Patents
Literature
34results about How to "Avoid off-target effects" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for preparing CAR-T cell by CRISPR/Cas9
InactiveCN104894068AEasy to operateImprove editing efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementForeign genetic material cellsAntibody moleculeCar t cells
The invention relates to a method for preparing a CAR-T cell by CRISPR / Cas9. The method comprises integrating a CAR molecule into a first intron of a human 19th chromosome AAVS1 site by a CRISPR / Cas9 technology, and integrating antibody molecules of various tumor surface antigens into a human T cell genome AAVS1 site by CRISPR / Cas9. The method realizes accurate integration of the CAR molecule into a human T cell genome specific safe port site, does not influence human normal gene functions, and prevents a series of clinical risks such as viral vector safety hidden trouble and genetic toxicity and immunogenicity caused by insertion of an exogenous gene into a genome.
Owner:NANJING KAEDI BIOTECH INC
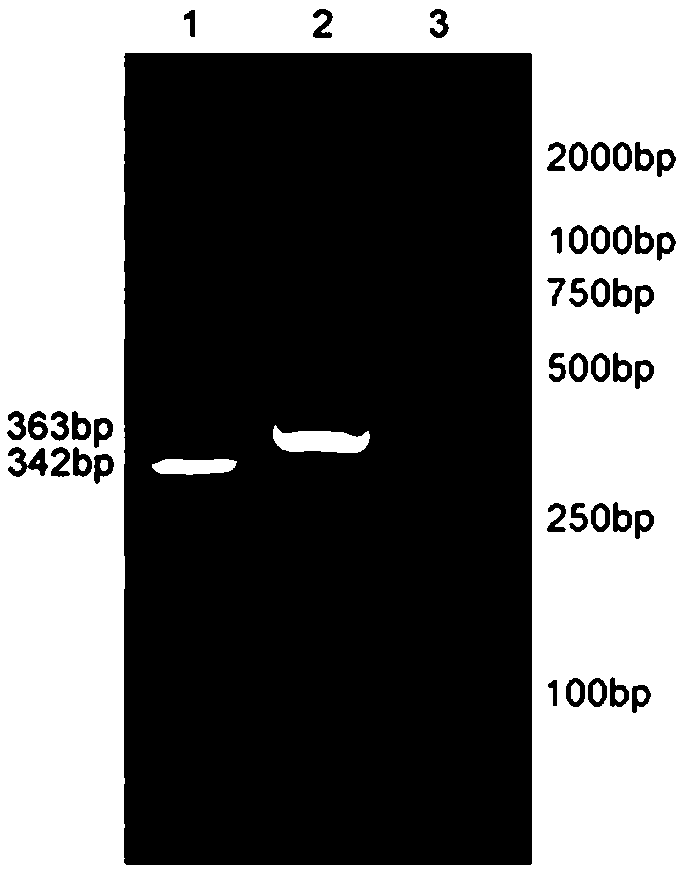
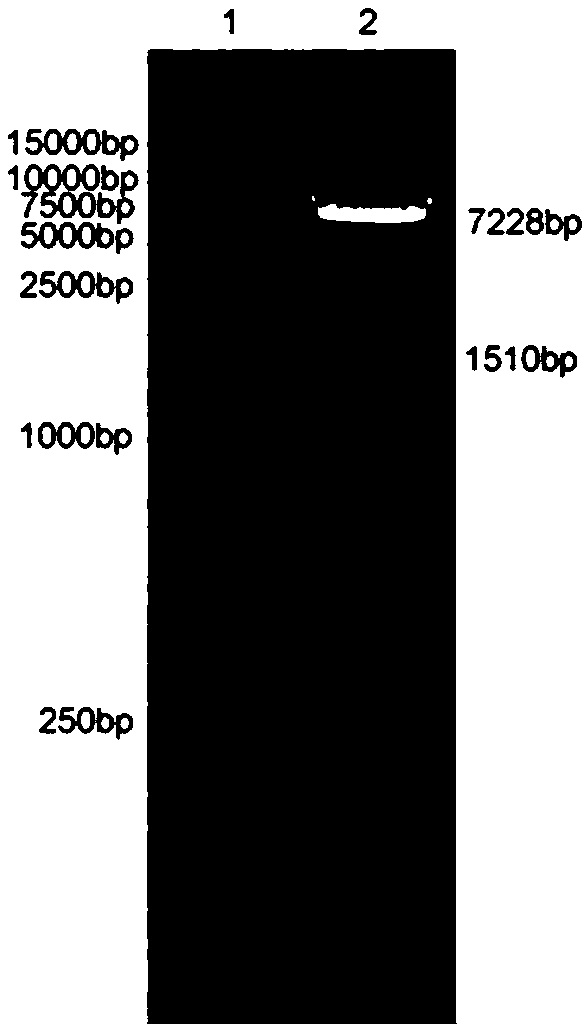
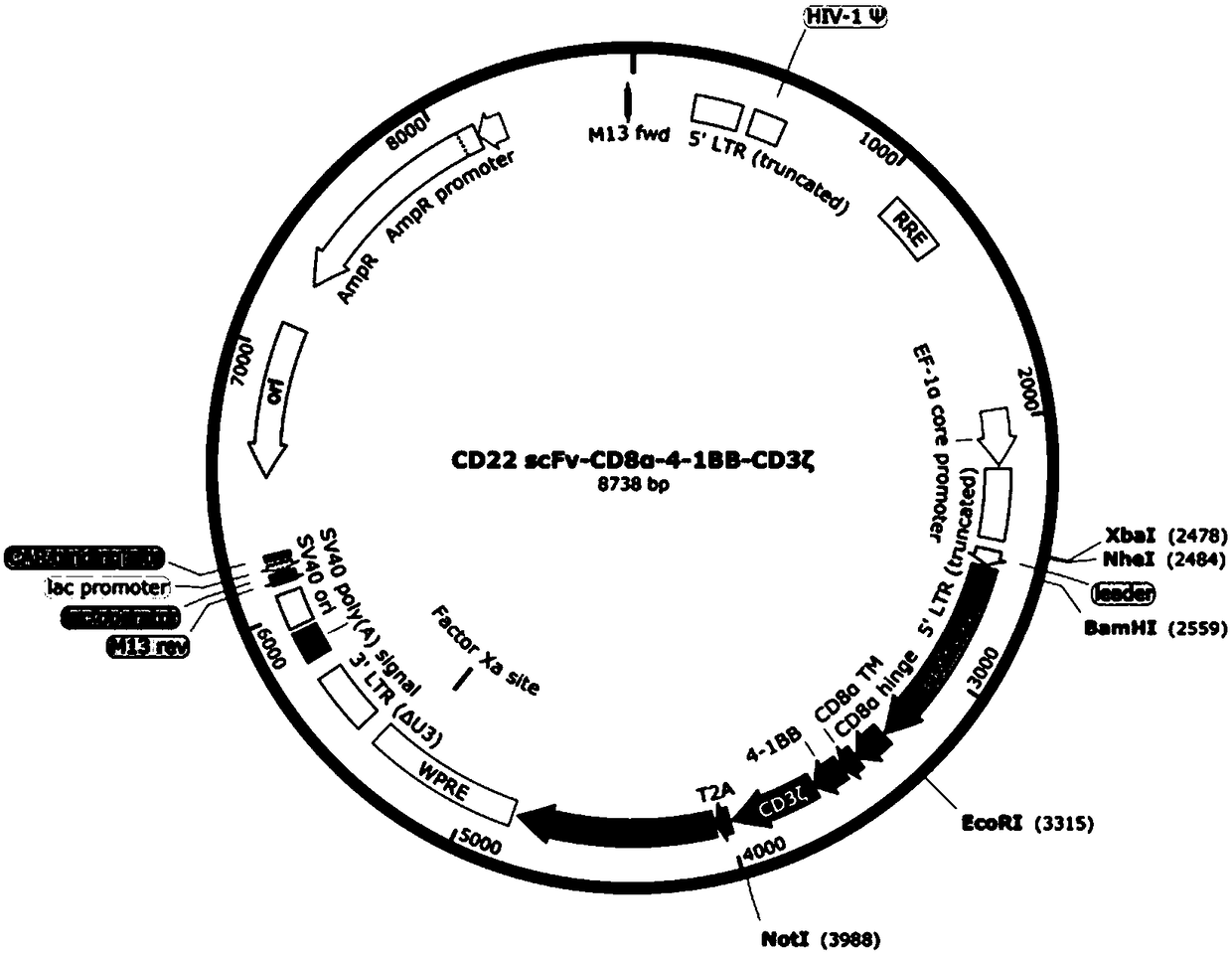
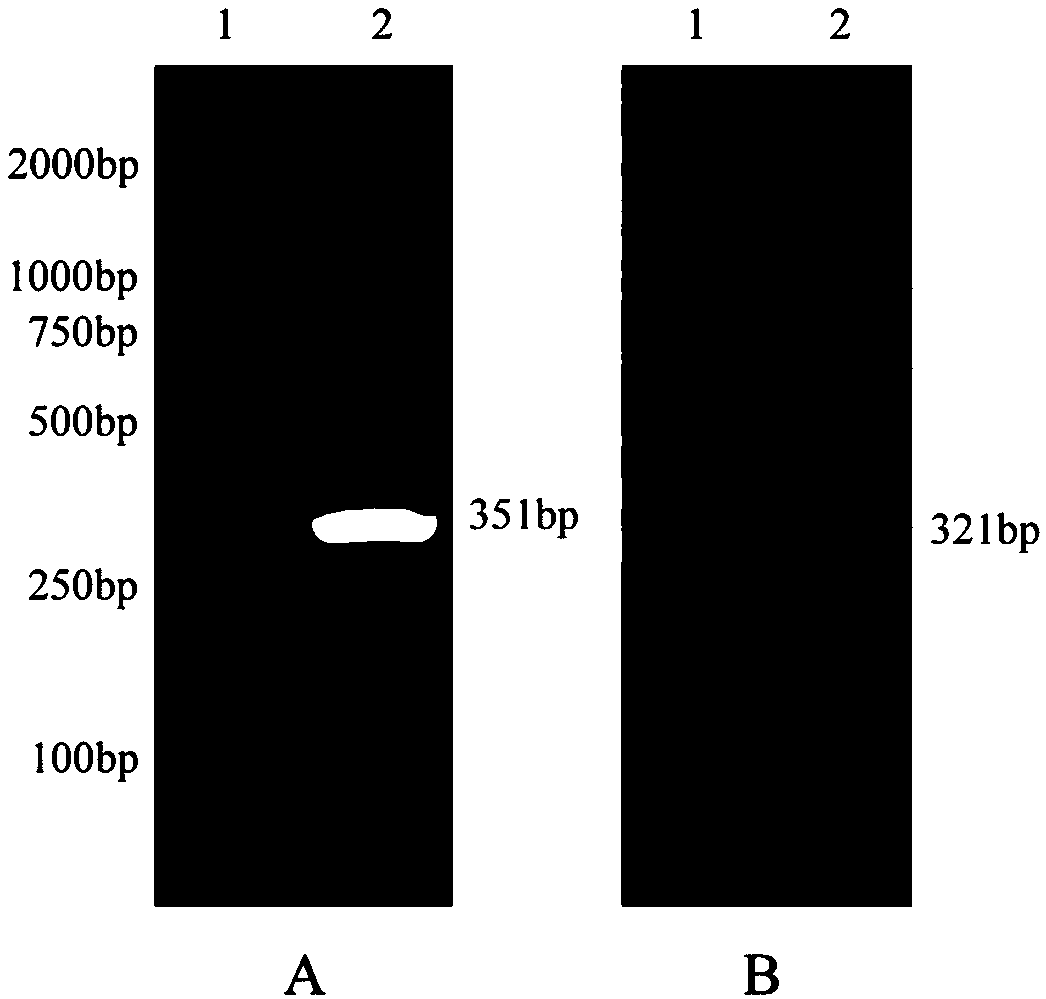
Chimeric antigen receptor targeting CD22 and application of chimeric antigen receptor
ActiveCN108715859AGood killing effectNo lethal effectPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigenOn cells
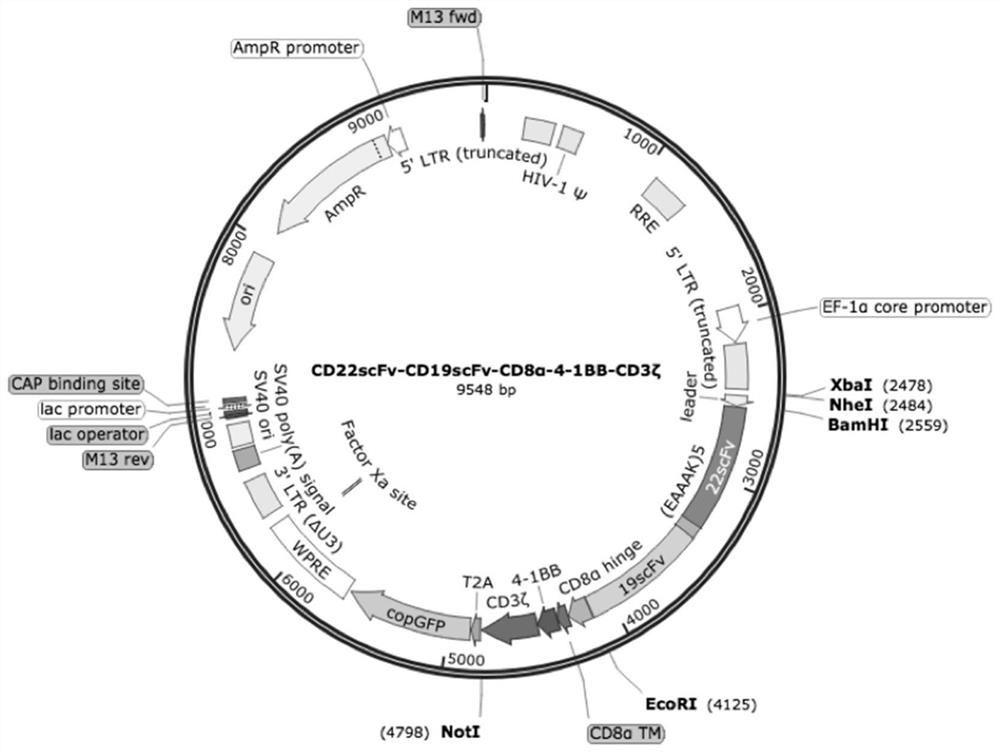
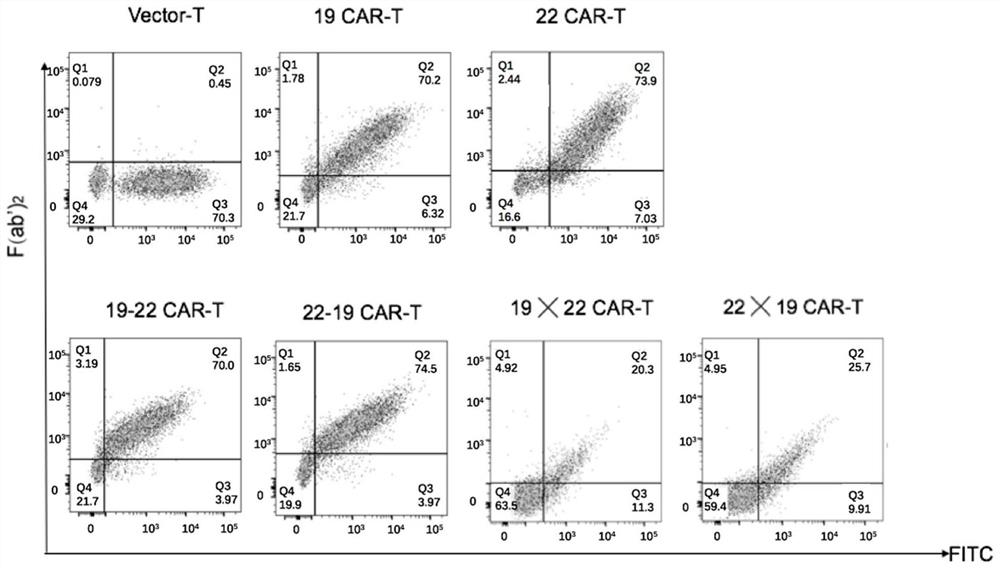
The invention provides a nucleic acid molecule for encoding a chimeric antigen receptor targeting CD22. The chimeric antigen receptor comprises an extracellular region, a transmembrane region and a intracellular signal transduction region, the extracellular region encoded by the nucleic acid molecule comprises a CD22 binding domain, and the CD22 binding domain is amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 3. By using flow cytometry, a degranulation analysis experiment and ELISA to detect cell factors secreted by a T cell, a fact that the CAR-T cell has a high lethal effect on B cell lymphoma cells and acute B cell lymphoma cell leukemia cells expressing CD22 and hardly has a lethal effect on cells which do not express CD22, and an off-target effect is prevented effectively is proved. The chimeric antigen receptor CD22scFv-CD8alpha-4-1BB-CD3zeta can be used for treating CD22<+>B cell hematologic neoplasms and is applicable to combined treatment with a CD19 CAR-T cell.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD DISEASES HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
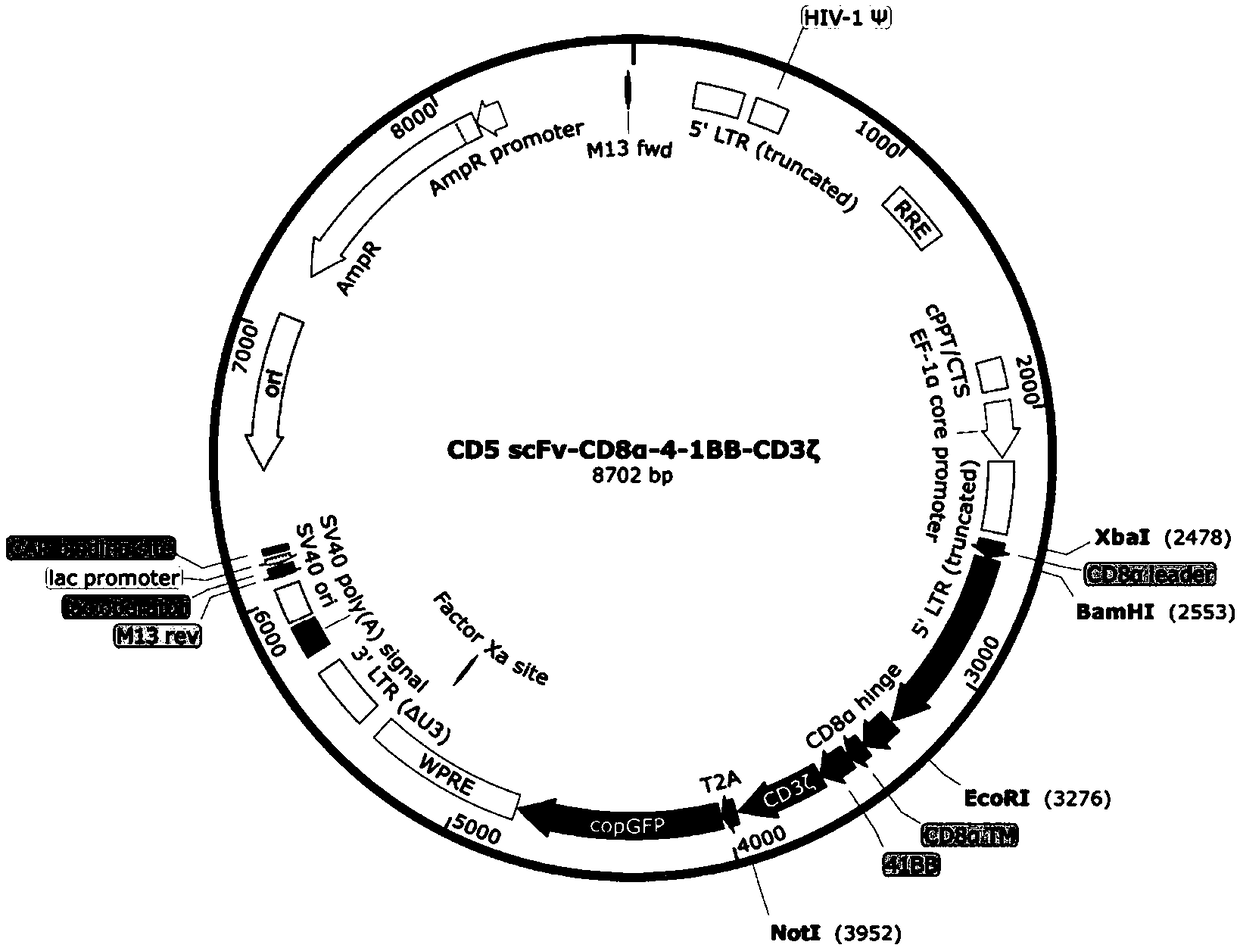
Chimeric antigen receptor targeting CD5 and application thereof
ActiveCN109266667AGood killing effectNo lethal effectPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigenCD8
The present invention provides a nucleic acid molecule encoding a chimeric antigen receptor targeting CD5, the chimeric antigen receptor comprises an extracellular domain, a transmembrane domain and an intracellular signal transduction domain, and the extracellular domain encoded by the chimeric antigen receptor comprises a CD5 binding domain which is an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:3. The chimeric antigen receptor comprises an extracellular domain, a transmembrane domain and an intracellular signal transduction domain, and the extracellular domain encoded by the chimeric antigenreceptor comprises a CD5 binding domain which is an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:3. The cytokines secreted by NK cells were detected by flow cytometry, degranulation assay and ELISA. The results showed that the CD5 CAR NK cells had strong cytotoxic effect on hematological tumor cells expressing CD5, but had weak cytotoxic effect on cells not expressing CD5. The cytokines secreted by CD5CAR NK cells could effectively prevent the missed target effect. A chimeric antigen receptor CD5 scFv-CD8[alpha]-4-1BB-CD 3 Xi can be used in the treatment of lymphocytic hematologic tumors with positive CD 5.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD DISEASES HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
Early drug screening method based on fluorescence
PendingCN110530829AHigh detection sensitivityPracticalFluorescence/phosphorescenceMeasurement deviceFluorescence
