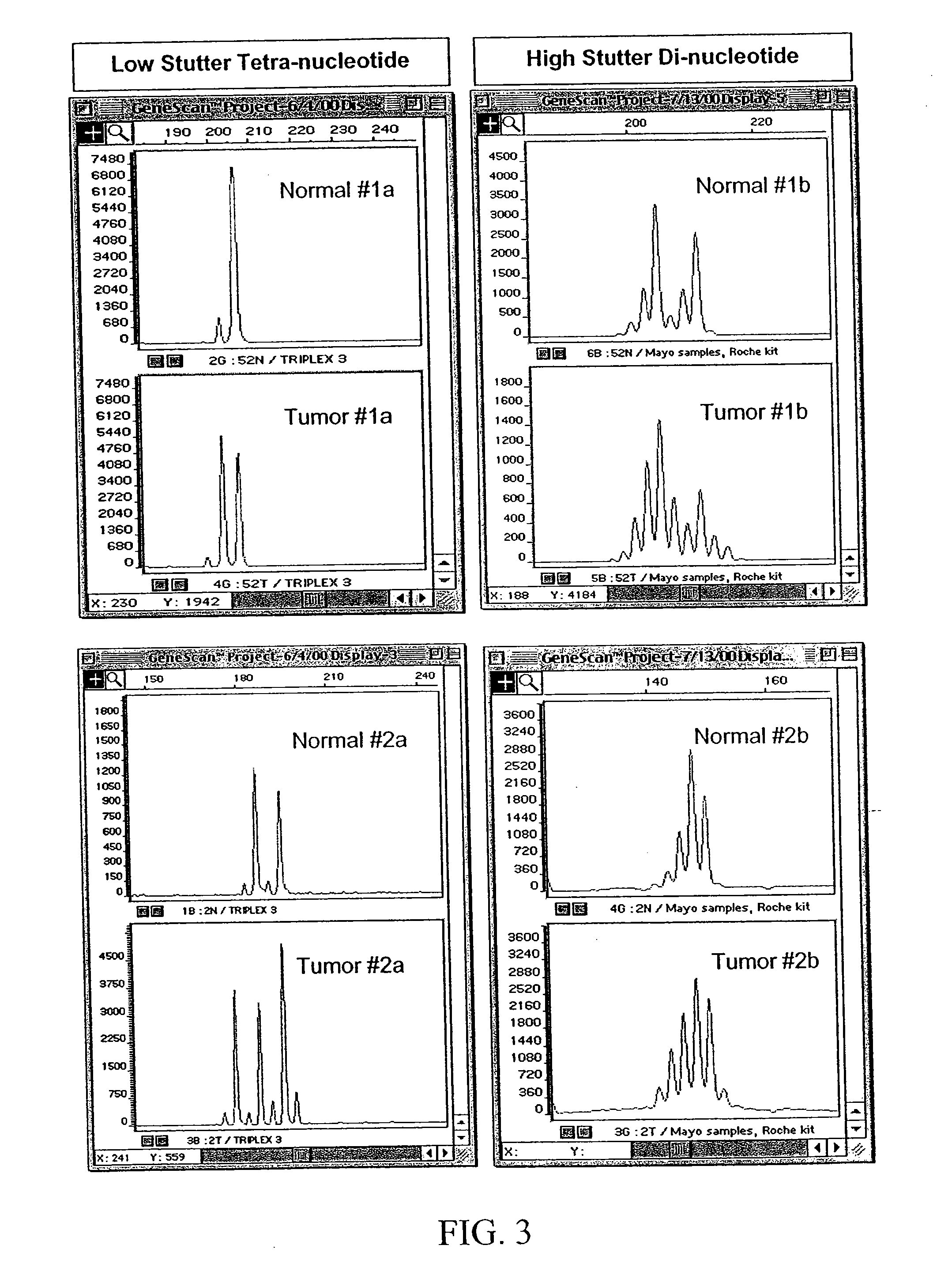
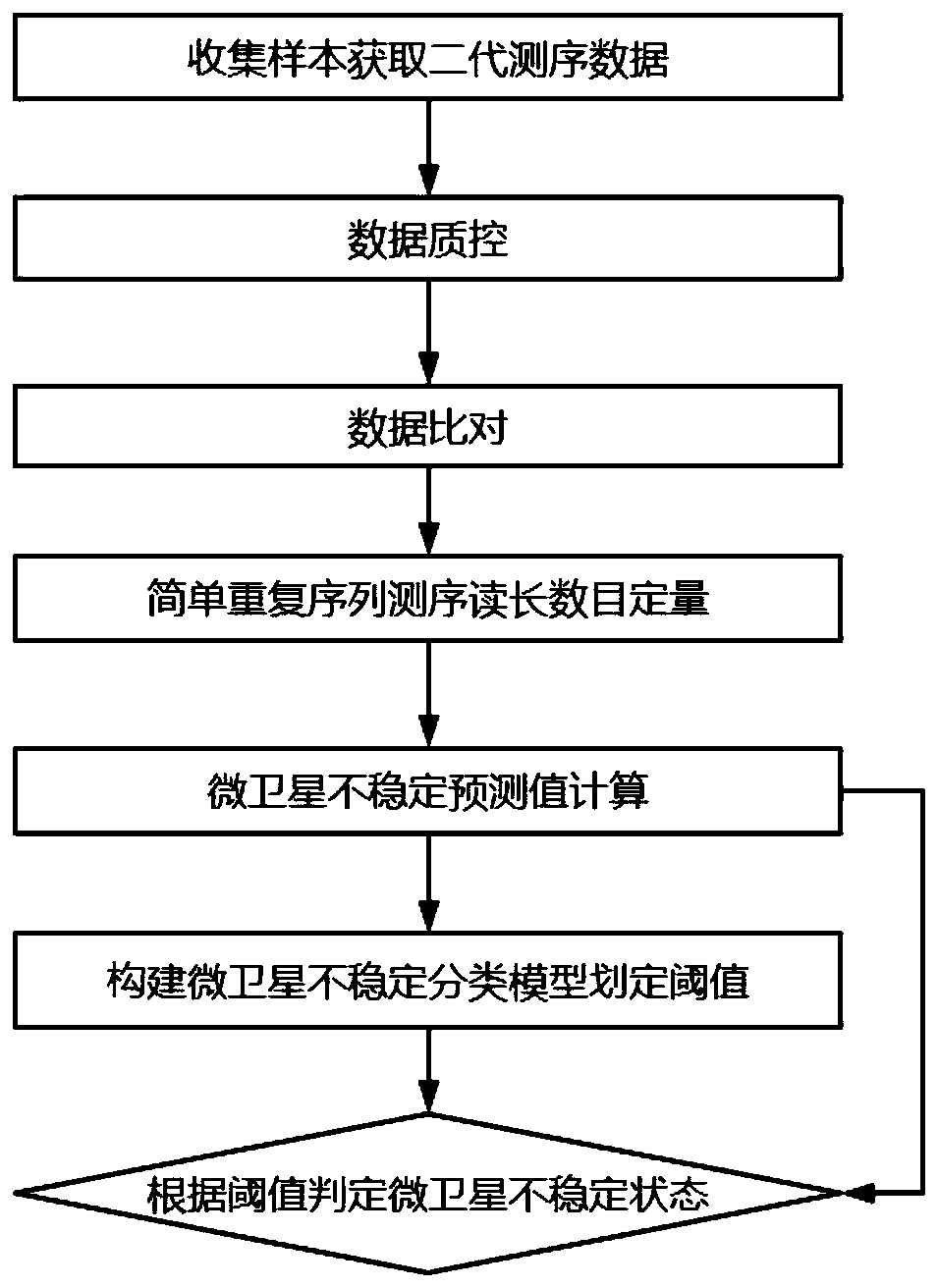
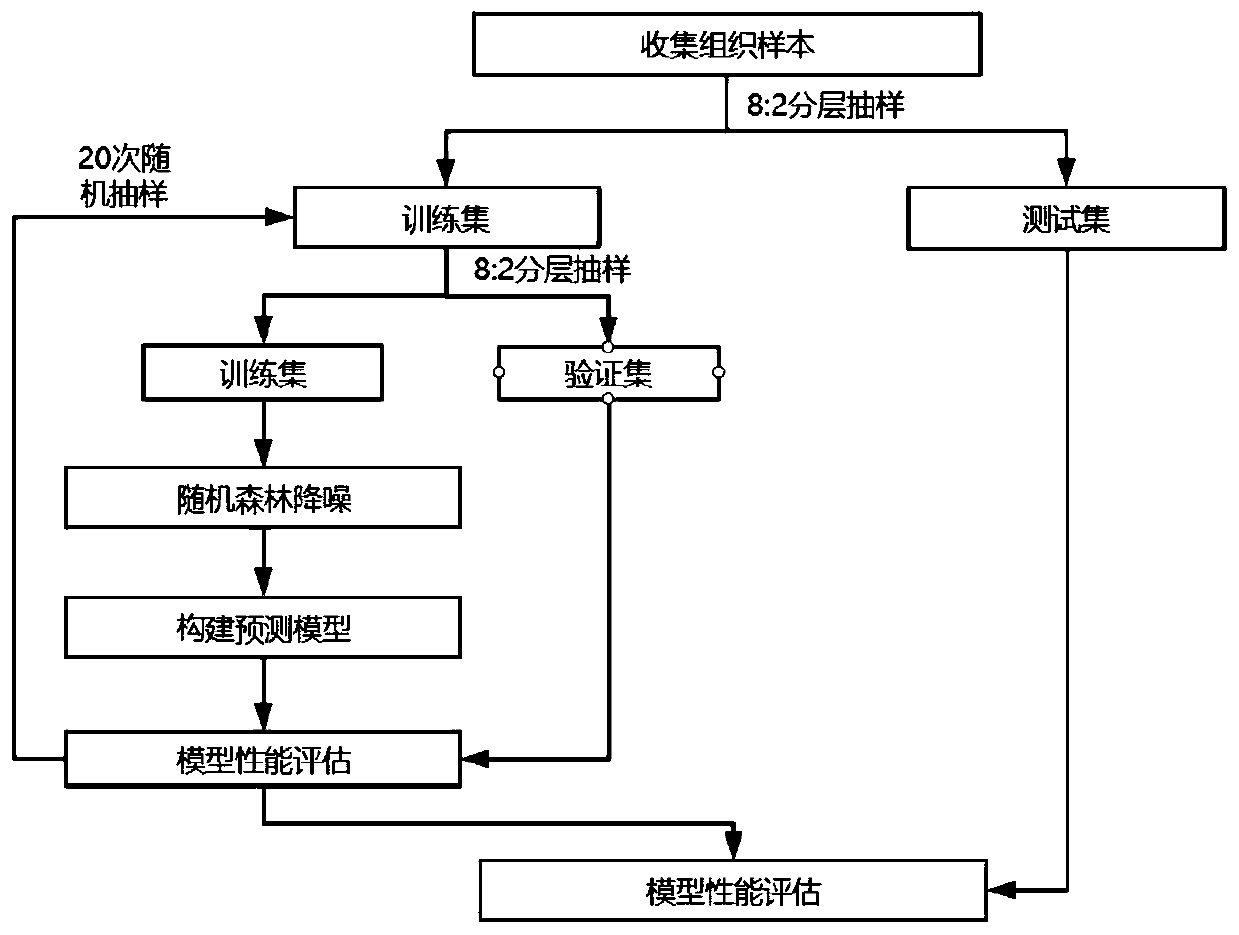
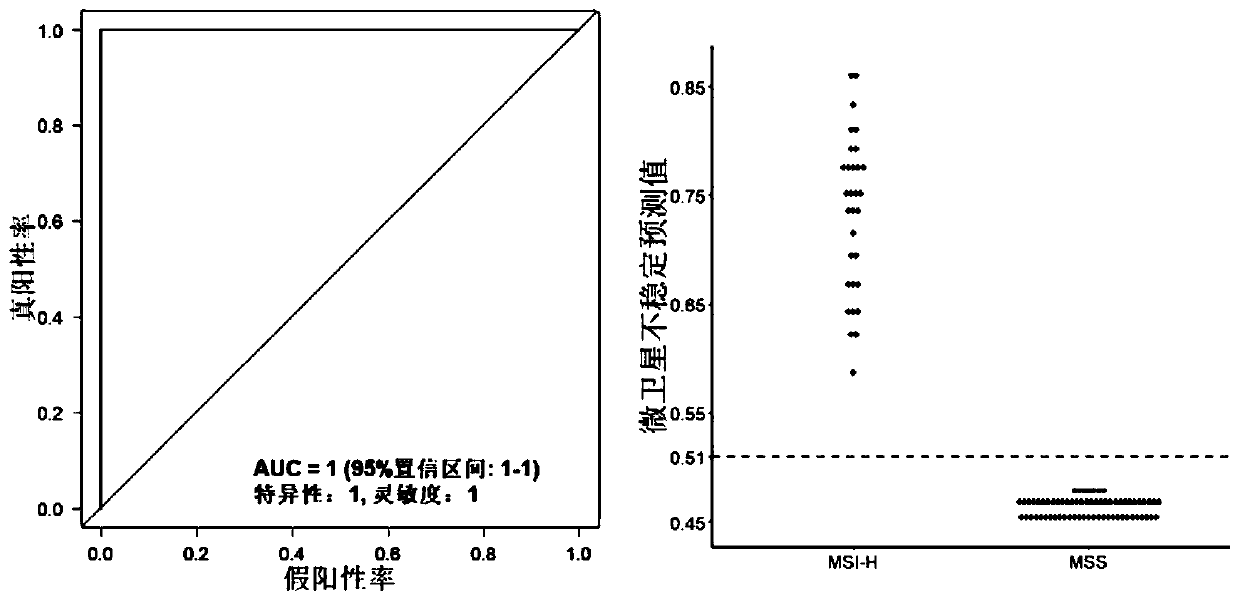
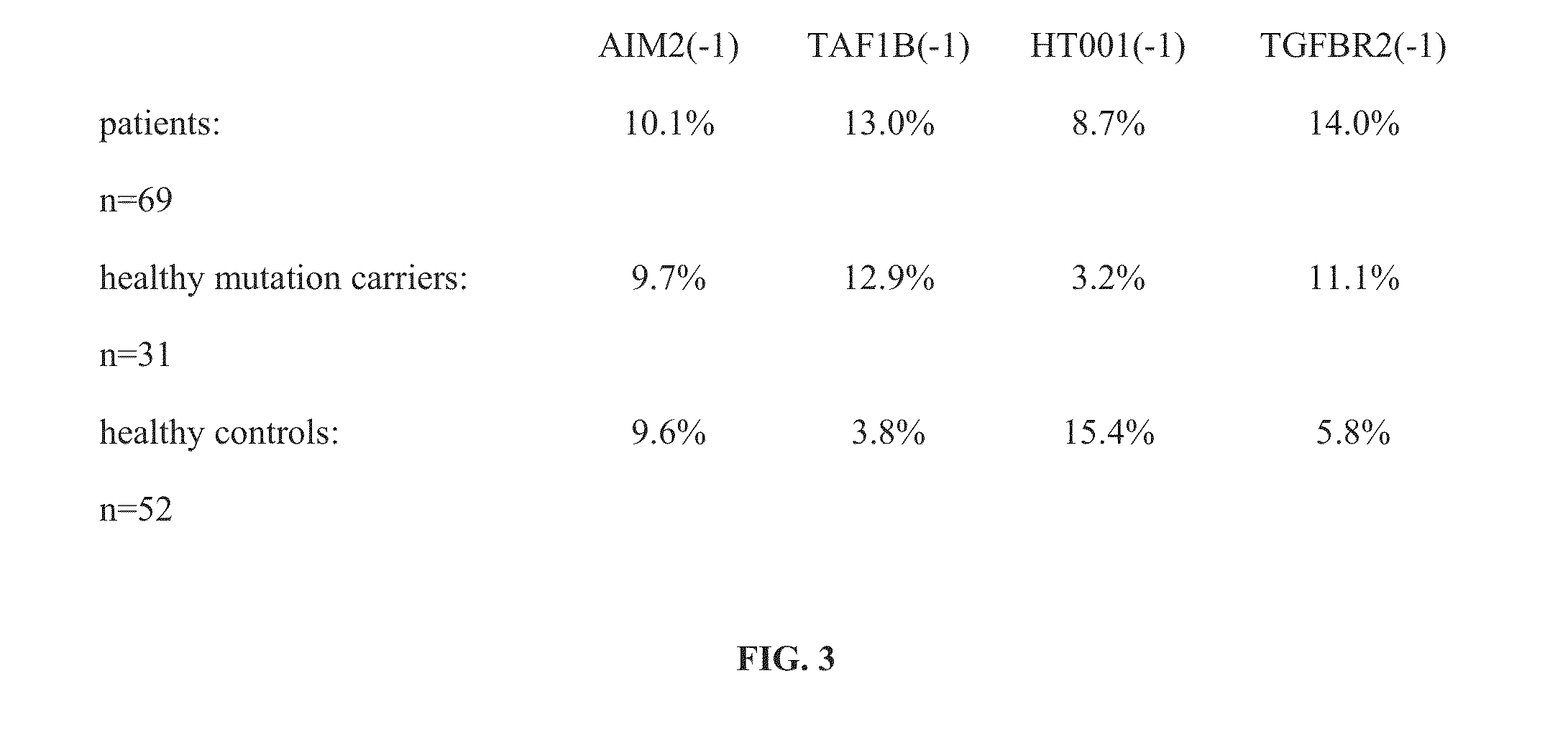
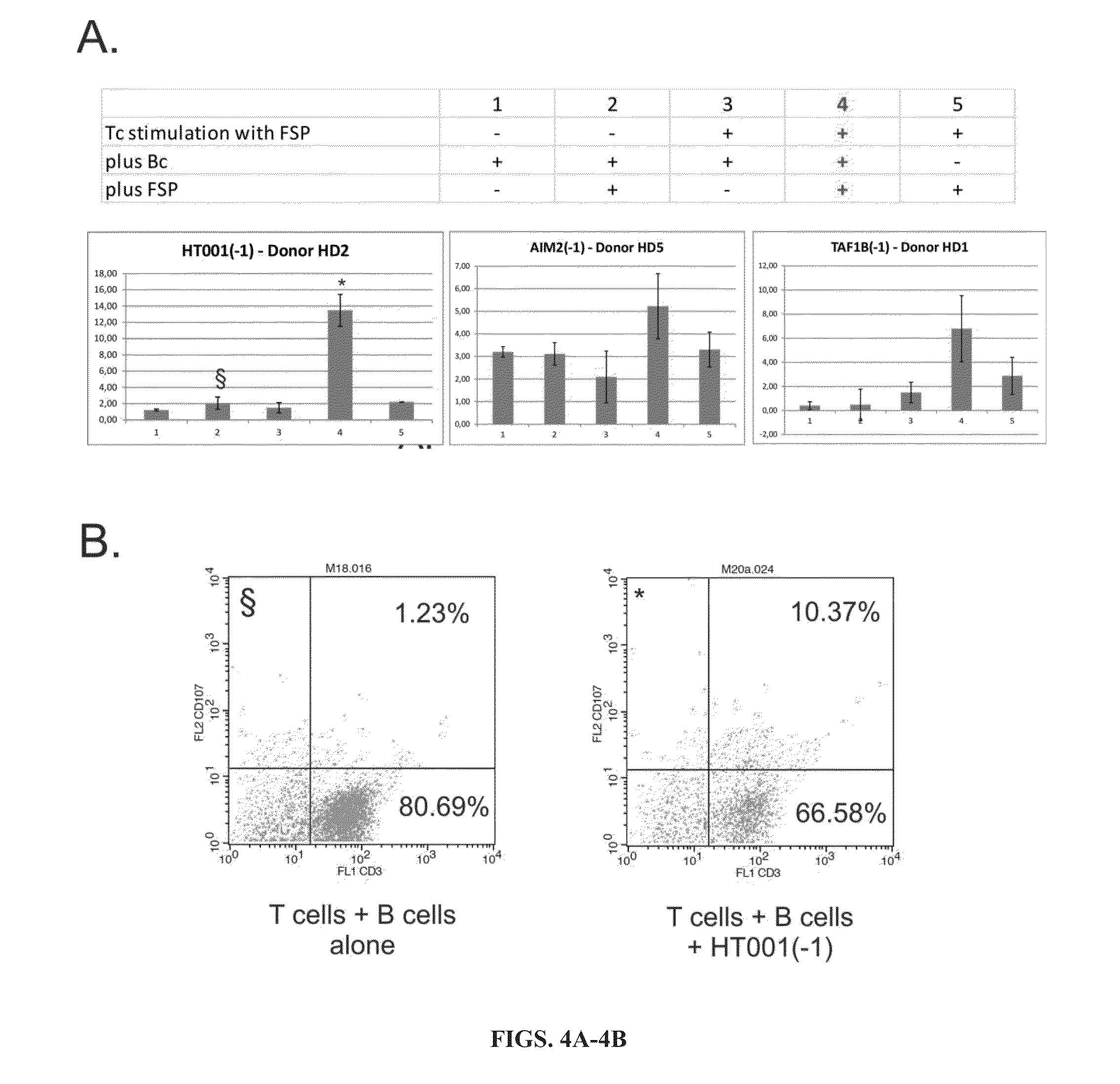
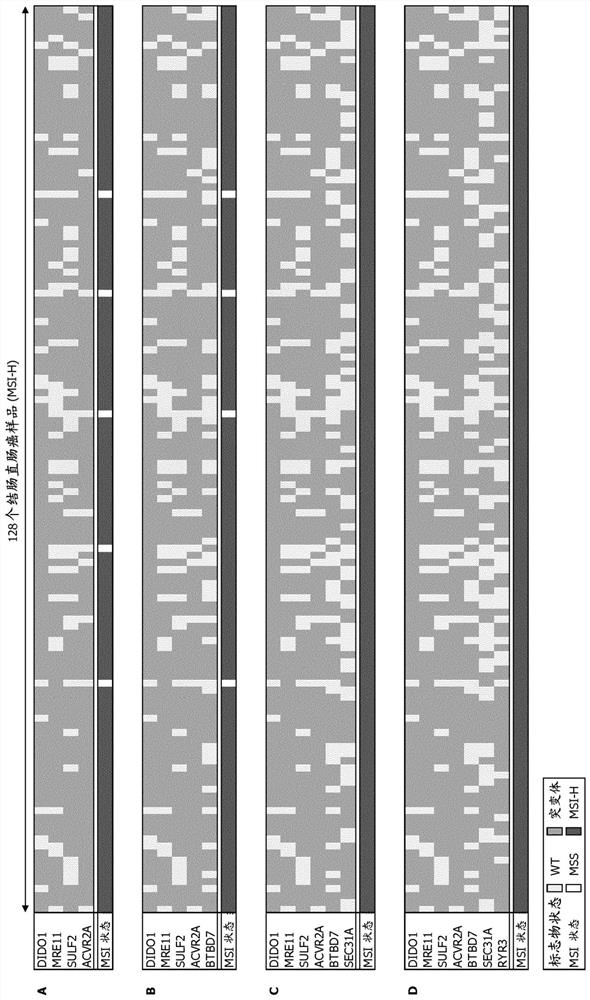
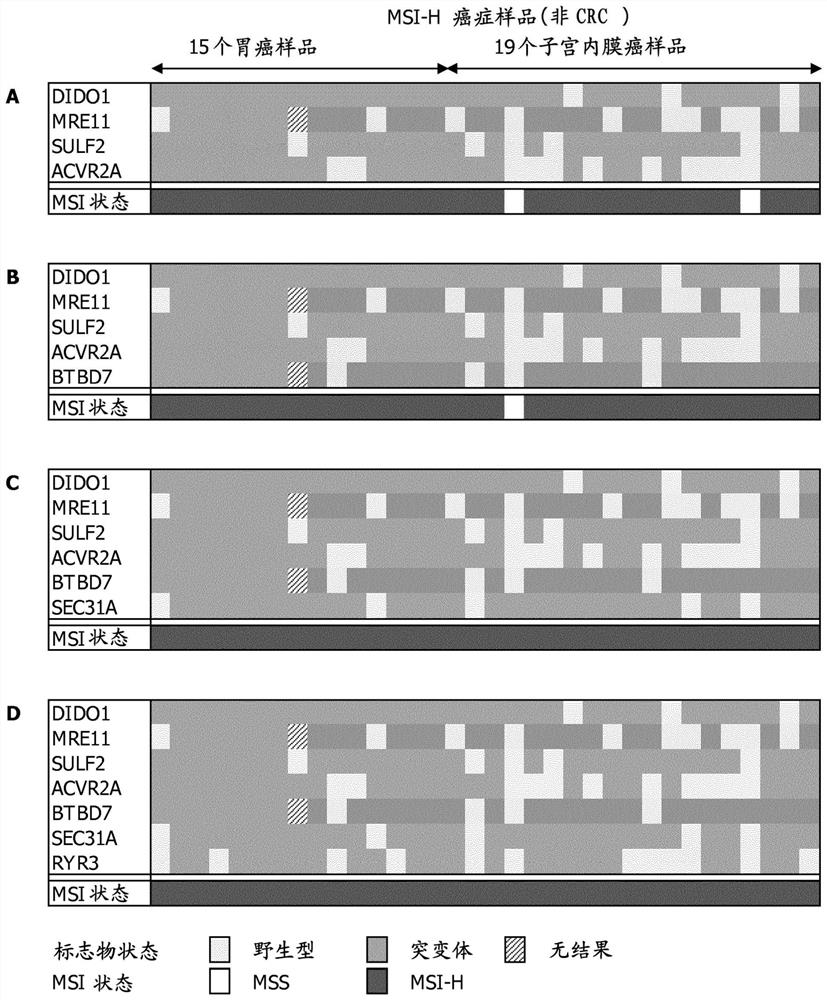
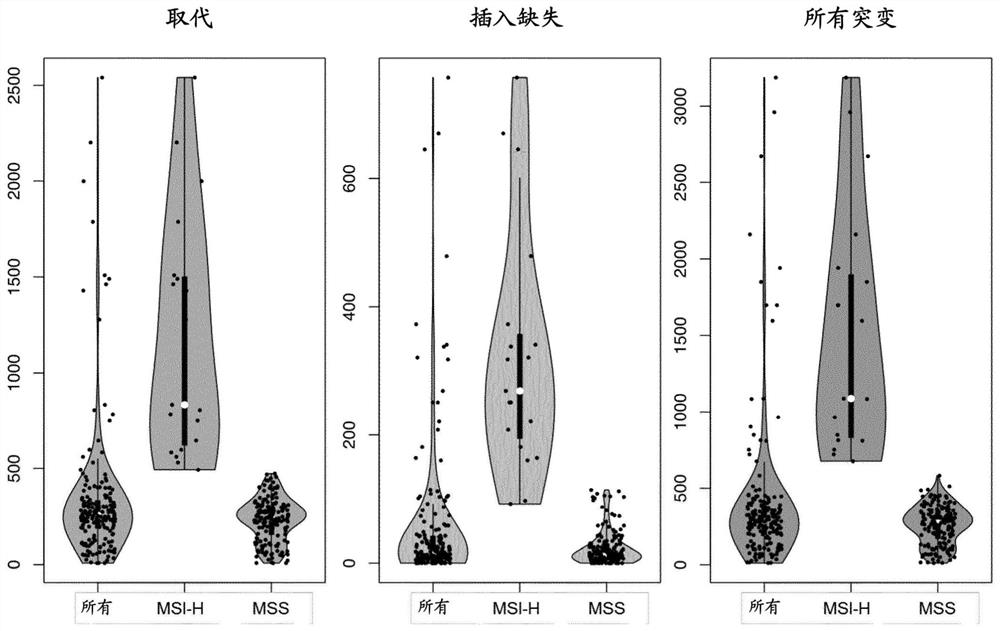
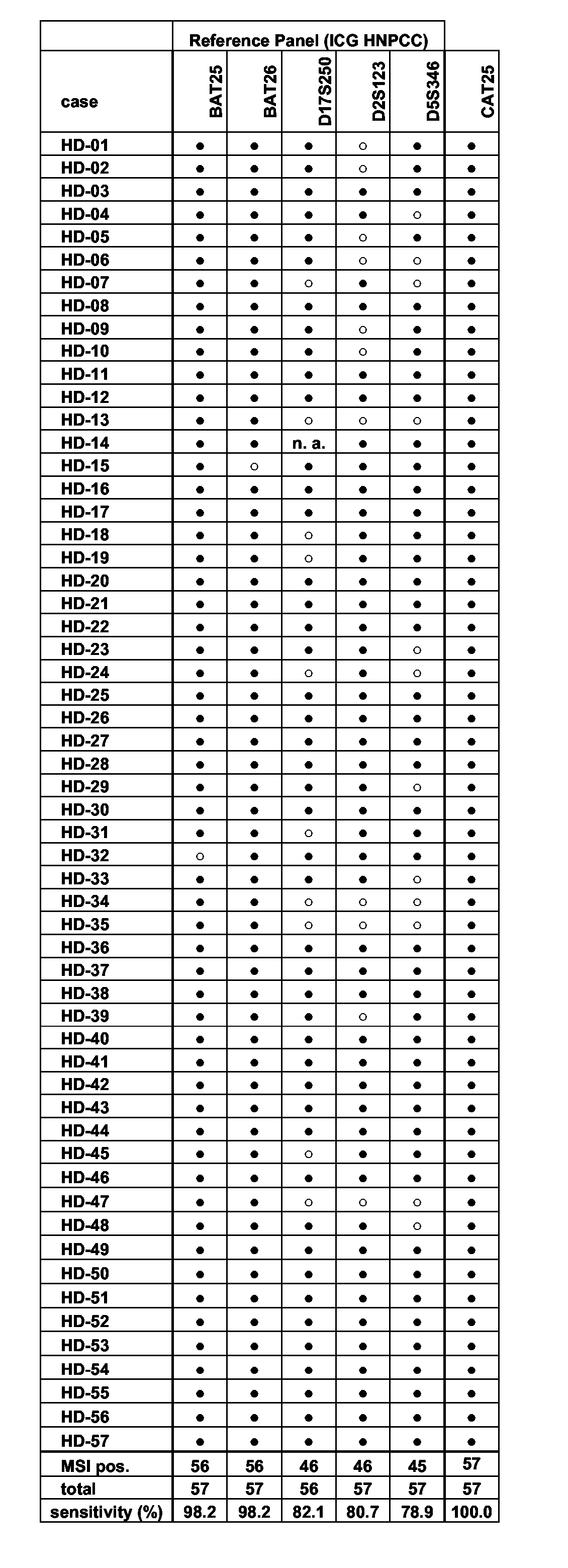
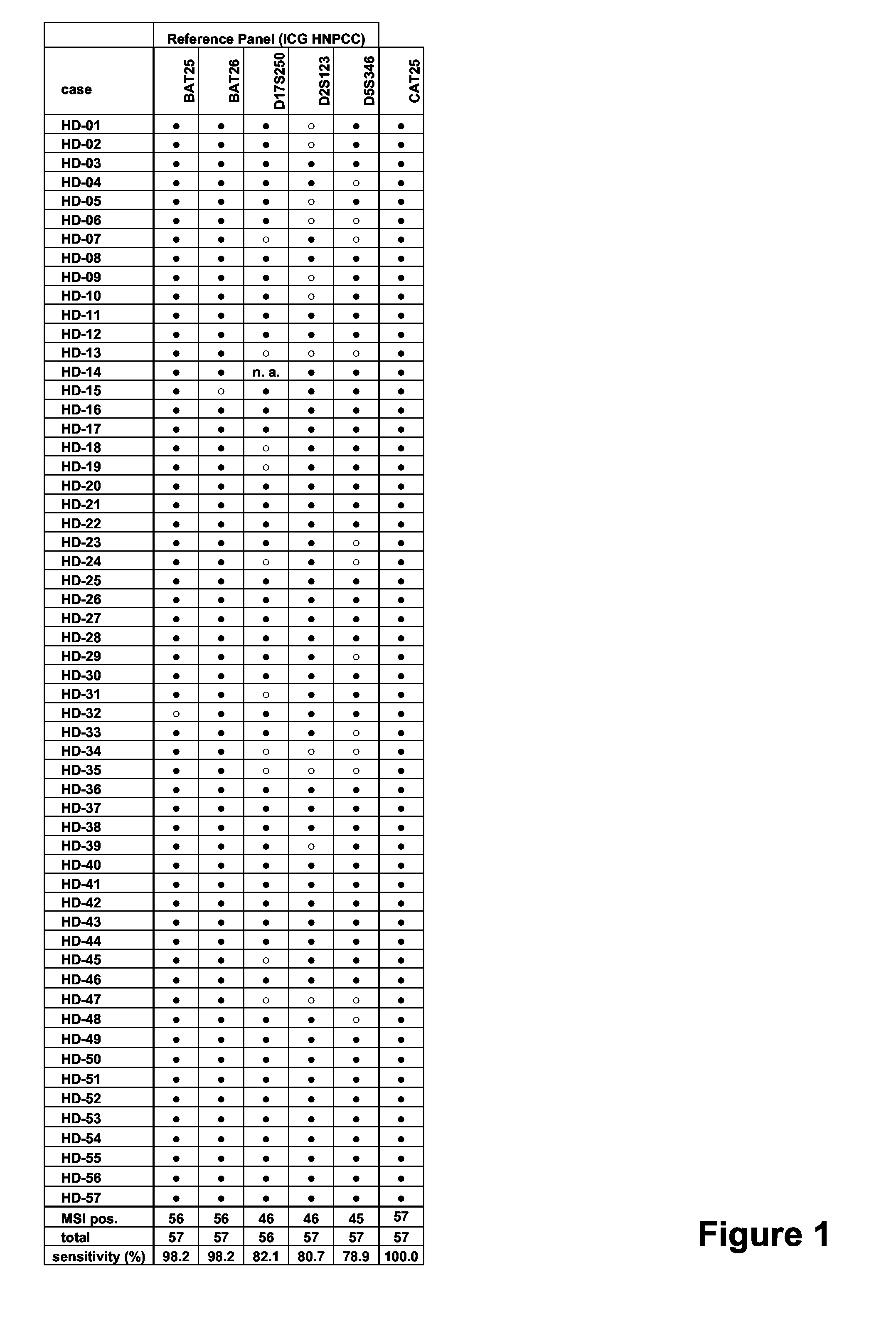
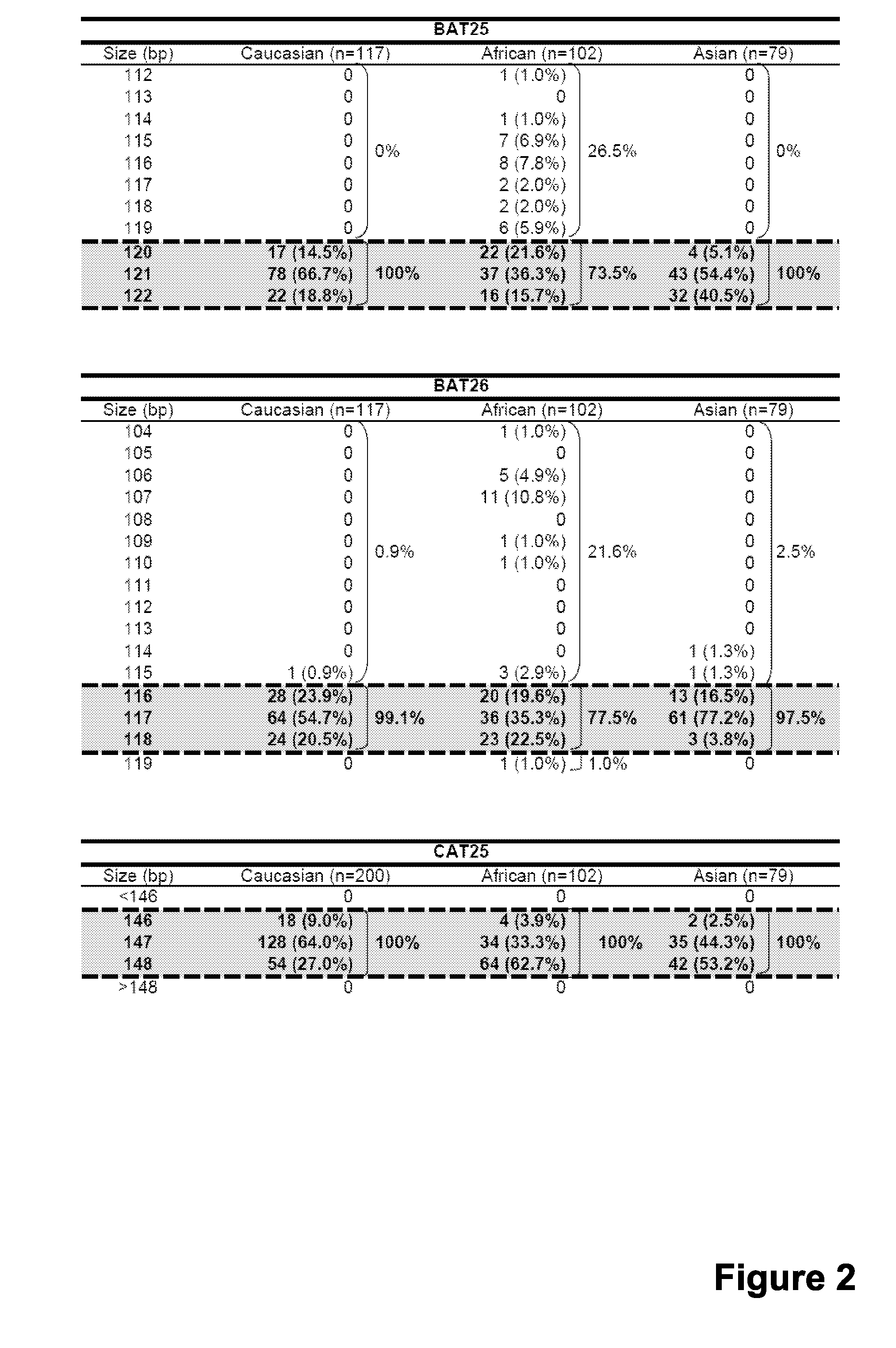
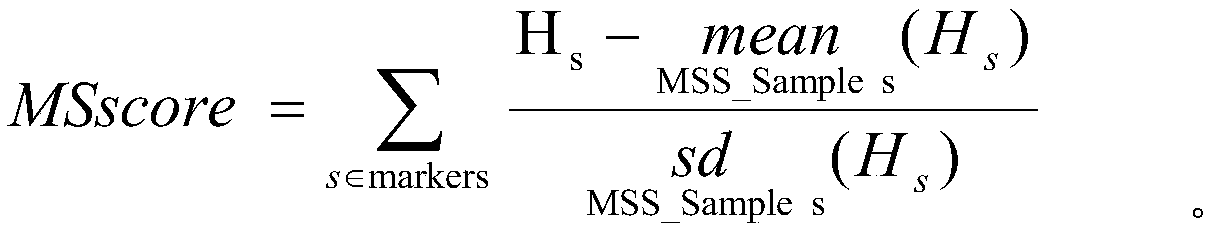Patents
Literature
153 results about "Microsatellite instability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
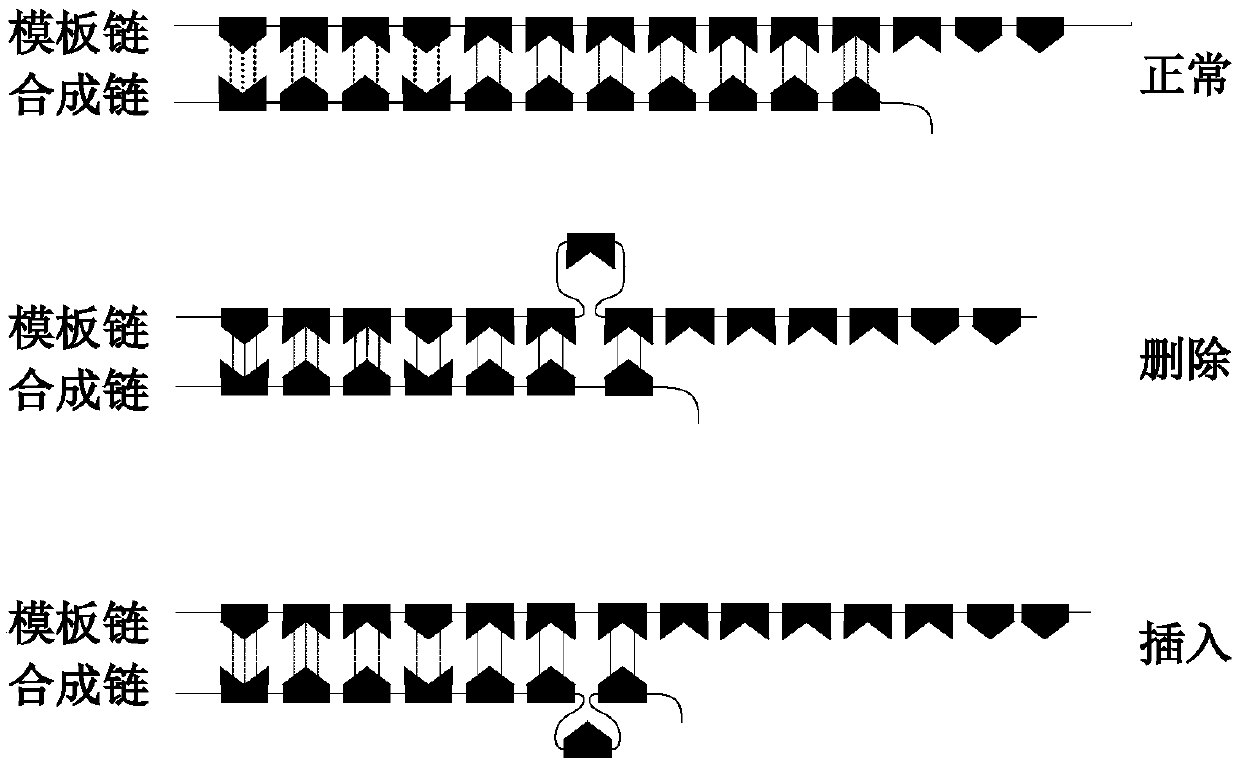
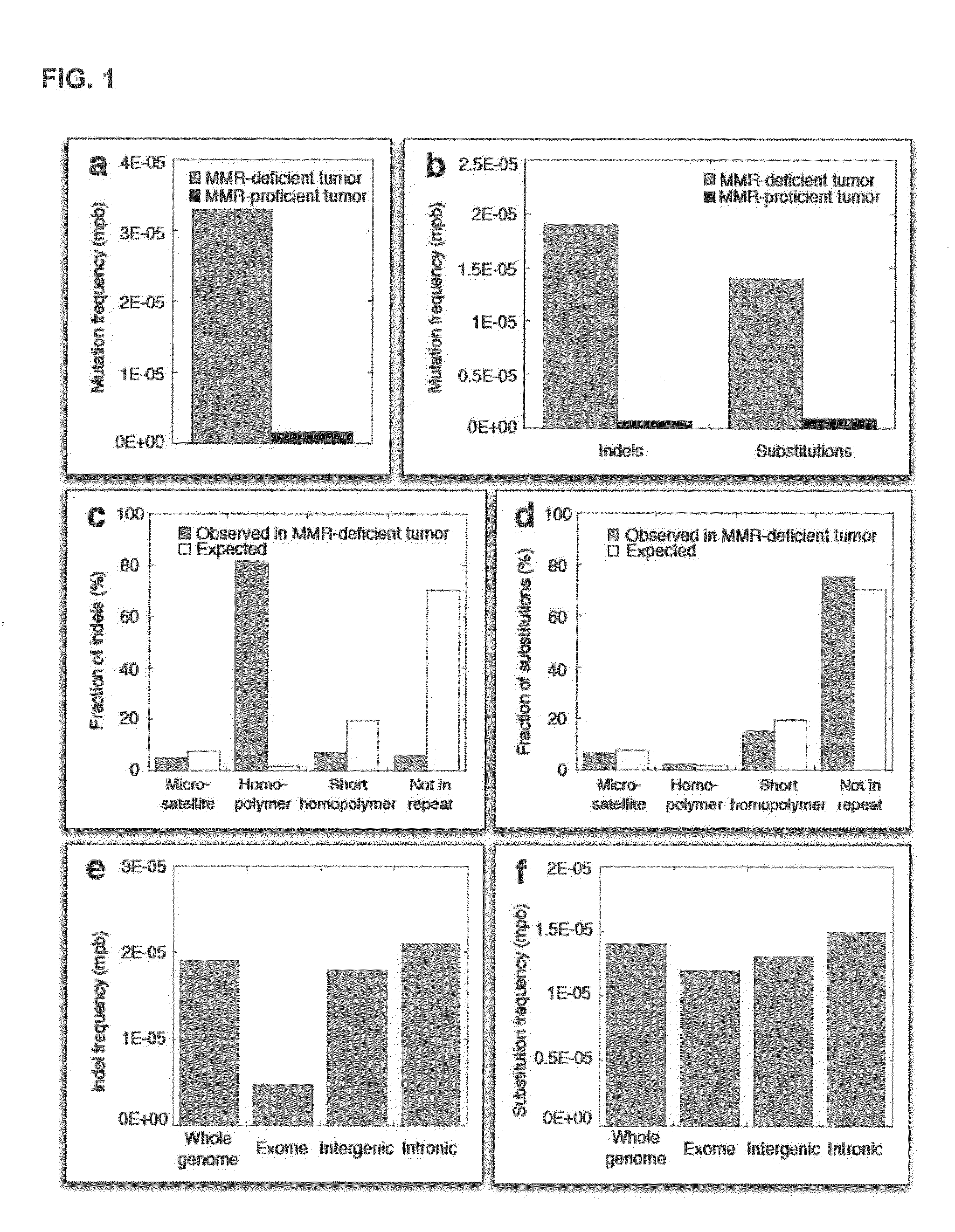
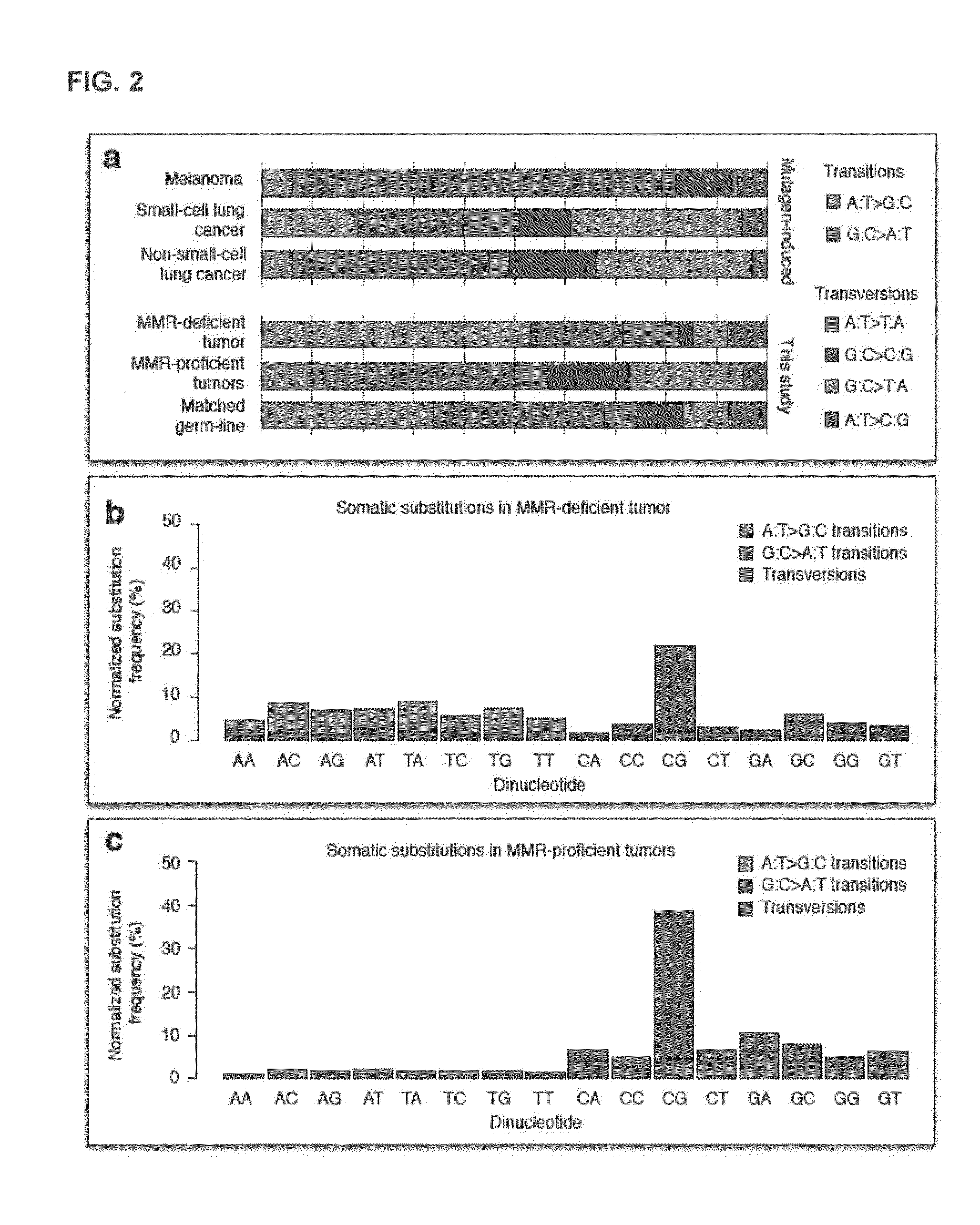
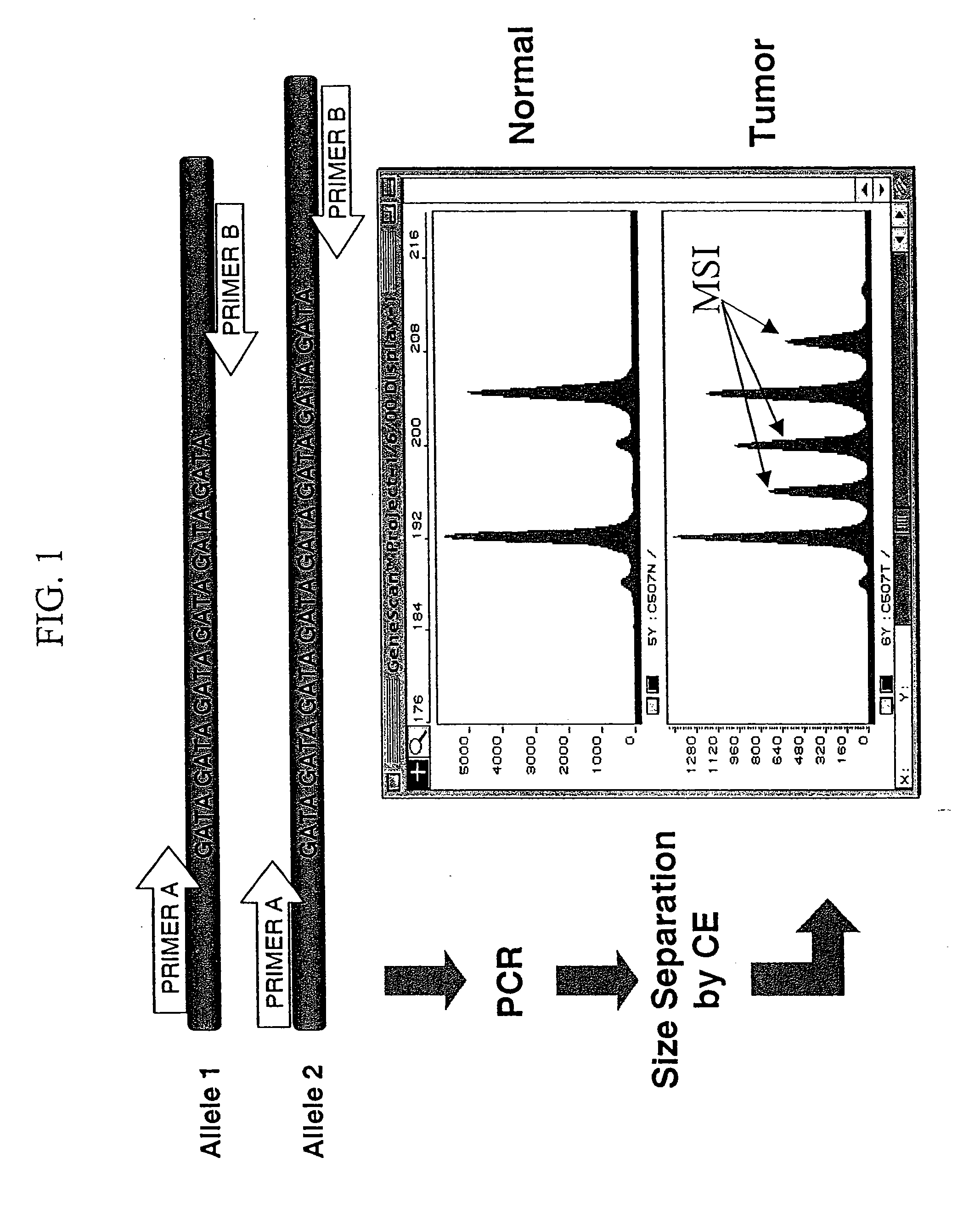
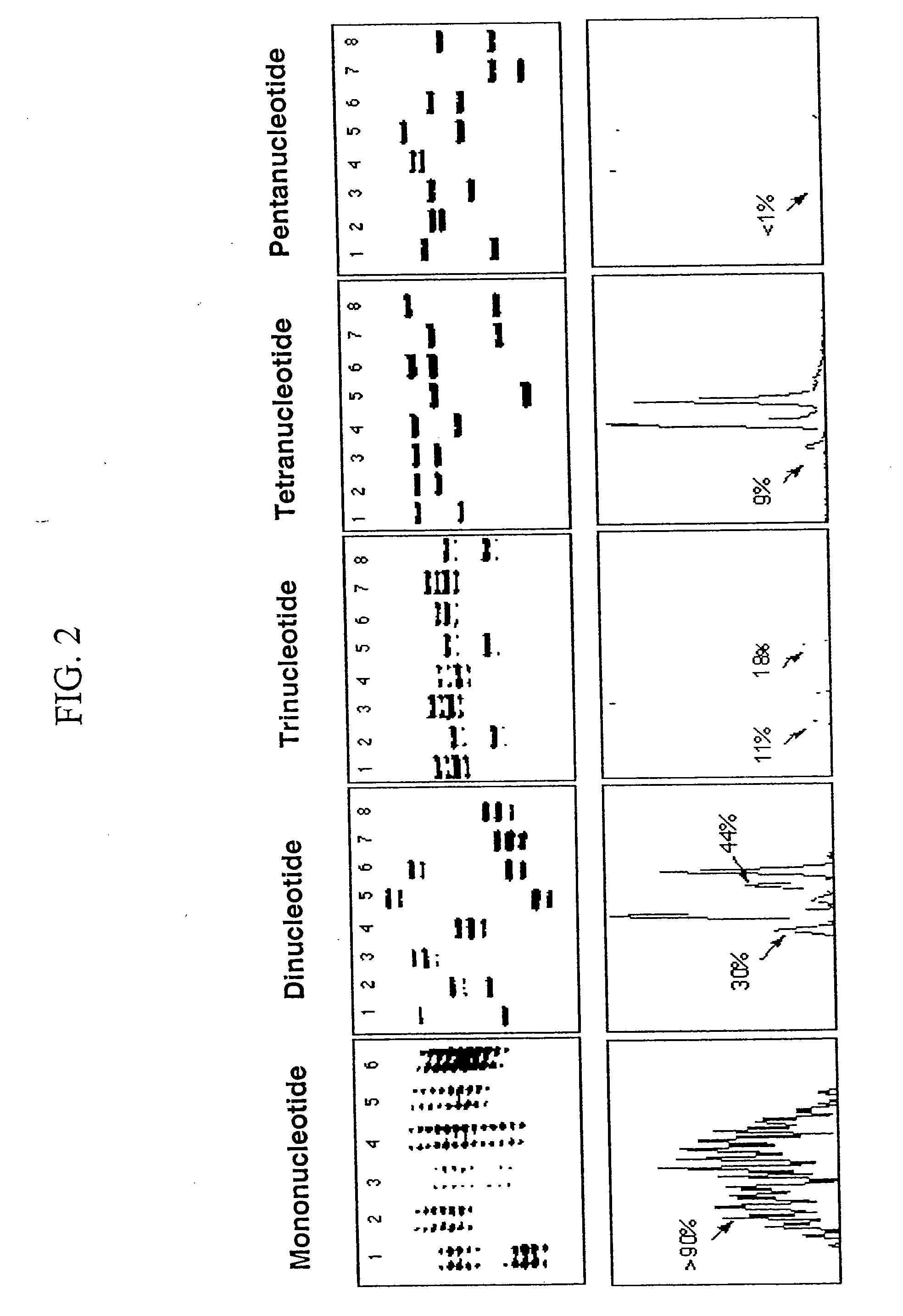
