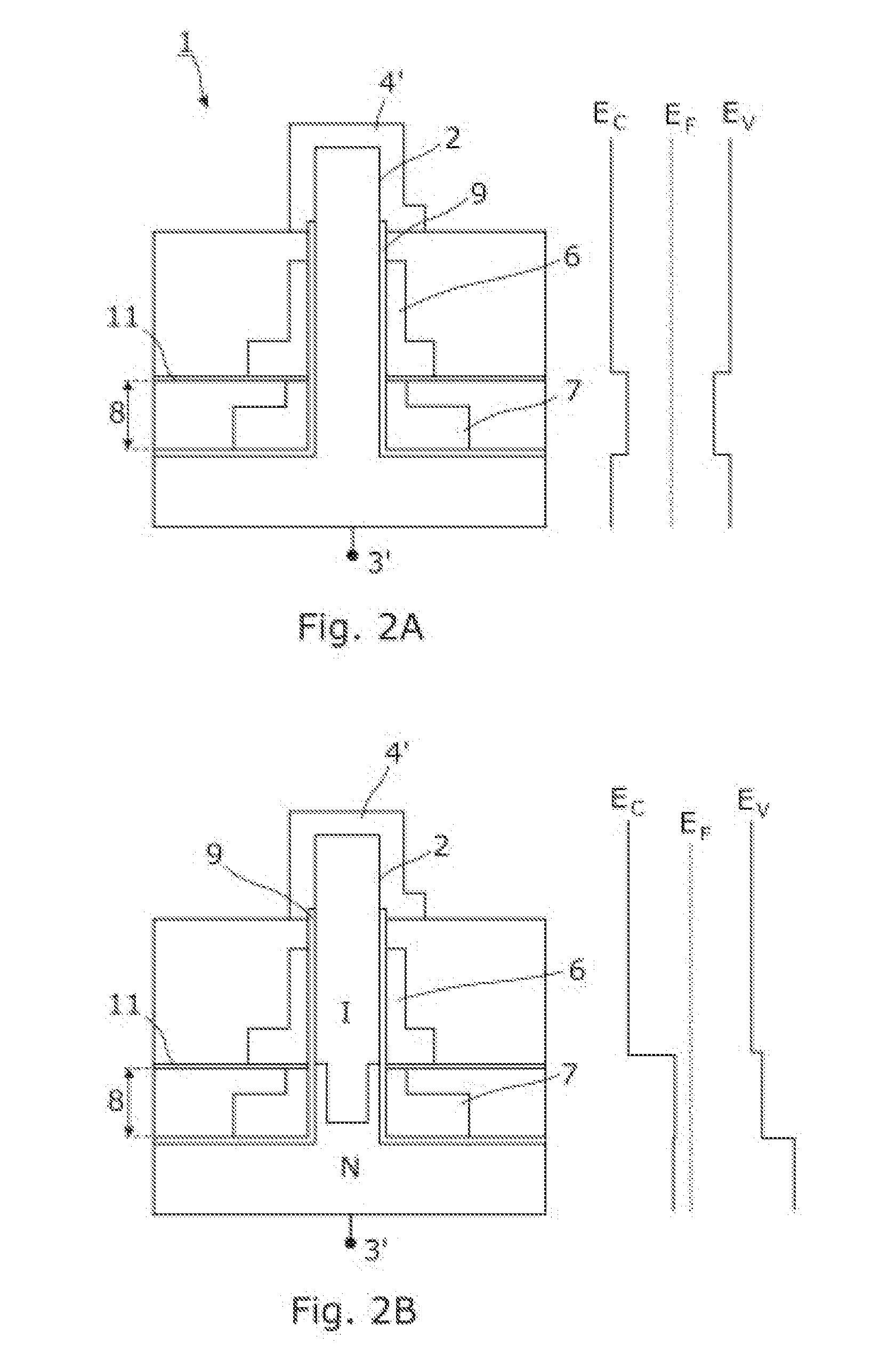
Nanowire field-effect device with multiple gates
InactiveUS20130264544A1Improve tunneling efficiencyIncrease ratingsNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsNanowire
The present invention relates to a semiconductor device (1) comprising: at least a nanowire (2) configured to comprise: at least a source region (3) comprising a corresponding source semiconductor material, at least a drain region (4) comprising a corresponding drain semiconductor material and at least a channel region (5) comprising a corresponding channel semiconductor material, the channel region (5) being arranged between the source region (3) and the drain region (4), at least a gate electrode (6) that is arranged relative to the nanowire (2) to circumferentially surround at least a part of the channel region (5), and at least a strain gate (7) that is arranged relative to the nanowire (2) to circumferentially surround at least a part of a segment of the nanowire (2), the strain gate (7) being configured to apply a strain to the nanowire segment (8), thereby to facilitate at least an alteration of the energy bands corresponding to the source region (3) relative to the energy bands corresponding to the channel region (5).
Owner:IBM CORP
Nitride semiconductor light emitting device
ActiveUS20120261687A1Improved in current distributionGood effectSemiconductor devicesActive layerLight emitting device
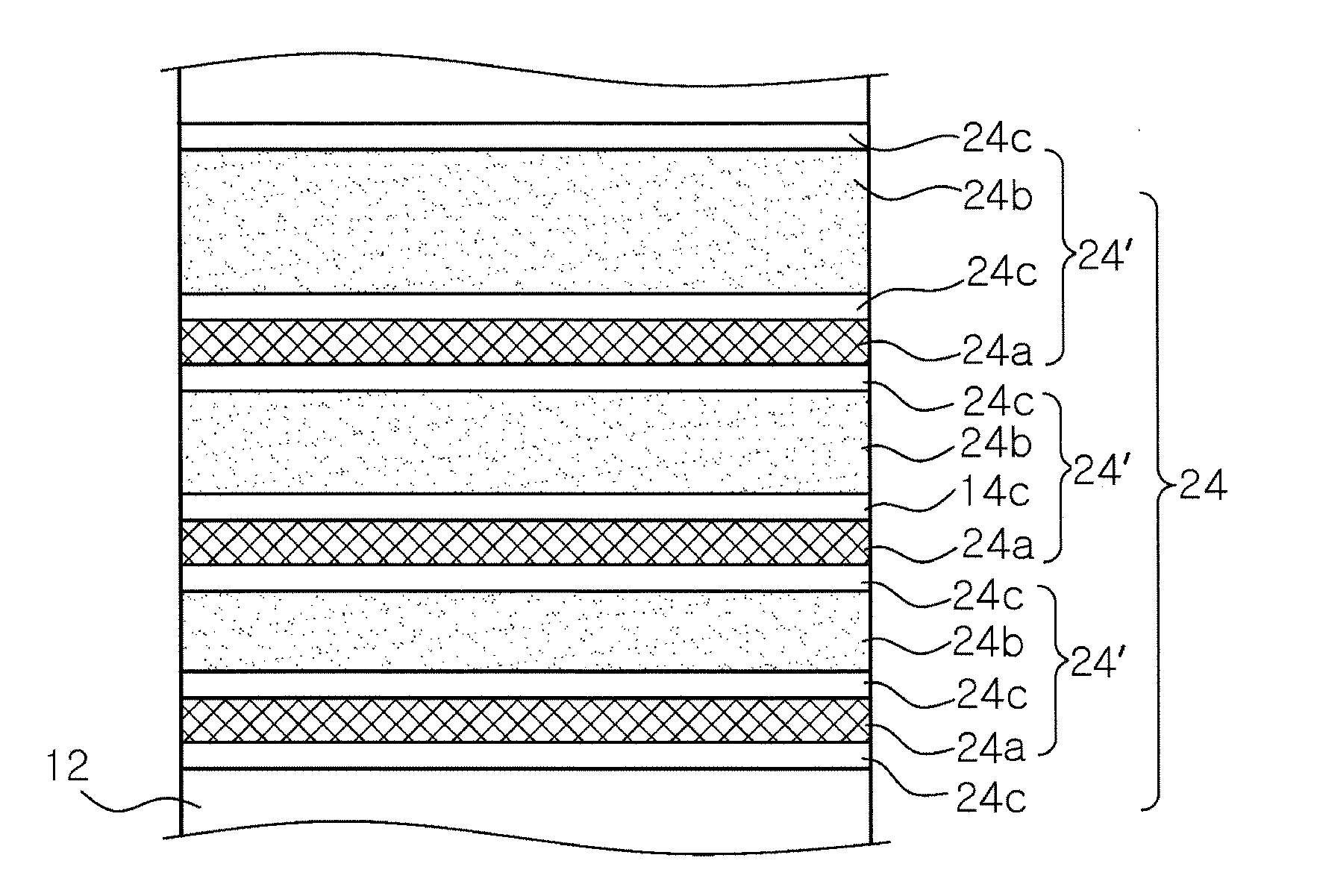
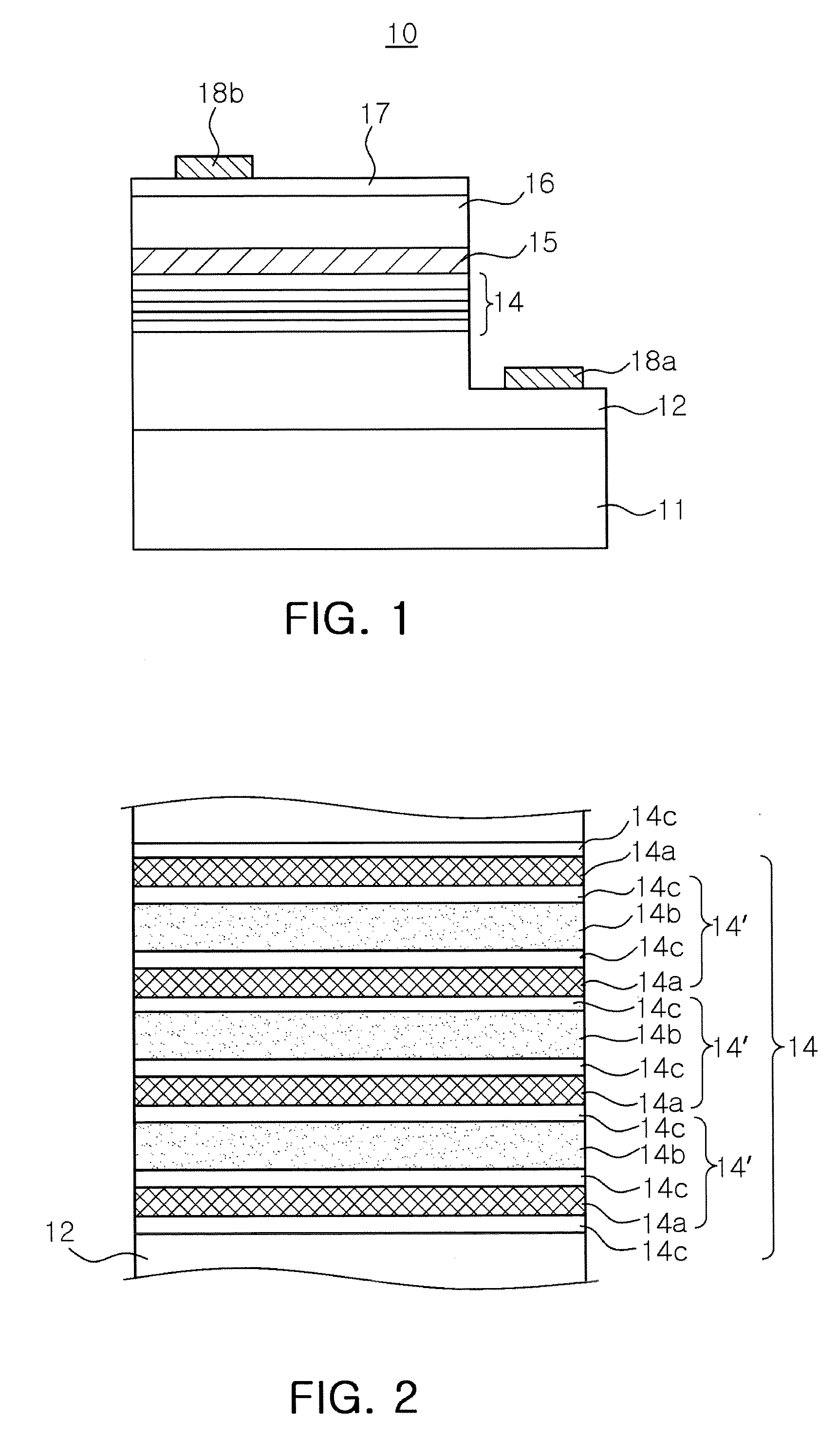
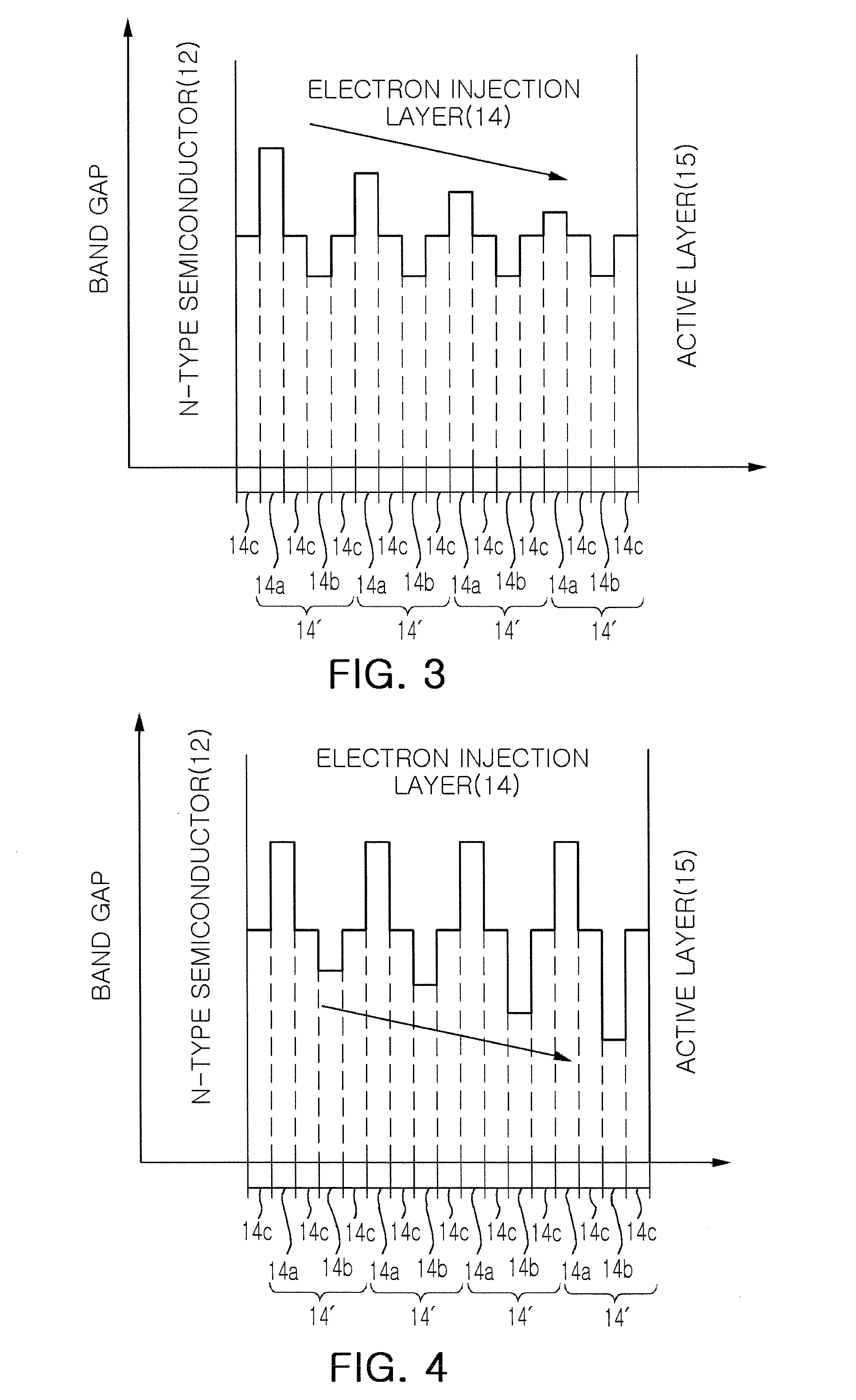
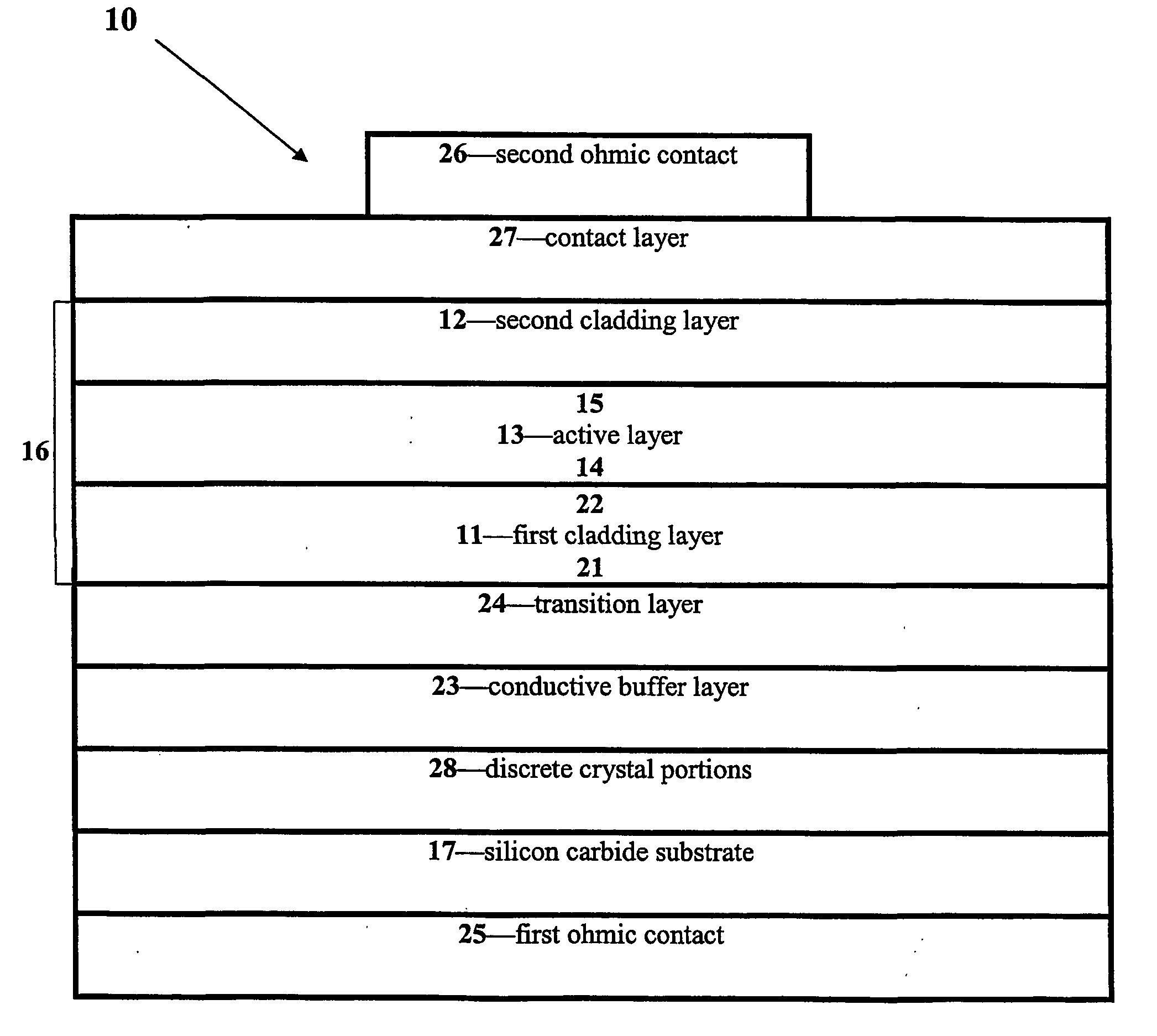
There is provided a nitride semiconductor light emitting device including: n-type and p-type nitride semiconductor layers; an active layer disposed between the n-type and p-type nitride semiconductor layers; and an electron injection layer disposed between the n-type nitride semiconductor layer and the active layer. The electron injection layer has a multilayer structure, in which three or more layers having different energy band gaps are stacked, and the multilayer structure is repetitively stacked at least twice. At least one layer among the three or more layers has a reduced energy band gap in individual multilayer structures in a direction toward the active layer, and the layer having the lowest energy band gap has an increased thickness in individual multilayer structures in a direction toward the active layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Group lll nitride emitting devices with gallium-free layers
