Saline-alkali soil resistant nitrogen fixation rhizobium japonicum and application thereof
A technology for saline-alkali soil and slow rhizobium, which is applied in the field of agricultural microorganisms, can solve problems such as inability to apply to alkaline soil, and achieves the effects of strong nitrogen fixation ability, increased total nitrogen content, and increased nitrogen content.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1 Isolation and purification of strains
[0039] Collect the nodules on the soybean roots cultivated in the rocky desertification area of Xingyi, Guizhou, select fresh and full nodules, soak the nodules in sterile water for 5-6 minutes in the ultra-clean bench, remove the impurities on the surface, and use 75% anhydrous ethanol. After surface disinfection for 3 to 5 minutes, disinfect with 3.5% NaClO for 8 minutes, and then rinse it with sterile water for 9 to 10 times; then cut a single root nodule with a sterilized knife, and then clamp the root nodule with tweezers. The solid YMA medium was streaked and cultured upside down in a constant temperature incubator at 28°C for 5 to 7 days until clear colonies grew. The obtained rhizobia monoclones were streaked and purified 3-4 times until clear monoclones were grown, single colonies were picked to transfer slants, and stored at 4°C at low temperature, and the obtained strains were named as Dian strains.
[0040...
Embodiment 2
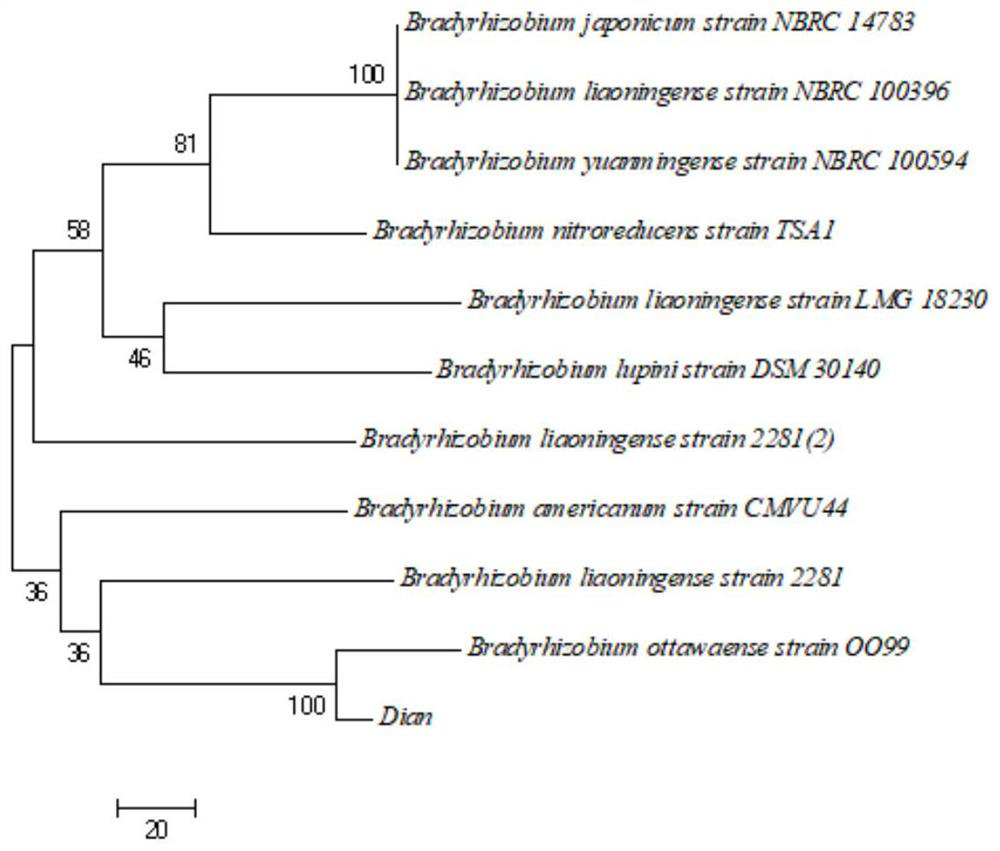
[0042] Example 2 Identification of bacterial strains
[0043] 1. Morphological identification of strains
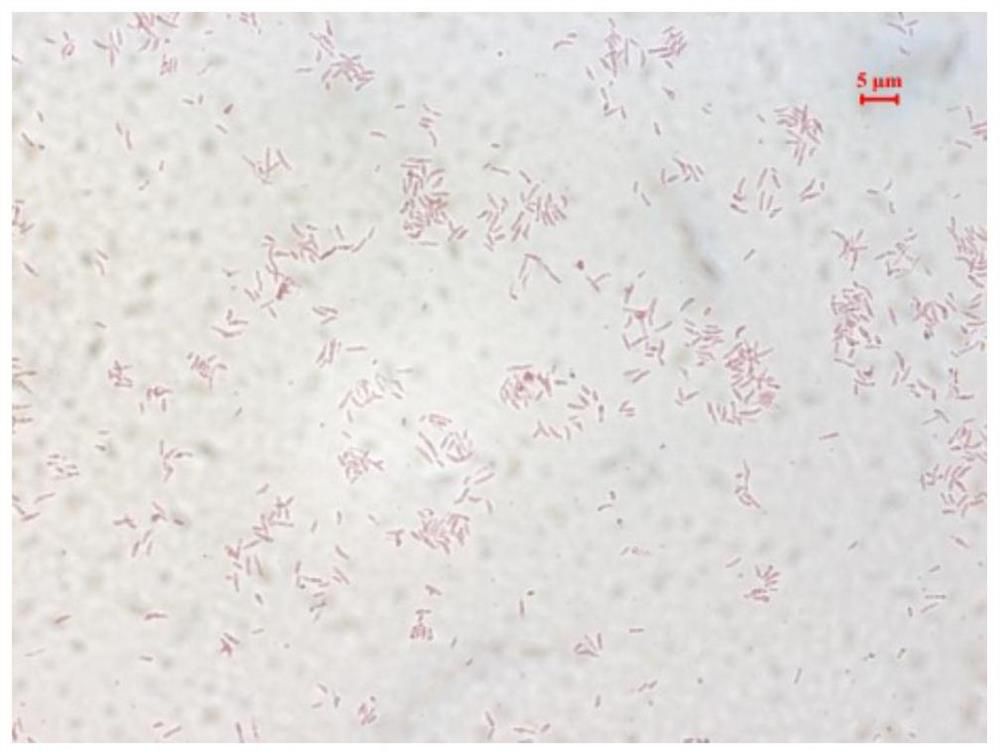
