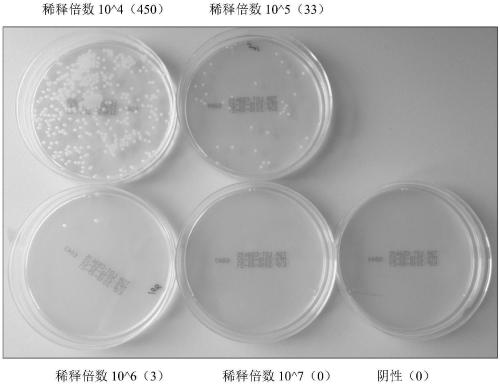
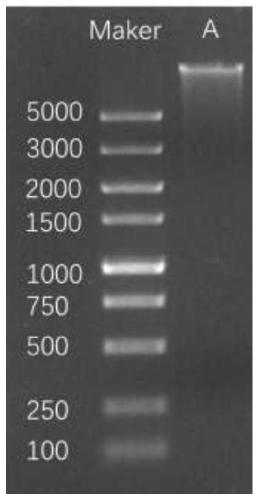
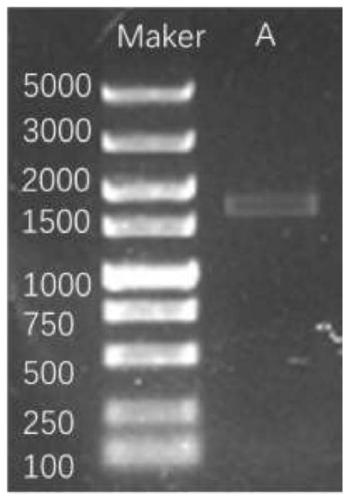
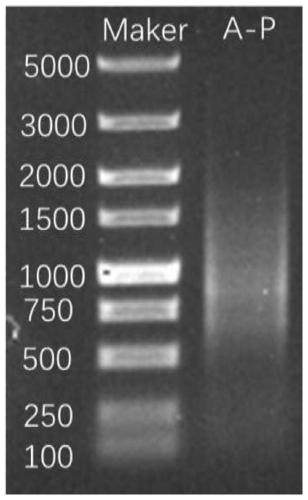
Patents
Literature
33 results about "Bacterial 16S" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
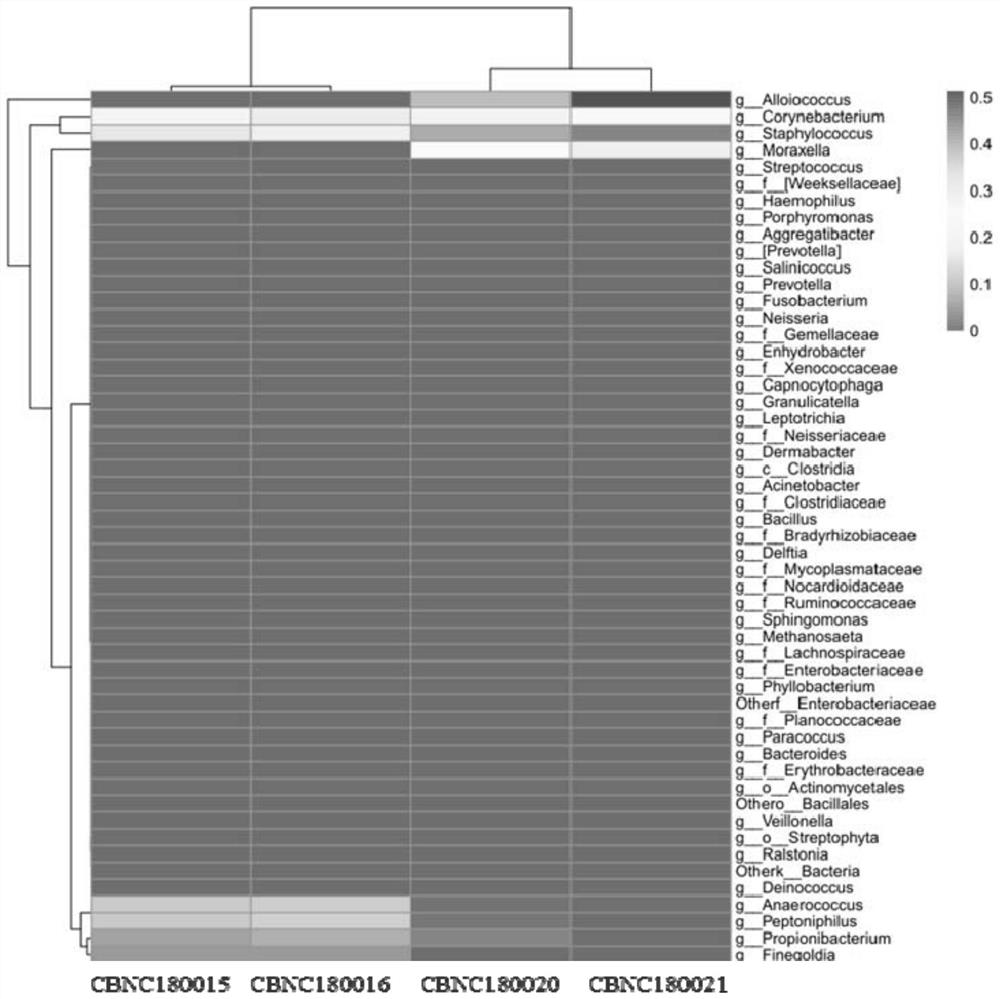
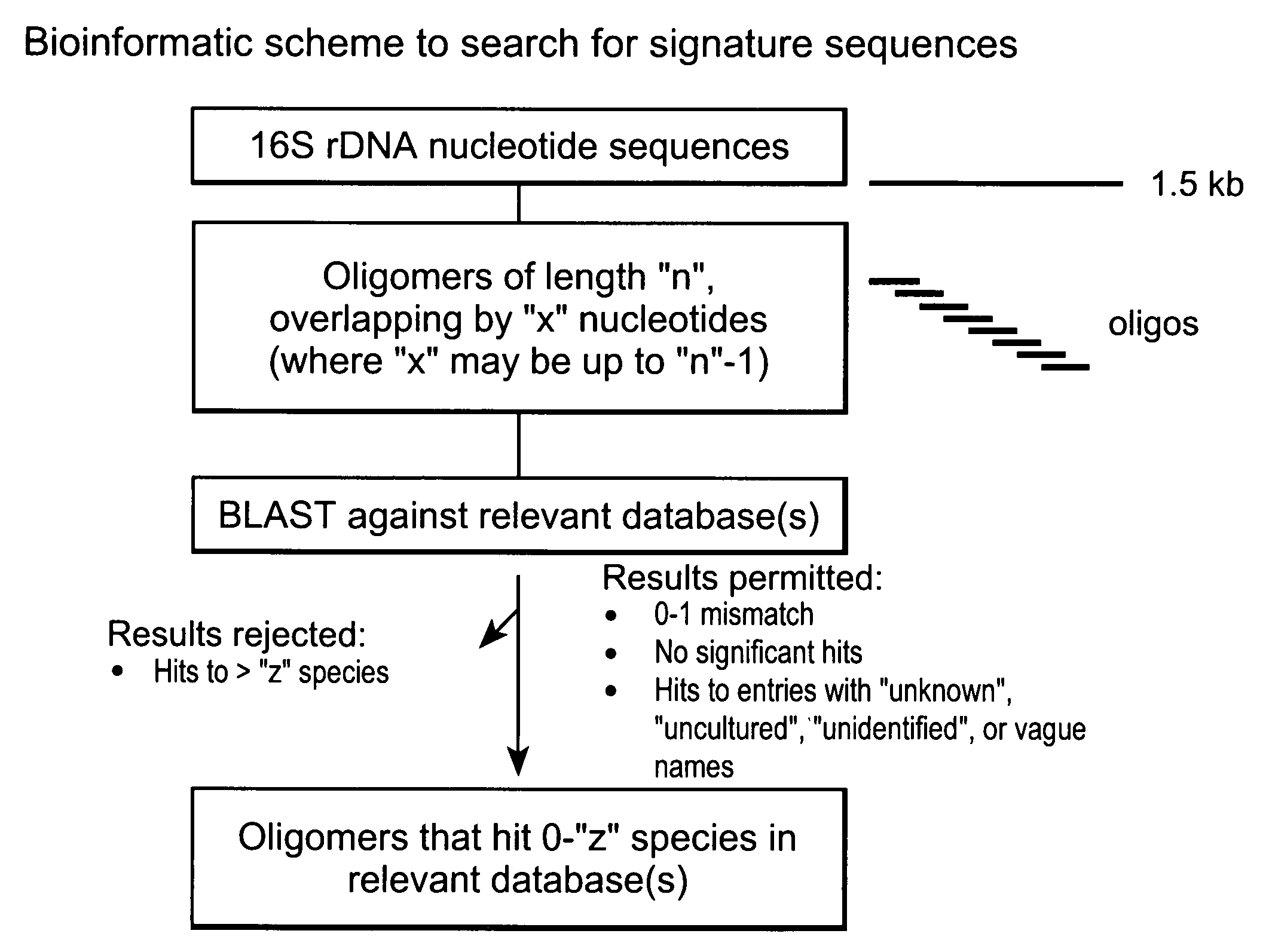
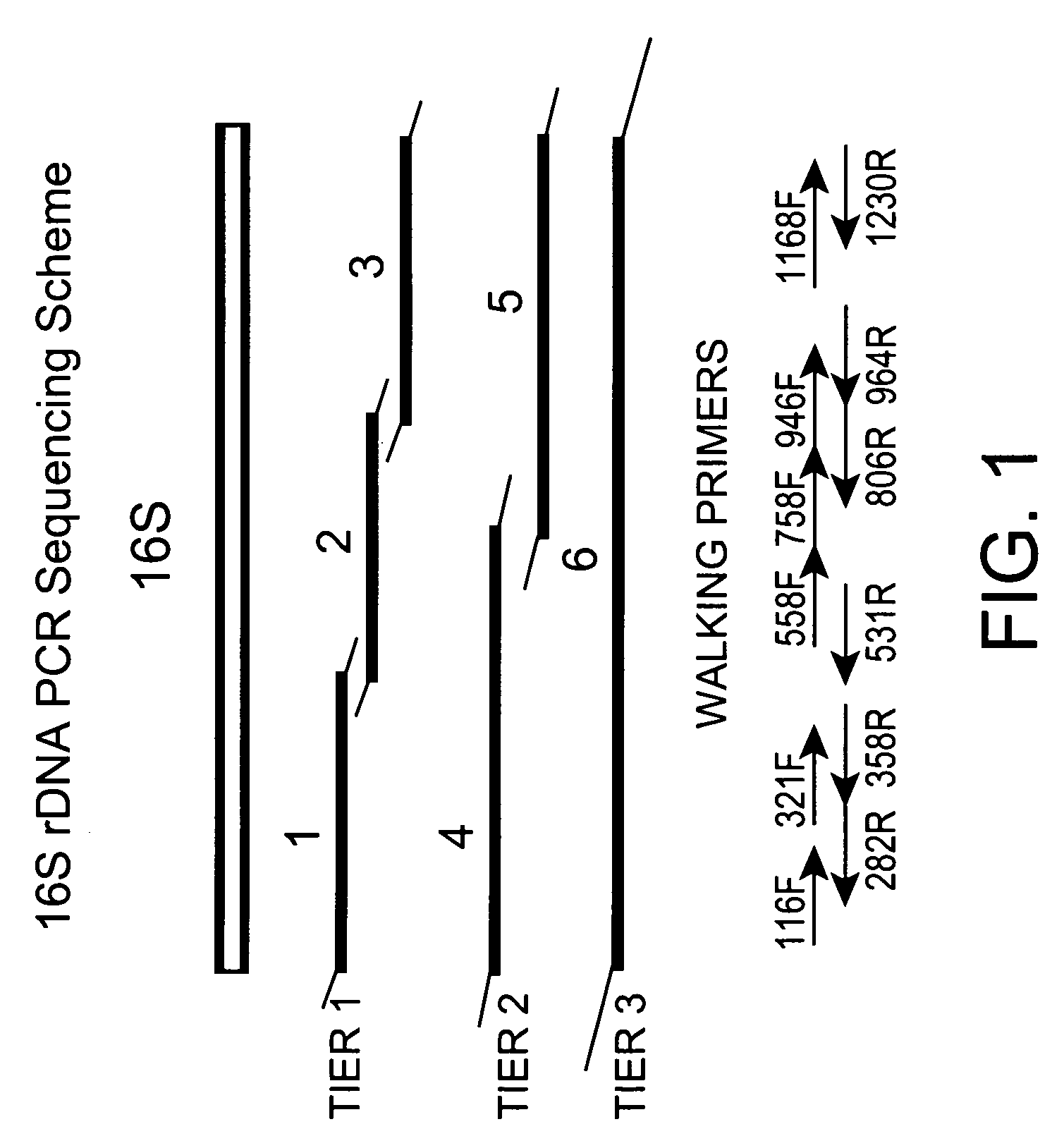
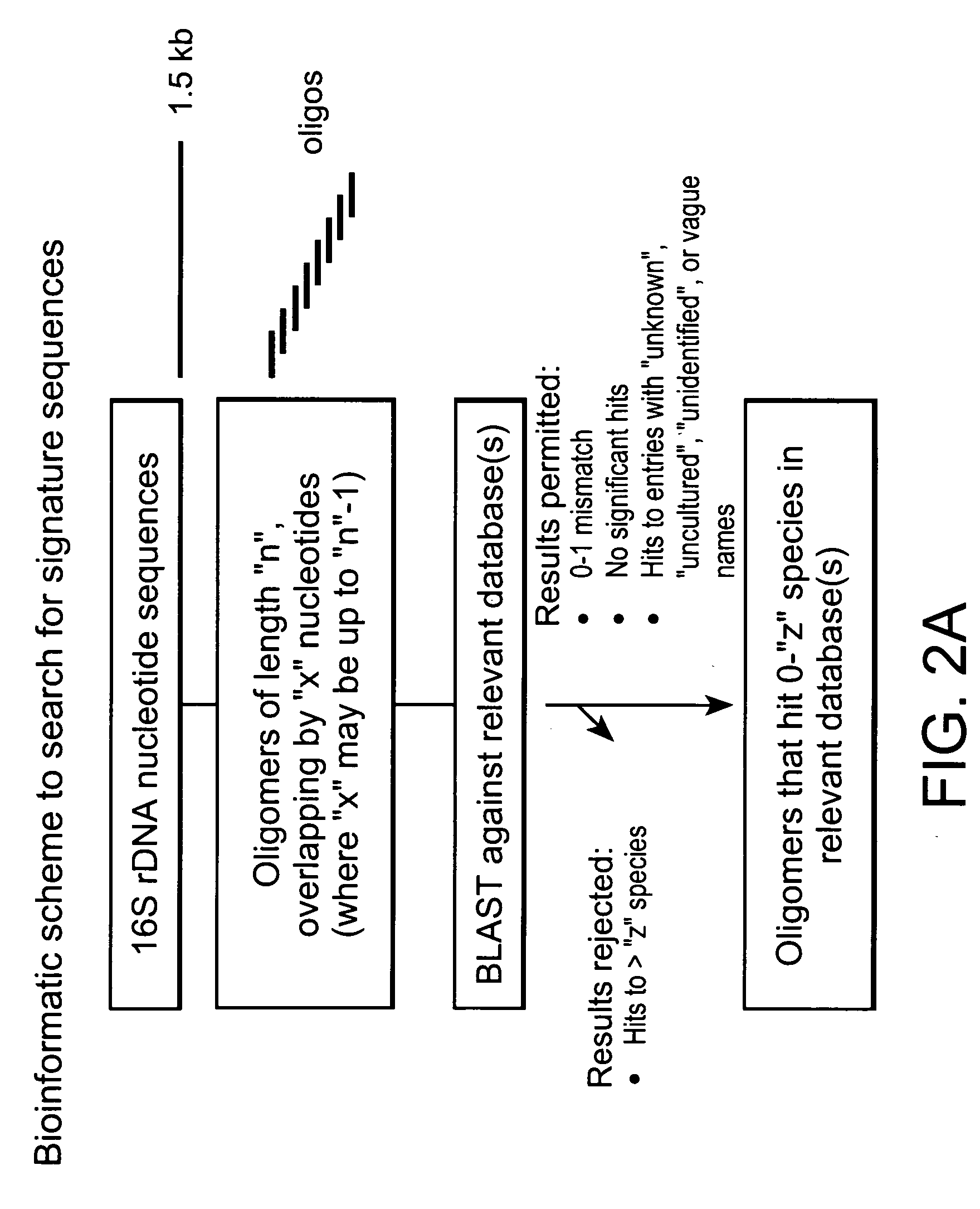
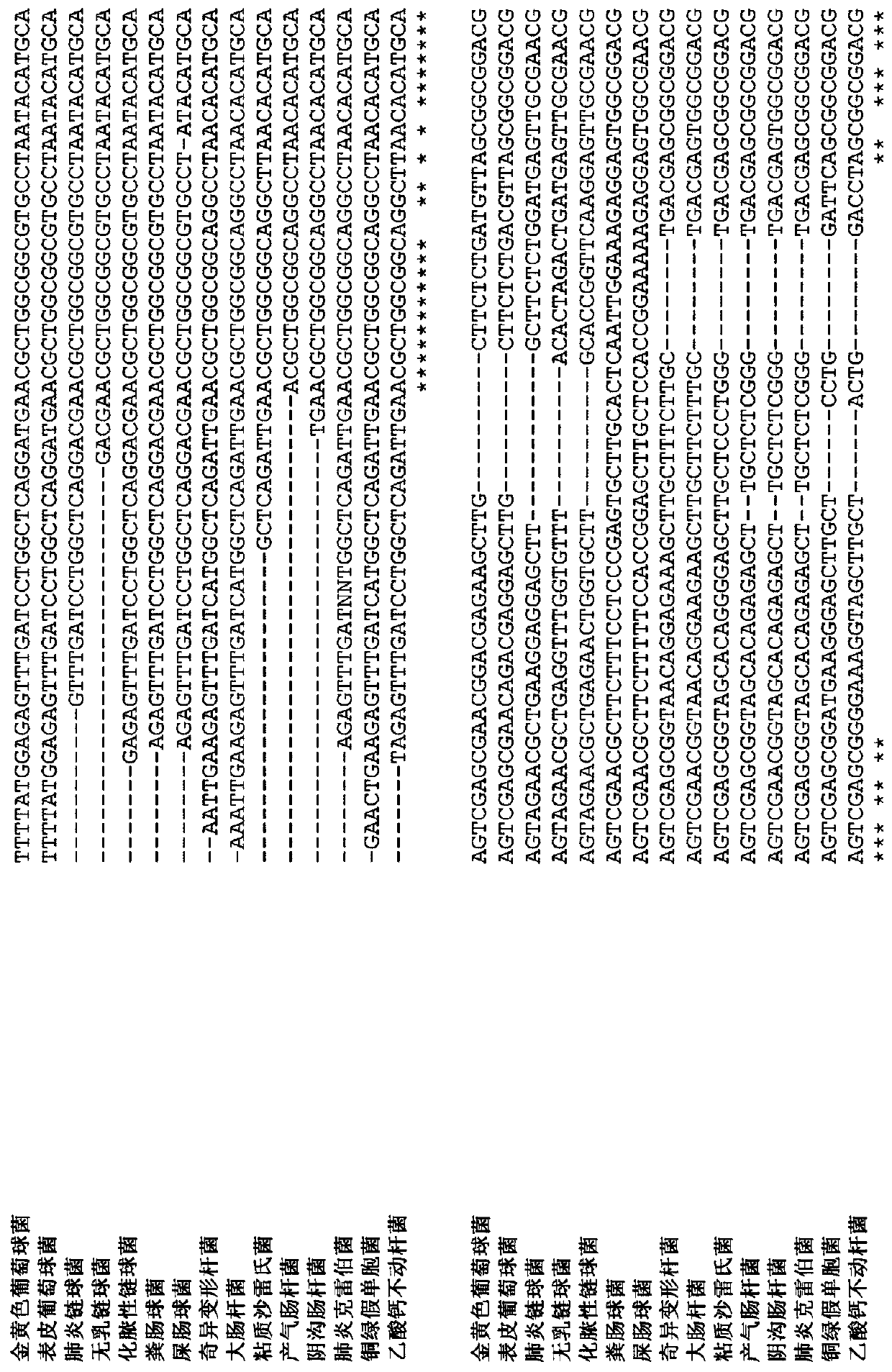
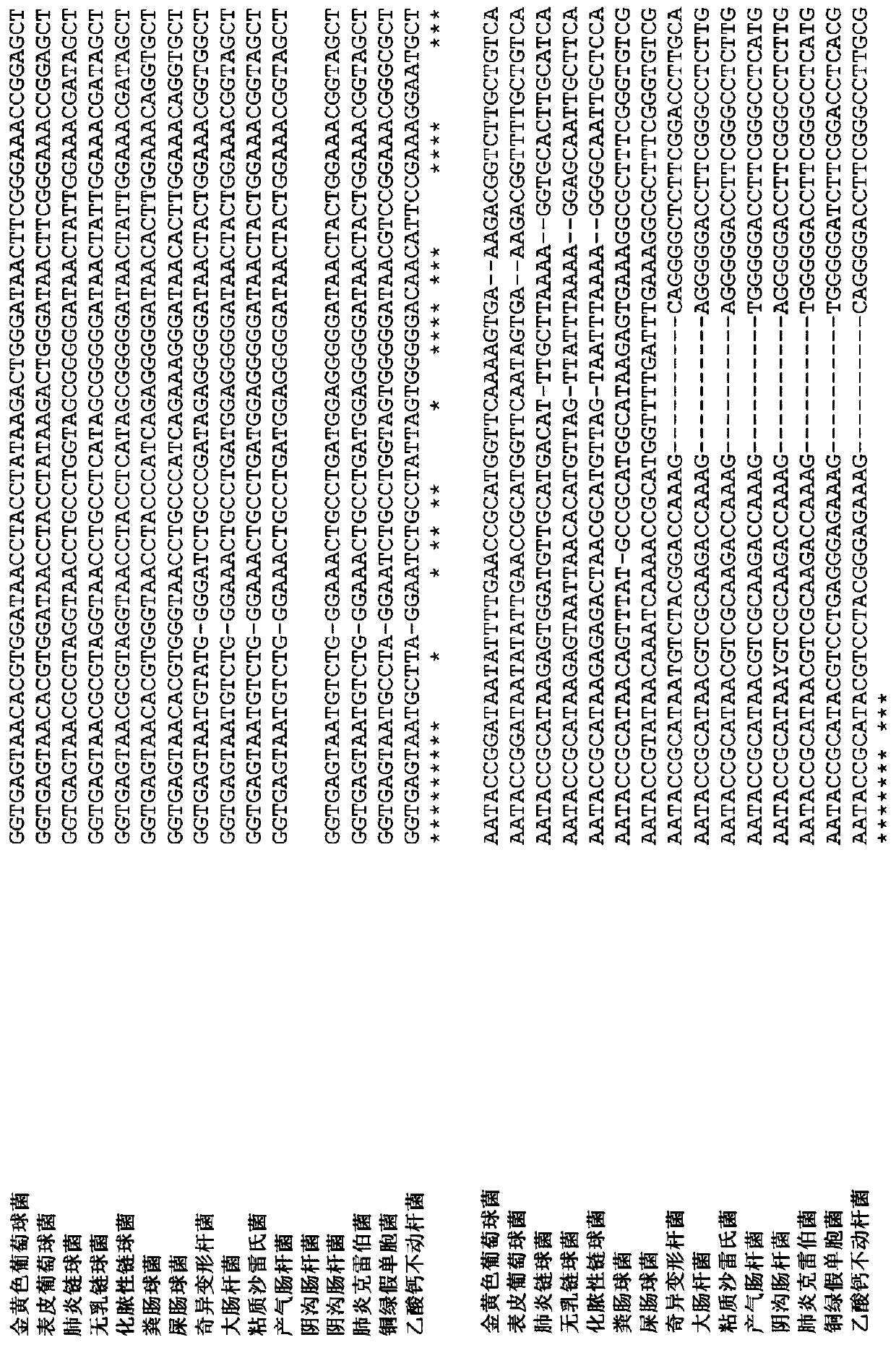
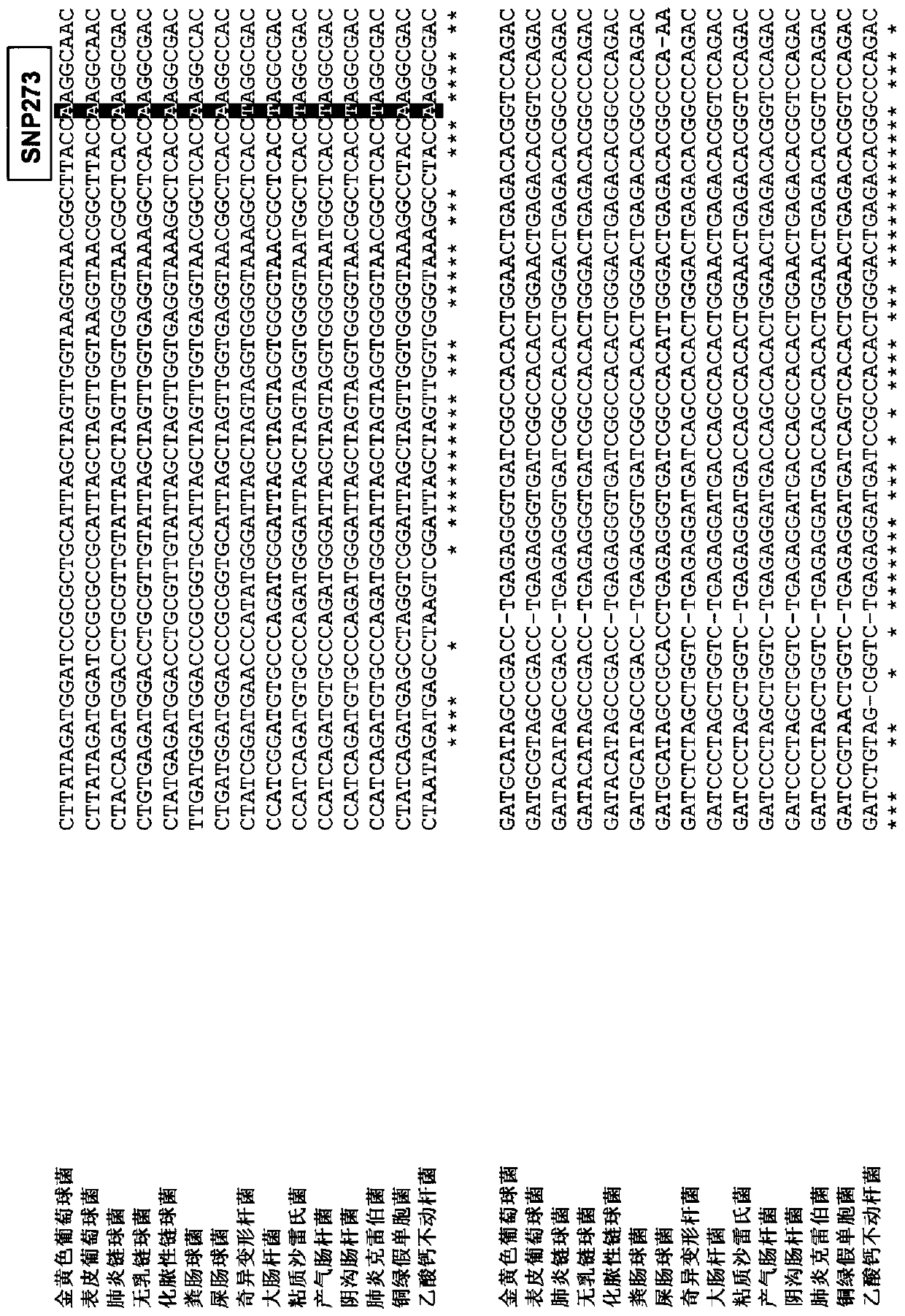
Genus, group, species and/or strain specific 16S rDNA sequences
InactiveUS20060046246A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismStrain specificity
Materials and methods for identifying unique sites in bacterial 16S and 23S rDNA are provided, as well as specific unique sequences of 16S rDNA in select bacteria. The distinguishing moieties will enable rapid differentiation between families, genera, groups, species, strains, subspecies, and isolates of microorganisms. Such differentiation can be performed by using rapid screening kits in combination with in silico analysis for diagnostic, prognastic, epidemiologic, phylogenetic, and other purposes.
