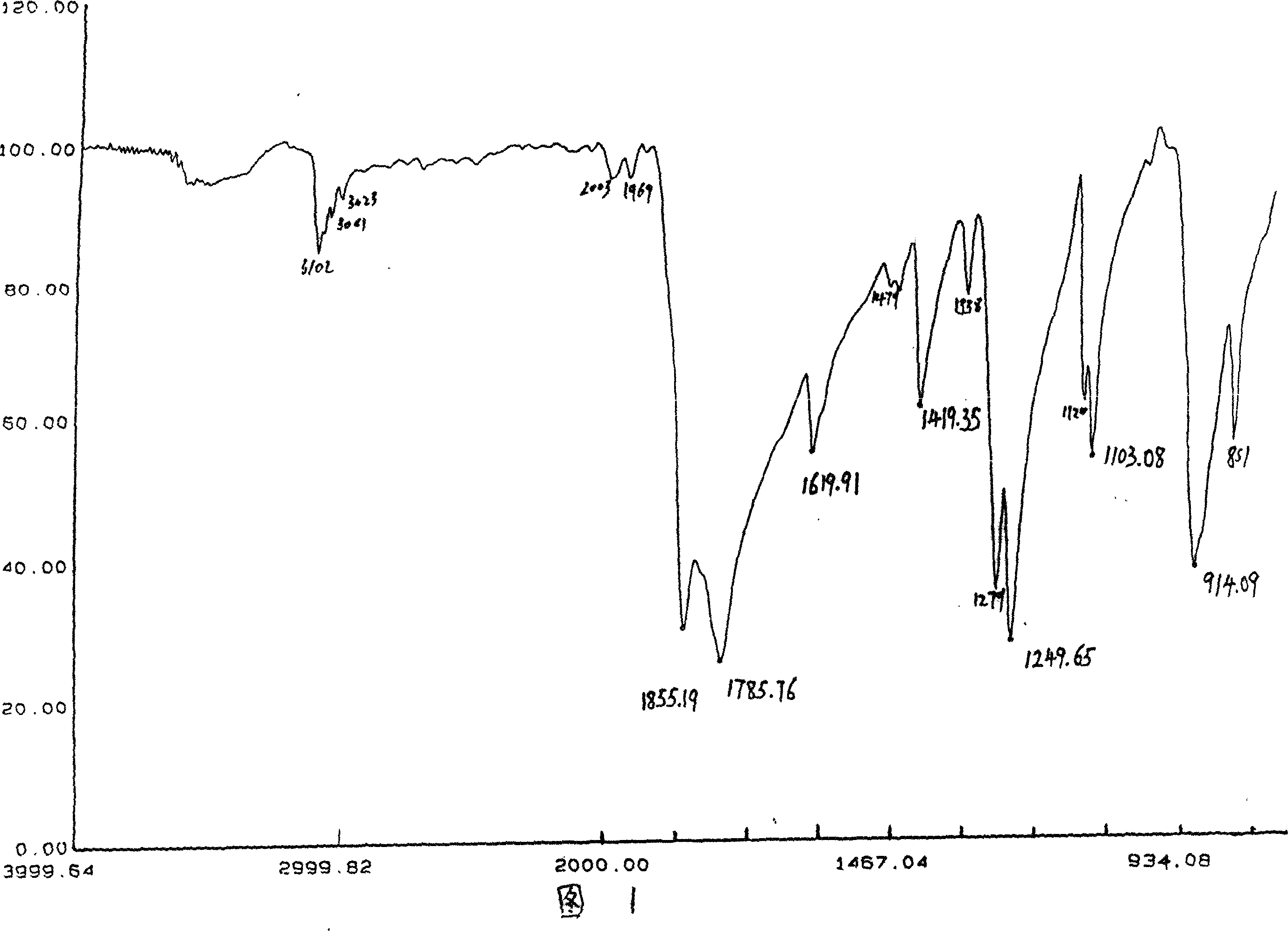
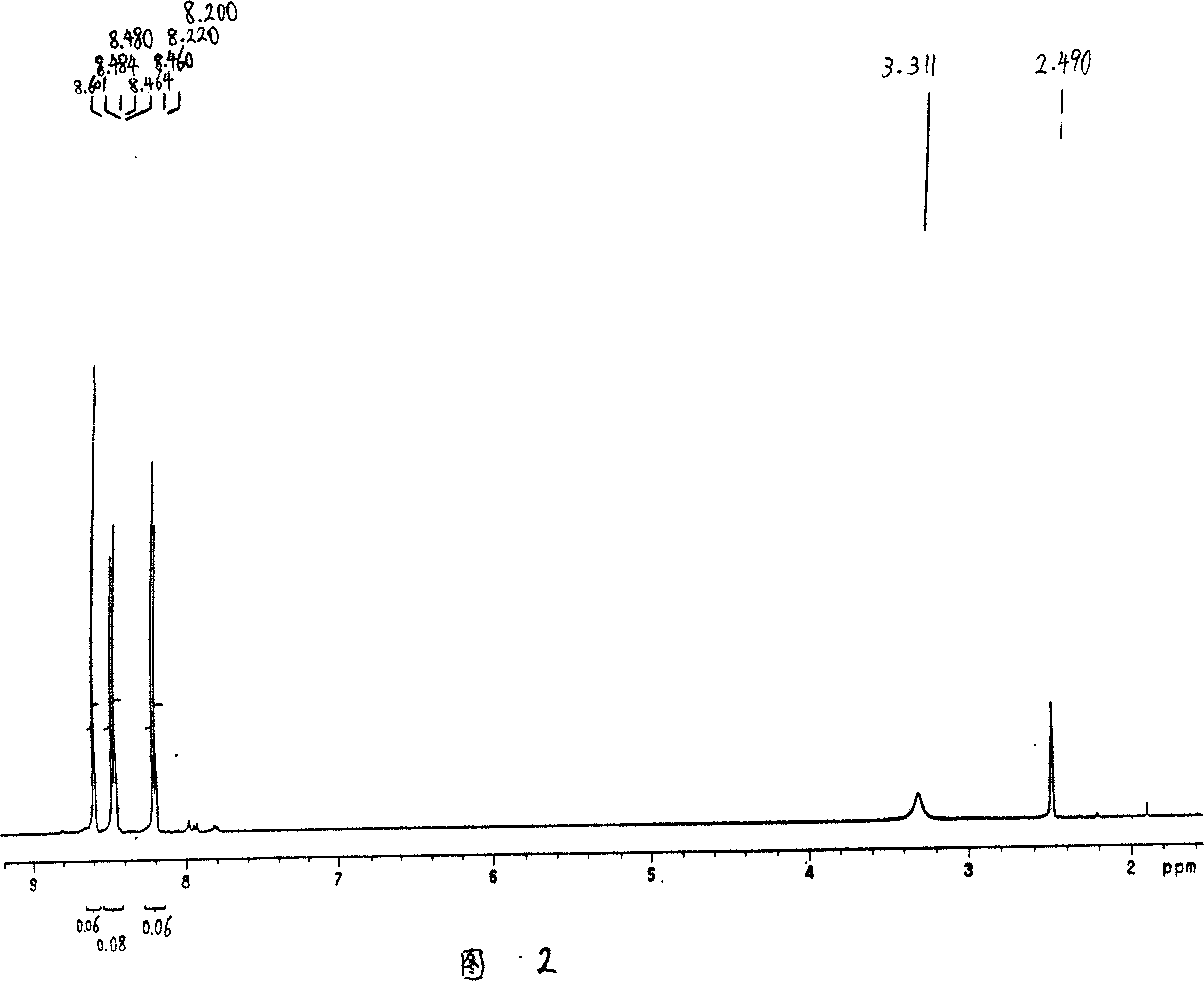
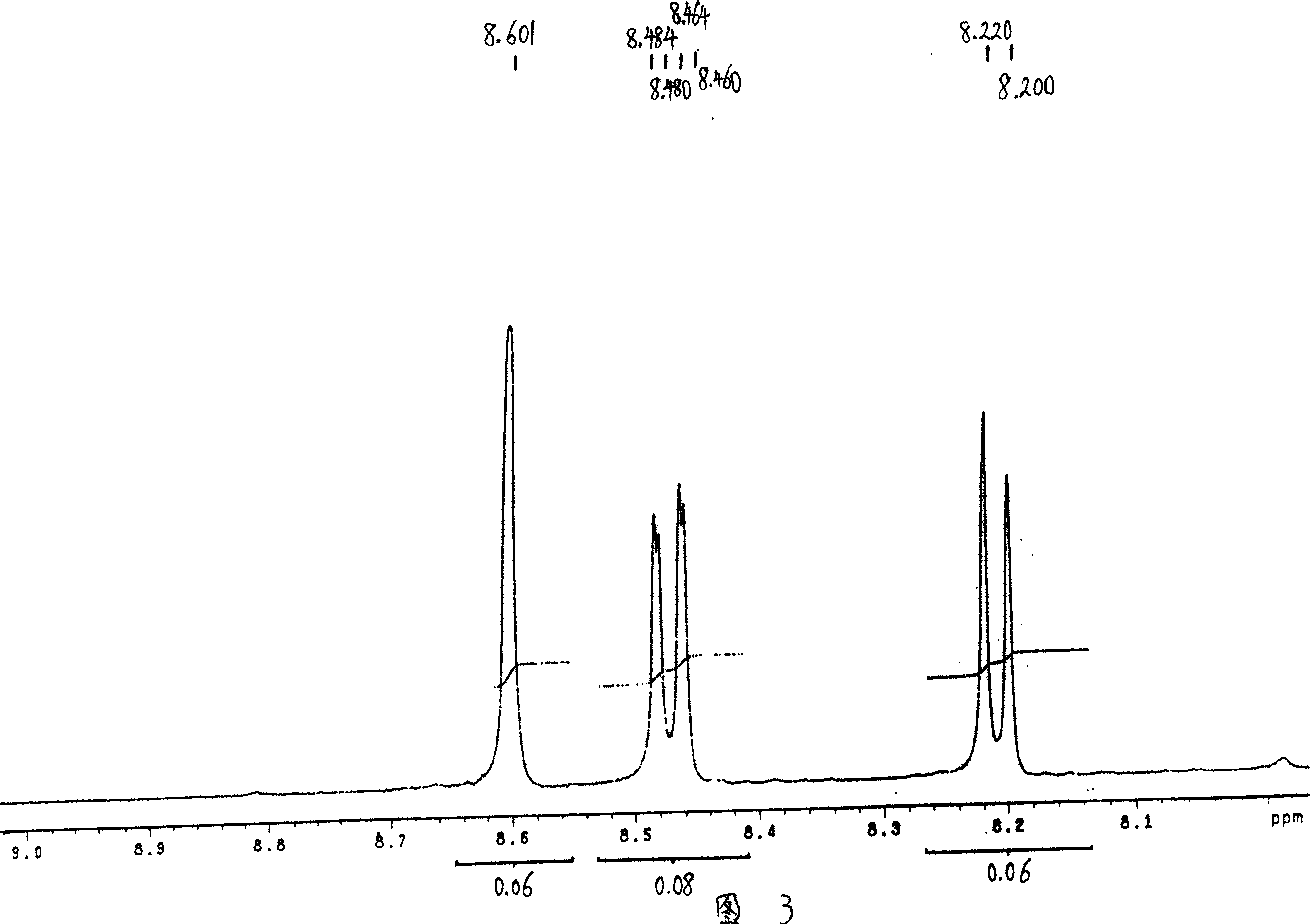
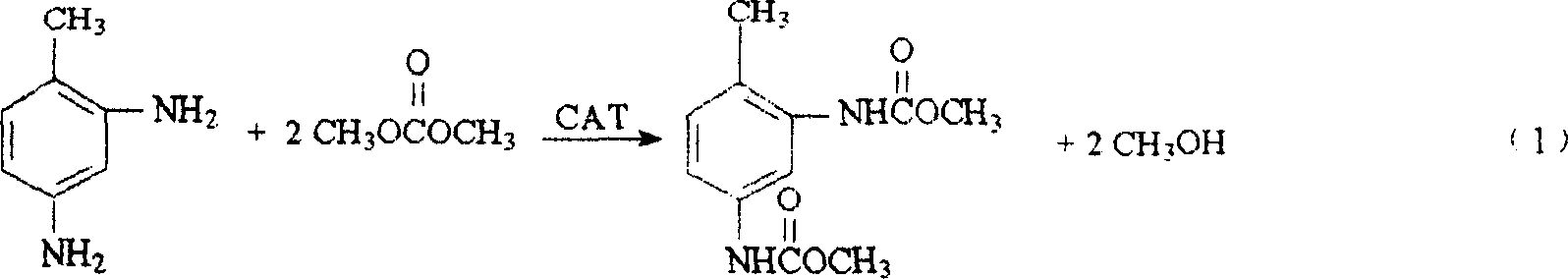
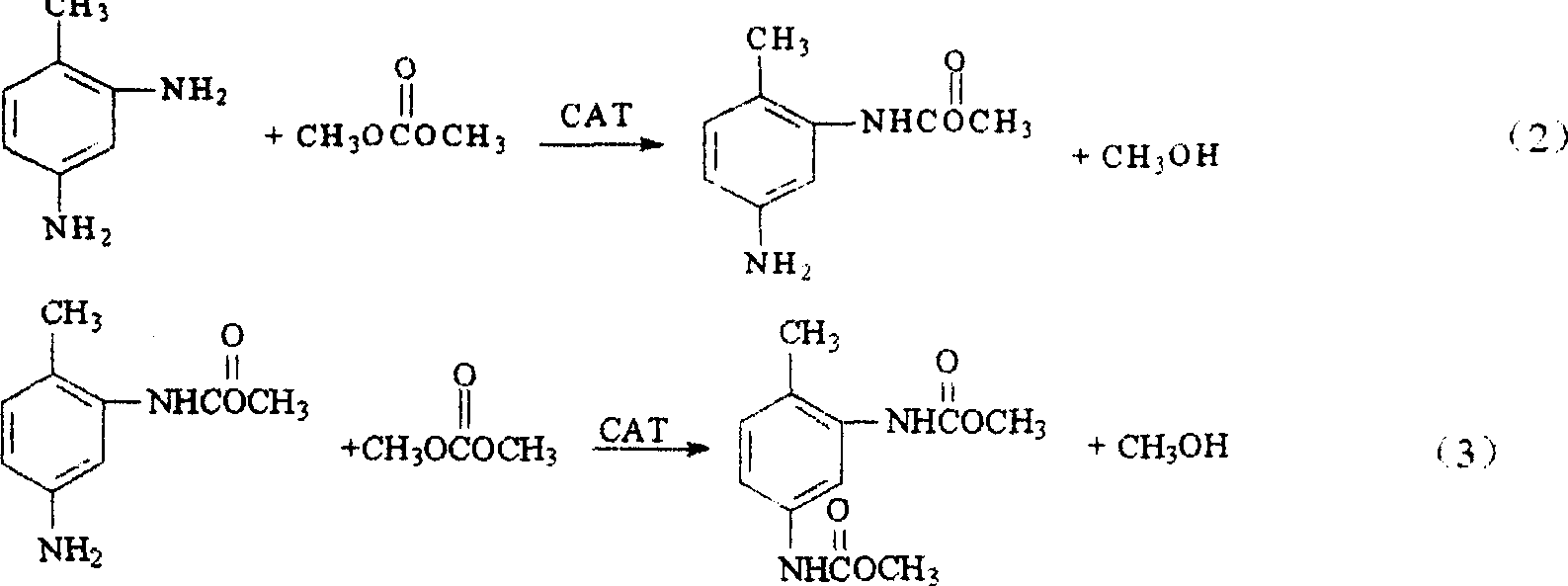
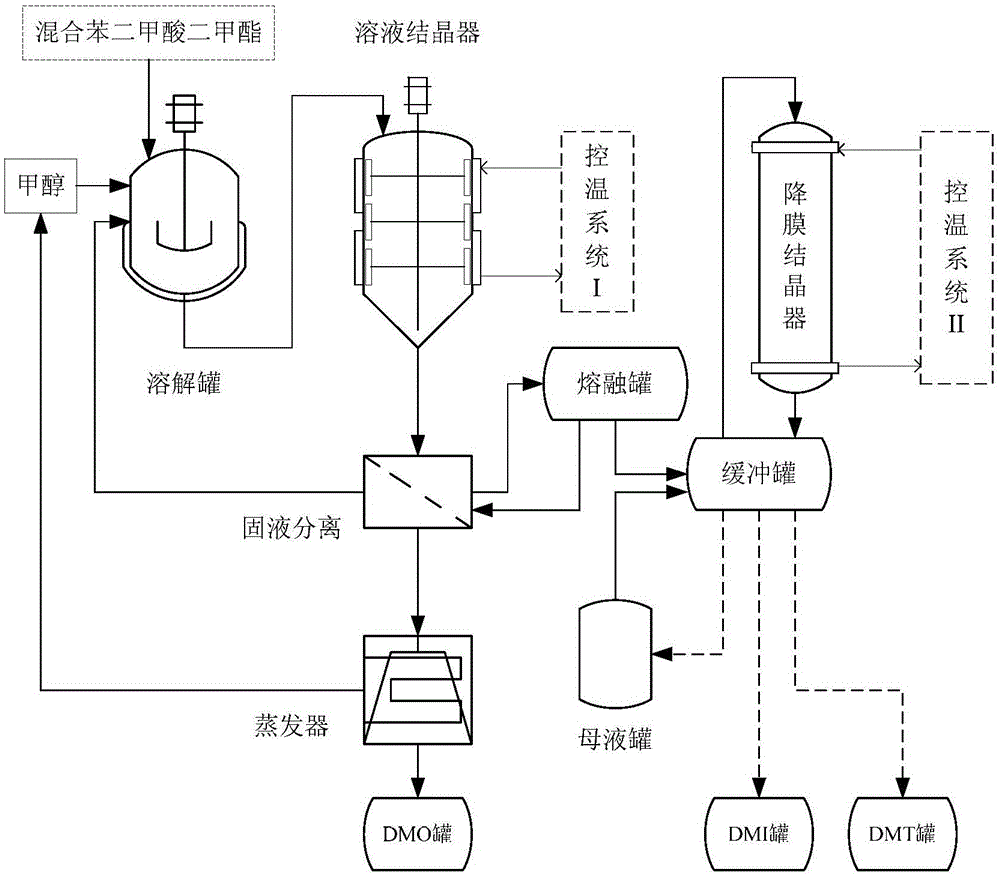
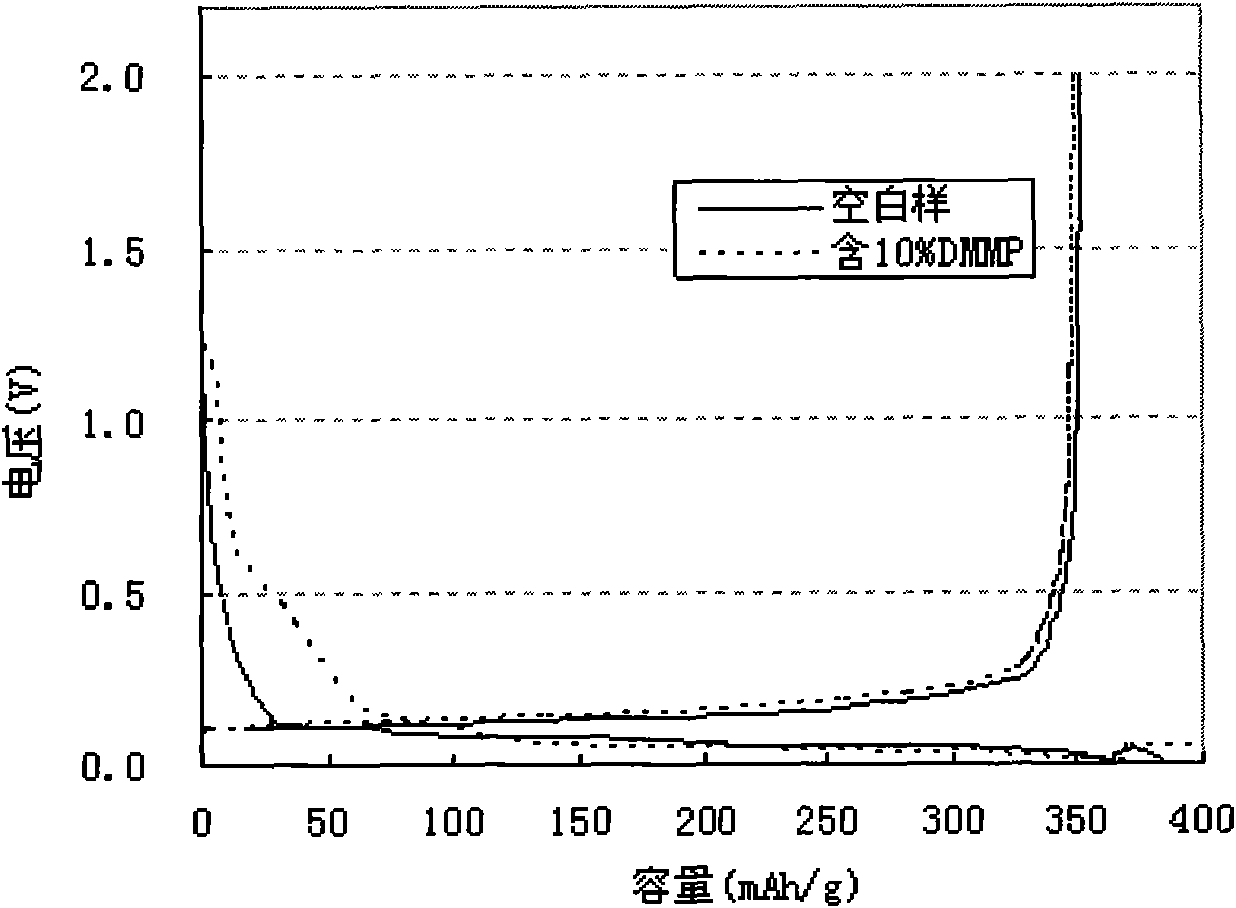