The invention relates to an early drug screening method based on fluorescence. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, providing target cells which stably express ion channel targets; 2, carrying out incubation on a voltage-sensitive dye and drugs with different concentrations together with the target cells; 3, measuring a fluorescence baseline value and a time-varying value of the incubated cells by utilizing a fluorescence measurement device; and 4, carrying out data fitting on the obtained values and determining whether the drugs have an exciting effect or an inhibiting effect on the ion channel targets. By utilizing the method, dozens of ion channel targets can be subjected to drug screening with an intermediate flux through utilizing a microplate reader with low cost; and theearly drug screening method is particularly applicable to early drug screening.
Owner:ICE BIOSCI INC +1
Multifunctional slow virus carrier capable of restraining endogenesis target genes and simultaneously expressing exogenous genes
InactiveCN102344939AEliminate negative effectsGood curative effectFermentationGenetic engineeringWild typeGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a multifunctional slow virus carrier capable of restraining endogenesis target genes and simultaneously expressing exogenous genes. The carrier is formed by a genetic engineering technology, is composed by two promoters and two corresponding multi-cloning sites for inserting shRNA and genes, can utilize an RNA interference technology to restrain the cell endogenesis genes, and simultaneously can recover the expression of the cell endogenesis genes through importing the exogenous genes, and accordingly, the normal phenotype of the whole cell is recovered. The technology overcomes a plurality of difficult points of the RNA technology, such as the RNA interference specificity and efficient infection cells are ensured, and stable expression can be realized in the cells. Consequently, base researchers can more accurately express the status of the target genes in a signal path and a plurality of unknown functions, the carrier also can be used for restraining the target gene with defect endogenesis functions, so efficient importing is realized, the wild type target genes with the endogenesis functions are stably expressed, and a very powerful tool is provided for gene treatment.
Owner:聂凌云
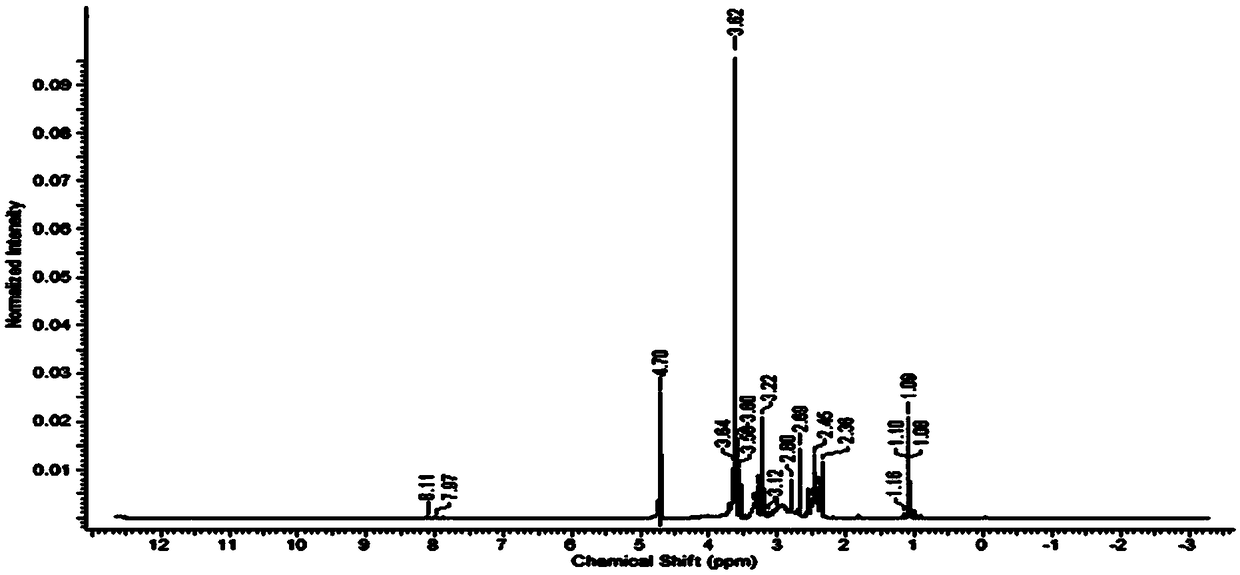
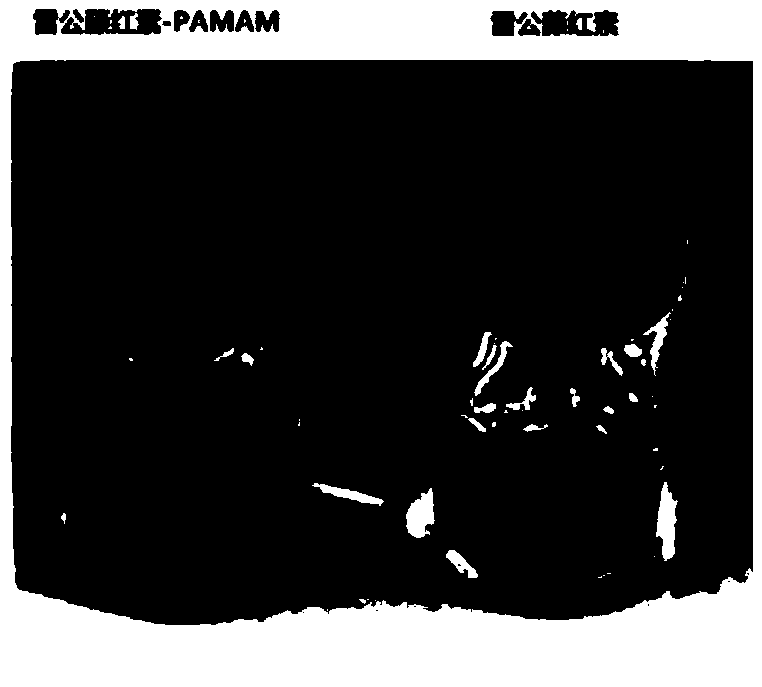
A kind of tripterine-dendrimer conjugate and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN108888774BAvoid off-target effectsHigh selectivityOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDendrimerAptamer
The invention discloses a tripterine-dendritic macromolecular conjugate, a preparation method thereof and an application, and relates to a tripterine. The tripterine-dendritic macromolecular conjugatecomprises a center dendritic polyamide-organic polyamidoaminedendrimer nano-carrier, polyethylene glycol, surface targeting ligands and the tripterine. The preparation method of the conjugate includes the steps: performing partial carboxylation on amidogen on the surface of PAMAM (polyamidoaminedendrimers) by butanedioic anhydride; dialyzing and freeze-drying a partial carboxylation object to obtain a PAMAM-COOH derivative; activating the PAMAM-COOH derivative by EDC / NHS, and modifying the activated derivative by the polyethylene glycol; dialyzing the modified derivative to obtain the PAMAM-PEG-COOH derivative; activating the PAMAM-PEG-COOH derivative by EDC / NHS; connecting the activated PAMAM-PEG-COOH derivative with EpCAM targeting aptamers; removing unreacted aptamers in an ultra-filtering manner to obtain a multifunctional PAMAM derivative; dissolving the tripterine by solvents; activating the dissolved tripterine by EDC / NHS; covalently complexing the activated tripterine on the surface of the PAMAM derivative; dialyzing a complexed object to obtain the conjugate.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Targeting responsive release system and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN111588704AAvoid off-target effects or leakage of active substancesAddressing poor treatment outcomesAntipyreticAnalgesicsBiophysicsBiomedical engineering
The invention provides a targeting responsive release system. The targeting responsive release system comprises a chimeric apoptotic corpuscle, the chimeric apoptotic corpuscle comprises an apoptoticcorpuscle membrane and mesoporous nanoparticles wrapped in the apoptotic corpuscle membrane, the apoptotic corpuscle membrane is an apoptotic corpuscle membrane derived from immune cells, and the mesoporous nanoparticles are loaded with active substances. The system provides an effective means for constructing a specific treatment product with a targeted delivery function and an accurate drug release function.
