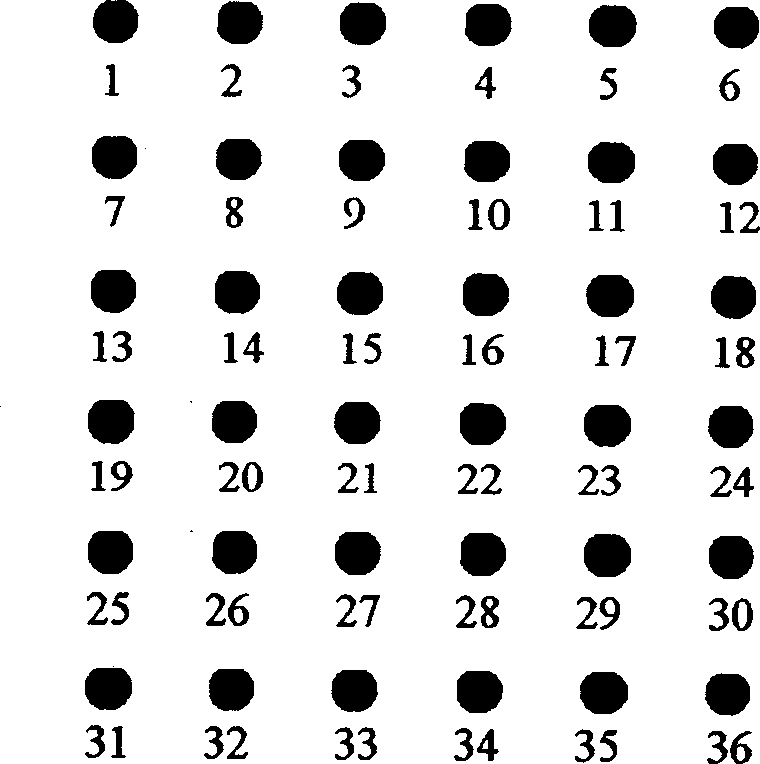Method for detecting aquatic animal pathogenic bacteria by using ribosome interoperonic region probe
A technology for probe detection and aquatic animals, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, biological testing, material inspection products, etc., can solve the problems of difficult identification of probes and unsatisfactory identification results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0137] Sample: A certain batch of exported live fish. Routine microbial culture and biochemical detection revealed suspected colonies of Clostridium perfringens.
[0138] 1. DNA extraction
[0139] Take one gram each of the epidermis, kidney tissue, liver tissue, and heart of the sample fish scales, mix and shake after homogenization, take 1 mL of the homogenate solution and let it stand in an ice bath for 5 minutes, then centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 5 minutes at room temperature, Discard the supernatant, add 100 μL lysozyme solution, incubate at 37°C for 10 minutes, add 500 μl TE buffer, shake and mix well. Add the same volume of Tris saturated phenol with a pH value of 8.0, shake vigorously at 12,000 rpm, centrifuge for 3 minutes, absorb the supernatant, and repeat the phenol extraction. Aspirate the supernatant, add 0.1 times the volume of sodium acetate (2mol / L), mix well, add an equal volume of ice ethanol, mix well, let stand at low temperature for 30 minutes, and cent...
Embodiment 2
[0175] Sample: A certain batch of exported live fish. Routine microbial culture and biochemical detection revealed suspected colonies of Edward tarda.
[0176] 1. DNA extraction
[0177] 2. PCR amplification of 16S-23S rRNA gene fragment
[0178] 3. Hybridization of the target gene amplification product with the probe on the nylon membrane
[0179] 4. ELISA color development of hybridization positive spots
[0180] The ELISA of the hybridization spots was performed according to the instructions of Roche Digoxigenin DNA Labeling and Detection Kit.
[0181] *Result interpretation
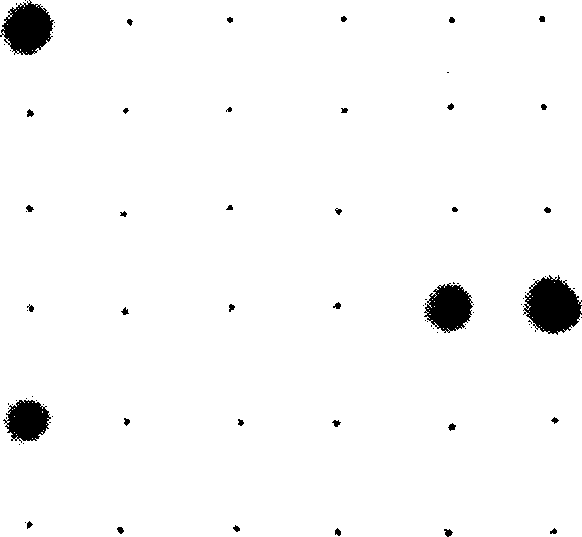
[0182] Interpretation of hybridization results Probe site 10 (Edwardia tarda probe 1 Etar1) and probe site 11 (Edwardia tarda probe 2 Etar2) on the nylon membrane are all dark blue spots, indicating positive hybridization results. The sample contained Edwardsiella tarda, see image 3 .
[0183] After 2 days, routine microbial culture was used to conclude that Edwardsiella lentus was contained i...
Embodiment 3
[0185]Sample: A certain batch of imported live fish. Suspected colonies of Vibrio vulnificus were detected by routine microbial culture and biochemical detection.
[0186] 1. DNA extraction
[0187] 2. PCR amplification of 16S-23S rRNA gene fragment
[0188] 3. Hybridization of the target gene amplification product with the probe on the nylon membrane
[0189] 4. ELISA color development of hybridization positive spots
[0190] The ELISA of the hybridization spots was performed according to the instructions of Roche Digoxigenin DNA Labeling and Detection Kit.
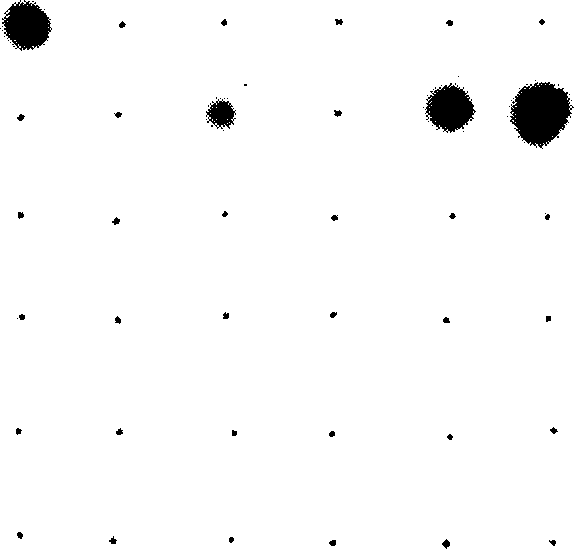
[0191] * Interpretation of results Interpretation of hybridization results Probe site 32 (Vibrio vulnificus probe 1 VvulI1p1) and probe site 33 (Vibrio vulnificus probe 2 VvulI1p2) on the nylon membrane are all dark blue, which means positive hybridization As a result, it was shown that the sample contained Vibrio vulnificus, see Figure 4 .
[0192] After 5 days, routine microbial culture was used to conclude that...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com