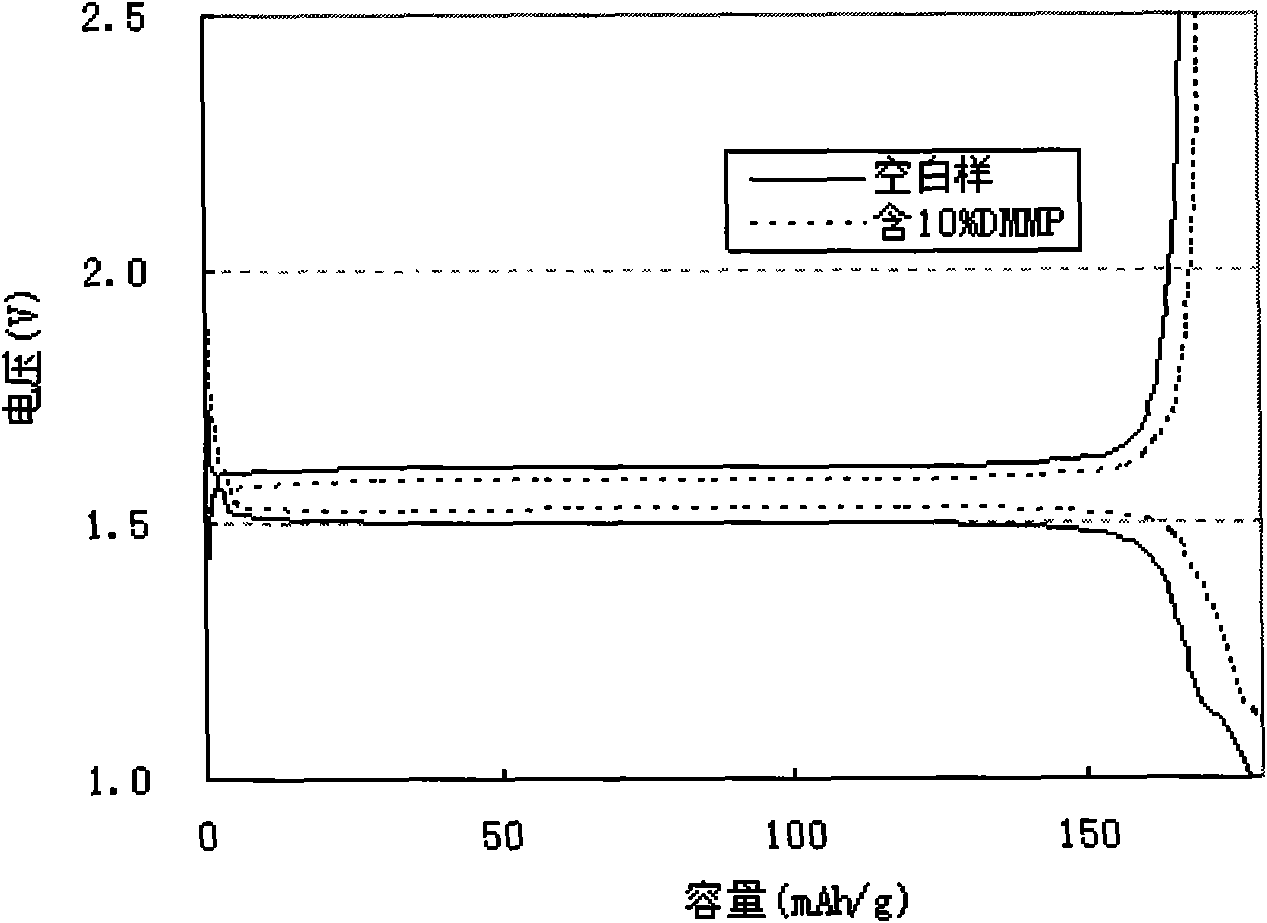
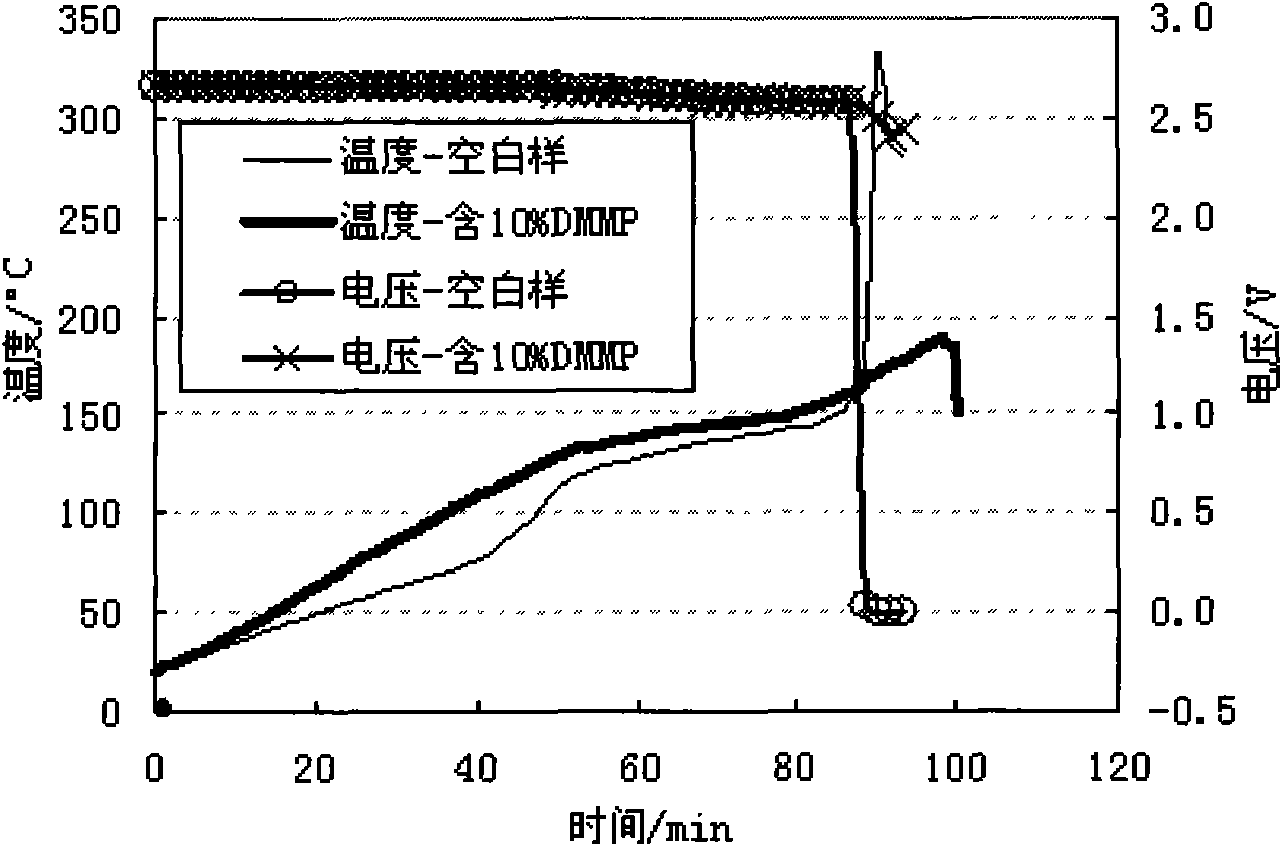
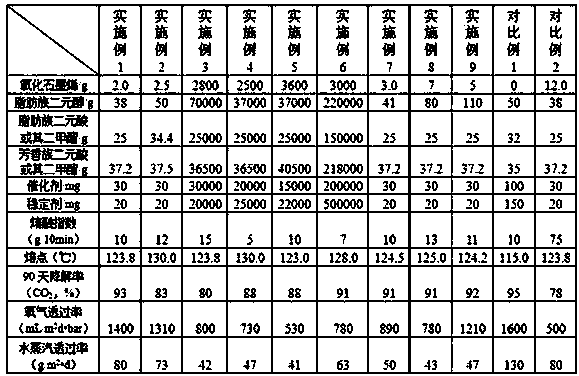
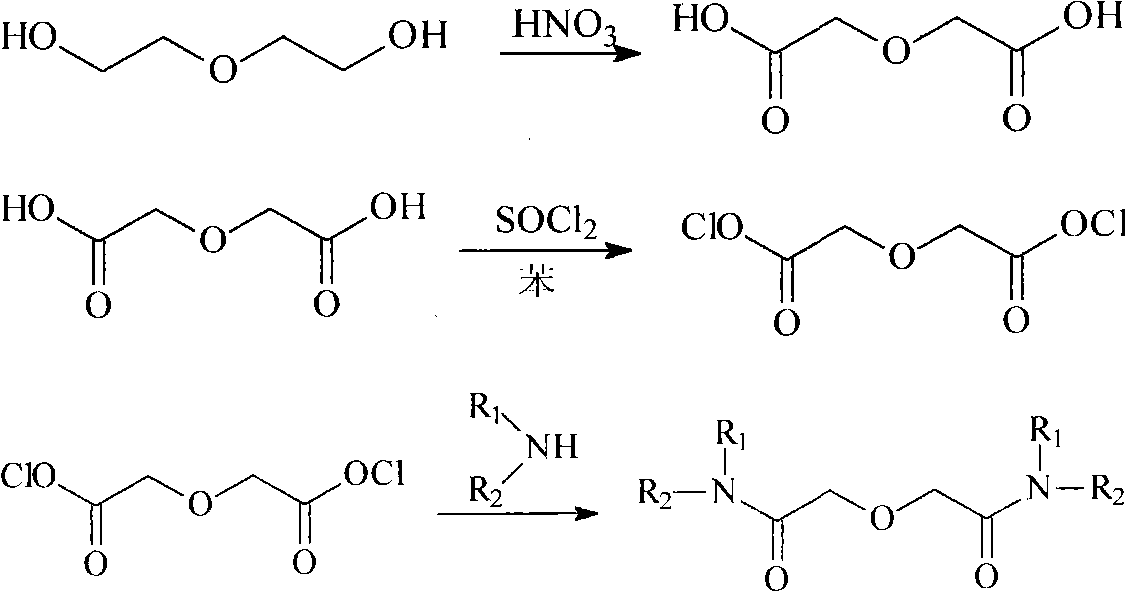
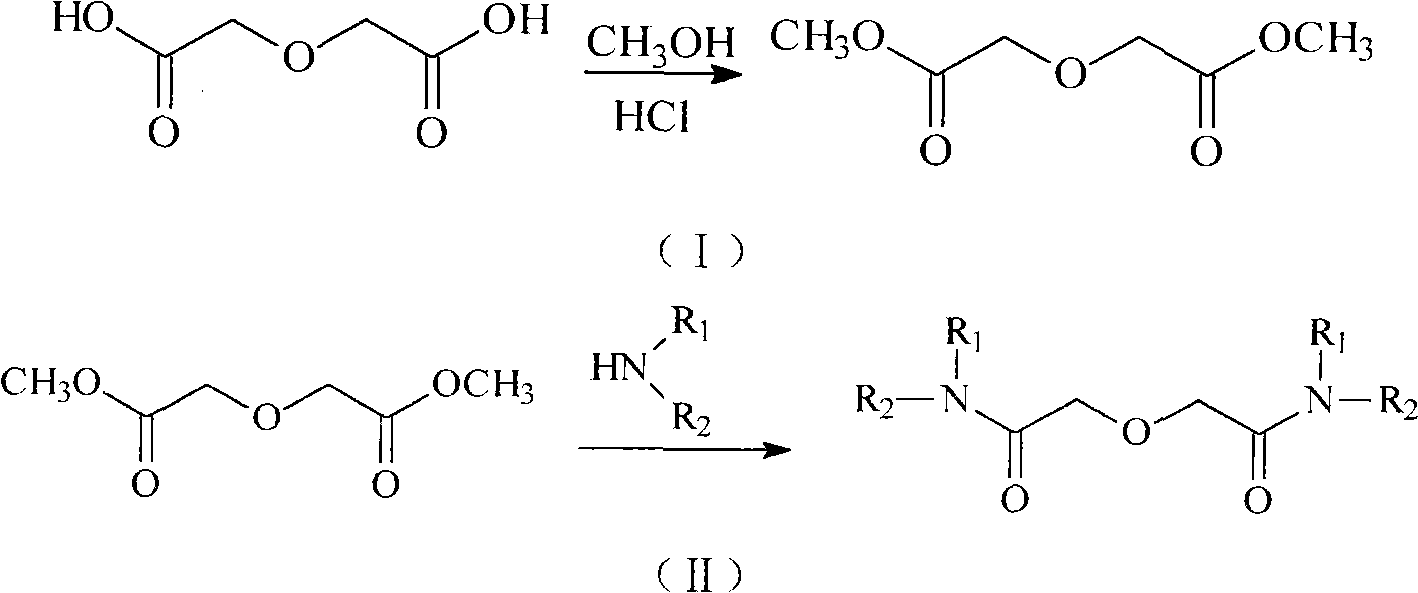
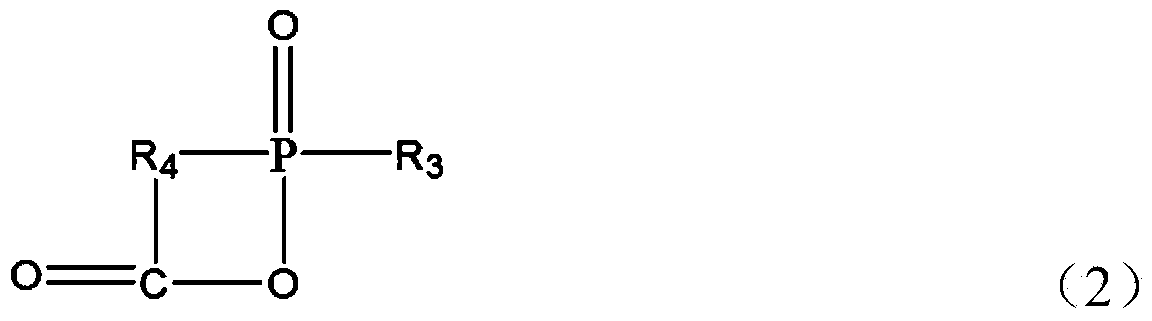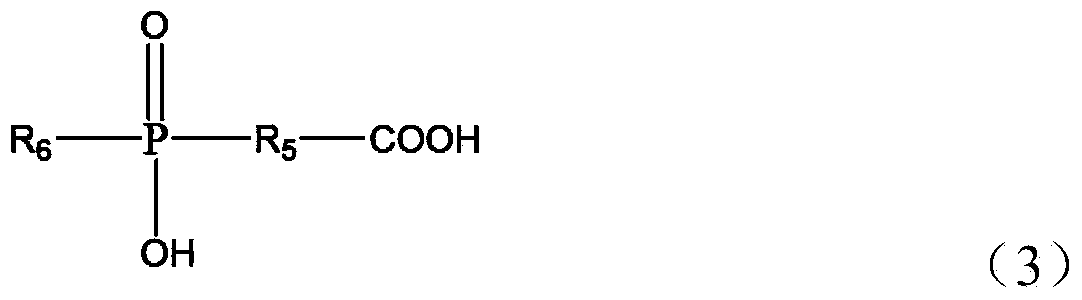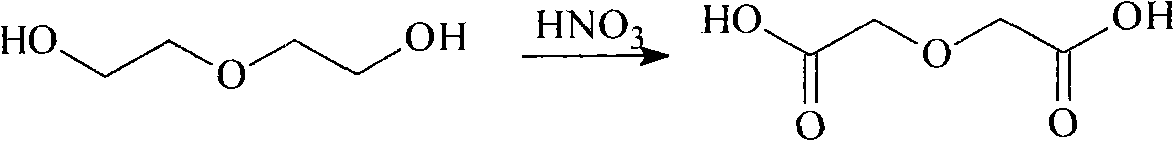Patents
Literature
419 results about "Dimethyl ester" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dimethyl Esters (also known as Dibasic Esters, DBE, and DMEs*) are readily biodegradable, low odor, low VOC solvents used in a wide variety of industrial and specialty applications.