Owner:XIAN TISSUE ENG & REGENERATIVE MEDICINE RES INST
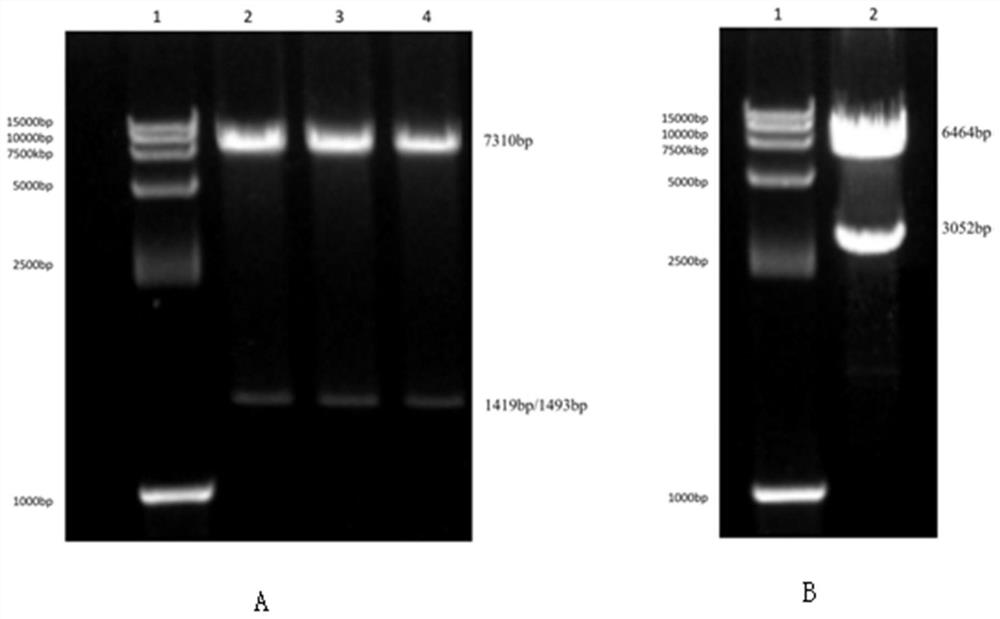
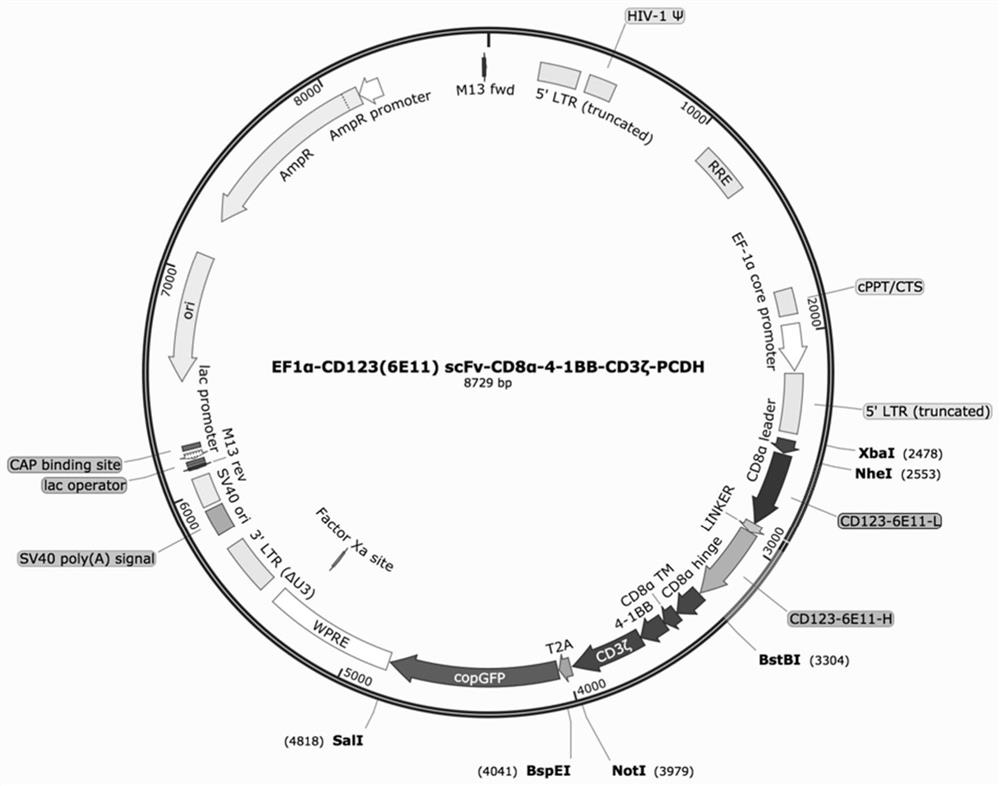
Chimeric antigen receptor targeting CD123 and double-target chimeric antigen receptor containing chimeric antigen receptor targeting CD123
ActiveCN112979820AStrong in vitro killing effectAvoid off-target effectsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleic acid vectorSingle-Chain AntibodiesCD33
The invention discloses a nucleic acid molecule for coding a chimeric antigen receptor targeting CD123. The chimeric antigen receptor comprises an extracellular region, a transmembrane region and an intracellular signal transduction region; the extracellular region coded by the chimeric antigen receptor comprises a CD123 binding structural domain; the CD123 binding structural domain is an anti-CD123 single-chain antibody variable region fragment; and the anti-CD123 single-chain antibody variable region fragment is an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.13 or a sequence with 90%-99% identity with the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.13, an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.14 or a sequence with 90%-99% identity with the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.14, or an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.15 or a sequence with 90%-99% identity with the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.15. According to the nucleic acid molecule for coding the chimeric antigen receptor targeting the CD123, the chimeric antigen receptor can be used for treating CD123+ and / or CD33+ hematologic tumors, so that the off-target effect is effectively prevented, the treatment effect is better, and escape is not prone to occurring.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD DISEASES HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
Tripterine-dendritic macromolecular conjugate, preparation method thereof and application
ActiveCN108888774AAvoid off-target effectsHigh selectivityOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAptamerFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a tripterine-dendritic macromolecular conjugate, a preparation method thereof and an application, and relates to a tripterine. The tripterine-dendritic macromolecular conjugatecomprises a center dendritic polyamide-organic polyamidoaminedendrimer nano-carrier, polyethylene glycol, surface targeting ligands and the tripterine. The preparation method of the conjugate includes the steps: performing partial carboxylation on amidogen on the surface of PAMAM (polyamidoaminedendrimers) by butanedioic anhydride; dialyzing and freeze-drying a partial carboxylation object to obtain a PAMAM-COOH derivative; activating the PAMAM-COOH derivative by EDC / NHS, and modifying the activated derivative by the polyethylene glycol; dialyzing the modified derivative to obtain the PAMAM-PEG-COOH derivative; activating the PAMAM-PEG-COOH derivative by EDC / NHS; connecting the activated PAMAM-PEG-COOH derivative with EpCAM targeting aptamers; removing unreacted aptamers in an ultra-filtering manner to obtain a multifunctional PAMAM derivative; dissolving the tripterine by solvents; activating the dissolved tripterine by EDC / NHS; covalently complexing the activated tripterine on the surface of the PAMAM derivative; dialyzing a complexed object to obtain the conjugate.