Owner:BIOMERIEUX INC +1
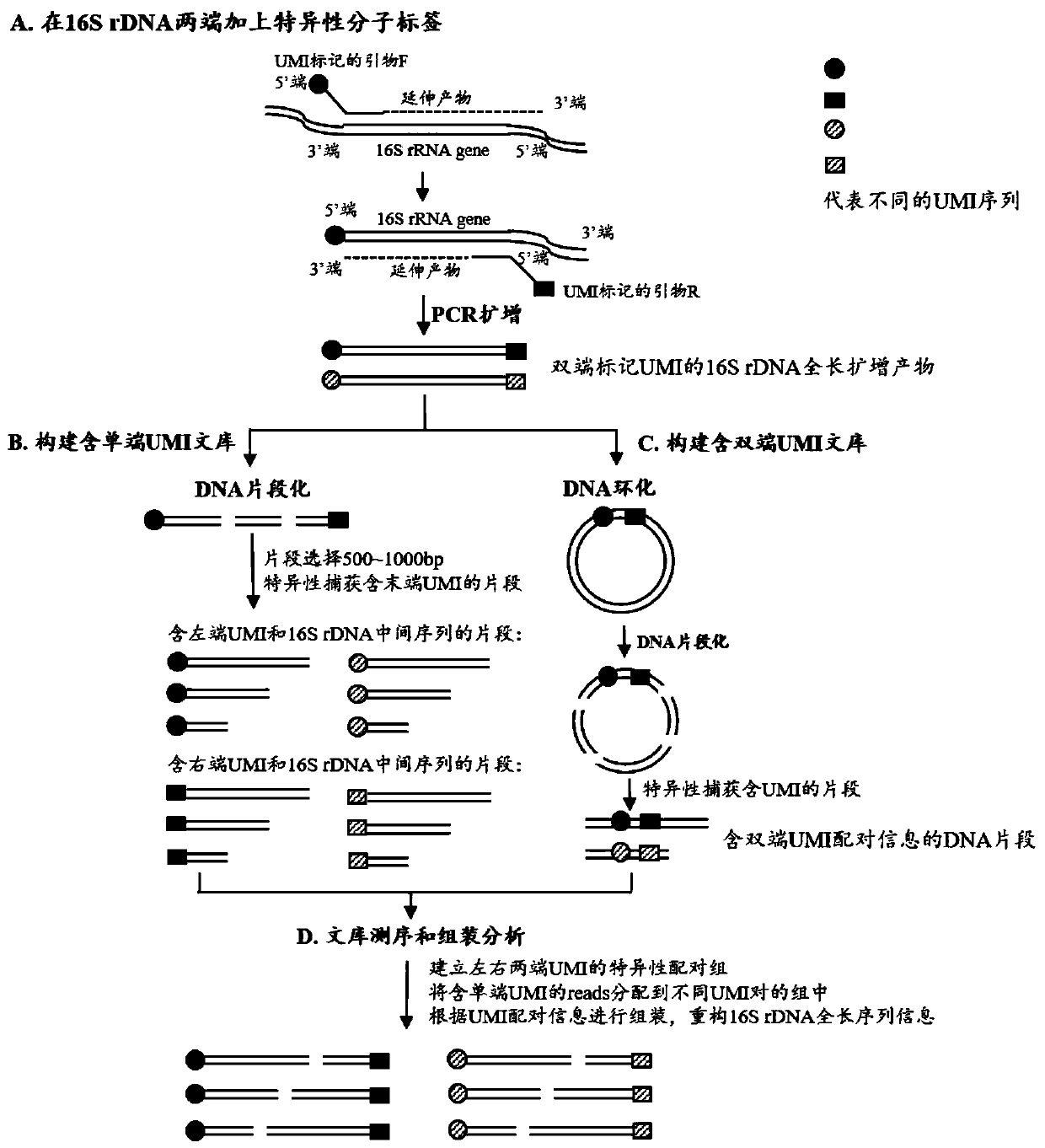
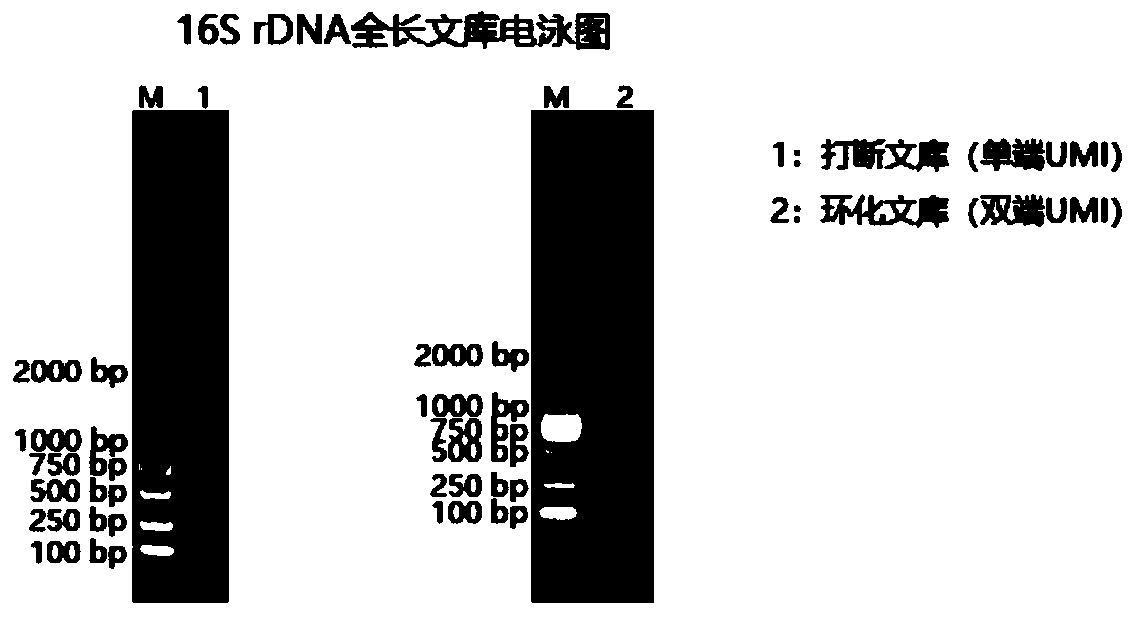
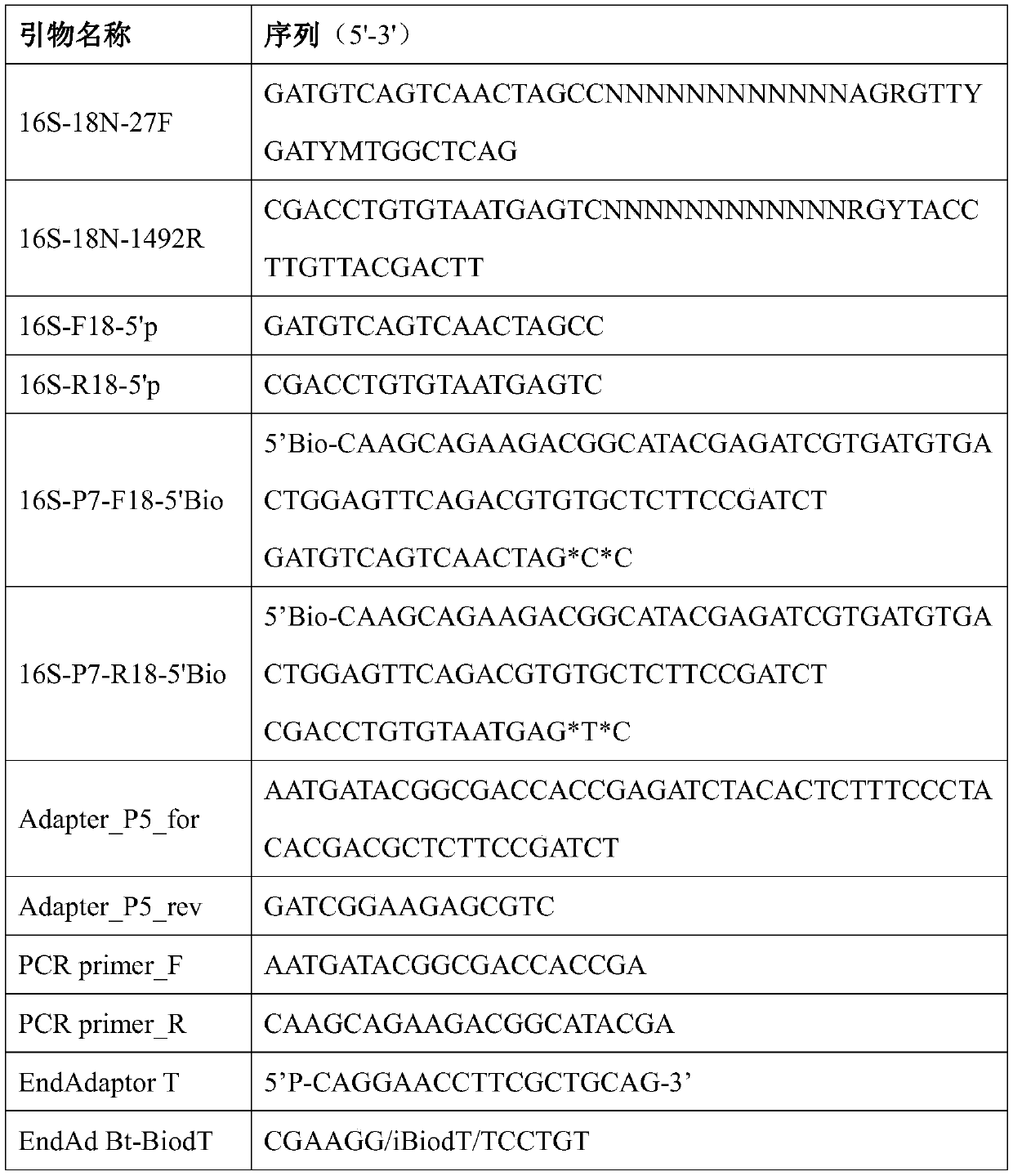
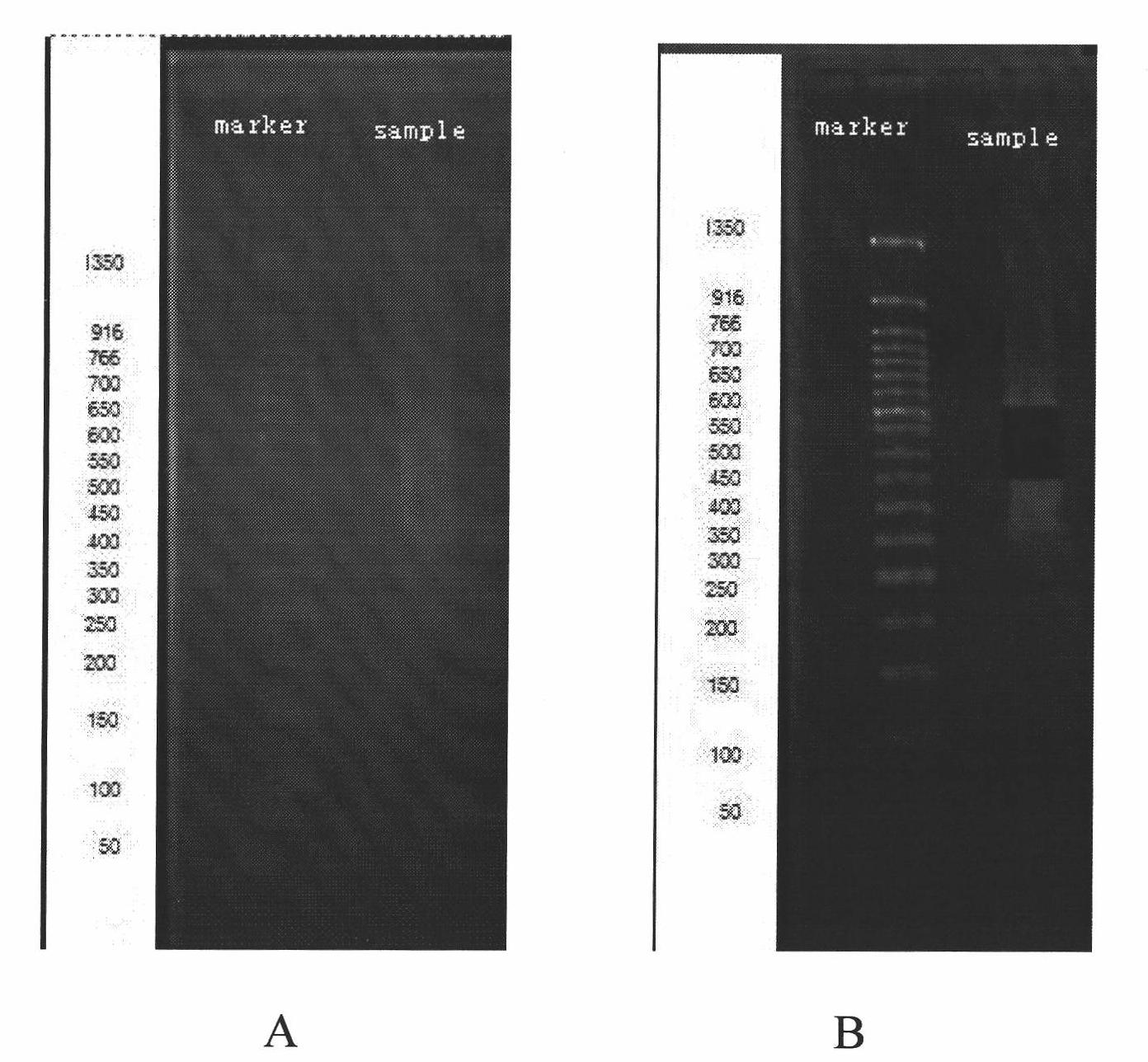
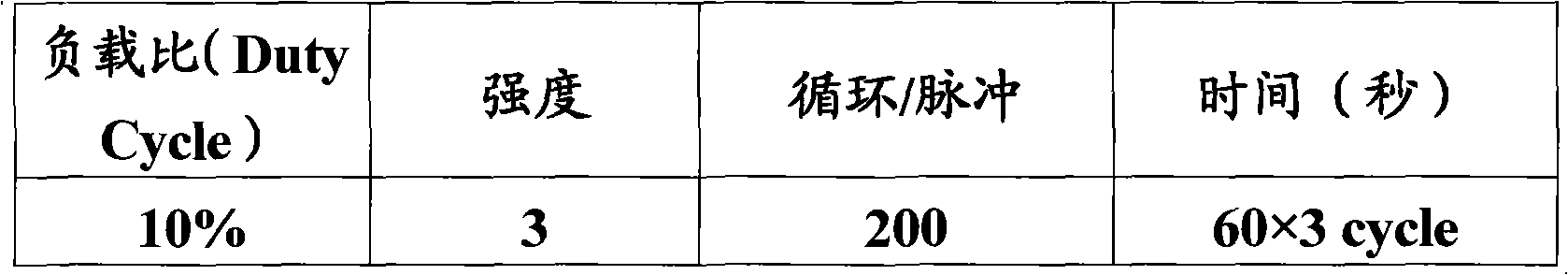
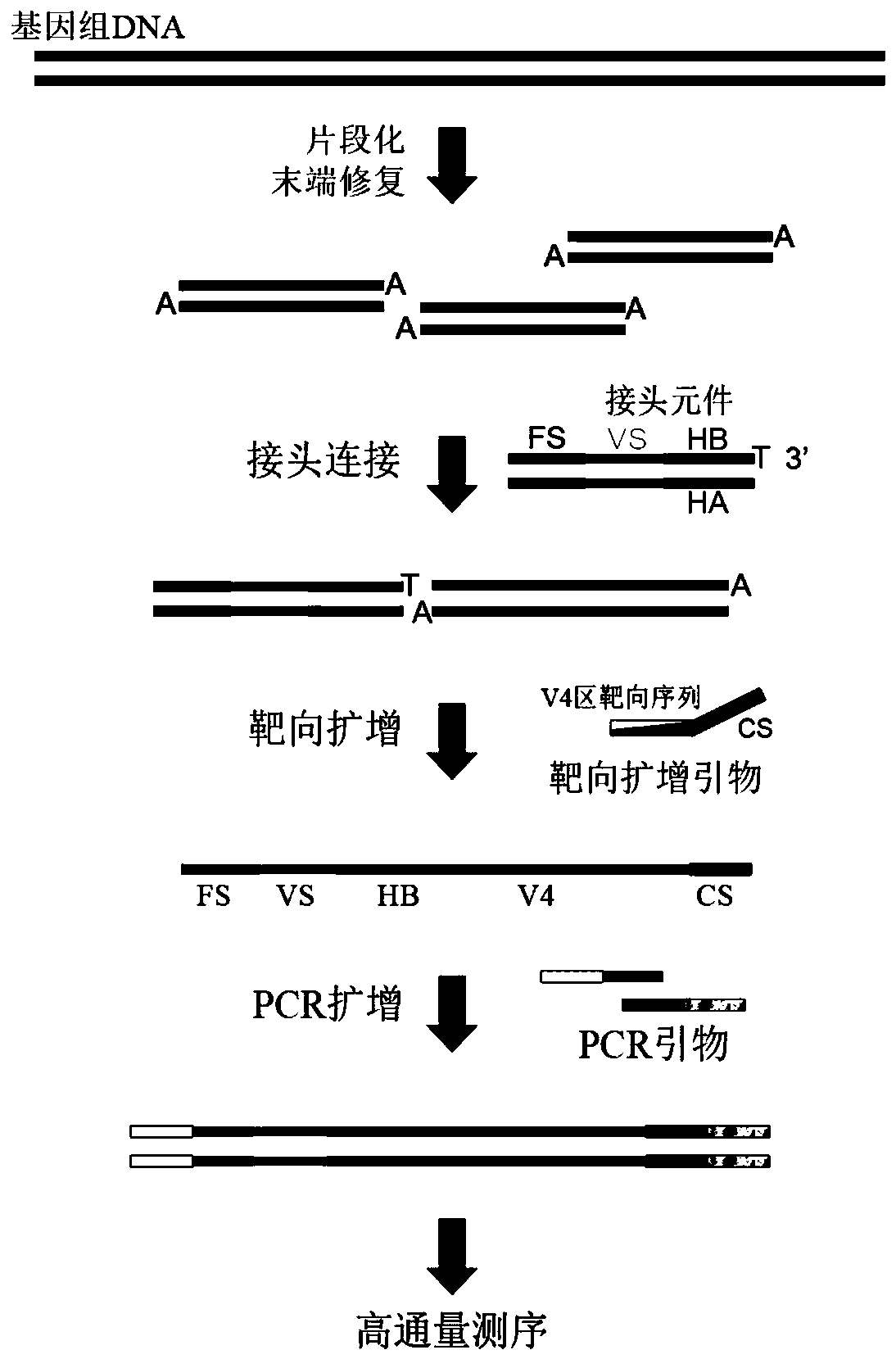
Method for constructing bacterium 16S rDNA overall-length high-throughput sequencing library
PendingCN110004210AHigh sequencing throughputLower Sequencing CostsMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationMicroorganismBacterial 16S
The invention relates to a method for constructing a bacterium 16S rDNA overall-length high-throughput sequencing library, and relates to the field of microorganism high-throughput sequencing. The method comprises the steps of firstly, adding unique molecular identifiers (UMIs) which are composed of random base groups to the two ends of each 16S rDNA template molecule, conducting PCR amplificationto obtain multiple copied 16S rDNA overall-length amplicons with two ends containing specific UMIs, randomly breaking and connecting joints of the sequencing library, and conducting paired-end sequencing to obtain the UMI sequences and corresponding 16S rDNA fragment sequences; besides, through cyclizing of the 16S rDNA overall-length amplicons and sequencing, obtaining UMI pairing information oftwo ends of the same molecule; conducting reads assembly according to the same UMI and pairing UMI information to increase the splicing length accordingly, and finally conducting assembly to obtain 16S rDNA overall-length sequence information. The method is low in cost, high in accuracy and suitable for high-throughput sequencing platforms; meanwhile, the method can effectively eliminate the influence of PCR amplification preferences, amplification errors and sequencing errors through the UMIs, and thus the bacterium population abundance in a sample is more precisely quantified.
Owner:杭州进一生物科技有限公司
Method for detecting enteritis pathogenic bacteria
ActiveCN102154450AAvoid damageCause drug resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesRibosomal DNA
The invention relates to a method for detecting bacteria, in particular to a method for detecting enteritis pathogenic bacteria. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) extracting DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of one or more bacteria samples; (2) amplifying full length of 16S rDNA (ribosomal DNA) of a sample by using a primer of 16S rDNA of bacteria; (3) breaking an amplified PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) product; (4) repairing ends of the broken product from each bacteria sample and connecting deoxyadenosine at the end 3' of the product, and then connecting different PCR-free joints; (5) sequencing a connection product by using a second-generation sequencing technology to obtain a sequence of the connection product; and (6) comparing the sequence with 16S rDNA reference sequences of all existing bacteria to determine types of bacteria existing in each sample.
