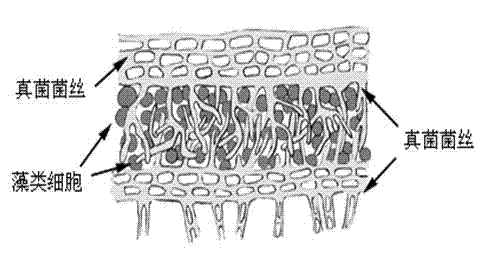
Harvesting method of microalgae mediated by fungus
A harvesting method and microalgae technology, applied in the field of renewable bio-energy, can solve the problems of high cost, high energy consumption, unsuitable for large-scale production applications, etc., and achieve the effect of controlling costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Oleaginous algal strains—Chlorella ( Cholorella vulgaris ) for local screening, and its autotrophic medium formula is as follows.
[0041] The formula of the above-mentioned autotrophic medium is: K 2 HPO 4 ·3H 2 O 0.04g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.075g / L, CaCl 2 2H 2 O 0.036g / L, citric acid 0.006g / L, ferric ammonium citrate 0.006g / L, EDTA 0.001g / L, NaNO 3 1.5g / L, Na 2 CO 3 0.02g / L, A5 trace element solution 1.5ml / L, of which A5 trace element solution composition: H 3 BO 3 2.86g / L, MnCl 2 4H 2 O 1.81g / L, ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.222g / L, NaMoO 4 2H 2 O 0.39g / L, CuSO 4 ·5H 2 O 0.079g / L, and CoCl 2 ·6H 2 O 0.05g / L.
[0042] The formula of the heterotrophic medium is the same as above, and the organic carbon source is added to the initial reducing sugar concentration of 20 g.L -1 .
[0043] By the method described in step 1, inoculate the strong individual colony of Chlorella grown on solid medium into a 250 mL shaker flask for shaking culture, and the temperatu...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Oil-bearing algal strains—Scenedes (Scenedesmus sp.) For local screening, the formula of the autotrophic medium is as follows.
[0048] The formula of the above-mentioned autotrophic medium is: K 2 HPO 4 ·3H 2 O 0.04g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.075g / L, CaCl 2 2H 2 O 0.036g / L, citric acid 0.006g / L, ferric ammonium citrate 0.006g / L, EDTA 0.001g / L, NaNO 3 1.5g / L, Na 2 CO 3 0.02g / L, A5 trace element solution 1.5ml / L, of which A5 trace element solution composition: H 3 BO 3 2.86g / L, MnCl 2 4H 2 O 1.81g / L, ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.222g / L, NaMoO 4 2H 2 O 0.39g / L, CuSO 4 ·5H 2 O 0.079g / L, and CoCl 2 ·6H 2 O 0.05g / L.
[0049] The formula of the heterotrophic medium is the same as above, and the organic carbon source is added to the initial reducing sugar concentration of 22 g.L -1 .
[0050] By the method described in step 1, inoculate the strong individual colony of Chlorella grown on solid medium into a 250 mL shaker flask for shaking culture, and the temperature ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com