InactiveUS20040051108A1Maintain good propertiesImprove emission efficiencyTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureElectromagnetic spectrum
The present invention is a semiconductor structure for light emitting devices that can emit in the red to ultraviolet portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. The semiconductor structure includes a first cladding layer of a Group III nitride, a second cladding layer of a Group III nitride, and an active layer of a Group III nitride that is positioned between the first and second cladding layers, and whose bandgap is smaller than the respective bandgaps of the first and second cladding layers. The semiconductor structure is characterized by the absence of gallium in one or more of these structural layers.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
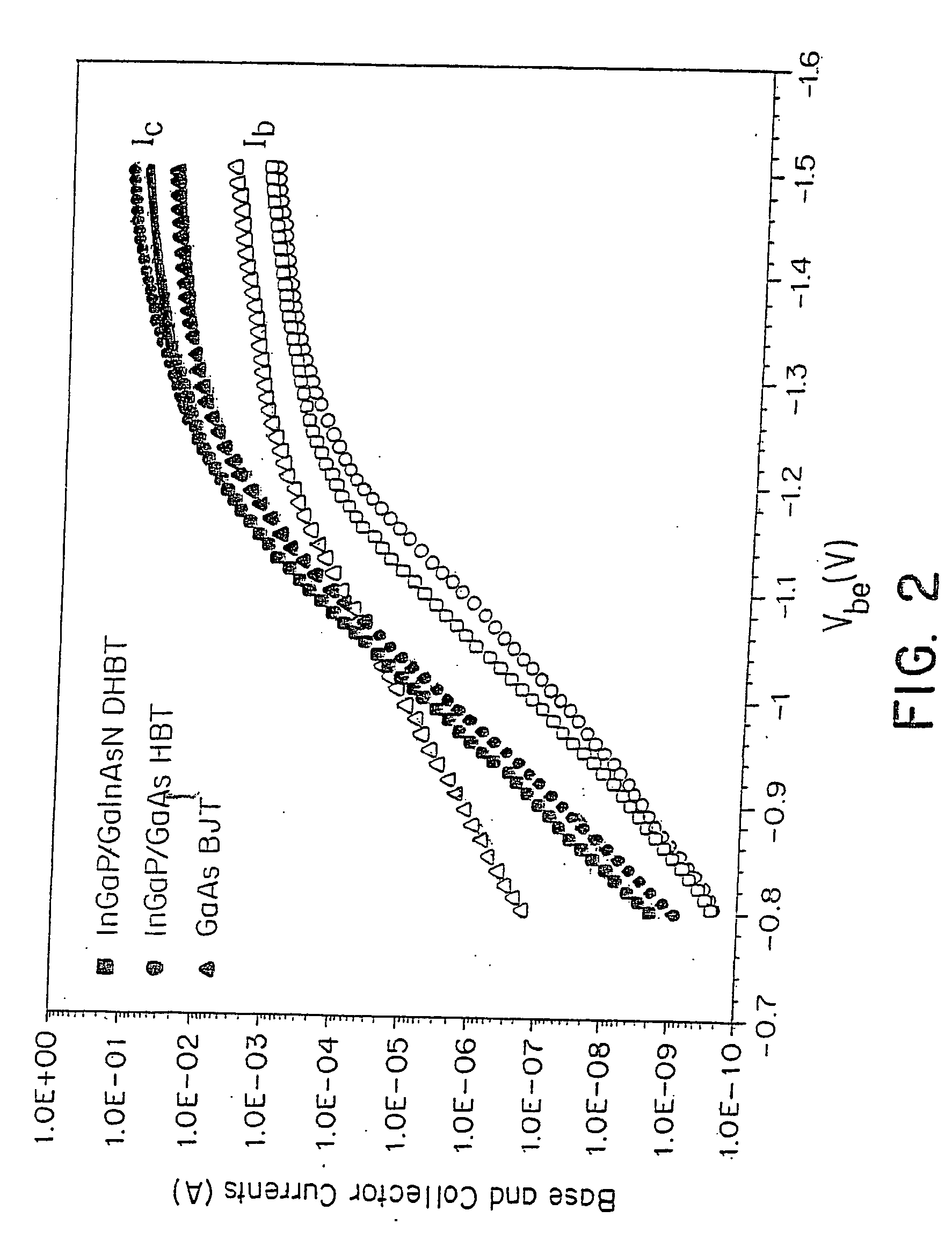
Bipolar transistor with graded base layer
InactiveUS20050139863A1Lower bandgapLow resistivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionSemiconductor materials
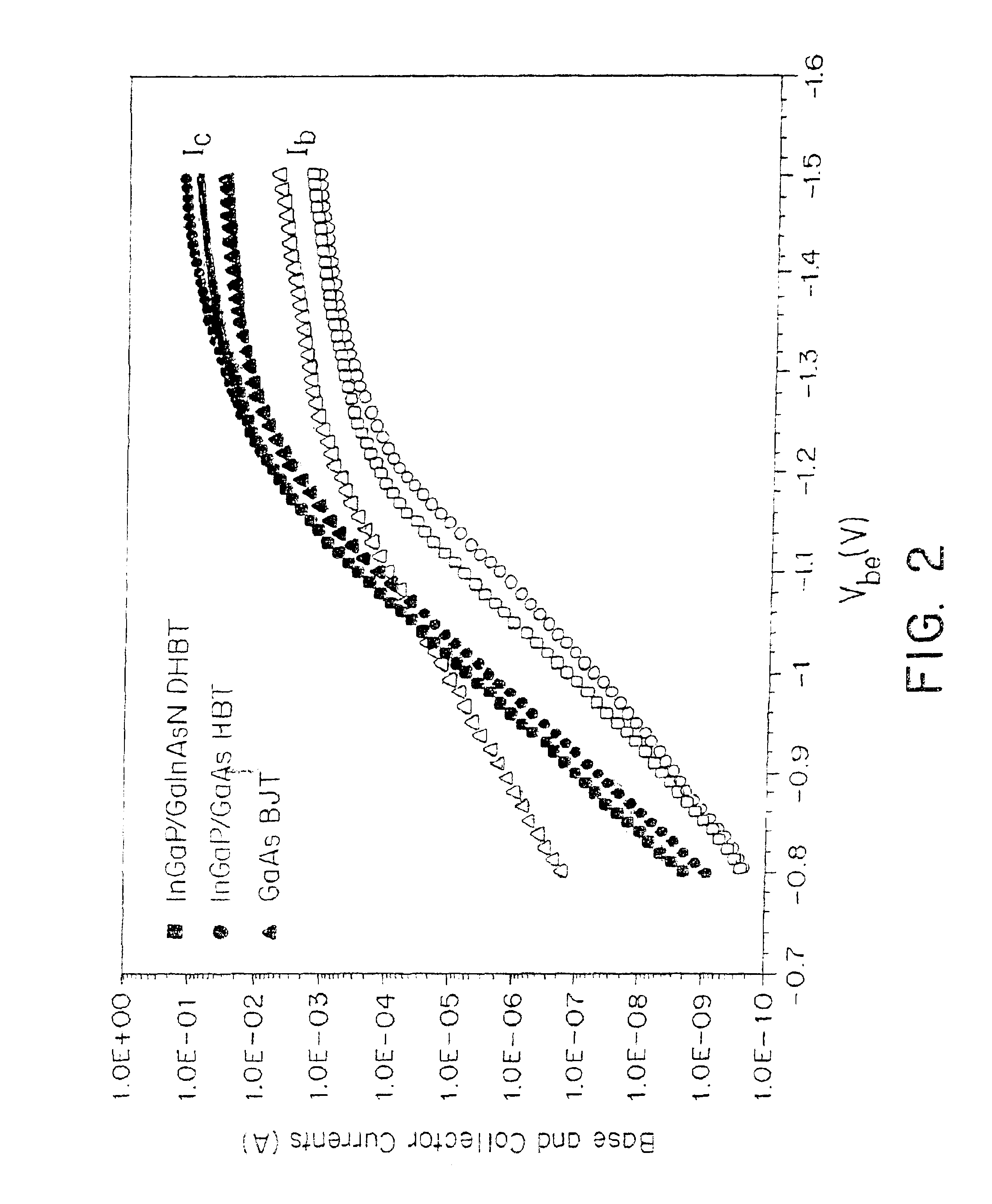
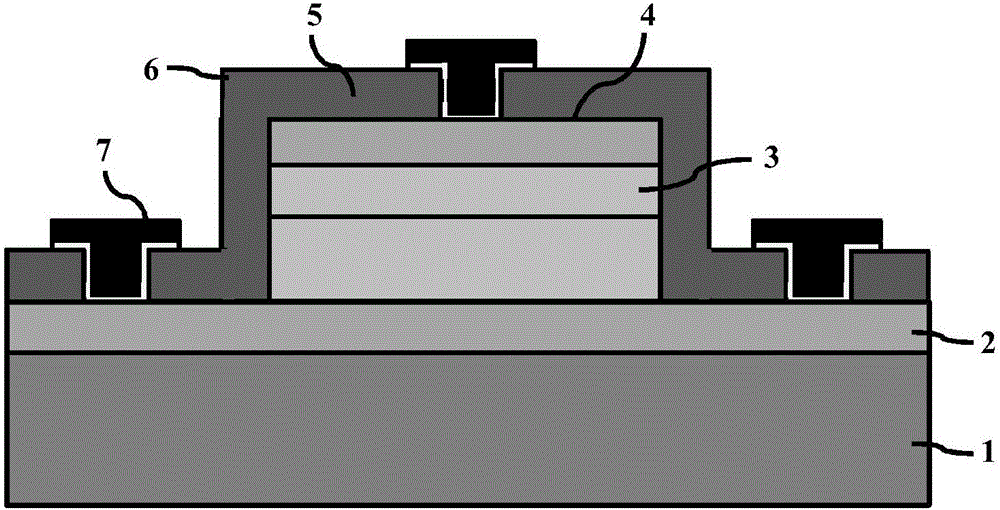
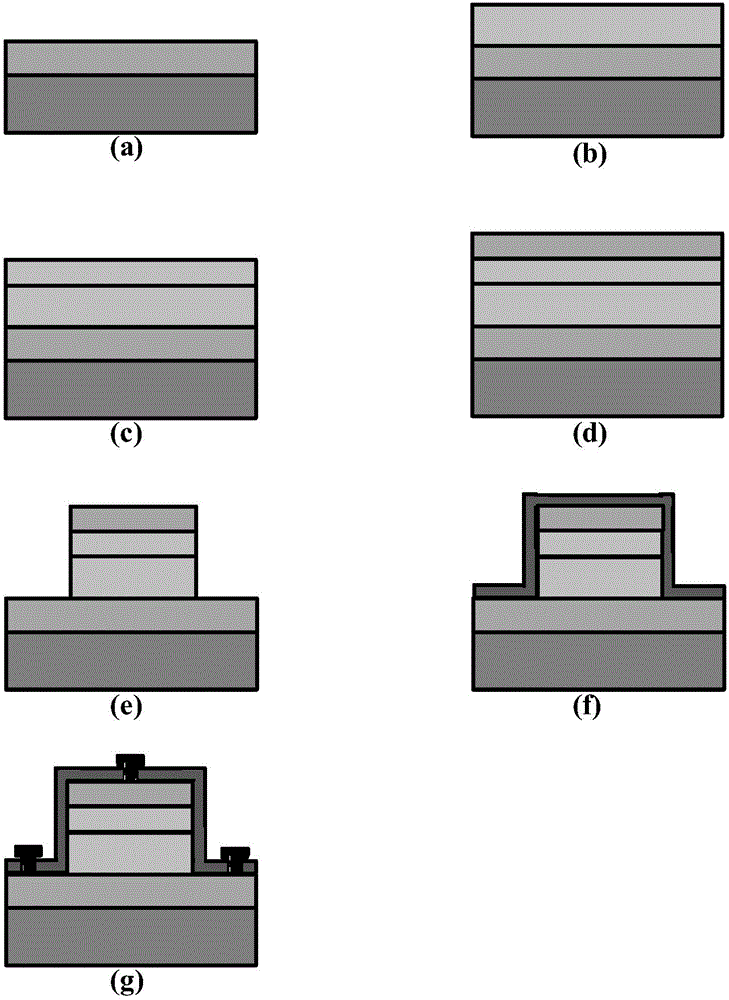
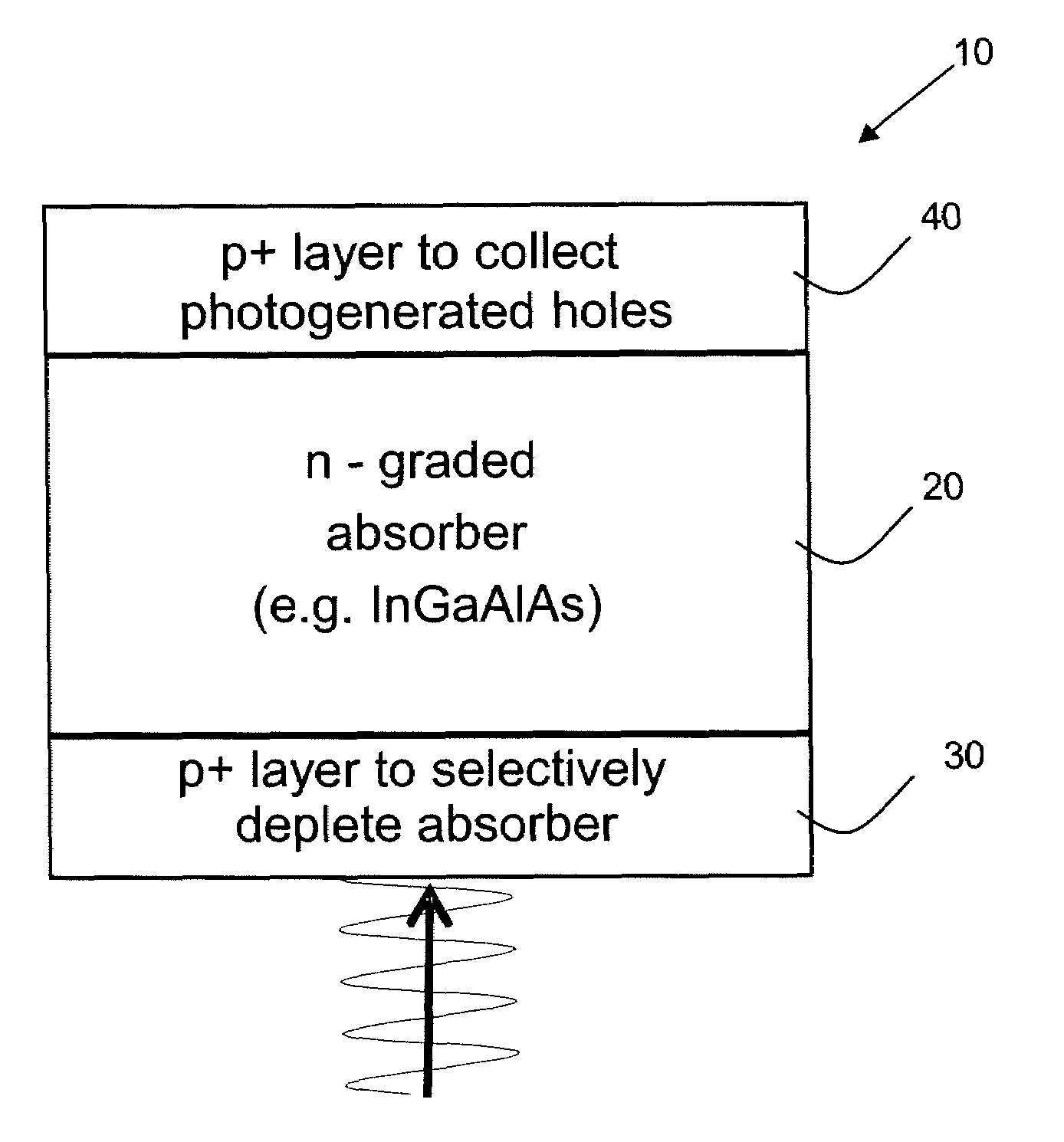
A semiconductor material which has a high carbon dopant concentration includes gallium, indium, arsenic and nitrogen. The disclosed semiconductor materials have a low sheet resistivity because of the high carbon dopant concentrations obtained. The material can be the base layer of gallium arsenide-based heterojunction bipolar transistors and can be lattice-matched to gallium arsenide emitter and / or collector layers by controlling concentrations of indium and nitrogen in the base layer. The base layer can have a graded band gap that is formed by changing the flow rates during deposition of III and V additive elements employed to reduce band gap relative to different III-V elements that represent the bulk of the layer. The flow rates of the III and V additive elements maintain an essentially constant doping-mobility product value during deposition and can be regulated to obtain pre-selected base-emitter voltages at junctions within a resulting transistor.