Owner:深圳华大因源医药科技有限公司
Multiple PCR primer pair combination for bacterium determination and determination method
InactiveCN106244699ASensitive identificationEfficient identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMicrobiologyBacterial 16S
The invention belongs to the field of biological technologies and provides a multiple PCR primer pair combination for bacterium determination which can be used for next generation sequencing of bacteria and a bacterium determination method. The primer pair combination is utilized to amplify V1-V8variable zones of a bacterium 16S rDNA, effectively obtains variable zone sequences; the bacterial species can be sensitively and efficiently determined by combining next-generation sequencing and bioinformatic analysis.
Owner:上海华点云生物科技有限公司
Joint element for 16S rDNA variable-zone quantitative sequencing library construction and library construction method
InactiveCN109797438ACorrect amplification errorsCorrect sequencing errorsMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary linkersMicroorganismPhosphate
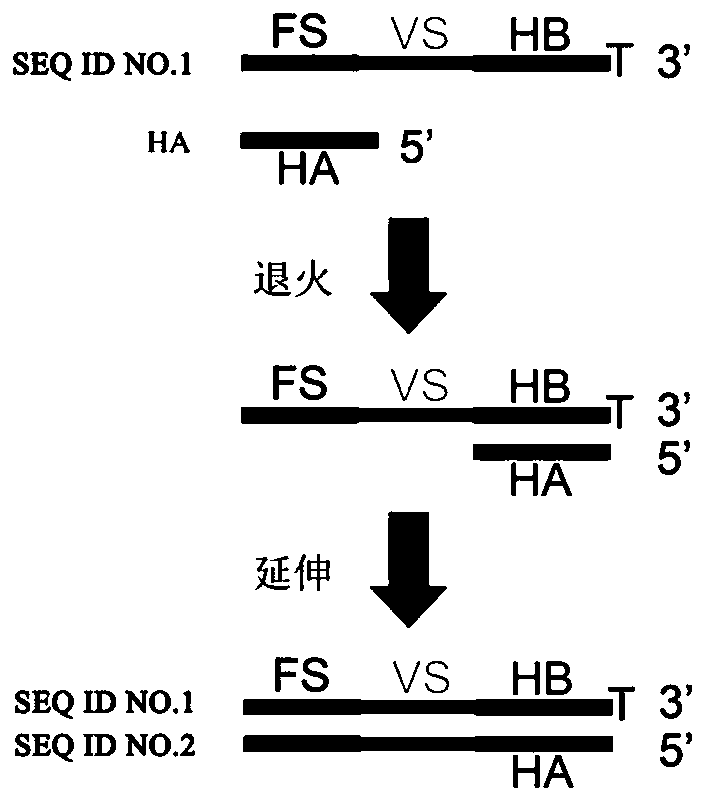
The invention discloses a joint element for 16S rDNA variable-zone quantitative sequencing library construction and a library construction method. Firstly, a double-strand DNA fragment is subjected toblunt end repair, a phosphate group is added to the 5' terminal, adenine A is added to the 3' terminal, and the joint element is connected to the processed DNA fragment through a binding reaction, wherein the joint element comprises two complementary paired DNA oligonucleotide chains, the sequence of one chain from 5' to 3' sequentially comprises a fixed sequence FS, a variable sequence VS and ahinge sequence B, the 3' terminal is a prominent basic group T, and the sequence and the other complementary sequence form a double-strand structure with one terminal provided with the single prominent basic group T. The joint element is a mixture of double-strand DNA containing variable sequences VS of different ucleotide sequences which are randomly distributed and combined. By means of the joint element, a quantitative sequencing library can be constructed from variable zones of bacterium 16S rDNA, microorganisms in samples are quantitatively detected, and identification of bacterial strains is achieved.
