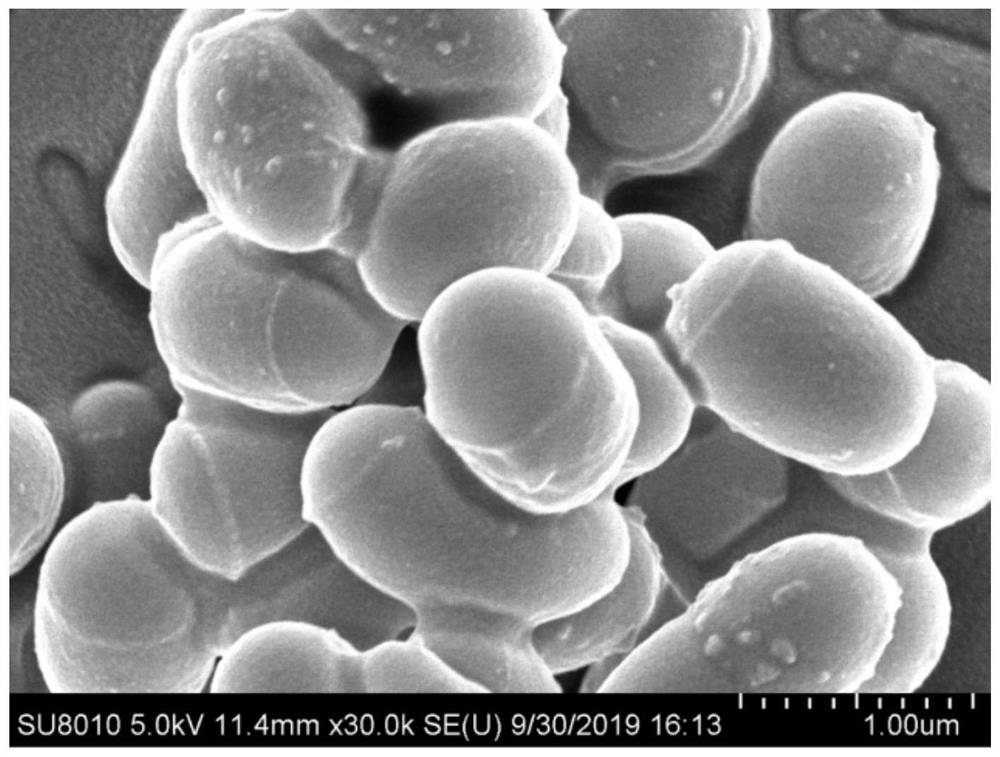
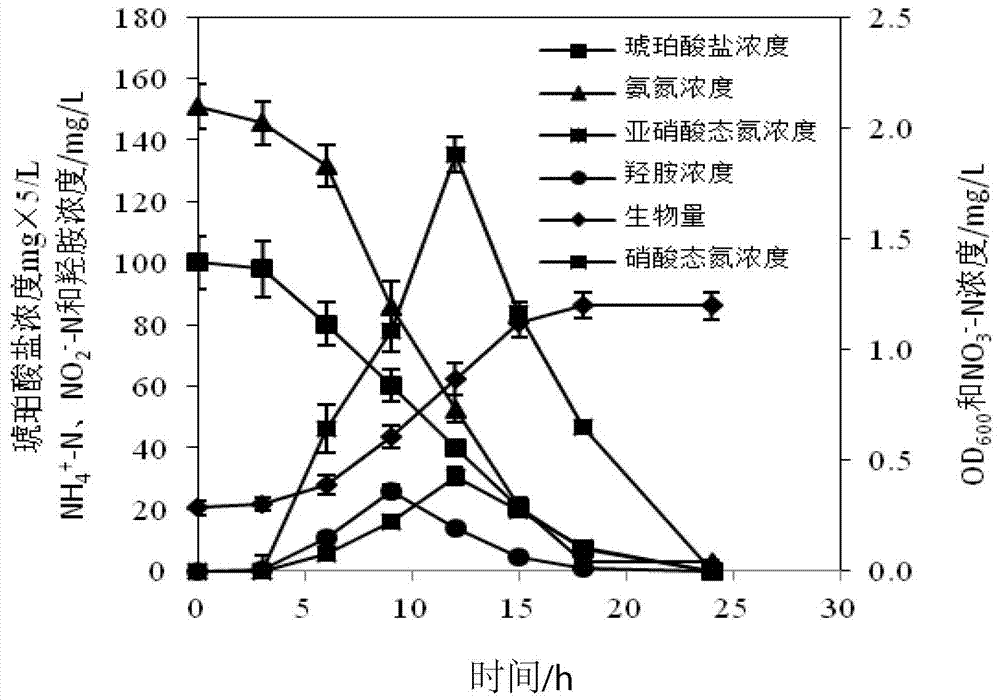
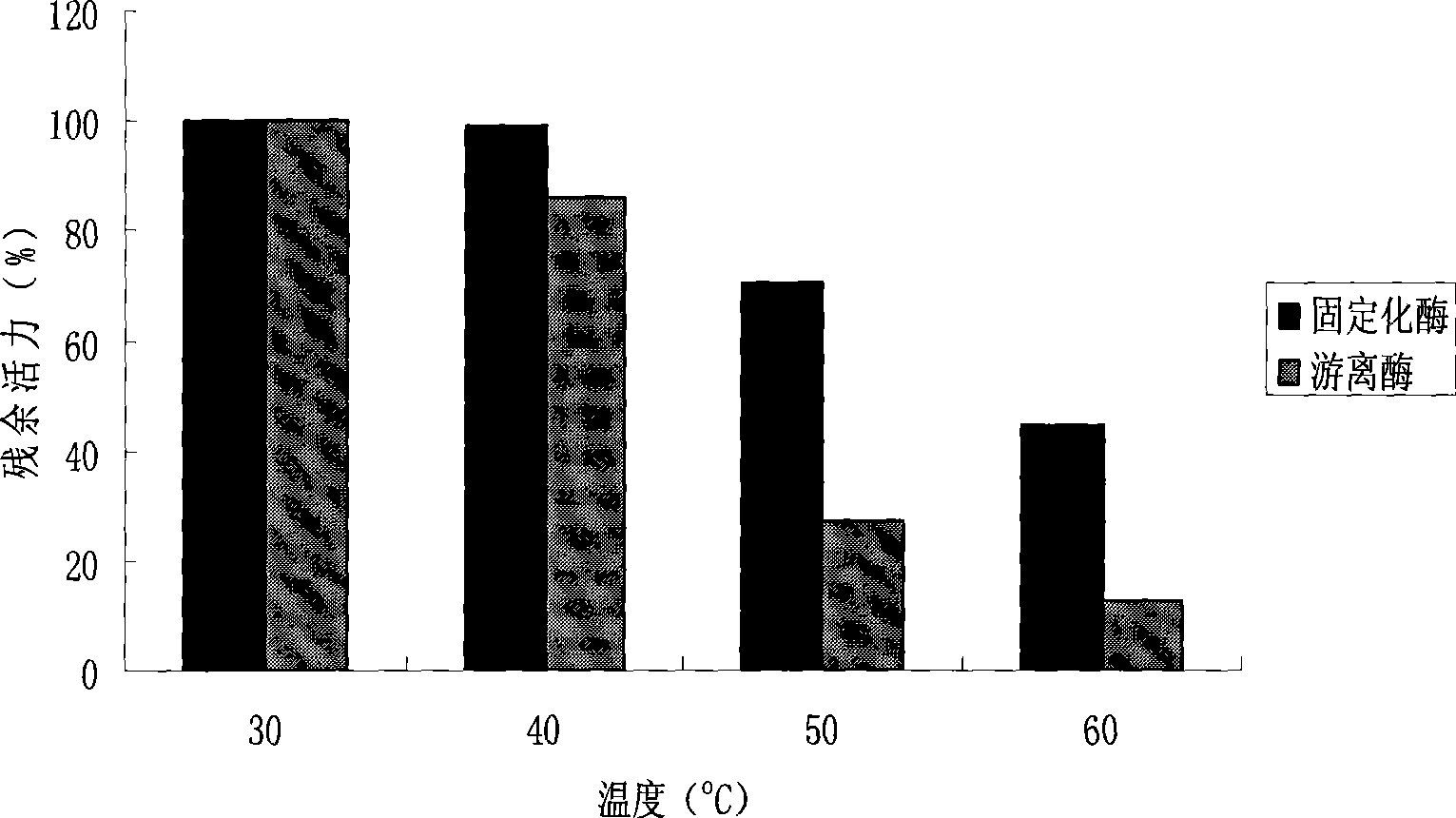
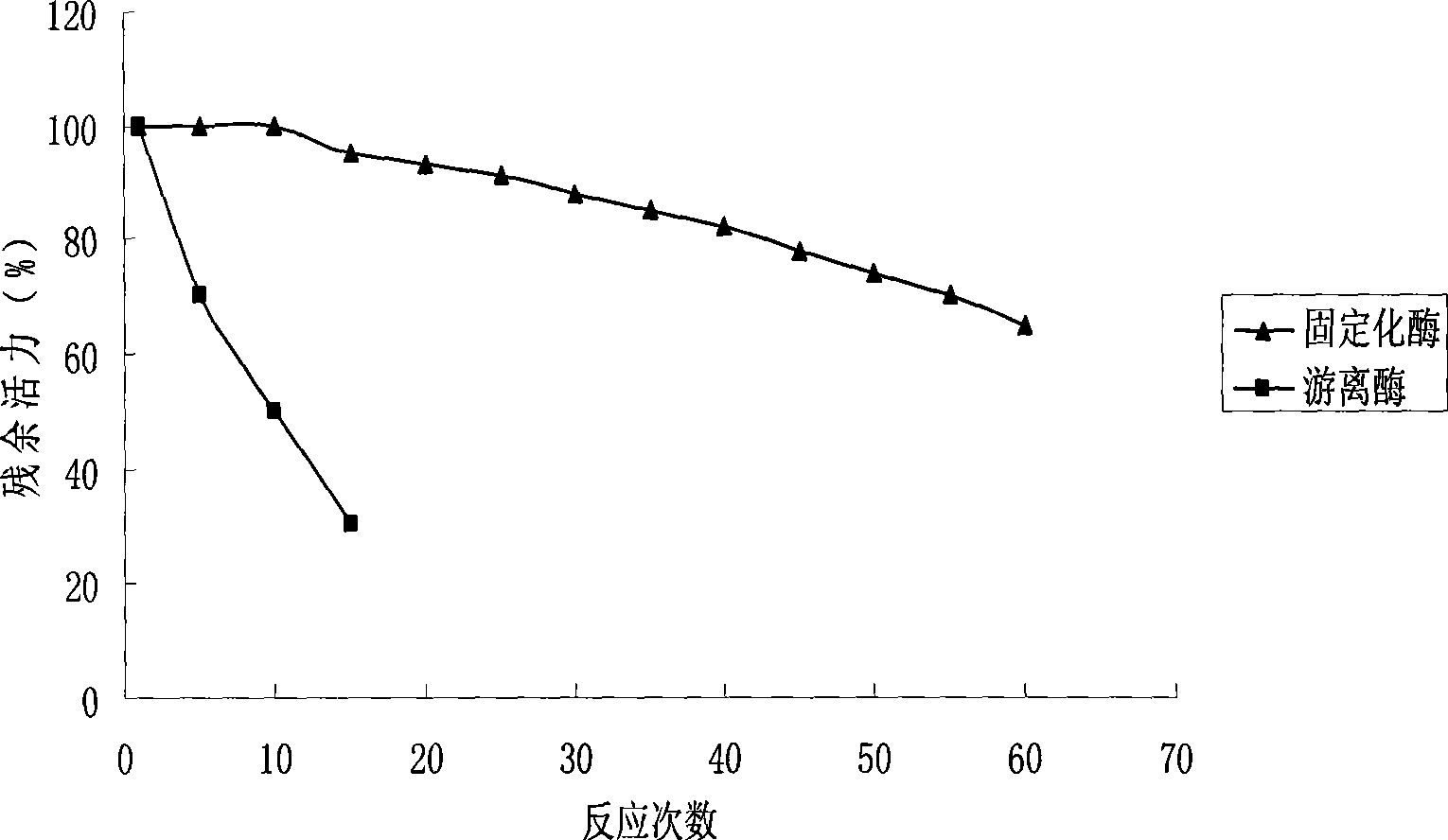
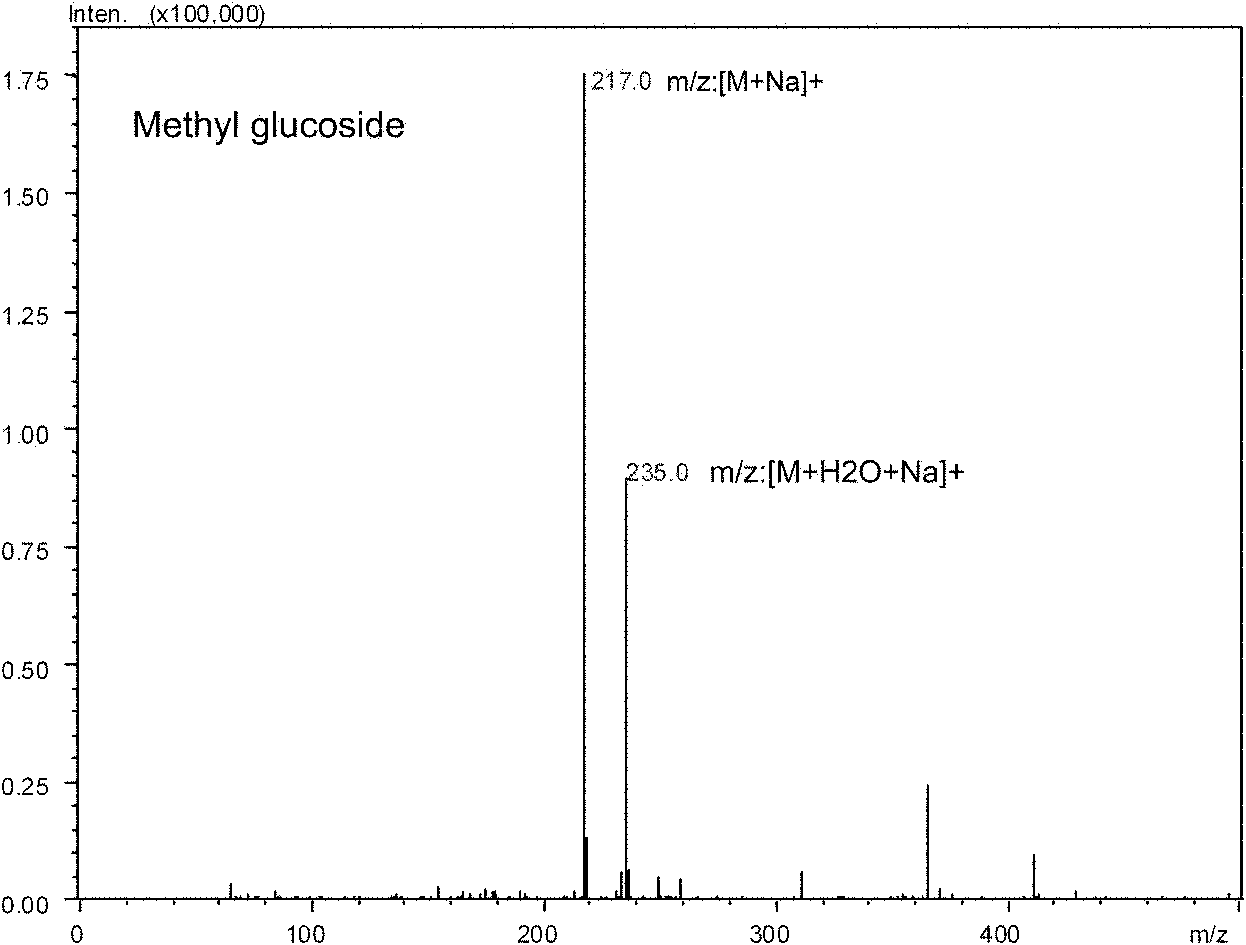
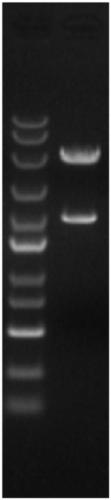
Patents
Literature
65 results about "Arthrobacter sp." patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nitrogen-fixing arthrobacterium and application thereof
ActiveCN103333837AHigh statistical analysisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobial agentNitrogen
The invention discloses a nitrogen-fixing arthrobacterium and application thereof. The nitrogen-fixing arthrobacterium is Arthrobacter sp. GD601, which is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center by a preservation number of CGMCC No.7779. The Arthrobacter sp. GD601 CGMCC No.7779 provided by the invention can be colonized in rhizosphere of a crop, and has a quite high nitrogen-fixing potential; the nitrogen-fixing arthrobacterium has a wide application prospect in inoculation agent, microbial agent and bio-organic fertilizer production for vegetable industrialized seedling production.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
High-efficiency Atrazine degrading bacteria and application and screening method thereof
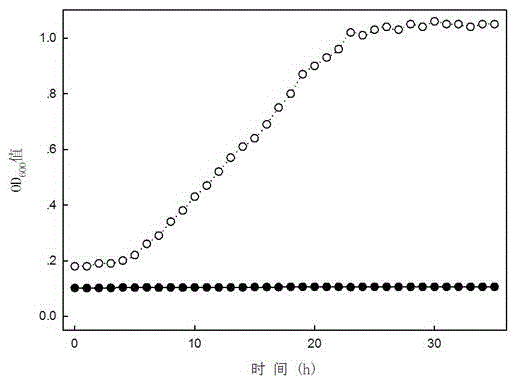
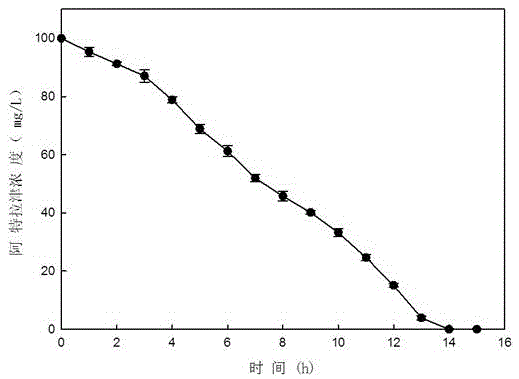
The invention relates to high-efficiency Atrazine degrading bacteria and an application and screening method thereof. The bacteria are ZXY-2, belong to Arthrobacter, are preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center and have the preservation number of CGMCC No.10937 and the preservation date of July 1st, 2015. The bacteria can grow with Atrazine as the unique carbon and nitrogen source, and Atrazine with the initial concentration of 100 mg / L can be completely degraded within 14 hours. The strain Arthrobacter sp. ZXY-2 has the optimal growth temperature of 30 DEG C to 35 DEG C, the optimal growth pH of 8.0 to 9.0 and the optimal growth table rotating speed of 100 r / min to 200 r / min. The bacteria can be used for rapidly repairing the pollution of Atrazine pesticide.
