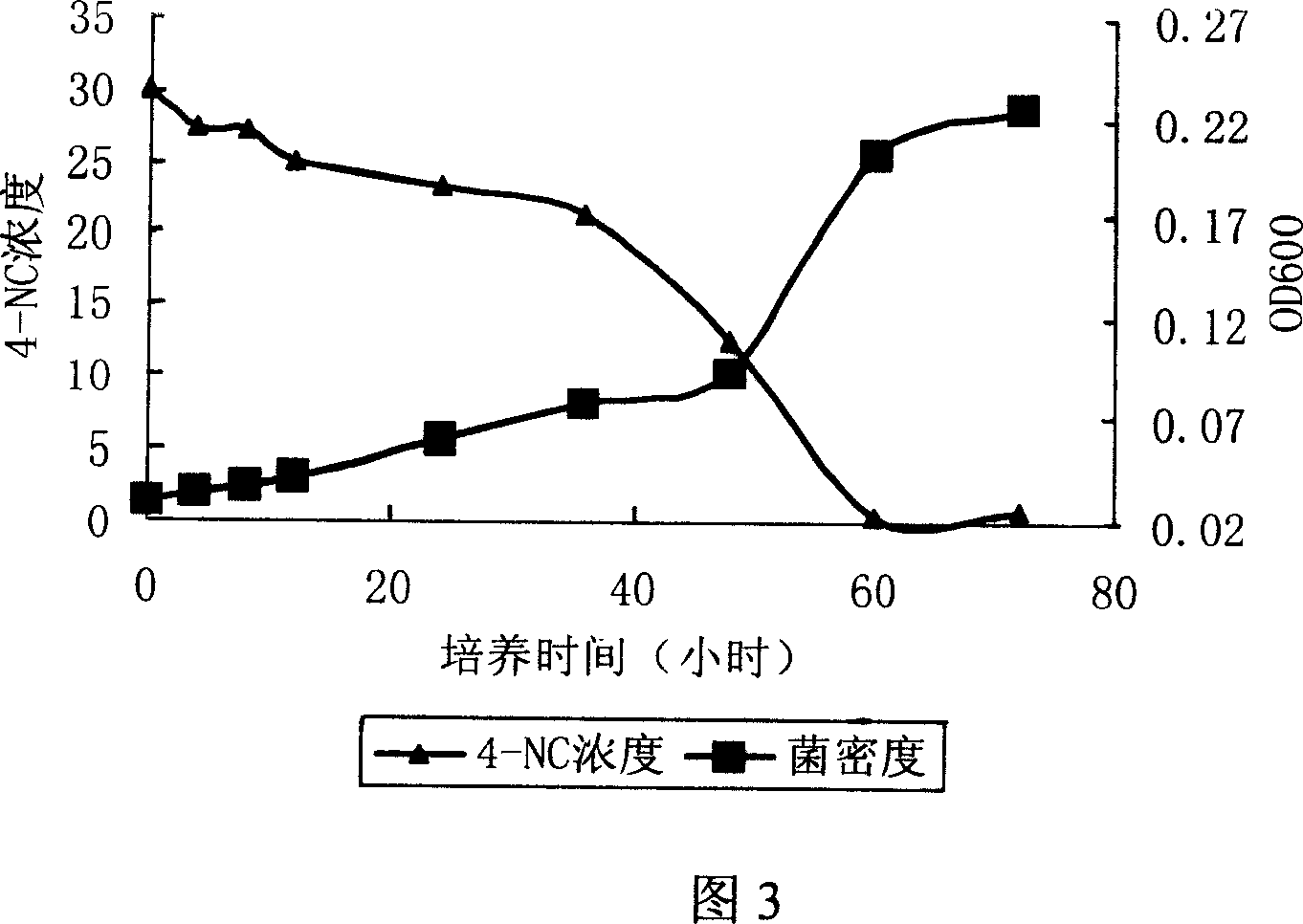
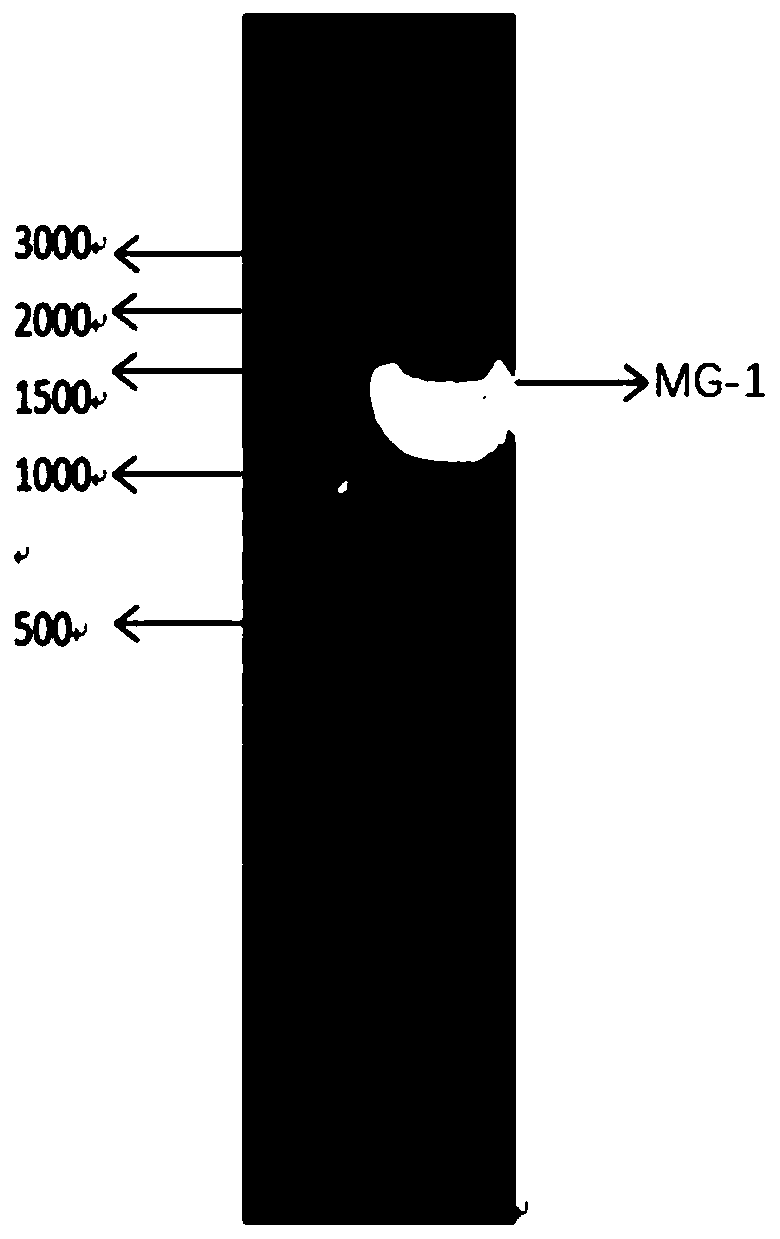
Patents
Literature
36 results about "Ochrobactrum sp." patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
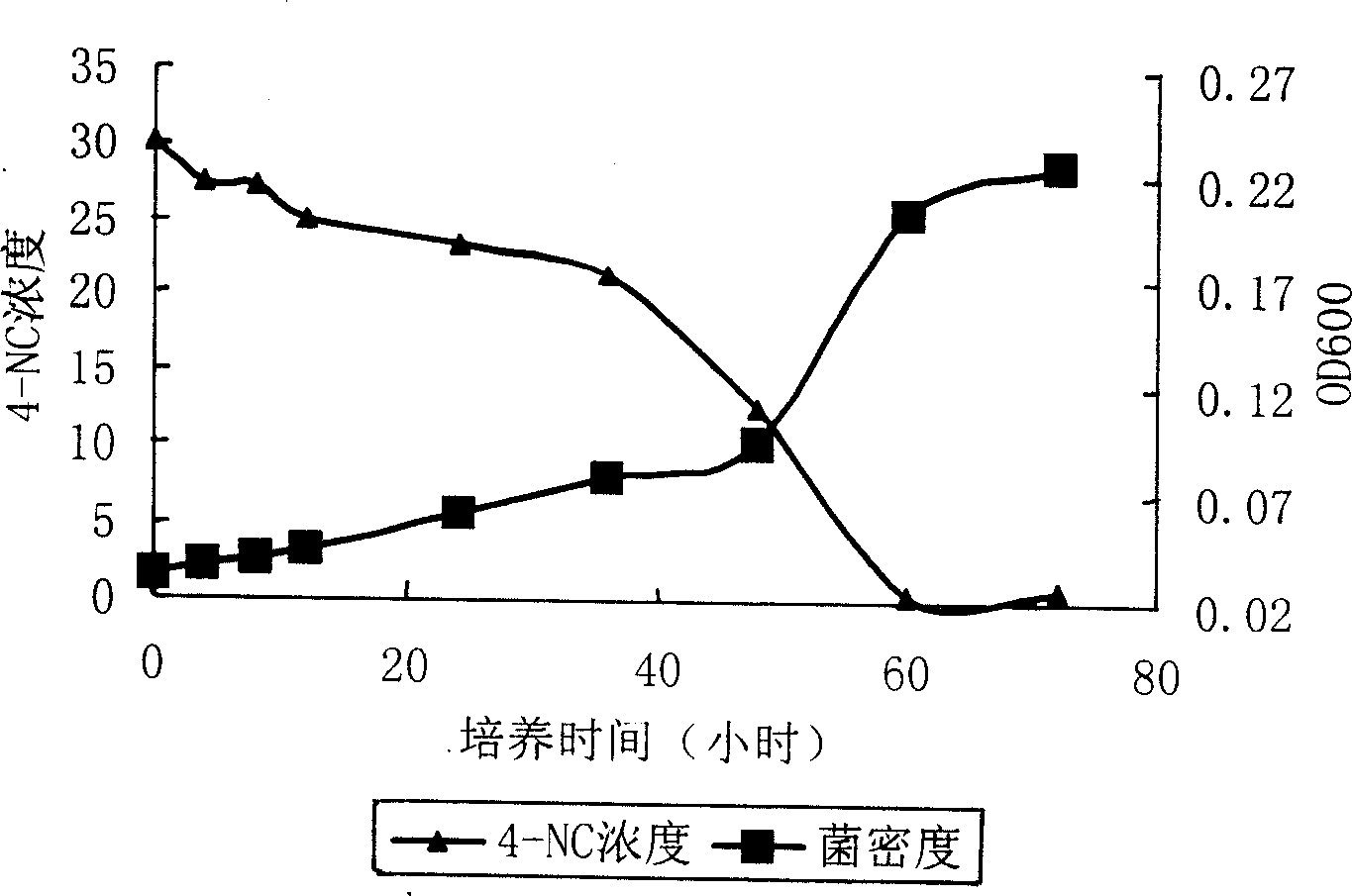
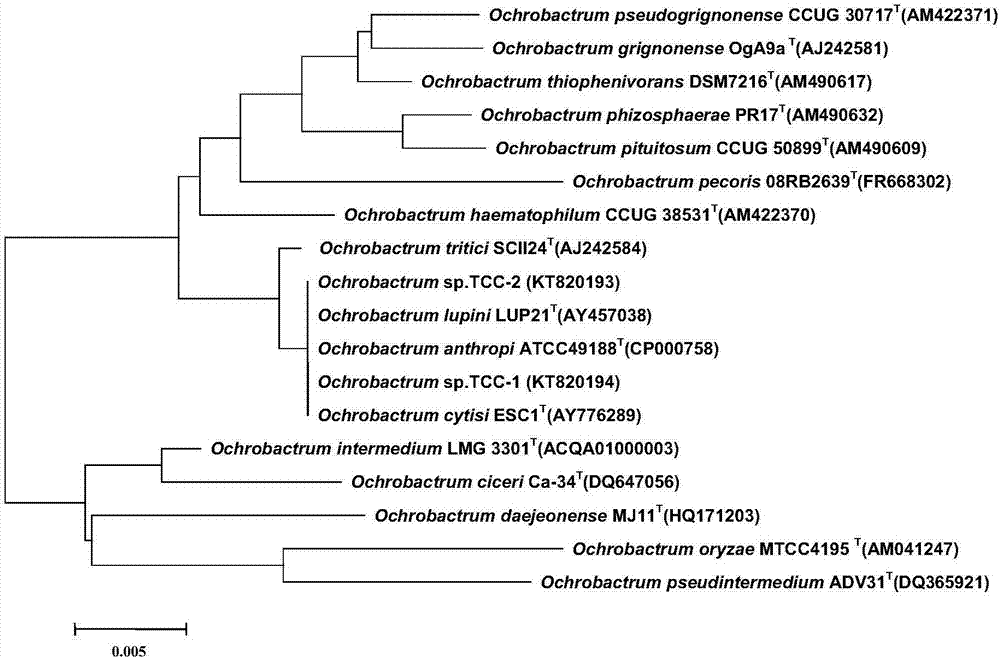
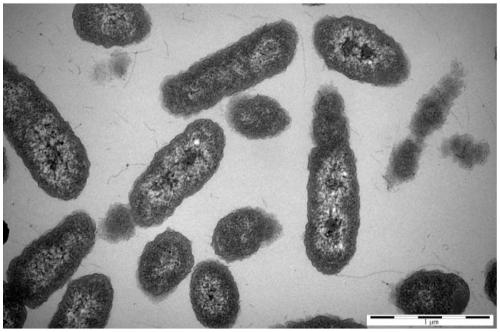
Ochrobactrum spp. belongs to the Brucellaceae and is known to be isolated from Leguminosae nodules (2, 3). Its name is derived from the Greek ochros, meaning pale yellow; this is the characteristic color of Ochrobactrum colonies. The organism has the potential to colonize an exceptionally wide variety of habitats (4–8).
Mixed inoculant for degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollutants
InactiveCN102776135AStrong growthImprove reproductive abilityBacteriaWater contaminantsOchrobactrum sp.Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
The invention relates to a rehabilitation technology of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollutants (PAHs), particularly discloses a mixed inoculant for degrading PAHs. The mixed inoculant comprises indigenous mixed bacteria, wherein the indigenous mixed bacteria comprise Pseudomonas sp. B08, Pseudomonas sp. BM, Bacillus sp. BYB, Bacillus sp. B07, Ochrobactrum sp. ZHL4, Gordonia sp. BGDS and Mycobacterium sp. BFZG. The mixed inoculant disclosed herein can be added according to an inoculation quantity of 5-10%, and when the initial concentration of PAHs is 180.67mgL<-1>, the total degradation rate of PAHs after being processed for 9 days can reach 91.21%.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Degradation bacteria for highly effective degrading organophosphorus pesticide and its use
The invention provides a strain of degrading bacterium for effectively degrading organic phosphoric pesticide, the bacterium has a name of Ochrobactrum sp. and a docket number of CGMCC No.1221. The bacterium can be used for degrading organic phosphoric pesticide and nitrogen-containing aromatic hydrocarbons substance, thus used for the biological purification of water body, soil or agricultural products contaminated by these substances.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Composite microbial inoculum, immobilization method and application thereof
InactiveCN102321549AAnti-toxicEfficient degradationBacteriaDispersed particle separationOchrobactrum sp.Rhizobium sp.
