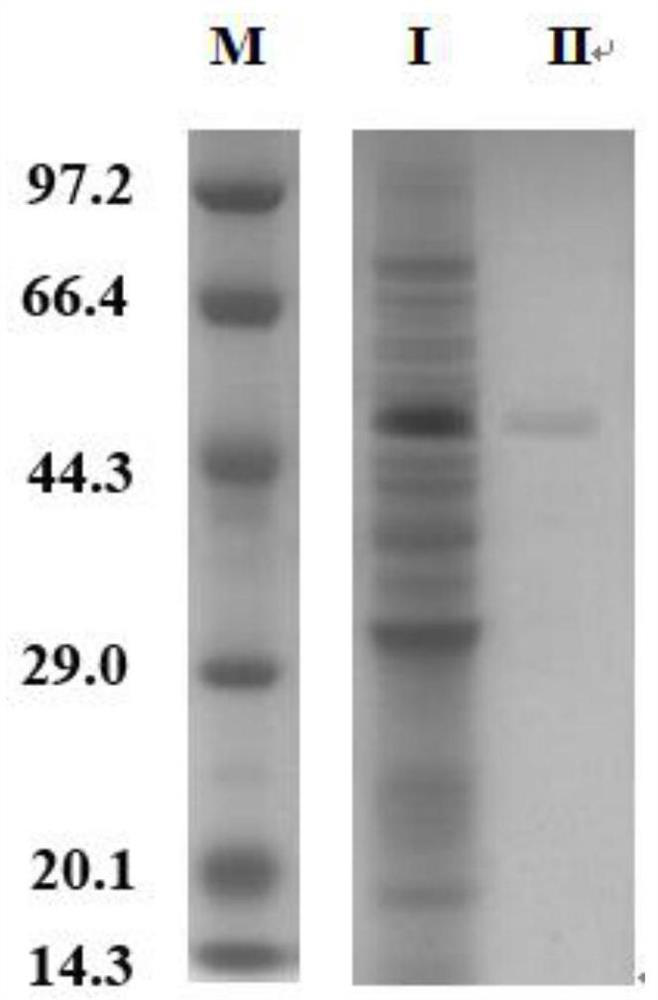
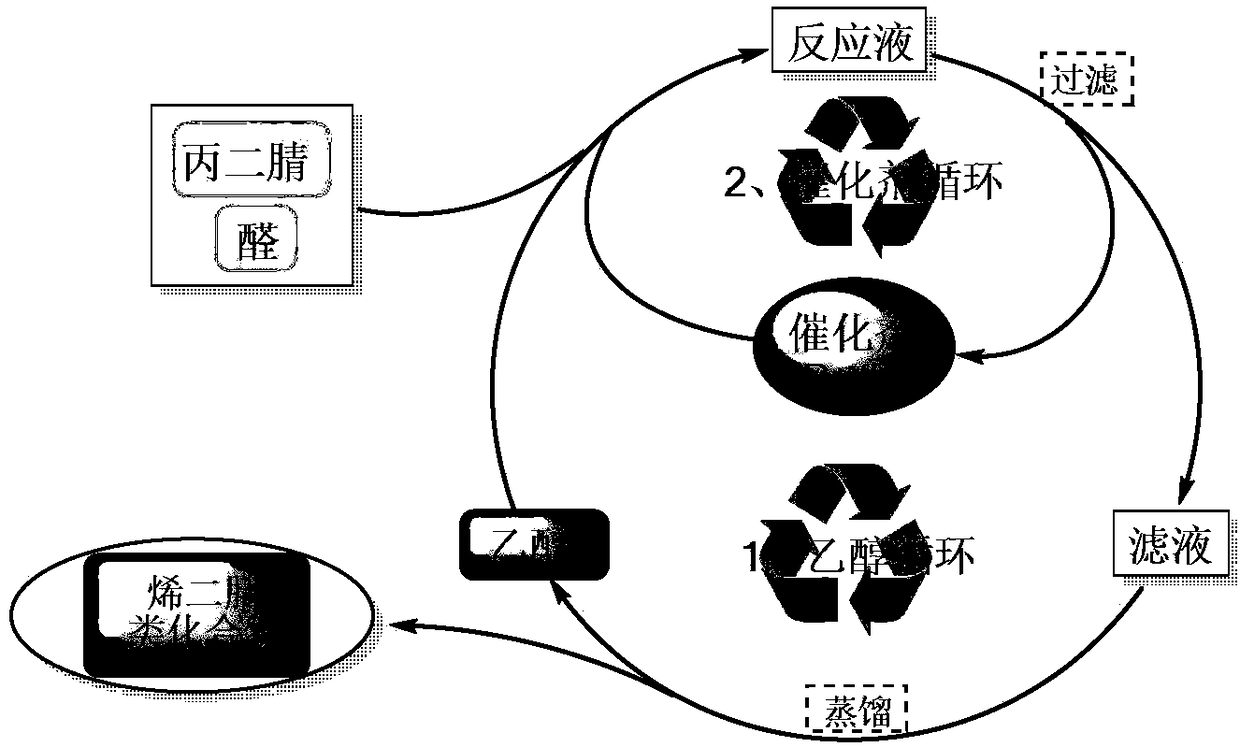
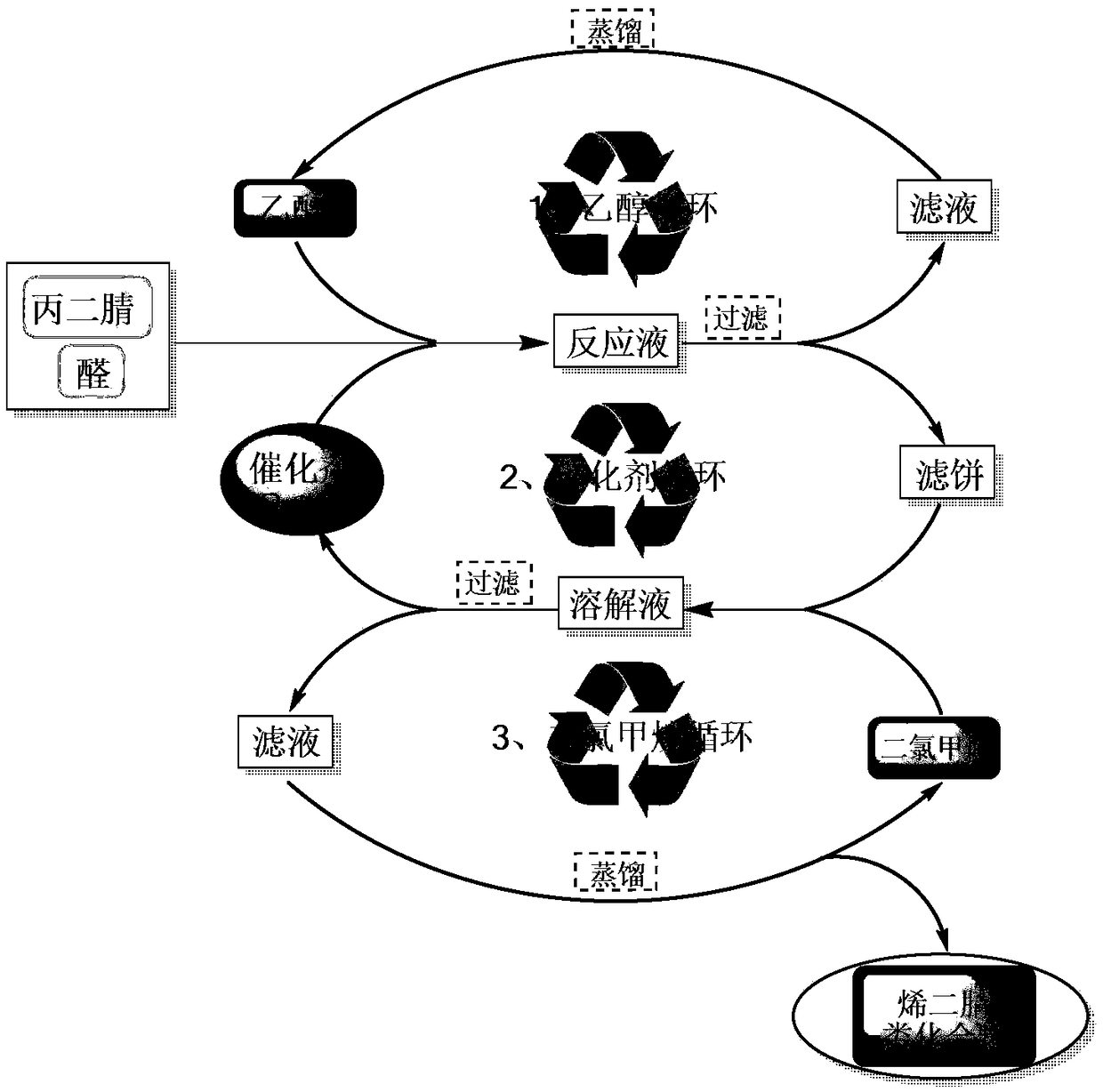
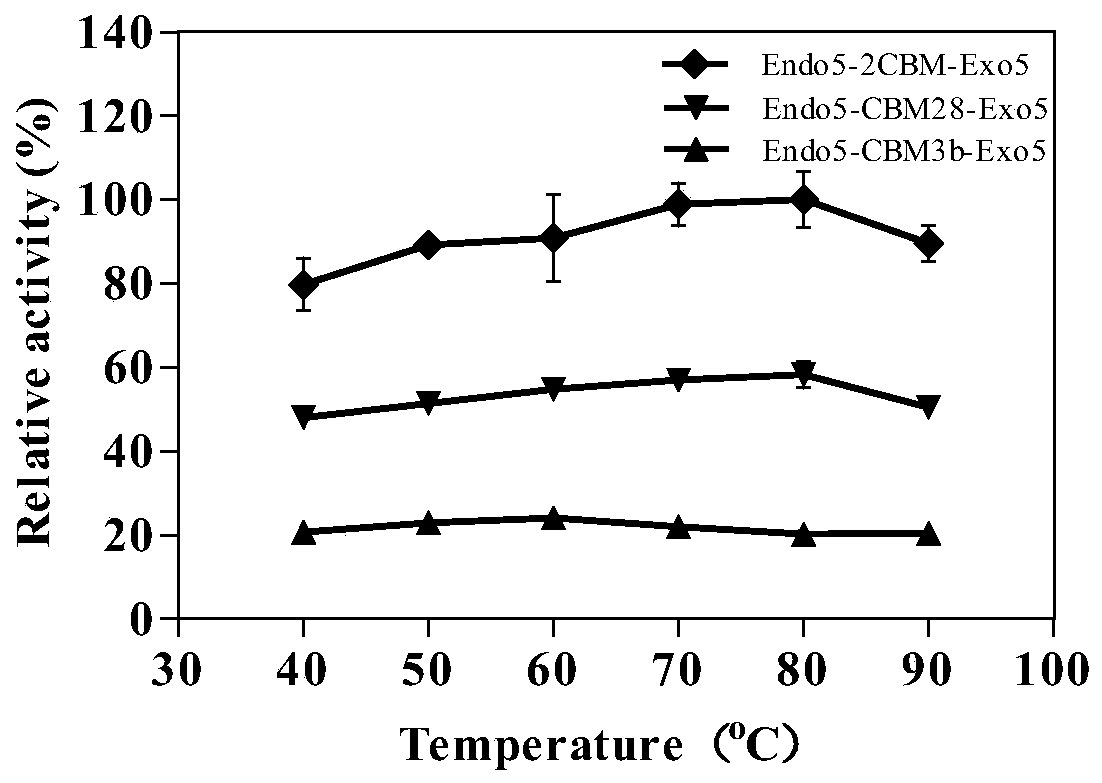
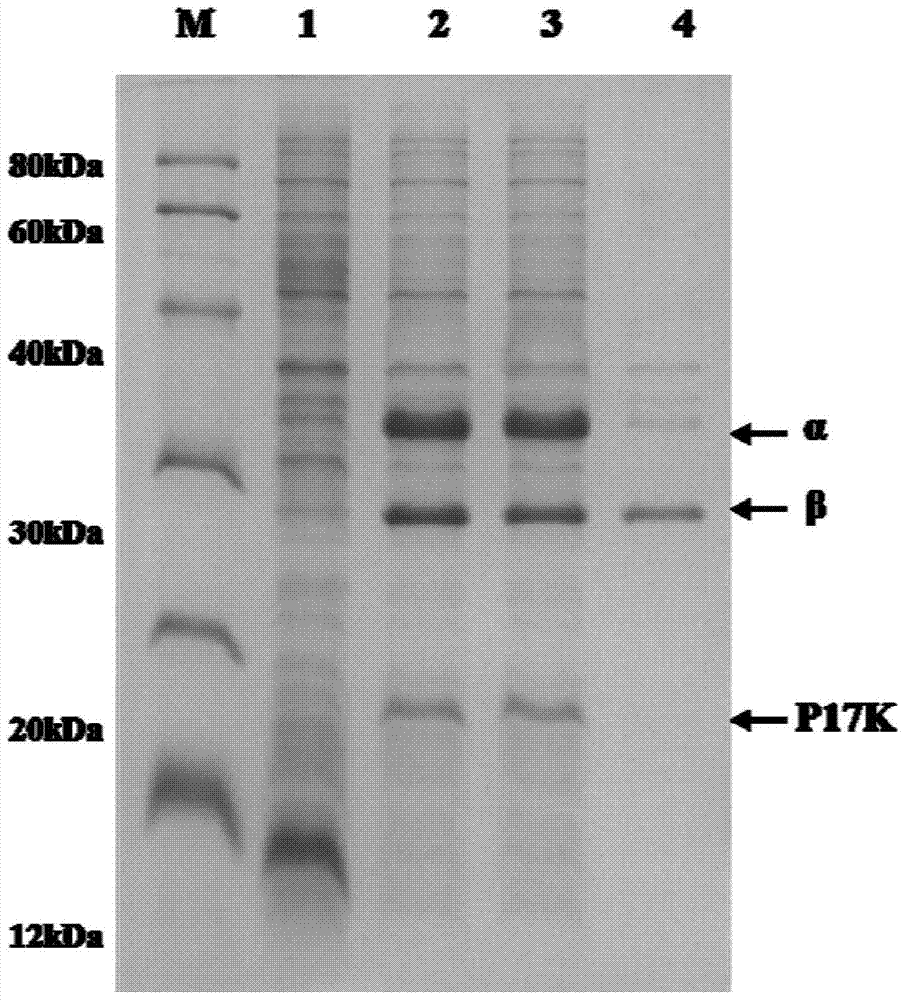
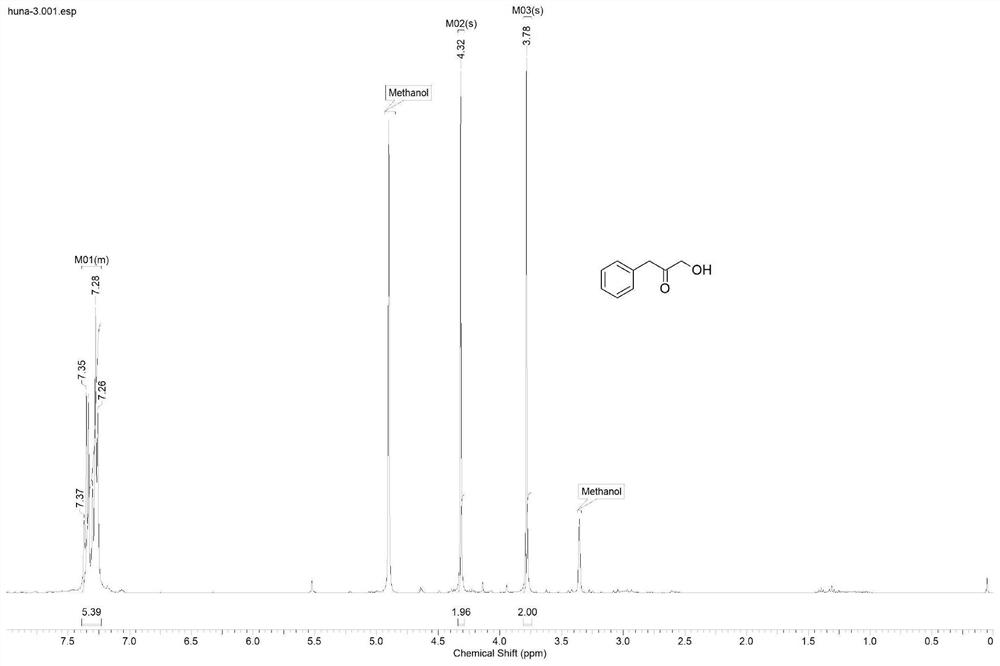
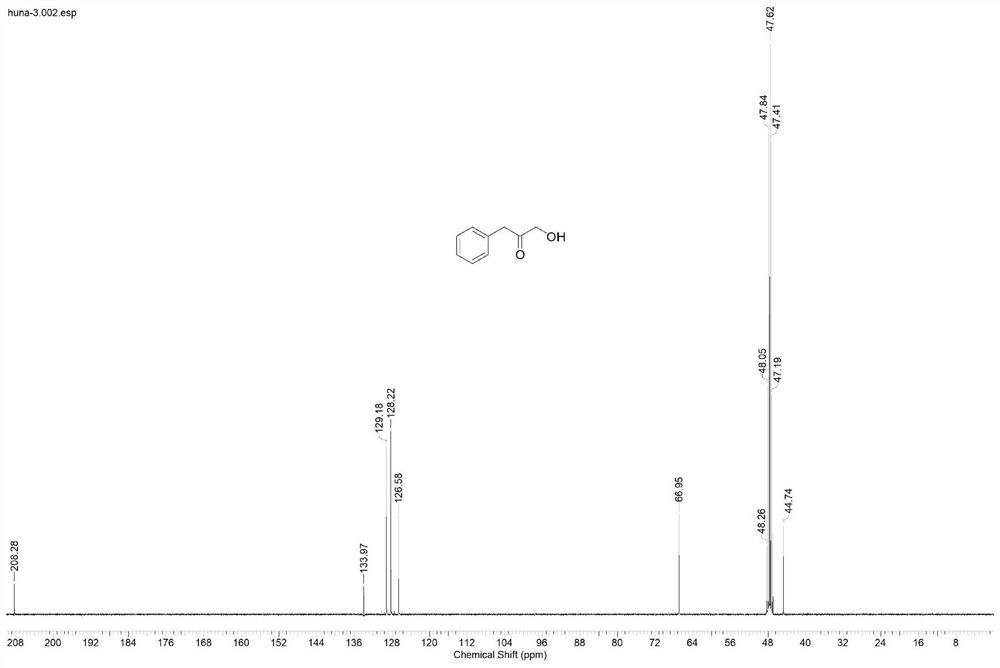
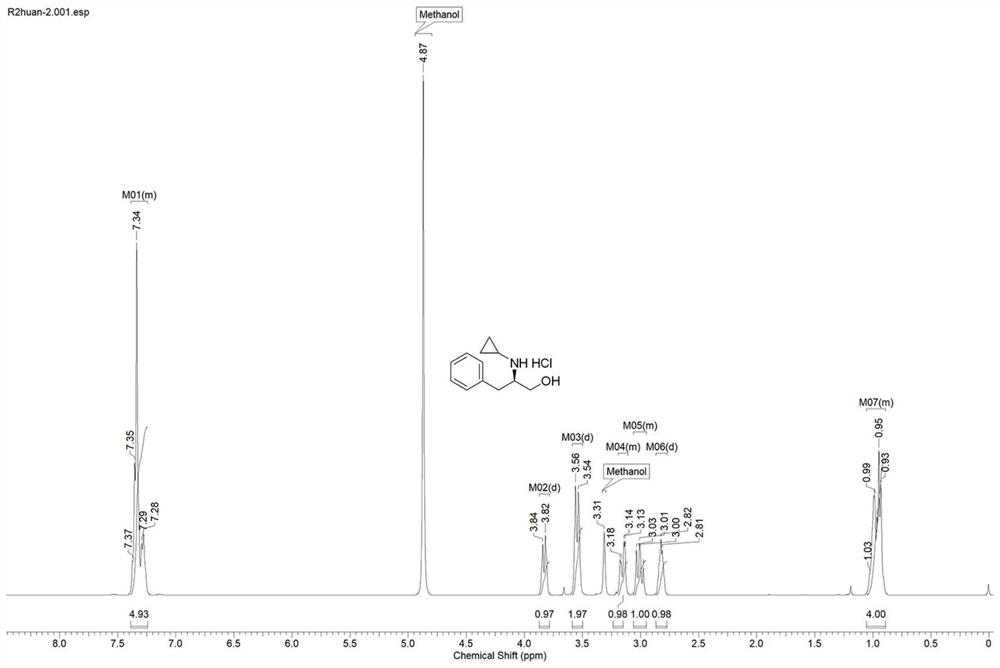
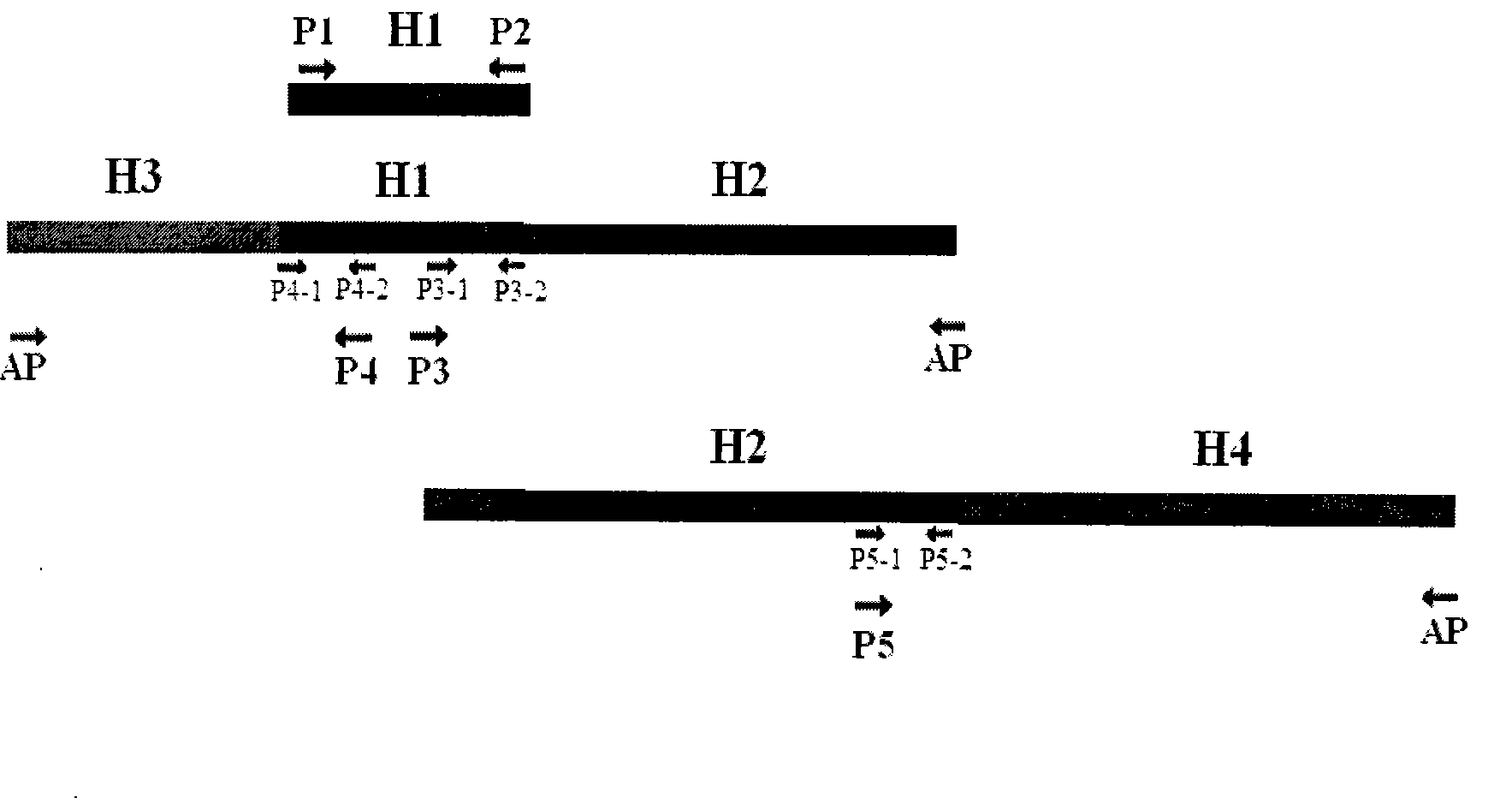
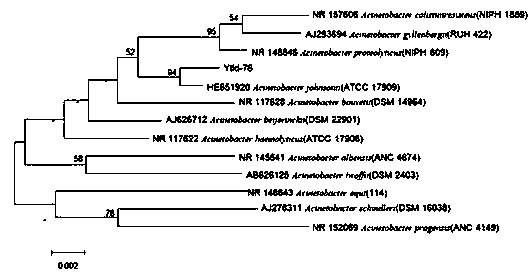
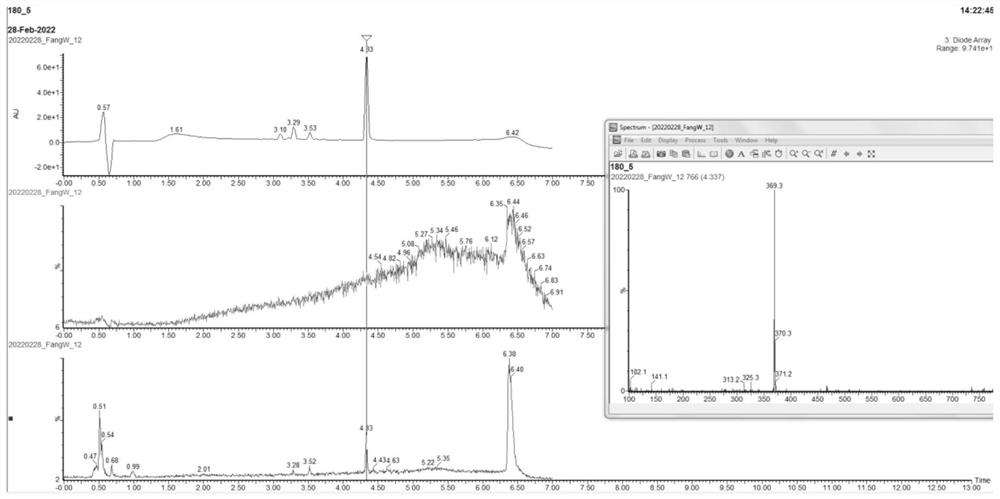
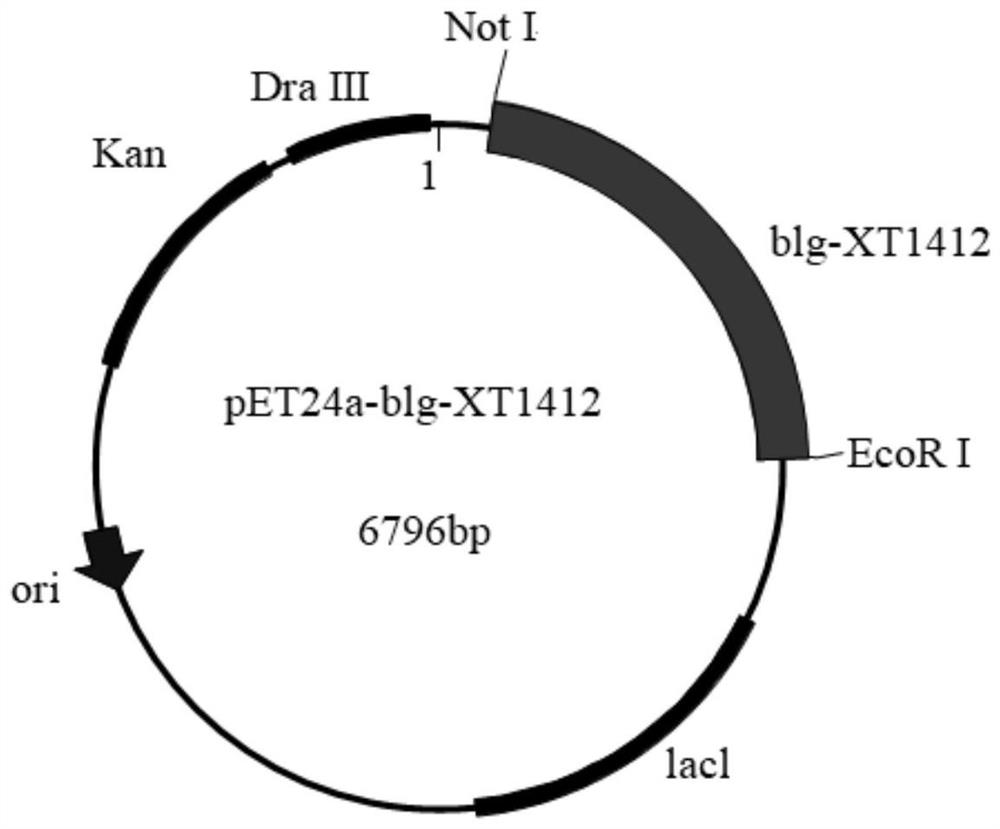
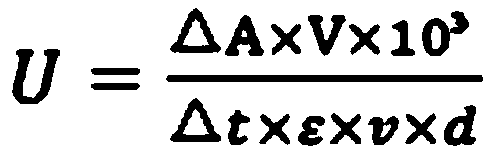Patents
Literature
52results about How to "Broad substrate spectrum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Paracoccus aminovorans HPD-2 and use thereof in soil remediation
ActiveCN101348773ABroad substrate spectrumPromote degradationBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismSoil remediation
The invention relates to a Paracoccus aminovorans HPD-2. The strain has been preserved in a depository authority specified by the State Intellectual Property Office; the collection date is July, 3rd, 2008; the name of the depository authority is China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center of the China Committee of Culture Collection for Microorganisms; and the collection number is CGMCC No.2568. The degrading bacterium has wide substrate spectrum and good degradability on PAHs in the environment.
