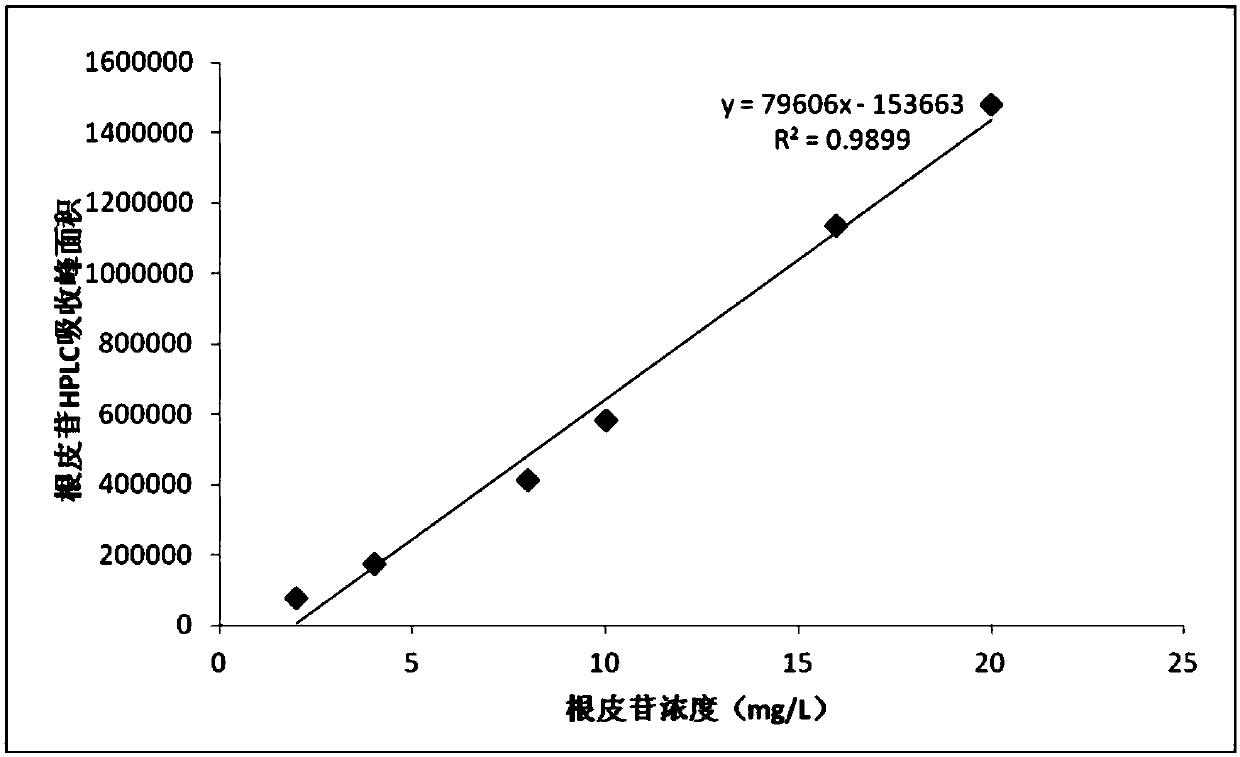
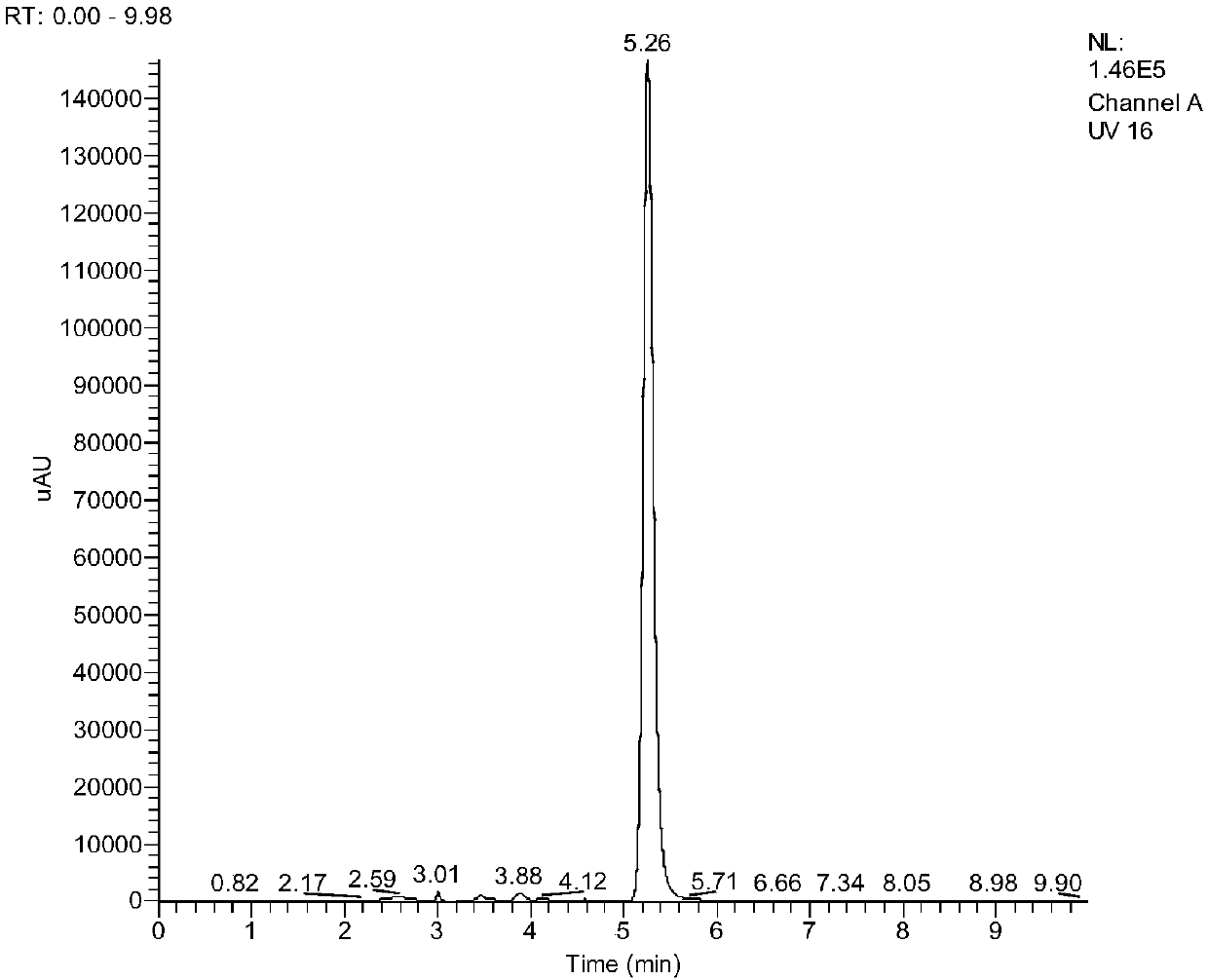
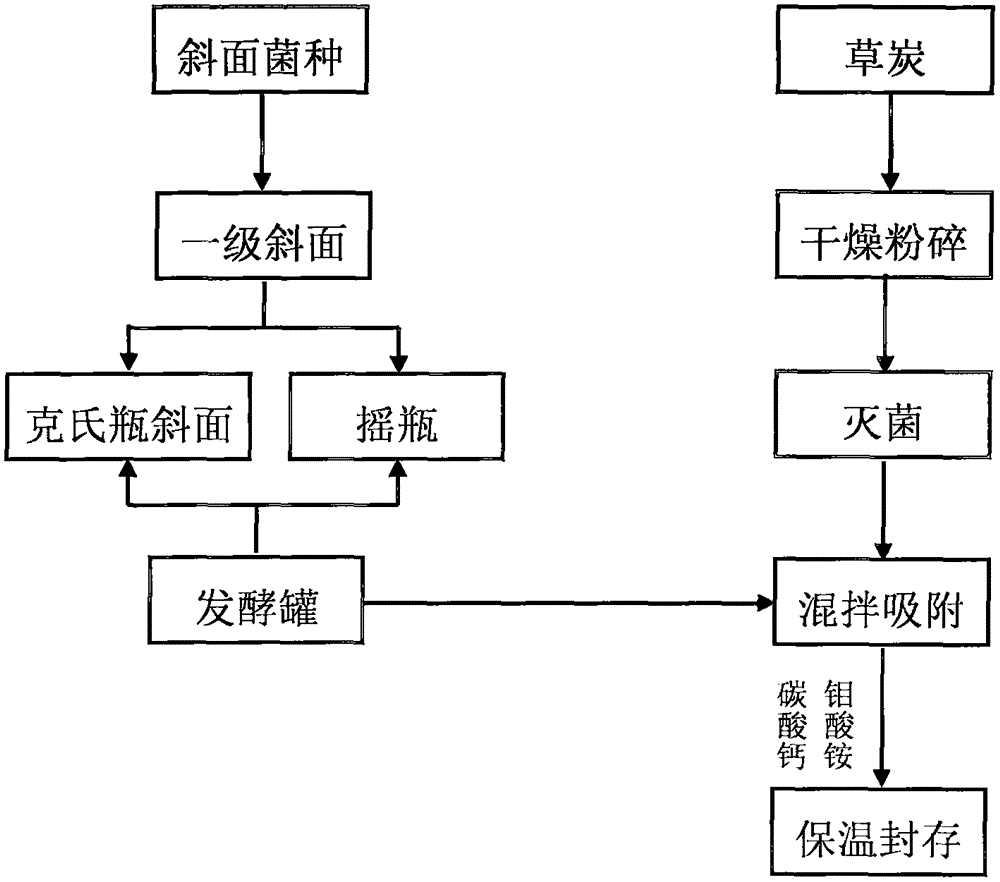
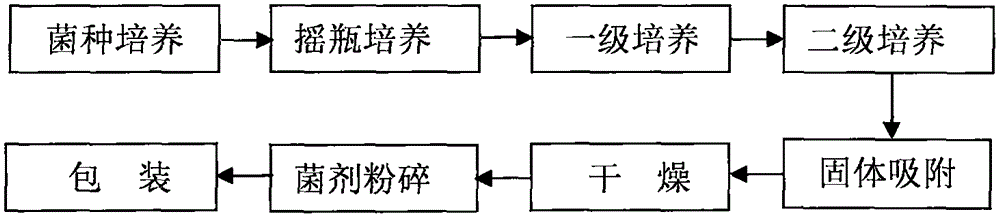
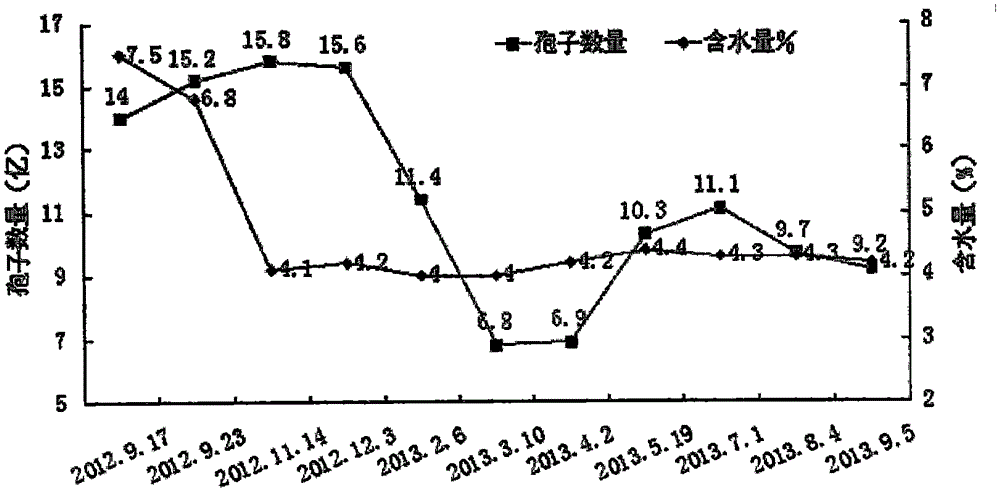
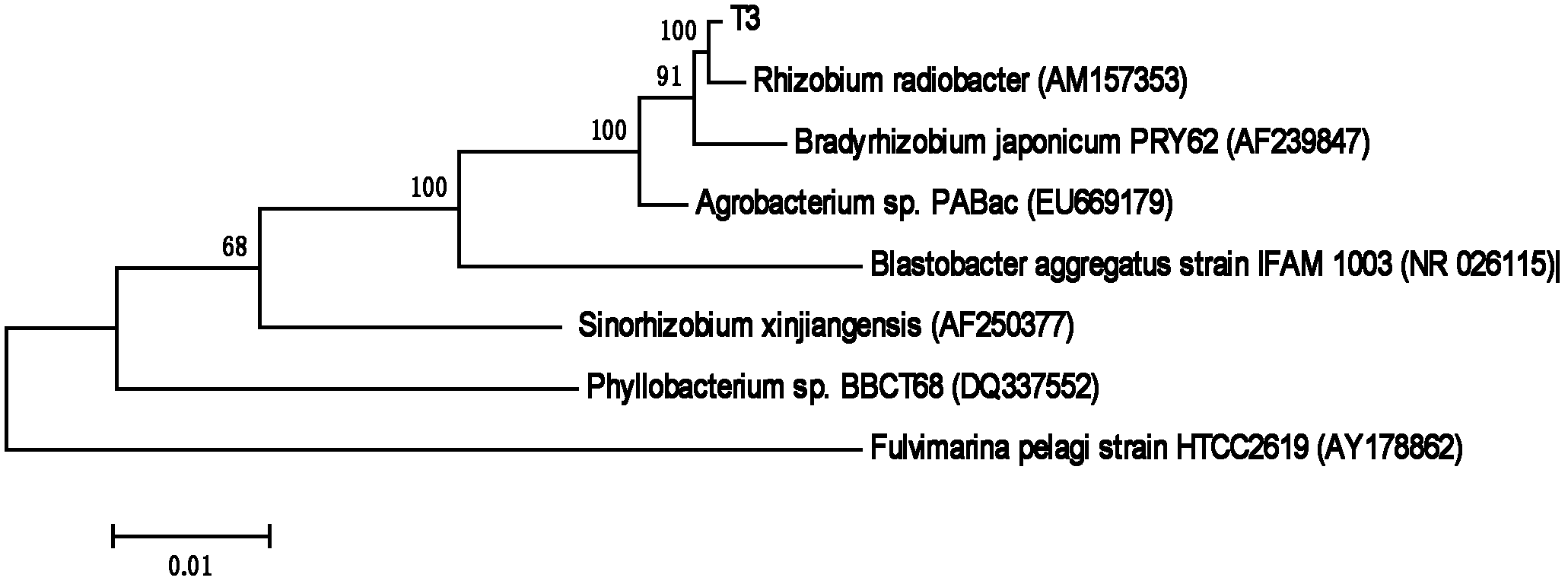
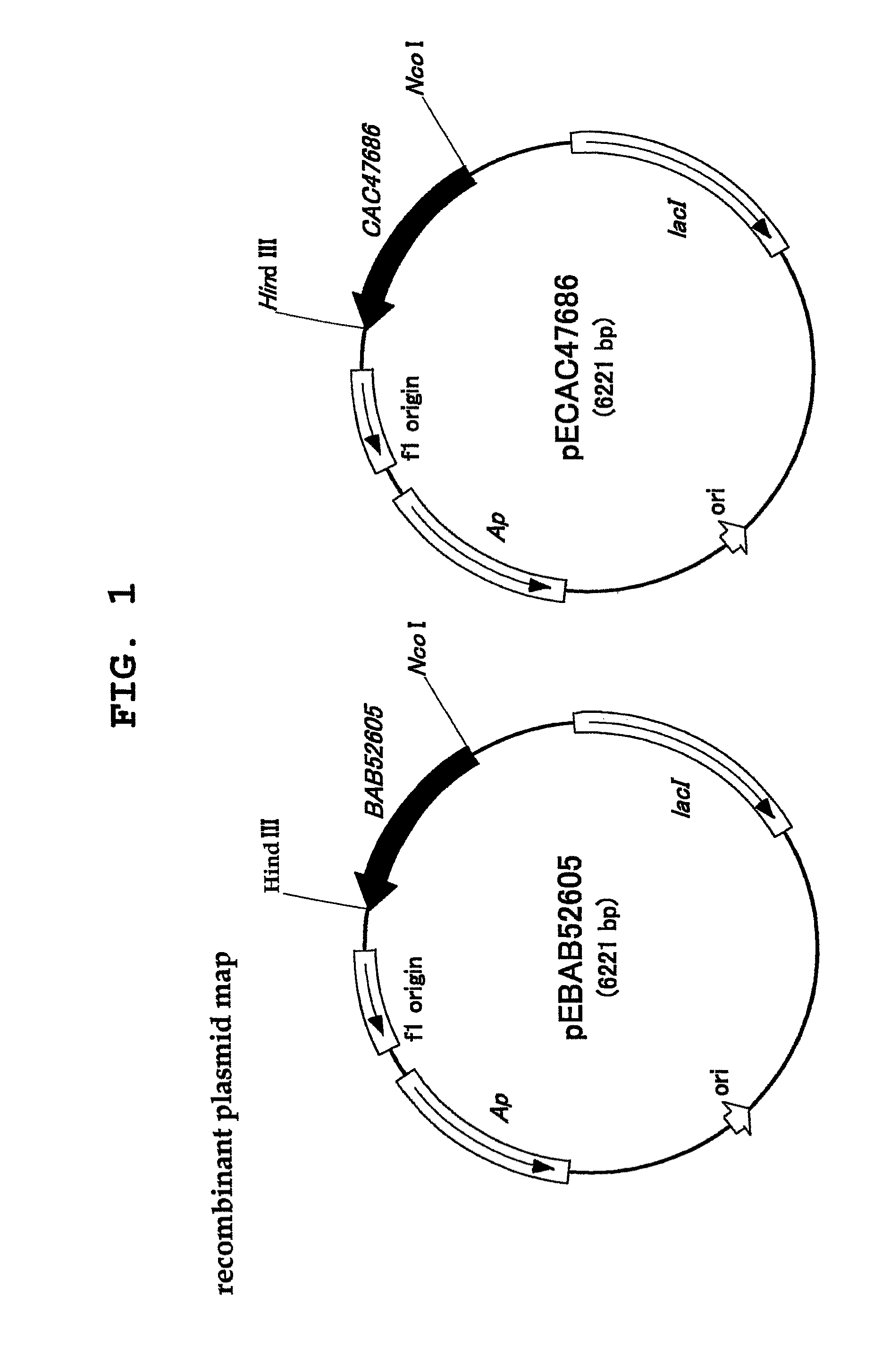
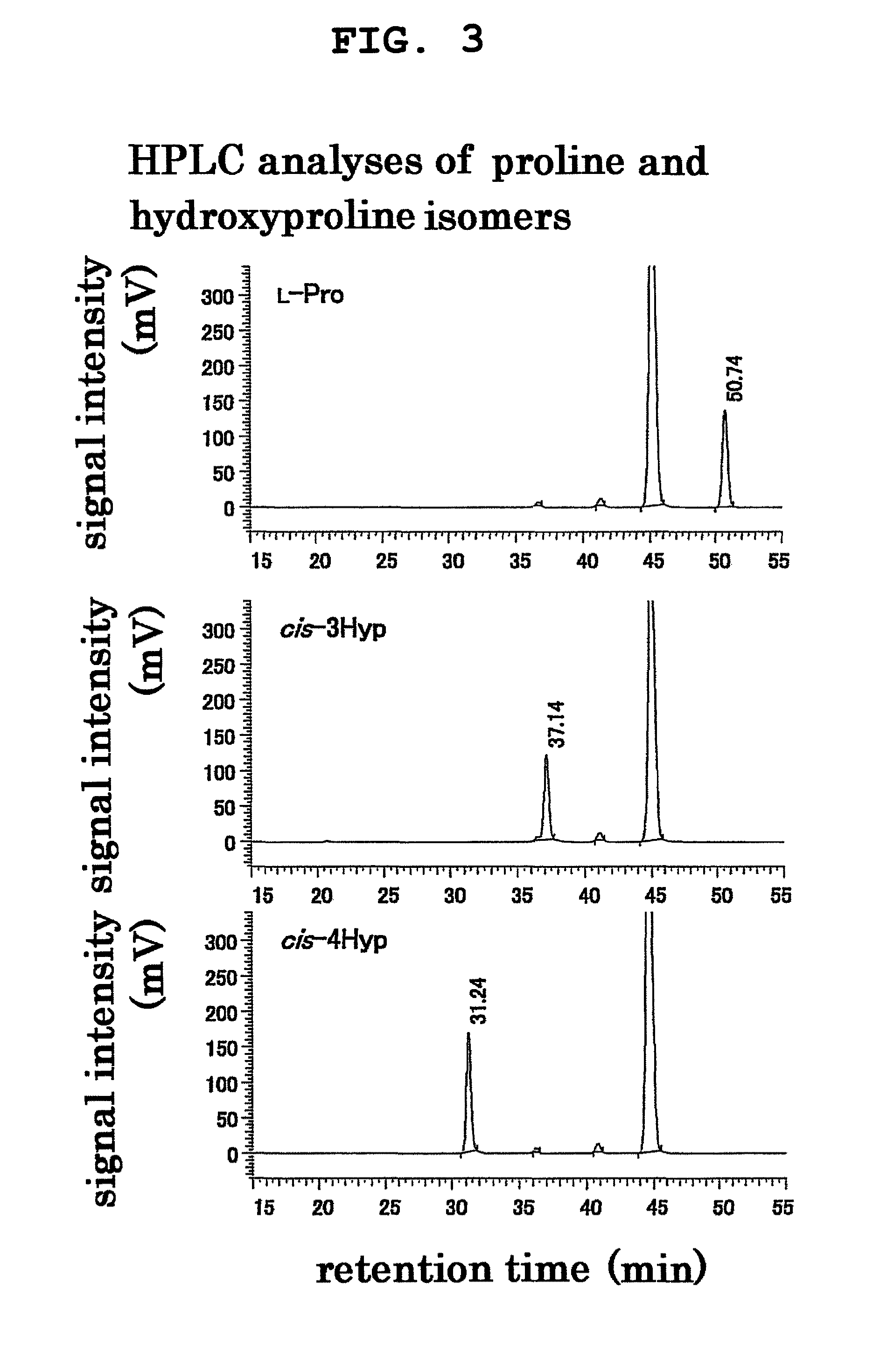
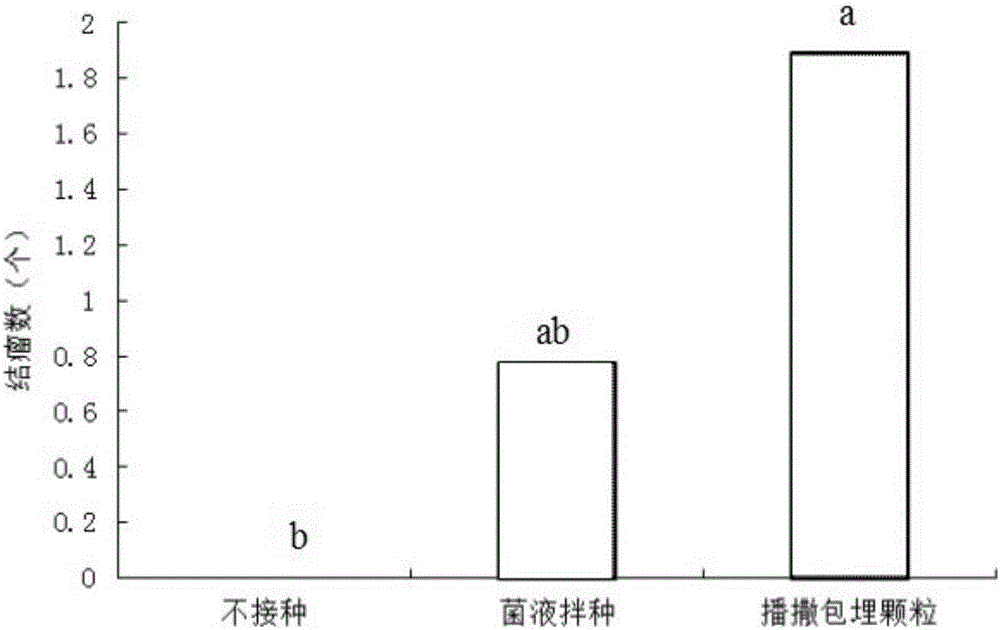
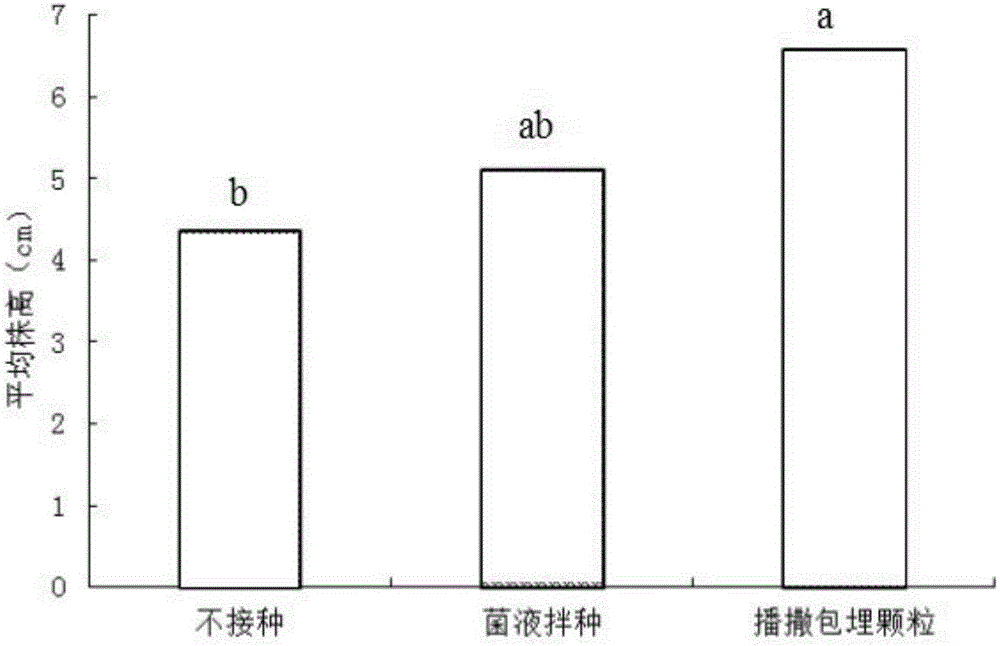
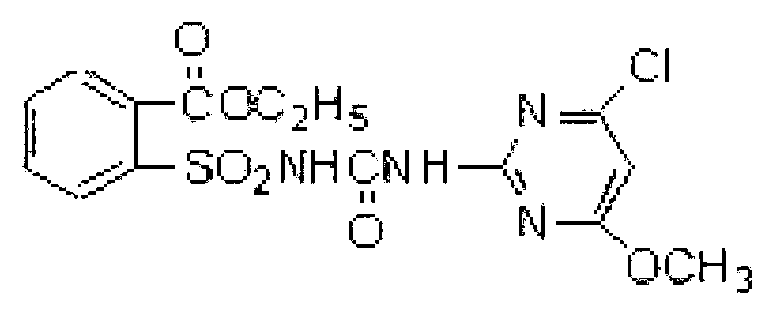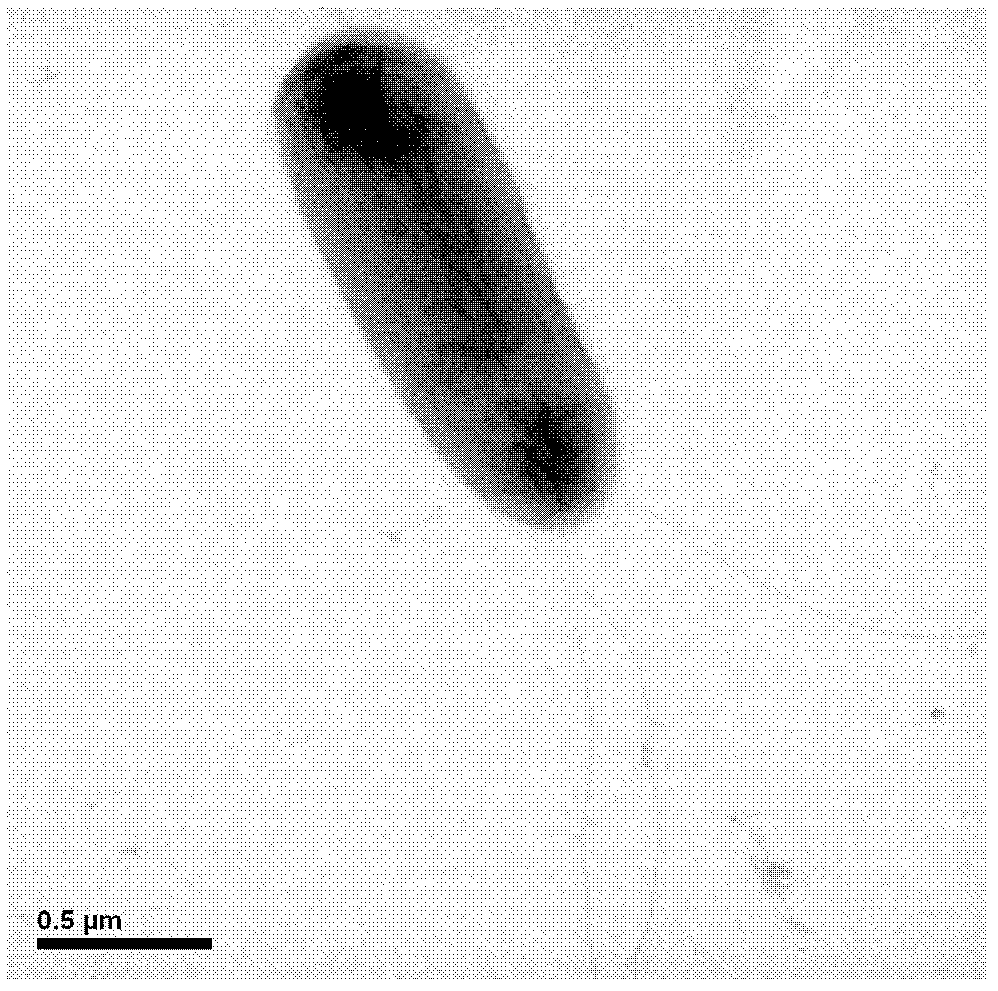Patents
Literature
155 results about "Rhizobium sp." patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
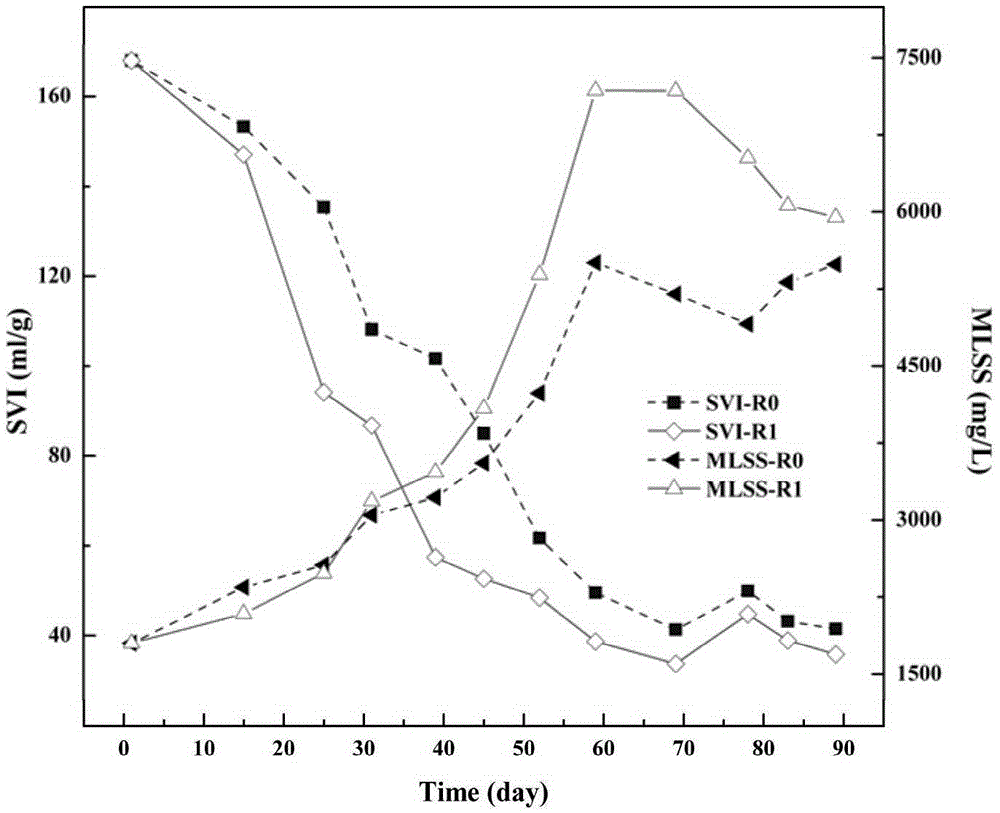
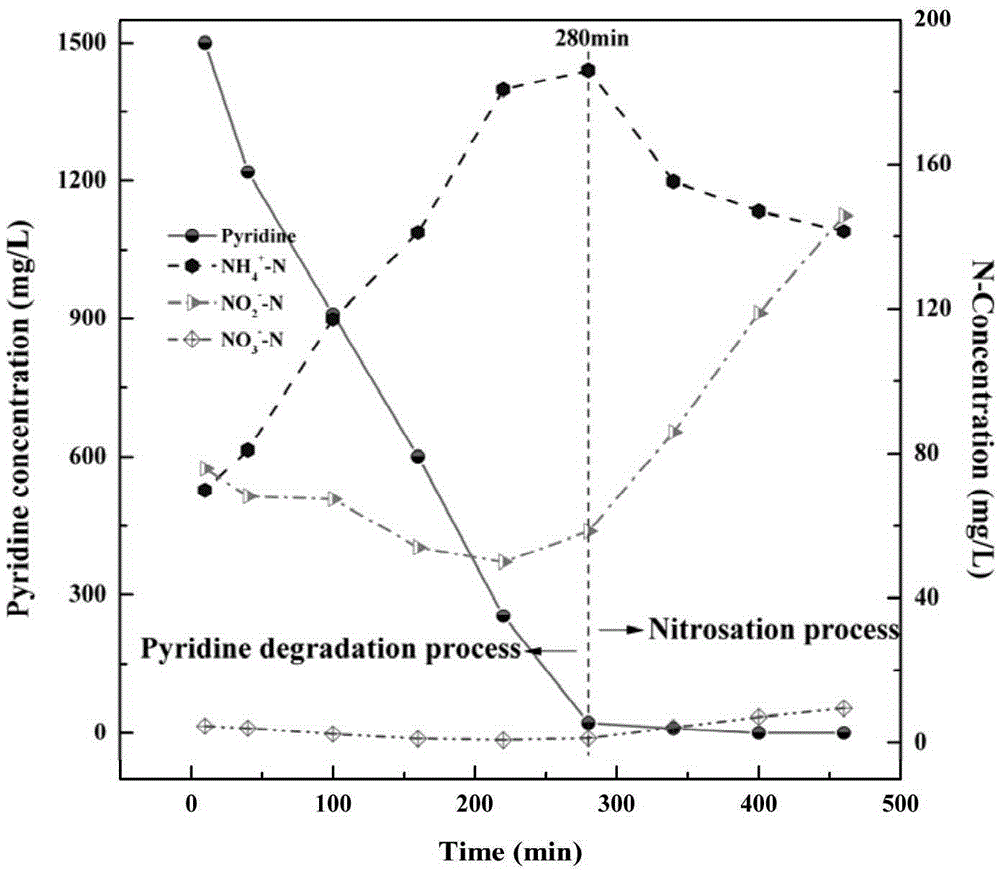
Method for accelerating aerobic sludge granulation by aid of charcoal