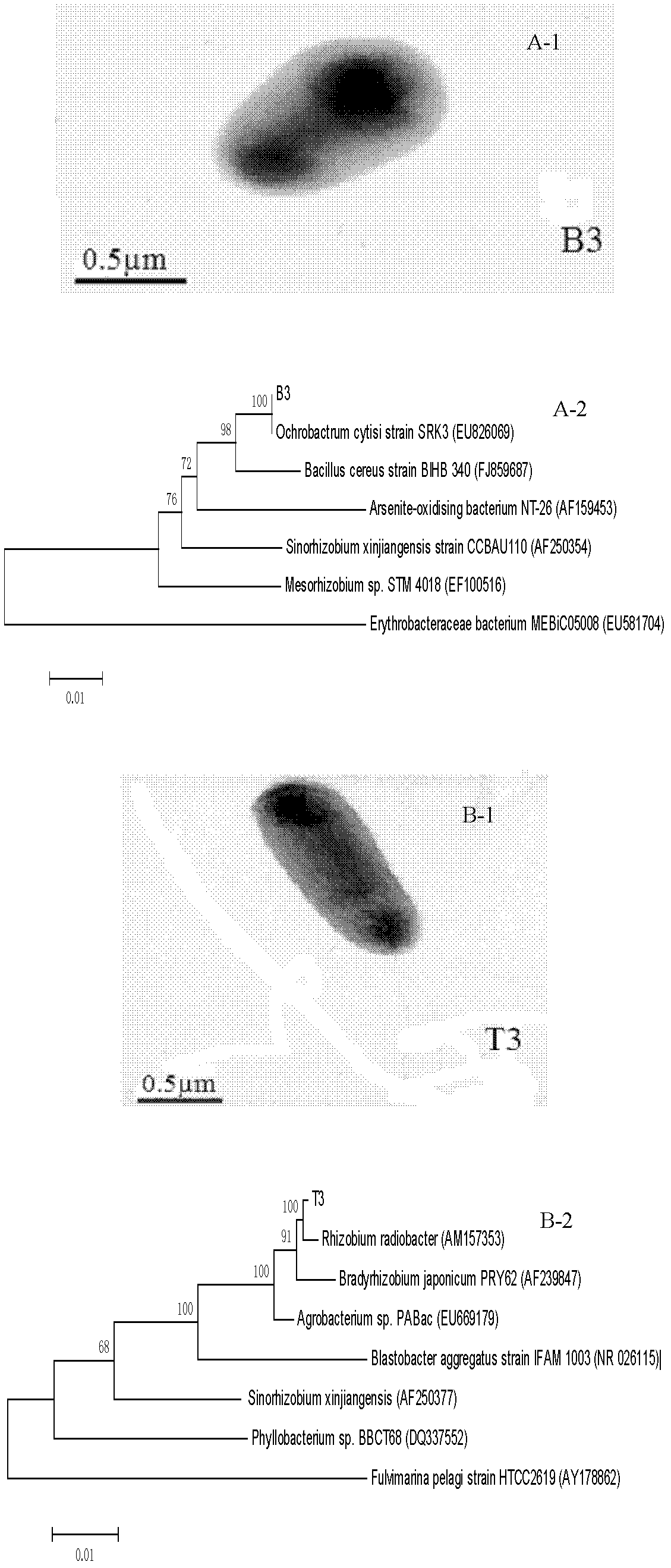
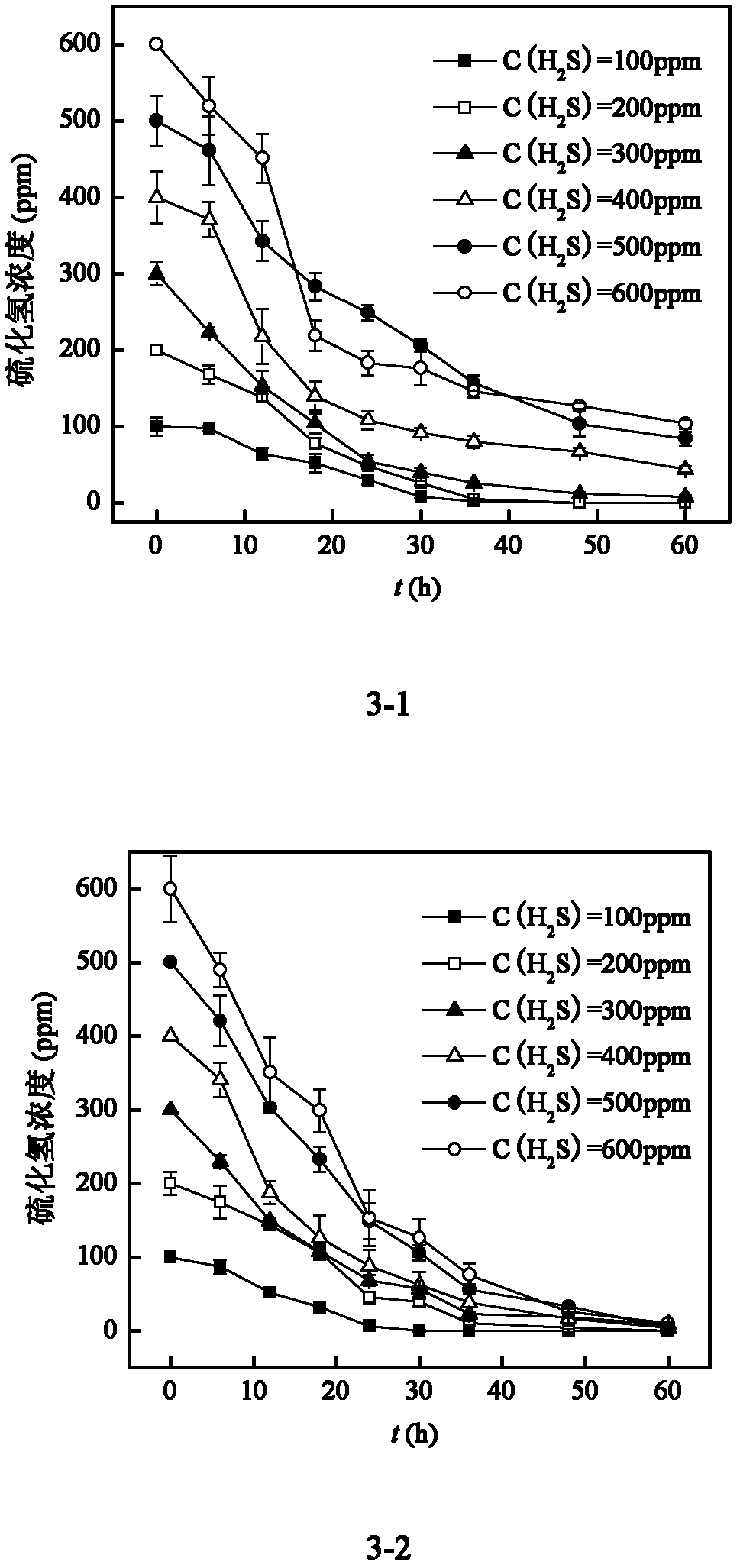
The invention discloses a composite microbial inoculum, and an immobilization method and application thereof. The composite microbial inoculum is prepared from an Ochrobactrum sp.B3 mycetocyte microbial suspension and a Rhizobium sp.T3 mycetocyte microbial suspension, wherein the concentration of the Ochrobactrum sp.B3 mycetocyte microbial suspension is 0.15-0.2g / L, and the concentration of the Rhizobium sp.T3 is 0.15-0.2g / L. The immobilization method of the composite microbial inoculum has the advantages of simple technique, and cheap and accessible raw materials, and is beneficial to large-scale production. The composite microbial inoculum immobilized cell granules have the advantages of high mechanical strength, high elasticity and stable enzymic activity, have certain toxin immunity in a reaction system, have strong tolerance to temperature and pH value, and can still efficiently degrade H2S waste gas after being used repeatedly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Quinolone antibiotic degrading bacterium and application thereof
ActiveCN106929442AEffectively remove pollutionEliminate pollutionBacteriaWater contaminantsFifth floorLivestock manure
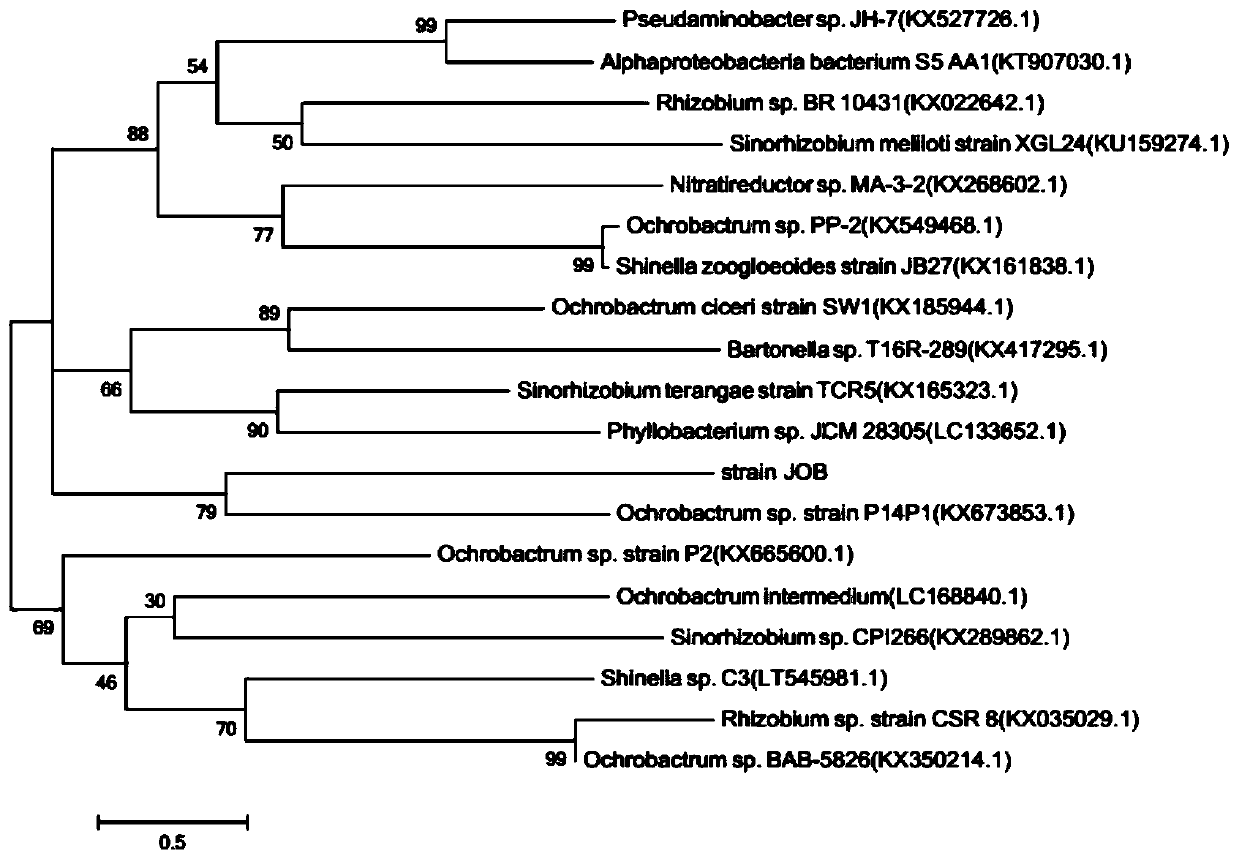
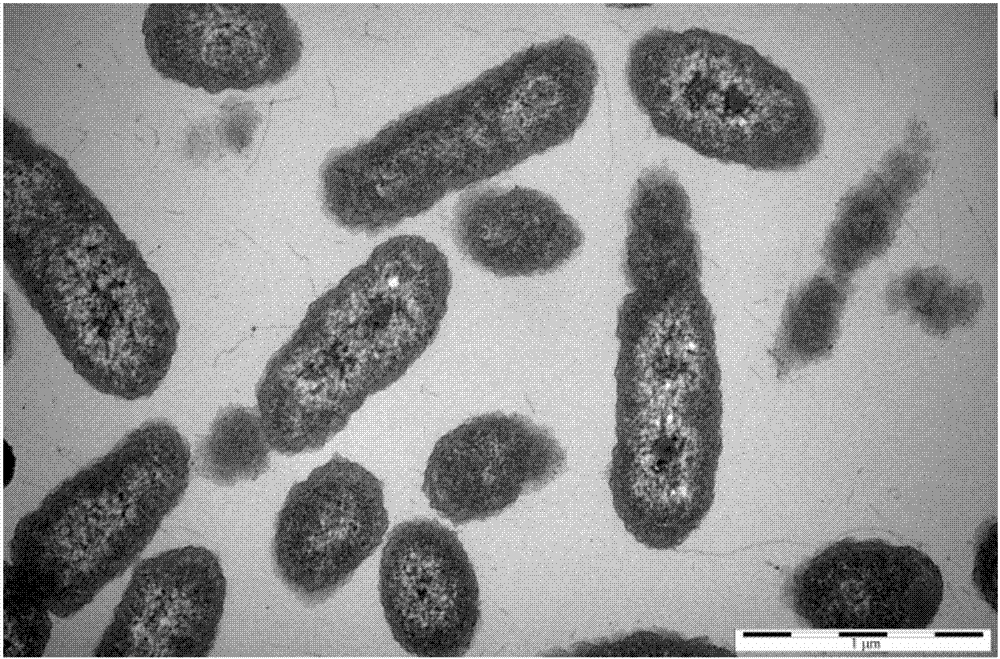
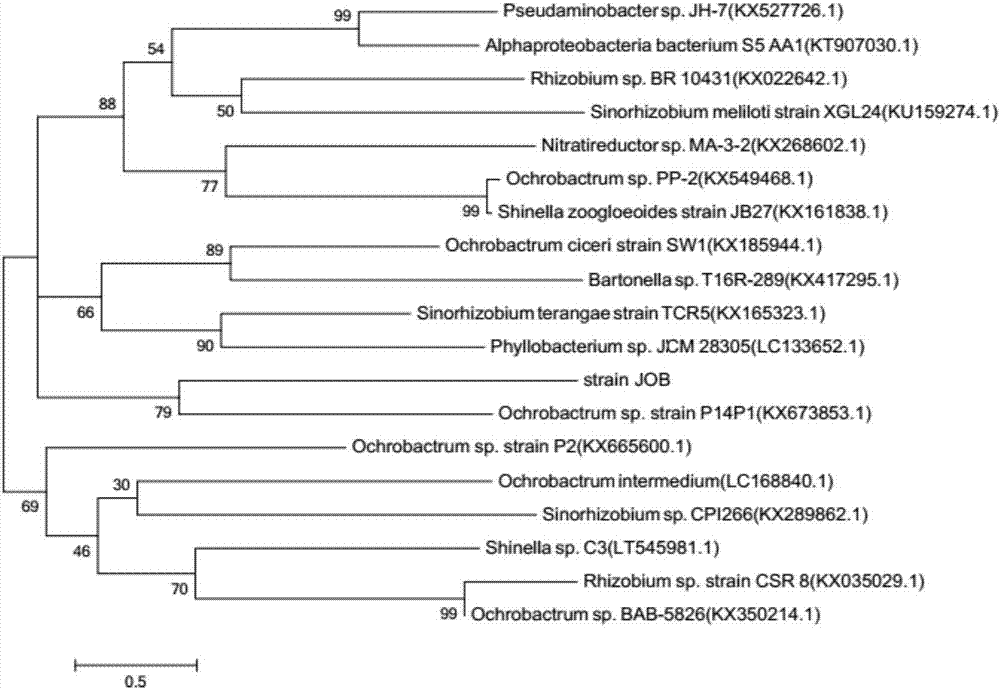
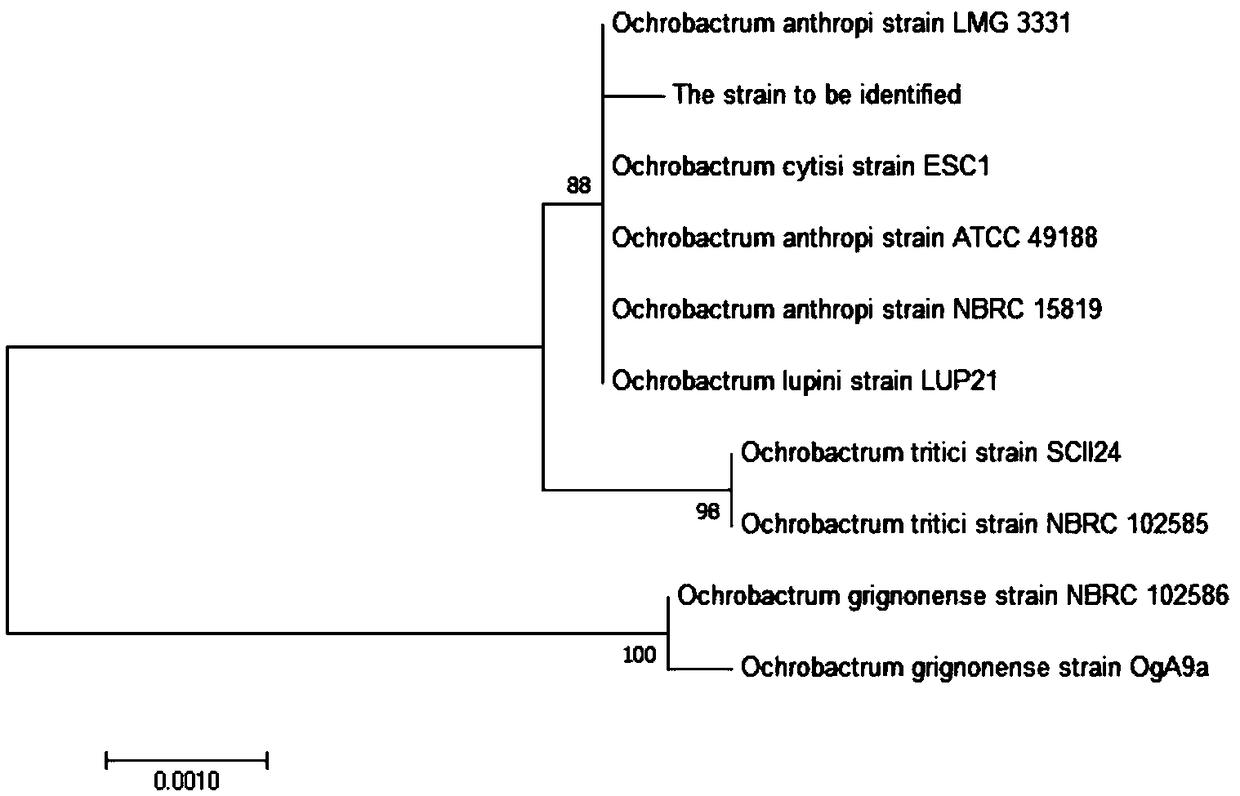
The invention discloses a quinolone antibiotic degrading bacterium and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of biological treatment of environmental pollutants. The degrading bacterium is obtained by domestication and purification of livestock manure, and is named as Ochrobactrum sp. JOB, and was preserved in Guangdong Microbiological Culture Collection Center (GDMCC), Guangdong Province Institute of Microbiology on the fifth floor, No.59 Building, No.100 Courtyard, Xianlie Middle Road, Guanzhou City on December 21st, 2016, with a preservation number of GDMCC NO:60132. The degrading bacterium disclosed by the invention is prepared into bacterium suspension or an immobilized microbial agent which can be used for effectively removing quinolone antibiotic pollution in different environmental media such as a water body and soil; compared with a physical absorption method, a chemical degradation method and the like, the quinolone antibiotic degrading bacterium has the advantages of high efficiency, energy conservation, environment friendliness and the like; particularly, a bacterial body is immobilized by using an embedding agent, so that the life of the bacterial body is prolonged; the microbial agent has an excellent action effect and high ability of adaptation to environment.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Method for treating industrial chromium-containing waste water by bacteria
InactiveCN101676224AHarm reductionHigh removal rateWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentOchrobactrum sp.Microorganism
The invention relates to a technology for treating industrial chromium-containing waste water by using microorganism and adsorbing agent in a combining way. Ochrobactrum sp. CTS-325 (with the collection number of CGMCC 1715) strain is inoculated into the mixed liquid of the industrial chromium-containing waste water and nutrient; then, after full reaction, adsorbing material is used for absorbingCr(III); and finally, desorption is carried out, and chromium can be recovered. The method has high treatment efficiency and no secondary pollution, leads the processes of reduction and adsorption tobe carried out at the room temperature, ensures the operation to be simpler and more convenient, and greatly reduces the running cost.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Petroleum degrading bacterium capable of degrading heavy crude oil as well as separation method and application of petroleum degrading bacterium
ActiveCN108949634APromote degradationGood removal effectBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationMicrobial agentBioremediation
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbes and environmental protection and in particular relates to a petroleum degrading bacterium capable of degrading heavy crude oil as well as a separation method and application of the petroleum degrading bacterium. The petroleum degrading bacterium belongs to Ochrobactrum sp. in taxonomy, is collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on May 7, 2018, and has a collection number of CGMCC No. 15739. The petroleum degrading bacterium is capable of growing under the conventional condition by taking heavy crude oil withhigh content of asphalt and resins as a unique carbon source and capable of degrading and removing petroleum pollutants; energy, carbon sources, heat sources and the like do not need to be manually added, the process requirement is low, the application cost is low, and secondary pollution is avoided; and the degradation rate of the heavy crude oil can reach 20% or higher within 7 days, the degradation efficiency is high, the petroleum pollutants in the environment can be rapidly degraded, and the petroleum degrading bacterium is applied to bioremediation of petroleum-contaminated soil or waterand can also be applied to preparing a composite microbial agent with other strains so as to be used for efficiently completely removing the petroleum pollutants in the environment.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
Method for treating sewage water having heavy metallic ion Cd2+ and Cu2+ by using bacteria 575