Owner:中科华鲁土壤修复工程有限公司
Pseudomonas aeruginosa and application thereof
InactiveCN102533589AStrong emulsifying abilityGood ability to degrade polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonsBacteriaTransportation and packagingCarbon sourceResting Cell
The invention discloses a pseudomonas aeruginosa CCTCCM208114 and application of the pseudomonas aeruginosa in petroleum pollutant degradation. The pseudomonas aeruginosa provided by the invention has the following characteristics that: 1) the pseudomonas aeruginosa has high-efficient petroleum hydrocarbon degradation capability; 2) the pseudomonas aeruginosa is capable of co-metabolizing fluorene in an inorganic salt culture medium in the presence of n-tetradecane; 3) a resting cell system of the pseudomonas aeruginosa has good polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation capability and can tolerate high polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon concentration; 4) the pseudomonas aeruginosa has a wide substrate spectrum; and 5) the pseudomonas aeruginosa grows in an LB (Luria Bertani) culture medium or an inorganic salt culture medium (straight-chain paraffin or polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon serves as the unique carbon source and energy source) and can generate biological surfactant. The pseudomonas aeruginosa can be widely applied to the field of bioremediation of petroleum compound pollution and is suitable for large-area popularization and application.
Owner:DAQING OILFIELD CO LTD
Strain of Enterobacter cloacae and its application in the preparation of 2,3-butylene glycol
ActiveCN102226159AIncrease concentrationImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesProduction rateCellulose
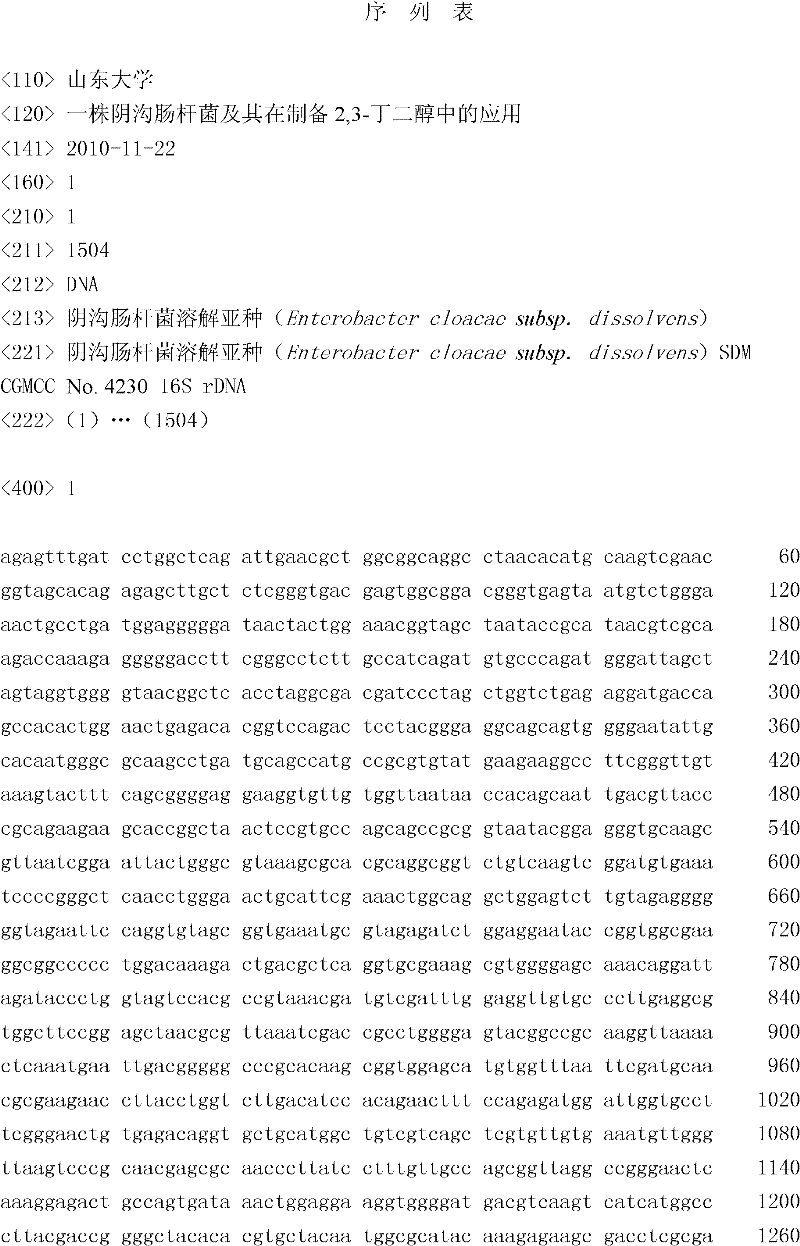
The invention discloses a strain of Enterobacter cloacae subsp. dissolvens SDM and its application in the preparation of 2,3-butylene glycol. The preservation number of the Enterobacter cloacae subsp. dissolvens SDM is CGMCC No.4230. Pentose, hexose, molasses, starch raw material hydrolysate, lignocellulose raw material hydrolysate are utilized in the strain provided by the invention with high transformation rate, high product concentration and wide substrate spectrum. According to the invention, the application of the strain of Enterobacter cloacae in the preparation of 2,3-butylene glycol has advantages of simple operation method, low cost and high efficiency; the output of 2,3-butylene glycol by the fermentation cylinder fed batch fermentation can reach 125-162 g / L; the transformation rate accounts for 90-95% of the theoretical transformation rate; the maximum productivity of 2,3-butylene glycol is 4.1 g / (L<.>h). Thus, the invention has a great prospect for industrial popularization and application.
Owner:上海肆芃科技有限公司
Hydantoinase and carbamoyl hydrolase producing strain, bienzyme gene and application thereof for preparing L-amino acid
InactiveCN101215533AImprove thermal stabilityGood substrate toleranceBacteriaHydrolasesChemical synthesisHydrolase Gene
The invention relates to a new microbe Bacillus fordii MH602 strain which can simultaneously produce hydantoinase and L-N-carbamyl hydrolase, hydantoinase produced by strain, L-N-carbamyl hydrolase gene and an application for preparing serial optical pure L-amino acid through the strain. The hydantoinase and L-N-carbamyl hydrolase that are produced by Bacillus fordii MH602 strain can overcome the defect of worse activity and heat stability of hydantoinase and L-N-carbamyl hydrolase in the L-amino acid procedure prepared by prior biologically inverted DL-5 substitution hydantoin or N-hydantoin amino acid, which is all provided with wide substrate spectrum, can catalyze a plurality of substrates and has better substrate selectivity for aromatic hydantoin. The applying operation for preparing L-amino acid by Bacillus fordii MH602 is simple and stable in operation, good in repeatability, which realizes stable and cheap preparation of L-amino acid and is beneficial to do large-scale preparation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for obtaining high-vitality superspectrum beta-lactam enzyme by directional anagenesis in vitro
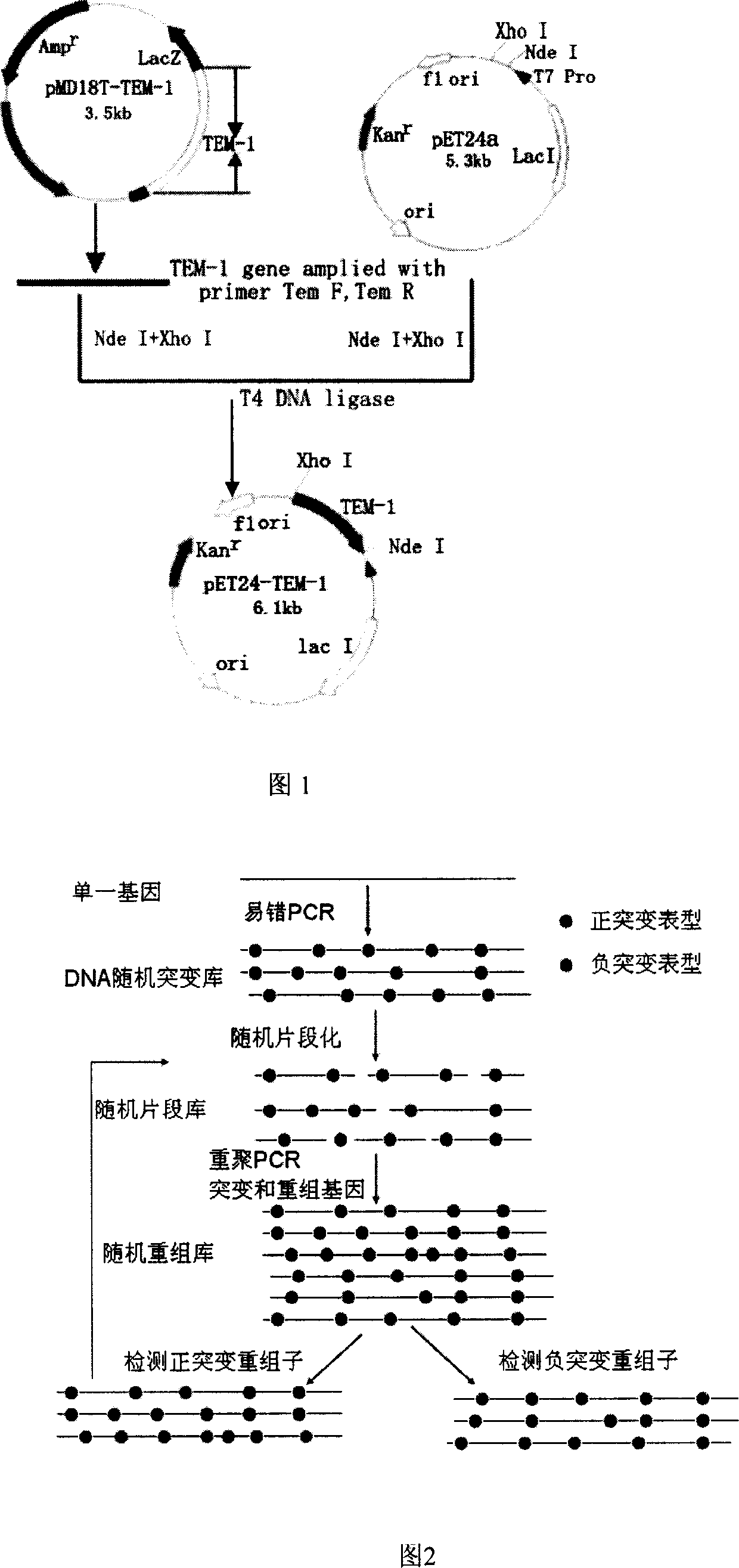
InactiveCN101104858ABroad substrate spectrumIncrease productionBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyCefotaxime
The method to prepare high active extended spectrum beta-lactamase through directed evolution in vitro of the invention belongs to medical bioengineering technical field. In particular, the invention adopts two directed evolution strategies of error-prone PCR and DNA shuffling to transform a lab strain plant which contains TEM-1 gene. The substrate spectrum enzymes of the mutated strain plant and the wild strain plant, and the activity of the substrate spectrum enzymes are compared, showing that the original substrate spectrum is enlarged because of mutation and the degradability of the third representative generation of beta-lactam antibiotics ceftazidime (CAZ) and the cefotaxime (CTX) is improved from zero to a specific activity of 43IU / mg to 78IU / mg.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
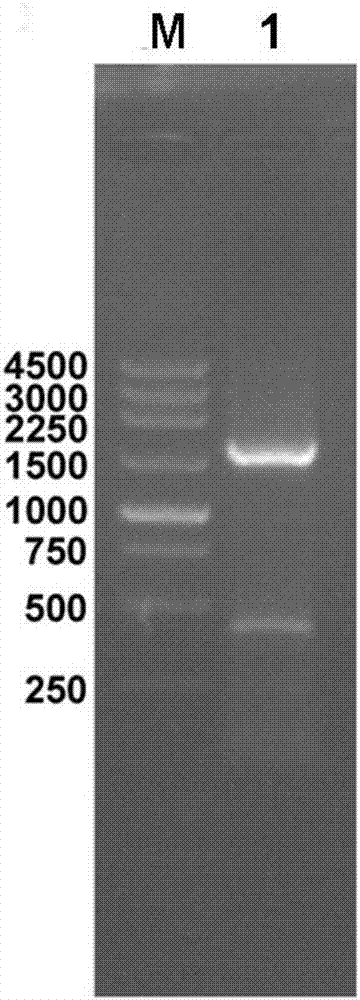
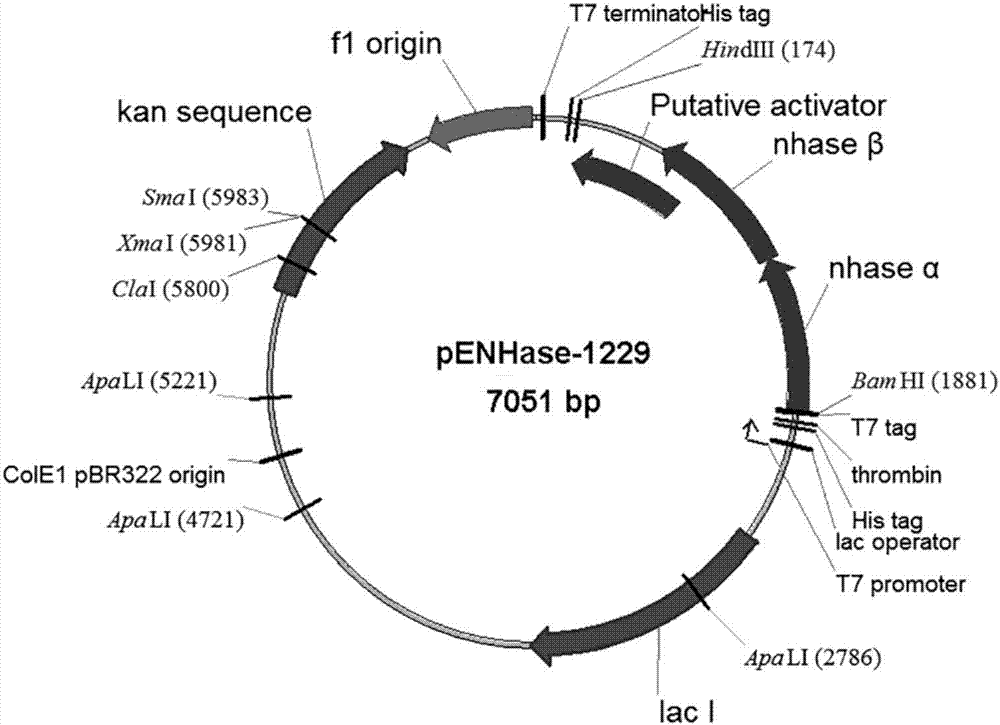
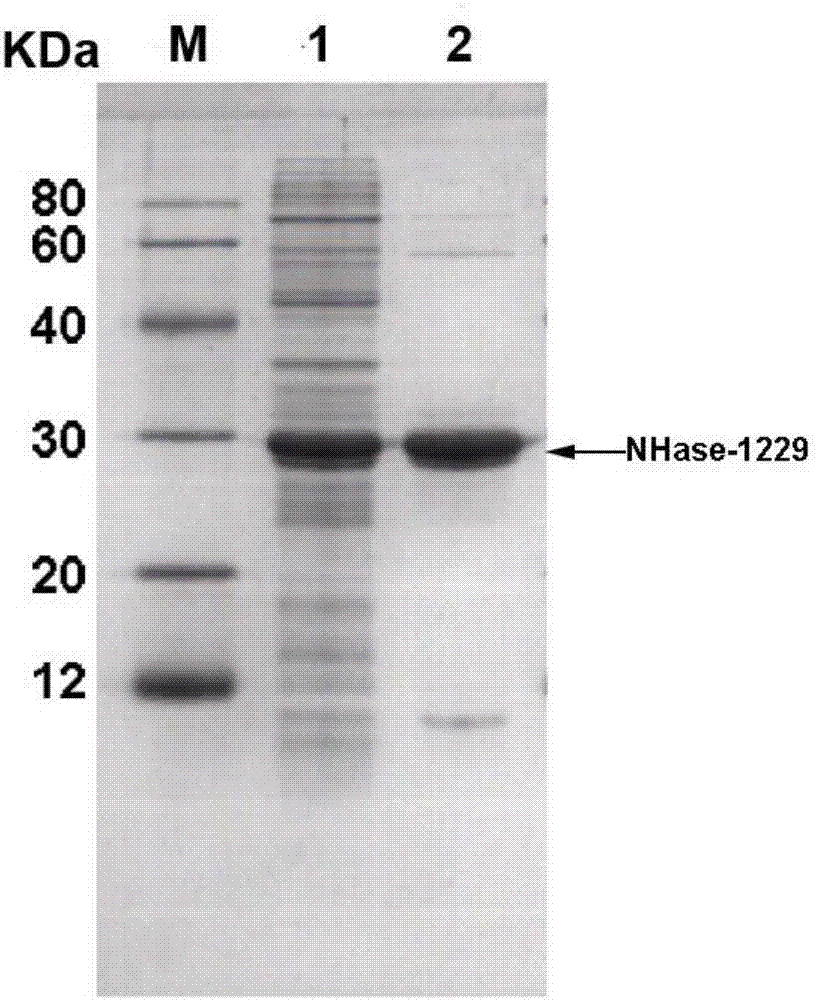