Method for preparing 1,2-cyclohexane cyclohexanedimethanol dibasic ester
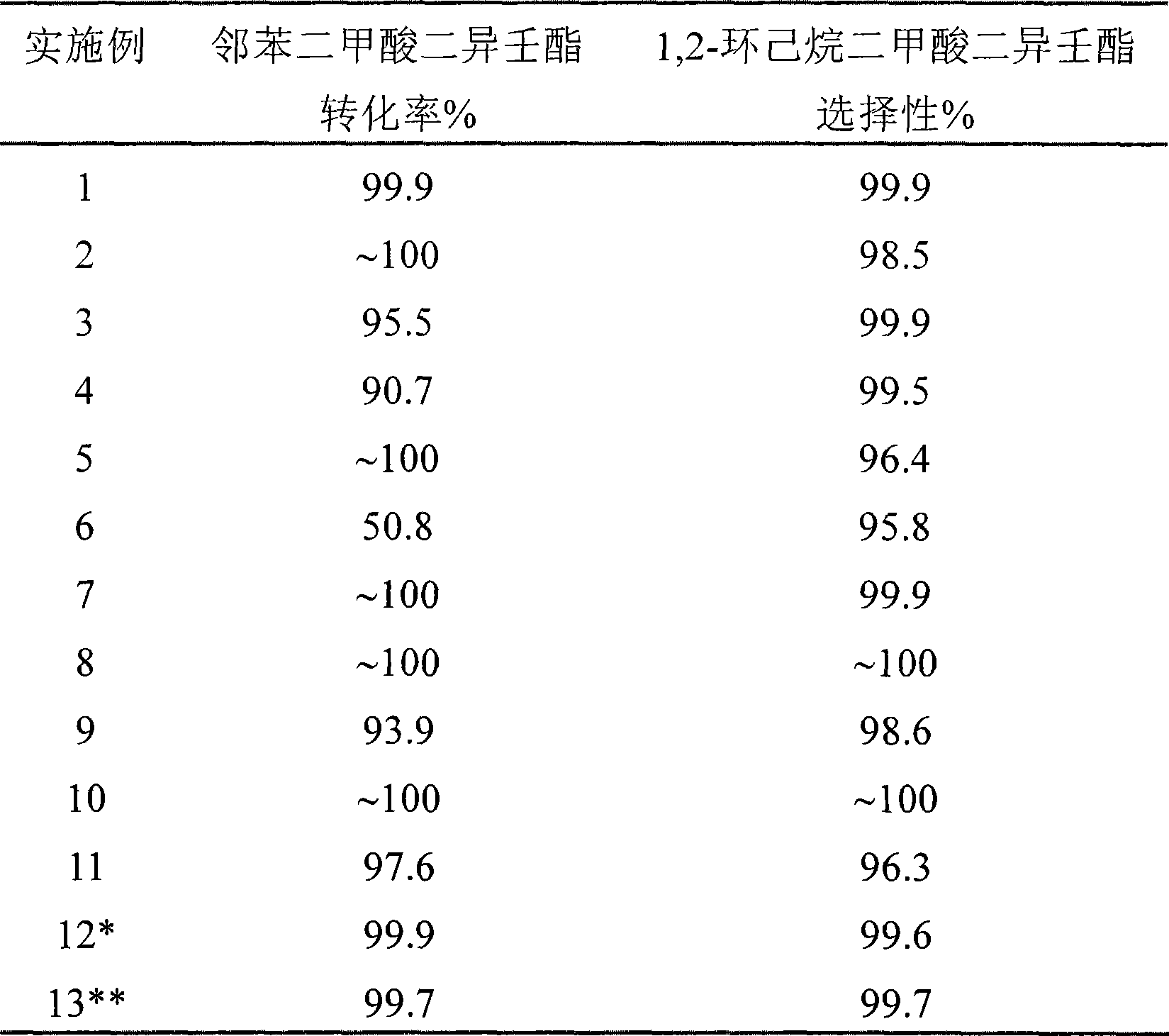
ActiveCN101417950AHigh selectivityLow reaction pressureOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationReaction temperatureDibasic ester
The invention relates to a method for preparing 1, 2-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid ester of binary, comprising a reaction system composed by binary phthalate ester, hydrogen and a catalyst; the reaction temperature ranges from 100 to 250 DEG C; the reaction pressure ranges from 3.0 to 12.0 Mpa; the molar ratio of H2 and X ranges from 50 to 450; the liquid space velocity of binary phthalate ester ranges from 0.1 to 2.5 h<-1>; the catalyst uses Al2O3, ZrO2, TiO2 or SiO2-Al2O3 as vehicle, and load active component can be Ru, Pt, Pd, Rh, Fe, Co, Ni and Cu; the binary phthalate ester is diisonynol phthalate, diisooctyl phthalate or dibutyl phthalate; the product 1, 2-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid ester of binary is 1, 2-cyclohexane diisononyl dimethyl ester, 1, 2-cyclohexane diisooctyl dimethyl ester or 1, 2-cyclohexane dibutyl dimethyl ester.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-fullness high-resolution environment protection polyureshane sublight uarnish
InactiveCN1483777AIncreased weight percentageReduce weightPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsKetoneSolvent
The present invention relates to a high-fullness high-distinctness environment-protecting type polyurethane matte varnish. Said varnish consists of the paint component, polyurethane solidifying agent component and diluting agent component according to the ratio of 1:0.5:0.6-0.8. The polyurethane solidifying agent component contains 50-70 wt% of tolylene diisocyanate trimer, and the rest is the affixture of 80% of tolylene diisocyanate and 20% of trimethylol propane, the paint component contains 15-25% of short oil soya alkyd resin whose solid content is 80%, 50-60% of modified saturated polyester resin, 0-5% of castor oil, 10-12% of aldehyde ketone resin whose solid content is 60%, 3-5% of flatting silica, 0.3-1.0% of teflon wax and 4%-10% of conventional adjuvant and solvent, and the diluting agent component contains 70-80% of butyl acetate, 10-20% of mixed diacid dimethyl ester and 10-15% of isophorone.
Owner:SHENZHEN FEIYANG JUNYAN TECH DEV
Combustion-resisting electrolyte of lithium secondary cell and its lithium cell
InactiveCN101079505AImprove flame retardant performanceSafe storageSecondary cellsCombustionPhosphate
The invention discloses a flame-proof electrolyte and its lithium battery for secondary lithium battery, which is characterized by the following: adopting one or more phosphosubester (such as methyl acid phosphate dimethyl ester, ethyl phosphate diethyl ester and its derivant) as pure solvent or solvent component; reducing the price of electrolyte with incombustibility, low toxicity and high conductivity; improving the combusting safety effectively.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Preparing method of 3,4,3',4'-biphenyltetracarbosylic dianhydride
InactiveCN101016284AEasy to recycleReduce processingOrganic chemistryReaction temperatureAcetonitrile
The invention discloses a making method of 3.4.3'.4'-biphenyl tetracarboxylic dianhydride, which comprises the following steps: adopting 4-chlorophthalandione anhydride as raw material; preparing 4-chlorophthalandione dimethyl ester, 3.3'.4.4'-biphenyl tetracarboxylic tetramethyl ester, 3.3'.4.4'-biphenyl tetracarboxylic acid and 3.3'.4.4'-biphenyl tetracarboxylic dianhydride; coupling; hydrolyzing; refining; (1) adopting p-toluenesulfonic acid as esterifying catalyst in the preparing procedure of 4-chlorophthalandione dimethyl ester; (2) adopting acetonitrile as solvent in the coupling procedure; (3) purifying hydrolytic 3.3'.4.4'-biphenyl tetracarboxylic acid through deionized water in the refining procedure; (4) washing and purifying 3.3'.4.4'-biphenyl tetracarboxylic dianhydride through acetone.
Owner:北京益利精细化学品有限公司
Preparation method of cationic dyeable flame-retardant polyester resin
The invention discloses a preparation method of cationic dyeable flame-retardant polyester resin. The manufacturing method is characterized by comprising the following steps: performing an esterification reaction on a halogen-free copolymerized phosphorus-based flame retardant, ethylene glycol and a composite catalyst to prepare an esterification solution of the halogen-free copolymerized flame retardant; performing ester exchange reaction on sulfoisophthalic acid dimethyl ester and the ethylene glycol to prepare a sulfonate-based bis(hydroxyethyl) isophthalate solution; performing an esterification reaction on terephthalic acid (or dimethyl terephthalate), the ethylene glycol and auxiliaries, then adding a catalyst, a stabilizer, the auxiliaries, the esterification solution of the phosphorus-based flame retardant (or a prepolymer solution of the phosphorus-based flame retardant) and the sulfonate-based bis(hydroxyethyl) isophthalate solution, performing condensation polymerization reaction, and cooling and dicing after the end of reaction to prepare the cationic dyeable flame-retardant polyester resin. The cationic dyeable flame-retardant polyester resin prepared by the method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of good spinnability, polyester fiber cationic dye boiling dyeing under normal pressure conditions, complete chromatogram and strong dye adhesion.
Preparation method of diethyl succinate
InactiveCN101323566AImprove protectionMild control conditionsOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationAlcoholDistillation
The invention discloses a preparation method of butane diacid dimethyl ester. The preparation process comprises the following steps of: (1) the rate of raw materials and a catalyst and dosage quality rate thereof is: butane diacid : industrial ethanol : absolute ethyl alcohol : the catalyst is equal to 1 : 0.8 to 1.1 : 0.1 to 0 : 0.01 to 0.02; 1) putting butane diacid, industrial ethyl alcohol of 20 percent of total amount and the catalyst into an esterification kettle and increasing temperature to 120 DEG C; 2) inputting residual industrial ethanol continuously for 8 hours to 9 hours, maintaining the temperature of the kettle at 115 DEG C to 120 DEG C and the temperature of the top of distillation device less than 105 DEG C; 4) sampling to detect acid value and inputting absolute ethyl alcohol when the acid value is 40mgKOH / g to 48mgKOH / g; 5) sampling to detect acid value after an hour and stopping heating when the acid value is 10mgKOH / g to 15mgKOH / g; 6) reducing the temperature to 80 DEG C after ethyl alcohol is withdrawn from the kettle by opening vacuum; 7) separating the catalyst from the materials cooled to 80 DEG C and putting the catalyst into an alkaline washing kettle; 8) inputting alkali solution of proper amount and mixing for 20 minutes to 40 minutes under temperature of 60 DEG C to 70 DEG C; 9) placing stilly for layering and emitting the lower water layer; 10) adding crude product after the alkaline washing into a rectification kettle, raising the temperature to 150 DEG C to 170 DEG C and dehydrating; 11) opening vacuum and collecting distillate of 160 DEG C to 190 DEG C which is the final product.
Owner:SHENZHEN FEIYANG IND CO LTD
Telomerase delivery by biodegradable Nanoparticle
InactiveUS20090142408A1Effectively crossControl releasePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsAge related diseaseHydrophilic polymers
A therapeutic compound consisting of human telomerase, its catalytic subunit hTert, or a known variant of either, and a biodegradable nanoparticle carrier, which can be administered to cells in a cell culture or in a living animal, is provided herein. The therapeutic compound is envisioned as a method for treating a wide variety of age-related diseases such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, aplastic anemia, dyskeratosis congenita, arteriosclerosis, macular degeneration, osteoporosis, Alzheimer's, diabetes type 2, and any disease that correlates with telomere shortening and may be corrected or ameliorated by lengthening telomeres. The therapeutic compound is also envisioned as method for potentially treating more generic problems of human aging. The nanoparticle carrier is comprised of certain biodegradable biocompatible polymers such as poly(lactide-co-glycolide), poly(lactic acid), poly(alkylene glycol), polybutylcyanoacrylate, poly(methylmethacrylate-co-methacrylic acid), poly-allylamine, polyanhydride, polyhydroxybutyric acid, polycaprolactone, lactide-caprolactone copolymers, polyhydroxybutyrate, polyalkylcyanoacrylates, polyanhydrides, polyorthoester or a combination thereof. The nanoparticle may incorporate a targeting moiety to direct the nanoparticle to a particular tissue type or a location within a cell. The nanoparticle may incorporate a plasticizer to facilitate sustained release of telomerase such as L-tartaric acid dimethyl ester, triethyl citrate, or glyceryl triacetate. A nanoparticle of the present invention can further contain a polymer that affects the charge or lipophilicity or hydrophilicity of the particle. Any biocompatible hydrophilic polymer can be used for this purpose, including but not limited to, poly(vinyl alcohol).
Owner:SARAD MATTHEW
Ester exchange catalysis method
ActiveCN103204777AHigh yieldOvercoming complexityMolecular sieve catalystsPreparation from organic carbonatesMolecular sieveHeteroatom
The invention discloses an ester exchange catalysis method. Specifically, phenol, dimethyl ester, a solvent and a catalyst are mixed and subjected to a contact reaction. The method is characterized in that the catalyst is a soluble zinc salt modified heteroatom molecular sieve.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Supported catalyst used in selective synthesis, and preparation method and purpose thereof
ActiveCN102218330AExpand the scope of selectionTo achieve selective regulationOrganic compound preparationPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionActive componentCatalyst support
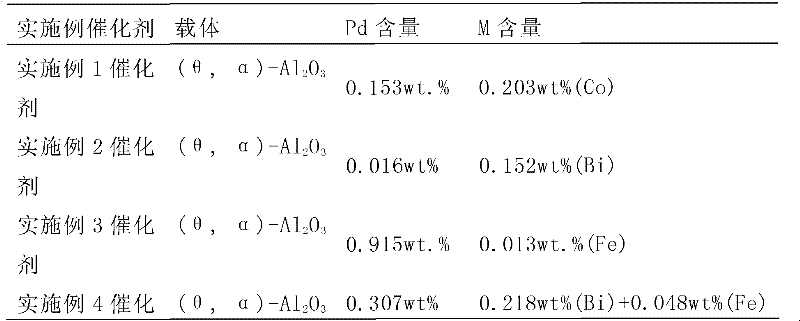
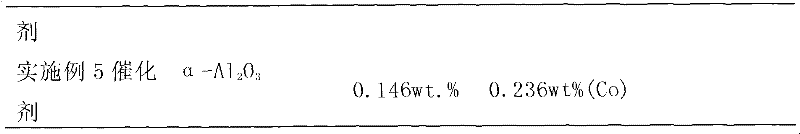
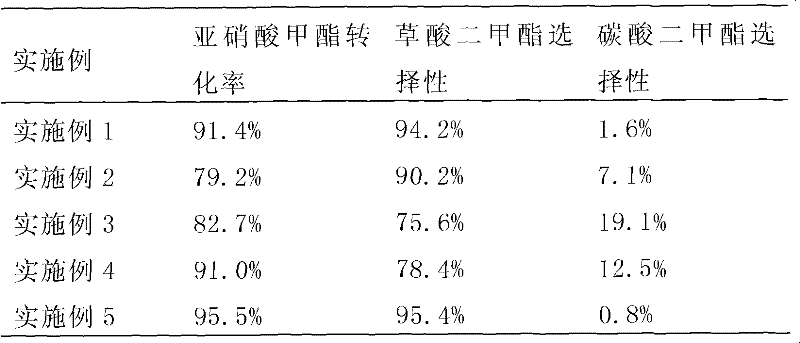
The invention relates to a supported catalyst used in selective synthesis. The catalyst comprises a main active component, an auxiliary active component, and a catalyst carrier. The main active component is Pd and / or its oxide, wherein the weight percentage content of the main active component is 0.01% to 1.0%. The auxiliary active component is at least one of the metals of Fe, Ni, Co, and Bi, and / or at least one of the oxides of the metals of Fe, Ni, Co, and Bi, wherein the weight percentage content of the auxiliary active component is 0.01% to 0.5%. The left component is Al2O3, which is thecatalyst carrier. The invention also relates to a preparation method and a purpose of the catalyst. As an experiment result, with the adding of the catalyst, relative selectivity of mesoxalic dimethyl ester and dimethyl carbonate in reaction products can be modulated.