InactiveCN101063096AImprove securityCause secondary pollutionBacteriaWater/sewage treatmentOchrobactrum sp.Sewage
The invention discloses a method with effective enriched heavy metal ion Cd2+ and Cu2+ strain to treat waste water with heavy metal ion Cd2+ and Cu2+, which is characterized by the following: preserving the strain in Chinese typical culture preserved center with preserved number at CCTCC NO: M207050 and name as Ochrobium 575 (Ochrobactrum sp. 575); culturing Ochrobactrum sp. 575 single bacterial colony as OD not less than 0. 6 bacterial liquid; adding the bacterial liquid into waste water with Cd2+, Cu2+ heavy metal ion with 0. 5-1% proportion; utilizing the property of effective enriched heavy metal ion Cd2+ and Cu2+; decreasing the content of heavy metal ion; reaching the goal of treating waste water.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Synergistic effect of multiple bacterial strains on degradation of polyphenol pollutants and research method thereof
InactiveCN103060419APromote degradationImprove degradation efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStudy methodsBacterial strain
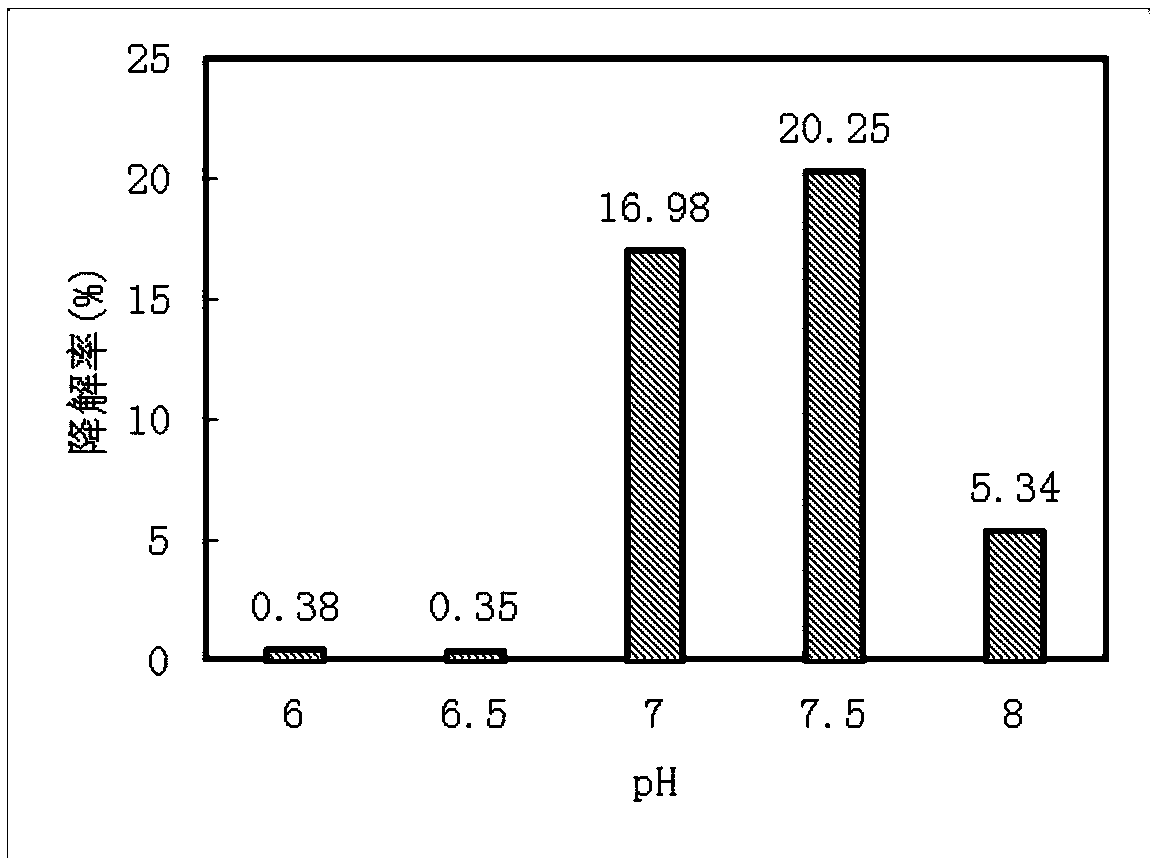
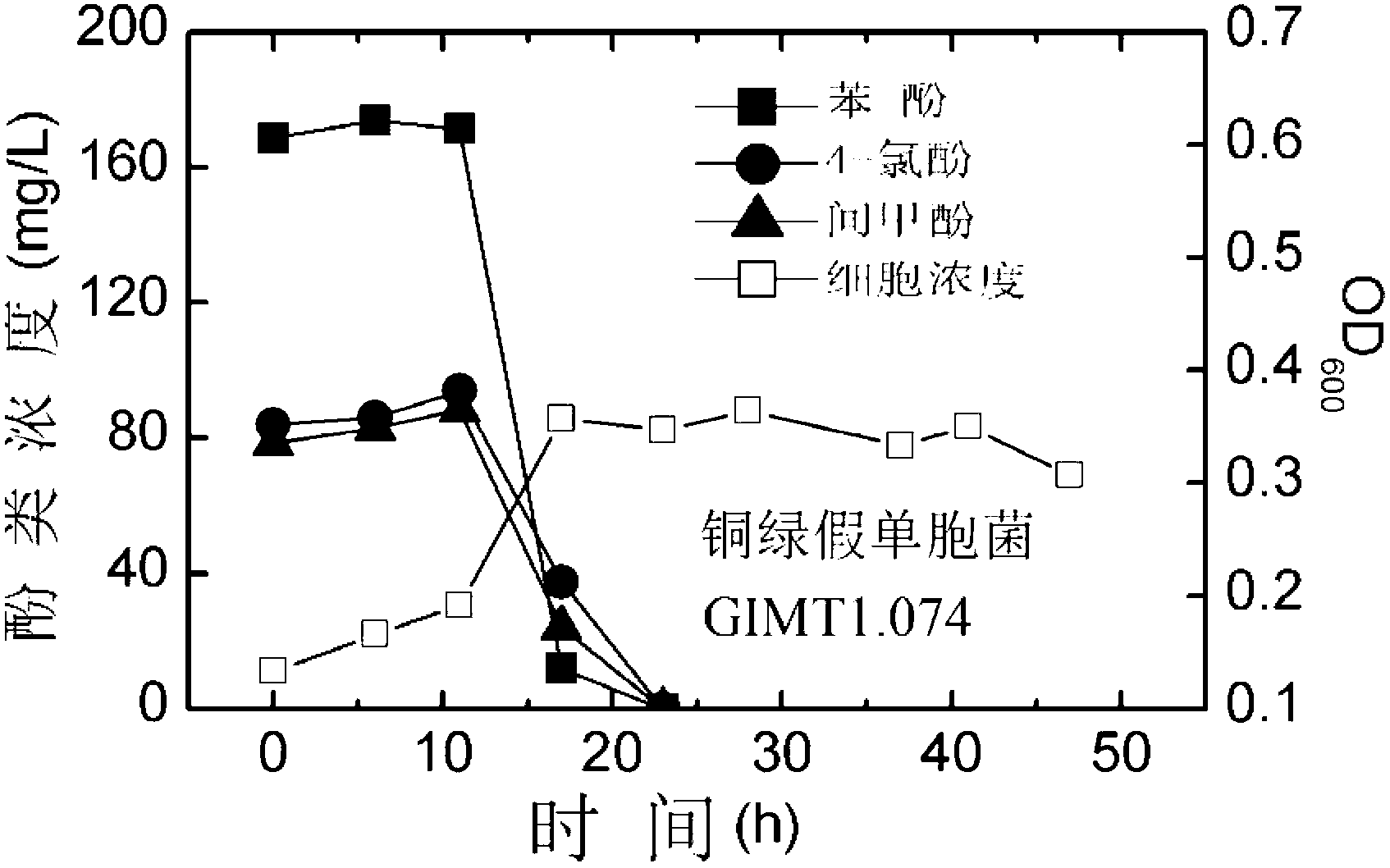
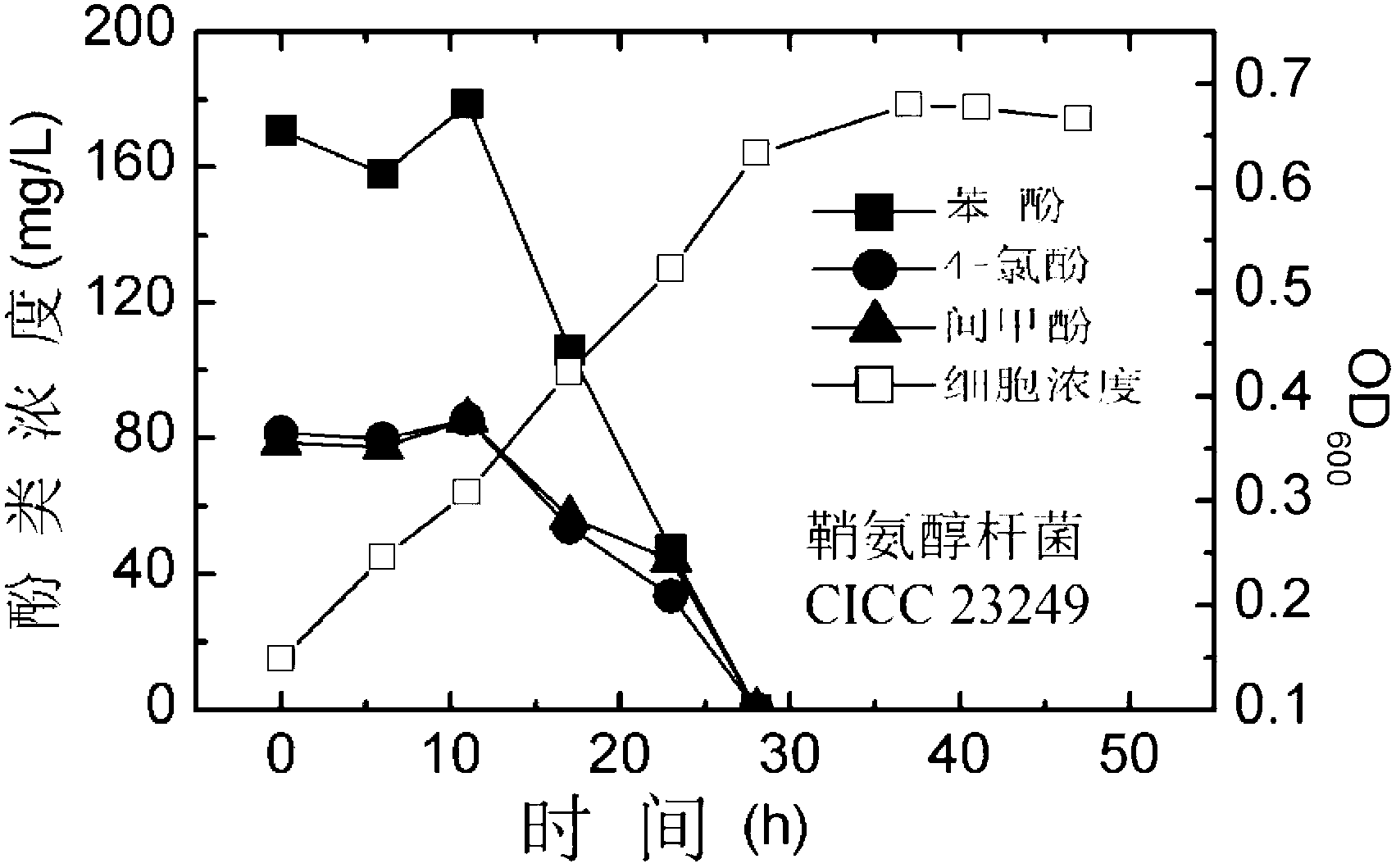
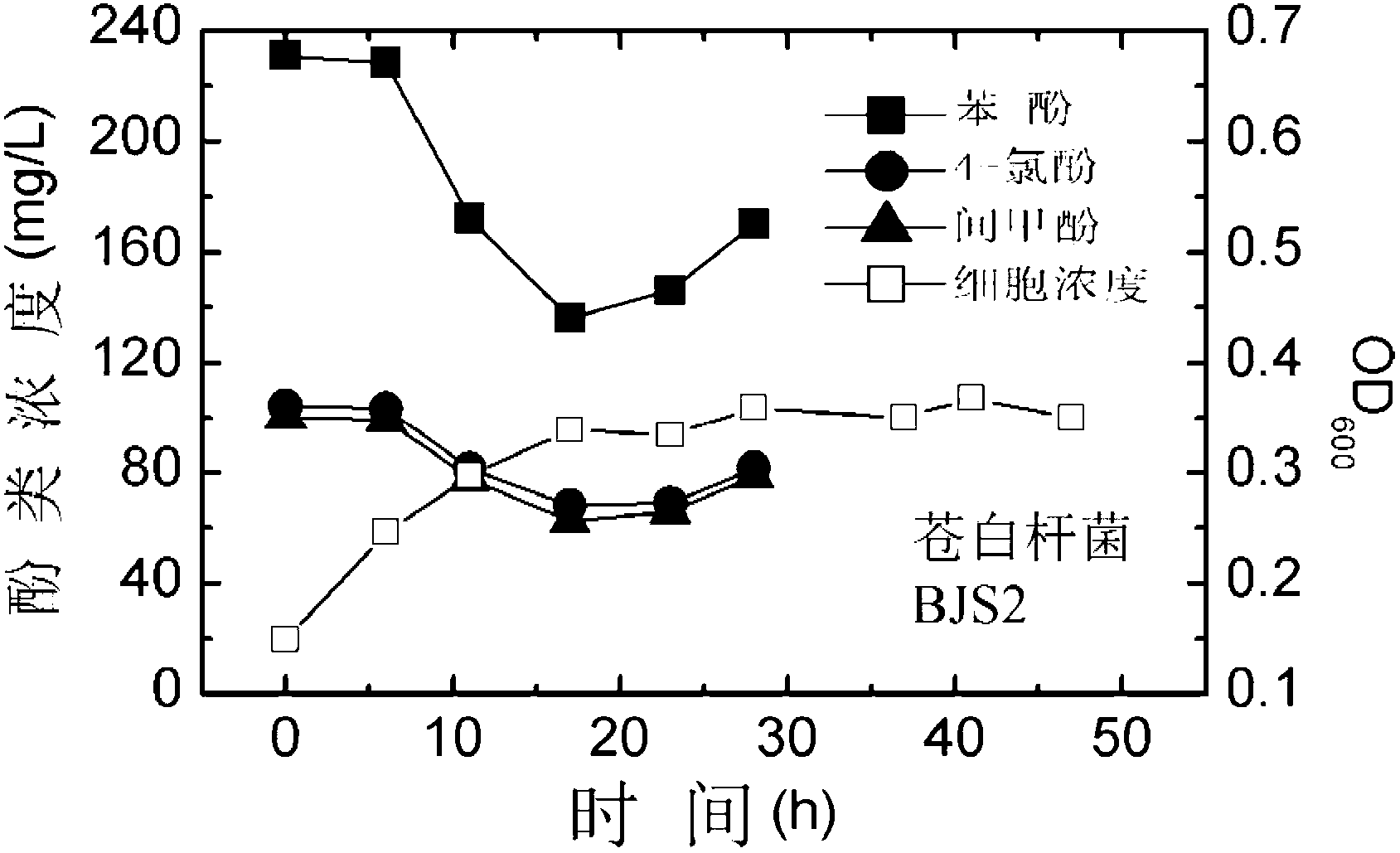
The invention relates to a synergistic effect of multiple bacterial strains on degradation of polyphenol pollutants and a research method thereof. According to the invention, a bacterial suspension is prepared from one or a mixture of two or three selected from the group consisting of pseudomonas aeruginosa GIMT1.074, sphingobacterium multivorum CICC 23249 and ochrobactrum sp. BJS2; then the bacterial suspension is inoculated to inorganic a salt medium containing phenol, meta-cresol and 4-chlorophenol with different concentrations for culture; parts of a culture solution are taken out at different time intervals to measure concentrations of phenol, meta-cresol and 4-chlorophenol in the culture solution so as to determine degradation rates at different times, and cell concentrations in the culture solution are measured to investigate growth conditions of different cells. According to research on synergistic degradation effects of the three phenol degrading bacteria, a mixed bacterial strain has superior capability in degradation of mixed phenolic pollutants and has much better degradation efficiency and effects compared to every individual bacterial strain; moreover, biomass of the mixed bacterial strain is increased to two times of the biomass of an original optimal bacterial strain, i.e., the pseudomonas aeruginosa GIMT1.074.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Compound microorganism live bacteria preparation for enhancing activated sludge, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN103421692AEasy to manufactureLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesActivated sludgeLiquid medium
The invention discloses a compound microorganism live bacteria preparation for enhancing activated sludge, a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation contains Bacillus fusiformis, Comamonas sp. and Ochrobactrum sp.. The preparation method comprises the following steps: first, Bacillus fusiformis, Comamonas sp. and Ochrobactrum sp. after inclined plane activation are inoculated in liquid mediums respectively, and cultured at the temperature of 30 DEG C-37 DEG C for 40-54 h to obtain a microorganism bacteria liquid; second, the microorganism bacteria liquids obtained from the first step are mixed uniformly, dried at the temperature of 40 DEG C-60 DEG C, and the processes of crushing to 15-50 meshes and sieving are performed. The preparation can enhance activated sludge performances effectively and rapidly in applications as an activated sludge COD-degrading enhancer in the papermaking wastewater treatment process. The preparation can degrade papermaking wastewater COD efficiently and improve wastewater chromaticity and water quality.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND +1
High-tolerance phenylamine degrading bacterium and application thereof
ActiveCN104560777AHighly biodegradable treatment functionReduce processing costsBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyHigh concentration
The invention discloses a high-tolerance phenylamine degrading bacterium MC-01(Ochrobactrum sp. MC-01), and belongs to an Ochrobactrum sp. type bacteria. The high-tolerance phenylamine degrading bacterium MC-01 is collected in the common microorganism center of the China committee for culture collection of microorganisms, the collection number is CGMCC 1.12930, and the collection date is June 10, 2014. The high-tolerance phenylamine degrading bacterium MC-01 disclosed by the invention has biodegradation function on phenylamine wastewater under the condition of high concentration; the phenylamine degradation rate of the strain can reach 99%, and no secondary environmental pollution is caused, no other chemical agents need to be added, and thus the treatment cost of the wastewater is greatly reduced and a wide application prospect is achieved. The high-tolerance phenylamine degrading bacterium MC-01 disclosed by the invention is helpful for solving the problem of a biological phenylamine wastewater treatment system under the condition of high concentration and has very high application value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Biochar-based bacterial composite soil conditioner as well as preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN108192631AImprove fertilitySimple structureAgriculture tools and machinesBacteriaBacillus cereusArthrobacter sp.