Owner:宜兴环保产业有限公司
A kind of preparation method of cyclic adenosine monophosphate
InactiveCN102268469APromote circulationReduce formationMicroorganismsFermentationTricarboxylic acidArthrobacter sp.
The present invention provides a method of preparing cyclic adenosine monophosphate, which includes the use of Arthrobacter sp. as an engineering bacterium, and the addition of precursors, inhibitors of glycolytic pathway and / or activators of tricarboxylic acid cycle into a fermentation medium, so as to acquire the cyclic adenosine monophosphate by fermentation. Further provided is a use of precursors, inhibitors of glycolytic pathway and / or activators of tricarboxylic acid cycle for preparing cyclic adenosine monophosphate by Arthrobacter sp.. The present invention inhibits the excessive glycolysis, increases the flux of pentose phosphate pathway, and enhances the tricarboxylic acid cycle by the addition of precursors, inhibitors of glycolytic pathway and / or activators of tricarboxylic acid cycle, so as to redistribute rationally the metabolic flux of central metabolic pathways, make the carbon flux more efficiently direct to the target product - cyclic adenosine monophosphate, and synthesize cyclic adenosine monophosphate by using carbon source efficiently.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Coding beta-galactosidase gene and expression and application thereof
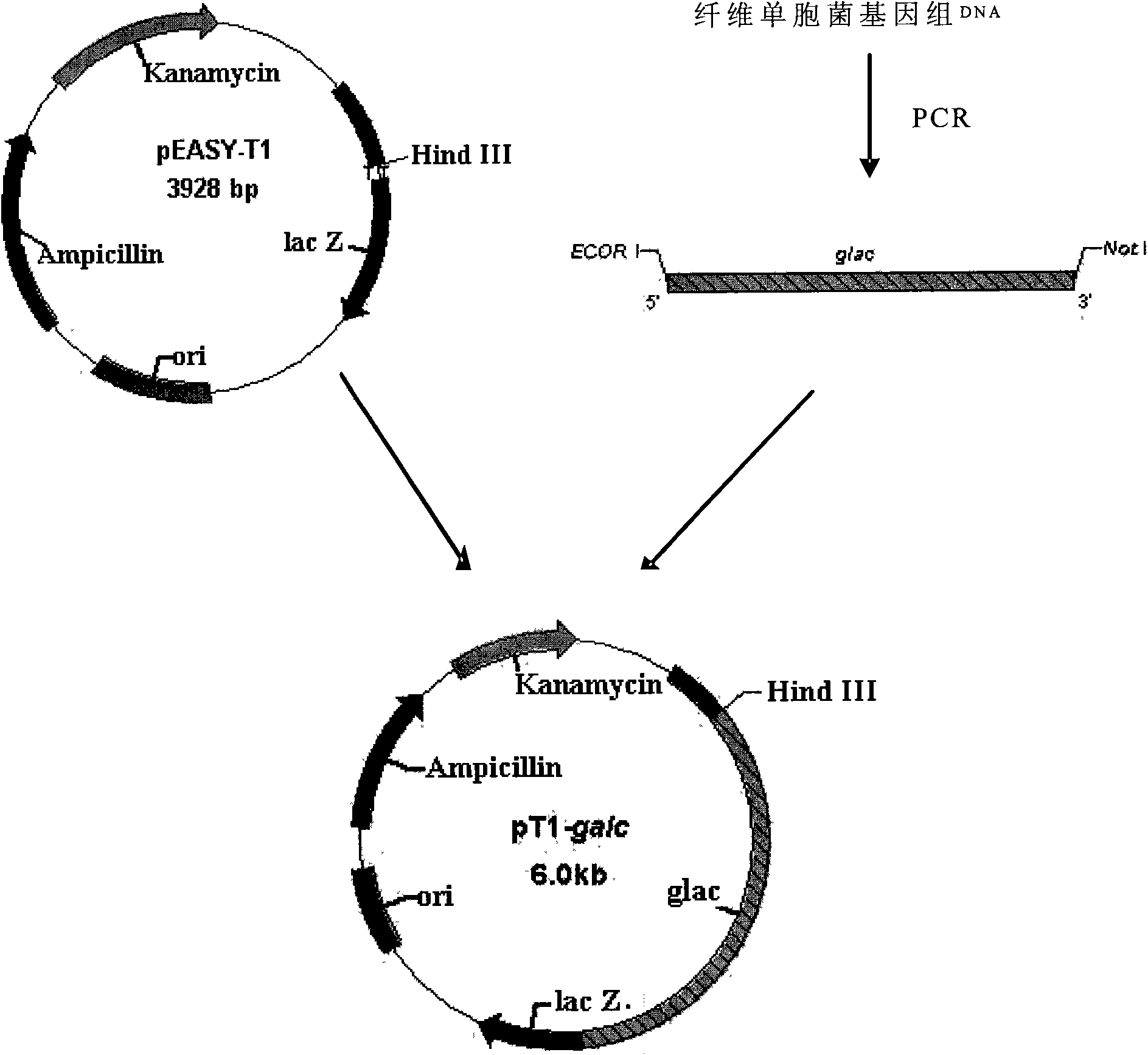
The invention discloses a coding beta-galactosidase gene and an expression and an application thereof. The invention sieves and clones a beta-galactosidase gene (SEQ ID NO:1) coming from Cellulononas sp. from Sinkiang soil. The DNA overall length of the beta-galactosidase gene group is 2076bp, and (G+C) percent content is 72.9% and the beta-galactosidase gene group is deduced to encode 629 amino acid. The beta-galactosidase encoded by genes has the highest similarity with the beta-galactosidase from Arthrobacter sp., and the similarity is 59%. Enzymology property measurements indicate that the beta-galactosidase of the invention is neutral normal-temperature enzyme. Most of the beta-galactosidase of other Arthrobacter sp. reported by documents belongs to low-temperature psychrophilic enzyme which is obvious different from the beta-galactosidase of the invention in terms of enzymology properties.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Bacterial strain capable of degrading pyridine and ammonia nitrogen, preparation method and application of bacterial strain
InactiveCN105713862APromote degradationGrowth inhibitionWater treatment parameter controlBacteriaHigh concentrationEndurance capacity
The invention discloses a bacterial strain capable of degrading pyridine and ammonia nitrogen. The bacterial strain is characterized by being preserved in CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) on April 25th, 2014, the preservation number is CCTCC M2014165, and the bacterial strain belongs to arthrobacter sp. and is named as Arthrobacter ureafaciens CZ3. The bacterial strain has efficient degradation capacity on high-concentration pyridine and has very high endurance capacity and efficient removal capacity on the environmental pollutant ammonia nitrogen, does not produce secondary pollution and is safe to use. The bacterial strain has broad application prospect and very high popularization value in the aspects of treatment of industrial wastewater containing high-concentration pyridine and biological treatment of wastewater containing high-concentration ammonia nitrogen.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for fermentation production of cyclic adenosine monophosphate by controlling dissolved oxygen content at two phases
ActiveCN102899372AImprove utilization efficiencyIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationGrowth phaseControl manner
The invention provides a method for fermentation production of cyclic adenosine monophosphate by controlling the dissolved oxygen content at two phases. The method adopts the two-phase dissolved oxygen content control manner to carry out batch fermentation in order to produce the cyclic adenosine monophosphate, fermentation strains are Arthrobacter sp having a preservation number of CGMCC No.3584, the dissolved oxygen in a thallus growth phase is 20-30%, and the dissolved oxygen is 5-10% after the thallus amount stabilizes. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of substantial improvement of the output of the cyclic adenosine monophosphate, no need of the addition of extra equipment in the fermentation process, saving of the electric energy for stirring and air supply in the later fermentation phase, and suitableness for industrialized production.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Phthalate degrading strain and application thereof
ActiveCN102864102APromote degradationEfficient degradation abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyArthrobacter sp.