Owner:IQE KC
Bipolar transistor with graded base layer
InactiveUS6847060B2Easy to manageImprove RF performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThermoelectric device junction materialsHeterojunctionSemiconductor materials
A semiconductor material which has a high carbon dopant concentration includes gallium, indium, arsenic and nitrogen. The disclosed semiconductor materials have a low sheet resistivity because of the high carbon dopant concentrations obtained. The material can be the base layer of gallium arsenide-based heterojunction bipolar transistors and can be lattice-matched to gallium arsenide emitter and / or collector layers by controlling concentrations of indium and nitrogen in the base layer. The base layer can have a graded band gap that is formed by changing the flow rates during deposition of III and V additive elements employed to reduce band gap relative to different III-V elements that represent the bulk of the layer. The flow rates of the III and V additive elements maintain an essentially constant doping-mobility product value during deposition and can be regulated to obtain pre-selected base-emitter voltages at junctions within a resulting transistor.
Owner:IQE KC
GeSn-GeSi material based heterogeneous phototransistor and fabrication method thereof
InactiveCN105789347ANarrow detection wavelengthNarrow detection wavelength rangeFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesCMOSHeterojunction
The invention discloses a GeSn-GeSi material based heterogeneous phototransistor and a fabrication method thereof. A collector and an emitter of the transistor both adopt a GeSi material, a light absorption region and a base region both adopt a GeSn material, an emitter region, the base region, the light absorption region and a collector region are sequentially and vertically arranged, and a passivation layer encircles the peripheries of the emitter region, the base region, the light absorption region and the collector region. According to the fabrication method of the transistor, the GeSn material is grown by a low-temperature solid-source molecular beam epitaxial process, and the fabrication method is a standard complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) fabrication method. The GeSn material with a high light absorption coefficient forms heterojunctions in the light absorption region, the GeSi emitter region and the collector region, the light sensitivity and light current during detection of an infrared light signal by the transistor are improved, and the GeSn-GeSi material based heterogeneous phototransistor has high light absorption rate.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Electronically tunable and reconfigurable hyperspectral photon detector
InactiveUS7652252B1Wavelength agility and tunabilityMinimum powerSpectrum investigationSolid-state devicesTerrainLength wave
Electronically tunable and reconfigurable hyperspectral IR detectors and methods for making the same are presented. In one embodiment, a reconfigurable hyperspectral sensor (or detector) detects radiation from about 0.4 μm to about 2 μm and beyond. This sensor is configured to be compact, and lightweight and offers hyperspectral imaging capability while providing wavelength agility and tunability at the chip-level. That is, the sensor is used to rapidly image across diverse terrain to identify man-made objects and other anomalies in cluttered environments.