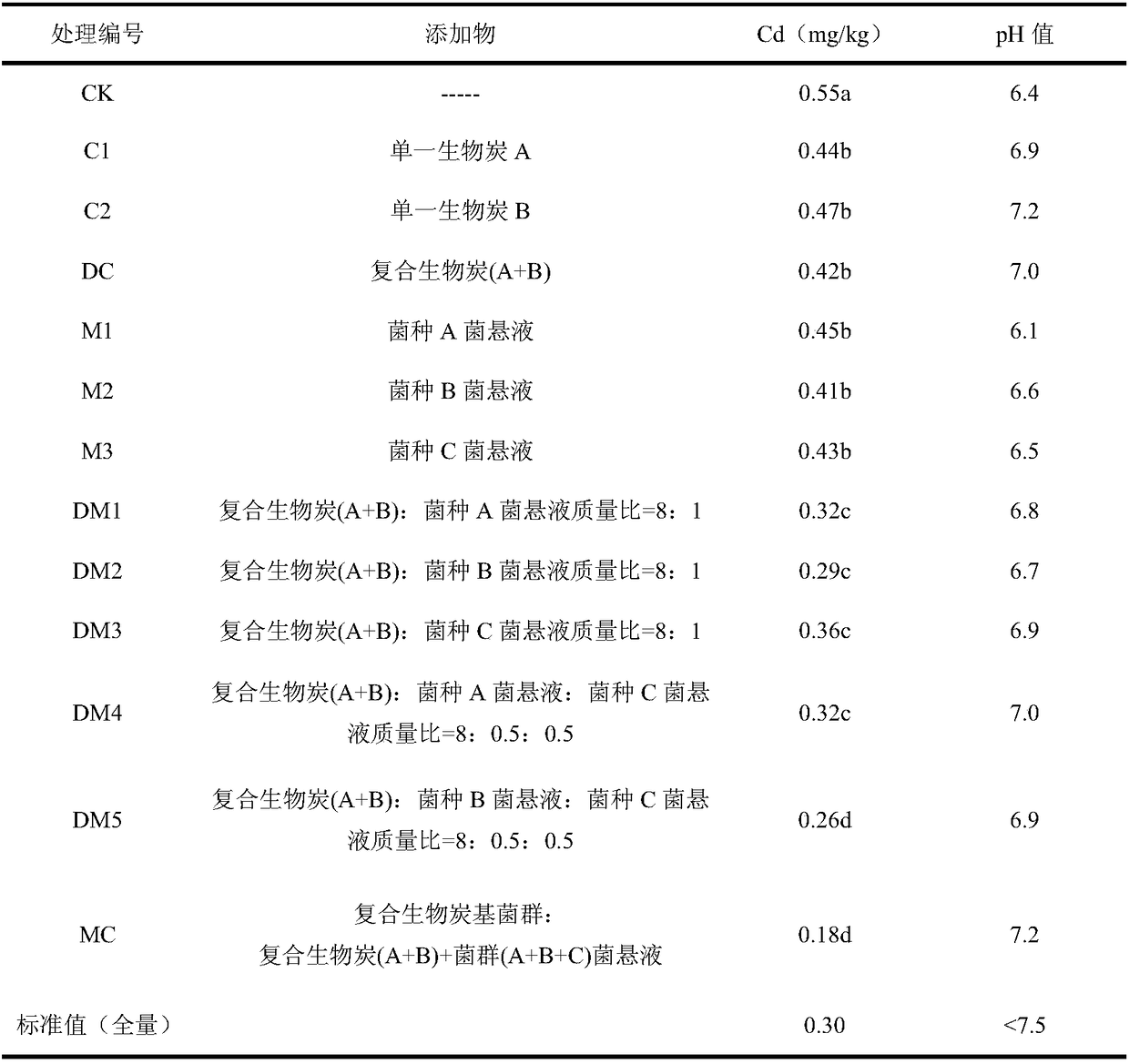
The invention discloses a biochar-based bacterial composite soil conditioner as well as preparation and application thereof. A preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) domestication of bacteria: sequentially inoculating bacillus cereus, ochrobactrum sp. and arthrobacter sp. into a Cd-containing inorganic salt culture solution with a gradient concentration respectively for domestication and cultivation; and mixing the domesticated and cultured bacterial solutions to prepare a bacterial suspension for later use; and (2) preparation of the biochar-based bacterial composite soil conditioner: taking biochar to be mixed with the bacterial suspension, adding antagonistic elements of heavy metals in soil, then performing shaking cultivation, filtering and washing. The biochar-based bacterial composite soil conditioner provided by the invention is simple in preparation method and low in cost; microorganisms in the preparation have high tolerance to the heavy metal Cd, so that the preparation has good remediation effect on the heavy metals in the soil, and is stable, long-acting, and less affected by the environment; the invention is an in-situ chemistry-combined microbial passivation remediation technology effectively applied to heavy metal-contaminated soil in farmlands.
Owner:HUNAN HENGKAI ENVIRONMENT TECH INVESTMENT CO LTD
Compound enzyme preparation and ochrobactrum assisted kitchen waste new high-temperature composting technology
PendingCN112522143AEfficient fermentationHeating up fastCalcareous fertilisersBio-organic fraction processingHuminBacterial strain
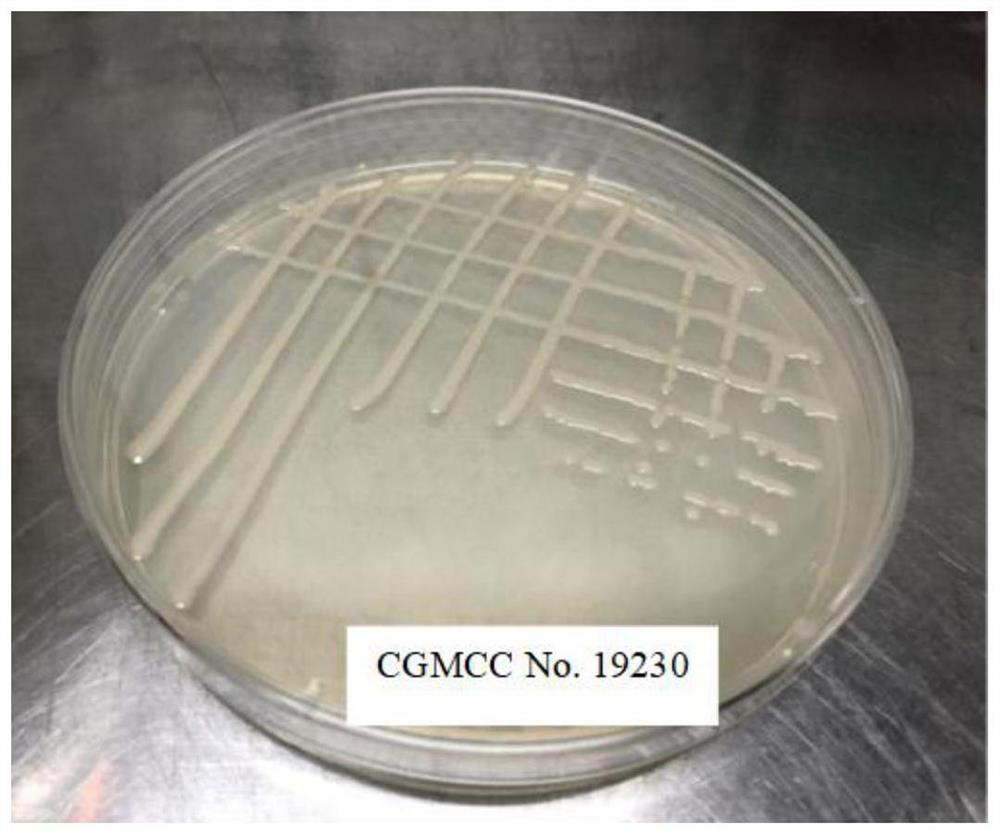
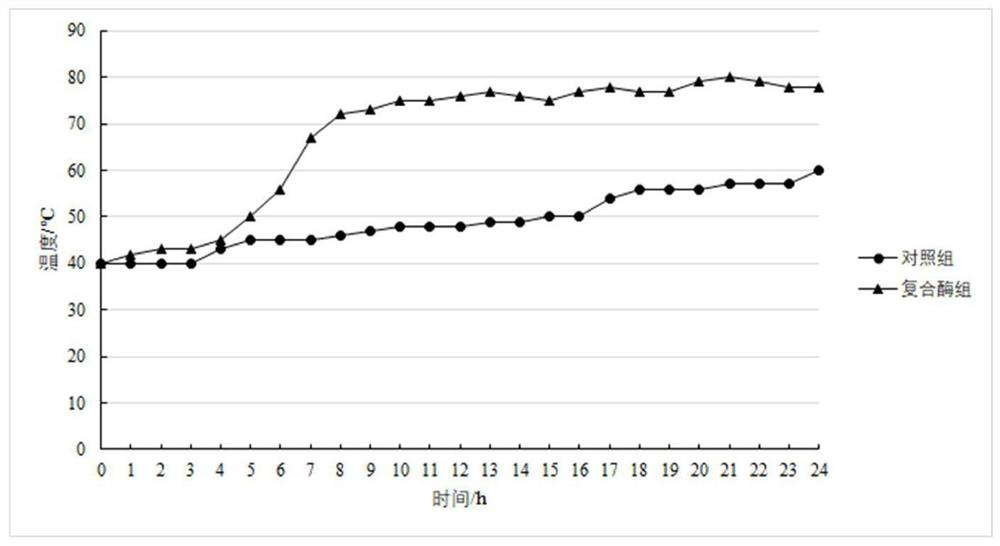
The invention relates to the field of microbial technology and environmental engineering, and discloses a compound enzyme preparation and ochrobactrum assisted kitchen waste new high-temperature composting technology. The preservation number of the ochrobactrum is CGMCC No.19230 and the ochrobactrum is classified and named as ochrobactrum sp. The compound enzyme preparation and bacterial strain cooperated high-temperature composting technology is used for performing high-temperature aerobic composting treatment on various organic matters such as kitchen waste, agricultural product tailings, slaughter house waste and the like, so that the organic matters are completely humified, dehydrated and dried, the weight is reduced by 70-92%, and finally, an organic fertilizer with excellent qualityis formed. The new high-temperature composting technology also relates to special pretreatment means such as physical cutting, enzymatic hydrolysis, bacterial strain metabolism rapid heat production and the like, so that a compost heap can be rapidly heated to 70 DEG C or above within 8 hours, a high-temperature stage of composting is rapidly started, various high-temperature strains are rapidly turned into absolute dominant strains in a compost heap system, and on the basis, a semi-continuous compost fermentation technology capable of supplementing and discharging materials every day is realized.
Owner:榆林鹤翼航天航空科技创新有限责任公司 +1
A composite bacterium agent for reducing a doxycycline concentration and a drug-resistant gene in a composting process and applications thereof
A composite bacterium agent for reducing a doxycycline concentration and a drug-resistant gene in a composting process and applications thereof are disclosed and belong to the technical fields of antibiotics and drug-resistant gene removing. The composite bacterium agent includes Ochrobactrum sp., Burkholderia sp., and Candida sp.. The mass ratio of freeze-dried powder of the Ochrobactrum sp., theBurkholderia sp., and the Candida sp. is 1-2:1-2:1-2. Through adding the composite bacterium agent into compost, residual doxycycline in livestock excrement can be efficiently degraded, the drug-resistant gene residual in the compost is effectively degraded, and safety of a compost product is improved. Through inoculation of the composite bacterium agent, the doxycycline degradation rate is 46.40%, and the tetracycline drug-resistant gene removal rate is 38.71%. Compost inoculated with the composite bacterium agent has higher doxycycline degradation effects and a lower drug-resistant gene content than compost not inoculated with the composite bacterium agent so that the composite bacterium agent has a good application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