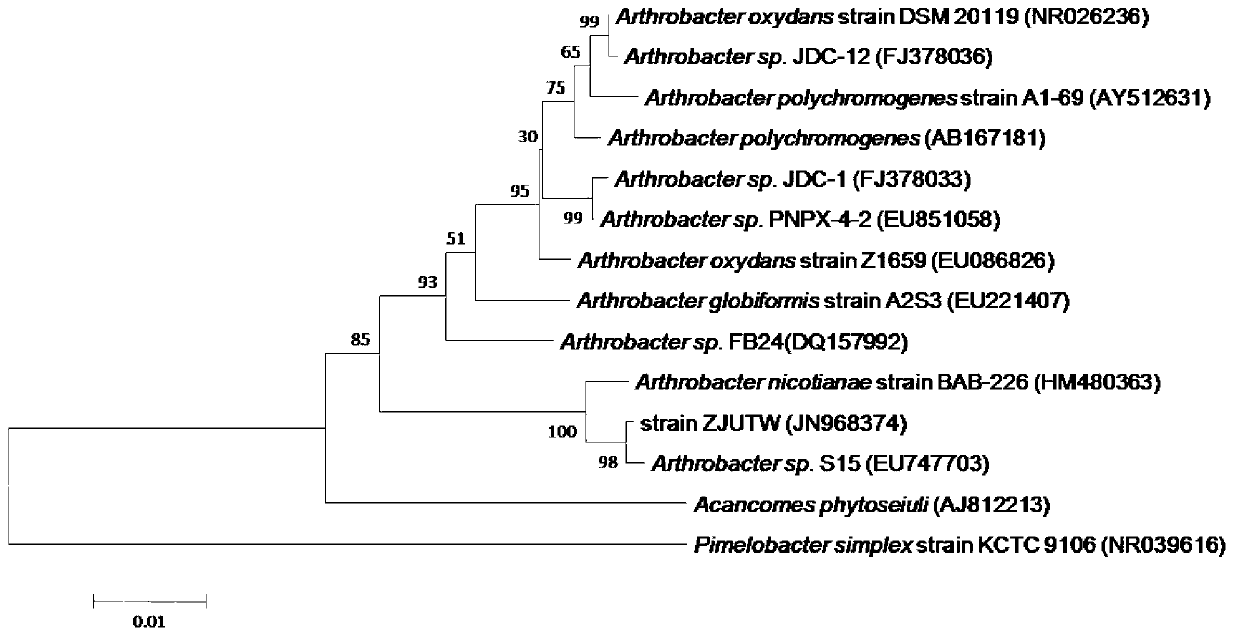
The invention provides a strain Arthrobacter sp.ZJUTW with high phthalate degrading property and an application of the strain. The strain is conserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (address: Wuhan University, Wuhan City, China 430072), the preservation number (CGMCC No) is 2012246 and the conservation date is June 24, 2012. The new strain with high phthalate degrading property is provided, the diethyl phthalate (DEP) and dibutyl phthalate (DBP) degrading conditions of resting cells are optimized and the environmental pollution problem of phthalate compounds can be effectively solved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
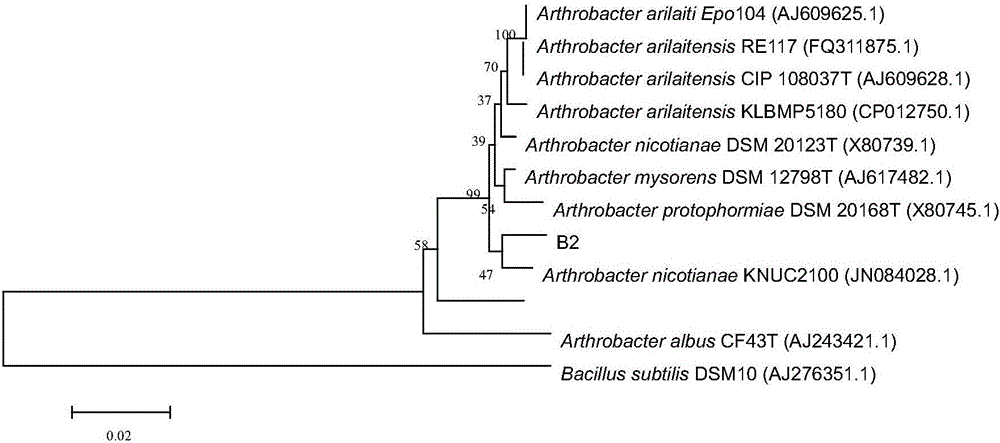
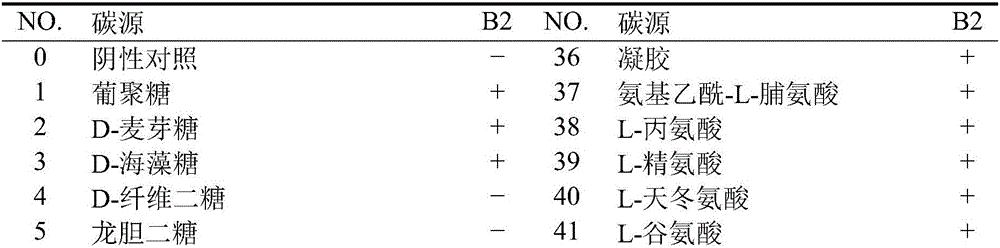
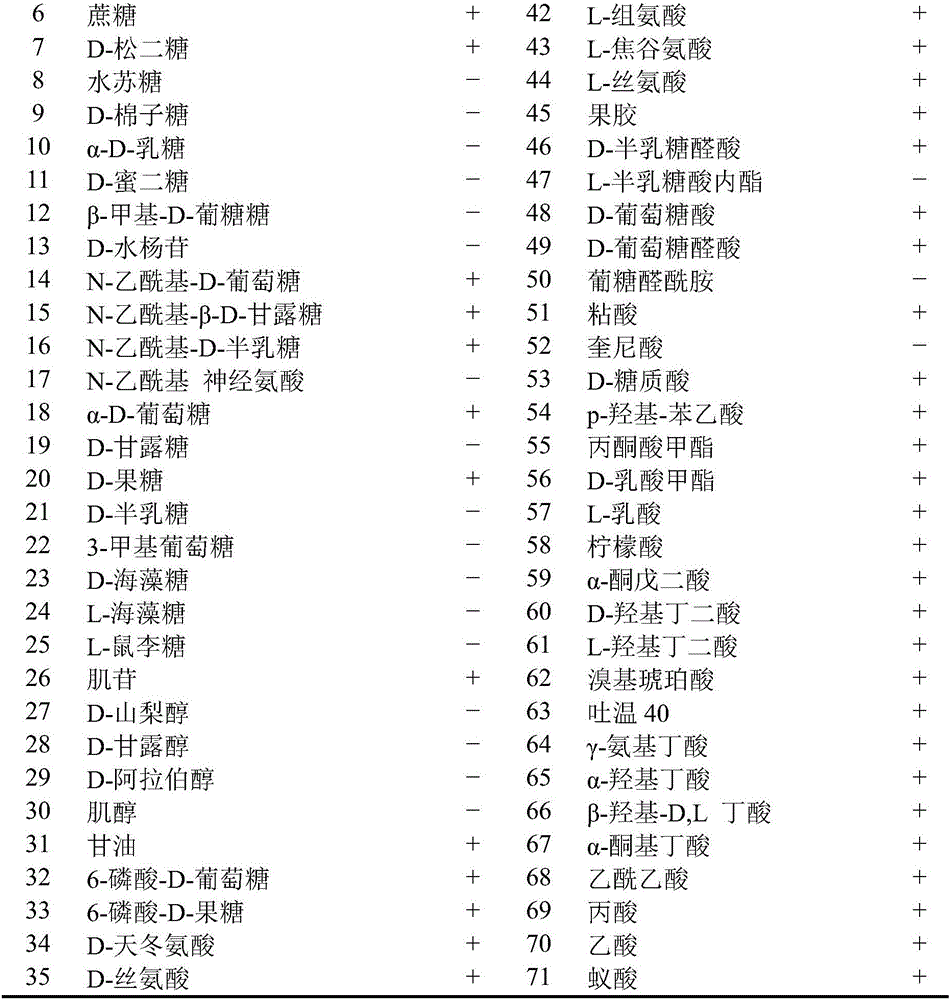
Strain of Arthrobacter sp. B2 and application thereof to nitrogen-containing sewage degradation
ActiveCN106399191AWith heterotrophic-aerobic denitrification functionBacteriaWater contaminantsNitriteOxygen
The invention provides a strain of Arthrobacter sp. B2 and application thereof to nitrogen-containing sewage degradation. The Arthrobacter sp. B2 is preserved in CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) on September 14, 2016, and has the preservation number of CCTCC NO:2016485. The Arthrobacter sp. B2 has high denitrification capability under the aerobic condition; the nitratlon reaction and the denitrification reaction are realized; the organic matters in the water body and organic matters of ammonia nitrogen, nitrite nitrogen and the like can be effectively degraded in the sewage treatment oxidation pond; the water body purification treatment is realized. Therefore the prepared strain of the Arthrobacter sp. B2 is applied to sewage treatment and culture waste water purification industry. The degradation rate of the nitrate is 87.6 percent; the nitrite degradation rate is 84.5 percent.
Owner:朗境环保科技有限公司
Microbial preparation for soil remediation
ActiveCN108624582AImprove compactionImprove adsorption capacityContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganism based processesMicrobial agentArthrobacter sp.
Owner:江苏世邦生物工程科技有限公司
Compound microbial soil remediation agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
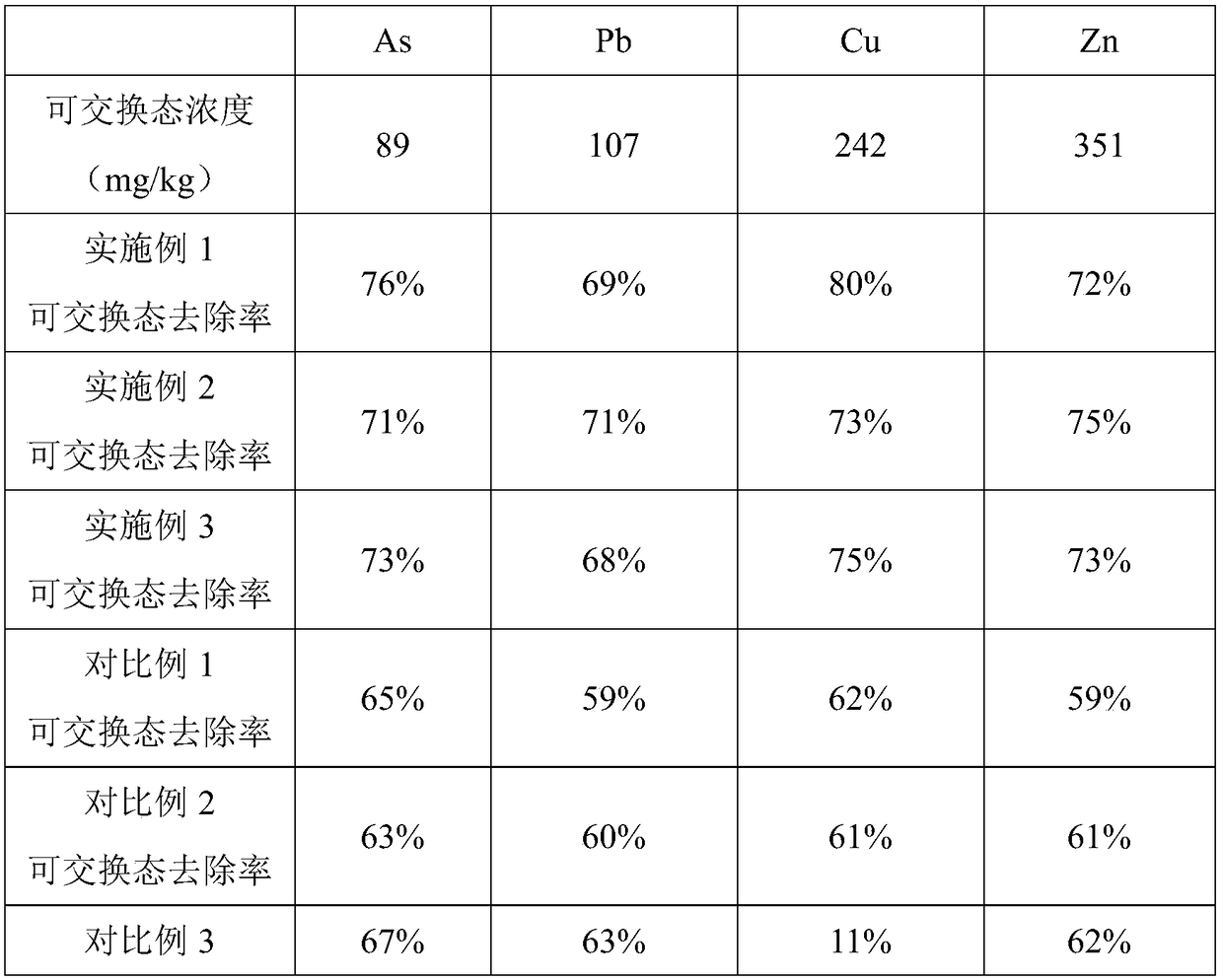
ActiveCN108441451AReduce contentEfficient degradationBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationAmylaseMicrobial agent