Nitrile hydratase as well as encoding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a nitrile hydratase as well as an encoding gene and application thereof. The nitrile hydratase is prepared from an alpha subunit and a beta subunit, wherein an amino acid sequence of the alpha subunit is shown as SEQ ID NO.4, and an amino acid sequence of the beta subunit is shown as SEQ ID NO.5. According to the nitrile hydratase as well as the encoding gene and the application thereof, a nitrile hydratase gene is cloned from acid-producing Klebsiella spp KCTC 1686, and the nitrile hydratase with high expression level, high activity, wide substrate spectrum and chiral selectivity is successfully obtained after the gene is expressed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Heat-resistant nitrile hydratase, engineering bacteria and application thereof in production of amide by catalyzing hydration reaction of nitrile compounds
InactiveCN107881163AHigh expressionHigh activityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousEscherichia coli
The invention discloses heat-resistant nitrile hydratase, engineering bacteria and application thereof in production of amide by catalyzing hydration reaction of nitrile compounds. The heat-resistantnitrile hydratase contains alpha-subunit coding genes with a base sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.4, beta-subunit coding genes with a base sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.5, and active element coding genes with a base sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.6. The nitrile hydratase genes are cloned from aurantimonas manganoxydans SI859A and successfully subjected to heterologous expression in E. coli BL21 (DE3), so as to obtain nitrile hydratase with high expression quantity and high activity and proteins with specific activities reaching 404.5U / mg. The nitrile hydratase has high catalytic activity on aromatic nitrile compounds and aliphatic nitrile compounds, and is a kind of nitrile hydratase with wide substrate spectrum, high thermal stability and excellent industrial application potential.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
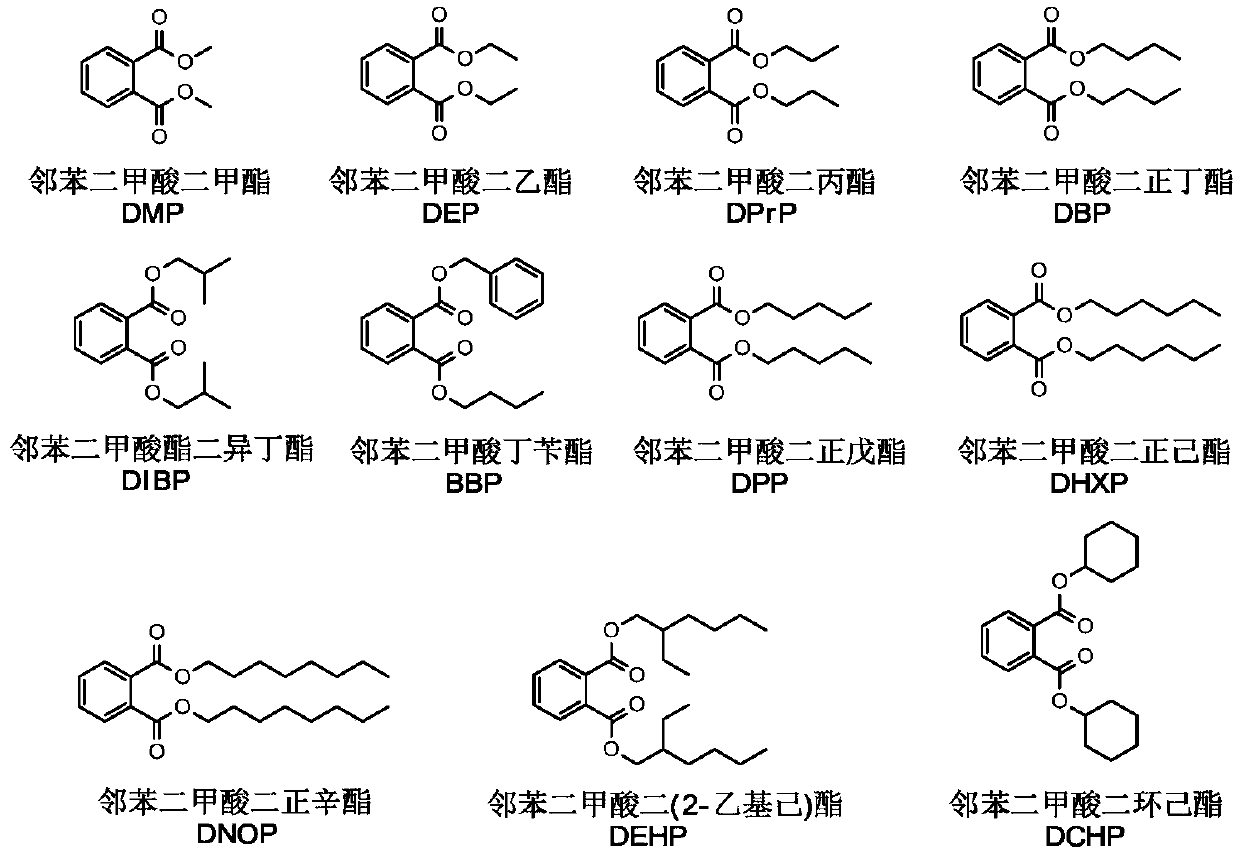
DEHP (di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate) hydrolase, gene and application of hydrolase
ActiveCN110373345APromote degradationBroad substrate spectrumBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyCatalytic effect
The invention relates to Gordonia polyisoprenivorans, DEHP (di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate) hydrolase expressed by Gordonia polyisoprenivorans, a coding gene and amino acid sequence of the DEHP hydrolase,a recombinant expression vector and recombinant expression transformant containing the gene sequence, a recombinase of the DEHP hydrolase, a preparation method of the recombinase, and a method of degrading PAEs (phthalate esters) by the recombinase. Compared with the prior art, the DEHP hydrolase has the advantages of wide substrate spectrum, good catalytic effect, mild reaction condition, good environmental friendliness and the like; therefore, the DEHP hydrolase is well applicable to biological remediation of soil and biodegradation of pollutants.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel 17 beta-hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase, gene and application thereof
ActiveCN109306342ALess by-productsShort conversion timeOxidoreductasesFermentationAndrostaneCarbonyl group
The invention discloses a novel 17 beta-hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase (17 beta-HSDcab) derived from candida albicans 7103 and a coding gene thereof; the enzyme is utilized as a biocatalyst to catalyse a substrate 17-carbonyl steroid compound to synthesize a 17 beta-hydroxyl steroid compound. The enzyme has a wide substrate spectrum, and especially has very high activity for androstane-4-alkene-3,17-diketone, androstane-4,9(11)-diene-3,17-diketone. A recombinant bacterium resting cell is taken as a biocatalyst, androstane-4-alkene-3,17-diketone is taken as a substrate, so that a target producttestosterone with a high yield is obtained with relatively high substrate feeding concentration, by-products are less, and the yield is not lower than 95%; and moreover, the conversion time is short,the used biocatalyst is less in dosage, and the space time yield is far higher than the current reported level.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
New (R)-transaminase from Fusarium oxysporum and application thereof
InactiveCN104630171ABroad amino donor substrate spectrumIncrease vitalityBacteriaTransferasesFusarium oxysporumNucleotide
The invention discloses a new (R)-transaminase and application thereof. The (R)-transaminase derives from Fusarium oxysporum Fo5176 (named HFO), the gene nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID No.1 and the amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID No.2. The new (R)-transaminase HFO is a strict (R) stereoselective Omega-transaminase, has a broad substrate spectrum, and has great application potential in bio-production of chiral amines and unnatural amino acids.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Kluyveromyces lactis mutant strain as well as glycosidase and application thereof
The invention relates to a kluyveromyces lactis mutant strain as well as glycosidase and an application thereof. With kluyveromyces lactis ATCC 8585 as an initial strain, the kluyveromyces lactis mutant strain is obtained through composite mutagenesis; the glycosidase, which is produced by the mutant strain, is good in stability and reserves high-temperature activity, and meanwhile, the glycosidase, which conforms to natural standard specifications and source safety, is applicable to industrial production. The invention also provides polynucleotide, a recombinant vector containing the polynucleotide, a host cell containing the recombinant vector and a composition containing the glycosidase. In addition, the invention also provides a method for producing the glycosidase and hydrolyzing a material containing a glucosidic bond.