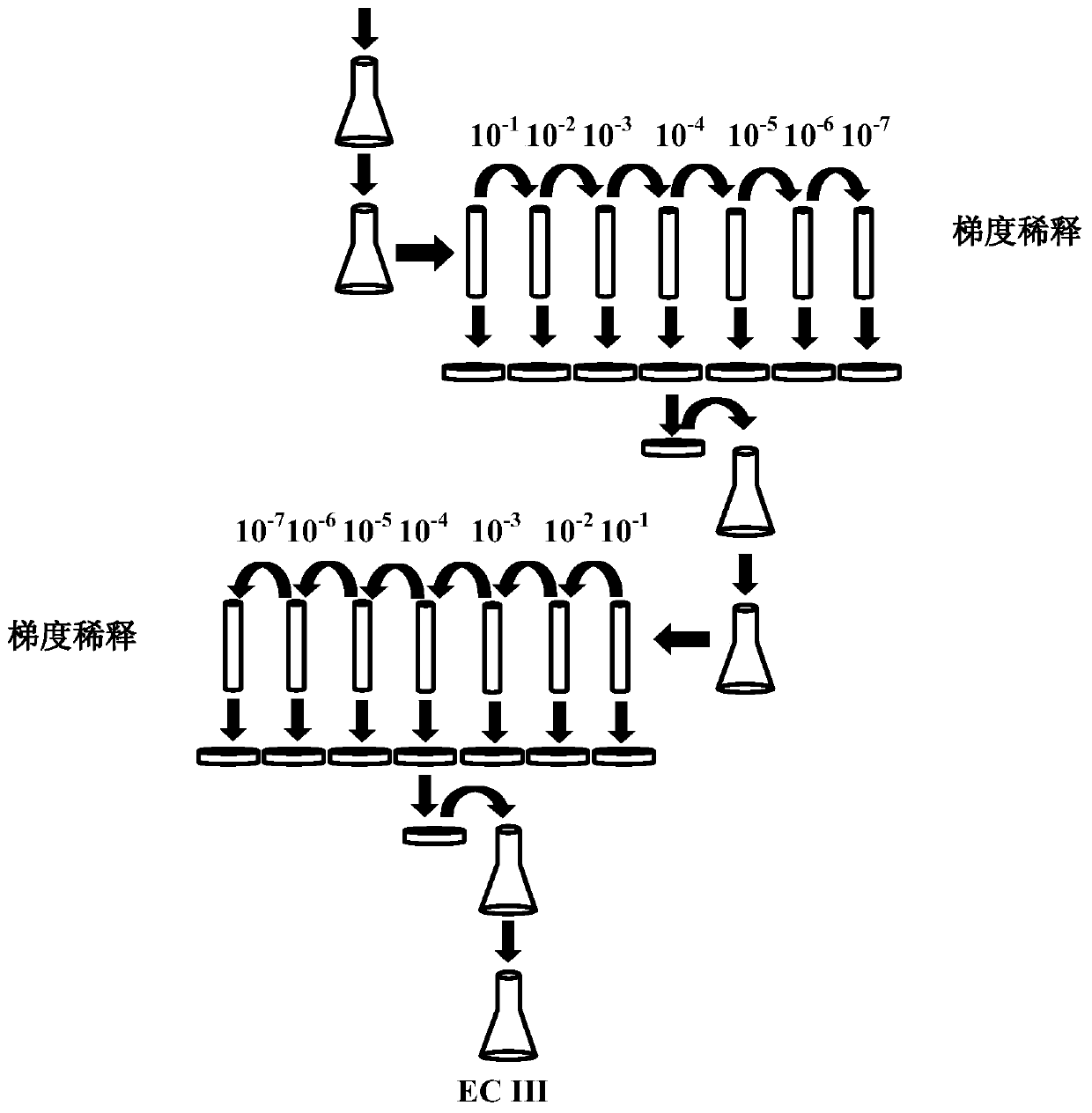
Method for separating and purifying Ochrobactrum sp. bacterium used for reducing Cr6+
InactiveCN101215522AIncrease formation rateSimple ingredientsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesOchrobactrum sp.Microorganism
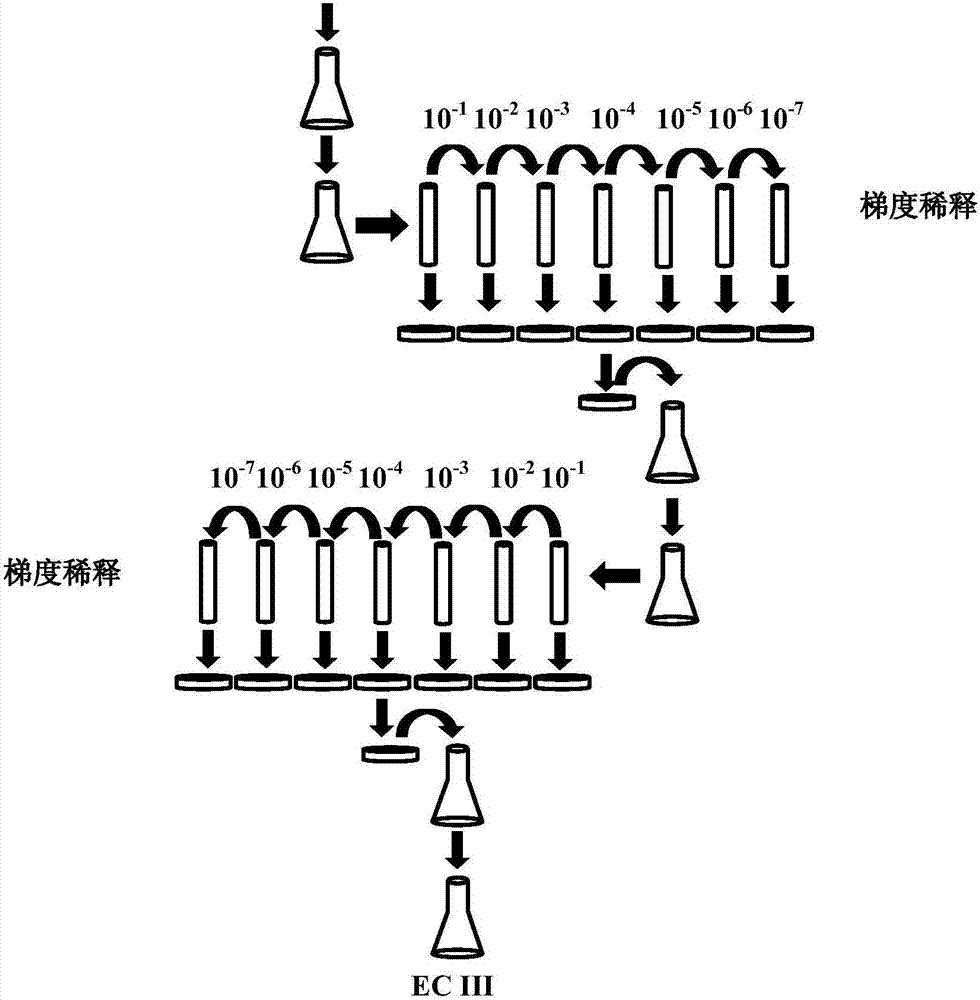
The invention discloses a method for separation and purification of Ochrobactrum sp. with deoxidizing Cr 6+, which solves the problem of that prior microorganism is difficult to isolated culture when microorganism disposes alkali waste water with Cr 6+. Picking alkali waste soil sample with Cr 6+ which is inoculated on organic LB medium to process enriched culture generation, adopting selective liquid medium Cr-G which is improved by inventor to process passage culture, and then adopting single-layer flat-plate and improved solid medium to process streak culture. The invention is capable of realizing separation and purification of Ochrobactrum sp. with deoxidizing Cr 6+ in alkality environment, adopting single-layer solid medium and optimize culture condition, wherein culture component is simple and formation rate of bacterial colony is higher.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
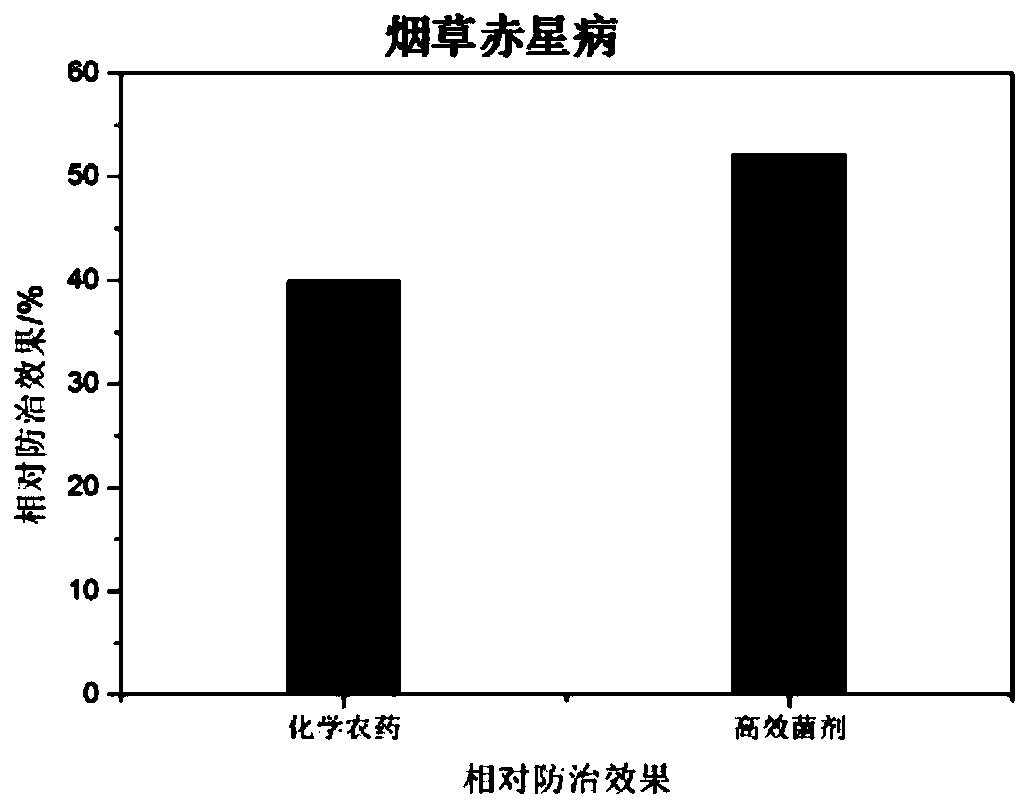
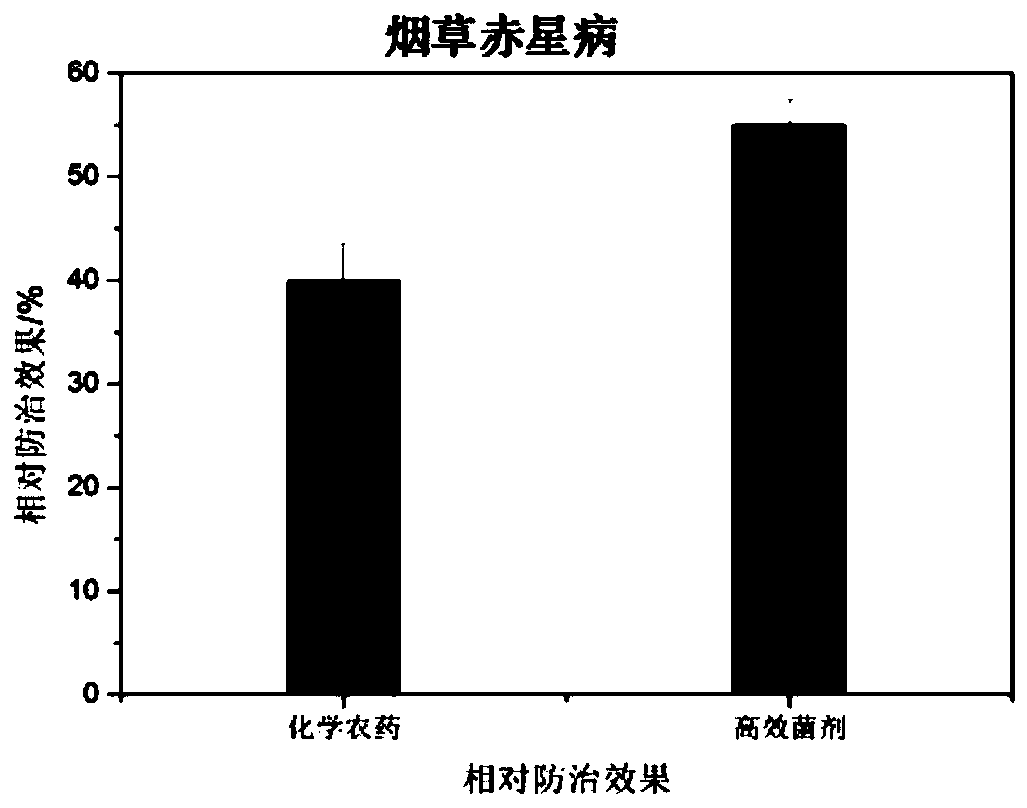
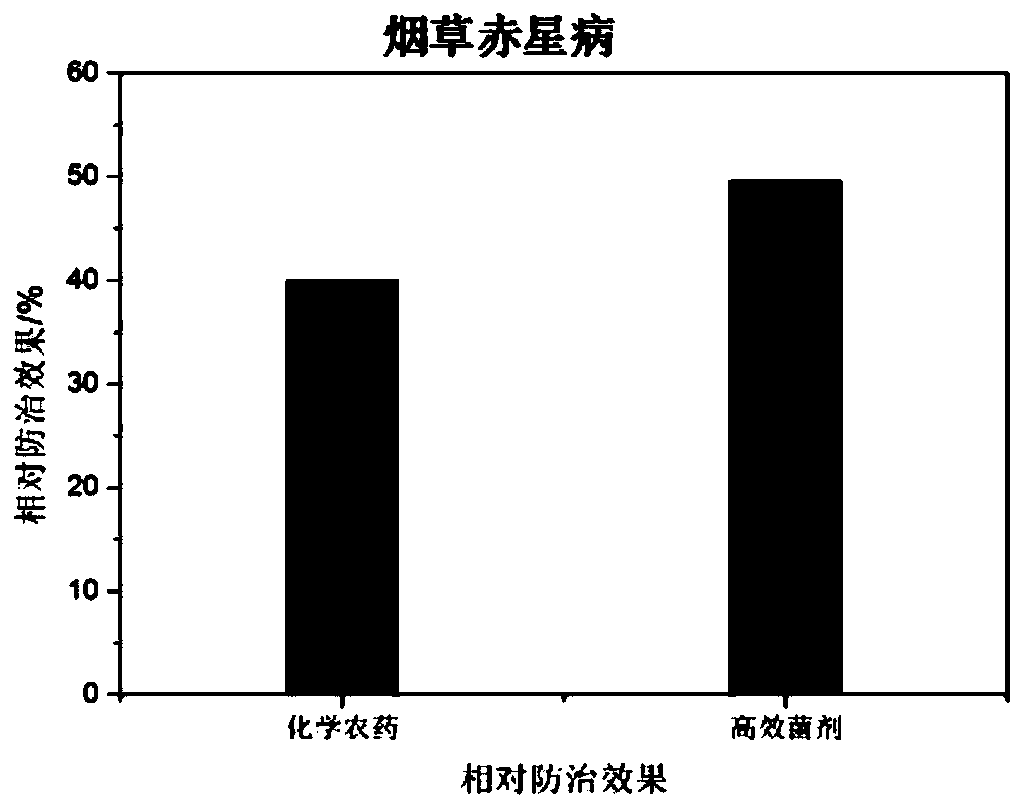
Microbial agent for preventing and controlling brown spot of tobaccos and preparation method of microbial agent
The invention discloses a mixed microbial agent for preventing and controlling brown spot of tobaccos and a preparation method of the mixed microbial agent, and belongs to the technical field of biological pesticide. The mixed microbial agent comprises 15-25% of Achromobacter, 5-15% of Enterobacter sp., 5-15% of Ochrobactrum sp., 40-60% of Stenotrophomonas sp. and 5-15% of Bacillus subtilis. The preparation method of the mixed microbial agent comprises the step of preparing the composite microbial agent from the Achromobacter, Enterobacter sp., Ochrobactrum sp., Stenotrophomonas sp. and Bacillus subtilis at a volume ratio, and the application mode of the microbial agent comprises the steps: adopting spray application, and spraying the microbial agent to both sides of leaves. It is proved through experiments that the prepared microbial agent has a high inhibitory effect on pathogenic bacteria of tobacco brown spot, and a good disease prevention effect on tobacco brown spot is achieved;and the microbial agent has low cost, a good effect and environmental protection, and therefore good prospects for biopesticide development are achieved.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO CENTRAL SOUTH AGRICULTURAL EXPERIMENTAL STATION +1
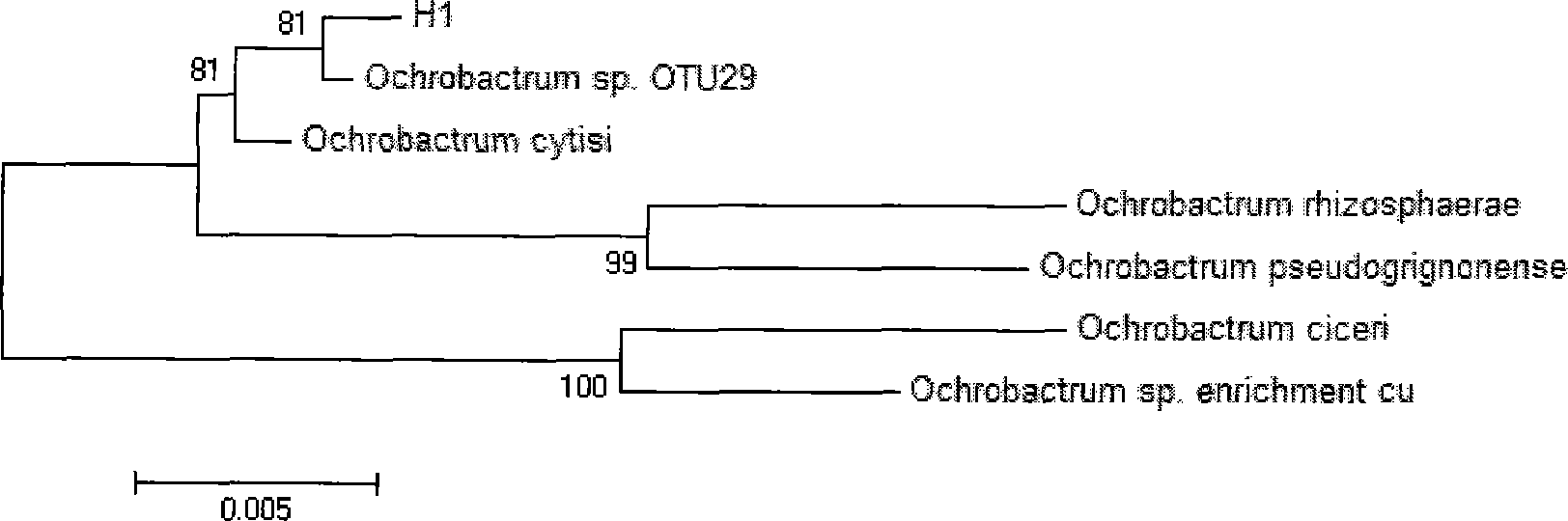
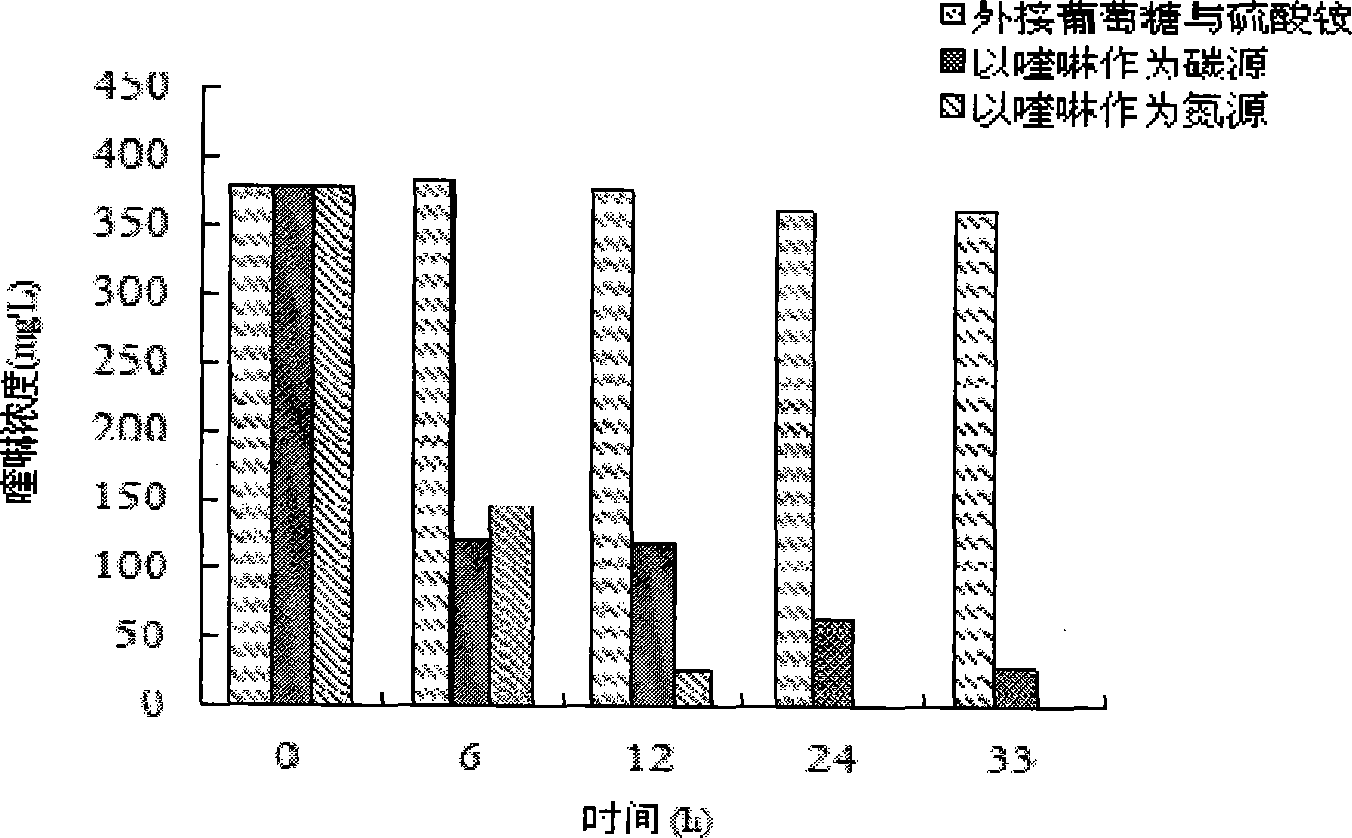
Application of Ochrobactrum sp. bacterial (H1) in quinoline degradation
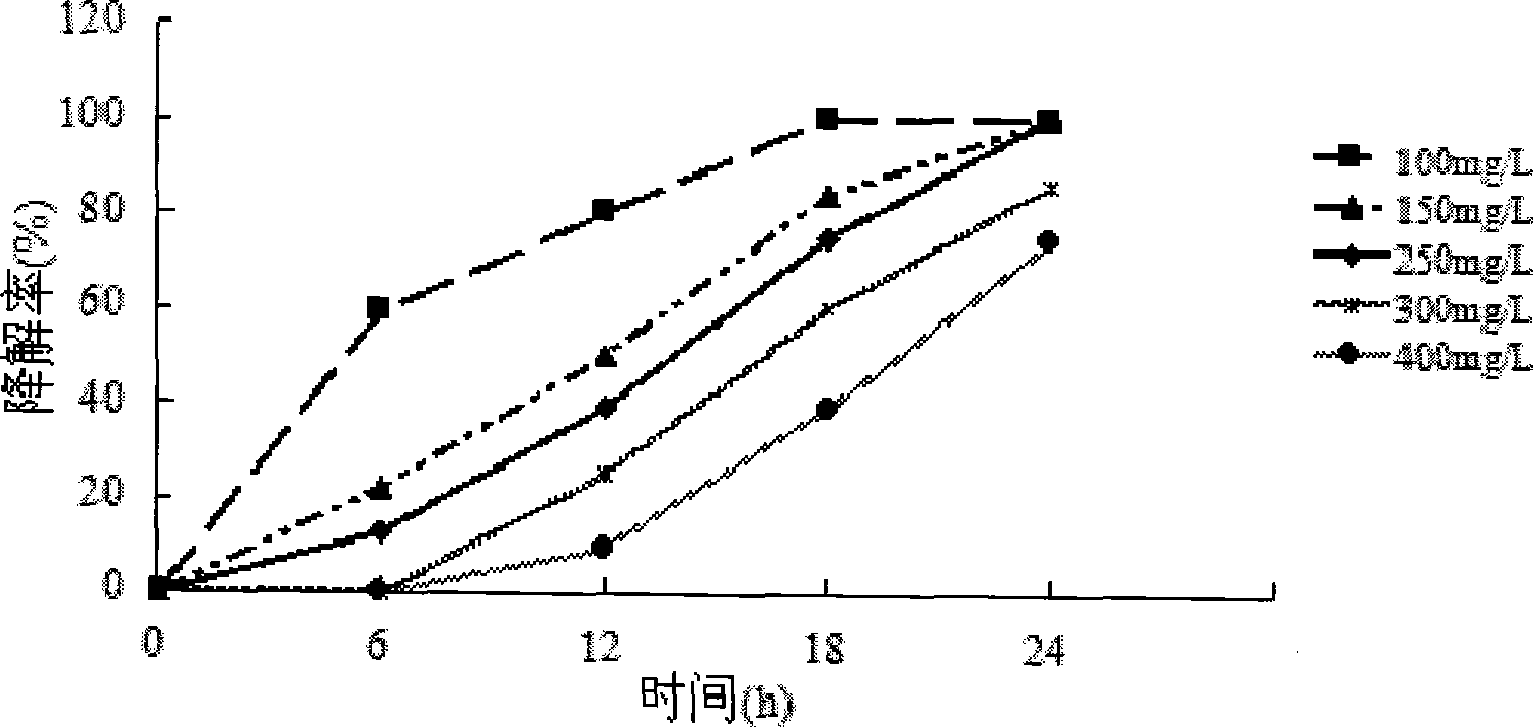
The present invention relates to an application of bacterial in quinoline degradation, wherein the bacterial is Ochrobactrum sp.. According to the present invention, the optimum degradation conditions are screened, wherein the optimum bacterial H1 growth temperature through utilizing quinoline is 30 DEG C, the initial growth pH value is 5.0, and a shaking table rotation speed is 150 r / min; the bacterial H1 meets a first order kinetic model when the initial quinoline concentration is within 250 mg / L, wherein a first order reaction rate is proportional to a quinoline concentration, the reaction that the bacterial grows through