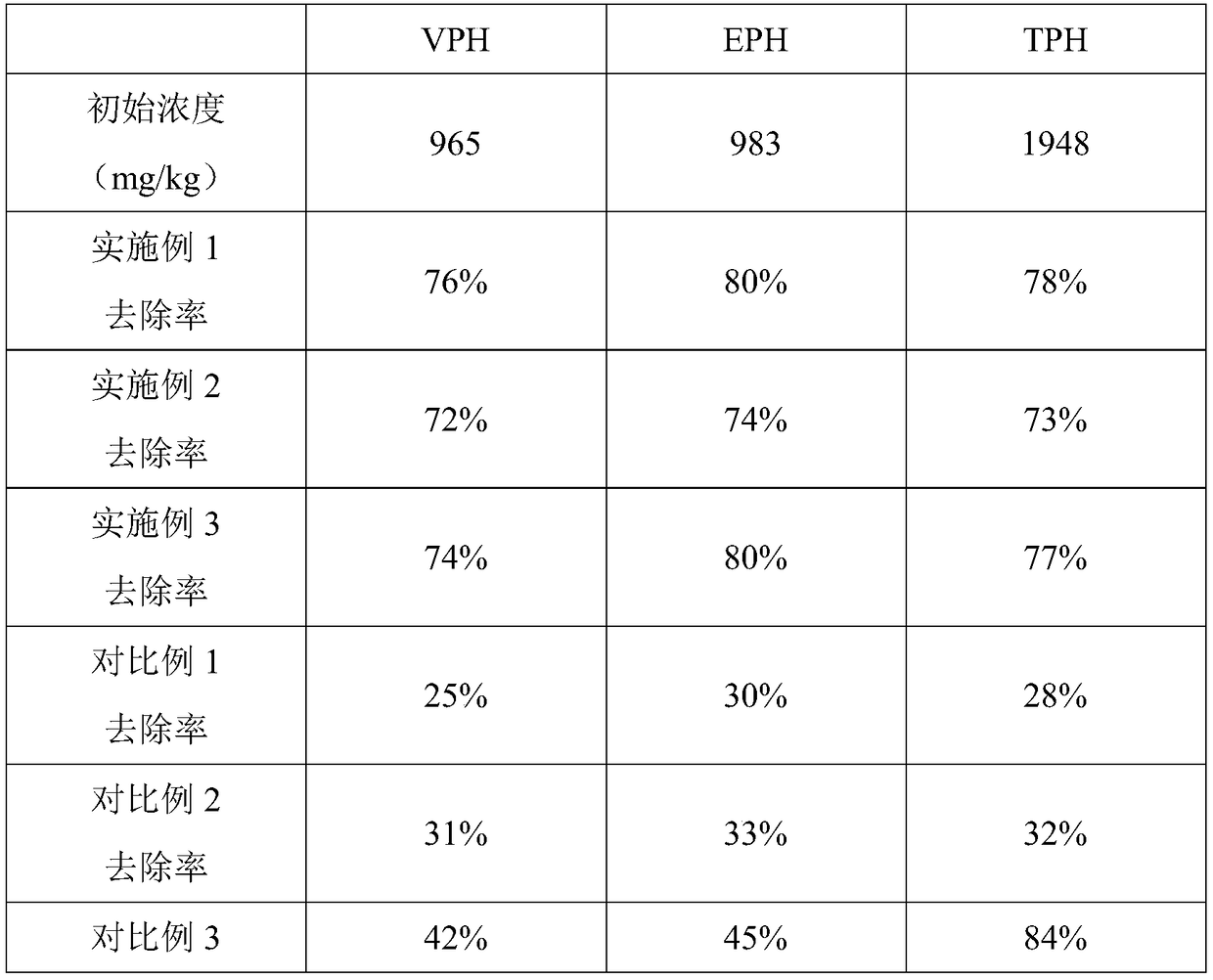
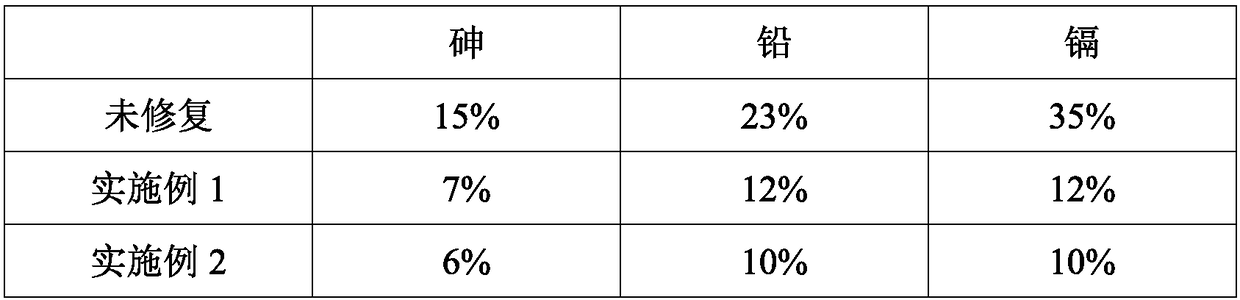
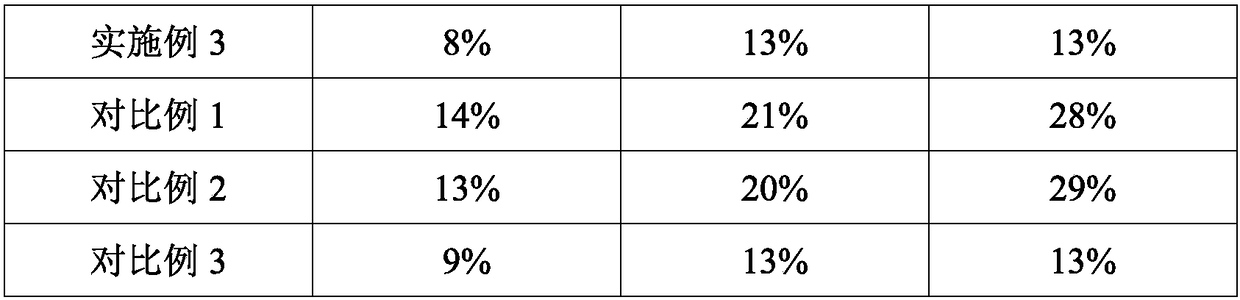
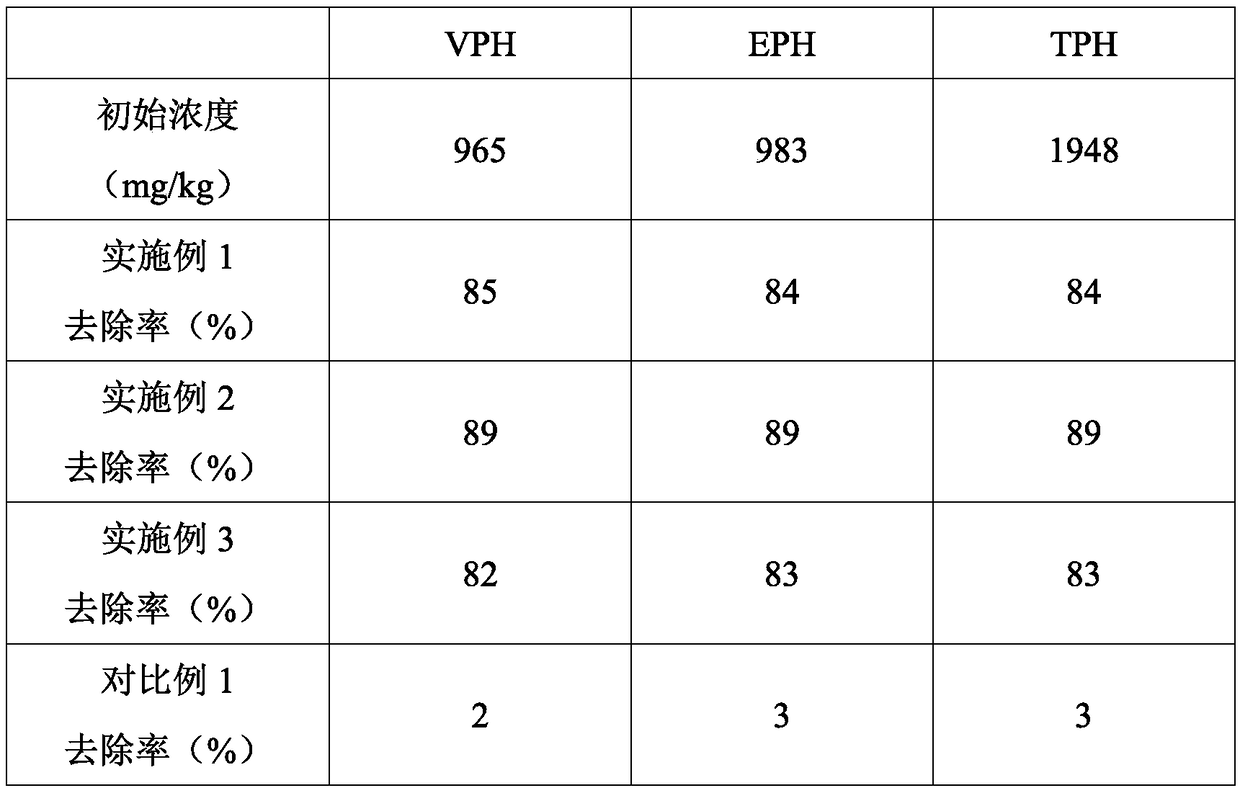
The invention discloses a compound microbial soil remediation agent. The agent comprises an arthrobacter sp. LHM7719 agent, a Bacillus subtilis microbial agent and compound enzyme, wherein the compound enzyme comprises glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and beta-amylase. The invention also discloses a preparation method and an application of the compound microbial soil remediation agent. Thearthrobacter sp. LHM7719 is applied to the soil remediation field and can significantly reduce the content of heavy metals including arsenic, lead and cadmium in soil after being matched with Bacillus subtilis and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and efficiently degrade petroleum hydrocarbon in the soil after being matched with the beta-amylase, so that the agent has good application prospects.
Owner:江苏世邦生物工程科技有限公司
Method for converting indole by phenol hydroxylase genetic engineering strains to prepare indigotine
InactiveCN101851649AImprove conversion abilityBroad substrate spectrumBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliDry weight
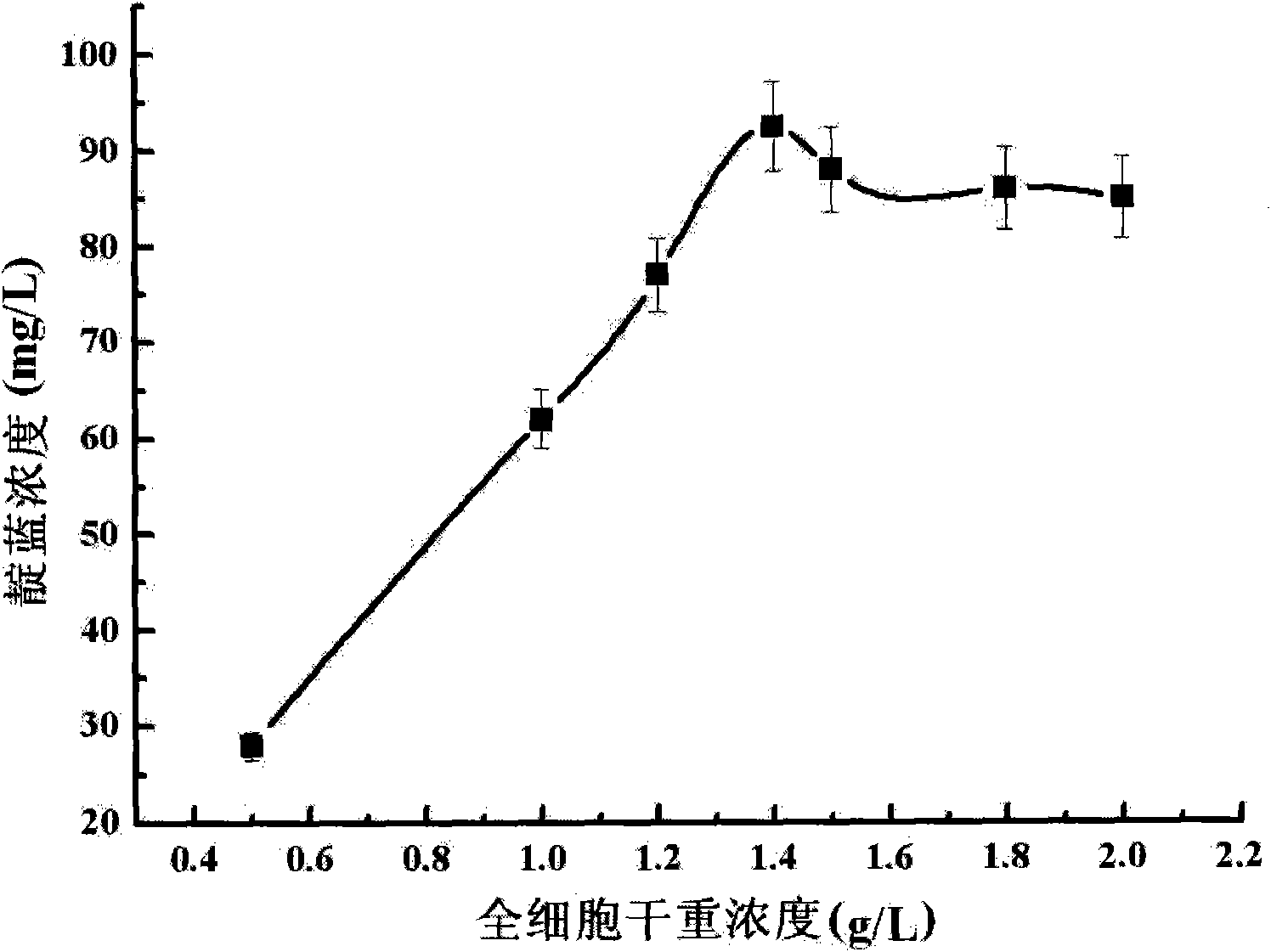
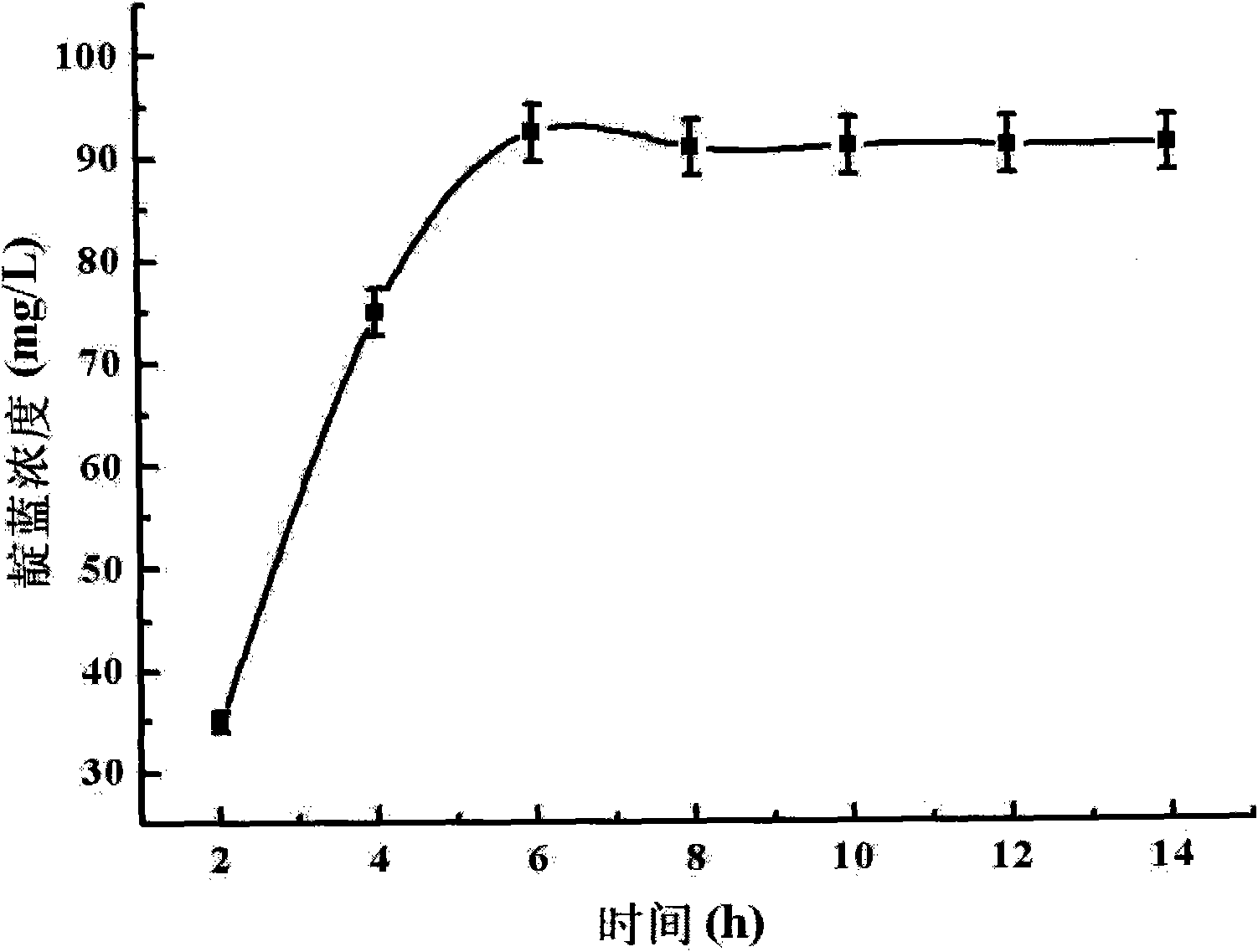
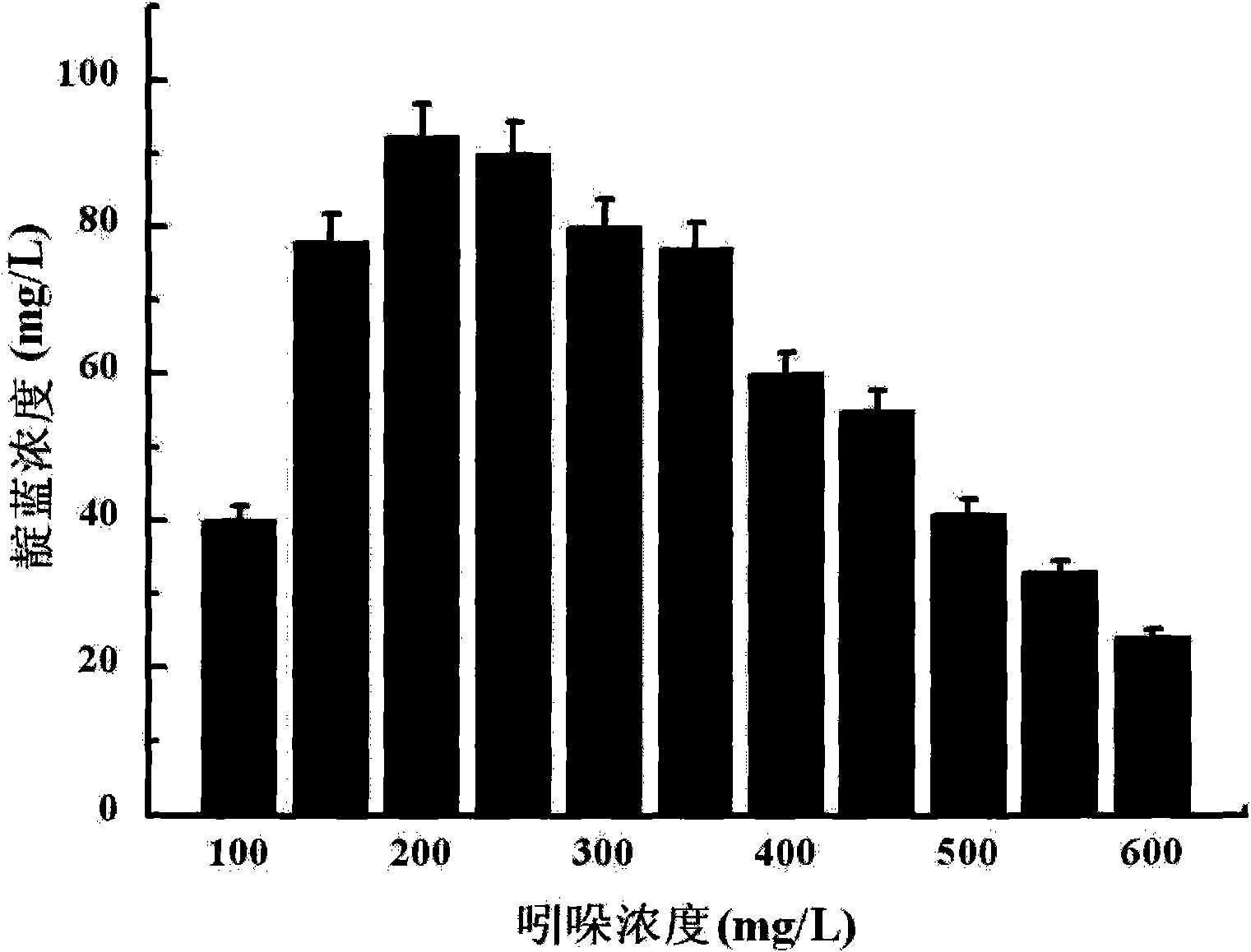
The invention relates to a method for converting indole to prepare indigotine by engineering strains formed by recombining phenol hydroxylase genes into colon bacillus, which belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining phenol hydroxylase gene full-length sequences with the total length of 5490bp and the Genbank registration number of FJ610336 in high-efficient phenol-degrading bacteria Arthrobacter sp.W1 with the GenBank registration number of EU339930; connecting the phenol hydroxylase gene full-length sequences to carrier plasmids (pET28a (+) Vector); and converting the phenol hydroxylase gene full-length sequences into host cell colon bacillus to construct phenol hydroxylase genetic engineering strains. The full-cell dry weight concentration of the phenol hydroxylase genetic engineering strains in a biological conversation reaction solution is between 1 and 2 g / L, the indole concentration is between 100 and 600 mg / L, the glucose concentration is between 0.5 and 2 mmol / L, the rotation speed of a shaking table is controlled between 50 to 200 r / min at a temperature between 20 and 40 DEG C, and the oscillating reaction lasts 2 to 14 hours. The biological conversation method of the invention has the advantages of mild reaction condition, high product concentration and short production period, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for recovering herbicide atrazine-polluted soil by using degradable bacteria