Owner:PUJING CHEM IND SHA +1
Method for preparing magnetic/hollow double-shell layer print adsorbent by emulsion polymerization
InactiveCN103204966AGood magnetic response propertiesEasy to separateOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesHexadecaneCross-link
The invention relates to a method for preparing magnetic / hollow double-shell layer print adsorbent by emulsion polymerization and belongs to the technical field of the preparation of environment function materials. Attapulgite is used as stabilizer; a few Fe3O4 nanometer particles are used as a magnetic separation carrier; a dispersion solution of hydrophilic Fe3O4 nanometer particles and attapulgite is used as a water phase; and a mixture of organic solvent hexadecane, cross-linking agent styrene, template molecule cyhalothrin, initiator azo isobutyric dimethyl ester and functional monomers acrylamide and tetra-vinyl pyridine is used as an oil phase. The water phase and the oil phase are mixed to prepare stable oil-in-water emulsion in an ultrasonic manner; and the magnetic hollow double-shell layer print polymer is prepared by emulsion polymerization. The magnetic hollow double-shell layer print polymer can be applied to selective recognition and separation of cyhalothrin in an aqueous solution. The magnetic hollow double-shell layer print polymer has a hollow double-layer structure, wherein the hollow structure can be used for effectively increasing adsorption capacity; the strength of the obtained printer polymer is enabled to be high by the inorganic particle layer in the shell layer; and the recognition points are unlikely to be damaged.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
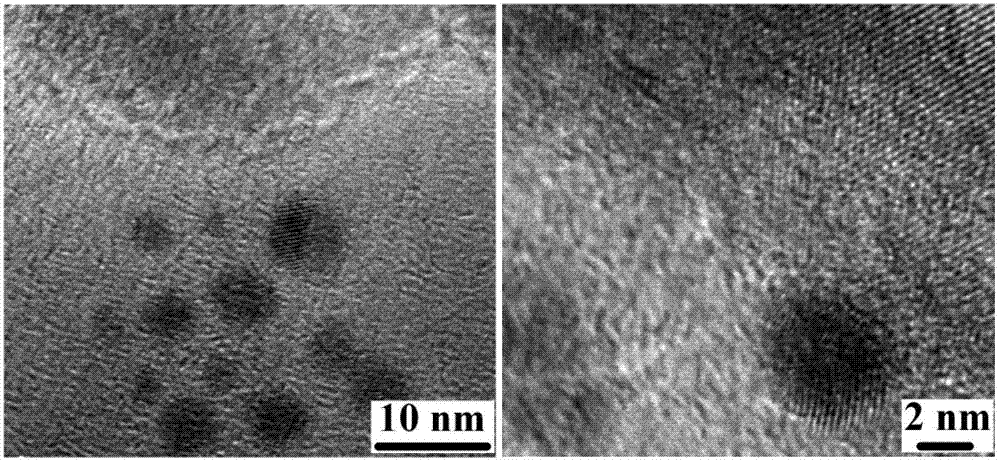
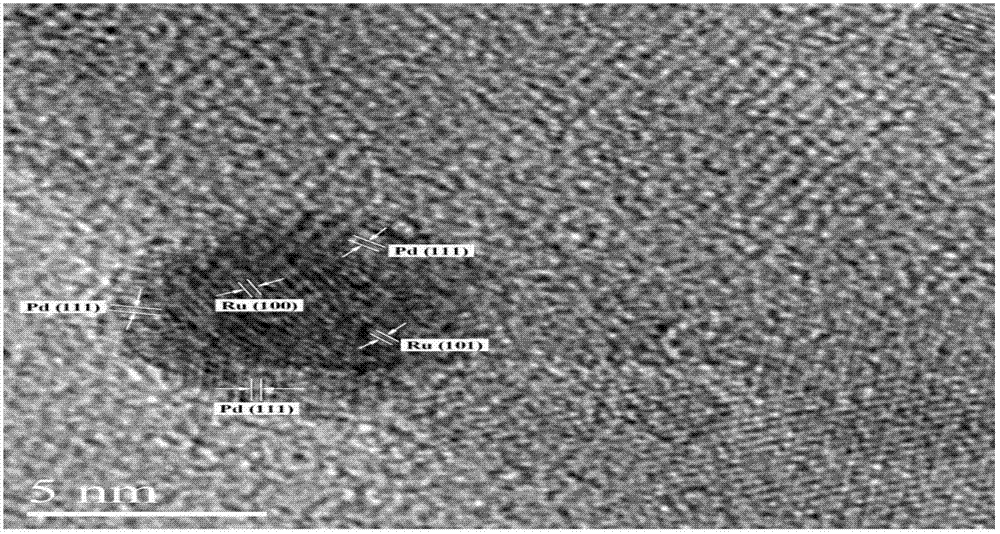
Low-content supported ruthenium-palladium bimetal hydrogenation catalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103157468ACatalytic selective hydrogenation performance improvement and enhancementLow costOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationDimethyl terephthalateActive component
The invention belongs to the technical field of catalysts and particularly relates to a low-content supported ruthenium-palladium bimetal hydrogenation catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the catalyst comprises the following steps: preparing a ruthenium monometal solution and a palladium monometal solution; under ultrasonic conditions, supporting the two active components (ruthenium and palladium) of the metal catalyst on the surface of an aluminum oxide carrier by respectively adopting a co-impregnation method and a fractional impregnation method; and washing, drying, roasting, and performing other treatment processes to finally obtain the low-content supported ruthenium-palladium bimetal hydrogenation catalyst. According to the invention, the method is low in cost; and the prepared bimetal hydrogenation catalyst has high selective hydrogenation activity, and shows excellent catalytic activity, favorable catalytic stability and high 1,4-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester (CHDM) yield when being used in the reaction process of preparing CHDM through selective hydrogenation of dimethyl terephthalate.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method for preparing 2,4-toluene diamino menthyl formate
InactiveCN1488623AEasy to operateLow costCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationAcetic acidDistillation
The invention discloses a producing method of 2, 4-toluene diamino methyl ester formate. It uses zinc acetate as catalyst, it is produced by reacting 2, 4- diamino toluene and dimethyl ester carbonate. The process adopts non-isothermal operation, the reaction is carried on in high pressure kettle uncontinuously. In reaction period, no materials is added in or pulled out, only need to control the temperature, the pressure is correspondent to the temperature. Separates the filtered material, the filtering temperature is control within 60í½90íµ, carries on decompression distillation to the liquid, the vacuum rate is 7í½12mmHg, the temperature is 35í½80íµ, gets the product TDC after instilling out the DMC and carbinol.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Method to make single-layer pet bottles with high barrier and improved clarity
InactiveUS20060246245A1Reduce yellownessEnvelopes/bags making machineryGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsPolyesterXylylene
The present invention comprises a blend of polyester and a partially aromatic polyamide with an ionic compatibilizer and a cobalt salt. This blend can be processed into a container that has both active and passive oxygen barrier and carbon dioxide barrier properties at an improved color and clarity than containers known in the art. The partially aromatic polyamide is preferably meta-xylylene adipamide. The ionic compatibilizer is preferably 5-sodiumsulfoisophthalic acid or 5-zincsulfoisophthalic acid, or their dialkyl esters such as the dimethyl ester (SIM) and glycol ester (SIPEG). The cobalt salt is selected form the class of cobalt acetate, cobalt carbonate, cobalt chloride, cobalt hydroxide, cobalt naphthenate, cobalt oleate, cobalt linoleate, cobalt octoate, cobalt stearate, cobalt nitrate, cobalt phosphate, cobalt sulfate, cobalt (ethylene glycolate), or mixtures of two or more of these. The partially aromatic polyamide is present in a range from about 1 to about 10 wt. % of said composition. The ionic compatibilizer is present in a range from about 0.1 to about 2.0 mol-% of said composition. The cobalt salt is present in a range from about 20 to about 500 ppm of said composition.
Owner:TREVIRA HLDG GMBH
Low-temperature curing color coiled material paint and method for preparing same
ActiveCN101531860ASuitable for continuous roller coatingMeet the hardness and toughnessPolyester coatingsLow temperature curingSolvent
The invention relates to a paint composition, in particular to a low-temperature curing paint used for manufacturing color steel plates and a method for preparing the same. The method comprises the following steps: adding 45 to 60 weight percent of saturated polyester resin, 3 to 5 weight percent of fully-methylated amino resin and 3 to 5 weight percent of partially-methylated amino resin into a reaction kettle; while stirring, adding 3 to 5 weight percent of propylene glycol ether acetate, 2 to 5 weight percent of binary acid dimethyl ester, 2 to 0.5 weight percent of closed cooling catalyst, 0.2 to 0.5 weight percent of open cooling catalyst, 5 to 10 weight percent of trimethyl benzene solvent to the mixture; after stirring the mixture evenly, adding 0.3 to 0.8 weight percent of dispersant to the mixture, and then adding 20 to 40 weight percent of filling pigment and 0.3 to 0.8 weight percent of wax powder while stirring; and after the mixture is dispersed evenly, performing sanding in a sand mill, and then performing paint and color mixing process to obtain the finished product, namely the low-temperature curing color coiled material paint. The method can solve the problems that the prior high-temperature baking curing paint has high curing temperature to cause energy sources waste.
Owner:JIANGSU LANLING POLYMER MATERIAL CO LTD
Graphene oxide/aliphatic-aromatic copolyester and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103642015AImprove conductivityDoes not generate static electricityTrans esterificationPolymer science
The invention discloses graphene oxide / aliphatic-aromatic copolyester. The graphene oxide / aliphatic-aromatic copolyester comprises the following raw materials by weight: 0.06 to 0.5% of graphene oxide, 40 to 65% of aliphatic dihydric alcohol, 32 to 57% of diacid or dimethyl ester thereof, 0.01 to 0.2% of a catalyst and 0.01 to 0.18% of a stabilizing agent. A preparation method for the graphene oxide / aliphatic-aromatic copolyester comprises the following steps: pretreatment of graphene oxide; transesterification; and condensation polymerization. The prepared graphene oxide / aliphatic-aromatic copolyester has good conductivity and does not generate static electricity in the production process of a blown film; due to addition of graphene oxide, melt strength is improved, film rupture hardly occurs during processing, and stability of production of a film material is improved.