Microsatellite instability (MSI) is the condition of genetic hypermutability (predisposition to mutation) that results from impaired DNA mismatch repair (MMR). The presence of MSI represents phenotypic evidence that MMR is not functioning normally.
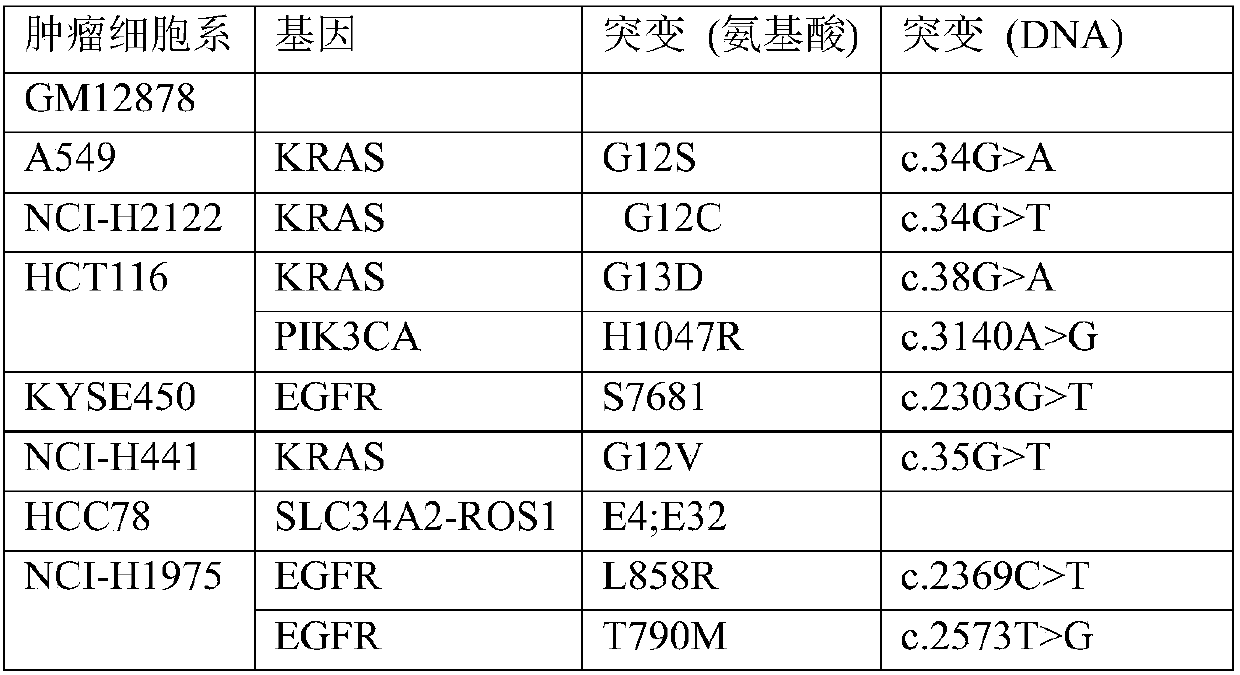
Tumor cell microsatellite instable state complex amplification system and detection kit
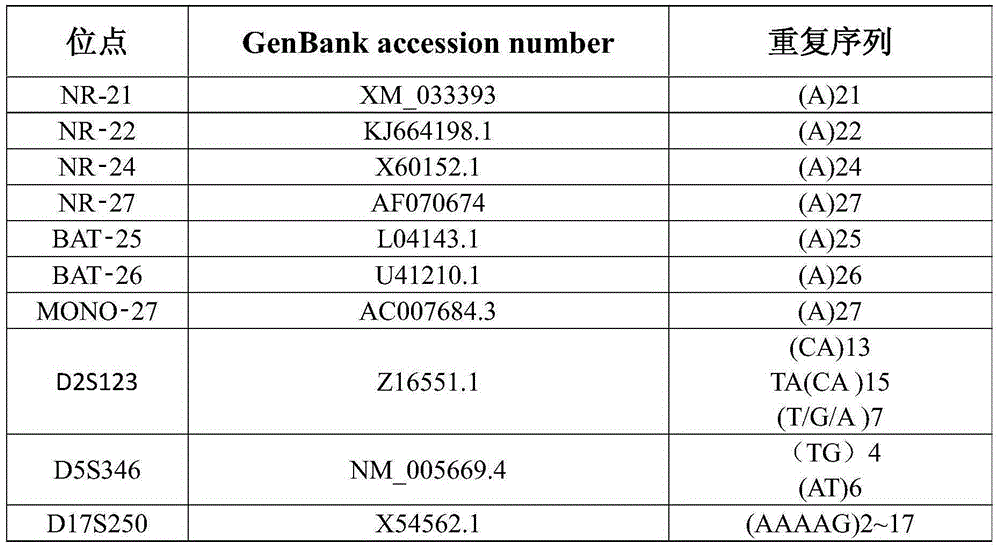
ActiveCN102230004AHigh sensitivityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementTrue positive rateWilms' tumor
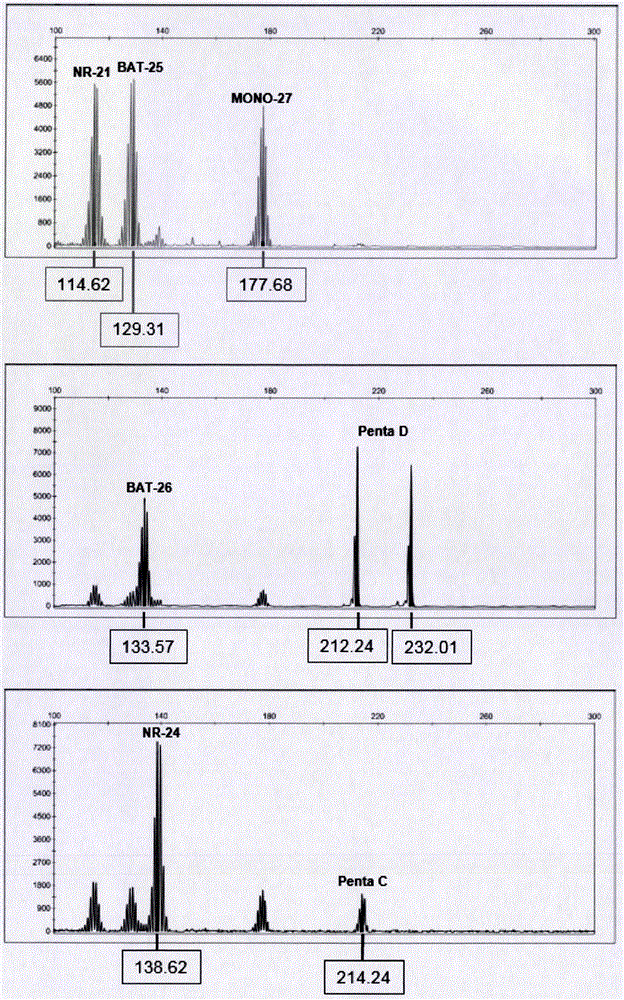
The invention relates to a tumor cell microsatellite instable state complex amplification system and a detection kit and belongs to the field of biotechnology. In the invention, 8 quasi-monomorphic nucleotide repeated loci with high sensitivity and specificity (including NR-21, NR-22, NR-24, NR-27, BAT-25, BAT-26, MONO-27 and CAT-25) are selected to detect microsatellite instability (MSI). Meanwhile, an amelo (AMEL) is added and a 9-loci multiplex amplification system is constructed, so the result is more accurate. The addition of the gender determining locus can prevent an experiment operator from mixing up samples and delivering wrong results to a certain extent. In the invention, the operation is simple, and large-scale promotion is convenient. With the success of the development of the kit, the method can be used for batch production; the use conditions of the method can be modularized; automatic equipment is applied in the whole process, so the whole process is independent of theoperational experiment of people; and the total detection time is about 6 hours.