InactiveCN105417689AShorten the time of granulationImprove settlement performanceWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsSequencing batch reactorActivated sludge
The invention discloses a method for accelerating aerobic sludge granulation by the aid of charcoal. The method includes that pyridine degradation bacteria Rhizobium sp. NJUST18 and ordinary activated sludge are used as compound inocula for the aerobic granular sludge, the charcoal is used as a crystal nucleus for the aerobic granular sludge in a sequencing batch reactor form, and quick forming of the pyridine degradation aerobic granular sludge can be promoted. The method has the advantages that the aerobic granular sludge with a pyridine degradation function can grow by the aid of pyridine which is a unique carbon source and a unique nitrogen source, granules have regular shapes and are good in sedimentation after the cultivated granular sludge is mature, reaction systems are high in sludge concentration, the high-concentration pyridine can be degraded and is subjected to synchronous nitrosation, and the cultivation time of the aerobic granular sludge for treating wastewater difficult to biodegrade can be effectively shortened.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
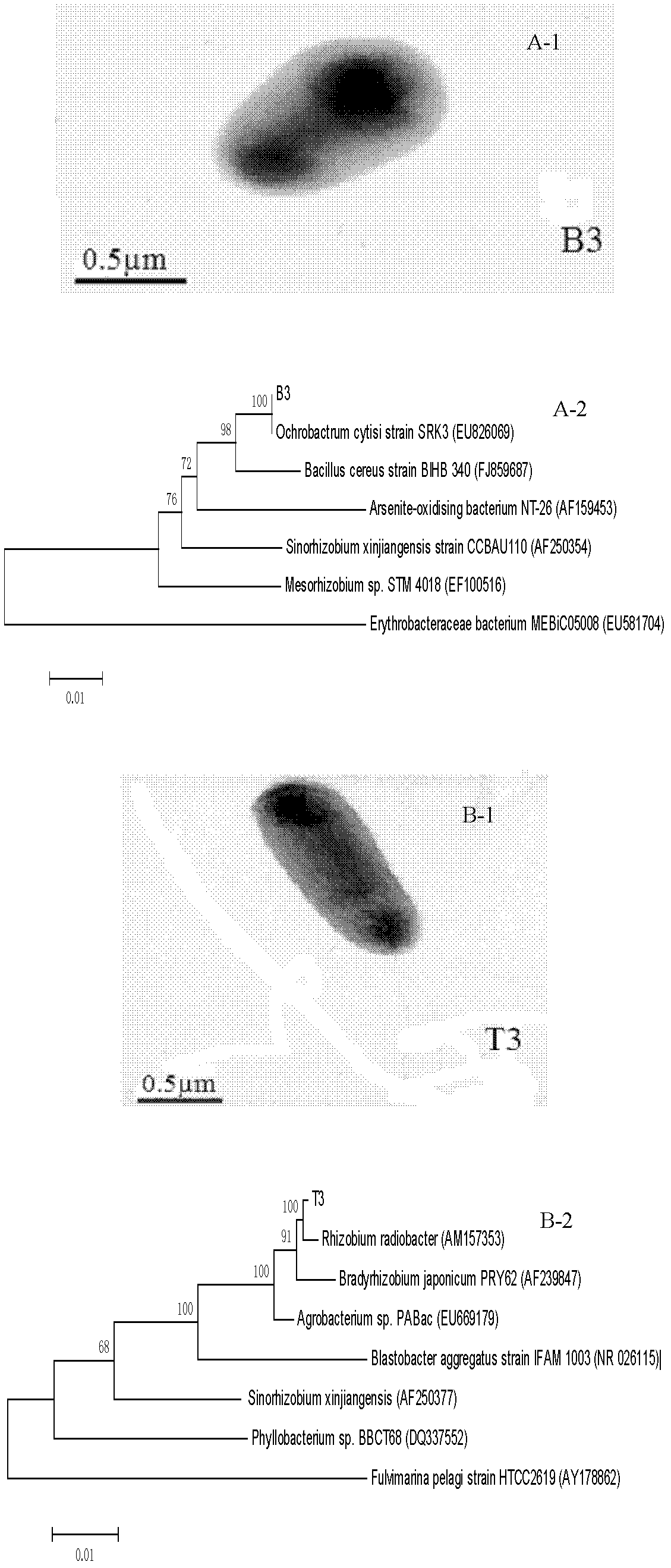
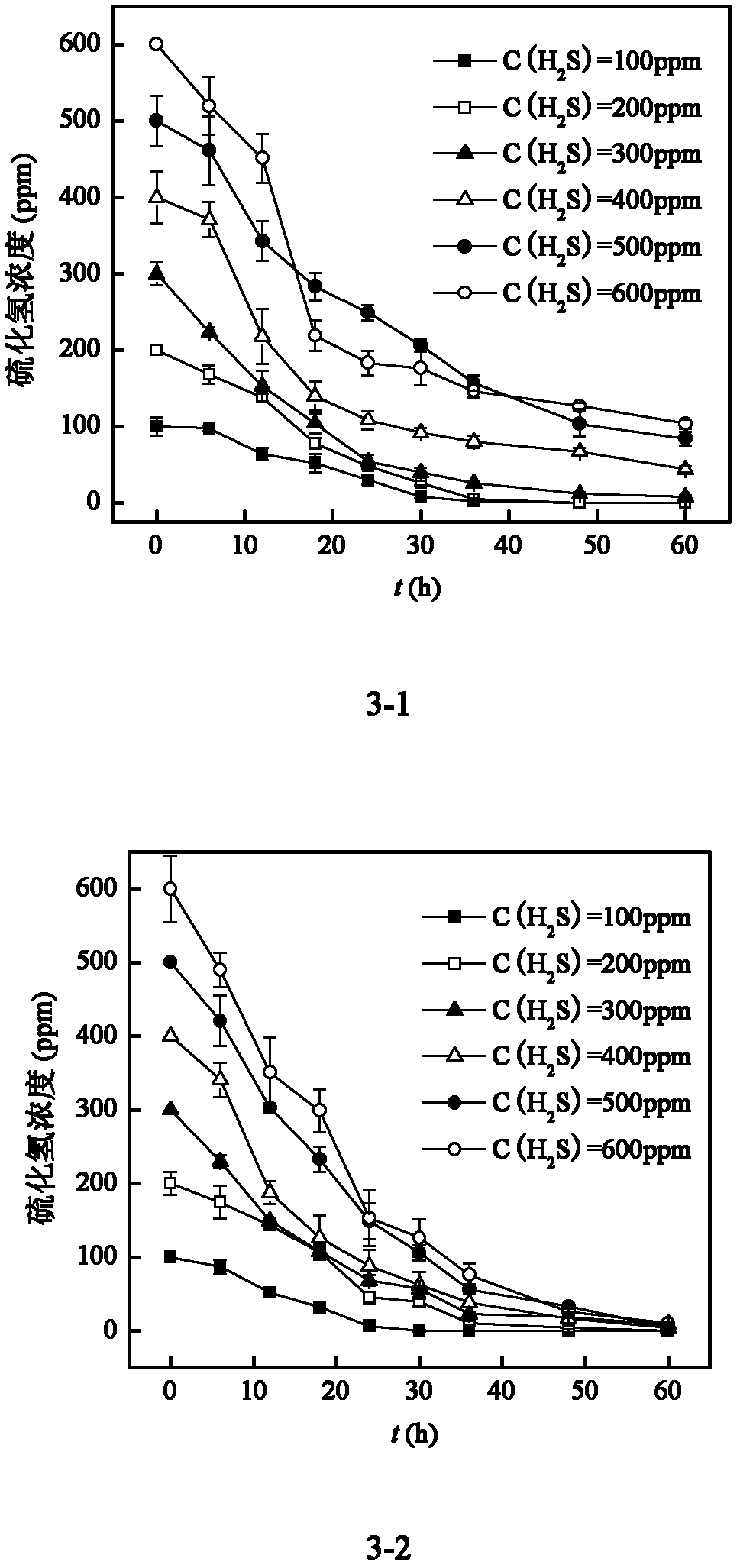
Composite microbial inoculum, immobilization method and application thereof
InactiveCN102321549AAnti-toxicEfficient degradationBacteriaDispersed particle separationOchrobactrum sp.Rhizobium sp.
