Triclocarban degrading bacterial strain and application thereof
A technology of triclocarban and degrading bacteria, applied in bacteria, biological water/sewage treatment, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problem of affecting the reproductive ability and endocrine system of animals, inducing the generation and transfer of microbial resistance genes, affecting the activity of aquatic organisms, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1 3
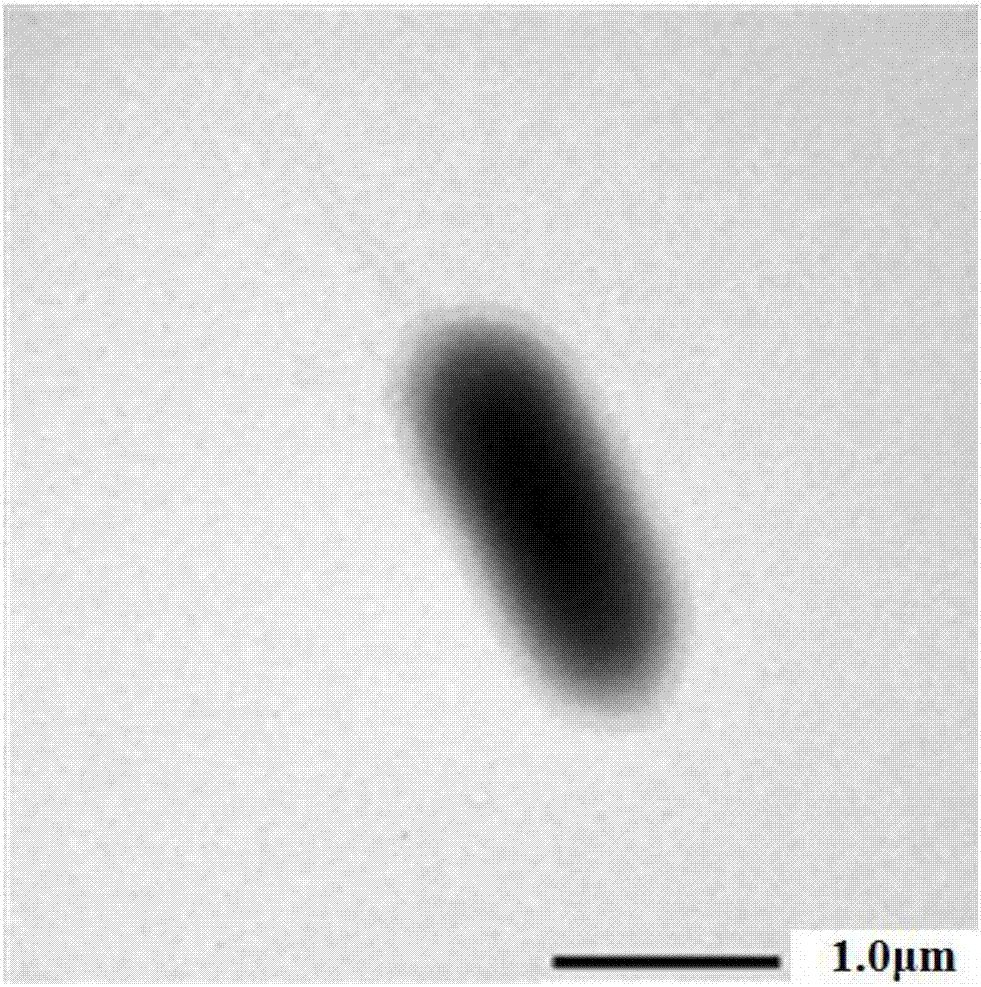
[0034] Example 1 Isolation and identification of triclocarban-degrading bacteria TCC-1 and its aerobic degradation of triclocarban
[0035] 1.1 Strain isolation and purification
[0036]The source of the bacteria was collected from the remaining sludge of a sewage treatment plant in Beijing. 20mg / L TCC was added to a 150mL Erlenmeyer flask as a mother liquor. First, the acetone was volatilized to remove, and then 50mL of sterilized basal salt medium (containing 0.05 % yeast extract), respectively insert about 5g of mud-water mixture samples, and place them in a constant temperature shaker at 30°C for cultivation, with a rotation speed of 150rpm. After culturing for 7-8 days, the culture medium was prepared in a similar manner, and 10% of the volume of the enriched solution was transferred to fresh culture medium. After 5 consecutive transfers, the degradation effect of the enrichment solution was measured. The strains were isolated and purified by dilution plate method and s...