Owner:BEIJING MICROREAD GENE TECH
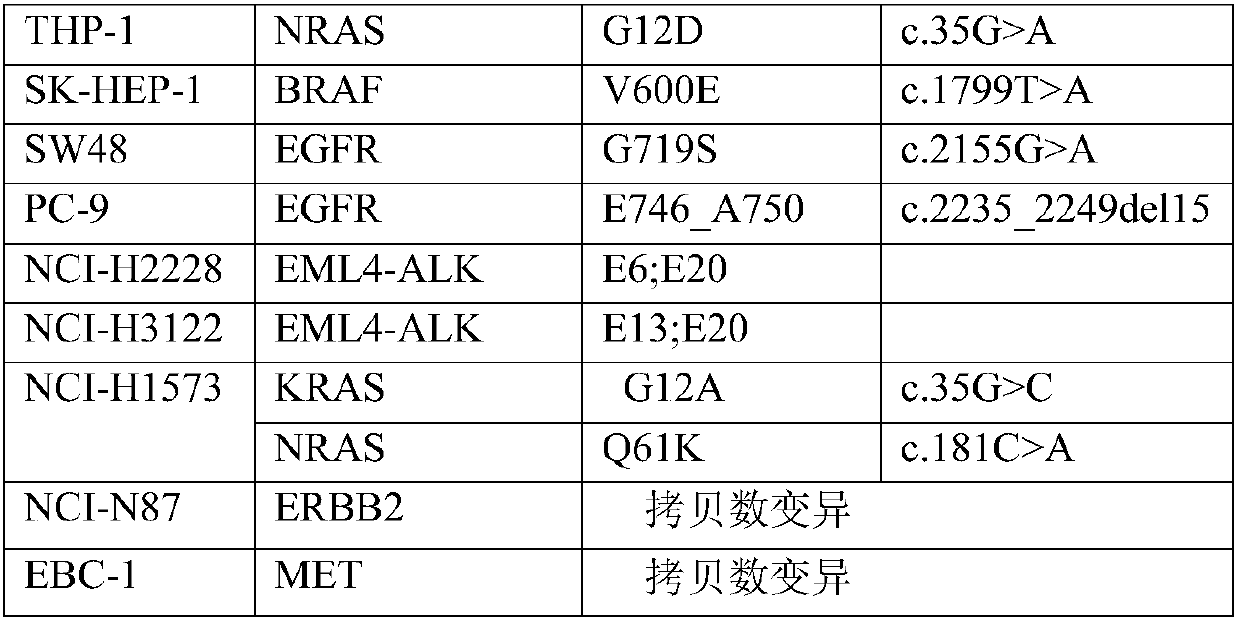
Next generation sequencing-based detection panel and detection kit for pan-cancer targeting, chemotherapy and immune drugs and application thereof
ActiveCN109609647AReduce data volumeImprove uniformityMicrobiological testing/measurementGenes mutationCancer targeting
The invention discloses a next generation sequencing-based detection panel and detection kit for pan-cancer targeting, chemotherapy and immune drugs and application thereof. The detection panel includes gene mutations related to pan-cancer type, treatment and prognosis, tumor mutation load calculation related exon regions and microsatellite instability sites. According the technical solution of the present invention, the detection panel includes the gene mutations related to pan-cancer type, treatment and prognosis, the tumor mutation load calculation related exon regions and the microsatellite instability sites, and the gene information included is comprehensive; a variety of tumor mutations can be jointly detected; and the detection panel and detection kit can be used for the concomitantdiagnosis of targeted drugs, chemotherapeutics or immune drugs to obtain accurate results.
Owner:ZHENYUE BIOTECHNOLOGY JIANGSU CO LTD
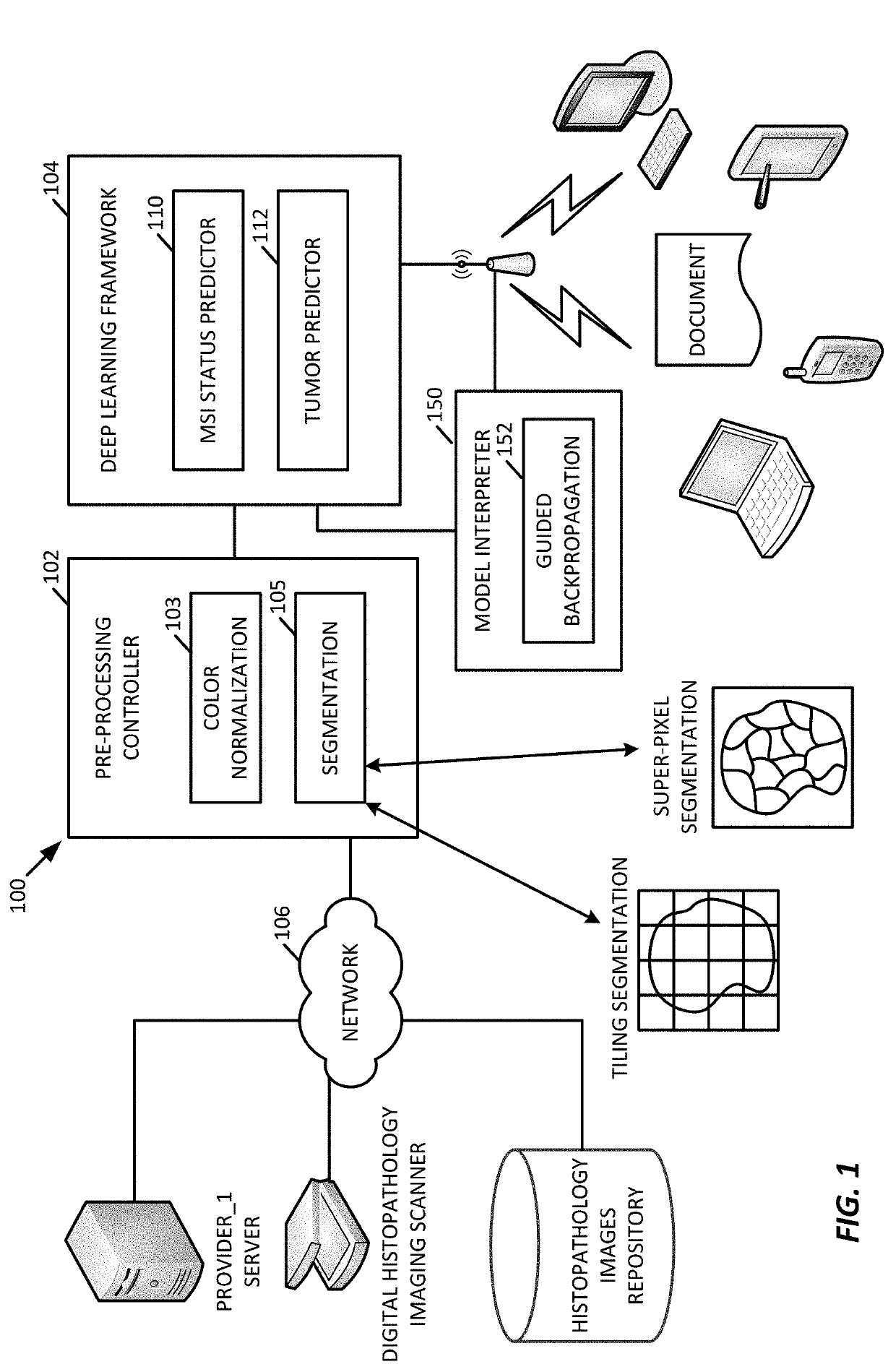
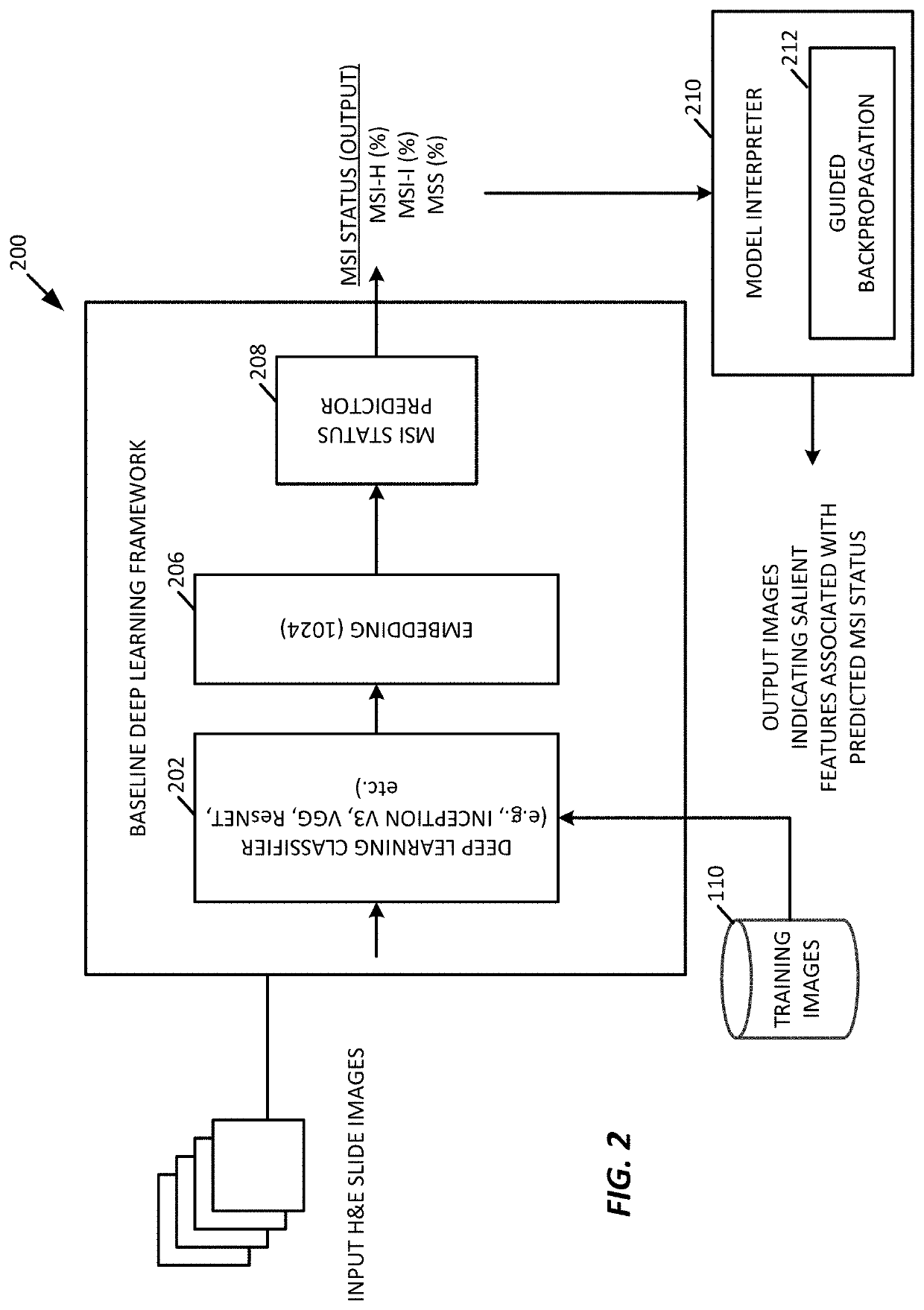
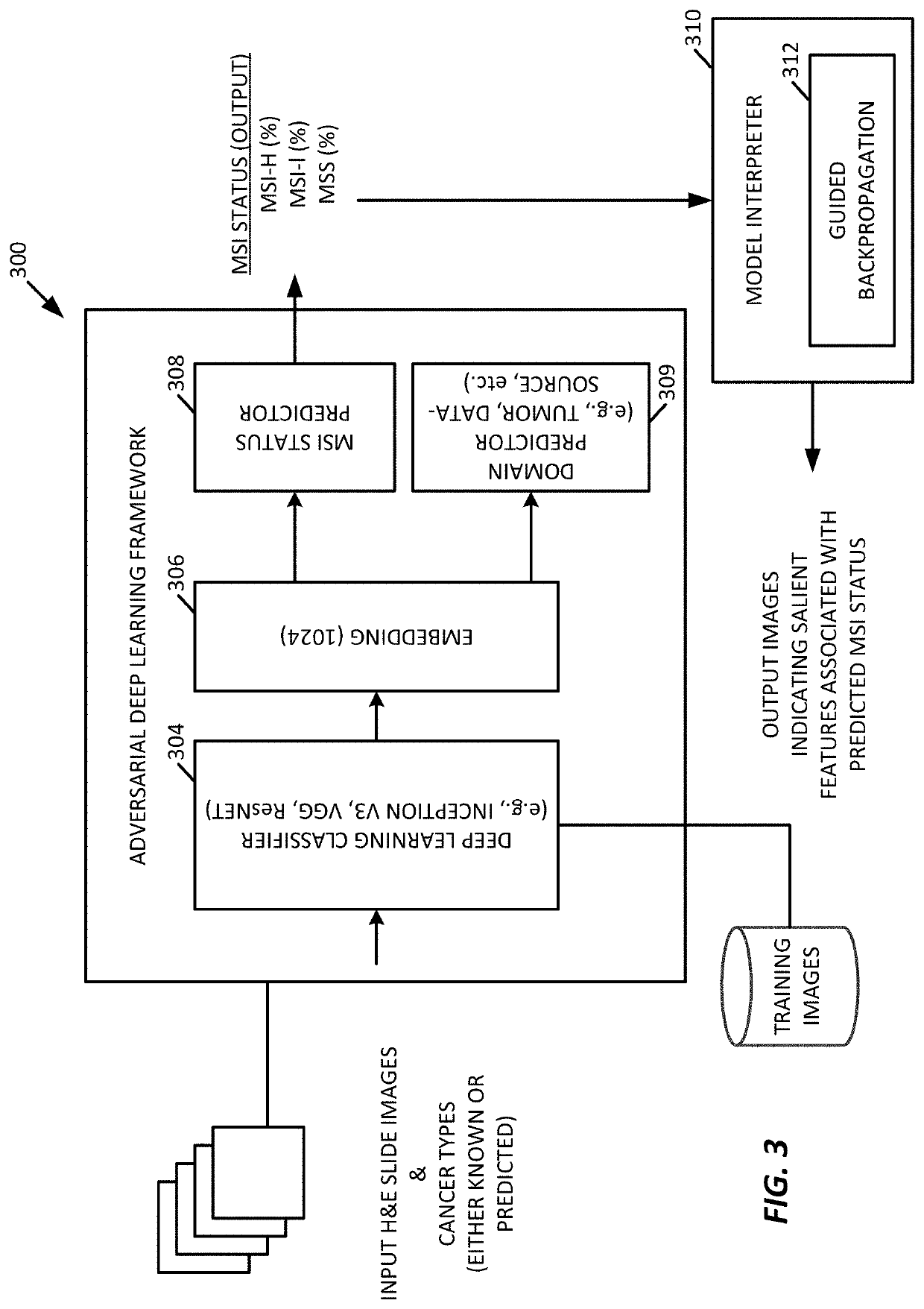
Generalizable and Interpretable Deep Learning Framework for Predicting MSI from Histopathology Slide Images
ActiveUS20190347557A1Facilitate visual interpretationImprove versatilityImage enhancementImage analysisAlgorithmDecision taking
A generalizable and interpretable deep learning model for predicting microsatellite instability from histopathology slide images is provided. Microsatellite instability (MSI) is an important genomic phenotype that can direct clinical treatment decisions, especially in the context of cancer immunotherapies. A deep learning framework is provided to predict MSI from histopathology images, to improve the generalizability of the predictive model using adversarial training to new domains, such as on new data sources or tumor types, and to provide techniques to visually interpret the topological and morphological features that influence the MSI predictions.