[0044] The Dian strain isolated in Example 1 was inoculated on YMA solid medium for cultivation, and recorded. After culturing for 5 to 7 days under the optimum growth conditions of pH 7.0 and temperature of 28 °C, the isolated and purified strain Dian was subjected to single colony state observation, mainly including colony size, color, transparency, wetness, colony surface state, and colony edge. state. At the same time, for the Dian strain in the logarithmic growth phase, the morphology of the bacteria was observed by light microscope after smear staining.
[0045] The result is as figure 1 shown, indicating that the Dian strain is Gram-negative, short rod-shaped, without spores, most of which are motile. Grow on solid YMA medium plate, the colony shape is approximately round, milky white, translucent, neat edge, more sticky, colony diameter of 0.8mm ~ 1mm.
[004...
Embodiment 3
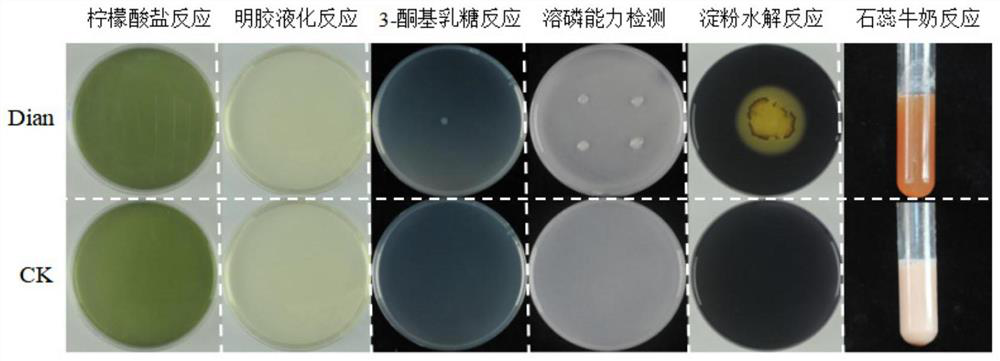
[0055] Example 3 Performance identification of soybean rhizobia Dian strain
[0056] Prepare 1L YMA liquid medium, divide it into 3 conical flasks, and sterilize it at 121°C for 20min; pipette 100μL of the rhizobial liquid that has been purified and reach the logarithmic growth phase into the triangle containing YMA medium. In the bottle, shake at 180 r / min overnight on a shaker at 28 °C to the OD of the bacterial solution 600 After the value reaches 0.6±0.05, it is divided into sterilized 50mL centrifuge tubes, centrifuged at 5000rpm in a centrifuge for 10min, taken out, poured off the supernatant, and resuspended with low nitrogen nutrient solution to obtain a bacterial suspension for later use.
[0057] Take 5 μL of the prepared rhizobia suspension on the soluble starch solid medium for spot plate inoculation, incubate in a constant temperature incubator at 28°C for 3 to 5 days until obvious single clones appear, and evenly add iodine solution on the plate, around the colon...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com