Patents
Literature
36results about How to "Nodulation rate is high" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Rhizobium and application thereof
ActiveCN105274030ANodulation rate is highImprove survival rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlant noduleDry weight
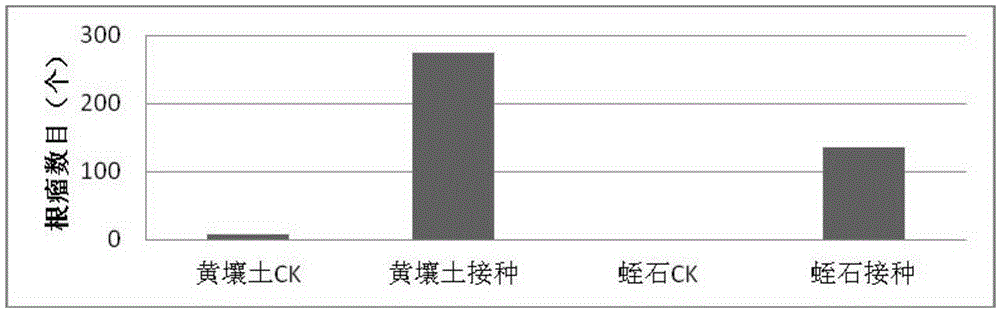
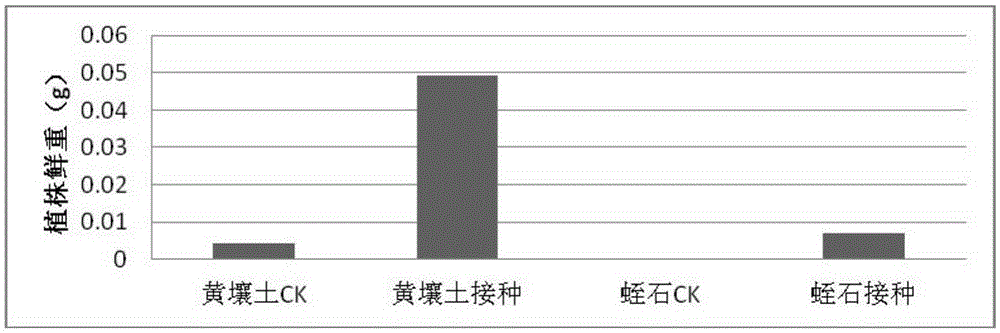
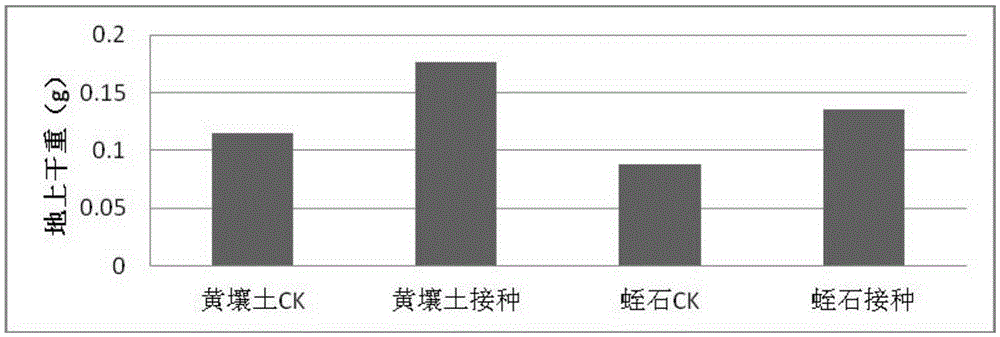
The invention relates to a (Bradyrhizobium sp.) LX-JX01 and application thereof. A preparation method of an inoculant for the (Bradyrhizobium sp.) LX-JX01 includes the steps of preparing a liquid DM culture medium, preparing a solid DM culture medium, activating a strain and culturing the rhizobium. The strain can be in nodulation and symbiosis with Dalbergia odorifera. When the inoculant for the Dalbergia odorifera rhizobium LX-JX01 is used for planting Dalbergia odorifera seedlings, nodulation number root nodules is increased by 3823% than a control group, fresh weight of the root nodules is increased by 1038%, dry weight of portions, above the ground, of plants is increased by 47.22%, and seedling height and plant stem diameter are increased by 1030% and 42.3% respectively, so that the inoculant can promote growing of Dalbergia odorifera. Consequently, the inoculant has wide application prospect in planting of artificial forest of Dalbergia odorifera.
Owner:领先生物农业股份有限公司
Soybean slower-growing rhizobium with broad-spectrum nodulation characteristics, application thereof and composite rhizobium agent prepared from same
InactiveCN109735468AHas broad-spectrum nodulation propertiesGood matching affinityBacteriaFabaceae cultivationMicrobial agentKlebsiella oxytoca
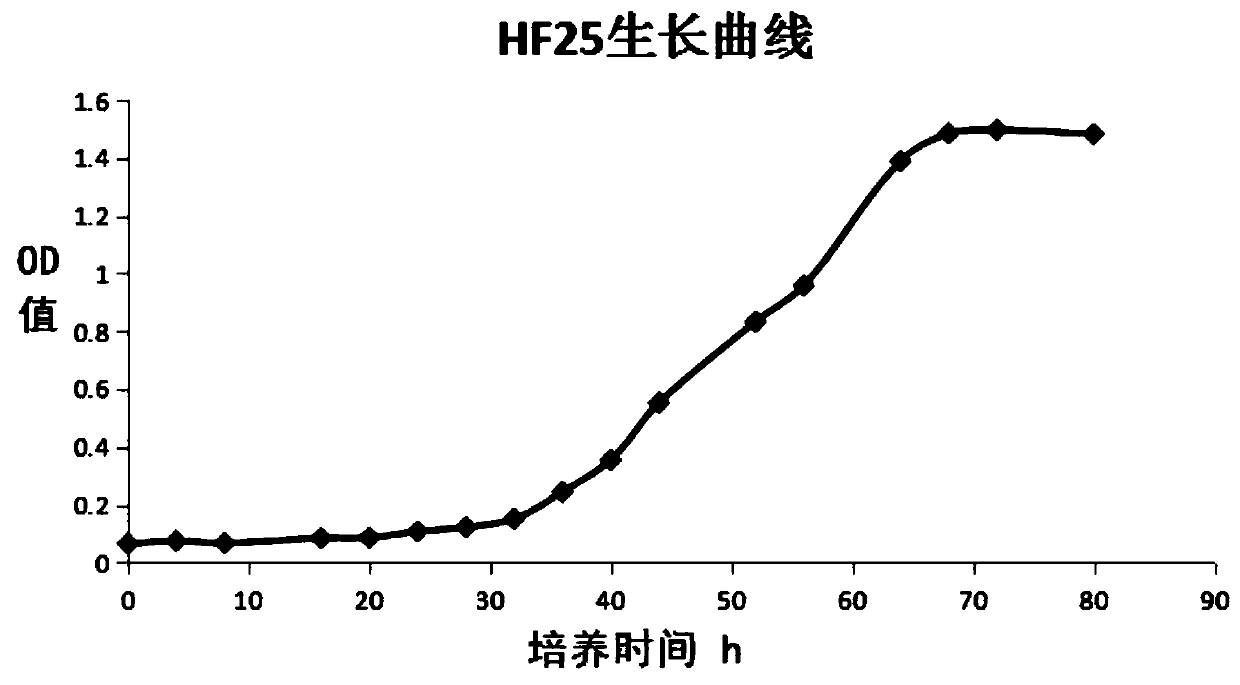
The invention relates to a soybean slower-growing rhizobium with broad-spectrum nodulation characteristics, application thereof and a composite rhizobium agent prepared from the same, and belongs to the technical field of agricultural microorganisms. In order to solve the problems that the soybean nodule bacteria are low in nodulation rate and poor in nitrogen fixing effect, the invention providesa Japanese Bradyrhizobium japonicum HF25, the preservation number is CGMCC No.14857, the bacterial strain has high matching affinity, nodulation competitiveness and nodulation and nitrogen fixation capacity. The invention further provides the composite rhizobium agent which is prepared from Japanese Bradyrhizobium japonicum HF25 and Klebsiella oxytoca ASP-15, two kinds of bacteria are compounded,and the nodulation and nitrogen fixation capacity is significantly improved; the composite rhizobium agent is applied to soybean planting, compared with soybeans which are not applied with a microbial agent, the number of soybean nodules is increased by 170%, the number of pods per plant is increased by 37.3%, and the hundred-grain weight of soybeans is increased by 5.5%.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY HEILONGJIANG ACADEMY OF SCI
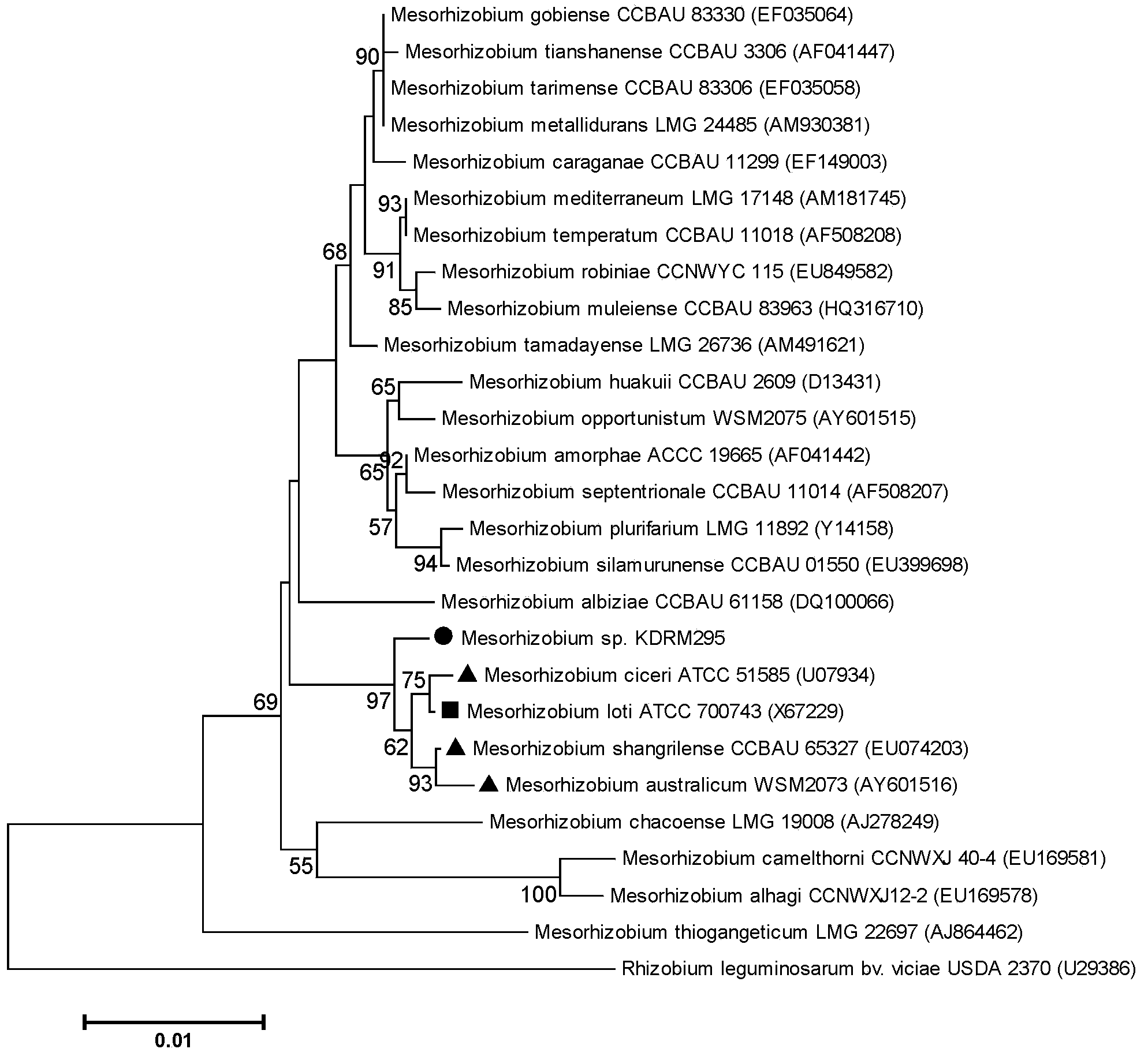
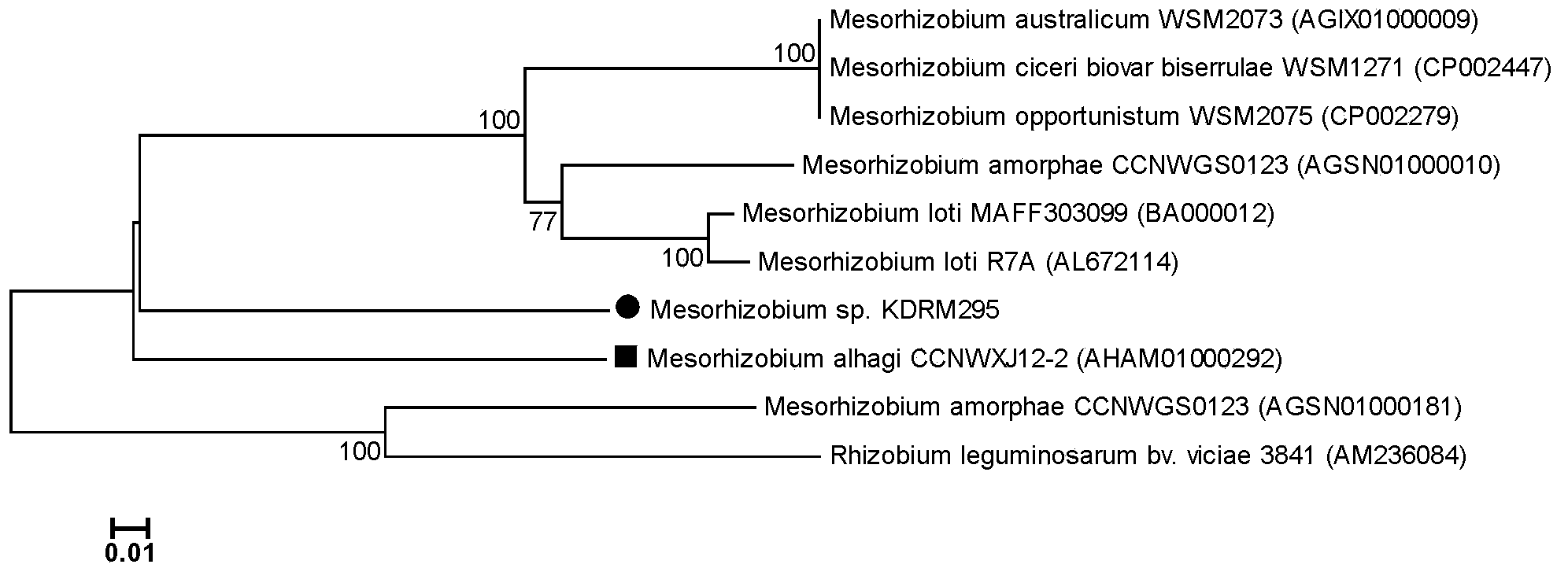
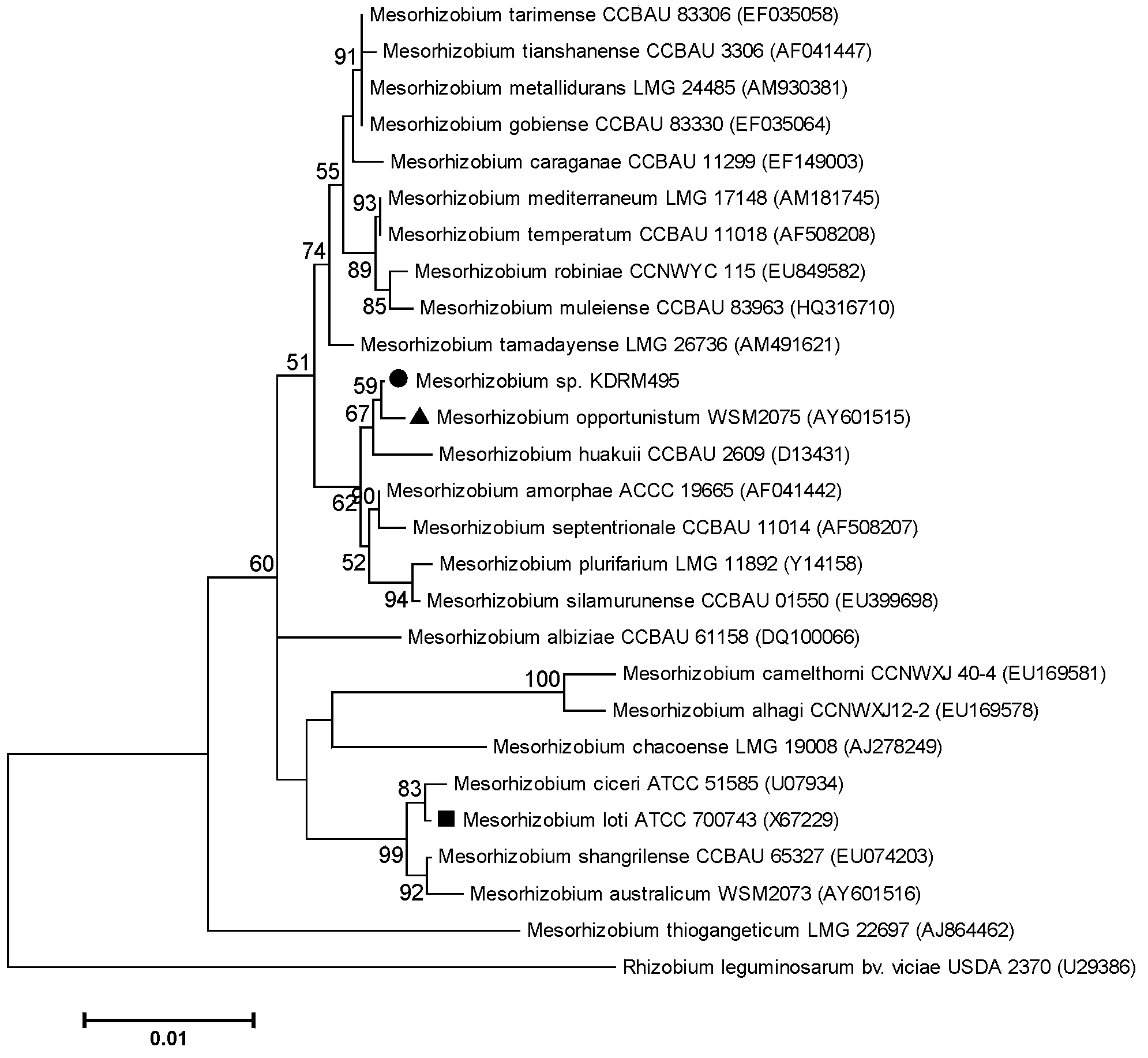
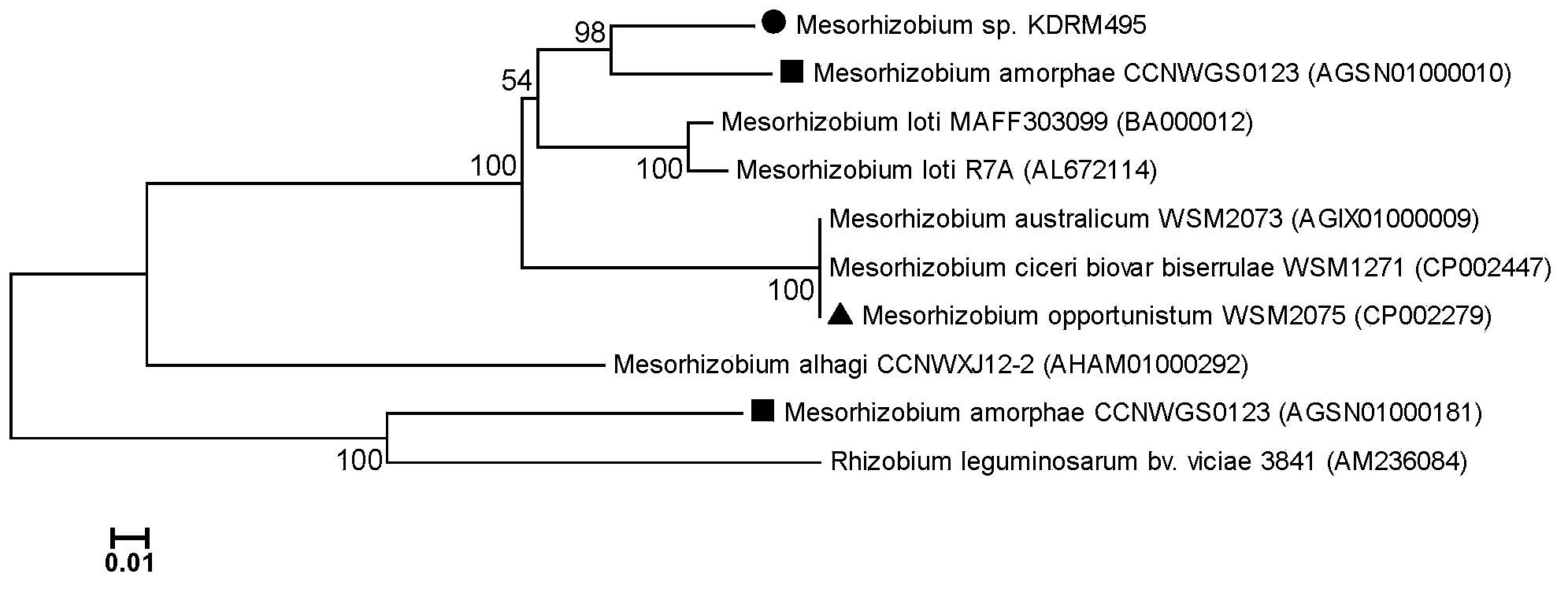
Mesorhizobium KDRM295 and application thereof
ActiveCN103045500AReduce inhibitionNodulation rate is highPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyPlant nodule
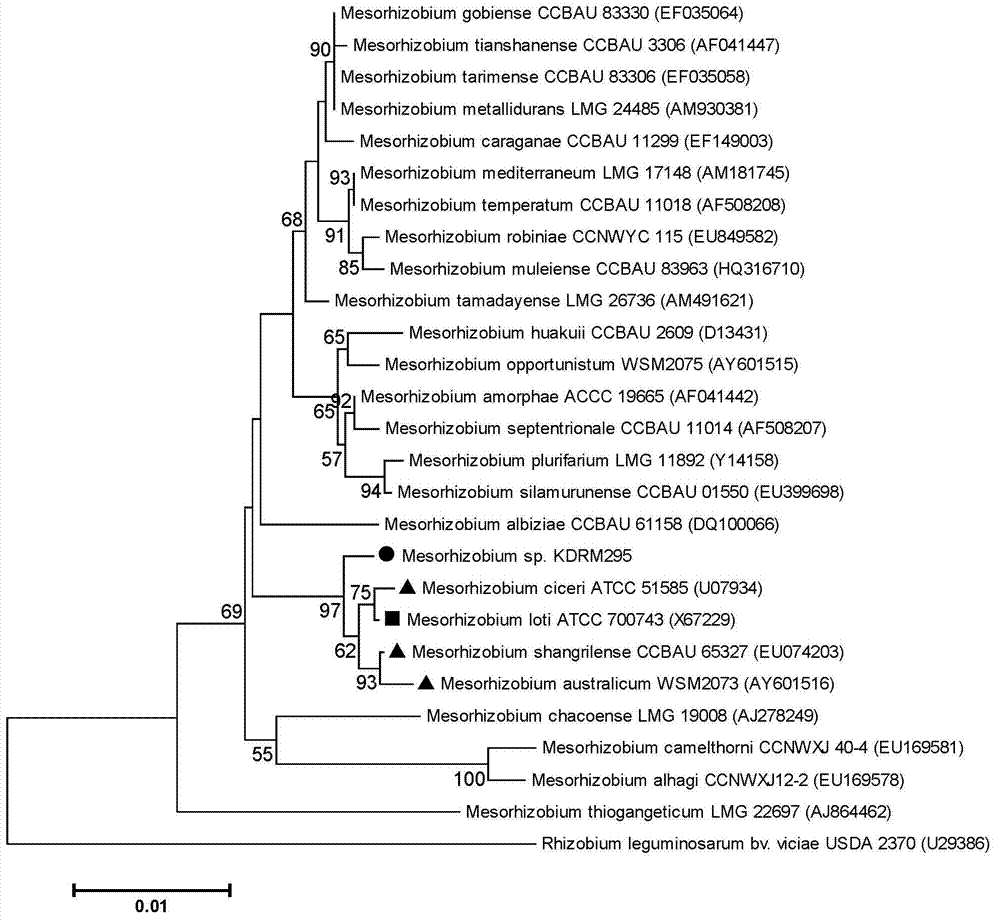
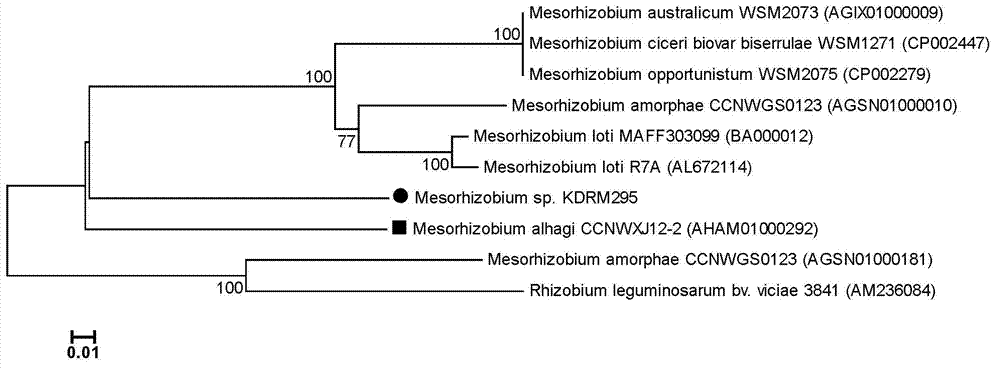