Owner:HRL LAB
Visible light catalytic material, and preparation method and application thereof
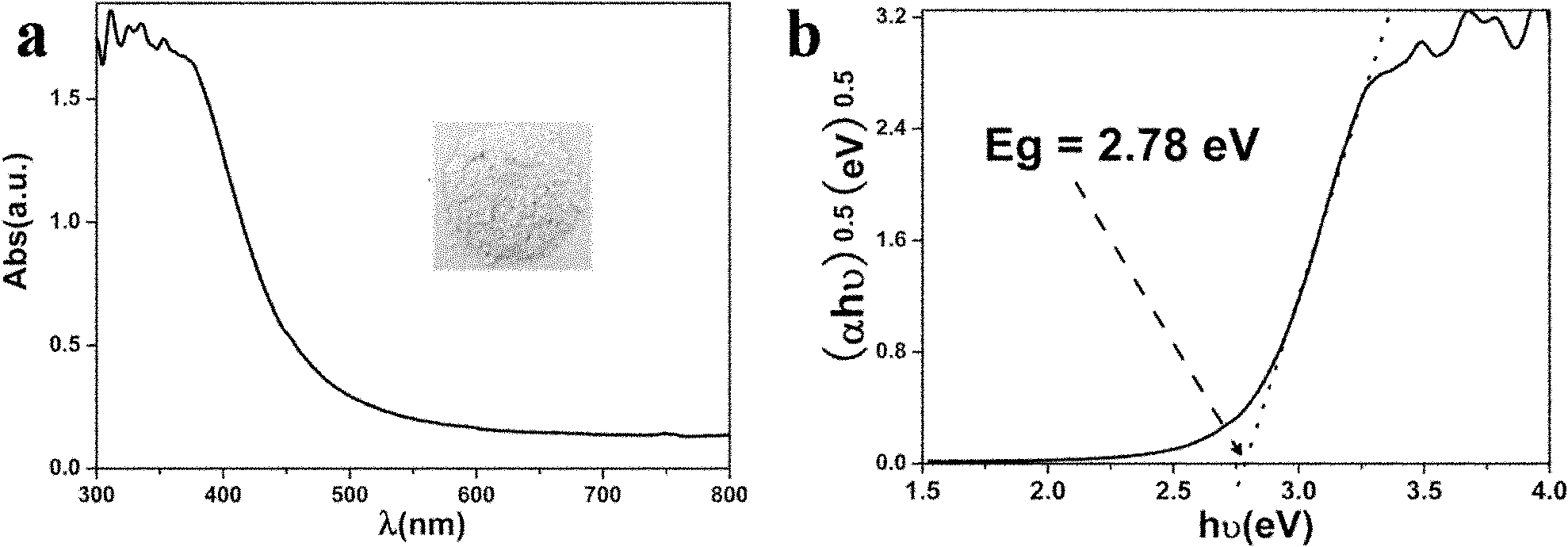
ActiveCN102080262AFast transferEasy to separatePolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsCrystallinityElectronic band structure
The invention discloses a visible light catalytic material used for environmental purification and a preparation method thereof. The visible light catalytic material is an indirect gas semiconductor with a dispersed energy band structure, is a crystalline nano material, comprises the chemical formula of Bi2Sn2O7, has the corresponding optical band gap width of 2.68 to 2.78eV and exhibits high visible light catalytic performance. In the preparation method provided by the invention, Bi2Sn2O7 nanoparticles can be prepared from readily-available raw materials with low cost under moderate conditions only by one-step hydrothermal reaction so as to avoid the coarsening and aggregation of the high-temperature sintered crystal particles; the preparation method is simple to operate; parameters are adjustable in a reaction process, and the crystallinity and material phase compositions of the product are easy to control; in addition, the sample provided by the invention exhibits high stability inphotocatalysis cycle tests of dye degradation and harmful gas purification, and is favorable for industrial application.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nano compound with multilayer structure, and applications thereof
InactiveCN106944153ALower TiO2 bandgapBroaden the Absorbing BoundaryWater/sewage treatment by irradiationPhotodynamic therapyMagnetic coreNanometre
The invention provides a nano compound with a multilayer structure, and applications thereof. The multilayer structure is composed of an inner core layer, an insolating layer, a main functional layer, and a double modified layer from inside to outside; the general structure formula of the nano compound is FeO-SiO<2>-TiO<2>-(X+FA); the inner core layer FeO is magnetic Fe3O4 or magnetic Fe2O3 or a mixture of magnetic Fe3O4 and Fe2O3; the isolating layeris SiO2; the main functional layer is TiO2; X in the double modified layer (X+FA) is one element selected from Zn, La, and Ce; FA is used for representing folic acid. The nano compound possesses magnetism, visible light responsiveness, bio specificity, and enhanced photocatalytic activity, and can be used in the photocatalysis field; steps are simple; operation is simple; and practicality is high.
Owner:TAISHAN MEDICAL UNIV
Naphthalene-diimide-heterocycle-naphthalene diimide oligomers as organic semiconductors and transistors therefrom
InactiveUS20140021448A1Unexpectedly stable performanceHigh and/or superior electron mobility valuesOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesOligomerOrganic semiconductor
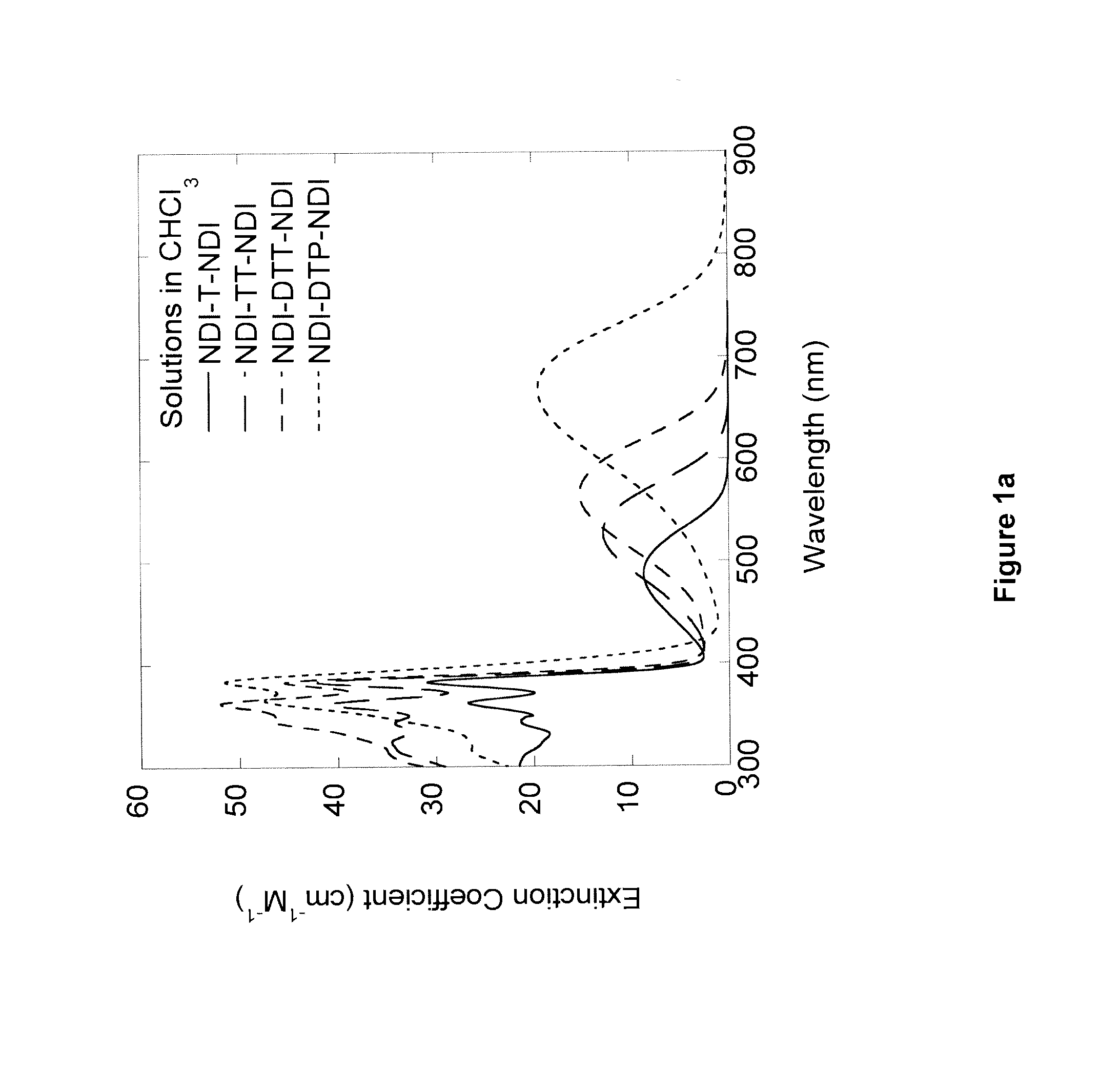
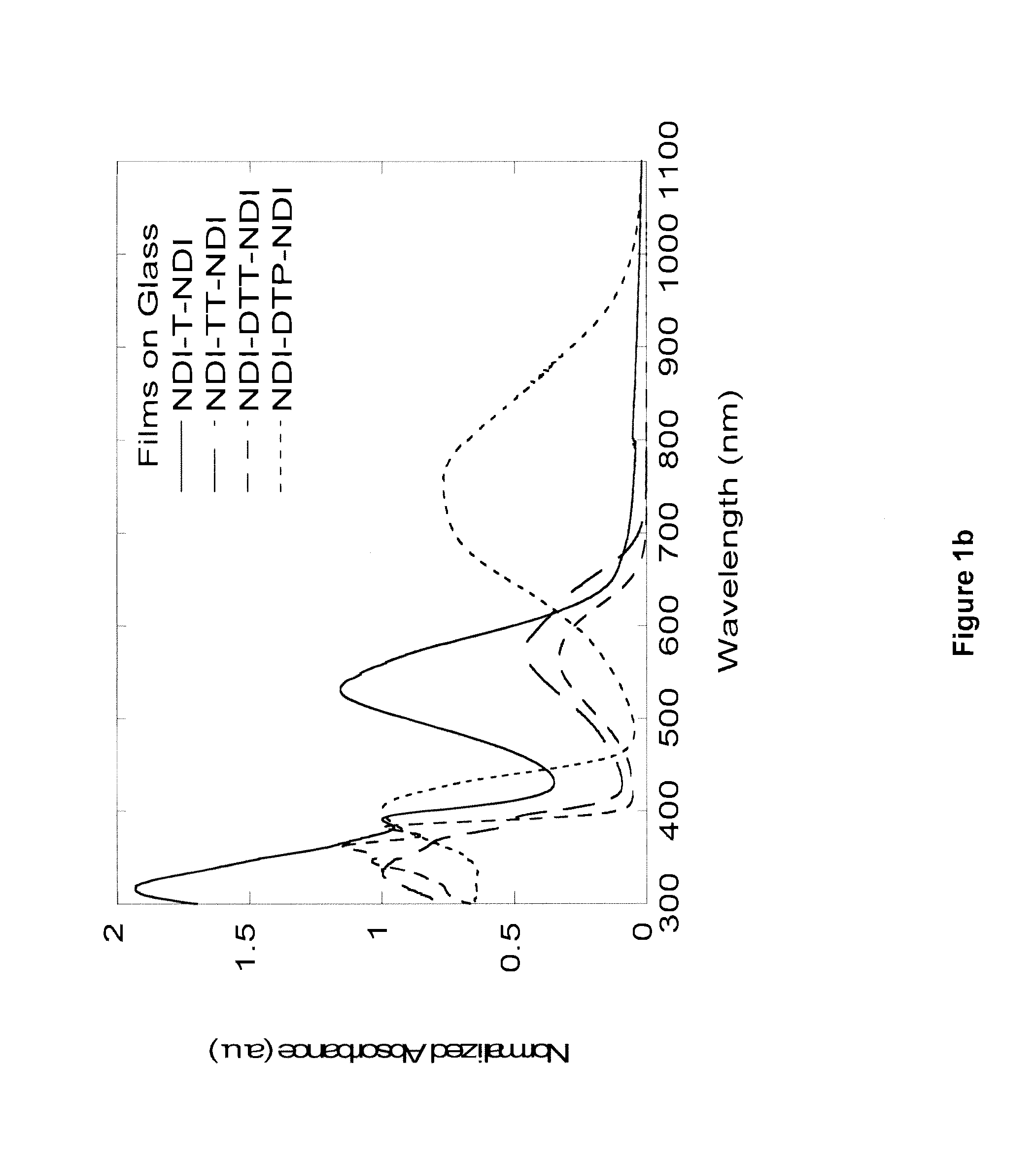
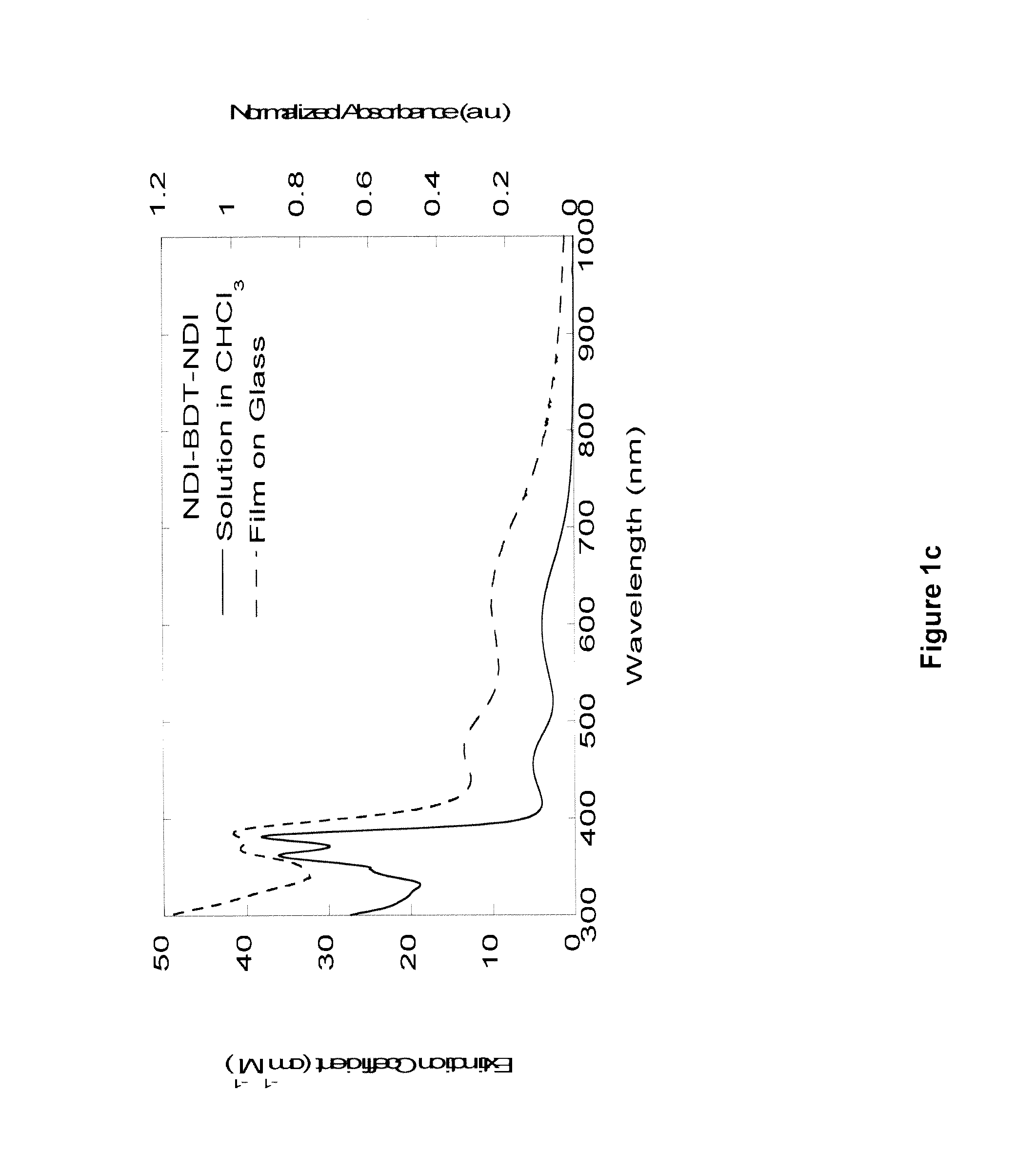