InactiveCN102989761AImprove degradation efficiencyProlong degradation timeContaminated soil reclamationSaccharumSucrose
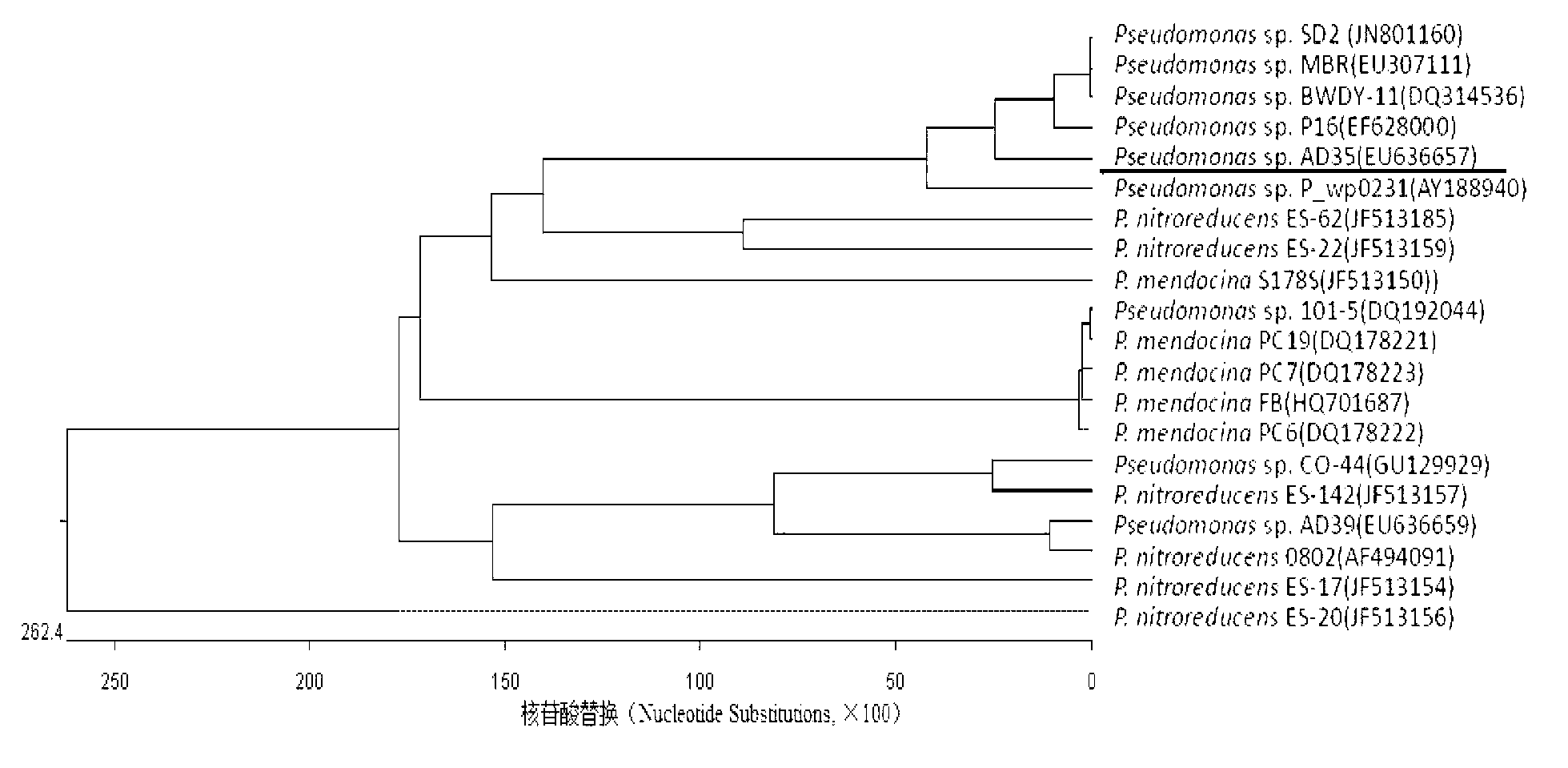
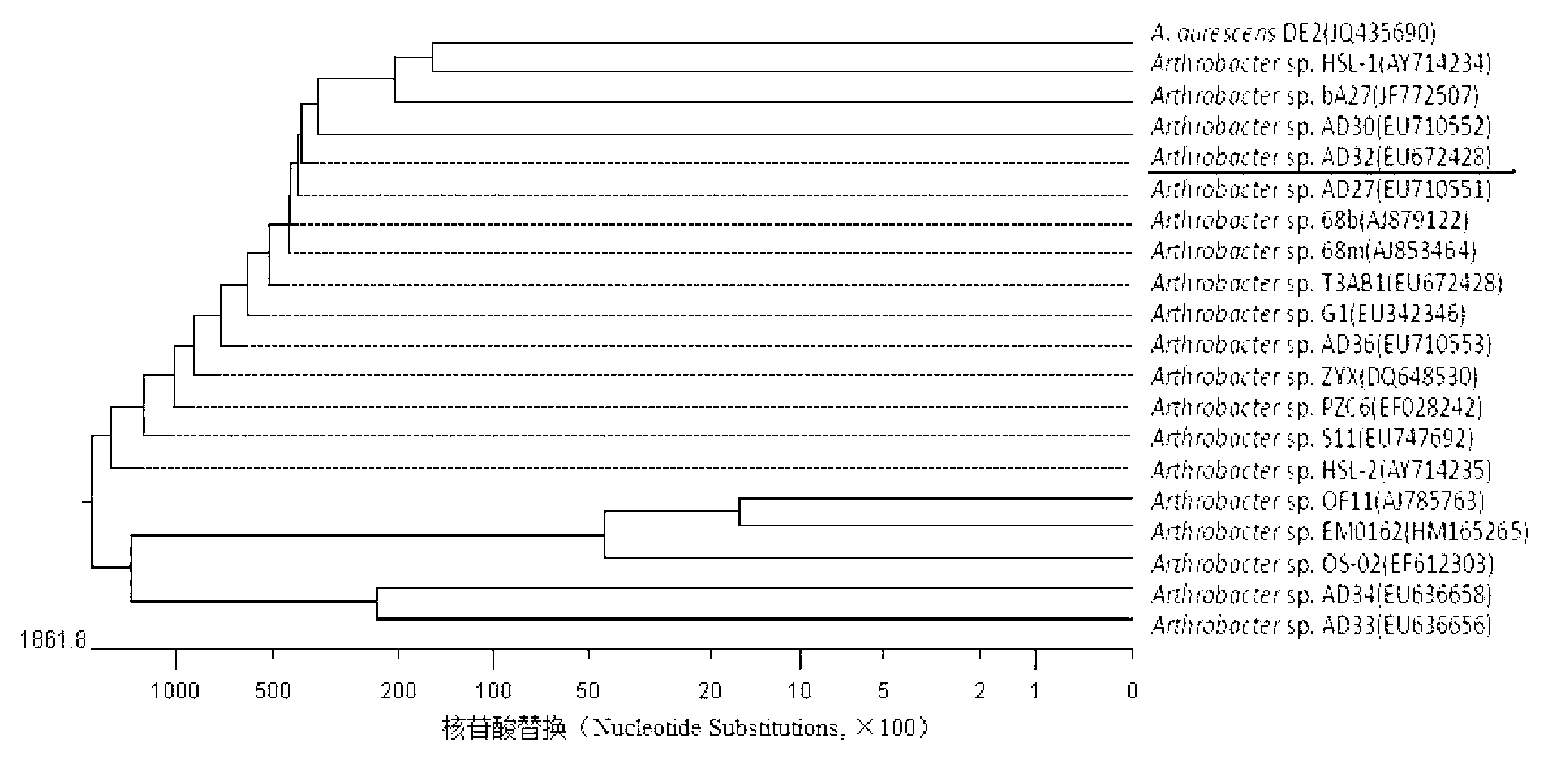
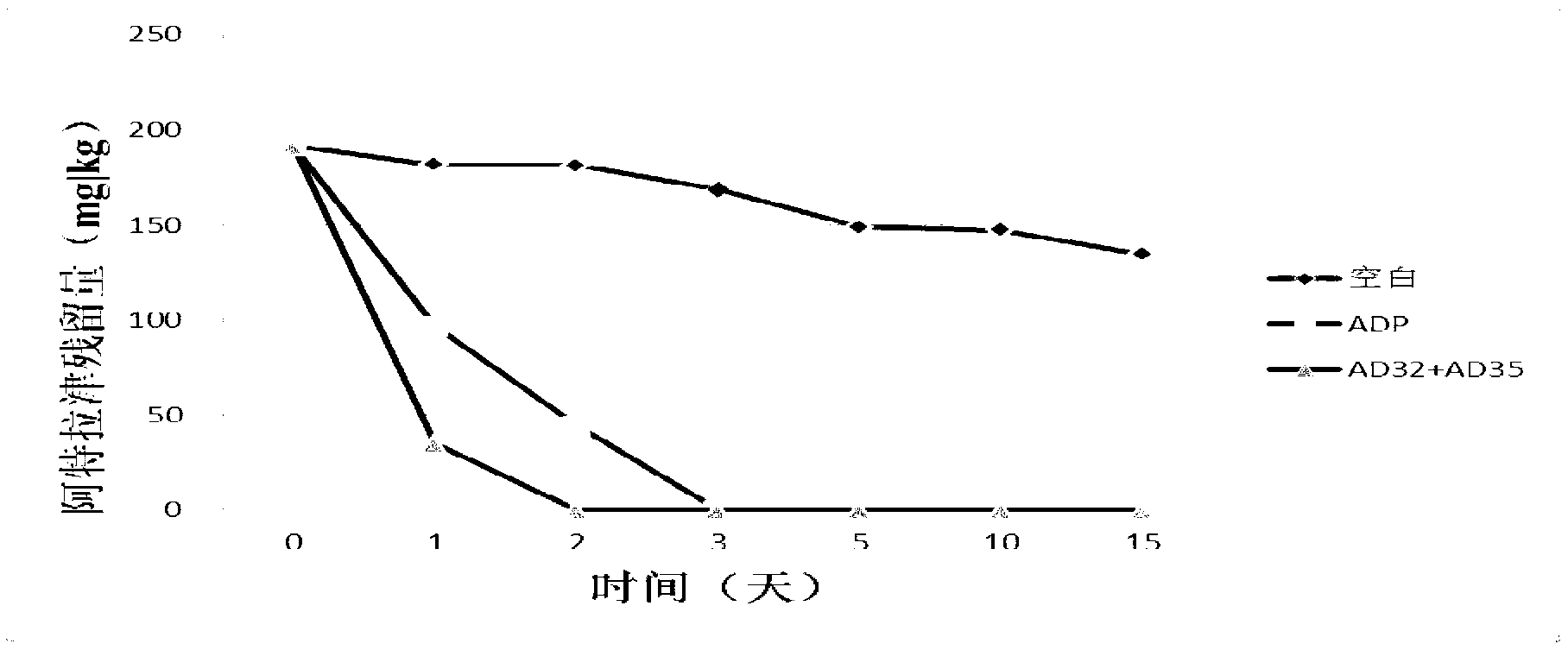
The invention relates to a method for separating and identifying two bacterial strains of degradable herbicide atrazine, and carrying out bioremediation on polluted soil with an atrazine concentration of 200mg / kg by using mixed bacteria of the two bacterial strains, belonging to the field of polluted soil recovery. The used bacterial strains are respectively arthrobacterium (Arthrobacter sp.) AD32 and pseudomonas (Pseudomonas sp.) AD35; a proper amount of cane sugar (1g / L-3g / L) and phosphate (0.3g / L) are added into the bacterium suspension when the soil is recovered; and after the soil is processed for two days in 30 DEG C, the removing rate of the atrazine is 100%.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Arthrobacterium and application thereof in degradation of aflatoxin
ActiveCN103981132AEfficient degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAflatoxin degradationMicrobiology
The invention discloses an arthrobacterium and an application thereof in degradation of aflatoxin and provides an arthrobacterium (Arthrobacter sp.) L15 which is assigned the accession number CGMCC No.8869. An experiment in the invention proves that the arthrobacterium L15 is discovered in the invention. Aflatoxin can be degraded efficiently when a fermentation liquor of the arthrobacterium L15 is added to the aflatoxin and dissolving and uniform mixing are carried out. The arthrobacterium L15, used as a biological material for degrading aflatoxin, has good application prospects in exploitation of not only novel biodegradation inoculants but also novel biodegradation sterile preparations.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Biochar-based bacterial composite soil conditioner as well as preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN108192631AImprove fertilitySimple structureAgriculture tools and machinesBacteriaBacillus cereusArthrobacter sp.