The invention discloses a composite microbial inoculum, and an immobilization method and application thereof. The composite microbial inoculum is prepared from an Ochrobactrum sp.B3 mycetocyte microbial suspension and a Rhizobium sp.T3 mycetocyte microbial suspension, wherein the concentration of the Ochrobactrum sp.B3 mycetocyte microbial suspension is 0.15-0.2g / L, and the concentration of the Rhizobium sp.T3 is 0.15-0.2g / L. The immobilization method of the composite microbial inoculum has the advantages of simple technique, and cheap and accessible raw materials, and is beneficial to large-scale production. The composite microbial inoculum immobilized cell granules have the advantages of high mechanical strength, high elasticity and stable enzymic activity, have certain toxin immunity in a reaction system, have strong tolerance to temperature and pH value, and can still efficiently degrade H2S waste gas after being used repeatedly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Rhizobium and microbial inoculum, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104911127AIncrease contentImprove the environmentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFungicide
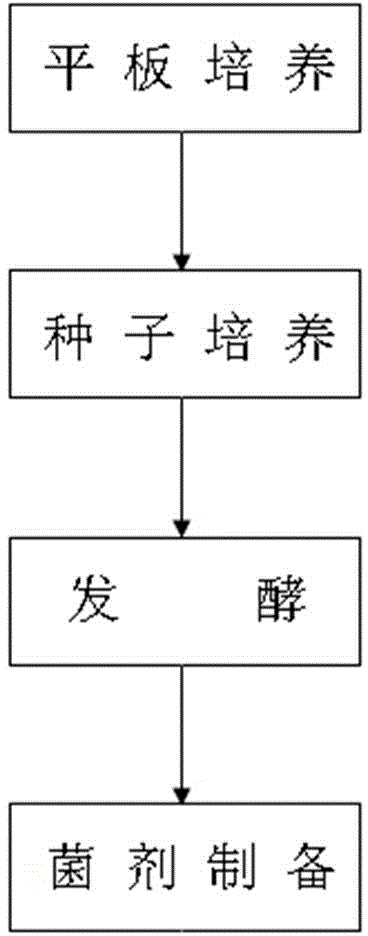
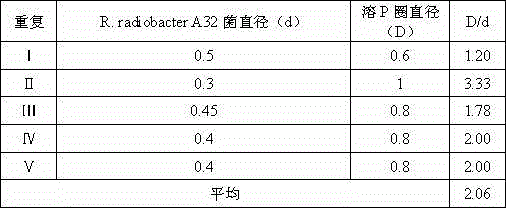
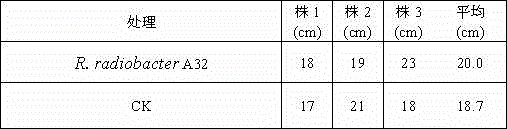
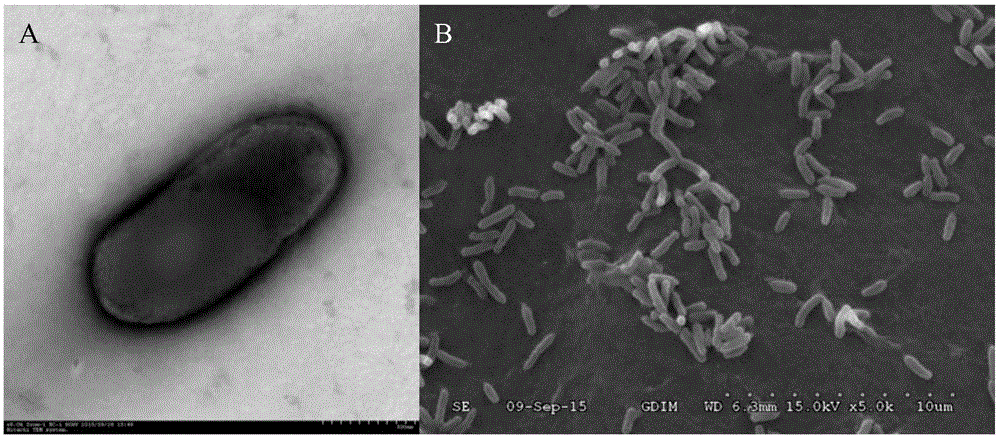
The invention discloses a rhizobium and microbial inoculum, preparation method and application thereof. The rhizobium is a Rhizobium radiobacter A32, the preservation department of the rhizobium is the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), the preservation date of the rhizobium is November 21, 2014, and the preservation serial number is CGMCC, No.10031. The rhizobium belongs to the kingdom of bacteria, the phylum of mycetozoan, the class of alpha-mycetozoan, the order of rhizobia, the family of rhizobia and the genus of rhizobia. The rhizobium is microbial inoculum which has active components and is obtained after plate culture, seed culture and fermentation are conducted on the radioactive rhizobium. Bacillus is microbial inoculum which has active components and is prepared through plate culture, seed culture, fermentation and fungicide preparation. The microbial inoculum is used for phosphate solubilizing and potassium solubilizing of soil and increase of the amount of soil mineral nitrogen.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI +2
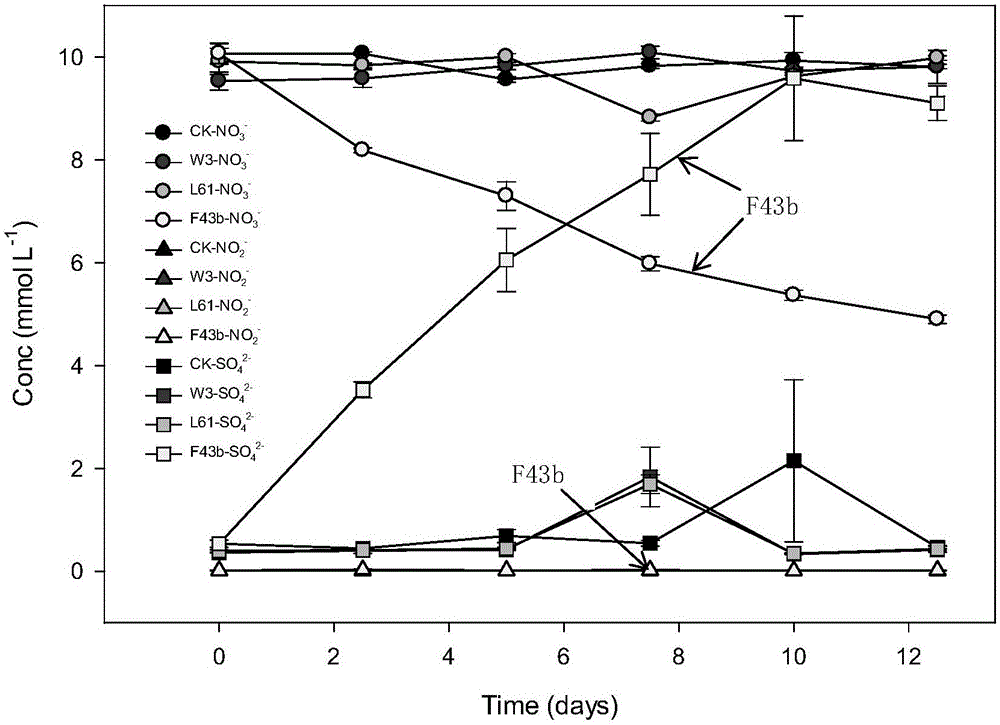
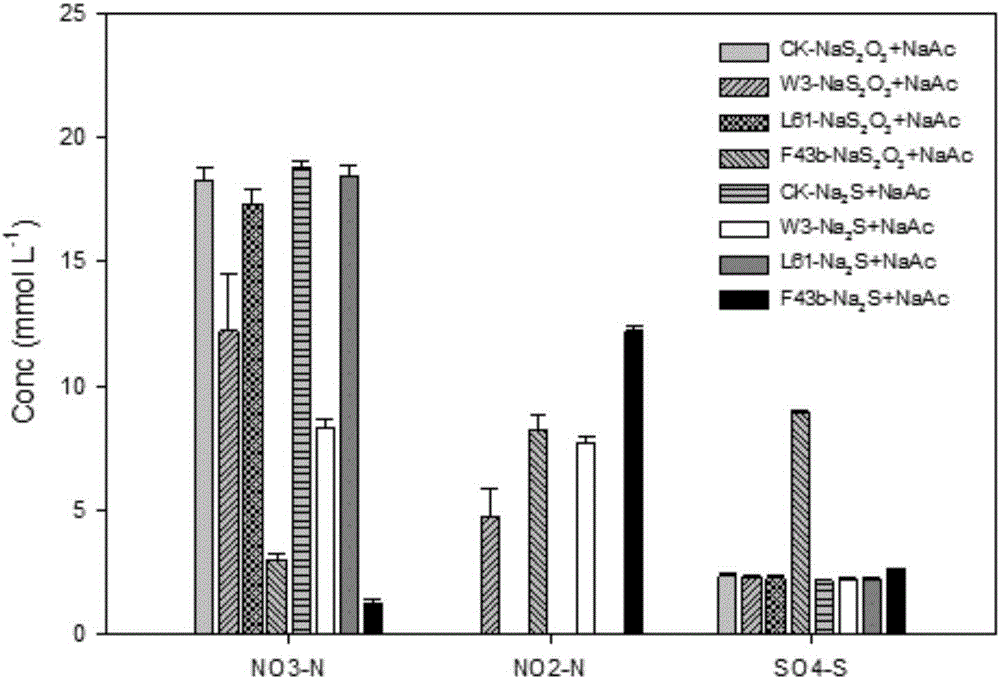
Facultatively autotrophic sulfur oxidation denitrification rhizobium F43b and application thereof
The invention discloses a facultatively autotrophic sulfur oxidation denitrification rhizobium F43b and an application thereof. The Rhizobium sp. F43b<T> is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) Wuhan University in Wuhan in China on March 30, 2016 with the preservation number of CCTCC NO:M 2016158. The Rhizobium sp. F43b<T> is facultatively autotrophic rhizobium with sulfur oxidation and denitrification functions, can remove COD, nitrates and sulfides from polluted water or deposits, realizes simultaneous removal of carbon, nitrogen and sulfur from the polluted water or deposits, and provides bacterial strains and microbial preparations for river restoration and carbon, nitrogen and sulfur wastewater treatment, and researches of the rhizobium provide theoretic guidance for river restoration and removal of carbon, nitrogen and sulfur.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
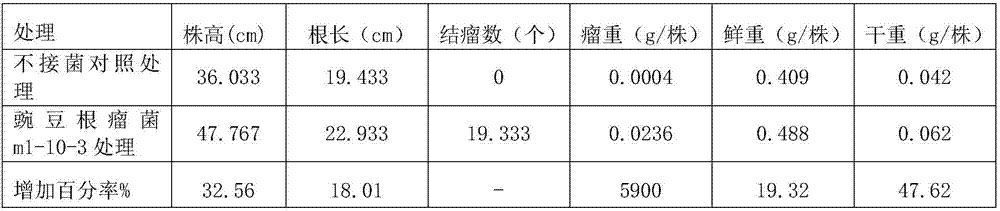
Rhizobium capable of promoting hairy vetch growth and application thereof
ActiveCN107164261AThe effect of increasing production is obviousImprove practicalityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsRhizobium leguminosarumMicroorganism
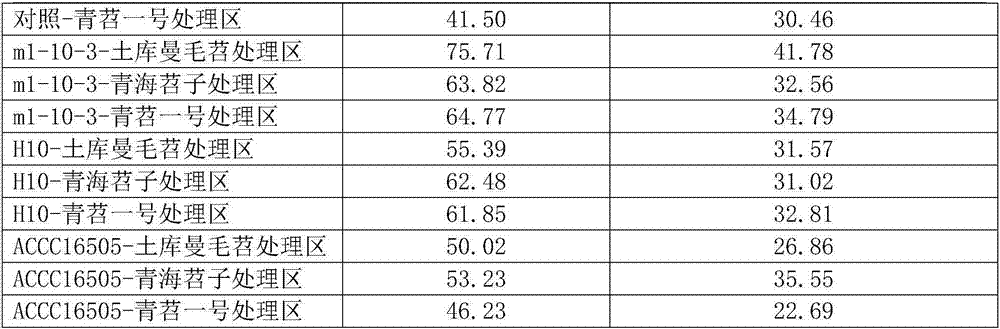
The invention discloses rhizobium leguminosarum capable of promoting hairy vetch growth and an application thereof. The strain number of the rhizobium leguminosarum is m1-10-3, and the preservation number of the rhizobium leguminosarum in the General Microbiology Center of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms is CGMCC No.11877. An experiment proves that the plant height and the fresh weight ratio of the hairy vetch inoculated with the rhizobium leguminosarum m1-10-3 are obviously improved in comparison with those of the hairy vetch which is not inoculated with the rhizobium, the hairy vetch which is inoculated with rhizobium leguminosarum H10 and the hairy vetch which is inoculated with rhizobium leguminosarum ACCC16505. The rhizobium leguminosarum has a wide application prospect field in the hairy vetch planting industry.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Bacterium capable of degrading pesticides chlorimuron-ethyl and carbendazim and application thereof
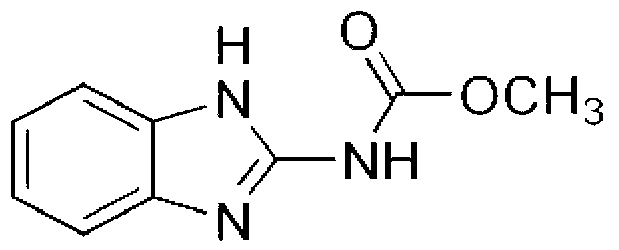
The invention discloses a bacterium capable of degrading pesticides chlorimuron-ethyl and carbendazim and an application of the bacterium. The bacterium capable of degrading pesticides chlorimuron-ethyl and carbendazim is rhizobium sp. LD1616 and the preservation number of the bacterium is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.7775. The rhizobium sp. LD1616 with the preservation of CGMCC NO.7775, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages that the degradation rate of the bacterium to chlorimuron-ethyl (45mg / L) is up to 71.56% in 7 days in an inorganic salt culture medium and the degradation rate of the bacterium to carbendazim (100mg / L) is up to 24.92% in 5 days, which indicates that the bacterium is capable of efficiently degrading the chlorimuron-ethyl and the carbendazim and has a broad application prospect in the remediation of soil polluted by residual pesticides chlorimuron-ethyl and carbendazim.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Rhizobium and application thereof
ActiveCN105274030ANodulation rate is highImprove survival rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlant noduleDry weight
The invention relates to a (Bradyrhizobium sp.) LX-JX01 and application thereof. A preparation method of an inoculant for the (Bradyrhizobium sp.) LX-JX01 includes the steps of preparing a liquid DM culture medium, preparing a solid DM culture medium, activating a strain and culturing the rhizobium. The strain can be in nodulation and symbiosis with Dalbergia odorifera. When the inoculant for the Dalbergia odorifera rhizobium LX-JX01 is used for planting Dalbergia odorifera seedlings, nodulation number root nodules is increased by 3823% than a control group, fresh weight of the root nodules is increased by 1038%, dry weight of portions, above the ground, of plants is increased by 47.22%, and seedling height and plant stem diameter are increased by 1030% and 42.3% respectively, so that the inoculant can promote growing of Dalbergia odorifera. Consequently, the inoculant has wide application prospect in planting of artificial forest of Dalbergia odorifera.