Owner:KINGFA SCI & TECH CO LTD +1
Treatment and resource-reclaiming process for waste water from production of dimethyl isophthalate-5-sulfonic acid
ActiveCN1837078ASave raw materialsAvoid secondary pollutionWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeWater/sewage treatment by sorptionRelationship - FatherDistillation
The invention discloses a father and resource method about m-phthalic acid dimethyl ester-5-sulfonic acid produced waste-water.the steps is passing the m-phthalic acid dimethyl ester-5-sulfonic acid produced waste-water of filter preconditioning to adsorbing column loaded acrylate adsorbing resin; after adding alkali in adsorbing water for neutralization, distillation recovery by carbinol and adsorption handling by activated carbon, and then can be discharged; the acrylate adsorbing resin which is adsorbed the organic matter of m-phthalic acid dimethyl ester-5-sulfonic acid produced waste-water can be desorbed by hot water, the desorption liquid can recover the m-phthalic acid dimethyl ester-5-sulfonic acid crystal by evaporation, condensation and crystallization. The CODCr in disposal waste-water of the open method of this invention is fell from 180000mg / L to about 100mg / L, the m-phthalic acid dimethyl ester-5-sulfonic in waste-water can be recovered as product, the purity can reach to primary standard; not only saving the raw material, but also avoiding secondary pollution. The final discharged waste-water accord with national sewage discharge standard, hasing distinct environmental, economic and social benefit.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
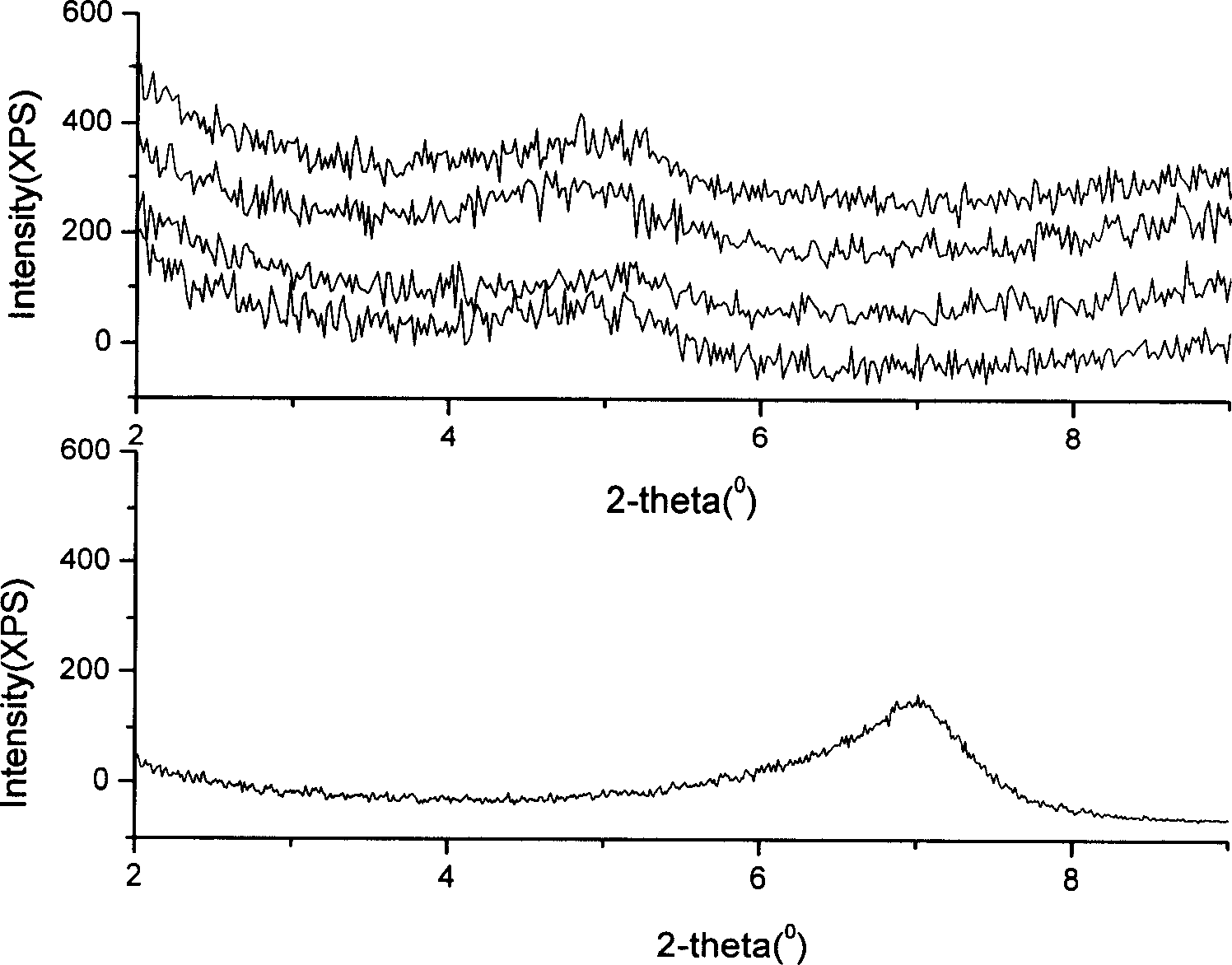
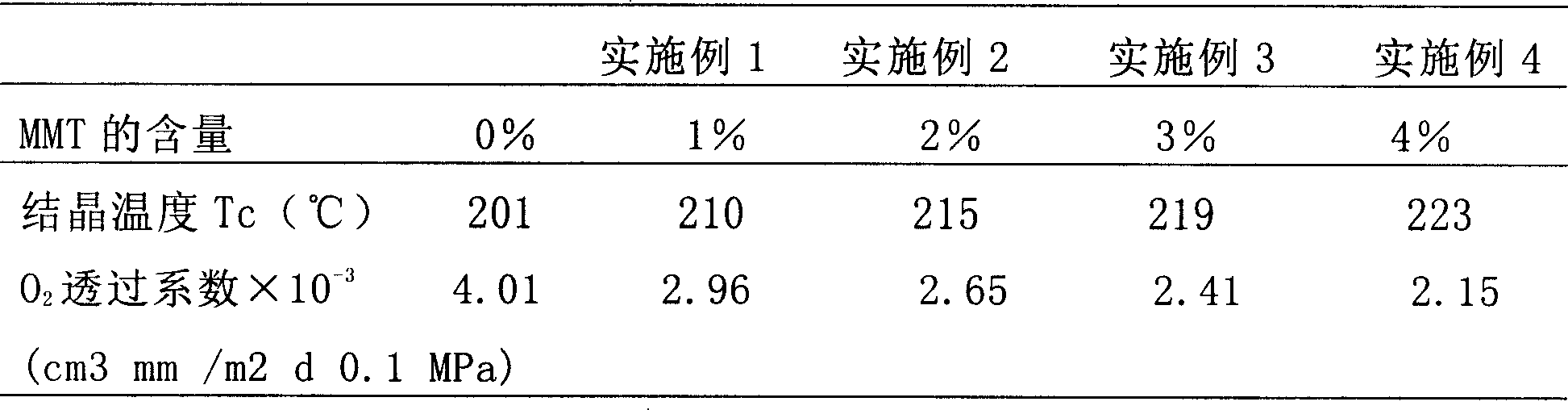
Montmorillonite modified polyester and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101200575AIncrease interface areaHigh molecular weightDimethyl terephthalateMontmorillonite
The present invention provides a preparation method of imvite modified polyester, including the following steps: (a) aqueous mixture of 1 to 4wtg. imvite original soil, 50 to 80wtg. glycol and 50 to 500wtg. water is provided; (b) the aqueous mixture in step (a) is mixed with 40 to 50wtg. terephthalic acid dimethyl ester; (c) the mixture in step (b) is polymerized under the temperature of 160 to 290 DEG C so as to obtain the imvite modified polyester. The present invention also provides composite material prepared by the method. The polyester composite material has excellent air barrier property and crystallization property.
Owner:SHANGHAI GENIUS ADVANCED MATERIAL (GRP) CO LTD
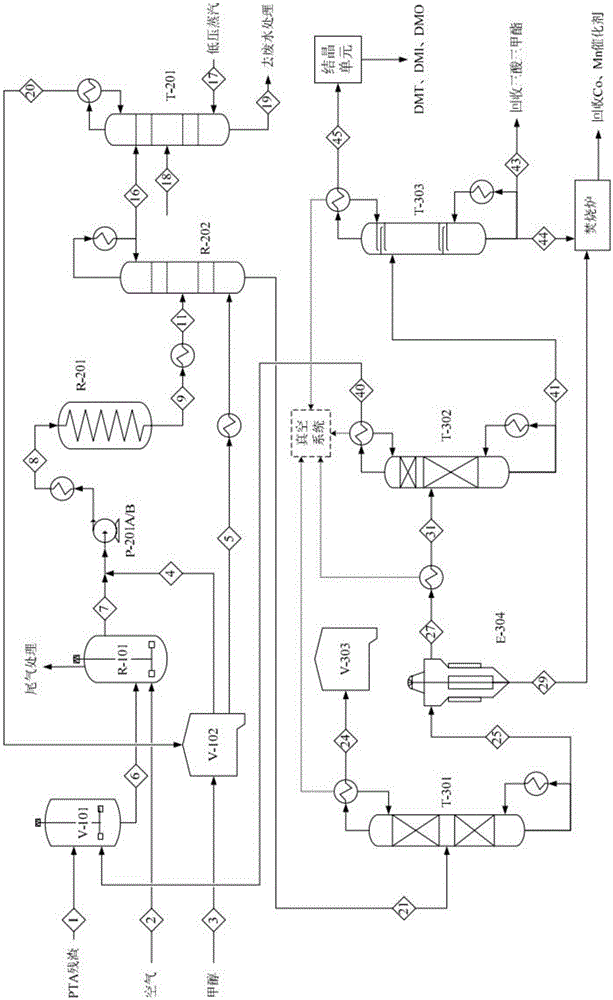
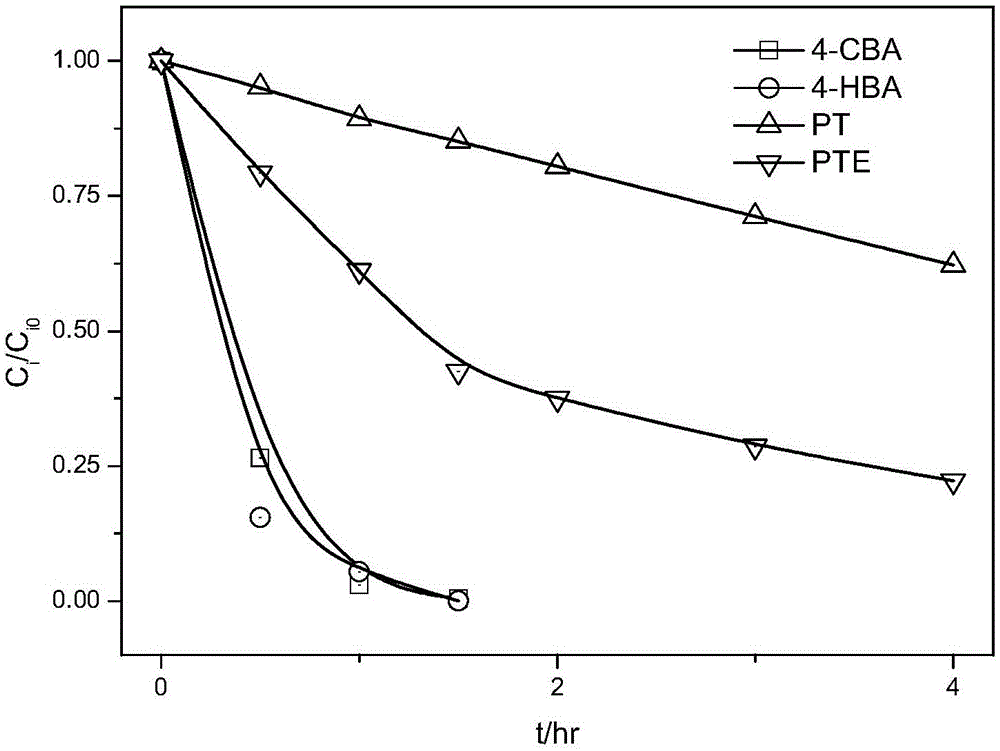
Method for methyl esterification recovery and recycle of PTA oxidation residue
InactiveCN105017022ARealize resource utilizationHigh purityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationDimethyl terephthalateMethyl benzoate
The invention discloses a method for methyl esterification recovery and recycle of PTA oxidation residue. The method comprises 1, primary oxidation treatment, 2, secondary methyl esterification treatment, and 3, tertiary rectification treatment, wherein methyl benzoate is recovered by primary reduced pressure rectification, methyl toluate is recovered by secondary reduced pressure rectification, mixed benzenedicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester is recovered by tertiary reduced pressure rectification, and dimethyl terephthalate, dimethyl isophthalate and dimethyl phthalate are respectively recovered by mixed benzenedicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester crystallization treatment. The method effectively recovers BA, IPA, TA, PT, 4-CBA, 4-HBA, OPA and TMA of the PTA oxidation residue, can produce high purity methyl benzoate, mixed benzenedicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester and trimethyl trimellitate products and realizes separation and recovery of DMT, DMI and DMO products from mixed benzenedicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester by crystallization.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Lithium ion battery
InactiveCN101662046AEfficiency is not affectedUnaffected capacityCell electrodesSecondary cellsSolventElectric potential
The invention discloses a lithium ion battery which comprises an anode piece, a cathode piece, an isolation film and electrolyte, wherein the anode piece comprises an anode flow collection body and ananode diaphragm which is attached on the anode flow collection body and contains an anode active substance, the cathode piece comprises a cathode flow collection body and a cathode diaphragm which isattached on the cathode flow collection body and contains a cathode active substance, an electrolyte solvent contains methylphosphoric acid dimethyl ester, and the cathode active substance is lithiumtitanate. In the lithium ion battery, the lithium titanate can not generate a reduction reaction with the methylphosphoric acid dimethyl ester because the platform electric potential of the lithium titanate is about 1.5V (Li+ / Li relatively) and is higher than the reduction electric potential of 1.2V (Li+ / Li relatively) of the methylphosphoric acid dimethyl ester, and the first-time efficiency andthe capacity of the lithium ion battery are not influenced.
Owner:DONGGUAN AMPEREX TECH
Continuous esterification production method for mixed dibasic acid dimethyl ester
InactiveCN101891610AFully contactedImprove conversion rateOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationRoom temperatureEsterification reaction
The invention discloses a continuous esterification production method for mixed dibasic acid dimethyl ester. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) pre-esterifying, namely, mixing dibasic acid and methanol in a mole ratio of 1:2-3 and performing pre-esterification at the normal temperature and normal pressure to obtain a pre-esterified material; (2) pre-heating the methanol, namely, pressurizing and pre-heating the methanol to form overheated methanol gas with the temperature of between 145 and 155 DEG C; and (3) continuously esterifying, namely, adding the pre-esterified material into a continuous esterification reactor, of which the middle part is provided with a catalyst reaction bed, from the top, adding the overheated methanol gas into the continuous esterification reactor from the bottom, performing a reverse flow reaction on the ascending methanol gas and the descending pre-esterified material on the catalyst reaction bed, and continuously discharging the mixed dibasic acid dimethyl ester which is generated by the esterification from the bottom of the esterification reactor.