utilizing quinoline belongs to the first order reaction within the concentration range, the specific growth rate is increased along with concentration increase, and bacterial growth is not limited by the concentration within the concentration range; after the bacterial H1 is immobilized by using sodium alginate, a 400 mg / L quinoline degradation rate can be 87.5% within 24h; and the crude enzyme solution in the bacterial cell is extracted, wherein the crude enzyme solution can induce catechol 1,2-dioxygenase (C12O), nitrogen heterocyclic ring is firstly oxidized into quinolone during quinoline metabolism, and then the nitrogen heterocyclic ring is subjected to chain opening to form benzaldehyde, xylene, 2-pentanone, hydroxyphenyl propionic acid and other intermediate products.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
Identification and culture methods for Cr(VI) reducing bacteria
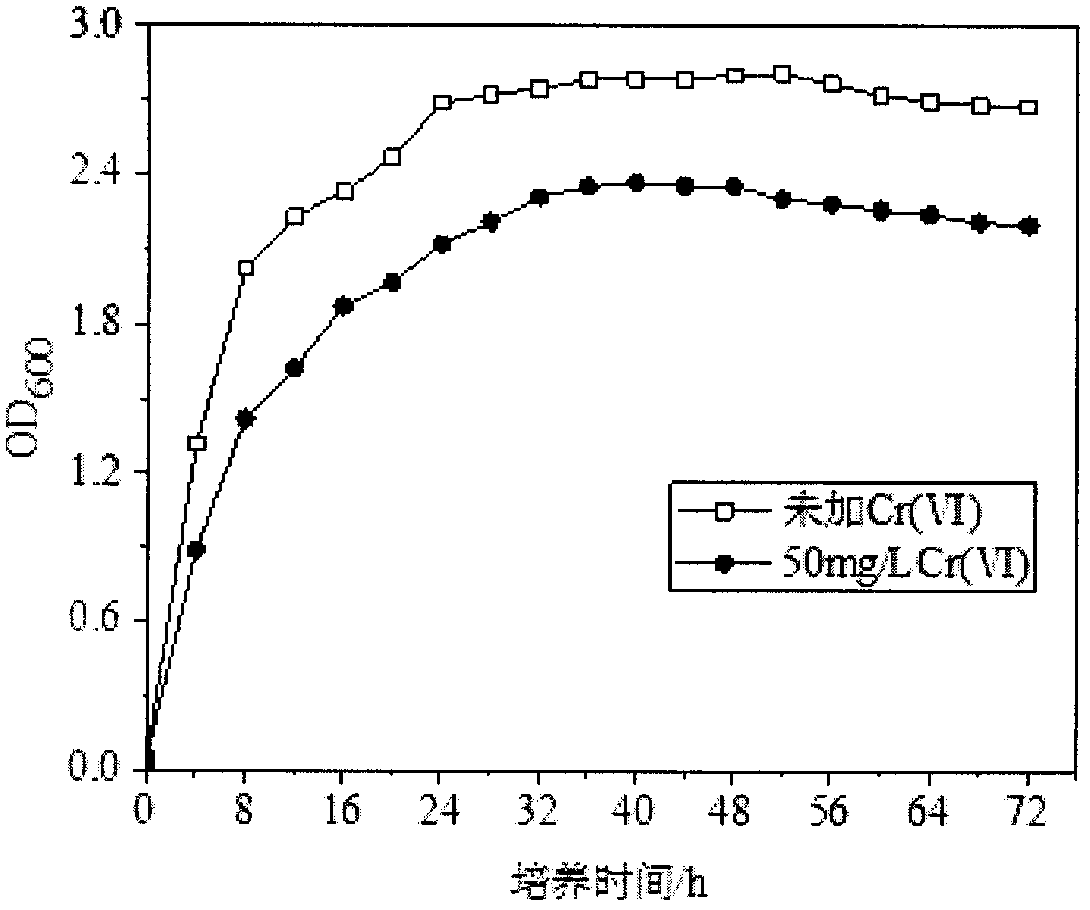
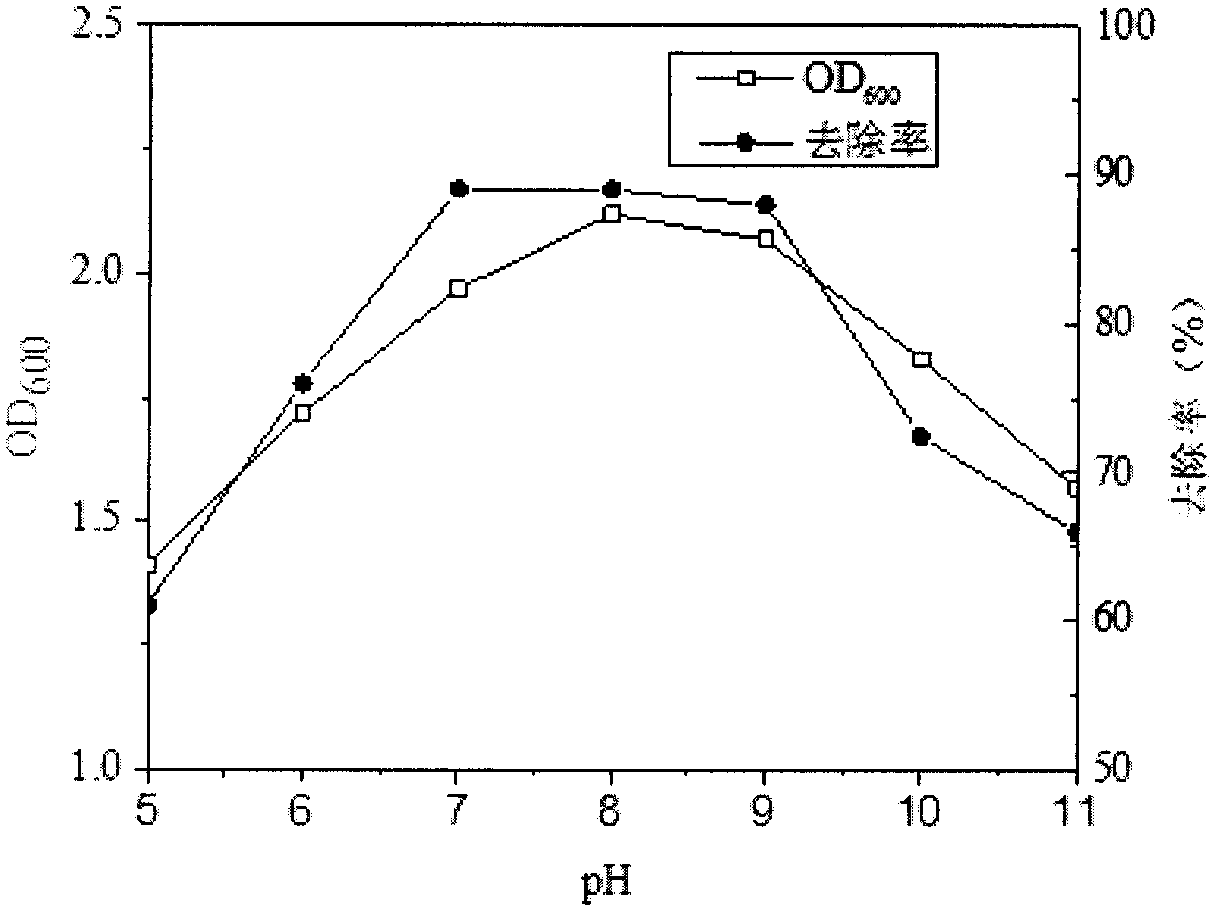
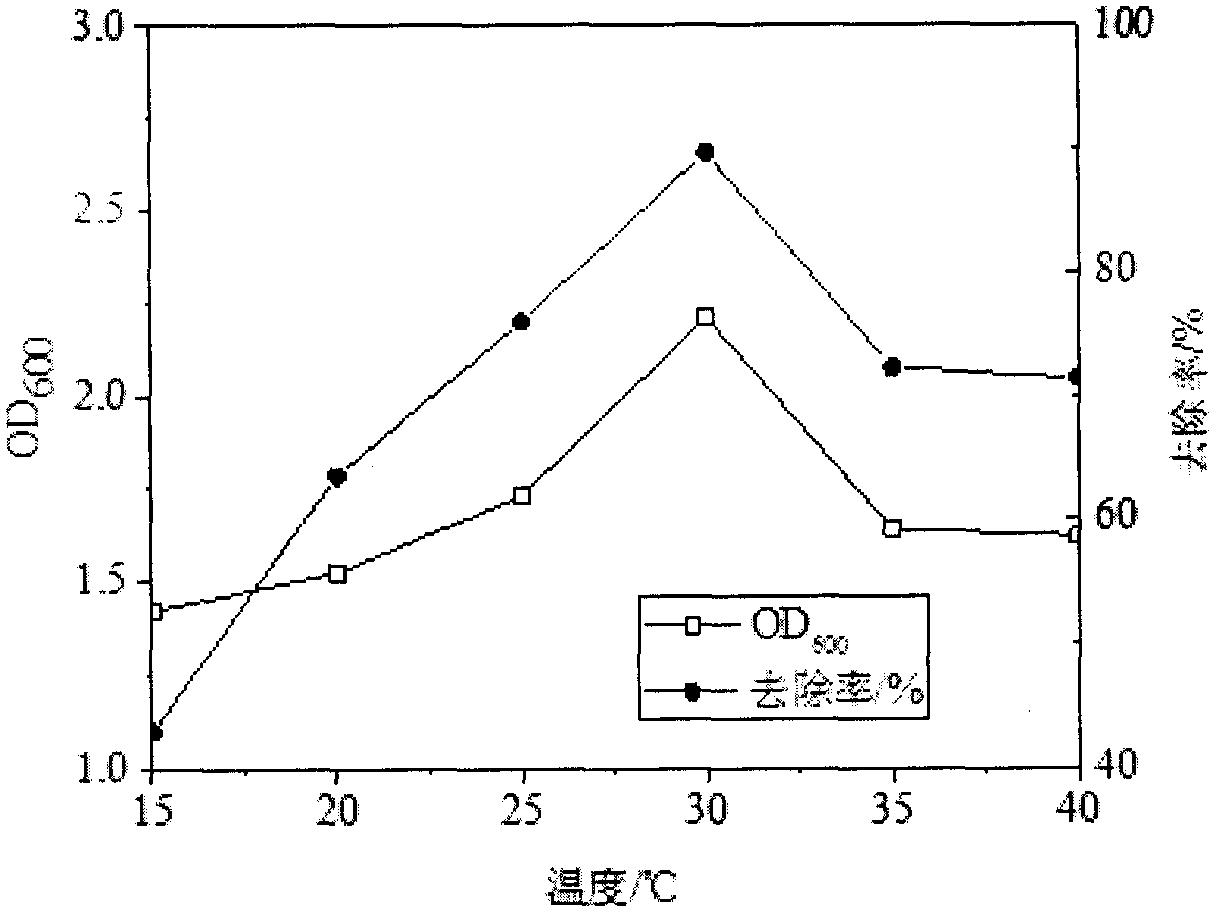
The invention discloses identification and culture methods for Cr(VI) reducing bacteria. The methods comprise the following steps: screening and separating Cr(VI) reducing bacteria from chromium-containing soil at a drain outlet of a sewer line of an electroplate factory by adopting a microbial separation and purification method; selecting a ZJ-8, the Cr(VI) removal rate of which reaches 73%, growing in a 150 mg / L Cr(VI) solution as an experimental strain; identifying the ZJ-8 by means of a physiological and biochemical method and a 16s rDNA sequencing method; and separately studying influenceof initial Cr(VI) concentration, pH, temperature and the like on bacterial growth and Cr(VI) removal effect. The ZJ-8 screened by the invention has a relatively high Cr(VI) removal ability in a relatively high metabolic activity condition. The ZJ-8 is a ram-negative bacillus which is Ochrobactrum sp through identification. The ZJ-8 has the relatively high Cr(VI) removal ability, and the removal rate of Cr(VI) can reach 89.4% after 50 mg / L Cr(VI) is treated in 72 hours under the conditions that the pH is 7-9, the inoculum size is 6% (volume fraction) and the temperature is 30 DEG C. The bacteria are expected to be applied to repairing chromium polluted water and soil.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Compound microorganism live bacteria preparation for enhancing activated sludge, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN103421692BEasy to manufactureLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesActivated sludgeLiquid medium
The invention discloses a compound microorganism live bacteria preparation for enhancing activated sludge, a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation contains Bacillus fusiformis, Comamonas sp. and Ochrobactrum sp.. The preparation method comprises the following steps: first, Bacillus fusiformis, Comamonas sp. and Ochrobactrum sp. after inclined plane activation are inoculated in liquid mediums respectively, and cultured at the temperature of 30 DEG C-37 DEG C for 40-54 h to obtain a microorganism bacteria liquid; second, the microorganism bacteria liquids obtained from the first step are mixed uniformly, dried at the temperature of 40 DEG C-60 DEG C, and the processes of crushing to 15-50 meshes and sieving are performed. The preparation can enhance activated sludge performances effectively and rapidly in applications as an activated sludge COD-degrading enhancer in the papermaking wastewater treatment process. The preparation can degrade papermaking wastewater COD efficiently and improve wastewater chromaticity and water quality.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND CO LTD +1
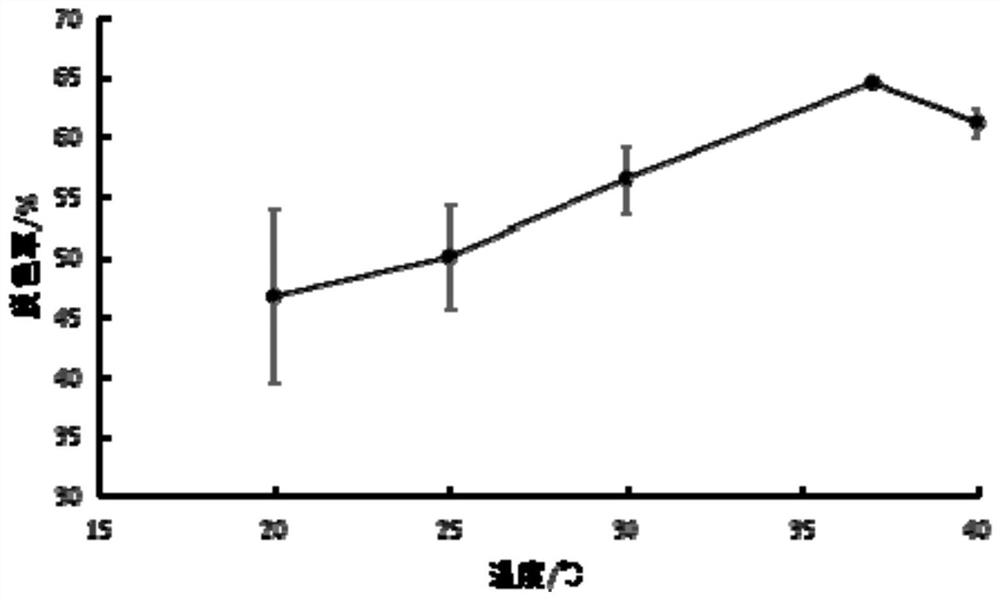
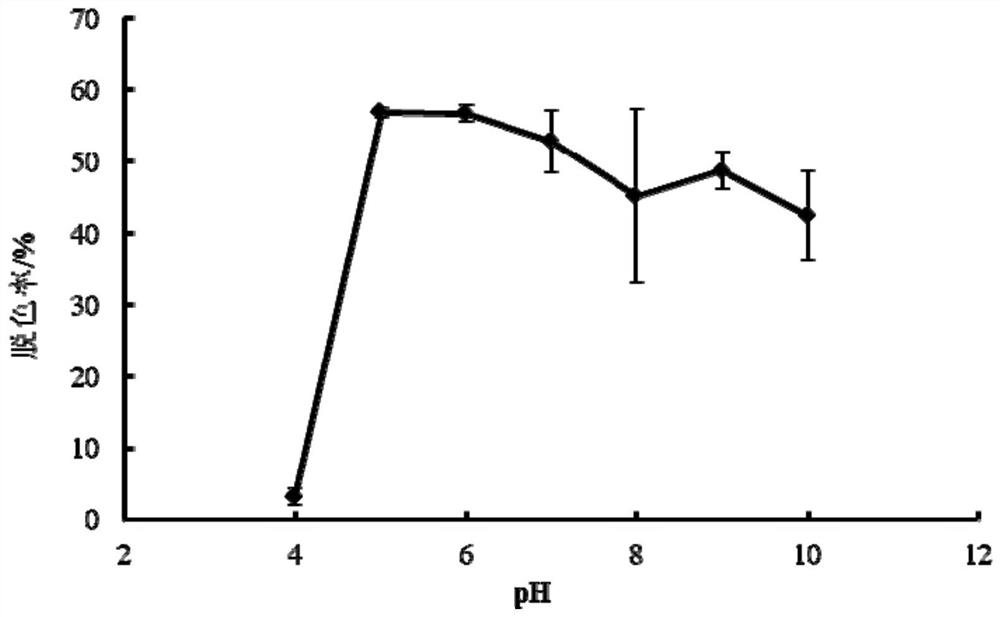
Ochrobactrum sp. ZTS-1 strain and application thereof
ActiveCN111378598AFast decolorizationWide range of temperature adaptationBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyOchrobactrum sp.