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Compositions and methods for treating toll-like receptor-driven inflammatory diseases
InactiveUS20200362052A1Inhibit productionPrevent immunosuppressionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsAntiendomysial antibodiesAutoantibody
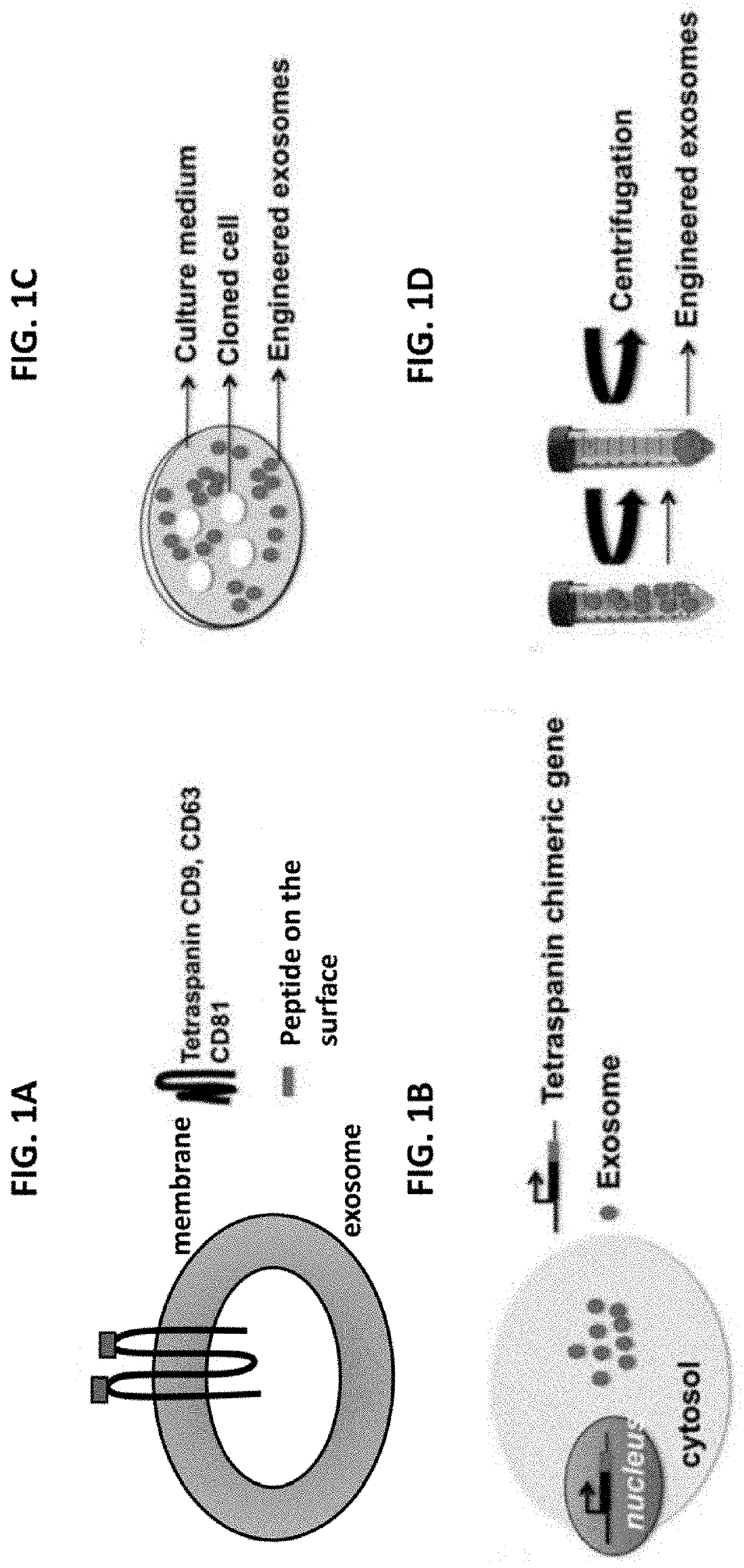
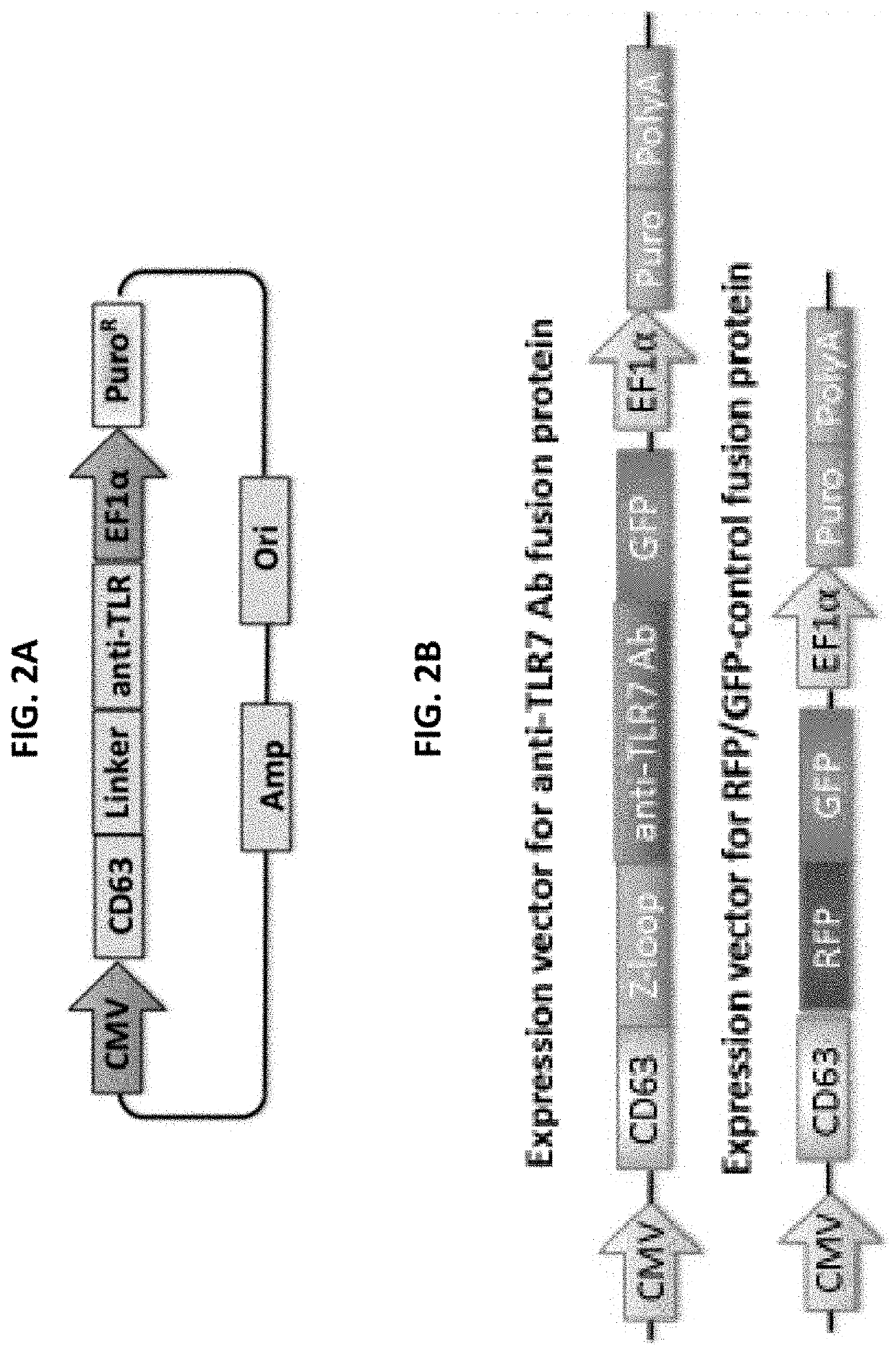
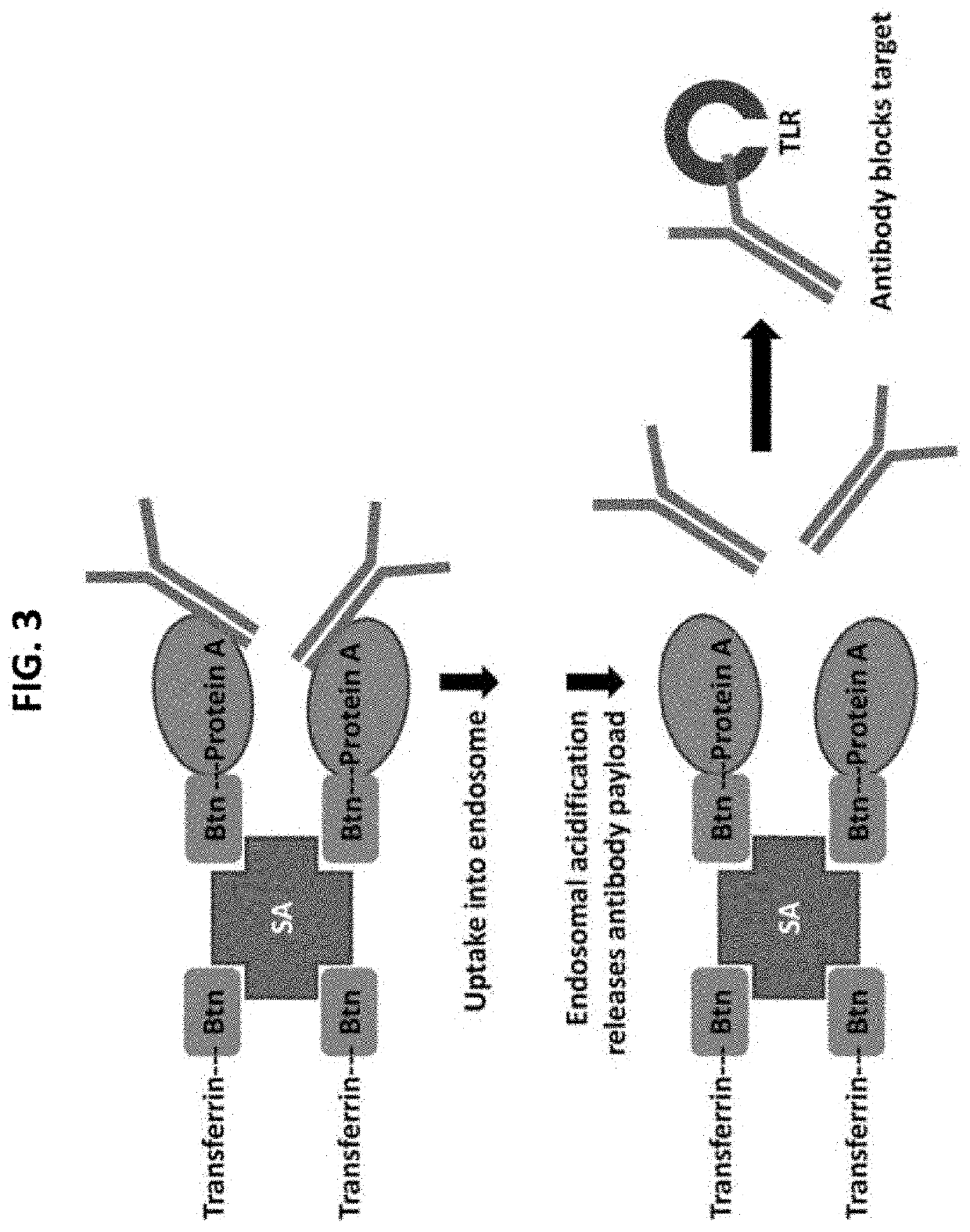
Many disorders wherein inflammation is a hallmark such as rheumatoid arthritis, sepsis, or cancer, are chronic and impose a significant burden on family and society due to their high morbidity and mortality. Each year the United States government spends $2.6T to treat chronic Inflammatory diseases, which are linked to 70% of the deaths every year. Protein therapeutics, such as anti-TNFα antibodies that selectively block the TNFα cascade, have become the mainstay therapy for the management of chronic inflammatory diseases. Despite the promise of these early studies, concerns about the side effects of these protein drugs, including induction of auto-antibodies and immuno-suppression, may limit the applications to disease treatments. Thus, there is a need to develop new drugs and delivery systems for the prevention and treatment of inflammatory diseases. The present invention relates to extracellular vesicle composition, system, and methods for treating Toll-like receptor-driven inflammatory disease.
Owner:SOUVIE BIODELIVERY LLC
Chimeric antigen receptor targeting CD22 and CD19 and application thereof
ActiveCN112442508AGood killing effectAvoid off-target effectsPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyT cellCombined treatment
The invention discloses a nucleic acid molecule encoding a chimeric antigen receptor targeting CD22 and CD19. The chimeric antigen receptor comprises an extracellular region, a transmembrane region and an intracellular signal transduction region, wherein the extracellular region encoded by the chimeric antigen receptor comprises a CD22 and CD19 binding domain, and the CD22 and CD19 binding domainis composed of an antibody single-chain variable region fragment of CD22 and an antibody single-chain variable region fragment of CD19; and the antibody single-chain variable region fragment of CD22 and the antibody single-chain variable region fragment of CD19 are arranged in the sequence of an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 9, an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 10, an amino acidsequence shown in SEQ ID No. 11 or an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 12. The chimeric antigen receptor disclosed by the invention can be used for treating CD19 <+> and CD22 <+> B cell bloodtumors and combined treatment with CD19 CAR-T cells or CD22 CAR-T cells.