Owner:领先生物农业股份有限公司
Fulvic acid and rhizobium biological type leguminous plant seed coating agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102070368AIncrease productionHigh activityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPlanting seedRhizobium
The invention relates to a fulvic acid and rhizobium biological type leguminous plant seed coating agent and a preparation method thereof. The fulvic acid and rhizobium biological type leguminous plant seed coating agent is characterized by comprising fulvic acid, a rhizobium culture solution, a film forming agent, trophic factors and the balance of water as raw materials. The preparation method comprises following steps of: adding 5-8% of film forming agent into the balance of water, and heating to 75-85 DEG C to slowly dissolve the film forming agent; then, adding 3-5% of dispersing agent, and adding 0.5-1.0% of trophic factors after the dispersing agent is dissolved; adding 0.03-1.0% of fulvic acid, and cooling to 28 DEG C or so; and finally, adding 3-5% of rhizobium culture solution, and uniformly mixing to obtain the product of fulvic acid and rhizobium biological type leguminous plant seed coating agent. The product has the advantages and effects of promoting the growth of rhizobia, enhancing stress resistance, obviously increasing the survival rate of rhizobia and the competitiveness of pannonibacter phragmitetus, reducing the use amount of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, protecting the environment, improving product quality and ensuring food safety.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Rhizobium astragula capable of effectively fixing nitrogen and culture method and application thereof
ActiveCN102174429AHigh nitrogen contentWide variety of sourcesBiocidePlant growth regulatorsAstragalus sinicusNitrogen
The invention relates to rhizobium astragula capable of effectively fixing nitrogen and a culture method and application thereof. The rhizobium astragula CGMCC No.4347 is cultured by the steps of strain activation, seed culture, fermentation culture and the like. The invention has the following beneficial effects: when the fermentation culture medium improved by the invention is adopted for culturing, the viable count of the fermentation liquor is far higher than that in the prior art; compared with the bacteria which are not inoculated on astragalus sinicus, the rhizobium astragula agent can ensure the fresh weight of the astragalus sinicus plants to be increased by more than 241%, the nitrogen content of the plants to be increased by more than 86% and the yield to be increased by more than 47% after being inoculated on the astragalus sinicus; compared with the existing produced strains, the rhizobium astragula agent ensures the fresh weight of the astragalus sinicus plants to be increased by more than 58%, the nitrogen content of the plants to be increased by more than 18% and the yield to be increased by more than 12%, thus being an excellent strain for production of the rhizobium astragula and inoculation of the astragalus sinicus; and the culture method is simple and practical, and the raw materials have wide sources and low price and are suitable for large-scale industrialized production.
Owner:领先生物农业股份有限公司
Rhizobium strain, microbial agent containing rhizobium strain and application thereof
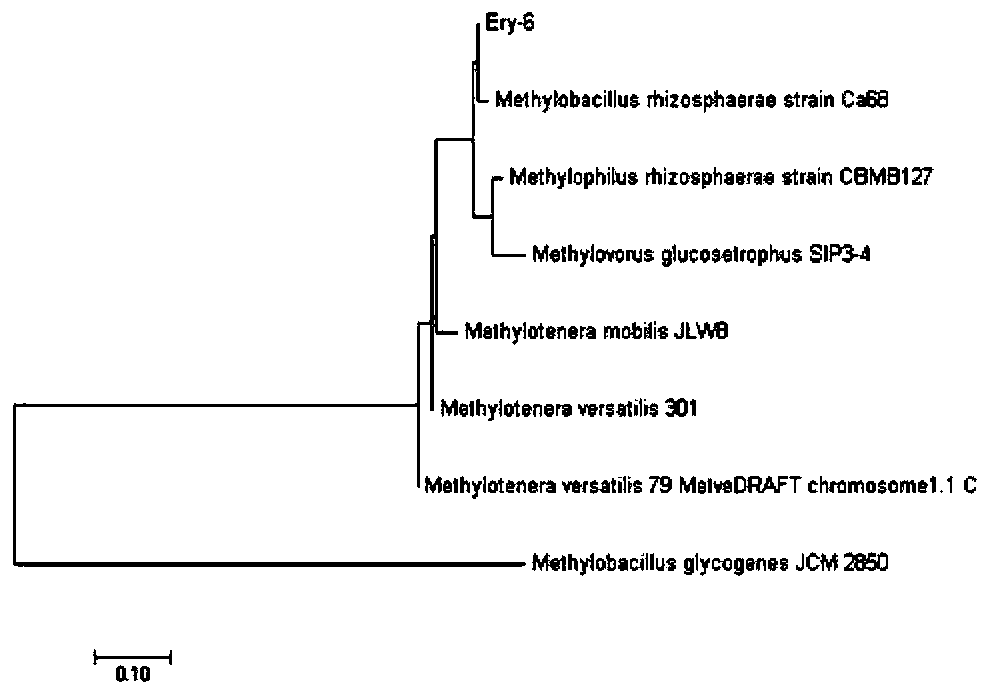
The invention relates to a rhizobium strain, namely Rhizobium sp. Ery-6). The Rhizobium sp. Ery-6 is preserved at China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) under the preservation number of CCTCC M 2019729. The invention further provides a microbial agent containing the Rhizobium sp. Ery-6 and a preparation method of the microbial agent; and moreover, the invention still further provides application of the microbial agent in erythromycin degradation. The Rhizobium sp. Ery-6 provided by the invention has very strong degradation ability on erythromycin, so that the Rhizobium sp. Ery-6 cangrow by taking the erythromycin as the sole carbon source. In 48 hours, the Rhizobium sp. Ery-6 is capable of reaching an erythromycin degradation rate up to 79.78% on erythromycin of which the concentration is 100 mg / L in an inorganic salt medium as well as an erythromycin degradation rate up to 37.3% on erythromycin of which the concentration is 1000 mg / L in an organic salt medium; and thus, theRhizobium sp. Ery-6 has a good development and application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Rhizobium strain and application thereof
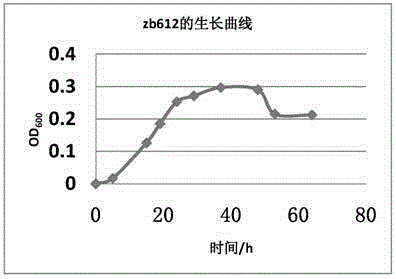
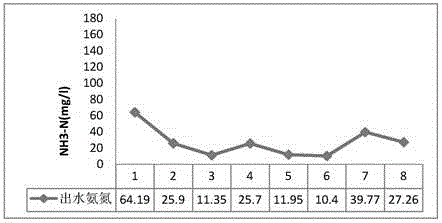
ActiveCN104830724ASolve the problem of segment processingHas the characteristic of removing ammonia nitrogenTreatment using aerobic processesBacteriaRhizobium sp.Oil sludge
The invention discloses a rhizobium strain and its application. The rhizobium strain is named as Rhizobium sp., the strain number is zb612, and preservation number is CGMCC No. 10721. The rhizobium strain was preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) at the No.3, 1 West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District of Beijing on April 15th, 2015. The strain provided by the invention can be used in onsite real nitrogen removal from sewage so as to raise the effect of removing ammonia nitrogen from oil sludge. The rhizobium provided by the invention has the characteristic of removing ammonia nitrogen. According to the rhizobium strain, organic carbon can be used as the sole carbon source and ammonia nitrogen is used as the sole nitrogen source so as to carry out metabolism, and ammonia nitrogen is directly converted to N2 through heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification so as to finish nitrogen removal. Thus, problems of aerobiotic nitrification and anoxic denitrification sectional treatment in traditional biological removal of nitrogen are solved.
Owner:水艺环保集团股份有限公司
Nutrient film protecting agent of rhizobium japonicum and production method thereof
InactiveCN101818119AServe as nutritionPlay a role in film formationMicroorganism based processesMicroorganism preservationCarboxymethyl celluloseSodium molybdate
The invention relates to a nutrient film protecting agent of rhizobium japonicum and a production method thereof. The nutrient film protecting agent of rhizobium japonicum is prepared by selecting the raw materials of PVP (Polyvinylpyrrolidone) K30, PVP S630, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, peptone, bovine serum albumin and sodium molybdate and reacting under a certain reaction condition; the nutrient film protecting agent of rhizobium japonicum, a liquid rhizobium japonicum agent and soybean seeds are mixed and stirred according to a certain proportion; and after the soybean seeds are coated and stored for two days, each soybean seed can ensure 100,000 live rhizobium japonicums. The invention has wide needed raw material sources, simple production process and low cost, can play roles of nutrition, film formation and protection in the rhizobium japonicum, and can ensure that the liquid rhizobium japonicum agent is preserved for one year at normal temperature; the live bacterium quantity is not smaller than 2,000,000,000 / ml, and the nitrogen fixing activity is not reduced.
Owner:哈尔滨奥龙奇康科技发展有限公司
Special humic acid-urea coated rhizobium fertilizer for soybean and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104130077AExtend the fertilizer periodIncrease profitSuperphosphatesOrganic fertilisersEcological environmentCoated urea
Owner:安徽莱姆佳生物科技股份有限公司
Rhizobium strain and application thereof
The invention discloses a rhizobium strain and an application thereof. The rhizobium strain is rhizobium indigoferae NM60 of which the CGMCC ((China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No is 4647. Rhizobium indigoferae NM60 can promote the growth of different kinds of hairy vetches, the strain has better symbiotic nodulation capability with each kind of hairy vetch, the strain is determined as the broad-spectrum nodulation strain of vetch and can be used to prepare green manure; and the strain has higher practicability and popularization and has a wide application prospect in the planting of vetch.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Microbial agent and soil modifying agent produced by fermentation thereof
ActiveCN101629156BImprove adaptabilityImprove fertilityFungiAgriculture tools and machinesBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
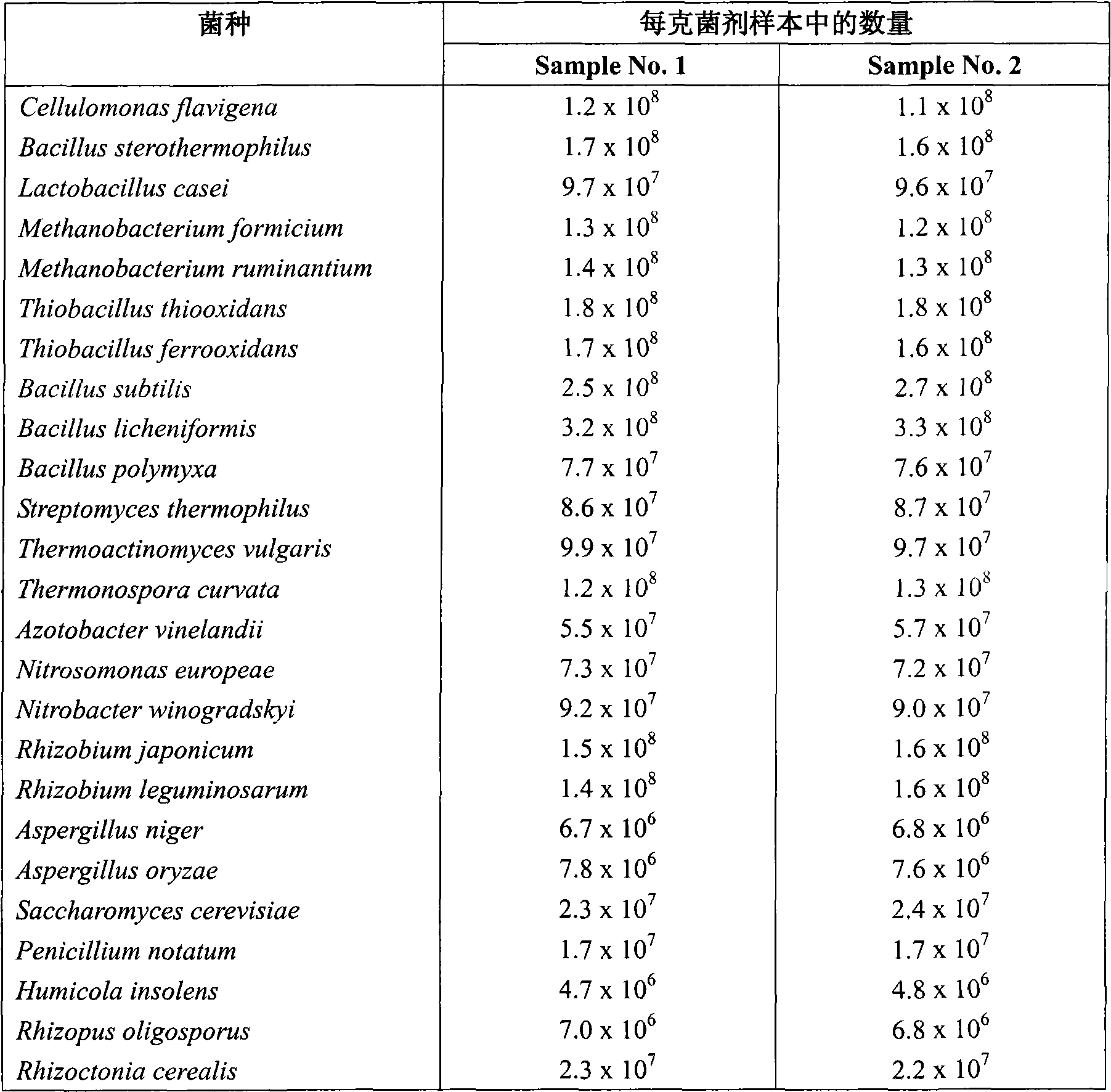
The invention relates to a microbial agent used for producing a soil modifying agent by fermentation, consisting of fiber monad, bacillus, lactobacillus, methanobacteria, thiobacillus, streptomycete, high-temperature actinomyces, high-temperature monad, azotobacteria, nitration monad, nitration bacilus, rhizobium, koji mold, leaven, blue mold, detritus mold, rhizopus as well as mycorrhizal fungi and substrate. In addition, the invention also relates to a soil modifying agent produced by the fermentation of the microbial agent, application thereof and the like.