Owner:WEIFANG YUANLI CHEM
Production of carbaminate by amine reacted with dimethyl ester carbonate
InactiveCN1424309AEasy to separateHigh purityCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationCarbamateMethyl carbonate
A process for preparing aminoformate from amine and dimethyl carbonate (DMC) features that under the existance of ionic liquid as solvent and catalyst system, the amine and DMC take part in catalytic oxo reaction at 40-200 deg.C for 0.5-5 hr. Its advantages are high output rate (more than 98%), high purity (more than 98%), high reaction activity, and easy recovery and cyclic use of catalyst.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
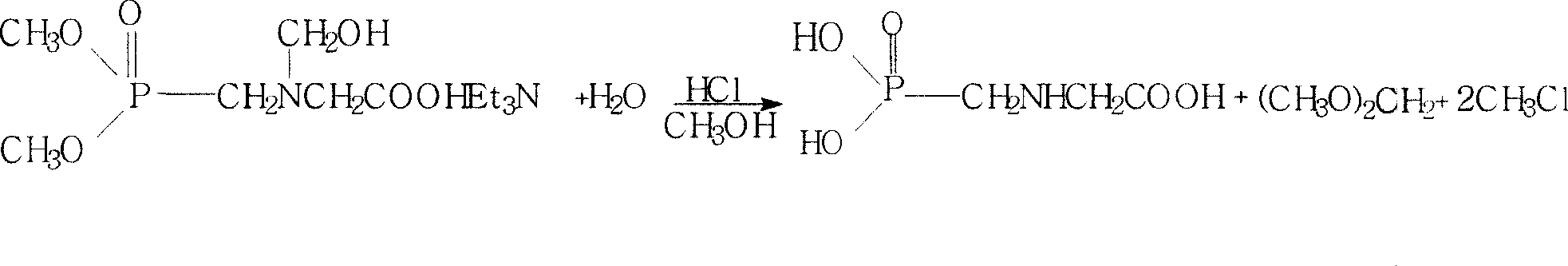
Method for preparing tiotropium bromide
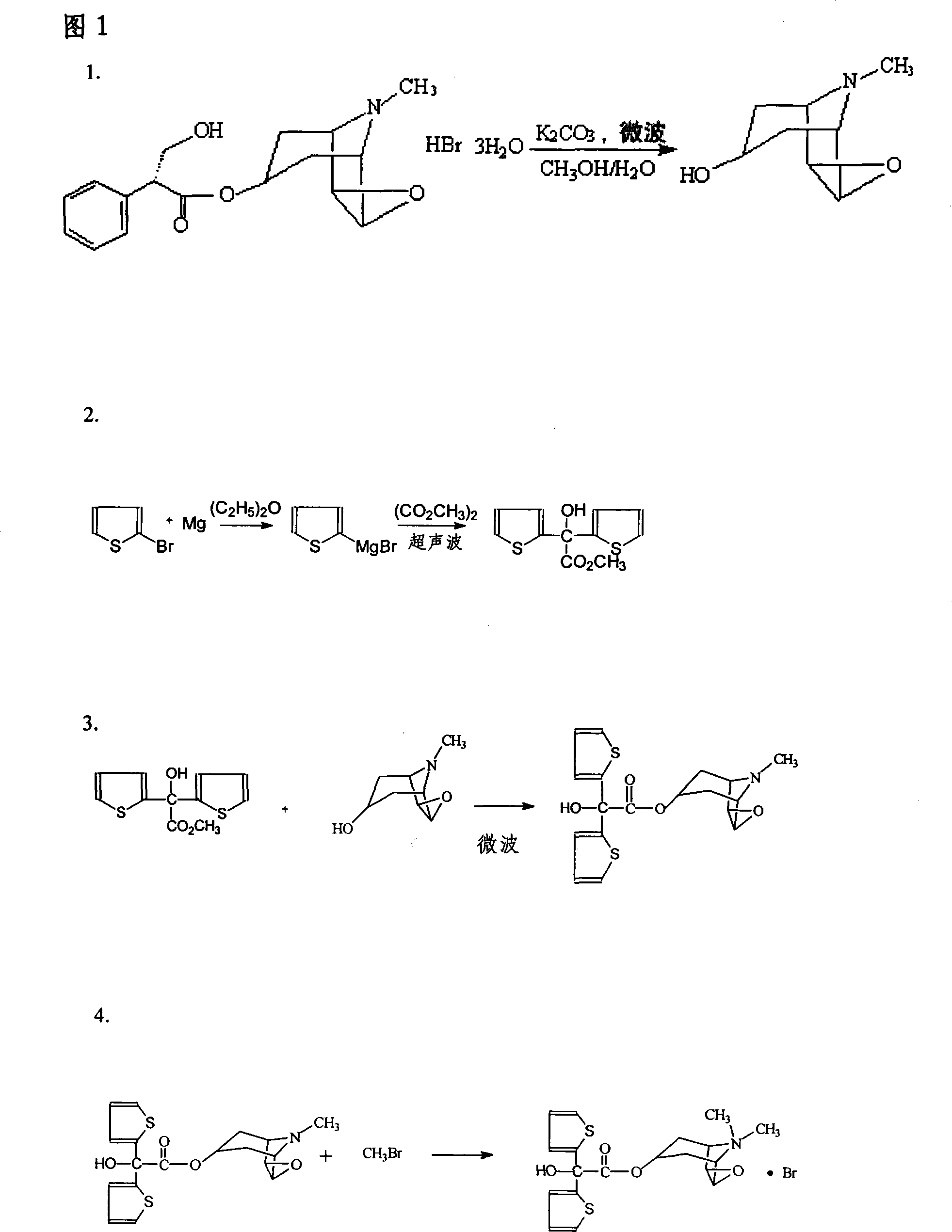
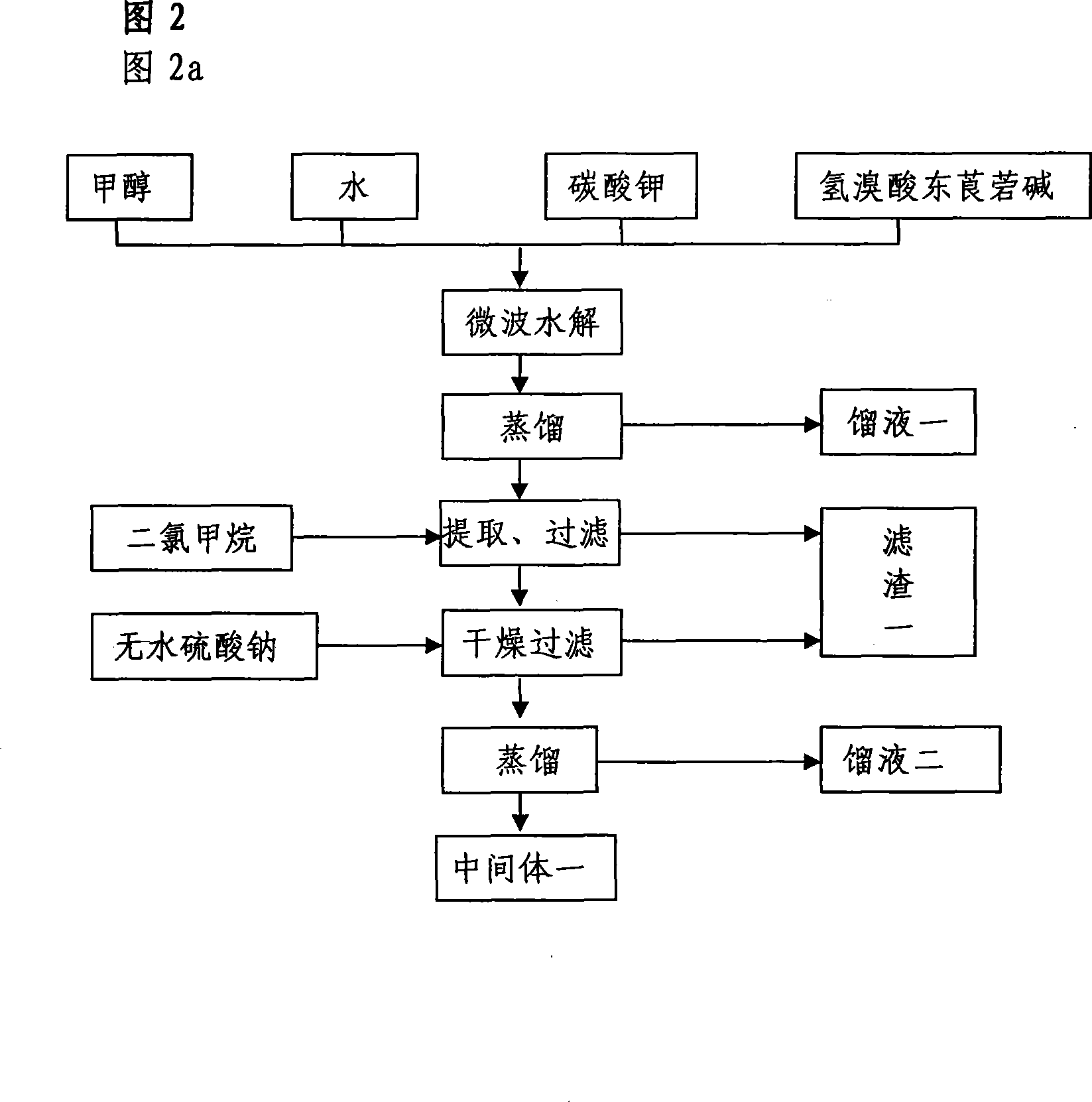
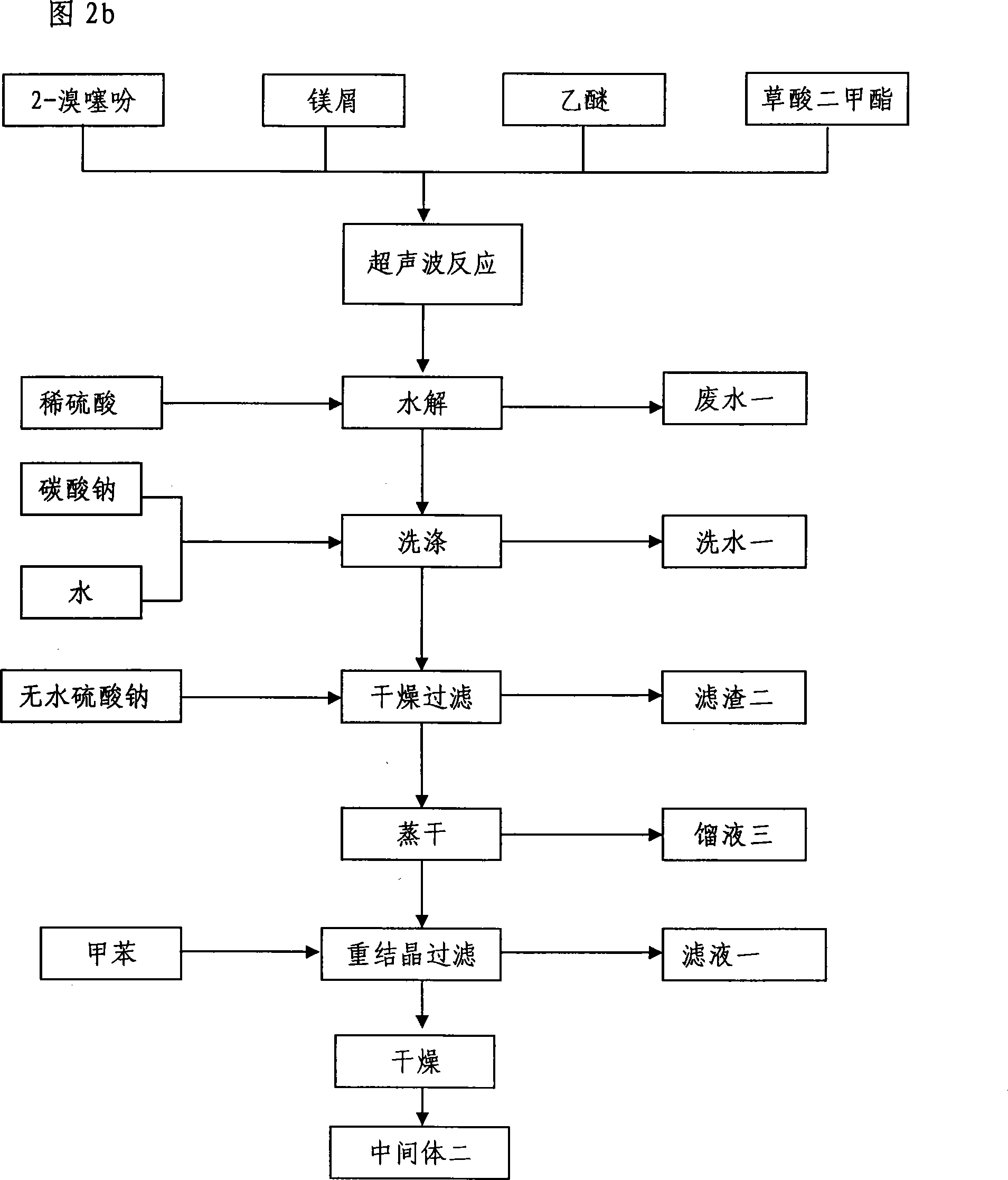
The invention relates to the application of microwave and ultrasonic technologies in synthesizing tiotropium bromide anhydride, in particular to a method for preparing the refined product of a finished product, namely, tiotropium bromide anhydride through crystallization and recrystallization processes by using a crude product of tiotropium bromide prepared through bromization reaction after hydrolytic reaction of scopolamine hydrobromide under microwave function, substitution and coupling reaction of bromothiophene, magnesium, and oxalic acid dimethyl ester under the microwave function, and condensation reaction of scopine and thiophen methyl glycollate under the microwave function. Using the invention to prepare tiotropium bromide anhydride, not only the reaction time is short, the side reaction is less, and the yield rate is high in the room temperature condition, but also the product quality is stable, controllable, safe and effective.
Owner:HONGYI SCI & TECH CO LTD NANCHANG
Basic aqueous easily-soluble modified polyesters and preparation method
The present invention discloses alkali soluble modified polyester and the preparation method. The production method includes esterification and condensation reactions and is characterized in that in the reaction, terephthalic acid dimethyl ester or terephthalic acid and ethylene alcohol are first component and second component, and m-phthalic acid ester with metallic sulphonate respectively is thirdcomponent; metatitanic acid ester is catalyst, phosphorus compound is stabilizer and alkali metal compound is assistant additive. The polyester copolymer provided by the present invention is characterized in that the viscosity is 0.40 to 0.65dl / g (including 0.40dl / g, 0.55dl / g, 0.65dl / g); wherein, the content of stibium compound is less than or equal to 100ppm in the unit of stibium atom relatively to polyester. The polyester copolymer produced by the present invention has excellent heat resistance, full alkali solubility and good spinning performance.
Owner:TORAY FIBER RES INST(CHINA) CO LTD
Graphene oxide/aliphatic-aromatic copolyester and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses graphene oxide / aliphatic-aromatic copolyester. The graphene oxide / aliphatic-aromatic copolyester comprises the following raw materials by weight: 2 to 10% of graphene oxide, 40 to 65% of aliphatic dihydric alcohol, 32 to 57% of diacid or dimethyl ester thereof, 0.01 to 0.2% of a catalyst and 0.01 to 0.18% of a stabilizing agent. A preparation method for the graphene oxide / aliphatic-aromatic copolyester comprises the following steps: pretreatment of graphene oxide; transesterification; and condensation polymerization. The prepared graphene oxide / aliphatic-aromatic copolyester is biodegradable, has a high barrier property and can be extensively used in the fields of food and medicines; since the graphene oxide / aliphatic-aromatic copolyester is a biodegradable barrier material, used graphene oxide / aliphatic-aromatic copolyester can be subjected to composting after discarding, thereby reducing pollution to the environment.