Owner:JUVENTAS CELL THERAPY LTD
FLT3 chimeric antigen receptor and application thereof
ActiveCN108251442AGood killing effectAvoid off-target effectsPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyCD8Flt3 mutation
The invention discloses an encoding chimeric antigen receptor nucleic acid molecule. The chimeric antigen receptor comprises an extracellular region, a transmembrane domain and an intracellular signaltransduction domain, wherein the encoded extracellular region comprises an FLT3 binding structural domain, and the FLT3 binding structural domain is an FLT3 ligand or an amino acid sequence with the90 to 99% identity as the FLT3 ligand. A flow cytometry, a degranulation analysis experiment and cytokines secreted by ELISA detection T cells prove that T cells modified by the chimeric antigen receptor have a strong killing effect of leukemia cells for expressing FLT3, especially have a specific killing effect on AML cells carrying FLT3 mutant and can effectively prevent an off-target effect. The chimeric antigen receptor FLT3L-CD8 alpha-4-1BB-CD3 zeta disclosed by the invention can be applied to treating FLT3+leukemia, especially leukemia carrying the FLT3 mutant.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD DISEASES HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
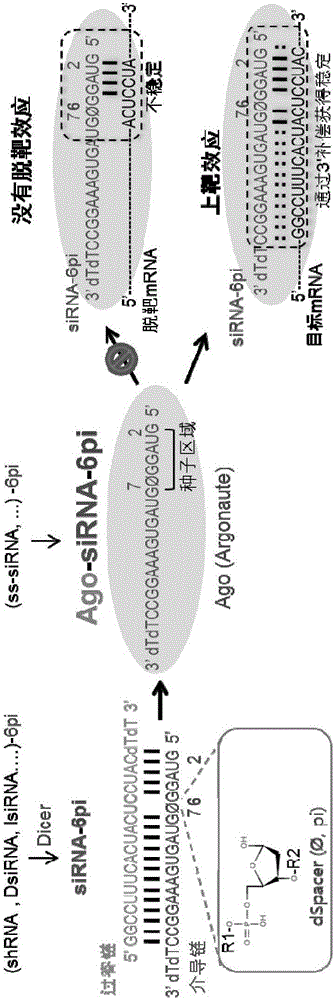
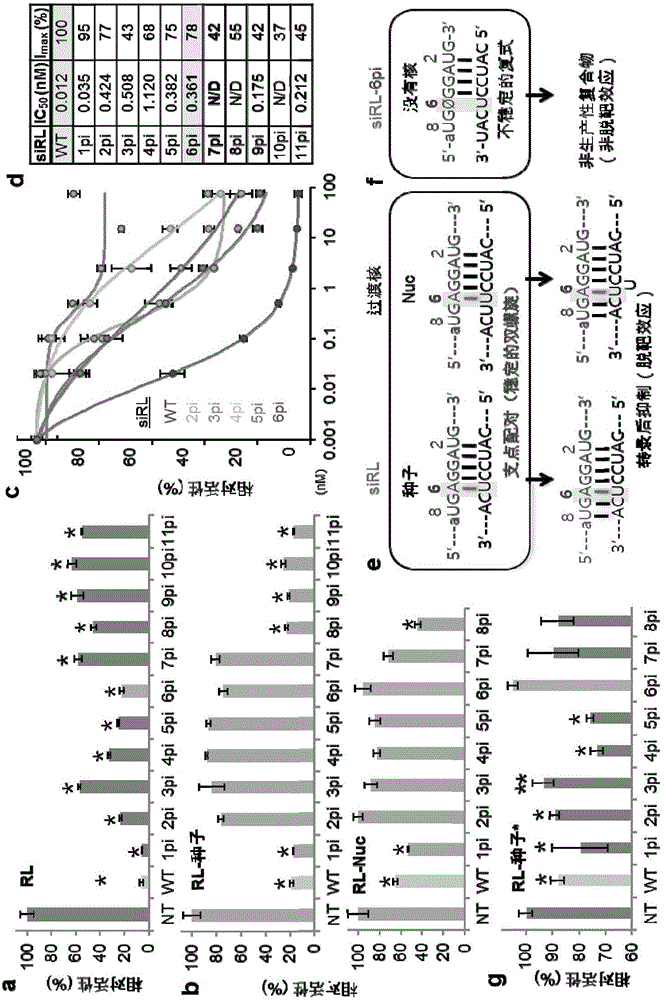
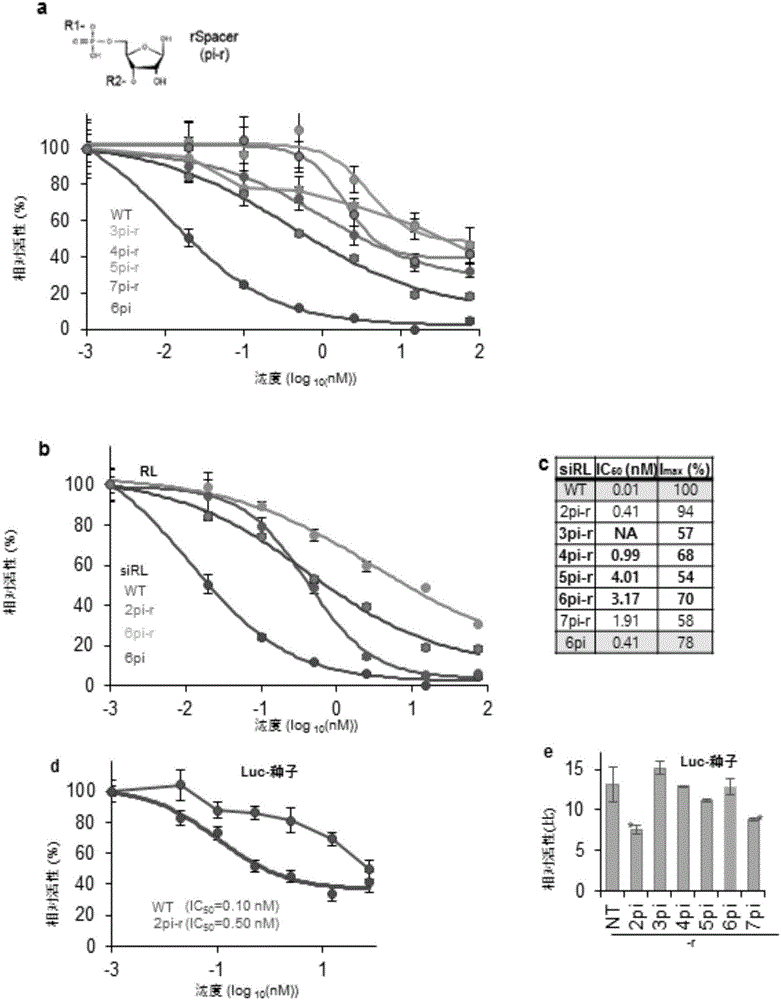
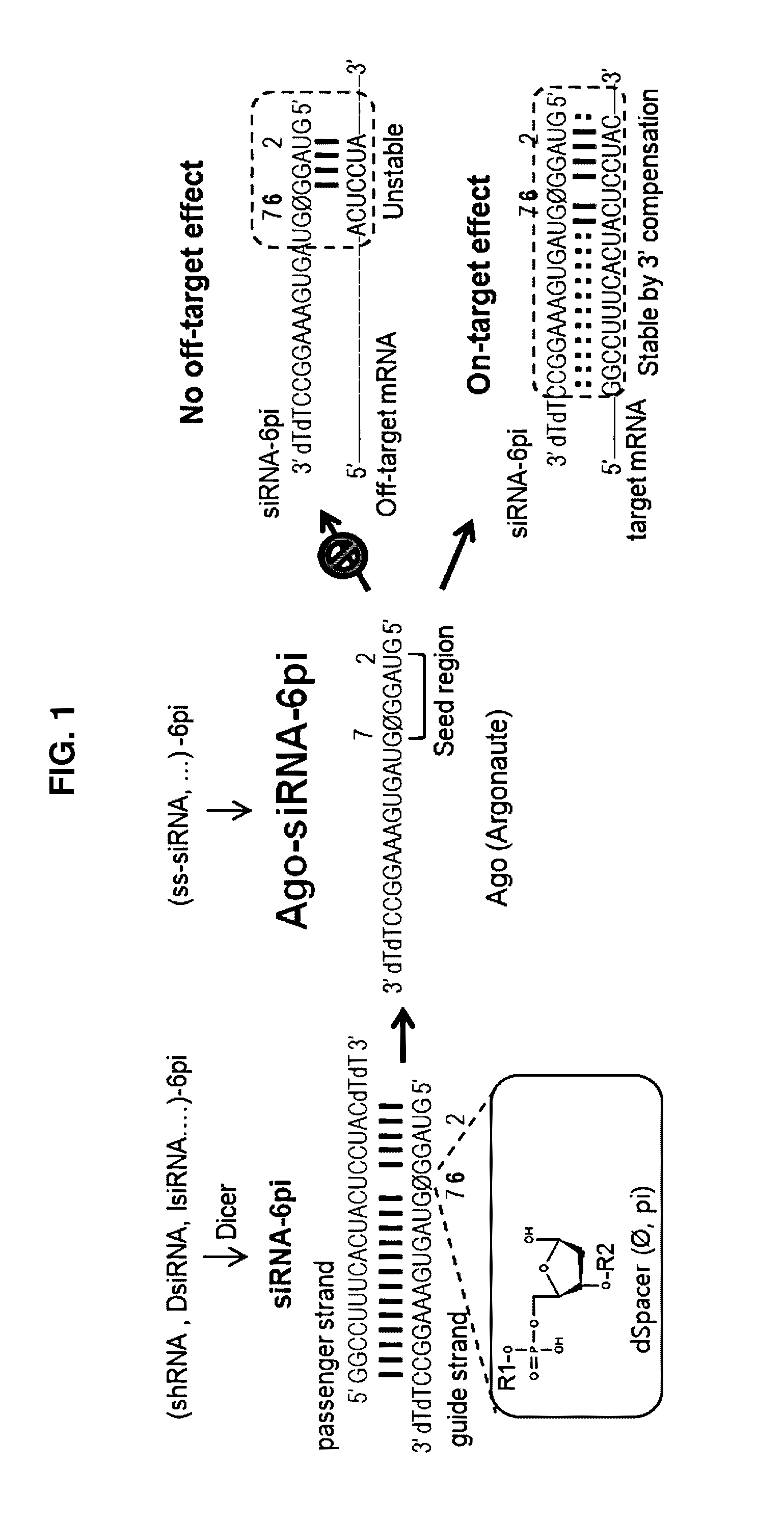
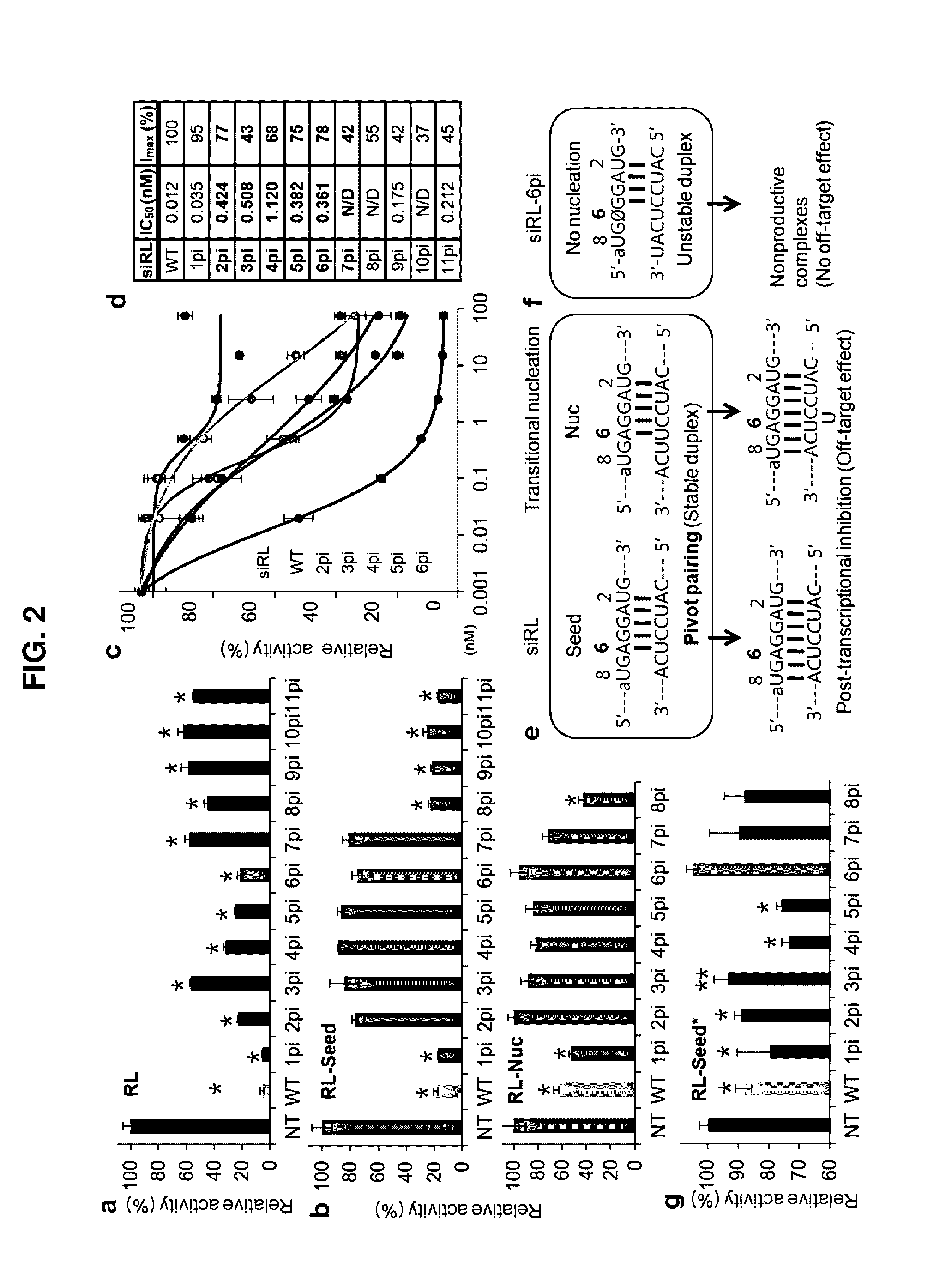
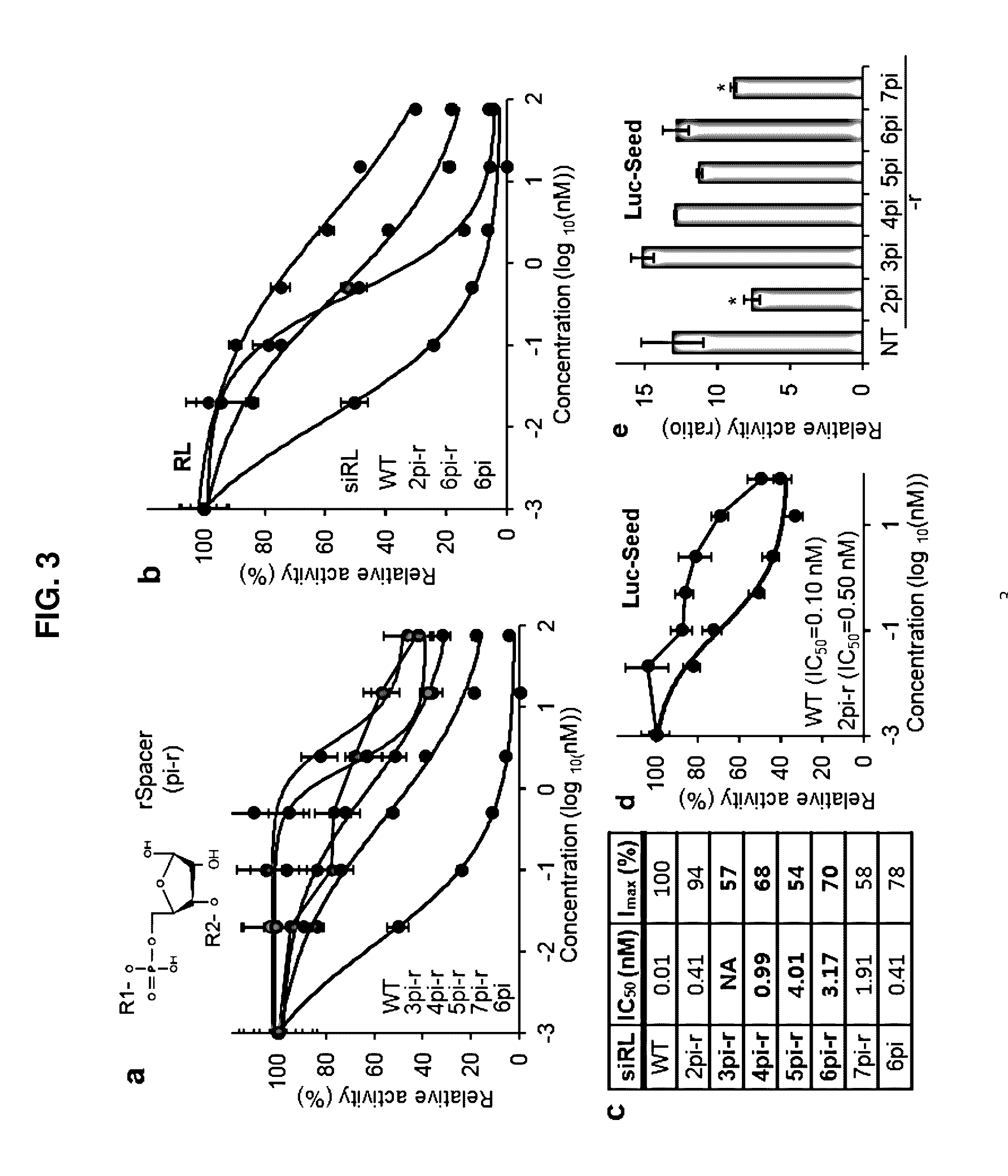
Nucleic acid inducing RNA interference modified for preventing off-target, and use thereof
ActiveCN105829535AInhibition of off-target effectsSelectiveActivity regulationGenetic material ingredientsSingle strandDouble strand
The present invention relates to a nucleic acid inducing RNA interference modified for preventing off-target, and a use thereof, and more specifically, to a nucleic acid inducing RNA interference, modified by replacing, by a spacer capable of no base pairing, 5' terminal and 3' terminal regions in at least one single strand of the double strand of the nucleic acid inducing RNA interference. The nucleic acid inducing RNA interference of the present invention can provide: a nucleic acid having a novel modified form for preventing an off-target effect generated when inhibiting the expression of a target gene by an RNA interference phenomenon; and a method for selectively inhibiting the expression of a target gene by using the same. In addition, the nucleic acid inducing RNA interference according to the present invention solves the inaccuracy and side effects due to off-target, which are the problems of a known nucleic acid inducing RNA interference, by providing a nucleic acid inducing RNA interference as a novel modified form having target selectivity and specificity by preventing an off-target effect while inhibiting the expression of a target gene, and thus can be used, without worries, in the research of a technique for inhibiting the expression of a gene and in gene therapy.