Owner:董颖军
Chitin deacetylase
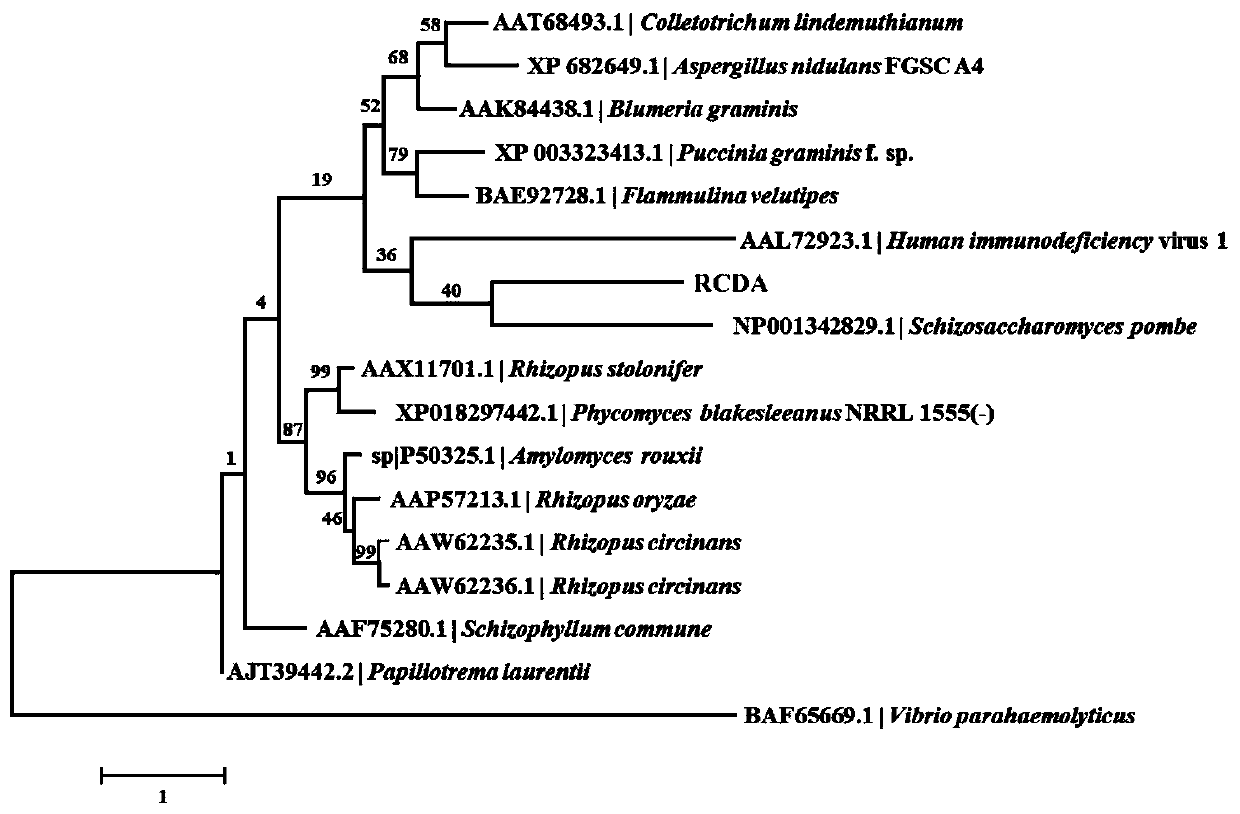
InactiveCN111172141ABroad substrate spectrumHigh activityHydrolasesFermentationRhodococcus equiChitin deacetylase
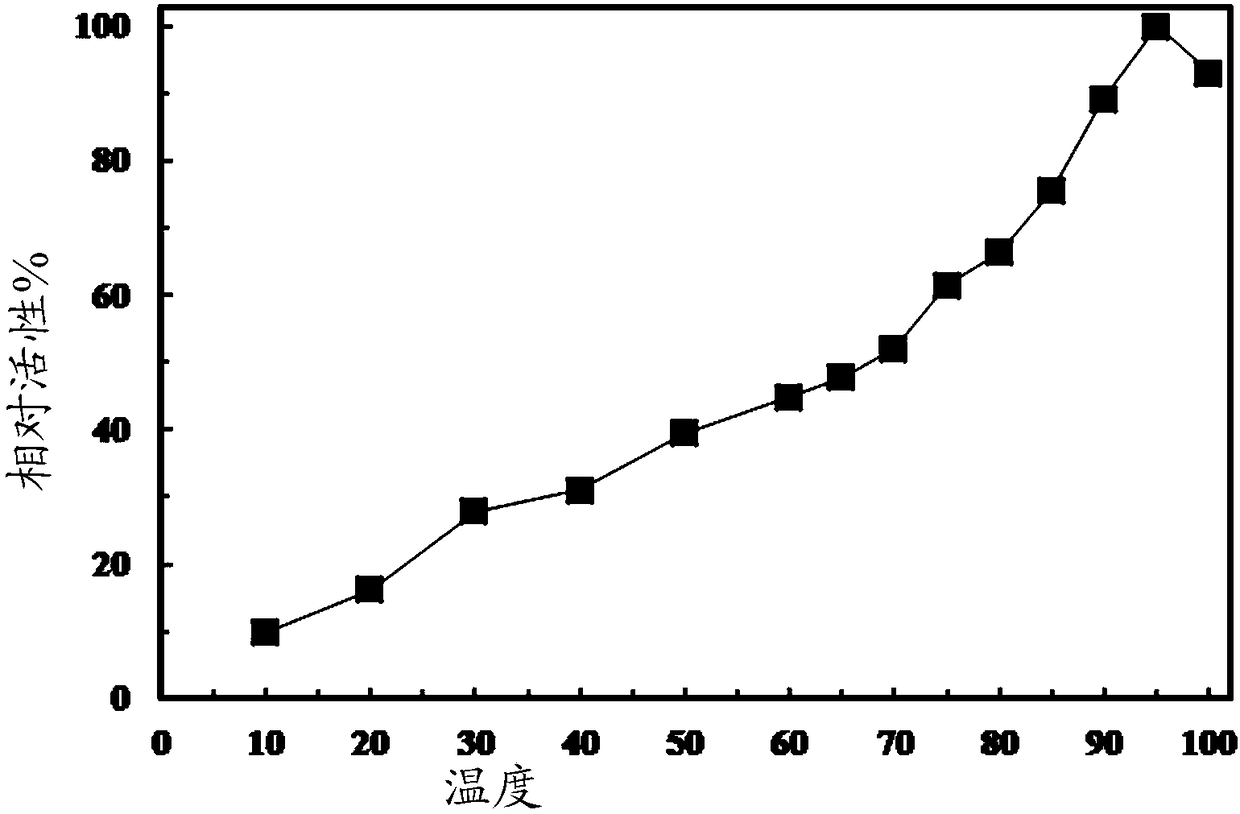
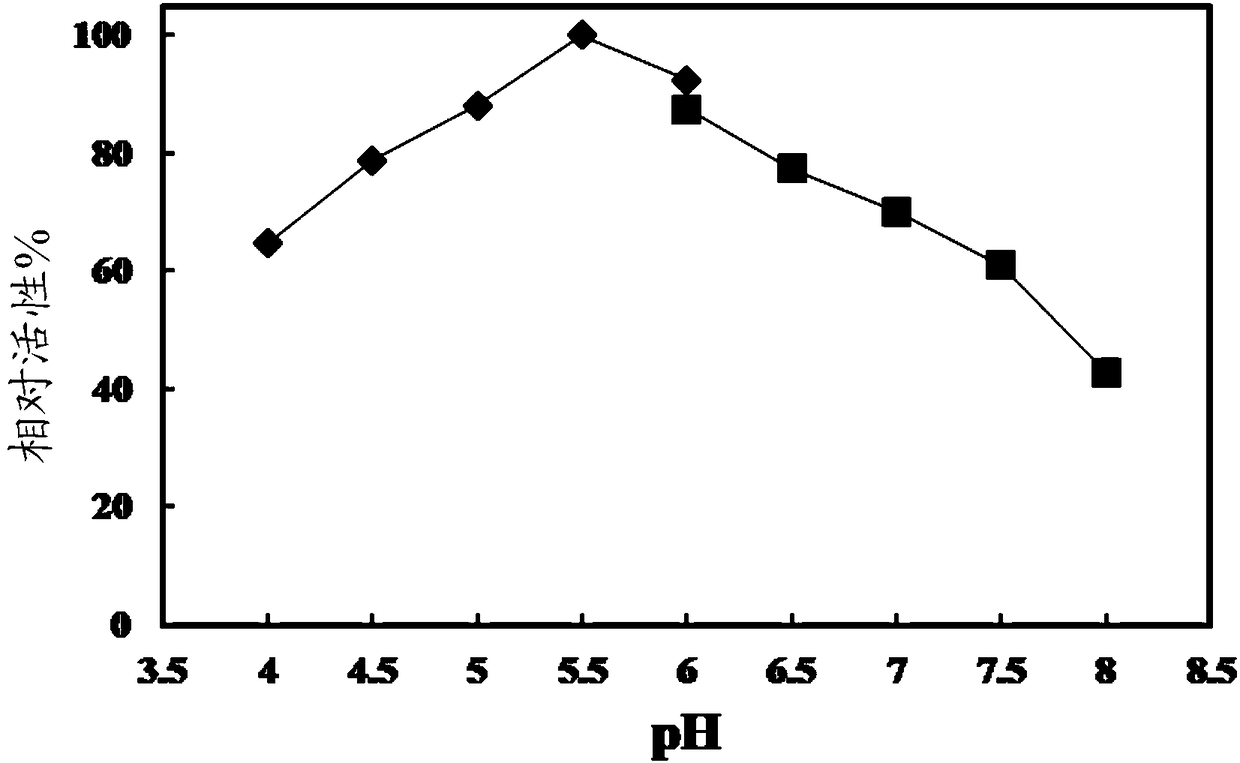
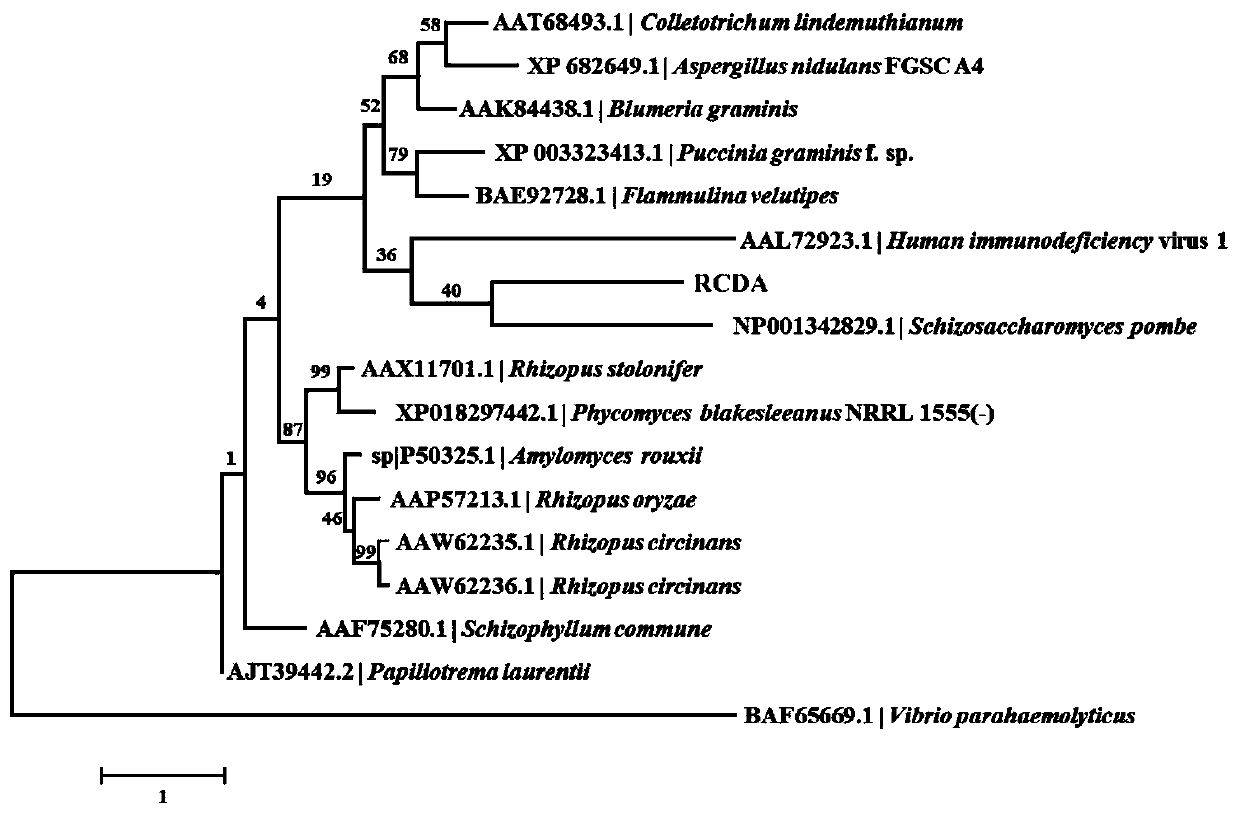
The invention belongs to the technical field of protease, and particularly relates to chitin deacetylase. The chitin deacetylase RCDA derives from Rhodococcus equi, has an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO.1 in a sequence table, is a novel protein sequence reported for the first time at present, has relatively low similarity with a protein sequence of the reported chitin deacetylase andhas a relatively wide substrate spectrum; and the chitin deacetylase has the characteristics that metal ion influence is low, and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
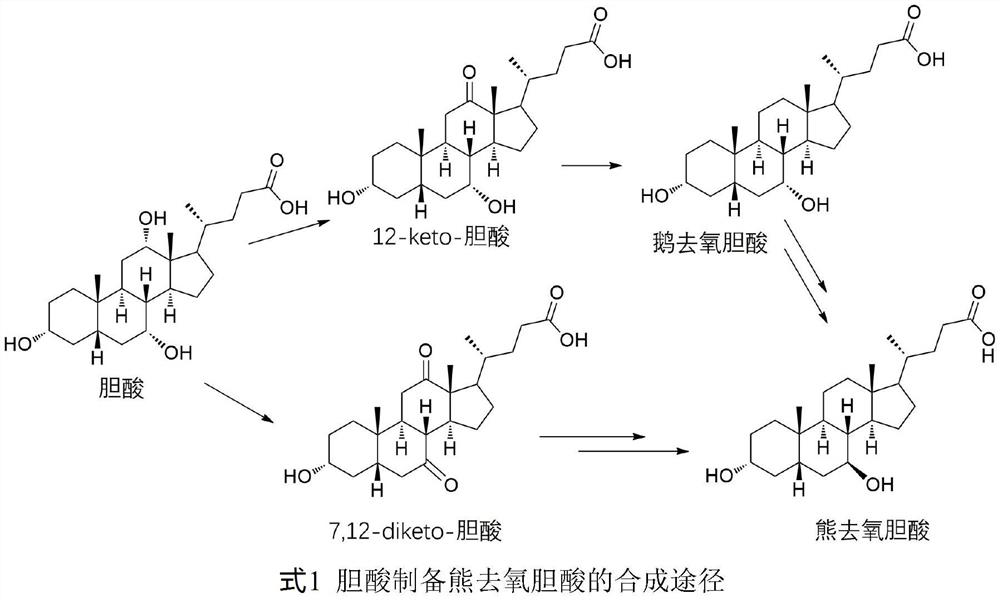
12-hydroxycholic acid dehydrogenase and application thereof
ActiveCN111826358ABroad substrate spectrumHigh activityMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesEscherichia coliCholic acid
The invention discloses a novel 12-hydroxycholic acid dehydrogenase derived from Eggerthella lenta and an encoding gene of the novel 12-hydroxycholic acid dehydrogenase. The novel 12-hydroxycholic acid dehydrogenase is used as a biocatalyst for catalyzing cholic acid and a derivative 12-hydroxyl thereof for oxidizing into a carbonyl substrate. The gene for encoding the enzyme has low homology withthe currently known 12-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, has high enzyme activity on 12-hydroxycholic acid and derivatives thereof, does not need to add antibiotics in the process of culturing and expressing escherichia coli of the gene, does not utilize traditional isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) for induction, and efficient expression can be achieved. In the conversion process, afterthalli are concentrated, the substrate concentration can reach 200 g / L and is achieved with the conversion rate greater than 95%, no organic solvent is used in the reaction process, and the conversionmethod is green and environmentally friendly.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
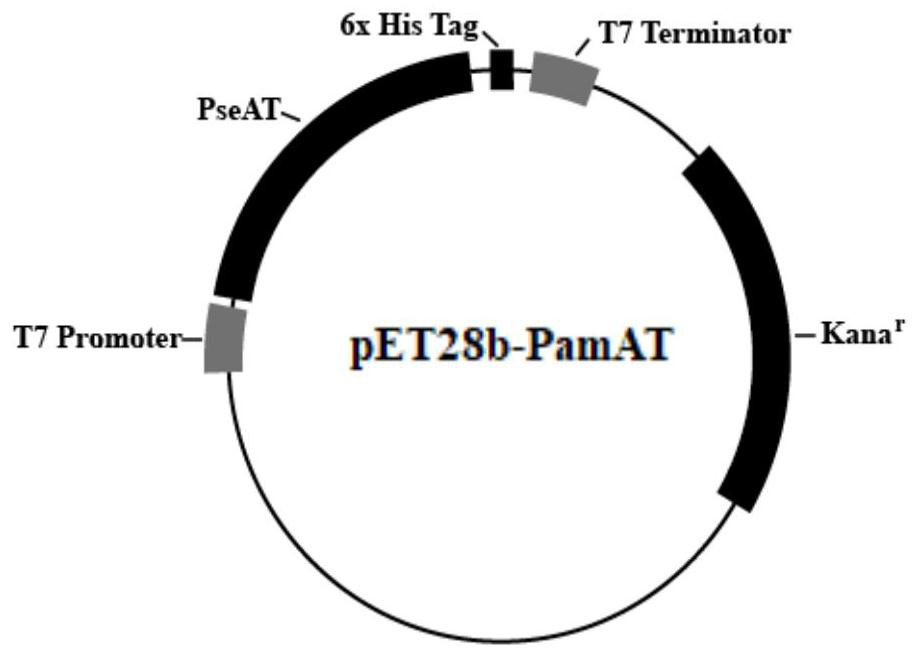
R-transaminase derived from pseudonocardia ammoxidation and synthesis method of R-transaminase
PendingCN112522228AEfficient synthesisBroad substrate spectrumTransferasesFermentationNucleotideAmino acid
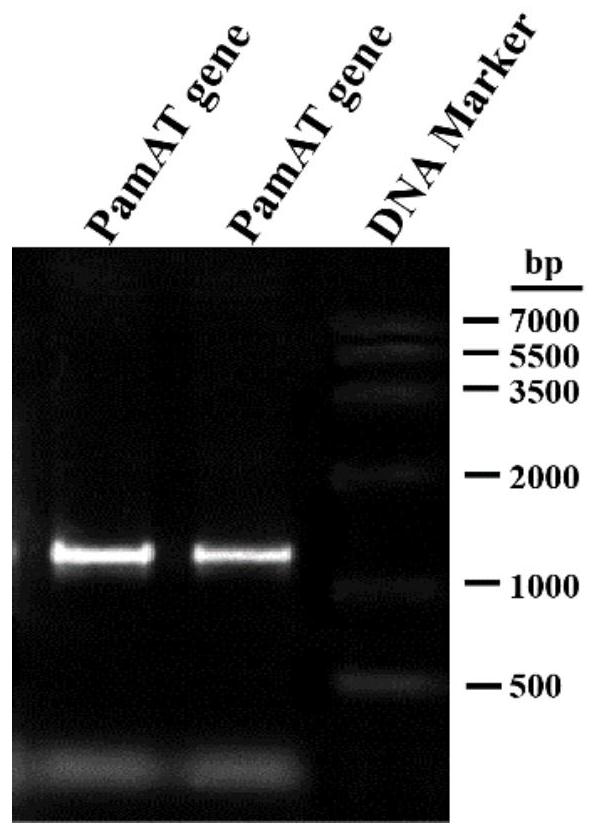
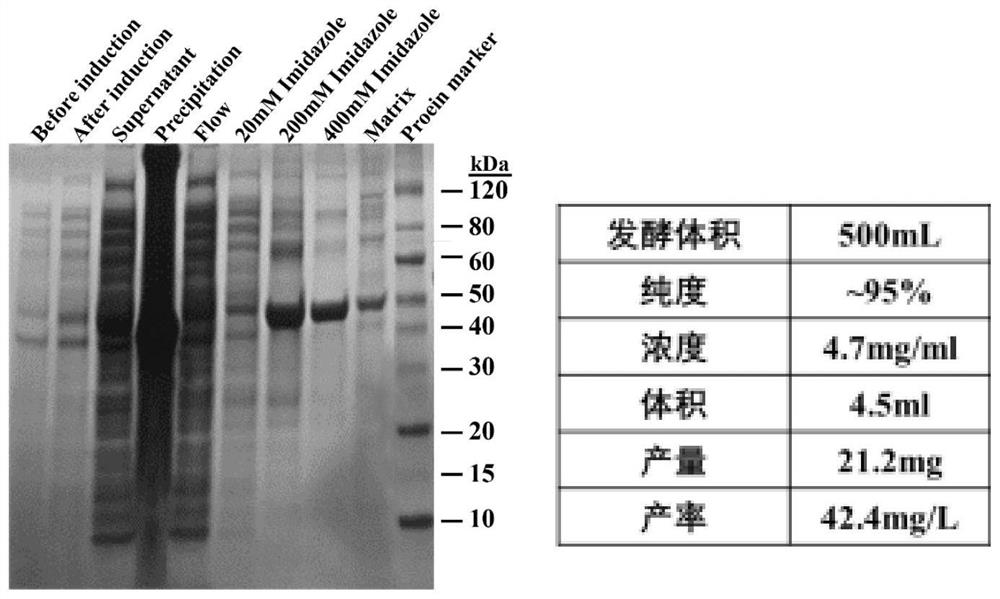
The invention discloses R-transaminase derived from pseudonocardia ammoxidation and a synthesis method thereof. The R-transaminase is named as PamAT, the nucleotide sequence of a gene is shown as SEQNO.1, the amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ NO.2, and the R-transaminase contains the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ NO.2 or is provided with at least 90% of identity with the SEQ NO.2 or is subjected to substitution, deletion or addition of one or more amino acids; and the high stereoselectivity means that the content of one stereoisomer is at least about 1.1 times that of the other stereoisomer. The R-transaminase has high stereoselectivity, has a wide substrate spectrum and has great application potential in the aspect of biological manufacturing of chiral amine and non-natural amino acid.
Owner:JIANGSU OCEAN UNIV
Amidase XAM, and encoding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN111944794AIncrease enzyme activityBroad substrate spectrumHydrolasesFermentationChemical industryHydroxamic acid
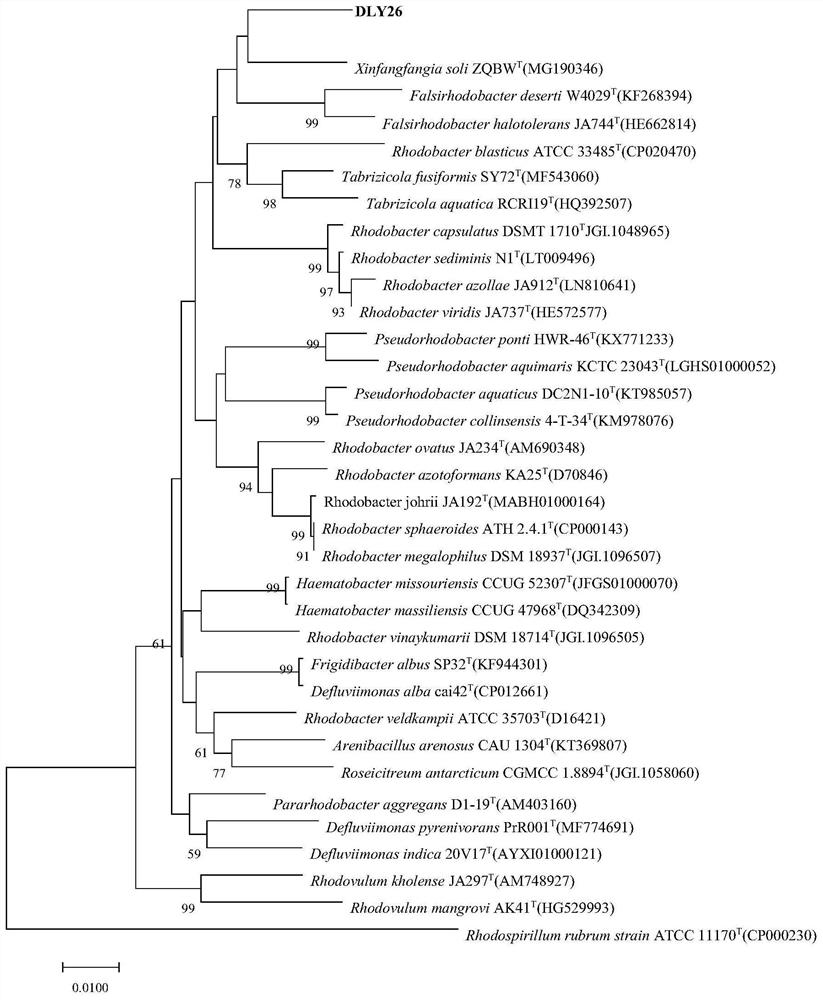
