Biomarker panel and methods for detecting microsatellite instability in cancers
A technology for biomarkers and biological samples, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, determination/inspection of microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of repeated scoring of single homopolymers, high cost, low sensitivity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
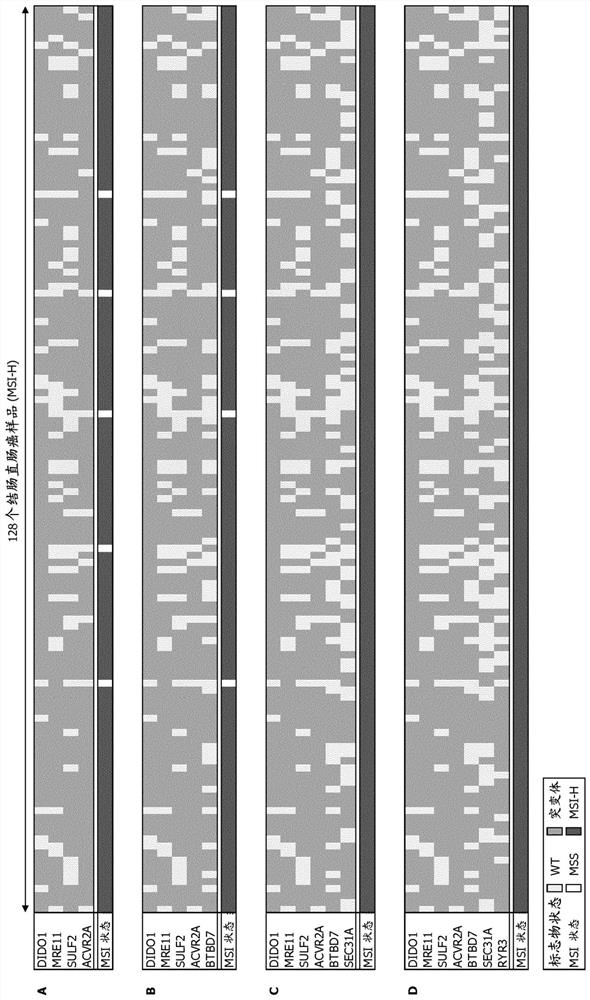
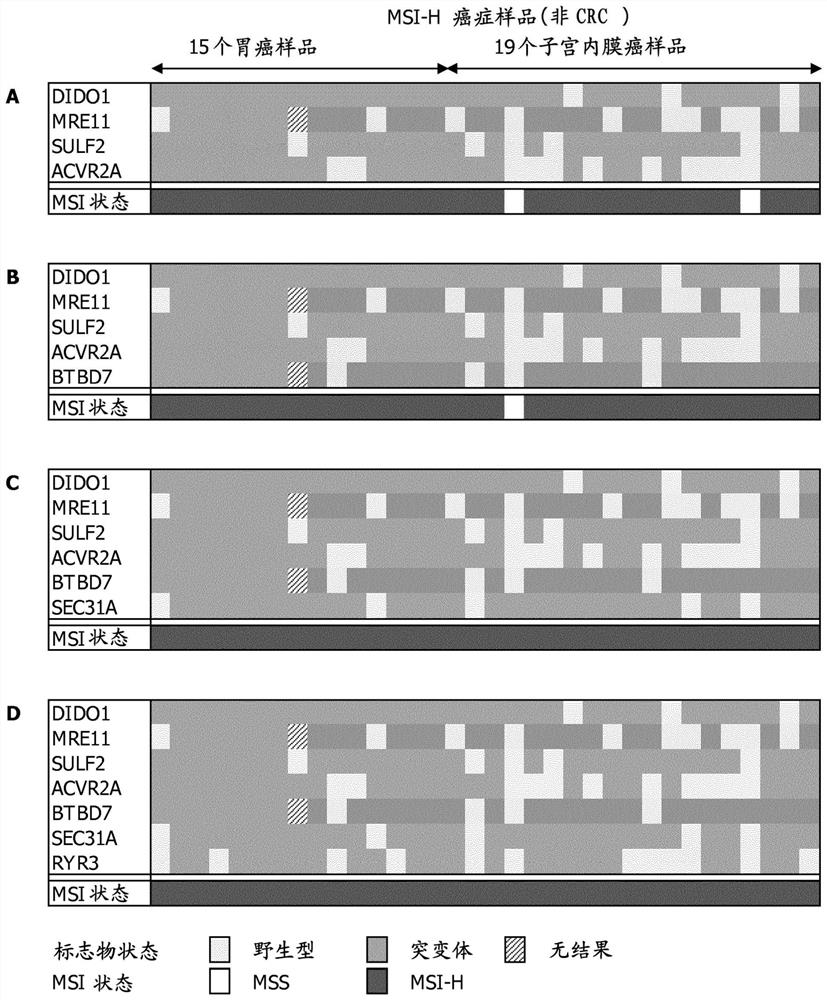
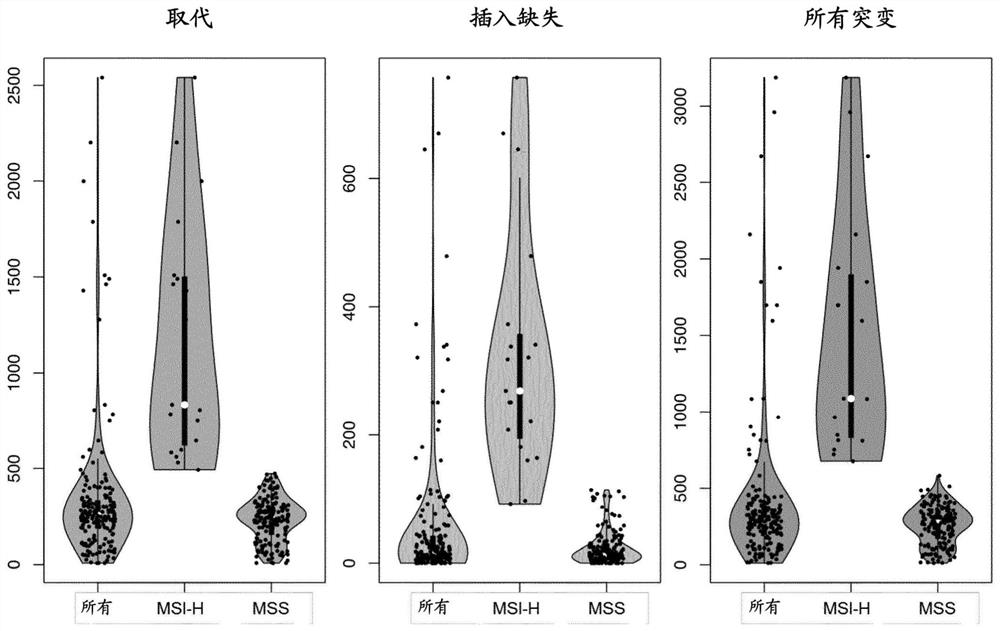
[0211] 1. Detection of microsatellite instability (microsatellite instability) in cancer samples with a new collection of highly sensitive markers Instability, MSI)
[0212] It is not easy to derive a minimum set of 4 markers from any given set of markers. For example, Zhao et al., 2014, eLife, described Sequenom analysis of 18 MSI-H samples using a panel of 59 markers revealed that the markers were called mutants in an average of 44.26% of the samples. Despite the high performance of this large panel of markers in detecting MSI status, a random set of 4 selected markers derived from it was less effective than the core set including ACRV2A, DIDO1, MRE11, SULF2 proposed here. Theoretical performance is much worse. Such randomly selected panels are additionally susceptible to the disadvantage that they may contain markers that show race-dependent differences in homopolymeric regions, such as that observed for the marker TMEM65 for the Caribbean population. This discrepancy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com