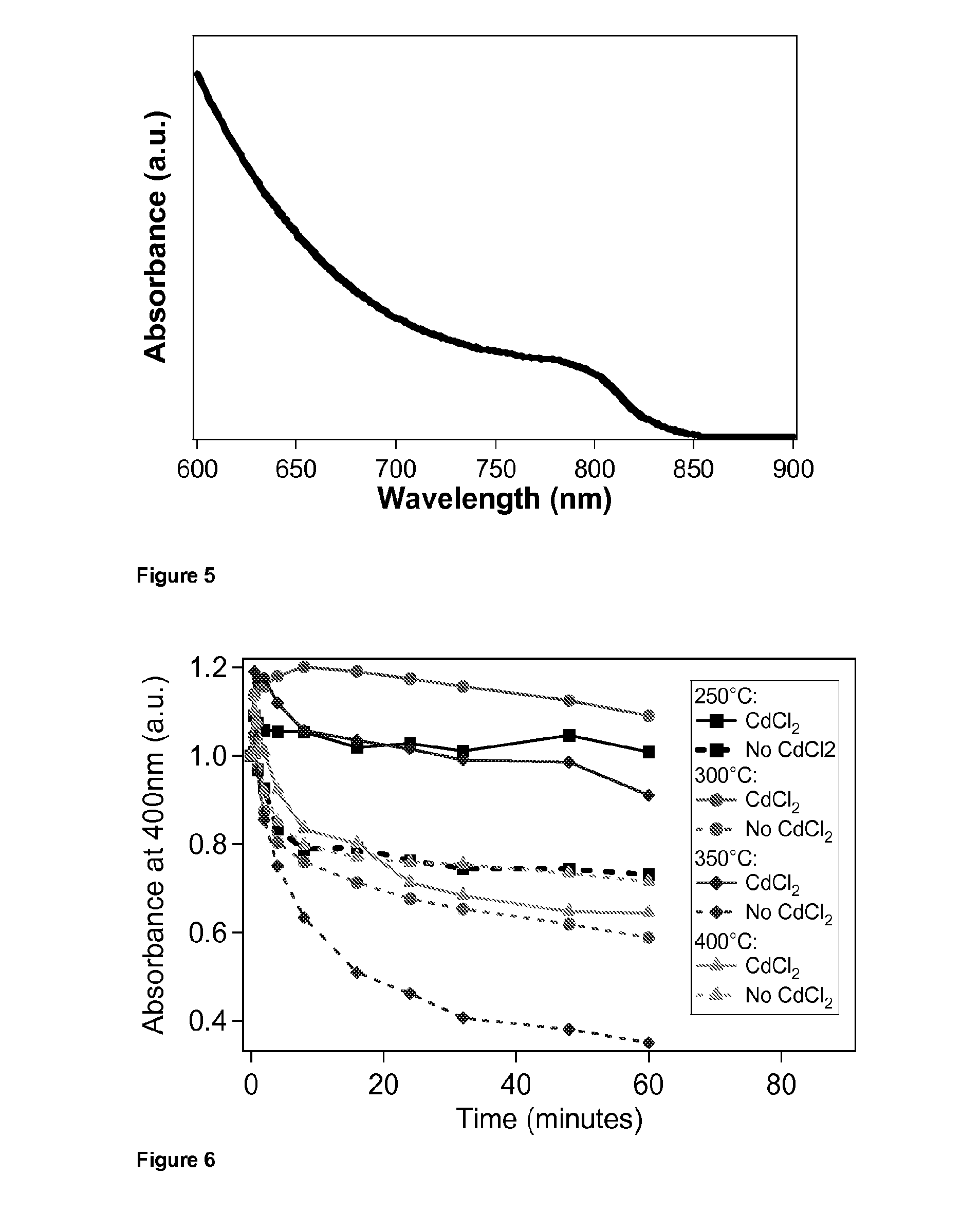
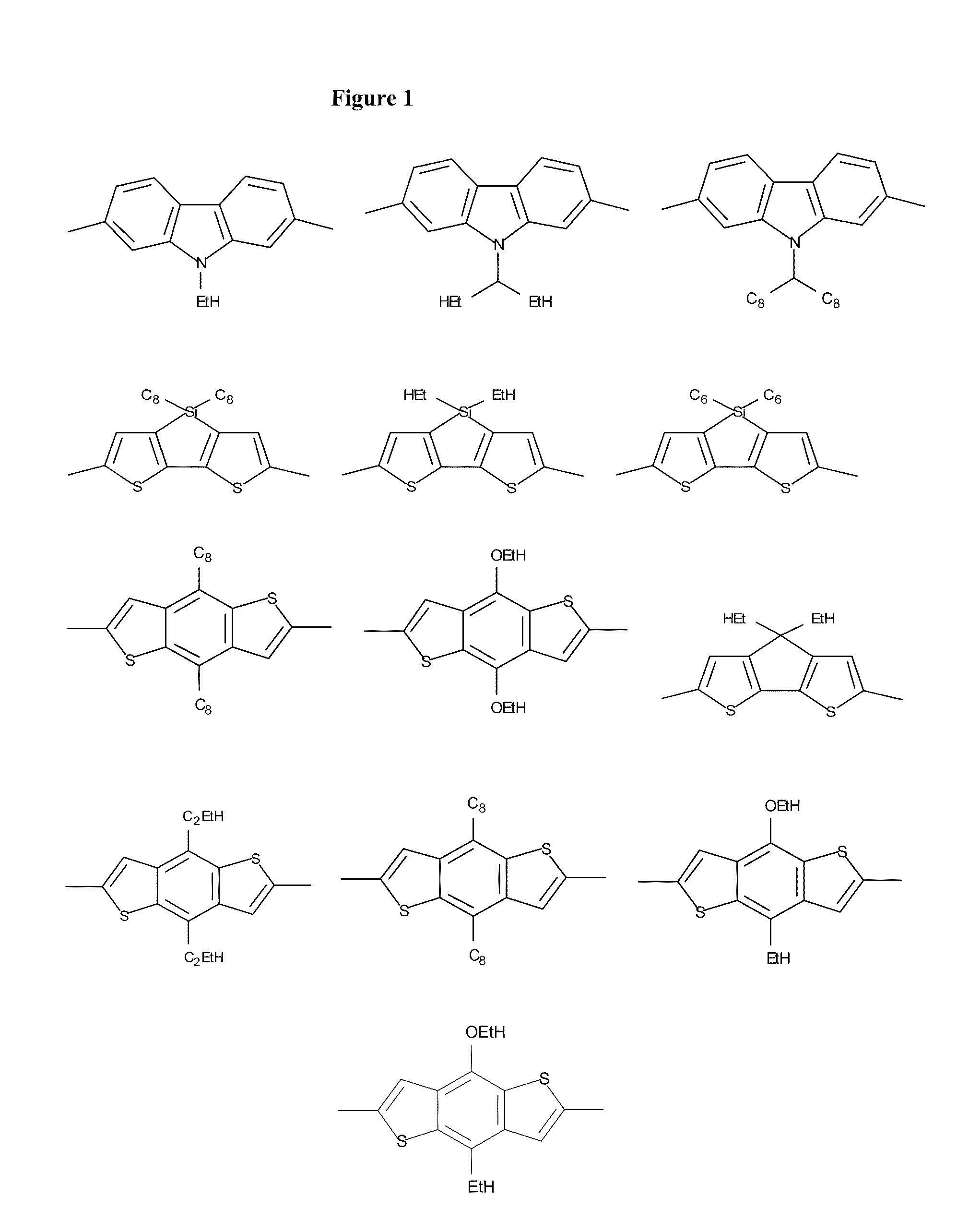
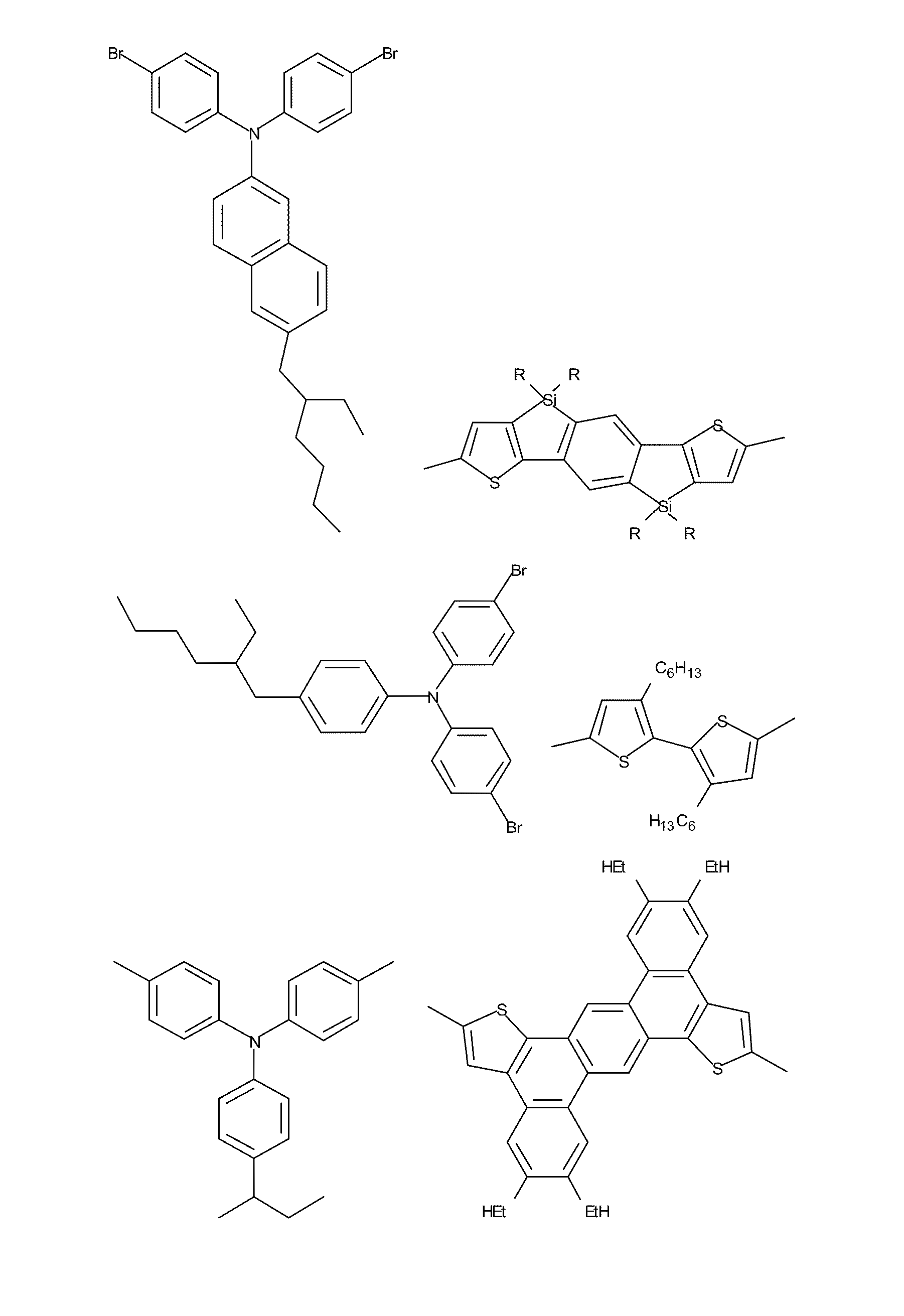
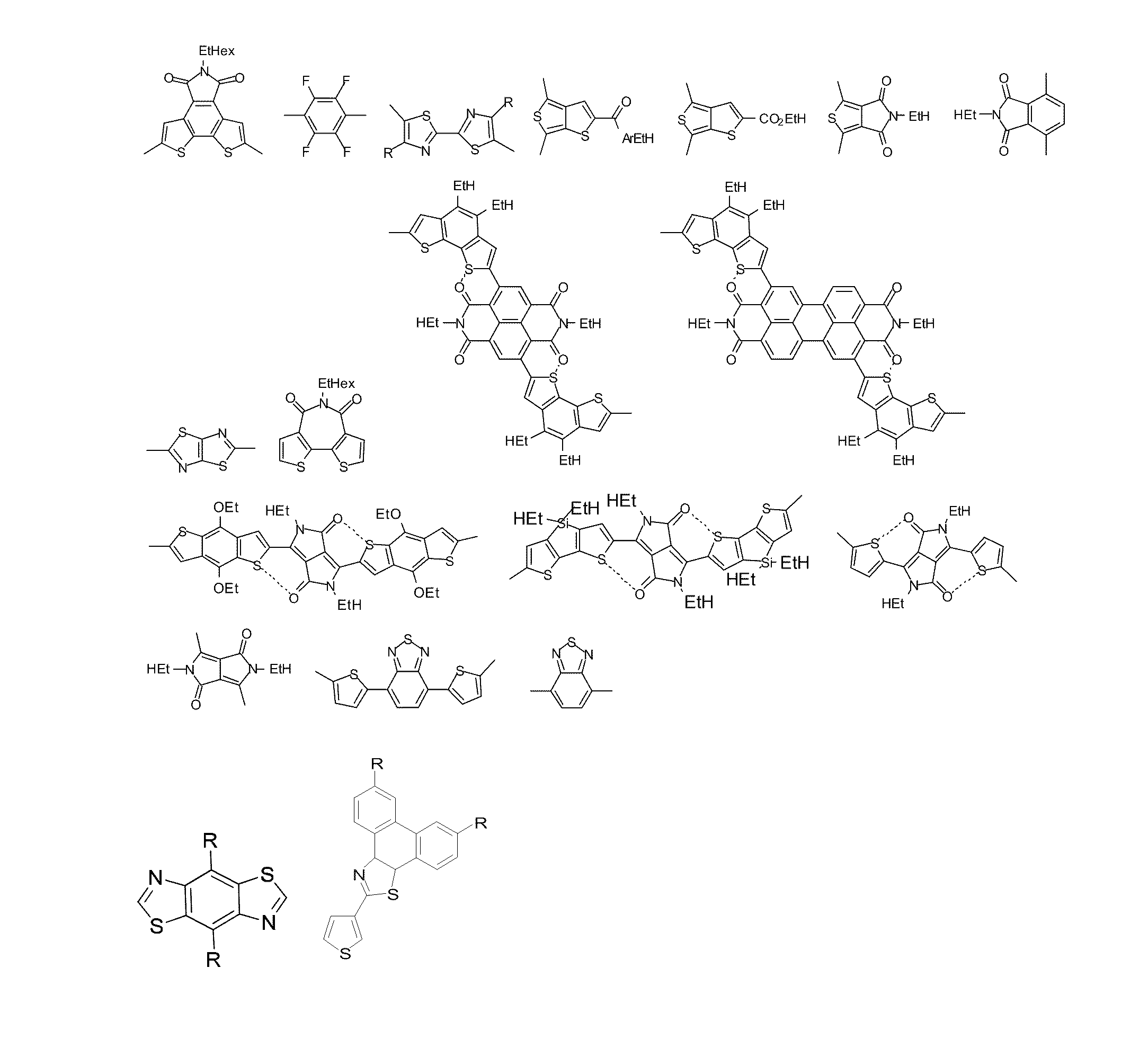Patents
Literature
258results about How to "Increase charge mobility" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
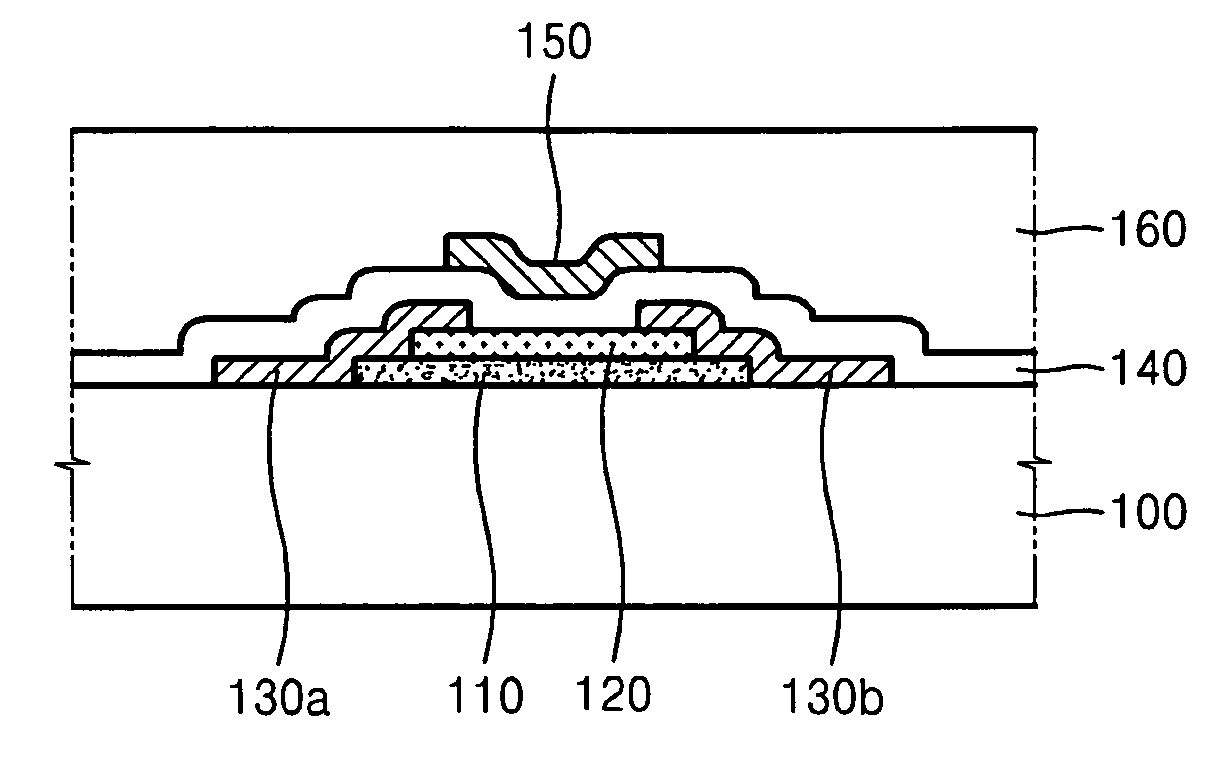
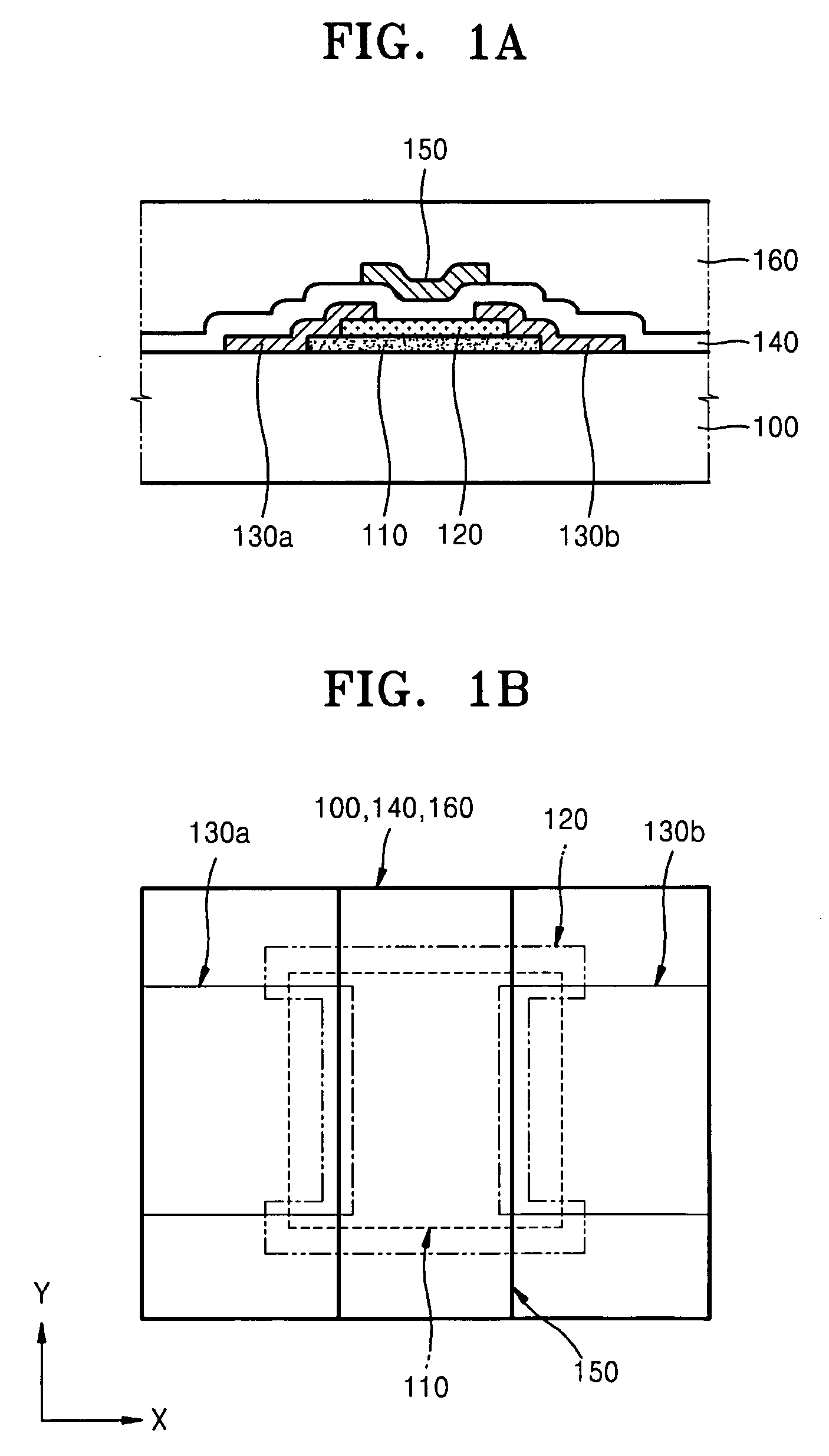
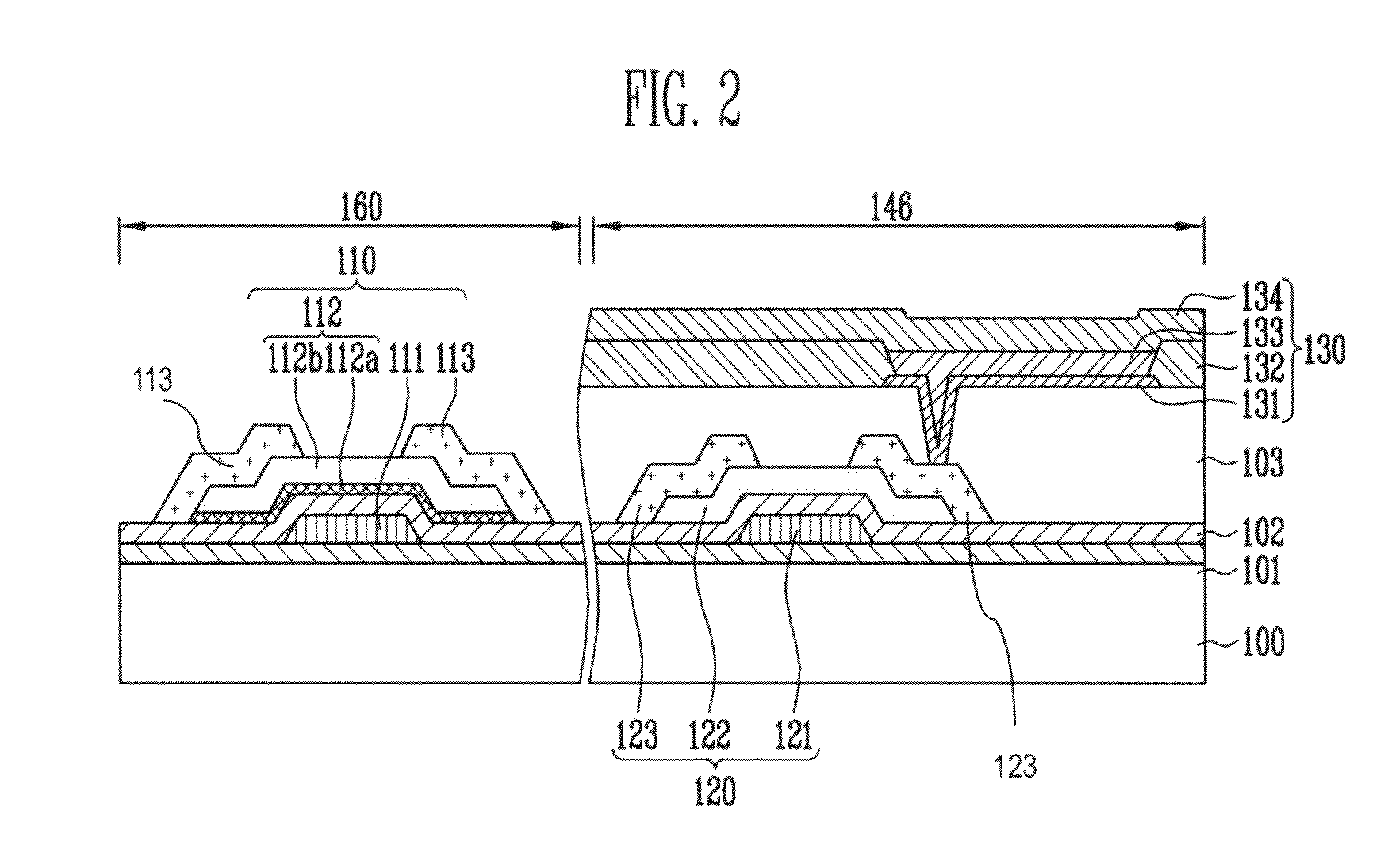
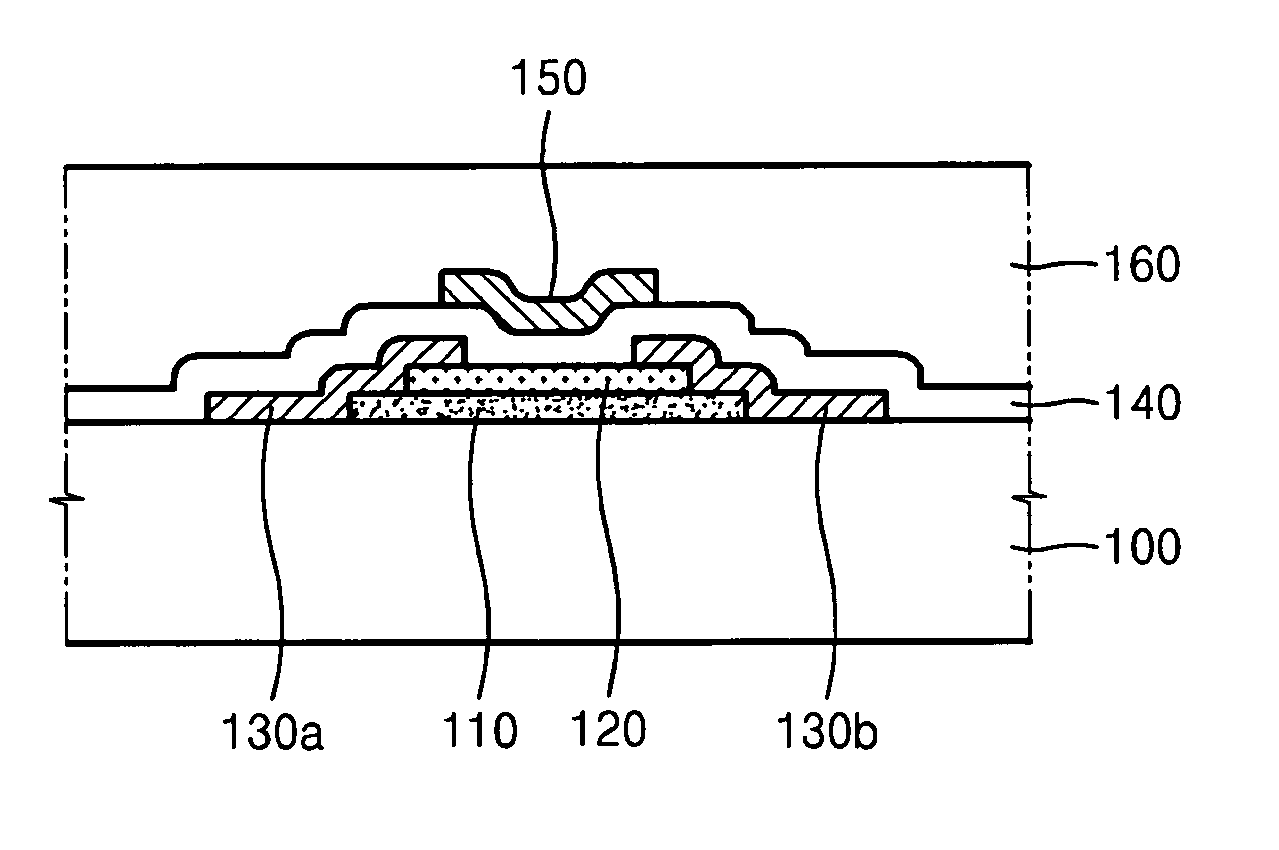
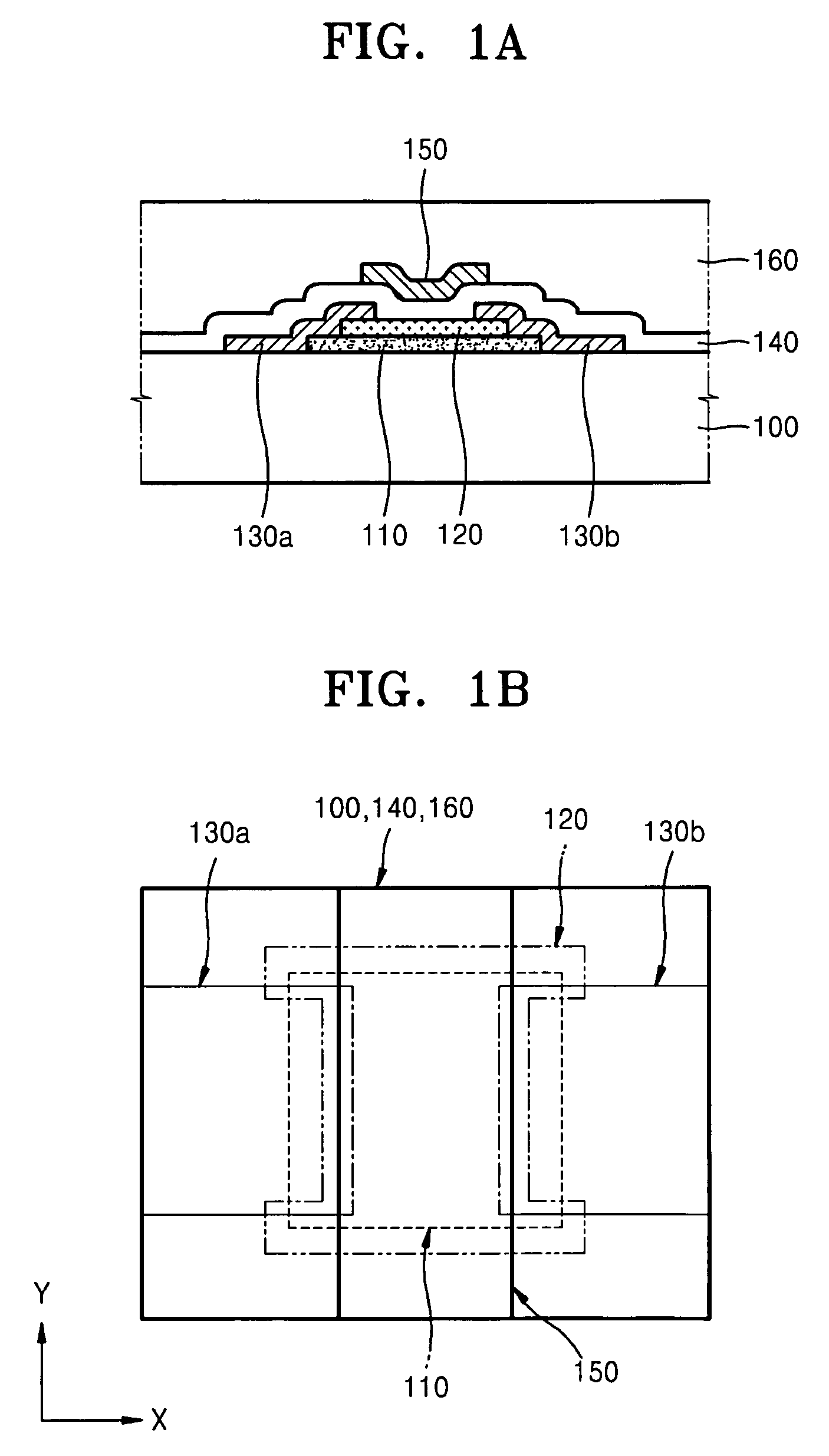
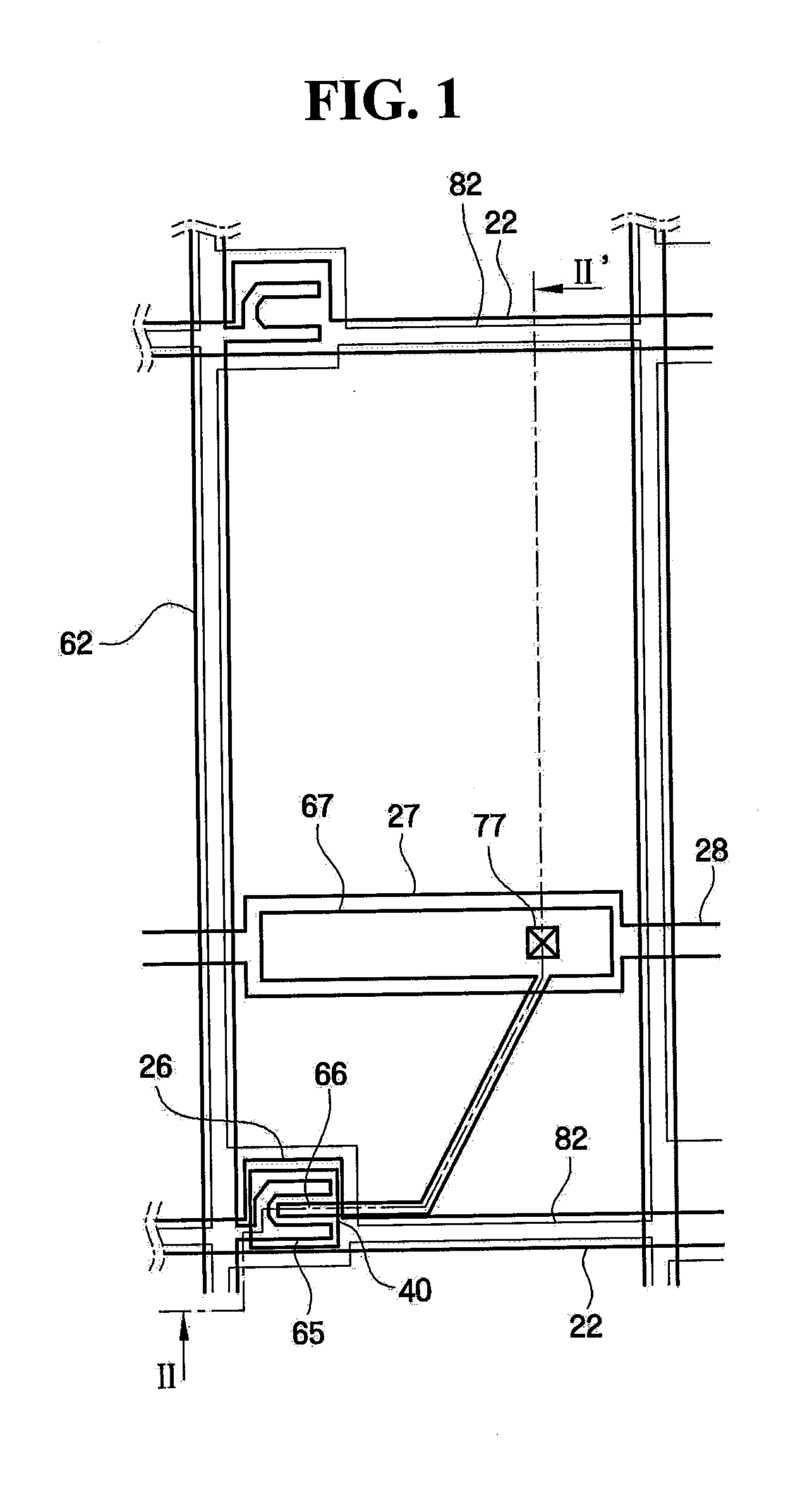
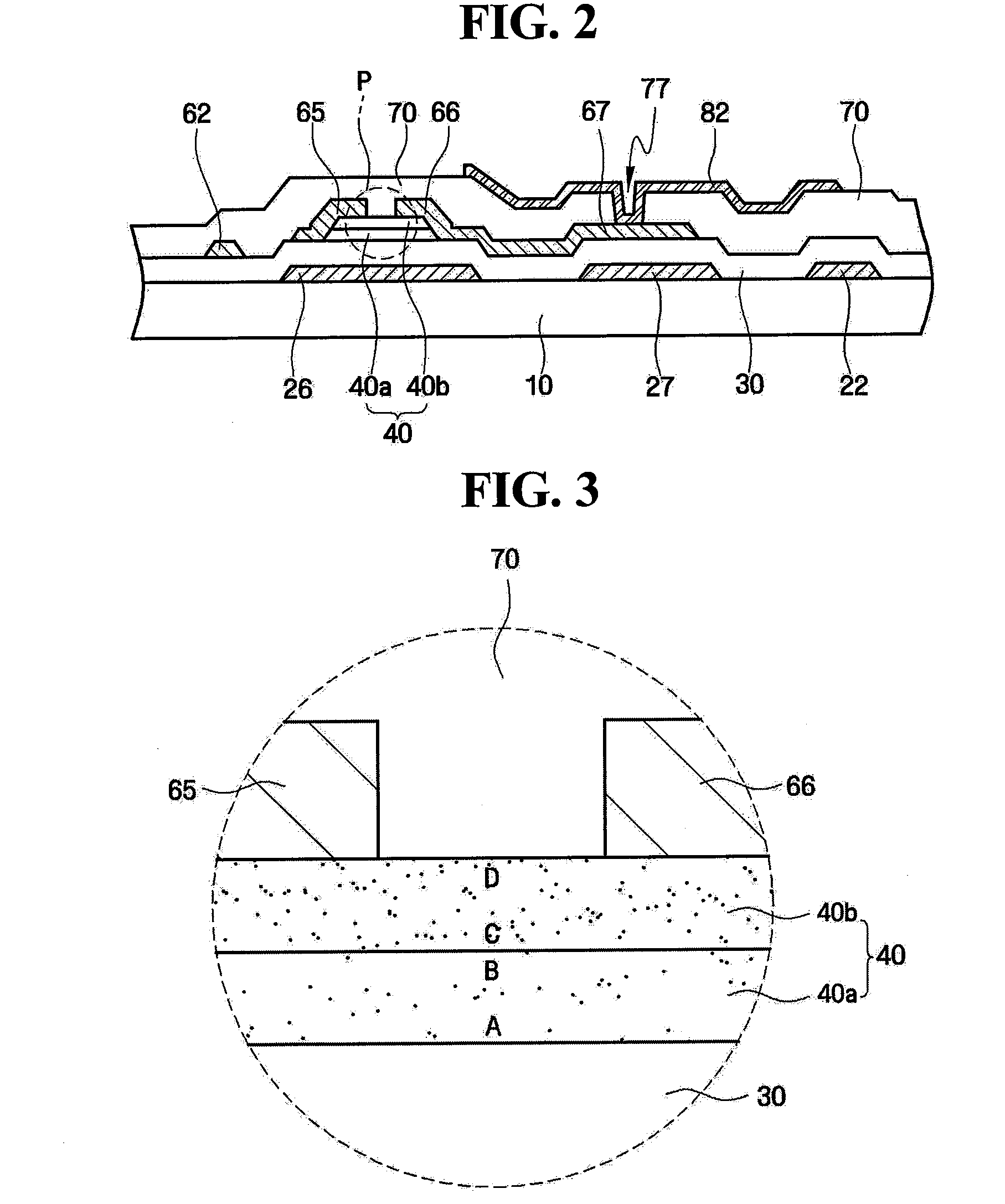
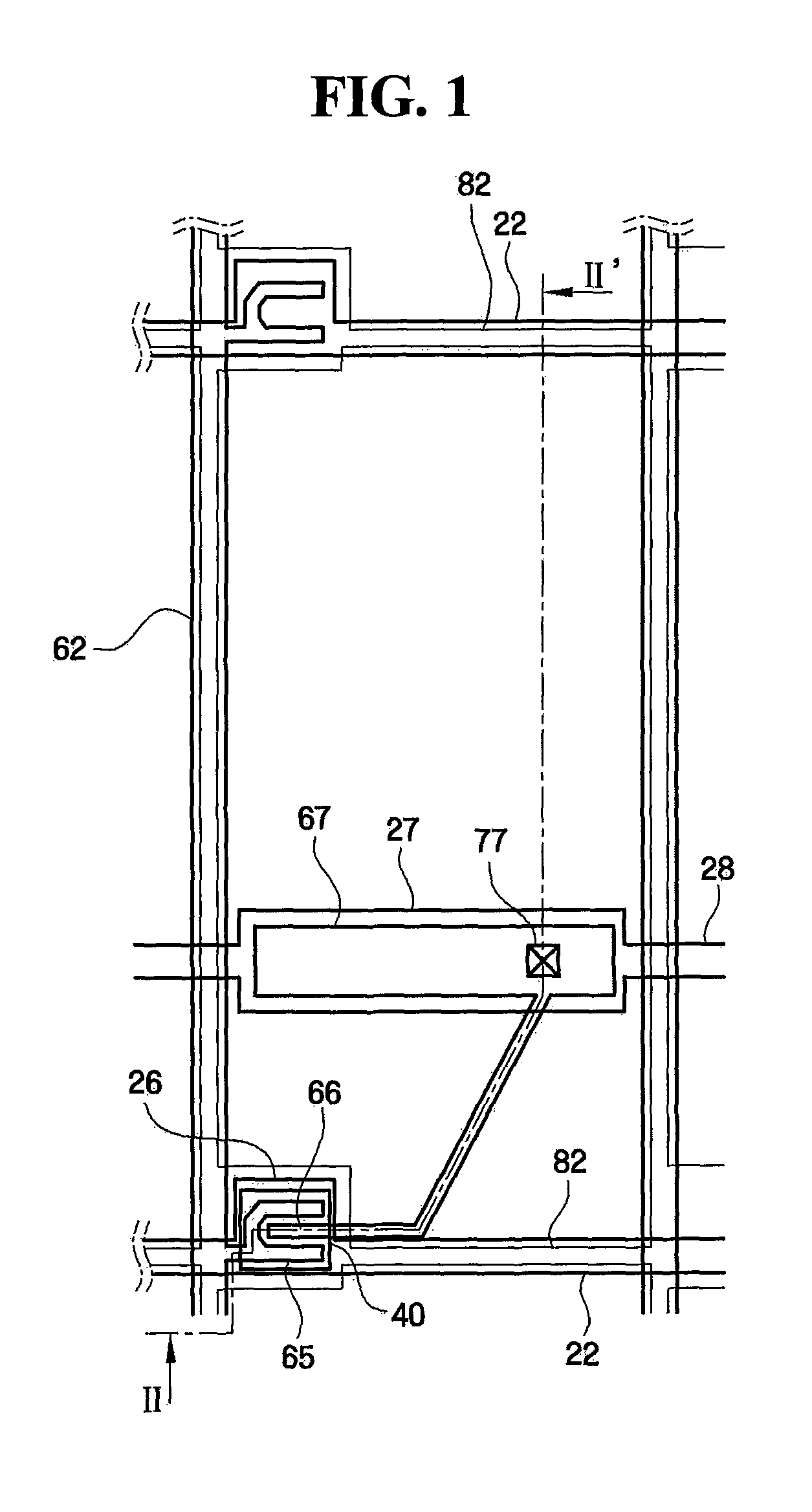
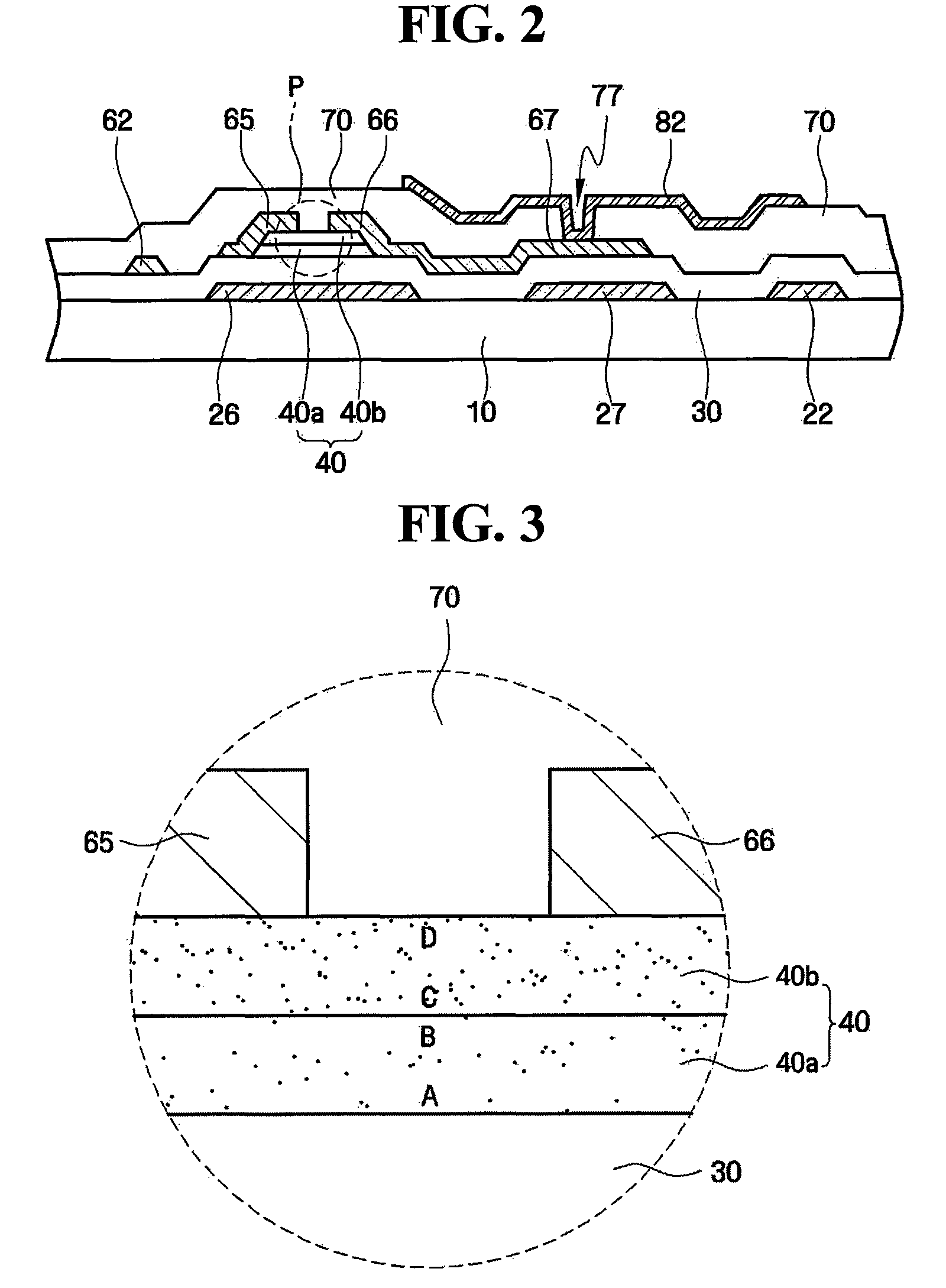
Thin film transistor and method of forming the same
ActiveUS20080197350A1Reduce layeringReduce degradationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
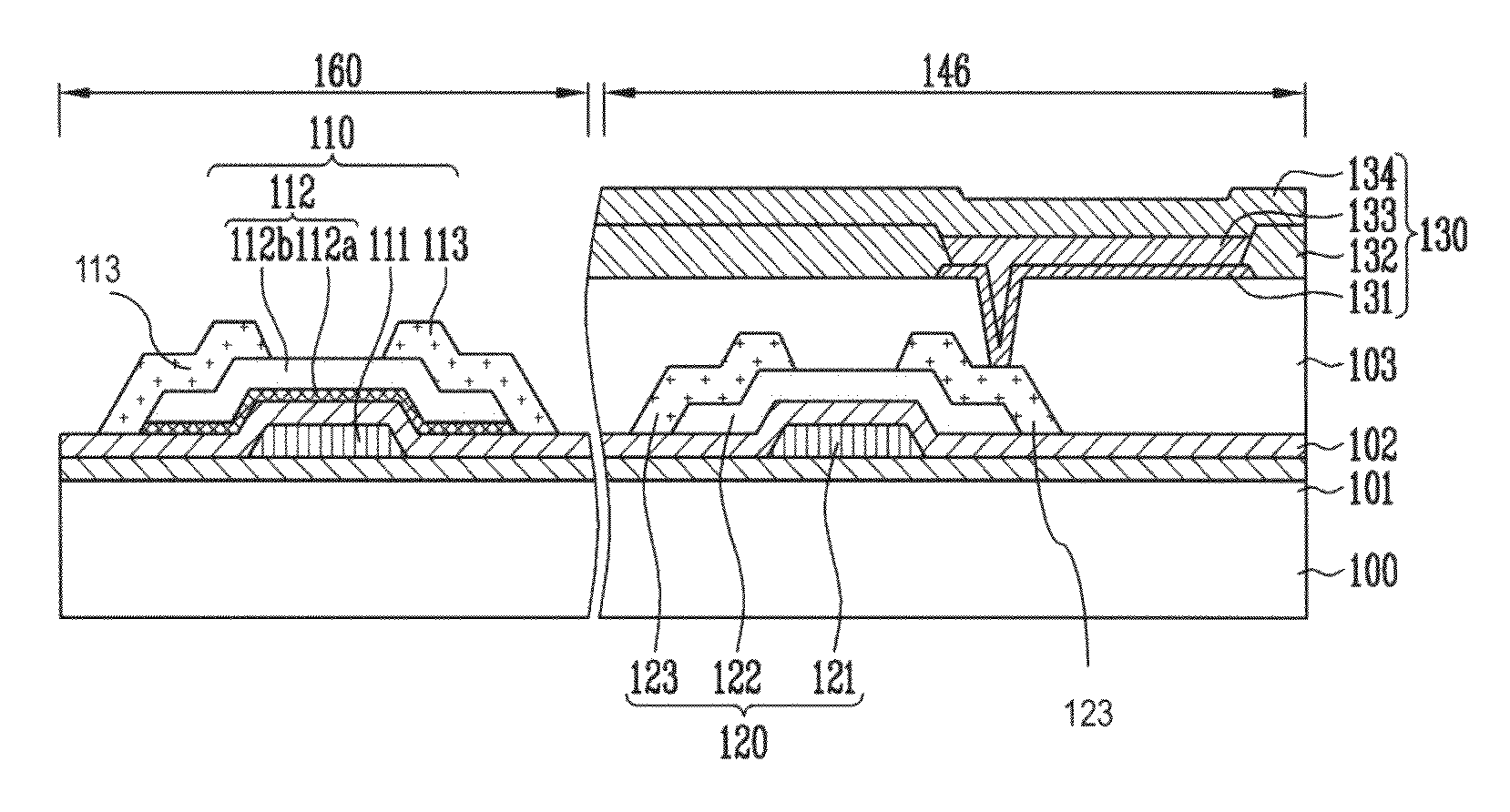
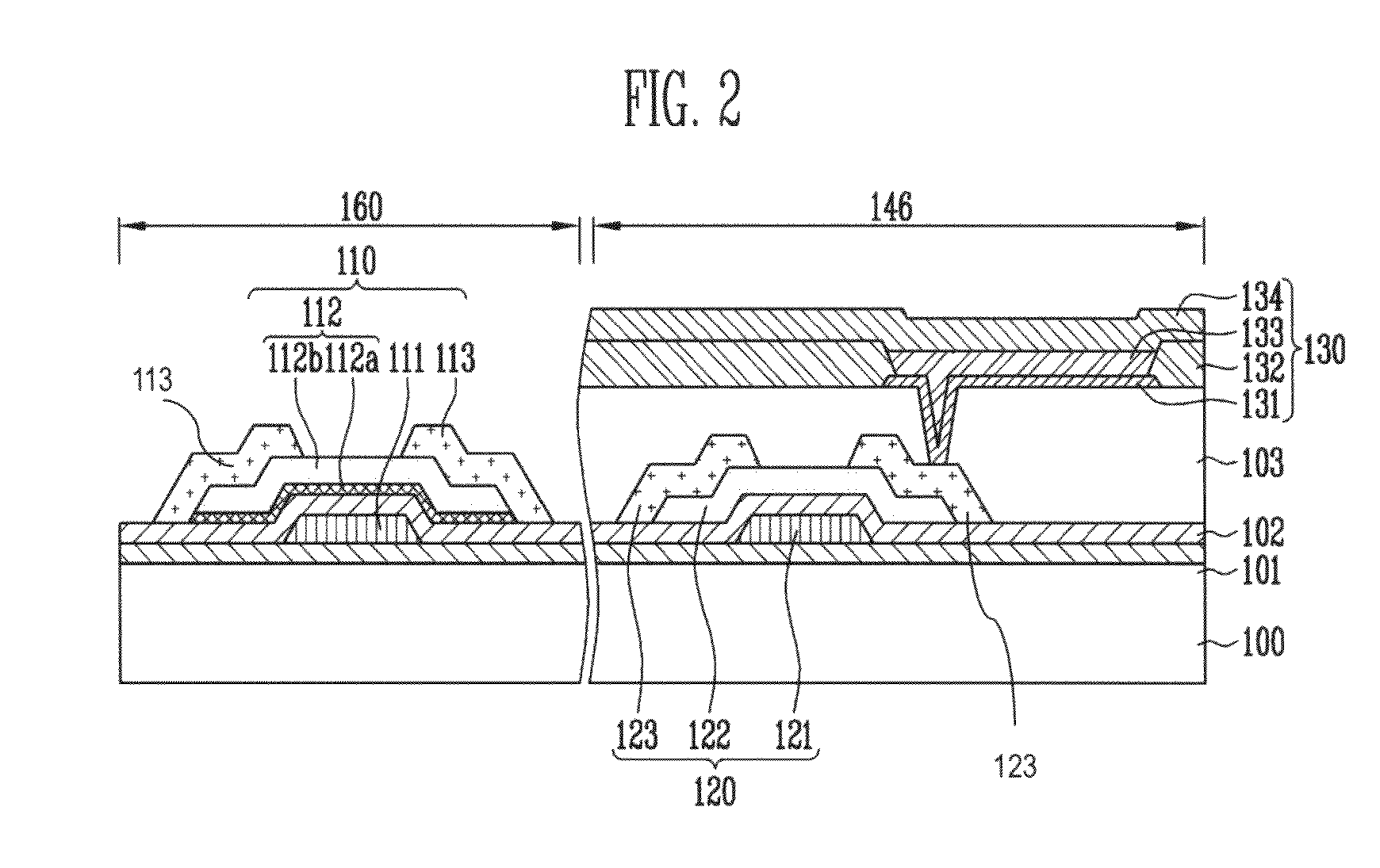
A thin film transistor (TFT) may include a channel layer, a source electrode, a drain electrode, a protective layer, a gate electrode, and / or a gate insulating layer. The channel layer may include an oxide semiconductor material. The source electrode and the drain electrode may face each other on the channel layer. The protective layer may be under the source electrode and the drain electrode and / or may cover the channel layer. The gate electrode may be configured to apply an electric field to the channel layer. The gate insulating layer may be interposed between the gate electrode and the channel layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
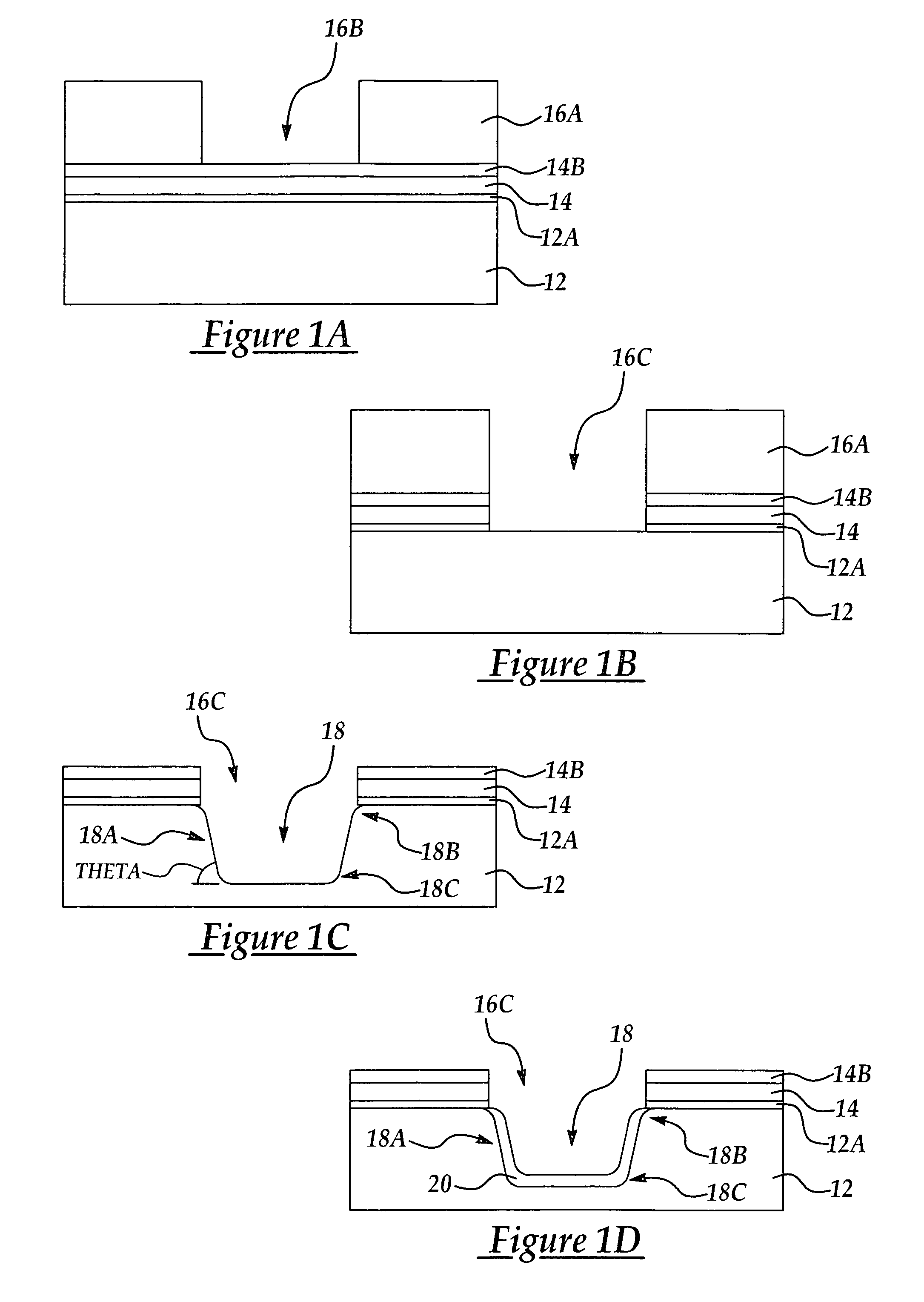
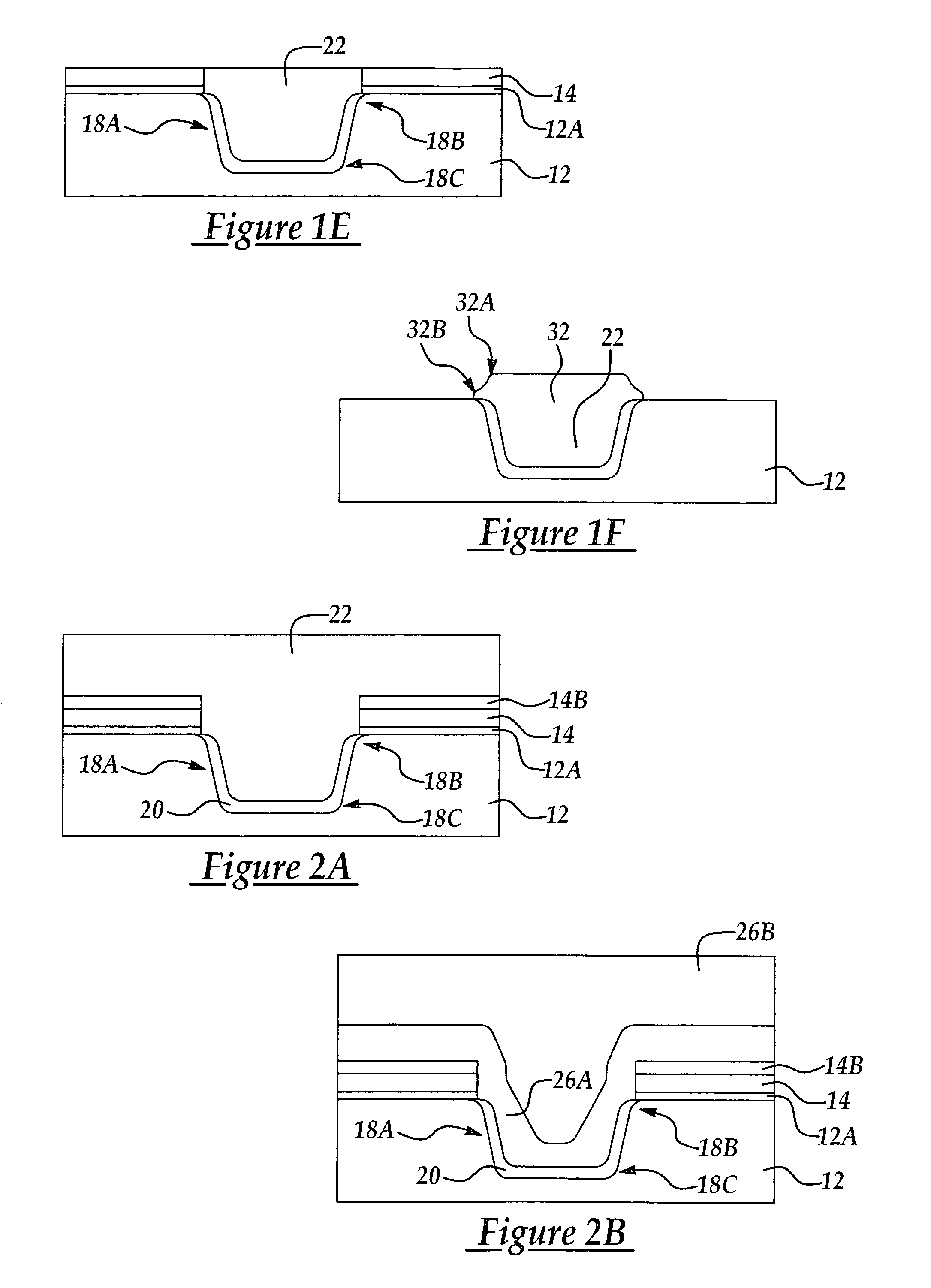
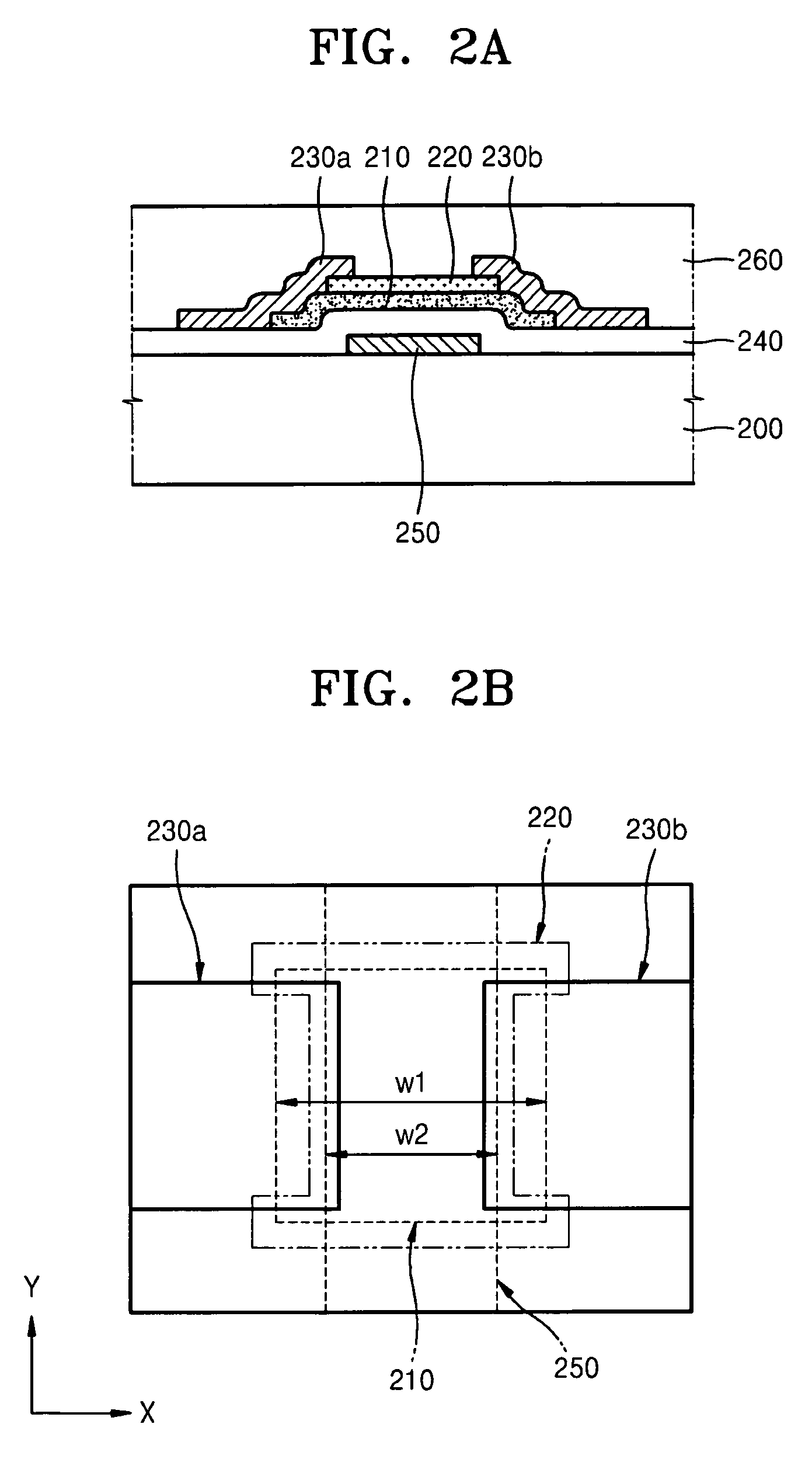
Method of achieving improved STI gap fill with reduced stress
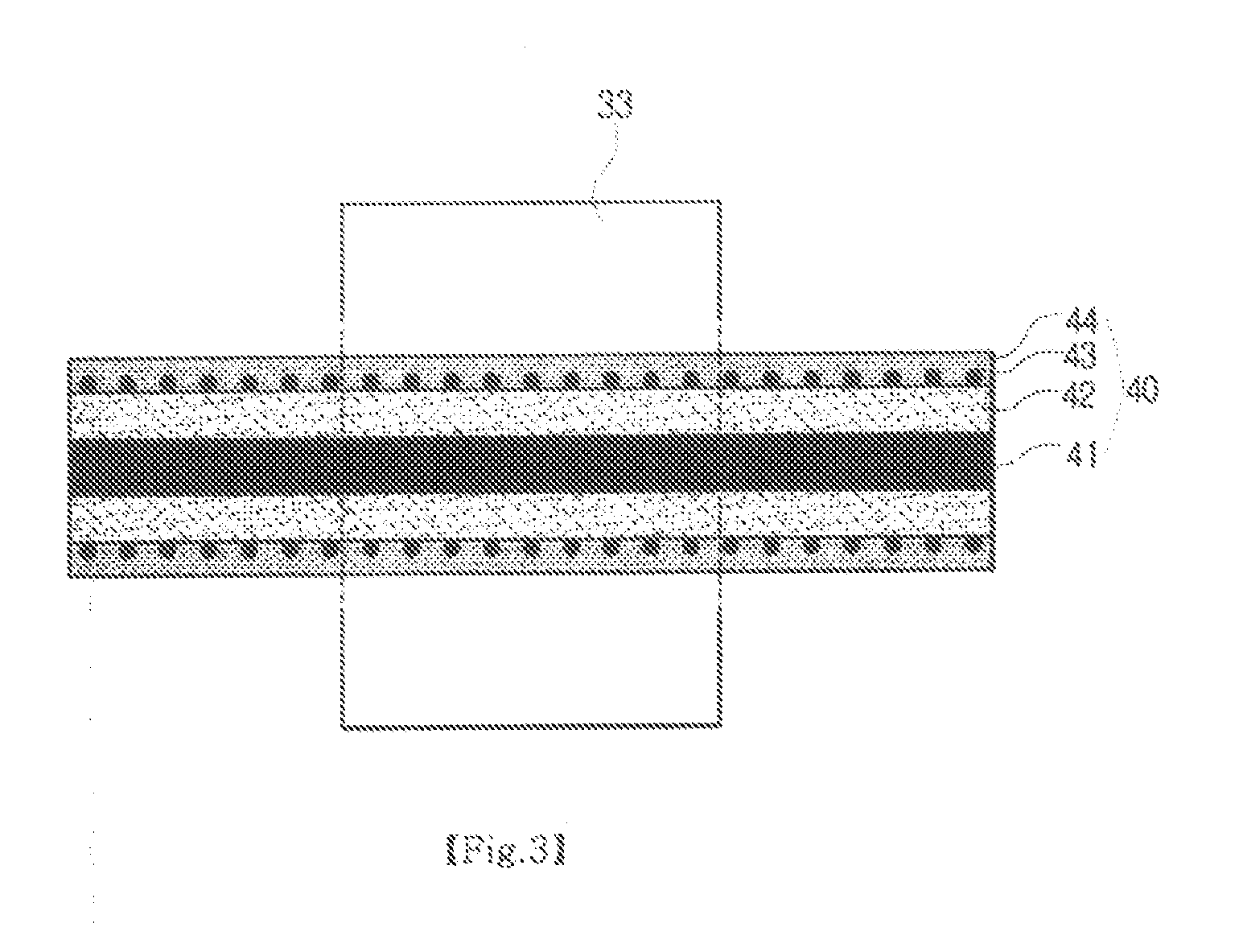
InactiveUS7118987B2Relieve pressureIncrease charge mobilityStentsBalloon catheterEngineeringSilicon dioxide
A shallow trench isolation (STI) structure and method of forming the same with reduced stress to improve charge mobility the method including providing a semiconductor substrate comprising at least one patterned hardmask layer overlying the semiconductor substrate; dry etching a trench in the semiconductor substrate according to the at least one patterned hardmask layer; forming one or more liner layers to line the trench selected from the group consisting of silicon dioxide, silicon nitride, and silicon oxynitride; forming one or more layers of trench filling material comprising silicon dioxide to backfill the trench; carrying out at least one thermal annealing step to relax accumulated stress in the trench filling material; carrying out at least one of a CMP and dry etch process to remove excess trench filling material above the trench level; and, removing the at least one patterned hardmask layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
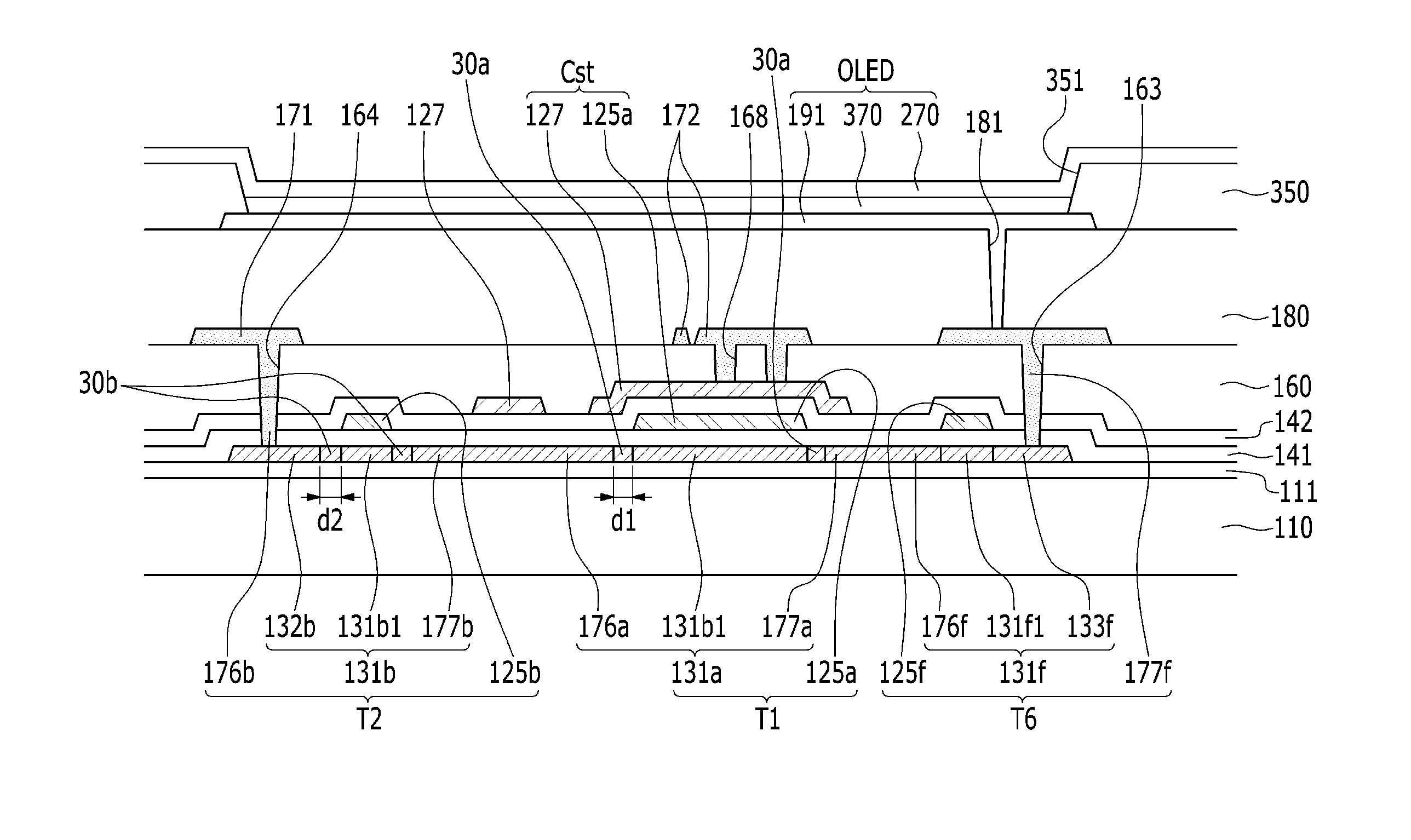
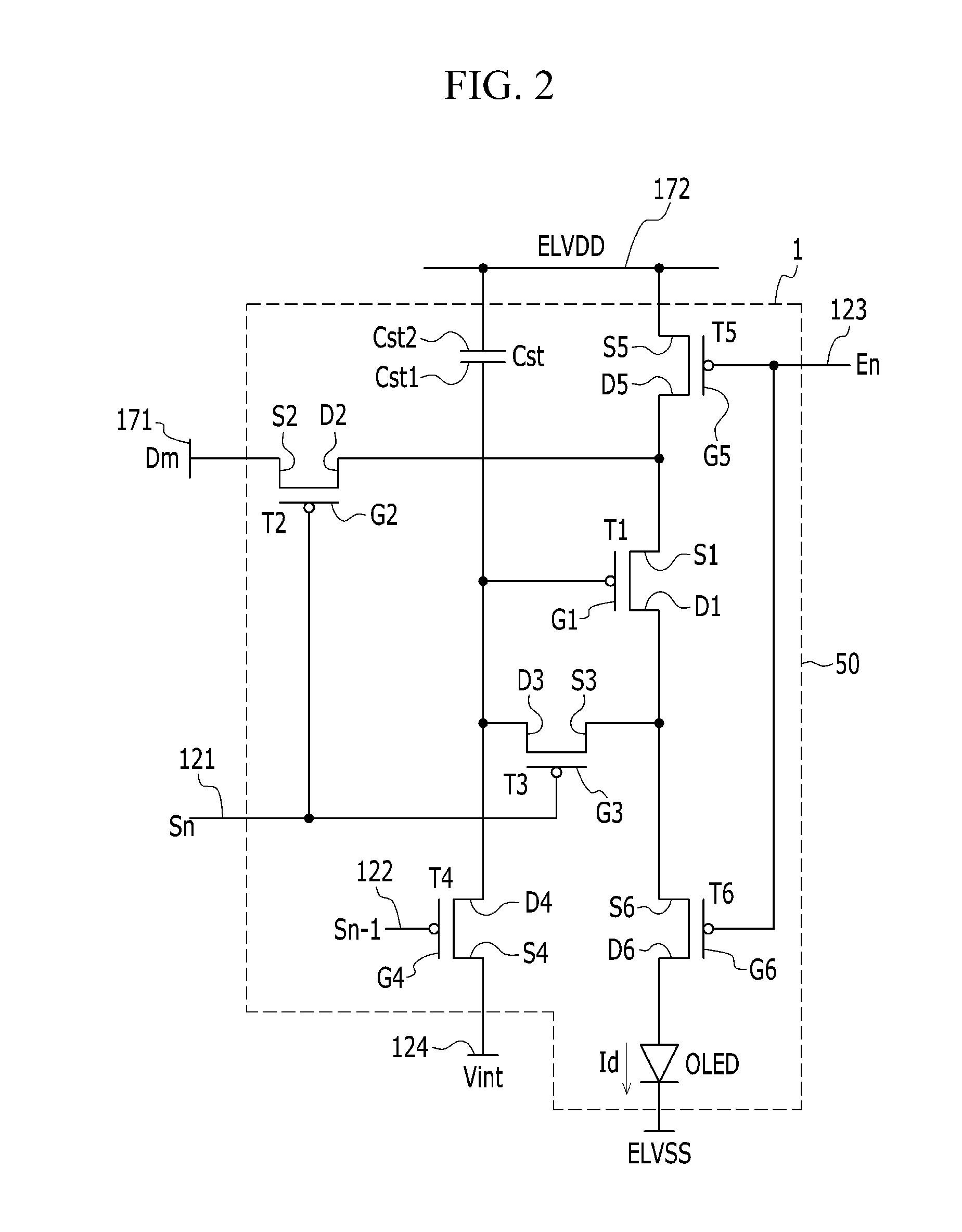
Organic light emitting display device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100176383A1High carrier concentrationStable and uniform functional propertyElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceLight-emitting diode