Owner:武汉康测科技有限公司
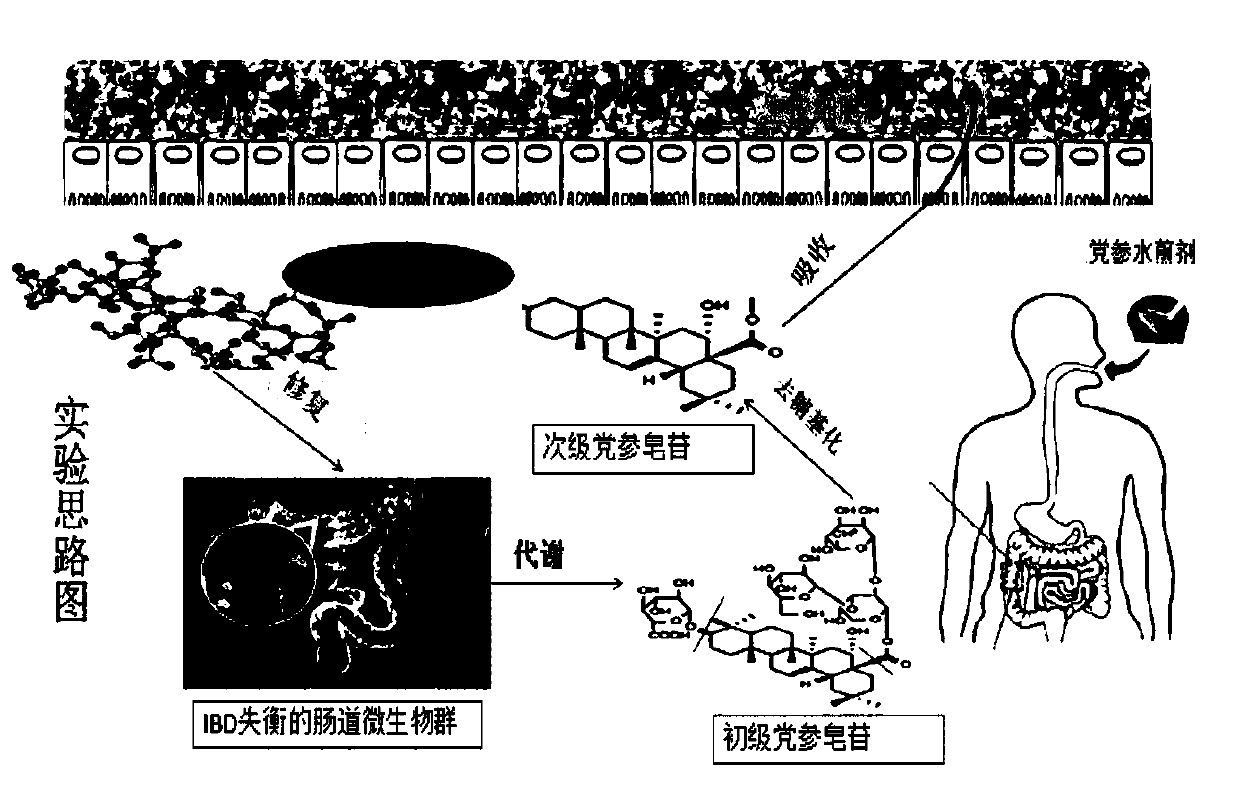
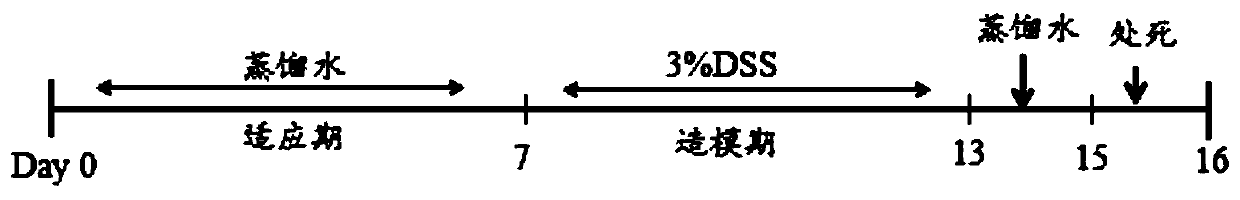
Application of codonopsis pilosula polysaccharide as medicine for regulating intestinal flora of human body
InactiveCN109745336AImprove macroscopic pathologySimple structureOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemDiseaseBacteroides
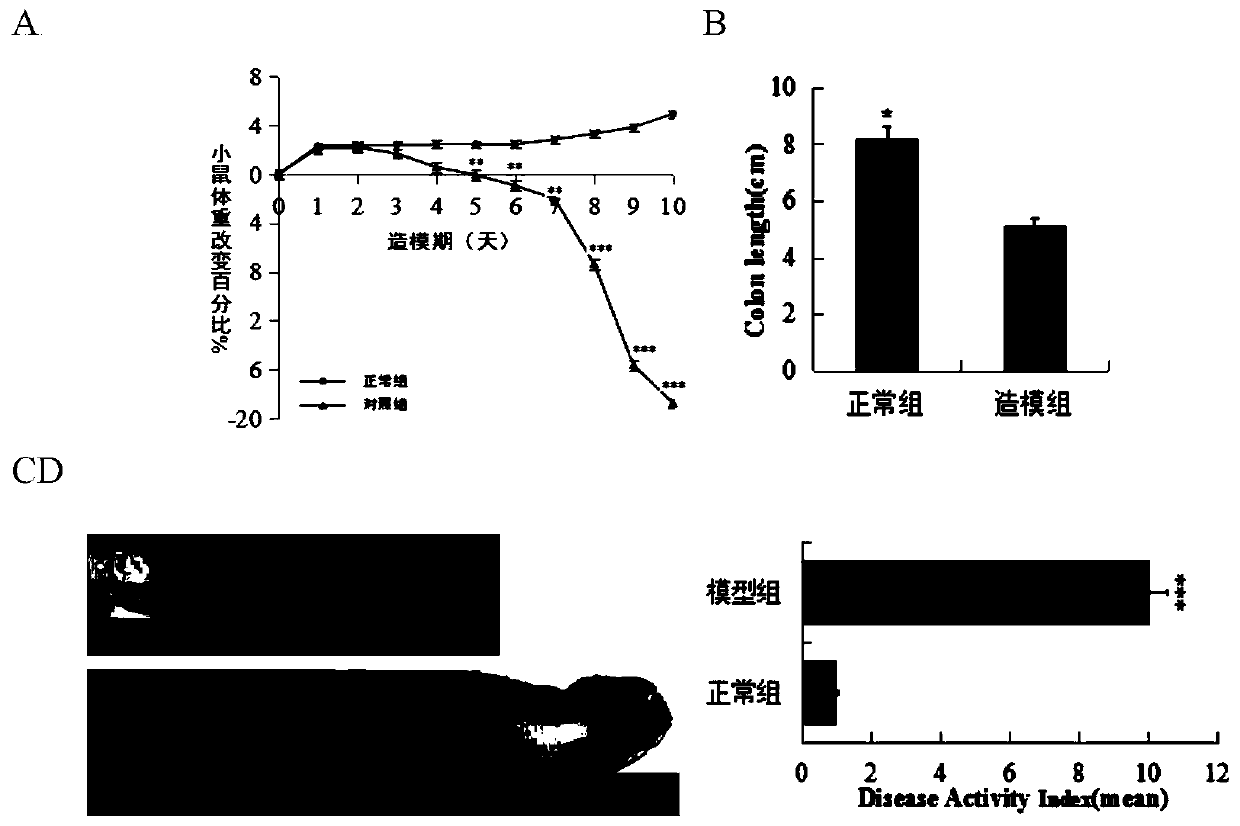
The invention provides an application of codonopsis pilosula polysaccharide as medicine for regulating intestinal flora of human body, namely the application of codonopsis pilosula polysaccharide as medicine, food or health products for preventing colitis. An acute colitis mouse model is established by using fructo-oligosaccharide, codonopsis pilosula polysaccharide and codonopsis pilosula saponinto be respectively prevented in a healthy mouse model for 21 days and adopting 3% dextran sodium sulfate to be induced for 7 days. The remission of three drugs to macroscopical pathological symptomsof colitis is compared by evaluating changes of body weight, colon length, pathological index of disease, histological section and myeloperoxidase activity of experimental mice and the like. The regulation of drug on intestinal flora of colitis mice is investigated by using the Illumina MiSeq 250 sequencing platform based on the variable region of 16S V3-V4, and dominant bacteria in each drug intervention group are identified, which shows the absorption of the highest exposure amount of monomer saponin in codonopsis pilosula saponin in serum and the cecum, clarifies the mechanism that codonopsis pilosula polysaccharide plays a role in the treatment of diseases by changing the action of intestinal flora on saponin metabolism.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Multiple-PCR rapid detection method of salmonella and escherichia coli
ActiveCN104711365AReduce the proportionHigh densityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliNucleotide
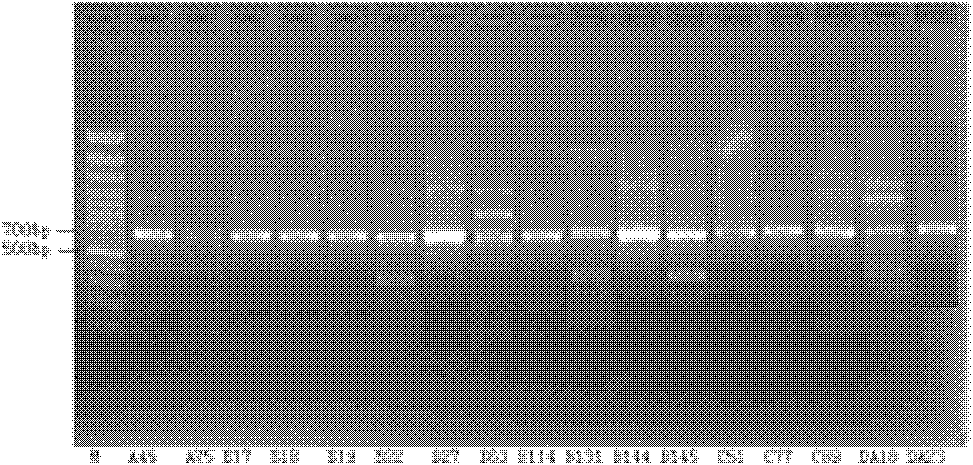
The invention discloses a multiple-PCR rapid detection method of salmonella and escherichia coli. A primer for performing multiple-PCR rapid detection on salmonella and escherichia coli O78 comprises (1) a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO:2, SEQ ID NO:3, SEQ ID NO:4 and SEQ ID NO:5; or (2) a nucleotide sequence having the basic sequence homology with the nucleotide sequence in (1) and having the function as same as that of the nucleotide sequence in (1). According to the detection method, specific genes of salmonella and escherichia coli O78 and a part of sequences of bacteria 16s rDNA are amplified once by using the multiple-PCR technology, and a PCR amplification product is detected by means of agarose gel electrophoresis. According to the method, the problems of long period (4-7 days) of a traditional pathogenic bacteria detection technology, tedious and complicated operations and relatively-low specificity and sensitivity are solved.
Owner:青岛智测检验检测有限公司
Preparation method of endophytic bacterial diversity 16SrDNA amplicon
InactiveCN107312847AReduce the proportionImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationBacteroidesBarcode
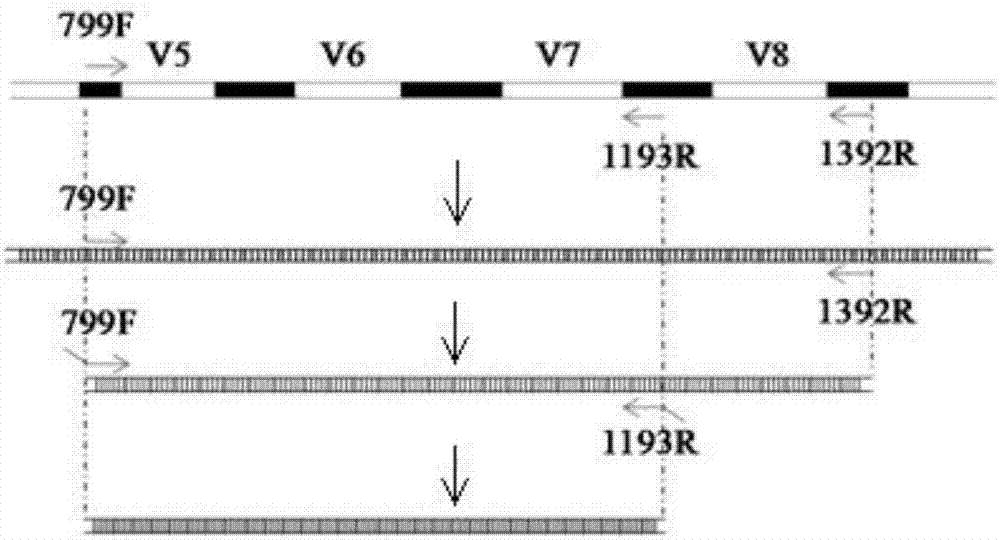
The invention provides a set of primers for high-throughput sequencing. The primers comprise a primer pair 799F / 1193R in allusion to V5-V7 variable fragments of an endophytic bacterium 16S rDNA and Barcode sequences connected with the 5' ends of the primer pair 799F / 1193R, wherein the sequence of 799F is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, the sequence of 1193R is shown in SEQ ID NO: 4, the Barcode sequence connected with the 5' end of the 799F is selected from sequences shown in SEQ ID NO: 5-28, and the Barcode sequence connected with the 5' end of the 1193R is selected from sequences shown as SEQ ID NO: 29-52. V5-V7 variable regions of the endophytic bacterium 16S rDNA are specifically amplified through two rounds of nested PCR, and the amplicon having the Barcode sequences at the 5' ends and applicable to the current second-generation high-throughput sequencing platform is obtained. After the adoption of the method provide by the invention for researching the endophytic bacterial diversity, the amplification efficiency of the endophytic bacterium 16S rDNA can be significantly improved, the proportion of host data in sequencing data is greatly reduced and the research cost is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI MAJORBIO BIO PHARM TECH
16S rDNA based preparation method of bacteria nucleic acid fingerprint characteristic spectrums and application thereof
InactiveCN103060431AValid identificationUndisturbedMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEnzymatic digestionSuper absorbent
The invention discloses a method for preparing bacteria 16S rDNA fingerprint spectrums. The method comprises the steps of PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification, SAP (super absorbent polymer) enzymatic digestion, transcription and nuclease digestion, purification, mass spectrometer detection and the like. A nucleic acid fingerprint spectrum database of common bacteria is created based on the method. According to the mass spectrum peak chart generated through experiments, the bacteria to be detected can be classified and identified and the results can be widely applied to the fields of bacteria classification and identification, genetic evolution analysis, drug resistance screening application, import and export inspection and the like.
Owner:向华
Analysis method for diversity of oral cavity flora and disease-associated flora marker
InactiveCN106636423AShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSaliva sampleFlora
The invention provides an analysis method for the diversity of oral cavity flora based on a second-generation high throughput sequencing technology and a disease-associated flora marker. The method comprises the following steps of (1) extracting a DNA of a to-be-detected saliva sample; (2) preparing a PCR reaction system, and carrying out PCR amplified reaction of V1-V2 regions of bacteria 16S rDNA, wherein the PCR reaction system comprises a PCR amplification template, a universal primer pair and the like; (3) carrying out detection of a target segment of a PCR product and purification of the PCR product; (4) carrying out second-generation high throughput sequencing on the purified PCR product and detecting the species of microorganisms in the saliva sample; (5) sequencing by using an Ion Torrent PGM sequencing system; and (6) carrying out bioinformatics analysis by using a FLASH, QIIME, usearch61. The diversity and the difference of the oral cavity flora of a patient are detected through the second-generation high throughput sequencing technology, so that the analysis method has the advantages that the composition and the functions of the flora can be more deeply analyzed in more detail by using the new-generation high throughput technology in comparison with a traditional flora detection method.
Owner:杨俊杰
Method for detecting aquatic animal pathogenic bacteria by using ribosome interoperonic region probe
InactiveCN1877327AAccurate identificationRapid identificationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesAquatic animal
The invention discloses a bacteria detecting technology which comprises designing special probes with biological information, including designing 34 pieces oligonucleotide as filtered probes and the corresponding PCR and hybridizing reacting conditions; enlarging via PCR and marking bacteria 16s-23srRNA gene interval array with Digoxin, and hybridizing the PCR products and a group of special oligonucleotide probes; after enzyme-linked immunoassay color-rendering, identifying whether has aquatic infectious pathogeny bacteria from the sample.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV +1
Antisense antibacterial method and composition
The invention relates to compositions comprising oligomers antisense to bacterial 16S or 23S rRNA and capable of selectively modulating the biological activity thereof, and methods for their use. More particularly, the invention relates to antisense oligomers directed to 16S or 23S rRNA found in one or more particular bacteria, or generally conserved among bacteria in general, and to pharmaceutical compositions and methods of treatment comprising the same.