Owner:宋彦耕
Rhizobium sp. and application thereof
The invention discloses Rhizobium sp. and application thereof. The Rhizobium sp. is preserved in CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) on March 11, 2016, and the preservation number of the Rhizobium sp. is CGMCC No. 12205. The Rhizobium sp. has the advantages that the Rhizobium sp. can efficiently inhibit the formation of a pathogen biofilm and inhibit pathogen virulence factors, the fermentation products or metabolites of the Rhizobium sp. can be effectively used as the active components of pathogen biofilm inhibitors, the Rhizobium sp. and the fermentation products or metabolites thereof can be used to effectively inhibit the formation of the pathogen biofilm and control the toxicity of pathogens, and accordingly the Rhizobium sp. can be effectively used for treating bacterial infection so as to enhance the susceptibility of the pathogens to common medicine and enhance a treatment effect.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and application thereof
ActiveCN107937310APromote degradationStable colonizationPlant growth regulatorsBiocideRhizobacteriaBacterial strain
The invention relates to the field of agricultural microorganisms, and in particular relates to a rhizobium pusense capable of degrading apple autotoxin phlorizin and application thereof. A rhizobiumpusense YIC4105 is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on November 2rd, 2017 with the preservation number of CGMCC No.14852. The bacterial strain is separatedfrom sesbania rhizosphere soil naturally distributed at the Yellow River delta and is obtained through artificial separation and purification; the bacterial strain has relatively strong capability ofdegrading phlorizin and can be stabilized and colonized at rhizosphere of apples; and successive cropping obstacle of an apple seedling caused by accumulation of phlorizin can be effectively preventedby utilizing the bacterial strain, so that the rhizobium provided by the invention has good prospect of being developed into a microbiological inoculants or bacterial fertilizer capable of promotingcrop growth.
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for making alfalfa rhizobium inoculant and rhizobium inoculant made through same and application thereof
InactiveCN105462873AImprove liquidityUniform and firm adsorptionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnvironmentally friendlyMaterials science
The invention provides a method for making alfalfa rhizobium inoculant and rhizobium inoculant made through the method and application thereof. The method includes the following steps that S1, bacterium liquid of alfalfa rhizobia is acquired; S2, powder containing kaolin powder and bentonite powder is acquired, and the particle size of the kaolin powder and the bentonite powder ranges from 20 microns to 100 microns; S3, the bacterium liquid and the powder are mixed, dried and smashed so that powder where the alfalfa rhizobium inoculant is adsorbed to can be acquired. The alfalfa rhizobium inoculant has the advantages that the number of effective living bacteria is high, the storage life is long, and the alfalfa rhizobium inoculant is environmentally friendly and suitable for commercial and industrial production.
Owner:克劳沃(北京)生态科技有限公司
Rhizobium sp. T3 and applications thereof in microbial degradation hydrogen sulfide
ActiveCN102321548AStrong toleranceEfficient hydrogen sulfide degradation abilityBacteriaDispersed particle separationMicroorganismLiquid cell
The invention discloses rhizobium sp. T3 which is preserved in China typical culture collection center, the preservation date is April, 2nd 2011, the preservation number is CCTCC No.M2011105, and the preservation address is Wuhan University in Wuhan, China. The application comprises the following step: by taking hydrogen sulfide as the only sulfur source and energy source, culturing the bacterial liquid obtained from the amplification culture of rhizobium sp.T3 selectively for 2-3 days at the temperature of 25-40 DEG C under an enclosed condition with the pH of 4.0-9.0, thus hydrogen sulfide is resolved, wherein the concentration of bacterial liquid cells is 200-300mg / L, and the initial concentration of hydrogen sulfide is 150-600ppm. The bacterial strain provided by the invention has efficient and high-tolerance hydrogen sulfide degradation capability, also can adapt to complex actual conditions, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
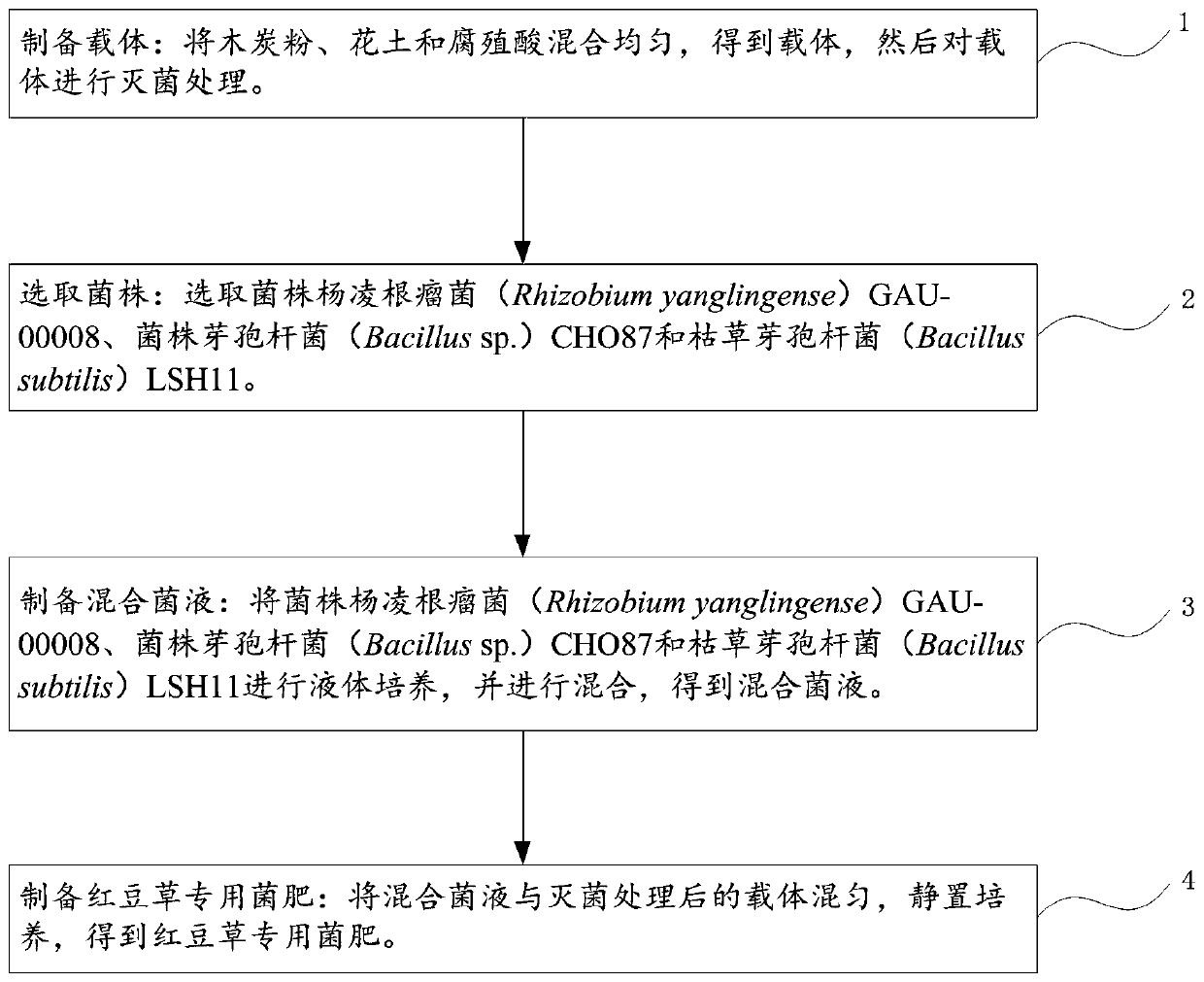
Special bacterial fertilizer for sainfoin and preparation method of special bacterial fertilizer
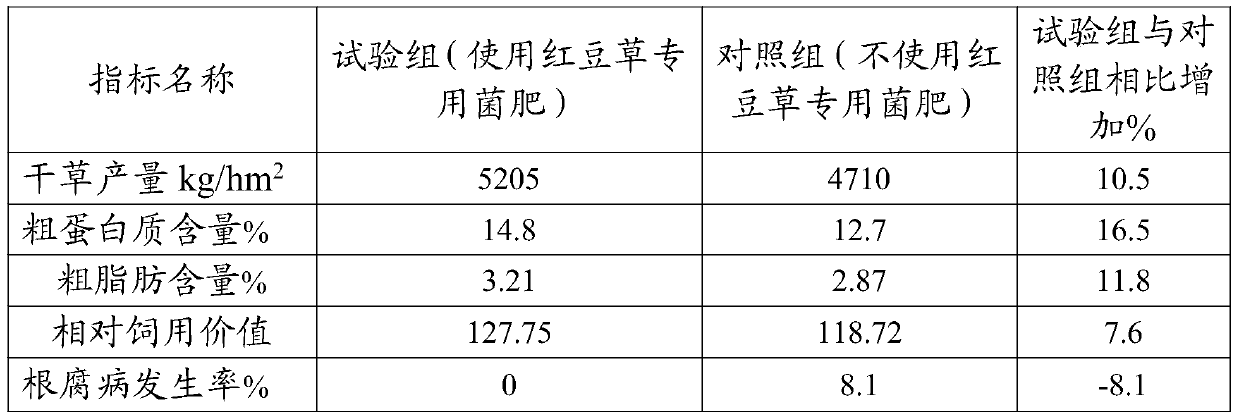
The invention discloses a special bacterial fertilizer for sainfoin, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The special bacterial fertilizer for sainfoin comprises a strain of Rhizobiumyanglingense GAU-00008, a strain of Bacillus sp. CHO87, a stain of Bacillus subtilis LSH11 and a vector. According to the invention, through a synergistic effect of the three strains, sufficient effective root nodules can be formed at root parts of sainfoin; and meanwhile, soil is activated, so that absorption of crops to other nutrient elements is promoted, a nutrition structure of plants is improved, growth of the plants is regulated and promoted, and disease resistance of the plants is enhanced.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Rhizobium and application thereof
ActiveCN109097305AEcological securityExpand sourceAgriculture tools and machinesBacteriaRoot noduleDecomposition
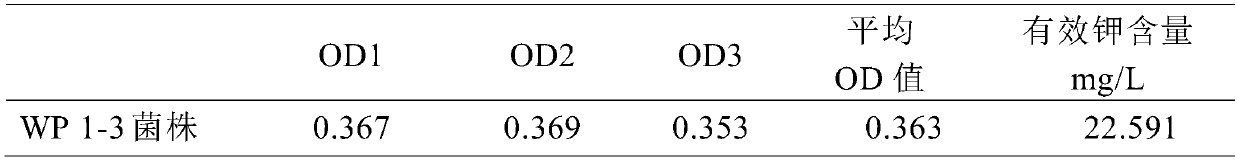
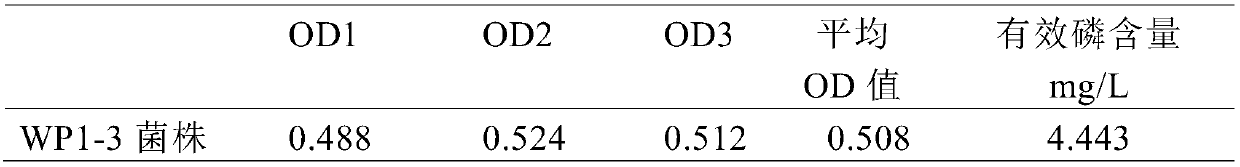
The invention discloses a rhizobium sp. WP 1-3, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.14472. In addition, the invention further discloses the application of the rhizobium to decomposition of potassium in soil and decomposition of insoluble phosphorus in the soil. The rhizobium is a dominant strain screened by taking potash feldsparf as a potassium source, the strain is capable of transforming the insoluble potassium in the aluminosilicate in the soil into a soluble component in the processes of growth and propagation, and promoting the decomposition of the insoluble potassium to increase thesource of the phosphorus in the soil. In addition, the strain further has an effect of fixing nitrogen, and provides the necessary nitrogen for the growth and metabolism of a plant.
Owner:XIAN UNVERSITY OF ARTS & SCI
L-proline cis-4-hydroxylase and use thereof to produce cis-4-hydroxy-L-proline
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO BIO CO LTD
Preparation method of alfalfa rhizobia immobilized embedded granule formation and application thereof
InactiveCN106754500AEasy to addNo loss of activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh activityDrug biological activity
The invention discloses preparation and application of a novel alfalfa rhizobia immobilized embedded granule formation, and belongs to the field of agricultural microbe application. An immobilized cell technology is a method for immobilizing microbial cells in some special materials, preparing granules to form a limited space, enabling the thallus to keep biological activity in a certain time and realizing proliferation. At present, the alfalfa rhizobia is widely applied to the fields such as medicines, foods, fermentation industry, wastewater treatment and the like, preliminary study in a rhizobium japonicum embedding aspect is realized, while the preparation and application of the alfalfa rhizobia embedded immobilized granules is still a blank at present. According to the novel alfalfa rhizobia immobilized embedded granules developed in the invention, the alfalfa rhizobia is conveniently added by alfalfa cultivation enterprises, and the activity of fungicides is not lost in the compounding, processing, granulating and transportation and storage processes. Therefore, alfalfa rhizobia bacterial manure can be easily used by farmer households, and the main technical bottleneck difficulty of a high-tolerance high-activity alfalfa rhizobia seed embedding technique is broken.
