Microsatellite instability sequencing data analysis method and apparatus, and computer readable medium
A technology for sequencing data and instability, applied in the field of gene detection, can solve the problem of low sensitivity to microsatellite instability, and achieve the effect of improving detection sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
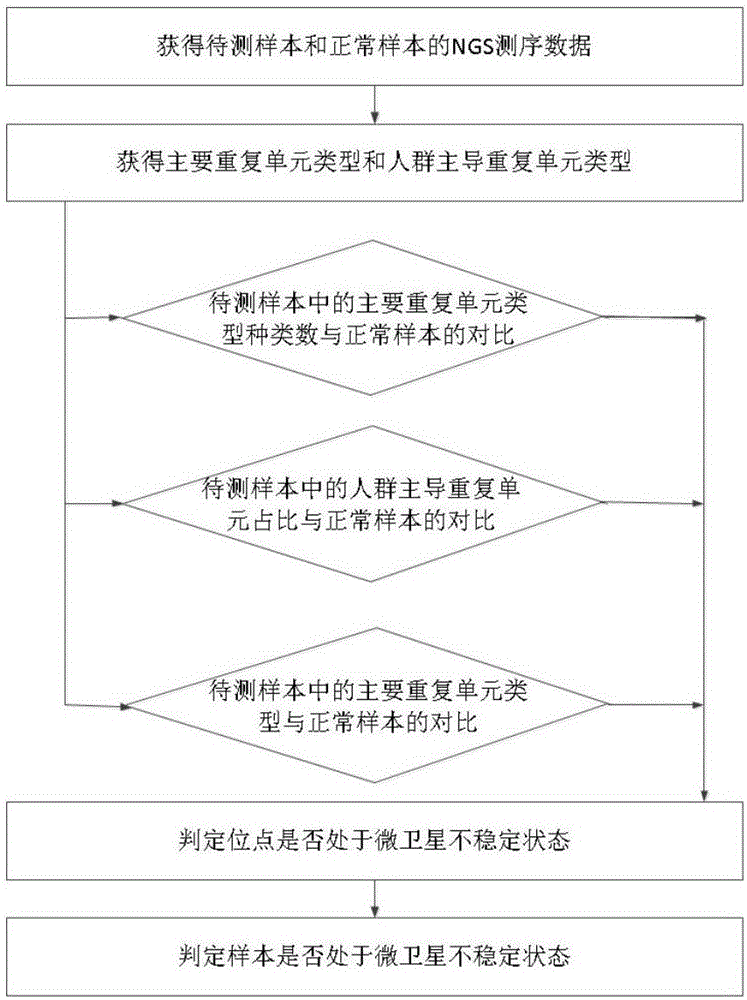
[0122] The preliminary screening of embodiment 1 locus
[0123] In the following, the present invention demonstrates the application of the analysis process and the MSI site screening method with examples. We performed high-throughput sequencing on the tumor tissue samples of 2,000 Chinese individuals suffering from solid tumors and the corresponding negative control samples of whole blood. The target genomic interval of the detection was the whole exon region of 422 cancer-related genes, and Intronic regions of some common gene fusions. The detection uses the liquid phase capture method to enrich the target DNA. The sequencing process is a common next-generation sequencing method, and its brief description is as follows: extract DNA from tissue samples and whole blood samples of each patient to obtain genomic DNA; Fragmentation to 200-350 base pairs; end repair, addition of adenine, library adapter ligation and other operations on fragmented DNA molecules; obtained DNA libr...
Embodiment 2
[0130] Example 2 Data Analysis of the Unstable State of Microsatellite Sites
[0131] Whole blood samples from 100 healthy people in Example 1 and 163 colorectal cancer clinical samples that had undergone Promega PCR microsatellite detection were used to perform sequencing analysis of microsatellite loci, and the sequencing process was carried out on an illumina next-generation sequencer Carried on.