Owner:TEMPUS LABS INC
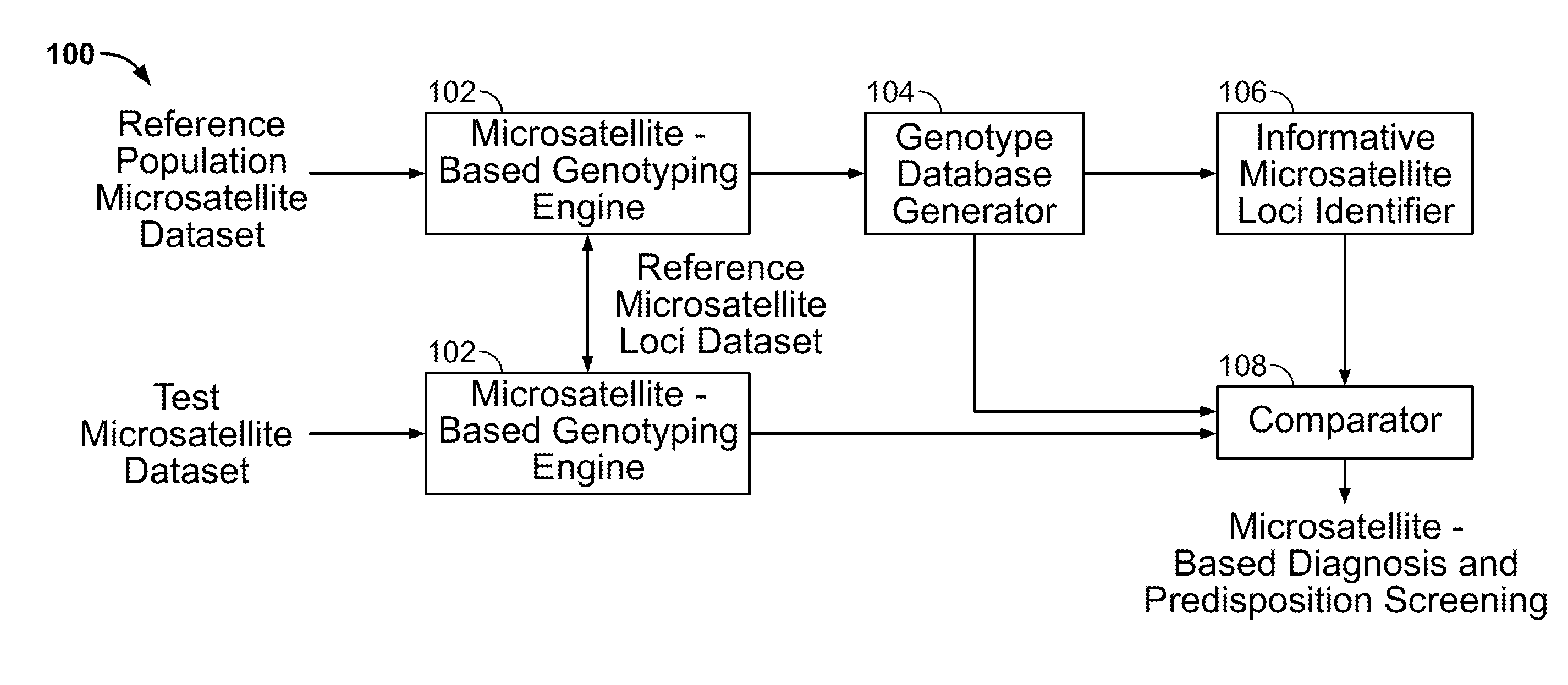
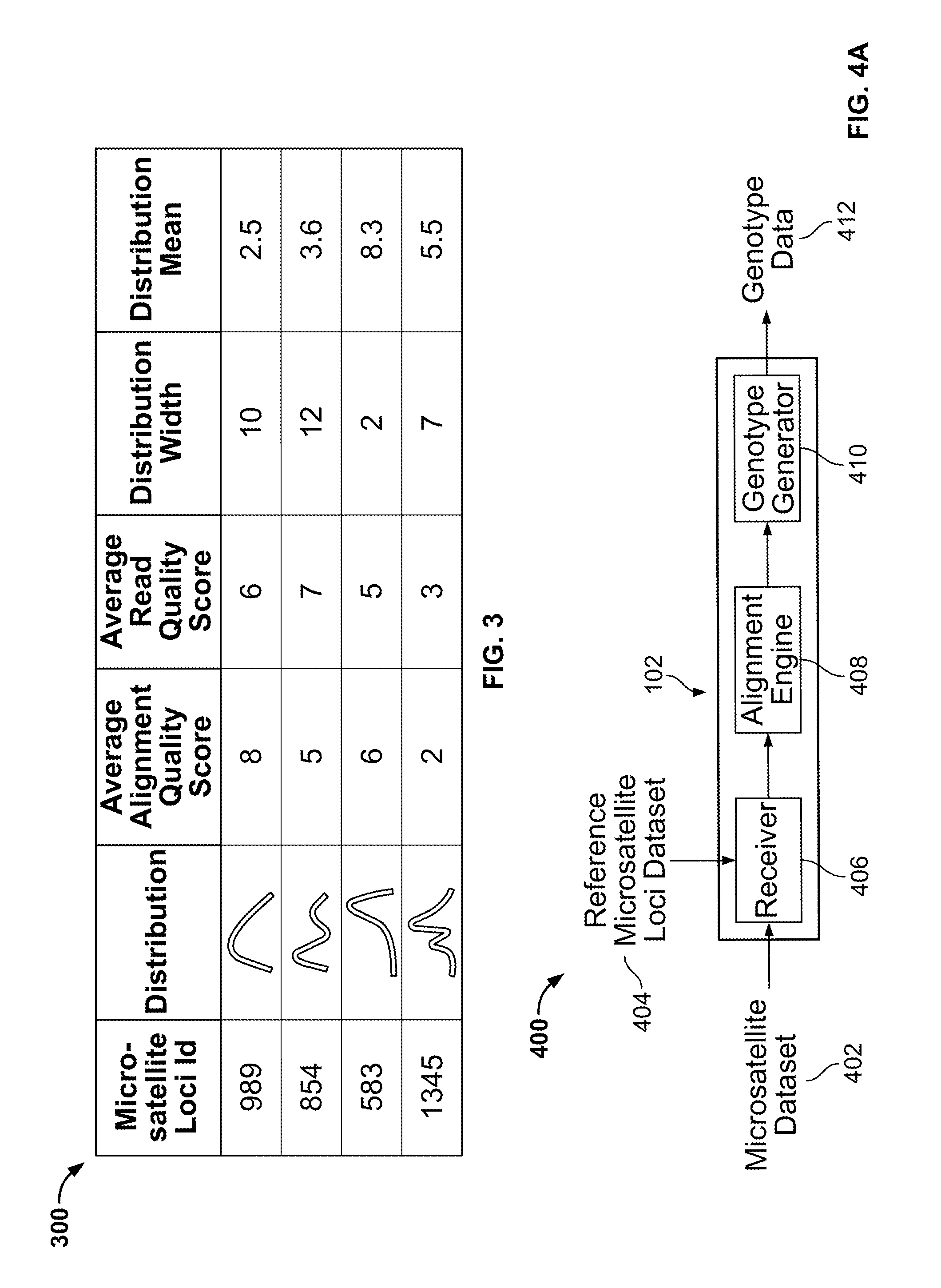
Methods and Compositions for Identifying Global Microsatellite Instability and for Characterizing Informative Microsatellite Loci
The disclosure provides methods and systems for assessing microsatellites, for identifying informative microsatellite loci, and for using microsatellite data. Microsatellite information has numerous uses including, for example, to characterize disease risk, to predict responsiveness to therapy, and to non-invasively diagnose subjects.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
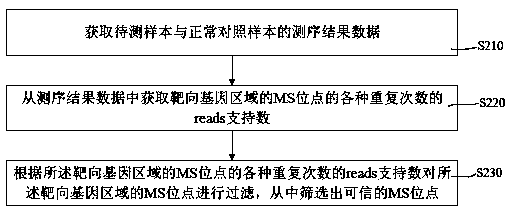
Microsatellite instability sequencing data analysis method and apparatus, and computer readable medium
ActiveCN107526944AImprove throughputHigh sensitivityBiostatisticsProteomicsAnalysis methodMicrosatellite Stable
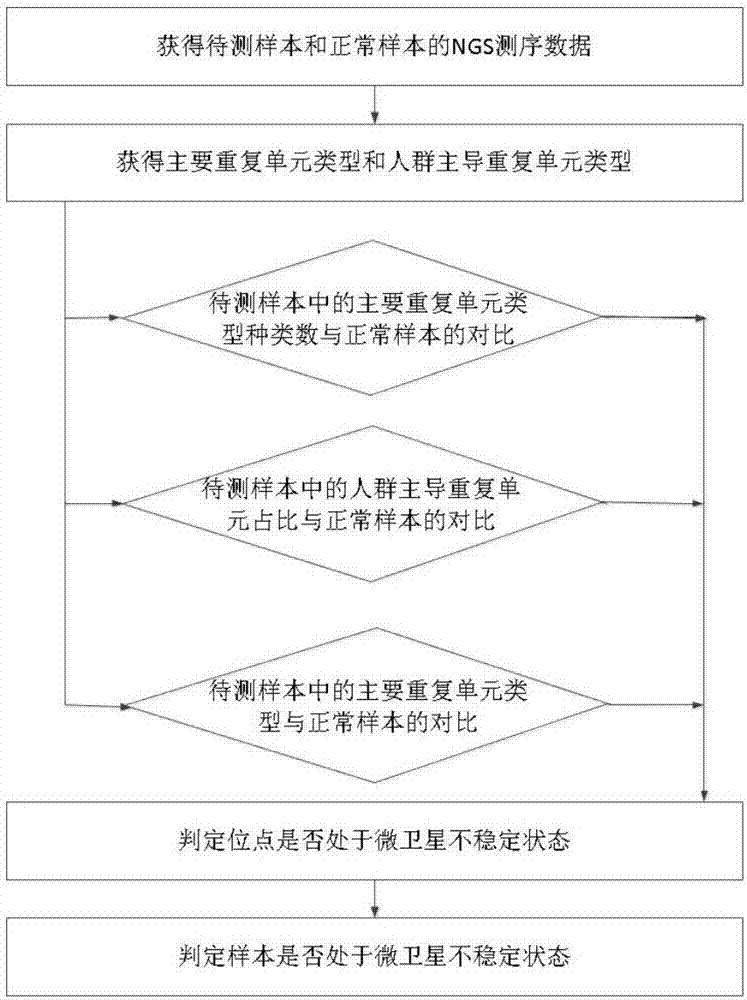
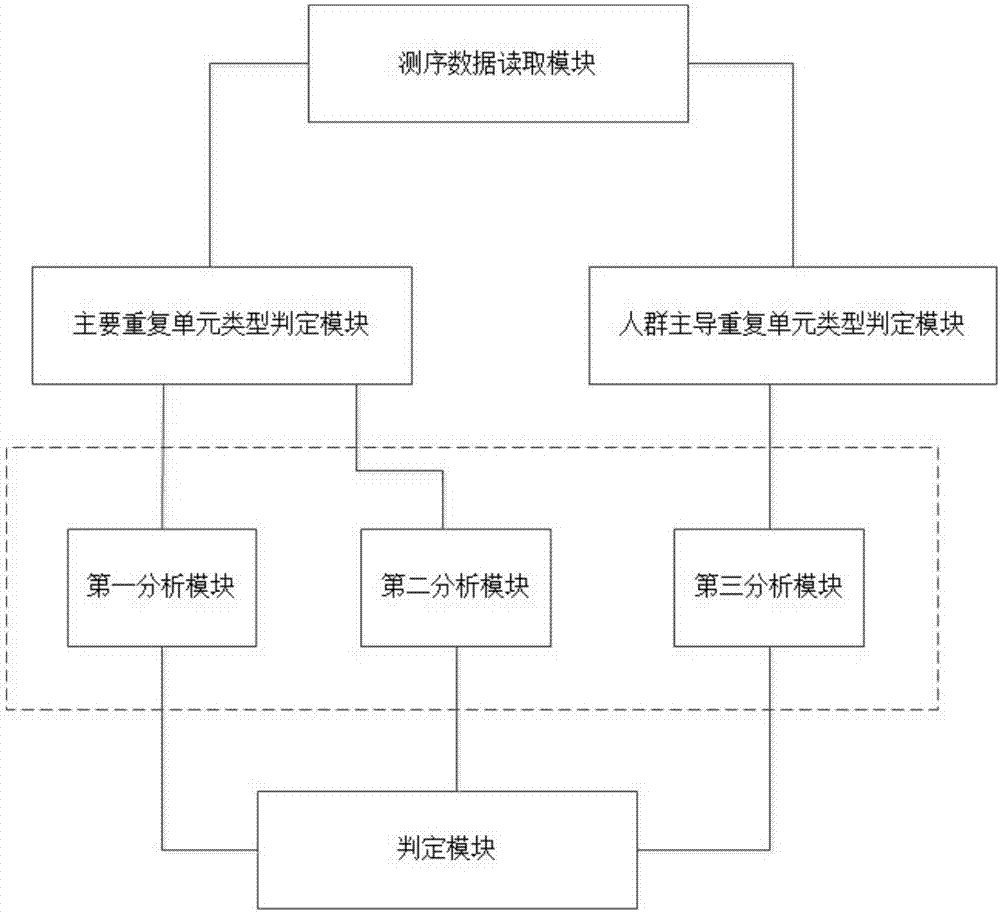
The invention provides a microsatellite instability sequencing data analysis method and apparatus, and a computer readable medium. Whether a situation of microsatellite instability exists or not can be determined by utilizing an NGS sequencing result; the analysis calculation method can remarkably improve detection sensitivity under the condition of not reducing specificity; a stable or instable state of each MSI site can be assessed in a quick, automatic, high-flux, high-sensitivity and high-specificity manner; and in combination with states of all MSI sites in each sample, the sample is comprehensively assessed as MSS, MSI-L or MSI-H.
Owner:GENESEEQ TECH INC
System for analyzing MSI (microsatellite instability) state during tumor immunotherapy
InactiveCN106834479AProvide accuratelyAccurately provide test reportsMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescencePD-L1
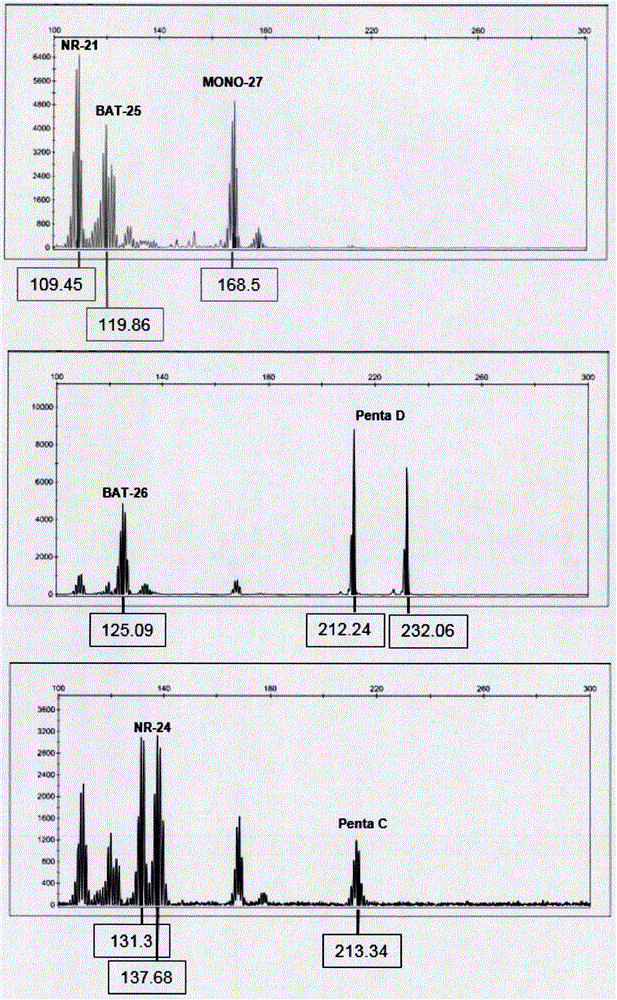
The invention relates to analysis of the MSI (microsatellite instability) state which can serve as an auxiliary diagnosis marker for tumor immunotherapy (PD-1 / PD-L1). The MSI of tumor cells of human beings is detected on the basis of a fluorescent PCR platform, and five of more mononucleotide repeat loci (NR-21, NR-24, BAT-25, BAT-26 and MONO27) reported in documents and internationally are selected for analysis of the MSI state. Besides, two pentanucleotide repeat loci (Penta C and Penta D) are selected for quality control of samples and are mainly used for detecting mixing and pollution of the samples. A fluorescently labeled primer is adopted, and besides, 7 loci are amplified; by comparison with other products, the amplification conditions are simplified, amplification can be performed on common PCR equipment, signals are stronger in combination with capillary electrophoresis analysis, the operation is simple, economical and practical properties are realized, the MSI state of a patient who receives or is going to receive tumor immunotherapy (PD-1 / PD-L1) can be detected within short time, and guiding significance is given as soon as possible for clinical treatment.
Owner:QIAGEN SUZHOU TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE CO LTD
A second generation sequencing-based method for detecting microsatellite stabilization and genomic changes through plasma
ActiveCN109207594ANon-invasiveReal-timeHealth-index calculationMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseNon invasive
The invention relates to a second generation sequencing-based method for detecting microsatellite instability (MSI) and genomic changes through plasma, a device implementing the method, uses of the method especially in non-invasive diagnosis, prognostic assessment, selection of treatment regimens or genetic screening in patients with cancer, preferably colorectal cancer (e. G., bowel cancer), gastric cancer and endometrial cancer. microsatellite instability (MSI) sites with high sensitivity and specificity associated with cancer, preferably colorectal cancer (e.g., bowel cancer), gastric or endometrial cancer, based on the detection method are obtained. The present invention also relates to a kit used in plasma microsatellite instability detection and use of detection reagents in preparation of the kit. The plasma MSI detection method is provided for that first time, which enables a microsatellite (MS) state of a sample to be judged with high accuracy and sensitivity.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BURNING ROCK DX CO LTD
Microsatellite instability determination system and related methods
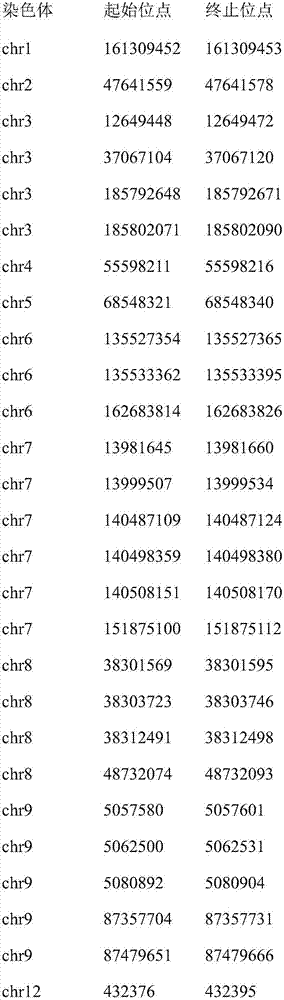
Methods and systems for determining microsatellite instability (MSI) directly from microsatellite region mappings for specific loci in the genome are provided. Techniques include an MSI assay that may be deployed in a paired form, that is, as tumor sample and matched normal sample MSI assay, or an unpaired form, that is, as a tumor-only MSI assay. The techniques provide an automated process for MSI determination by mapping read counts in tumor samples and normal samples and comparing the two, for an identified set of 43 microsatellite loci.
Owner:TEMPUS LABS INC
Microsatellite instability site combination, detection kit and application of microsatellite instability site combination
ActiveCN107513565AIncreased sensitivitySolve problems prone to low sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsGeneticsTrue positive rate
The invention provides a microsatellite instability site combination, a detection kit and application of the microsatellite instability site combination. By the used microsatellite instability site combination, after next-generation sequencing (NGS) detection, a sequencing result about one or more microsatellite sites capable of indicating an MSI state can be generated as input data. The method can be used for accurately defining the MSI state is high, low or stable, and has the characteristics of high sensitivity and specificity as well as repeatability in comparison to existing analysis methods.
Owner:GENESEEQ TECH INC
Process for microsatellite instability detection
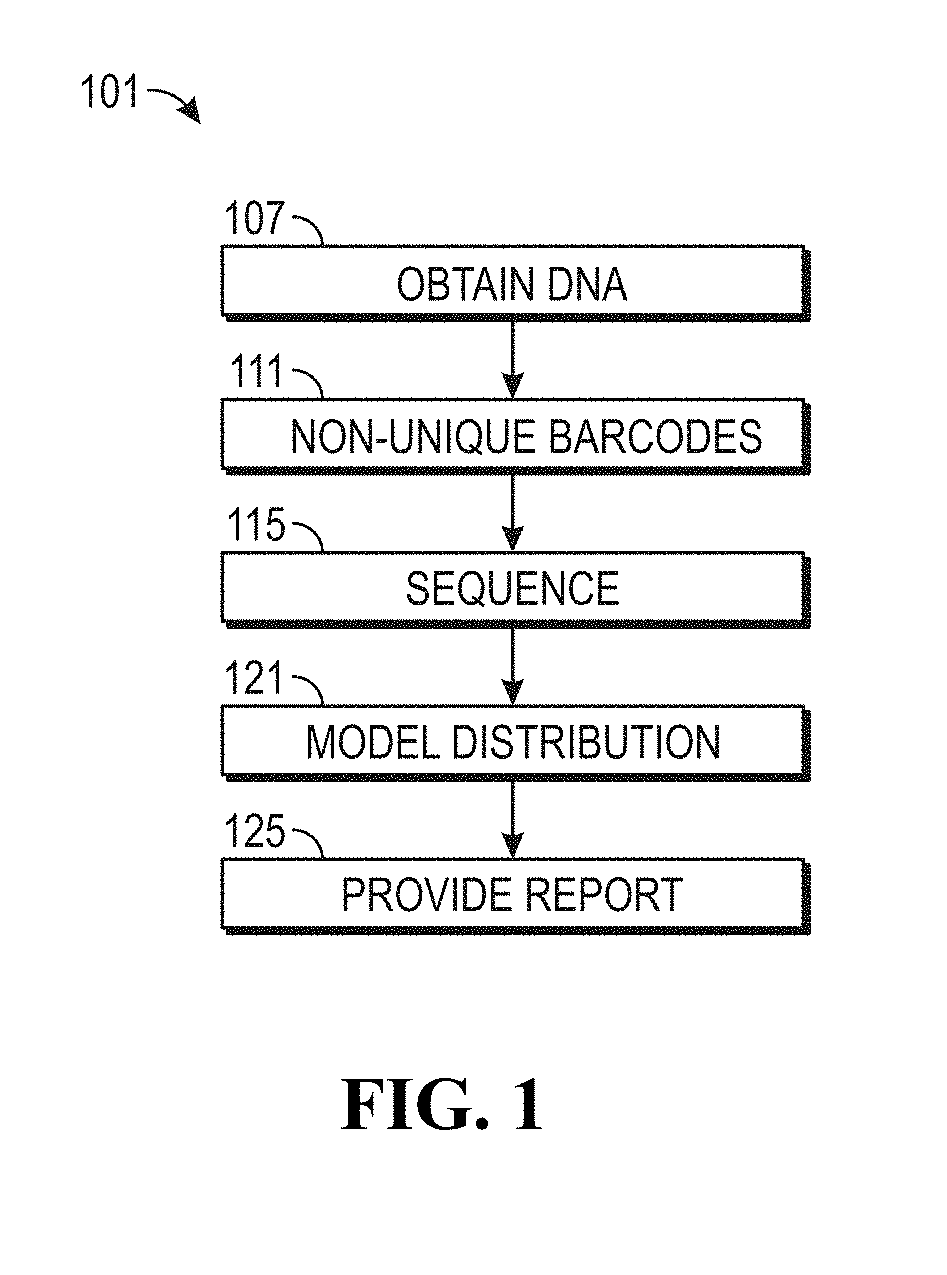
ActiveUS20190169685A1Useful in detectionIncrease the burdenTherapiesHealth-index calculationCell freeNucleotide
The invention provides methods for determining the MSI status of a patient by liquid biopsy with sample preparation using hybrid capture and non-unique barcodes. In certain aspects, the invention provides a method of detecting microsatellite instability (MSI). The method includes obtaining cell-free DNA (cfDNA) from a sample of blood or plasma from a patient and sequencing portions of the cfDNA to obtain sequences of a plurality of tracts of nucleotide repeats in the cfDNA. A report is provided describing an MSI status in the patient when a distribution of lengths of the plurality of tracts has peaks that deviate significantly from peaks in a reference distribution.