Embodiment 2 3
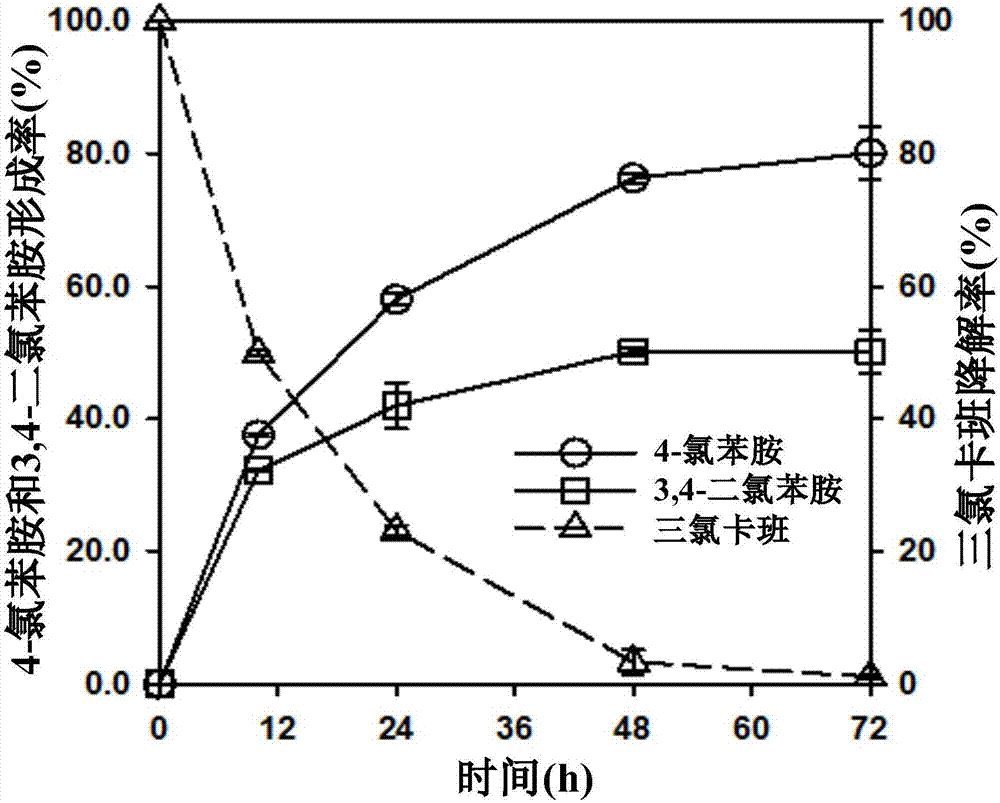
[0046] Example 2 Triclocarban-degrading bacteria TCC-1 anaerobically degrades triclocarban, 4,4'-dichlorophenylurea and diphenylurea
[0047] Preparation of anaerobic medium: Supplement 1.5mM potassium nitrate and 15mM sodium acetate into the basal salt medium. After fully dissolving, inject high-purity nitrogen gas to remove oxygen, seal the culture bottle with anaerobic plug, and sterilize at high temperature and high pressure.
[0048] In the anaerobic medium prepared above, 5 mg / L of triclocarban, 4,4'-dichlorophenylurea and diphenylurea were respectively added in the form of mother liquor, and the bacterial strain TCC- 1 Inoculate into anaerobic basal salt medium, the initial OD600 value is about 0.035, each group has 3 repetitions, and observe the change of biomass and the degradation of the above substrates.
[0049] Continuously monitor the conversion of triclocarban, 4,4'-dichlorophenylurea and diphenylurea Figure 5 and 6 As shown, the results show that the tricloc...
Embodiment 3 3
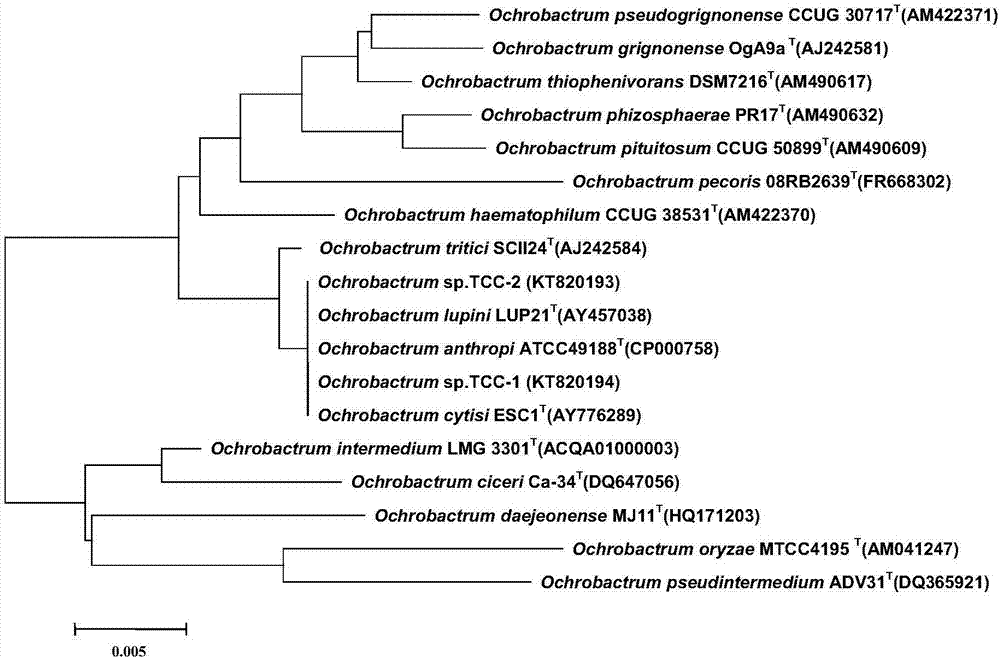
[0050] Example 3 Cloning of the degrading gene tccA of the triclocarban-degrading bacteria TCC-1
[0051] 3.1 Extraction of bacterial genome total DNA
[0052] After the triclocarban-degrading bacterium TCC-1 was cultured in large quantities, the CTAB method was used to extract high-purity, large-segment genomic DNA. The extraction method was referred to the "Refined Molecular Biology Experiment Guide" edited by F. Osper et al.
[0053] 3.2 Digestion of total DNA
[0054] The total DNA of Ochrobactrum sp.TCC-1 was partially digested with Sau3AI.
[0055] 3.3 Recovery of DNA fragments
[0056] The digested DNA fragments were separated and purified by electrophoresis (TAE buffer), and recovered using a DNA recovery kit (Tiangen, Beijing). The recovered DNA was dissolved in TE buffer (pH 8.0) and placed at -20°C preservation.
[0057] 3.4 Enzyme linkage
[0058] Establish the following reaction system: pUC118(BamHI) (TaKaRa, Code: D3321) 0.5μL
[0059] Recover 5 μL of DNA f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com