Owner:DAQING BRANCH OF HEILONGJIANG ACAD OF SCI
New applications of Rhizobium W33 strain
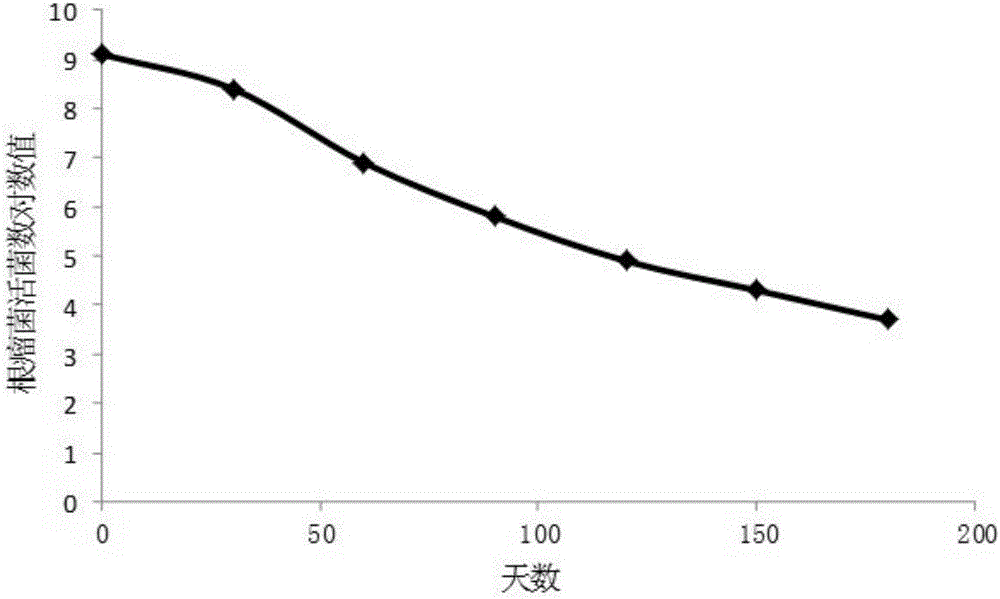
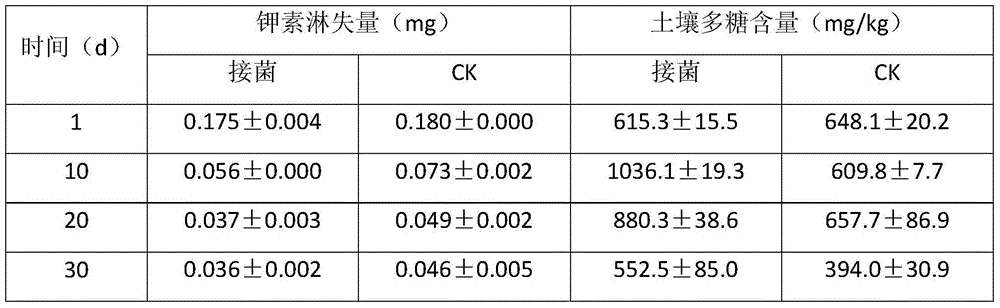
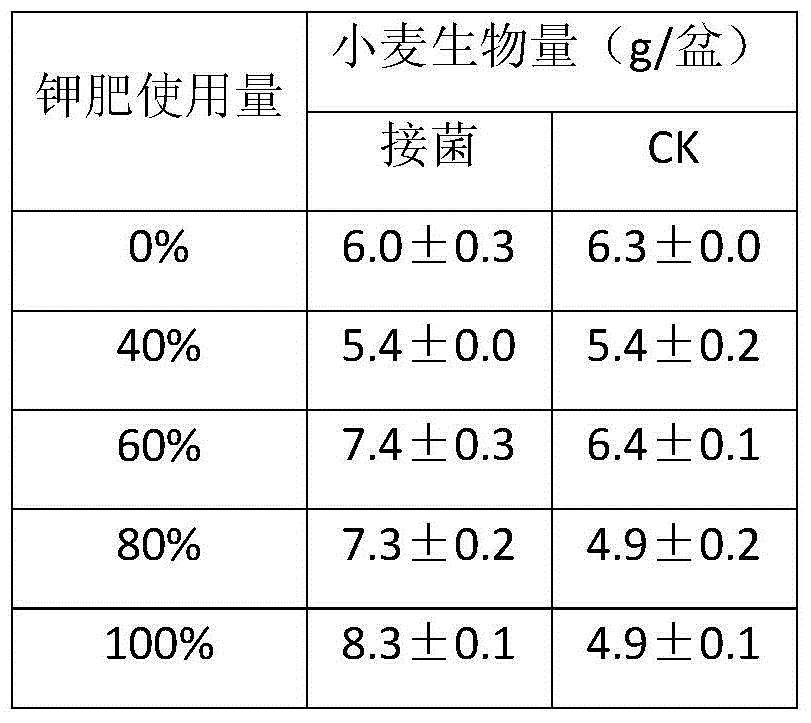
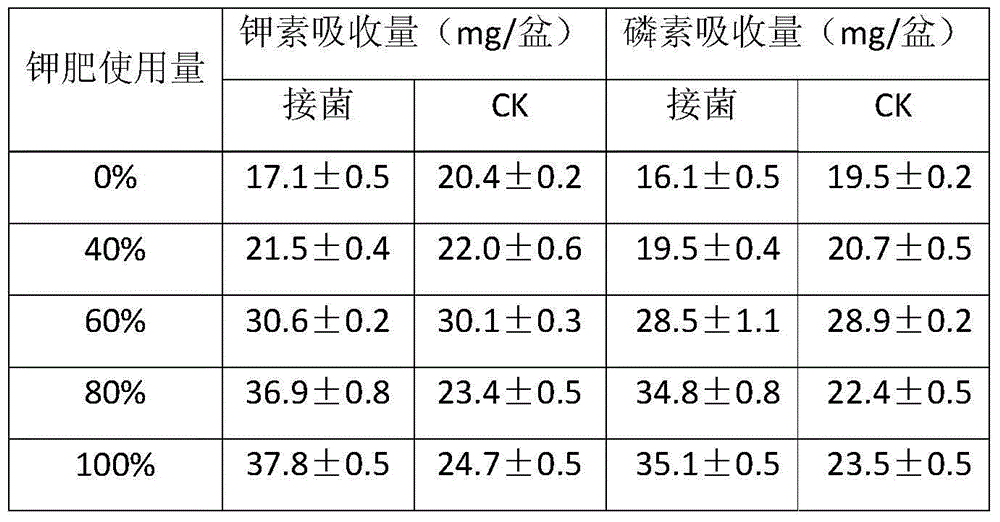
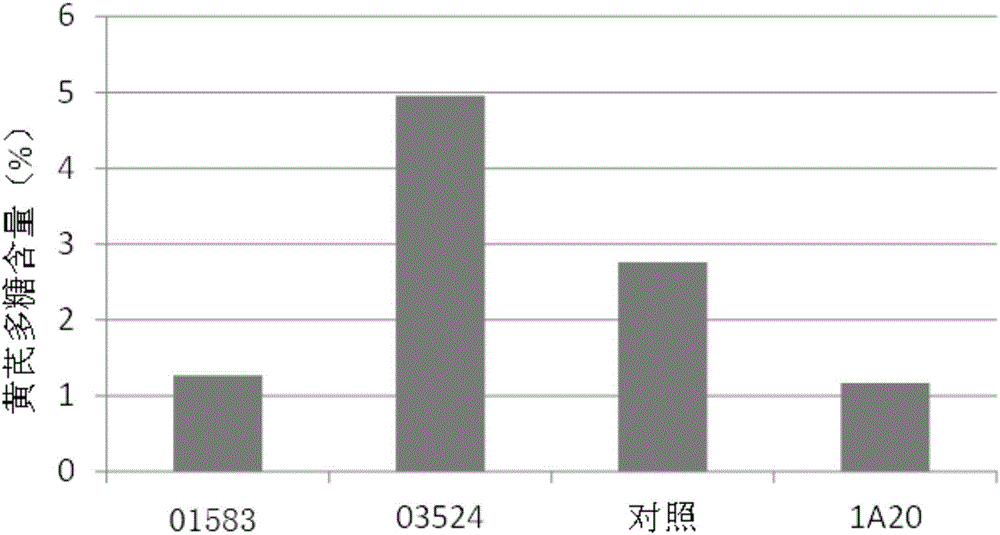
ActiveCN105418204APotassium leaching decreasedHigh in polysaccharidesBacteriaClimate change adaptationBacteroidesPotassium
The present invention belongs to the fields of agriculture and agricultural technology and Rhizobium applications, and discloses new applications of a Rhizobium sp. W33 strain. According to the present invention, the Rhizobium sp. W33 is adopted as a raw material, and bacterial activation is performed to prepare a bacterial suspension, wherein the bacterial suspension is inoculated in a potassium-containing liquid culture medium so as to absorb the potassium in the solution, and the bacterial suspension is inoculated in soil so as to reduce potassium fertilizer leaching loss, significantly promote plant growth and absorption on potassium and phosphorus, and improve potassium fertilizer absorption and utilization rate.
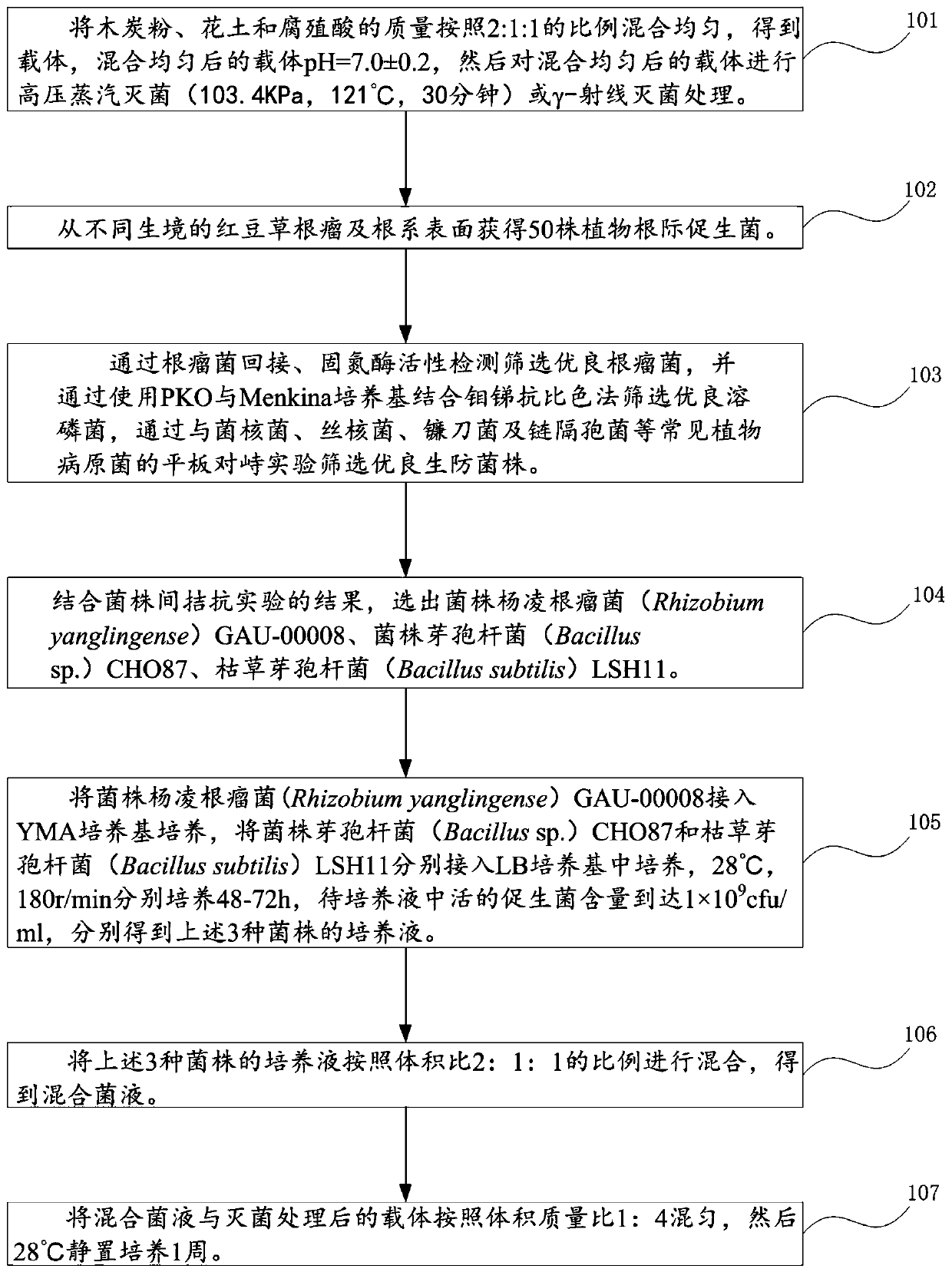
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Selenized microbial exopolysaccharide, and preparation method and uses thereof
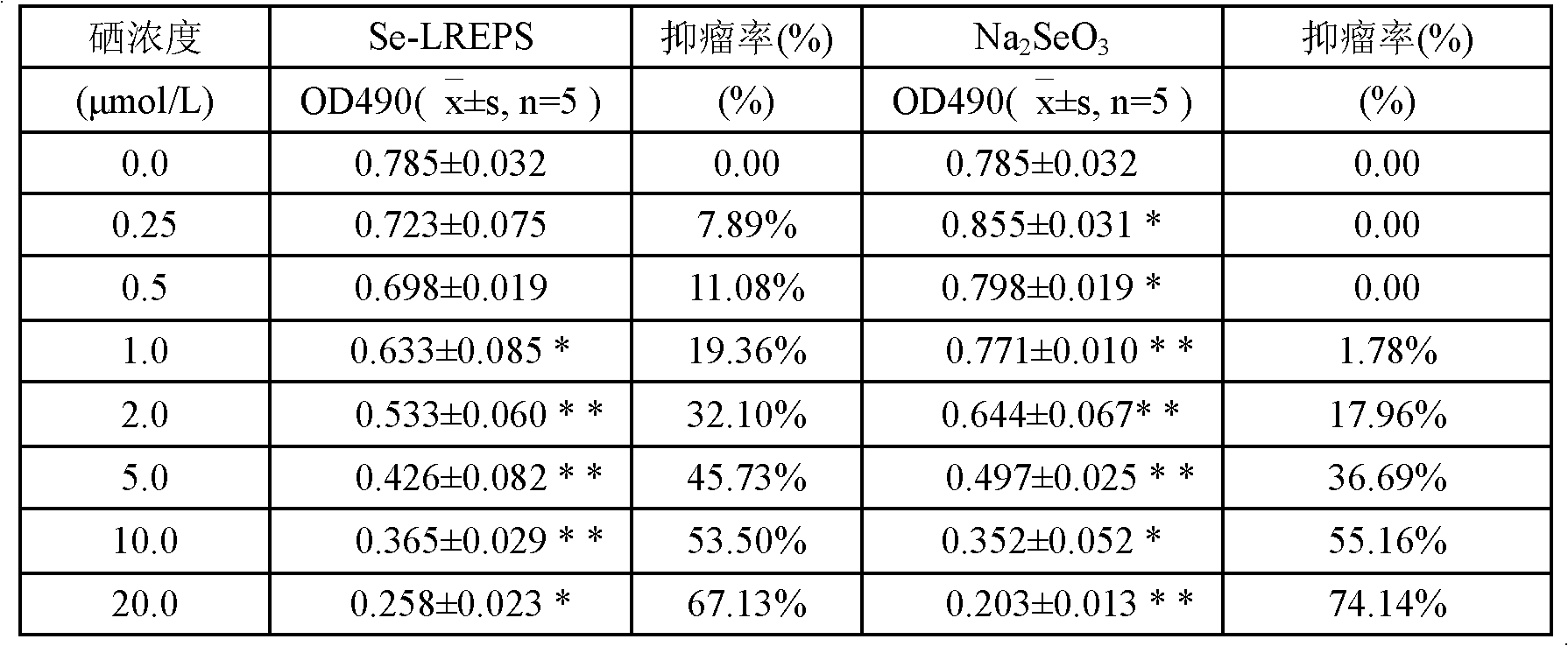
InactiveCN102633899ANo generationShort reaction time for selenizationOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsFreeze-dryingRhizobium sp.