The various inventions and / or their embodiments disclosed herein relate to certain naphthalene diimide (NDI) compounds wherein the NDI groups are bonded to certain subclasses of bridging heteroaryl (hAr) groups, such as the “NDI-hAr-NDI” oligomeric compounds, wherein hAr is a heteroaryl group chosen to provide desirable electronic and steric properties, and the possible identities of the “Rz” terminal peripheral substituent groups are described herein. Transistor and inverter devices can be prepared.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
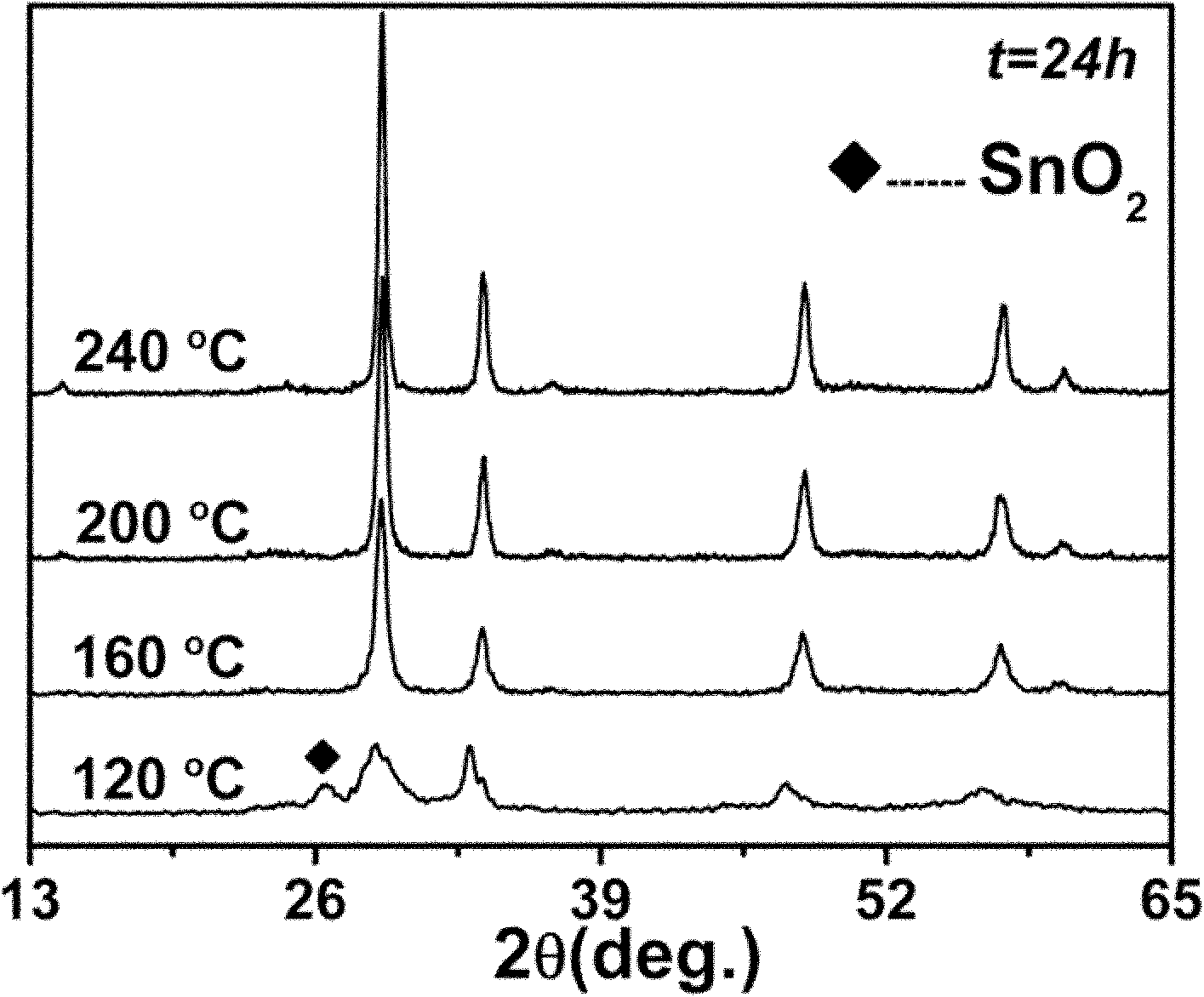
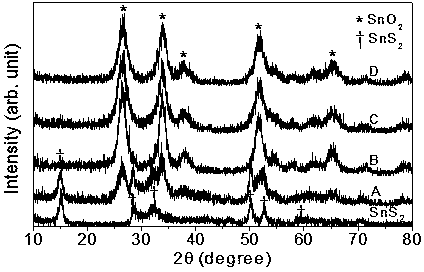
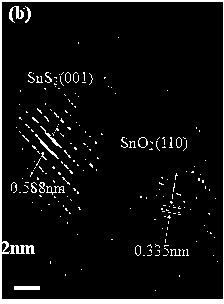
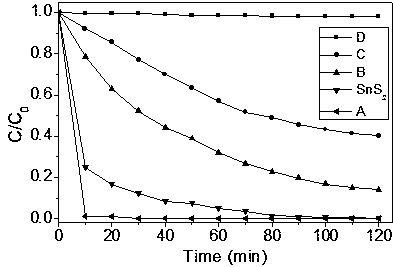
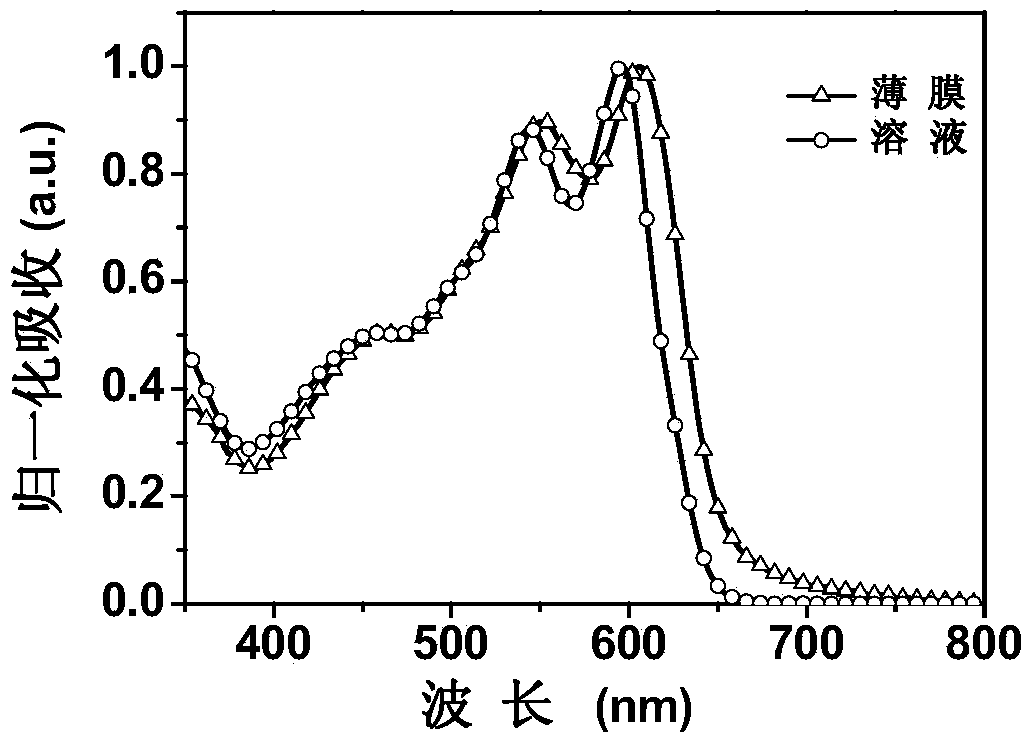
Preparation method for SnO2-based composite visible light photocatalyst
InactiveCN103861618ALower bandgapImprove photocatalytic efficiencyPhysical/chemical process catalystsHeterojunctionVisible light photocatalytic
The invention provides a preparation method for a SnO2-based composite visible light photocatalyst, belonging to the technical field of preparation of a novel nano material and a composite photocatalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing SnS2 nano particles by a hydrothermal method; then partially oxidizing the SnS2 nano particles by using H2O2 under a hydrothermal environment to prepare the visible light photocatalyst with a SnO2 / SnS2 heterojunction composite structure. According to the preparation method, the SnO2 and the SnS2 are compounded to realize the absorption and the catalysis under visible light, and the problem that visible light photocatalysis can not be realized by a traditional TiO2 photocatalyst is solved; the prepared composite heterojunction structure is combined tightly so as to be good for transferring photon-generated carriers on two energy bands and separating the photon-generated carriers.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Polymer photovoltaic material, preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN104031245AEasy to prepareEasy to purifyFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesSolubilityPolymer science
The invention discloses a polymer photovoltaic material, a preparation method and use thereof. The molecule of the polymer material takes two-dimensional conjugate dibenzothiophene or naphtho-bithiophene as a donor, and takes thiophene and pyrrole diketone and derivatives thereof as receptors, and the polymer material has a structure shown in a formula (I) or a formula (II). The polymer material is simple in preparation and easy to purify, and has good solubleness in common organic solvents (for example, dichloromethane, trichloromethane, tetrahydrofuran, chlorobenzene or o-dichlorobenzene and the like). The film with high quality can be prepared by using a liquid method. The macromolecule is applied to a donor material of a solar battery, the energy conversion efficiency exceeds 7.5%, and the open-circuit voltage exceeds 1V.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
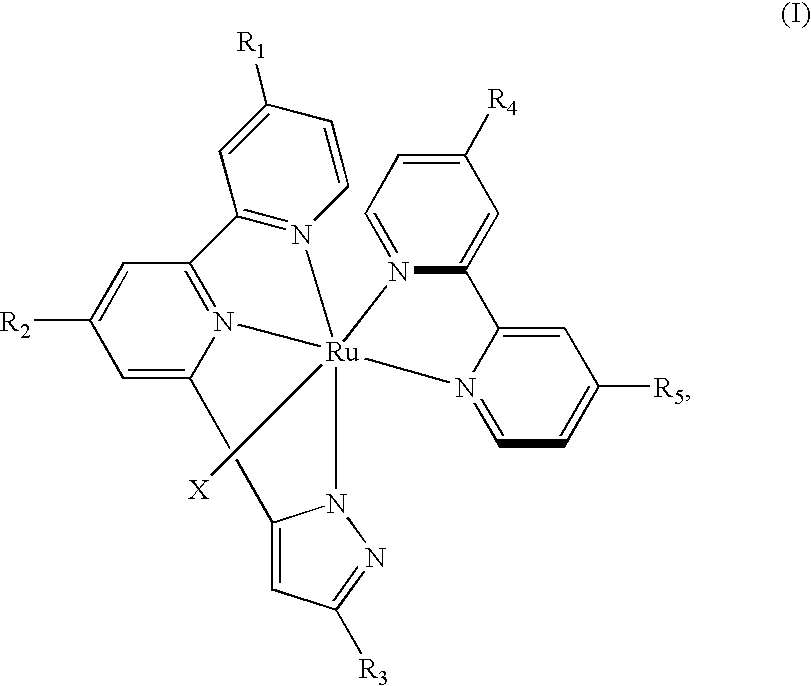
Ruthenium complexes with tridentate heterocyclic ligand and dye-sensitized solar cells using the same
ActiveUS20080114174A1Lower bandgapPromoting metal-to-ligand charge transfer (MLCT) transitionRuthenium organic compoundsElectrolytic capacitorsPhosphoric acidCarboxylic acid