The invention relates to mesorhizobium KDRM295 which is separated from acacia root nodule, contains ACC deaminase, and can efficiently nodulate and promote growth of the acacia, and an application thereof. The mesorhizobium KDRM295 is now preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) with the preservation number of CCTCCNO: M2012331. The mesorhizobium KDRM295 contains ACC deaminase which can decompose ACC into alpha-ketobutyrate and NH3, reduce the level of plant cell for synthesizing ethylene, lighten the inhibition effect of ethylene to infection of the root nodule, improve the nodulation rate of root nodule and acacia and the level of symbiotic nitrogen fixation, provide high-level nitrogen for the growth of the acacia on the barren wasteland without fertilization, promote the growth of acacia seeding, and increase mature biomass for the acacia, thereby realizing high yield of the acacia mature with low inoculation investment, and playing a role of raising seeding and afforestation for acacia.
Owner:ZHONGYING CHANGJIANG INTERNATIONAL NEW ENERGY INVESTMENT CO LTD
Mesorhizobium kowhaii and culture method thereof, astragalus membranaceus rhizobium agent and method and application of astragalus membranaceus rhizobium agent
ActiveCN113005059ANodulation rate is highStrong nitrogen fixation abilityBacteriaFabaceae cultivationHorticultureNitrogen fertilizer
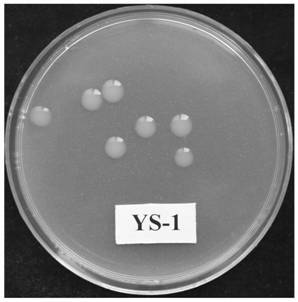
The invention provides a mesorhizobium kowhaii and Astragalus mongholicus rhizobium agent, a method and an application, and belongs to the technical field of microbial agents. The mesorhizobium kowhaii YS-1 provided by the invention has the preservation number of CGMCC No.20571, and has the characteristics of high nodulation rate and strong nitrogen fixation capability, can significantly improve the summarized nodulation number, effective nodulation number and nodulation weight of astragalus membranaceus, reduces the use amount of chemical nitrogen fertilizer in astragalus membranaceus planting, reduces the pollution of nitrogen fertilizer to the environment, and plays a significant role and has important and profound significance on production of green food and high yield, high efficiency and low consumption of agriculture.
Owner:INST OF SOIL FERTILIZER & WATER SAVING AGRI GANSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Saline-alkali soil resistant nitrogen fixation rhizobium japonicum and application thereof
ActiveCN114456981AHigh nitrogen contentIncrease productionPlant growth regulatorsBiocidePlant noduleEcological environment
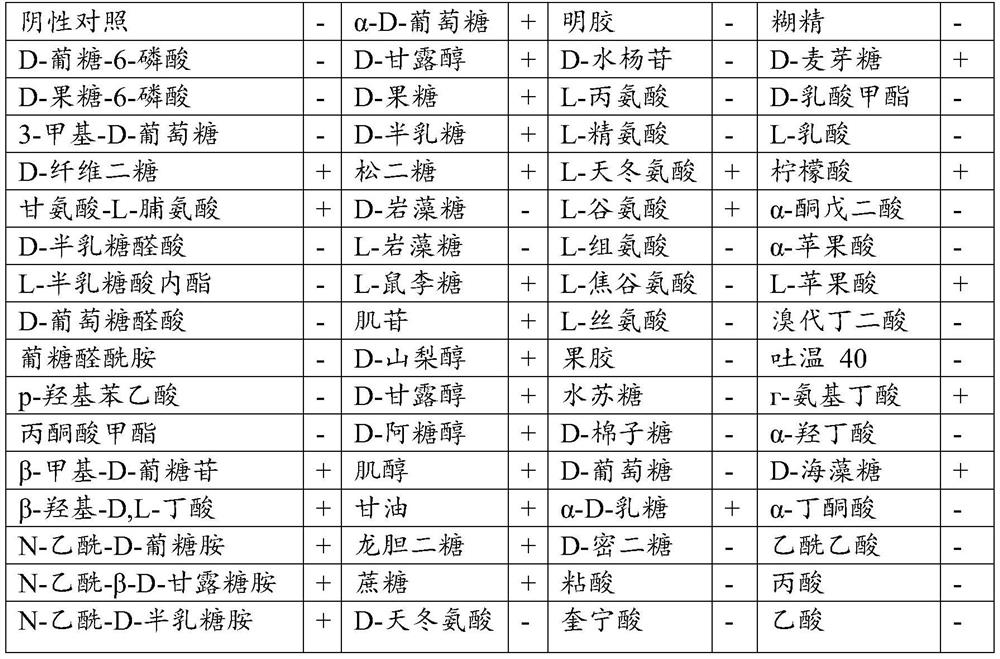
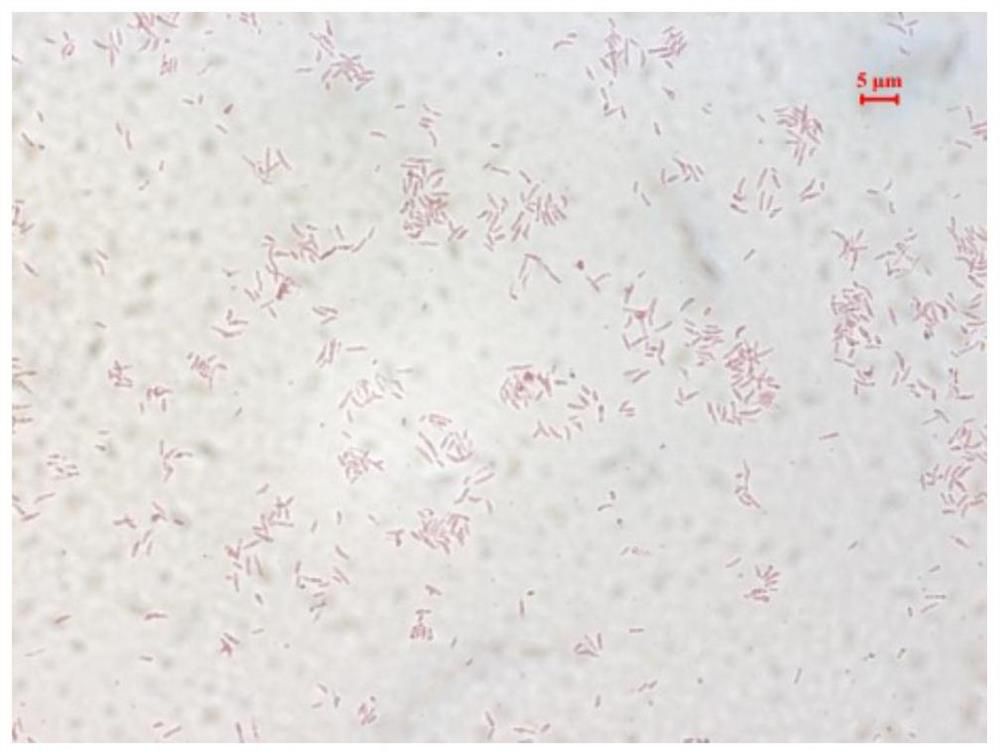
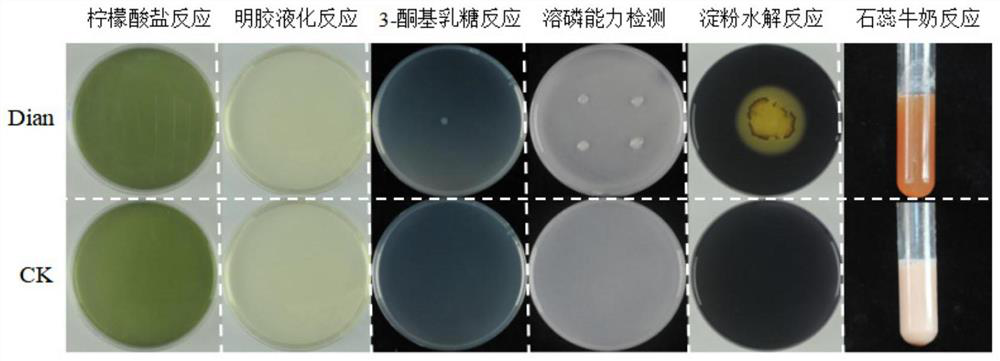
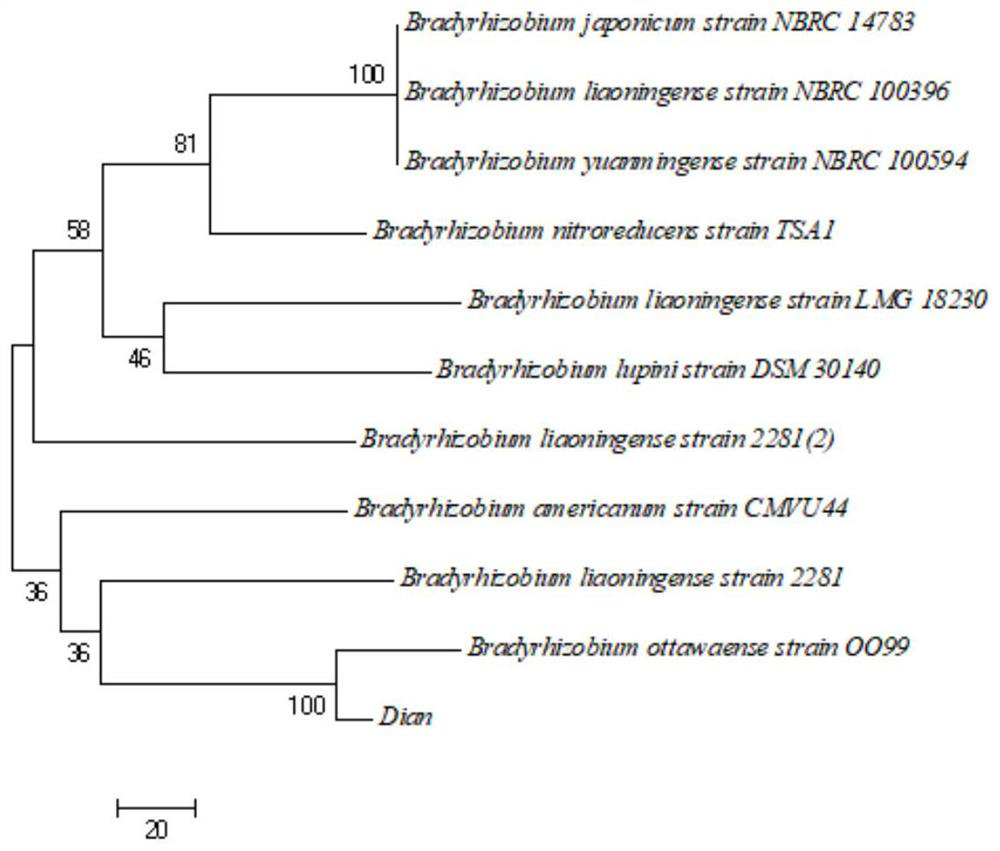
The invention discloses a nitrogen-fixing bradyrhizobium japonicum strain resistant to saline-alkali soil and application of the bradyrhizobium japonicum strain. According to the invention, a strain of bradyrhizobium taihuae Dian strain is obtained through separation and is preserved in Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center on January 11, 2022, and the preservation number is GDMCC No: 62202. Researches show that the strain has the characteristics of high nodulation rate and strong nitrogen fixation capability, and can optimize the micro-ecological environment of alkaline soil crop root growth; the Dian strain is adopted to treat plants, soybean nodulation and nitrogen fixation can be effectively promoted, plant nitrogen nutrition is increased, plant growth is promoted, and the biomass, root nodule number and nitrogen content of soybean plants can be remarkably improved. The strain is especially suitable for cultivation and production of soybeans in stony desertification areas, expands a strain resource library of nitrogen-fixing rhizobium, is beneficial to promoting nodulation and nitrogen fixation of plants, and increases nitrogen nutrition of the plants.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