The invention discloses amidase XAM, and an encoding gene and application thereof. The protein provided by the invention is from Xinfangfangia sp., is an amidase tag family amidase, is named XAM protein and is the protein having an amino acid sequence disclosed by a sequence 1 in a sequence table. The invention also provides application of the XAM protein as the amidase. The invention also provides application of the XAM protein in hydroxamic acid production. The invention has a great application prospect in relevant medical care fields, chemical industry fields and the like.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
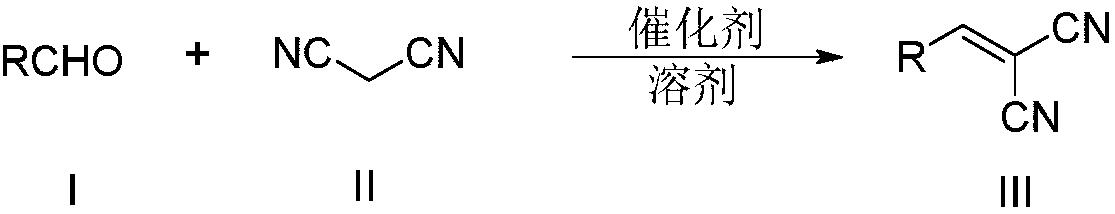
Synthesis method of alkenyl dinitrile compounds
ActiveCN108383755AIncrease pressureReduce pollutionCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationSynthesis methodsSolvent
The invention discloses a synthesis method of alkenyl dinitrile compounds. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking substituted aldehyde and malononitrile as raw materials, takingRu / C as a catalyst, carrying out a reaction at 20-60 DEG C in ethanol, and carrying out separation and purification on the reaction liquid after the reaction to obtain an alkenyl dinitrile compound. The Ru / C catalyst used in the synthesis method is cheap and is easy to obtain; the Ru / C catalyst is a heterogeneous catalytic system in the reaction, so that the catalyst and a solvent are very convenient to recycle and can be repeatedly used; the reaction raw materials are diverse and cheap, are easily available, and are suitable for the synthesis of various substituted alkenyl dinitrile compounds. The post-treatment is simple, the product purity is good, and the yield is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Scopulariopsis brevicaulis and application thereof
ActiveCN103013841BBroad substrate spectrumPromote degradationFungiContaminated soil reclamationPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonChemical compound
The invention discloses Scopulariopsis brevicaulis and application thereof. A preservation serial number of Scopulariopsis brevicaulis 4Z is CGMCCNo.6870 (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center). Scopulariopsis brevicaulis has a wider substrate spectrum, has good degradation ability on organic aromatic compounds, particularly polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in an environment, and can be applied to treatment of environmental pollution, for example, Scopulariopsis brevicaulis can act as a bioremediation reagent for soil polluted by the organic aromatic compounds for wide use.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Mutant chitosanase with high temperature stability
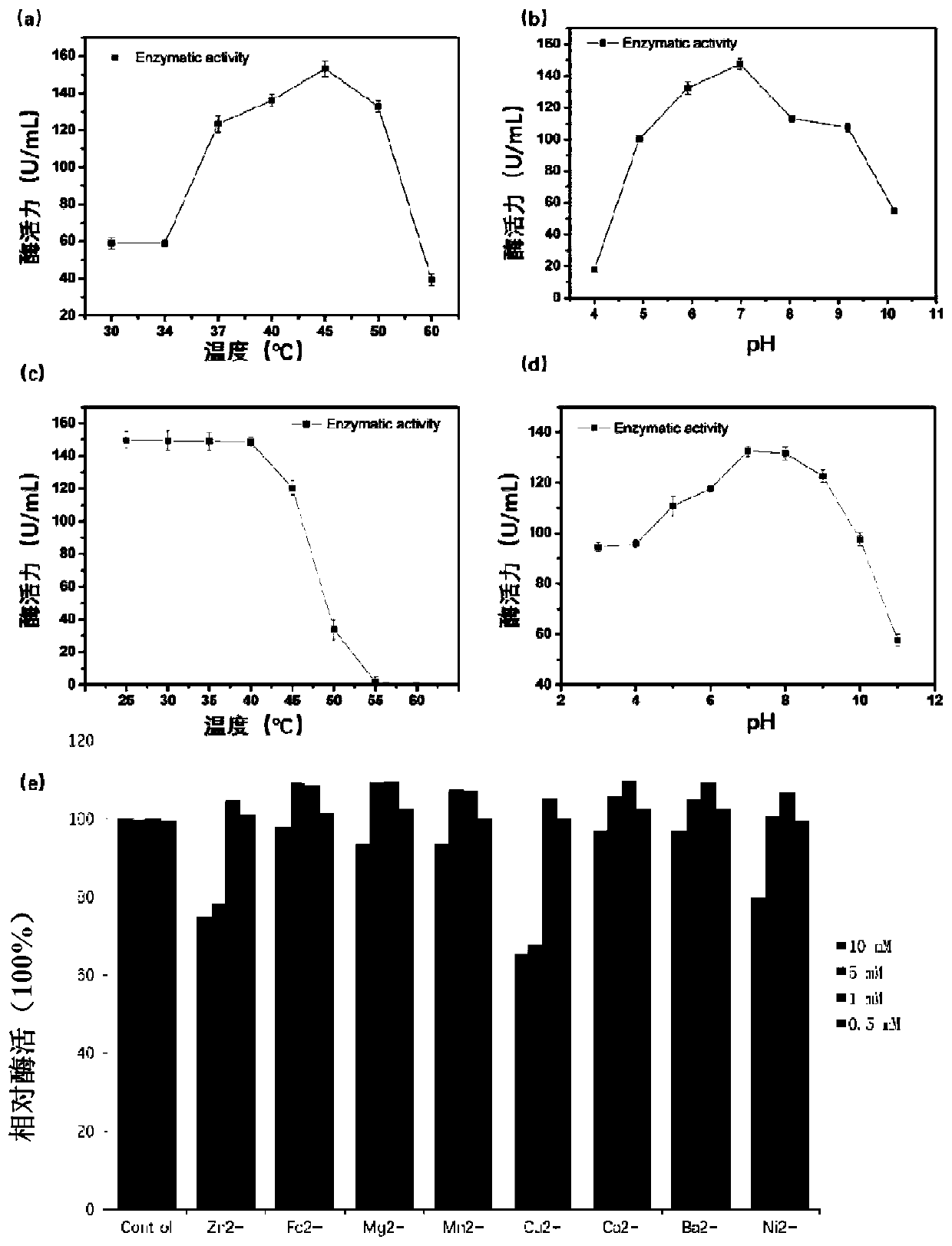
PendingCN114752584ABroad substrate spectrumImprove temperature stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHydrolysate
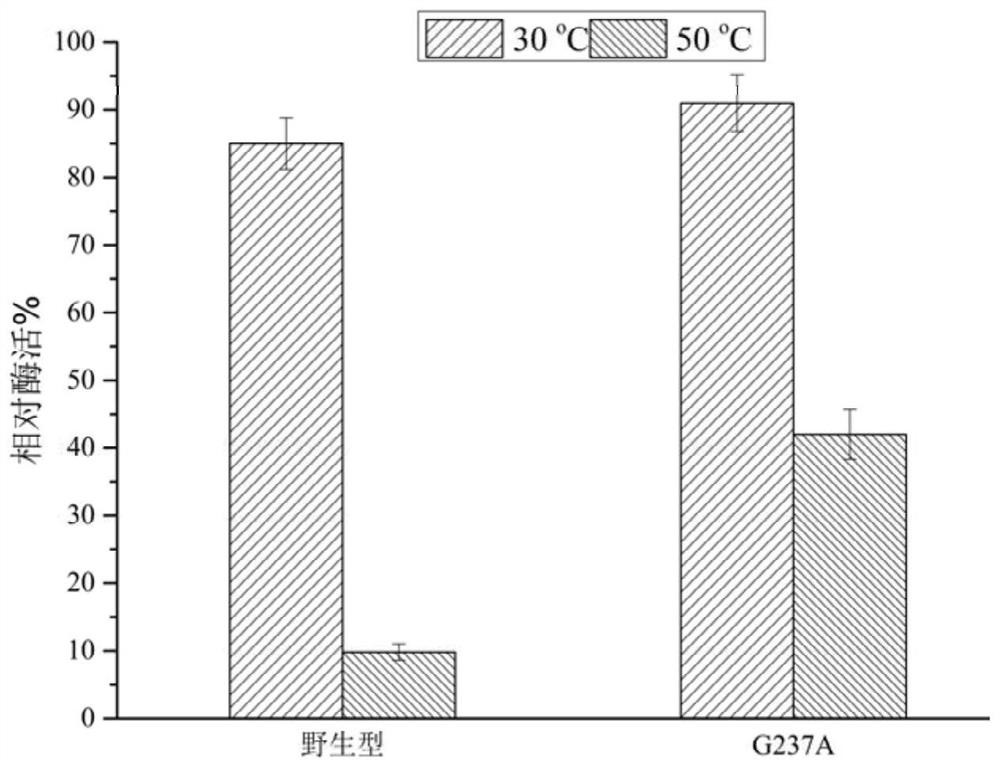
The invention relates to gene cloning, site-specific mutagenesis and gene recombination technologies, and particularly discloses a novel mutant of a 46 family glycoside hydrolase chitosanase (SaCsn46A) cloned from streptomyces avermitilis, and the enzyme is composed of 271 amino acids which comprise 34 amino acid signal peptides. By analyzing a high-unfolding free energy site on a zymoprotein structure, a mutation site is selected for mutation, and a chitosanase mutant with improved temperature stability is screened out. According to the invention, glycine at the 237th position of an original enzyme SaCsn46A is mutated into alanine (G237A), and the mutant is expressed in escherichia coli Rosetta. Compared with the wild chitosanase, the temperature stability of the mutant enzyme is 4.8 times higher than that of the wild chitosanase. A thin-layer chromatographic analysis result shows that enzyme hydrolysates are mainly glucosamine GlcN and (GlcN) 2.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Acidic high-temperature-resistant recombinant cellulase and application thereof
ActiveCN110358755AAcid-resistant and high-temperature resistantGreat advantageBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCellulaseFilter paper
