Method for pretreating wastewater obtained from antibiotic production
A technology for antibiotic wastewater and production wastewater, which is applied in natural water treatment, water/sewage treatment, water treatment parameter control, etc. It can solve the problems of severe and harsh treatment conditions, low antibiotic residues, and reduce the biological toxicity of antibiotic production wastewater.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
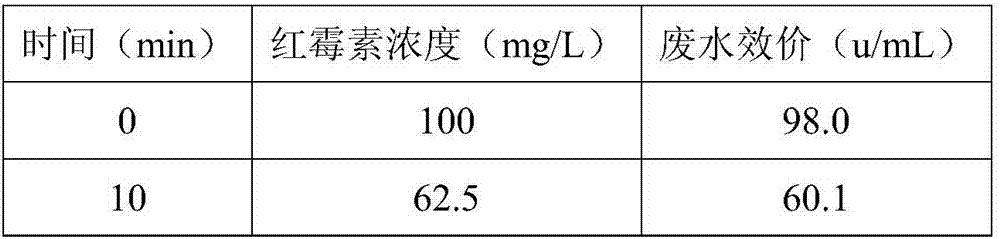
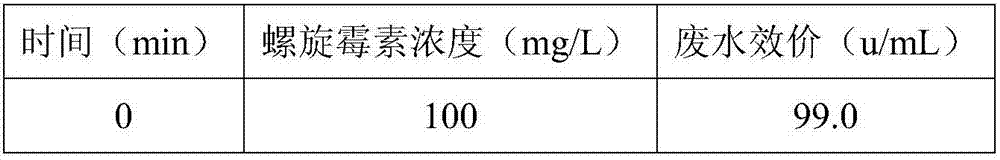
[0099] The treatment of embodiment 1 streptomycin simulated wastewater
[0100] 1. Preparation of streptomycin simulated wastewater
[0101] Streptomycin sulfate standard substance was dissolved in ultrapure water to prepare streptomycin simulated wastewater solution, wherein the concentration of streptomycin sulfate in the streptomycin simulated wastewater solution was 100mg / L.
[0102] In the embodiment of the present invention, 50 mg of streptomycin sulfate standard substance was dissolved in 500 mL of ultrapure water to make streptomycin simulated waste water for subsequent use.
[0103] 2. Preparation of solid base catalyst (CaO-MgO composite metal oxide)
[0104] 2-1) Mix calcium acetate with ultrapure water, stir and dissolve evenly, and prepare an aqueous solution of calcium acetate, wherein the ratio of the mass of calcium acetate to the volume of ultrapure water is 7.36:100, that is, dissolve in 100ml of ultrapure water 7.36 g calcium acetate.
[0105] In the embo...
Embodiment 1A
[0124] The treatment of embodiment 1A streptomycin simulated wastewater
[0125] 1. Preparation of streptomycin simulated wastewater
[0126] Same as Example 1.
[0127] 2. Preparation of solid base catalyst (CaO-MgO composite metal oxide)
[0128] 2-1) Mix calcium acetate with ultrapure water, stir and dissolve evenly, and prepare an aqueous solution of calcium acetate, wherein the ratio of the mass of calcium acetate to the volume of ultrapure water is 2.78:100, that is, dissolve in 100ml of ultrapure water 2.78 g calcium acetate.
[0129] In the embodiment of the present invention, 2.78g of calcium acetate was dissolved in 100mL of ultrapure water to prepare an aqueous solution of calcium acetate for subsequent use.
[0130] 2-2) Weigh light MgO (10g) calcined at 500°C for 8 hours, place it in an aqueous solution of calcium acetate, and carry out impregnation treatment at a stirring rate of 300rpm, and stop stirring after impregnating for 6 hours, wherein the mass of MgO...
Embodiment 1B
[0139] The treatment of embodiment 1B streptomycin simulated wastewater
[0140] 1. Preparation of streptomycin simulated wastewater
[0141] Same as Example 1.
[0142] 2. Preparation of solid base catalyst (CaO-MgO composite metal oxide)
[0143] 2-1) Mix calcium acetate with ultrapure water, stir and dissolve evenly, and prepare an aqueous solution of calcium acetate, wherein the ratio of the mass of calcium acetate to the volume of ultrapure water is 7.9:100, that is, dissolve in 100ml of ultrapure water 7.9 g calcium acetate.
[0144] In the embodiment of the present invention, 7.9g of calcium acetate was dissolved in 100mL of ultrapure water to prepare an aqueous solution of calcium acetate for subsequent use.
[0145] 2-2) Weigh light MgO (10g) calcined at 500°C for 8 hours, place it in an aqueous solution of calcium acetate, and carry out impregnation treatment at a stirring rate of 300rpm, and stop stirring after impregnating for 6 hours, wherein the mass of MgO is...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com