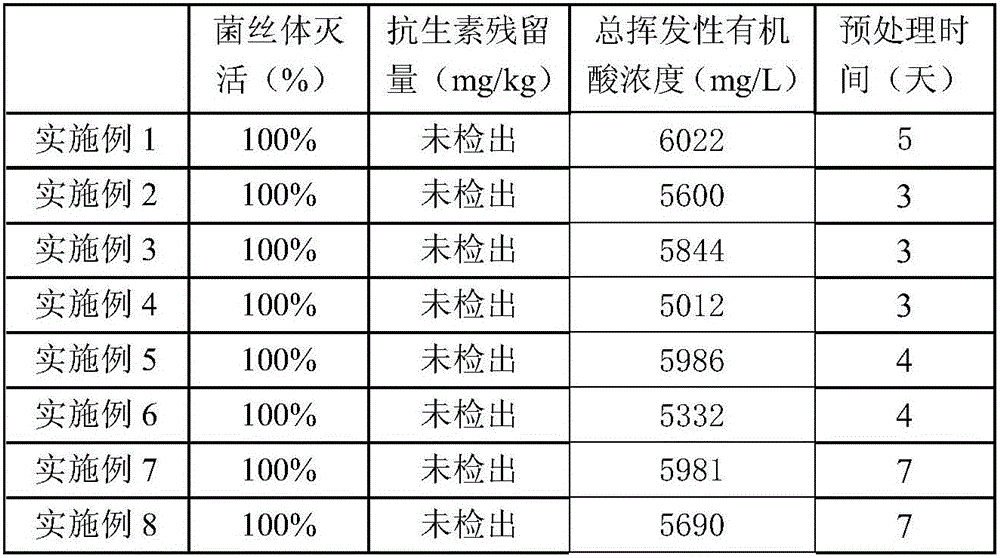
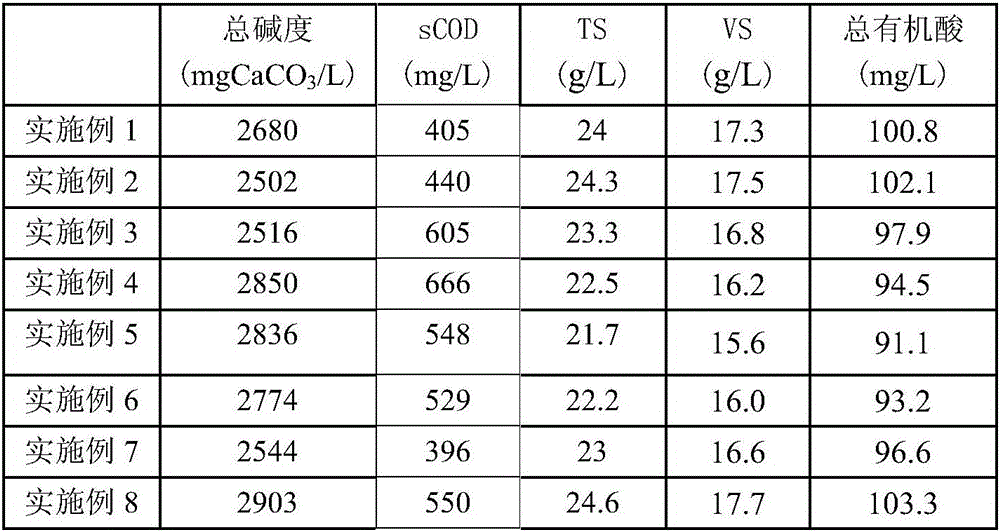
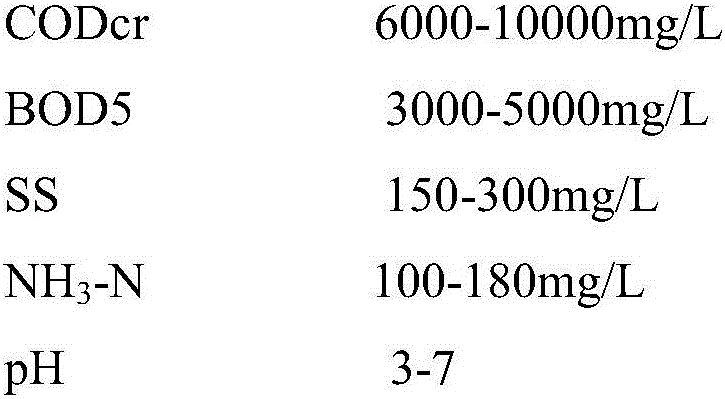Method for harmless treatment of ferment antibiotic fungus residues
A technology of antibiotic residues and antibiotics, applied in the field of harmless treatment of antibiotic residues, can solve the problems of difficult release of intracellular organic matter, difficulty in fully utilizing, low efficiency of methane production steps, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0096] The harmless treatment of embodiment 1 oxytetracycline bacterium slag
[0097] 1. Preparation of strains and sludge
[0098] 1-1) Preparation of thermophilic acid-producing bacteria
[0099] The thermophilic strains in Table 2 were inoculated on LB agar culture (tryptone 10g / L, yeast extract 5g / L, sodium chloride 10g / L, agar 15-20g / L, pH7), respectively, at 55°C Under anaerobic culture; then select the colonies with good growth status (big colonies) and inoculate them in fresh LB liquid medium (tryptone 10g / L, yeast extract 5g / L, sodium chloride 10g / L, pH7 ), anaerobic enrichment culture at 55°C until the biomass of the strains in the liquid medium increased to (1-2)×10 8 Bacteria / ml; then the culture solution of 7 strains of thermophilic bacteria was mixed in proportion to obtain thermolytic acid-producing bacteria, which were inoculated in the reactor to start the ultra-high temperature anaerobic fermentation treatment, among which 7 strains of thermophilic bacteria...
Embodiment 2
[0145] The harmless treatment of embodiment 2 penicillin scum
[0146] 1. Preparation of strains and sludge
[0147] 1-1) Preparation of thermophilic acid-producing bacteria