Disclosed is an organic light emitting display device and a method of manufacturing the same. The organic light emitting display device includes the thin film transistor of the drive unit that has the activation layer formed in a structure where the first oxide semiconductor layer and the second oxide semiconductor layer are stacked, the thin film transistor of the pixel unit that has the activation layer formed of the second oxide semiconductor layer, and the organic light emitting diode coupled to the thin film transistor of the pixel unit. The thin film transistor of the drive unit has channel formed on the first oxide semiconductor layer having a higher carrier concentration than the second oxide semiconductor layer, having a high charge mobility, and the thin film transistor of the pixel unit has a channel formed on the second oxide semiconductor layer, having a stable and uniform functional property.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
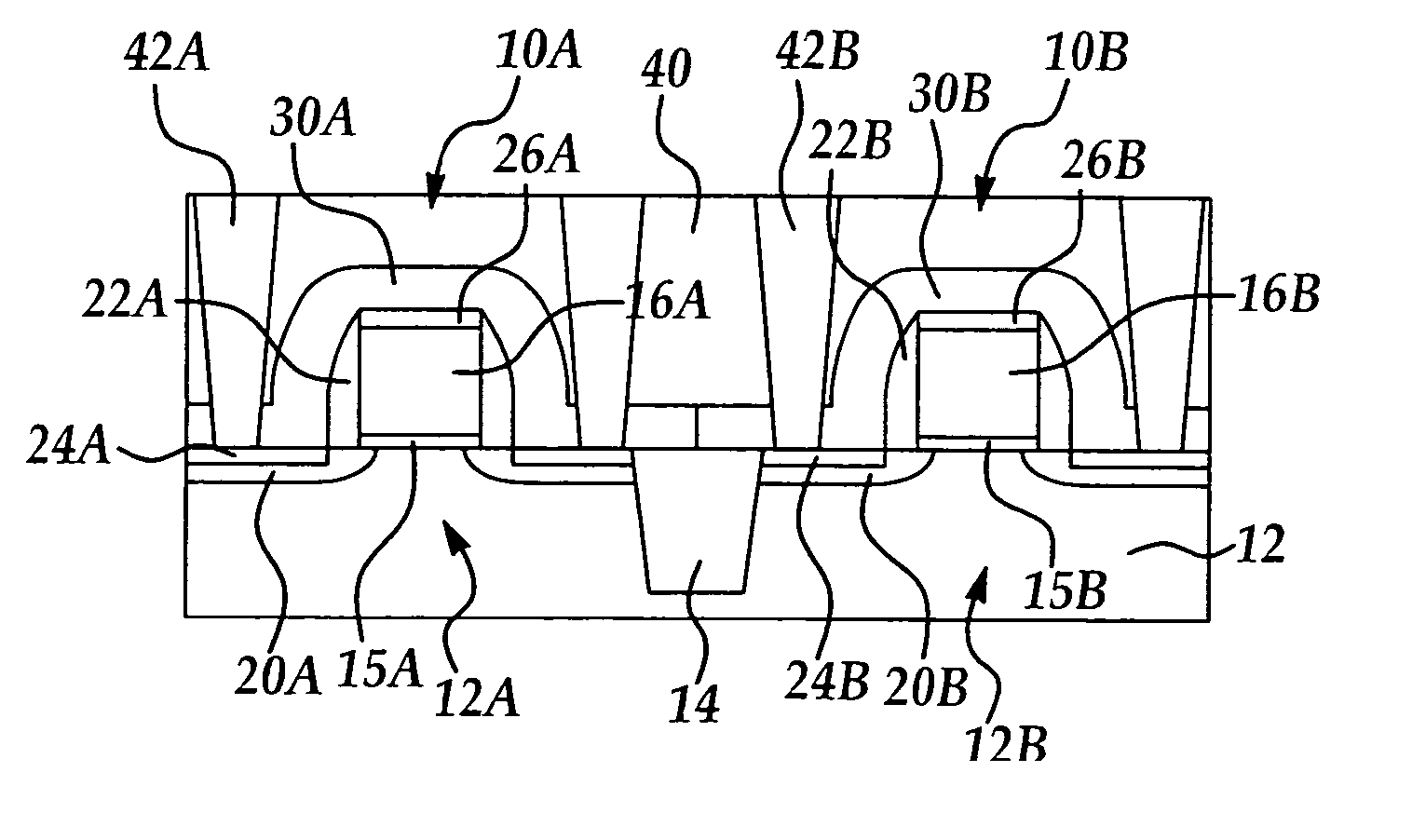
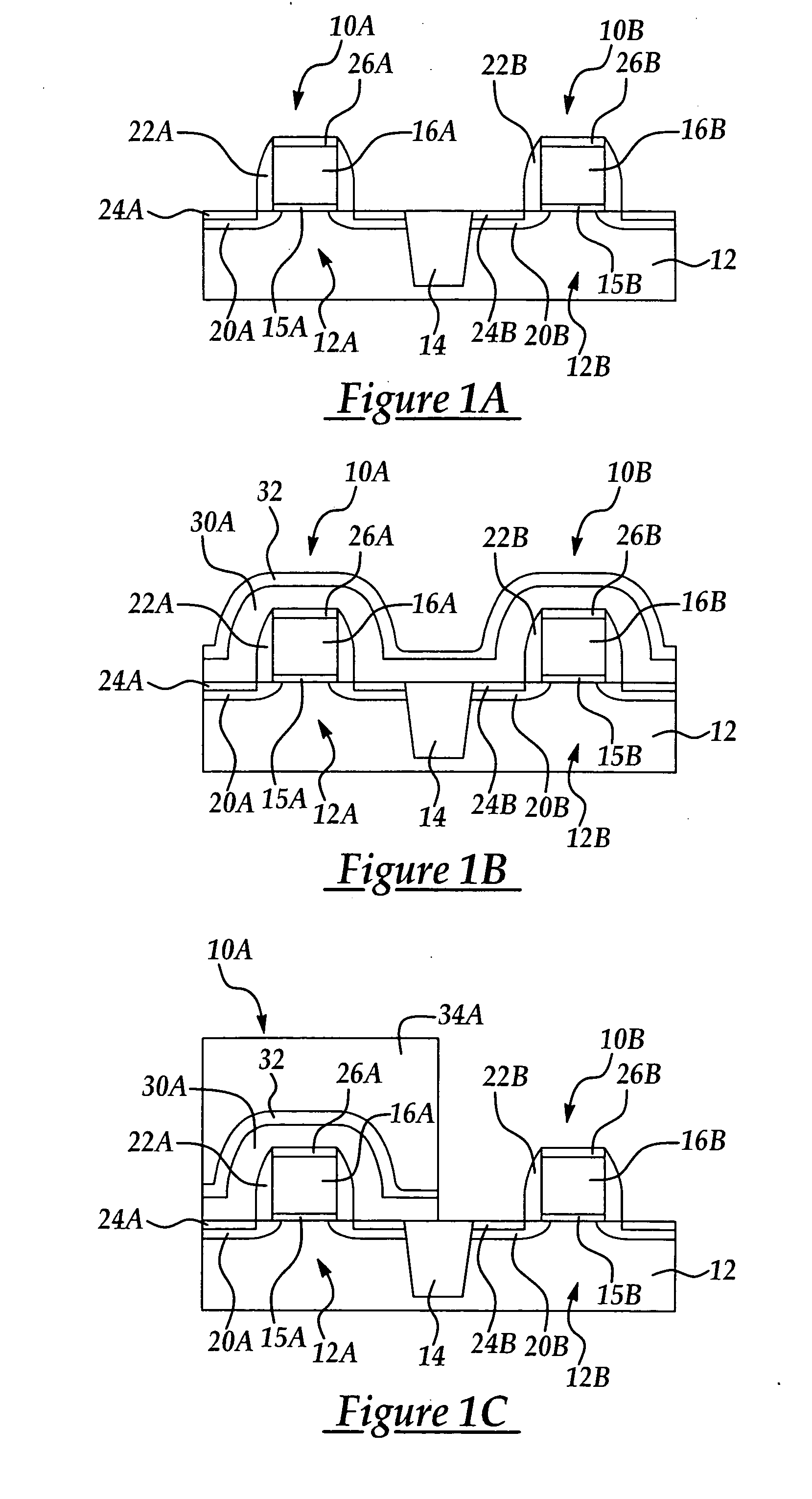
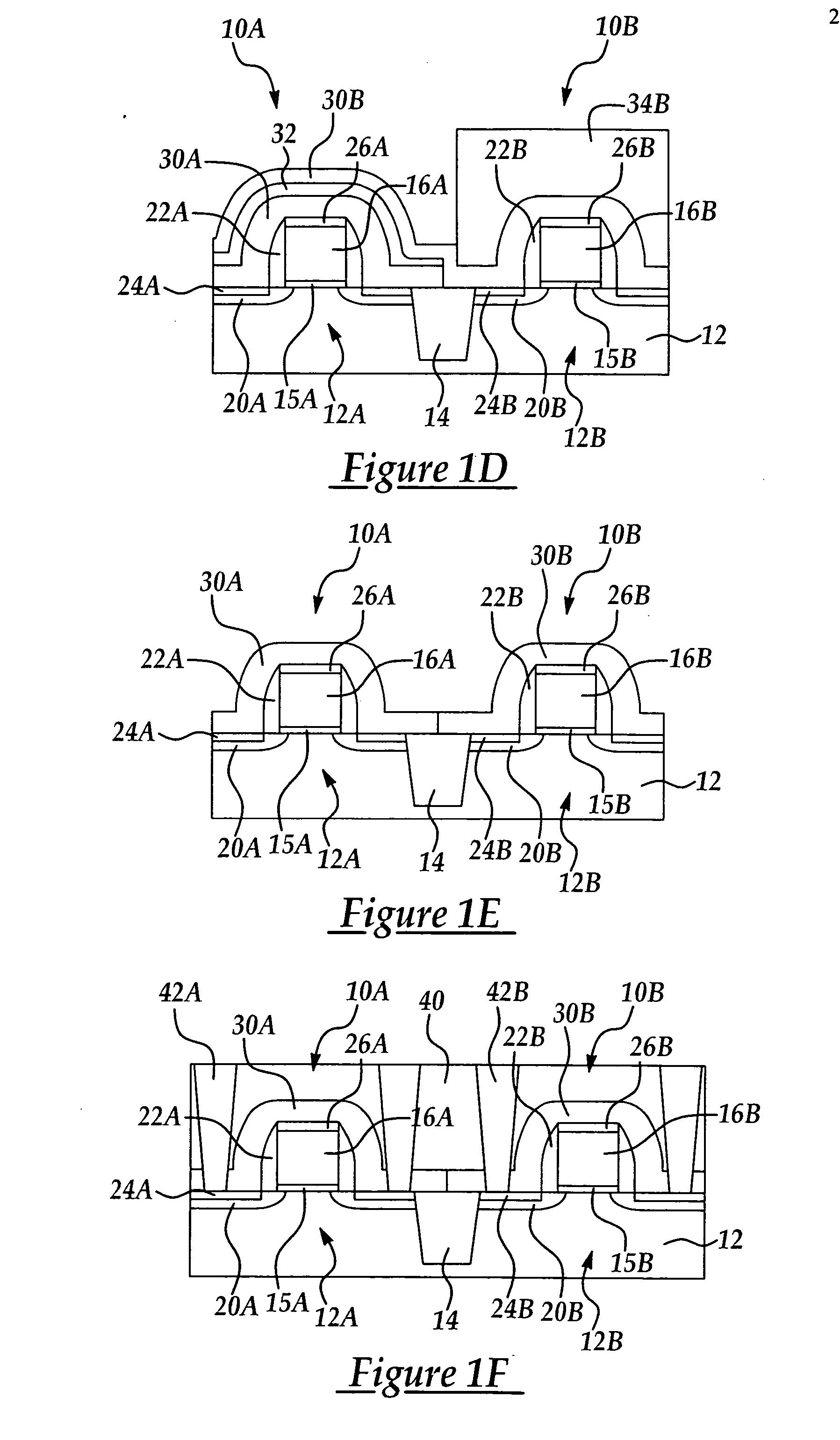
Local stress control for CMOS performance enhancement
InactiveUS20050214998A1Increase charge mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCMOSPerformance enhancement
A semiconductor device and method for forming the same for improving charge mobility in NMOS and PMOS devices simultaneously, the method including forming a first dielectric layer including a stress type selected from the group consisting of tensile stress and compressive stress over the respective PMOS and NMOS device regions; removing a portion of the first dielectric layer overlying one of the PMOS and NMOS device regions; forming a second dielectric layer including a stress type opposite from the first dielectric layer stress type over the respective PMOS and NMOS device regions; and, removing a portion of the second dielectric layer overlying one of the PMOS and NMOS device regions having an underlying first dielectric layer to form a compressive stress dielectric layer over the PMOS device region and a tensile stress dielectric layer over the NMOS device region.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
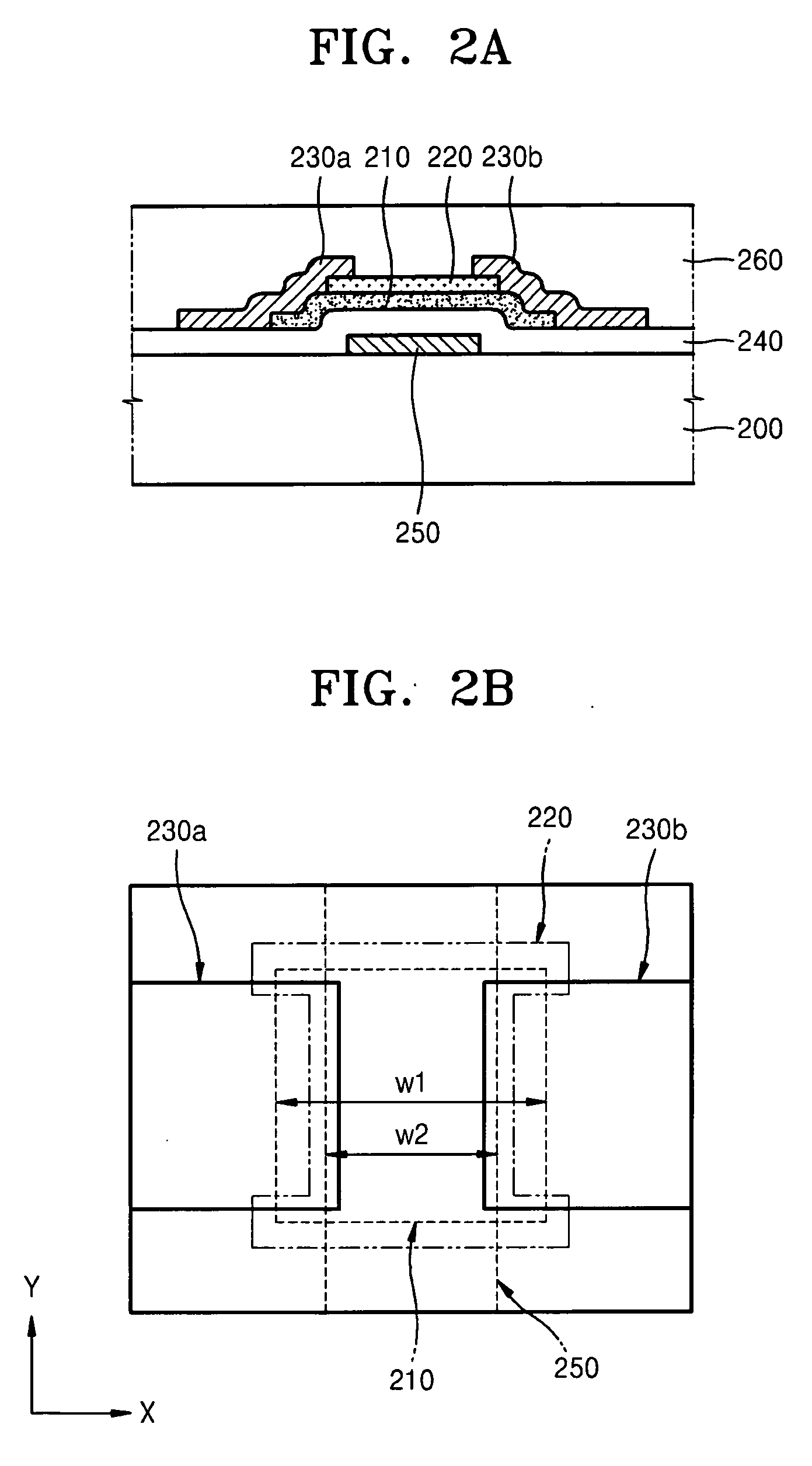
Thin film transistor and method of forming the same
ActiveUS7910920B2Reduce layeringReduce degradationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Polymers with low band gaps and high charge mobility
InactiveUS20070020526A1Increase currentImprove efficiencyNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesSystems approachesPolymer
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Polymers with low band gaps and high charge mobility
ActiveUS20070014939A1Increase currentImprove efficiencyNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesPolymerChemistry
Owner:RAYNERGY TEK INC
Organic thin film transistor comprising multi-layered gate insulator
ActiveUS20050001210A1Increase charge mobilityReduce driveTransistorMaterial nanotechnologyGate insulatorOptoelectronics
An organic thin film transistor (OTFT) comprising a gate electrode, a gate insulating film, an organic active layer and a source / drain electrode, or a gate electrode, a gate insulating film, a source / drain electrode and an organic active layer, sequentially formed on a substrate, wherein the gate insulating film is a multi-layered insulator comprising a first layer of a high dielectric material and a second layer of an insulating organic polymer compatible with the organic active layer, the second layer being positioned directly under the organic active layer. The OTFT of the present invention shows low threshold and driving voltages, high charge mobility, and high Ion / Ioff, and it can be prepared by a wet process.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Polymers with low band gaps and high charge mobility