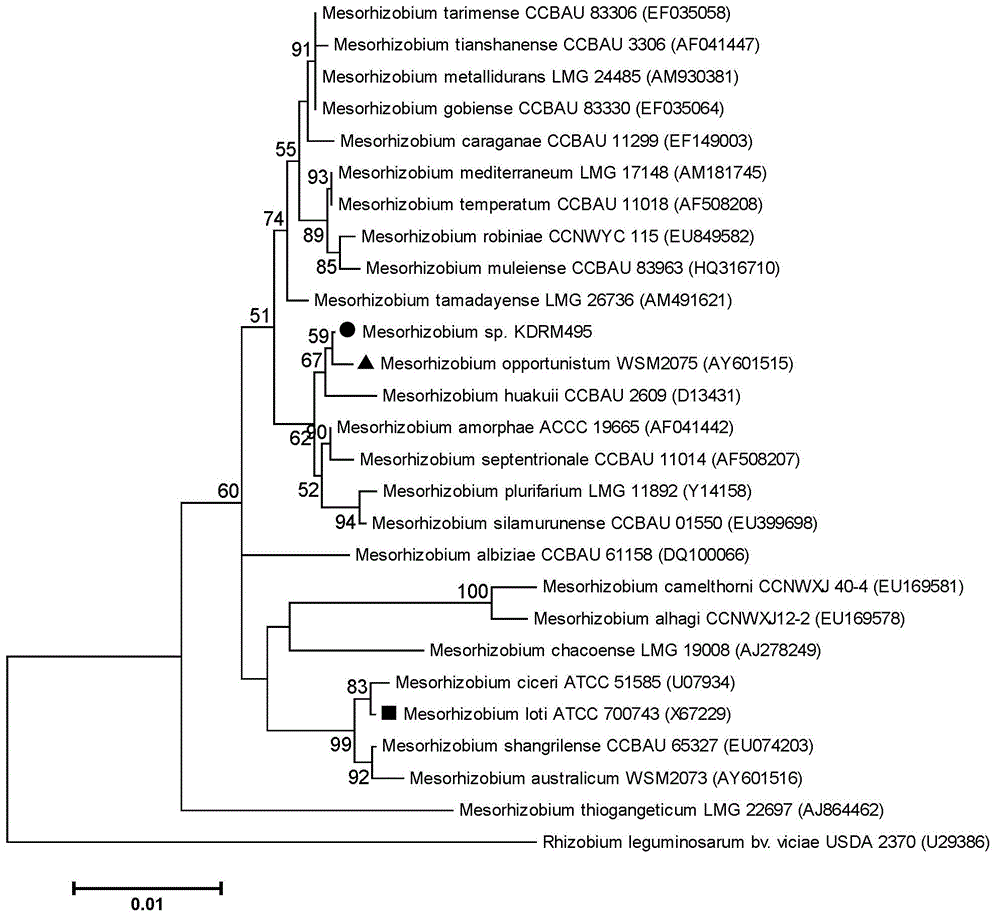
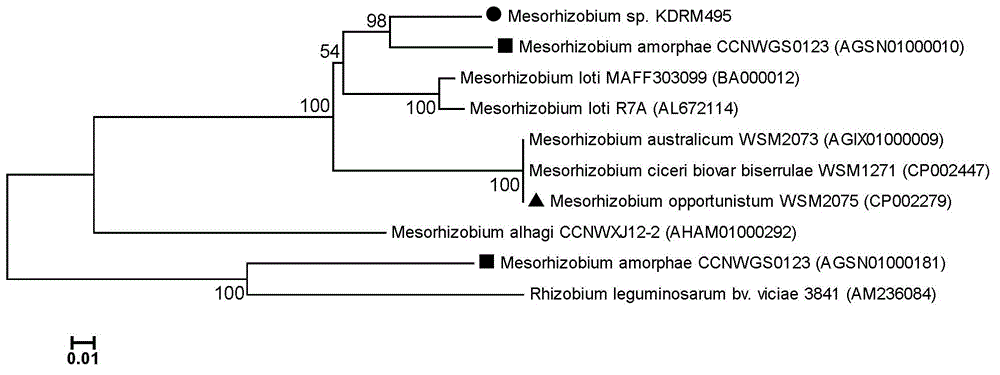
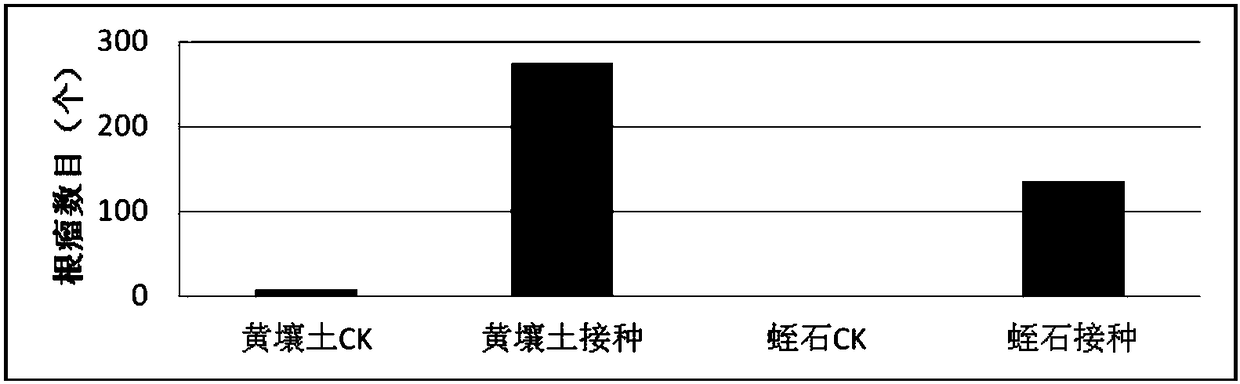
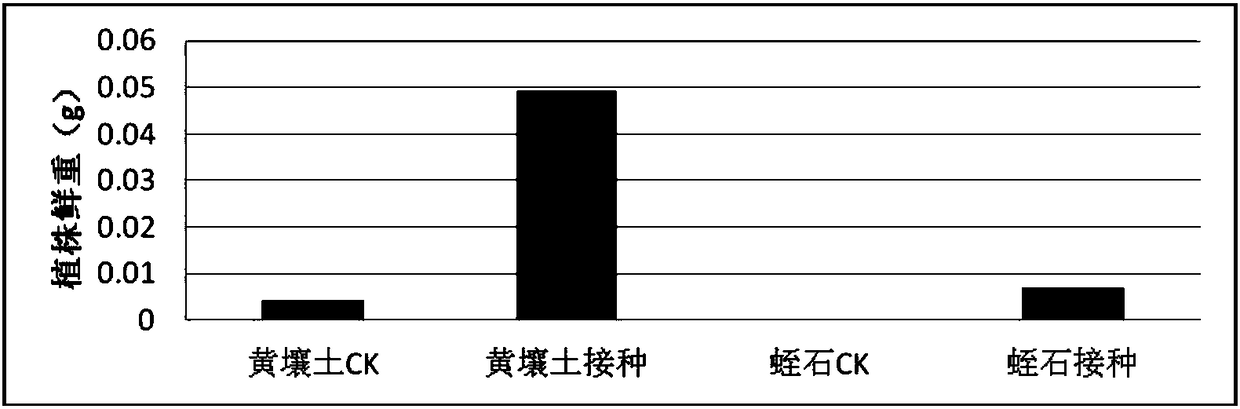
Mesorhizobium KDRM495 and application thereof
ActiveCN102978139AReduce inhibitionNodulation rate is highBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPlant nodulePlant cell
The invention relates to mesorhizobium KDRM495 and application thereof. The mesorhizobium KDRM495 is separated from acacia root nodule, contains ACC deaminase, and can efficiently nodulate and promotes acacia growth. A mesorhizobium KDRM495 strain is collected in CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection), and the collection number is CCTCC No: M2012333. The mesorhizobium KDRM495 disclosed by the invention contains the ACC deaminase which can decompose ACC into alpha-ketobutyrate and NH3, lowers the level of synthesizing ethylene from plant cells, reduces the inhibiting effect of ethylene on rhizobium infestation, enhances the nodulation rate and symbiotic nitrogen fixation level of rhizobia and acacia, provides the high-level nitrogen for the growth of the acacia on unfertilized sterile wastelands, promotes the growth of acacia seedlings and increases the biomass of acacia lumbers, thereby achieving the high yield of the acacia lumbers through low-cost inoculation investment and playing a role in the aspect of acacia seedling culture and forestation.
Owner:ZHONGYING CHANGJIANG INTERNATIONAL NEW ENERGY INVESTMENT CO LTD
A kind of rhizobia and its application
ActiveCN105274030BNodulation rate is highImprove survival rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyRoot nodule
The invention relates to Bradyrhizobium sp. LX‑JX01 and its application. The preparation method of the bradyrhizobium LX-JX01 bacterial agent of the present invention comprises the steps of liquid DM medium preparation, solid DM medium preparation, strain activation and rhizobia culture. The strain can nodulate symbiosis with Dalbergia balata. When Dalbergia japonica LX-JX01 bacterial agent of the present invention was used to plant Dalbergia japonica seedlings, its nodule nodule number increased by 3823% compared with the control, the fresh weight of nodules increased by 1038%, the dry weight of the aboveground part of the plant increased by 47.22%, and the seedling height and plant diameter are increased by 1030% and 42.3% respectively, therefore, the bacterial agent of the present invention can promote the growth of Dalbergia balsamicum. Therefore, the fungal agent of the present invention has broad application prospect in the plantation of Dalbergia balsamanii artificial forest.
Owner:领先生物农业股份有限公司
Chinese milk vetch microbial fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104230421AImprove the effect of increasing productionIncrease crop yieldBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationFertilizerChemistry
The invention discloses a Chinese milk vetch microbial fertilizer. The Chinese milk vetch microbial fertilizer is prepared by mixing a solid biological fertilizer with mycorrhiza fungi in a weight ratio of 9 to 1, wherein the solid biological fertilizer is formed by fermenting a liquid bacterial liquid in a carrier substrate; and a bacterial strain of the liquid bacterial liquid is formed by mixing and inoculating bradyrhizobium and agrobacterium in mesorhizobium huakuii of the Chinese milk vetch. The invention further provides a preparation method of the Chinese milk vetch microbial fertilizer.