Owner:KINGFA SCI & TECH CO LTD +1
Resource recycling method of glyphosate mother liquor
InactiveCN101792216AImprove economyEasy to handleBiocideGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPhosphorous acidSeparation technology
The invention particularly relates to a resource recycling method of glyphosate mother liquor, which separates each component of mother liquor generated from producing glyphosate by a phosphorous acid dimethyl ester method by a multistage membrane separation technology, sufficiently recycles each useful component, reduces wastewater treatment capacity and realizes resource recycling. The method comprises the following steps: preparing the glyphosate mother liquor in glyphosate production by the phosphorous acid dimethyl ester method; removing solid impurities and viscous components by microfiltration, ultrafiltration and the like, and then continuously entering all stages of membrane separation devices for separating and concentrating; each stage of membrane separation device has different functions, wherein the first-stage membrane separation device separates and concentrates for obtaining a solution A being rich in mineral salt of sodium chloride or ammonia chloride and the like; the second-stage membrane separation device separates and concentrates for obtaining a solution B being rich in sodium hydroxide; the third-stage membrane separation device separates and concentrates for obtaining a solution C being rich in phosphorous acid; and the forth-stage membrane separation device separates and concentrates for obtaining a solution D being rich in glyphosate, and the rest is a solution E being rich in other impurities and byproducts.
Owner:HANGZHOU TIAN CHUANG ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Method for synthesizing diamide compound (R1R2NCO) 2CH2OCH2
InactiveCN102020579AFor long-term storageReduce pollutionOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationHydrogen chlorideDiglycolic acid
The invention discloses a novel method for synthesizing a diamide compound (R1R2NCO) 2CH2OCH2, which comprises the following steps of: with a hydrogen chloride gas as a catalytic agent, catalyzing diglycolic acid and methanol to prepare diglycolic acid dimethyl ester; and reacting the diglycolic acid dimethyl ester with amine to produce the corresponding 3-oxa-pentanediamide. Reaction conditions are mild, and operation steps are simple because of omitting the preparation of acyl chloride; the prepared ester can be stored for long, which is convenient for increasing production efficiency; environment pollution is lower without exhausting a large quantity of sulfur dioxide or hydrogen chloride gas.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
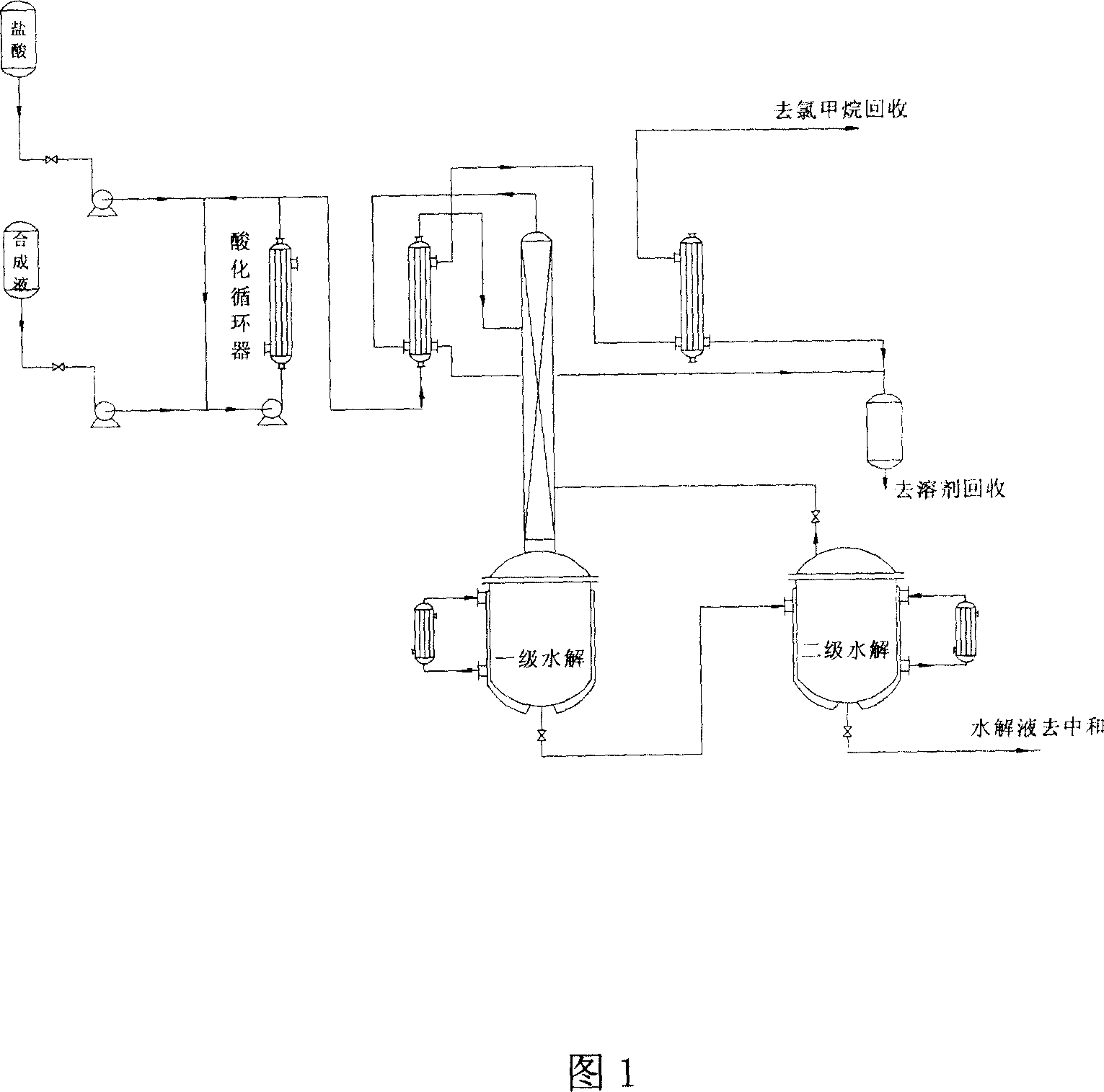
Continuous synthesis of glyphosate by dimethyl ester
Continuous synthesis of glyphosate by dimethyl ester is carried out by taking paraformaldehyde, amino acetic acid and dimethyl ester as raw materials to obtain synthetic liquid, acidizing it with hydrochloric acid, mixing, entering into hydrolytic reactive zone, reacting in hydrolytic reactor continuously, acidizing synthetic liquid, hydrolyzing in hydrolytic reactive zone continuously, forming into glyphosate salt, batching continuously and neutralization crystallizing to obtain the final product. It realizes continuous hydrolysis and simplifies process and can be used in large-scale production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG XINAN CHEM INDAL GROUP
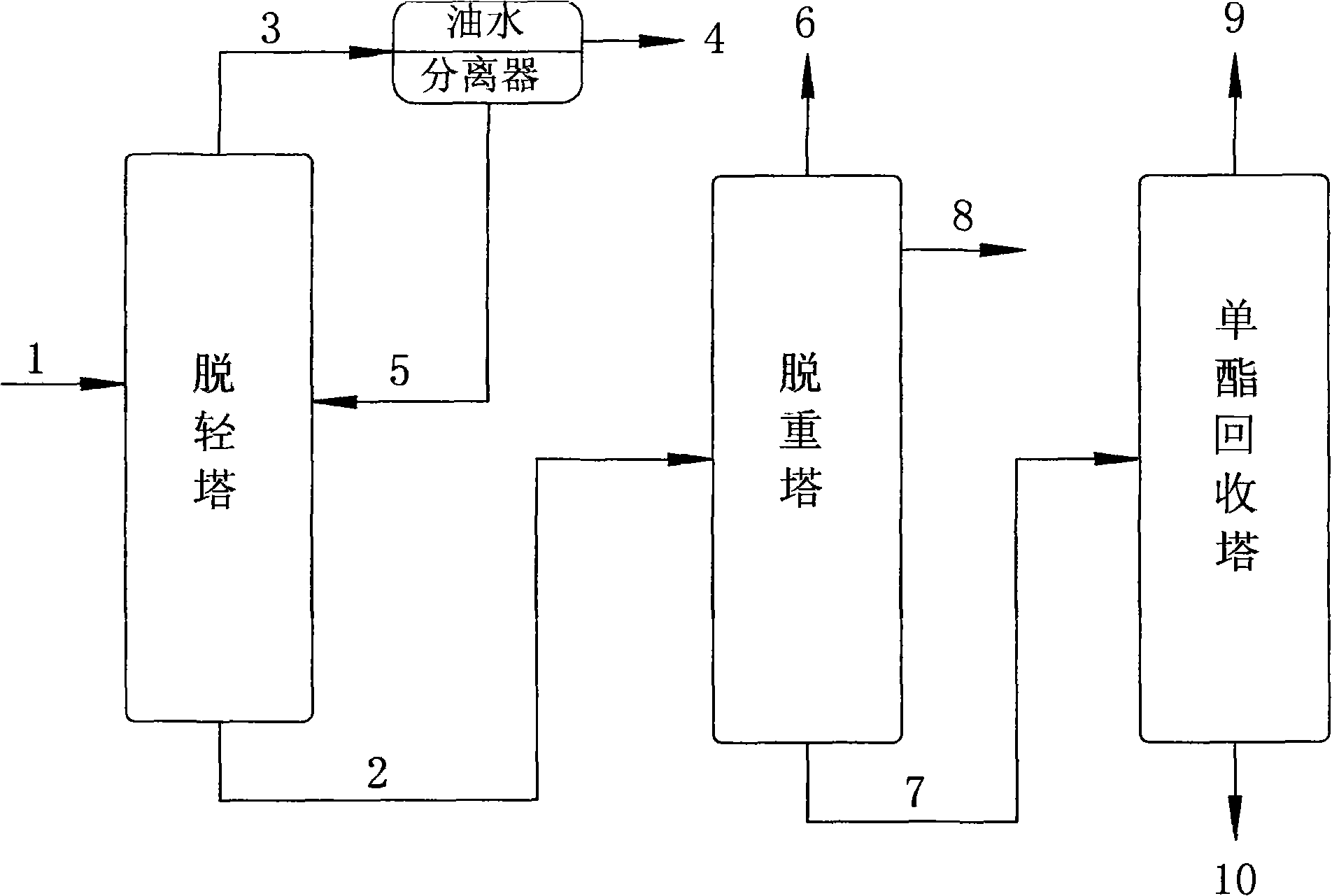
Method for refining dibasic acid dimethyl ester plasticizer
ActiveCN101525446AHigh purityQuality improvementOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationPlasticizerTar
The invention discloses a method for refining a dibasic acid dimethyl ester plasticizer, which comprises the following steps: dibasic acid dimethyl ester plasticizer crude product is refined by adopting a continuous decompression and rectification light-component and heavy-component removing method, after being filtered, the plasticizer crude product firstly enters a lightness-removing column, the lightness-removing column performs decompression operation to remove light components on the top of the lightness-removing column, the bottom materials of the lightness-removing column enter a weight-removing column to remove weight components, the weight-removing column performs decompression operation to remove monoester and little tar in the plasticizer crude product, and the top of the weight-removing column extracts the refined plasticizer produce. The plasticizer product has high purity, stable quality, lower energy consumption, simple operation and high product yield and reduces the generation of tar and environmental pollution.
Owner:WEIFANG YUANLI CHEM
Novel rare earth europium complex and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105801608ANovel preparation methodEasy to operateGroup 3/13 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesLuminescent compositionsRare earthPhenanthroline
The invention discloses a novel rare earth europium complex and a preparation method thereof. The method includes the following steps of firstly, conducting acylation reaction with acetophenone and benzenedicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester as the raw materials to obtain beta-diketone ligand; secondly, using beta-diketone ligand obtained in the first step as the first ligand and phenanthroline as the second ligand to obtain the rare earth europium complex. The preparation method is easy to operate and implement, and the prepared novel rare earth europium complex is novel in structure, has high heat stability and meanwhile has the advantages of being high in fluorescent strength, long in fluorescent service life and the like.
Owner:河南索顿新材料有限公司
Preparing method for mixed dibasic acid ester from adipic acid production waste liquid and treatment method for the waste liquid
ActiveCN101016245ADecomposition is safe and reliableOxidation process is safe and reliableOrganic compound preparationMultistage water/sewage treatmentHydrogenWastewater
The invention discloses a making method of binary acid ester through waste liquid of adipic acid and disposing method of waste liquid, which comprises the following steps: adding concentrated nitric acid into BI waste liquid; decomposing butylacetic acid hydrogen peroxidate into hydroxy capronate under 70-110 deg.c; aerating NO2 into decomposing liquid to trigger oxidization reaction; maintaining temperature between 70 and 110 deg.c; condensing reactant to 20-50%; evaporating DBA waste liquid to 20-50% under normal pressure; flashing with BI oxidizing condensate; cooling to 50-70 deg.c; reacting composite liquid and esterified carbinol with the same weight to extract; washing extracting phase; rectifying in the vacuum under 20-60kPa; rectifying rough composite dibasic acid dimethyl ester under 2-15kPa; evaporating water to 20-50%; circulating in the esterifying autoclave to do secondary esterification; making total transmitting rate of diacid over 90%.
Owner:QINGDAO ECSS SOFT TECH +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com