InactiveUS20070017571A1Increase currentImprove efficiencyNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesSystems approachesPolymer
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
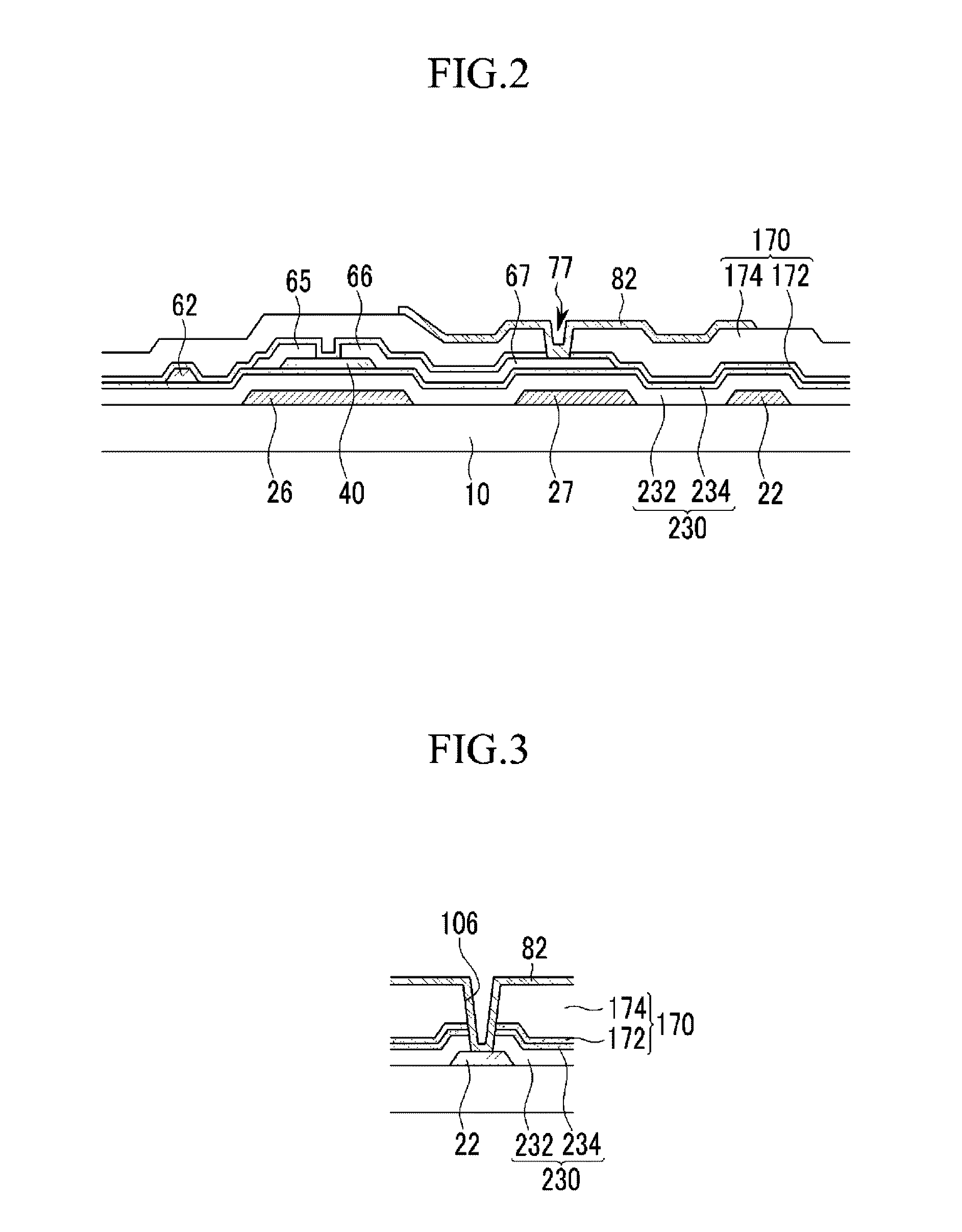
Thin film transistor display panel and manufacturing method of the same
ActiveUS20110297930A1Improve reliabilityShape stableTransistorSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceSemiconductor
A TFT display panel having a high charge mobility and making it possible to obtain uniform electric characteristics with respect to a large-area display is provided as well as a manufacturing method thereof. A TFT display panel includes a gate electrode formed on an insulation substrate, a first gate insulting layer formed of SiNx on the gate electrode, a second gate insulting layer formed of SiOx on the first gate insulting layer, an oxide semiconductor layer formed to overlap the gate electrode and having a channel part, and a passivation layer formed of SiOx on the oxide semiconductor layer and the gate electrode, and the passivation layer includes a contact hole exposing the drain electrode. The contact hole has a shape in which the passivation layer of a portion directly exposed together with a metal occupies an area smaller than the upper passivation layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Polymers with low band gaps and high charge mobility
ActiveUS7772485B2Increase currentImprove efficiencyOrganic chemistryNanoinformaticsPolymer scienceRepeat unit
Owner:RAYNERGY TEK INC
Polycyclic benzothiadiazole non-fullerene acceptor material, preparation method thereof and application of material
ActiveCN109134513AImprove solubilityPromote absorptionOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesSolubilityOrganic solar cell
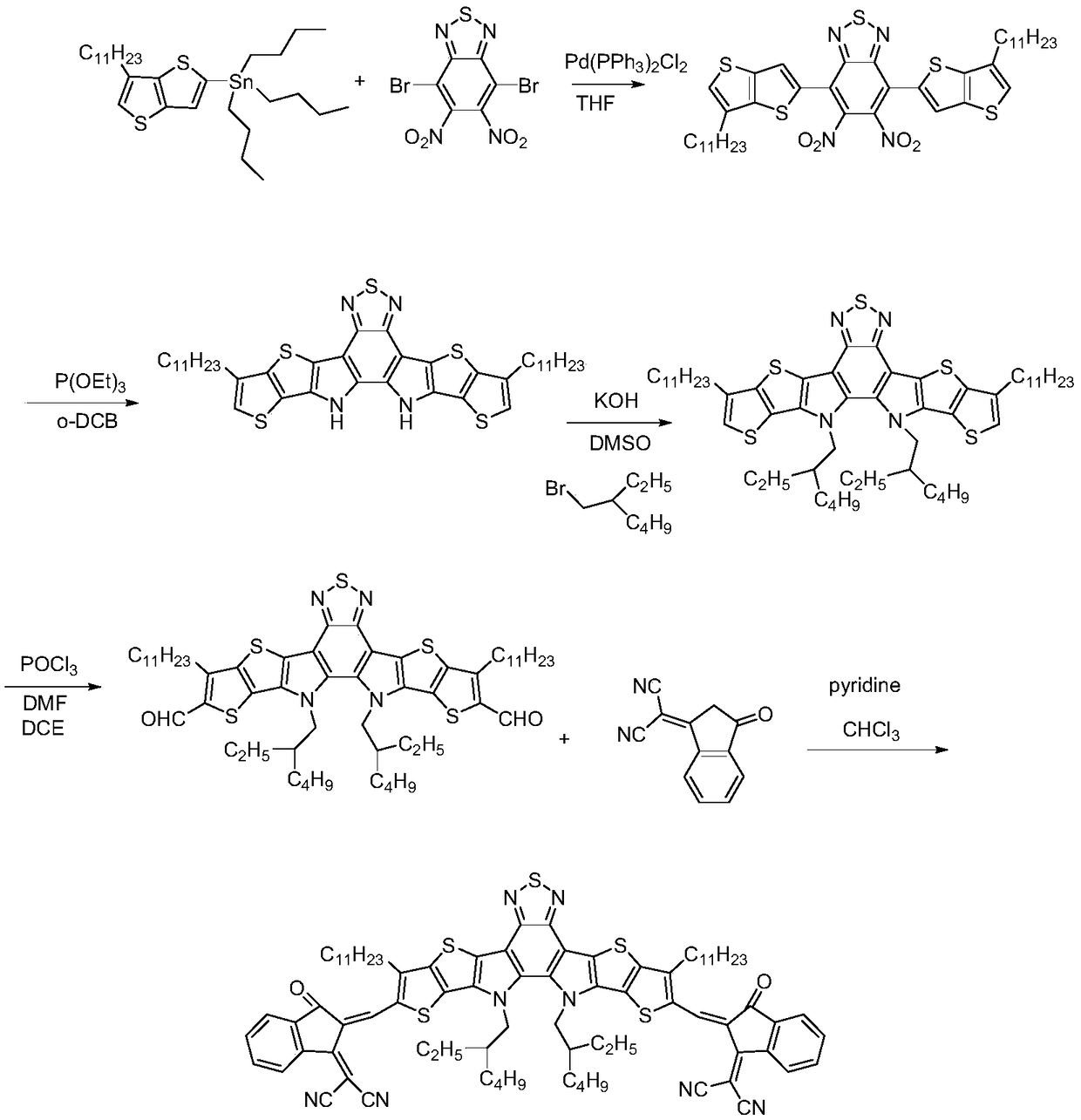
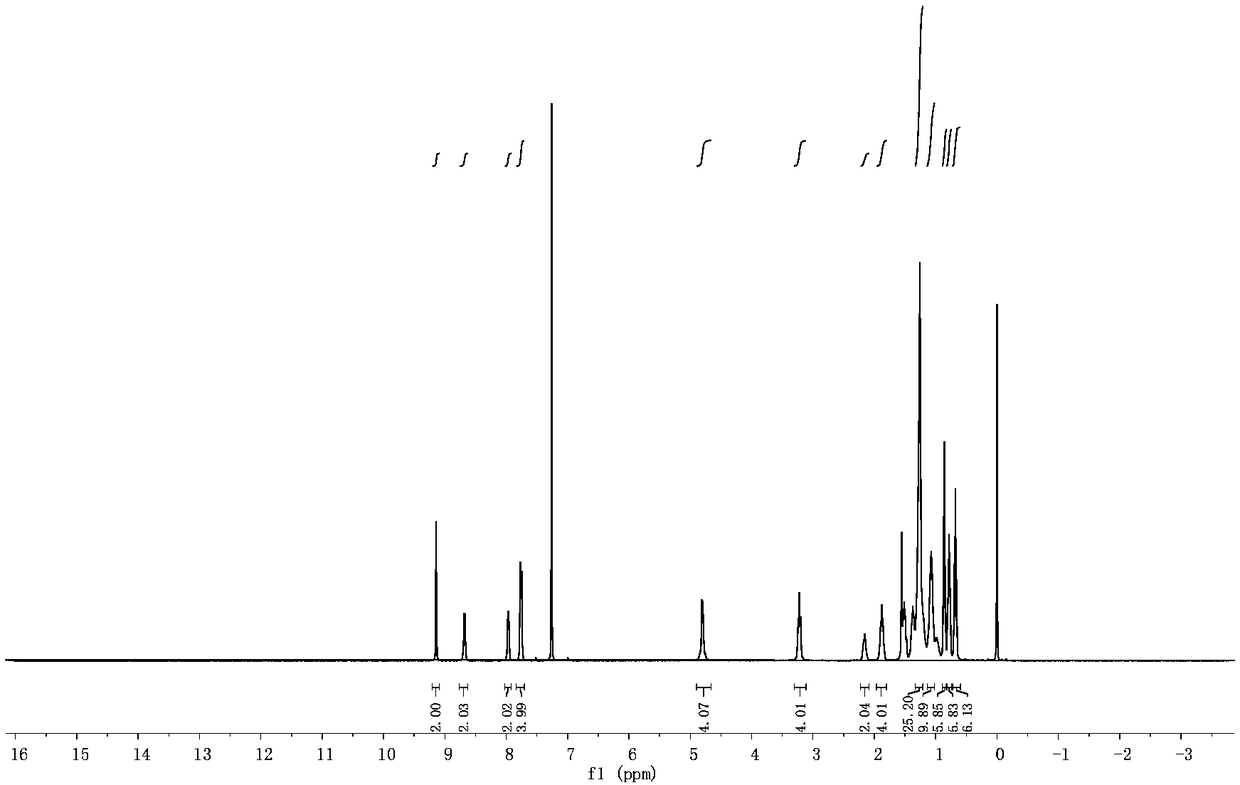
The invention discloses a polycyclic benzothiadiazole non-fullerene acceptor material, a preparation method thereof and an application of the material. The polycyclic benzothiadiazole non-fullerene acceptor material comprises a polycyclic benzothiadiazole center core and electrophilic end groups, the polycyclic benzothiadiazole center core is of a nitrogen bridge trapezoidal polycyclic structure,the electrophilic end groups are connected to two ends of the center core, 4, 7-dibromo-5, 6-binitro benzothiadiazole serves as a raw material in the preparation process, Stille coupling and Vilsmeier-Haack reaction are sequentially performed to obtain the polycyclic benzothiadiazole center core, and end-group structures are introduced by Knoevenagel reaction to obtain the polycyclic benzothiadiazole non-fullerene acceptor material. The acceptor material is good in solubility and easily processed into a film, has a good photoelectric conversion function and is used for preparing an organic solar battery device, and photoelectric conversion efficiency reaches nearly 16% of single battery conversion efficiency.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Thin film transistor array substrate and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20100051933A1Increase charge mobilityUniform characteristicsTransistorSolid-state devicesOptoelectronicsOxygen