Owner:HUBEI ZHENGJIA MICROBE PROJECT & TECH
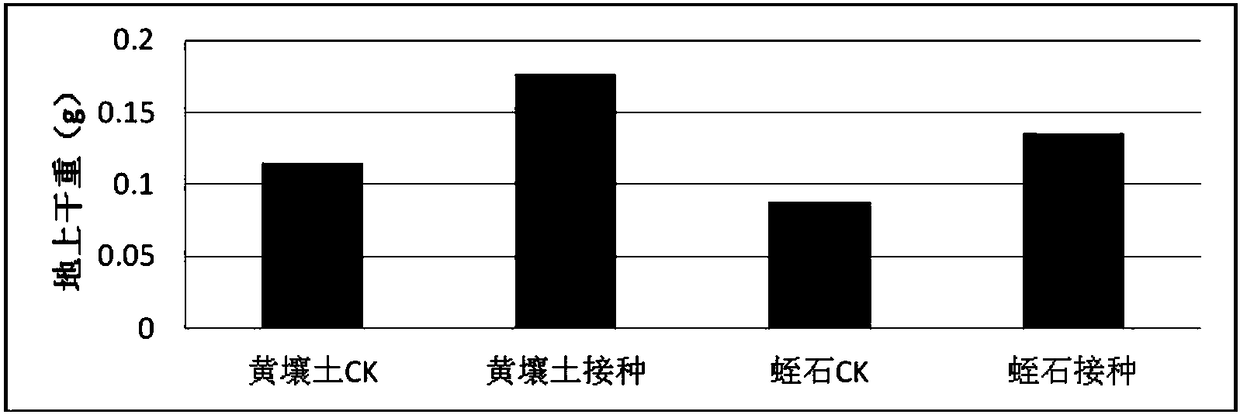
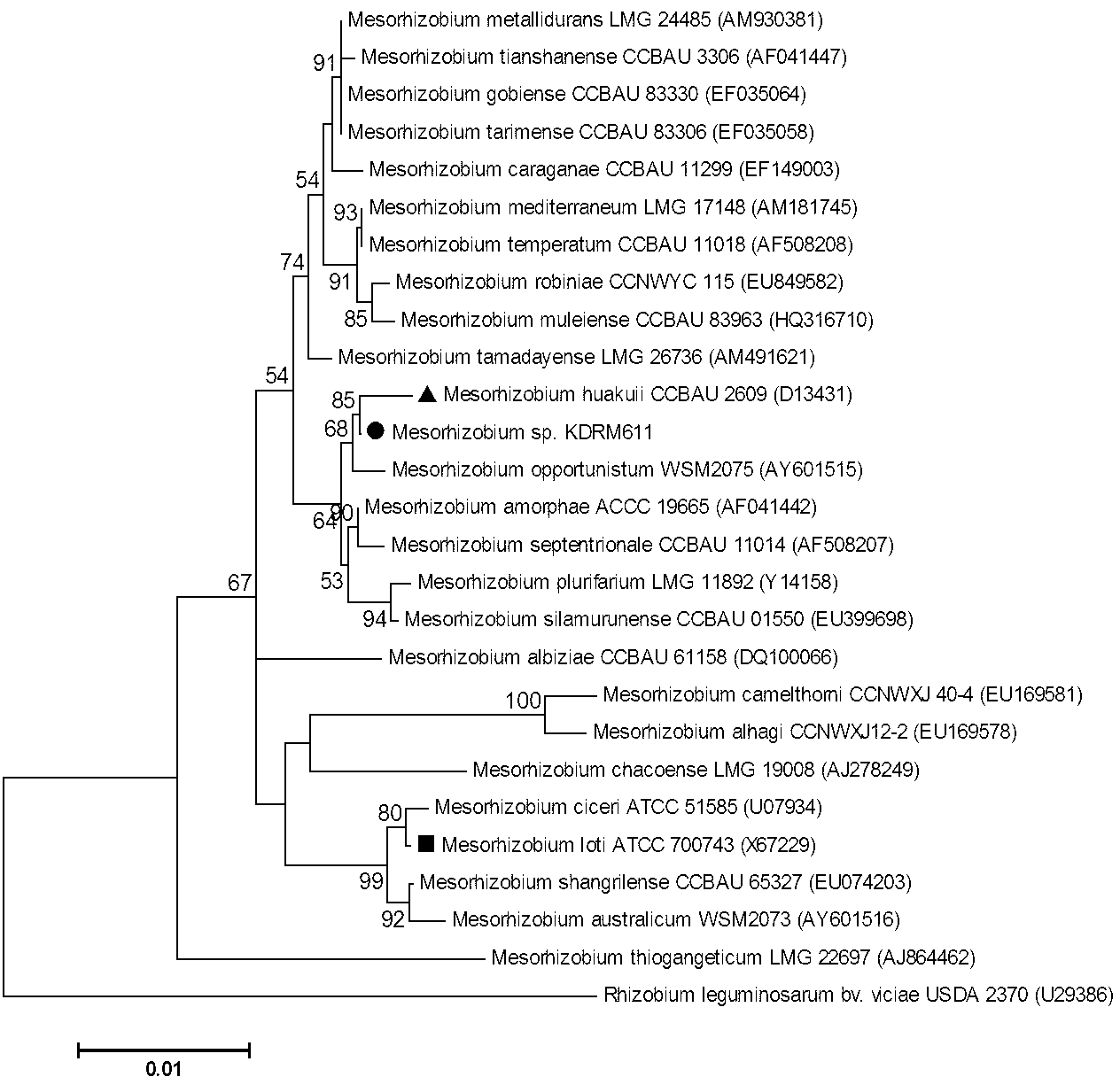
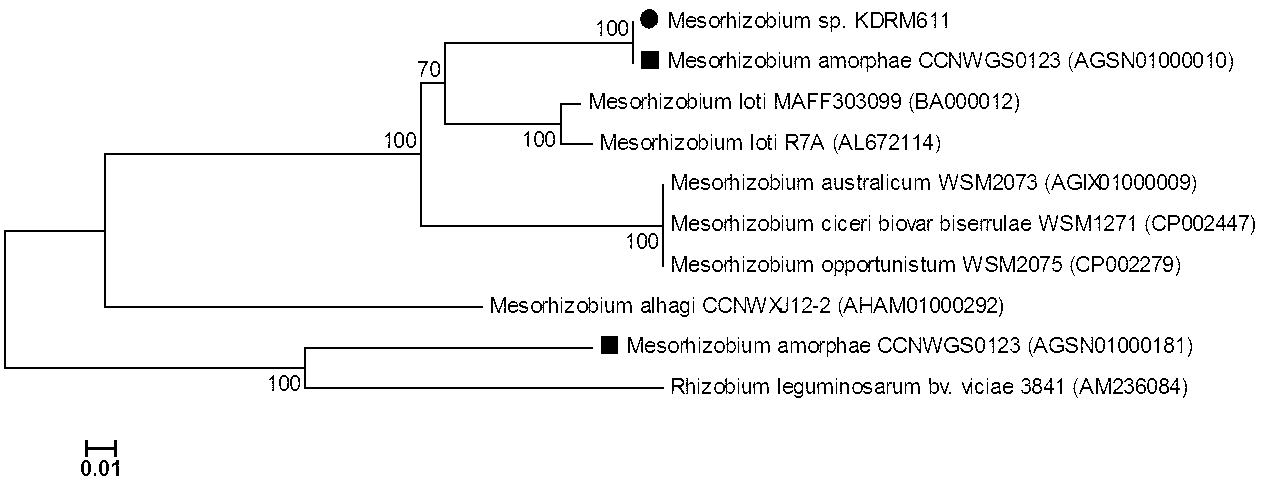
Mesorhizobium KDRM611 and application thereof
ActiveCN103013856AReduce inhibitionNodulation rate is highBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlant nodulePlant cell
The invention relates to Mesorhizobium KDRM611 and the application of the Mesorhizobium KDRM 565. The Mesorhizobium KDRM611 is separated from Robinia pseudoacacia root nodule, contains ACC deaminase and can effective carry out nodulation and promote the growth of the Robinia pseudoacacia. The Mesorhizobium KDRM 611 strain is preserved in China Center for Type CultureCollection with the preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2012335. The Mesorhizobium KDRM 611 disclosed by the invention contains the ACC deaminase which can decompose ACC into alpha-ketobutyrate and NH3, reduce the level of synthesizing ethylene with plant cells, reduce an inhibition function of ethylene on rhizobium infection, improve the nodulation rate of rhizobium and the Robinia pseudoacacia and the level of symbiotic nitrogen fixation, provide high-level nitrogen for the growth of the Robinia pseudoacacia on non-fertilized barren wasteland, promote the growth of seedlings of the Robinia pseudoacacia and increase the biomass of mature the Robinia pseudoacacia, thereby realizing high yield of the mature Robinia pseudoacacia by using inoculation with low cost, and playing a role in Robinia pseudoacacia culture and forestation.
Owner:ZHONGYING CHANGJIANG INTERNATIONAL NEW ENERGY INVESTMENT CO LTD
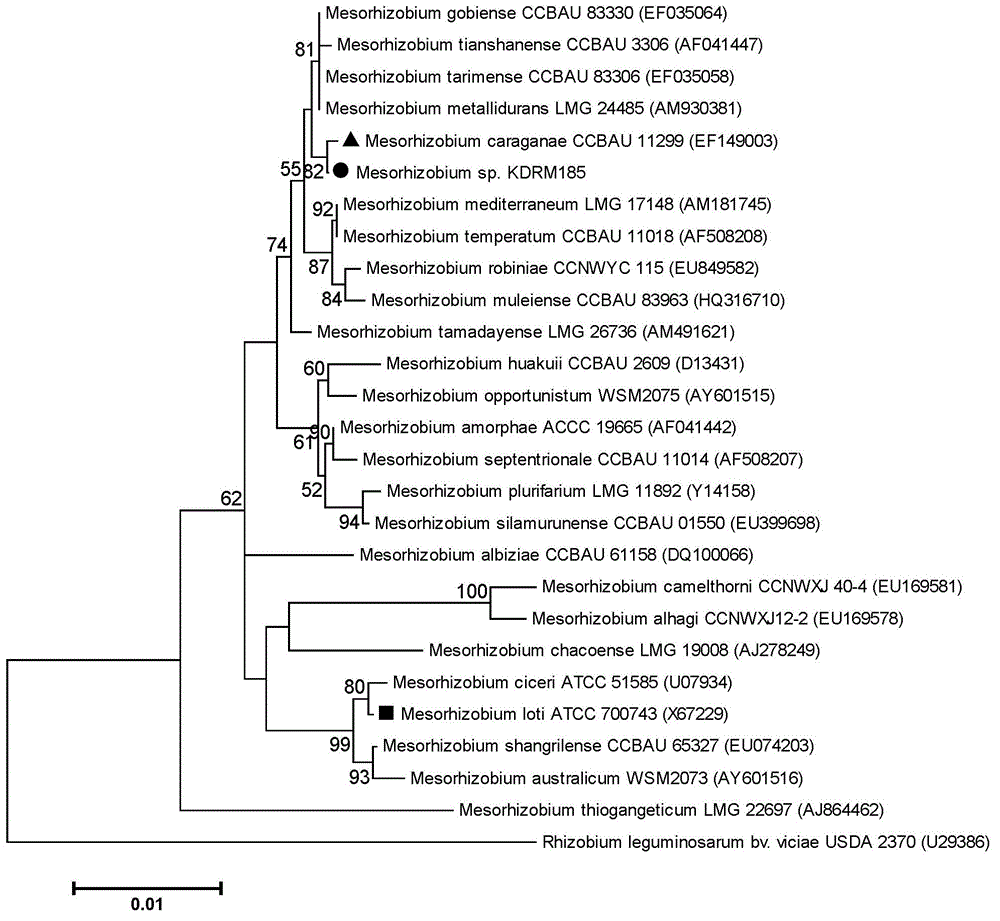
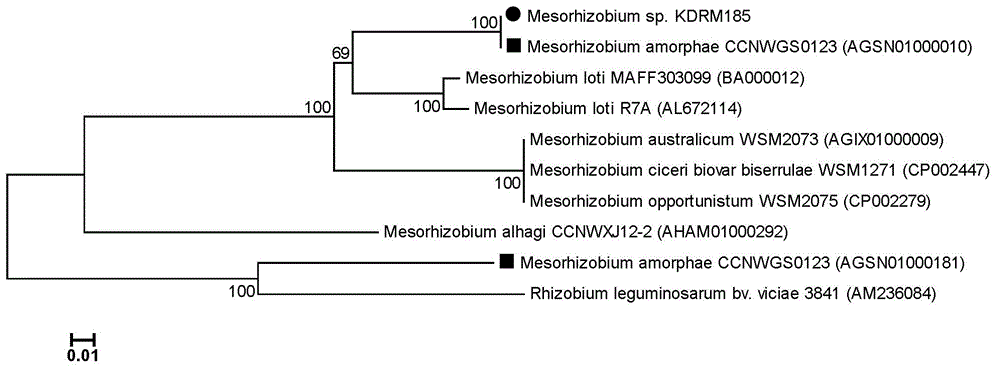
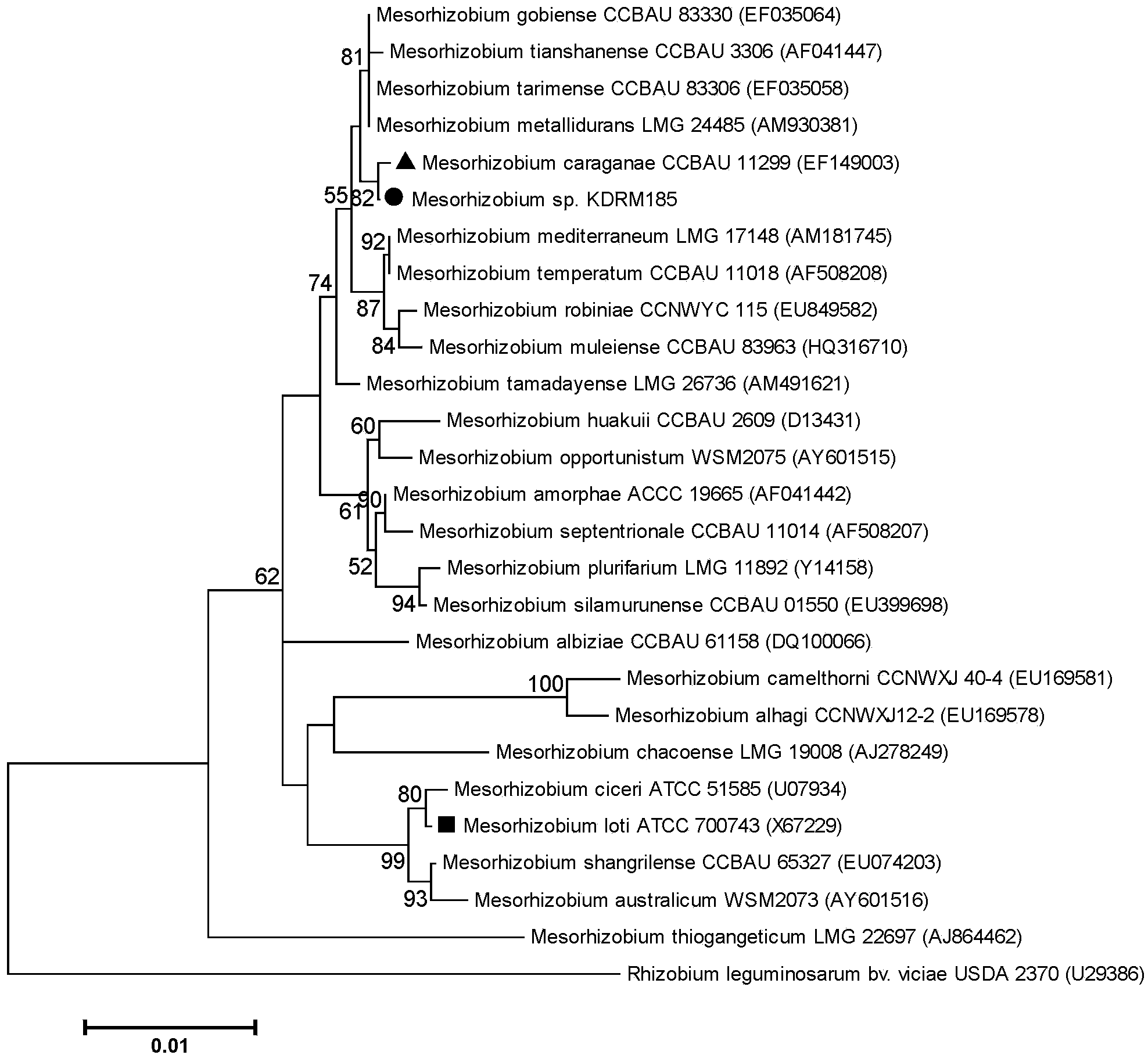
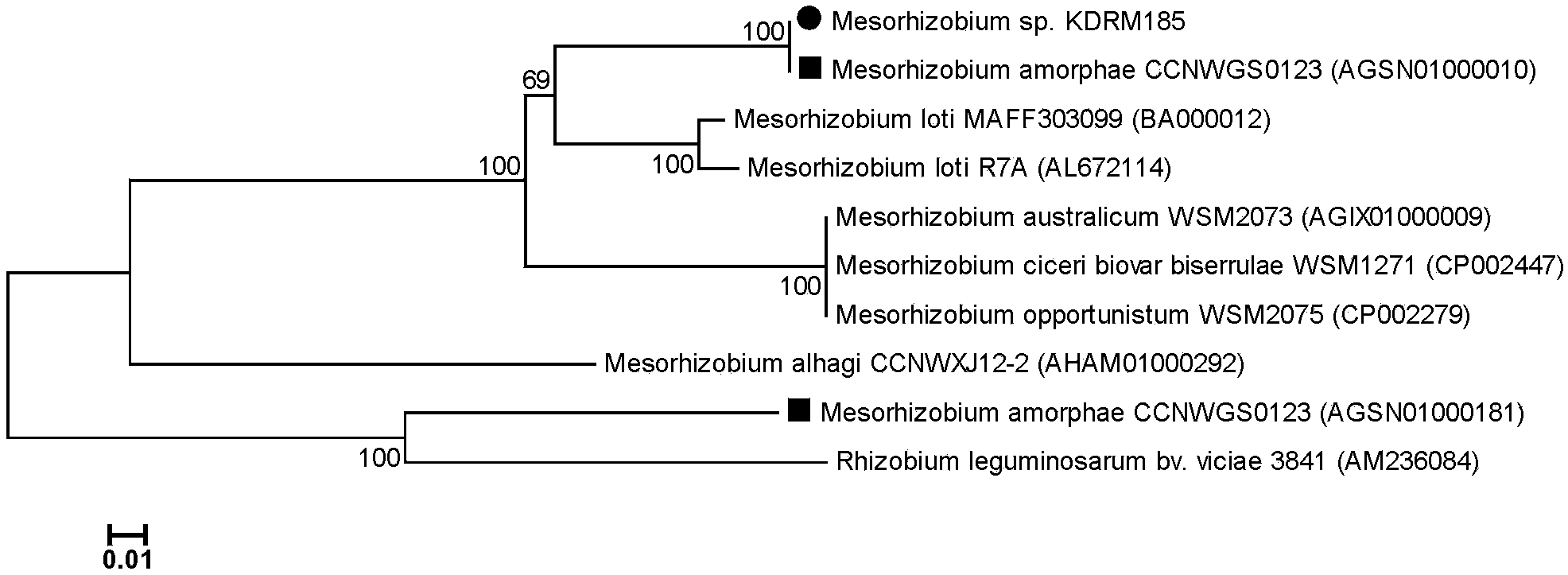
Mesorhizobium KDRM185 and application thereof
ActiveCN102978138AReduce inhibitionNodulation rate is highBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlant nodulePlant cell
The invention relates to a mesorhizobium KDRM185 capable of being separated from an acacia root nodule, containing ACC deaminase, efficiently nodulating and promoting acacia growth and application thereof. A mesorhizobium KDRM185 strain is collected in CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection), and the collection number is CCTCC No: M2012329. The mesorhizobium KDRM185 disclosed by the invention contains the ACC deaminase and can decompose the ACC into alpha-ketobutyrate and NH3, lower the level of plant cells on synthesizing ethylene, reduce the inhibiting effect of the ethylene on rhizobium infestation, enhance the nodulation rate and symbiotic nitrogen fixation level of rhizobia and acacia, provide high-level nitrogen for the growth of the acacia on unfertilized sterile wastelands, promote the growth of acacia seedlings and increase the biomass of acacia lumbers, thereby achieving the high yield of the acacia lumbers through low-cost inoculation investment and playing a role in acacia seedling culture and forestation.