The invention provides a selenized microbial exopolysaccharide and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of: adding micromolecular Rhizobium sp. exopolysaccharide to nitric acid solution, stirring, adding selenous acid and barium chloride, adding sulfuric acid dropwise, removing precipitates by centrifugation, regulating the pH of supernatant to 7 by sodium hydroxide, putting the supernatant in a dialysis bag for dialysis, concentrating the dialysate under reduced pressure and then adding edible alcohol, separating out selenized microbial exopolysaccharide, and collecting and freeze-drying the selenized microbial exopolysaccharide to obtain selenized micromolecular microbial exopolysaccharide. The content of selenium in the exopolysaccharide can reach 586 to 790 mu g / g according to measurement; mice tests show that the exopolysaccharide has excellent antitumor activity; and the exopolysaccharide can be used in preparing antitumor medicines and healthcare products.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Rhizobium and application thereof
InactiveCN106591183APromote growthImprove qualityPlant growth regulatorsBiocideAstragalus polysaccharideMicroorganism
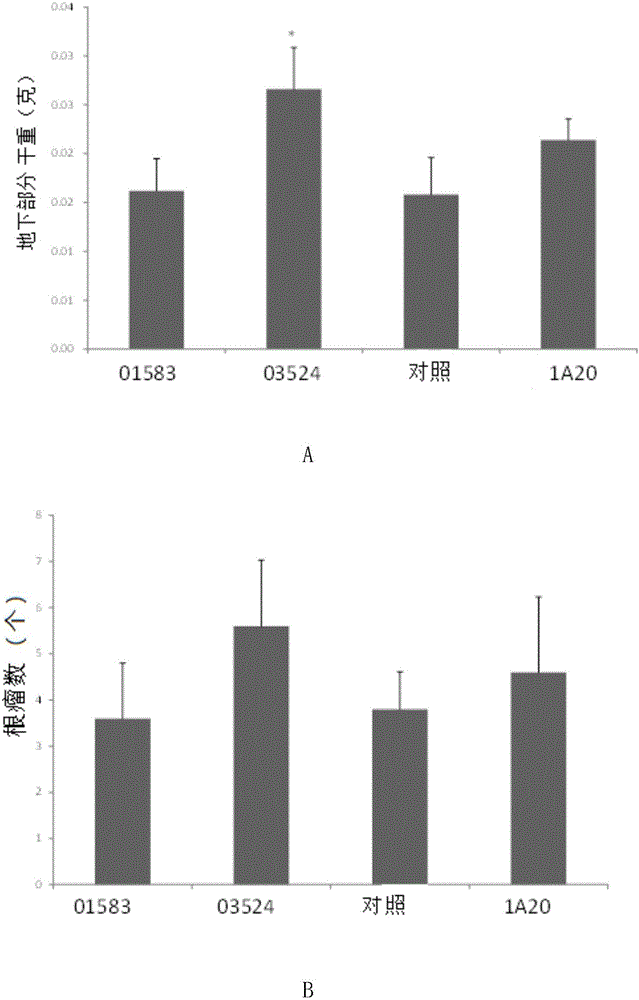
The invention discloses a rhizobium and application thereof. The rhizobium provided by the invention is northern Mesorhizobium septentrionale CCBAU 03524, of which the preservation number in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center is CGMCC No.11015. Experiments show that the northern Mesorhizobium septentrionale CCBAU 03524 CGMCC No.11015 has important application value in promoting growth of astragalus plants and / or improving quality of astragalus and / or raising seedlings of astragalus plants; the promotion of the growth of astragalus plants is reflected as increase of the number of nodules and / or increase of dry weight of underground parts; the improvement of the quality of astragalus is reflected as increase of percentage of astragalus polysaccharide in astragalus root.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV +1
Method of purifying water, suitable bacteria for said method and use thereof
InactiveCN1420848ALow costReduce energy consumptionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismBiology
A method of purifying waste water biologically by using three particularly suitable bacteria: Bacillus sp. DT-1, Pseudomonas azelaica, DT-2, and / or Rhizobus sp. DT-5, or mixed populations thereof. The invention further relates to the bacteria and the mixed populations and use thereof in purifying waste water. The invention further relates to a bioreactor including the bacteria.
Owner:克莱沃有限公司
Rhizobium pumilum and application of rhizobium pumilum in preparation of water-soluble beta-1,3 glucan
ActiveCN112358985AIncrease production capacityEase of industrial productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
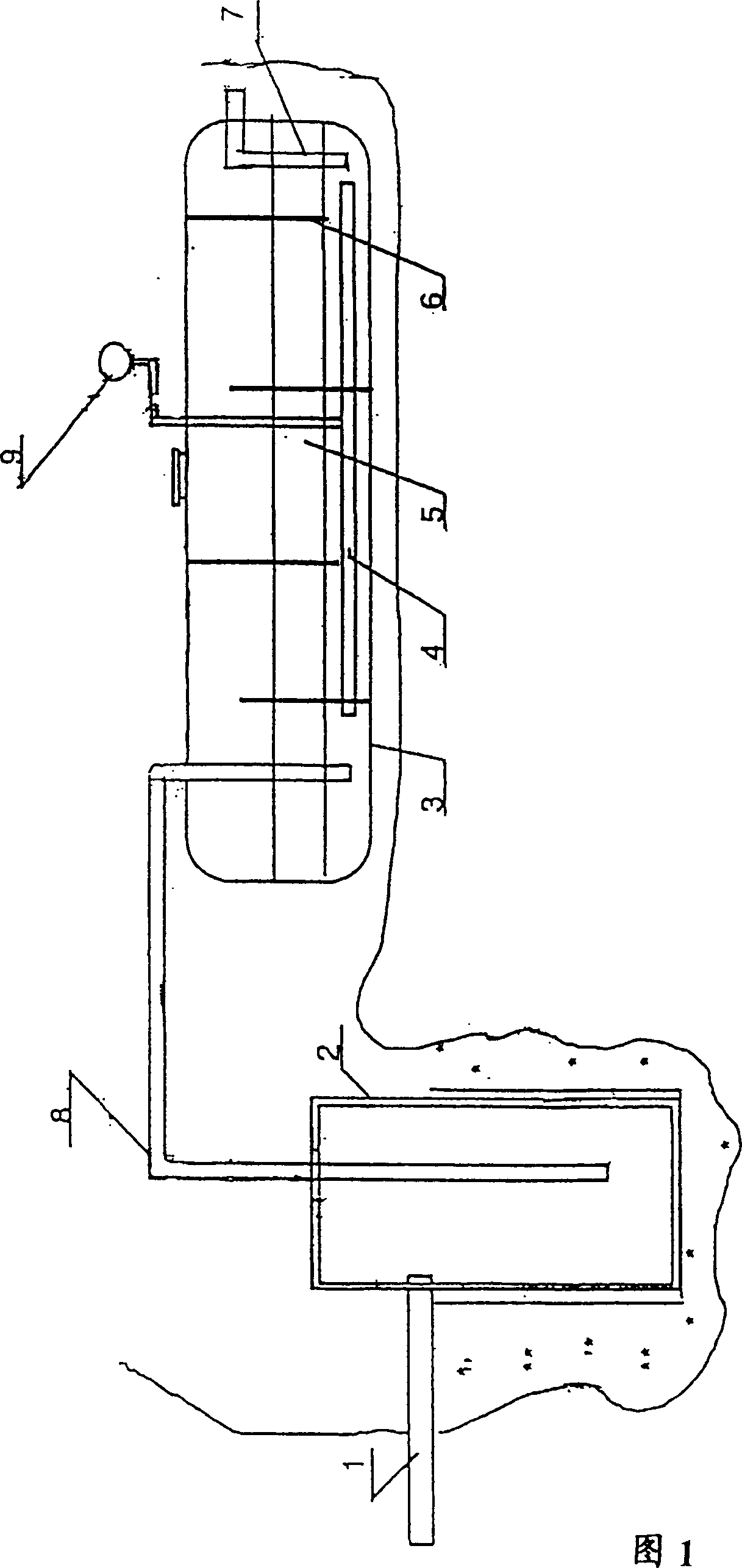
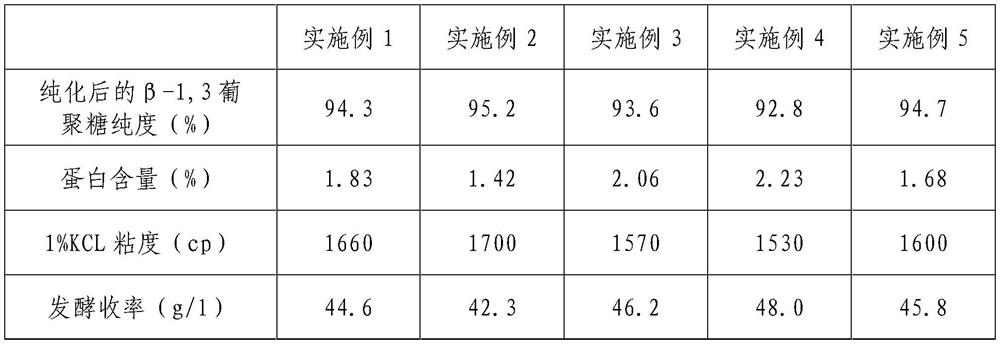
The invention belongs to microbial fermentation, and particularly relates to rhizobium pumilum and an application of the rhizobium pumilum in preparation of water-soluble beta-1,3 glucan. A method comprises the following process steps: inoculating rhizobium pumilum with the preservation number of CGMCC No.19764 into a sterilized culture solution containing a carbon source, a nitrogen source and other necessary nutrient substances, ventilating, stirring and fermenting at the temperature of 28-32 DEG C, and finishing the fermentation when the fermentation period does not exceed 70 hours to prepare fermentation liquor containing beta-1, 3 glucan. The method solves the problems of tedious process, low product yield and the like in the prior art, and the product has the advantages of high yield, high product viscosity, good water solubility, low fermentation cost and the like.
Owner:河北沣川生物科技有限公司
Rhizobium and application thereof in degrading nonyl phenol in water environment
ActiveCN112522131AEfficient degradationReduce concentrationBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyHigh concentration
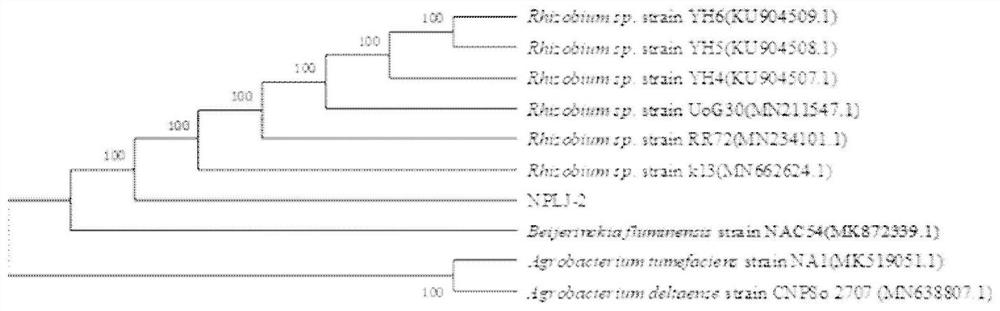
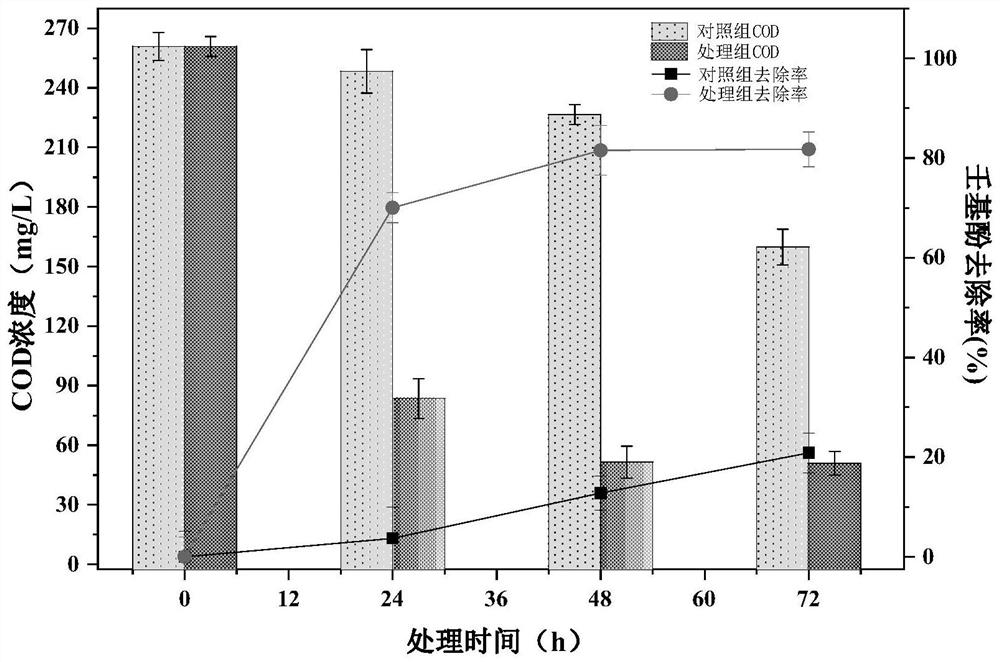
The invention discloses rhizobium named as Rhizobium sp. NPLJ-2. The Rhizobium sp. NPLJ-2 is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on October 19th, 2020 with the preservation number ofCCTCC M 2020603. The invention also discloses application of the rhizobium in degrading nonyl phenol in a water environment. The rhizobium disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the biodegradation rate of the nonyl phenol with the initial concentration of 100 mg / L in a water body under an aerobic condition can reach 80% or above, the biodegradation time is effectively shortened, and meanwhile, COD contributed by the nonyl phenol in sewage is also effectively reduced; and the nonyl phenol in the sewage is quickly and efficiently degraded by utilizing a biological method, and the rhizobium has important significance for treatment of high-concentration environmental hormone-nonyl phenol in the sewage.
Owner:NANJING JIANGDAO INST OF ENVIRONMENT RES CO LTD
Free-living nitrogen fixing bacterium MBC8 and application thereof
The invention discloses a free-living nitrogen fixing bacterium MBC8 (Rhizobium galegae), which was preserved with preservation number CGMCC No.10824 on May, 19, 2015 by China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center. The strain still can exist, reproduce and have nitrogen fixing activity under drought, great temperature difference, saline-alkaline disasters and strong ultraviolet radiation. A bacterial agent prepared by using the strain can be applied to ecological systems under drought, great temperature difference, saline-alkaline disasters and strong ultraviolet radiation, can increase nitrogen accumulation of the ecological systems, can play a role of improving soil environments, can improve physiological activity of microbes and plants and can increase net primary productivity.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com