A thin film transistor array substrate having a high charge mobility and that can raise a threshold voltage, and a method of fabricating the thin film transistor array substrate are provided. The thin film transistor array substrate includes: an insulating substrate; a gate electrode formed on the insulating substrate; an oxide semiconductor layer comprising a lower oxide layer formed on the gate electrode and an upper oxide layer formed on the lower oxide layer, such that the oxygen concentration of the upper oxide layer is higher than the oxygen concentration of the lower oxide layer; and a source electrode and a drain electrode formed on the oxide semiconductor layer and separated from each other.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Nonvolatile memory electronic device including nanowire channel and nanoparticle-floating gate nodes and a method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20100276667A1Increase charge mobilityHighly integratedNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanowireNanoparticle
A nonvolatile memory electronic device including nanowire channel and nanoparticle-floating gate nodes, in which the nonvolatile memory electronic device, which comprises a semiconductor nanowire used as a charge transport channel and nanoparticles used as a charge trapping layer, is configured by allowing the nanoparticles to be adsorbed on a tunneling layer deposited on a surface of the semiconductor nanowire, whereby charge carriers moving through the nanowire are tunneled to the nanoparticles by a voltage applied to a gate, and then, the charge carriers are tunneled from the nanoparticles to the nanowire by the change of the voltage that has been applied to the gate, whereby the nonvolatile memory electronic device can be operated at a low voltage and increase the operation speed thereof.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY CO LTD
Method of achieving improved STI gap fill with reduced stress
InactiveUS20050170606A1Relieve pressureImprove CMOS device charge mobilityStentsBalloon catheterFilling materialsEngineering
A shallow trench isolation (STI) structure and method of forming the same with reduced stress to improve charge mobility the method including providing a semiconductor substrate comprising at least one patterned hardmask layer overlying the semiconductor substrate; dry etching a trench in the semiconductor substrate according to the at least one patterned hardmask layer; forming one or more liner layers to line the trench selected from the group consisting of silicon dioxide, silicon nitride, and silicon oxynitride; forming one or more layers of trench filling material comprising silicon dioxide to backfill the trench; carrying out at least one thermal annealing step to relax accumulated stress in the trench filling material; carrying out at least one of a CMP and dry etch process to remove excess trench filling material above the trench level; and, removing the at least one patterned hardmask layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Organic light emitting diode display and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20140117340A1Increase mileageReduce leakage currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceEngineering
An organic light emitting diode display device includes a substrate including a pixel portion and a peripheral portion, a semiconductor layer including a pixel switching semiconductor layer and a driving semiconductor layer formed on the pixel portion, and a peripheral switching semiconductor layer formed on the peripheral portion. A first gate insulating layer is formed on the semiconductor layer. A peripheral switching gate electrode is formed on the first gate insulating layer of the peripheral portion, and a pixel switching gate electrode and a driving gate electrode are formed on the first gate insulating layer of the pixel portion. A length of a peripheral switching low concentration doping region formed in the peripheral switching semiconductor layer may be larger than a length of a pixel switching low concentration doping region and a driving low concentration doping region formed in the pixel switching semiconductor layer and the driving semiconductor layer, respectively.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
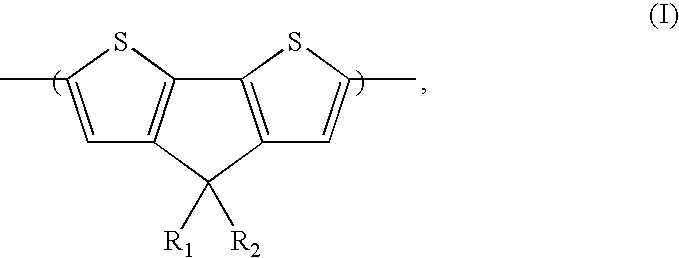
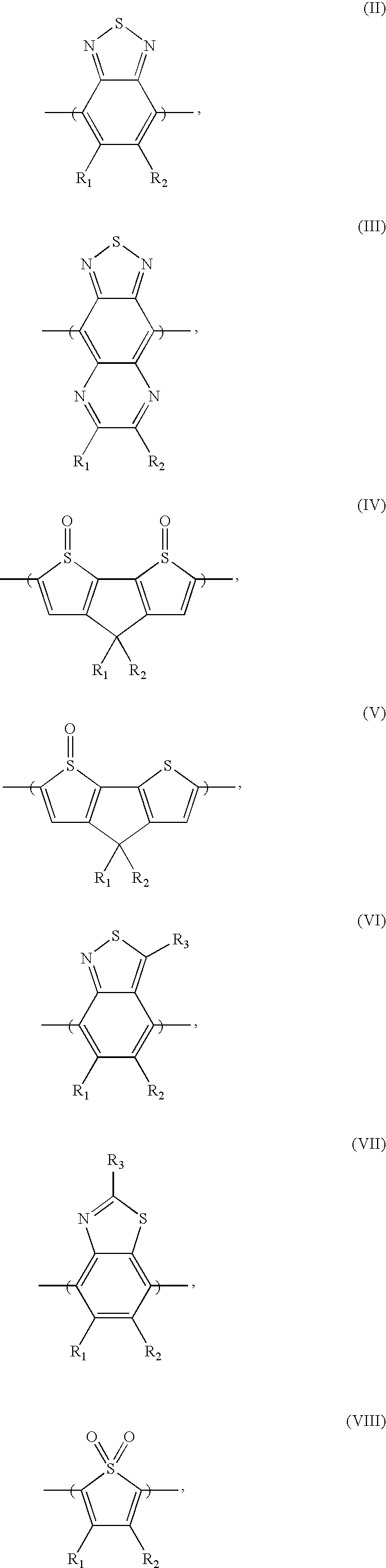
Heteroacene compound, organic thin film including a heteroacene compound and electronic device including an organic thin film
InactiveUS20090043113A1Increase charge mobilityEasy to processOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesOrganic filmRoom temperature
A heteroacene compound, an organic thin film including a heteroacene compound and an electronic device including a thin film are provided. The heteroacene compound is a compound having six rings fused together in a compact planar structure. The compound may be used in an organic thin film and / or applied to electronic devices using a deposition process or a room-temperature solution process.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Sintered device
InactiveUS20130280854A1High charge mobilityFew defectMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureRepeated treatmentNanoparticle deposition
A method for the production of an inorganic film on a substrate, the method comprising: (a) depositing a layer of nanoparticles on the substrate by contacting the substrate with a nanoparticle dispersion; (b) treating the deposited layer of nanoparticles to prevent removal of the nanoparticles in subsequent layer depositing steps; (c) depositing a further layer of nanoparticles onto the preceding nanoparticle layer on the substrate; (d) repeating treatment step (b) and deposition step (c) at least one further time; and (e) optionally thermally annealing the multilayer film produced following steps (a) to (d); wherein the method comprises at least one thermal annealing step in which the layer or layers of nanoparticles are thermally annealed.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG +1
Organic electronic devices and polymers, including photovoltaic cells and diketone-based polymers
InactiveUS20110204341A1Better electronic and photonic devicesBetter solar cells or photovoltaic devicesGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesDiketonePolymer science
Owner:SOLVAY USA
Oxide semiconductor devices, methods of manufacturing oxide semiconductor devices, display devices having oxide semiconductor devices, methods of manufacturing display devices having oxide semiconductor devices
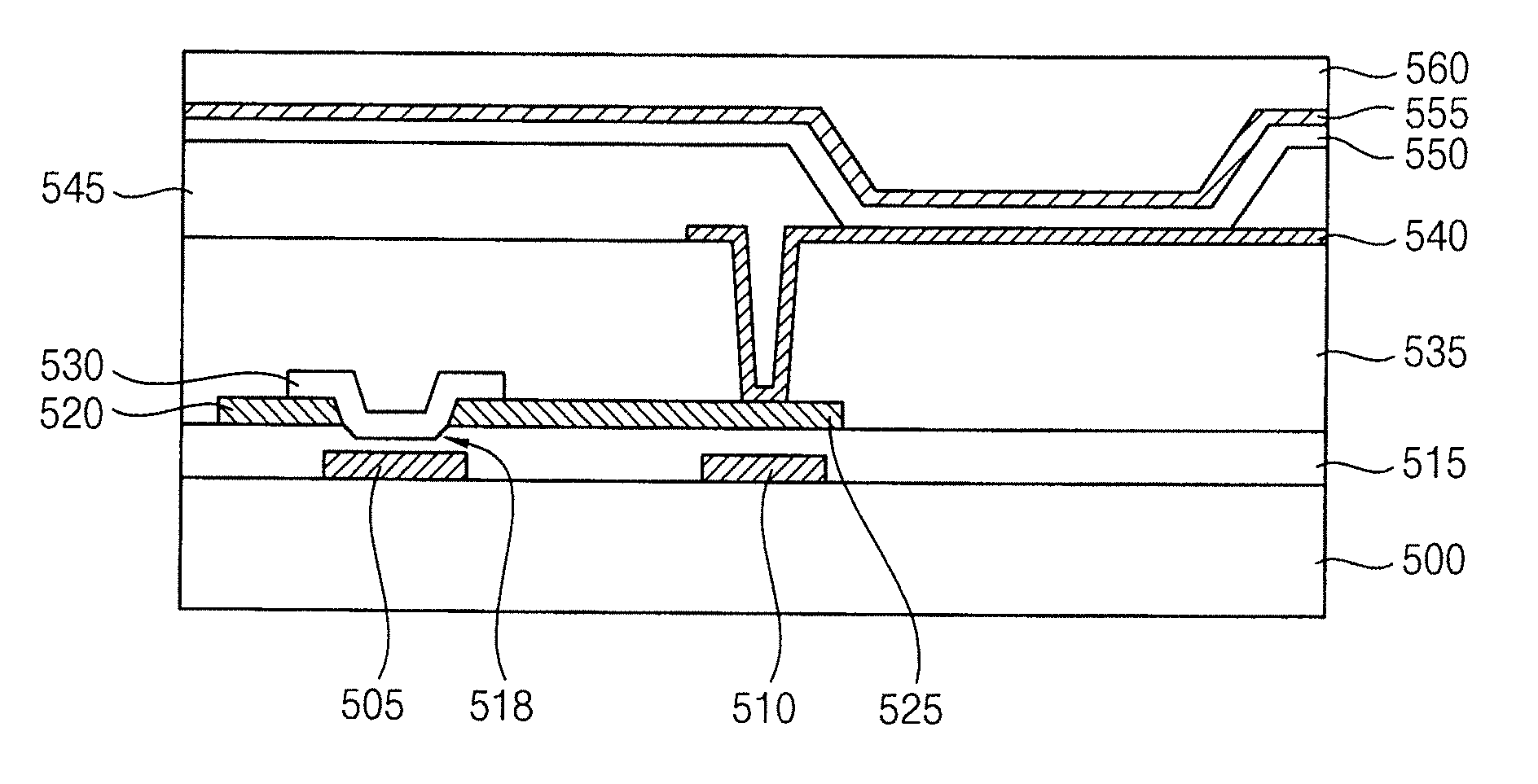
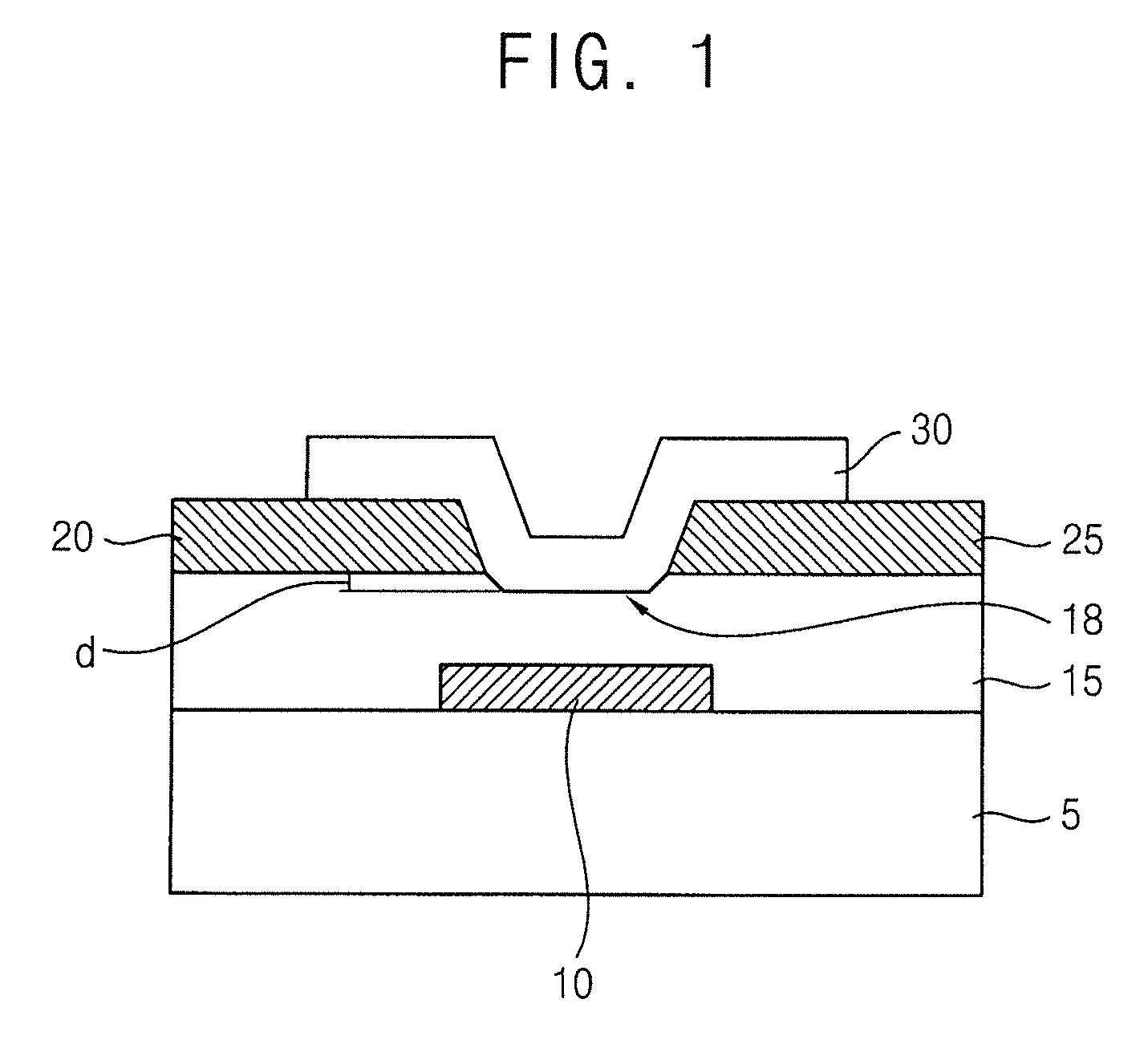
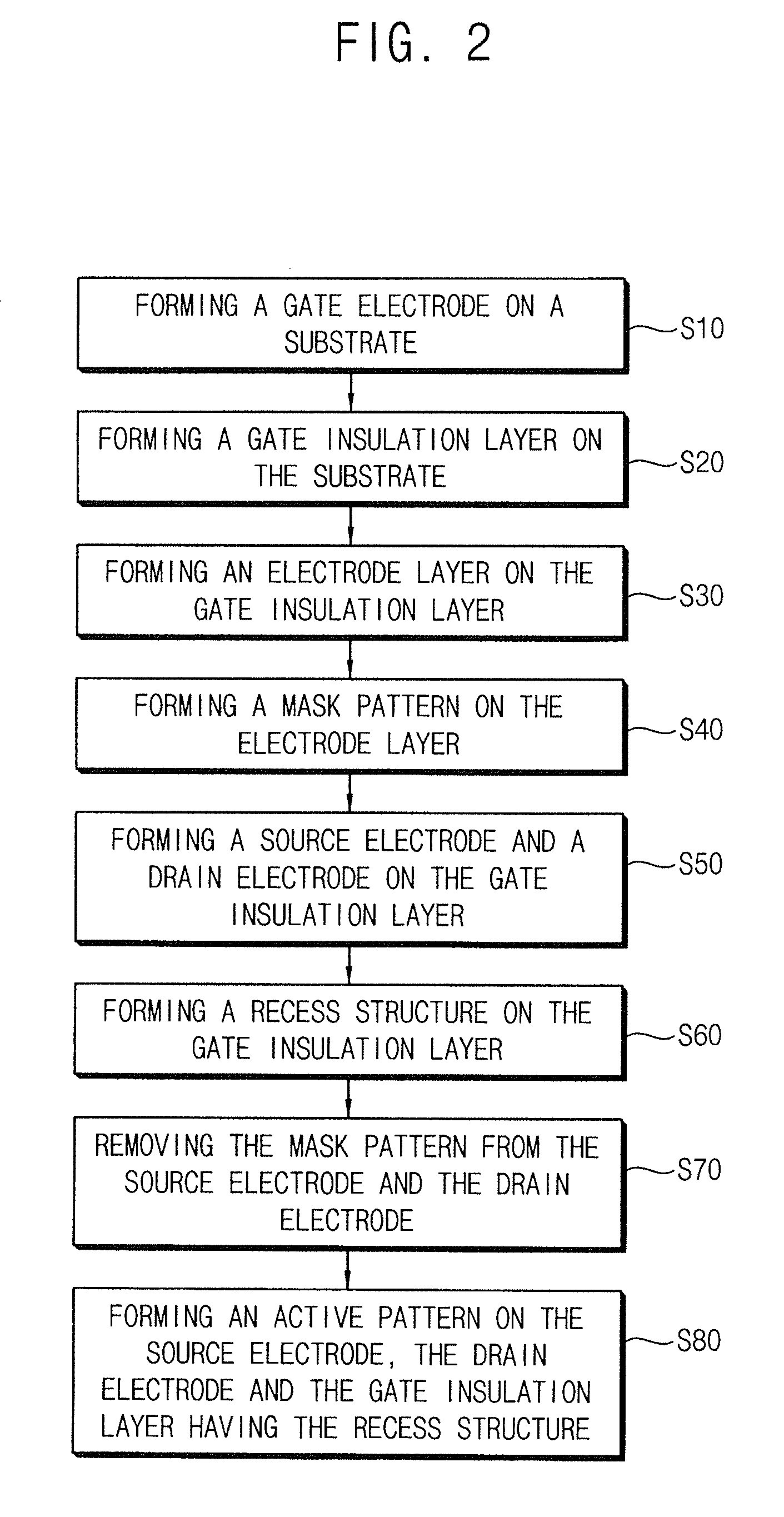
InactiveUS20120292610A1Improve electrical characteristicsIncrease charge mobilityTransistorSolid-state devicesInsulation layerDisplay device
An oxide semiconductor device includes a gate electrode on a substrate, a gate insulation layer on the substrate, the gate insulation layer having a recess structure over the gate electrode, a source electrode on a first portion of the gate insulation layer, a drain electrode on a second portion of the gate insulation layer, and an active pattern on the source electrode and the drain electrode, the active pattern filling the recess structure.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Heteroacene compound, organic thin film comprising the compound, and electronic device comprising the thin film