[0148] Except that the inoculation ratio of the 7 strains of thermolytic acid-producing bacteria is 0.8:1:1.2:1:1.2:0.8:1, the rest are the same as step 1-1) in Example 1.
[0149] In the present invention, Sarcina, Clostridium, Anaerobaculum, Coprothermobacter, Fervidobacterium, Caloranerobacter, the proportioning of Thermus in the thermophilic acid-producing bacteria except 0.8:1:1.2:1:1.2:0.8:1, the dosage proportioning is (0.8 -1.2):(0.8-1.2):(0.8-1.2):(0.8-1.2):(0.8-1.2):(0.8-1.2):(0.8-1.2) are applicable to the present invention.
[0150] 1-2) Preparation of medium temperature digested sludge and municipal surplus sludge
[0151] Medium temperature digested sludge, municipal residual sludge are the same as in step 1-2) in embodiment 1;
[0152] 2. Start-up treatment of ultra-high temperature anae...
Embodiment 3
[0172] The harmless treatment of embodiment 3 cephalosporin slag
[0173] 1. Preparation of strains and sludge
[0174] 1-1) Preparation of thermophilic acid-producing bacteria
[0175] Except that the inoculation ratio of the 7 strains of thermolytic acid-producing bacteria is 1:1.2:1:0.8:0.8:1:1.2, the rest are the same as step 1-1) in Example 1.
[0176] In the present invention, arcina, Clostridium, Anaerobaculum, Coprothermobacter, Fervidobacterium, Caloranerobacter, the proportioning of Thermus except 1:1.2:1:0.8:0.8:1:1.2 in the thermophilic acid-producing bacteria, the dosage proportioning is (0.8 -1.2):(0.8-1.2):(0.8-1.2):(0.8-1.2):(0.8-1.2):(0.8-1.2):(0.8-1.2) are applicable to the present invention.
[0177] 1-2) Preparation of medium temperature digested sludge and municipal surplus sludge
[0178] Medium temperature digested sludge, municipal residual sludge are the same as in step 1-2) in embodiment 1;
[0179] 2. Start-up treatment of ultra-high temperature ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com