Owner:AVI BIOPHARMA
Detection method of germs in traditional zymotic soybean paste
InactiveCN101619355AAvoid churnDo not change the contentMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMicroorganismMicrobiology
The invention relates to a detection method of germs in soybean paste, in particular to a detection method of germs in traditional zymotic soybean paste, solving the problem that the prior PCR-DGGE technology can not accurately detect the germs in the traditional zymotic soybean paste. The detection method comprises the following steps: (1) the DNA extraction of a germ common gene group of a traditional zymotic soybean paste sample; (2) a V3 section of 16S rDNA of PCR amplified germs; and (3) the PCR-DGGE of the germs. The method of the invention thoroughly clear up other contents of the traditional zymotic soybean paste except microbial cells while avoiding the loss of the species and the amount of microorganism whenever possible, and the whole detection process does not change the DNA content, reduces the final analysis bias and ensures the precision of a detection result.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis technique for detection of bacterial community structure in rice wine wheat koji
InactiveCN102277432AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBacteroidesCommunity structure
The invention discloses a method for detecting the bacterial community structure in rice wine wheat koji by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis technology. The genomic DNA of the wheat koji sample is extracted by the benzyl chloride method, the bacterial 16S rDNA V3 region is amplified by PCR, and the DGGE electrophoresis band is separated. Secondary PCR and T-cloning after rubber tapping and recovery, selection of positive clones for DGGE band comparison, sequencing after correct comparison, and obtaining relevant microbial information from GenBank. The invention is simple, fast and has good repeatability, and has good guiding significance for analyzing the dominant bacteria and functional microorganisms in rice wine wheat koji.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
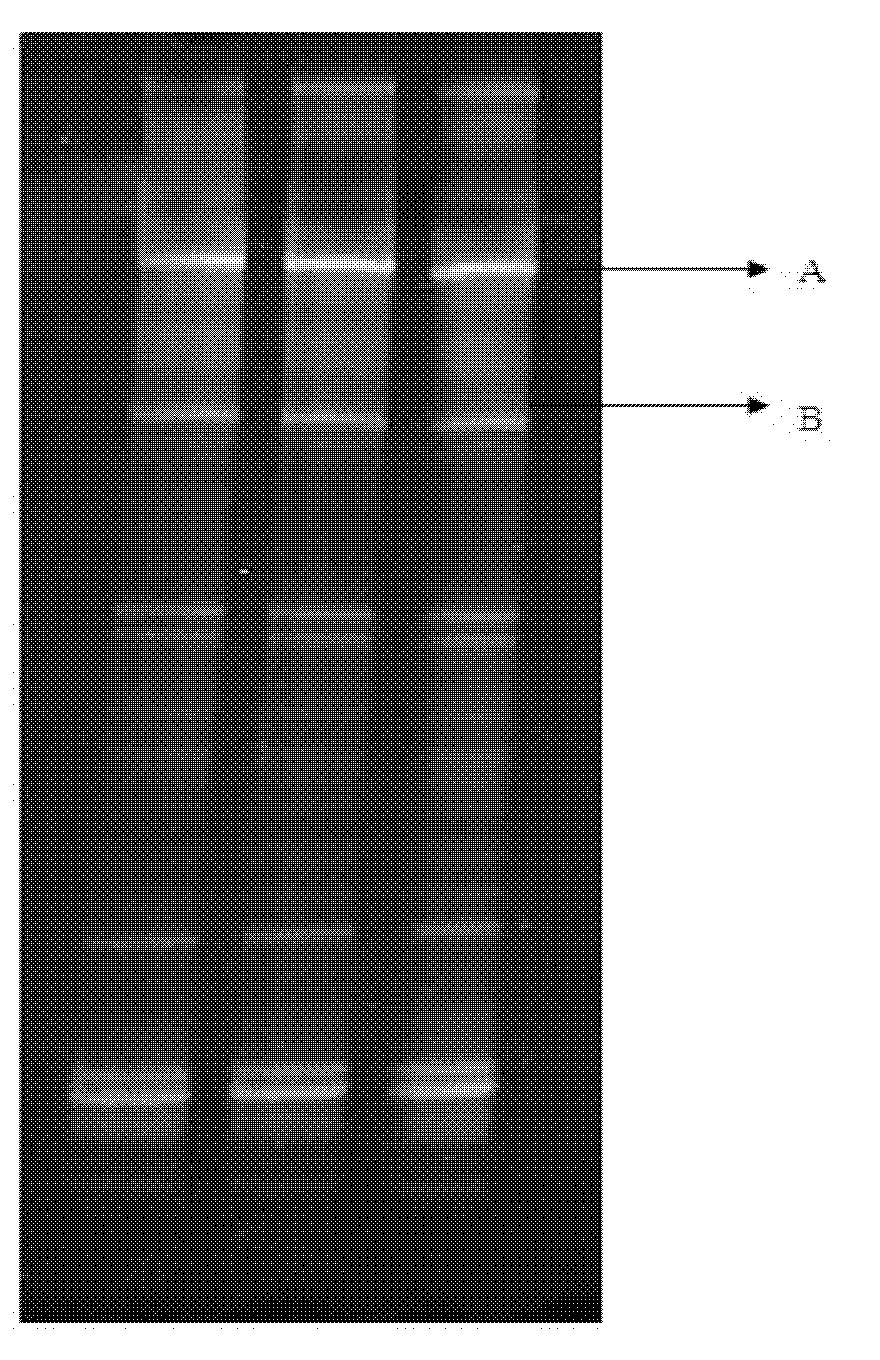
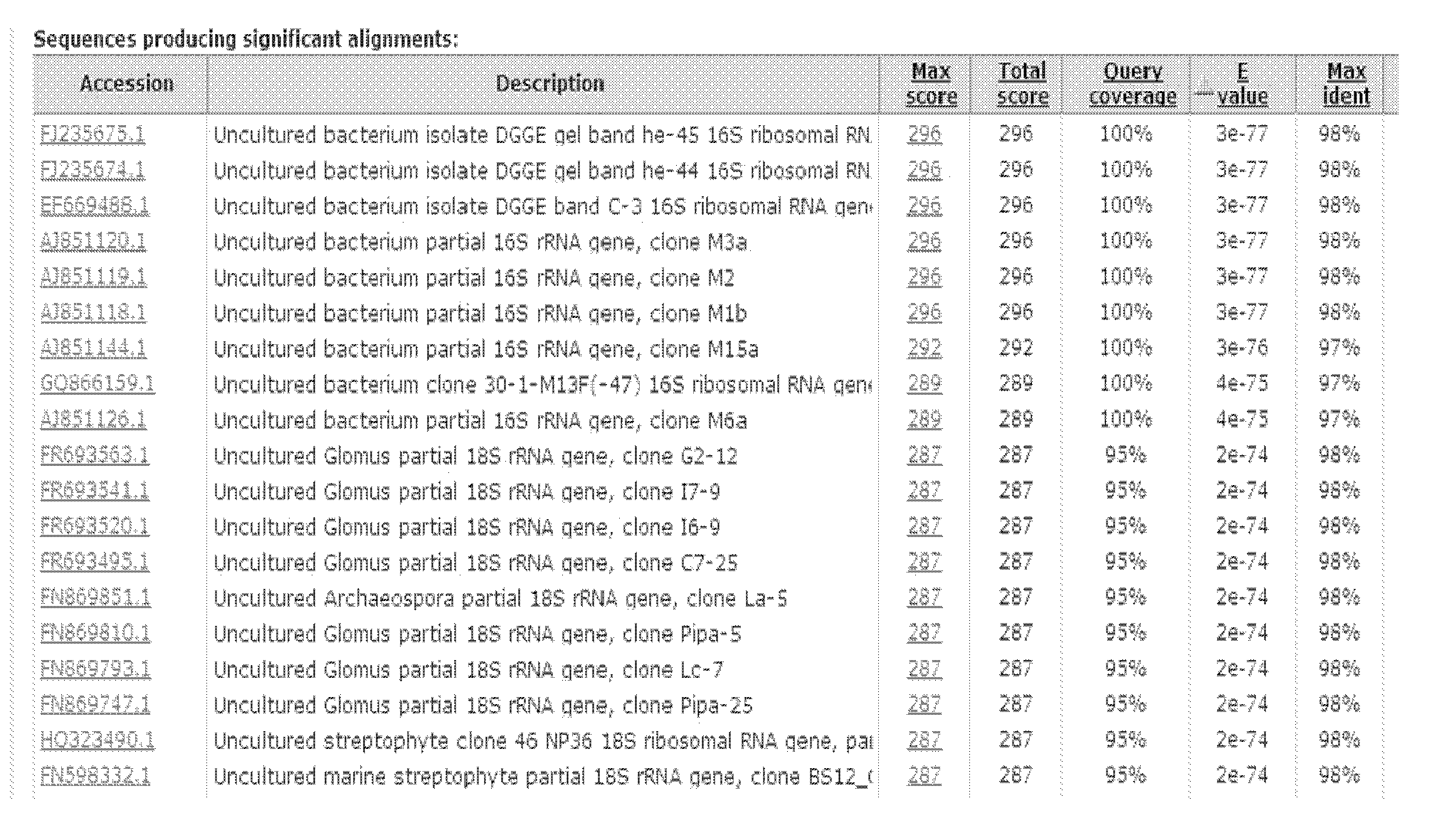
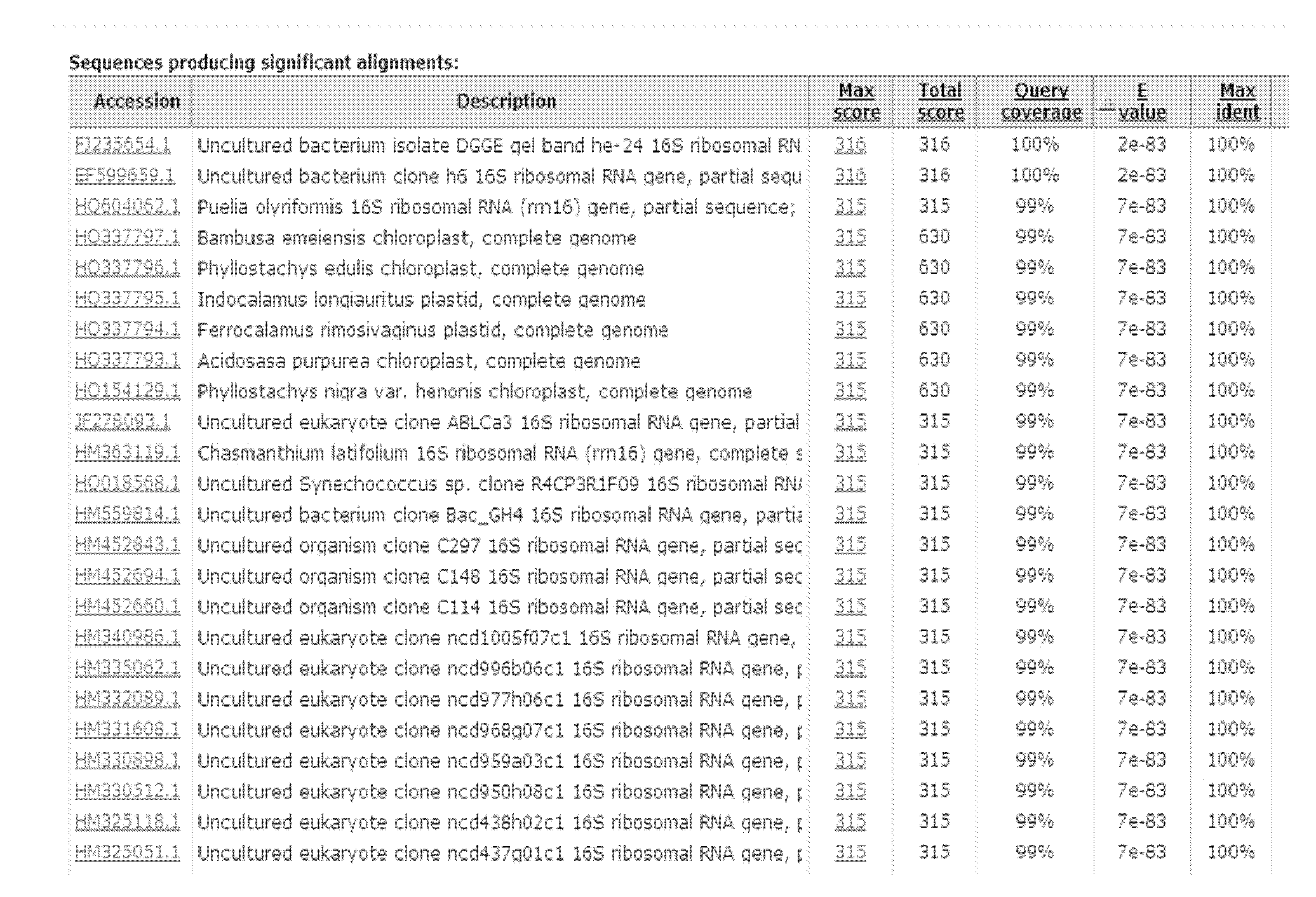
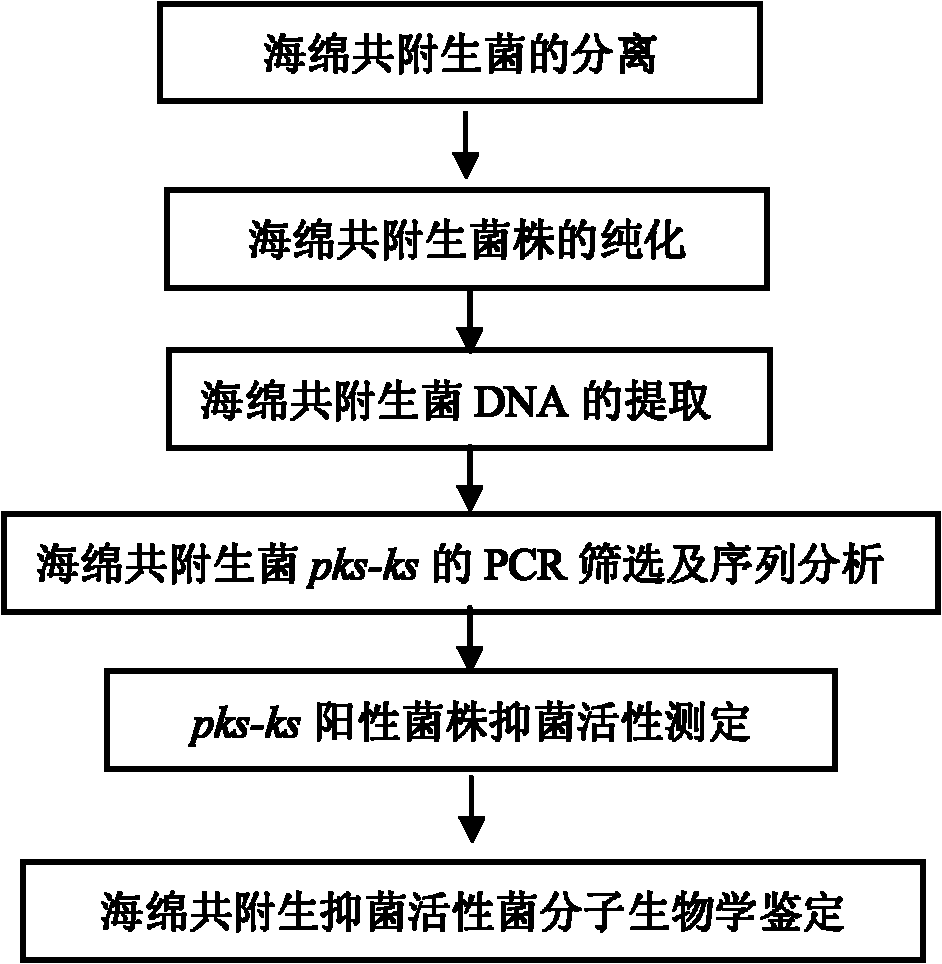
Method for screening sponge-associated antibacterial active strains
InactiveCN101871009AImprove purposeReliable resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening methodMicrobiology
The invention relates to a method for screening sponge-associated antibacterial active strains, combining marine bacteria pks gene molecular biology screening with antibacterial activity detection. The method comprises the following steps of: first, separating and purifying sponge-associated strains, extracting sponge-associated strain DNA as templates by a phenol-chloroform method; taking a ks region universal primer GB1 / GB2 of bacterial pks gene as a primer to perform polymerase chain reaction for amplifying the pks gene fragment; obtaining a 690bp fragment of sponge-associated bacterial, sequencing, then submitting to Gengank and carrying out Blast analysis; measuring the antibacterial activity of pks positive strains; taking screened antibacterial active strains having 690bp target fragments as templates; taking 16SrDNA universal primer 27f / 1492r as a primer; carrying out polymerase chain reaction to amplify the target fragments and sequencing identification; submitting obtained sequence to Genbank; and carrying out Blast analysis to determine the species of pks gene fragment positive sponge-associated antibacterial active strains.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Tracing method of probiotics in dairy product
InactiveCN107058482AImprove the extraction effectHelp removeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGenomic DNA
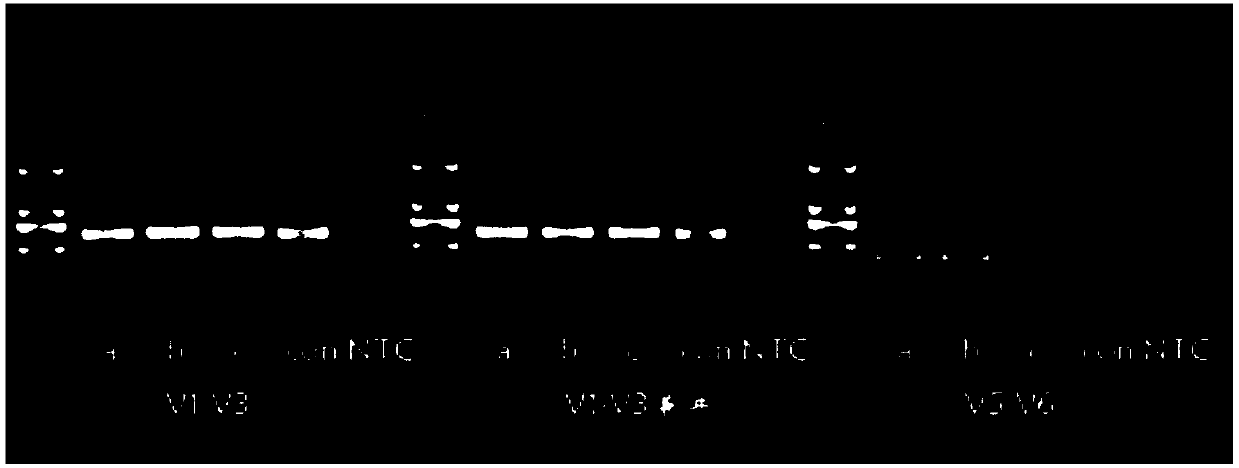
The invention belongs to the technical field of detection, relates to a tracing method of probiotics in a dairy product, and particularly relates to a tracing method of probiotics in the dairy product on an Illumina Miseq sequencing platform. The method comprises the following steps: (1) sample pretreatment: adding sodium citrate and sodium hydroxide into a to-be-detected sample, mixing and centrifuging, discarding supernatant, and adding lysozyme into precipitates for incubation; (2) genomic DNA extraction of the pretreated sample; (3) 16S rRNA PCR amplification: aiming at v1-v3 regions and v5-v6 regions of bacterium 16s rDNA, and designing a primer for PCR amplification; and (4) Illumina Miseq sequencing: performing Illumina Miseq sequencing to the PCR product. Analysis on bacterial strain types and abundance of probiotics contained in food of market fermented dairy products, probiotic milk powder and the like is conducted by utilizing the Illumina Miseq sequencing platform, showing that the practical abundance of probiotics in the solid probiotic products is basically identical with the labeling, and the practical sequencing in the fermented type probiotic product has great difference from that of the labeled bacterial strain.
Owner:PLANTS & ANIMALS & FOOD TESTING QUARANTINE TECH CENT SHANGHAI ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU +1
Biomarkers and uses thereof
Owner:MICROBIO PTY LTD
Method for analyzing children autism intestinal flora diversity and specific primer pair
