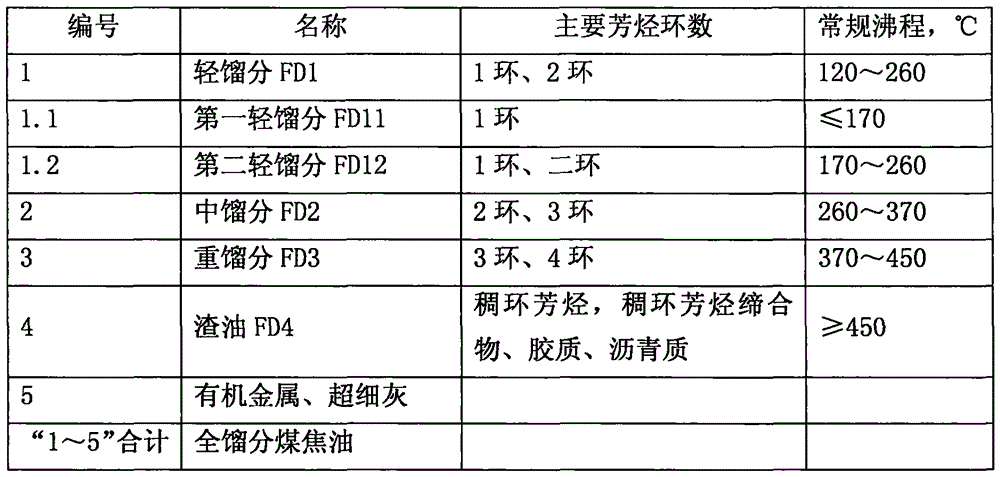
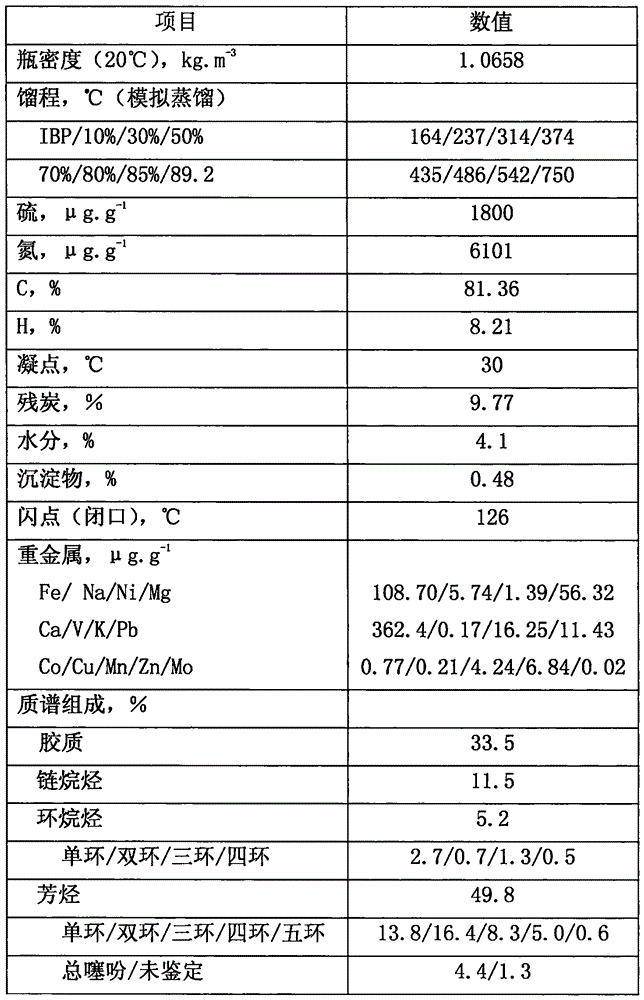
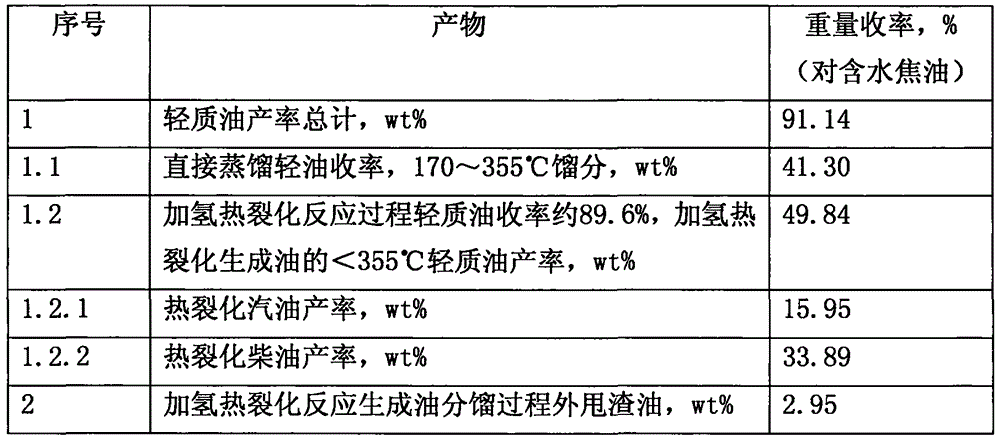
Inferior hydrocarbon hydrogenated thermal cracking method for setting hydrogenated aromatic hydrocarbon light-saturation reaction process
A technology for hydrogenation reaction and reaction process, which is applied in hydrotreating process, treatment of hydrocarbon oil, petroleum industry, etc., can solve problems such as slow speed, aggravation of liquid phase property deterioration and viscosity increase in the process of suspended bed thermal cracking reaction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0866] Based on Comparative Example 1, the low-quality hydrocarbon HDS hydrogenation aromatic hydrocarbon shallow saturation reaction process, that is, the first hydrogenation reaction process R10, was added.
[0867] According to the present invention, the mixed fraction FOMD is used as inferior hydrocarbon HDS, and before the inferior hydrocarbon HDS enters the hydrothermal cracking reaction process, that is, the second hydrogenation reaction process R20, the first hydrogenation reaction process R10 completes the shallow saturation of hydrogenated aromatics Reaction, under the condition of strengthening the hydrogenation reaction function based on liquid phase reaction, the hydrogenation aromatic hydrocarbon shallow saturation reaction R10R of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons is carried out, so that the middle aromatic ring of some polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons is saturated, and HDS carries out the carbon residue removal reaction. Produce simultaneously the methylene bridg...
Embodiment 2
[0886] Embodiment 1 was improved by adopting Chinese patent ZL201210022921.9, a method for hydrogenation and lightening of heavy oil with low hydrogen content using hydrogen-donating hydrocarbons.
