Fermentation medium, bacterial strain and production method for fermentation production of adenosine cyclophosphate
A fermentation medium and cyclic adenosine monophosphate technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of expensive raw materials, complicated process, and many by-products, and achieve the effect of low raw material cost, simple operation, and many by-products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
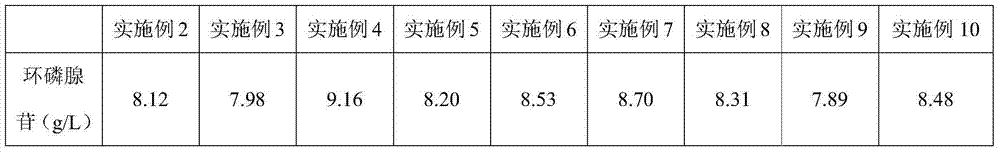
Examples
Embodiment 1
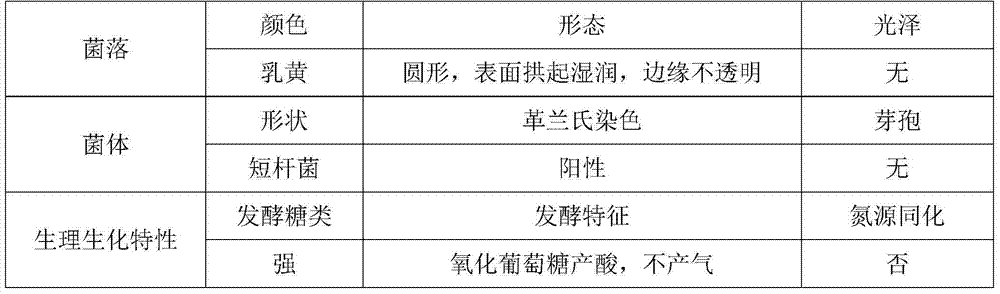
[0022] This embodiment is a screening method for bacterial strains that ferment and produce cyclic adenosine monophosphate, comprising the following steps:
[0023] Soil samples collected from a soil rich in organic matter are inoculated in an enrichment medium with hypoxanthine as a substrate for enrichment and isolation culture. Focusing on the appearance of the colony, observe the shape of the bacteria with a microscope, and obtain a number of Arthrobacter strains. After multiple purifications, they were respectively inserted into the slope, and stored in the refrigerator at 4°C for later use. The five purified strains were selected and named A.sp01, A.sp02, A.sp03, A.sp04, A.sp5 respectively.
[0024] A.sp01, A.sp02, A.sp03, A.sp04, A.sp5 strains were respectively inoculated in 100mL microbial enrichment medium for shaking culture at 42°C, and the conversion of hypoxanthine was measured every day. After complete conversion, the conversion time was recorded, and A.sp01 had...
Embodiment 2
[0052] The fermentation medium for producing cyclic adenosine monophosphate in this example includes the following mass fractions: glucose 5%, peptone 0.5%, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 1%, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 1%, magnesium sulfate 0.3%, urea 1%, purine base 0.3%; pH natural.
[0053] The method for fermentatively producing cyclic adenosine monophosphate of the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0054] 1) Inoculate the A.sp01 strain on the prepared slant medium, and incubate at a constant temperature of 30°C for 48 hours until a large number of colonies grow;
[0055] 2) Pick colonies and inoculate them in the seed medium for 3 days with shaking at 28°C and 160rpm;
[0056] 3) Inoculate the seed liquid in step 2) into the fermentation medium at an inoculum amount of 5% for fermentation and culture, and ferment and cultivate for 60 hours at 28°C and 60% dissolved oxygen.
Embodiment 3
[0058] The fermentation medium for producing cyclic adenosine monophosphate in this example includes the following mass fractions: glucose 5%, peptone 0.5%, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 1%, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 1%, magnesium sulfate 0.3%, urea 1%, purine base 0.3%; pH natural.
[0059] The method for fermentatively producing cyclic adenosine monophosphate of the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0060] 1) Inoculate the A.sp01 strain on the prepared slant medium, and incubate at a constant temperature of 33°C for 42 hours until a large number of colonies grow;
[0061] 2) Pick colonies and inoculate them in the seed medium for 1 day with shaking at 37°C and 160rpm;
[0062] 3) Inoculate the seed solution in step 2) into the fermentation medium at an inoculum amount of 5% for fermentation and culture, and ferment and cultivate for 65 hours at 32°C and 62% dissolved oxygen.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com