Owner:ENCODEGEN CO LTD
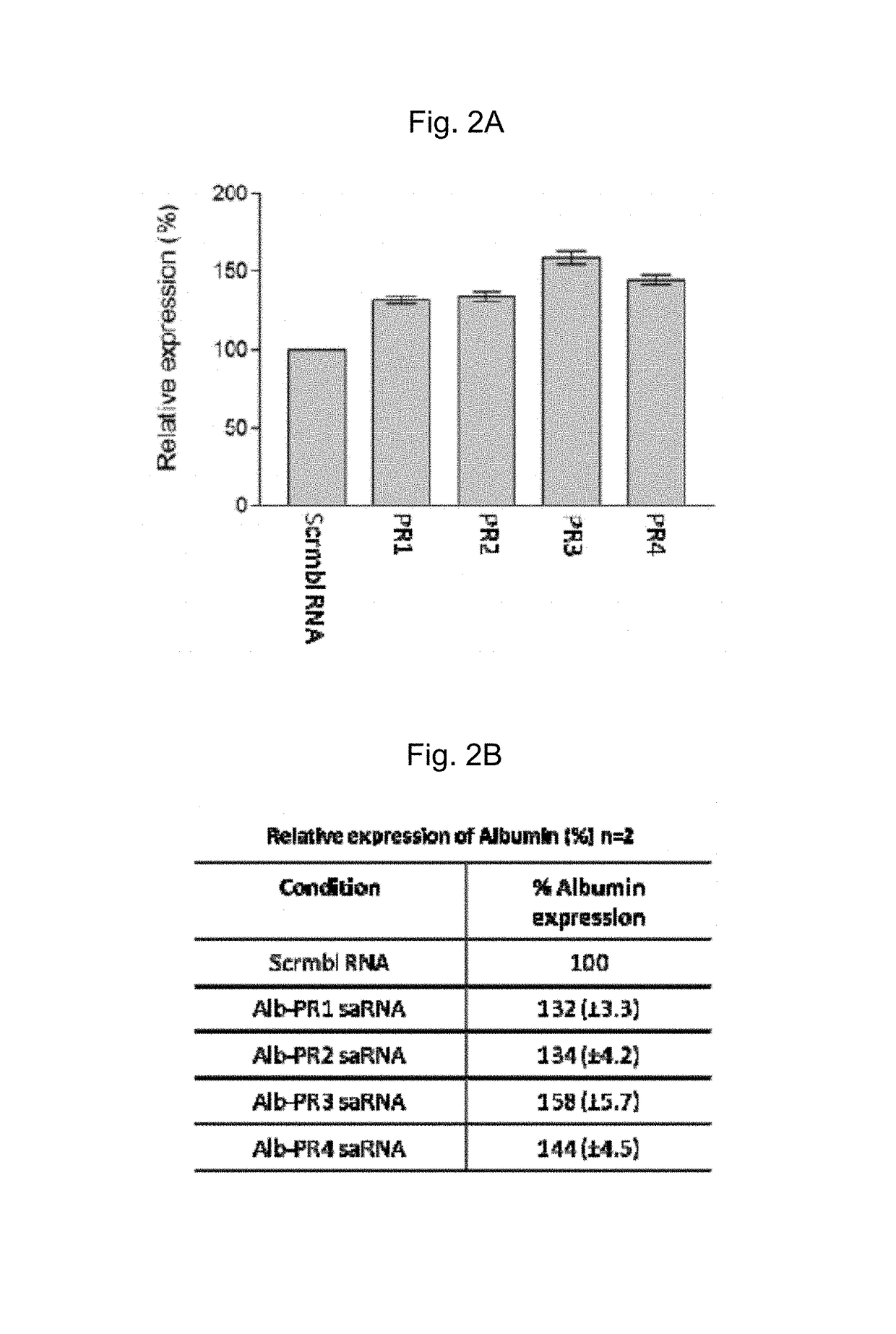
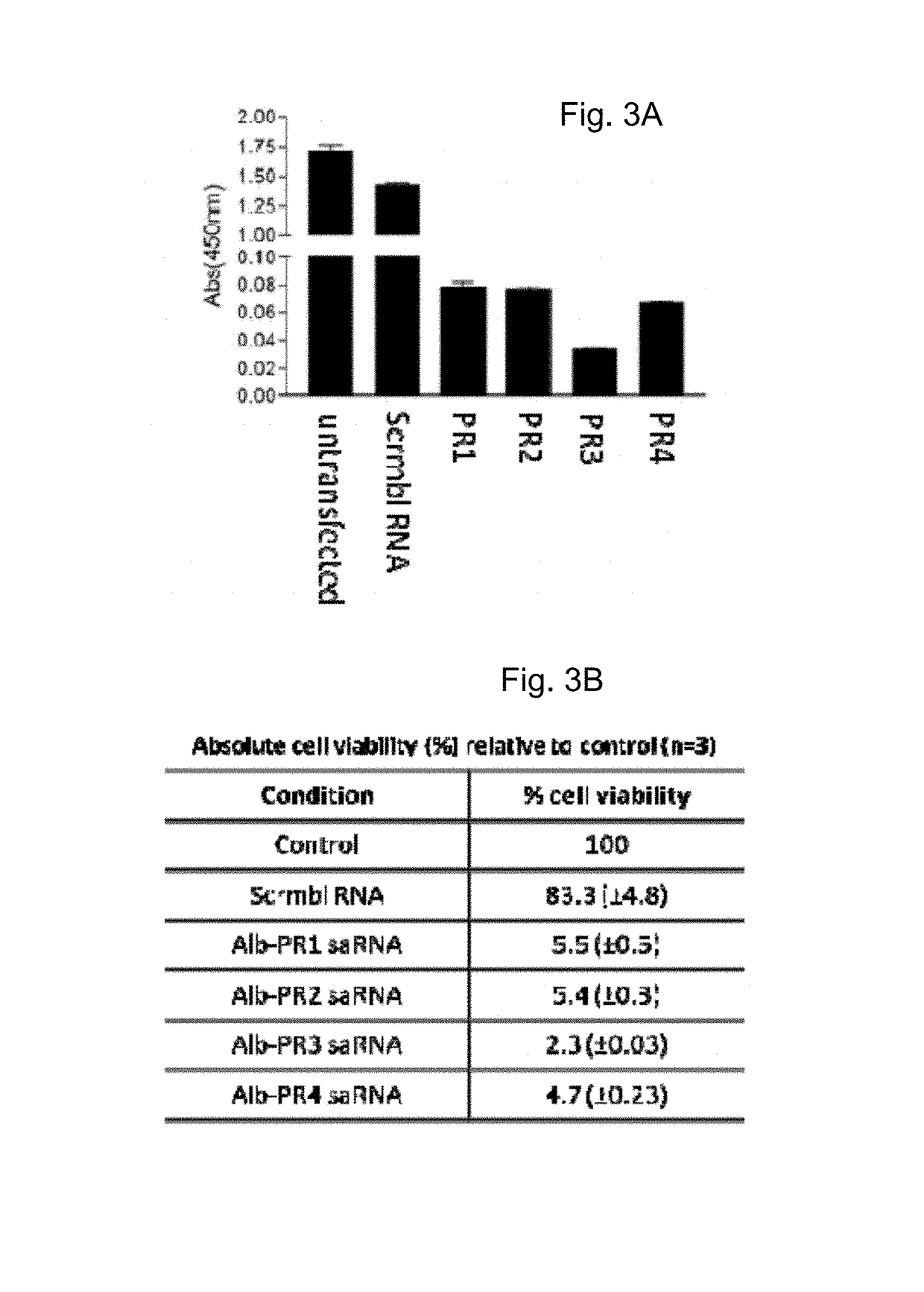
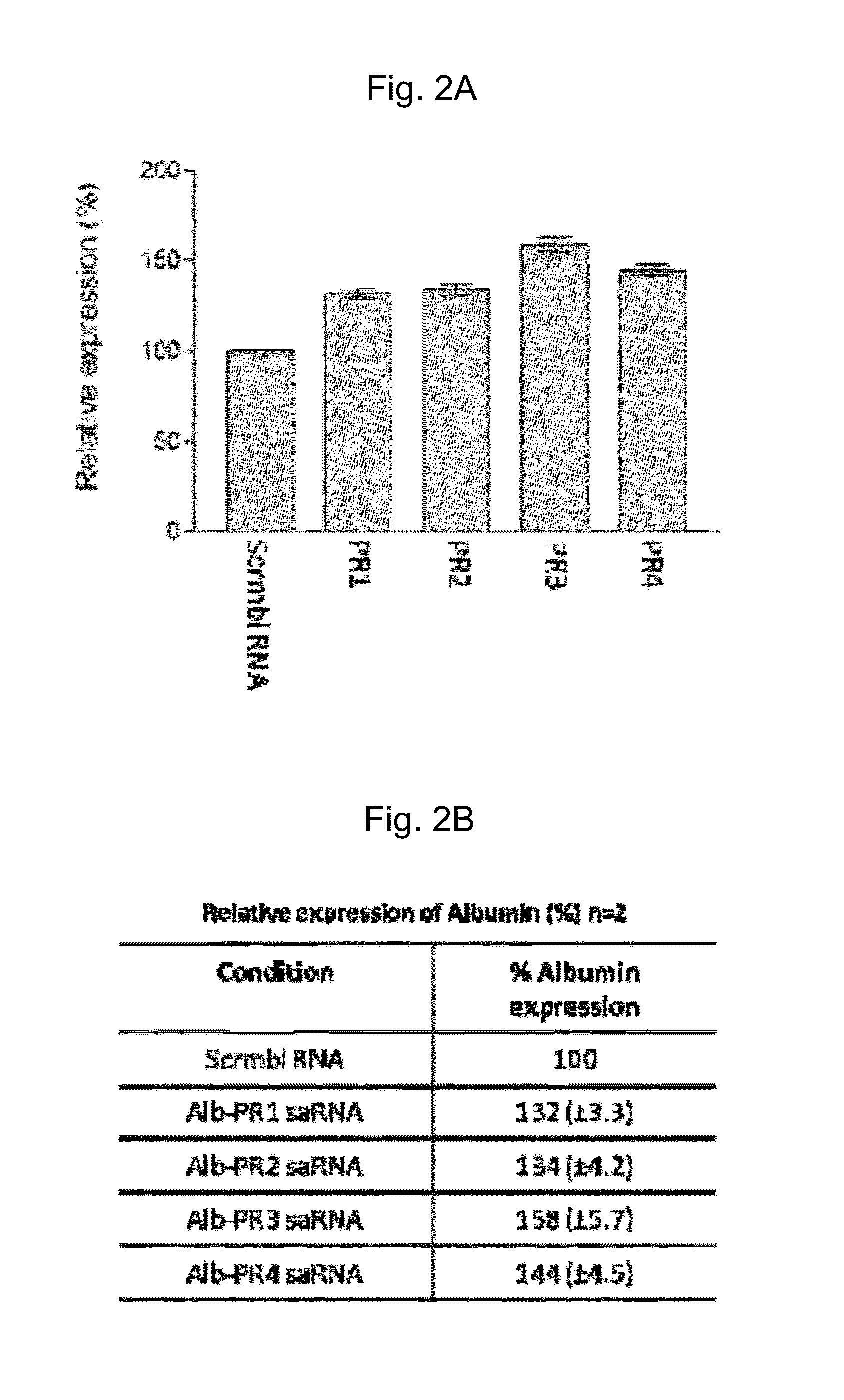
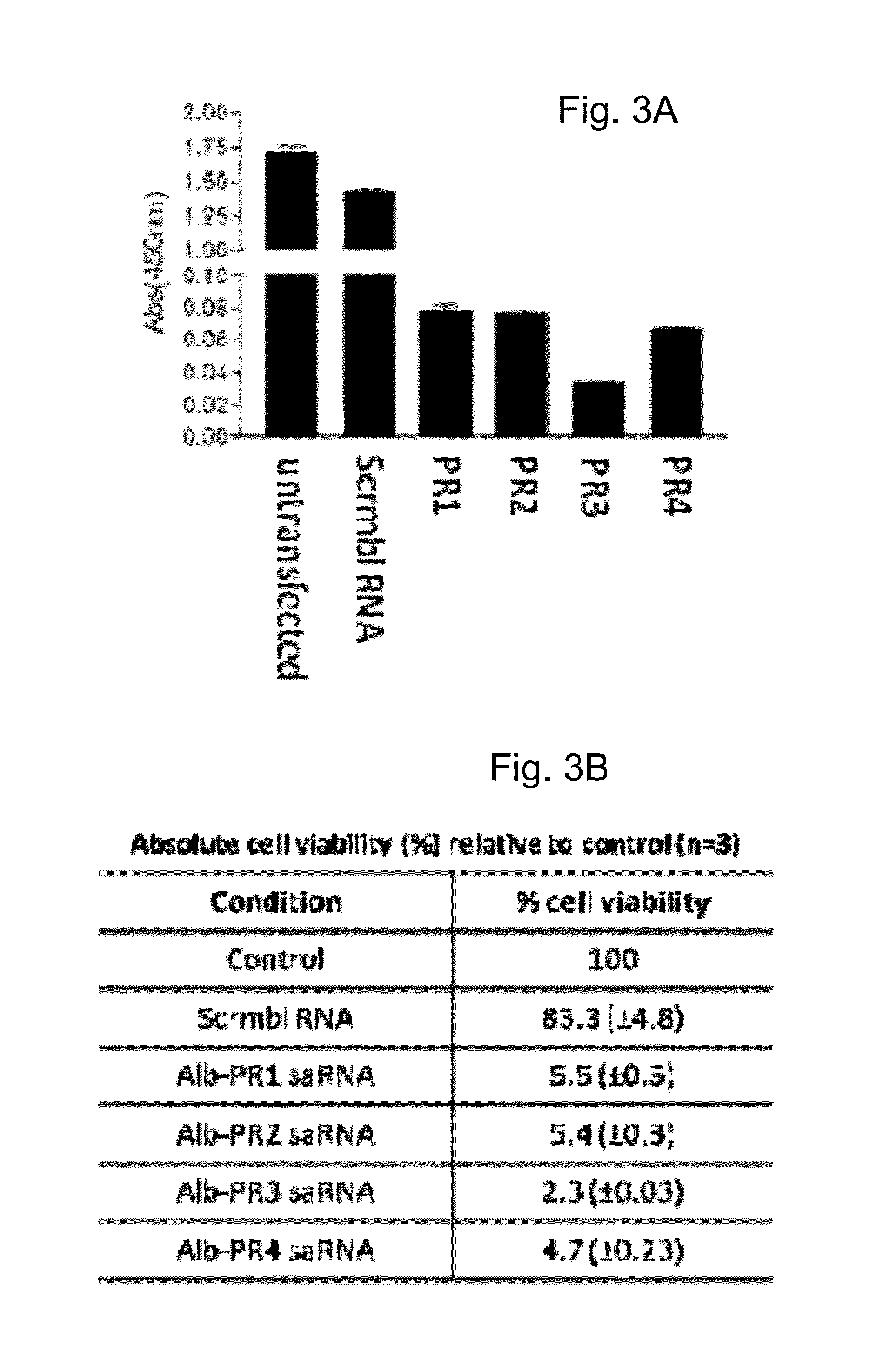
Albumin production and cell proliferation
ActiveUS9745579B2ModulationReduce Polycomb-levelsSugar derivativesDigestive systemDiseaseHypoproteinemia
The present invention provides short activating RNA molecules which up-regulate albumin production. The present invention also provides methods of up-regulating albumin production, such methods involving the use of short activating RNA molecules capable of increasing the expression of albumin. The present invention also provides the use of the short activating RNA molecules in therapy, such as treating or preventing a hyperproliferative disorder and / or a disorder characterised by hypoalbuminemia.
Owner:MINA THERAPEUTICS
Sorafenib-gene co-loaded nano-drug for cancer treatment as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112263565AAvoid off-target effectsAvoid clearingGenetic material ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCancer cellCholesterol
The invention provides a sorafenib gene co-loaded nano-drug for cancer treatment as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The sorafenib gene co-loaded nano-drug comprises a nano-aggregate wrapped by a targeting lipid layer; the targeting lipid layer comprises sorafenib, phospholipid, a targeting substance and cholesterol; and the nano-aggregate is shUSP22 wrapped by an active oxygen response material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: coating shUSP22 with the active oxygen response material to prepare the nano-aggregate; and loading the targeting lipid layeron a surface of the nano-aggregate to obtain the sorafenib gene co-loaded nano-drug. The application is an application of the sorafenib gene co-loaded nano-drug in preparation of drugs for treating cancers. The sorafenib gene co-loaded nano-drug can effectively improve active oxygen level in cancer cells, inhibit expression of USP22 in liver cancer cells, efficiently kill the liver cancer cells,prolong blood circulation time of sorafenib and inhibit tumor growth.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Primer probe composition, kit containing primer probe composition and detection method of primer probe composition
ActiveCN114058742AStrong specificityAvoid off-target effectsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationViral testPcr method
The invention discloses a primer probe composition, a kit containing the primer probe composition and a detection method of the primer probe composition, belonging to the technical field of virus detection. The primer probe composition comprises specific primers and probes aiming at the influenza A virus, the influenza B virus and the respiratory syncytial virus. The specific primer and the probe have good specificity. High-specificity, high-sensitivity and high-efficiency detection on the influenza A virus, the influenza B virus and the respiratory syncytial virus can be realized by adopting the kit and a Q-PCR method.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KEFEN BIOTECH CO LTD
Nucleic acid inducing RNA interference modified for preventing off-target, and use thereof
ActiveUS20160304878A1Avoid off-target effectsSelectively expressionActivity regulationGenetic material ingredientsSingle strandDouble strand
The present invention relates to an RNA interference-inducing nucleic acid and the use thereof, and more particularly to an RNA interference-inducing nucleic acid comprising at least one single strand of double strands, the at least one single strand comprising a modification substituted to a spacer, which is unable to form a base pair, in the 5′ end or the 3′ end region. The RNA interference-inducing nucleic acid of the present invention is a novel modified form of nucleotide provided to prevent off-target effects, offering a method to selectively repress target gene expression. In addition, according to the present invention, the RNA interference-inducing nucleic acid provides novel modified forms with target selectivity and specificity as a method to block the off-target effects while silencing the target gene expression, whereas the usage of conventional RNA interference-inducing nucleic acids cause inaccuracy and adverse effects through off-targets, thereby the RNA interference-inducing nucleic acid was offered to solve the problem, wherein it will be widely used as a method for repressing gene expression in research and for gene therapy without concerning the off-target effects.