Owner:PERSONAL GENOME DIAGNOSTICS INC
Novel markers for detecting microsatellite instability in cancer and determining synthetic lethality with inhibition of the dna base excision repair pathway
InactiveCN104379765AMicrobiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsSynthetic lethalityWilms' tumor
The present application relates to the field of cancer, particularly to mismatch repair (MMR-)deficient tumors. New markers are presented herein that have a high sensitivity to detect whether a tumor is mismatch repair deficient or not. The markers are particularly mutations in microsatellite regions. Accordingly, methods are provided for diagnosing microsatellite instability of a tumor, comprising determining the presence of these markers. Further, kits are provided to detect the presence of these markers (or subsets thereof) in a sample.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW +1
Microsatellite biomarker combination, detection kit and use thereof
ActiveCN109182525AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationStomach cancerBiomarker (petroleum)
The present invention relates to biomarker combinations, kits for detecting them, and their use in microsatellite instability (MSI) detection and cancer, preferably colorectal cancer (e.g., bowel cancer), gastric cancer or endometrial cancer, prognostic assessment, treatment regimen selection or genetic screening in plasma samples. A method for detecting plasma MSI is provided for the first time,which enables a microsatellite (MS) state of a sample to be judged with high accuracy and sensitivity.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BURNING ROCK DX CO LTD
Method and device for detecting instability of microsatellite locus
ActiveCN107058551AIncrease the number of sitesReduce false positivesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisInstabilityData treatment
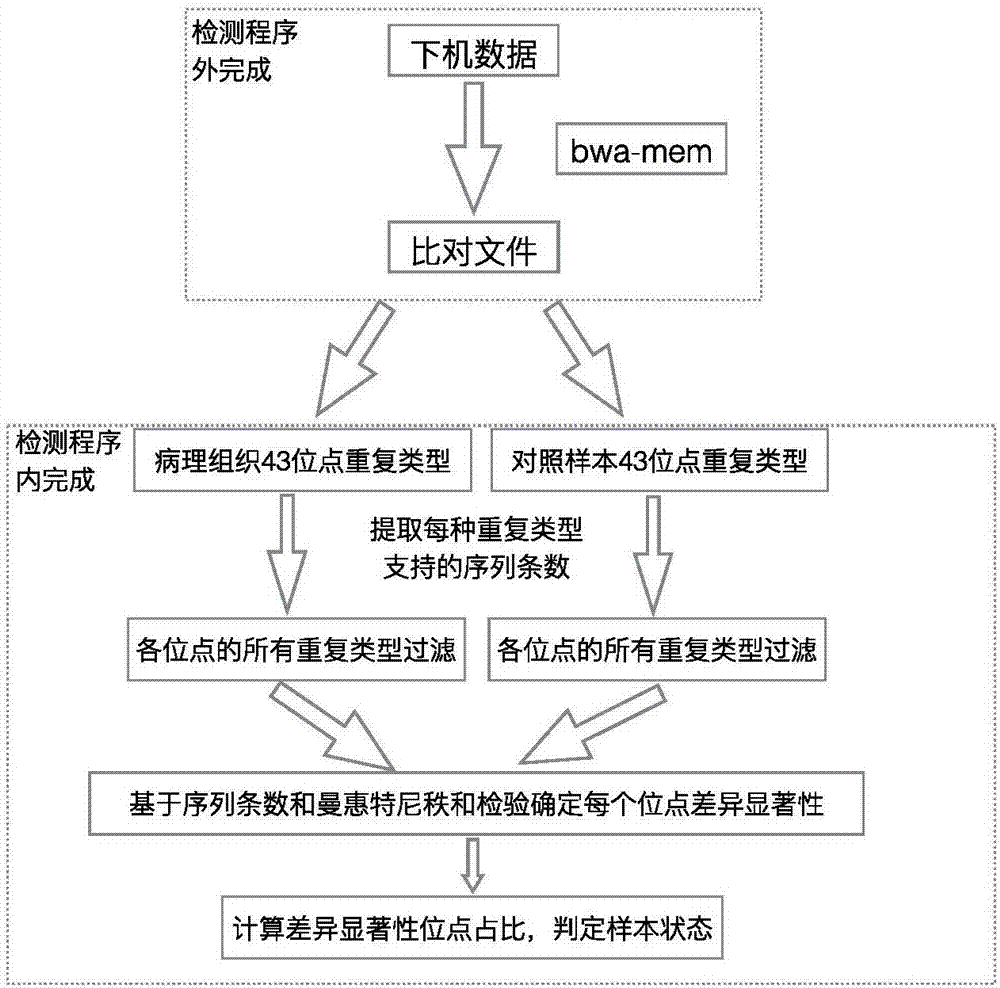
The invention discloses a method and device for detecting instability of a microsatellite locus, wherein the method comprises the steps of S1, treating a sample; S2, processing data, to be specific, using comparison software to compare determined sequences to a reference genome to obtain a comparison file, allowing non-matched sequences to form soft cut-off, ranking according to comparison positions, and using the software samtools to establish an index; S3, detecting the instability of the microsatellite locus, to be specific, using locus coverage rates having significant differences to determine the microsatellite instability of the sample. By using the method and device in connection with high-throughput sequencing techniques for capturing a target area, the quantity of loci for detection can be increased greatly; differences between a pathological sample and a control sample are judged, the microsatellite stability of the sample is determined through the differences in connection with statistical testing, and chances for false positives and false negatives to occur in the detection of microsatellite locus stability in the prior art are slimmed.
Owner:天津诺禾致源生物信息科技有限公司
Microsatellite instability detecting system and method based on genome sequencing
ActiveCN109637590AReduce limitationsRelieve painSequence analysisInstrumentsGenomic sequencingWhole genome sequencing
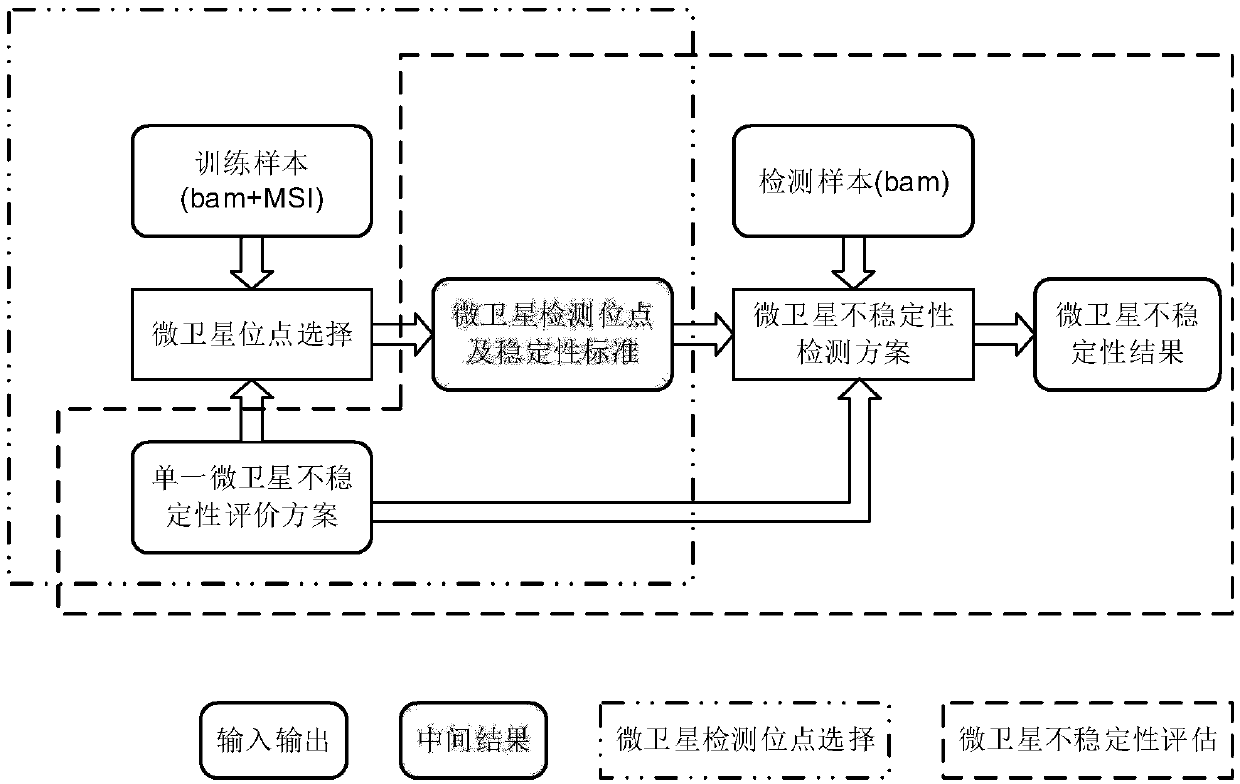
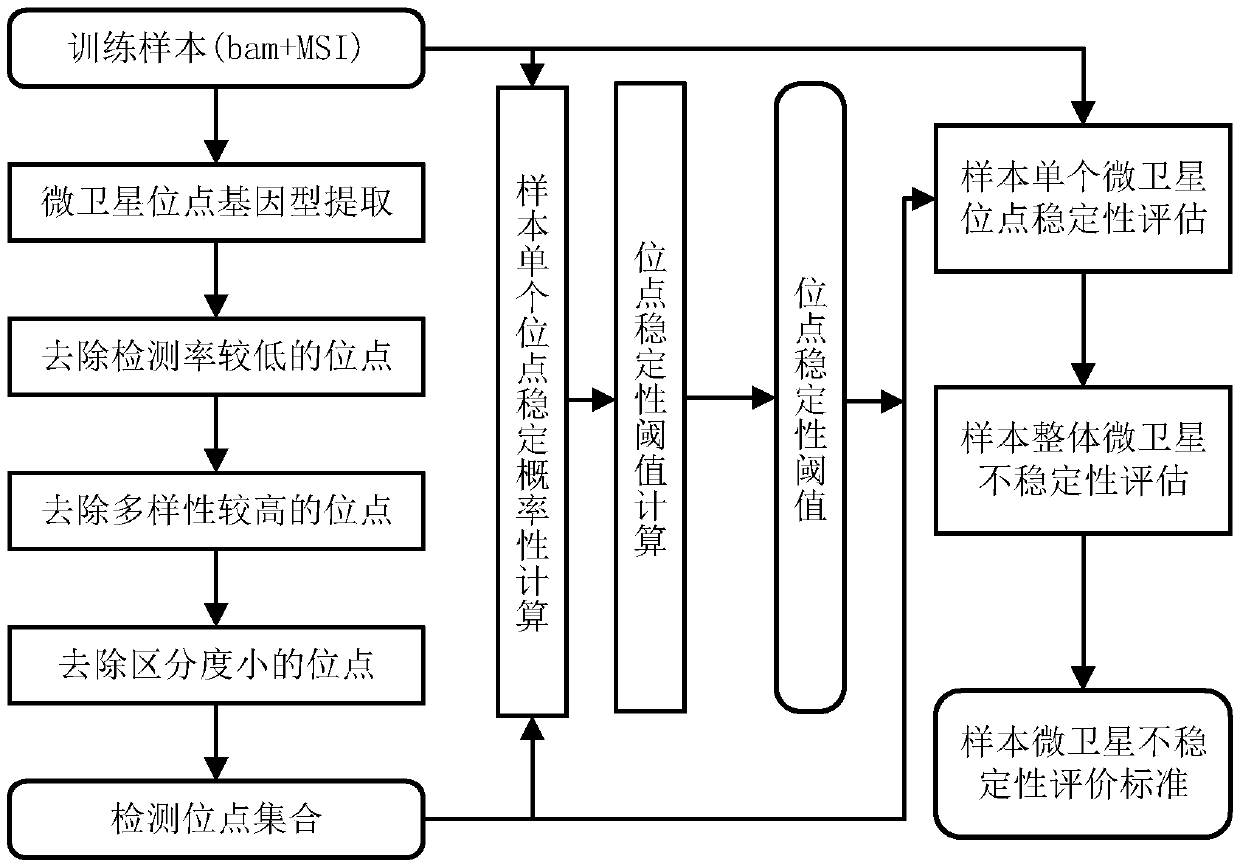
The invention discloses a microsatellite instability detecting system and method based on genome sequencing. The method comprises the steps that microsatellite detecting site selection is conducted, wherein an effective detecting site is selected according to sequencing data of a certain tumor sample, the threshold value of the instability of a single microsatellite corresponding to the effectivedetecting site and the evaluation standard of the instability of the microsatellite of a certain tumor sample are computed; microsatellite instability detection is conducted on a detected sample according to the threshold value of the instability of the single microsatellite corresponding to the effective detecting site and the evaluation standard of the instability of the microsatellite of the certain tumor sample. The system and the method have the advantages that the system and the method do not rely on a control sample, the pain on a detected person caused by sampling can be reduced, all genetic information of the detected person is included in the control sample, the probability of privacy leakage of the detected person can be reduced by not using the control sample, and the detectioncost can be reduced by not detecting the control sample; the operation is convenient, the cost is low, and the confidence level is high.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Gene panel used for detecting breast cancer gene mutation, detection method used for detecting breast cancer gene mutation and application of gene panel
InactiveCN111647648AComprehensive immunotherapyComprehensive treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisHuman DNA sequencingGenome human
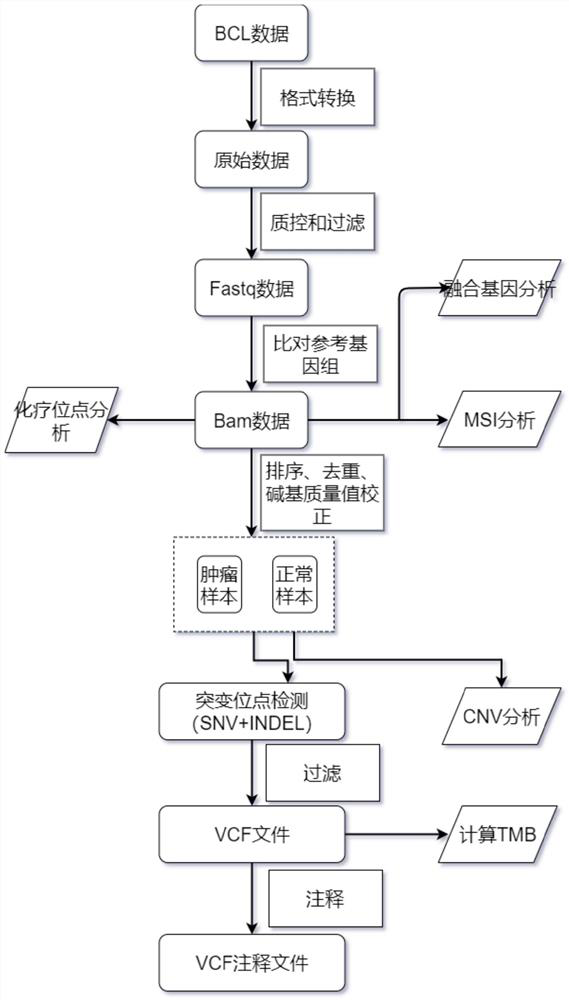
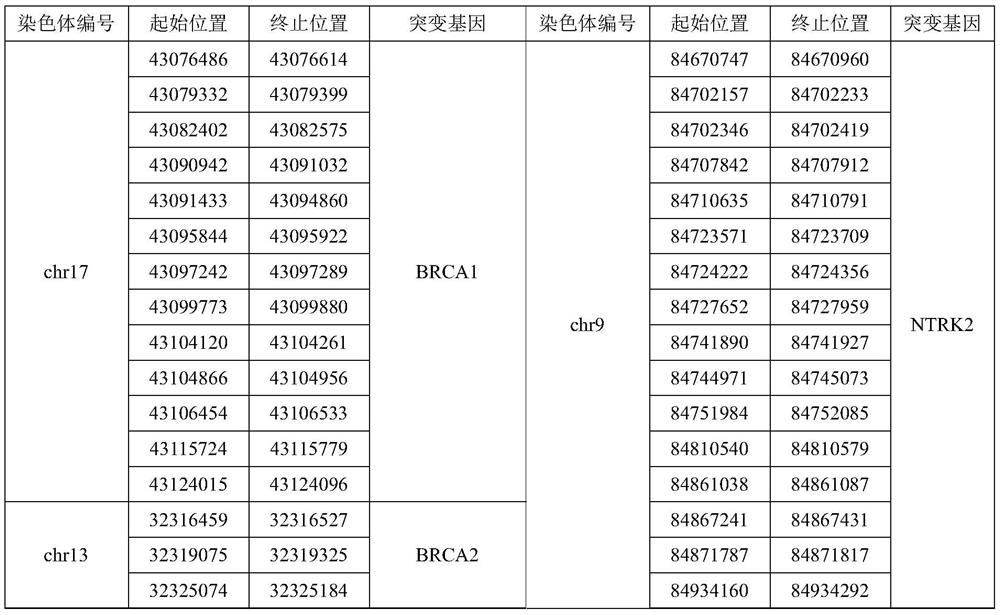
The invention relates to a gene panel used for detecting breast cancer gene mutation, and a detection method and application of the gene panel. The panel disclosed by the invention comprises 54419 pieces of targeted DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) probes. The targeted DNA comprises the exon regions of 445 pieces of genes on the human genomes, 2573 pieces of MSI (microsatellite instability) sites and 566 position intervals used for detecting gene fusion. The detection method in the invention can be used for detecting SNV (single nucleotide variation), Indel (Insertion and Deletion), CNV (Copy Number Variation), Fusion, MSI, TMB (Tumor Mutational Burden), HLA (human leucocyte antigen) parting and the like of a tumor somatic cell multi-site DNA mutation. An optimal individual treatment medicine and scheme can be conveniently selected according to the genome features of patients in a breast cancer immunotherapy process.
Owner:北斗生命科学(广州)有限公司 +1
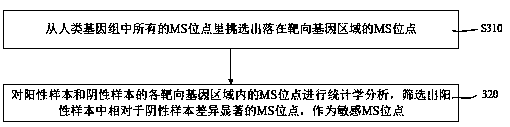
Microsatellite unstable site screening and analysis model construction method and device
InactiveCN110797078AImprove featuresHigh sensitivityBiostatisticsProteomicsMutation detectionMicrosatellite Stable
The invention provides a microsatellite unstable site screening and analysis model construction method and device. The method comprises the following steps of: S1, taking a microsatellite site of a reference genome as a candidate MS site, S2, selecting a plurality of samples with known microsatellite instability detection state information as training set samples, carrying out mutation detection on candidate MS site areas of the training set samples, respectively recording mutation types and numbers, and calculating information entropy of mutation of each candidate MS site, and S3, correlatingthe microsatellite instability detection state information with the entropy of the information entropy of the mutation of each candidate MS site, selecting an entropy threshold of each candidate MS site for distinguishing the microsatellite instability detection result, and screening out the candidate MS site with a high distinguishing degree as an MSI site. According to the scheme, the problemsof low detection efficiency caused by excessive fixed MSI sites and low detection specificity and sensitivity caused by incapability of covering all types of samples in the prior art are solved.
Owner:BEIJING GENEPLUS TECH +1
Colon cancer microsatellite instability detection kit based on next generation sequencing platform
InactiveCN105256057AImprove throughputHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrosatellite StableEnzyme
The invention discloses a colon cancer microsatellite instability detection kit based on a next generation sequencing platform. The colon cancer microsatellite instability detection kit comprises 4.5-6.5mu l of a primer panel solution, wherein the concentration of solute in the primer panel solution is 45-55 mmole / L; the primer panel solution comprises primers of 10 microsatellite loci; the kit further comprises 8-10mu l of Master Mix and 1.3-1.7ml of non-enzyme water; Master Mix comprises 3-7mu l of 10*LA Taq Buffer and 3-5mu l of 2-4mmol / L dNTPs, and 0.5-1mu l of LA Taq enzyme. By adopting the kit disclosed by the invention, all MSI loci of multiple samples can be simultaneously detected by sequencing once, influence caused by artificial operation can be reduced, and the detection result reliability can be improved.