Owner:ZHONGYING CHANGJIANG INTERNATIONAL NEW ENERGY INVESTMENT CO LTD
Compound microbial agent suitable for saline-alkali soil in arid and semi-arid regions and application of compound microbial agent
ActiveCN114304187AGood synergyGood effectBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBacillus licheniformisAlkali soil
The invention provides a compound microbial agent suitable for saline-alkali soil in arid and semi-arid regions and application of the compound microbial agent. The compound microbial agent disclosed by the invention comprises alfalfa rhizobium, functional water-retaining peptide and drought-enduring bacteria, wherein the drought-tolerant bacteria are endophytic bacillus flexus CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.21705, and the functional water retention peptide is prepared by fermenting bacillus licheniformis CGMCC No.8821. The compound microbial agent disclosed by the invention can be used for improving the activity of crop root systems and the drought resistance and saline-alkali resistance of crops, is particularly suitable for crop planting in arid and semi-arid climate regions, obviously improves the nitrogen fixation performance of crops under arid conditions, obviously improves the adaptive capacity of crop root systems under water drought and saline-alkali stress, improves the stress resistance of crops, and improves the yield of crops. The purposes of improving the soil performance and increasing the yield are achieved, and the method has important significance on improvement of the ecological planting environment of saline-alkali soil in arid and semi-arid regions and sustainable development of modern agriculture.
Owner:领先生物农业股份有限公司
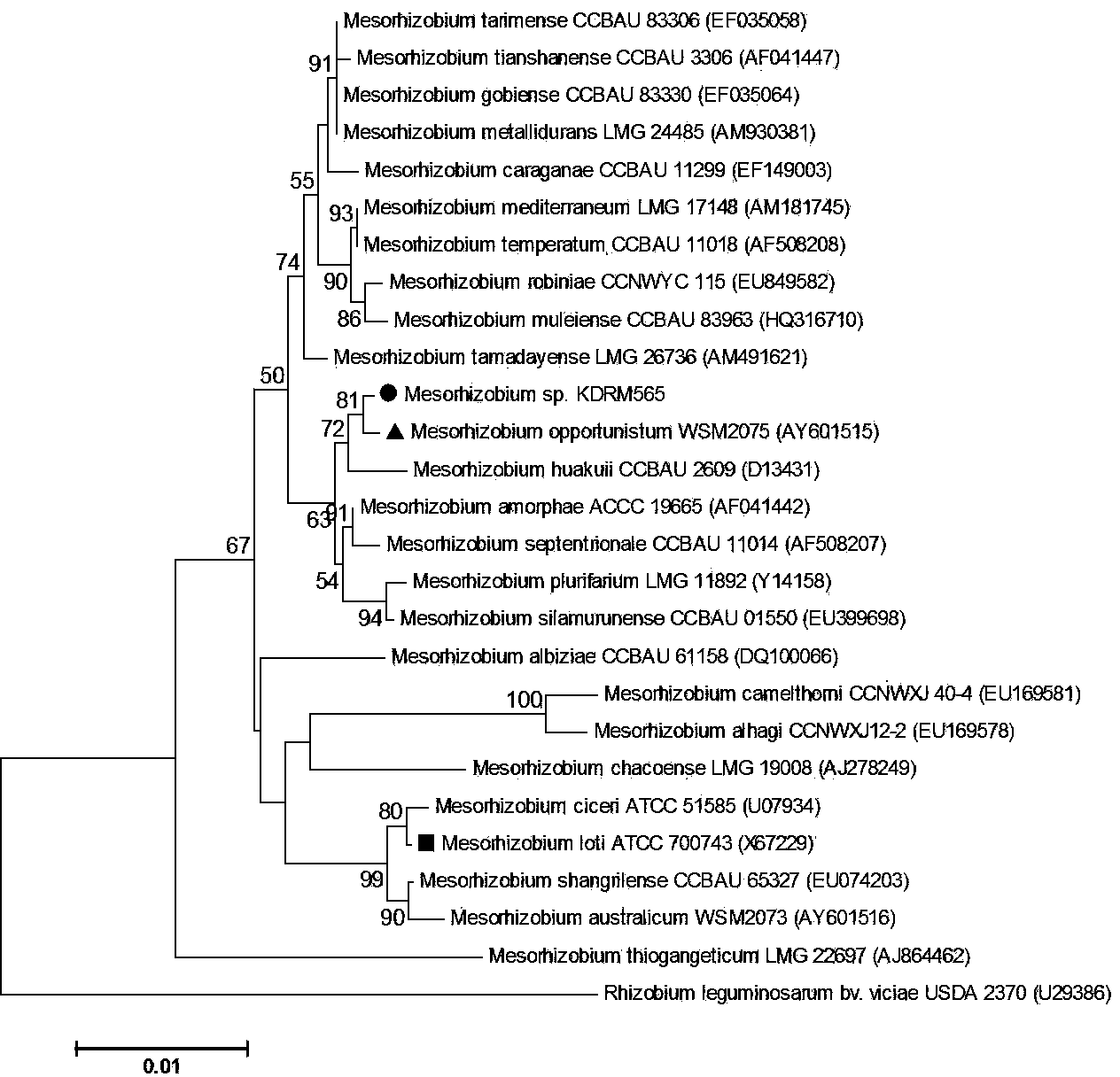
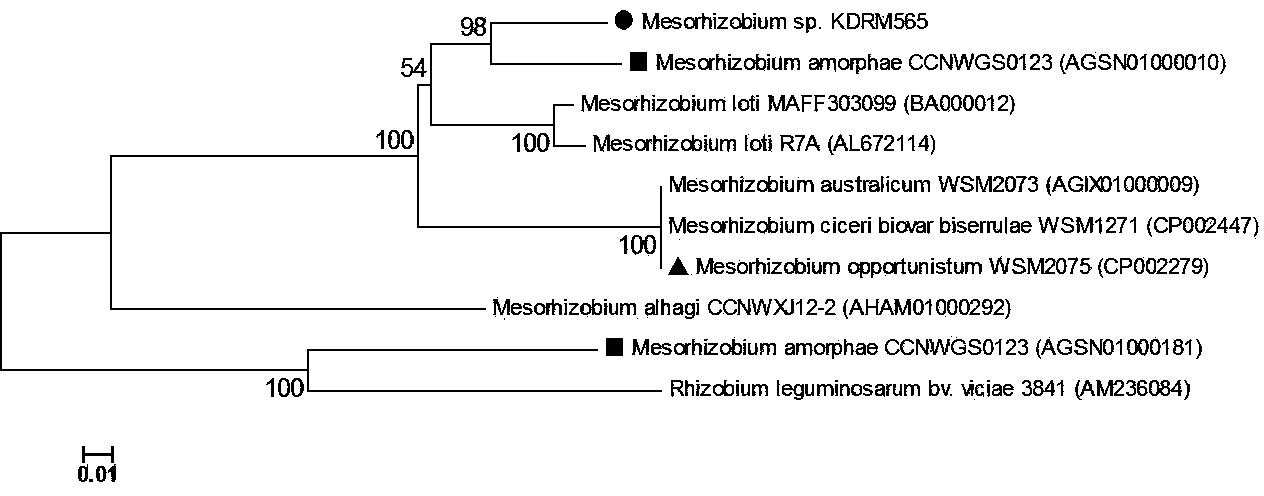
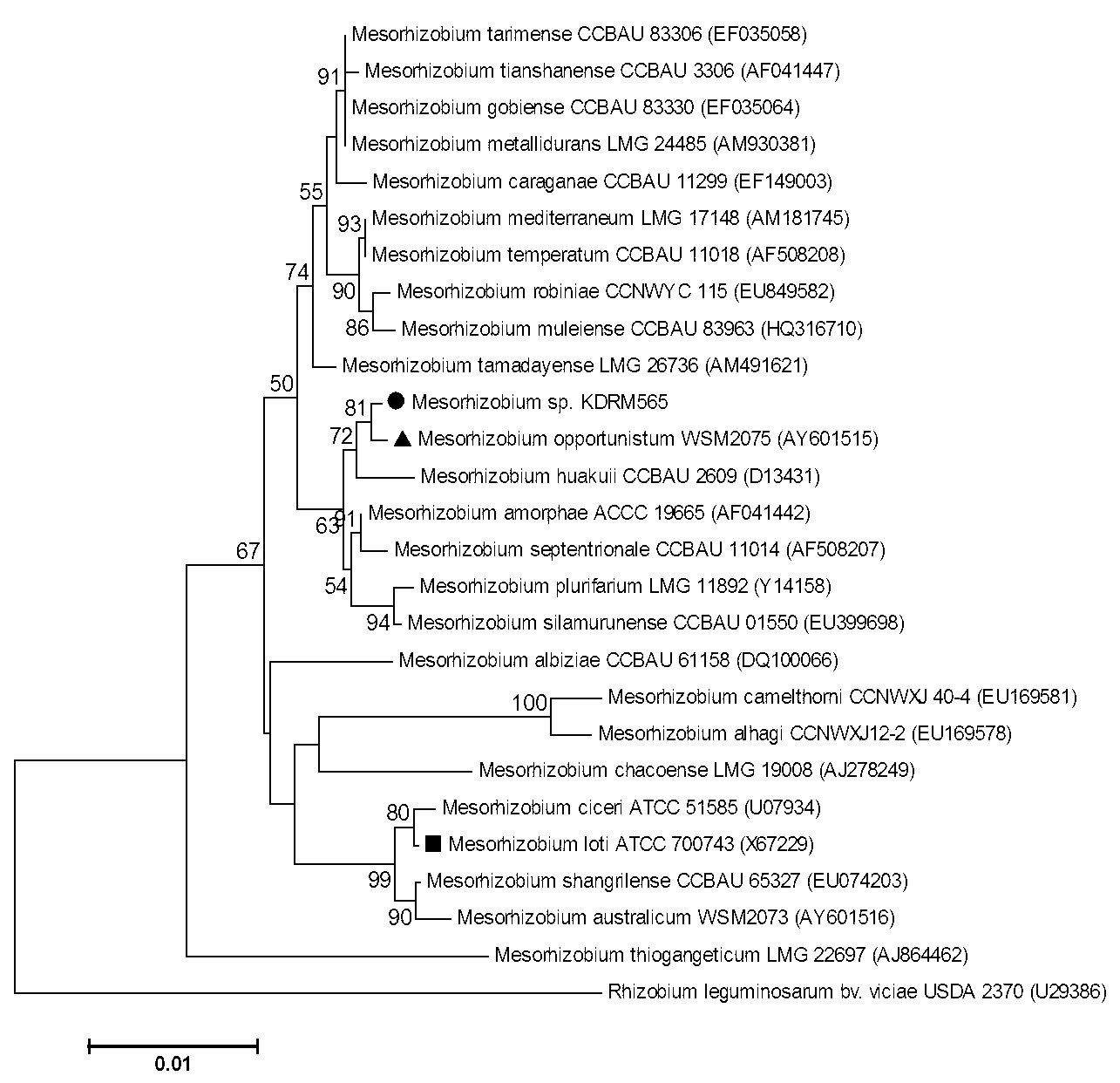
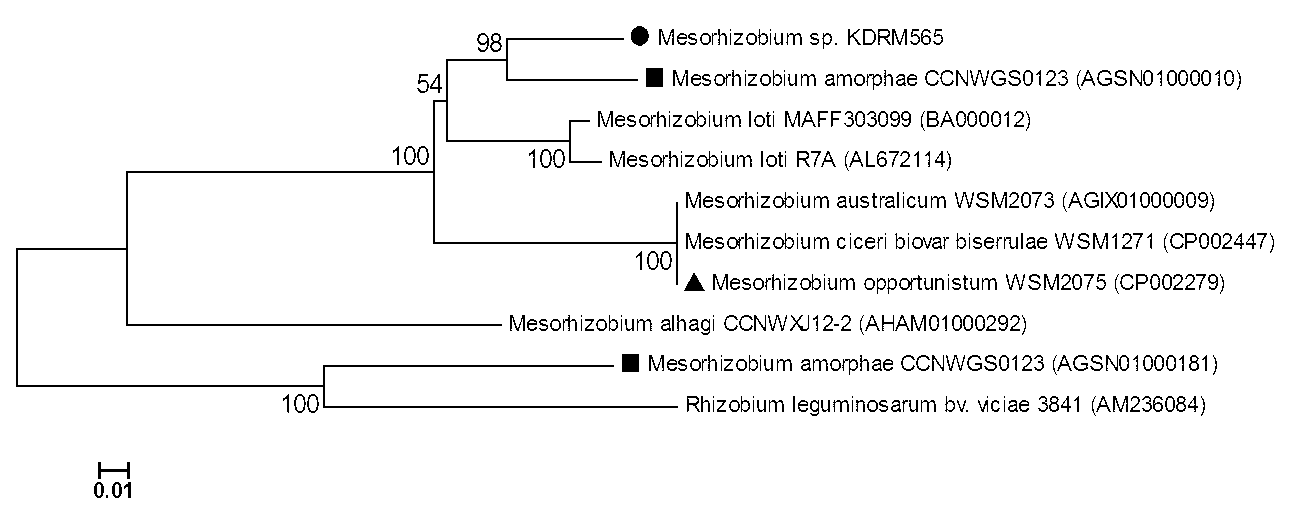
Mesorhizobium KDRM 565 and application thereof
ActiveCN103013857BReduce inhibitionNodulation rate is highPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyPlant nodule
The invention relates to Mesorhizobium KDRM 565 and the application of the Mesorhizobium KDRM 565, wherein the Mesorhizobium KDRM 565 is separated from Robinia pseudoacacia root nodule, contains ACC deaminase and can be used for effective carrying out nodulation and promote growth of Robinia pseudoacacia. The Mesorhizobium KDRM 565 strain is preserved in China Center for Type CultureCollection with the preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2012334. The Mesorhizobium KDRM 565 disclosed by the invention contains ACC deaminase which can decompose ACC into alpha-ketobutyrate and NH3, reduce the level of synthesizing ethylene with plant cells, reduce an inhibition function of ethylene on rhizobium infection, improve the nodulation rate of rhizobium and Robinia pseudoacacia and the level of symbiotic nitrogen fixation, provide high-level nitrogen for the growth of the Robinia pseudoacacia on non-fertilized barren wasteland, promote the growth of seedlings of Robinia pseudoacacia and increase the biomass of mature Robinia pseudoacacia, thereby realizing the high yield the matureRobinia pseudoacacia by using inoculation with low cost, and playing a role in Robinia pseudoacacia culture and forestation.