Owner:ENCODEGEN CO LTD
A kind of erbb2 single-chain antibody, chimeric antigen receptor targeting human erbb2, recombinant vector, recombinant cell and application
ActiveCN110396131BGood killing effectAvoid off-target effectsBlood/immune system cellsImmunoglobulinsAntigenSingle-Chain Antibodies
The invention provides an ErbB2 single-chain antibody, a chimeric antigen receptor targeting human ErbB2, a recombinant vector, a recombinant cell and an application, belonging to the technical field of tumor immunotherapy. The ErbB2 single-chain antibody has the characteristics of SEQ ID No. The amino acid sequence shown in .1; the chimeric antigen receptor targeting human ErbB2 has the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 3; the recombinant vector includes a gene encoding the chimeric antigen receptor and Initial vector; the recombinant cells include natural killer cells and the recombinant vector. The ErbB2 single chain antibody of the present invention can specifically recognize tumor antigens, avoid the off-target effect of CAR-NK cells, and have a good tumor cell killing effect; the recombinant cells have a high ability to continuously kill tumor cells and reduce Risk of cytokine storm.
Owner:BEIJING DCTY BIOTECH CO LTD +1
Crispr/cas9 system and its application of the trp gene of Bemisia tabaci med cryptic species
ActiveCN106086008BAvoid off-target effectsThe effect is long-lasting and stableMicroinjection basedPeptidesMutantNuclear gene
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, in particular to a CRISPR / cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats / associated proteins) system of a bemisia tabaci MED cryptic species TRP gene and an application of the CRISPR / cas9 system. By overcoming an off-target effect by optimizing a synthetic primer of a target site of sgRNA of a bemisia tabaci MED cryptic species TRP sequence, the expression of a target gene can be inhibited from a nuclear gene level, so that a durable and stable effect is achieved and a durable and stable mutant type is formed.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
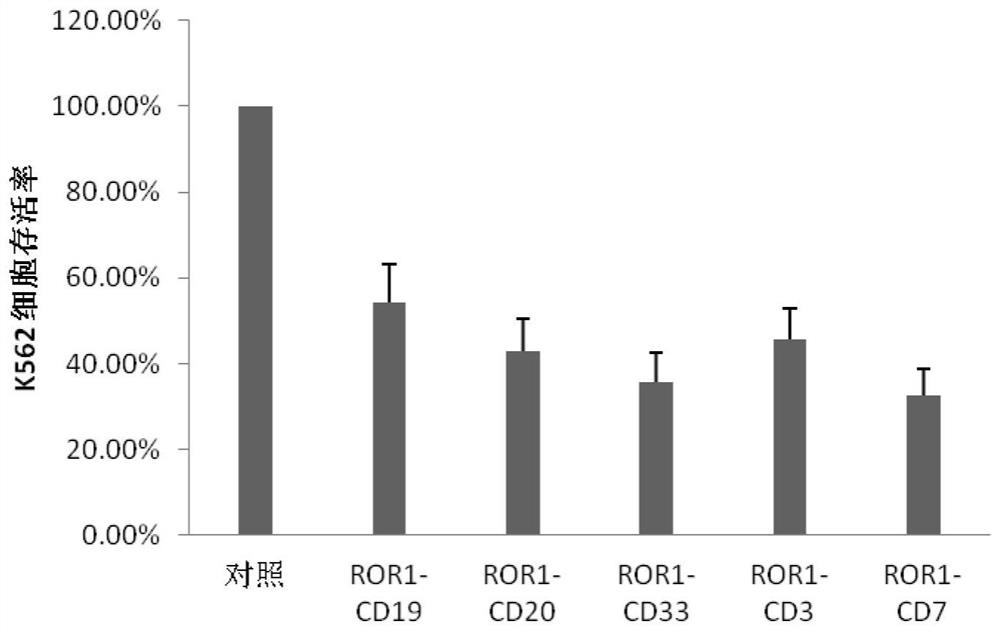
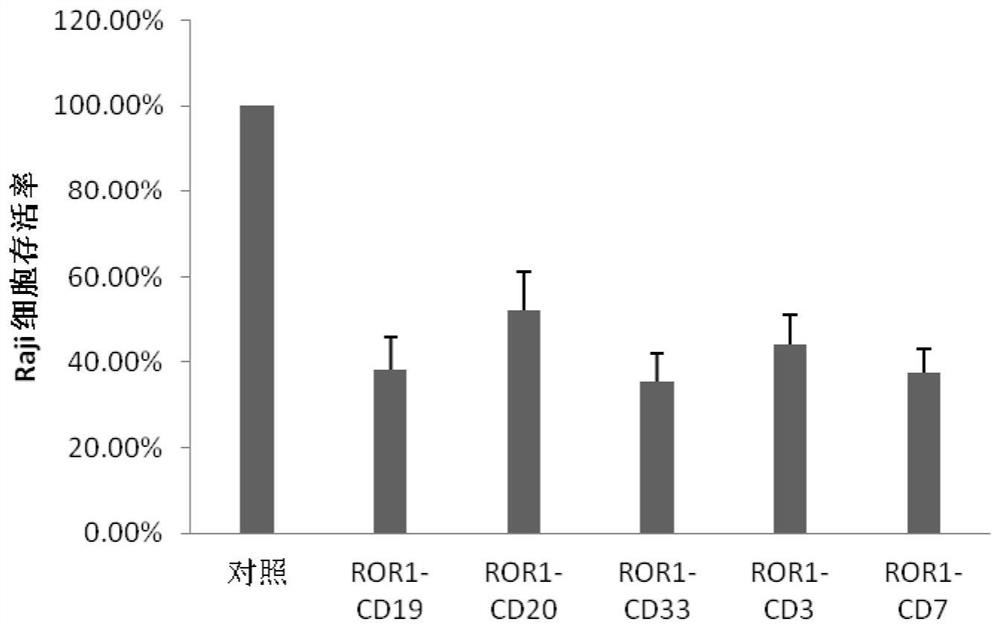
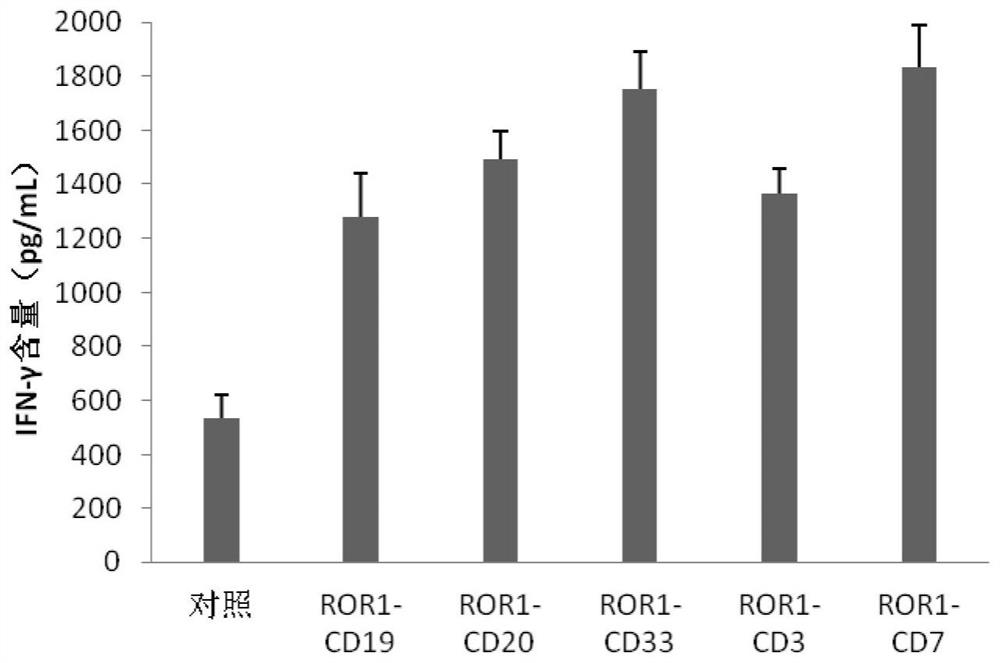
Bispecific chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) targeting ROR1 and CD33 and application thereof
ActiveCN114133457AImprove tumor targetingAvoid off-target effectsPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyCD3Signalling molecules
The invention provides a bispecific chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) targeting ROR1 and CD33 and application thereof, the bispecific chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) has the following structure: ROR1 scFv-CD33 scFv-H-TM-C-CD3 zeta, in which '-' is a connecting peptide or a peptide bond; h is a hinge area; tM is a transmembrane domain; c is a costimulatory signal molecule; cD3zeta is an intracellular signal transduction sequence. The chimeric antigen receptor can inhibit tumor growth in vivo and in vitro, prolong the life cycle, promote cytokine secretion and play a synergistic anti-tumor role.
Owner:郑州源创基因科技有限公司 +2
A Sorafenib-gene co-loaded nano-medicine for cancer treatment and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN112263565BAvoid off-target effectsAvoid clearingGenetic material ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCancer cellCholesterol
The present invention provides a Sorafenib-gene-co-loaded nano-medicine for cancer treatment and its preparation method and application, wherein Sorafenib-gene-co-loaded nano-medicine includes nano-aggregates wrapped by targeting lipid layer ; The targeting lipid layer includes Sorafenib, phospholipids, targeting substances and cholesterol; the nano-aggregates are shUSP22 encapsulated by active oxygen responsive materials. The above preparation method includes the following steps: wrapping shUSP22 with active oxygen corresponding materials to prepare nano-aggregates; loading the targeting lipid layer on the surface of nano-aggregates to obtain sorafenib-gene co-carrying nano-medicines. The above application is the application in the preparation of medicines for treating cancer. The sorafenib-gene co-loaded nano-medicine of the present invention can effectively increase the level of active oxygen in cancer cells, inhibit the expression of USP22 in liver cancer cells, efficiently kill liver cancer cells, prolong the blood circulation time of sorafenib, and inhibit tumor growth.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A chimeric antigen receptor immune cell and its preparation method and application
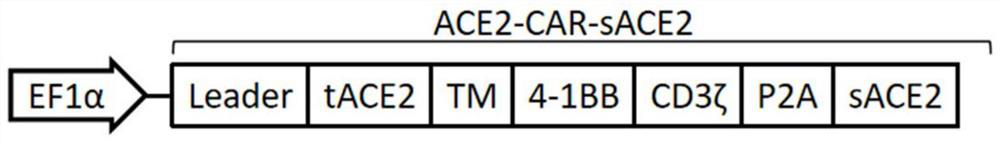
ActiveCN111560076BAvoid off-target effectsReduce riskSsRNA viruses positive-senseImmunoglobulins against virusesCritically illCompetitive binding
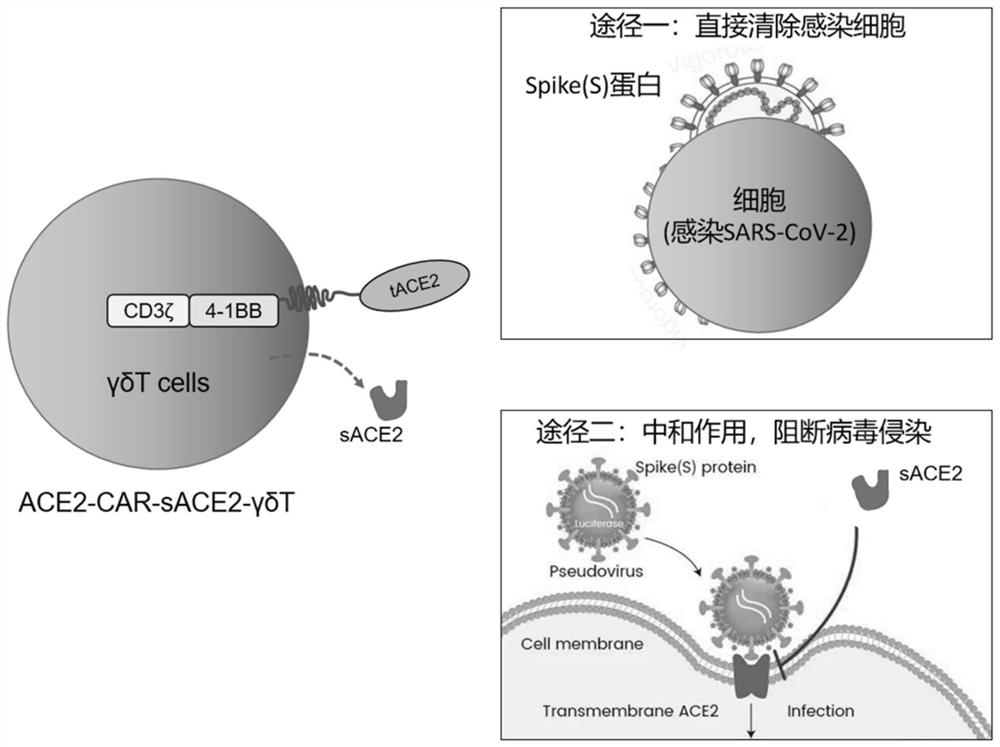
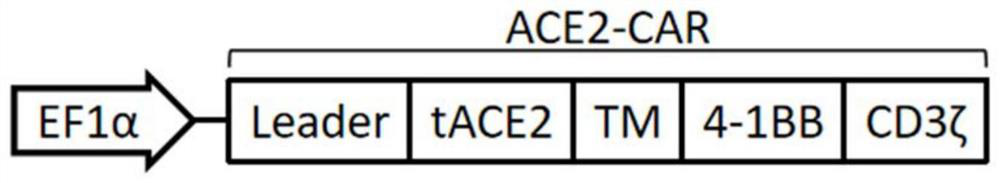
The invention provides a chimeric antigen receptor immune cell and a preparation method and application thereof. The expressed CAR molecule includes a signal peptide, a binding receptor of the coronavirus spike glycoprotein, a hinge region, a transmembrane domain, and a costimulatory structure. domain and signaling domain; the CAR molecule also includes secretory ACE2, which is connected to the carboxyl terminus of the signaling domain through a linking peptide; the immune cells expressing the CAR molecule have the ability to target and clear the cells infected by the new coronavirus, and Release secreted ACE2 molecules to competitively bind to the viral S protein to achieve allogeneic reinfusion to treat people infected with COVID-19 and prevent the transformation from mild to critically ill. It also has universal curative effect on other viruses bound by ACE2 receptors, and has strategic reserve value It provides new methods and ideas for the treatment of many major human diseases such as tumors and immune diseases.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BIO GENE TECH CO LTD
flt3 chimeric antigen receptor and its application
ActiveCN108251442BGood killing effectAvoid off-target effectsPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigen receptorsFlt3 mutation
The invention discloses a nucleic acid molecule encoding a chimeric antigen receptor, the chimeric antigen receptor comprises an extracellular region, a transmembrane region and an intracellular signal transduction region, and the encoded extracellular region comprises a FLT3 binding A structural domain, the FLT3 binding domain is a FLT3 ligand or an amino acid sequence having 90-99% identity with the FLT3 ligand. Through flow cytometry, degranulation analysis experiments, and ELISA detection of cytokines secreted by T cells, it was proved that the T cells modified by the chimeric antigen receptor had a strong killing effect on leukemia cells expressing FLT3, especially for those carrying FLT3 mutant AML cells have a specific killing effect, effectively preventing off-target effects. The chimeric antigen receptor FLT3L-CD8α-4-1BB-CD3ζ of the present invention can be used for FLT3 + Treatment of leukemia, especially leukemia with FLT3 mutation.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD DISEASES HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
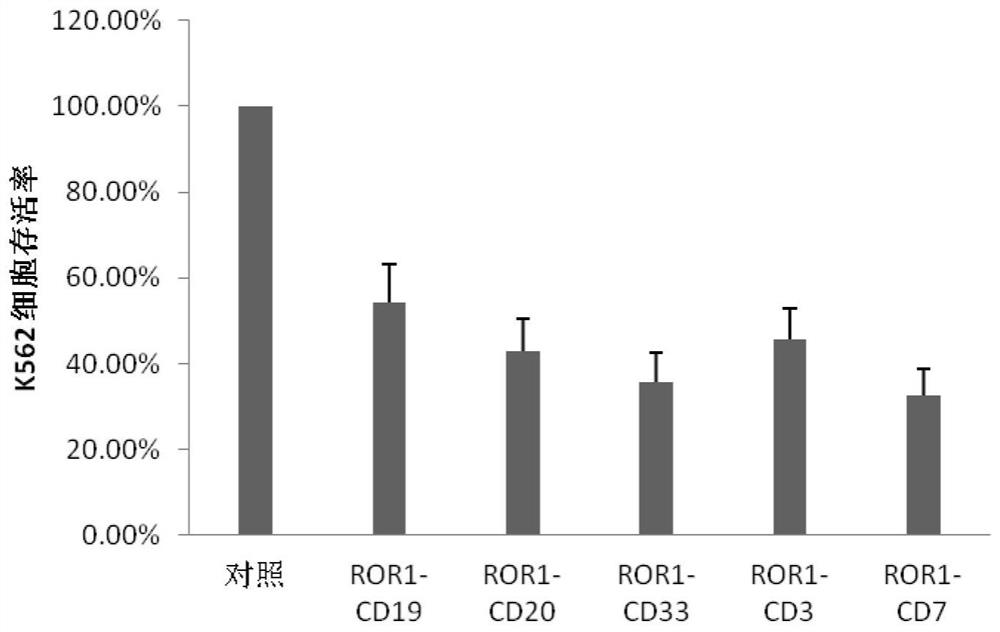
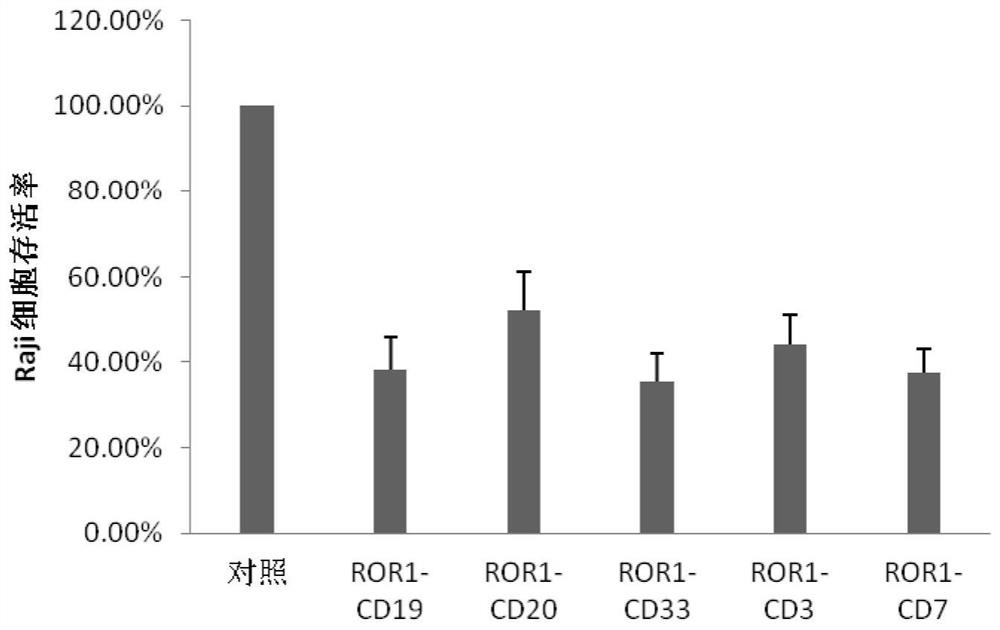
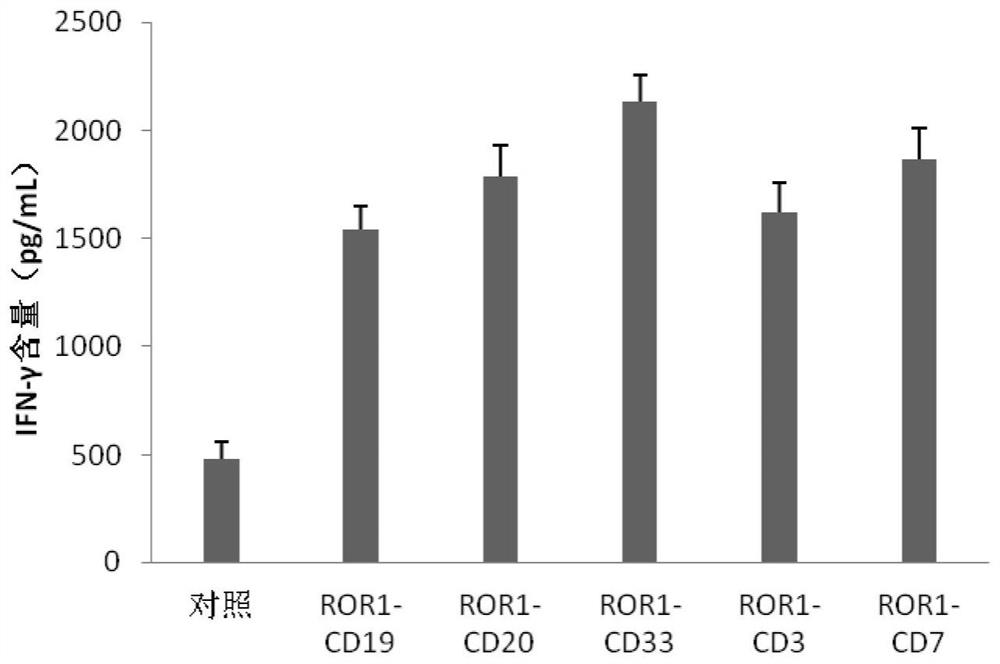
Bispecific chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) targeting ROR1 and CD7 and application thereof
ActiveCN114057896AImprove expression levelExtend the life cyclePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilySignalling moleculesOncology
The invention provides a bispecific chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) targeting ROR1 and CD7 and application thereof, the bispecific chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) has the following structure: ROR1 scFv-CD7 scFv-H-TM-C-CD3 zeta, in which "-" is a connecting peptide or a peptide bond; H is a hinge area; TM is a transmembrane domain; C is a costimulatory signal molecule; and CD3zeta is an intracellular signal transduction sequence. The chimeric antigen receptor can inhibit tumor growth in vivo and in vitro, prolong the life cycle, promote cytokine secretion and play a synergistic anti-tumor role.