The invention discloses a biochar-based bacterial composite soil conditioner as well as preparation and application thereof. A preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) domestication of bacteria: sequentially inoculating bacillus cereus, ochrobactrum sp. and arthrobacter sp. into a Cd-containing inorganic salt culture solution with a gradient concentration respectively for domestication and cultivation; and mixing the domesticated and cultured bacterial solutions to prepare a bacterial suspension for later use; and (2) preparation of the biochar-based bacterial composite soil conditioner: taking biochar to be mixed with the bacterial suspension, adding antagonistic elements of heavy metals in soil, then performing shaking cultivation, filtering and washing. The biochar-based bacterial composite soil conditioner provided by the invention is simple in preparation method and low in cost; microorganisms in the preparation have high tolerance to the heavy metal Cd, so that the preparation has good remediation effect on the heavy metals in the soil, and is stable, long-acting, and less affected by the environment; the invention is an in-situ chemistry-combined microbial passivation remediation technology effectively applied to heavy metal-contaminated soil in farmlands.
Owner:HUNAN HENGKAI ENVIRONMENT TECH INVESTMENT CO LTD
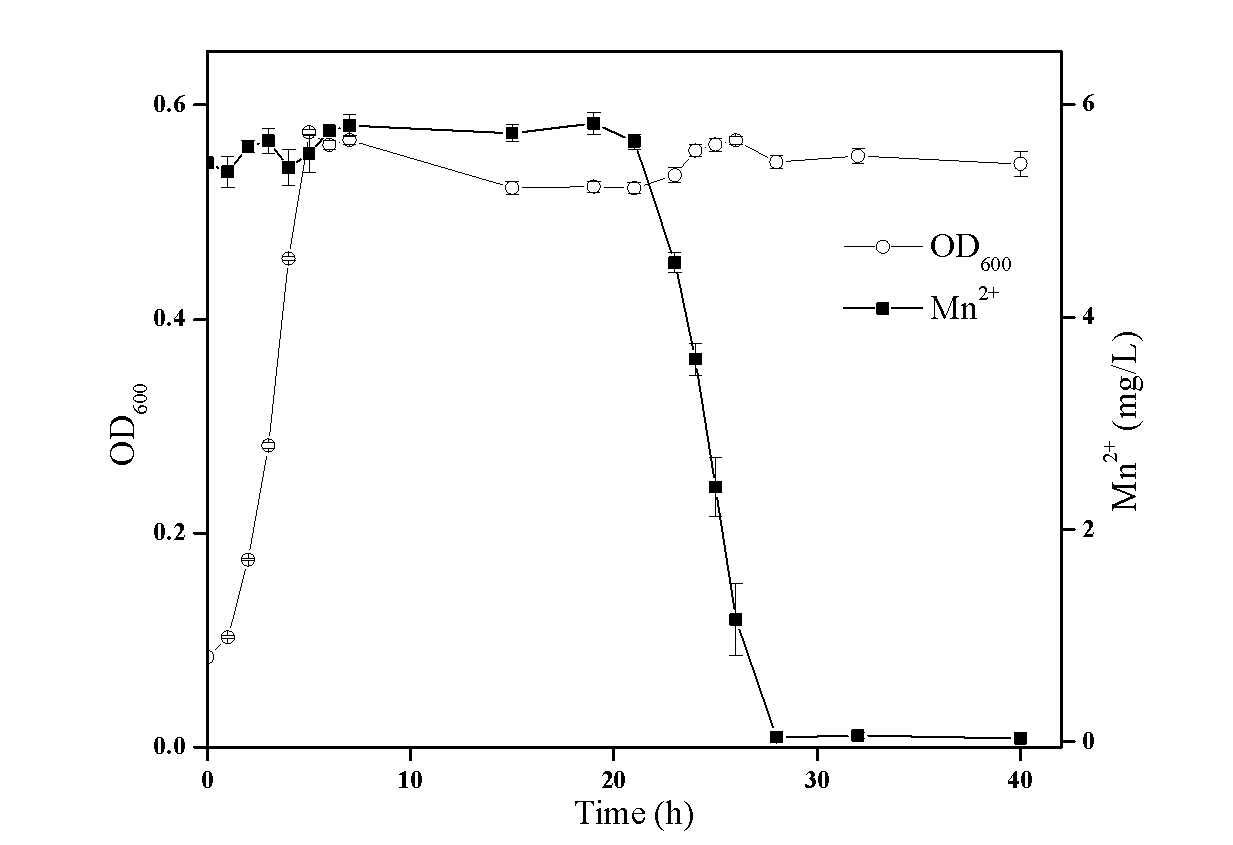
Manganese oxidizing composite microbial system and application thereof
The invention discloses a composite microbial system capable of oxidizing Mn2+ and an application of the composite microbial system in a water body or a solid matrix. The composite microbial system can oxidize Mn2<+> in the water body or the solid matrix to generate manganese oxide insoluble in water. The Mn2<+> oxidizing composite microbial system comprises two bacterial strains belonging to different categories: Arthrobacter sp. QXT-31 and Sphingopyxis sp. QXT-31B, respectively. The preserve numbers are respectively CGMCC No.6631 and CMGCC No.6947. The Arthrobacter sp. QXT-31 and Sphingopyxis sp. QXT-31B provided by the invention are used to oxidize Mn2<+> in the natural water body, and the operating temperature (10-30 DEG C) is in a normal temperature range, the operating pH value (6.5-8.5) is in a neutral range, and high Mn2<+> oxidizing efficiency is obtained.
Owner:清华苏州环境创新研究院
Biochemical preparation for treating threonine fermentation sewage
ActiveCN105921099AReduce dosageShorten the timeOther chemical processesSilicon compoundsBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention relates to a biochemical preparation for treating threonine fermentation sewage. The biochemical preparation is characterized by comprising a physical adsorbent and a composite microbial agent, wherein the composite microbial agent is prepared from the following raw materials by a volume ratio: 6 to 7 parts of arthrobacter sp., 5 to 7 parts of pseudomonas stutzeri, 5 to 7 parts of rhodococcus sp., 4 to 5 parts of bacillus amyloliquefaciens, 4 to 5 parts of clostridium papyrosolvens and 3 to 4 parts of scenedesmus obliquus. The biochemical preparation contains multiple microorganisms having good degrading capability to recalcitrant pollutants; various strains are reasonably matched to realize a good degrading effect; the biochemical preparation has a broad application prospect.
Owner:内蒙古阜丰生物科技有限公司
Arthrobacter for producing beta-fructofuranosidase and application of arthrobacter
ActiveCN106148243AImprove the ability to convert into lactulose oligosaccharidesIncrease vitalityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNitroso
The invention relates to arthrobacter for producing beta-fructofuranosidase and application of the arthrobacter. The Arthrobacter sp. BLCY-004 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on August 16th, 2016, the address is the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, No. 3, No.1 Yard, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 12855. The arthrobacter is separated from soil, the high-producing strain of high-producing beta-fructofuranosidase is obtained by means of mutagenic treatment technologies such as ultraviolet mutagenesis, nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis and the like and is named as BLCY-004, the enzyme activity reaches 1100U / ml and is improved by more than 50% as compared with that of conventional beta-fructofuranosidase, the capacity that sucrose is converted into lactosucrose can be highly improved by applying the arthrobacter to production of lactosucrose, and production cost is lowered significantly.
Owner:SHANDONG BAILONG CHUANGYUAN BIO TECH
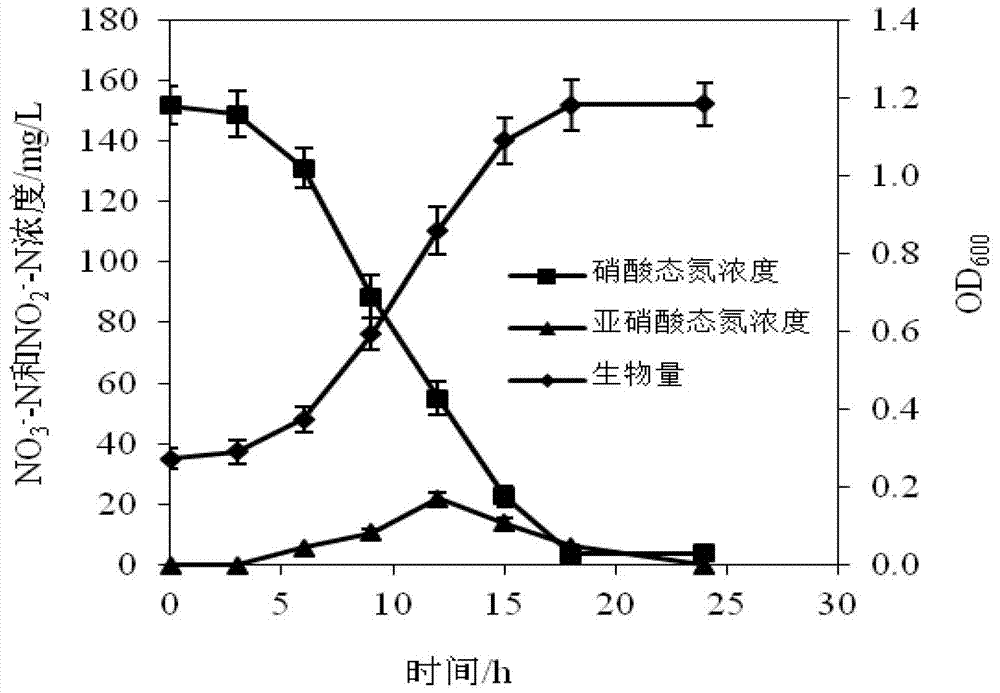
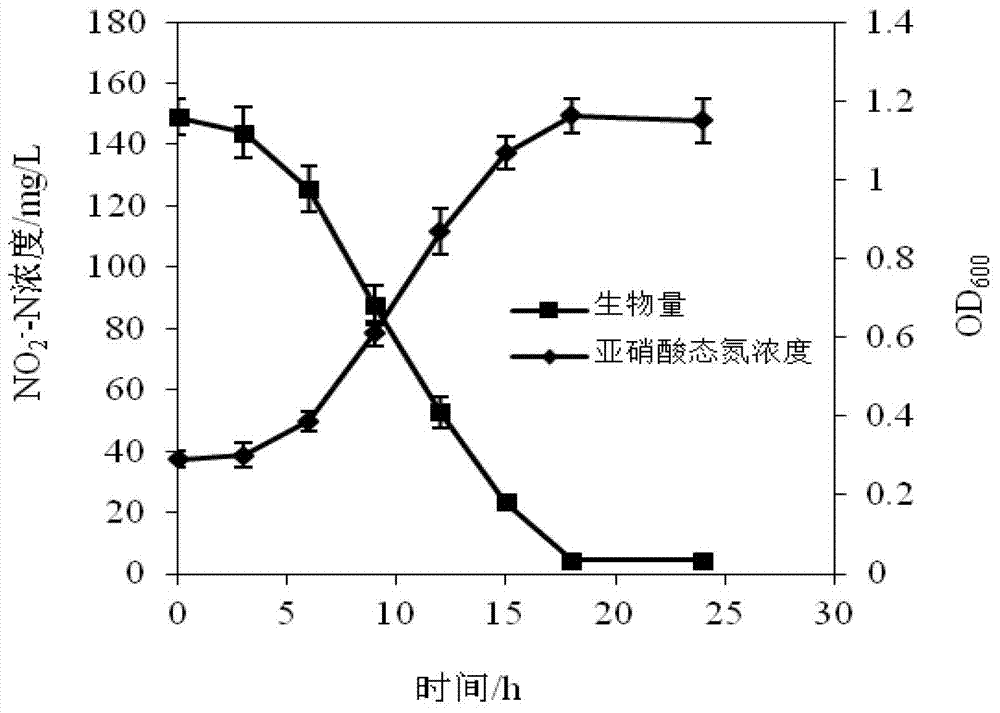
Heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification arthrobacterium and application thereof
ActiveCN107245463AWide pH rangeWide range of temperature adaptationBacteriaWater contaminantsHigh concentrationNitrogen gas
The invention discloses a heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification arthrobacterium and application in denitrification of wastewater. The bacteria strain is Arthrobacter sp. WZUF01, and is preserved into Common Microorganism Center of China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center; the registration number in the collection center is CGMCC NO.14012. The bacteria strain has the advantages that the nitrogen in the nitrogen-containing wastewater is removed, the pH (potential of hydrogen) and temperature application ranges are broader, the carbon and nitrogen mass ratio is lower, and the higher content of dissolved oxygen can be endured; the high concentration of ammonia can be endured, the wastewater with NH4<+>-N concentration more than 300mg / L from a culture farm after anaerobic digestion can be treated, the treatment result meets the pollutant emission standard of livestock and poultry culture industry (GB18596-2001), and the final product is nitrogen; the gathering ability is good; the Arthrobacter sp. WZUF01 has greater application potential in the actual nitrogen removal of the wastewater.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
Arthrobacter sp. and application thereof in aspect of biological control of bacterial wilt of tomato
ActiveCN106520595ADescription SurvivalGood Growth InhibitionBiocideCalcareous fertilisersFungicideRalstonia solanacearum
The invention discloses arthrobacter sp. and application thereof in aspect of biological control of bacterial wilt of tomato. 16SrRNA of the arthrobacter sp. has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1. The invention also discloses a screening method of the arthrobacter sp. as well as preparation methods of a tomato bacterial wilt antagonistic fungicide and a tomato bacterial wilt antagonistic breeding medium. According to the invention, by separating and screening tomato bacterial wilt antagonistic bacteria and by conducting control effect experiments, a strain, which has an antagonistic action on the tomato bacterial wilt, is separated and screened out; firstly, through culture and propagation, the finished fungicide product is prepared, and then, mushroom residues, obtained from edible fungi cultivation, are fermented and rotten and are mixed with other substrates according to a certain proportion, so that the breeding medium is prepared; the biocontrol fungicide and the breeding medium are organically combined; the arthrobacter sp. has the advantages of being rich in available resources, low in cost, capable of preventing secondary pollution to environment when used for controlling the bacterial wilt and the like; therefore, an effective way is provided for solving the soil-borne disease, namely the bacterial wilt of tomato.