ActiveUS7816673B2Increase charge mobilityEasy to processLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic chemistryElectricitySolubility
A heteroacene compound includes a di-thieno-benzo-thieno-thiophene derivative, in which all six rings may be fused together, an organic thin film including the same, and an electronic device that includes the thin film as a carrier transport layer. The compound of example embodiments may have a compact planar structure to thus realize improved solvent solubility and processability. When the compound is applied to electronic devices, a deposition process or a room-temperature solution process may be applied, and as well, intermolecular packing and stacking may be efficiently realized, resulting in improved electrical properties, including increased charge mobility.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
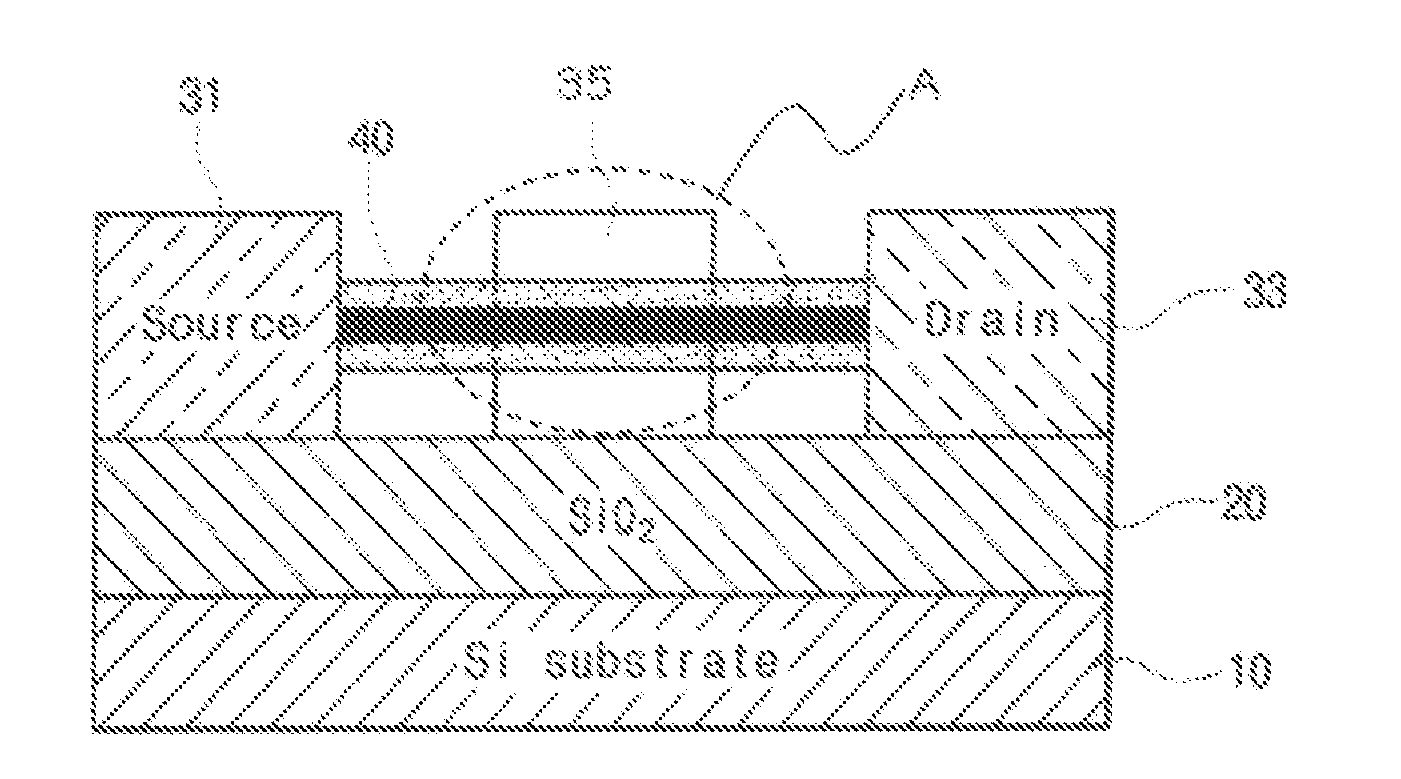
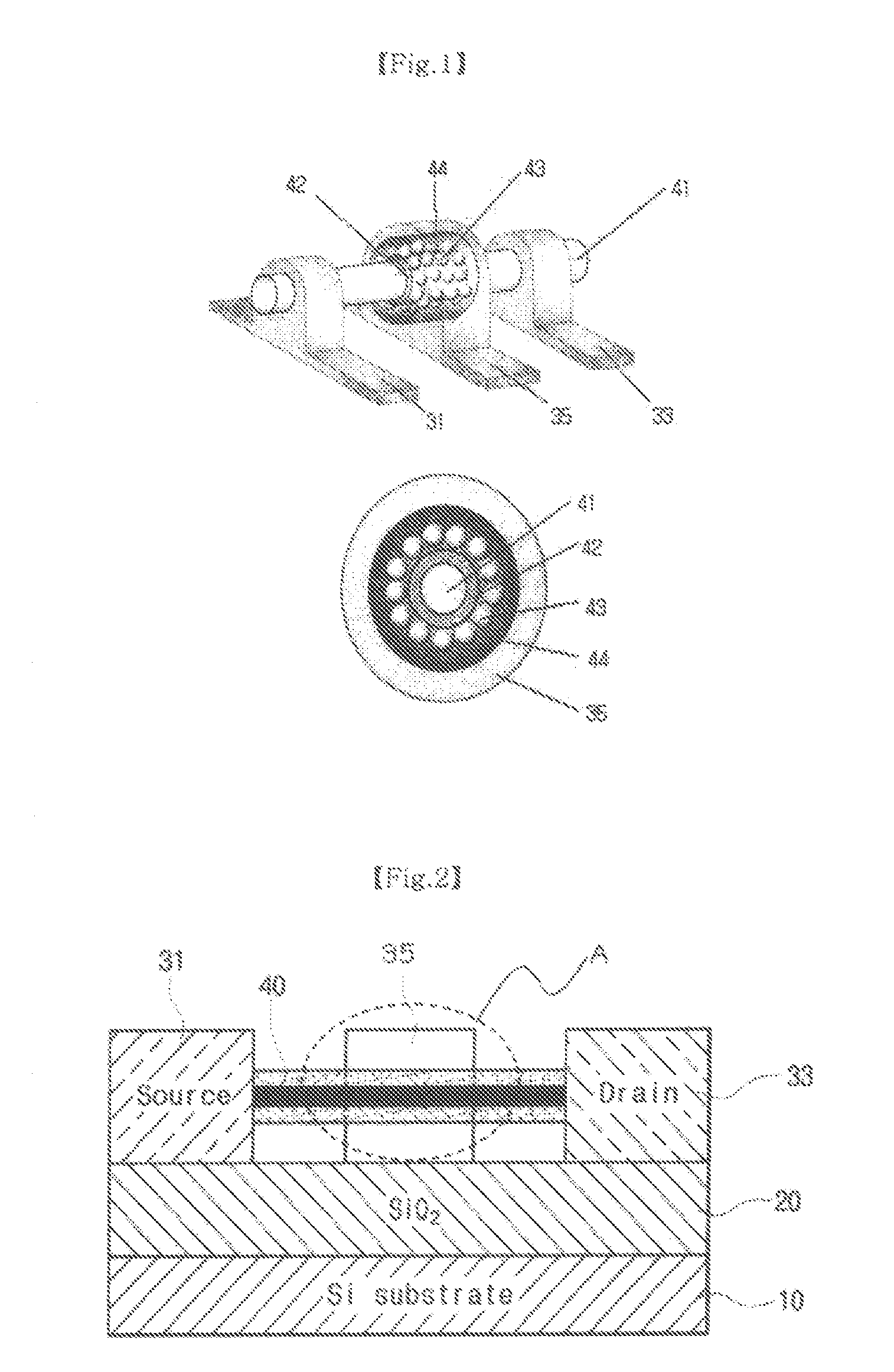
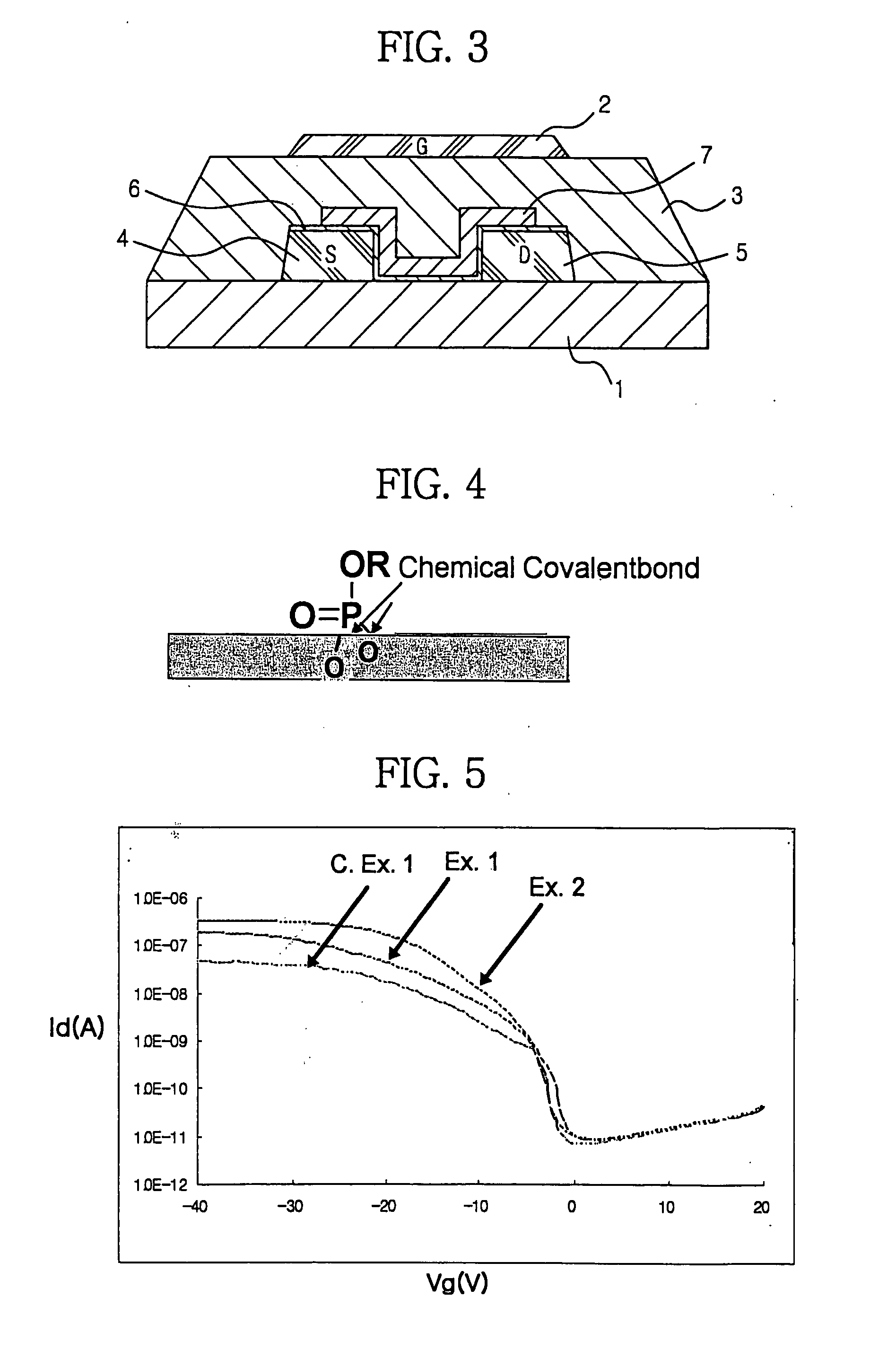
Method of fabricating organic thin film transistor using self assembled monolayer-forming compound containing dichlorophosphoryl group
InactiveUS20080105866A1Improve electrical performanceImprove work functionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSelf-assembled monolayerWork function
Disclosed is a method of fabricating an organic thin film transistor including a substrate, a gate electrode, a gate insulating layer, metal oxide source / drain electrodes, and an organic semiconductor layer, in which the surface of the metal oxide source / drain electrodes or of the metal oxide source / drain electrodes and gate insulating layer is treated with a self assembled monolayer-forming compound containing a dichlorophosphoryl group. According to the method of example embodiments, the work function of the metal oxide of the source / drain electrodes may be increased to be higher than that with no SAM-forming electrode, thus making it possible to fabricate an improved organic thin film transistor having increased charge mobility.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electro-optical devices using dynamic reconfiguration of effective electrode structures
ActiveUS20110216257A1Reduce aberrationImprove performance of lensStatic indicating devicesFixed grillesOptical propertyElectric field
Variable liquid crystal devices for controlling the propagation of light through a liquid crystal layer use a frequency dependent material to dynamically reconfigure effective electrode structures in the device. The frequency of a drive signal that generates an electric field in the device may be varied, and the frequency dependent material has different charge mobilities for the different frequencies. At a low charge mobility, the frequency dependent material has little effect on the existing electrode structures. However, at a high charge mobility, the frequency dependent material appears as an extension of the fixed electrodes, and may be used to change the effective electrode structure and, thereby, the spatial profile of the electric field. This, in turn, changes the optical properties of the liquid crystal, thus allowing the optical device to be frequency controllable.