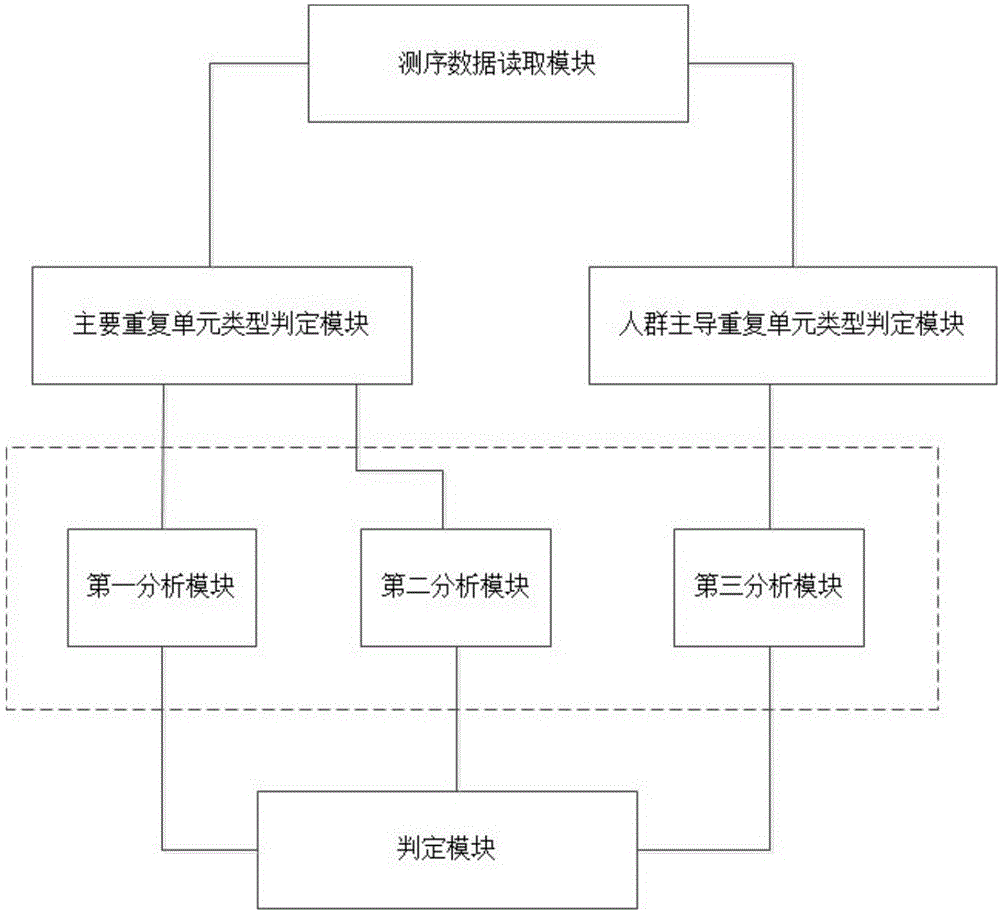
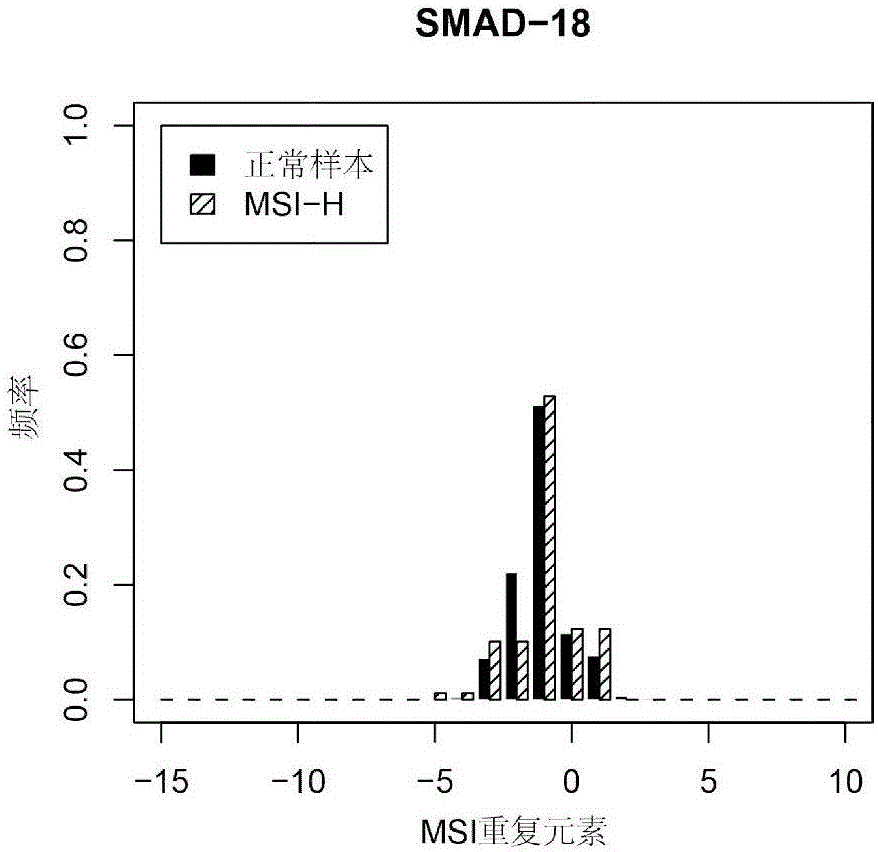
[0132] First, after processing the off-machine sequencing data of normal population and patient samples, reads that can cover 22 MSI loci are found, and then these reads are classified according to the number of single base repeats in the microsatellite loci. Classes and numbers accumulate. The main repeat unit types at each site corresponding to normal samples and patient samples were counted, and the population-dominated repeat unit types on all normal samples were counted. The average value and standard deviation of the main repeat unit types on the 22 MSI sites were counted...
Embodiment 3
[0142] The microsatellite instability analysis of embodiment 3 site combination
[0143] In order to demonstrate the superiority of the 22 microsatellite instability sites combined with biological indicators proposed by the present invention, the 22 microsatellite sites obtained by screening were compared with the 22 randomly selected sites in the remaining sites in the 96 candidate sites. sites, compared in terms of accuracy in defining microsatellite instability in patients.
[0144] Control Experiment 1: Figure 6 22 randomly selected microsatellite instability points (numbered in Table 2 are respectively 39, 88, 43, 34, 25, 56, 63, 69, 42, 32, 28, 45, 59, 98, 44 , 50, 85, 99, 67, 53, 52, and 66 MSI sites), only the analysis results obtained from the determination condition of "the number of main repeat unit types". The classification of MSS, MSI-L, and MSI-H in the figure is based on the judgment results of the Promega kit, and each data point is 163 clinical samples t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com