Owner:湖南宏雅基因技术有限公司
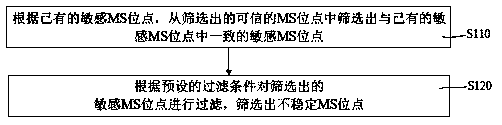
Microsatellite instability detection device, computer equipment and computer storage medium
The invention relates to a microsatellite instability detection device capable of improving result accuracy, computer equipment and a computer storage medium. The microsatellite instability detectiondevice screens out a sensitive MS site consistent with existing sensitive MS site data from screened credible MS loci according to the existing sensitive MS site data; filtering the screened sensitiveMS site, and screening unstable MS sites; and carrying out scoring analysis on the unstable MS sites of a tumor sample. According to the microsatellite instability detection method, the problems existing in the traditional technology are fully considered, on the basis of sensitive MS site data established in the earlier stage, a more accurate result can be obtained by using a lower sequencing data volume, and due to the small data volume, the whole processing flow is faster and higher in efficiency, and the occurrence of false positive and false negative results can be effectively reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI ORIGIMED CO LTD
Novel markers for detecting microsatellite instability in cancer and determining synthetic lethality with inhibition of the DNA base excision repair pathway
ActiveUS20150045369A1Increase costAccurate diagnosisBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementSynthetic lethalityInstability
Described are mismatch repair (MMR-)deficient tumors. Markers are presented herein having a high sensitivity to detect whether a tumor is mismatch repair deficient or not. The markers are particularly mutations in microsatellite regions. Accordingly, methods and materials are provided for diagnosing microsatellite instability of a tumor. Such a method comprises determining the presence of these markers. Further, kits are provided to detect the presence of these markers (or subsets thereof) in a sample.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW +1
Detection of microsatellite instability and its use in diagnosis of tumors
InactiveUS20070117136A1Microbiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyAbnormal tissue growthNeoplasm diagnosis
Methods and kits are disclosed for use in the analysis of microsatellite instability in genomic DNA. Methods and kits are also disclosed which can be used to detect microsatellite instability DNA present in biological materials, such as tumors. The methods and kits of the present invention can be used to detect or diagnose diseases associated with microsatellite instability, such as certain types of cancer.
Owner:PROMEGA CORP
Microsatellite instability prediction method and application thereof
ActiveCN111304303AImprove performanceImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGeneticsScreening method
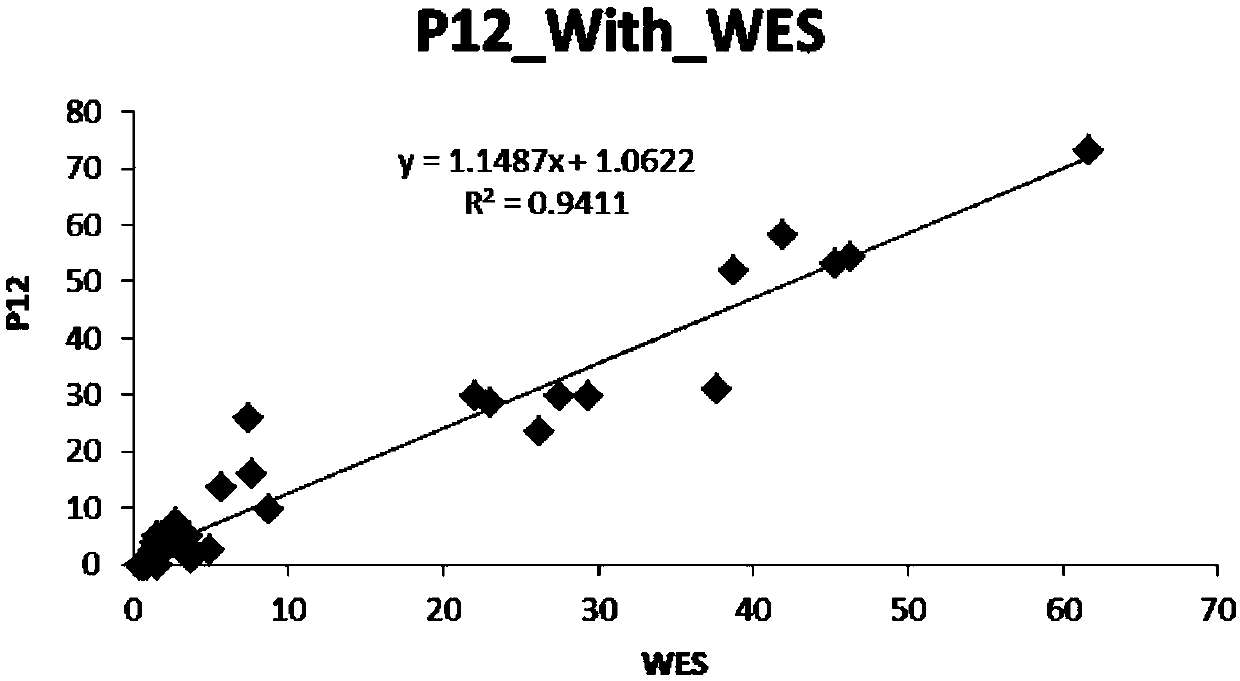
The invention discloses a microsatellite instability detection and prediction method, a related site screening method, a model construction method and an application. The site screening method comprises the following steps: i) determining a microsatellite instability predicted value of a candidate microsatellite site in a sample; and / or ii) screening sites or site combinations for microsatellite instability detection by using one or more indicators including the microsatellite instability predicted value of the candidate microsatellite site; wherein the microsatellite instability predicted value is a quantified value of an abundance difference between a major allele type and a minor allele type in the candidate microsatellite site. The method provided by the invention is high in accuracy,and can accurately and stably detect the MSI state only on the basis of a single tumor sample.
Owner:BERRY ONCOLOGY CO LTD
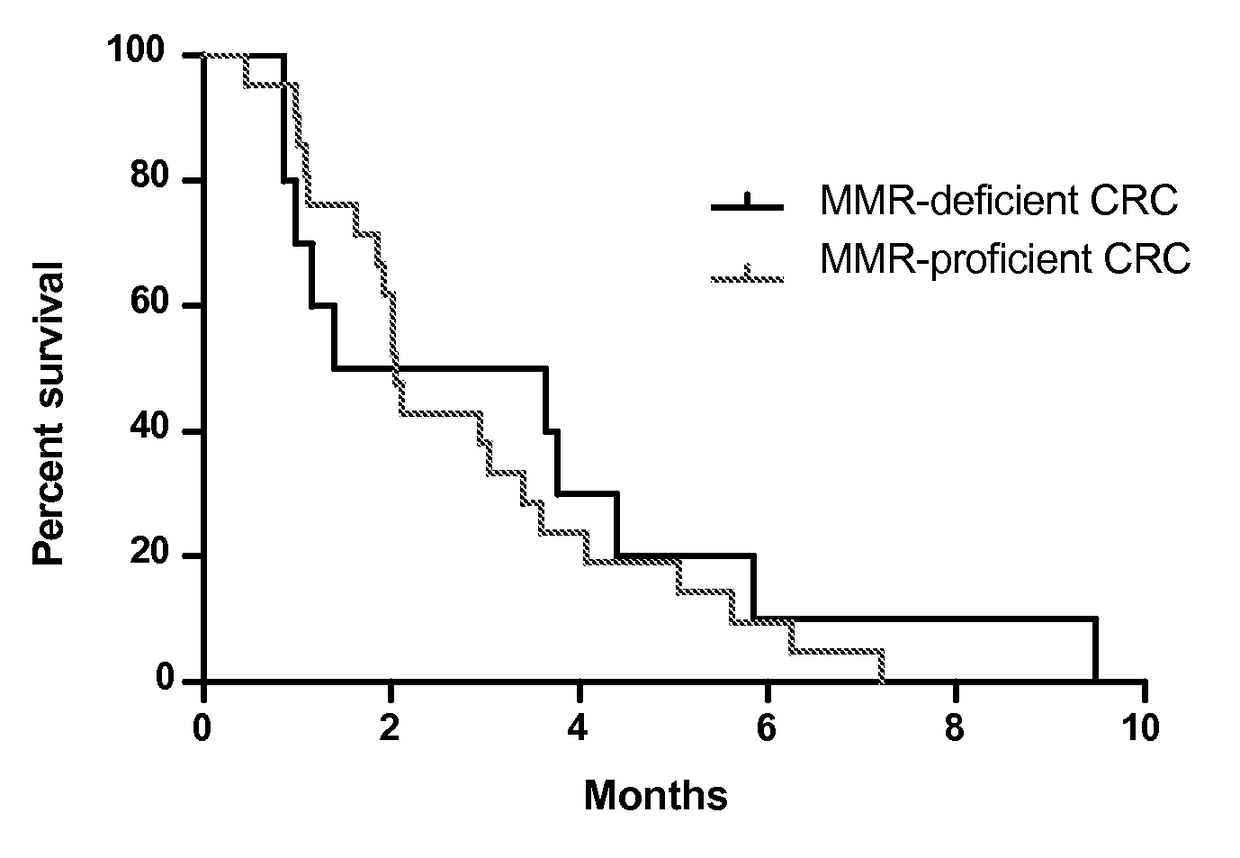
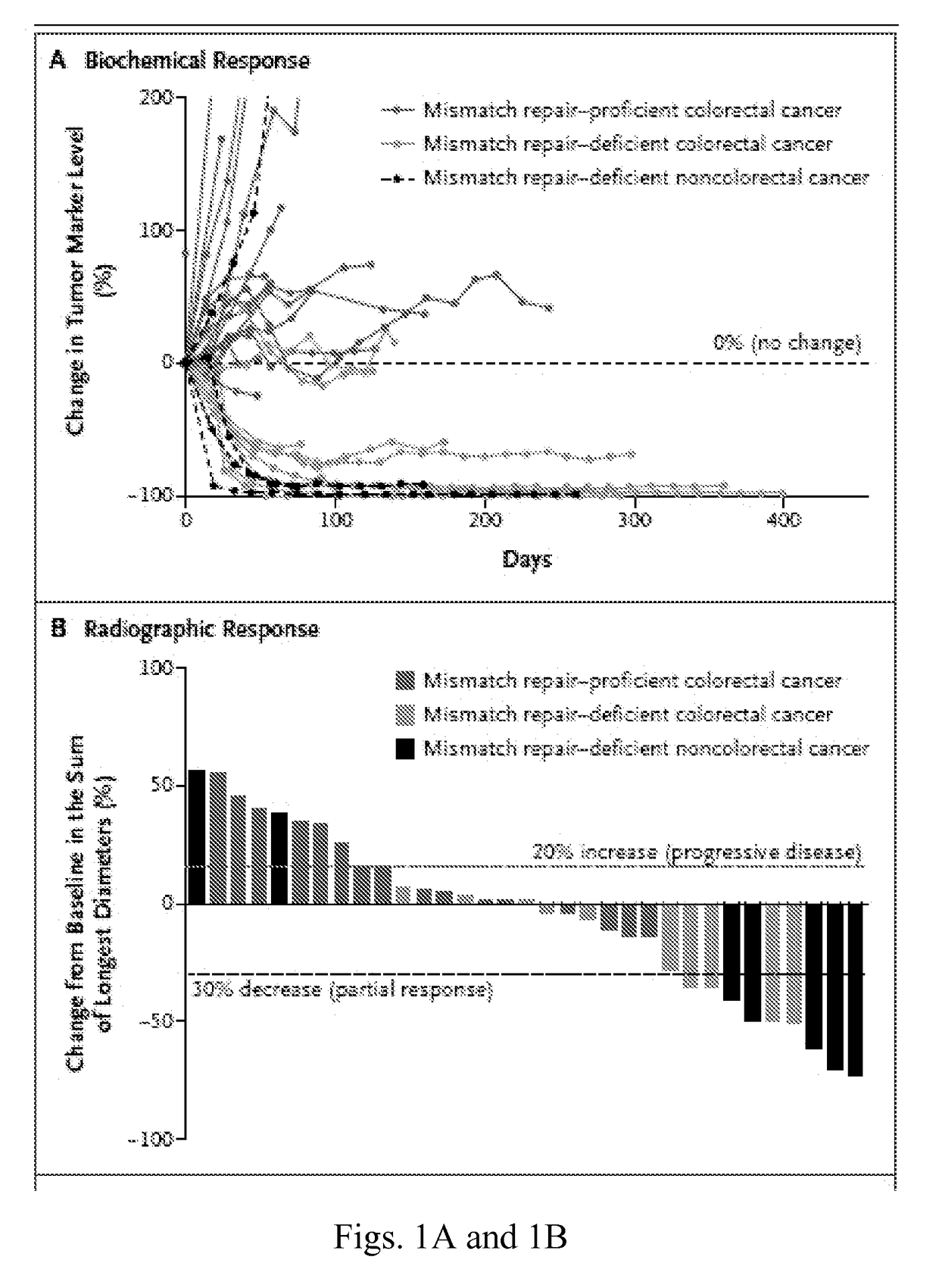
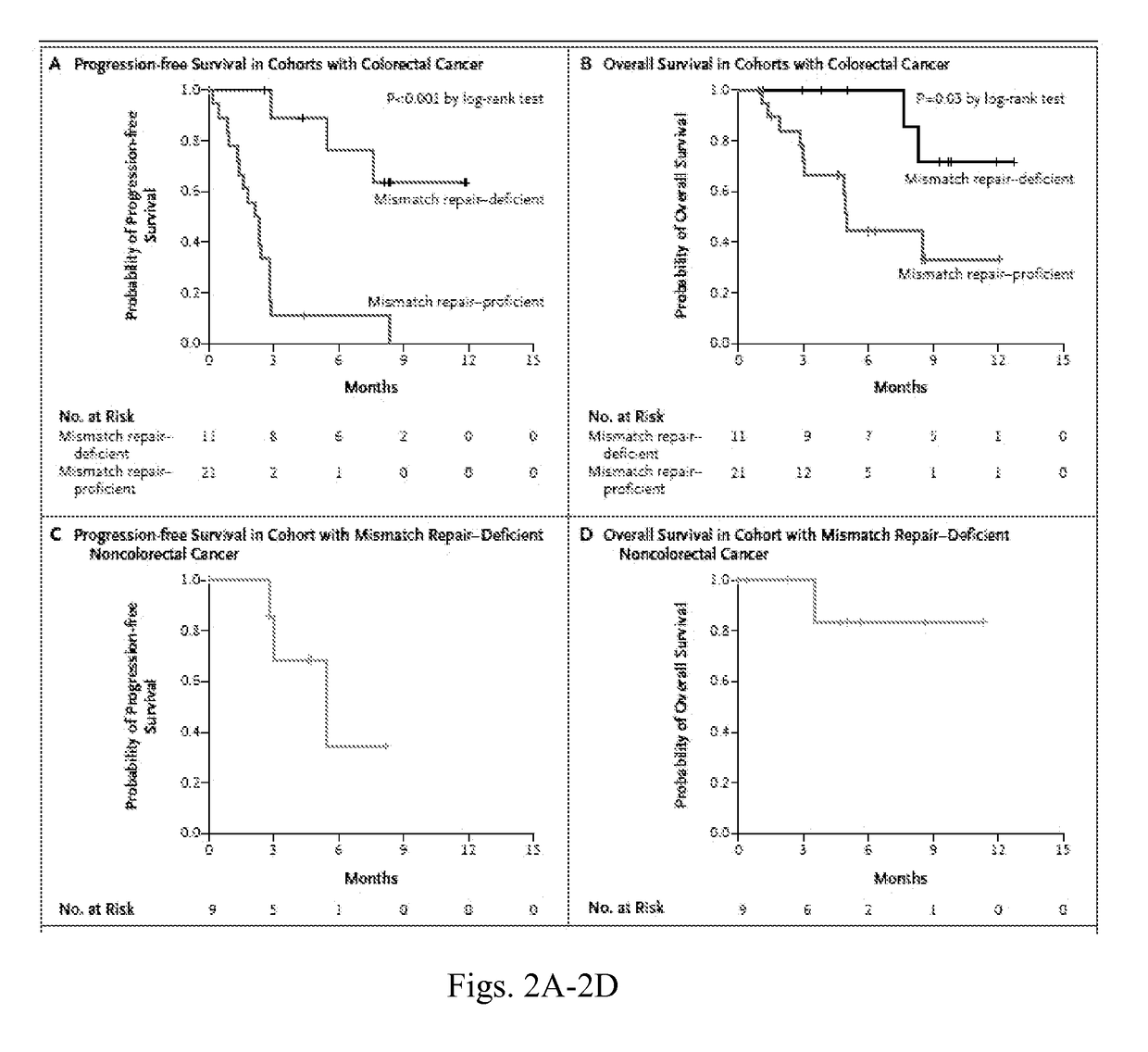
Checkpoint Blockade and Microsatellite Instability
InactiveUS20170267760A1High mutational burdenMicrobiological testing/measurementDigestive systemProgrammed deathImmune tolerance
Blockade of immune checkpoints such as cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) and programmed death-1 (PD-1) shows promise in patients with cancer. Inhibitory antibodies directed at these receptors have been shown to break immune tolerance and promote anti-tumor immunity. These agents work particularly well in patients with a certain category of tumor. Such tumors may be particularly susceptible to treatment because of the multitude of neoantigens which they produce.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
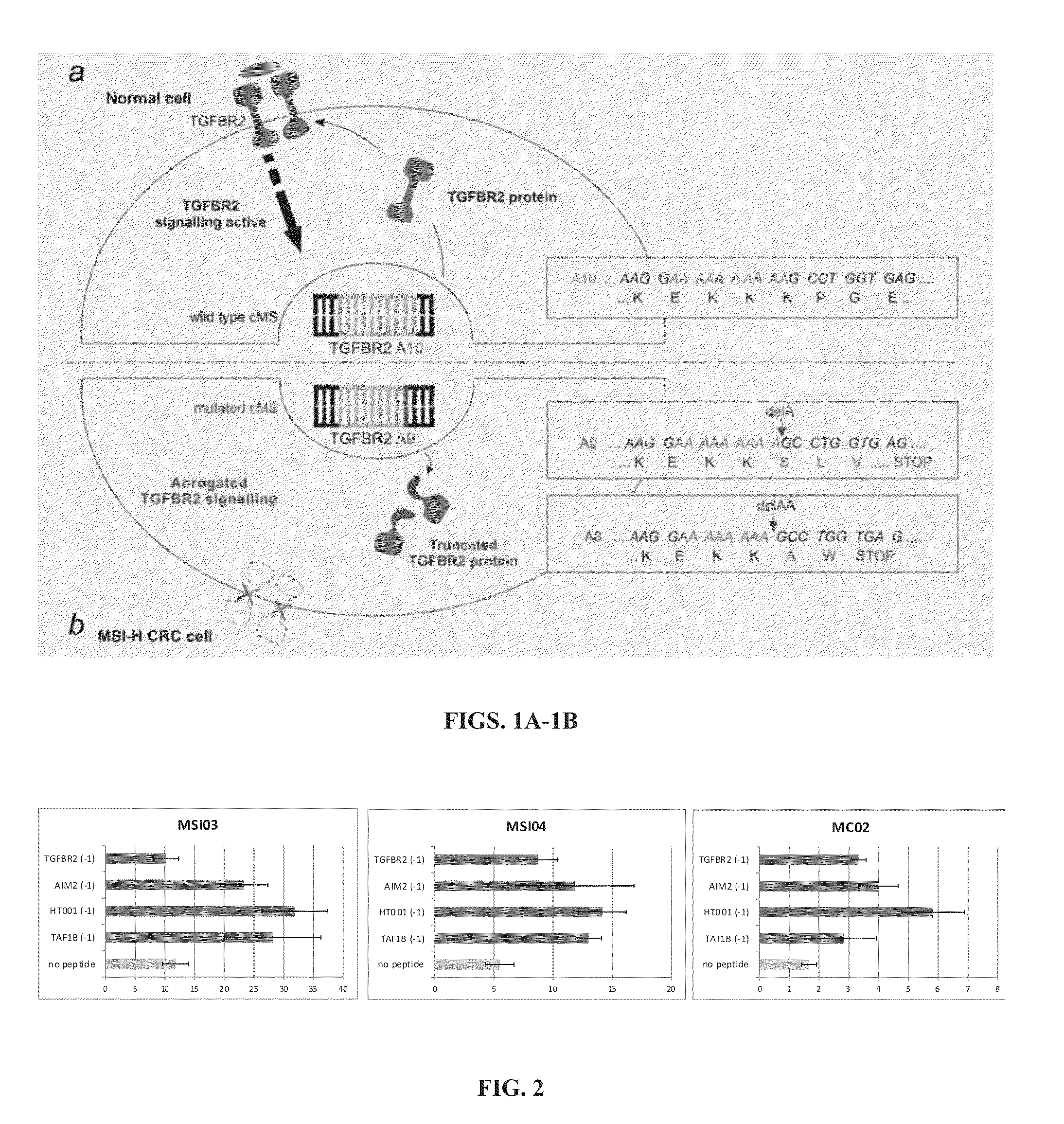
Msi-specific frameshift peptides (FSP) for prevention and treatment of cancer
Described is a vaccine for prevention and treatment of cancer characterized by microsatellite instability (MSI). The vaccine contains an MSI-specific frameshift peptide (FSP) generating humoral and cellular responses against tumor cells or a nucleic acid encoding said FSP. The vaccine of the present invention is particularly useful for the prevention / treatment of colorectal cancer, endometrial cancer, gastric cancer or small bowel cancer.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF HEIDELBERG
Compounds and Methods for Assessment of Microsatellite Instability (Msi) Status
ActiveUS20080096197A1Effective strategySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrosatellite StableBiology
The present invention provides a method for assessment of the Microsatellite Instability (MSI) status of medically relevant conditions associated with MSI phenotype such as e.g. neoplastic lesions. The method is based on the analysis of a monomorphic T25 (CAT25) mononucleotide repeat located in the 3′-UTR of the Caspase 2 (CASP2) gene. Based on the determination of the length of the named mononucleotide repeat the presence or absence of MSI may be assessed. Determination of the length is performed in a single PCR procedure. Alternatively an enhanced assessment could be performed by combining the CAT25 marker with further markers such as BAT25 and BAT26 in a single multiplex PCR process.
