Fungus strain for degrading polyurethane plastic and culture method and application of fungus strain
A technology of polyurethane and bacterial strains, which is applied in the field of bacterial strain culture and fungal strains, and can solve problems such as biodegradation of PU that have not been found
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1: Isolation and screening of fungal strain A.flavus G10:
[0035] S110. Isolating a fungal strain from the gut of a cricket.
[0036] Specifically, the cricket may be "Gryllus bimaculatus" cricket. Specifically, fungal strains were isolated from the gut of crickets.
[0037] S120, using PU as the sole carbon source, culturing the fungal strain in a liquid medium to obtain a culture solution;
[0038] Specifically, by dissolving each segment of the cricket gut in sterile saline solution and incubating the gut in a liquid medium.
[0039] Among them, the preparation method of the liquid medium is: add 0.7g KH to 1000ml deionized water 2 PO4, 7.7gK 2 HPO 4 , 0.7g MgSO 4 ·7H 2 0, 1.0gNH 4 NO 3 , 0.005g NaCl, 0.002g FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 0.002g ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 0.001gxx. Liquid media were sterilized by autoclaving at 121°C for 15 minutes before use.
[0040] S130. Dilute the culture solution containing the fungal strain and spread it on solidified nutrient a...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Example 2: Identification of fungi
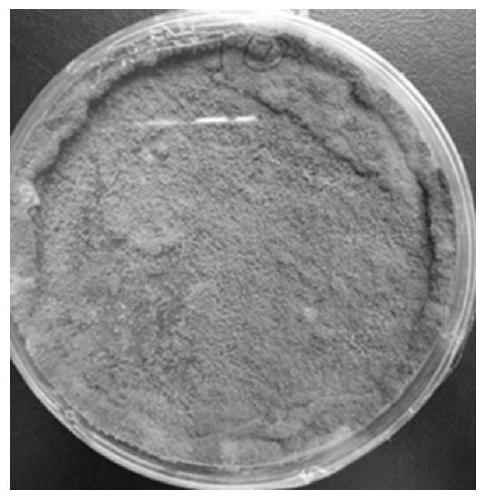
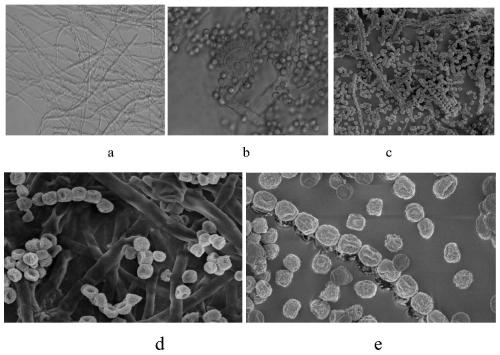
[0045] DNA from degrading fungal strains was isolated at room temperature (25-28°C), purified and plated on malt extract agar (MEA) plates. Morphological characterization was performed by light microscopy and stereo electron microscopy. The PU-degrading fungus isolated by molecular morphology and phylogenetic analysis was identified as Aspergillus flavus G10.
[0046] Specifically, the identification method is: morphological characterization by optical microscope and stereo electron microscope. In internal transcribed spacer (ITS5 / ITS4), large subunit (LR0R / LR5), RNA polymerase II second largest subunit (fRPB2-5f / fRPB2-7cR), calmodulin (CAL-228F / CAL2Rd) and β- for molecular identification. Tubulin (T1 / T2) sequence method. The ITS sequence data generated in this study were subjected to BLAST searches in GenBank's nucleotide database (www http: / / blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / ) to identify their most likely closely related taxa. Single-ge...
Embodiment 3
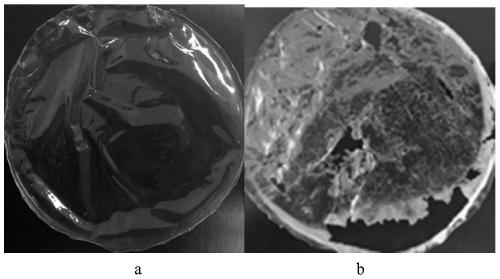
[0047] Embodiment 3: The method for degrading polyurethane plastics using fungal strain A.flavus G10:
[0048] Cultivation conditions: The conditions in the incubator were maintained at a temperature of 24±2°C, a relative humidity of 75±2%, and a light ratio of 8:10 to cultivate 300 crickets. There were a total of 6 small incubators in one incubator. There are 50 crickets in an incubator.
[0049] Among them, the control group: 150 healthy adult crickets were raised under the control conditions that the temperature was 24±2°C, the relative humidity was 75±2%, and the light ratio was 8:10, and fed with wheat bran, wheat germ and yeast powder. The ratio is 10:3:1 respectively. Also add 0.2% of the total amount of vitamin powder and water.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com