[0887] In the coal tar FOO separation section FRAC, coal tar FOO is separated into a light fraction FOL mainly composed of hydrocarbons with a conventional boiling point of 60-355°C, and a medium-low temperature coal tar middle fraction FOM mainly composed of hydrocarbons with a conventional boiling point of 355-435°C And the heavy fraction FOD mainly composed of hydrocarbons with a conventional boiling point greater than 435°C, the heavy fraction FOD is used as inferior hydrocarbon HDS; the light fraction FOL and the middle fraction FOM enter the prehydrogenation process RFOLM to be converted into hydrogenation reaction effluent RFOLM-P, and The hydrogen reaction effluent RFOLM-P enters the thermal high-pressure separation process RFOLM-P-THPS to be separated into thermal high-sepa...
Embodiment 3
[0916] Based on Example 2, combined application of a hydrothermal cracking method for producing low-carbon single six-membered ring hydrocarbons from high-aromatic hydrocarbons disclosed in Chinese patent application CN105623724A, a second product solution was formed for Example 2. Compared with Example 2, the hydrocarbon components in the second hydrogenation reaction effluent R20P with a conventional boiling point of 290-355°C are returned to the first hydrogenation reaction process R10 as cracked cycle oil instead of being used as a hydrogenation upgrading reaction process The use of R60 raw materials, the effect is:
[0917] ① For the first hydrogenation reaction process R10, the total amount of hydrogen-donating hydrocarbons is increased, which can further increase the ratio KSH of "weight of hydrogen-donating hydrocarbons / weight of coal tar heavy oil HDS";
[0918] ② Utilize the "selective cracking function" of the hydrothermal cracking reaction process to maximize the p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com