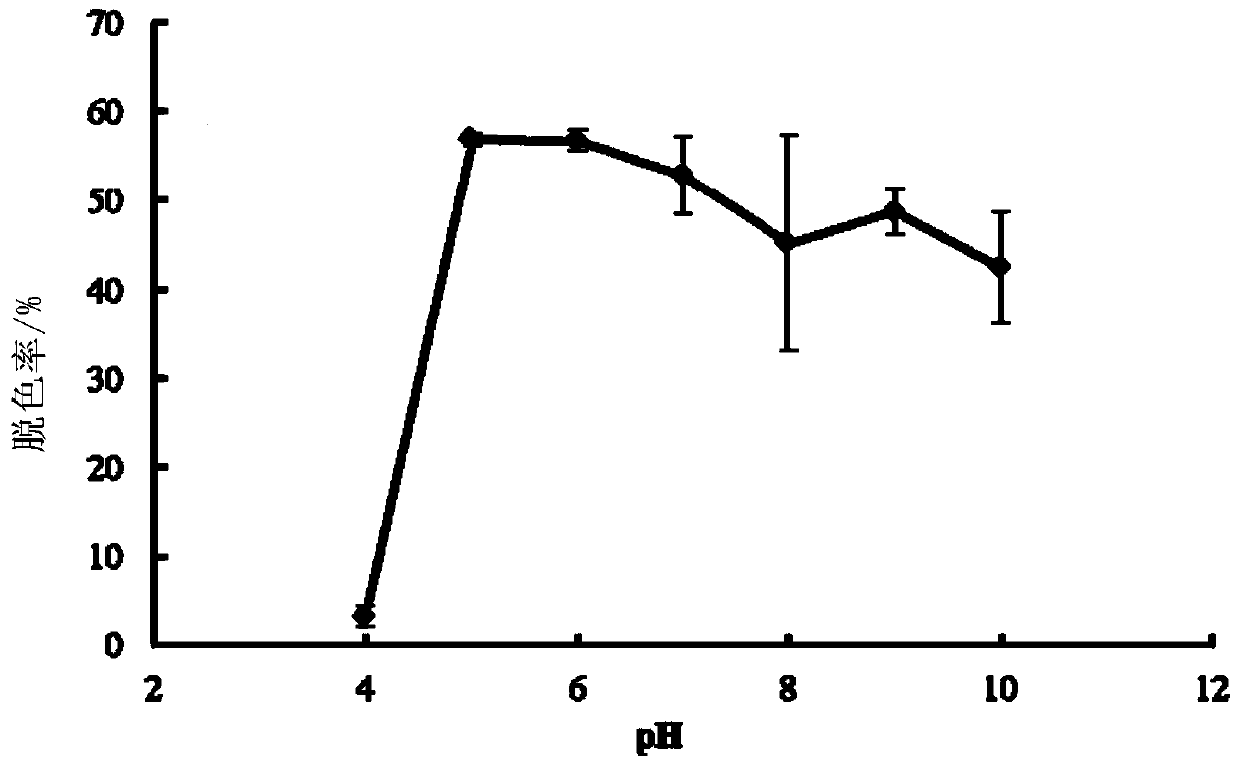
The invention relates to the field of biology, and in particular relates to an Ochrobactrum sp. ZTS-1 strain and an application thereof. The strain is preserved at China Center for Type Culture Collection, the address is Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, the postcode is 430072, the preservation date is January 10, 2020, the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M2020034, and the classification name is Ochrobactrum sp.ZTS-1. The strain has the characteristics of rapid decolorization of crystal violet, a wide temperature adaptation range and a wide pH value adaptation range in the decolorization of crystal violet dyes, and has broad application prospects.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Efficient plant growth promoting bacterium and application thereof in research and development of bio-compound fertilizer
ActiveCN105112331AIncrease profitReduce dosagePlant growth regulatorsBacteriaHuman healthPlant growth
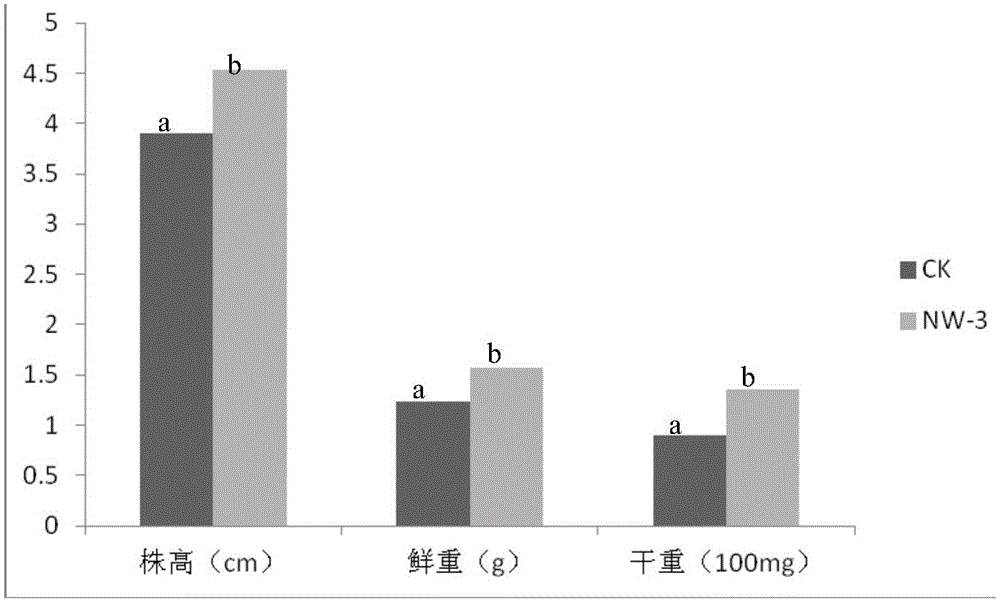
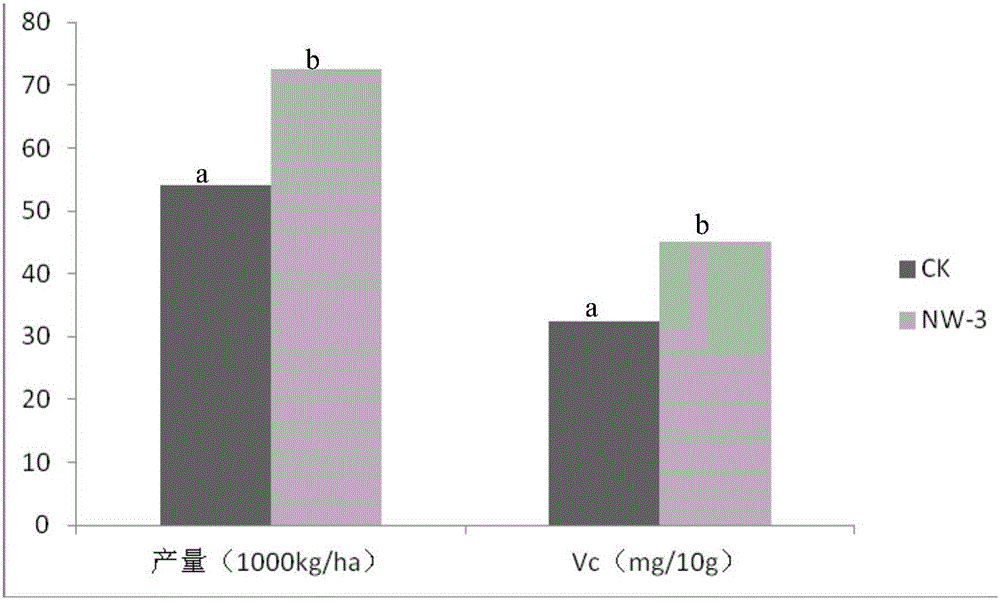
The invention provides an efficient plant growth promoting bacterium Ochrobactrum sp.NW-3 which is collected under number of CGMCC No.10858. The efficient plant growth promoting bacterium is used for producing hormone IAA, ACC deaminase and ironophore and is further used for producing products and bio-fertilizer for promoting plant growth. By the microbial fertilizer, soil pollution, water pollution and threat to human health caused by chemical fertilizer can be reduced greatly, soil can be improved, soil fertility can be enhanced, agricultural non-point source pollution can be reduced, green agriculture can be developed, and sustainable development of agriculture can be promoted, so that the bio-compound fertilizer has wide application prospect and huge market potential.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
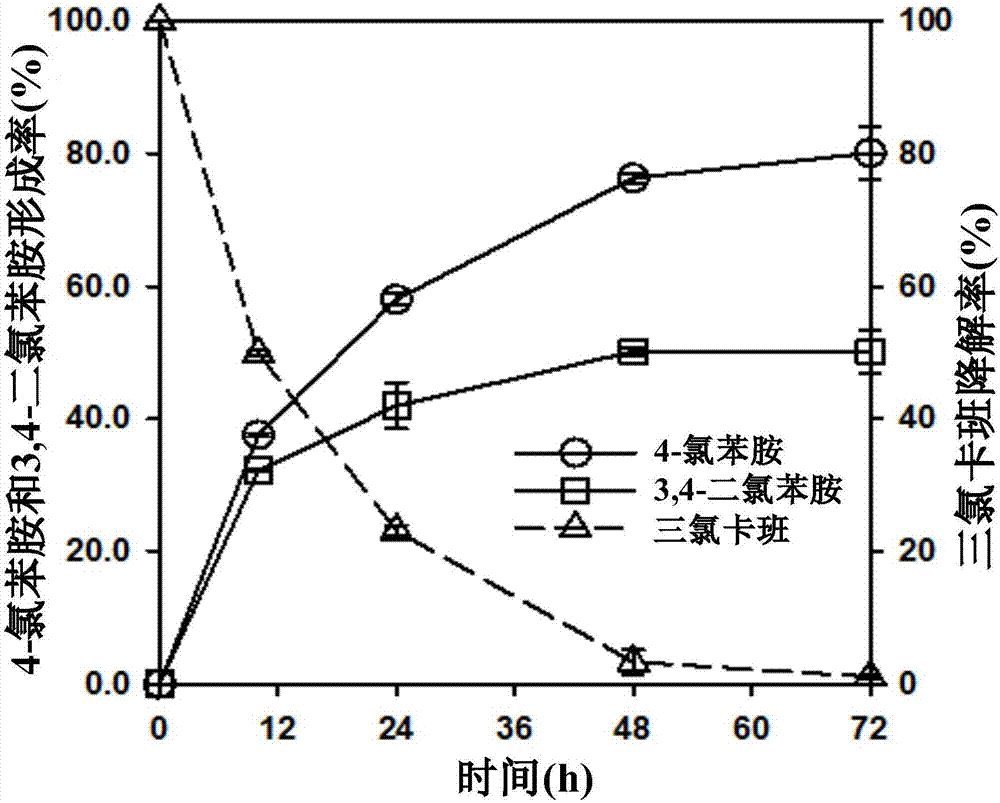
Triclocarban degrading bacterial strain and application thereof
PendingCN107312731ARich varietyAdapt to engineering applicationsBacteriaWater contaminantsOchrobactrum sp.Microorganism
The invention discloses a triclocarban degrading bacterial strain and the application thereof. The triclocarban degrading bacterial strain is Ochrobactrum sp., and has the collection number of CGMCC No.14087. The invention further provides the application of the triclocarban degrading bacterial strain to the field of microbial degradation. The triclocarban degrading bacterial strain has the effective degradation temperature range of 20-40 DEG C and the effective pH range of 5.2-9.0, has the degradation ability under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions, can be well adapted to engineering application under a natural condition, and can degrade multiple types of amido bond-containing substrates.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
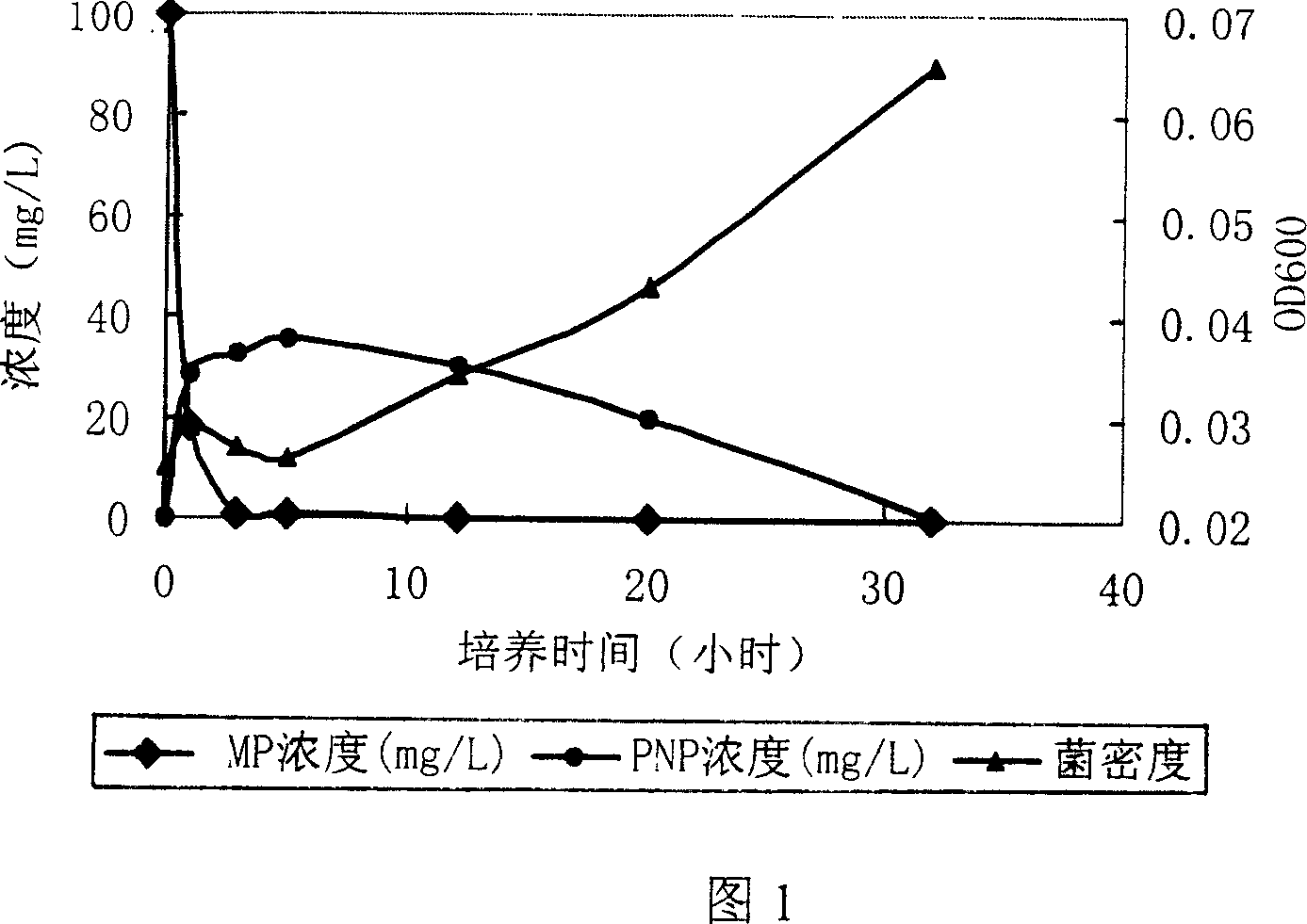
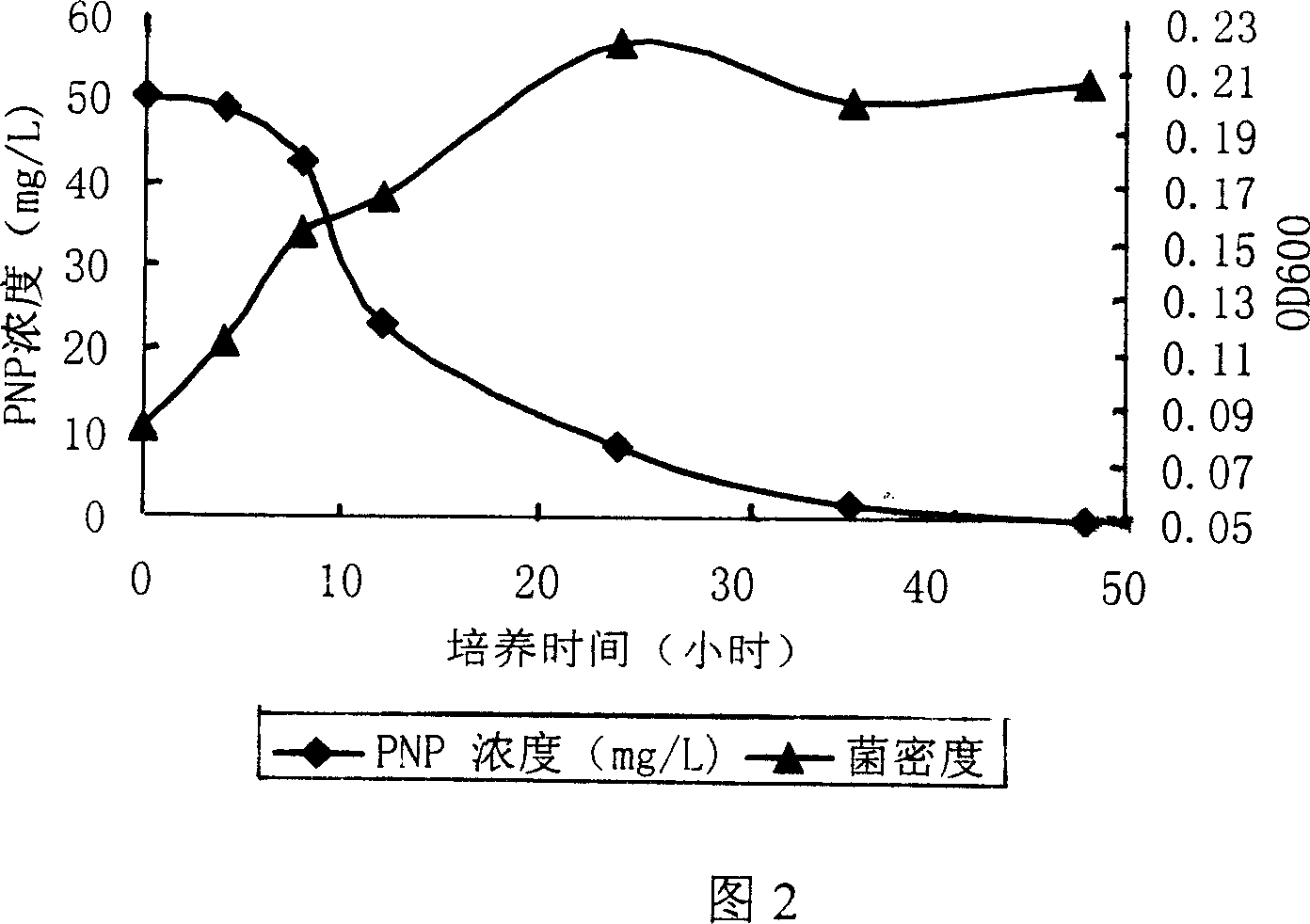
Degradation bacteria for highly effective degrading organophosphorus pesticide and its use
The invention provides a strain of degrading bacterium for effectively degrading organic phosphoric pesticide, the bacterium has a name of Ochrobactrum sp. and a docket number of CGMCC No.1221. The bacterium can be used for degrading organic phosphoric pesticide and nitrogen-containing aromatic hydrocarbons substance, thus used for the biological purification of water body, soil or agricultural products contaminated by these substances.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Low-temperature cellulose degrading bacterium
InactiveCN110241059AEfficient degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCelluloseOchrobactrum sp.
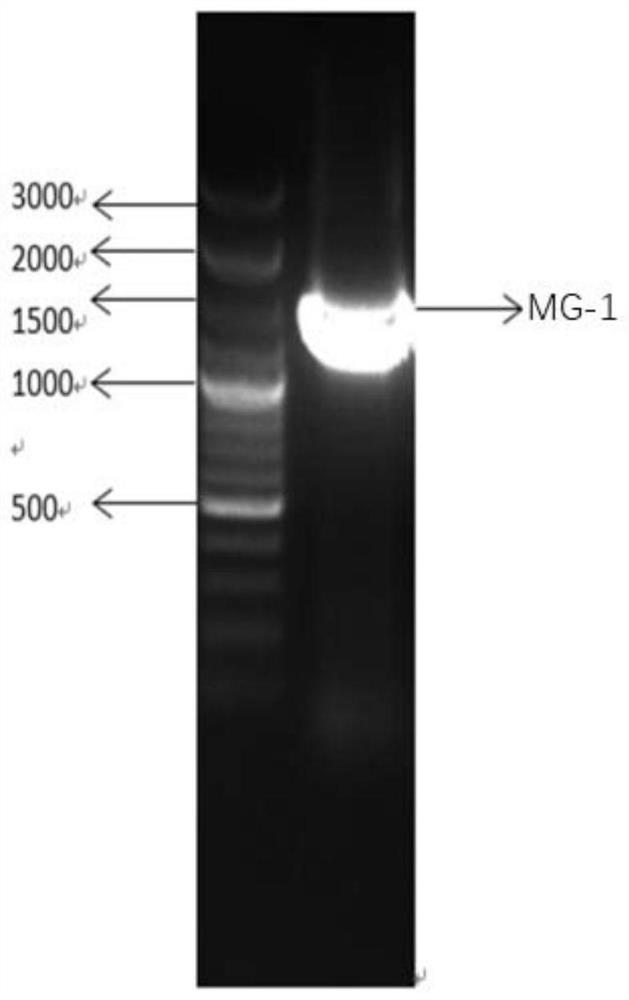
The invention discloses a low-temperature cellulose degrading bacterium, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The strain MG-1 is ochrobactrum sp., and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 18079. The strain MG-1 can grow well at 4-35 DEG C and secrete filter paper enzyme, endo-beta-1,4-glucanase, exo-beta-1,4-glucanase and other cellulases. After the strain MG-1 is cultured for 30 days at 16 DEG C, the degradation rate of the strain MG-1 to corn stalks reaches 22.30%; the strain MG-1 can be used for strain resource development for decay-promoting bacterial agents for corn stalk field-returning in a low temperature area.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
A Low-Temperature Cellulose Degrading Bacteria
ActiveCN111893065BEfficient degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyOchrobactrum sp.