The invention discloses three kinds of acidic high-temperature-resistant recombinant cellulase and application thereof. Amino acid sequences of the three kinds of recombinant cellulase are shown in SEQIDNO:1-3 respectively. The three kinds of recombinant cellulase have the highest enzyme activity of 1.54 U / mg to CMC-Na and the highest vitality of 0.167 U / mg to Avicel under the conditions that thepH value is 4.0-5.0 and the temperature is 60-80 DEG C. The vitality of the three kinds of recombinant cellulase basically remains unchanged under the conditions that the temperature is 75 DEG C and the pH value is 4.0-4.5 after heat preservation is carried out for 2 hours. The three kinds of recombinant cellulase can directly degrade the CMC-Na, crystalline cellulose, filter paper and other natural lignocellulose such as rice straw and wheat straw, and the highest vitality of the three kinds of recombinant cellulase to the rice straw reaches 0.106 U / mg. Compared with the prior art, the threekinds of recombinant cellulose have greater superiority, can effectively degrade the natural lignocellulose, and have potential industrial application value.
Owner:HUAIYIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Nitrile hydratase and its coding gene and application
ActiveCN104450657BHigh expressionHigh activityDepsipeptidesFermentationKlebsiella sppChiral selectivity
The invention discloses a nitrile hydratase as well as an encoding gene and application thereof. The nitrile hydratase is prepared from an alpha subunit and a beta subunit, wherein an amino acid sequence of the alpha subunit is shown as SEQ ID NO.4, and an amino acid sequence of the beta subunit is shown as SEQ ID NO.5. According to the nitrile hydratase as well as the encoding gene and the application thereof, a nitrile hydratase gene is cloned from acid-producing Klebsiella spp KCTC 1686, and the nitrile hydratase with high expression level, high activity, wide substrate spectrum and chiral selectivity is successfully obtained after the gene is expressed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Enzymatic synthesis of chiral amino alcohol compounds
ActiveCN114381441AHigh catalytic activityImprove conversion rateBacteriaOrganic compound preparationEnzymatic synthesisKetone
The invention discloses a method for generating an optical pure chiral amino alcohol compound by catalyzing a reaction between alpha-hydroxy ketone and small molecule amine through a biocatalyst. More specifically, the invention provides a method for generating chiral amino alcohol by catalyzing reductive amination reaction of different types of alpha-hydroxy ketones and small molecular amine through imine reductase. The method has the remarkable characteristics of mild reaction conditions, good stereoselectivity, no pollution and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Preparation method of transaminase mutant and chiral amine compound
PendingCN114875006AIncrease enzyme activityStrong ability to withstand extreme environmentsBacteriaTransferasesEnzyme catalysisAmino acid mutation
The invention provides a transaminase mutant and a preparation method of a chiral amine compound. The transaminase mutant comprises (a) a protein with an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1; or (b) a protein with an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 or SEQ ID NO: 3; or (c) a protein which is subjected to amino acid mutation and has a transaminase function on at least one of the following sites of the amino acid sequence in (b): Y89, L380, N86, Y85, T91, P83, K90, S417, S424, F301, G164, T452 and the like; and (d) protein which has more than 80% of homology with the amino acid sequence limited by any one of (a), (b) or (c) and has a transaminase function. The method can solve the problem of low transaminase activity in the prior art, and is suitable for the field of enzyme catalysis.