Owner:INST OF GARDENING ANHUI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Tetracycline antibiotics degrading arthrobacterium and application thereof
ActiveCN108707559APromote degradationReduce residual concentrationBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationBacterial strainArthrobacter sp.
The invention relates to the field of environment protection, and discloses a tetracycline antibiotics degrading arthrobacterium and application thereof. The classification name of the tetracycline antibiotics degrading arthrobacterium is Arthrobacter sp.. The Arthrobacter sp. is tetracycline antibiotics degrading arthrobacterium, can effectively degrade various tetracycline antibiotics, has the best oxytetracycline degrading effect, and has the good degrading effect for tetracycline and aureomycin. The bacterial strain OTC-16 can grow under the pH of 6.0-9.0 and under the temperature of 20-35DEG C, the application range is wide, and the tetracycline antibiotics degrading arthrobacterium can be used for repairing tetracycline antibiotics pollution.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Method for preparing S type cyclopentenone by sol-gel embedding immobilized enzyme
InactiveCN101418291AHigh activityImprove stabilityMicroorganism based processesOn/in organic carrierSilanesKetone
The invention discloses a method for preparing S-type cyclopentenone from a sol gel embedded immobilized enzyme. The method comprises the following steps: 1) using an organic silane reagent as a precursor to react with water under the catalysis of acid or alkali so as to generate a sol; 2) adding a buffer solution containing enzyme powder into the mixture, and mixing, keeping stand for aging, and drying the mixture to obtain the sol gel embedded immobilized enzyme; and 3) using the sol gel embedded immobilized enzyme as a catalyst to perform enantiomeric separation reaction with cyclopentenone in an organic phase so as to obtain the S-type cyclopentenone. The method is characterized in that the used lipase is Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Arthrobacter sp. and Acinetobacter sp.; the precursor is gamma-methacryloyl-oxypropyl-trimethoxysilane or alkyl-trimethoxysilane, or a mixture of the gamma-methacryloyl-oxypropyl-trimethoxysilane or the alkyl-trimethoxysilane and n-methyl silicate or ethyl orthosilicate; and the cyclopentenone is allyl alcohol ketone or propargyl alcohol ketone. The vitality, the stability, the enantioselectivity and the like of the immobilized enzyme related in the invention are significantly improved in the split reaction of the cyclopentenone.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Compound bacterial agent applied to straw mulching and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105238714ASimple methodCombination newBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicromonospora sp.Decomposition
The invention discloses a compound bacterial agent applied to straw mulching. The compound bacterial agent comprises 1.0*10<9>cfu / g-8.0*10<9>cfu / g of Bacillus sp.CZ5, 1.0*10<8>cfu / g-6.0*10<9>cfu / g of Arthrobacter sp.WH16, 1.0*10<9>cfu / g-2.0*10<10>cfu / g of Streptomyces sp.WH36 and 1.0*10<7>cfu / g-5.0*10<8>cfu / g of Micromonospora sp.WH13. The invention further provides a preparation method of the compound bacterial agent applied to straw mulching. Compared with the prior art, the compound bacterial agent applied to straw mulching has the advantage that purposes of quick decomposition of straw, suppression of soil pathogens and increase of crop yield are achieved under synergistic effect of various straw degradation bacteria / biocontrol bacteria.
Owner:上海原本生物科技有限公司
Microbes for alkyl glycoside synthesis and application thereof
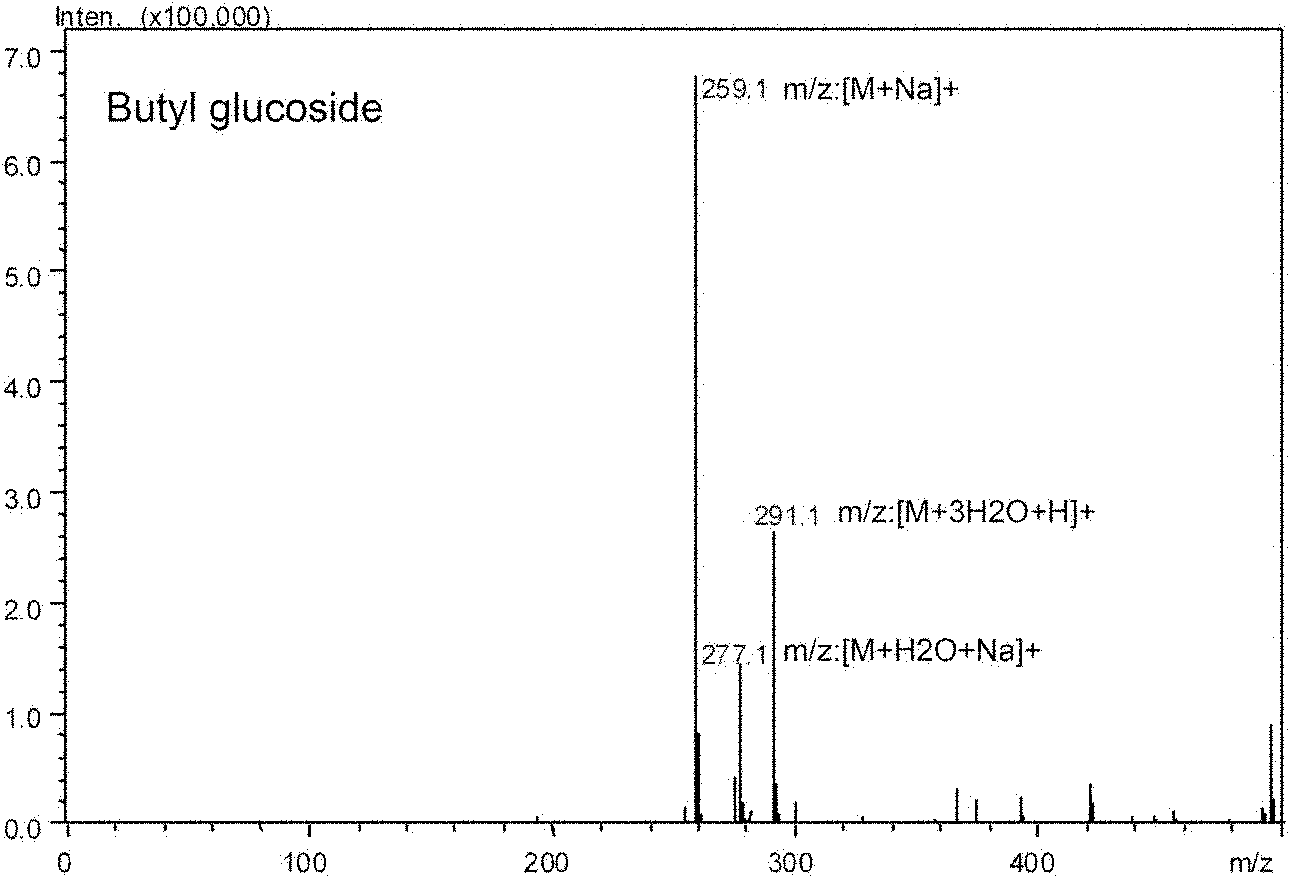
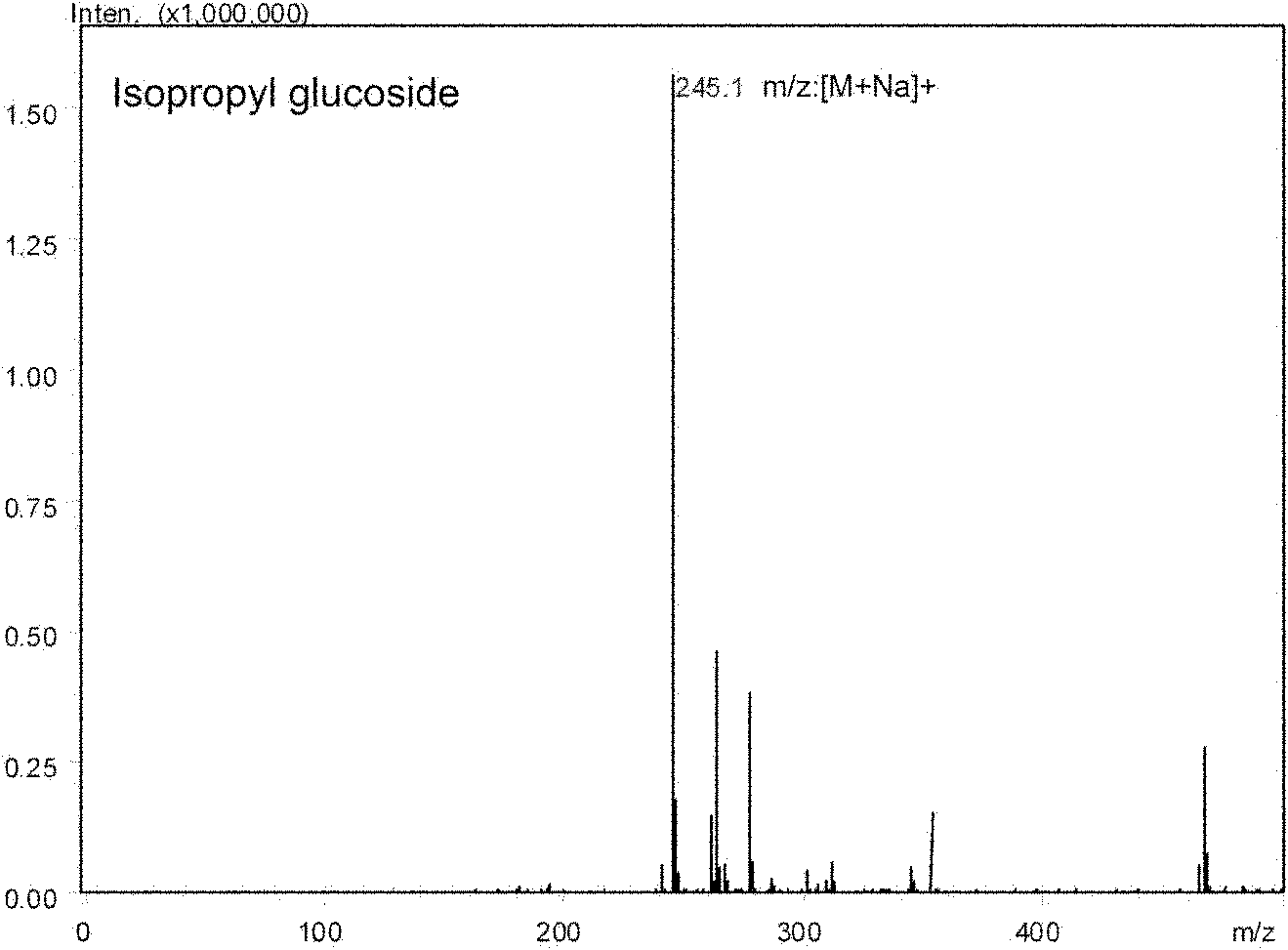
The invention relates to microbes having a high-efficiency transglycosylation activity and application thereof. The microbes are Arthrobacter sp.DL001. Strains or broth of Arthrobacter sp.DL001 can realize high-efficiency transglycosylation to glycosyl acceptors in the presence of glycosyl donors and thus a novel effective method for preparing carbohydrates and glycosides by biotransformation reactions is provided. The novel effective method can realize high-efficiency, cheap and eco-friendly preparation of carbohydrates and glycosides and is an effective approach of industrial production of carbohydrates and glycosides.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG IND TECH RES INST CO LTD DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Marine microorganism Arthrobacter sp. YJ34 dextranase producing gene and recombinant engineering bacterium thereof
InactiveCN109679974AEfficient expressionHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliMicroorganism
The invention provides a marine microorganism Arthrobacter sp. YJ34 dextranase producing gene. An enzyme gene sequence is 1923 bp in total length, ATG is taken as an initial codon, TAG is taken as a terminal codon, and GC base content is 59.23 percent. The invention further discloses a dextranase gene recombinant engineering bacterim obtained through cloning of the dextranase gene and efficient expression in escherichia coli. The invention belongs to the technical field of enzymology and enzyme engineering. The recombinant engineering bacterium is built through gene cloning and sequencing, anda purified recombinant enzyme is obtained by induced expression and purification of a recombinant enzyme. The enzyme activity and enzyme stability are improved greatly. The optimal reaction temperature of the enzyme is 55 DEG C as determined according to the enzymatic property, and the optimal acting pH is 7.5.
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH
Fermentation medium, bacterial strain and production method for fermentation production of adenosine cyclophosphate
ActiveCN103571779ASolve complex processLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismAdenosine
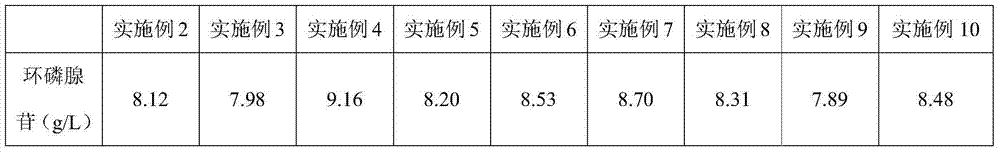
The invention discloses a fermentation medium, a bacterial strain and a production method for fermentation production of adenosine cyclophosphate. The medium comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 5-15% of glucose, 0.5-1% of peptone, 1-6% of monopotassium phosphate, 1-6% of dipotassium phosphate, 0.3-0.6% of magnesium sulfate, 1-6% of urea, and 0.3-0.6% of purine base. The bacterial strain is Arthrobacter sp.A.sp01; the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M 2013431; the preservation data is September 17, 2013; the preservation authority is the China center for type culture collection; the preservation address is Wuhan university in China. The fermentation medium disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being simple to operate, low in raw material cost, safe and environment-friendly, and can be applied to industrial production. An experiment proves that the content of the adenosine cyclophosphate obtained by the production method disclosed by the invention is at least more than 7.8g / L, and can be up to 9.16g / L. A new route is opened for fermentation production of the adenosine cyclophosphate by employing microorganisms.