The invention discloses a low-temperature cellulose-degrading bacterium, which belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The strain MG-1 belongs to the genus Ochrobactrum sp., and the preservation number is CGMCC No.18079. The MG-1 strain provided by the present invention can grow well at 4°C-35°C and secrete filter paper enzyme, endo-β-1,4-glucanase, exo-β-1,4-glucanase and cellulases such as β‑glucosidase. Cultivated at 16°C for 30 days, the degradation rate of the strain MG‑1 for corn stalks reached 22.30%, which can be used as a strain resource for the development of rot-promoting bacteria for corn stalk returning to the field in low-temperature areas.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Ochrobactrum and application thereof
InactiveCN102433275AImprove qualityReduce pollutionBacteriaTobacco treatmentOchrobactrum sp.Microorganism
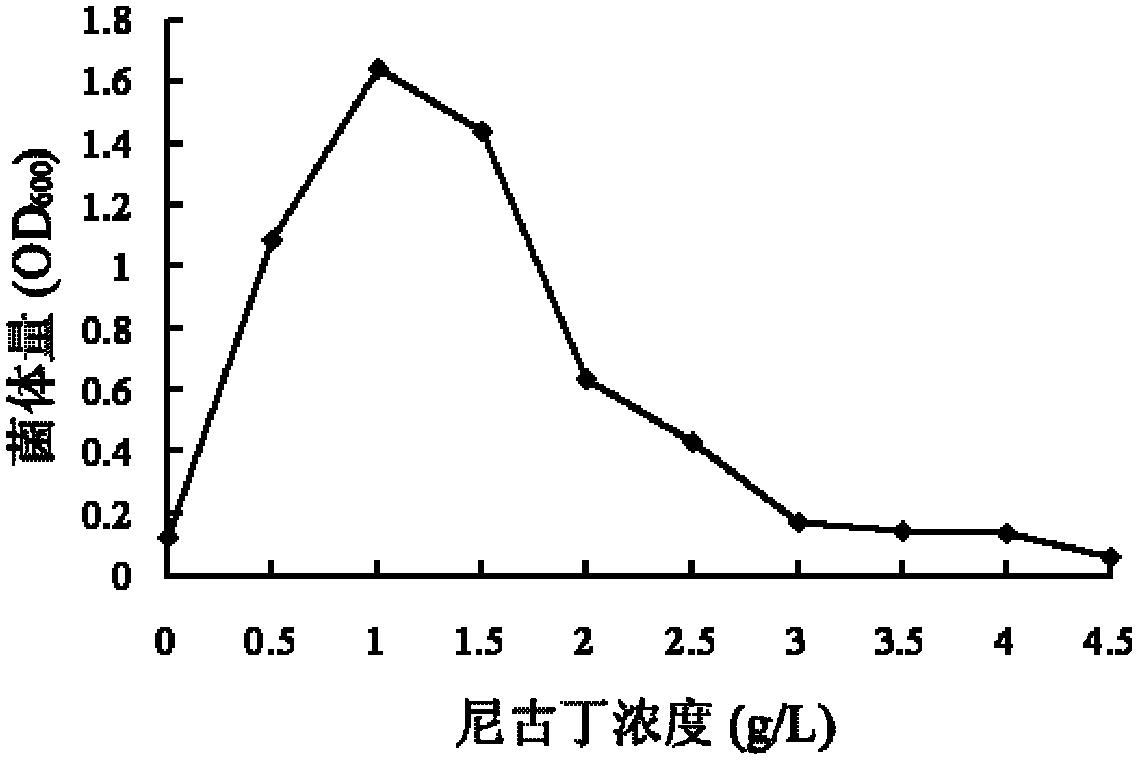
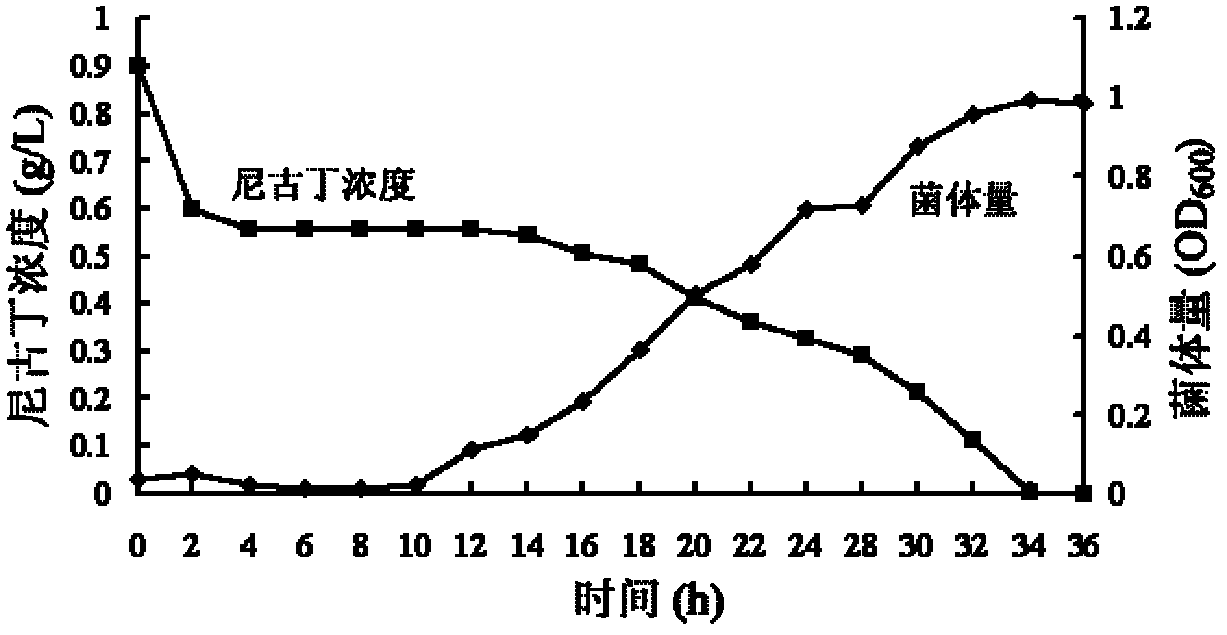
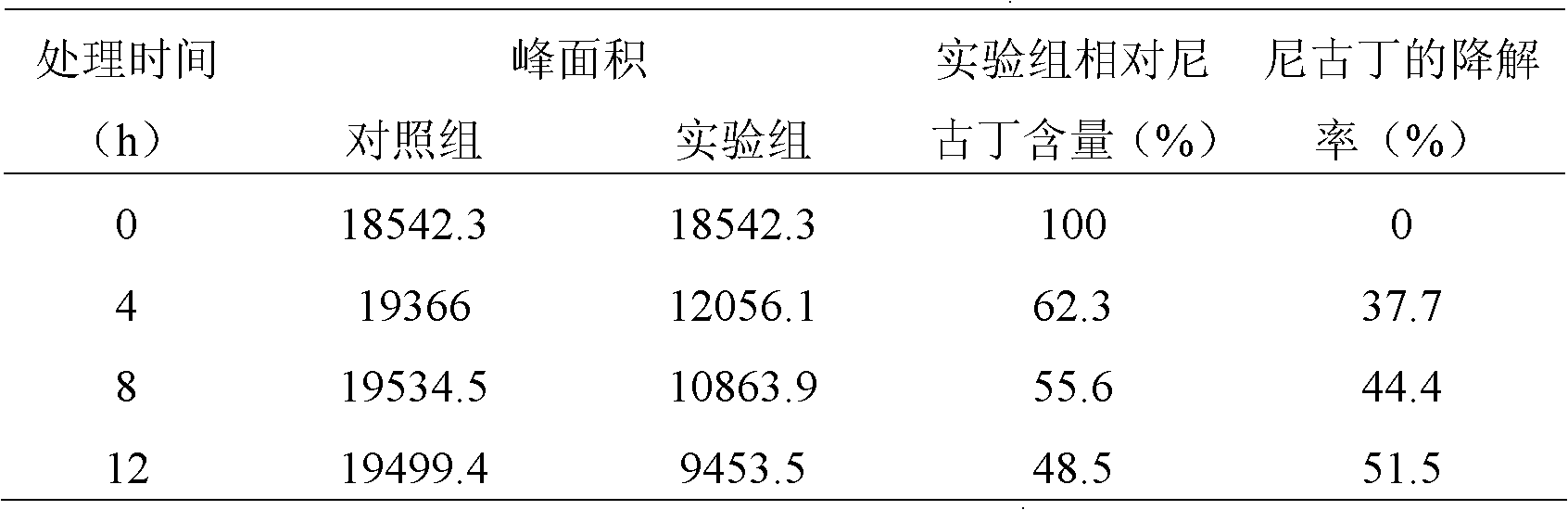
The invention relates to ochrobactrum and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of applied microbiology. The ochrobactrum sp.4-40 disclosed by the invention was preserved in CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection) on 3rd, November, 2011 with the preservation number of CGMCC No.5442. The ochrobactrum sp.4-40 has the capability of metabolizing nicotine and can growat the concentration of the nicotine as high as 4.5g / L. By culturing the ochrobactrum sp.4-40 in a large amount, a biocatalyst using a complete cell of the strain is used for completely degrading pure nicotine and can be used for reducing the content of the nicotine in tobacco leaves simultaneously. The ochrobactrum sp.4-40 disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the nicotine in tobacco and tobacco wastes can be degraded and the harm of cigarettes on a human body and the pollution to the environment are reduced.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Microbial agent for deodorizing livestock and poultry manure as well as preparation method and application of microbial agent
ActiveCN114410512APhysiological characteristics are clearReduce productionBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaBiotechnologyStaphylococcus lactis
The invention provides a livestock and poultry manure deodorizing composite microbial inoculant and a preparation method and application thereof. The livestock and poultry manure deodorizing microbial agent comprises the following bacterial strains in parts by cell number of each bacterial strain accounting for the total cell number of compound bacteria: 15-20 parts of Ochrobactrum sp.DSM717; 10 to 20 parts of Rummaliibacillus pycnus DSM 15030, and 10 to 20 parts of an additive, 10 to 20 parts of Brevibacillus fuszeri DSM9887, and 10 to 20 parts of a mixture of the brevibacillus fuszeri DSM9887; 10 to 15 parts of Enterococcus faecalis DSM2981, 10 to 15 parts of Eurococcus faecalis DSM2981; 5 to 10 parts of Methylobacter aminos JCM 8240, 5 to 10 parts of Metylobacter aminos JCM 8240, 5 to 10 parts of Metylobacter aminos JCM 10 to 15 parts of an Acinetobacter indicus DSM 100979, 10 to 15 parts of an Acinetobacter indicus DSM 100979; the preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing the following raw materials in parts by weight: 15-20 parts of bacillus velezensis CGMCC NO.23309; and 10 to 20 parts of Lactococcus lactis CGMCC NO.22594, and 10 to 20 parts of Lactococcus lactis CGMCC NO.22594. The microbial agent disclosed by the invention can treat foul smell from the source, and the strains do not have antagonism, so that the microbial agent is good in synergistic effect, high in foul smell removal rate and effective for a long time.
Owner:BIOGAS SCI RES INST MIN OF AGRI
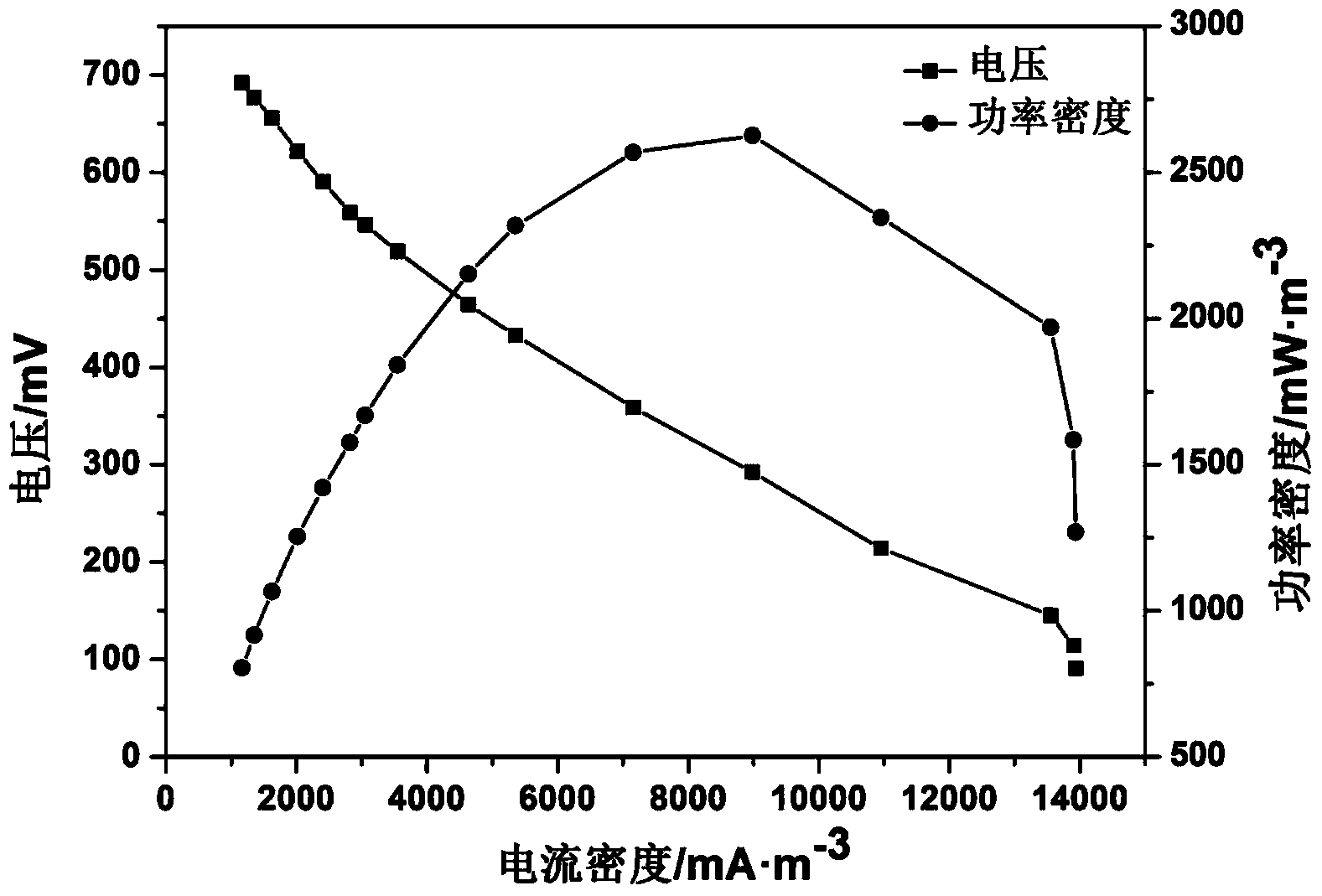
Application of ochrobactrum in preparation of microbial fuel cell, and device and method for preparing microbial fuel cell
ActiveCN103627661AImprove electrochemical activityLower requirementBacteriaCell electrodesOchrobactrum sp.Electricity
The invention discloses application of ochrobactrum in preparation of a microbial fuel cell, and a device and a method for preparing the microbial fuel cell. The ochrobactrum (Ochrobactrum sp.5753rd-generation) is preserved by the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M2013549, and the preservation date is November 6, 2013. The ochrobactrum can transfer electrons to an extracellular electron acceptor under an anaerobic condition, and can utilize xylose as a single carbon source to generate electric energy; the ochrobactrum is strong in electricity production activity, and has a good application prospect in recycling utilization of a biological energy source.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
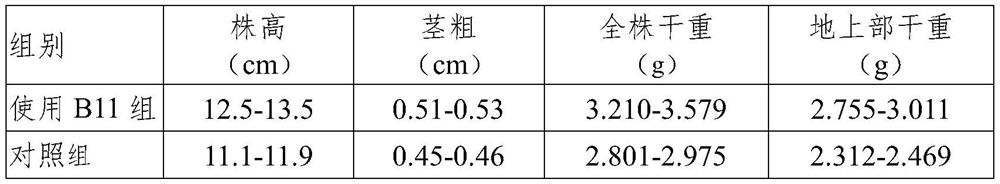
Growth regulation and control method for high-density seedling culture of melons, bacterial strain and application of bacterial strain
ActiveCN114514834ASolve growth problemsReduce labor costsBacteriaGraftingBiotechnologyOchrobactrum sp.
The invention belongs to the technical field of high-density seedling raising, and relates to a growth regulation and control method for high-density seedling raising of melons, a strain and application of the strain, the strain is an ochrobactrum B11 strain, the strain is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection, the address is Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 430072, the preservation date is July 23, 2021, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M2021925; the Ochrobactrum sp. B11 strain is used for regulating and controlling the growth of scions and rootstocks in high-density seedling culture of melons, so that the high-density seedling culture efficiency of the melons can be improved, and the cost is saved.
Owner:INST OF GARDENING ANHUI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
A kind of Paleobacterium ochrobactrum sp.ZTS-1 bacterial strain and its application
ActiveCN111378598BFast decolorizationWide range of temperature adaptationBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyOchrobactrum sp.
The invention relates to the field of biology, in particular to a strain of Ochrobactrum sp. ZTS‑1 and its application. The strain is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, address: Wuhan University, Wuhan, China; zip code 430072, the preservation date is January 10, 2020, the preservation number is: CCTCC NO: M2020034, and the taxonomic name is Ochrobactrum sp.ZTS‑ 1. In decolorization of crystal violet dyes, the strain has the characteristics of rapid decolorization of crystal violet, wide range of temperature adaptation and wide range of pH value adaptation, and has broad application prospects.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
A strain of quinolone antibiotic degrading bacteria and its application
ActiveCN106929442BEffectively remove pollutionEliminate pollutionBacteriaWater contaminantsOchrobactrum sp.Fungicide
The invention discloses a quinolone antibiotic-degrading bacterium and its application, belonging to the technical field of biological treatment of environmental pollutants. The degrading bacterium was domesticated and purified from livestock and poultry feces, named Ochrobactrum sp. JOB, and was preserved in Guangdong Province on December 21, 2016, Building 59, Compound No. 100, Xianlie Middle Road, Guangzhou City. Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center of the Institute of Microbiology, collection number: GDMCC NO: 60132. In the present invention, degrading bacteria are made into bacterial suspension or immobilized bacterial agent, which can effectively remove quinolone antibiotic pollution in different environmental media such as water body and soil, and have high efficiency, energy saving and environmental protection compared with methods such as physical adsorption and chemical degradation. advantage. In particular, using the embedding agent to fix the bacteria, prolong the life of the bacteria, the effect of the bacteria agent is good, and the ability to adapt to the environment is strong.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com