A ruthenium complex having a chemical formula of RuL1L2X is provided. The chemical formula includes a structural formula represented by the following Formula (I):in which, X is a monodentate anion ligand, L1 and L2 respectively represent a heterocyclic tridentate ligand with a structure shown in the following structural formula (II):and a bipyridine ligand derivative with a structure shown in the following structural formula (III):in which R1, R2, R4 and R5 of L1 and L2 are the same or different substituents and represent alkyl, alkoxy, aminoalkyl, haloalkanes or substituted phenyl group, carboxylic acid group or acid radical salt thereof, sulfonic acid group or acid radical salt thereof, phosphoric acid group or acid radical salt thereof or hydrogen atom. R3 represents perhalogenated alkyl group, alkoxy, alkyl, amino, halogens, or hydrogen atom. The ruthenium complexes are suitable for being used as dye-sensitizers for fabricating dye-sensitized solar cells.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
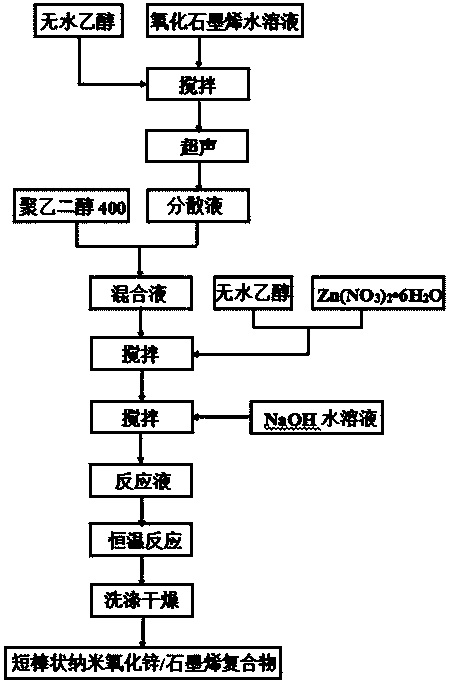
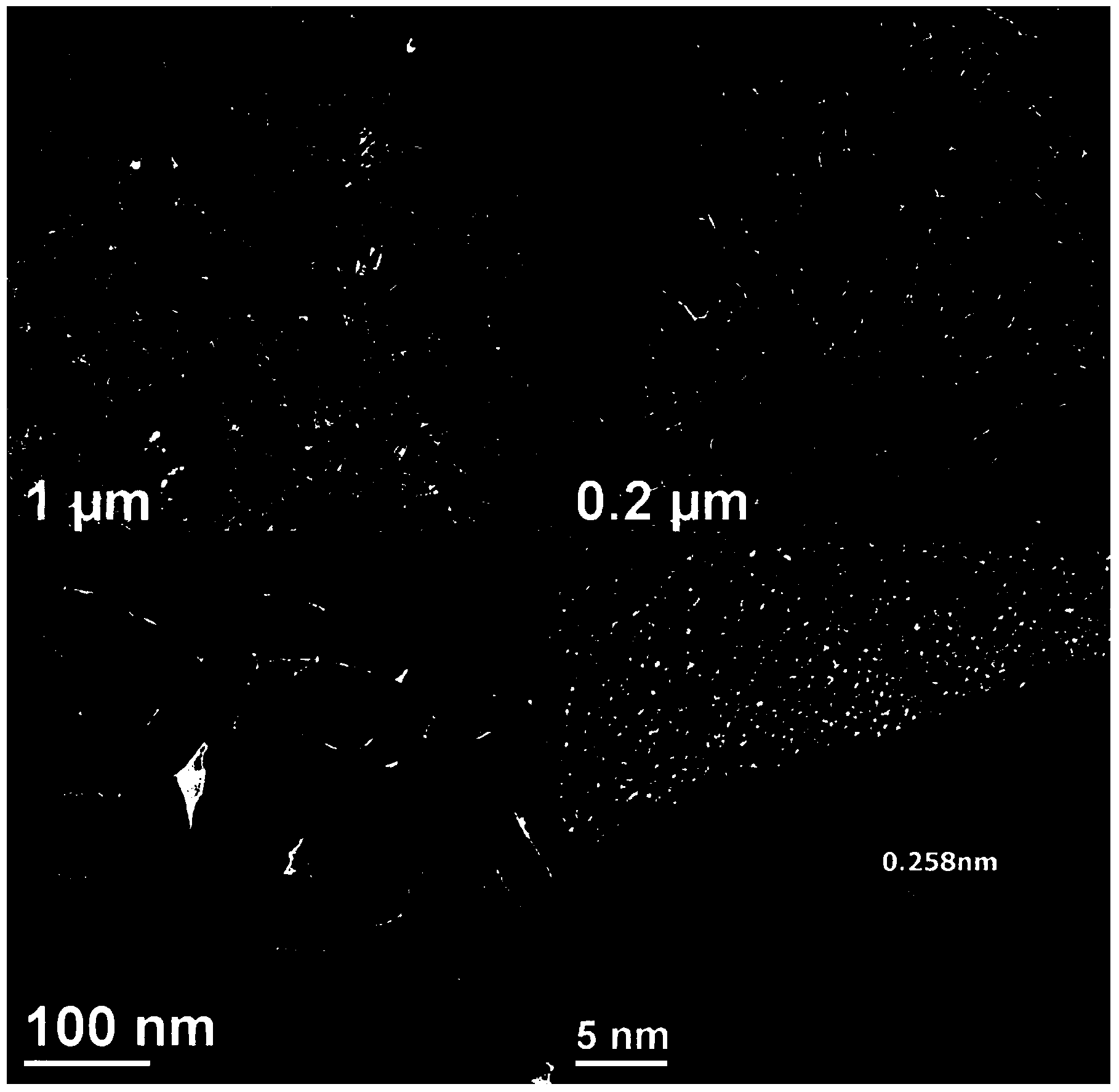
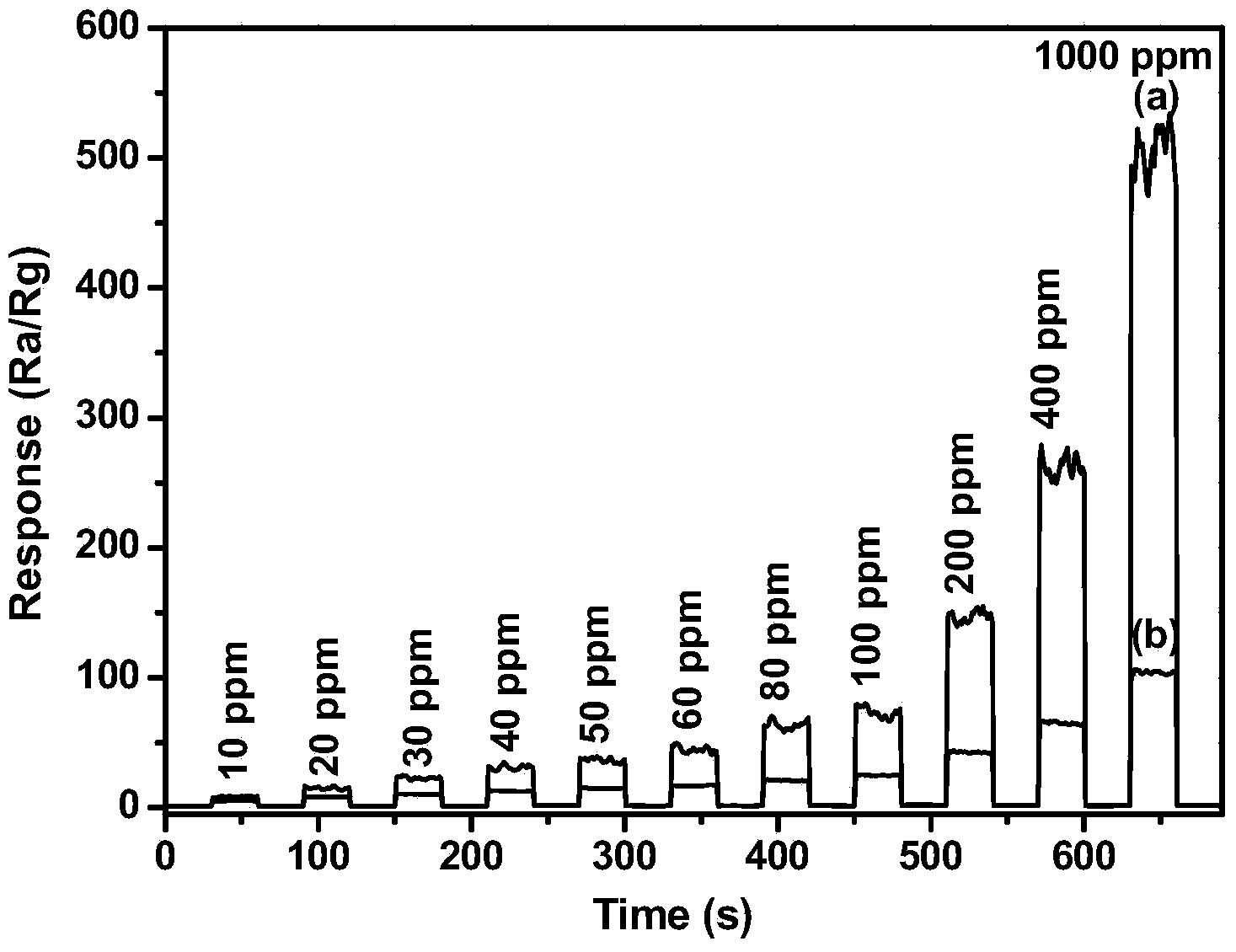
Short-bar-shaped nano-zinc oxide/graphene compound and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104076073AEasy to operateImprove gas sensing performanceMaterial nanotechnologyMaterial electrochemical variablesAlcoholGas detector
The invention discloses a short-bar-shaped nano-zinc oxide / graphene compound and a preparation method thereof. Nano-zinc oxide in the compound is uniformly supported on the surface of a graphene sheet layer and shaped as a short bar. The preparation method of the compound comprises the following steps: dispersing a graphene oxide aqueous solution in absolute ethyl alcohol, and subsequently carrying out ultrasonic treatment to obtain a uniform dispersion liquid; adding a surface surfactant, namely polyethylene glycol 400, into the dispersion liquid to obtain a mixed liquid; dissolving Zn(NO3)2.6H2O in the absolute ethyl alcohol, and then adding to the mixed liquid; and adjusting pH of the mixed liquid to 9-10, then carrying out constant-temperature reaction in a sealed reaction kettle, and washing and drying a product after the reaction is ended to obtain a target product. The preparation method of the compound is a soft chemical method which is simple to operate, can be used for preparing the target product with excellent gas-sensitive property, and is good in application prospect in the field of gas-sensitive sensors.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
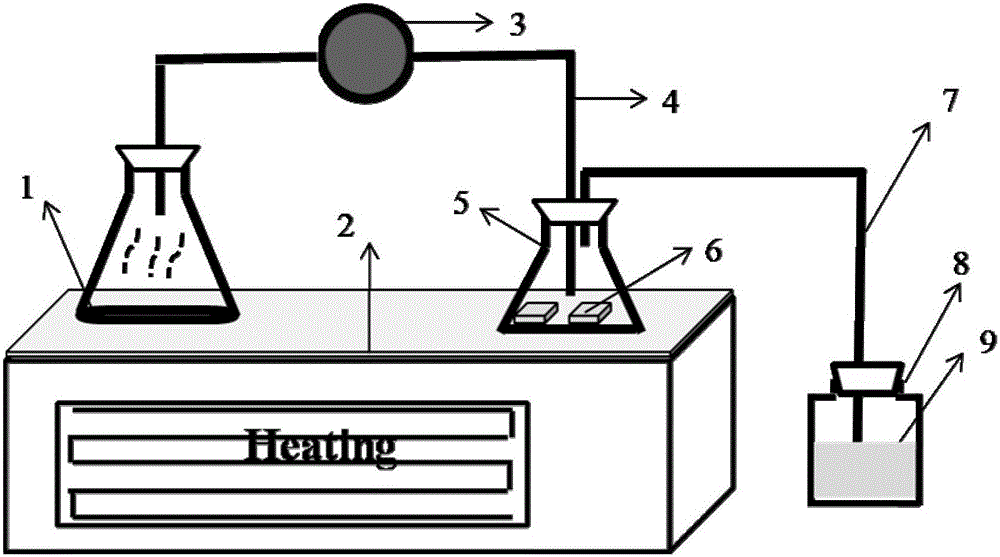
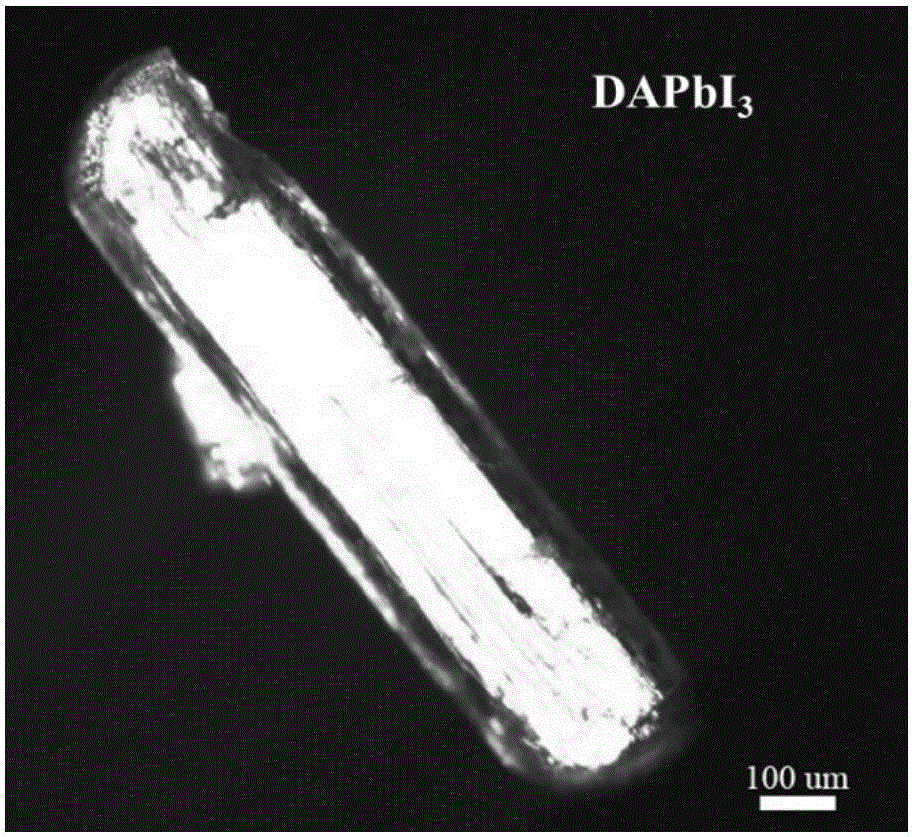
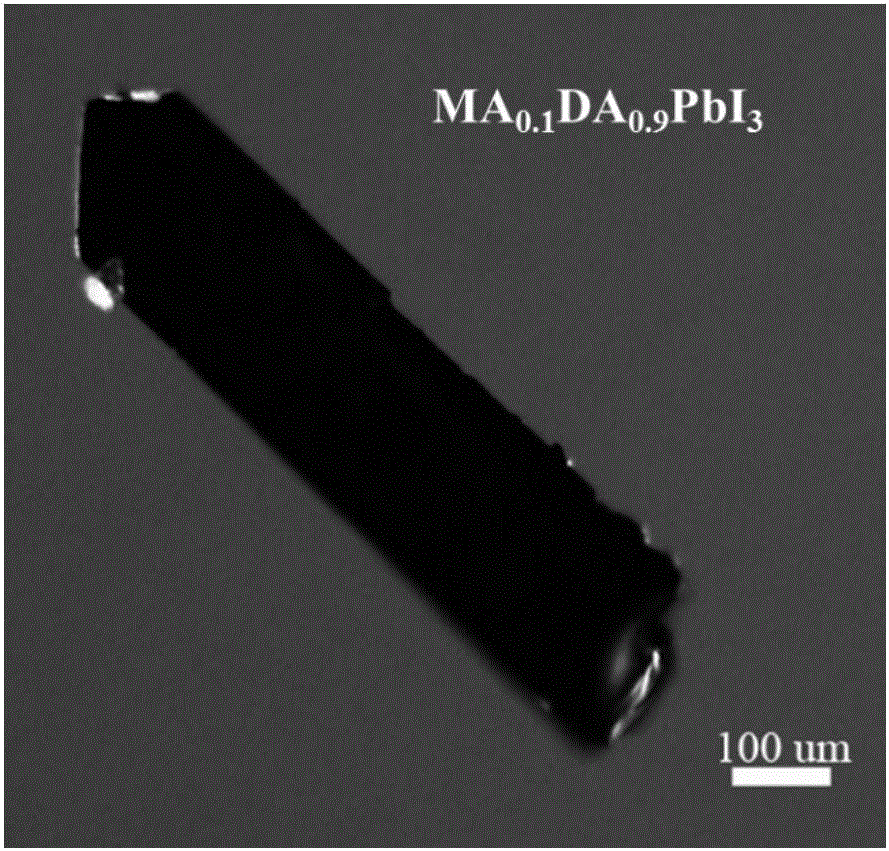
Organic and inorganic composite perovskite single crystal induced transformation method and device based on methylamine atmosphere
InactiveCN106757371AUniversalLower bandgapPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsPhotovoltaic detectorsSingle crystal