Owner:ZHONGYING CHANGJIANG INTERNATIONAL NEW ENERGY INVESTMENT CO LTD
A Cassia rhizobia txr2 and its application
InactiveCN109337847BNodulation rate is highStrong nitrogen fixation abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEcological environment
The invention discloses a rhizobia TXR2 and an application thereof, belonging to the technical field of microbes. The strain is isolated and purified from fresh root nodules of Cassia forage, and detected by PCR nodA gene, and identified by 16S rDNA molecular biology, identified as Bradyrhizobium ( Bradyrhizobium ), and named it Tianyuan 2. It was deposited in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on April 10, 2018, with the preservation number CCTCC NO: M2018193. The rhizobia TXR2 of the present invention has been proved by the laboratory potted back grafting test that it has the characteristics of high-efficiency nodulation and strong nitrogen fixation ability, and the inoculation of the rhizobia can significantly improve the number of nodules, nitrogen fixation efficiency of nodules, biomass and plant nitrogen of Cassia herb Content, and then achieve the effect of fertilizing the soil and improving the ecological environment.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
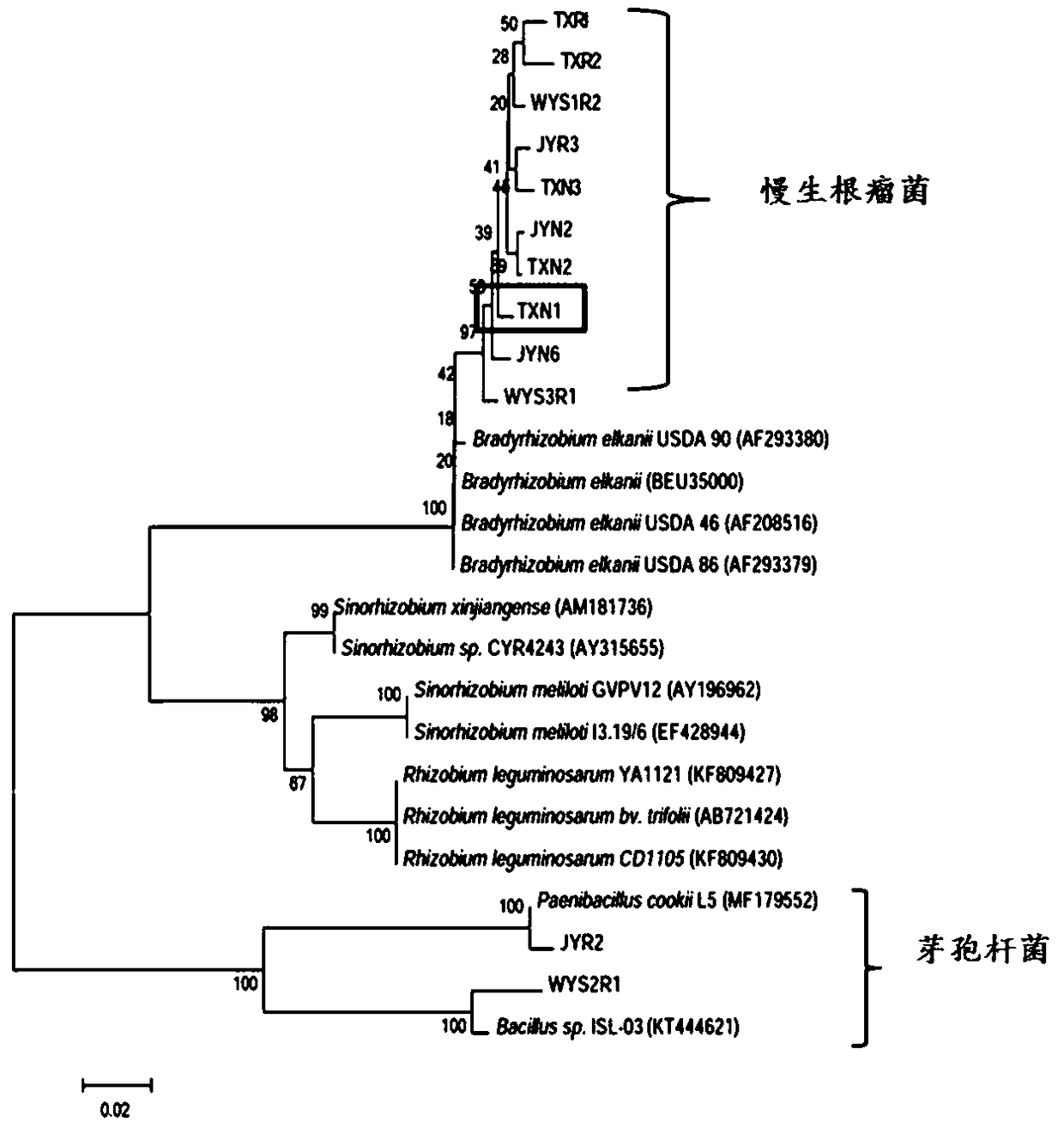
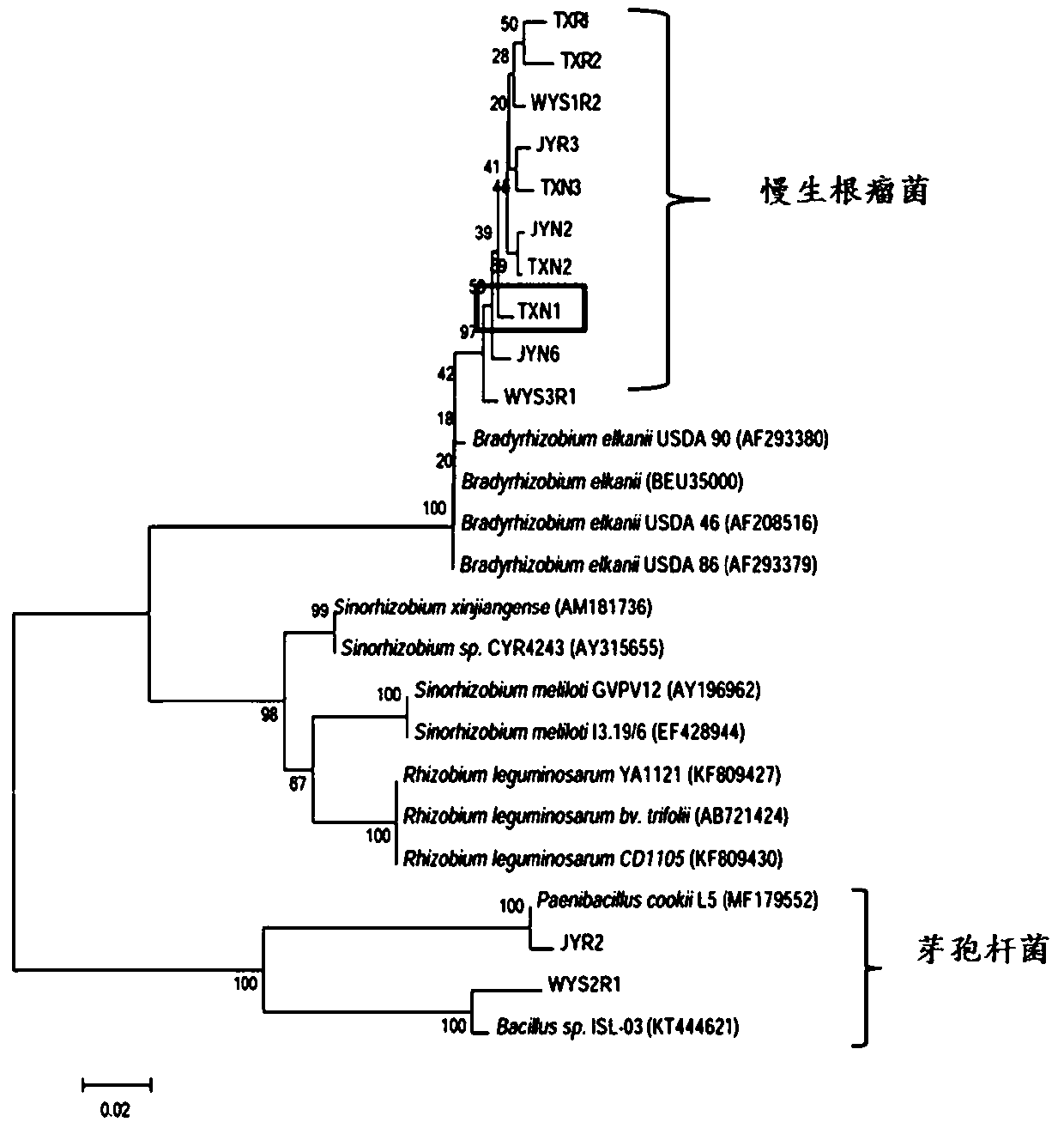
Cassia rhizobium strain TXN1 and application thereof
InactiveCN109294962ANodulation rate is highStrong nitrogen fixation abilityPlant growth regulatorsBiocidePlant noduleEcological environment
The invention discloses a cassia rhizobium strain TXN1 and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of microorganism. The cassia rhizobium strain TXN1 is obtained by being separated andpurified from fresh nodules of cassia grasses and performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection on nodA (nodulation protein A) gene as well as 16S rDNA (ribosomal deoxyribonucleic acid identification) molecular biological detection, determined to be a new strain of Bradyrhizobium and named as Tianyu-1. The cassia rhizobium strain TXN1 is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collectionin April 10, 2018 with a preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2018191. Laboratory pot culture inoculation experiments prove that the cassia rhizobium strain TXN1 has the advantages of efficient nodulation and large nitrogen fixing capacity; inoculation of the cassia rhizobium strain TXN1 can significantly increase the number of root nodules, the root nitrogen fixing efficiency, the biomass and the plant nitrogen content of cassia grasses and further achieve the effects of increasing soil fertility and improving the ecological environment.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Mesorhizobium KDRM295 and application thereof
ActiveCN103045500BReduce inhibitionNodulation rate is highPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyPlant nodule
Owner:ZHONGYING CHANGJIANG INTERNATIONAL NEW ENERGY INVESTMENT CO LTD
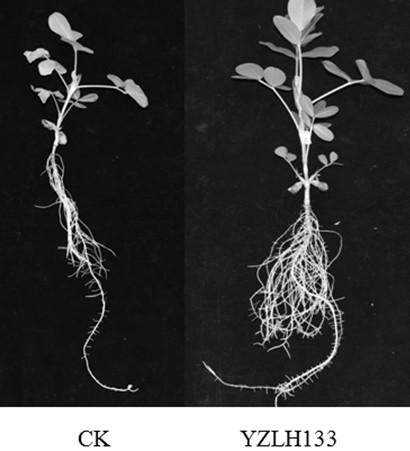
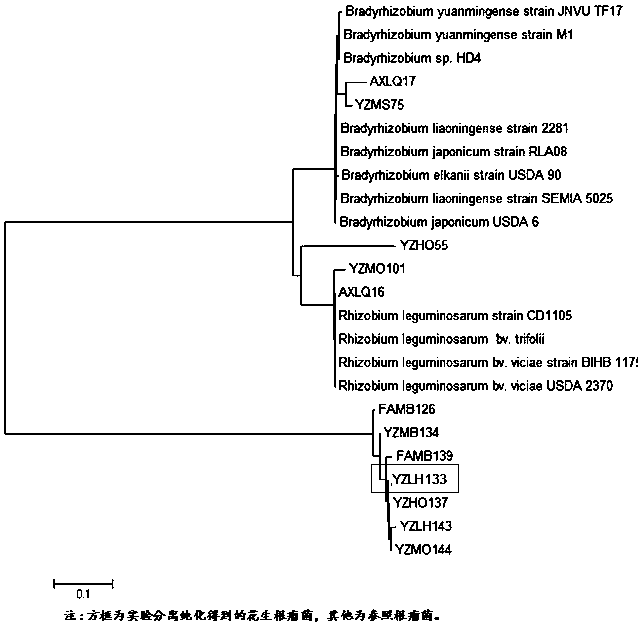
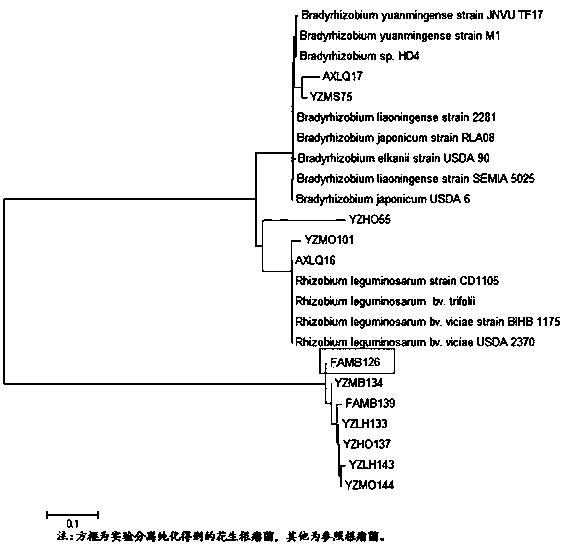
Rhizobium YZLH133 and application thereof
InactiveCN109439589ANodulation rate is highStrong nitrogen fixation abilityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsRoot nodulePhylogenetic profiling
The invention discloses a rhizobium YZLH133 and application thereof. The strain is a new strain which is captured from the soil in Youxi District, Fujian Province through Longhua peanut variety, is separated and purified from fresh nodules, is determined to be Bradyrhizobium through phylogenetic analysis by testing part sequences of 16s rDNA of the strain, and is named Funong 3#. A laboratory hydroponic tieback test and a large field tieback experiment prove that the rhizobium YZLH133 disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of efficient nodulation and strong nitrogen fixing capacity; the biomass and the yield of peanuts can be improved by inoculating the rhizobium; and the rhizobium is applicable to acid soil in South China to serve as one of the measures for conventional cultivation of the peanuts.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
A kind of rhizobia yzm0144 and its application
InactiveCN109355234BNodulation rate is highStrong nitrogen fixation abilityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsRoot nodulePhylogenetic profiling
The invention discloses a rhizobia YZM0144 and its application. The strain is obtained from the rhizobia in the soil of Youxi area, Fujian Province through a new variety of MO peanut, and the rhizobia is separated and purified from fresh nodules, and the strain is of 16s rDNA partial sequence was determined, and through phylogenetic analysis, it was identified as Bradyrhizobium ( Bradyrhizobium ) of the new strain and named it Funong No. 4. The rhizobia YZM0144 of the present invention has the characteristics of high-efficiency nodulation and strong nitrogen fixation ability through laboratory hydroponic backgrafting tests and field backgrafting experiments. Inoculation of the rhizobia can increase peanut biomass and yield, and can be applied to acidic soil in South China , as one of the measures for conventional cultivation of peanuts.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
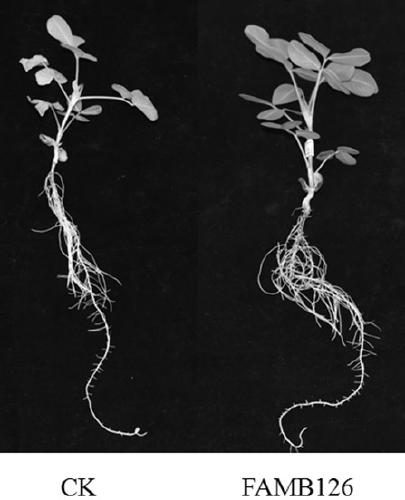
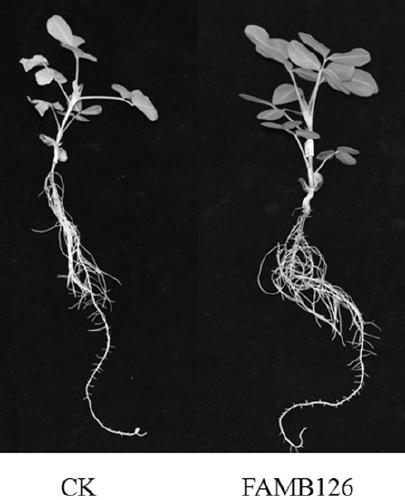
A kind of rhizobia famb126 and its application
InactiveCN109355235BNodulation rate is highStrong nitrogen fixation abilityPlant growth regulatorsBiocideRoot nodulePhylogenetic profiling
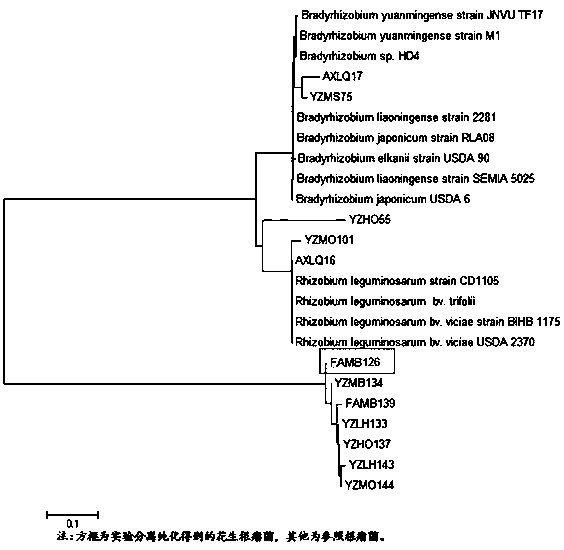
The invention discloses a rhizobia FAMB126 and its application. The strain is obtained from the rhizobia in the soil of Anxi area, Fujian Province by Minhua No. 8 peanut variety, and the rhizobia is separated and purified from fresh nodules, and the strain of 16s The rDNA partial sequence was determined, and through phylogenetic analysis, it was determined to be Bradyrhizobium ( Bradyrhizobium ) of the new strain and named it Funong 2. The rhizobia FAMB126 of the present invention has been proved to have the characteristics of high-efficiency nodulation and strong nitrogen fixation ability through laboratory hydroponic backgrafting tests and field backgrafting experiments. Inoculation of the rhizobia FAMB126 can increase peanut biomass and yield, and can be applied to acidic soil in South China , as one of the measures for conventional cultivation of peanuts.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Mesorhizobium KDRM495 and application thereof
ActiveCN102978139BReduce inhibitionNodulation rate is highBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPlant nodulePlant cell
The invention relates to mesorhizobium KDRM495 and application thereof. The mesorhizobium KDRM495 is separated from acacia root nodule, contains ACC deaminase, and can efficiently nodulate and promotes acacia growth. A mesorhizobium KDRM495 strain is collected in CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection), and the collection number is CCTCC No: M2012333. The mesorhizobium KDRM495 disclosed by the invention contains the ACC deaminase which can decompose ACC into alpha-ketobutyrate and NH3, lowers the level of synthesizing ethylene from plant cells, reduces the inhibiting effect of ethylene on rhizobium infestation, enhances the nodulation rate and symbiotic nitrogen fixation level of rhizobia and acacia, provides the high-level nitrogen for the growth of the acacia on unfertilized sterile wastelands, promotes the growth of acacia seedlings and increases the biomass of acacia lumbers, thereby achieving the high yield of the acacia lumbers through low-cost inoculation investment and playing a role in the aspect of acacia seedling culture and forestation.