Owner:ASYMCHEM LIFE SCI TIANJIN
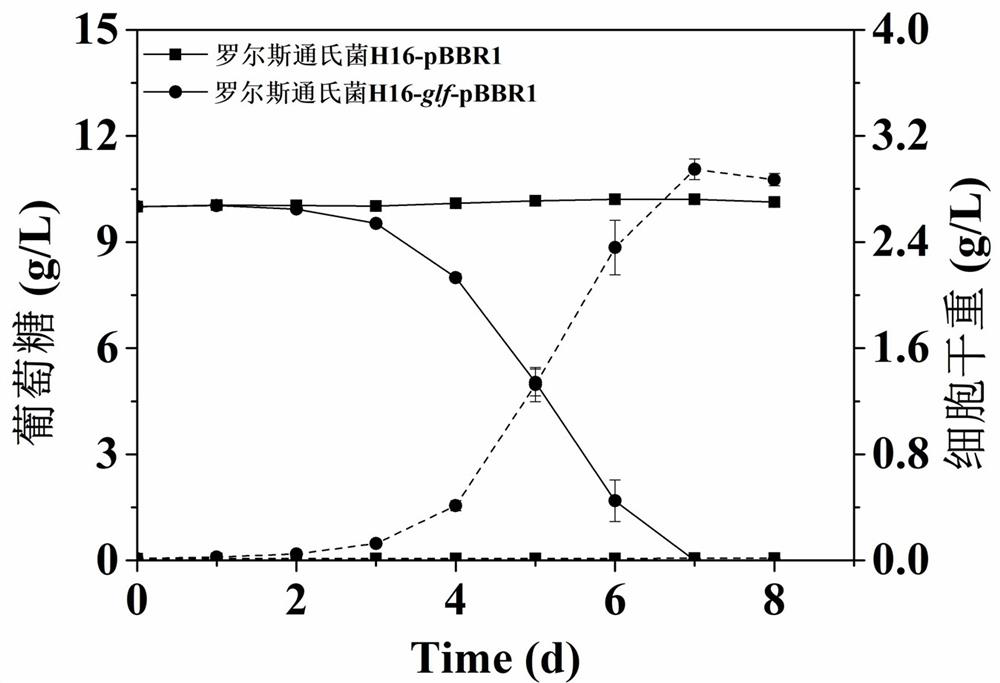
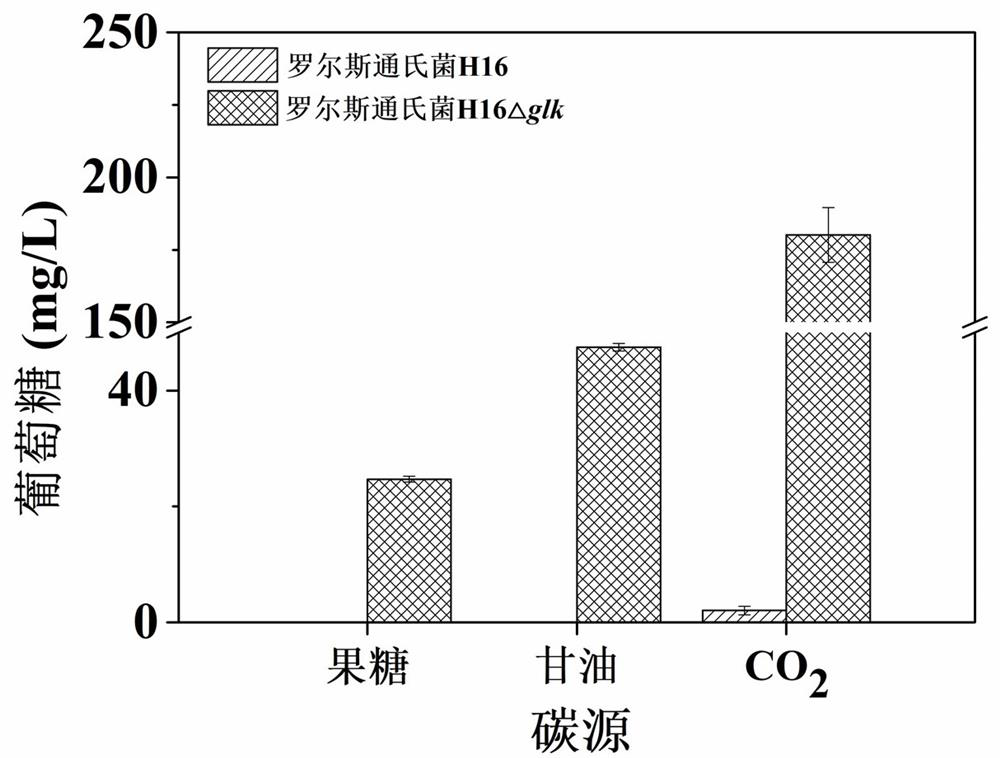
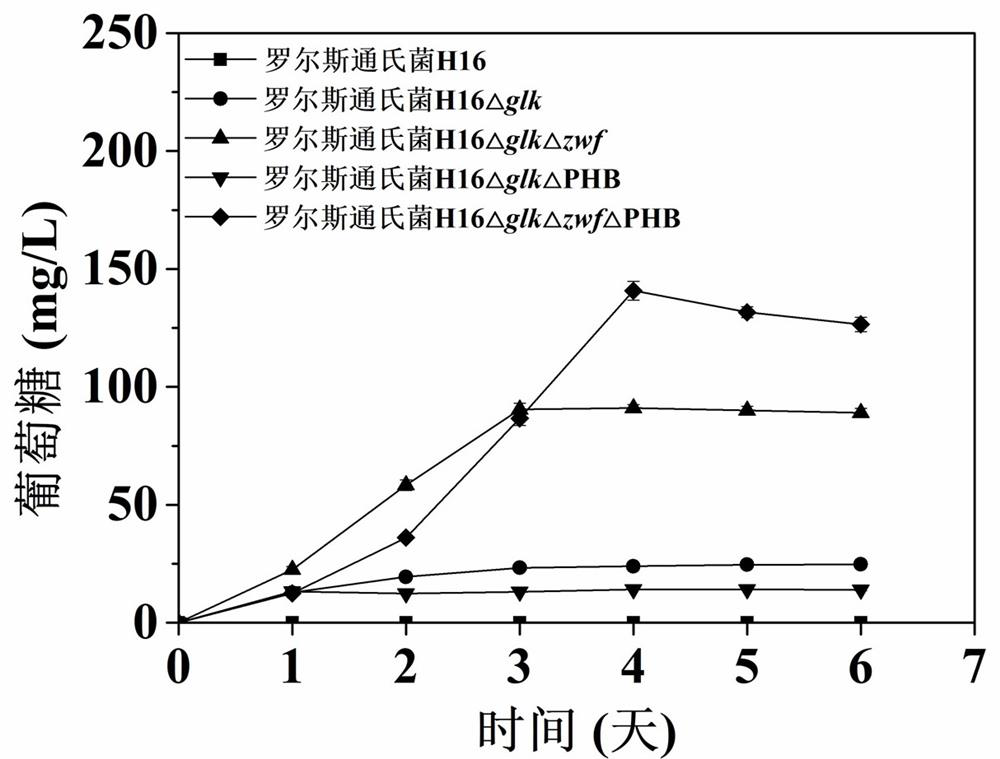
Ralstonia engineering bacteria for producing glucose and fermentation production method
ActiveCN114806998ARealize accumulationEfficient fixing capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHydroxybutyric acidFructose
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, in particular to a glucose-producing Ralstonia engineering bacterium and a fermentation production method. According to the invention, by knocking out a glucokinase gene (glk) in Ralstonia H16, the accumulation of the product glucose is realized when fructose, glycerol and carbon dioxide (CO2) are used as unique carbon sources. And then, the supply of product precursors glucose-6-phosphoric acid and glucose-1-phosphoric acid in the mutant Ralstonia cells is improved by blocking the diversion of carbon flow by an Enter-Doudoroff (ED) pathway and a phosphopentose poly ([R]-3 hydroxybutyric acid) (PHB) synthesis pathway. Fermentation is carried out by using fructose, glycerol and CO2 as unique carbon sources, and the highest yields of glucose respectively reach 140.8 mg / L, 73.9 mg / L and 253.3 mg / L.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Hydantoinase and carbamoyl hydrolase producing strain, bienzyme gene and application thereof for preparing L-amino acid
InactiveCN101215533BStable productionAvoid inhibitionBacteriaHydrolasesChemical synthesisHydrolase Gene
The invention relates to a new microbe Bacillus fordii MH602 strain which can simultaneously produce hydantoinase and L-N-carbamyl hydrolase, the hydantoinase and L-N-carbamyl hydrolase produced by the strain, and an application for preparing serial optical pure L-amino acid through the strain. The hydantoinase and L-N-carbamyl hydrolase that are produced by Bacillus fordii MH602 strain can overcome the defect of worse activity and heat stability of the hydantoinase and L-N-carbamyl hydrolase in the L-amino acid preparation process by prior biologically inverting DL-5 substituted hydantoin or N-hydantoinamino acid, which has wide substrate spectrum, and can catalyze a plurality of substrates and have better substrate selectivity for aromatic hydantoin. For the natural amino acid and non-protein amino acid which are difficult to produce by a fermentation method or a chemosynthesis method, the preparation of L-amino acid by using the Bacillus fordii MH602 is simple and stable in operation, good in repeatability, which realizes stable and cheap preparation of L-amino acid and facilitates to scale production.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Strain for producing tyrosine ammonia lyase and application of strain
ActiveCN111424005ABroaden the channels of strainsGood genetic stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesActive agentTyrosine
The invention relates to a strain for producing tyrosine ammonia lyase and an application of the strain, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The strain is classified and named as Acinetobacterjohnsonii, is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on May 15, 2020, and has a preservation number of CGMCC No.19831. The strain provided by the invention has good hereditary stability and low culture cost, the generated tyrosine ammonia lyase has high enzyme activity, and the strain has a wide applicable substrate spectrum and can be directly used for direct conversion and synthesis of p-hydroxycinnamic acid and p-hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives. During catalytic synthesis, addition of a surfactant, an organic solvent and other membrane penetrating agents is not needed, introduction of exogenous impurities is avoided, extraction and separation operation is facilitated, and advantages are achieved for industrial application.
Owner:SHANDONG YANGCHENG BIOLOGY TECH CO LTD
Recombinant escherichia coli KLUGIN73 and application thereof
PendingCN114606173ARealize one-time hydrolysisBroad substrate spectrumBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliEnzymatic hydrolysis
The invention discloses recombinant escherichia coli KLUGIN73 and application thereof. The preservation number of the recombinant escherichia coli KLUGIN73 is CCTCC (China Center For Type Culture Collection) NO: M 2022248. The thermophilic glycosidase generated by the escherichia coli KLUGIN73 has the capacity of hydrolyzing glucoside and rhamnoside, the substrate spectrum is wide, one-time hydrolysis of disaccharide of icariin can be achieved, the reaction condition is simple and single, and the cost of enzymatic hydrolysis of icariin is greatly reduced; according to the process for hydrolyzing icariin, the target product, namely icariin, is single, no by-product is generated, and the yield of the product is close to 100%; the recombinant glycosidase disclosed by the invention can completely hydrolyze 10mM icariin in a pure water phase, and the concentration of the recombinant glycosidase is far more than 1000 times of the solubility of the recombinant glycosidase in water, so that a process for producing icaritin by hydrolyzing icariin through an enzyme method has higher industrial application value.
Owner:董颖军
An extreme thermophilic bacterium and its application in high temperature composting fermentation
ActiveCN110819554BBroad substrate spectrumImprove qualityBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaHuminEngineering
The invention relates to the field of microbial technology and environmental engineering, and discloses an extreme thermophile and its application in high-temperature composting fermentation. The extreme thermophile is named GW-2, and its preservation number is CGMCC 18012, and the classification of microorganisms is named for Chelativorans composti . The strain of the present invention can grow normally in the range of 40-105°C, pH 5-11, and salinity 0-7%, can utilize various carbon sources and nitrogen sources for growth, and has a very broad substrate spectrum. The strain of the present invention combined with the special high-temperature composting process of the present invention can be used for high-temperature aerobic composting treatment of various organic matter such as kitchen waste, agricultural product tailings, slaughterhouse waste, etc., so that the organic matter is completely humified, dehydrated and dried, and loses weight by 70- 92%, finally forming a high-quality organic fertilizer.
Owner:HANGZHOU XIUCHUAN TECH CO LTD
A tyrosine ammonia lyase-producing strain and its application
ActiveCN111424005BBroaden the channels of strainsGood genetic stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesActive agentTyrosine
The invention relates to a strain producing tyrosine ammonia-lyase and its application, which belongs to the field of biotechnology. The strain is classified and named as Acinetobacter johnsonii, and has been preserved in China's microbial strains on May 15, 2020 General Microbiology Center of the Preservation Management Committee, deposit number: CGMCC No.19831. The bacterial strain provided by the present invention has good genetic stability, low cultivation cost, high enzymatic activity of tyrosine ammonia-lyase, and wide applicable substrate spectrum. There is no need to add membrane-permeable agents such as surfactants and organic solvents during synthesis, avoiding the introduction of foreign impurities, which is conducive to extraction and separation operations, and has advantages in industrial applications.
Owner:SHANDONG YANGCHENG BIOLOGY TECH CO LTD
Amidase xam and its encoding gene and application
ActiveCN111944794BIncrease enzyme activityBroad substrate spectrumHydrolasesGenetic engineeringChemical industryHydroxamic acid
The invention discloses amidase XAM and its coding gene and application. The protein provided by the present invention is derived from Xinfangfangia sp., is an amidase tag family amidase, named XAM protein, and is a protein composed of the amino acid sequence shown in Sequence 1 in the sequence listing. The invention also protects the use of XAM protein as amidase. The invention also protects the use of XAM protein in the production of hydroxamic acid. The present invention has great application prospects for related medical fields, chemical industry fields and the like.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
A method for enzyme-catalyzed selective amidation and hydrazide modification of polypeptide C-terminus
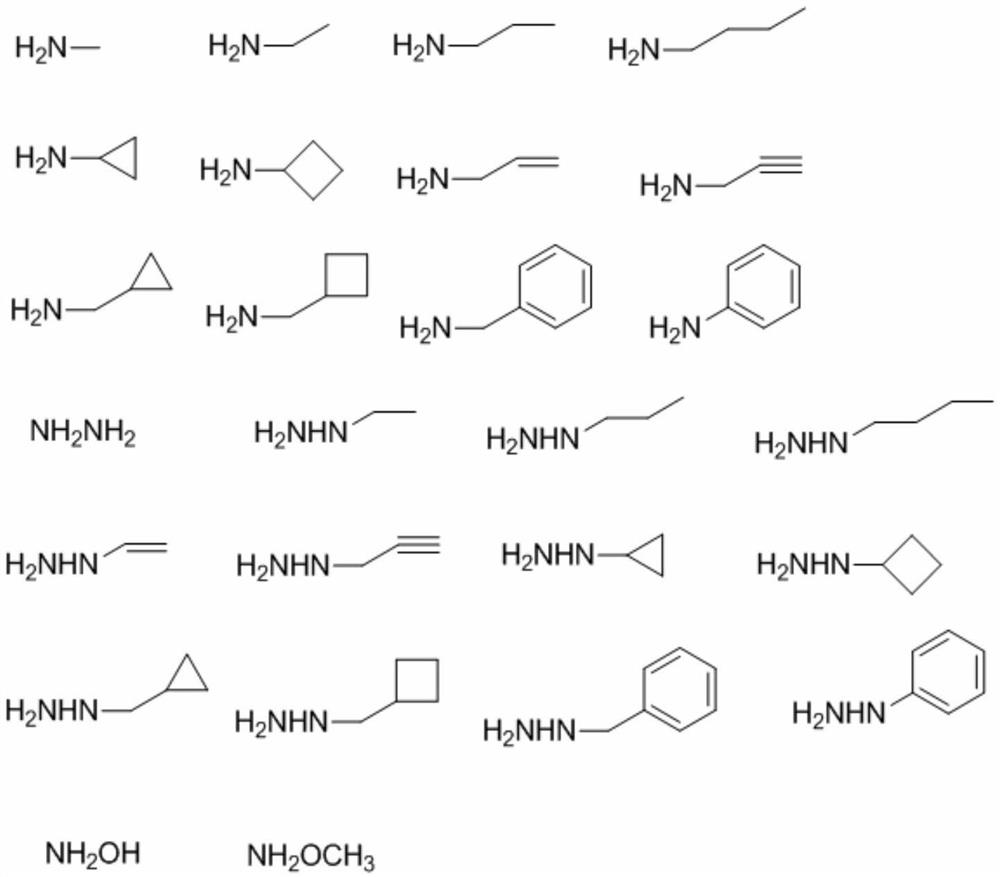
The invention discloses an enzyme-catalyzed polypeptide C-terminal selective amidation and hydrazidation modification method. The present invention provides a method for amidation and / or hydrazidation modification of the C-terminal amino acid of a polypeptide, which uses a specific protein to amidate and / or hydrazidate the C-terminal amino acid of the polypeptide; the specific protein is SEQ The protein shown in ID No.1. This method can be used to achieve amidation and / or hydrazidation modification of the C-terminal amino acid of the polypeptide, and it is an aqueous reaction with mild conditions. The C-terminal is selectively modified without affecting other modification groups on the side chain, and the side chain does not need to be protected. , with a wide substrate spectrum and no restriction on the amino acid sequence of the substrate polypeptide. Any amino acid at the terminal end of the modified polypeptide can be modified except proline.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com