The invention relates to organic and inorganic composite perovskite single crystal induced transformation method and device based on a methylamine atmosphere. The method comprises the following steps: putting an organic and inorganic composite perovskite single crystal into the methylamine atmosphere; and carrying out induced treatment for 3h to 36h at the temperature of 40 DEG C-150 DEG C. The invention further provides a device for inducing the signal crystal to transform by methylamine gas. After a wide-band gap perovskite material induces the transformation, an optical absorption range is greatly expanded and the photoelectric properties are greatly improved; and the wide-band gap perovskite material can be widely applied to the fields of solar batteries, photoelectric detectors and the like. The method and equipment are simple, the price is low and the preparation is efficient.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
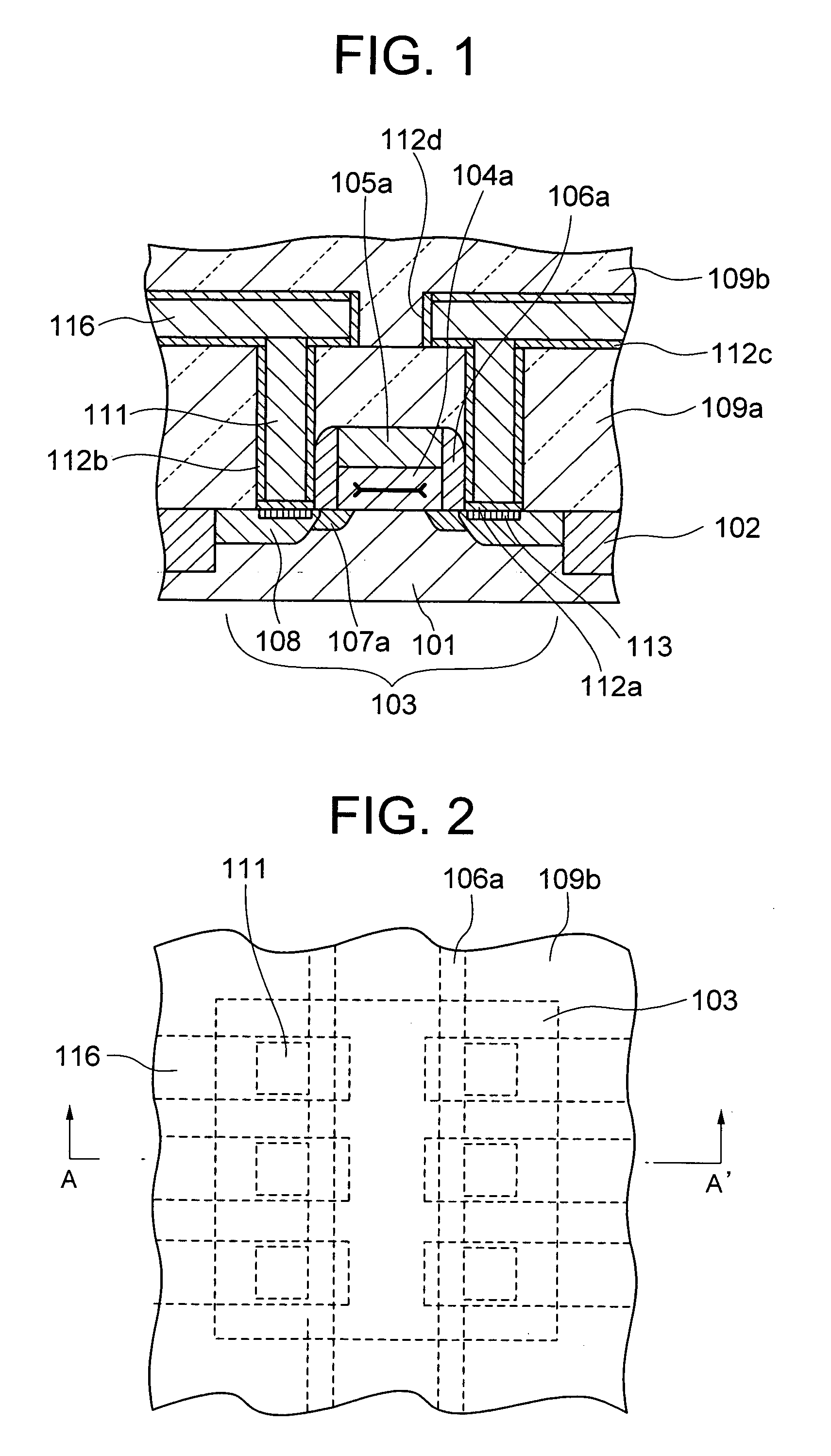
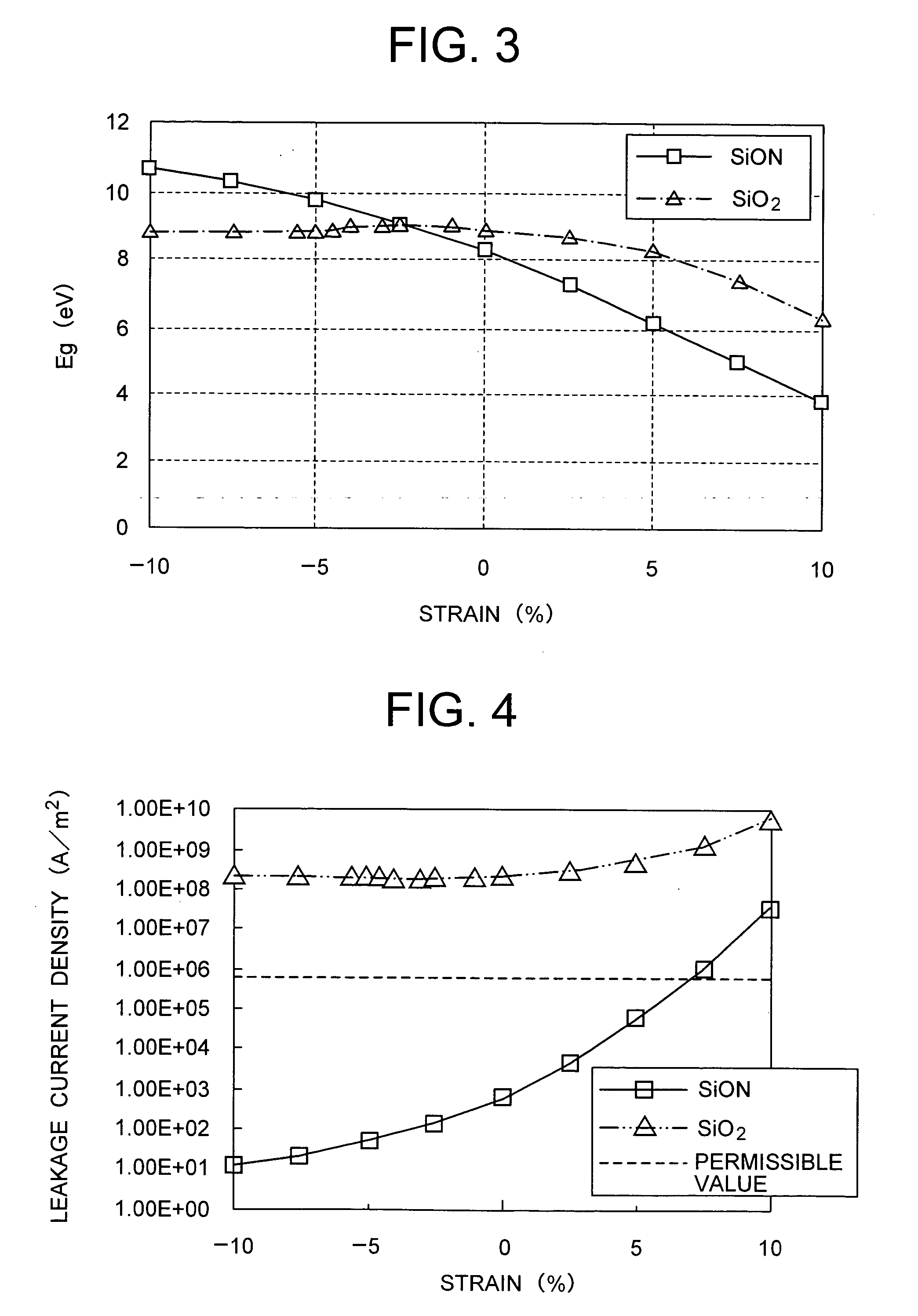
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050051855A1Satisfactory characteristicNot easy to flowTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDevice materialSemiconductor
A semiconductor device constitutes an electric field effect type transistor having a semiconductor substrate, a gate insulating layer formed on the substrate and a gate electrode formed on the gate insulating layer. The gate insulating layer is mainly formed of silicon oxynitride (SiON) and a strain state of the gate insulating layer is a compressed strain state.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
TiO2-xNx Nanotubes and Method for Preparing the Same
InactiveUS20100044630A1Controlled electronic structureReduced band gapMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNitrogen atomNitrogen gas
TiO2-xNx (0.01≦x≦0.2) nanotubes and a method for preparing the same are disclosed. More particularly, TiO2-xNx (0.01≦x≦0.2) nanotubes doped with nitrogen atoms by treating TiO2 nanotubes through nitrogen plasma to partially substitute oxygen portion of TiO2 nanotube with nitrogen, and a method for preparing the same are disclosed. The TiO2-xNx (0.01≦x≦0.2) nanotube of the present invention is prepared by doping nitrogen on a TiO2 nanotube to control an electronic structure and reduce a band gap of the TiO2 nanotube, so that the prepared TiO2-xNx (0.01≦x≦0.2) nanotube exhibits improved conductivity and extended light absorption range from a UV ray area up to a visible light area, thus having more enhanced applicable performance in optical and / or electrochemical aspects.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
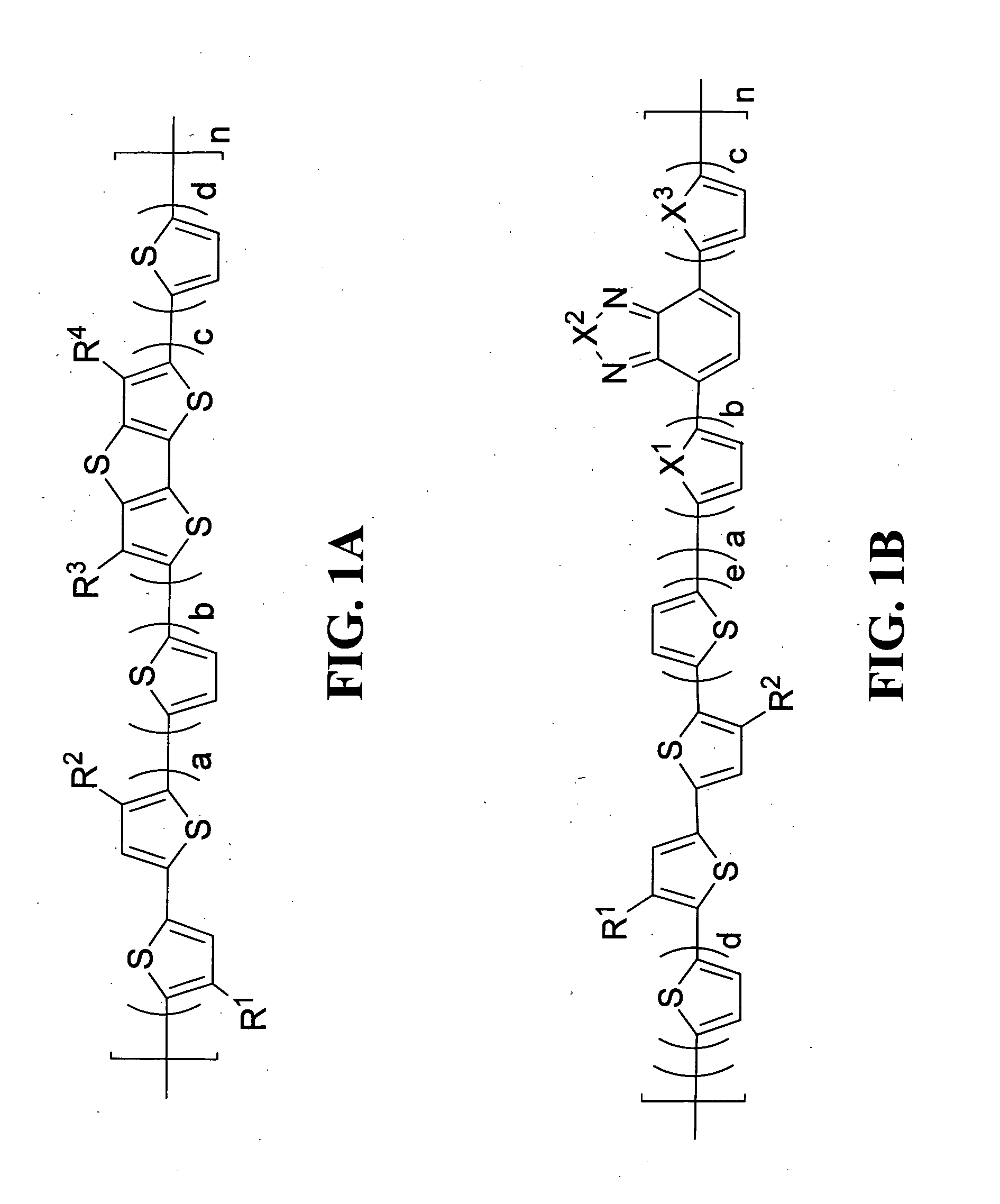
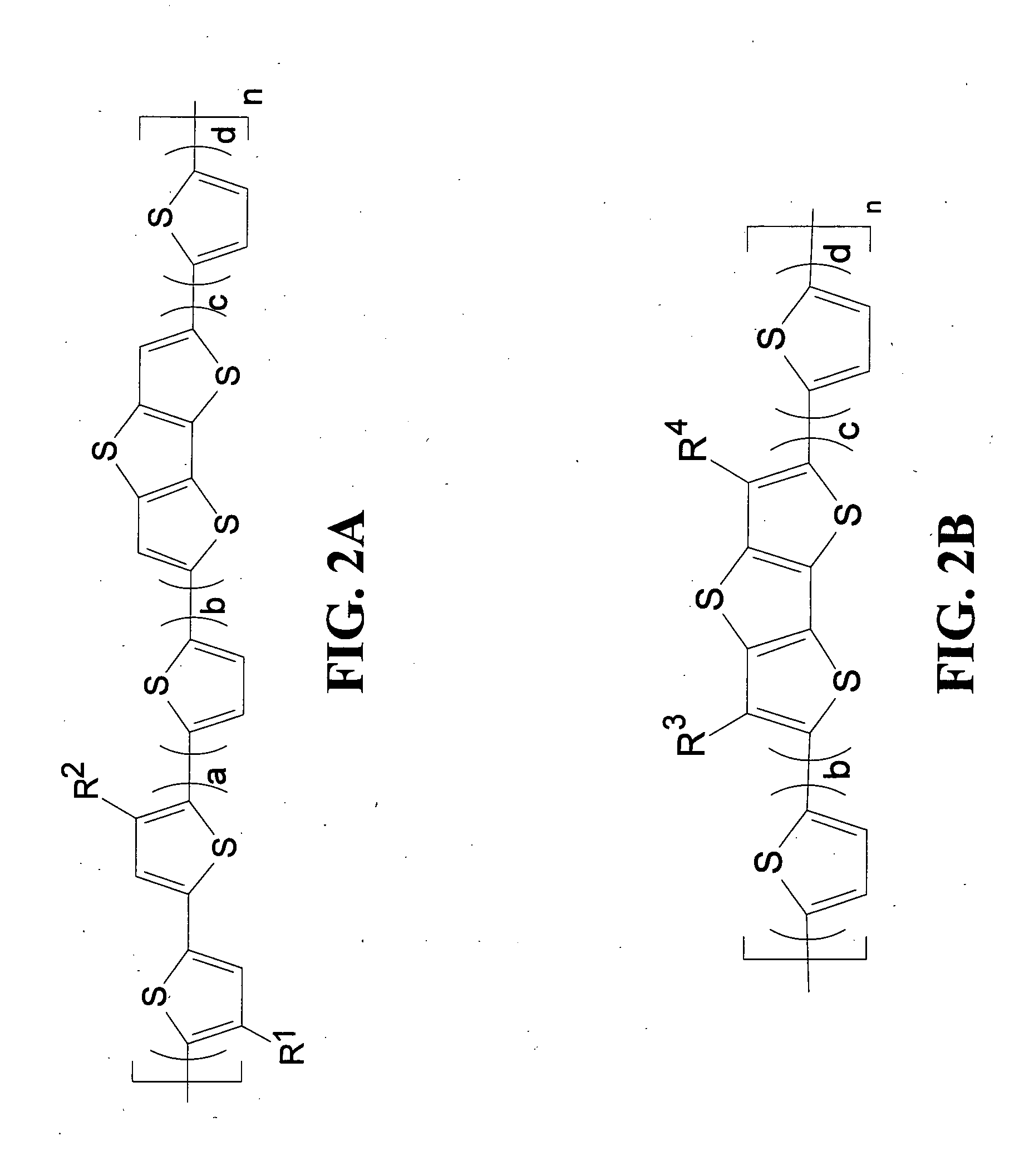
Polymeric semiconductors, devices, and related methods
InactiveUS20120156829A1Increase charge mobilityLower bandgapTransistorOrganic chemistryPolymer scienceSide chain
A polymer comprises a polymeric chain represented by formula (I) or (II). In formula (I), a, b, c, d, and n are integers, a from 0 to 3, b from 1 to 5, c from 1 to 3, d from 1 to 5, and n from 2 to 5000; R1 and R2 are side chains; R3 and R4 are each independently II or a side chain; and when a is 0, R3 and R4 are side chains. In formula (II), a, b, c, d, e, and n are integers, a from 1 to 3, b and c being independently 0 or 1, d and e being independently 1 or 2, and n from 2 to 5000; R1 and R2 are side chains except —COOalkyl; and X1, X2 and X3 are independently O, S, or Se. Semiconductors and devices comprising the polymer are also provided.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