Owner:ROCHE MTM LAB AG
Microsatellite instability detection site screening method based on single tumor sample high-throughput sequencing
ActiveCN110910957ACheck comprehensivelyHigh-precision detectionData visualisationProteomicsGeneticsTumor Sample
The invention discloses a microsatellite instability detection site screening method based on single tumor sample high-throughput sequencing. The method is based on an optimized microsatellite site state mark, and the machine learning techniques are employed for modeling analysis of each microsatellite site; whether each sample is in a microsatellite unstable state or not is detected by utilizingthe percentage that effective sites are judged as microsatellite unstable sites, so the microsatellite instable state is detected only by utilizing tumor sample sequencing data, the stability of a plurality of microsatellite sites can be judged with high precision, and the accurate and stable microsatellite instable state gene detection is realized.
Owner:求臻医学科技(浙江)有限公司
Methods of Identifying Microsatellite Instability
ActiveUS20190194731A1Improve the level ofMicrobiological testing/measurementTumor SampleWilms' tumor
The present invention relates to methods and kits for identifying microsatellite instability (MSI) in a sample. In particular it relates to identifying microsatellite instability in a tumor sample, which may be from a subject suspected of having colorectal cancer or Lynch syndrome. The methods and kits can be used to identify mismatch repair defects. More particularly the invention relates to a panel of markers for a sequencing based MSI test, that can differentiate between MSI-H and MSS CRCs. The invention also allows for determination of biological significance, differentiating between PCR and sequencing errors and MSI induced indels / mutations.
Owner:CANCER RES TECH LTD
Checkpoint Blockade and Microsatellite Instability
InactiveUS20170313775A1Microbiological testing/measurementDigestive systemProgrammed deathImmune tolerance
Blockade of immune checkpoints such as cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) and programmed death-1 (PD-1) shows promise in patients with cancer. Inhibitory antibodies directed at these receptors have been shown to break immune tolerance and promote anti-tumor immunity. These agents work particularly well in patients with a certain category of tumor. Such tumors may be particularly susceptible to treatment because of the multitude of neoantigens which they produce.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
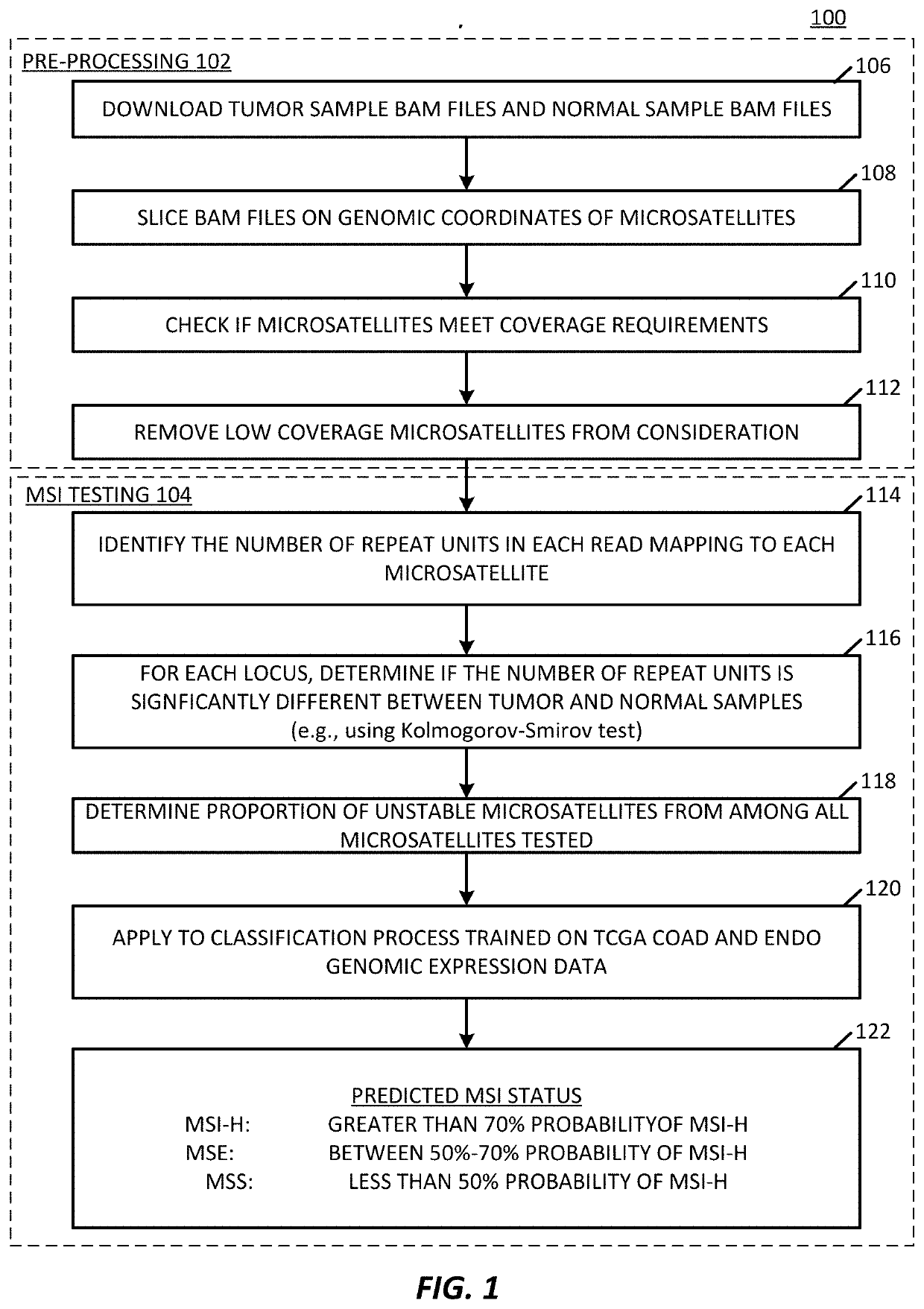
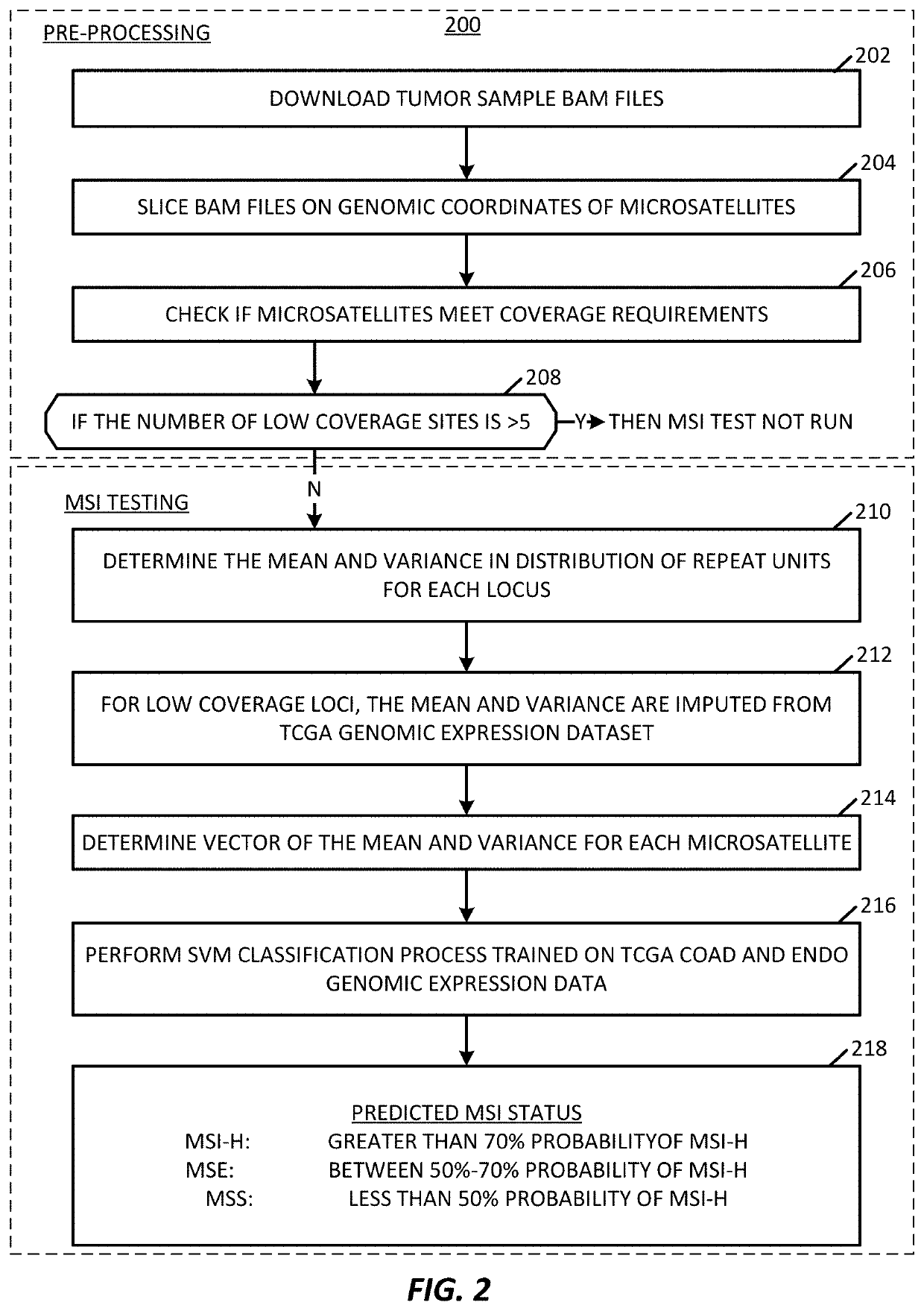
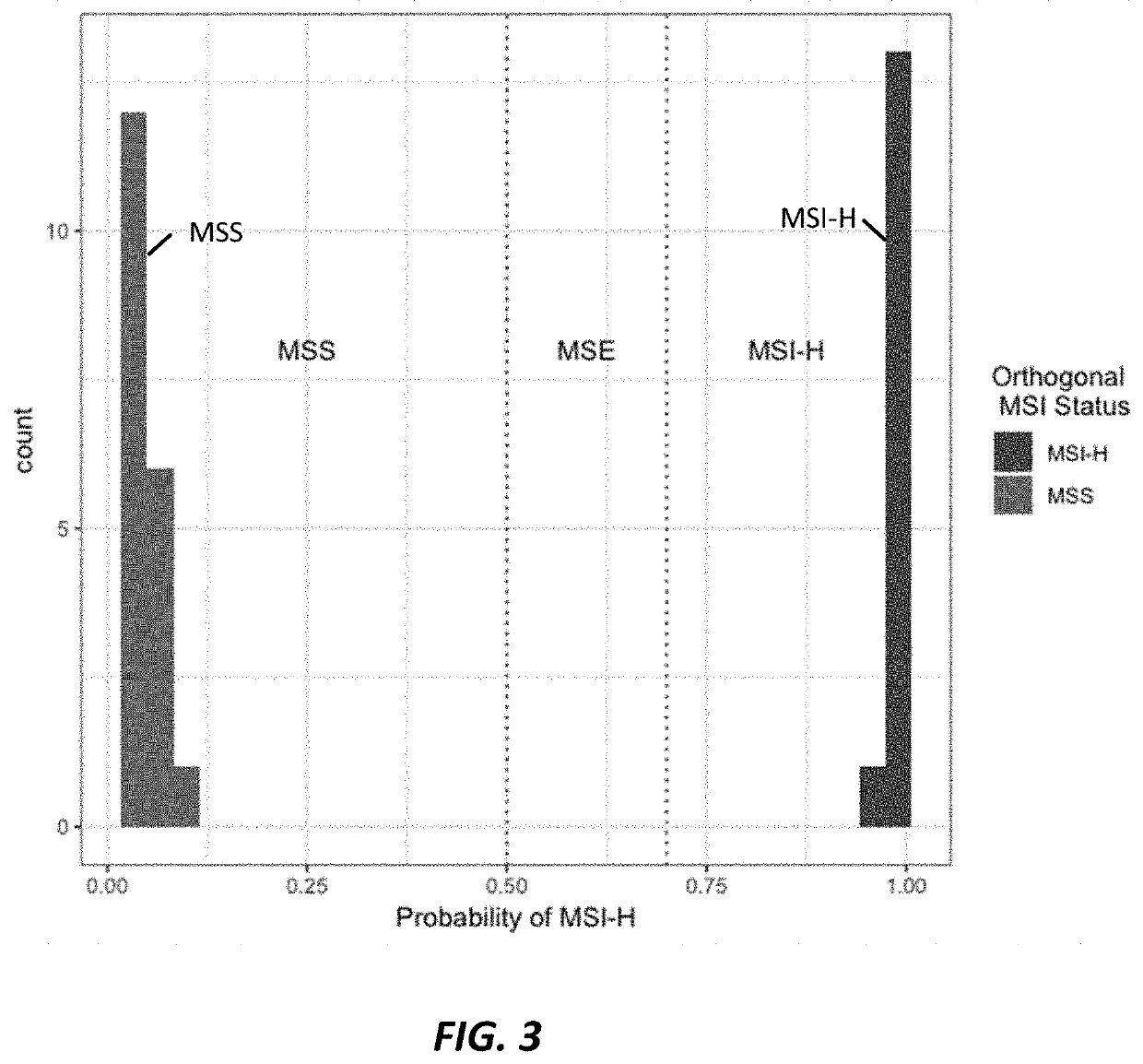
Microsatellite instability detection
For some cancers, microsatellite instability (MSI) in cell-free DNA can indicate the presence of a cancer in a subject. Subjects can generate a DNA sample for analysis to determine a likelihood that MSI exists and, thereby, determine a likelihood that the sample includes cancer. A system determines a likelihood that the sample includes MSI by selecting a set of markers from the sample and determining if those markers include MSI associated with cancer. The system determines if a marker is significant in by calculating: a viability score, a significance score, an entropy score, and a divergence score. The processing system determines an instability score representing a likelihood that the sample includes MSI based on the determined marker significances. Based on the instability score, the processing system can determine that a sample includes MSI and inform a method of treatment for the subject.
Owner:GRAIL LLC
Method for detecting blood microsatellite instability based on second generation sequencing technology
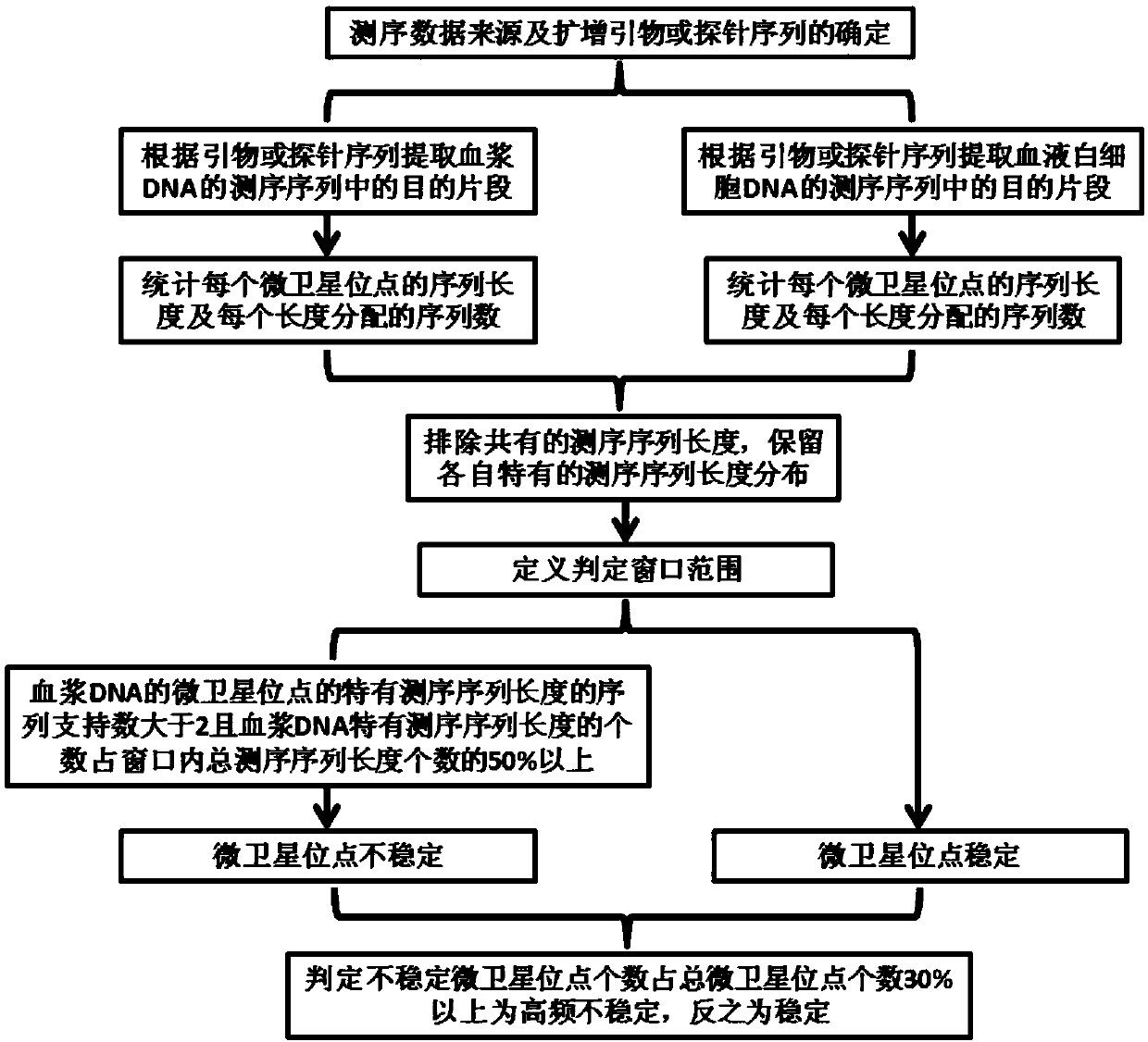
InactiveCN109584961AImprove consistencyResolve detectionBiostatisticsSequence analysisMicrosatellite StableTumor tissue
The invention discloses a method for detecting blood microsatellite instability based on a second-generation sequencing technology, which comprises the following steps: respectively determining the length and the number of each sequence corresponding to the same microsatellite locus to be detected in second-generation sequencing data of plasma DNA and blood leukocyte DNA, determining the length ofthe sequencing sequence with difference by comparison. Determining the sequence length L corresponding to the primer and / or the probe and the length L'of the corresponding microsatellite locus to bedetected in the known genome, and if the number of sequences with different sequencing sequence lengths is more than 2 in the judgment range window of L-L'(X (L+L'), and accounts for more than 50% ofthe total sequence length in the judgment range window, the microsatellite locus is judged to be unstable, and conversely, the microsatellite locus is judged to be stable. Repeating the process to judge the stability of a plurality of microsatellite loci so as to detect the microsatellite instability of the sample. The method for detecting blood microsatellite instability based on second generation sequencing technology can complete the detection only by extracting the blood of the patient without depending on tumor tissues.
Owner:GENEIS TECH BEIJING CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com