Owner:冬青(天津)生物科技有限公司
Chimeric antigen receptor targeting BCMA and application thereof
PendingCN114790462AGood killing effectAvoid off-target effectsPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilySingle-Chain AntibodiesAntibody fragments
The invention discloses a nucleic acid molecule for coding a chimeric antigen receptor targeting BCMA, the chimeric antigen receptor comprises an extracellular region, a transmembrane region and an intracellular signal transduction region, the extracellular region coded by the chimeric antigen receptor comprises a BCMA binding structural domain, the BCMA binding structural domain is a single-chain antibody fragment specifically binding to BCMA, and the intracellular signal transduction region is a single-chain antibody fragment specifically binding to BCMA. The single-chain antibody fragment comprises a light chain variable region amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 1 and a heavy chain variable region amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 2. The T cell modified by the chimeric antigen receptor has a very strong killing effect on multiple myeloma cells expressing BCMA, almost has no killing effect on cells not expressing BCMA, and effectively prevents an off-target effect. The chimeric antigen receptor disclosed by the invention can be used for treatment of BCMA + multiple myeloma cell hematologic tumors and combined treatment of CAR-T cells such as CD38, CD138 and CD19.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD DISEASES HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
A primer-probe composition, a kit comprising the same, and a detection method thereof
ActiveCN114058742BStrong specificityAvoid off-target effectsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCytotoxicityRespiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
The invention discloses a primer probe composition, a kit containing the same and a detection method thereof, belonging to the technical field of virus detection. The specific primers and probes of cellular virus, the specific primers and probes have good specificity, adopt the test kit of the present invention, the Q-PCR method can realize the synthesis of influenza A virus, influenza B virus and respiratory tract High specificity, high sensitivity and high efficiency detection of cytomegalovirus.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KEFEN BIOTECH CO LTD
CD123-targeted chimeric antigen receptors and dual-target chimeric antigen receptors containing CD123-targeted chimeric antigen receptors
ActiveCN112979820BStrong in vitro killing effectAvoid off-target effectsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleic acid vectorSingle-Chain AntibodiesCD33
The invention discloses a nucleic acid molecule encoding a chimeric antigen receptor targeting CD123, the chimeric antigen receptor comprises an extracellular region, a transmembrane region and an intracellular signal transduction region, and the encoded extracellular region comprises CD123 binding domain, the CD123 binding domain is an anti-CD123 single-chain antibody variable region fragment; the anti-CD123 single-chain antibody variable region fragment is the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.13 or has 90 A sequence with %-99% identity, the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.14 or a sequence with 90%-99% identity therewith, or the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. % identity sequence. The chimeric antigen receptor of the present invention can be used for CD123 + and / or CD33 + The treatment of hematological tumors can effectively prevent off-target effects, make the treatment effect better, and avoid escape.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD DISEASES HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
Chimeric antigen receptor capable of simultaneously targeting CD19 and CD20 and application of chimeric antigen receptor
ActiveCN113549155AGood killing effectAvoid off-target effectsPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyCD20Antigen receptors
The invention discloses a nucleic acid molecule for coding a chimeric antigen receptor capable of simultaneously targeting CD19 and CD20. The chimeric antigen receptor comprises an extracellular region, a transmembrane region and an intracellular signal transduction region, wherein the extracellular region coded by the chimeric antigen receptor comprises CD19 and CD20 binding structural domains, and the CD20 binding structural domain in the CD19 and CD20 binding structural domains is an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. Experiments prove that the T cell modified by the chimeric antigen receptor has a strong killing effect on CD19 <+>, CD20 <+> and CD19 <+> / CD20 <+> B cell lymphoma cells and B cell lymphoma leukemia cells, almost has no killing effect on cells which do not express CD19 and CD20, and effectively prevents an off-target effect. The chimeric antigen receptor disclosed by the invention can be used for treatment of CD19 + B cell and CD20 + B cell hematologic tumors and combined treatment with CD19 CAR-T cells or CD20 CAR-T cells.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD DISEASES HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
Albumin production and cell proliferation
ActiveUS20160145618A1ModulationReduce Polycomb-levelsOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemDiseaseHypoproteinemia
The present invention provides short activating RNA molecules which up-regulate albumin production. The present invention also provides methods of up-regulating albumin production, such methods involving the use of short activating RNA molecules capable of increasing the expression of albumin. The present invention also provides the use of the short activating RNA molecules in therapy, such as treating or preventing a hyperproliferative disorder and / or a disorder characterised by hypoalbuminemia.
Owner:MINA THERAPEUTICS
HLA-G specific chimeric antigen receptor, nucleic acid encoding HLA-G specific chimeric antigen receptor, expression plastid of HLA-G specific chimeric antigen receptor, cell expressing HLA-G specific chimeric antigen receptor, application of cell and composition
PendingCN112707967AExcellent ability to specifically bind tumor cellsEffective treatmentNucleic acid vectorImmunoglobulinsAntigenWhite blood cell
The invention discloses an HLA-G specific chimeric antigen receptor, nucleic acid encoding the HLA-G specific chimeric antigen receptor, an expression plastid of the HLA-G specific chimeric antigen receptor, a cell expressing the HLA-G specific chimeric antigen receptor, an application of the cell and a composition, The present invention relates to the HLA-G specific chimeric antigen receptor, an isolated nucleic acid, the expression plastid of the HLA-G specific chimeric antigen receptor, the cell expressing the HLA-G specific chimeric antigen receptor, a pharmaceutical composition for treatment of cancer, and the application of the cell expressing the HLA-G specific chimeric antigen receptor. The HLA-G specific chimeric antigen receptor and a human leukocyte antigen G are specifically bound. The cell expressing the HLA-G specific chimeric antigen receptor is obtained by transducing the HLA-G specific chimeric antigen receptor into an immune cell. The pharmaceutical composition for treatment of cancer comprises the cell expressing the HLA-G specific chimeric antigen receptor and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. Therefore, the cell expressing the HLA-G specific chimeric antigen receptor can be used for inducing tumor cell death of mammals.
Owner:CHINA MEDICAL UNIV HOSPITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com