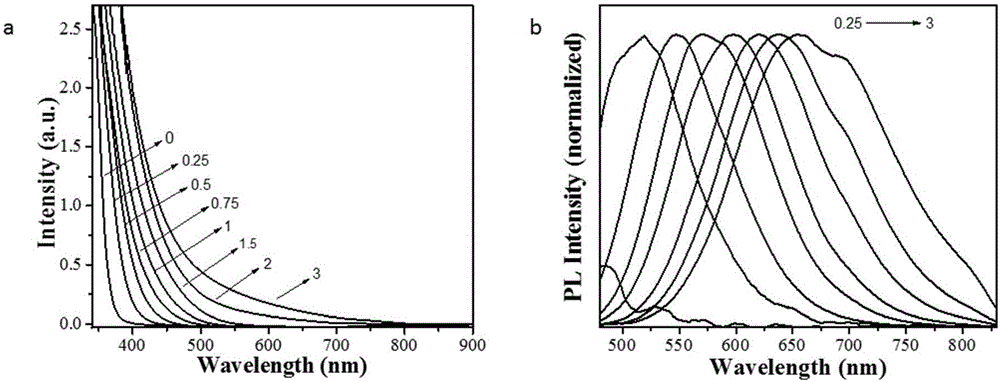
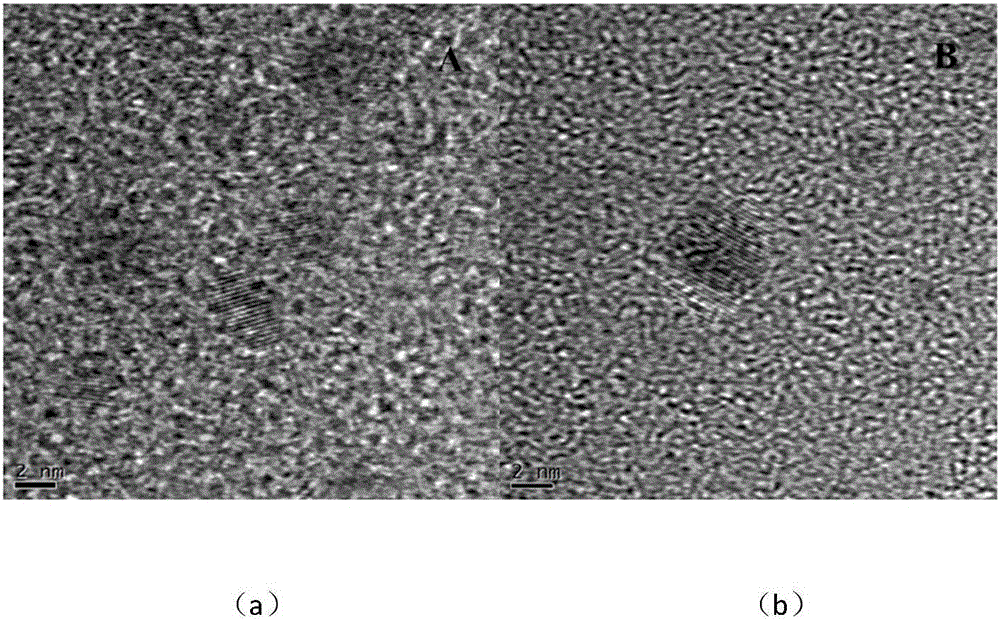
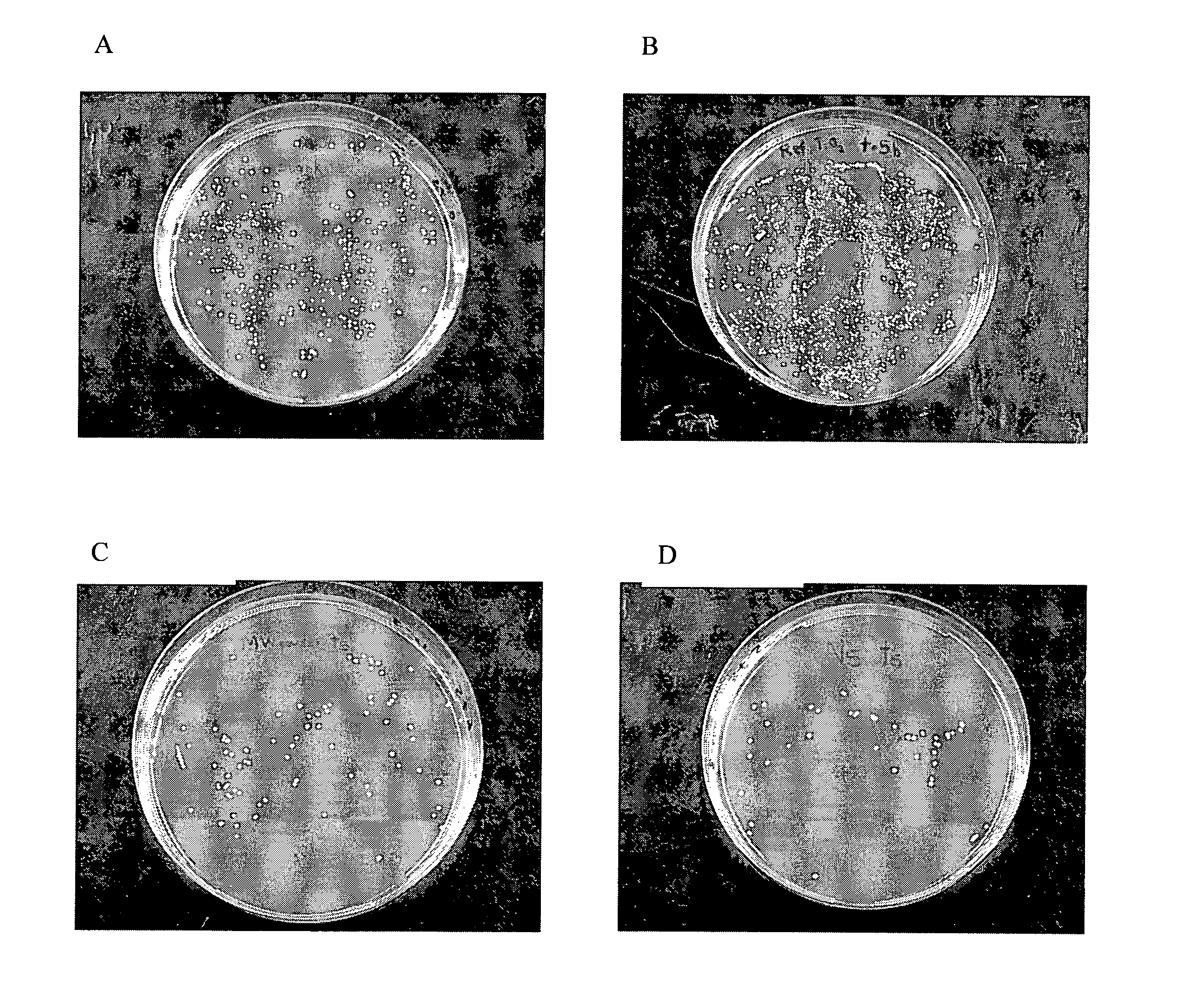
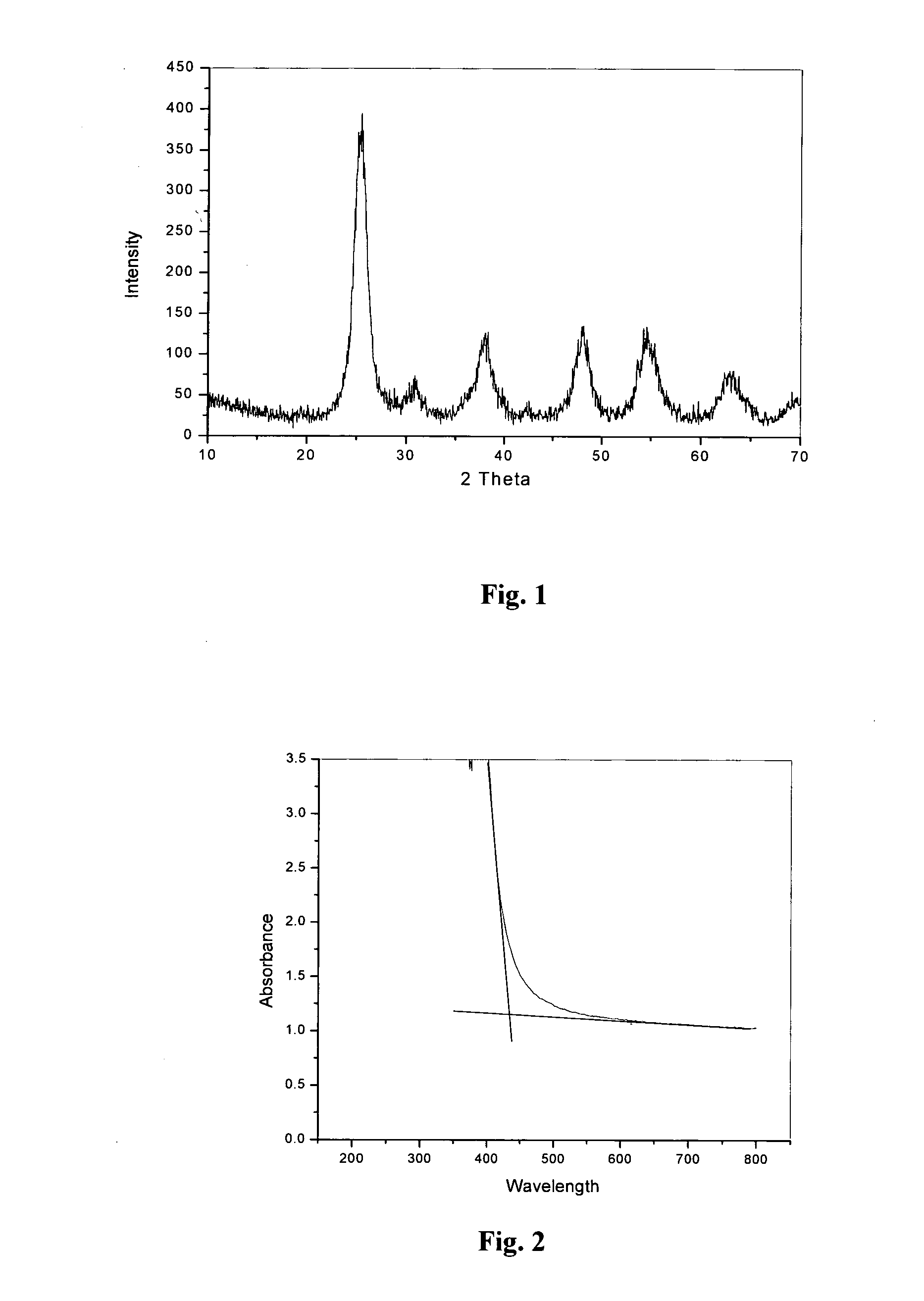
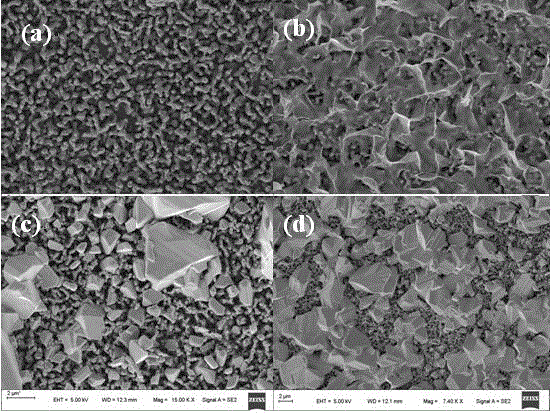
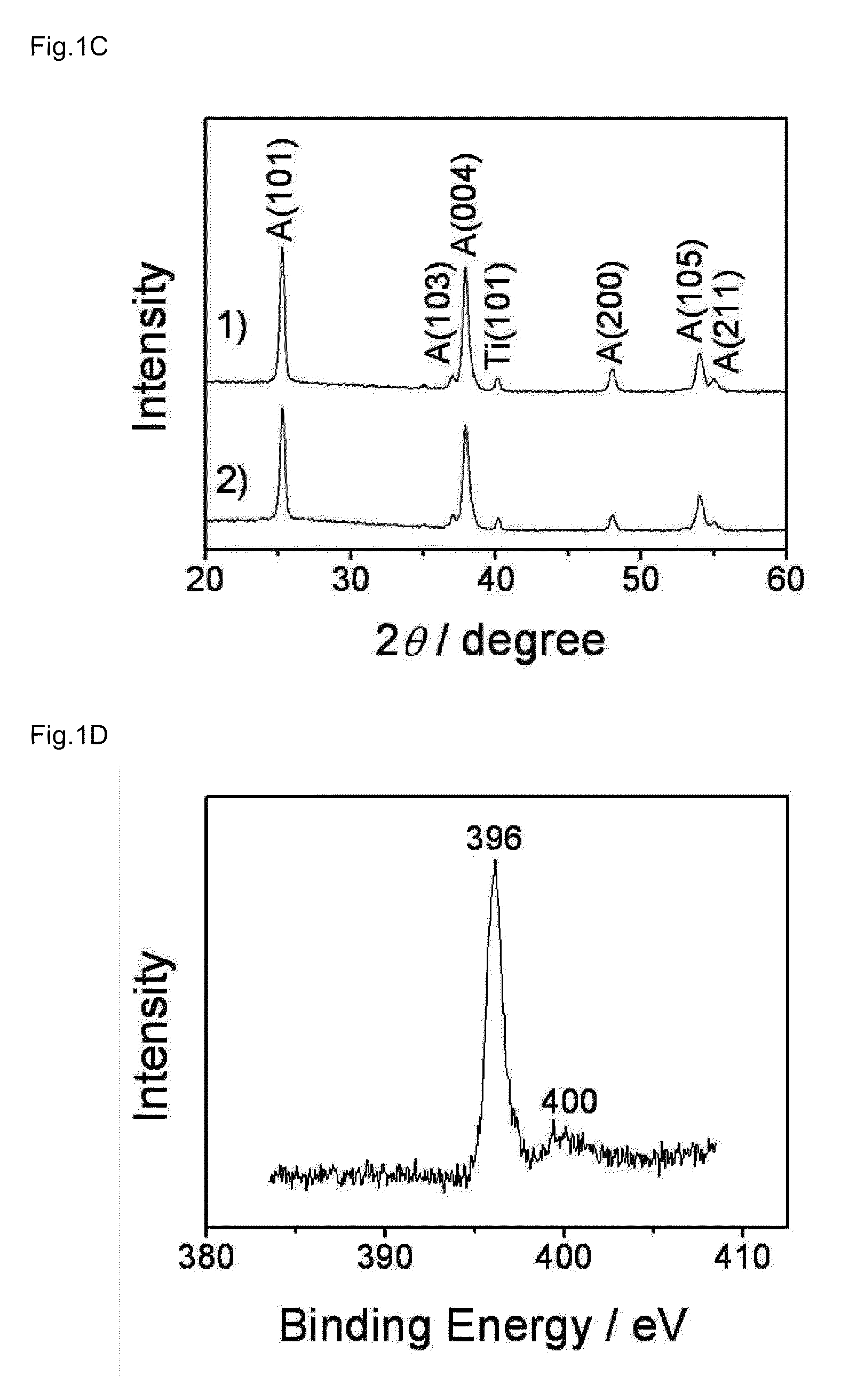
Preparation method and application for palladium-modified titanium dioxide with three-dimensional flower-like structure exposure [001] crystal face
InactiveCN105032406AExpand the scope of absorptionInhibitory complexWater/sewage treatment by irradiationEnergy based wastewater treatmentWastewaterPhotocatalytic degradation
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application for palladium-modified titanium dioxide with a three-dimensional flower-like structure exposure [001] crystal face. The preparation method is characterized by comprising: a step I, preparing titanium dioxide with a three-dimensional flower-like structure exposure [001] crystal face; and a step II, preparing palladium-modified titanium dioxide with a three-dimensional flower-like structure exposure [001] crystal face. According to the preparation method and the application for the palladium-modified titanium dioxide with the three-dimensional flower-like structure exposure [001] crystal face provided by the invention, the method is simple and easy to implement; conditions are gentle; operation is simple; the preparation period is short; the preparation success rate is high; photocatalytic activity under a visible light condition is high; raw materials are economical and available; and the palladium-modified titanium dioxide can realize mass production, is easy to recycle and reuse, and can be applied to photocatalytic degradation on wastewater pollutants.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
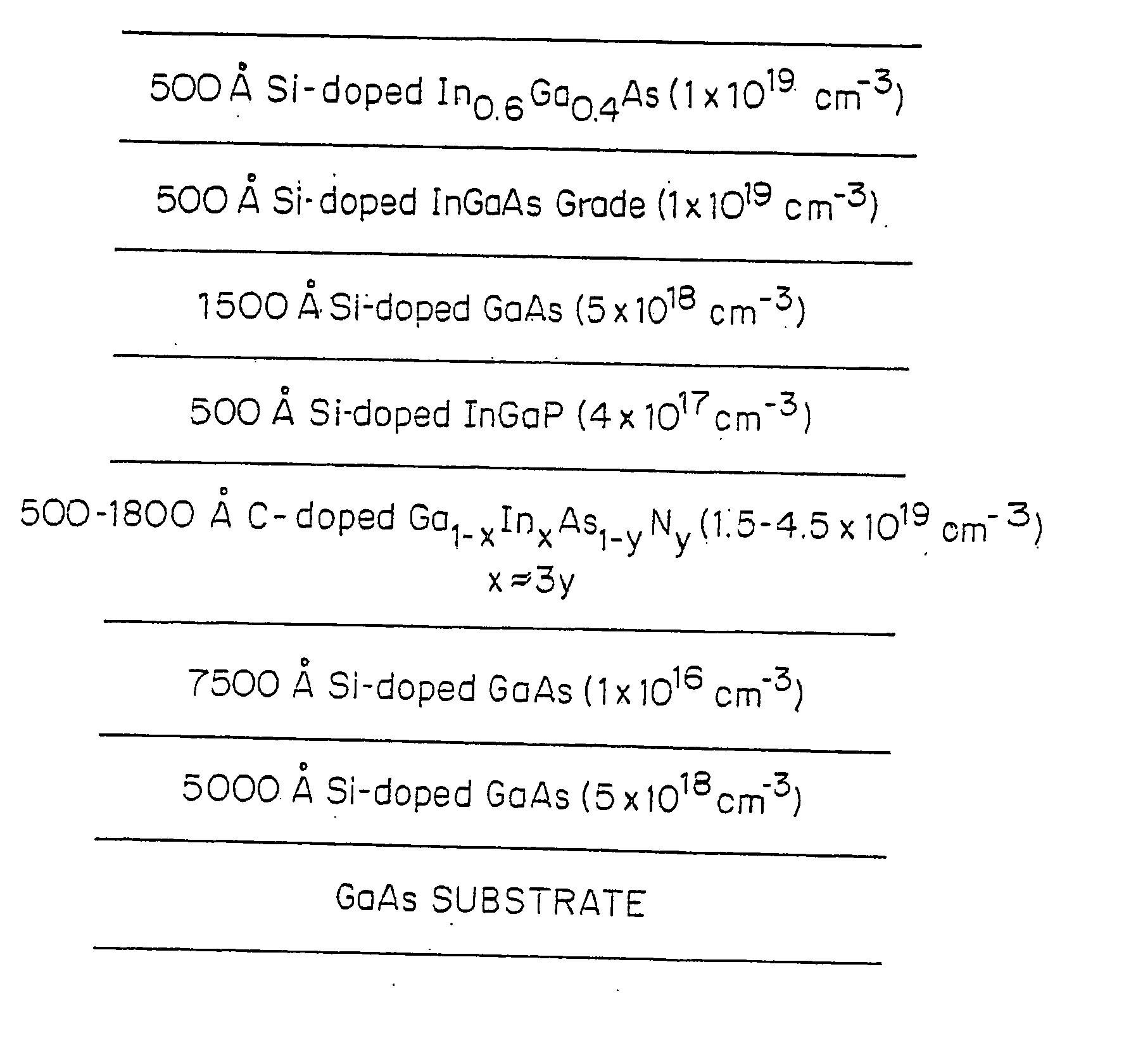



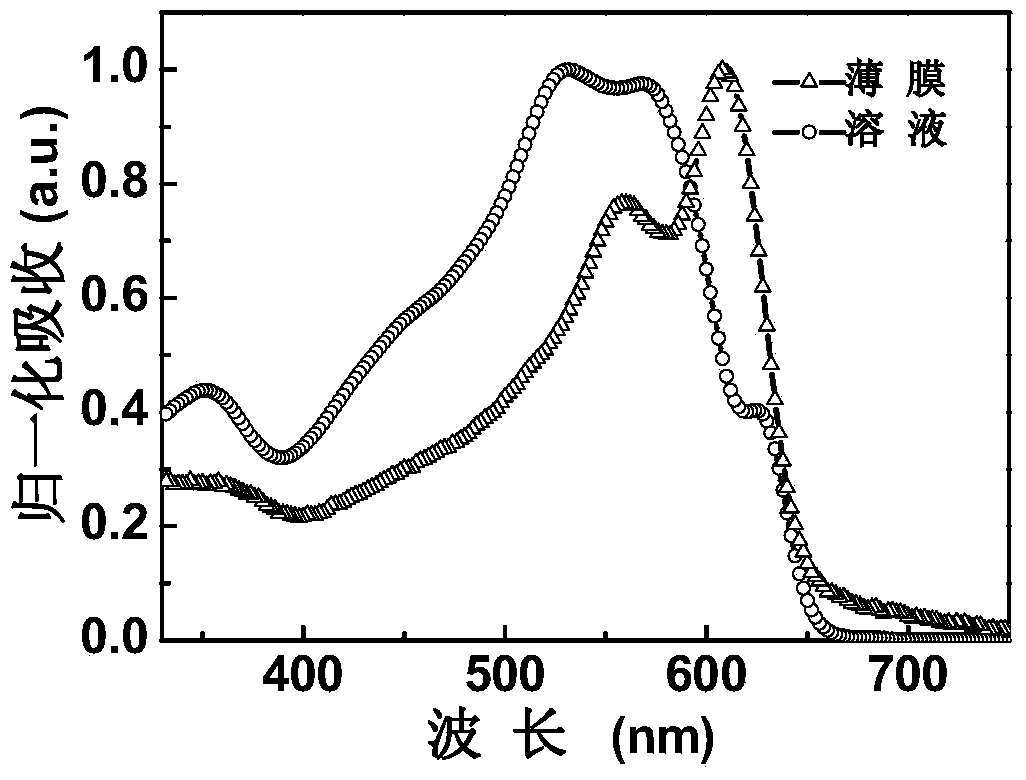
![Preparation method and application for palladium-modified titanium dioxide with three-dimensional flower-like structure exposure [001] crystal face Preparation method and application for palladium-modified titanium dioxide with three-dimensional flower-like structure exposure [001] crystal face](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/b51e76fc-e8b7-4064-8e34-1796a08328ed/HDA0000756349890000011.PNG)
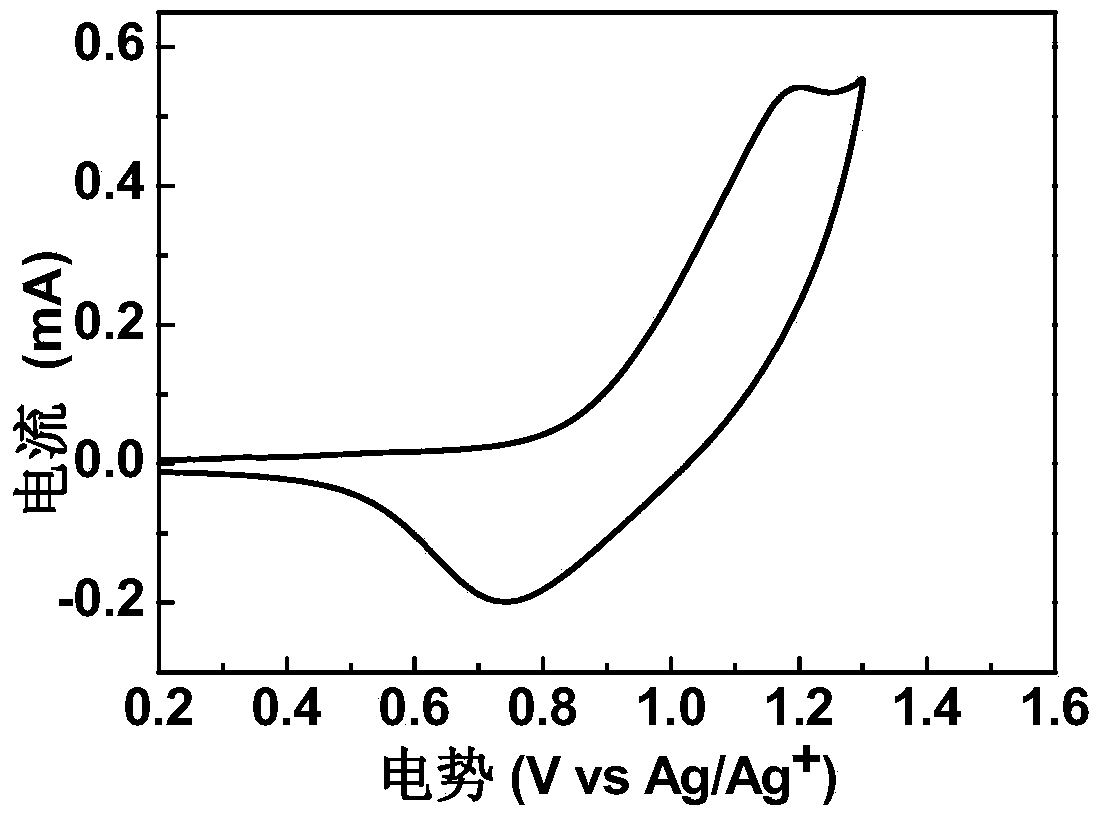
![Preparation method and application for palladium-modified titanium dioxide with three-dimensional flower-like structure exposure [001] crystal face Preparation method and application for palladium-modified titanium dioxide with three-dimensional flower-like structure exposure [001] crystal face](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/b51e76fc-e8b7-4064-8e34-1796a08328ed/HDA0000756349890000012.PNG)
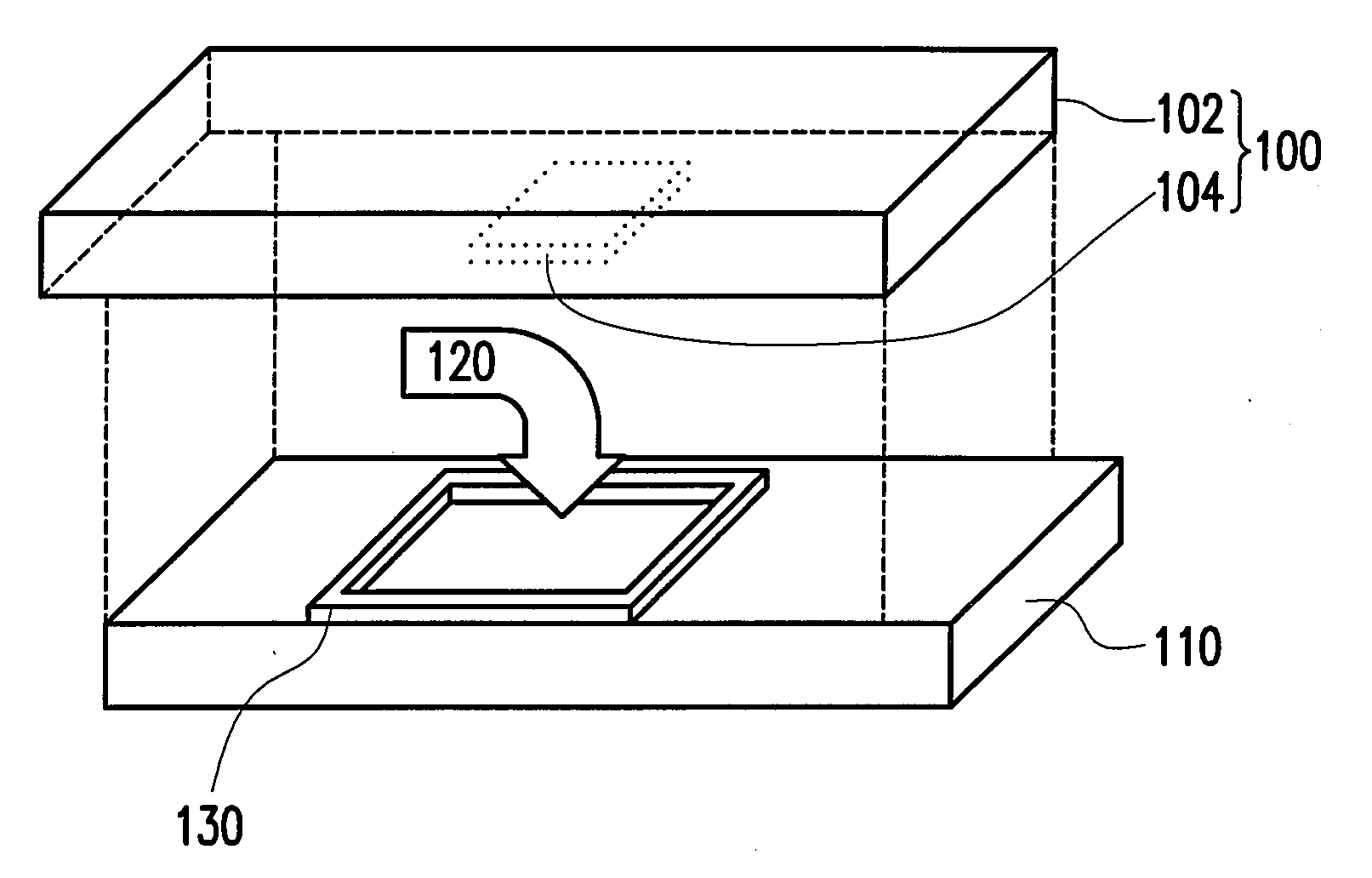
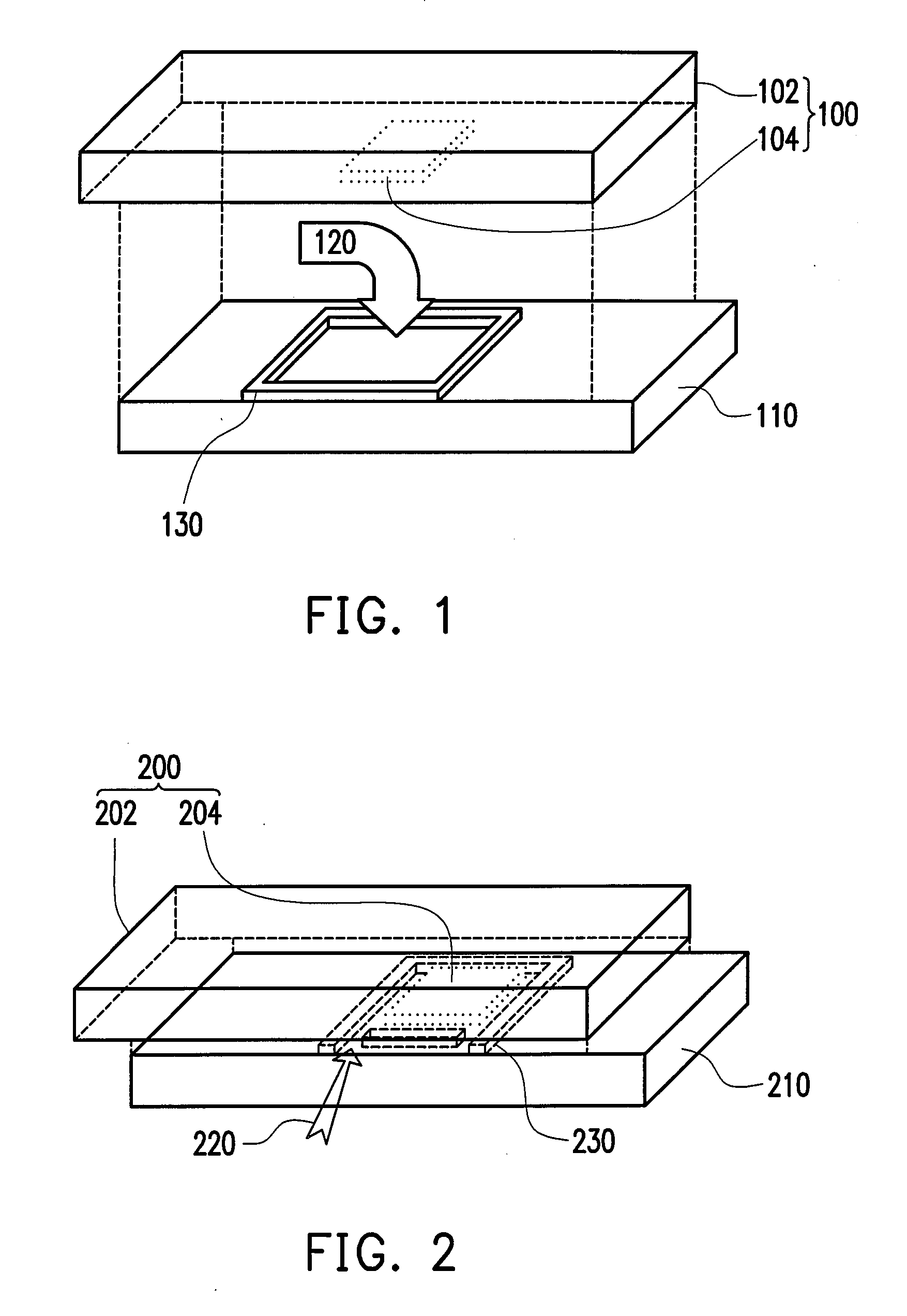
![Preparation method and application for palladium-modified titanium dioxide with three-dimensional flower-like structure exposure [001] crystal face Preparation method and application for palladium-modified titanium dioxide with three-dimensional flower-like structure exposure [001] crystal face](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/b51e76fc-e8b7-4064-8e34-1796a08328ed/HDA0000756349890000021.PNG)