InactiveCN107058564AShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationInformation analysisFeces
The invention provides a method for analyzing children autism intestinal flora diversity and a specific primer pair. The method comprises the following steps: 1) extracting DNA of a to-be-detected stool sample; 2) configuring a PCR reaction system and performing PCR amplified reaction in bacteria 16S rDNA V1-V2 areas, wherein the PCR reaction system comprises a PCR amplification template, a universal primer pair and the like; 3) detecting a target fragment of a PCR product and purifying the PCR product; 4) performing second-generation high-throughput sequencing on the purified PCR product and detecting the types of microorganisms in the stool sample; 5) sequencing by utilizing an I11umina MiSeq sequencing system; 6) performing bio-information analysis by utilizing FLASH, QIIME and usearch61. The method provided by the invention has the benefits that through a second-generation high-throughput sequencing technology, the intestinal flora diversity of a diseased patient and the difference are detected; compared with a traditional flora detection method, the compositions and the functions of floras can be more detailedly and deeply analyzed by applying the new-generation high-throughput technology.
Owner:QILU CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF SHANDONG UNIV
Nest PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection method for peanut pseudomonas solanacearum
InactiveCN103614475AReduce distractionsStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrophoresesAssay
The invention relates to a nest PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection method for peanut pseudomonas solanacearum, which comprises the following steps of performing a first round of PCR amplification by use of a universal primer L1 / L2 for a bacterial 16S-23S rDNA ITS sequence by adopting a sample DNA as a template; performing a second round of PCR amplification by use of a designed pair of specific primers W1 / W2 for identifying the peanut pseudomonas solanacearum by adopting the product of the first round of PCR as a template; performing electrophoresis detection on the amplification product, wherein if a 374bp specific strip appears, the detected pathogenic bacterium is determined to be peanut pseudomonas solanacearum. In the nest PCR detection method for peanut pseudomonas solanacearum, provided by the invention, the detection sensitivity on the germ genome DNA is 10fg, and the shortcomings of the methods such as biological assay, enzyme linked immunosorbent assay technology, conventional PCR and the like can be overcome. The invention provides a quick, sensitive and specific detection method for peanut pseudomonas solanacearum, which can be applied to the early diagnosis of field peanut pseudomonas solanacearum and is of great significance to the early detection and timely prevention of the disease.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION FAAS
Method for detecting bacteria by amplifying conserved region sequence of 16S rDNA
InactiveCN109554441AQuick checkEfficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerEscherichia coli
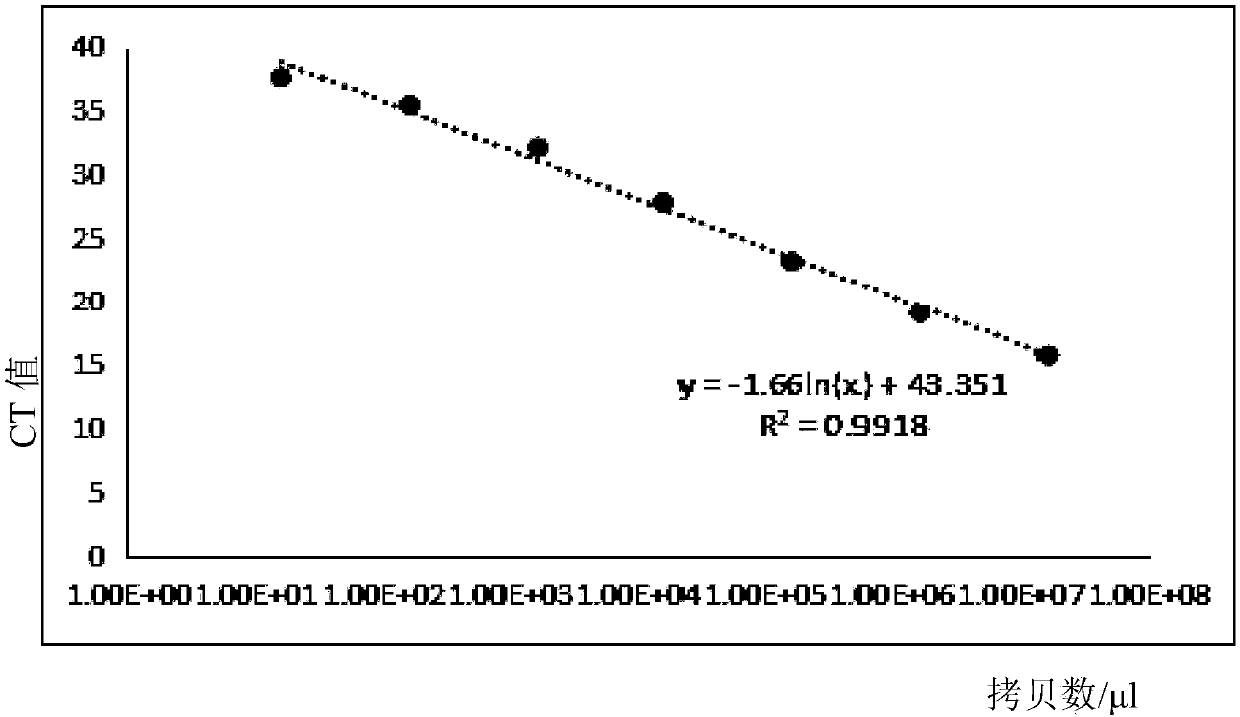
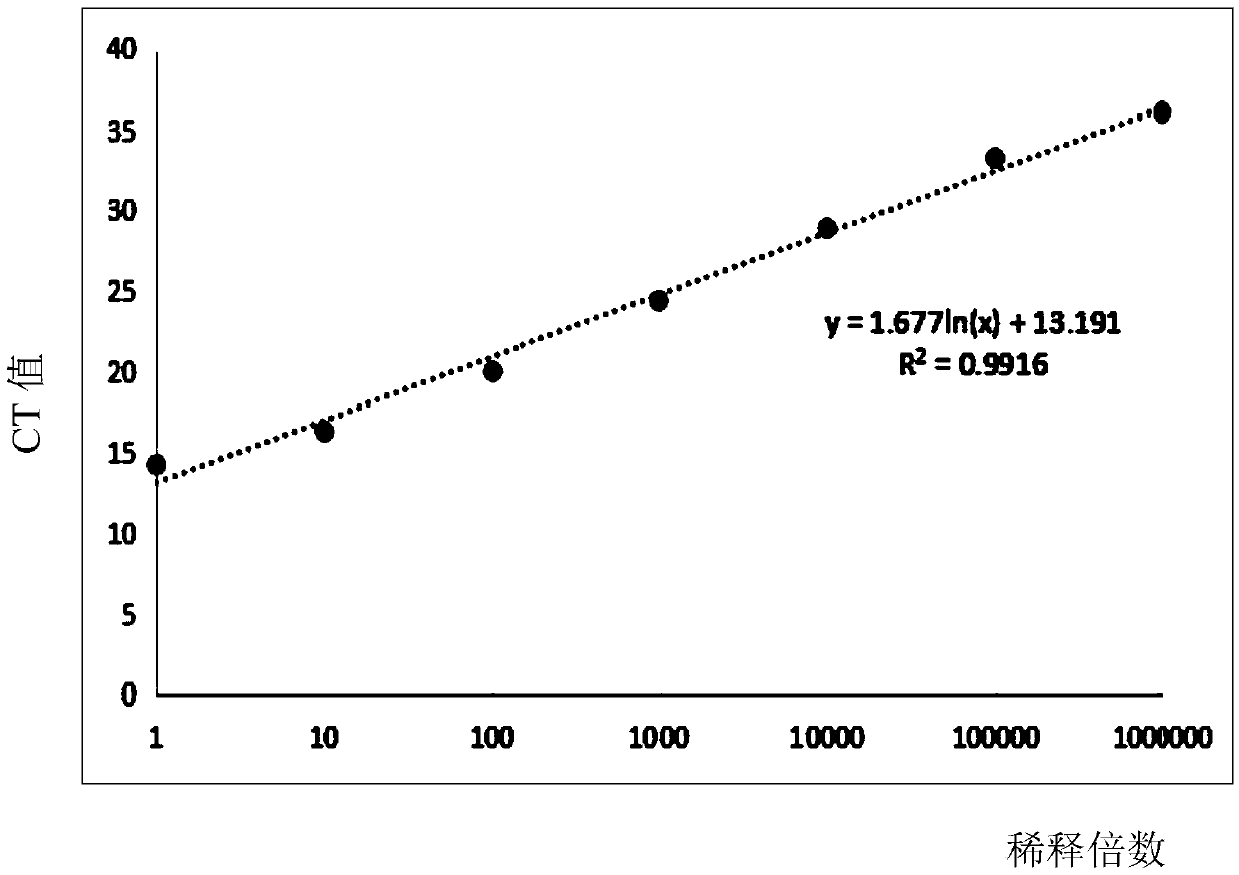
Provided is a method for detecting bacteria by amplifying a conserved region sequence of 16S rDNA. The conserved region sequence of bacteria 16S rDNA is amplified by an RT-PCR method. A standard product is a pUC57 plasmid containing a part of conserved region sequence of 16S rDNA. A PCR reaction system contains 200 nM forward primer and 200 nM reverse primer, a proper amount of a template is added, a standard curve is established by the pUC57 plasmid containing a part of conservative region sequence of 16S rDNA, and then the concentration of bacteria is calculated according to the CT value ofa sample to be tested. According to the method, when the threshold value is set at 10000, the CT value of the sample to be tested is less than 35 and the Tm is between 83.6 DEG C-85 DEG C, bacterial contamination exists, the escherichia coli concentration limit which can be detected is 3-33 cfu / [mu]l, the DNA copying number limit which can be detected is about 1.6*10<2> copies, and the result canbe obtained in 2 h.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV +1
Library-building sequencing method for detecting full length of bacterial 16S rDNA
ActiveCN110452974ASuitable for structure detectionAccurate ecological structureMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisMicroorganismSpecies level
The invention discloses a library-building sequencing method for detecting full length of bacterial 16S rDNA. By adding a molecular tag UMI to each sample, a ligation library and a splicing library are separately amplified, the two libraries are sequenced, the data is extracted by recognizing the UMI combination, and the full length sequence of 16S rDNA was assembled, and the species type is determined by comparing the databases. The library-building method of the invention is suitable for the detection of the flora structure of all types of samples, and can upgrade the traditional flora structure identification from a genus level to a species level, compared with the genus level, the species level has the advantage that an ecological structure of environmental microorganisms can be more accurately determined, which facilitates deep research, and method realizes the detection of specific bacterial species in samples.