Owner:POINT FINANCIAL
Organic light emitting display device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS8436342B2Increase charge mobilityHigh concentrationElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceLight-emitting diode
Disclosed is an organic light emitting display device and a method of manufacturing the same. The organic light emitting display device includes the thin film transistor of the drive unit that has the activation layer formed in a structure where the first oxide semiconductor layer and the second oxide semiconductor layer are stacked, the thin film transistor of the pixel unit that has the activation layer formed of the second oxide semiconductor layer, and the organic light emitting diode coupled to the thin film transistor of the pixel unit. The thin film transistor of the drive unit has channel formed on the first oxide semiconductor layer having a higher carrier concentration than the second oxide semiconductor layer, having a high charge mobility, and the thin film transistor of the pixel unit has a channel formed on the second oxide semiconductor layer, having a stable and uniform functional property.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Polymers with low band gaps and high charge mobility
InactiveUS20070158620A1Increase currentImprove efficiencyNanoinformaticsConductive materialSystems approachesPolymer
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Composition for dielectric thin film, metal oxide dielectric thin film using the same and preparation method thereof
ActiveUS20080079075A1Improve electrical performanceLow working voltageTransistorLiquid organic insulatorsDielectric thin filmsElectron
This invention pertains to a composition for a dielectric thin film, which is capable of being subjected to a low-temperature process. Specifically, the invention is directed to a metal oxide dielectric thin film formed using the composition, a preparation method thereof, a transistor device comprising the dielectric thin film, and an electronic device comprising the transistor device. The electronic device to which the dielectric thin film has been applied exhibits excellent electrical properties, thereby satisfying both a low operating voltage and a high charge mobility.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
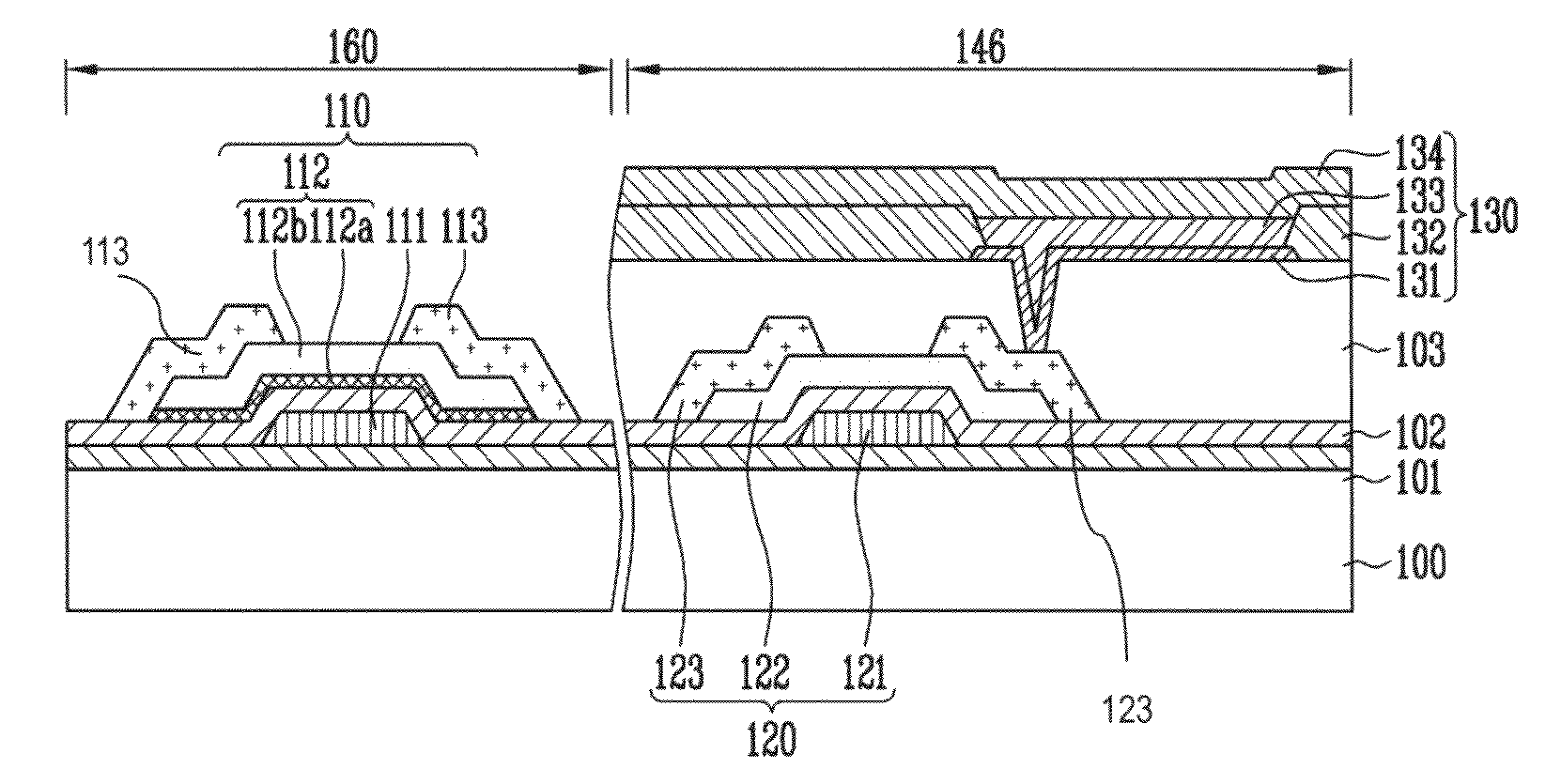
Thin film transistor, method of forming the same and flat panel display device having the same
InactiveUS20100148155A1Increase charge mobilityExtend your lifeTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringFlat panel display
A thin film transistor (TFT), a method of forming the same and a flat panel display device having the same are disclosed. The TFT includes a buffer layer and a semiconductor layer which are sequentially disposed on a substrate, a gate pattern including an insulating pattern and a gate electrode pattern which are sequentially disposed on the semiconductor layer, source and drain regions defining a portion of the semiconductor layer below the gate pattern as a channel area, formed by doping the semiconductor layer disposed at both sides of the gate pattern with impurities, and extending from both sides of the channel area, a passivation layer which covers the entire surface of the substrate having the gate pattern, a first metal electrode which penetrates a portion of the passivation layer disposed on the source area and a portion of the source region below the portion of the passivation