Rhizobium astragula capable of effectively fixing nitrogen and culture method and application thereof
The technology of a rhizobium rhizobia and a culturing method is applied in the field of high-efficiency nitrogen-fixing rhizobium rhizobia. Inexpensive effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Embodiment 1: the cultivation of milk vetch rhizobia CGMCC No.4347
[0064] The cultivation steps are as follows:
[0065] Prepare slant medium: accurately weigh according to mannitol 10g / L, yeast extract 1.0g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.5g / L, magnesium sulfate 0.5g / L, sodium chloride 0.2g / L, and agar 18g / L. Take mannitol, yeast extract, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, magnesium sulfate, sodium chloride and agar, and then dissolve it in water. After the dissolution is complete, use acid or alkali to adjust the pH to 6.8-7.0, then add water to reach the above concentration, and mix well Afterwards, it was divided into test tubes, and after autoclaving at a temperature of 121° C. for 30 minutes, the test tubes were placed obliquely while hot to make slant medium.
[0066] Preparation of seed medium: Accurately weigh mannitol, yeast Ointment, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, magnesium sulfate, sodium chloride, and then dissolved in water, adjusted to pH 6.8-7.0 wi...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Embodiment 2: Optimizing the fermentation medium of milk vetch rhizobia CGMCC No.4347
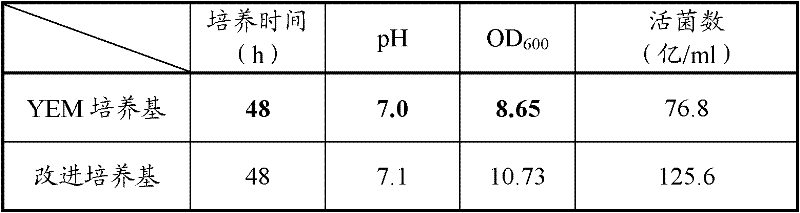
[0072] Choose cheap industrial by-product soybean molasses as carbon source to replace part of carbon source mannitol in YEM medium; choose sodium glutamate as nitrogen source to replace part of nitrogen source yeast extract in YEM medium. The optimization of the fermentation medium was carried out in the same culture method as in Example 1.
[0073] Among them, soybean molasses needs to be hydrolyzed first. The specific method is: dilute concentrated sulfuric acid (18.4mol / L) with water to 1mol / L, then mix equal volumes of soybean molasses with a solid content of 60% and diluted 1mol / L sulfuric acid, and sterilize at a temperature of 121°C. hydrolysis.
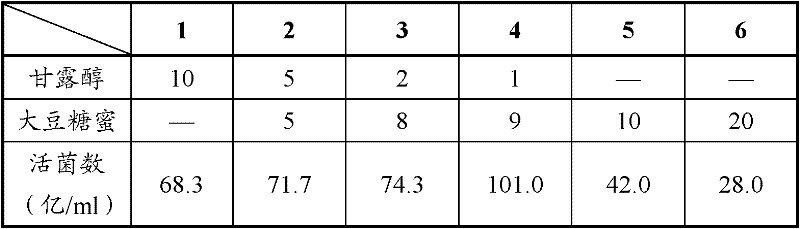
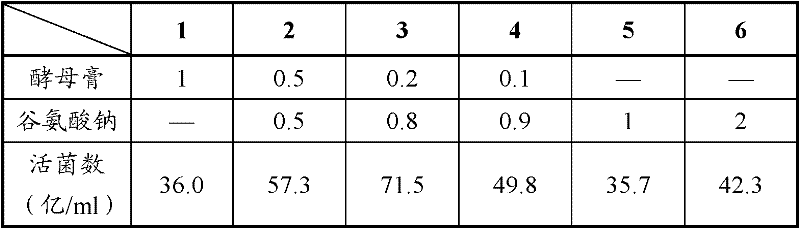
[0074] Table 1 shows the test results when only the carbon source is changed without changing other components in the existing YEM medium.
[0075] Table 1: CGMCC No.4347 medium for rhizobia CGMCC No.4347
[0076] Carbon source ...
Embodiment 3
[0087] Embodiment 3: the preparation of solid milk vetch rhizobium CGMCC No.4347 bacterial agent
[0088] Peat treatment: Dry the peat naturally, then crush it, pass through a 100-mesh sieve, adjust the pH to 7.0 with quicklime powder, and sterilize at 121°C for 1 hour.
[0089] The acquisition of the milk vetch rhizobium CGMCC No.4347 microbial agent containing peat: the liquid milk vetch rhizobium CGMCC No.4347 bacterial agent obtained in Example 1 and the treated sterilized, dry, pH 7.0~7.2 The peat was mixed according to the weight ratio of 1:2.5, and then multiplied and cultured at 28° C. for 24 hours to obtain solid milk vetch rhizobium CGMCC No.4347 inoculum, and the number of viable bacteria was more than 500 million / g.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com