Owner:HENAN INST OF SCI & TECH
Arthrobacter sp. expression plasmid and application thereof
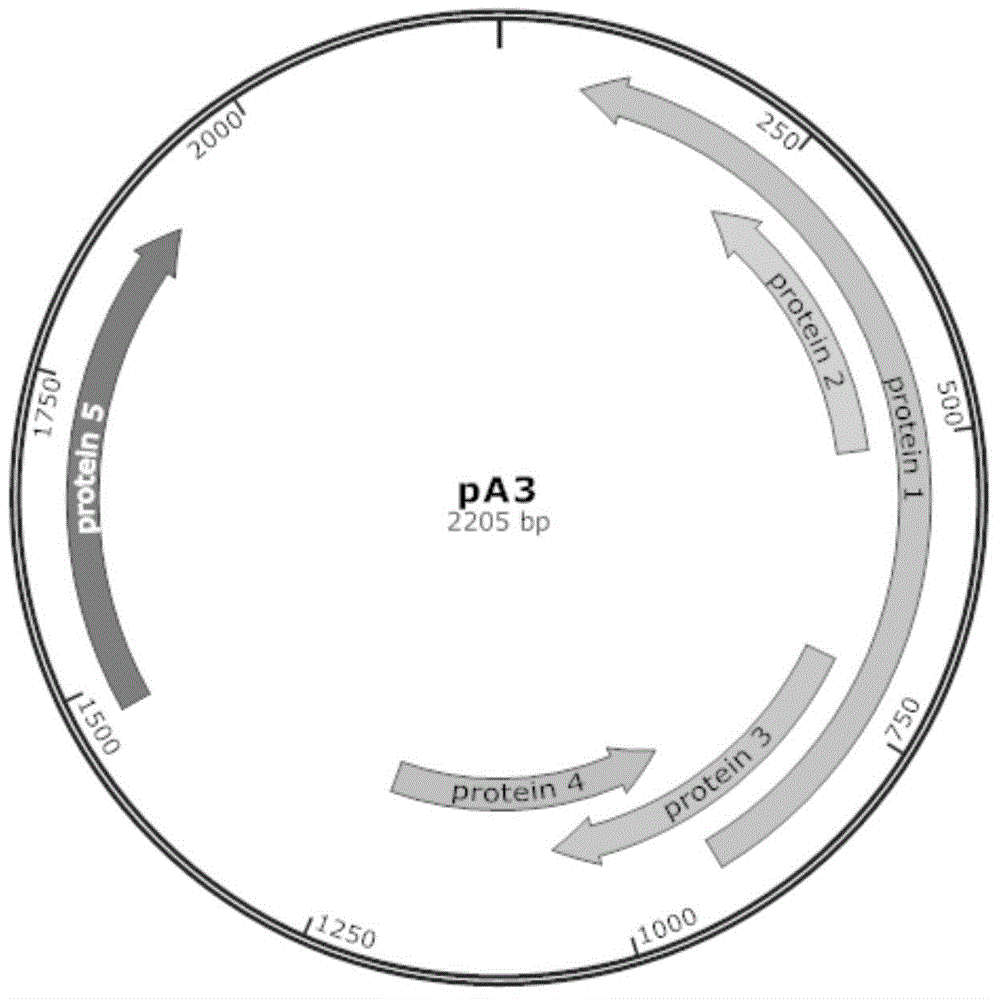
ActiveCN104962574AIncrease productionGreen fluorescence is obviousMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliResistant genes
The invention discloses an Arthrobacter sp. expression plasmid, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The plasmid disclosed in the invention is annular in shape, and the nucleotide sequence of the plasmid is represented by SEQ ID NO:1, comprises an Arthrobacter sp. promoter sequence, a multiple cloning site sequence, a replicating sequence in Arthrobacter sp., a kanamycin resistant gene sequence, an Escherichia coli replicating sequence and an amicillin resistant gene sequence, and can autonomously replicate in Escherichia coli and Arthrobacter sp.. The plasmid is used to express ghprt gene in the Arthrobacter sp. of CGMCC3584, and the cAMP output of the plasmid is 65.2% higher than that of original strain.
Owner:南京趣酶生物科技有限公司 +1
Arthrobacter sp. PL-410 and application thereof in producing chondroitin lyase
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganisms, in particular to arthrobacter pseudoarthrobacter PL-410 and application of the arthrobacter pseudoarthrobacter PL-410 in production of chondroitin lyase. The preservation number of the pseudoarthrobacter sp. PL-410 provided by the invention is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.22736, and the preservation number of the pseudoarthrobacter sp. PL-410 is CGMCC No.22736. The pseudoarthrobacter sp. PL-410 disclosed by the invention can be used for preparing chondroitin lyase (AC type), and the chondroitin lyase can be used for researching the structure of chondroitin sulfate and constructing a chondroitin sulfate oligosaccharide library, can also be applied to the field of medicines, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Arthrobacter CW9 and its purpose
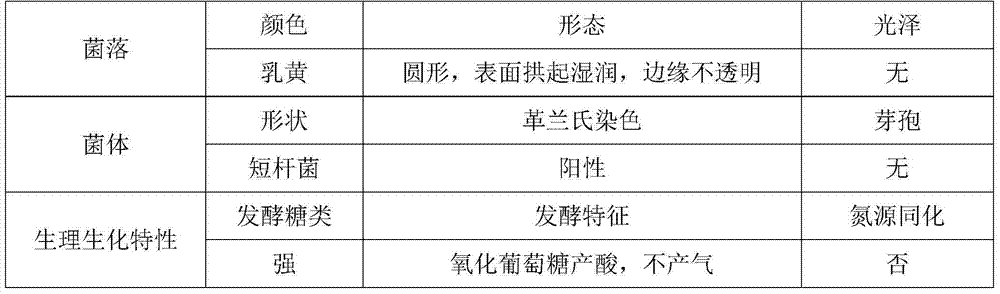
ActiveCN102485884ASimple and efficient method for screening strain CW9Has a prebiotic effectBacteriaClimate change adaptationBiotechnologySprouted Seeds
The invention relates to Arthrobacter CW9 (Arthrobacter sp. CW9) with CGMCC of No.4197. The bacterial strain is Gram positive bacteria without spore, capsule and motion. The colony on a 2216E flat possesses the characteristics of yellow, circle, intermediate protrusion, smoothness and moisture; The aerobic strain possesses optimum growth temperature of 26 DEG C and the optimum pH value of 7.6; the concentration for NaCl resistance is 10%, the optimum salinity is 1%, the growth can not generated without NaCl. The Arthrobacter CW9 can be used for raising the metamorphosis rate and survival rateof seawater crustaceans larvae. The bacterial strain screening method of the present invention is concise and high efficient, the Arthrobacter possesses probiotic function on the crustaceans larvae, the production method as well as the storage and transportation are simple, the application method is also simple; the Arthrobacter is employed only in crustaceans animal zoea one-stage, so that the metamorphosis rate of the post-larvae can be enhanced and stabilized, and the sprout seed output can be greatly increased.
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH
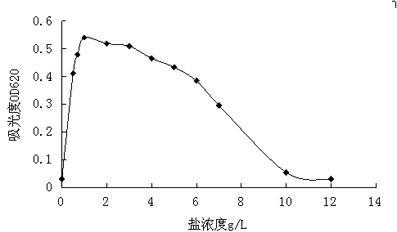
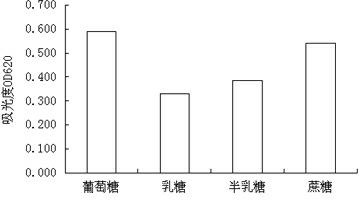
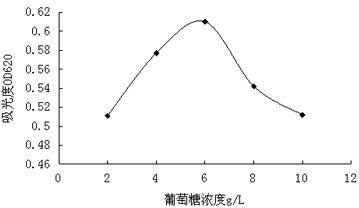
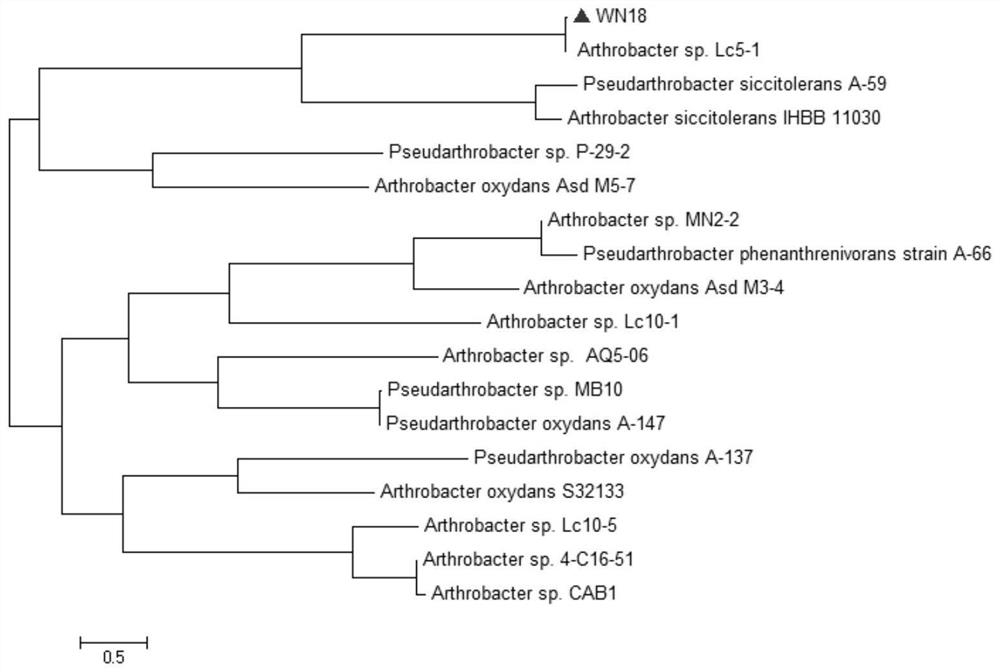
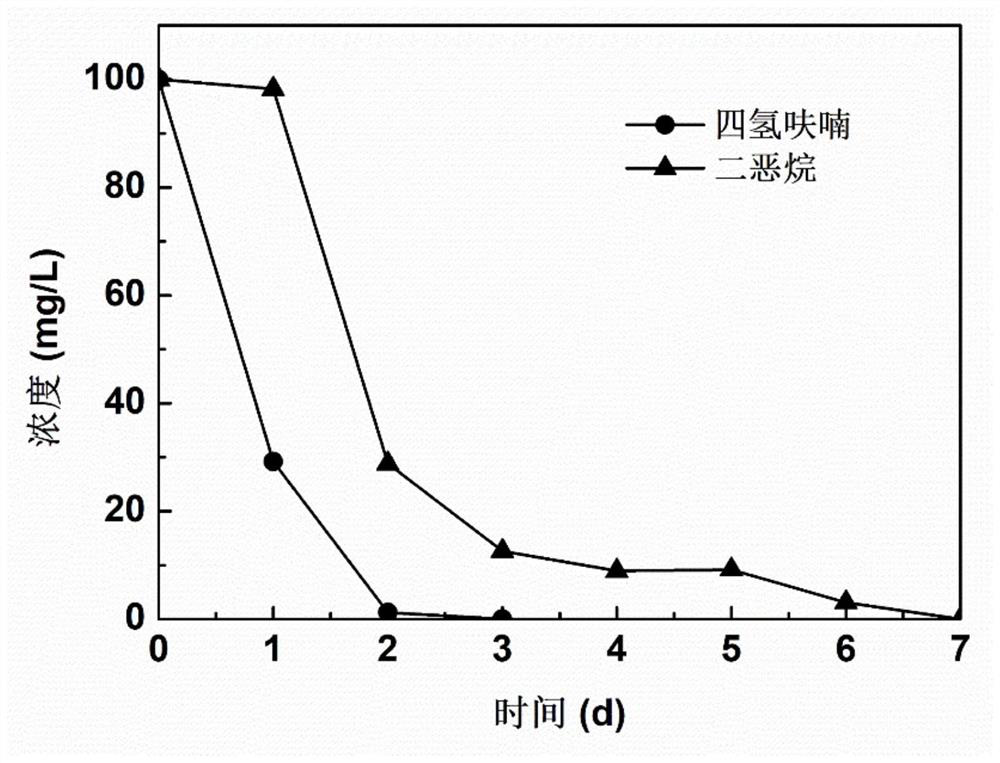
Arthrobacter sp. WN18 and application thereof
ActiveCN111793587ARapid metabolic degradationEfficient metabolic degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyHigh concentration
The invention provides an Arthrobacter sp. WN18. The Arthrobacter sp. WN18 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on June 24, 2020 at No.3, Yard No.1, Beichen WestRoad, Chaoyang District, Beijing, and has a preservation number of CGMCC NO.20135. The strain has the capability of efficiently degrading dioxane and the relatively high environmental adaptability under the condition that tetrahydrofuran is used as a primary substrate, and the reaction activity of the strain can be kept in high-concentration dioxane and tetrahydrofuran. The strain provides an excellent strain resource for biological treatment of the dioxane polluted environment.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY +1
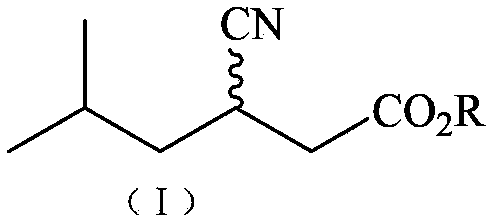
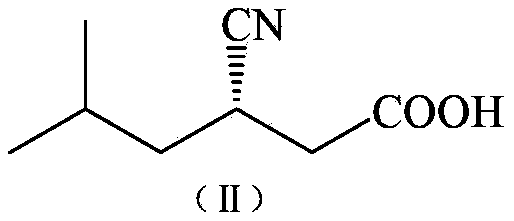
Arthrobacterium ZJB-09277 and application thereof in preparing (S)-3-cyan-5-methyl caproic acid
ActiveCN103114054BAtom economy is highHigh potential for industrial applicationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesArthrobacter sp.Hydrolysis
The invention discloses arthrobacterium ZJB-09277 (Arthrobacter sp. ZJB-09277) and an application thereof in preparing (S)-3-cyan-5-methyl caproic acid. The arthrobacterium is preserved in the Chinese Typical Culture Collection Center which is located in Wuhan College, Wuhan, China, the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2012419, and the preservation date is October 22nd, 2012. The invention further provides a novel strain for preparing the (S)-3-cyan-5-methyl caproic acid in a stereoselectivity hydrolysis mode. An important chiral intermediate of pregabalin, namely, the (S)-3-cyan-5-methyl caproic acid can be prepared from the strain. The preparation method of the (S)-3-cyan-5-methyl caproic acid disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high atom economy, mild condition, environmental-friendliness, and has higher industrial application potentials.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com