layer to be electrically connected with the source region, and a second metal electrode which penetrates a portion of the passivation layer disposed on the drain area and a portion of the drain region below the portion of the passivation layer to be electrically connected with the drain region. According to the present invention, a metal is infiltrated into source and drain regions to disperse an electric current when a TFT operates, and thus charge mobility is improved, and damage of a drain region caused by the excessive current density is prevented, leading to the long lifespan and excellent performance.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
Thin film transistor array substrate and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS8283666B2Increase charge mobilityUniform characteristicsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxygenSemiconductor
A thin film transistor array substrate having a high charge mobility and that can raise a threshold voltage, and a method of fabricating the thin film transistor array substrate are provided. The thin film transistor array substrate includes: an insulating substrate; a gate electrode formed on the insulating substrate; an oxide semiconductor layer comprising a lower oxide layer formed on the gate electrode and an upper oxide layer formed on the lower oxide layer, such that the oxygen concentration of the upper oxide layer is higher than the oxygen concentration of the lower oxide layer; and a source electrode and a drain electrode formed on the oxide semiconductor layer and separated from each other.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Organic thin-film transistors
ActiveUS20070148812A1High carrier mobilityIncrease charge mobilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic filmCharge carrier mobility
Methods are disclosed for improving organic thin-film transistor (OTFT) performance by acid doping of the semiconducting layer. The semiconducting polymer comprising the semiconductor layer is doped with an acid, especially a Lewis acid, either during or after polymerization of the polymer, but prior to application of the polymer onto the OTFT. Also disclosed are OTFTs having enhanced charge carrier mobility produced by these methods.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Image stabilization and shifting in a liquid crystal lens
InactiveUS20120257131A1Easy to controlEnhanced electric field controlStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsOptical propertyImage stabilization
Variable liquid crystal devices for controlling the propagation of light through a liquid crystal layer use a frequency dependent material to dynamically reconfigure effective electrode structures in the device. The frequency of a drive signal that generates an electric field in the device can be varied, and the frequency dependent material has different charge mobilities for the different frequencies. At a low charge mobility, the frequency dependent material has little effect on the existing electrode structures. However, at a high charge mobility, the frequency dependent material appears as an extension of the fixed electrodes, and can be used to change the effective electrode structure and, thereby, the spatial profile of the electric field. This, in turn, changes the optical properties of the liquid crystal, thus allowing the optical device to be frequency controllable.
Owner:POINT FINANCIAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com