Owner:ZHONGYING CHANGJIANG INTERNATIONAL NEW ENERGY INVESTMENT CO LTD
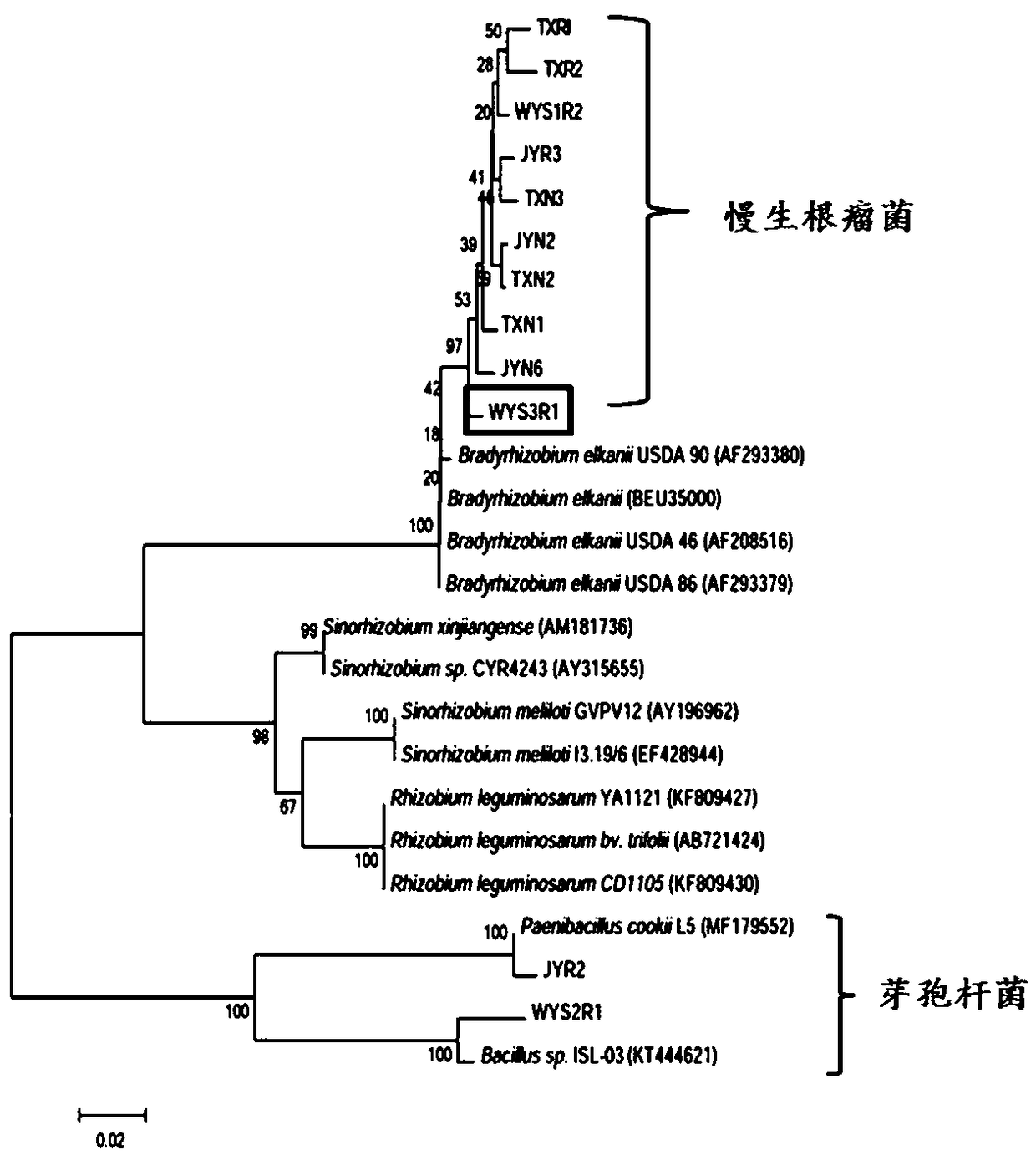
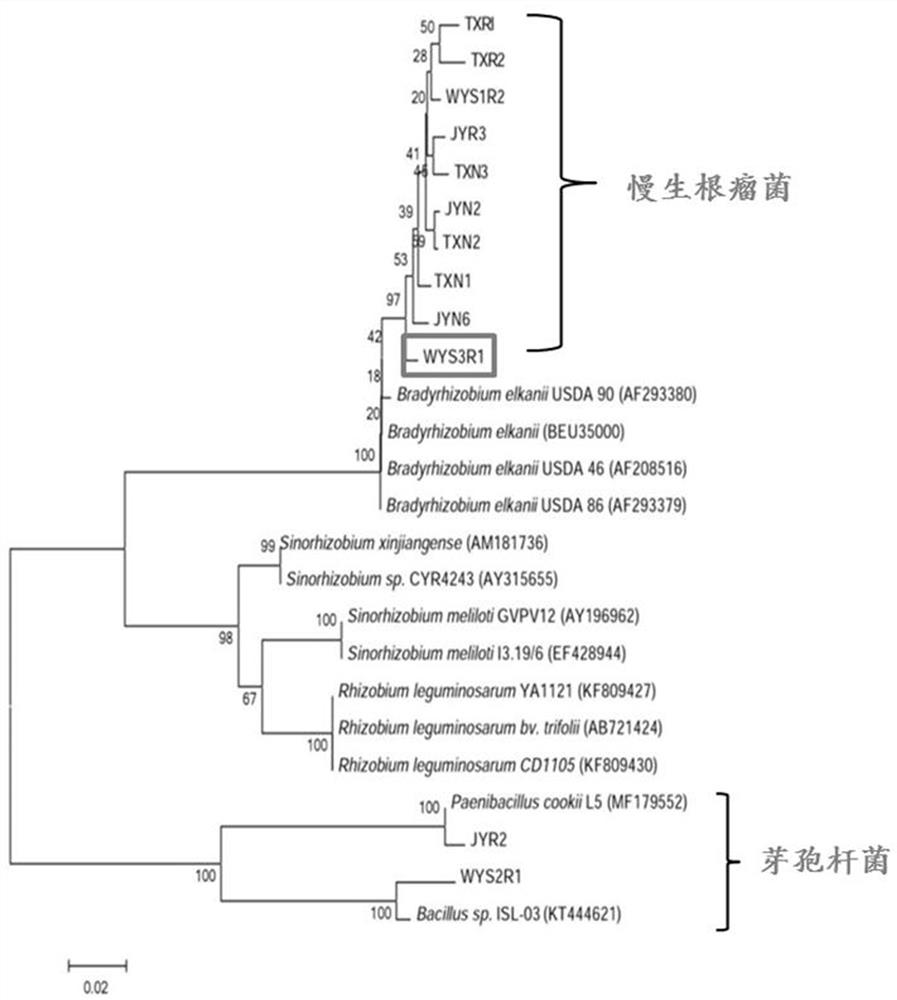
Chamaecrista bradyrhizobiumsp. WYS3R1 and application thereof
InactiveCN109439590ANodulation rate is highStrong nitrogen fixation abilityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMicroorganismRoot nodule
The invention discloses chamaecrista bradyrhizobiumsp. WYS3R1 and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. A strain line is separated and purified from fresh chamaecrista grass nodule; nodA gene is detected by PCR; a novel strain line of Bradyrhizobium is determined by biological assay of 16S rDNA molecule and is named as Wuyuan 1. The chamaecrista bradyrhizobiumsp. WYS3R1 was preserved in China Center for Type CultureCollection on April 10th, 2018, with a preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2018190. The bonsai tieback test in a laboratory proves that the bradyrhizobiumsp. WYS3R1 disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of efficient nodulation and nitrogen fixation capabilities; by inoculating the bradyrhizobiumsp., nodule number, nodule nitrogen fixation efficiency and the biomass of chamaecrista grass and nitrogen content of plants can be obviously improved, and further the effects of culturing soil fertility and improving ecological environment are realized.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
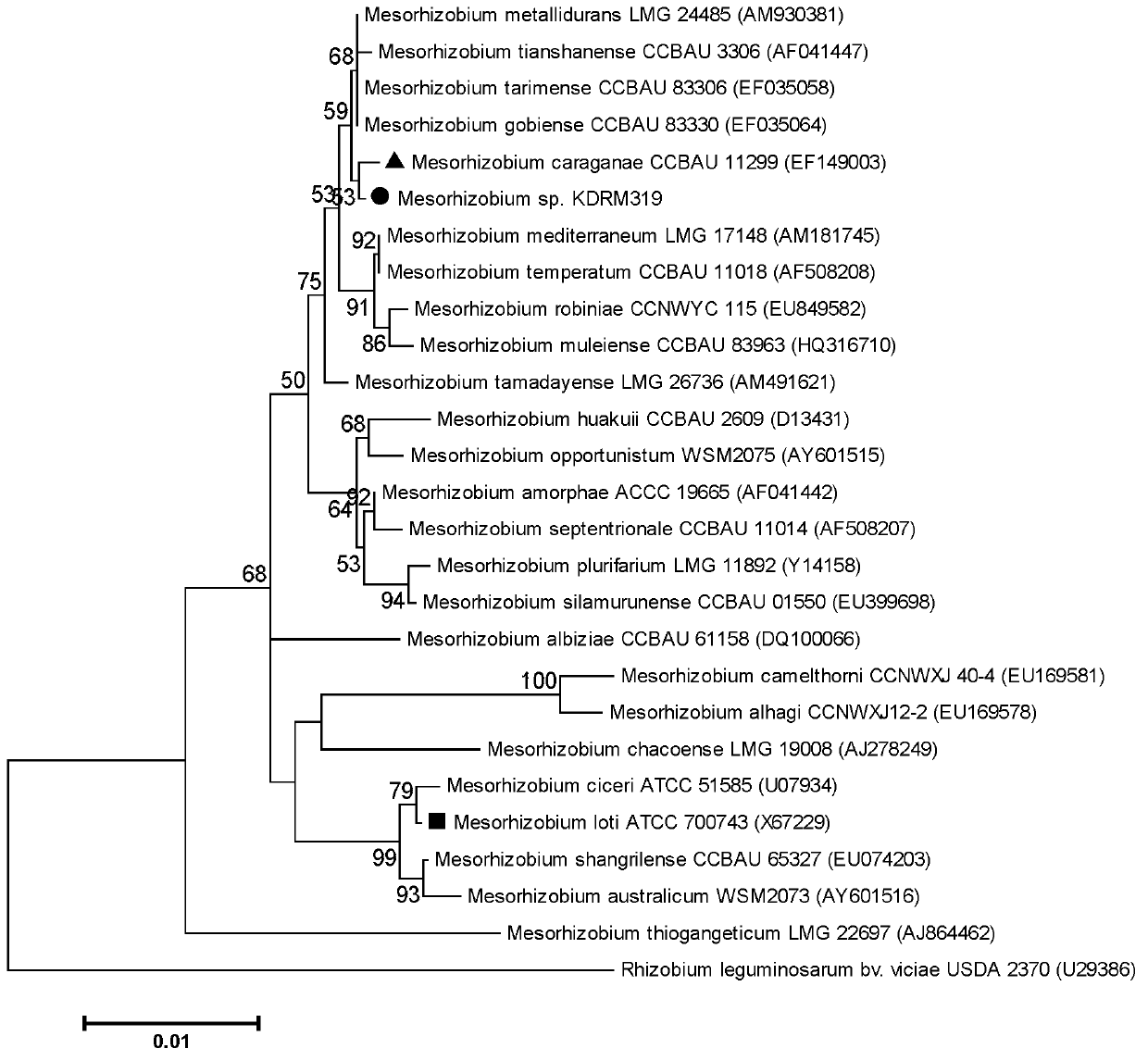
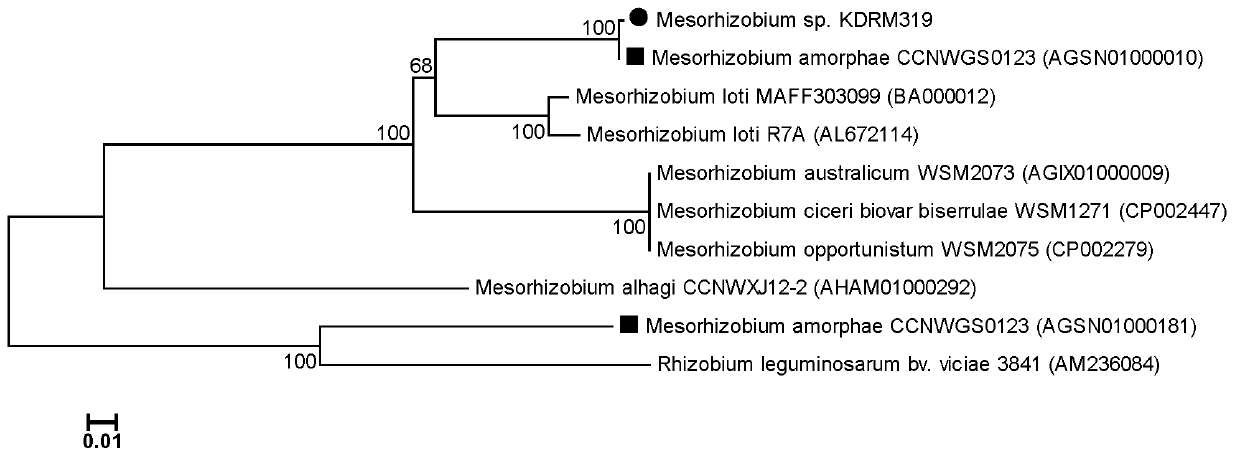
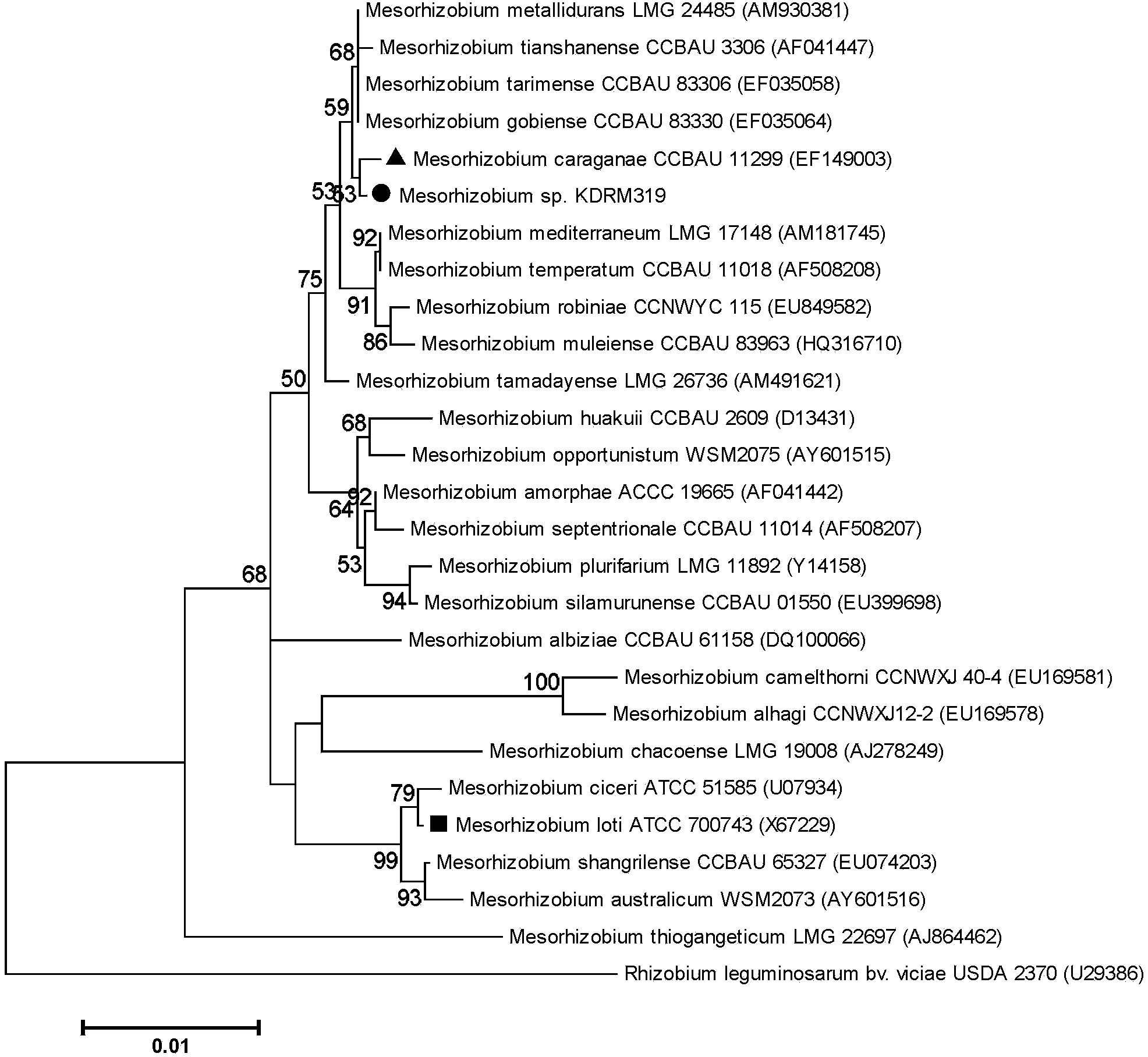
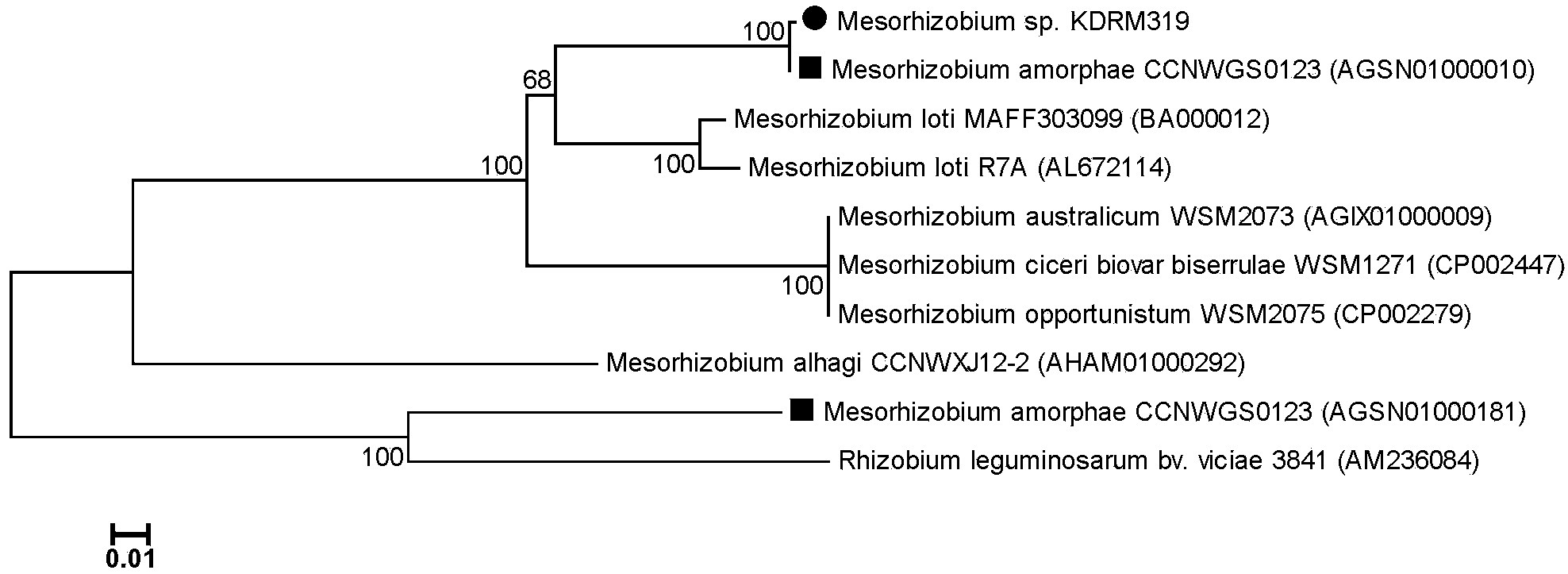
Mesorhizobium KDRM319 and application thereof
ActiveCN102978137AReduce inhibitionNodulation rate is highBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPlant nodulePlant cell
The invention relates to mesorhizobium KDRM319 and application thereof. The mesorhizobium KDRM319 is separated from acacia root nodule, contains ACC deaminase and can efficiently nodulate and promote acacia growth. A mesorhizobium KDRM319 strain is collected in CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection), and the collection number is CCTCC NO.M2012332. The mesorhizobium KDRM319 disclosed by the invention contains the ACC deaminase which can decompose ACC into alpha-ketobutyrate and NH3, lowers the level of synthesizing ethylene from plant cells, reduces the inhibiting effect of ethylene on rhizobium infestation, enhances the nodulation rate and symbiotic nitrogen fixation level of rhizobia and acacia, provides the high-level nitrogen for the growth of the acacia on unfertilized sterile wastelands, promotes the growth of acacia seedlings and increases the biomass of acacia lumbers, thereby achieving the high yield of the acacia lumbers through low-cost inoculation investment and playing a role in the aspect of acacia seedling culture and forestation.
