Complex microbial agent for composting fermentation and application thereof
A compound bacterial agent and composting technology, which is applied in the field of biological fermentation and microorganisms, can solve the problems of not reaching the compound bacterial agent, the total number of live bacteria in the product is not high, and the strain is not functional, so as to reduce unpleasant odor and improve the quality of compost products , The effect of reducing the cost of agricultural production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] 1.1 Microbial agent preparation
[0024] 1.1.1 Incline culture: the original strains of Phanerochaete chrysosporium, Streptomyces grisea, Bacillus subtilis, methylotrophic Bacillus and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (the above-mentioned strains are common strains in the art, and can be obtained commercially) were respectively inoculated on corresponding solid medium, Phanerochaete chrysosporium was cultivated at 28-30° C. for 3-5 days, Streptomyces grisea was cultivated at 28-30° C. for 5-7 days, and Bacillus subtilis, methylotrophic Bacillus and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens are cultured at 30-37°C for 2-3 days to activate the strains.
[0025] 1.1.2 Primary seed culture: Wash the activated slant with sterile physiological saline and transfer it to a sterile Erlenmeyer flask for shaking culture. Bacillus subtilis, methylotrophic Bacillus and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens were cultured at 30°C and 180r / mmin for 48 hours to obtain a first-grade seed solution;
[0026] Phanerocha...
Embodiment 2
[0045] The difference from Example 1 is that the mixing ratio during the preparation of the composite bacterial agent is: solid bacterial agents of Phanerochaete chrysosporium, Streptomyces grisea, Bacillus subtilis, methylotrophic Bacillus and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens according to 2:2:1:1:1 ratio mix well.
[0046] Composting raw materials and methods, sampling and assay methods are all the same as in Example 1.
[0047] 2.1 Experimental results
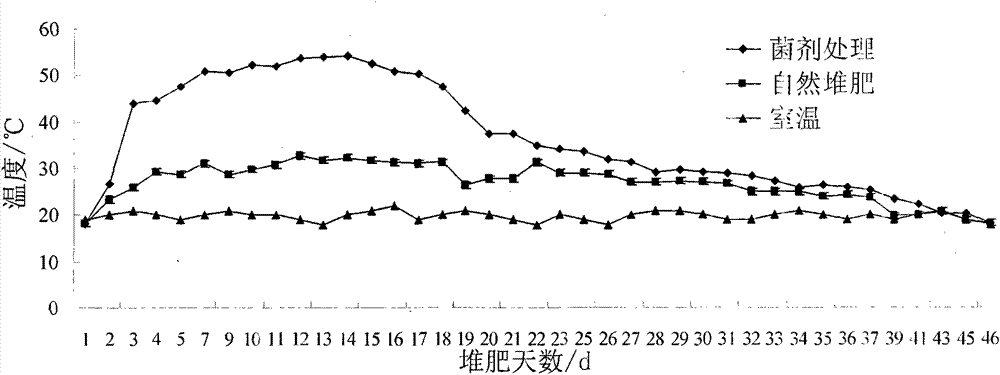
[0048] 2.1.1 Changes in temperature during composting
[0049] The compost inoculated with bacteria also enters the pyrolysis stage (>45°C) on the second day after composting (see figure 2 ), the high temperature period lasted 18 days, 2 days longer than Example 1.
[0050] 2.1.2 Changes in lignocellulose content during composting
[0051] It can be seen from Table 2 that at the end of composting, the degradation rates of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin in the compost added with bacterial agents increased by 32.5%, 22.48%...
Embodiment 3
[0055] The difference from Example 1 is that the mixing ratio during the preparation of the composite bacterial agent is: solid bacterial agents of Phanerochaete chrysosporium, Streptomyces grisea, Bacillus subtilis, methylotrophic Bacillus and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens according to 2:1:2:1:2 ratio mix well.
[0056] Composting raw materials and methods, sampling and assay methods are all the same as in Example 1.
[0057] 2.1 Experimental results
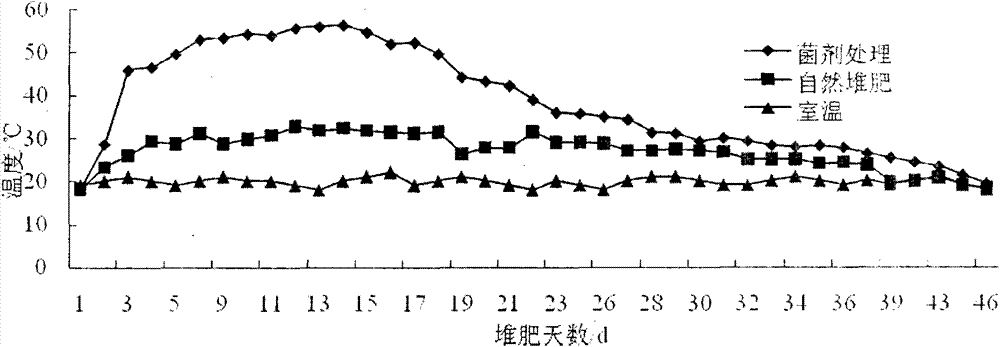
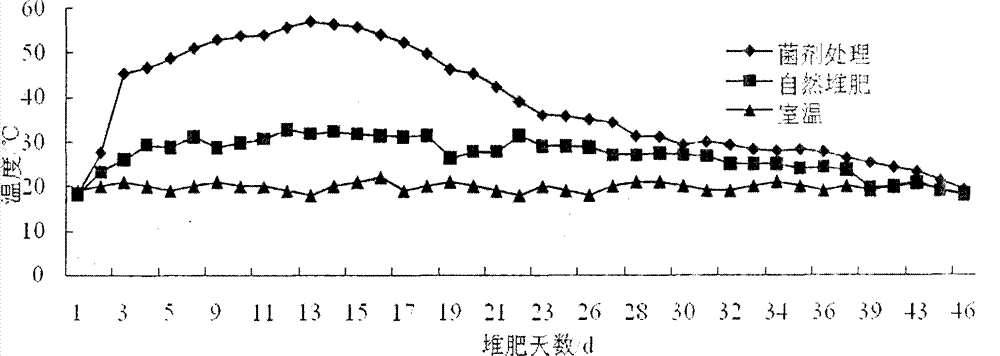
[0058] 2.1.1 Changes in temperature during composting
[0059] The compost inoculated with bacteria also enters the pyrolysis stage (>45°C) on the second day after composting (see image 3 ), the high temperature period lasted 17 days, which was extended by 1 day than in Example 1.
[0060] 2.1.2 Changes in lignocellulose content during composting
[0061] It can be seen from Table 3 that at the end of composting, the degradation rates of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin in the compost added with bacterial agents increased ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com