Owner:北京群峰纳源健康科技有限公司
Fast nucleic acid extraction, sequencing and identification method based on bacterial 16S rDNA sequence
InactiveCN111154847ARapid Integrated IdentificationMicrobiological testing/measurementA-DNANucleic acid sequencing
The invention discloses a fast nucleic acid extraction, sequencing and identification method based on a bacterial 16S rDNA sequence, and belongs to the technical field of nucleic acid sequencing and identification methods. The method comprises the following steps of (1) extracting DNA in a sample; (2)performing PCR amplification reaction in a PCR reaction kit by using the DNA extracted in the step(1) as a DNA template to be detected and using a universal primer for 16S rDNA sequence amplification; and (3) analyzing a PCR amplification product. A bacterial genome crude extraction method with the advantages of wide application range, high flux, high positive detection rate and low cost is provided, and is used for PCR amplification of bacterial 16S rDNA; then, sequencing and strain identification are performed; the whole operation is fast, simple and convenient; the requirements on equipment are low; the bacterial 16S rDNA full-length sequence can be amplified; gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria can be covered; the identification success rate is high; the strain quantity requirement is low; in addition, the flux is high; and the method can be used for treating hundreds of samples at the same time.
Owner:北京睿博兴科生物技术有限公司
Primers for Amplification and Sequencing of Eubacterial 16S rDNA for Identification
InactiveUS20110159488A1Simple systemSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesGenus
The invention relates to oligonucleotides for the qualitative and / or quantitative amplification and / or the sequencing of 16S rDNA-genes, as well as of fragments thereof and RNA derived thereof. It relates to their use as primers in amplification reactions and in sequencing, in particular in combination for the identification of the genus / species / strain of the bacterial sample or clinical isolate.
Owner:SMARTGENE
Bacterium 16SrDNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) 500 fragment gene sequencing and dblast database analytical method
InactiveCN104099420ASimple methodAccurate dataMicrobiological testing/measurementCapillary electrophoresisBatch processing
A bacterium 16SrDNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) 500 fragment gene sequencing and dblast database analytical method comprises the following steps: step 1, extracting a bacterium DNA sample; step 2, performing bacterium 16SrDNA500 fragment gene amplification; step 3, purifying a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) product; step 4, cycling a sequencing reaction; step 5, a purifying a product of the sequencing reaction; step 6, preparing a capillary electrophoresis sample and performing capillary electrophoresis; and step 7.1, establishing gene testing quality analyzing and receiving standard. The method has the advantages of convenience, batch processing, accurate data and high stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI ROCHE PHARMA
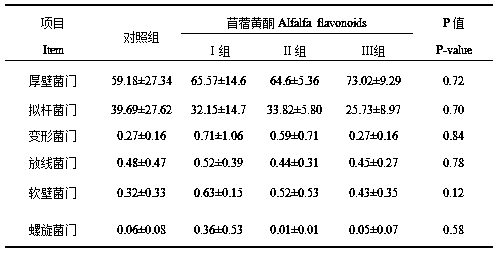
Method for predicting influences of alfalfa flavonoid on weaned pig colon microflora and application of alfalfa flavonoid
InactiveCN109735637AIncrease abundanceIncrease the amount addedMicrobiological testing/measurementAccessory food factorsPig farmsBacteroides
The invention relates to the field of application of alfalfa flavonoid, in particular to a method for predicting the influences of the alfalfa flavonoid on weaned pig colon microflora and the application of the alfalfa flavonoid. Weaned pig colons fed with the alfalfa flavonoid with different concentrations are bought from a pig farm; content of the colons fed with the different kinds of alfalfa flavonoid is collected, and DNA of microorganisms in the content of the colons is extracted; the DNA of the extracted colon microorganisms is used as a template, a bacterium 16S universal primer is adopted, and fluorogenic quantitative PCR detection is carried out; fluorogenic quantitative PCR products are collected respectively, a sodium hydroxide solution is used for denaturation, a single-chainDNA segment is generated, and a Miseq library is established; Miseq sequencing is carried out according to the Miseq library, and double-end sequence data obtained after Miseq sequencing is analyzed.The alfalfa flavonoid has a certain influence effect on forming of the colon flora, 0.2% of the alfalfa flavonoid is added, and the influence effect on the forming of the colon flora is obvious.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
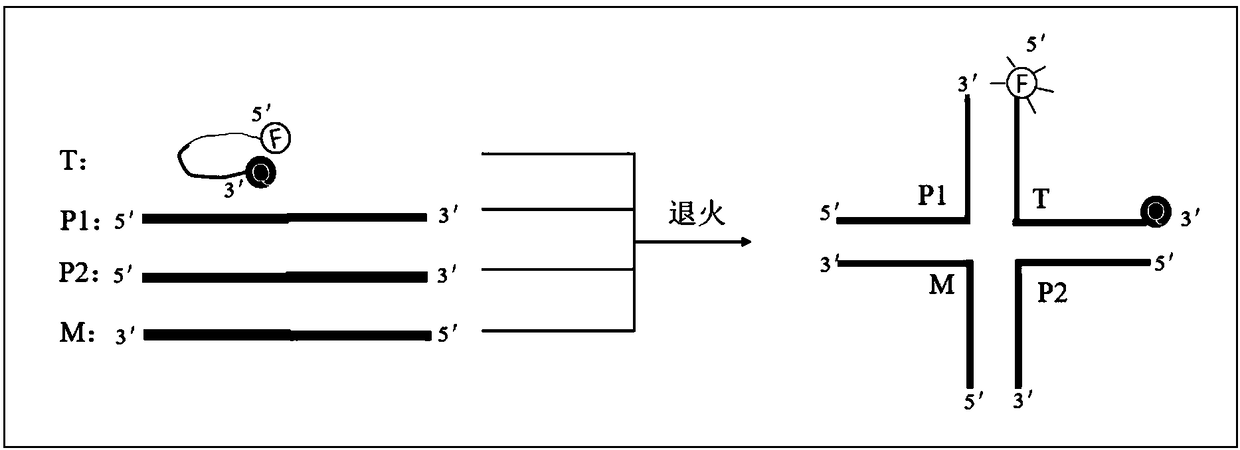
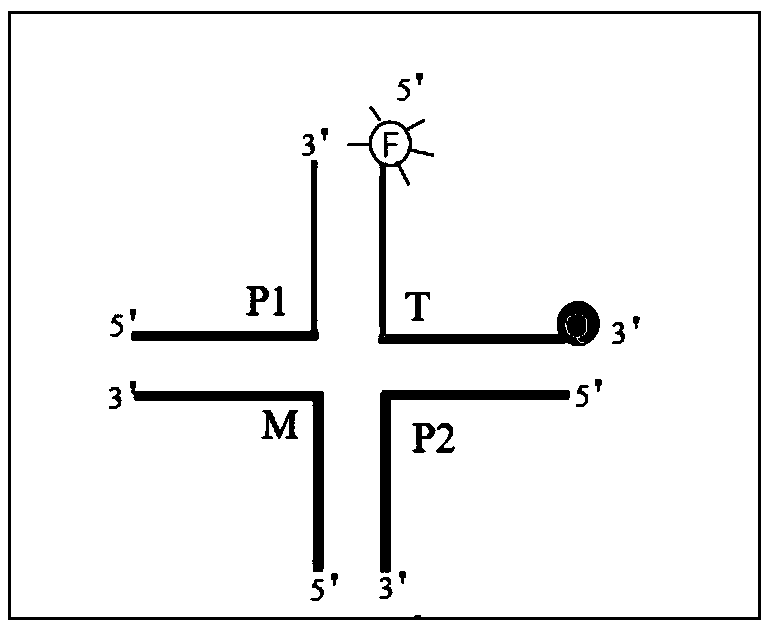
Screening method of gene polymorphism detection probe
ActiveCN108359713ASave time and costSave R&D costsMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence designFluorescence
The invention relates to a screening method of a gene polymorphism detection probe. The method comprises the following steps of (1) designing a universal probe according to a bacterium 16S rDNA conserved region; designing a template sequence containing a mutation site; (2) designing a plurality of pairs of screening primers P1 and a plurality of screening primers P2 covering polymorphism sites according to the base sequence of the mutation site of a gene to be tested of a GeneBank database; (3) gradually taking one pair of primers in the plurality of pairs of screening primers P1 and the plurality of screening primers P2 obtained and designed in the step (2) one by one to perform annealing reaction with the universal probe and the template sequence designed and obtained in the step (1); performing screening to obtain the preferable template sequence; (4) according to the preferable template sequence, synthesizing the matched fluorescent probe, i.e., the final preferable probe. The screening method of the gene polymorphism detection probe can avoid the problems of high cost and low research and development efficiency caused by screening of a great number of probes can be avoided.
Owner:深圳会众生物技术有限公司
A kind of method and detection kit for nasal flora detection
ActiveCN108866220BReduce distractionsDesigned for high amplification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationHigh homologyFlora
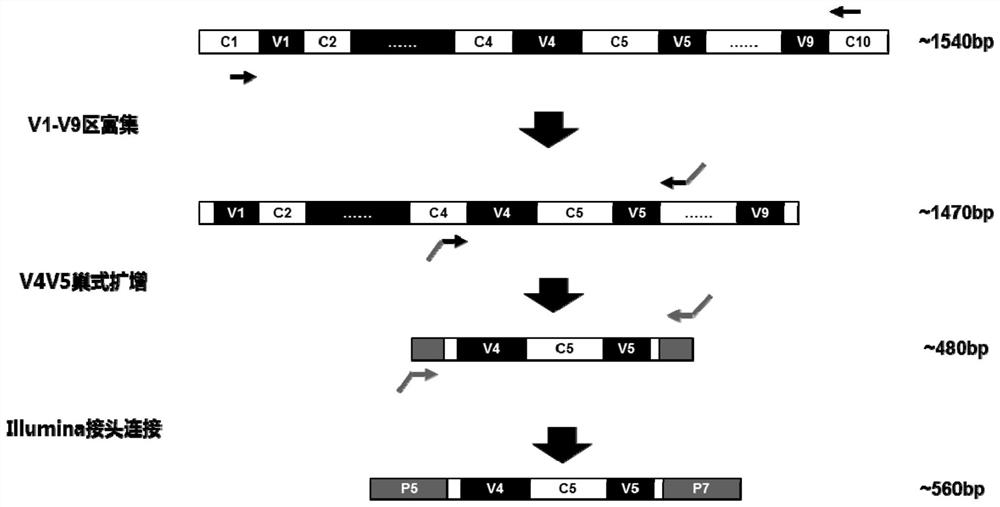
The invention discloses a method for detecting nasal flora and a detection kit. The present invention provides a set of primers for the detection of sample flora, including primers for amplifying the V4-V5 region of bacterial 16S rDNA and primers for amplifying the V1-V9 region of bacterial 16S rDNA; the present invention first uses the amplification efficiency The V1‑V9 primers with high specificity and low human homology first enrich the 16S rDNA fragment, and then use nested PCR to amplify the target segment V4V5 double fragment, which overcomes the need to directly amplify the V4V5 segment. The amplification primers have high homology with the human genome sequence. When amplifying nasal swab samples with high human gDNA content, there will be serious non-specific amplification problems.
Owner:CAPITALBIO CORP
A kind of nested PCR detection method of Ralstonia solanacearum in peanut
InactiveCN103614475BHigh sensitivityReduce distractionsMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrophoresesSpecific detection
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION FAAS
Method for analyzing plant endophytic bacteria flora by primers targeting V5V6 region
ActiveCN112126694AAccurate analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a method for analyzing a plant endophytic bacteria flora by primers targeting the V5V6 region. The invention provides a primer pair for analyzing a plant endophytic bacteria flora, the primer pair is composed of a primer A and a primer B, and a target sequence is the full length or part of the V5-V6 region of bacterial 16S rDNA, wherein the primer A is a single-stranded DNAmolecule with a nucleotide sequence shown as a sequence 1 in a sequence table, the primer B corresponds to plant mitochondrion 18S rDNA, three continuous differential nucleotides exist between the 3'end of the primer B and the plant mitochondrion 18S rDNA, and the number of differential nucleotides between the full length of the primer B and the plant mitochondrion 18S rDNA is larger than or equal to 4. According to the method, a pure plant endophytic bacteria flora 16S amplicon is obtained by utilizing the primer pair, and DNA polymerase which has hot start activity and does not have 3'->5'exonuclease correction activity, and a sequencing experiment platform for amplifying the endophytic bacteria flora in a pollution-free manner is established in combination with a second-generation sequencing platform.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A method for analyzing plant endophytic bacterial flora with primers in the v5v6 region
ActiveCN112126694BAccurate analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideFlora
The invention discloses a method for analyzing plant endophytic bacterial flora with V5V6 region primers. The present invention provides a pair of primers for analyzing plant endophytic bacterial flora, consisting of primer A and primer B, the target sequence is the full length or part of the V5-V6 region of bacterial 16S rDNA; the primer A is a nucleotide sequence For the single-stranded DNA molecule shown in Sequence 1 in the sequence listing, the primer B corresponds to the plant mitochondrial 18S rDNA, and the 3' end of the primer B has 3 consecutive different nucleotides from the plant mitochondrial 18S rDNA, and the primer B The difference between the full length and plant mitochondrial 18S rDNA is greater than or equal to 4 nucleotides. The present invention uses the above primer pair and DNA polymerase with hot start activity and no 3'→5' exonuclease correction activity to obtain pure 16S amplicon of endophytic bacterial flora in plants; A sequencing experiment platform for contamination-free amplification of endophytic bacterial flora was established.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com