Owner:ZHONGYING CHANGJIANG INTERNATIONAL NEW ENERGY INVESTMENT CO LTD
Rhizobium YZM0144 and application thereof
InactiveCN109355234ANodulation rate is highStrong nitrogen fixation abilityPlant growth regulatorsBiocidePlant noduleBradyrhizobium species
The invention discloses rhizobium YZM0144 and application thereof. The rhizobium YZM0144 is obtained by collecting rhizobium in soil of Youxi area of Fujian Province through a MO peanut novel variety,the rhizobium is separated and purified from fresh nodules, a 16s rDNA partial sequence of a strain is determined and identified as a novel strain of Bradyrhizobium by a phylogenetic analysis, and the rhizobium is named as Funong No. 4. The rhizobium YZM0144 proves that the rhizobium has the advantages of high-efficiency nodulation and strong nitrogen-fixing ability through laboratory hydroponicreturning experiments and field returning experiments, inoculation of the rhizobium can increase peanut biomass and yield, and the rhizobium can be applied to acid soil in South China as one of the measures for the routine cultivation of peanuts.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Mesorhizobium KDRM185 and application thereof
ActiveCN102978138BReduce inhibitionNodulation rate is highBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlant nodulePlant cell
Owner:ZHONGYING CHANGJIANG INTERNATIONAL NEW ENERGY INVESTMENT CO LTD
A Rhizobium wys3r1 Strain of Cassia and Its Application
InactiveCN109439590BNodulation rate is highStrong nitrogen fixation abilityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsEcological environmentBradyrhizobium
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Mesorhizobium KDRM 565 and application thereof
ActiveCN103013857AReduce inhibitionIncreased nodulation rates and levels of symbiotic nitrogen fixationPlant growth regulatorsBiocideRhizobiumSeedling
The invention relates to Mesorhizobium KDRM 565 and the application of the Mesorhizobium KDRM 565, wherein the Mesorhizobium KDRM 565 is separated from Robinia pseudoacacia root nodule, contains ACC deaminase and can be used for effective carrying out nodulation and promote growth of Robinia pseudoacacia. The Mesorhizobium KDRM 565 strain is preserved in China Center for Type CultureCollection with the preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2012334. The Mesorhizobium KDRM 565 disclosed by the invention contains ACC deaminase which can decompose ACC into alpha-ketobutyrate and NH3, reduce the level of synthesizing ethylene with plant cells, reduce an inhibition function of ethylene on rhizobium infection, improve the nodulation rate of rhizobium and Robinia pseudoacacia and the level of symbiotic nitrogen fixation, provide high-level nitrogen for the growth of the Robinia pseudoacacia on non-fertilized barren wasteland, promote the growth of seedlings of Robinia pseudoacacia and increase the biomass of mature Robinia pseudoacacia, thereby realizing the high yield the matureRobinia pseudoacacia by using inoculation with low cost, and playing a role in Robinia pseudoacacia culture and forestation.
Owner:ZHONGYING CHANGJIANG INTERNATIONAL NEW ENERGY INVESTMENT CO LTD
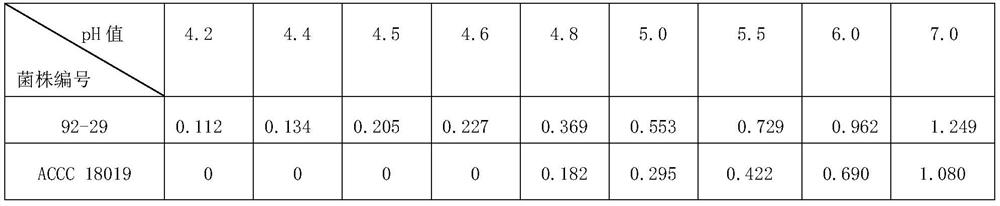
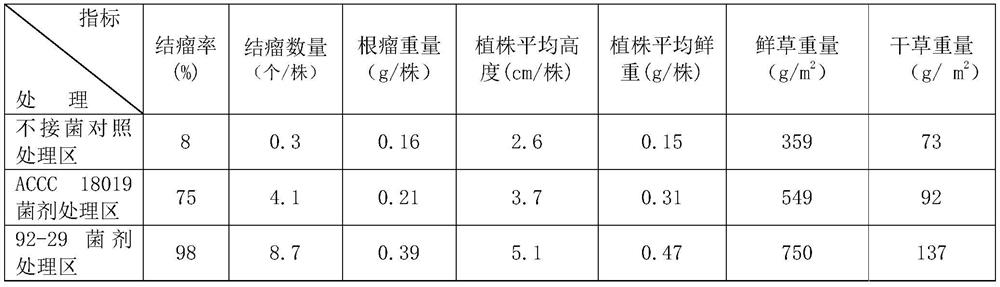
Method for promoting the growth of clover and/or increasing the yield of clover and inoculum used therefor
ActiveCN108841761BPromote growthIncrease productionPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyFungicide
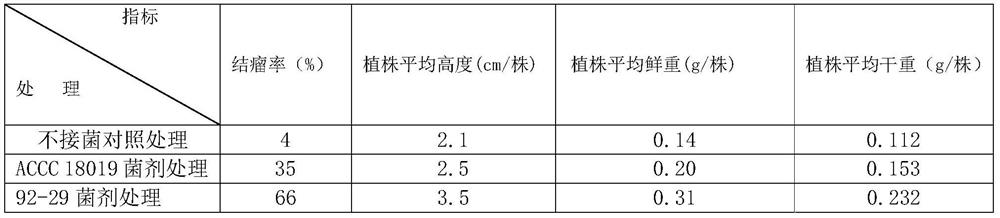
The invention discloses a method for promoting the growth of clover and / or increasing the yield of clover and the bacterial agent used therein. The method for promoting the growth of clover and / or increasing the yield of clover comprises the step of mixing the seeds of clover with the inoculum before sowing the soil; the inoculation contains the metabolites of Rhizobium clover or / and the Rhizobium clover ; The strain number of the Rhizobium clover bacteria is 92-29, and its preservation number in the General Microorganism Center of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee is CGMCC No.15533. Clover rhizobia 92-29 of the present invention significantly promotes the growth of clover and significantly improves the output of clover under acidic soil conditions: improve the plant height, nodulation rate, root nodule number and / or root nodule weight of clover; increase the plant fresh weight and dry weight of clover Heavy, increases clover's fresh grass yield and dry grass yield. The invention has broad application prospects in the clover planting industry.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
A Cassia rhizobia txn1 and its application
InactiveCN109294962BNodulation rate is highStrong nitrogen fixation abilityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPlant noduleEcological environment
The invention discloses a strain of rhizobia TXN1 and its application, belonging to the technical field of microbes. The strain is isolated and purified from fresh root nodules of Cassia forage, and detected by PCR nodA gene, and identified by 16S rDNA molecular biology, identified as Bradyrhizobium ( Bradyrhizobium ), and named it Tianyu No. 1. It was deposited in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on April 10, 2018, and the deposit number is CCTCC NO: M2018191. The nitrogen-fixing bacterium strain TXN1 of the present invention proves that it has the characteristics of high-efficiency nodulation and strong nitrogen fixation ability through laboratory pot plant backgrafting experiments, and the inoculation of the rhizobia can significantly increase the number of nodules, nitrogen fixation efficiency of nodules, biomass and The nitrogen content of the plant can be increased to achieve the effect of fertilizing the soil and improving the ecological environment.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
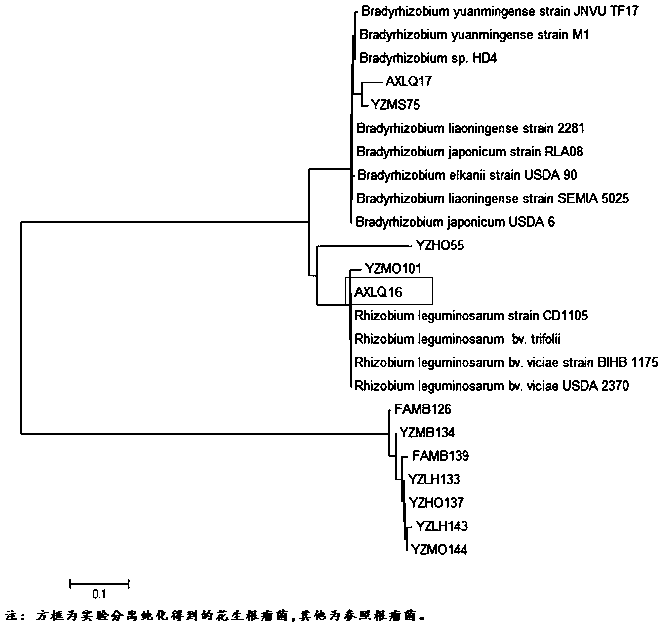
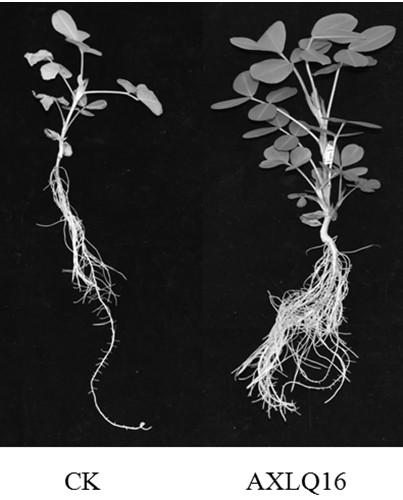
A kind of rhizobia axlq16 and its application
InactiveCN109486711BNodulation rate is highStrong nitrogen fixation abilityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsRoot noduleSouth china
The invention discloses a kind of rhizobia AXLQ16 and its application. The strain is obtained from the rhizobia in the soil of Anxi area, Fujian Province by Minhua No. 11 peanut variety, the rhizobia is separated and purified from fresh nodules, and the The 16S rDNA partial sequence was determined, and through phylogenetic analysis, it was identified as the genus Rapid-growing Rhizobium ( Rhizobium ) of the new strain and named it Funong No. 1. The rhizobia AXLQ16 of the present invention has been proved to have the characteristics of high-efficiency nodulation and strong nitrogen fixation ability through laboratory hydroponic backgrafting tests and field backgrafting experiments. Inoculation of the rhizobia AXLQ16 can increase peanut biomass and yield, and can be applied to acidic soil in South China , as one of the measures for conventional cultivation of peanuts.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Mesorhizobium KDRM319 and application thereof
ActiveCN102978137BReduce inhibitionNodulation rate is highBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPlant nodulePlant cell
The invention relates to mesorhizobium KDRM319 and application thereof. The mesorhizobium KDRM319 is separated from acacia root nodule, contains ACC deaminase and can efficiently nodulate and promote acacia growth. A mesorhizobium KDRM319 strain is collected in CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection), and the collection number is CCTCC NO.M2012332. The mesorhizobium KDRM319 disclosed by the invention contains the ACC deaminase which can decompose ACC into alpha-ketobutyrate and NH3, lowers the level of synthesizing ethylene from plant cells, reduces the inhibiting effect of ethylene on rhizobium infestation, enhances the nodulation rate and symbiotic nitrogen fixation level of rhizobia and acacia, provides the high-level nitrogen for the growth of the acacia on unfertilized sterile wastelands, promotes the growth of acacia seedlings and increases the biomass of acacia lumbers, thereby achieving the high yield of the acacia lumbers through low-cost inoculation investment and playing a role in the aspect of acacia seedling culture and forestation.
Owner:ZHONGYING CHANGJIANG INTERNATIONAL NEW ENERGY INVESTMENT CO LTD
Rhizobium FAMB126 and application thereof
InactiveCN109355235ANodulation rate is highStrong nitrogen fixation abilityPlant growth regulatorsBiocideRhizobiumBiomass
The invention discloses rhizobium FAMB126 and application thereof. The rhizobium FAMB126 is obtained by collecting rhizobium in soil of Anxi area of Fujian Province through a peanut variety of MinhuaNo.8, the rhizobium is separated and purified from fresh nodules, a 16s rDNA partial sequence of a strain is determined and identified as a novel strain of Bradyrhizobium by a phylogenetic analysis, and the rhizobium is named as Funong No. 2. The rhizobium FAMB126 proves that the rhizobium has the advantages of high-efficiency nodulation and strong nitrogen-fixing ability through laboratory hydroponic returning experiments and field returning experiments, inoculation of the rhizobium can increase peanut biomass and yield, and the rhizobium can be applied to acid soil in South China as one of the measures for the routine cultivation of peanuts.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com